How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: November 30, 2023
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a struggle. Before you can even begin to expect to earn their business, you need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on what your product or service promises.

Sure, you could say that you're great at X or that you're way ahead of the competition when it comes to Y. But at the end of the day, what you really need to win new business is cold, hard proof.
One of the best ways to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. In fact, HubSpot’s 2020 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so compelling that they are the fifth most commonly used type of content used by marketers.

Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what you need to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic. To jump to different areas of this post, click on the links below to automatically scroll.

Case Study Definition
Case study templates, how to write a case study.
- How to Format a Case Study
Business Case Study Examples
A case study is a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it's common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client. Perhaps the success you're highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers and help you attract new clients.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why write a case study?
I know, you’re thinking “ Okay, but why do I need to write one of these? ” The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples. Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain Complex Topics or Concepts
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies and show how they can be applied in a practical way. You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that shows how your product solved their issue and how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar successful results.
2. Show Expertise
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build Trust and Credibility
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework. They can have confidence in the solutions you’ve presented because they’ve read through as you’ve explained the problem and outlined step-by-step what it took to solve it. All of these elements working together enable you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create Social Proof
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof . People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — putting your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes work together to help you gain more clients. Plus you can even use quotes from customers featured in these studies and repurpose them in other marketing content. Now that you know more about the benefits of producing a case study, let’s check out how long these documents should be.
How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved. This may be easier said than done, but it's important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader's interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers. We’ve also seen brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience.
Ultimately, the length of your case study should be determined by the amount of information necessary to convey the story and its impact without becoming too long. Next, let’s look at some templates to take the guesswork out of creating one.
To help you arm your prospects with information they can trust, we've put together a step-by-step guide on how to create effective case studies for your business with free case study templates for creating your own.
Tell us a little about yourself below to gain access today:
And to give you more options, we’ll highlight some useful templates that serve different needs. But remember, there are endless possibilities when it comes to demonstrating the work your business has done.
1. General Case Study Template

Do you have a specific product or service that you’re trying to sell, but not enough reviews or success stories? This Product Specific case study template will help.
This template relies less on metrics, and more on highlighting the customer’s experience and satisfaction. As you follow the template instructions, you’ll be prompted to speak more about the benefits of the specific product, rather than your team’s process for working with the customer.
4. Bold Social Media Business Case Study Template

You can find templates that represent different niches, industries, or strategies that your business has found success in — like a bold social media business case study template.
In this template, you can tell the story of how your social media marketing strategy has helped you or your client through collaboration or sale of your service. Customize it to reflect the different marketing channels used in your business and show off how well your business has been able to boost traffic, engagement, follows, and more.
5. Lead Generation Business Case Study Template

It’s important to note that not every case study has to be the product of a sale or customer story, sometimes they can be informative lessons that your own business has experienced. A great example of this is the Lead Generation Business case study template.
If you’re looking to share operational successes regarding how your team has improved processes or content, you should include the stories of different team members involved, how the solution was found, and how it has made a difference in the work your business does.
Now that we’ve discussed different templates and ideas for how to use them, let’s break down how to create your own case study with one.
- Get started with case study templates.
- Determine the case study's objective.
- Establish a case study medium.
- Find the right case study candidate.
- Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
- Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
- Download a case study email template.
- Define the process you want to follow with the client.
- Ensure you're asking the right questions.
- Layout your case study format.
- Publish and promote your case study.
1. Get started with case study templates.
Telling your customer's story is a delicate process — you need to highlight their success while naturally incorporating your business into their story.
If you're just getting started with case studies, we recommend you download HubSpot's Case Study Templates we mentioned before to kickstart the process.
2. Determine the case study's objective.
All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives.
Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring. In other words, what will the client have succeeded in doing by the end of the piece?
The client objective you focus on will depend on what you want to prove to your future customers as a result of publishing this case study.
Your case study can focus on one of the following client objectives:
- Complying with government regulation
- Lowering business costs
- Becoming profitable
- Generating more leads
- Closing on more customers
- Generating more revenue
- Expanding into a new market
- Becoming more sustainable or energy-efficient
3. Establish a case study medium.
Next, you'll determine the medium in which you'll create the case study. In other words, how will you tell this story?
Case studies don't have to be simple, written one-pagers. Using different media in your case study can allow you to promote your final piece on different channels. For example, while a written case study might just live on your website and get featured in a Facebook post, you can post an infographic case study on Pinterest and a video case study on your YouTube channel.
Here are some different case study mediums to consider:
Written Case Study
Consider writing this case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form for readers to fill out before downloading the piece, allowing this case study to generate leads for your business.
Video Case Study
Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers.
Infographic Case Study
Use the long, vertical format of an infographic to tell your success story from top to bottom. As you progress down the infographic, emphasize major KPIs using bigger text and charts that show the successes your client has had since working with you.
Podcast Case Study
Podcasts are a platform for you to have a candid conversation with your client. This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success.
4. Find the right case study candidate.
Writing about your previous projects requires more than picking a client and telling a story. You need permission, quotes, and a plan. To start, here are a few things to look for in potential candidates.
Product Knowledge
It helps to select a customer who's well-versed in the logistics of your product or service. That way, he or she can better speak to the value of what you offer in a way that makes sense for future customers.
Remarkable Results
Clients that have seen the best results are going to make the strongest case studies. If their own businesses have seen an exemplary ROI from your product or service, they're more likely to convey the enthusiasm that you want prospects to feel, too.
One part of this step is to choose clients who have experienced unexpected success from your product or service. When you've provided non-traditional customers — in industries that you don't usually work with, for example — with positive results, it can help to remove doubts from prospects.
Recognizable Names
While small companies can have powerful stories, bigger or more notable brands tend to lend credibility to your own. In fact, 89% of consumers say they'll buy from a brand they already recognize over a competitor, especially if they already follow them on social media.
Customers that came to you after working with a competitor help highlight your competitive advantage and might even sway decisions in your favor.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
Most importantly at this point, however, is getting your subject's approval. When first reaching out to your case study candidate, provide them with the case study's objective and format — both of which you will have come up with in the first two steps above.
To get this initial permission from your subject, put yourself in their shoes — what would they want out of this case study? Although you're writing this for your own company's benefit, your subject is far more interested in the benefit it has for them.
Benefits to Offer Your Case Study Candidate
Here are four potential benefits you can promise your case study candidate to gain their approval.
Brand Exposure
Explain to your subject to whom this case study will be exposed, and how this exposure can help increase their brand awareness both in and beyond their own industry. In the B2B sector, brand awareness can be hard to collect outside one's own market, making case studies particularly useful to a client looking to expand their name's reach.
Employee Exposure
Allow your subject to provide quotes with credits back to specific employees. When this is an option for them, their brand isn't the only thing expanding its reach — their employees can get their name out there, too. This presents your subject with networking and career development opportunities they might not have otherwise.
Product Discount
This is a more tangible incentive you can offer your case study candidate, especially if they're a current customer of yours. If they agree to be your subject, offer them a product discount — or a free trial of another product — as a thank-you for their help creating your case study.
Backlinks and Website Traffic
Here's a benefit that is sure to resonate with your subject's marketing team: If you publish your case study on your website, and your study links back to your subject's website — known as a "backlink" — this small gesture can give them website traffic from visitors who click through to your subject's website.
Additionally, a backlink from you increases your subject's page authority in the eyes of Google. This helps them rank more highly in search engine results and collect traffic from readers who are already looking for information about their industry.
6. Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
So you know what you’re going to offer your candidate, it’s time that you prepare the resources needed for if and when they agree to participate, like a case study release form and success story letter.
Let's break those two down.
Case Study Release Form
This document can vary, depending on factors like the size of your business, the nature of your work, and what you intend to do with the case studies once they are completed. That said, you should typically aim to include the following in the Case Study Release Form:
- A clear explanation of why you are creating this case study and how it will be used.
- A statement defining the information and potentially trademarked information you expect to include about the company — things like names, logos, job titles, and pictures.
- An explanation of what you expect from the participant, beyond the completion of the case study. For example, is this customer willing to act as a reference or share feedback, and do you have permission to pass contact information along for these purposes?
- A note about compensation.
Success Story Letter
As noted in the sample email, this document serves as an outline for the entire case study process. Other than a brief explanation of how the customer will benefit from case study participation, you'll want to be sure to define the following steps in the Success Story Letter.
7. Download a case study email template.
While you gathered your resources, your candidate has gotten time to read over the proposal. When your candidate approves of your case study, it's time to send them a release form.
A case study release form tells you what you'll need from your chosen subject, like permission to use any brand names and share the project information publicly. Kick-off this process with an email that runs through exactly what they can expect from you, as well as what you need from them. To give you an idea of what that might look like, check out this sample email:
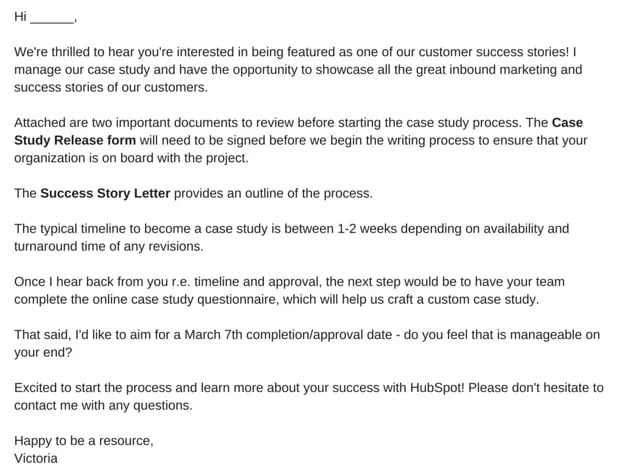
8. Define the process you want to follow with the client.
Before you can begin the case study, you have to have a clear outline of the case study process with your client. An example of an effective outline would include the following information.
The Acceptance
First, you'll need to receive internal approval from the company's marketing team. Once approved, the Release Form should be signed and returned to you. It's also a good time to determine a timeline that meets the needs and capabilities of both teams.
The Questionnaire
To ensure that you have a productive interview — which is one of the best ways to collect information for the case study — you'll want to ask the participant to complete a questionnaire before this conversation. That will provide your team with the necessary foundation to organize the interview, and get the most out of it.
The Interview
Once the questionnaire is completed, someone on your team should reach out to the participant to schedule a 30- to 60-minute interview, which should include a series of custom questions related to the customer's experience with your product or service.
The Draft Review
After the case study is composed, you'll want to send a draft to the customer, allowing an opportunity to give you feedback and edits.
The Final Approval
Once any necessary edits are completed, send a revised copy of the case study to the customer for final approval.
Once the case study goes live — on your website or elsewhere — it's best to contact the customer with a link to the page where the case study lives. Don't be afraid to ask your participants to share these links with their own networks, as it not only demonstrates your ability to deliver positive results and impressive growth, as well.
9. Ensure you're asking the right questions.
Before you execute the questionnaire and actual interview, make sure you're setting yourself up for success. A strong case study results from being prepared to ask the right questions. What do those look like? Here are a few examples to get you started:
- What are your goals?
- What challenges were you experiencing before purchasing our product or service?
- What made our product or service stand out against our competitors?
- What did your decision-making process look like?
- How have you benefited from using our product or service? (Where applicable, always ask for data.)
Keep in mind that the questionnaire is designed to help you gain insights into what sort of strong, success-focused questions to ask during the actual interview. And once you get to that stage, we recommend that you follow the "Golden Rule of Interviewing." Sounds fancy, right? It's actually quite simple — ask open-ended questions.
If you're looking to craft a compelling story, "yes" or "no" answers won't provide the details you need. Focus on questions that invite elaboration, such as, "Can you describe ...?" or, "Tell me about ..."
In terms of the interview structure, we recommend categorizing the questions and flowing them into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, and how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context. That helps match the customer's need with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes. Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you've collected and actually turn it into something, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. Where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
To help you get a handle on this step, it's important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study. They can be very visual, which you'll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated mostly through video or photos, with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections we suggest, which we'll cover in more detail down below:
- Title: Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle: Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary : A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject: An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives: A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped: A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results: A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes: Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans: Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call to Action (CTA): Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible. Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you've completed your case study, it's time to publish and promote it. Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas:
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier in this article, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF. To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client's success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they'd like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people here from your homepage with a "Case Studies" or "Testimonials" button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
Format for a Case Study
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

Image Source
The title is one of the most important parts of your case study. It should draw readers in while succinctly describing the potential benefits of working with your company. To that end, your title should:
- State the name of your custome r. Right away, the reader must learn which company used your products and services. This is especially important if your customer has a recognizable brand. If you work with individuals and not companies, you may omit the name and go with professional titles: “A Marketer…”, “A CFO…”, and so forth.
- State which product your customer used . Even if you only offer one product or service, or if your company name is the same as your product name, you should still include the name of your solution. That way, readers who are not familiar with your business can become aware of what you sell.
- Allude to the results achieved . You don’t necessarily need to provide hard numbers, but the title needs to represent the benefits, quickly. That way, if a reader doesn’t stay to read, they can walk away with the most essential information: Your product works.
The example above, “Crunch Fitness Increases Leads and Signups With HubSpot,” achieves all three — without being wordy. Keeping your title short and sweet is also essential.
2. Subtitle

Your subtitle is another essential part of your case study — don’t skip it, even if you think you’ve done the work with the title. In this section, include a brief summary of the challenges your customer was facing before they began to use your products and services. Then, drive the point home by reiterating the benefits your customer experienced by working with you.
The above example reads:
“Crunch Fitness was franchising rapidly when COVID-19 forced fitness clubs around the world to close their doors. But the company stayed agile by using HubSpot to increase leads and free trial signups.”
We like that the case study team expressed the urgency of the problem — opening more locations in the midst of a pandemic — and placed the focus on the customer’s ability to stay agile.
3. Executive Summary

The executive summary should provide a snapshot of your customer, their challenges, and the benefits they enjoyed from working with you. Think it’s too much? Think again — the purpose of the case study is to emphasize, again and again, how well your product works.
The good news is that depending on your design, the executive summary can be mixed with the subtitle or with the “About the Company” section. Many times, this section doesn’t need an explicit “Executive Summary” subheading. You do need, however, to provide a convenient snapshot for readers to scan.
In the above example, ADP included information about its customer in a scannable bullet-point format, then provided two sections: “Business Challenge” and “How ADP Helped.” We love how simple and easy the format is to follow for those who are unfamiliar with ADP or its typical customer.
4. About the Company

Readers need to know and understand who your customer is. This is important for several reasons: It helps your reader potentially relate to your customer, it defines your ideal client profile (which is essential to deter poor-fit prospects who might have reached out without knowing they were a poor fit), and it gives your customer an indirect boon by subtly promoting their products and services.
Feel free to keep this section as simple as possible. You can simply copy and paste information from the company’s LinkedIn, use a quote directly from your customer, or take a more creative storytelling approach.
In the above example, HubSpot included one paragraph of description for Crunch Fitness and a few bullet points. Below, ADP tells the story of its customer using an engaging, personable technique that effectively draws readers in.

5. Challenges and Objectives

The challenges and objectives section of your case study is the place to lay out, in detail, the difficulties your customer faced prior to working with you — and what they hoped to achieve when they enlisted your help.
In this section, you can be as brief or as descriptive as you’d like, but remember: Stress the urgency of the situation. Don’t understate how much your customer needed your solution (but don’t exaggerate and lie, either). Provide contextual information as necessary. For instance, the pandemic and societal factors may have contributed to the urgency of the need.
Take the above example from design consultancy IDEO:
“Educational opportunities for adults have become difficult to access in the United States, just when they’re needed most. To counter this trend, IDEO helped the city of South Bend and the Drucker Institute launch Bendable, a community-powered platform that connects people with opportunities to learn with and from each other.”
We love how IDEO mentions the difficulties the United States faces at large, the efforts its customer is taking to address these issues, and the steps IDEO took to help.
6. How Product/Service Helped
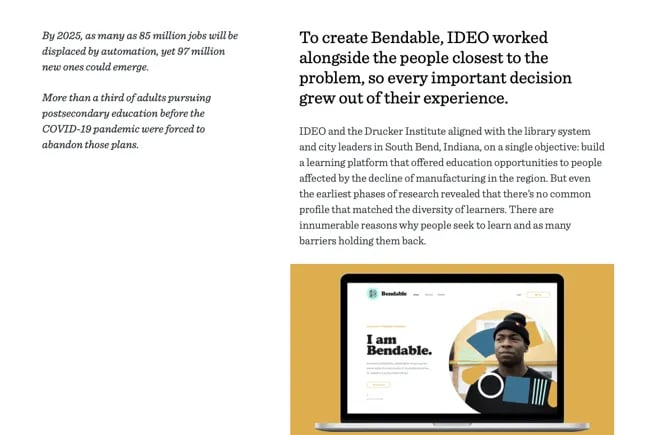
This is where you get your product or service to shine. Cover the specific benefits that your customer enjoyed and the features they gleaned the most use out of. You can also go into detail about how you worked with and for your customer. Maybe you met several times before choosing the right solution, or you consulted with external agencies to create the best package for them.
Whatever the case may be, try to illustrate how easy and pain-free it is to work with the representatives at your company. After all, potential customers aren’t looking to just purchase a product. They’re looking for a dependable provider that will strive to exceed their expectations.
In the above example, IDEO describes how it partnered with research institutes and spoke with learners to create Bendable, a free educational platform. We love how it shows its proactivity and thoroughness. It makes potential customers feel that IDEO might do something similar for them.

The results are essential, and the best part is that you don’t need to write the entirety of the case study before sharing them. Like HubSpot, IDEO, and ADP, you can include the results right below the subtitle or executive summary. Use data and numbers to substantiate the success of your efforts, but if you don’t have numbers, you can provide quotes from your customers.
We can’t overstate the importance of the results. In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and result.
8. Supporting Visuals or Quotes

Let your customer speak for themselves by including quotes from the representatives who directly interfaced with your company.
Visuals can also help, even if they’re stock images. On one side, they can help you convey your customer’s industry, and on the other, they can indirectly convey your successes. For instance, a picture of a happy professional — even if they’re not your customer — will communicate that your product can lead to a happy client.
In this example from IDEO, we see a man standing in a boat. IDEO’s customer is neither the man pictured nor the manufacturer of the boat, but rather Conservation International, an environmental organization. This imagery provides a visually pleasing pattern interrupt to the page, while still conveying what the case study is about.
9. Future Plans
This is optional, but including future plans can help you close on a more positive, personable note than if you were to simply include a quote or the results. In this space, you can show that your product will remain in your customer’s tech stack for years to come, or that your services will continue to be instrumental to your customer’s success.
Alternatively, if you work only on time-bound projects, you can allude to the positive impact your customer will continue to see, even after years of the end of the contract.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Not every case study needs a CTA, but we’d still encourage it. Putting one at the end of your case study will encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
It will also make it easier for them to reach out, if they’re ready to start immediately. You don’t want to lose business just because they have to scroll all the way back up to reach out to your team.
To help you visualize this case study outline, check out the case study template below, which can also be downloaded here .
You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down your findings into a compelling story. And after all of that, you're left with a little piece of sales enabling gold — a case study.
To show you what a well-executed final product looks like, have a look at some of these marketing case study examples.
1. "Shopify Uses HubSpot CRM to Transform High Volume Sales Organization," by HubSpot
What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. This reflects a major HubSpot value, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why Shopify uses HubSpot and is accompanied by a short video and some basic statistics on the company.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the additional text on the page. So, while case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
2. "New England Journal of Medicine," by Corey McPherson Nash
When branding and design studio Corey McPherson Nash showcases its work, it makes sense for it to be visual — after all, that's what they do. So in building the case study for the studio's work on the New England Journal of Medicine's integrated advertising campaign — a project that included the goal of promoting the client's digital presence — Corey McPherson Nash showed its audience what it did, rather than purely telling it.
Notice that the case study does include some light written copy — which includes the major points we've suggested — but lets the visuals do the talking, allowing users to really absorb the studio's services.
3. "Designing the Future of Urban Farming," by IDEO
Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, he or she is greeted with a big, bold photo, and two very simple columns of text — "The Challenge" and "The Outcome."
Immediately, IDEO has communicated two of the case study's major pillars. And while that's great — the company created a solution for vertical farming startup INFARM's challenge — it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, those pillars are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and additional visuals.
4. "Secure Wi-Fi Wins Big for Tournament," by WatchGuard
Then, there are the cases when visuals can tell almost the entire story — when executed correctly. Network security provider WatchGuard can do that through this video, which tells the story of how its services enhanced the attendee and vendor experience at the Windmill Ultimate Frisbee tournament.
5. Rock and Roll Hall of Fame Boosts Social Media Engagement and Brand Awareness with HubSpot
In the case study above , HubSpot uses photos, videos, screenshots, and helpful stats to tell the story of how the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame used the bot, CRM, and social media tools to gain brand awareness.
6. Small Desk Plant Business Ups Sales by 30% With Trello
This case study from Trello is straightforward and easy to understand. It begins by explaining the background of the company that decided to use it, what its goals were, and how it planned to use Trello to help them.
It then goes on to discuss how the software was implemented and what tasks and teams benefited from it. Towards the end, it explains the sales results that came from implementing the software and includes quotes from decision-makers at the company that implemented it.
7. Facebook's Mercedes Benz Success Story
Facebook's Success Stories page hosts a number of well-designed and easy-to-understand case studies that visually and editorially get to the bottom line quickly.
Each study begins with key stats that draw the reader in. Then it's organized by highlighting a problem or goal in the introduction, the process the company took to reach its goals, and the results. Then, in the end, Facebook notes the tools used in the case study.
Showcasing Your Work
You work hard at what you do. Now, it's time to show it to the world — and, perhaps more important, to potential customers. Before you show off the projects that make you the proudest, we hope you follow these important steps that will help you effectively communicate that work and leave all parties feeling good about it.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally published in February 2017 but was updated for comprehensiveness and freshness in July 2021.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![guidelines for case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![guidelines for case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![guidelines for case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Article Writing Affordable Article Writing Services
- Blog Writing Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Product Description Website that optimise your visibility
- Website Writing Website that optimise your visibility
- Proofreading Website that optimise your visibility
- Translation Website that optimise your visibility
- Agriculture Affordable Article Writing Services
- Health & Beauty Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Automotive Website that optimise your visibility
- Sports & fitness Website that optimise your visibility
- Real Estate Website that optimise your visibility
- Entertainment Website that optimise your visibility
- Blogs Affordable Article Writing Services
- Samples Blogs that optimise your visibility
- Case Study Website that optimise your visibility

“How to Write Case Studies: A Comprehensive Guide”
Case studies are essential for marketing and research, offering in-depth insights into successes and problem-solving methods. This blog explains how to write case studies, including steps for creating them, tips for analysis, and case study examples. You'll also find case study templates to simplify the process. Effective case studies establish credibility, enhance marketing efforts, and provide valuable insights for future projects.
Case studies are detailed examinations of subjects like businesses, organizations, or individuals. They are used to highlight successes and problem-solving methods. They are crucial in marketing, education, and research to provide concrete examples and insights.
This blog will explain how to write case studies and their importance. We will cover different applications of case studies and a step-by-step process to create them. You’ll find tips for conducting case study analysis, along with case study examples and case study templates.
Effective case studies are vital. They showcase success stories and problem-solving skills, establishing credibility. This guide will teach you how to create a case study that engages your audience and enhances your marketing and research efforts.
What are Case Studies?
1. Definition and Purpose of a Case Study
Case studies are in-depth explorations of specific subjects to understand dynamics and outcomes. They provide detailed insights that can be generalized to broader contexts.
2. Different Types of Case Studies
- Exploratory: Investigates an area with limited information.
- Explanatory: Explains reasons behind a phenomenon.
- Descriptive: Provides a detailed account of the subject.
- Intrinsic : Focuses on a unique subject.
- Instrumental: Uses the case to understand a broader issue.
3. Benefits of Using Case Studies
Case studies offer many benefits. They provide real-world examples to illustrate theories or concepts. Businesses can demonstrate the effectiveness of their products or services. Researchers gain detailed insights into specific phenomena. Educators use them to teach through practical examples. Learning how to write case studies can enhance your marketing and research efforts.
Understanding how to create a case study involves recognizing these benefits. Case study examples show practical applications. Using case study templates can simplify the process.
5 Steps to Write a Case Study
1. Identifying the Subject or Case
Choose a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure the subject has a clear narrative and relevance to your audience. The subject should illustrate key points and provide substantial learning opportunities. Common subjects include successful projects, client stories, or significant business challenges.
2. Conducting Thorough Research and Data Collection
Gather comprehensive data from multiple sources. Conduct interviews with key stakeholders, such as clients, team members, or industry experts. Use surveys to collect quantitative data. Review documents, reports, and any relevant records. Ensure the information is accurate, relevant, and up-to-date. This thorough research forms the foundation for how to write case studies that are credible and informative.
3. Structuring the Case Study
Organize your case study into these sections:
- Introduction: Introduce the subject and its significance. Provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Background: Provide context and background information. Describe the subject’s history, environment, and any relevant details.
- Case Presentation: Detail the case, including the problem or challenge faced. Discuss the actions taken to address the issue.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and discuss the findings. Highlight key insights, patterns, and outcomes.
- Conclusion: Summarize the outcomes and key takeaways. Reflect on the broader implications and lessons learned.
4. Writing a Compelling Introduction
The introduction should grab the reader’s attention. Start with a hook, such as an interesting fact, quote, or question. Provide a brief overview of the subject and its importance. Explain why this case is relevant and worth studying. An engaging introduction sets the stage for how to create a case study that keeps readers interested.
5. Providing Background Information and Context
Give readers the necessary background to understand the case. Include details about the subject’s history, environment, and any relevant circumstances. Explain the context in which the case exists, such as the industry, market conditions, or organizational culture. Providing a solid foundation helps readers grasp the significance of the case and enhances the credibility of your study.
Understanding how to write a case study involves meticulous research and a clear structure. Utilizing case study examples and templates can guide you through the process, ensuring you present your findings effectively. These steps are essential for writing informative, engaging, and impactful case studies.
How to Write Case Study Analysis
1. Analyzing the Data Collected
Examine the data to identify patterns, trends, and key findings. Use qualitative and quantitative methods to ensure a comprehensive analysis. Validate the data’s accuracy and relevance to the subject. Look for correlations and causations that can provide deeper insights.
2. Identifying Key Issues and Problems
Pinpoint the main issues or challenges faced by the subject. Determine the root causes of these problems. Use tools like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to get a clear picture. Prioritize the issues based on their impact and urgency.
3. Discussing Possible Solutions and Their Implementation
Explore various solutions that address the identified issues. Compare the potential effectiveness of each solution. Discuss the steps taken to implement the chosen solutions. Highlight the decision-making process and the rationale behind it. Include any obstacles faced during implementation and how they were overcome.
4. Evaluating the Results and Outcomes
Assess the outcomes of the implemented solutions. Use metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure success. Compare the results with the initial objectives and expectations. Discuss any deviations and their reasons. Provide evidence to support your evaluation, such as before-and-after data or testimonials.
5. Providing Insights and Lessons Learned
Reflect on the insights gained from the case study. Discuss what worked well and what didn’t. Highlight lessons that can be applied to similar situations. Provide actionable recommendations for future projects. This section should offer valuable takeaways for the readers, helping them understand how to create a case study that is insightful and practical.
Mastering how to write case studies involves understanding each part of the analysis. Use case study examples to see how these elements are applied. Case study templates can help you structure your work. Knowing how to make a case study analysis will make your findings clear and actionable.
Case Study Examples and Templates
1. Showcasing Successful Case Studies
Georgia tech athletics increase season ticket sales by 80%.
Georgia Tech Athletics aimed to enhance their season ticket sales and engagement with fans. Their initial strategy involved multiple outbound phone calls without targeting. They partnered with Salesloft to improve their sales process with a more structured inbound approach. This allowed sales reps to target communications effectively. As a result, Georgia Tech saw an 80% increase in season ticket sales, with improved employee engagement and fan relationships.
WeightWatchers Revamps Enterprise Sales Process with HubSpot
WeightWatchers sought to improve their sales efficiency. Their previous system lacked automation, requiring extensive manual effort. By adopting HubSpot’s CRM, WeightWatchers streamlined their sales process. The automation capabilities of HubSpot allowed them to manage customer interactions more effectively. This transition significantly enhanced their operational efficiency and sales performance.
2. Breakdown of What Makes These Examples Effective
These case study examples are effective due to their clear structure and compelling storytelling. They:
- Identify the problem: Each case study begins by outlining the challenges faced by the client.
- Detail the solution: They explain the specific solutions implemented to address these challenges.
- Showcase the results: Quantifiable results and improvements are highlighted, demonstrating the effectiveness of the solutions.
- Use visuals and quotes: Incorporating images, charts, and client testimonials enhances engagement and credibility.
3. Providing Case Study Templates
To assist in creating your own case studies, here are some recommended case study templates:
1. General Case Study Template
- Suitable for various industries and applications.
- Includes sections for background, problem, solution, and results.
- Helps provide a structured narrative for any case study.
2. Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Focuses on presenting metrics and data.
- Ideal for showcasing quantitative achievements.
- Structured to highlight significant performance improvements and achievements.
3. Product-Specific Case Study Template
- Emphasizes customer experiences and satisfaction with a specific product.
- Highlights benefits and features of the product rather than the process.
4. Tips for Customizing Templates to Fit Your Needs
When using case study templates, tailor them to match the specific context of your study. Consider the following tips:
- Adapt the language and tone: Ensure it aligns with your brand voice and audience.
- Include relevant visuals: Add charts, graphs, and images to support your narrative.
- Personalize the content: Use specific details about the subject to make the case study unique and relatable.
Utilizing these examples and templates will guide you in how to write case studies effectively. They provide a clear framework for how to create a case study that is engaging and informative. Learning how to make a case study becomes more manageable with these resources and examples.
Tips for Creating Compelling Case Studies
1. Using Storytelling Techniques to Engage Readers
Incorporate storytelling techniques to make your case study engaging. A compelling narrative holds the reader’s attention.
2. Including Quotes and Testimonials from Participants
Add quotes and testimonials to add credibility. Participant feedback enhances the authenticity of your study.
3. Visual Aids: Charts, Graphs, and Images to Support Your Case
Use charts, graphs, and images to illustrate key points. Visual aids help in better understanding and retention.
4. Ensuring Clarity and Conciseness in Writing
Write clearly and concisely to maintain reader interest. Avoid jargon and ensure your writing is easy to follow.
5. Highlighting the Impact and Benefits
Emphasize the positive outcomes and benefits. Show how the subject has improved or achieved success.
Understanding how to write case studies involves using effective storytelling and visuals. Case study examples show how to engage readers, and case study templates help organize your content. Learning how to make a case study ensures that it is clear and impactful.
Benefits of Using Case Studies
1. Establishing Authority and Credibility
How to write case studies can effectively establish your authority. Showcasing success stories builds credibility in your field.
2. Demonstrating Practical Applications of Your Product or Service
Case study examples demonstrate how your product or service solves real-world problems. This practical evidence is convincing for potential clients.
3. Enhancing Marketing and Sales Efforts
Use case studies to support your marketing and sales strategies. They highlight your successes and attract new customers.
4. Providing Valuable Insights for Future Projects
Case studies offer insights that can guide future projects. Learning how to create a case study helps in applying these lessons effectively.
5. Engaging and Educating Your Audience
Case studies are engaging and educational. They provide detailed examples and valuable lessons. Using case study templates can make this process easier and more effective. Understanding how to make a case study ensures you can communicate these benefits clearly.
Writing effective case studies involves thorough research, clear structure, and engaging content. By following these steps, you’ll learn how to write case studies that showcase your success stories and problem-solving skills. Use the case study examples and case study templates provided to get started. Well-crafted case studies are valuable tools for marketing, research, and education. Start learning how to make a case study today and share your success stories with the world.
What is the purpose of a case study?
A case study provides detailed insights into a subject, illustrating successes and solutions. It helps in understanding complex issues.
How do I choose a subject for my case study?
Select a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure it has a clear narrative.
What are the key components of a case study analysis?
A case study analysis includes data collection, identifying key issues, discussing solutions, evaluating outcomes, and providing insights.
Where can I find case study templates?
You can find downloadable case study templates online. They simplify the process of creating a case study.
How can case studies benefit my business?
Case studies establish credibility, demonstrate practical applications, enhance marketing efforts, and provide insights for future projects. Learning how to create a case study can significantly benefit your business.

I am currently pursuing my Masters in Communication and Journalism from University of Mumbai. I am the author of four self published books. I am interested inv writing for films and TV. I run a blog where I write about film reviews.
More details for blogs

How to Create Interactive Content and Boost Engagement
Learn how to create interactive content to engage your audience. Discover tools, strategies, and benefits of using interactive elements.

How to Use Canva to Mass Produce Viral Content
Discover how to use Canva to mass produce viral content with these expert tips and strategies. Boost your content creation game today!

SGE Ranking Strategies: How to Get Rankings on SGEs
Learn how to create answers that rank for SGE with our comprehensive guide on SGE ranking strategies. Powerful tips and examples!
Need assistance with something
Speak with our expert right away to receive free service-related advice.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Definition and Introduction
Case analysis is a problem-based teaching and learning method that involves critically analyzing complex scenarios within an organizational setting for the purpose of placing the student in a “real world” situation and applying reflection and critical thinking skills to contemplate appropriate solutions, decisions, or recommended courses of action. It is considered a more effective teaching technique than in-class role playing or simulation activities. The analytical process is often guided by questions provided by the instructor that ask students to contemplate relationships between the facts and critical incidents described in the case.
Cases generally include both descriptive and statistical elements and rely on students applying abductive reasoning to develop and argue for preferred or best outcomes [i.e., case scenarios rarely have a single correct or perfect answer based on the evidence provided]. Rather than emphasizing theories or concepts, case analysis assignments emphasize building a bridge of relevancy between abstract thinking and practical application and, by so doing, teaches the value of both within a specific area of professional practice.
Given this, the purpose of a case analysis paper is to present a structured and logically organized format for analyzing the case situation. It can be assigned to students individually or as a small group assignment and it may include an in-class presentation component. Case analysis is predominately taught in economics and business-related courses, but it is also a method of teaching and learning found in other applied social sciences disciplines, such as, social work, public relations, education, journalism, and public administration.
Ellet, William. The Case Study Handbook: A Student's Guide . Revised Edition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2018; Christoph Rasche and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Analysis . Writing Center, Baruch College; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
How to Approach Writing a Case Analysis Paper
The organization and structure of a case analysis paper can vary depending on the organizational setting, the situation, and how your professor wants you to approach the assignment. Nevertheless, preparing to write a case analysis paper involves several important steps. As Hawes notes, a case analysis assignment “...is useful in developing the ability to get to the heart of a problem, analyze it thoroughly, and to indicate the appropriate solution as well as how it should be implemented” [p.48]. This statement encapsulates how you should approach preparing to write a case analysis paper.
Before you begin to write your paper, consider the following analytical procedures:
- Review the case to get an overview of the situation . A case can be only a few pages in length, however, it is most often very lengthy and contains a significant amount of detailed background information and statistics, with multilayered descriptions of the scenario, the roles and behaviors of various stakeholder groups, and situational events. Therefore, a quick reading of the case will help you gain an overall sense of the situation and illuminate the types of issues and problems that you will need to address in your paper. If your professor has provided questions intended to help frame your analysis, use them to guide your initial reading of the case.
- Read the case thoroughly . After gaining a general overview of the case, carefully read the content again with the purpose of understanding key circumstances, events, and behaviors among stakeholder groups. Look for information or data that appears contradictory, extraneous, or misleading. At this point, you should be taking notes as you read because this will help you develop a general outline of your paper. The aim is to obtain a complete understanding of the situation so that you can begin contemplating tentative answers to any questions your professor has provided or, if they have not provided, developing answers to your own questions about the case scenario and its connection to the course readings,lectures, and class discussions.
- Determine key stakeholder groups, issues, and events and the relationships they all have to each other . As you analyze the content, pay particular attention to identifying individuals, groups, or organizations described in the case and identify evidence of any problems or issues of concern that impact the situation in a negative way. Other things to look for include identifying any assumptions being made by or about each stakeholder, potential biased explanations or actions, explicit demands or ultimatums , and the underlying concerns that motivate these behaviors among stakeholders. The goal at this stage is to develop a comprehensive understanding of the situational and behavioral dynamics of the case and the explicit and implicit consequences of each of these actions.
- Identify the core problems . The next step in most case analysis assignments is to discern what the core [i.e., most damaging, detrimental, injurious] problems are within the organizational setting and to determine their implications. The purpose at this stage of preparing to write your analysis paper is to distinguish between the symptoms of core problems and the core problems themselves and to decide which of these must be addressed immediately and which problems do not appear critical but may escalate over time. Identify evidence from the case to support your decisions by determining what information or data is essential to addressing the core problems and what information is not relevant or is misleading.
- Explore alternative solutions . As noted, case analysis scenarios rarely have only one correct answer. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind that the process of analyzing the case and diagnosing core problems, while based on evidence, is a subjective process open to various avenues of interpretation. This means that you must consider alternative solutions or courses of action by critically examining strengths and weaknesses, risk factors, and the differences between short and long-term solutions. For each possible solution or course of action, consider the consequences they may have related to their implementation and how these recommendations might lead to new problems. Also, consider thinking about your recommended solutions or courses of action in relation to issues of fairness, equity, and inclusion.
- Decide on a final set of recommendations . The last stage in preparing to write a case analysis paper is to assert an opinion or viewpoint about the recommendations needed to help resolve the core problems as you see them and to make a persuasive argument for supporting this point of view. Prepare a clear rationale for your recommendations based on examining each element of your analysis. Anticipate possible obstacles that could derail their implementation. Consider any counter-arguments that could be made concerning the validity of your recommended actions. Finally, describe a set of criteria and measurable indicators that could be applied to evaluating the effectiveness of your implementation plan.
Use these steps as the framework for writing your paper. Remember that the more detailed you are in taking notes as you critically examine each element of the case, the more information you will have to draw from when you begin to write. This will save you time.
NOTE : If the process of preparing to write a case analysis paper is assigned as a student group project, consider having each member of the group analyze a specific element of the case, including drafting answers to the corresponding questions used by your professor to frame the analysis. This will help make the analytical process more efficient and ensure that the distribution of work is equitable. This can also facilitate who is responsible for drafting each part of the final case analysis paper and, if applicable, the in-class presentation.
Framework for Case Analysis . College of Management. University of Massachusetts; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Rasche, Christoph and Achim Seisreiner. Guidelines for Business Case Analysis . University of Potsdam; Writing a Case Study Analysis . University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center; Van Ness, Raymond K. A Guide to Case Analysis . School of Business. State University of New York, Albany; Writing a Case Analysis . Business School, University of New South Wales.
Structure and Writing Style
A case analysis paper should be detailed, concise, persuasive, clearly written, and professional in tone and in the use of language . As with other forms of college-level academic writing, declarative statements that convey information, provide a fact, or offer an explanation or any recommended courses of action should be based on evidence. If allowed by your professor, any external sources used to support your analysis, such as course readings, should be properly cited under a list of references. The organization and structure of case analysis papers can vary depending on your professor’s preferred format, but its structure generally follows the steps used for analyzing the case.
Introduction
The introduction should provide a succinct but thorough descriptive overview of the main facts, issues, and core problems of the case . The introduction should also include a brief summary of the most relevant details about the situation and organizational setting. This includes defining the theoretical framework or conceptual model on which any questions were used to frame your analysis.
Following the rules of most college-level research papers, the introduction should then inform the reader how the paper will be organized. This includes describing the major sections of the paper and the order in which they will be presented. Unless you are told to do so by your professor, you do not need to preview your final recommendations in the introduction. U nlike most college-level research papers , the introduction does not include a statement about the significance of your findings because a case analysis assignment does not involve contributing new knowledge about a research problem.
Background Analysis
Background analysis can vary depending on any guiding questions provided by your professor and the underlying concept or theory that the case is based upon. In general, however, this section of your paper should focus on:
- Providing an overarching analysis of problems identified from the case scenario, including identifying events that stakeholders find challenging or troublesome,
- Identifying assumptions made by each stakeholder and any apparent biases they may exhibit,
- Describing any demands or claims made by or forced upon key stakeholders, and
- Highlighting any issues of concern or complaints expressed by stakeholders in response to those demands or claims.
These aspects of the case are often in the form of behavioral responses expressed by individuals or groups within the organizational setting. However, note that problems in a case situation can also be reflected in data [or the lack thereof] and in the decision-making, operational, cultural, or institutional structure of the organization. Additionally, demands or claims can be either internal and external to the organization [e.g., a case analysis involving a president considering arms sales to Saudi Arabia could include managing internal demands from White House advisors as well as demands from members of Congress].
Throughout this section, present all relevant evidence from the case that supports your analysis. Do not simply claim there is a problem, an assumption, a demand, or a concern; tell the reader what part of the case informed how you identified these background elements.
Identification of Problems
In most case analysis assignments, there are problems, and then there are problems . Each problem can reflect a multitude of underlying symptoms that are detrimental to the interests of the organization. The purpose of identifying problems is to teach students how to differentiate between problems that vary in severity, impact, and relative importance. Given this, problems can be described in three general forms: those that must be addressed immediately, those that should be addressed but the impact is not severe, and those that do not require immediate attention and can be set aside for the time being.
All of the problems you identify from the case should be identified in this section of your paper, with a description based on evidence explaining the problem variances. If the assignment asks you to conduct research to further support your assessment of the problems, include this in your explanation. Remember to cite those sources in a list of references. Use specific evidence from the case and apply appropriate concepts, theories, and models discussed in class or in relevant course readings to highlight and explain the key problems [or problem] that you believe must be solved immediately and describe the underlying symptoms and why they are so critical.
Alternative Solutions
This section is where you provide specific, realistic, and evidence-based solutions to the problems you have identified and make recommendations about how to alleviate the underlying symptomatic conditions impacting the organizational setting. For each solution, you must explain why it was chosen and provide clear evidence to support your reasoning. This can include, for example, course readings and class discussions as well as research resources, such as, books, journal articles, research reports, or government documents. In some cases, your professor may encourage you to include personal, anecdotal experiences as evidence to support why you chose a particular solution or set of solutions. Using anecdotal evidence helps promote reflective thinking about the process of determining what qualifies as a core problem and relevant solution .
Throughout this part of the paper, keep in mind the entire array of problems that must be addressed and describe in detail the solutions that might be implemented to resolve these problems.
Recommended Courses of Action
In some case analysis assignments, your professor may ask you to combine the alternative solutions section with your recommended courses of action. However, it is important to know the difference between the two. A solution refers to the answer to a problem. A course of action refers to a procedure or deliberate sequence of activities adopted to proactively confront a situation, often in the context of accomplishing a goal. In this context, proposed courses of action are based on your analysis of alternative solutions. Your description and justification for pursuing each course of action should represent the overall plan for implementing your recommendations.
For each course of action, you need to explain the rationale for your recommendation in a way that confronts challenges, explains risks, and anticipates any counter-arguments from stakeholders. Do this by considering the strengths and weaknesses of each course of action framed in relation to how the action is expected to resolve the core problems presented, the possible ways the action may affect remaining problems, and how the recommended action will be perceived by each stakeholder.
In addition, you should describe the criteria needed to measure how well the implementation of these actions is working and explain which individuals or groups are responsible for ensuring your recommendations are successful. In addition, always consider the law of unintended consequences. Outline difficulties that may arise in implementing each course of action and describe how implementing the proposed courses of action [either individually or collectively] may lead to new problems [both large and small].
Throughout this section, you must consider the costs and benefits of recommending your courses of action in relation to uncertainties or missing information and the negative consequences of success.
The conclusion should be brief and introspective. Unlike a research paper, the conclusion in a case analysis paper does not include a summary of key findings and their significance, a statement about how the study contributed to existing knowledge, or indicate opportunities for future research.
Begin by synthesizing the core problems presented in the case and the relevance of your recommended solutions. This can include an explanation of what you have learned about the case in the context of your answers to the questions provided by your professor. The conclusion is also where you link what you learned from analyzing the case with the course readings or class discussions. This can further demonstrate your understanding of the relationships between the practical case situation and the theoretical and abstract content of assigned readings and other course content.
Problems to Avoid
The literature on case analysis assignments often includes examples of difficulties students have with applying methods of critical analysis and effectively reporting the results of their assessment of the situation. A common reason cited by scholars is that the application of this type of teaching and learning method is limited to applied fields of social and behavioral sciences and, as a result, writing a case analysis paper can be unfamiliar to most students entering college.
After you have drafted your paper, proofread the narrative flow and revise any of these common errors:
- Unnecessary detail in the background section . The background section should highlight the essential elements of the case based on your analysis. Focus on summarizing the facts and highlighting the key factors that become relevant in the other sections of the paper by eliminating any unnecessary information.
- Analysis relies too much on opinion . Your analysis is interpretive, but the narrative must be connected clearly to evidence from the case and any models and theories discussed in class or in course readings. Any positions or arguments you make should be supported by evidence.
- Analysis does not focus on the most important elements of the case . Your paper should provide a thorough overview of the case. However, the analysis should focus on providing evidence about what you identify are the key events, stakeholders, issues, and problems. Emphasize what you identify as the most critical aspects of the case to be developed throughout your analysis. Be thorough but succinct.
- Writing is too descriptive . A paper with too much descriptive information detracts from your analysis of the complexities of the case situation. Questions about what happened, where, when, and by whom should only be included as essential information leading to your examination of questions related to why, how, and for what purpose.
- Inadequate definition of a core problem and associated symptoms . A common error found in case analysis papers is recommending a solution or course of action without adequately defining or demonstrating that you understand the problem. Make sure you have clearly described the problem and its impact and scope within the organizational setting. Ensure that you have adequately described the root causes w hen describing the symptoms of the problem.
- Recommendations lack specificity . Identify any use of vague statements and indeterminate terminology, such as, “A particular experience” or “a large increase to the budget.” These statements cannot be measured and, as a result, there is no way to evaluate their successful implementation. Provide specific data and use direct language in describing recommended actions.
- Unrealistic, exaggerated, or unattainable recommendations . Review your recommendations to ensure that they are based on the situational facts of the case. Your recommended solutions and courses of action must be based on realistic assumptions and fit within the constraints of the situation. Also note that the case scenario has already happened, therefore, any speculation or arguments about what could have occurred if the circumstances were different should be revised or eliminated.
Bee, Lian Song et al. "Business Students' Perspectives on Case Method Coaching for Problem-Based Learning: Impacts on Student Engagement and Learning Performance in Higher Education." Education & Training 64 (2022): 416-432; The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Georgallis, Panikos and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching using Case-Based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; Hawes, Jon M. "Teaching is Not Telling: The Case Method as a Form of Interactive Learning." Journal for Advancement of Marketing Education 5 (Winter 2004): 47-54; Georgallis, Panikos, and Kayleigh Bruijn. "Sustainability Teaching Using Case-based Debates." Journal of International Education in Business 15 (2022): 147-163; .Dean, Kathy Lund and Charles J. Fornaciari. "How to Create and Use Experiential Case-Based Exercises in a Management Classroom." Journal of Management Education 26 (October 2002): 586-603; Klebba, Joanne M. and Janet G. Hamilton. "Structured Case Analysis: Developing Critical Thinking Skills in a Marketing Case Course." Journal of Marketing Education 29 (August 2007): 132-137, 139; Klein, Norman. "The Case Discussion Method Revisited: Some Questions about Student Skills." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 30-32; Mukherjee, Arup. "Effective Use of In-Class Mini Case Analysis for Discovery Learning in an Undergraduate MIS Course." The Journal of Computer Information Systems 40 (Spring 2000): 15-23; Pessoa, Silviaet al. "Scaffolding the Case Analysis in an Organizational Behavior Course: Making Analytical Language Explicit." Journal of Management Education 46 (2022): 226-251: Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Schweitzer, Karen. "How to Write and Format a Business Case Study." ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-write-and-format-a-business-case-study-466324 (accessed December 5, 2022); Reddy, C. D. "Teaching Research Methodology: Everything's a Case." Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 18 (December 2020): 178-188; Volpe, Guglielmo. "Case Teaching in Economics: History, Practice and Evidence." Cogent Economics and Finance 3 (December 2015). doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/23322039.2015.1120977.
Writing Tip
Ca se Study and Case Analysis Are Not the Same!
Confusion often exists between what it means to write a paper that uses a case study research design and writing a paper that analyzes a case; they are two different types of approaches to learning in the social and behavioral sciences. Professors as well as educational researchers contribute to this confusion because they often use the term "case study" when describing the subject of analysis for a case analysis paper. But you are not studying a case for the purpose of generating a comprehensive, multi-faceted understanding of a research problem. R ather, you are critically analyzing a specific scenario to argue logically for recommended solutions and courses of action that lead to optimal outcomes applicable to professional practice.
To avoid any confusion, here are twelve characteristics that delineate the differences between writing a paper using the case study research method and writing a case analysis paper:
- Case study is a method of in-depth research and rigorous inquiry ; case analysis is a reliable method of teaching and learning . A case study is a modality of research that investigates a phenomenon for the purpose of creating new knowledge, solving a problem, or testing a hypothesis using empirical evidence derived from the case being studied. Often, the results are used to generalize about a larger population or within a wider context. The writing adheres to the traditional standards of a scholarly research study. A case analysis is a pedagogical tool used to teach students how to reflect and think critically about a practical, real-life problem in an organizational setting.
- The researcher is responsible for identifying the case to study; a case analysis is assigned by your professor . As the researcher, you choose the case study to investigate in support of obtaining new knowledge and understanding about the research problem. The case in a case analysis assignment is almost always provided, and sometimes written, by your professor and either given to every student in class to analyze individually or to a small group of students, or students select a case to analyze from a predetermined list.
- A case study is indeterminate and boundless; a case analysis is predetermined and confined . A case study can be almost anything [see item 9 below] as long as it relates directly to examining the research problem. This relationship is the only limit to what a researcher can choose as the subject of their case study. The content of a case analysis is determined by your professor and its parameters are well-defined and limited to elucidating insights of practical value applied to practice.
- Case study is fact-based and describes actual events or situations; case analysis can be entirely fictional or adapted from an actual situation . The entire content of a case study must be grounded in reality to be a valid subject of investigation in an empirical research study. A case analysis only needs to set the stage for critically examining a situation in practice and, therefore, can be entirely fictional or adapted, all or in-part, from an actual situation.
- Research using a case study method must adhere to principles of intellectual honesty and academic integrity; a case analysis scenario can include misleading or false information . A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy. A case analysis scenario may include misleading or false information intended to deliberately distract from the central issues of the case. The purpose is to teach students how to sort through conflicting or useless information in order to come up with the preferred solution. Any use of misleading or false information in academic research is considered unethical.
- Case study is linked to a research problem; case analysis is linked to a practical situation or scenario . In the social sciences, the subject of an investigation is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to generate new knowledge leading to a solution. Case analysis narratives are grounded in real life scenarios for the purpose of examining the realities of decision-making behavior and processes within organizational settings. A case analysis assignments include a problem or set of problems to be analyzed. However, the goal is centered around the act of identifying and evaluating courses of action leading to best possible outcomes.
- The purpose of a case study is to create new knowledge through research; the purpose of a case analysis is to teach new understanding . Case studies are a choice of methodological design intended to create new knowledge about resolving a research problem. A case analysis is a mode of teaching and learning intended to create new understanding and an awareness of uncertainty applied to practice through acts of critical thinking and reflection.
- A case study seeks to identify the best possible solution to a research problem; case analysis can have an indeterminate set of solutions or outcomes . Your role in studying a case is to discover the most logical, evidence-based ways to address a research problem. A case analysis assignment rarely has a single correct answer because one of the goals is to force students to confront the real life dynamics of uncertainly, ambiguity, and missing or conflicting information within professional practice. Under these conditions, a perfect outcome or solution almost never exists.
- Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis . The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem. For a case analysis assignment, your professor will often ask you to examine solutions or recommended courses of action based solely on facts and information from the case.
- Case study can be a person, place, object, issue, event, condition, or phenomenon; a case analysis is a carefully constructed synopsis of events, situations, and behaviors . The research problem dictates the type of case being studied and, therefore, the design can encompass almost anything tangible as long as it fulfills the objective of generating new knowledge and understanding. A case analysis is in the form of a narrative containing descriptions of facts, situations, processes, rules, and behaviors within a particular setting and under a specific set of circumstances.
- Case study can represent an open-ended subject of inquiry; a case analysis is a narrative about something that has happened in the past . A case study is not restricted by time and can encompass an event or issue with no temporal limit or end. For example, the current war in Ukraine can be used as a case study of how medical personnel help civilians during a large military conflict, even though circumstances around this event are still evolving. A case analysis can be used to elicit critical thinking about current or future situations in practice, but the case itself is a narrative about something finite and that has taken place in the past.
- Multiple case studies can be used in a research study; case analysis involves examining a single scenario . Case study research can use two or more cases to examine a problem, often for the purpose of conducting a comparative investigation intended to discover hidden relationships, document emerging trends, or determine variations among different examples. A case analysis assignment typically describes a stand-alone, self-contained situation and any comparisons among cases are conducted during in-class discussions and/or student presentations.
The Case Analysis . Fred Meijer Center for Writing and Michigan Authors. Grand Valley State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Ramsey, V. J. and L. D. Dodge. "Case Analysis: A Structured Approach." Exchange: The Organizational Behavior Teaching Journal 6 (November 1981): 27-29; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2017; Crowe, Sarah et al. “The Case Study Approach.” BMC Medical Research Methodology 11 (2011): doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-100; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Works
- Next: Writing a Case Study >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.

Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Heart Views
- v.18(3); Jul-Sep 2017
Guidelines To Writing A Clinical Case Report
What is a clinical case report.
A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine. Some reports contain an extensive review of the relevant literature on the topic. The case report is a rapid short communication between busy clinicians who may not have time or resources to conduct large scale research.
WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR PUBLISHING A CASE REPORT?
The most common reasons for publishing a case are the following: 1) an unexpected association between diseases or symptoms; 2) an unexpected event in the course observing or treating a patient; 3) findings that shed new light on the possible pathogenesis of a disease or an adverse effect; 4) unique or rare features of a disease; 5) unique therapeutic approaches; variation of anatomical structures.
Most journals publish case reports that deal with one or more of the following:
- Unusual observations
- Adverse response to therapies
- Unusual combination of conditions leading to confusion
- Illustration of a new theory
- Question regarding a current theory
- Personal impact.
STRUCTURE OF A CASE REPORT[ 1 , 2 ]
Different journals have slightly different formats for case reports. It is always a good idea to read some of the target jiurnals case reports to get a general idea of the sequence and format.
In general, all case reports include the following components: an abstract, an introduction, a case, and a discussion. Some journals might require literature review.
The abstract should summarize the case, the problem it addresses, and the message it conveys. Abstracts of case studies are usually very short, preferably not more than 150 words.
Introduction
The introduction gives a brief overview of the problem that the case addresses, citing relevant literature where necessary. The introduction generally ends with a single sentence describing the patient and the basic condition that he or she is suffering from.
This section provides the details of the case in the following order:
- Patient description
- Case history
- Physical examination results
- Results of pathological tests and other investigations
- Treatment plan
- Expected outcome of the treatment plan
- Actual outcome.
The author should ensure that all the relevant details are included and unnecessary ones excluded.
This is the most important part of the case report; the part that will convince the journal that the case is publication worthy. This section should start by expanding on what has been said in the introduction, focusing on why the case is noteworthy and the problem that it addresses.
This is followed by a summary of the existing literature on the topic. (If the journal specifies a separate section on literature review, it should be added before the Discussion). This part describes the existing theories and research findings on the key issue in the patient's condition. The review should narrow down to the source of confusion or the main challenge in the case.
Finally, the case report should be connected to the existing literature, mentioning the message that the case conveys. The author should explain whether this corroborates with or detracts from current beliefs about the problem and how this evidence can add value to future clinical practice.
A case report ends with a conclusion or with summary points, depending on the journal's specified format. This section should briefly give readers the key points covered in the case report. Here, the author can give suggestions and recommendations to clinicians, teachers, or researchers. Some journals do not want a separate section for the conclusion: it can then be the concluding paragraph of the Discussion section.
Notes on patient consent
Informed consent in an ethical requirement for most studies involving humans, so before you start writing your case report, take a written consent from the patient as all journals require that you provide it at the time of manuscript submission. In case the patient is a minor, parental consent is required. For adults who are unable to consent to investigation or treatment, consent of closest family members is required.
Patient anonymity is also an important requirement. Remember not to disclose any information that might reveal the identity of the patient. You need to be particularly careful with pictures, and ensure that pictures of the affected area do not reveal the identity of the patient.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
Your Step-By-Step Guide To Writing a Case Study

Creating a case study is both an art and a science. It requires making an in-depth exploration of your chosen subject in order to extract meaningful insights and understand the dynamics that more general surveys or statistical research might not uncover. At the same time, your case study also needs to be a compelling read to ensure those insights get attention from other people!
Unsurprisingly, the prospect of crafting an effective case study can be daunting. It calls for strategic planning, careful organization, and clear communication, all of which can be challenging even for experienced researchers. That's why we've created this step-by-step guide, which breaks the process down into manageable steps, demystifying the journey from defining your research question to sharing your findings. Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a first-timer, this guide aims to equip you with the necessary tools and tips to create a case study that's not just informative, but also engaging and impactful.
Are you ready to unlock the potential of case studies? Let's dive in!
What is a case study?

First, it's important to understand what a case study is – and what it isn't.
A case study is a thorough exploration of a specific subject or event over a certain time frame. Case studies are utilized in numerous fields, including sociology, psychology, education, anthropology, business, and the health sciences, and employ various research techniques to shed light on complex issues.
A case study does not provide absolute proof or conclusions that can be universally applied. Because it concentrates on one particular case or just a few cases, the findings might not apply to different contexts or subjects. Case studies also aren't ideal for determining cause-and-effect relationships as they do not use controlled conditions to separate and measure the impacts of different factors. Lastly, it must be said that a case study isn't just a random assortment of facts or observations; it necessitates a clear research question, a methodical approach to data collection and analysis, and a thoughtful interpretation of the results.
Getting started

Now that we've established the definition and purpose of a case study, let's explore the process by which one is created. You can produce a case study by following these nine steps:
1. Define the purpose of your case study
Before you start writing a case study, you need to define its purpose clearly. Ask yourself: What is the research question or problem you aim to solve? What insights are you looking to uncover? Your goals will guide your research design and influence your choice of case. This initial stage of introspection and clarification is crucial as it acts as a roadmap for your study.
2. Select the case to study
Once you've defined your research objective, the next step is to choose a suitable case that can help answer your research question. This might be a unique, critical, or representative instance. Unique cases offer the opportunity to observe and analyze a situation that is unusual or not well-understood. In contrast, a representative or typical case is often chosen because it represents other cases or a broader phenomenon.
In any case, be sure to justify your choice. Explain why the case is of interest and how it can contribute to the knowledge or understanding of the issue at hand. For instance, if you're studying the effects of corporate restructuring on employee morale, you might choose to focus on a company that recently underwent a significant restructure.
3. Conduct a thorough literature review
Performing a literature review involves a careful examination of relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources related to your research question or problem. In the process, you identify gaps in the current knowledge and determine how your case study can address them. By critically examining existing research, you will not only gain a comprehensive understanding of your chosen topic but also be able to refine your research question or hypothesis, if necessary.
4. Choose a methodological approach
The methodological approach used in your case study will depend on your research objectives and the nature of the case. Methodologies that can be employed in case studies include qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods .
Qualitative methods are often used when the goal is to explore, understand, or interpret certain phenomena. These involve approaches like interviews, focus groups, or ethnography. Quantitative methods, on the other hand, are used when the goal is to test hypotheses or examine relationships between variables. Quantitative approaches often include experiments. Also, surveys may be either qualitative or quantitative depending on the question design.
You may choose to use a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods (mixed methods) if it suits your research objectives.
5. Collect and organize your data
Data collection should be systematic and organized to maintain the integrity and reliability of your research. You need to plan how you will record and store your data to ensure that it's accessible and usable.
If you're conducting interviews or observations, consider using recording devices (with participant consent) to capture the data accurately. In addition, you may want to transcribe the recorded material for easier analysis. If you're using documents or archival records, develop a system for coding and categorizing the data.
6. Analyze the data
Analysis involves interpreting your data to draw out meaningful insights; it is in this stage that your findings start to take shape. Depending on the nature of your data and your research question, you might use any of a variety of analysis methods. For qualitative data, you might employ thematic analysis to identify key themes or grounded theory to generate a new theoretical framework. For quantitative data, you might use statistical analysis to identify patterns or correlations.
Always be open to unexpected findings. Your initial hypotheses might not be supported, or you might uncover new insights that you hadn't initially considered. Remember that all data, whether they fit neatly into your analysis or not, provide valuable insights and contribute to the holistic understanding of your case.
7. Write the case study report
After analyzing the data, it's finally time to compose your case study. In terms of structure, a typical case study might consist of an introduction, background information, the collected data (results), analysis of that data, and the conclusion. Here's a brief breakdown of each section:
- Introduction: The introduction should be brief but engaging, providing a clear statement of the research question or problem, explaining why the case was chosen, and outlining what the case study will cover.
- Background: The background provides the context for your case. Describe the case, its history, and any relevant information that will help readers understand the situation.
- Results: This section should provide a comprehensive account of what you found, without interpretation or opinion. Present your findings in a clear, organized manner. Use visuals such as charts or graphs if they aid comprehension.
- Analysis: This section should provide your interpretations and arguments. Discuss the patterns, themes, or relationships you've identified in your data. Explain what these findings mean in relation to your research question.
- Conclusion: Finally, summarize the key insights from your case study along with their implications. Discuss the limitations of your study and propose avenues for future research.
8. Review and revise
The process of writing a case study doesn't actually end when the report is written; you also need to review your writing for coherence, clarity, and correctness. Don't underestimate the importance of this step! Make sure the information flows logically and that your arguments are well-supported. Check for any grammar or spelling errors. Having a peer or mentor review your work can be incredibly helpful as they provide a fresh perspective and can catch mistakes you might have missed.
9. Get approval if required
If your case study involves human subjects, you may need to obtain approval from an ethical review board. You'll also need to obtain informed consent from your subjects and ensure you respect their privacy and confidentiality throughout the research process. Always follow your institution's ethical guidelines and any other relevant legislation .
Practical tips for writing a compelling case study

Getting through all those steps can feel like a formidable challenge, but here are some practical tips to make the process more manageable:
Be systematic and organized
Given the importance of detail in case studies, it's vital to be systematic and organized from the get-go. This means keeping meticulous records of your data, your sources, and any changes to your research design. A good practice is to maintain a research journal or log where you can record your process, thoughts, and reflections.
In addition, use technology to your advantage. Digital tools like citation managers can help you keep track of your sources and make formatting references a breeze, while spreadsheet or database software can assist in managing and organizing your data. Developing a consistent system for labeling and storing information at the outset will save you time and effort later when you need to retrieve data for analysis.
Stay focused
One common pitfall in research and writing is loss of focus: getting sidetracked by interesting but ultimately irrelevant digressions, which can be very easy, especially when you're dealing with a rich and complex case. Always remember your research question and objectives, and let these guide your study at every step. It's perfectly acceptable – and in fact advisable – to delineate what your study will not cover. Setting clear boundaries can help you stay focused and manage the scope of your study effectively.
Use visual aids
Visual aids such as charts, diagrams, or photographs can greatly enhance your case study. They provide readers with a break from the monotony of text and can communicate complex data or relationships more easily. For instance, if you're presenting a lot of numerical data, consider using a chart or graph. If you're describing a process or sequence of events, portraying it in a flowchart or timeline might be useful. Remember, the goal is to aid comprehension, so make sure your visual aids are clear, well-labeled, and integrated into the text.
Include direct quotes
If your case study involves interviews, including direct quotes can add depth and a sense of the personal to your findings. They provide readers with a firsthand perspective and make your case study more engaging.
When using quotes, be sure to integrate them smoothly into your text. Provide enough context so readers understand the quote's relevance. Also, remember to adhere to ethical guidelines– always respect confidentiality and anonymity agreements.
Maintain ethical standards
Ethics is a fundamental consideration in all research, including case studies. Ensure you have proper consent from participants, respect their privacy, and accurately present your findings without manipulation.
Misrepresenting data or failing to respect participants' rights can lead to serious ethical violations. Always follow your institution's ethical guidelines and any other relevant legislation. If in doubt, seek advice from a supervisor or your institution's ethics committee.
Acknowledge limitations
Every research study has limitations, which could relate to the research design, data collection methods, or other aspects of the study. Being transparent about the limitations of your study can enhance its credibility; moreover, not only does identifying limitations demonstrate your critical thinking and honesty, but it also helps readers accurately interpret your findings.
Finally, acknowledging the limitations of your work helps to set the stage for further research. By identifying aspects that your study couldn't address, you provide other researchers with avenues for building on your findings.
Learn from examples
Before you start writing your case study, it can be helpful to review some published case studies in your field. Different fields may have different conventions, and familiarizing yourself with case studies in your own field can help guide your writing. Look at the structure, tone, and style. Pay attention to how the authors present and analyze data, and how they link their findings back to the research question. You can also learn a lot from the strengths and weaknesses of previously published works. However, remember to develop your own unique voice and perspective – don't just mimic what others have done.
Design for triangulation
Triangulation involves using multiple data sources or methods to gain a more comprehensive and balanced understanding of your research topic. By coming at your research question from multiple directions, such as by examining different datasets or using different methods, you can increase the validity of your results and gain more nuanced insights.
For example, if you're studying the impact of a new teaching method in a school, you might observe classes, interview teachers, and also survey students. Each method will provide a slightly different perspective, and together, they allow you to develop a more complete picture of the teaching method's impact.
Practice reflexivity
Reflexivity involves reflecting on how your assumptions, values, or experiences might influence your research process and interpretations. As a researcher, it's essential to be aware of your potential biases and how they might shape your study.
Consider keeping a reflexivity journal where you can note your thoughts, feelings, and reflections throughout the research process. This practice can help you stay aware of your biases and ensure your research is as objective and balanced as possible.
Write for your audience
Always make sure that your writing is on target for your intended audience. If you're writing for an academic audience, for example, you'll likely use a more formal tone and include more detailed methodological information. If you're writing for practitioners or a general audience, you might use a more accessible language and focus more on practical implications.
Remember to define any technical terms or jargon, and provide sufficient context so your readers can understand your research. The goal is to communicate your findings effectively, regardless of who your readers are.
Seek feedback
Feedback is valuable for improving your case study. Consider sharing drafts with your peers, mentors, or supervisors and asking for their input. Fresh eyes can provide different perspectives, catch errors, or suggest ways to strengthen your arguments.
Remember, feedback is not personal; it's about improving your work. Be open to critique and willing to revise your work based on the feedback you receive.
Writing a case study is a meticulous process that requires clear purpose, careful planning, systematic data collection, and thoughtful analysis. Although it can be time-consuming, the rich, detailed insights a well-executed case study can provide make this study design an invaluable tool in research.
By following this guide and adopting its practical tips, you will be well on your way to crafting a compelling case study that contributes meaningful insights to your chosen field. Good luck with your research journey!
Header image by Kateryna Hliznitsova .
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
Plans and Pricing
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Business leadership
Communication & collaboration
CX / Customer experience
EX / Employee experience
Hybrid work
Productivity
Small business
Virtual events
Life @ RingCentral
RingCentral newsdesk
RingCentral products
Customer stories
Industry insights
Reports & research
Strategic partnerships
Working at RC Bulgaria
Already a partner?
Interested in partnering with us? Tell us a little about your business here .
Sales: (877) 768-4369
The ultimate guide to writing a good case study

Your prospect has done their research. They’ve made a list of requirements. They’ve compared several possible solutions (including yours). They’ve been to your website and had conversations with a salesperson. And they’ve narrowed their search down to your product and your competitor. On paper, both products look similar. But your prospect is still on the fence.
So what’s it going to take for them to go with yours?
Probably something that convinces them that your product gets results.
Enter the case study—tiebreaker extraordinaire, and your best friend.
In this post, we’ll look at:
- What a case study is and why you need one
- 3 elements of a good case study
- How to prep for a case study
- 5 steps to writing your case study
- Tips for making a good case study great
- 5 real-life case study examples
🔍 Are you looking for some case study examples? Check out this free eBook housing five case study examples.
📙 Get the eBook
What is a case study and why should you create one?
A case study is basically a document (it can be a video too) that outlines how a customer used your product to overcome a problem. It’s real-world proof that your product works and gets results.
If your product or service has helped customers get great results, a case study will help you showcase those results to your future customers. They’re an excellent way to attract more business, and can mean the difference between a lost opportunity and a really good end-of-quarter.
What makes a good case study?
First, it’s helpful to highlight what makes case studies bad: most are painfully boring. What they have in research and detail, they lack in a cohesive, consumable story. They list numbers and contain data, but the reader isn’t sure what it all means or why it’s relevant to their problem. They end up existing as technical documents that do little to persuade or excite anyone—and that’s unfortunate because they have the potential to be a powerful sales tool that can help you close big deals in the decision-making phase.
So how do you write a good one, then? Here are three characteristics every good case study should have:
It’s digestible
There’s no hard rule on how long a case study should be. But it’s always a good idea to ask “ How short can we make it? ” A good case study avoids the unnecessary minutiae, knows what it’s trying to say, and communicates it quickly and without ambiguity. With a few exceptions, effective case studies are concise and, clear.
It’s thorough
On the other side of the length equation, being thorough is also important. While the case study is all about making impressive claims about how a product helped someone achieve a certain result, it also needs to explain how it happened. Good case studies include key details that show how the customer got from A to B using the product—something you don’t get with customer reviews . Don’t make your reader work too hard to visualize the story. If you can use images and videos, use them!
It’s a story
Yes, case studies are sales tools. But the ones really worth reading tell a compelling story with a beginning, middle, and end. They beg to be read all the way through. Often, they present a problem that creates tension and demands a solution. And remember, in this story, the customer is the hero—not you.
6 steps to find a good case study
Before you start actually writing, there’s a bit of prep work you’ll need to do to make sure your case study is amazing. (This is where good customer service teamwork will really come in handy since your customer support team will have the best intel.)
1. Choose your customer
You may have many customers who’ve seen great results using your product. But you can’t just pick a name out of a hat and showcase their results; they may not be right for your audience or their results may not be typical. For example, don’t feature an enterprise company when most of your customers are small businesses. Or claiming that your clients have a 90% customer retention rate when most of them see 70% on average (still impressive, though). When considering which customer to use, start by creating a list of customers that meet these criteria:
They’ve seen good results with your product or service
The numbers are what really matter. So choose customers that have seen strong results using your product. But be careful about showcasing exceptionally good results if they’re not likely to be repeated by most.

RingCentral: W2O
They have a respected and recognizable brand
Strong brands give your product instant social proof. They prove that you’re established and trustworthy. That alone can make you a front-runner in the decision-making process. After all, if Big Brand X trusts you, so can a prospect.
They’re a typical customer
Good results don’t carry as much weight when they’re achieved by companies in other industries or verticals. Identify current customers that are similar to your target audience. If you sell enterprise software, choose enterprise customers. If you’re a consultant in the healthcare industry, choose a customer that works in healthcare.
With your list in hand, you can start reaching out. Picking up the phone can be a lot more effective than sending an email. It’s more personal, lets you build rapport, and is harder to ignore than an email.
Try to get in touch with customers who use or are very familiar with your product or service—someone who can speak to results. Tell them you’re interested in writing a case study and you’d love to hear more about the results they’ve achieved. Be clear about what the process involves on their part—whether it’s a list of questions in an email, a phone call, or if it involves a camera and crew.
If you’ve provided value, your customer is more likely to see you as a partner rather than a vendor and, hopefully, will be happy to participate. Remember, you’re also shining a spotlight on their own success. So it’s a win-win.
That said, you may hear “no” a few times, too. Don’t get discouraged. Some customers will decline for different reasons, regardless of the results they’ve achieved with your product.
Don’t just use a personal phone to call your customers and interview them. Use a communications app that has a phone calling feature instead. Not only would it show your business as the caller ID (instead of a shady phone number they’re not familiar with), some apps let you record conversations too to make it easy to go back and analyze your conversations (just remember to ask first).
2. Begin your research
Start collecting information about your customer. This is easier if you work as a team. From sales to marketing to customer service, everyone who’s been in touch with customer will have insight about their experience. They can help you understand what your customers do and sell, and what challenges they’re facing. Identify the stakeholders you need to speak with—anyone in the company who uses your product—from the CEO to the marketing intern. Collect stats, even ones you don’t think are relevant—they may be later.
3. Ask the right questions
Smart questions get insightful answers. Here are some examples of great questions to start with:
“What were some of the bigger challenges you faced before using our product?”
“How does our product help you reach your individual goals?”
“Which key metrics have improved most since using our product/service?”
“Which parts of your business have been impacted most, and how?”
“How long did it take to roll out our product?”
But don’t stop there. Use these questions to segue into deeper, more targeted questions that underscore the real-world benefits of your product. Let the conversation flow naturally—this is the magic of interviews. You can’t always plan for what interesting topics come up next.
4. Identify your target audience
Beyond your customer’s industry, consider who the target audience of the case study is. Who will see it? Who does it need to influence? While it’s often high-level executives who make large purchase decisions, employees at all levels can act as a champion for your product or brand. Your case study may have to persuade an IT worker that your product or service is going to make their job easier, while it needs to convince the CFO that they’ll see a real return on investment.
5. Identify the top three things you want to highlight
During the initial research phase, you’ve likely uncovered a lot of interesting information about your customer and their experiences with your product. While it might be tempting to use it all, your case study should quickly and clearly communicate the value of your product. Go through this information and identify the three most important business results you want to communicate in the case study.
Stats and key performance indicators (KPIs) to consider using in your case study:
- Ramp up time: How long did it take to get started with your product? Did it improve any other facet of their workflow?
- Sales results: How did the product impact your customer’s bottom line?
- Total return on investment (ROI): How long did it take to earn more than they spent on your product?
- Productivity increases: Which teams saw improvements in process and workflow? And now much?

Here’s how RollWorks shows off the amazing ROI that their customers, Payscale, got with them .
6. Choose your format
A case study doesn’t have to exist only as a PDF attachment in a late-stage deal email (although there’s nothing wrong with that). Consider the format. Think about who’s going to read it (or watch it). Do you want to turn this into fancy interactive content ? Does your prospect have the time and interest to dig into the details? Or do they just want the facts? Choose the format that you think best engages the audience that you’re selling to.
Report format
This long-form document has been the gold standard for B2B case studies for many years. This format is effective when the subject matter is complex and demands detail. Remember, a CTO who’s evaluating large-scale business communications platforms for a multi-year deal is going to want more information than a marketing manager who’s evaluating a new social media ad platform:
Here’s how Zendesk presented their case study with IDC as a report .
Keeping things short and sweet is often the best way to get your message heard. By focusing on the key points, you can highlight the biggest wins at just a glance. Most report format case studies can be easily condensed into a one-page document. This is ideal for prospects (and salespeople) who are short on time and prefer something they can quickly scan—like this Adzerk case study with Reddit :
Few things can tell a story the way that video can, and case studies are no exception. They give you an unmatched level of creative freedom and storytelling using music, lighting, pacing, and voice that can evoke emotions and persuade someone using more than just numbers and facts. And at just a couple of minutes long, they can do a lot of heavy lifting in not a lot of time.

Dropbox: Expedia
Infographic
People love infographics. They’re an excellent way to convey important data in a simple, eye-pleasing way. If your case study requires you to use a lot of data to prove a point—or if visualizing data can make the results more clear—building an infographic case study can be a great investment.

5 key steps for writing your case study
Congrats. You’ve done the research. You’ve made the calls. You’ve pored over all the details. Now, all you have to do is write. Here are five simple steps that’ll help you create a powerful case study that champions your customer and clearly showcases the real-world value of your products or services.
1. Introduce the customer
Set the stage for your case study with an introduction. Briefly explain who your customer is with a bit of background information that can include their industry, product, company size, and location. You don’t have to dig into the nuts and bolts of their business, but you do want the reader to understand who they are and what they do. The more color you can provide here, the more impactful it’ll be when you show the awesome results this customer saw because they chose you.
2. State the problem
Every product or service is a solution to a problem. Explain the problem (or problems) that you helped your customer overcome. Describe the larger impact of the issue. Maybe it was customers leaving. Perhaps it was bad leads—or good leads that were never followed up on. Use this as an opportunity to clearly show what was at stake, and make sure you leave the jargon out of it. Frame the problem in simple terms that any reader can understand.
3. Introduce your product
This is where you begin solving the problem. Briefly introduce your product and what it does. Start on a general level, then apply it to the challenge the customer was experiencing. Talk about which teams or individuals used your product and how they used it. Be sure to make the connection between the customer’s problem and your solution crystal clear.
4. Show results
The big reveal. What kind of results was your customer able to achieve using your product or service? Speak to how they solved the problem descriptively, but also with cold, hard numbers. Not everything can be measured in numbers (sometimes, peace of mind is a powerful benefit all on its own), but whenever you can, back up your story with the stats. At the very least, this will make it easy for a CFO—or a prospect who wants to buy—to justify buying your product.
For example:
The customer saw a 33% increase in web traffic, a large influx of social media activity, and a 10% boost in revenue over the duration of the campaign .
5. Prove it
Don’t forget to show your math. How you get the results is just as important as the results themselves. What specific steps were taken to get those results? Not only will this help validate your claims, it makes it easier to envision how the reader may be able to achieve them, too.
8 tips to write a great case study
1. avoid jargon .
As a subject matter expert in your line of work, it can be tempting to go into as much jargony detail as possible. This is normal as it’s often the language we use at work every day. But remember that your customer probably doesn’t speak that language. When in doubt, use an app like Hemingway to make sure you’re writing at a level that most people can understand.
2. Spend time on your title
It’s tempting to use the case study’s most interesting or impressive KPI as your title. But that also gives away the ending before the story begins, and skips details that are important for context in the process. Try writing a title that piques interest without being a spoiler.
3. Edit. Then edit again.
Once you’ve got your first draft completed (and the jargon removed), edit the case study. A few best practices here:
- Look for and eliminate unnecessary adjectives.
- Speak in an active voice.
- Look for details that get in the way of the story.
And then do it all over again until you can’t edit it down anymore without losing the essence of the story.
4. A picture is worth a thousand words
This is especially true when you’re talking about a block of text that’s trying to communicate a chunk of data. Well-designed charts, graphs, images, or infographics can do the heavy lifting of several pages of text in just seconds. They can also help break up large pieces of text, making the case study easier to read—and nicer to look at. After all, the end goal is to have these read all the way through.
Here’s an example of a graphic from a longer CPA Canada infographic (that includes a short case study embedded inside it):
5. Pull quotes
Hard data and results are good. But a customer quote is a great piece of social proof and adds a human element to your case study. And that makes your results more believable. Customer quotes can also be used outside of your testimonial too—try adding it on your website, landing pages, or email marketing campaigns or welcome emails to get more people to check out your products and buy online. Here’s an example of what that looks like:

6. Make it scannable
Some people will take the time to read your case study front to back and absorb every detail. Some won’t give it more than a single glance. And sometimes, that person is the decision-maker. Make the most important results easy to spot, read, and retain at a glance. Write headings that are descriptive—if someone just scanned them, would they be able to get the gist of the story? Consider putting a summary at the very beginning of the study, or call out impressive results in a larger font size.
7. Record your interviews
Ditch the pen and paper. If you’re conducting one-on-one interviews over the phone, you can save yourself a lot of time and energy by recording the conversation (with your customer’s consent, of course). There are tools that can make this easier too—you might find one or two in your marketing stack . For example, you could use RingCentral’s Zapier integration to transcribe your conversation into a text file.
8. Don’t forget the call to action (CTA)
Your prospect is excited because your case study has done an excellent job of showing how your product or service can help drive results for customers. Now, how do they get in touch with you to learn more? Whether it’s a button that links to your website, an email address, or a phone number, make sure there’s an easy way of getting in touch with you in the case study.
5 examples of great case studies from real-life companies
Mailchimp: make a connection in real life with postcards.
What we like about it: The title doesn’t give everything away all at once, and the case study tells a story with a beginning, middle, and end. The sections are clearly titled and organized, and the results are easy to find. As a bonus: the video adds a believable human element.

LinkedIn: How Adobe achieves alignment and ABM success with LinkedIn
What we like about it: It’s detailed without being a novella. It understands and speaks to the enterprise customer. The key points are in bullet format and easy to read. The important wins are highlighted. And the video makes the content easy to engage with.

Hootsuite: How Meliá became one of the most influential hotel chains on social media
What we like about it: The title makes you want to read the whole customer story. They’ve embdedded a well-produced video high on the page, so you can choose to watch it before you read on. The design and layout of the page makes the content and images easy to consume, and the results can’t be missed. Also, they weren’t shy about adding CTAs.
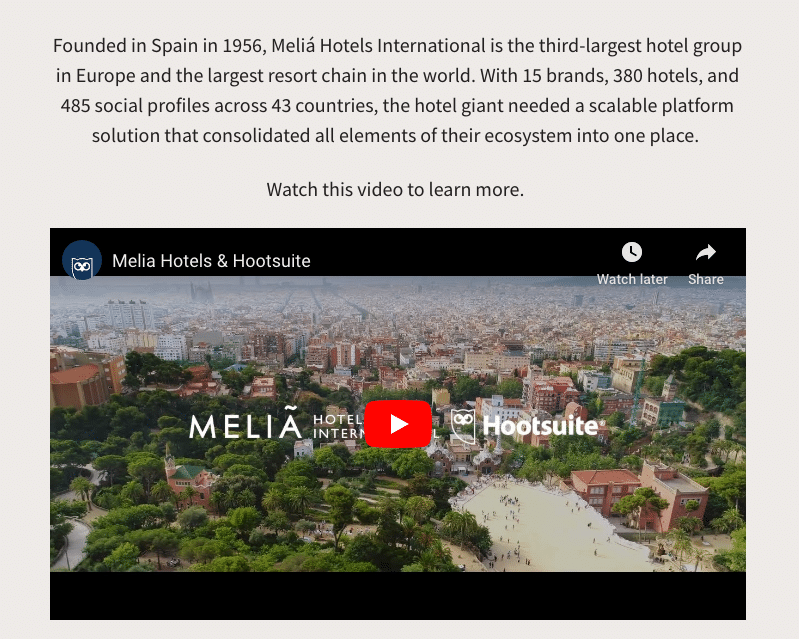
Slack: So yeah, we tried Slack
What we like about it: This case study follows the tried and true format of customer, problem, solution, and results. It uses humor and relatable characters throughout to support the story and keep your attention. And it’s only two minutes long so it gets the point across quickly.

Assetworks: South Carolina School Board Insurance Trust
What we like about it: This case study tackles the otherwise complex and technical topic, and simplifies it as an infographic using images to make the results clear. It’s concise and easy to follow because you can see the math without actually doing any math.
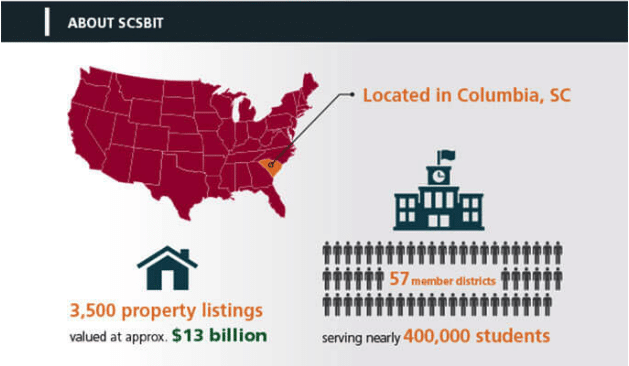
The final word on building a great case study…
Sure, an ad or boosted social media post (more on social media best practices here) can make someone aware of your brand or that your product exists, and a landing page can tell them how your product can solve their problem.
But there’s nothing quite as powerful as someone else singing your praises.
And that’s exactly what a case study does. Spend the time to do it right and it has the potential to deliver huge ROI no matter how big or small your company is. And not just once—but over and over again.
Originally published Feb 05, 2020, updated Oct 19, 2022

53 marketing quotes to inspire & motivate you
You can find inspirational or motivational quotes for pretty much any area of life. There are some great quotes out there for things like fitness, healthy eating, and relationships. You’ll often see some people put quotes on their desk to keep them focused at work. Others will even tattoo their favorite quotes so they always ...
Thank you for your interest in RingCentral.
Related content

11 business email etiquette best practices | RingCentral

10 powerful Zoom alternatives for video calling and conferencing

13 more effective alternatives to “just touching base” emails
- Do Not Sell My Personal Info

- ⋅
Google Case Study Shows Importance Of Structured Data
Google published a case study showing how structured data and optimizing URLs for crawling resulted in nearly doubling clicks from the SERPs

Google published a case study that shows how using structured data and following best practices improved discoverability and brought more search traffic. The case study was about the use of Video structured data but the insights shared are applicable across a range of content types.
The new case study is about an Indonesian publisher called Vidio.
How CDNs Can Cause Indexing Problems
One of the interesting points in the case study is about an issue related to how CDNs can link to image and video files with expiring URLs. The new documentation specifically mentions that it’s important that the CDN uses stable URLs and links to another Google documentation page that goes into more detail.
Google explains that some CDNs use quickly expiring URLs for video and thumbnail files and encourages publishers and SEOs to use just one stable URL for each video. Something interesting to note is that not only does this help Google index the files it also helps Google collect user interest signals.
This is what the documentation advises :
“Some CDNs use quickly expiring URLs for video and thumbnail files. These URLs may prevent Google from successfully indexing your videos or fetching the video files. This also makes it harder for Google to understand users’ interest in your videos over time. Use a single unique and stable URL for each video. This allows Google to discover and process the videos consistently, confirm they are still available and collect correct signals on the videos.”
Implementing The Correct Structured Data
Google highlighted the importance of using the correct structured data and validating it with Google’s structured data testing tool.
These are the results of the above work:
“Within a year of implementing VideoObject markup, Vidio saw improvements in impressions and clicks on their video pages. While the number of videos that Vidio published from Q1 2022 to Q1 2023 increased by ~30%, adding VideoObject markup made their videos eligible for display in various places on Google. This led to an increase of ~3x video impressions and close to 2x video clicks on Google Search. Vidio also used the Search Console video indexing report and performance report, which helped them to identify and fix issues for their entire platform.”
Indexing + Structured Data = More Visibility
The keys to better search performance were ensuring that Google is able to crawl the URLs, which is something that can easily be overlooked in the rush to correlate a drop in rankings to a recent algorithm update. Never rule anything out during a site audit.
Another thing the case study recommends that is important is to assure that the proper structured data is being used. Using the appropriate structured data can help make a webpage qualify for improved search visibility through one of Google’s enhanced search features like featured snippets.
Read Google’s case study:
How Vidio brought more locally relevant video-on-demand (VOD) content to Indonesian users through Google Search
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Anton Vierietin
I have 25 years hands-on experience in SEO and have kept on top of the evolution of search every step ...
Subscribe To Our Newsletter.
Conquer your day with daily search marketing news.
- Awards & Good Words
- Ikumi Crocoll
- Jaena Rae Cabrera
- Jess Schomberg
- Ryan Randall
- Announcements
- Lead Pipe Publication Process
- Style Guide
Using a Proposed Library Guide Assessment Standards Rubric and a Peer Review Process to Pedagogically Improve Library Guides: A Case Study
Library guides can help librarians provide information to their patrons regarding their library resources, services, and tools. Despite their perceived usefulness, there is little discussion in designing library guides pedagogically by following a set of assessment standards for a quality-checked review. Instructional designers regularly use vetted assessment standards and a peer review process for building high-quality courses, yet librarians typically do not when designing library guides. This article explores using a set of standards remixed from SUNY’s Online Course Quality Review Rubric or OSCQR and a peer review process. The authors used a case study approach to test the effectiveness of building library guides with the proposed standards by tasking college students to assess two Fake News guides (one revised to meet the proposed standards). Results indicated most students preferred the revised library guide to the original guide for personal use. The majority valued the revised guide for integrating into a learning management system and perceived it to be more beneficial for professors to teach from. Future studies should replicate this study and include additional perspectives from faculty and how they perceive the pedagogical values of a library guide designed following the proposed rubric.
Image: “Helpful”. Digital image created with Midjourney AI. By Trina McCowan CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Introduction
Library guides or LibGuides are a proprietary publishing tool for libraries and museums created by the company Springshare; librarians can use LibGuides to publish on a variety of topics centered around research (Dotson, 2021; Springshare, n. d.). For consistency, the authors will use the term library guides moving forward. Librarians can use Springshare’s tool to publish web pages to educate users on library subjects, topics, procedures, or processes (Coombs, 2015). Additionally, librarians can work with teaching faculty to create course guides that compile resources for specific classes (Berić-Stojšić & Dubicki, 2016; Clever, 2020). According to Springshare (n. d.), library guides are widely used by academic, museum, school, and public libraries; approximately 130,000 libraries worldwide use this library tool (Springshare, n. d.). The library guides’ popularity and continued use may stem from their ease of use as it eliminates the need to know a coding language to develop online content. (Bergstrom-Lynch, 2019).
Baker (2014) described library guides as the “evolutionary descendants of library pathfinders” (p. 108). The first pathfinders were paper brochures that provided suggested resources for advanced research. Often, librarians created these tools for the advanced practitioner as patrons granted access to the library were researchers and seasoned scholars. As the end users were already experts, there was little need for librarians to provide instruction for using the resources (Emanuel, 2013). Later, programs such as MIT’s 1970s Project Intrex developed pathfinders that presented students with library resources in their fields of interest (Conrad & Stevens, 2019). As technology advanced, librarians created and curated pathfinders for online access (Emanuel, 2013).
Today, due to the modernization of pathfinders as library guides and their ease of discoverability, students and unaffiliated online users often find these guides without the assistance of a librarian (Emanuel, 2013). Search engines such as Google can extend a library guide’s reach far beyond a single institutional website, drawing the attention of information experts and novice internet users alike (Brewer et al., 2017; Emanuel, 2013; Lauseng et al., 2021). This expanded access means a librarian will not always be present to help interpret and explain the library guide’s learning objectives. Stone et al. (2018) state that library guides should be built using pedagogical principles “where the guide walks the student through the research process” (p. 280). Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) argues that there has been an abundant focus on user-centered library design studies but little focus on learning-centered design. Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) advocates for more attention directed to learning-centered design principles as library guides are integrated into Learning Management Systems (LMS) such as Canvas and Blackboard (Berić-Stojšić & Dubicki, 2016; Bielat et al., 2013; Lauseng et al., 2021) and can be presented as a learning module for the library (Emanuel, 2013; Mann et al., 2013). The use of library guides as online learning and teaching tools is not novel; however, their creation and evaluation using instructional design principles are a recent development (Bergstrom-Lynch, 2019).
A core component of an instructional designer’s job is to ensure that online course development meets the institution’s standards for quality assurance (Halupa, 2019). Instructional designers can aid with writing appropriate course and learning objectives and selecting learning activities and assessments that align back to the module’s objectives. Additionally, they can provide feedback on designing a course that is student-friendly—being mindful of cognitive overload, course layout, font options, and color selection. Additionally, instructional designers are trained in designing learning content that meets accessibility standards (Halupa, 2019).
Instructional design teams and teaching faculty can choose from a variety of quality assurance standards rubrics to reference to ensure that key elements for online learning are present in the online course environment. Examples of quality assurance tools include Quality Matters (QM) Higher Education Rubric and SUNY’s Online Course Quality Review Rubric or OSCQR, a professional development course refreshment process with a rubric (Kathuria & Becker, 2021; OSCQR-SUNY, n.d.). QM is a not-for-profit subscribing service that provides education on assessing online courses through the organization’s assessment rubric of general and specific standards (Unal & Unal, 2016). The assessment process is a “collegial, faculty-driven, research-based peer review process…” (Unal & Unal, 2016, p. 464). For a national review, QM suggests three reviewers certified and trained with QM to conduct a quality review. There should be a content specialist and one external reviewer outside of the university involved in the process (Pickens & Witte, 2015). Some universities, such as the University of North Florida, submit online courses for a QM certificate with High-Quality recognition or an in-house review based on the standards earning High-Quality designation. For an in-house review at UNF, a subject matter expert, instructional designer, and trained faculty reviewer assess the course to provide feedback based on the standards (CIRT, “Online Course Design Quality Review”, n. d.; Hulen, 2022). Instructional designers at some institutions may use other pedagogical rubrics that are freely available and not proprietary. OSCQR is an openly licensed online course review rubric that allows use and/or adaptation (OSCQR-SUNY, n. d.). SUNYY-OSCQR’s rubric is a tool that can be used as a professional development exercise when building and/or refreshing online courses (OSCQR-SUNY, n.d.).
Typically, library guides do not receive a vetted vigorous pedagogical peer review process like online courses. Because library guides are more accessible and are used as teaching tools, they should be crafted for a diverse audience and easy for first-time library guide users to understand and navigate (Bergstrom-Lynch, 2019; Smith et al., 2023). However, Conrad & Stevens (2019) state: “Inexperienced content creators can inadvertently develop guides that are difficult to use, lacking consistent templates and containing overwhelming amounts of information” (p. 49). Lee et al. (2021) reviewed library guides about the systematic review process. Although this topic is complex, Lee et al. (2021) noted that there was a lack of instruction about the systematic review process presented. If instructional opportunities are missing from the most complex topics, one may need to review all types of library guides with fresh eyes.
Moukhliss aims to describe a set of quality review standards, the Library Guide Assessment Standards (LGAS) rubric with annotations that she created based on the nature of library guides, and by remixing the SUNY-OSCQR rubric. Two trained reviewers are recommended to work with their peer review coordinator to individually engage in the review process and then convene to discuss the results. A standard will be marked Met when both of the reviewers mark it as Met, noting the evidence to support the Met designation. In order for a standard to be marked as Met, the library guide author should show evidence of 85% accuracy or higher per standard. To pass the quality-checked review to receive a quality-checked badge, the peer review team should note that 85% of the standards are marked as “Met.” If the review fails, the library guide author may continue to edit the guide or publish the guide without the quality-checked badge. Details regarding the peer review process are shared in the Library Guide Assessment Standards for Quality-Checked Review library guide. Select the Peer Review Training Materials tab for the training workbook and tutorial.
Situational Context
The University of North Florida (UNF) Thomas G. Carpenter Library services an R2 university of approximately 16,500 students. The UNF Center for Instruction and Research Technology (CIRT) supports two online learning librarians. The online librarians’ roles are to provide online instruction services to UNF faculty. CIRT staff advocate for online teaching faculty to submit their online courses to undergo a rigorous quality review process. Faculty can obtain a High-Quality designation for course design by working with an instructional designer and an appointed peer reviewer from UNF, or they may opt to aim for a High-Quality review after three years of course implementation by submitting for national review with Quality Matters (Hulen, 2022). Currently, Moukhliss serves as a peer reviewer for online High-Quality course reviews.
After several High-Quality course reviews, Moukhliss questioned why there are no current vetted review standards for the various types of library guides reviewed and completed by trained librarians as there are for online courses and thus borrowed from The SUNY Online Course Quality Review Rubric OSCQR to re-mix as the Library Guide Assessment Standards Rubric with annotations .
Literature Review
The amount of peer-reviewed literature on library guide design is shockingly small considering how many library guides have been created. The current research focus has been on usability and user experience studies, although some researchers have begun to focus on instructional design principles. As Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) states, peer-reviewed literature addressing library guide design through the lens of instructional design principles is at a stage of infancy. Researchers have primarily focused on collecting data on usage and usability (Conrad & Stevens, 2019; Oullette, 2011; Quintel, 2016). German (2017), an instructional design librarian, argues that when the library guide is created and maintained through a learner-centered point of view, librarians will see library guides as “e-learning tools” (p. 163). Lee et al. (2021) noted the value of integrating active learning activities into library guides. Stone et al. (2018) conducted a comparison study between two library guides, one library guide as-is and the other re-designed with pedagogical insight. Stone et al. (2018) concluded that “a pedagogical guide design, organizing resources around the information literacy research process and explaining the ‘why’ and ‘how of the process, leads to better student learning than the pathfinder design” (p. 290). A library guide representative of a pathfinder design lists resources rather than explaining them. Lee and Lowe (2018) conducted a similar study and noted more user interaction when viewing the pedagogically designed guide vs. the guide not designed with pedagogical principles. Hence Stone (2018) and Lee and Lowe (2018) discovered similar findings.
Authors like German (2017) and Lee et al. (2021) have touched upon instructional design topics. For example, Adebonojo (2010) described aligning the content of a subject library guide to library sources shared in course syllabi. Still, the author does not expand to discuss any other instructional design principles. Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) thinks more comprehensively, advocating for the use of the ADDIE instructional design model (an acronym for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation) when building library guides. The analysis phase encourages the designer to note problems with current instruction. The design phase entails how the designer will rectify the learning gap from the analysis phase. The development phase entails adding instructional materials, activities, and assessments. The implementation phase involves introducing the materials to learners. The evaluation phase enables the designer to collect feedback and improve content based on suggestions. ADDIE is cyclical and iterative (Bergstrom-Lynch, 2019). Allen (2017) introduces librarians to instructional design theories in the context of building an online information literacy asynchronous course but does not tie in using these theories for building library guides.
As Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) focused on best practices for library guide design based on ADDIE, German et al. (2017) used service design thinking constructs to build effective instruction guides. The five core principles of service design thinking are “user-centered, co-creative, sequencing, evidencing, and holistic” (German et al., 2017, p. 163). Focusing on the user encourages the designer to think like a student and ask: What do I need to know to successfully master this content? The co-creator stage invites other stakeholders to add their perspectives and/or expertise to the guide. The sequencing component invites the librarian to think through the role of the librarian and library services before, during, and after instruction. German et al. (2017) advocates for information from each stage to be communicated in the library guide. Evidencing involves the librarian reviewing the library guide to ensure that the content aligns with the learning objective (German et al., 2017). Both authors advocate for instructional design methods but fall short of suggesting an assessment rubric for designing and peer-reviewing guides.
Smith et al. (2023) developed a library guide rubric for their library guide redesign project at the Kelvin Smith Library at Case Western Reserve University. This rubric focused heavily on accessibility standards using the Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool or WAVE. Although Smith et al. (2023) discuss a rubric, the rubric was crafted as an evaluation tool for the author of the guide rather than for a peer review process.
Although Bergstrom-Lynch (2019), German et al. (2017), and Smith et al. (2023) are pioneering best practices for library guides, they take different approaches. For example, Bergstrom-Lynch (2019) presents best practices for cyclical re-evaluation of the guide based on instructional design principles and derives their best practices based on their usability studies. The Smith et al. (2023) rubric emphasizes accessibility standards for ADA compliance—essential for course designers but a component of a more comprehensive rubric. German et al. (2017) emphasizes a user-centered design through the design thinking method. Moukhliss intends to add to the literature by suggesting using a remix of a vetted tool that course developers use as a professional development exercise with faculty. This OSCQR-SUNY tool envelopes the varying perspectives of Bergstrom-Lynch (2019), Smith et al. (2023), and German et al. (2017).
Strengths & Weaknesses of the Library Guide
As with any tool, library guides have their strengths and weaknesses. Positives include indications that library guides can play a positive role in improving students’ grades, retention, and overall research skills (Brewer et al., 2017; May & Leighton, 2013; Wakeham et al., 2012). Additionally, library guides are easy to build and update (Baker, 2014; Conrad & Stevens, 2019). They can accommodate RSS feeds, videos, blogs, and chat (Baker, 2014), are accessible to the world, and cover a vast range of library research topics. According to Lauseng et al. (2021), library guides are discoverable through Googling and integrated into online Learning Management Systems (LMS). These factors support the view that library guides hold educational value and should be reconsidered for use as an Open Education Resource (Lauseng et al., 2021).
However, there are no perfect educational tools. Library guide weaknesses include their underutilization largely due to students not knowing what they are or how to find them (Bagshaw & Yorke-Barber, 2018; Conrad & Stevens, 2019; Ouellette, 2011). Additionally, library guides can be difficult for students to navigate, contain unnecessary content, and overuse library jargon (Sonsteby & DeJonghe, 2013). Conrad & Stevens (2019) described a usability study where the students were disoriented when using library guides and reported that they did not understand their purpose, function, or how to return to the library homepage. Lee et al. (2021) and Baker (2014) suggest that librarians tend to employ the “kitchen sink” (Baker, 2014, p. 110) approach to build library guides, thus overloading the guide with unapplicable content.
Critical Pedagogy and Library Guides
In his publication titled “The Philosophy of the Oppressed,” Paulo Freire introduced the theory of critical pedagogy and asserted that most educational models have the effect of reinforcing systems of societal injustice through the assumption that students are empty vessels who need to be filled with knowledge and skills curated by the intellectual elite (Kincheloe, 2012; Downey, 2016). Early in the 21 st century, information professionals built upon the belief that “Critical pedagogy is, in essence, a project that positions education as a catalyst for social justice” (Tewell, 2015, p. 26) by developing “critical information literacy” to address what some saw as the Association of College and Research Libraries’ technically sound, but socially unaware “Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education” (Cuevas-Cerveró et al., 2023). In subsequent years, numerous librarians and educators have written about the role of information literacy in dismantling systems of oppression, citing the need to promote “critical engagement with information sources” while recognizing that knowledge creation is a collaborative process in which everyone engages (Downey, 2016, p. 41).
The majority of scholarly output on library guides focus on user-centered design rather than specifically advocating for critical pedagogical methods. Yet there are a few scholars, such as Lechtenberg & Gold (2022), emphasizing how the lack of pedagogical training within LIS programs often results in information-centric library guides rather than learner-centric ones. Their presentation at LOEX 2022 reiterates the importance of user-centered design in all steps of guide creation, including deciding whether a library guide is needed.
Additionally, the literature demonstrates that library guides are useful tools in delivering critical information literacy instruction and interventions. For instance, Hare and Evanson used a library guide to list open-access sources as part of their Information Privilege Outreach programming for undergraduate students approaching graduation (Hare & Evanson, 2018). Likewise, Buck and Valentino required students in their “OER and Social Justice” course to create a library guide designed to educate faculty about the benefits of open educational resources, partly due to students’ familiarity with the design and functionality of similar research guides (Buck & Valentino, 2018). As tools that have been used to communicate the principles of critical pedagogy, the evaluation of institutional library guides should consider how effectively critical pedagogy is incorporated into their design.
The Library Guide Assessment Standards (LGAS) Rubric
For the remixed rubric, Moukhliss changed the term “course” from OSCQR’s original verbiage to “library guide,” and Moukhliss dropped some original standards based on the differences between the expectations for an online course (i.e., rubrics, syllabus, etc.) and a library guide. Likewise, several standards were added in response to the pros and cons of the library guides, as found in the literature. Additionally, Moukhliss wrote annotations to add clarity to each standard for the peer review process. For example, Standard 2 in the remixed LGAS rubric prompts the reviewer to see if the author defines the term library guide since research has indicated that students do not know what library guides are nor how to find them (Bagshaw & Yorke-Barber, 2018; Conrad & Stevens, 2019; Ouellette, 2011). Standard 7 suggests that the librarian provide links to the profiles of other librarian liaisons who may serve the audience using the library guide. Standard 9 prompts the reviewer to see if the library guide links to the library university’s homepage to clarify Conrad & Stevens’s (2019) conundrum that the library guide is not the library homepage. These additional standards were added to ensure that users are provided with adequate information about the nature of library guides, who publishes them, and how to locate additional guides to address the confusion that Conrad & Stevens (2019) noted in their library guide usability study. Additionally, these added standards may be helpful for those who discover library guides through a Google search.
Moukhliss intends to use the additional standards to provide context about the library guide to novice users, thus addressing the issue of information privilege or the assumption that everyone starts with the same background knowledge. Standard 22 was added to negate adding unnecessary resources to the guide, which Baker (2014) and Conrad & Stevens (2019) cited as a common problem. Standard 27 encourages the use of Creative Commons attribution, as suggested by Lauseng et al. (2021). They found that not only faculty, staff, and students at the University of Illinois Chicago were using their Evidence Based Medicine library guide, but also a wider audience. Recognizing its strong visibility and significant external usage, they considered it a potential candidate for an Open Educational Resource (OER). As library guides are often found without the help of the librarian, Standard 28 suggests that reviewers check that library guide authors provide steps for accessing research tools and databases suggested in the library guide outside of the context of the guide. Providing such information may help to negate Conrad & Stevens’s (2019) findings regarding students’ feelings of disorientation while using a library guide and difficulty navigating to the library homepage from the guide.
Standard 30 was added so that students have a dedicated Get Help tab explaining the variety of ways the user can contact their library and/or librarians for additional assistance. Standard 31 was re-written so that the user could check for their understanding in a way appropriate for the guide (Lee et al., 2021), such as a low-stakes quiz or poll. Finally, Standard 32 encourages the user to provide feedback regarding the guide’s usefulness, content, design, etc., with the understanding that learning objectives follow an iterative cycle and are not stagnant. Student feedback can help the authoring librarian update and maintain the guide’s relevancy to users and will give students the opportunity to become co-creators of the knowledge they consume.
UNF’s LGAS Rubric for Quality-Checked Review library guide includes an additional tab for a Quality-Checked badge (available on the Maintenance Checklist/Test Your Knowledge tab) and a suggested maintenance checklist (See Maintenance Checklist/ Test Your Knowledge tab) for monthly review, twice-a-year, and yearly reviews. Moukhliss borrowed and remixed the checklist from the Vanderbilt University Libraries (current as of 8/21/2023). The Peer Review Training Materials tab includes a training workbook and training video on the LGAS rubric, the annotations, and the peer review process. Moukhliss provides a Creative Commons license to the library guide to encourage other institutions to reuse and/or remix at the LGAS’s Start Here page .
Methodology, Theoretical Model, and Framework
Moukhliss and McCowan used the qualitative case study methodology. Gephart (2004) stated, “Qualitative research is multimethod research that uses an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. . . . Qualitative research emphasizes qualities of entities —the processes and meanings that occur naturally” (pp. 454-455). Moukhliss and McCowan selected the exploratory multi-case study so that they could assess multiple student user/learning perspectives when accessing, navigating, and digesting the two library guides.
The theoretical model used for this study is the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle. This quality improvement model has evolved with input from Walter Shewart and Dr. Edward Deming (Koehler & Pankowski, 1996). The cycle walks a team through four steps: Plan, Do, Check, and Act. The Plan phase allows time for one to think through problems such as the lack of design standards for library guides. During the “Do” phase, Moukhliss selected and made a remix of the quality review tool SUNY OSCQR. Additionally, she selected a “kitchen sink” (Baker, 2014, p. 10) library guide and redesigned it with the proposed rubric. Moukhliss’s aim was only to remove dead links and/or outdated information when restructuring the guide. The only items deemed outdated were the CRAAP test learning object and selected books from the curated e-book list. The CRAAP test was removed, and no substitution of similar materials was made. The list of selected books was updated in the revised guide to reflect current publications. As Moukhliss restructured the guide, she decided to use tabbed boxes to chunk and sequence information to appease Standards 11, 12, 13, and 15. You may view this restructuring by comparing the original Fake News guide and the revised Fake News guide . The “Do” phase includes Moukhliss recruiting participants to evaluate the two library guides — the original Fake News guide with the Fake News Guide 2 revised to follow the suggested standards and peer review process. Moukhliss and McCowan submitted the library guide study proposal to the Institutional Review Board in November 2023, and the study was marked Exempt. In December 2023, Moukhliss recruited participants by emailing faculty, distributing flyers in the library, posting flyers on display boards, and adding a digital flyer to each library floor’s lightboard display. The librarians added the incentive of 10-dollar Starbucks gift cards to the first 15 students who signed consent forms and successfully completed the 30-minute recorded Zoom session (or until saturation was reached).
Moukhliss interviewed one test pilot (P1) and ten students (P2-P11) for this study and she noted saturation after her seventh interview but continued to ten participants to increase certainty. Although some may view this as a low sample population, the data aligns with the peer-reviewed literature. Hennick & Kaiser (2019) discuss saturation in in-depth interviews and point to Guest et al.’s (2006) study. Guest et al. (2006) determined that after reviewing data from 60 interviews deemed in-depth, they determined that saturation presented itself between Interviews 7-12 “at which point 88% of all themes were developed and 97% of important (high frequency) themes were identified” (Hennick & Kaiser, 2019, para. 5). The Questionnaire framework for this study is centered around Bloom’s Taxonomy. This taxonomy provides a framework of action verbs that align with the hierarchical levels of learning. Bloom’s taxonomy includes verbiage for learning objectives that align with the level of the learning outcomes of remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create. McCowan incorporated various levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy as she built the UX script used for this study. Moukhliss interchanged Fake News and Fake News 2 as Guide A and Guide B throughout the interview sessions. After each recorded Zoom session, Moukhliss reviewed the session and recorded the task completion times on the script, recorded the data to the scorecard, and updated data into the qualitative software NVivo. Both script and scorecard are available on the Library Guide Study page . Moukhliss created a codebook with participant information, assigned code names for everyone, and stored the codebook to a password protected file of her work computer to keep identifiable information secure. Moukhliss used the code names Participant 1, Participant 2, Participant 3, etc. and removed all personal identifiers as she prepared to upload the study’s data to a qualitative software system. For coding, the authors chose the NVivo platform, a qualitative assessment tool that can organize data by type (correspondence, observation, and interviews), enable the researcher(s) to easily insert notes in each file, and develop codes to discover themes. Moukhliss coded the interviews based on the LGAS (i.e., Standard 1, 2, 3, etc.). Additional codes were added regarding navigation and content. Moukhliss & McCowan reviewed the codes for themes and preferences regarding library guide design.
The “Check” phase guided Moukhliss and McCowan in considering the implementation of the LGAS rubric and peer review process for library guides at UNF. During this phase, they reviewed participants’ qualitative responses to the Fake News library guide and the Fake News 2 library guide. Data from the “Check” phase will drive Moukhliss & McCowan to make recommendations in the “Act” phase (Koehler & Pankowski, 1996), which will be discussed in the Conclusion.
Interviewees
Moukhliss worked with one test pilot and interviewed ten students for this study. The ten students’ majors were representative of the following: Nursing, Computer Science, Communications, Public Administration, Electrical Engineering, Information Technology, Health Sciences, Philosophy, and Criminal Justice. Participants included two first-year students, two sophomores, three juniors, two seniors, and one graduate student. Eight participants used their desktops, whereas two completed the study on their phones. When evaluating the familiarity of users with library guides, one participant noted they had never used a library guide before, two others stated they rarely used them, and another two students stated that they occasionally used them. Finally, five students stated they did not know whether they had ever used one or not.
Findings & Discussion
Overall, students were faster at navigating the Fake News 2 Revised guide vs. the original guide except for listing the 5 Types of Fake News. This may be because the 5 Types of Fake News were listed on the original guide’s first page. The overall successful mean navigability for the original guide was 39 seconds, whereas the revised guide’s mean was 22.2 seconds for the successful completion of a task. Moukhliss noted a pattern of failed completion tasks often linked back to poorly labeled sections of the new and revised guides.
Although the content was identical in both guides except for the removal of outdated information, dead website links from the original guide, and the updated list of e-books to the revised guide, the students’ overall mean confidence level indicated 4.2 for the original guide’s information vs a 4.4 for the revised guide. The mean recommendation likelihood level for the original guide is 6.4, whereas the mean recommendation likelihood level of the revised guide increased to 7.9.
Regarding library guide personal preferences for a course reading, one student indicated they would want to work off the old guide, and 9 others indicated wanting to work from the revised guide for the following reasons:
- Organization and layout are more effective.
- Information is presented more clearly.
- There is a tab for dedicated UNF resources.
- Easier to navigate.
- Less jumbled
- Easier to follow when working with peers.
Regarding perceptions of which guide a professor may choose to teach with, three chose the original guide, whereas the other seven indicated the revised guide. One student stated that the old guide was more straightforward and that the instructor could explain the guide if they were using it during direct instruction. Preferences for the revised guide include:
- More “interactive-ness” and quizzes
- Summaries are present.
- Presentation of content is better.
- Locating information is easier.
- The guide doesn’t feel like “a massive run-on sentence.”
- Ease for “flipping through the topics.”
- Presence of library consult and contact information.
Although not part of the interview questions, Moukhliss was able to document that eight participants were not aware that a library guide could be embedded into a Canvas course, and one participant was aware. Moukhliss is unaware of the other participant’s experiences with an embedded library guide. Regarding preferences for embedding the library guide in Canvas, one student voted for the old guide whereas nine preferred the revised guide. Remarks for the revised guide include the inclusion of necessary Get Help information for struggling students and for the guide’s ease of navigation.
Although not every standard from the LGAS rubric was brought up in conversation throughout the student interviews, the LGAS that were seen as positive and appreciated by students to integrate into a guide’s design include the following Standards: 4, 7, 11, 12, 15, 21, 22, 28, 30, and standards 31. It was noted through action that two students navigated the revised guide by the hyperlinked learning objectives and not by side navigation (Standard 5), thus indicating that Standard 5 may hold value for those who maneuvered the guide through the stated objectives. Moukhliss noted during her observations that one limitation to hyperlinking the object to a specific library guide page is when that page includes a tabbed box. The library guide author is unable to directly link to a specific sub-tab from the box. Instead, the link defaults to the first page of the box’s information. Thus, students maneuvering the guide expected to find the listed objective on the first tab of the tabbed box, and they did not innately click through the sub-tabs to discover the listed objective.
Through observation, Moukhliss noted that six students struggled to understand how to initially navigate the library guides using the side navigation functionality, but after time with the guide and/or Moukhliss educating them on side navigation, they were successful. Moukhliss noted that for students who were comfortable with navigating a guide or after Moukhliss educated them on navigating the guide, students preferred the sub-tabbed boxes of the revised guide to the organization of the original guide. The students found neither library guide perfect, but Moukhliss & McCowan noted there was an overall theme that organization of information and proper sequencing and chunking of the information was perceived as important by the students. Three students commented on appreciating clarification for each part of the guide, which provides leverage for proposed Standard 28.
Additionally, two students appreciated the library guide author profile picture and contact information on each page and three students positively remarked on the presence of a Get Help tab on the revised guide. One participant stated that professors want students to have a point of contact with their library liaisons, and they do not like “anonymous pages” (referring to the original guide lacking an author profile). The final participant wanted to see more consult widgets listed throughout the library guide. Regarding the Fake News 2 Guide, two students preferred that more content information and less information about getting started be present on the first page of the guide. Furthermore, images and design mattered, as one student remarked that they did not like the Fake News 2 banner, and several others disliked the lack of imagery on the first page of the Fake News 2 guide. For both guides, students consistently remarked on liking the Fake News infographics.
Those supporting the old guide or parts of the original guide, three students liked the CRAAP Test worksheet and wanted to see it in the revised guide, not knowing that the worksheet was deemed dated by members of the instruction team and thus removed by Moukhliss for that reason. One student wanted to see the CRAAP test worksheet repurposed to be a flowchart regarding fake news. Moukhliss noted that most of the students perceived objects listed on the original guide and revised guide to be current, relevant, and vetted. Eight participants did not question their usefulness or relevancy or whether the library guide author was maintaining the guide. Only one student pointed out that the old guide had a list of outdated e-books and that the list was refreshed for the new guide. Thus, Moukhliss’s observations may reinforce to library guide authors that library guides should be reviewed and refreshed regularly as proposed by Standard 22 —⎯ as most students from this study appeared to take for face value that what is presented on the guide to be not only vetted but continuously maintained.
Initial data from this study indicate that using the LGAS rubric with annotations and a peer review process may improve the learning experience for students, especially in relation to being mindful of what information to include in a library guide, as well as the sequencing and chunking of the information. Early data indicates students appreciate a Get Help section and want to see Contact Us and library liaison/author information throughout the guide’s pages.
Because six students initially struggled with maneuvering through a guide, Moukhliss & McCowan suggest including instructions on how to navigate in either the library guide banner and/or a brief introductory video for the Start Here page or both locations. Here is a screenshot of sample banner instructions:
As stated, Moukhliss noted that most students were not aware of the presence of library guides in their Canvas courses. This may indicate that librarians should provide direct instruction during one-shots in not only what library guides are and how to maneuver them, but directly model how to access an embedded guide within Canvas.
Library guides have considerable pedagogical potential. However, there are no widely-used rubrics for evaluating whether a particular library guide has design features that support its intended learning outcomes. Based on this study, librarians who adopt or adapt the LGAS rubric will be more likely to design library guides that support students’ ability to complete relevant tasks. At UNF, Moukhliss and McCowan plan to suggest to administration to employ the LGAS rubric and annotations with a peer review process and to consider templatizing their institution’s (UNF) library guides to honor the proposed standard that was deemed most impactful by the student participants. This includes recommending to library administration to include a Get Started tab for guide template(s) and to include placeholders for introductory text, a library guide navigation video tutorial, visual navigational instructions embedded in the guide’s banner, and the inclusion of the guide’s learning objectives. Furthermore, they propose an institutionally vetted Get Help tab that can be mapped to each guide. Other proposals include templatizing each page to include the following: a page synopsis, applicable explanations for accessing library-specific resources and tools from the library’s homepage, placeholders for general contact information, a link to the library liaison directory, a placeholder for the author bio picture, feedback, assessment, and a research consultation link or widget as well as instructions for accessing the library’s homepage.
Following the creation of a standardized template, Moukhliss plans to propose to recruit a team of volunteer peer reviewers (library staff, librarians, library administration) and provide training on the LGAS rubric, the annotations, and the peer review process. She will recommend all library guide authors to train on the proposed LGAS rubric and the new library guide template for future library guide authorship projects and for updating and improving existing guides based on the standards. The training will cover the rubric, the annotations, and the maintenance calendar checklists for monthly, bi-annually, and yearly review. All proposed training materials are available at the LGAS’s Start Here page .
Moukhliss and McCowan encourage other college and university librarians to consider using or remixing the proposed LGAS rubric for a quality-checked review and to conduct studies on students’ perceptions of the rubric to add data to this research. The authors suggest future studies to survey both students and faculty on their perspectives on using a quality assurance rubric and peer review process to increase the pedagogical value of a library guide. Moukhliss & McCowan encourage future authors of studies to report on their successes and struggles for forming and training library colleagues on using a quality-checked rubric for library guide design and the peer review process.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express our gratitude to Kelly Lindberg and Ryan Randall, our peer reviewers. As well, we would like to thank the staff at In The Library with the Lead Pipe, including our publishing editor, Jaena Rae Cabrera.
Adebonojo, L. G. (2010). LibGuides: customizing subject guides for individual courses. College & Undergraduate Libraries , 17 (4), 398–412. https://doi.org/10.1080/10691316.2010.525426
Allen, M. (2017). Designing online asynchronous information literacy instruction using the ADDIE model. In T. Maddison & M. Kumaran (Eds.), Distributed learning pedagogy and technology in online information literacy instruction (pp.69-90). Chandos Publishing.
Bagshaw, A. & Yorke-Barber, P. (2018). Guiding librarians: Rethinking library guides as a staff development tool links to an external site. Journal of the Australian Library and Information Association , 67 (1), 31–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750158.2017.1410629
Baker, R. L. (2014). Designing LibGuides as instructional tools for critical thinking and effective online learning. Journal of Library and Information Services in Distance Learning , 8 (3–4), 107–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/1533290X.2014.944423
Bergstrom-Lynch. (2019). LibGuides by design: Using instructional design principles and user-centered studies to develop best practices. Public Services Quarterly , 15 (3), 205–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228959.2019.1632245
Berić-Stojšić, & Dubicki, E. (2016). Guiding students’ learning with LibGuides as an interactive teaching tool in health promotion. Pedagogy in Health Promotion , 2 (2), 144–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/2373379915625324
Bielat, V., Befus, R., & Arnold, J. (2013). Integrating LibGuides into the teaching-learning process. In A. Dobbs, R. L. Sittler, & D. Cook (Eds.). U sing LibGuides to enhance library services: A LITA guide (pp. 121-142). ALA TechSource.
Brewer, L., Rick, H., & Grondin, K. A. (2017). Improving digital libraries and support with online research guides. Online Learning Journal , 21 (3), 135-150. http://dx.doi.org/10.24059/olj.v21i3.1237
Buck, S., & Valentino, M. L. (2018). OER and social justice: A colloquium at Oregon State University. Journal of Librarianship and Scholarly Communication , 6 (2). https://doi.org/10.7710/2162-3309.2231
CIRT. (n. d.) Online Course Design Quality Review. https://www.unf.edu/cirt/id-Quality-Review.html
Clever, K. A. (2020). Connecting with faculty and students through course-related LibGuides. Pennsylvania Libraries , 8 (1), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.5195/palrap.2020.215
Conrad, S. & Stevens, C. (2019). “Am I on the library website?: A LibGuides usability study. Information Technology and Libraries , 38 (3), 49-81. https://doi.org/10.6017/ital.v38i3.10977
Coombs, B. (2015). LibGuides 2. Journal of the Medical Library Association , 103 (1), 64–65. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.103.1.020
Cuevas-Cerveró, A., Colmenero-Ruiz, M.-J., & Martínez-Ávila, D. (2023). Critical information literacy as a form of information activism. The Journal of Academic Librarianship , 49 (6), 102786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2023.102786
Dotson, D. S. (2021). LibGuides Gone Viral: A Giant LibGuides Project during Remote Working. Science & Technology Libraries (New York, N.Y.) , 40 (3), 243–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/0194262X.2021.1884169
Downey, A. (2016). Critical information literacy: Foundations, inspiration, and ideas . Library Juice Press.
Emanuel, J. (2013). A short history of LibraryGuides and their usefulness to librarians and patrons. In A. Dobbs, R. L. Sittler, & D. Cook (Eds.). Using LibGuides to enhance library services: A LITA guide (pp. 3-20). ALA TechSource.
Gephart, R. P., Jr. (2004). Qualitative research and academy of management journal. Academy of Management Journal , 47 (4), 452–462. https://doi.org/10.5465.amj.2004.14438580
German, E. (2017). Information literacy and instruction: LibGuides for instruction: A service design point of view from an academic library. Reference & User Services Quarterly , 56 (3), 162-167. https://doi.org/10.5860/rusq.56n3.162
German, E., Grassian, E., & LeMire, S. (2017). LibGuides for instruction: A service design point of view from an academic library. Reference and User Services Quarterly , 56(3), 162–167. https://doi.org/10.5860/rusq.56n3.162
Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods , 18, 59–82. doi:10.1177/1525822X05279903
Halupa, C. (2019). Differentiation of roles: Instructional designers and faculty in the creation of online courses . International Journal of Higher Education , 8 (1), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v8n1p55
Hare, S., & Evanson, C. (2018). Information privilege outreach for undergraduate students. College & Research Libraries , 79 (6), 726–736. https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.79.6.726
Hennink, M., & Kaiser, B., (2019). Saturation in qualitative research, In P. Atkinson, S. Delamont, A. Cernat, J.W. Sakshaug, & R.A. Williams (Eds.), SAGE Research Methods Foundations. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781526421036822322
Hulen, K. (2022). Quality assurance drives continuous improvements to online programs. In S. Kumar & P. Arnold (Eds.), Quality in online programs: Approaches and practices in higher education . (pp. 3-22). The Netherlands: Brill. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004510852_001
Kathuria, H., & Becker, D. W. (2021). Leveraging course quality checklist to improve online courses. Journal of Teaching and Learning with Technology, 10 (1) https://doi.org/10.14434/jotlt.v10i1.31253
Kincheloe, J. (2012). Critical pedagogy in the twenty-first century: Evolution for survival. Counterpoints , 422 , 147–183.
Koehler, J. W. & Pankowski, J. M. (1996). Continual improvement in government tools & methods. St. Lucie Press.
Lauseng, D. L., Howard, C., Scoulas, J. M., & Berry, A. (2021). Assessing online library guide use and Open Educational Resource (OER) potential: An evidence-based decision-making approach. Journal of Web Librarianship , 15 (3), 128–153. https://doi.org/10.1080/19322909.2021.1935396
Lechtenberg, U. & Gold, H. (2022). When all you have is a hammer, everything looks like a LibGuide: Strengths, limitations, and opportunities of the teaching tool [Conference presentation]. LOEX 2022 Conference, Ypsilanti, MI, United States. https://vimeo.com/721358576
Lee, Hayden, K. A., Ganshorn, H., & Pethrick, H. (2021). A content analysis of systematic review online library guides. Evidence Based Library and Information Practice , 16 (1), 60–77. https://doi.org/10.18438/eblip29819
Lee, Y. Y., & Lowe, M. S. (2018). Building positive learning experiences through pedagogical research guide design. Journal of Web Librarianship , 12 (4), 205-231. https://doi.org/10.1080/19322909.2018.1499453
Mann, B. J., Arnold, J. L., and Rawson, J. (2013). Using LibGuides to promote information literacy in a distance education environment. In A. Dobbs, R. L. Sittler, & D. Cook (Eds.). U sing LibGuides to enhance library services: A LITA guide (pp. 221-238). ALA TechSource.
May, D. & Leighton, H. V. (2013). Using a library-based course page to improve research skills in an undergraduate international business law course. Journal of Legal Studies Education , 30 (2), 295-319. doi: 10.11n/jlse.12003
OSCQR – Suny Online Course Quality Review Rubric (n. d.). About OSCQR . https://oscqr.suny.edu/
Ouellette, D. (2011). Subject guides in academic libraries: A user-centred study of uses and perceptions. Canadian Journal of Information and Library Science, 35 (4), 436–451.10.1353/ils.2011.0024
Pickens, & Witte, G. (2015). Circle the wagons & bust out the big guns! Tame the “Wild West” of distance librarianship using Quality Matters TM Benchmarks. Journal of Library & Information Services in Distance Learning , 9 (1-2), 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/1533290X.2014.946352
Quintel, D. F. (2016, January/February). LibGuides and usability: What our users want. Computers in Libraries Magazine , 36 (1), 4-8.
Smith, E. S., Koziura, A., Meinke, E., & Meszaros, E. (2023). Designing and implementing an instructional triptych for a digital future. The Journal of Academic Librarianship , 49 (2), 102672–106277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2023.102672
Sonsteby, A. & DeJonghe, J. (2013). Usability testing, user-centered design, and LibGuides subject guides: A case study. J ournal of Web Librarianship , 7 (1), 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/19322909.2013.747366
SpringShare (n. d.). LibGuides. https://springshare.com/libguides/
Stone, S. M., Sara Lowe, M., & Maxson, B. K. (2018). Does course guide design impact student learning? College & Undergraduate Libraries , 25 (3), 280-296. https://doi.org/10.1080/10691316.2018.1482808
Tewell, E. (2015). A decade of critical information literacy: A review of the literature . Comminfolit , 9 (1), 24-43. https://doi.org/10.15760/comminfolit.2015.9.1.174
Unal, Z. & Unal, A. (2016). Students Matter: Quality Measurements in Online Courses. International Journal on E-Learning, 15 (4), 463-481. Waynesville, NC USA: Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE). Retrieved September 21, 2023 from https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/147317/ .
Wakeham, M., Roberts, A., Shelley, J. & Wells, P. (2012). Library subject guides: A case study of evidence-informed library development. Journal of Librarianship and Information Science , 44 (3), 199-207. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961000611434757
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Weekend Edition Sunday
- Latest Show
Sunday Puzzle
- Corrections
Listen to the lead story from this episode.
Politics chat: How voters are responding to Trump's felony conviction
by Ayesha Rascoe , Mara Liasson
The Americas
Mexico votes for a new president after a campaigning season plagued by violence.
by Eyder Peralta , Ayesha Rascoe
Middle East
Aid workers in gaza say nowhere is safe after israeli attacks on 'humanitarian zones'.
by Hadeel Al-Shalchi
Girls in the U.S. are getting their period earlier. Here's what parents should know
by Ayesha Rascoe , Maria Godoy
Bookstores have come under attack in Ukraine. But interest in reading is only growing
by Joanna Kakissis
25 years ago, Napster changed how we listen to music forever
by Ayesha Rascoe
What locals think of the proposal to build U.S.'s tallest building in Oklahoma City
by Graycen Wheeler

Sunday Puzzle NPR hide caption
Sunday Puzzle: Second in Line
by Will Shortz
Movie Interviews
A new animated film follows a lonely dog and his robot friend in new york city.
by Ayesha Rascoe , Matthew Schuerman , Andrew Craig
Conservative media sows doubt about the verdict in Trump's felony convictions
by Ayesha Rascoe , David Folkenflik
Supreme Court judge accused of bias towards Trump declines to recuse himself from case
by Ayesha Rascoe , Matthew Schuerman , Hiba Ahmad
Some states are adopting a new form of reading instruction to combat falling scores
by Juma Sei
A new movie tells the story of Kemba Smith Pradia, race and incarceration
Strange news, meet abby lampe, two-time champion of the cheese-wheel-chasing race, meet abby lampe, two-time champion of the chees-wheel-chasing race, 100 years ago, indigenous people were granted u.s. citizenship by law.
by Sandhya Dirks
The first professional women's hockey league in the U.S. has a winner
Music interviews, jon lampley, a veteran of stephen colbert's talk show, releases his debut album.
by D. Parvaz , Ayesha Rascoe , Ryan Benk
Searching for a song you heard between stories? We've retired music buttons on these pages. Learn more here.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The CARE guidelines for case reports help authors reduce risk of bias, increase transparency, and provide early signals of what works, for which patients, and under which circumstances. Case reports following the CARE guidelines support the measurement of (1) clinician- and patient-assessed outcomes, (2) effectiveness of Clinical Practice ...
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words. Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a real-life phenomenon or situation. Learn how to write a case study for your social sciences research assignments with this helpful guide from USC Library. Find out how to define the case, select the data sources, analyze the evidence, and report the results.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
5 Steps to Write a Case Study. 1. Identifying the Subject or Case. Choose a subject that aligns with your objectives and offers valuable insights. Ensure the subject has a clear narrative and relevance to your audience. The subject should illustrate key points and provide substantial learning opportunities.
The Case Study Handbook: A Student's Guide. Revised Edition. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Publishing, 2018; Christoph Rasche and Achim Seisreiner. ... Case study can represent an open-ended subject of inquiry; a case analysis is a narrative about something that has happened in the past. A case study is not restricted by time and can ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study analysis requires you to investigate a business problem, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidence. Preparing the Case. Before you begin writing, follow these guidelines to help you prepare and understand the case study: Read and Examine the Case Thoroughly
It is best to simply tell the story and let the outcome speak for itself. With these points in mind, let's begin the process of writing the case study: Title page: Title: The title page will contain the full title of the article. Remember that many people may find our article by searching on the internet.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
Designing and Conducting Case Studies. This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of ...
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. This case study example illustrates the benefits Thomson Reuters experienced ...
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
Case report can be classified as a single case report, two case reports or case series, which aggregate more than two cases in a report. Case reports are usually retrospective by nature, however, it can be prospectively designed, for example, applying a new diagnostic or management approach or guideline of a particular health condition to ...
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine. Some reports contain an extensive review of the relevant ...
Discuss the limitations of your study and propose avenues for future research. 8. Review and revise. The process of writing a case study doesn't actually end when the report is written; you also need to review your writing for coherence, clarity, and correctness. Don't underestimate the importance of this step!
6. Make it scannable. Some people will take the time to read your case study front to back and absorb every detail. Some won't give it more than a single glance. And sometimes, that person is the decision-maker. Make the most important results easy to spot, read, and retain at a glance.
This guide explains how to write a descriptive case study. A descriptive case study describes how an organization handled a specific issue. Case studies can vary in length and the amount of details provided. They can be fictional or based on true events. Why should you write one? Case studies can help others (e.g., students, other organizations,
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
This guide explains how to write a descriptive case study. A descriptive case study describes how an organization handled a specific issue. Case studies can vary in length and the amount of details provided. They can be fictional or based on true events. Why should you write one? Case studies can help others (e.g., students, other organizations ...
Evidence-based case study guidelines. The clinical case study may be defined as a detailed analysis of the therapy conducted with a couple or family that will be instructive, may be exemplary or cautionary, and stresses factors contributing to either success or failure of the treatment. Because evidence-based clinical case studies can be ...
60. SHARES. Google published a case study that shows how using structured data and following best practices improved discoverability and brought more search traffic. The case study was about the ...
The authors used a case study approach to test the effectiveness of building library guides with the proposed standards by tasking college students to assess two Fake News guides (one revised to meet the proposed standards). Results indicated most students preferred the revised library guide to the original guide for personal use.
Check the current status of services and components for Cisco's cloud-based Webex, Security and IoT offerings. Cisco Support Assistant. The Cisco Support Assistant (formerly TAC Connect Bot) provides a self-service experience for common case inquiries and basic transactions without waiting in a queue.
Medications ». Four medications received a conditional recommendation for use in the treatment of PTSD: sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine and venlafaxine. This website is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not render individual professional advice or endorse any particular treatment for any individuals.
Dive into this guide to discover how to market effectively on TikTok and achieve big results. Why Marketing on TikTok is a Game-Changer. In today's digital landscape, standing out is more challenging than ever. TikTok's unique format and vast user base provide a fresh and engaging way to reach potential customers. ... Case Study: Goodcall's ...
Exploring the carbon balance pattern from the perspective of urban spatial development pattern is an effective way to solve the urban carbon emissions reduction problem, promote high-quality economic development, and synergize the development of the regional "nature-economy" dual system. Taking 105 counties (districts) in Anhui Province as an example, based on the calculation of regional ...
Jon Lampley, a veteran of Stephen Colbert's talk show, releases his debut album. by D. Parvaz, Ayesha Rascoe, Ryan Benk. 7 min. Searching for a song you heard between stories?
Third-party scientific tests and studies; Case studies, testimonials, and reviews; Influencer or celebrity endorsements; Endorsements from trusted advisors; Hiya Health, for example, has an endorsement from a pediatric specialist for its vitamin gummies that are marketed at children. People are more likely to trust that the gummies are, in fact ...