

Case Examples
Examples of recommended interventions in the treatment of depression across the lifespan.

Children/Adolescents
A 15-year-old Puerto Rican female
The adolescent was previously diagnosed with major depressive disorder and treated intermittently with supportive psychotherapy and antidepressants. Her more recent episodes related to her parents’ marital problems and her academic/social difficulties at school. She was treated using cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
Chafey, M.I.J., Bernal, G., & Rossello, J. (2009). Clinical Case Study: CBT for Depression in A Puerto Rican Adolescent. Challenges and Variability in Treatment Response. Depression and Anxiety , 26, 98-103. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20457
Sam, a 15-year-old adolescent
Sam was team captain of his soccer team, but an unexpected fight with another teammate prompted his parents to meet with a clinical psychologist. Sam was diagnosed with major depressive disorder after showing an increase in symptoms over the previous three months. Several recent challenges in his family and romantic life led the therapist to recommend interpersonal psychotherapy for adolescents (IPT-A).
Hall, E.B., & Mufson, L. (2009). Interpersonal Psychotherapy for Depressed Adolescents (IPT-A): A Case Illustration. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 38 (4), 582-593. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374410902976338
© Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (Div. 53) APA, https://sccap53.org/, reprinted by permission of Taylor & Francis Ltd, http://www.tandfonline.com on behalf of the Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (Div. 53) APA.
General Adults
Mark, a 43-year-old male
Mark had a history of depression and sought treatment after his second marriage ended. His depression was characterized as being “controlled by a pattern of interpersonal avoidance.” The behavior/activation therapist asked Mark to complete an activity record to help steer the treatment sessions.
Dimidjian, S., Martell, C.R., Addis, M.E., & Herman-Dunn, R. (2008). Chapter 8: Behavioral activation for depression. In D.H. Barlow (Ed.) Clinical handbook of psychological disorders: A step-by-step treatment manual (4th ed., pp. 343-362). New York: Guilford Press.
Reprinted with permission from Guilford Press.
Denise, a 59-year-old widow
Denise is described as having “nonchronic depression” which appeared most recently at the onset of her husband’s diagnosis with brain cancer. Her symptoms were loneliness, difficulty coping with daily life, and sadness. Treatment included filling out a weekly activity log and identifying/reconstructing automatic thoughts.
Young, J.E., Rygh, J.L., Weinberger, A.D., & Beck, A.T. (2008). Chapter 6: Cognitive therapy for depression. In D.H. Barlow (Ed.) Clinical handbook of psychological disorders: A step-by-step treatment manual (4th ed., pp. 278-287). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Nancy, a 25-year-old single, white female
Nancy described herself as being “trapped by her relationships.” Her intake interview confirmed symptoms of major depressive disorder and the clinician recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Persons, J.B., Davidson, J. & Tompkins, M.A. (2001). A Case Example: Nancy. In Essential Components of Cognitive-Behavior Therapy For Depression (pp. 205-242). Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/10389-007
While APA owns the rights to this text, some exhibits are property of the San Francisco Bay Area Center for Cognitive Therapy, which has granted the APA permission for use.
Luke, a 34-year-old male graduate student
Luke is described as having treatment-resistant depression and while not suicidal, hoped that a fatal illness would take his life or that he would just disappear. His treatment involved mindfulness-based cognitive therapy, which helps participants become aware of and recharacterize their overwhelming negative thoughts. It involves regular practice of mindfulness techniques and exercises as one component of therapy.
Sipe, W.E.B., & Eisendrath, S.J. (2014). Chapter 3 — Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For Treatment-Resistant Depression. In R.A. Baer (Ed.), Mindfulness-Based Treatment Approaches (2nd ed., pp. 66-70). San Diego: Academic Press.
Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.
Sara, a 35-year-old married female
Sara was referred to treatment after having a stillbirth. Sara showed symptoms of grief, or complicated bereavement, and was diagnosed with major depression, recurrent. The clinician recommended interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a duration of 12 weeks.
Bleiberg, K.L., & Markowitz, J.C. (2008). Chapter 7: Interpersonal psychotherapy for depression. In D.H. Barlow (Ed.) Clinical handbook of psychological disorders: a treatment manual (4th ed., pp. 315-323). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Peggy, a 52-year-old white, Italian-American widow
Peggy had a history of chronic depression, which flared during her husband’s illness and ultimate death. Guilt was a driving factor of her depressive symptoms, which lasted six months after his death. The clinician treated Peggy with psychodynamic therapy over a period of two years.
Bishop, J., & Lane , R.C. (2003). Psychodynamic Treatment of a Case of Grief Superimposed On Melancholia. Clinical Case Studies , 2(1), 3-19. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534650102239085
Several case examples of supportive therapy
Winston, A., Rosenthal, R.N., & Pinsker, H. (2004). Introduction to Supportive Psychotherapy . Arlington, VA : American Psychiatric Publishing.
Older Adults
Several case examples of interpersonal psychotherapy & pharmacotherapy
Miller, M. D., Wolfson, L., Frank, E., Cornes, C., Silberman, R., Ehrenpreis, L.…Reynolds, C. F., III. (1998). Using Interpersonal Psychotherapy (IPT) in a Combined Psychotherapy/Medication Research Protocol with Depressed Elders: A Descriptive Report With Case Vignettes. Journal of Psychotherapy Practice and Research , 7(1), 47-55.
15 Famous Experiments and Case Studies in Psychology

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Psychology has seen thousands upon thousands of research studies over the years. Most of these studies have helped shape our current understanding of human thoughts, behavior, and feelings.
The psychology case studies in this list are considered classic examples of psychological case studies and experiments, which are still being taught in introductory psychology courses up to this day.
Some studies, however, were downright shocking and controversial that you’d probably wonder why such studies were conducted back in the day. Imagine participating in an experiment for a small reward or extra class credit, only to be left scarred for life. These kinds of studies, however, paved the way for a more ethical approach to studying psychology and implementation of research standards such as the use of debriefing in psychology research .
Case Study vs. Experiment
Before we dive into the list of the most famous studies in psychology, let us first review the difference between case studies and experiments.
- It is an in-depth study and analysis of an individual, group, community, or phenomenon. The results of a case study cannot be applied to the whole population, but they can provide insights for further studies.
- It often uses qualitative research methods such as observations, surveys, and interviews.
- It is often conducted in real-life settings rather than in controlled environments.
- An experiment is a type of study done on a sample or group of random participants, the results of which can be generalized to the whole population.
- It often uses quantitative research methods that rely on numbers and statistics.
- It is conducted in controlled environments, wherein some things or situations are manipulated.
See Also: Experimental vs Observational Studies
Famous Experiments in Psychology
1. the marshmallow experiment.
Psychologist Walter Mischel conducted the marshmallow experiment at Stanford University in the 1960s to early 1970s. It was a simple test that aimed to define the connection between delayed gratification and success in life.
The instructions were fairly straightforward: children ages 4-6 were presented a piece of marshmallow on a table and they were told that they would receive a second piece if they could wait for 15 minutes without eating the first marshmallow.
About one-third of the 600 participants succeeded in delaying gratification to receive the second marshmallow. Mischel and his team followed up on these participants in the 1990s, learning that those who had the willpower to wait for a larger reward experienced more success in life in terms of SAT scores and other metrics.
This case study also supported self-control theory , a theory in criminology that holds that people with greater self-control are less likely to end up in trouble with the law!
The classic marshmallow experiment, however, was debunked in a 2018 replication study done by Tyler Watts and colleagues.
This more recent experiment had a larger group of participants (900) and a better representation of the general population when it comes to race and ethnicity. In this study, the researchers found out that the ability to wait for a second marshmallow does not depend on willpower alone but more so on the economic background and social status of the participants.
2. The Bystander Effect
In 1694, Kitty Genovese was murdered in the neighborhood of Kew Gardens, New York. It was told that there were up to 38 witnesses and onlookers in the vicinity of the crime scene, but nobody did anything to stop the murder or call for help.
Such tragedy was the catalyst that inspired social psychologists Bibb Latane and John Darley to formulate the phenomenon called bystander effect or bystander apathy .
Subsequent investigations showed that this story was exaggerated and inaccurate, as there were actually only about a dozen witnesses, at least two of whom called the police. But the case of Kitty Genovese led to various studies that aim to shed light on the bystander phenomenon.
Latane and Darley tested bystander intervention in an experimental study . Participants were asked to answer a questionnaire inside a room, and they would either be alone or with two other participants (who were actually actors or confederates in the study). Smoke would then come out from under the door. The reaction time of participants was tested — how long would it take them to report the smoke to the authorities or the experimenters?
The results showed that participants who were alone in the room reported the smoke faster than participants who were with two passive others. The study suggests that the more onlookers are present in an emergency situation, the less likely someone would step up to help, a social phenomenon now popularly called the bystander effect.
3. Asch Conformity Study
Have you ever made a decision against your better judgment just to fit in with your friends or family? The Asch Conformity Studies will help you understand this kind of situation better.
In this experiment, a group of participants were shown three numbered lines of different lengths and asked to identify the longest of them all. However, only one true participant was present in every group and the rest were actors, most of whom told the wrong answer.
Results showed that the participants went for the wrong answer, even though they knew which line was the longest one in the first place. When the participants were asked why they identified the wrong one, they said that they didn’t want to be branded as strange or peculiar.
This study goes to show that there are situations in life when people prefer fitting in than being right. It also tells that there is power in numbers — a group’s decision can overwhelm a person and make them doubt their judgment.
4. The Bobo Doll Experiment
The Bobo Doll Experiment was conducted by Dr. Albert Bandura, the proponent of social learning theory .
Back in the 1960s, the Nature vs. Nurture debate was a popular topic among psychologists. Bandura contributed to this discussion by proposing that human behavior is mostly influenced by environmental rather than genetic factors.
In the Bobo Doll Experiment, children were divided into three groups: one group was shown a video in which an adult acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll, the second group was shown a video in which an adult play with the Bobo Doll, and the third group served as the control group where no video was shown.
The children were then led to a room with different kinds of toys, including the Bobo Doll they’ve seen in the video. Results showed that children tend to imitate the adults in the video. Those who were presented the aggressive model acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll while those who were presented the passive model showed less aggression.
While the Bobo Doll Experiment can no longer be replicated because of ethical concerns, it has laid out the foundations of social learning theory and helped us understand the degree of influence adult behavior has on children.
5. Blue Eye / Brown Eye Experiment
Following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, third-grade teacher Jane Elliott conducted an experiment in her class. Although not a formal experiment in controlled settings, A Class Divided is a good example of a social experiment to help children understand the concept of racism and discrimination.
The class was divided into two groups: blue-eyed children and brown-eyed children. For one day, Elliott gave preferential treatment to her blue-eyed students, giving them more attention and pampering them with rewards. The next day, it was the brown-eyed students’ turn to receive extra favors and privileges.
As a result, whichever group of students was given preferential treatment performed exceptionally well in class, had higher quiz scores, and recited more frequently; students who were discriminated against felt humiliated, answered poorly in tests, and became uncertain with their answers in class.
This study is now widely taught in sociocultural psychology classes.
6. Stanford Prison Experiment
One of the most controversial and widely-cited studies in psychology is the Stanford Prison Experiment , conducted by Philip Zimbardo at the basement of the Stanford psychology building in 1971. The hypothesis was that abusive behavior in prisons is influenced by the personality traits of the prisoners and prison guards.
The participants in the experiment were college students who were randomly assigned as either a prisoner or a prison guard. The prison guards were then told to run the simulated prison for two weeks. However, the experiment had to be stopped in just 6 days.
The prison guards abused their authority and harassed the prisoners through verbal and physical means. The prisoners, on the other hand, showed submissive behavior. Zimbardo decided to stop the experiment because the prisoners were showing signs of emotional and physical breakdown.
Although the experiment wasn’t completed, the results strongly showed that people can easily get into a social role when others expect them to, especially when it’s highly stereotyped .
7. The Halo Effect
Have you ever wondered why toothpastes and other dental products are endorsed in advertisements by celebrities more often than dentists? The Halo Effect is one of the reasons!
The Halo Effect shows how one favorable attribute of a person can gain them positive perceptions in other attributes. In the case of product advertisements, attractive celebrities are also perceived as intelligent and knowledgeable of a certain subject matter even though they’re not technically experts.
The Halo Effect originated in a classic study done by Edward Thorndike in the early 1900s. He asked military commanding officers to rate their subordinates based on different qualities, such as physical appearance, leadership, dependability, and intelligence.
The results showed that high ratings of a particular quality influences the ratings of other qualities, producing a halo effect of overall high ratings. The opposite also applied, which means that a negative rating in one quality also correlated to negative ratings in other qualities.
Experiments on the Halo Effect came in various formats as well, supporting Thorndike’s original theory. This phenomenon suggests that our perception of other people’s overall personality is hugely influenced by a quality that we focus on.
8. Cognitive Dissonance
There are experiences in our lives when our beliefs and behaviors do not align with each other and we try to justify them in our minds. This is cognitive dissonance , which was studied in an experiment by Leon Festinger and James Carlsmith back in 1959.
In this experiment, participants had to go through a series of boring and repetitive tasks, such as spending an hour turning pegs in a wooden knob. After completing the tasks, they were then paid either $1 or $20 to tell the next participants that the tasks were extremely fun and enjoyable. Afterwards, participants were asked to rate the experiment. Those who were given $1 rated the experiment as more interesting and fun than those who received $20.
The results showed that those who received a smaller incentive to lie experienced cognitive dissonance — $1 wasn’t enough incentive for that one hour of painstakingly boring activity, so the participants had to justify that they had fun anyway.
Famous Case Studies in Psychology
9. little albert.
In 1920, behaviourist theorists John Watson and Rosalie Rayner experimented on a 9-month-old baby to test the effects of classical conditioning in instilling fear in humans.
This was such a controversial study that it gained popularity in psychology textbooks and syllabi because it is a classic example of unethical research studies done in the name of science.
In one of the experiments, Little Albert was presented with a harmless stimulus or object, a white rat, which he wasn’t scared of at first. But every time Little Albert would see the white rat, the researchers would play a scary sound of hammer and steel. After about 6 pairings, Little Albert learned to fear the rat even without the scary sound.
Little Albert developed signs of fear to different objects presented to him through classical conditioning . He even generalized his fear to other stimuli not present in the course of the experiment.
10. Phineas Gage
Phineas Gage is such a celebrity in Psych 101 classes, even though the way he rose to popularity began with a tragic accident. He was a resident of Central Vermont and worked in the construction of a new railway line in the mid-1800s. One day, an explosive went off prematurely, sending a tamping iron straight into his face and through his brain.
Gage survived the accident, fortunately, something that is considered a feat even up to this day. He managed to find a job as a stagecoach after the accident. However, his family and friends reported that his personality changed so much that “he was no longer Gage” (Harlow, 1868).
New evidence on the case of Phineas Gage has since come to light, thanks to modern scientific studies and medical tests. However, there are still plenty of mysteries revolving around his brain damage and subsequent recovery.
11. Anna O.
Anna O., a social worker and feminist of German Jewish descent, was one of the first patients to receive psychoanalytic treatment.
Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim and she inspired much of Sigmund Freud’s works and books on psychoanalytic theory, although they hadn’t met in person. Their connection was through Joseph Breuer, Freud’s mentor when he was still starting his clinical practice.
Anna O. suffered from paralysis, personality changes, hallucinations, and rambling speech, but her doctors could not find the cause. Joseph Breuer was then called to her house for intervention and he performed psychoanalysis, also called the “talking cure”, on her.
Breuer would tell Anna O. to say anything that came to her mind, such as her thoughts, feelings, and childhood experiences. It was noted that her symptoms subsided by talking things out.
However, Breuer later referred Anna O. to the Bellevue Sanatorium, where she recovered and set out to be a renowned writer and advocate of women and children.
12. Patient HM
H.M., or Henry Gustav Molaison, was a severe amnesiac who had been the subject of countless psychological and neurological studies.
Henry was 27 when he underwent brain surgery to cure the epilepsy that he had been experiencing since childhood. In an unfortunate turn of events, he lost his memory because of the surgery and his brain also became unable to store long-term memories.
He was then regarded as someone living solely in the present, forgetting an experience as soon as it happened and only remembering bits and pieces of his past. Over the years, his amnesia and the structure of his brain had helped neuropsychologists learn more about cognitive functions .
Suzanne Corkin, a researcher, writer, and good friend of H.M., recently published a book about his life. Entitled Permanent Present Tense , this book is both a memoir and a case study following the struggles and joys of Henry Gustav Molaison.
13. Chris Sizemore
Chris Sizemore gained celebrity status in the psychology community when she was diagnosed with multiple personality disorder, now known as dissociative identity disorder.
Sizemore has several alter egos, which included Eve Black, Eve White, and Jane. Various papers about her stated that these alter egos were formed as a coping mechanism against the traumatic experiences she underwent in her childhood.
Sizemore said that although she has succeeded in unifying her alter egos into one dominant personality, there were periods in the past experienced by only one of her alter egos. For example, her husband married her Eve White alter ego and not her.
Her story inspired her psychiatrists to write a book about her, entitled The Three Faces of Eve , which was then turned into a 1957 movie of the same title.
14. David Reimer
When David was just 8 months old, he lost his penis because of a botched circumcision operation.
Psychologist John Money then advised Reimer’s parents to raise him as a girl instead, naming him Brenda. His gender reassignment was supported by subsequent surgery and hormonal therapy.
Money described Reimer’s gender reassignment as a success, but problems started to arise as Reimer was growing up. His boyishness was not completely subdued by the hormonal therapy. When he was 14 years old, he learned about the secrets of his past and he underwent gender reassignment to become male again.
Reimer became an advocate for children undergoing the same difficult situation he had been. His life story ended when he was 38 as he took his own life.
15. Kim Peek
Kim Peek was the inspiration behind Rain Man , an Oscar-winning movie about an autistic savant character played by Dustin Hoffman.
The movie was released in 1988, a time when autism wasn’t widely known and acknowledged yet. So it was an eye-opener for many people who watched the film.
In reality, Kim Peek was a non-autistic savant. He was exceptionally intelligent despite the brain abnormalities he was born with. He was like a walking encyclopedia, knowledgeable about travel routes, US zip codes, historical facts, and classical music. He also read and memorized approximately 12,000 books in his lifetime.
This list of experiments and case studies in psychology is just the tip of the iceberg! There are still countless interesting psychology studies that you can explore if you want to learn more about human behavior and dynamics.
You can also conduct your own mini-experiment or participate in a study conducted in your school or neighborhood. Just remember that there are ethical standards to follow so as not to repeat the lasting physical and emotional harm done to Little Albert or the Stanford Prison Experiment participants.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 70 (9), 1–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0093718
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63 (3), 575–582. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0045925
Elliott, J., Yale University., WGBH (Television station : Boston, Mass.), & PBS DVD (Firm). (2003). A class divided. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Films.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58 (2), 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0041593
Haney, C., Banks, W. C., & Zimbardo, P. G. (1973). A study of prisoners and guards in a simulated prison. Naval Research Review , 30 , 4-17.
Latane, B., & Darley, J. M. (1968). Group inhibition of bystander intervention in emergencies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 10 (3), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0026570
Mischel, W. (2014). The Marshmallow Test: Mastering self-control. Little, Brown and Co.
Thorndike, E. (1920) A Constant Error in Psychological Ratings. Journal of Applied Psychology , 4 , 25-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0071663
Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of experimental psychology , 3 (1), 1.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
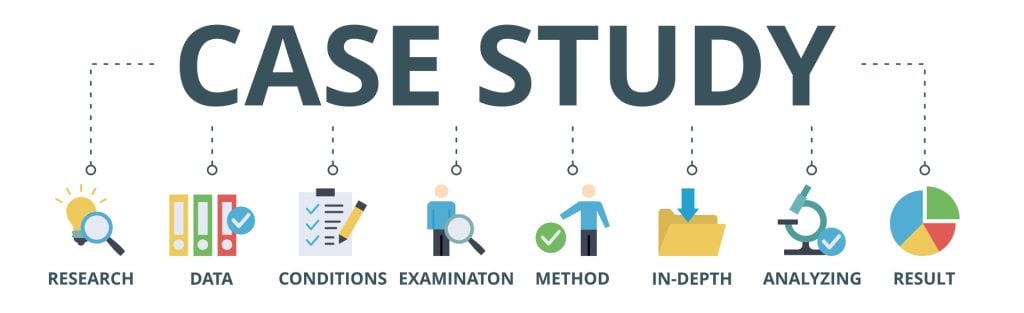
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Discourse Analysis

Phenomenology In Qualitative Research

Ethnography In Qualitative Research

Narrative Analysis In Qualitative Research
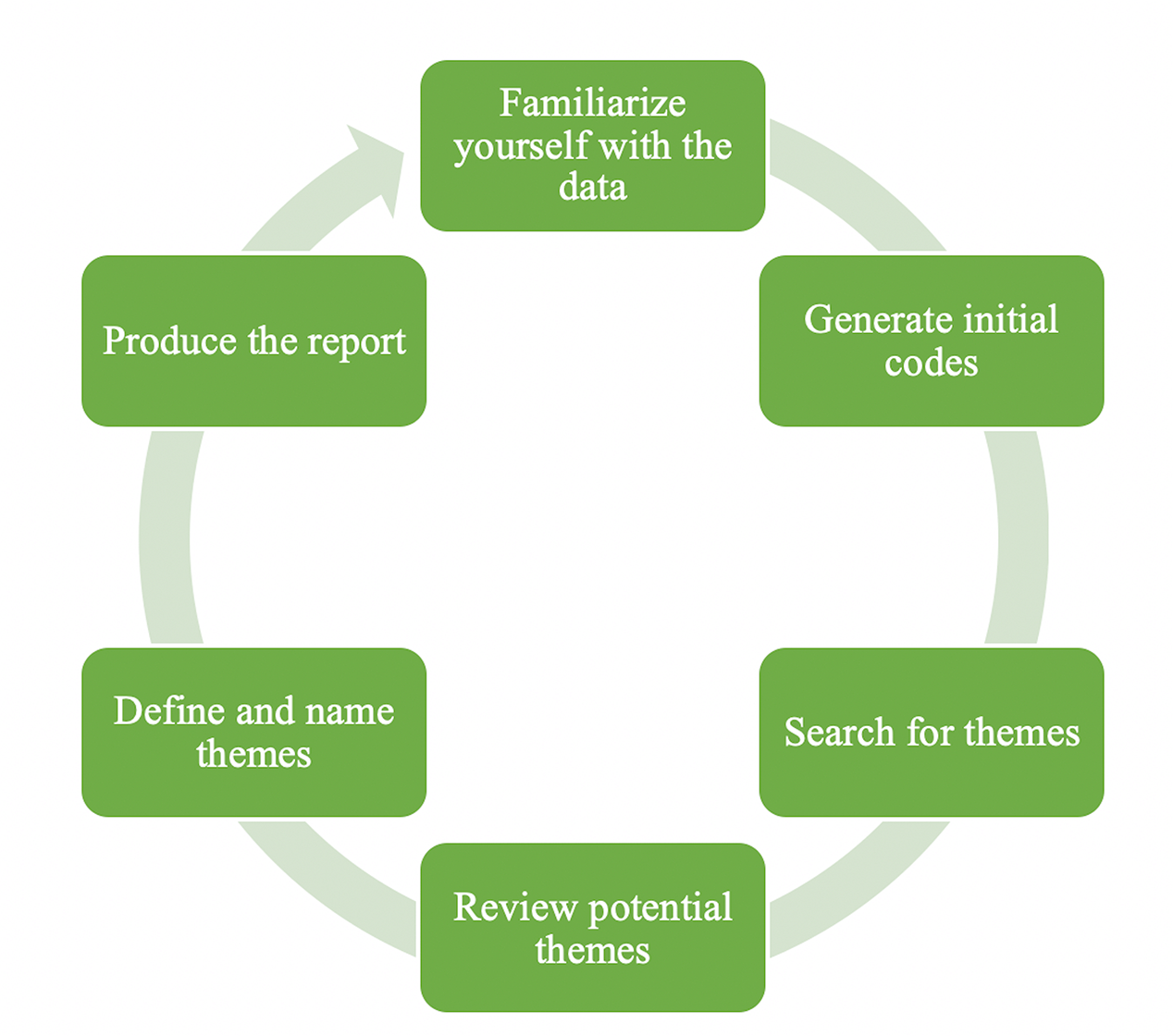
Thematic Analysis: A Step by Step Guide
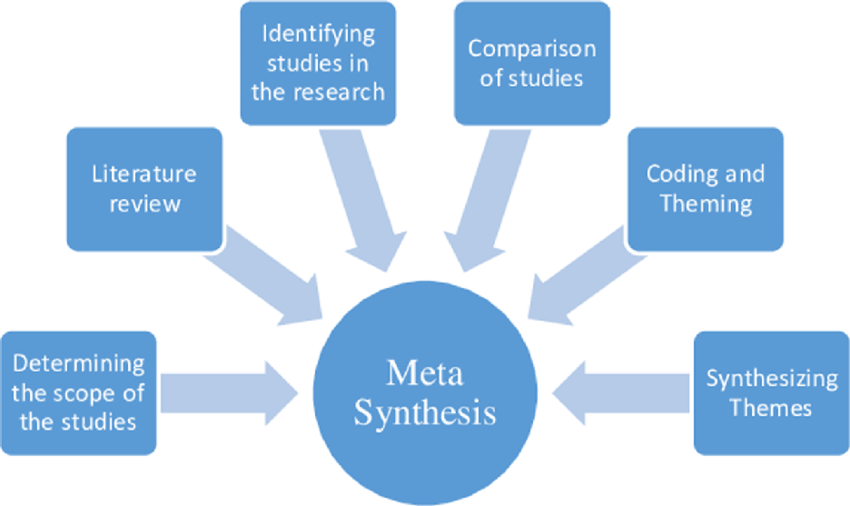
Metasynthesis Of Qualitative Research
How to Write a Case Conceptualization: 10 Examples (+ PDF)

Such understanding can be developed by reading relevant records, meeting with clients face to face, and using assessments such as a mental status examination.
As you proceed, you are forming a guiding concept of who this client is, how they became who they are, and where their personal journey might be heading.
Such a guiding concept, which will shape any needed interventions, is called a case conceptualization, and we will examine various examples in this article.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free . These science-based exercises will provide you with detailed insight into positive Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and give you the tools to apply it in your therapy or coaching.
This Article Contains:
What is a case conceptualization or formulation, 4 things to include in your case formulation, a helpful example & model, 3 samples of case formulations, 6 templates and worksheets for counselors, relevant resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
In psychology and related fields, a case conceptualization summarizes the key facts and findings from an evaluation to provide guidance for recommendations.
This is typically the evaluation of an individual, although you can extend the concept of case conceptualization to summarizing findings about a group or organization.
Based on the case conceptualization, recommendations can be made to improve a client’s self-care , mental status, job performance, etc (Sperry & Sperry, 2020).

- Summary of the client’s identifying information, referral questions, and timeline of important events or factors in their life . A timeline can be especially helpful in understanding how the client’s strengths and limitations have evolved.
- Statement of the client’s core strengths . Identifying core strengths in the client’s life should help guide any recommendations, including how strengths might be used to offset limitations.
- Statement concerning a client’s limitations or weaknesses . This will also help guide any recommendations. If a weakness is worth mentioning in a case conceptualization, it is worth writing a recommendation about it.
Note: As with mental status examinations , observations in this context concerning weaknesses are not value judgments, about whether the client is a good person, etc. The observations are clinical judgments meant to guide recommendations.
- A summary of how the strengths, limitations, and other key information about a client inform diagnosis and prognosis .
You should briefly clarify how you arrived at a given diagnosis. For example, why do you believe a personality disorder is primary, rather than a major depressive disorder?
Many clinicians provide diagnoses in formal psychiatric terms, per the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Some clinicians will state a diagnosis in less formal terms that do not coincide exactly with ICD-10 or DSM-5 codes. What is arguably more important is that a diagnostic impression, formal or not, gives a clear sense of who the person is and the support they need to reach their goals.
Prognosis is a forecast about whether the client’s condition can be expected to improve, worsen, or remain stable. Prognosis can be difficult, as it often depends on unforeseeable factors. However, this should not keep you from offering a conservative opinion on a client’s expected course, provided treatment recommendations are followed.

Download 3 Free Positive CBT Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to find new pathways to reduce suffering and more effectively cope with life stressors.
Download 3 Free Positive CBT Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Based on the pointers for writing a case conceptualization above, an example for summarizing an adolescent case (in this instance, a counseling case for relieving depression and improving social skills) might read as follows.
Background and referral information
This is a 15-year-old Haitian–American youth, referred by his mother for concerns about self-isolation, depression, and poor social skills. He reportedly moved with his mother to the United States three years ago.
He reportedly misses his life and friends in Haiti. The mother states he has had difficulty adjusting socially in the United States, especially with peers. He has become increasingly self-isolating, appears sad and irritable, and has started to refuse to go to school.
His mother is very supportive and aware of his emotional–behavioral needs. The youth has been enrolled in a social skills group at school and has attended three sessions, with some reported benefit. He is agreeable to start individual counseling. He reportedly does well in school academically when he applies himself.
Limitations
Behavioral form completed by his mother shows elevated depression scale (T score = 80). There is a milder elevation on the inattention scale (T score = 60), which suggests depression is more acute than inattention and might drive it.
He is also elevated on a scale measuring social skills and involvement (T score = 65). Here too, it is reasonable to assume that depression is driving social isolation and difficulty relating to peers, especially since while living in Haiti, he was reportedly quite social with peers.
Diagnostic impressions, treatment guidance, prognosis
This youth’s history, presentation on interview, and results of emotional–behavioral forms suggest some difficulty with depression, likely contributing to social isolation. As he has no prior reported history of depression, this is most likely a reaction to missing his former home and difficulty adjusting to his new school and peers.
Treatments should include individual counseling with an evidence-based approach such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT). His counselor should consider emotional processing and social skills building as well.
Prognosis is favorable, with anticipated benefit apparent within 12 sessions of CBT.
How to write a case conceptualization: An outline
The following outline is necessarily general. It can be modified as needed, with points excluded or added, depending on the case.
- Client’s gender, age, level of education, vocational status, marital status
- Referred by whom, why, and for what type of service (e.g., testing, counseling, coaching)
- In the spirit of strengths-based assessment, consider listing the client’s strengths first, before any limitations.
- Consider the full range of positive factors supporting the client.
- Physical health
- Family support
- Financial resources
- Capacity to work
- Resilience or other positive personality traits
- Emotional stability
- Cognitive strengths, per history and testing
- The client’s limitations or relative weaknesses should be described in a way that highlights those most needing attention or treatment.
- Medical conditions affecting daily functioning
- Lack of family or other social support
- Limited financial resources
- Inability to find or hold suitable employment
- Substance abuse or dependence
- Proneness to interpersonal conflict
- Emotional–behavioral problems, including anxious or depressive symptoms
- Cognitive deficits, per history and testing
- Diagnoses that are warranted can be given in either DSM-5 or ICD-10 terms.
- There can be more than one diagnosis given. If that’s the case, consider describing these in terms of primary diagnosis, secondary diagnosis, etc.
- The primary diagnosis should best encompass the client’s key symptoms or traits, best explain their behavior, or most need treatment.
- Take care to avoid over-assigning multiple and potentially overlapping diagnoses.
When writing a case conceptualization, always keep in mind the timeline of significant events or factors in the examinee’s life.
- Decide which events or factors are significant enough to include in a case conceptualization.
- When these points are placed in a timeline, they help you understand how the person has evolved to become who they are now.
- A good timeline can also help you understand which factors in a person’s life might be causative for others. For example, if a person has suffered a frontal head injury in the past year, this might help explain their changeable moods, presence of depressive disorder, etc.

Sample #1: Conceptualization for CBT case
This is a 35-year-old Caucasian man referred by his physician for treatment of generalized anxiety.
Strengths/supports in his case include willingness to engage in treatment, high average intelligence per recent cognitive testing, supportive family, and regular physical exercise (running).
Limiting factors include relatively low stress coping skills, frequent migraines (likely stress related), and relative social isolation (partly due to some anxiety about social skills).
The client’s presentation on interview and review of medical/psychiatric records show a history of chronic worry, including frequent worries about his wife’s health and his finances. He meets criteria for DSM-5 generalized anxiety disorder. He has also described occasional panic-type episodes, which do not currently meet full criteria for panic disorder but could develop into such without preventive therapy.
Treatments should include CBT for generalized anxiety, including keeping a worry journal; regular assessment of anxiety levels with Penn State Worry Questionnaire and/or Beck Anxiety Inventory; cognitive restructuring around negative beliefs that reinforce anxiety; and practice of relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation and diaphragmatic breathing .
Prognosis is good, given the evidence for efficacy of CBT for anxiety disorders generally (Hofmann, Asnaani, Vonk, Sawyer, & Fang, 2012).
Sample #2: Conceptualization for DBT case
This 51-year-old Haitian–American woman is self-referred for depressive symptoms, including reported moods of “rage,” “sadness,” and “emptiness.” She says that many of her difficulties involve family, friends, and coworkers who regularly “disrespect” her and “plot against her behind her back.”
Her current psychiatrist has diagnosed her with personality disorder with borderline features, but she doubts the accuracy of this diagnosis.
Strengths/supports include a willingness to engage in treatment, highly developed and marketable computer programming skills, and engagement in leisure activities such as playing backgammon with friends.
Limiting factors include low stress coping skills, mild difficulties with attention and recent memory (likely due in part to depressive affect), and a tendency to self-medicate with alcohol when feeling depressed.
The client’s presentation on interview, review of medical/psychiatric records, and results of MMPI-2 personality inventory corroborate her psychiatrist’s diagnosis of borderline personality disorder.
The diagnosis is supported by a longstanding history of unstable identity, volatile personal relationships with fear of being abandoned, feelings of emptiness, reactive depressive disorder with suicidal gestures, and lack of insight into interpersonal difficulties that have resulted in her often stressed and depressive state.
Treatments should emphasize a DBT group that her psychiatrist has encouraged her to attend but to which she has not yet gone. There should also be regular individual counseling emphasizing DBT skills including mindfulness or present moment focus, building interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance. There should be a counseling element for limiting alcohol use. Cognitive exercises are also recommended.
Of note, DBT is the only evidence-based treatment for borderline personality disorder (May, Richardi, & Barth, 2016). Prognosis is guardedly optimistic, provided she engages in both group and individual DBT treatments on a weekly basis, and these treatments continue without interruption for at least three months, with refresher sessions as needed.
Sample #3: Conceptualization in a family therapy case
This 45-year-old African-American woman was initially referred for individual therapy for “rapid mood swings” and a tendency to become embroiled in family conflicts. Several sessions of family therapy also appear indicated, and her psychiatrist concurs.
The client’s husband (50 years old) and son (25 years old, living with parents) were interviewed separately and together. When interviewed separately, her husband and son each indicated the client’s alcohol intake was “out of control,” and that she was consuming about six alcoholic beverages throughout the day, sometimes more.
Her husband and son each said the client was often too tired for household duties by the evening and often had rapid shifts in mood from happy to angry to “crying in her room.”
On individual interview, the client stated that her husband and son were each drinking about as much as she, that neither ever offered to help her with household duties, and that her son appeared unable to keep a job, which left him home most of the day, making demands on her for meals, etc.
On interview with the three family members, each acknowledged that the instances above were occurring at home, although father and son tended to blame most of the problems, including son’s difficulty maintaining employment, on the client and her drinking.
Strengths/supports in the family include a willingness of each member to engage in family sessions, awareness of supportive resources such as assistance for son’s job search, and a willingness by all to examine and reduce alcohol use by all family members as needed.
Limiting factors in this case include apparent tendency of all household members to drink to some excess, lack of insight by one or more family members as to how alcohol consumption is contributing to communication and other problems in the household, and a tendency by husband and son to make this client the family scapegoat.
The family dynamic can be conceptualized in this case through a DBT lens.
From this perspective, problems develop within the family when the environment is experienced by one or more members as invalidating and unsupportive. DBT skills with a nonjudgmental focus, active listening to others, reflecting each other’s feelings, and tolerance of distress in the moment should help to develop an environment that supports all family members and facilitates effective communication.
It appears that all family members in this case would benefit from engaging in the above DBT skills, to support and communicate with one another.
Prognosis is guardedly optimistic if family will engage in therapy with DBT elements for at least six sessions (with refresher sessions as needed).
Introduction to case conceptualization – Thomas Field
The following worksheets can be used for case conceptualization and planning.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Individual Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for individual clients.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Couples Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for couples.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Family Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for families.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Individual Counseling helps clients facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Couples Counseling helps couples facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Family Counseling helps families facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.

17 Science-Based Ways To Apply Positive CBT
These 17 Positive CBT & Cognitive Therapy Exercises [PDF] include our top-rated, ready-made templates for helping others develop more helpful thoughts and behaviors in response to challenges, while broadening the scope of traditional CBT.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
The following resources can be found in the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , and their full versions can be accessed by a subscription.
Analyzing Strengths Use in Different Life Domains can help clients understand their notable strengths and which strengths can be used to more advantage in new contexts.
Family Strength Spotting is another relevant resource. Each family member fills out a worksheet detailing notable strengths of other family members. In reviewing all worksheets, each family member can gain a greater appreciation for other members’ strengths, note common or unique strengths, and determine how best to use these combined strengths to achieve family goals.
Four Front Assessment is another resource designed to help counselors conceptualize a case based on a client’s personal and environmental strengths and weaknesses. The idea behind this tool is that environmental factors in the broad sense, such as a supportive/unsupportive family, are too often overlooked in conceptualizing a case.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others through CBT, check out this collection of 17 validated positive CBT tools for practitioners. Use them to help others overcome unhelpful thoughts and feelings and develop more positive behaviors.
In helping professions, success in working with clients depends first and foremost on how well you understand them.
This understanding is crystallized in a case conceptualization.
Case conceptualization helps answer key questions. Who is this client? How did they become who they are? What supports do they need to reach their goals?
The conceptualization itself depends on gathering all pertinent data on a given case, through record review, interview, behavioral observation, questionnaires completed by the client, etc.
Once the data is assembled, the counselor, coach, or other involved professional can focus on enumerating the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and limitations.
It is also often helpful to put the client’s strengths and limitations in a timeline so you can see how they have evolved and which factors might have contributed to the emergence of others.
Based on this in-depth understanding of the client, you can then tailor specific recommendations for enhancing their strengths, overcoming their weaknesses, and reaching their particular goals.
We hope you have enjoyed this discussion of how to conceptualize cases in the helping professions and that you will find some tools for doing so useful.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. For more information, don’t forget to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free .
- Hofmann, S. G., Asnaani, A., Vonk, I. J., Sawyer, A. T., & Fang, A. (2012). The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses. Cognitive Therapy and Research , 36 (5), 427–440.
- May, J. M., Richardi, T. M., & Barth, K. S. (2016). Dialectical behavior therapy as treatment for borderline personality disorder. The Mental Health Clinician , 6 (2), 62–67.
- Sperry, L., & Sperry, J. (2020). Case conceptualization: Mastering this competency with ease and confidence . Routledge.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
I found this very helpful and MORE understanding. I think I will often visit this page.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Youth Counseling: 17 Courses & Activities for Helping Teens
From a maturing body and brain to developing life skills and values, the teen years can be challenging, and mental health concerns may arise. Teens [...]

How To Plan Your Counseling Session: 6 Examples
Planning is crucial in a counseling session to ensure that time inside–and outside–therapy sessions is well spent, with the client achieving a successful outcome within [...]

Applied Positive Psychology in Therapy: Your Ultimate Guide
Without a doubt, this is an exciting time for positive psychology in therapy. Many academics and therapists now recognize the value of this fascinating, evolving [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (53)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (46)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (48)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (45)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

How to Write a Psychology Case Study: Expert Tips

Have you ever heard of Phineas Gage, a man whose life story became a legendary case study in the annals of psychology? In the mid-19th century, Gage, a railroad construction foreman, survived a near-fatal accident when an iron rod pierced through his skull, severely damaging his brain. What makes this tale truly remarkable is that, despite his physical recovery, Gage's personality underwent a dramatic transformation. He went from being a mild-mannered and responsible individual to becoming impulsive and unpredictable. This remarkable case marked the dawn of psychology's fascination with understanding the intricate workings of the human mind. Case studies, like the one of Phineas Gage, have been a cornerstone of our understanding of human behavior ever since.
Short Description
In this article, we'll unravel the secrets of case study psychology as the powerful tool of this field. We will explore its essence and why these investigations are so crucial in understanding human behavior. Discover the various types of case studies, gain insights from real-world examples, and uncover the essential steps and expert tips on how to craft your very own compelling study. Get ready to embark on a comprehensive exploration of this invaluable research method.
Ready to Uncover the Secrets of the Mind?
Our team of skilled psychologists and wordsmiths is here to craft a masterpiece from your ideas.
What Is a Case Study in Psychology
A case study psychology definition can be compared to a magnifying glass turned toward a single individual, group, or phenomenon. According to our paper writer , it's a focused investigation that delves deep into the unique complexities of a particular subject. Rather than sifting through mountains of data, a case study allows us to zoom in and scrutinize the details, uncovering the 'whys' and 'hows' that often remain hidden in broader research.
A psychology case study is not about generalizations or sweeping theories; it's about the intricacies of real-life situations. It's the detective work of the field, aiming to unveil the 'story behind the data' and offering profound insights into human behavior, emotions, and experiences. So, while psychology as a whole may study the forest, a case study takes you on a journey through the trees, revealing the unique patterns, quirks, and secrets that make each one distinct.
The Significance of Psychology Case Studies
Writing a psychology case study plays a pivotal role in the world of research and understanding the human mind. Here's why they are so crucial, according to our ' do my essay ' experts:
.webp)
- In-Depth Exploration: Case studies provide an opportunity to explore complex human behaviors and experiences in great detail. By diving deep into a specific case, researchers can uncover nuances that might be overlooked in broader studies.
- Unique Perspectives: Every individual and situation is unique, and case studies allow us to capture this diversity. They offer a chance to highlight the idiosyncrasies that make people who they are and situations what they are.
- Theory Testing: Case studies are a way to test and refine psychological theories in real-world scenarios. They provide practical insights that can validate or challenge existing hypotheses.
- Practical Applications: The knowledge gained from case studies can be applied to various fields, from clinical psychology to education and business. It helps professionals make informed decisions and develop effective interventions.
- Holistic Understanding: Case studies often involve a comprehensive examination of an individual's life or a particular phenomenon. This holistic approach contributes to a more profound comprehension of human behavior and the factors that influence it.
Varieties of a Psychology Case Study
When considering how to write a psychology case study, you should remember that it is a diverse field, and so are the case studies conducted within it. Let's explore the different types from our ' write my research paper ' experts:
- Descriptive Case Studies: These focus on providing a detailed description of a particular case or phenomenon. They serve as a foundation for further research and can be valuable in generating hypotheses.
- Exploratory Case Studies: Exploratory studies aim to investigate novel or scarcely explored areas within psychology. They often pave the way for more in-depth research by generating new questions and ideas.
- Explanatory Case Studies: These delve into the 'why' and 'how' of a particular case, seeking to explain the underlying factors or mechanisms that drive a particular behavior or event.
- Instrumental Case Studies: In these cases, the individual or situation under examination is instrumental in testing or illustrating a particular theory or concept in psychology.
- Intrinsic Case Studies: Contrary to instrumental case studies, intrinsic ones explore a case for its own unique significance, aiming to understand the specific details and intricacies of that case without primarily serving as a tool to test broader theories.
- Collective Case Studies: These studies involve the examination of multiple cases to identify common patterns or differences. They are helpful when researchers seek to generalize findings across a group.
- Longitudinal Case Studies: Longitudinal studies track a case over an extended period, allowing researchers to observe changes and developments over time.
- Cross-Sectional Case Studies: In contrast, cross-sectional case studies involve the examination of a case at a single point in time, offering a snapshot of that particular moment.
The Advantages of Psychology Case Studies
Learning how to write a case study offers numerous benefits, making it a valuable research method in the field. Here are some of the advantages:
- Rich Insights: Case studies provide in-depth insights into individual behavior and experiences, allowing researchers to uncover unique patterns, motivations, and complexities.
- Holistic Understanding: By examining a case in its entirety, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence human behavior, including psychological, environmental, and contextual aspects.
- Theory Development: Case studies contribute to theory development by providing real-world examples that can validate or refine existing psychological theories.
- Personalized Approach: Researchers can tailor their methods to fit the specific case, making it a flexible approach that can adapt to the unique characteristics of the subject.
- Application in Practice: The knowledge gained from case studies can be applied in various practical settings, such as clinical psychology, education, and organizational management, to develop more effective interventions and solutions.
- Real-World Relevance: Psychology case studies often address real-life issues, making the findings relevant and applicable to everyday situations.
- Qualitative Data: They generate qualitative data, which can be rich in detail and context, offering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Hypothesis Generation: Case studies can spark new research questions and hypotheses, guiding further investigations in psychology.
- Ethical Considerations: In some cases, case studies can be conducted in situations where experimental research may not be ethical, providing valuable insights that would otherwise be inaccessible.
- Educational Value: Case studies are commonly used as teaching tools, helping students apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios and encouraging critical thinking.
How to Write a Psychology Case Study
Crafting a psychology case study requires a meticulous approach that combines the art of storytelling with the precision of scientific analysis. In this section, we'll provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to create an engaging and informative psychology case study, from selecting the right subject to presenting your findings effectively.
Step 1: Gathering Information for Subject Profiling
To create a comprehensive psychology case study, the first crucial step is gathering all the necessary information to build a detailed profile of your subject. This profile forms the backbone of your study, offering a deeper understanding of the individual or situation you're examining.
According to our case study writing service , you should begin by collecting a range of data, including personal history, demographics, behavioral observations, and any relevant documentation. Interviews, surveys, and direct observations are common methods to gather this information. Ensure that the data you collect is relevant to the specific aspects of the subject's life or behavior that you intend to investigate.
By meticulously gathering and organizing this data, you'll lay the foundation for a robust case study that not only informs your readers but also provides the context needed to make meaningful observations and draw insightful conclusions.
Step 2: Selecting a Case Study Method
Once you have gathered all the essential information about your subject, the next step in crafting a psychology case study is to choose the most appropriate case study method. The method you select will determine how you approach the analysis and presentation of your findings. Here are some common case study methods to consider:
- Single-Subject Case Study: This method focuses on a single individual or a particular event, offering a detailed examination of that subject's experiences and behaviors.
- Comparative Case Study: In this approach, you analyze two or more cases to draw comparisons or contrasts, revealing patterns or differences among them.
- Longitudinal Case Study: A longitudinal study involves tracking a subject or group over an extended period, observing changes and developments over time.
- Cross-Sectional Case Study: This method involves analyzing subjects at a specific point in time, offering a snapshot of their current state.
- Exploratory Case Study: Exploratory studies are ideal for investigating new or underexplored areas within psychology.
- Explanatory Case Study: If your goal is to uncover the underlying factors and mechanisms behind a specific behavior or phenomenon, the explanatory case study is a suitable choice.
Step 3: Gathering Background Information on the Subject
In the process of learning how to write a psychology case study, it's essential to delve into the subject's background to build a complete and meaningful narrative. The background information serves as a crucial context for understanding the individual or situation under investigation.
To gather this information effectively:
- Personal History: Explore the subject's life history, including their upbringing, family background, education, and career path. These details provide insights into their development and experiences.
- Demographics: Collect demographic data, such as age, gender, and cultural background, as part of your data collection process. These factors can be influential in understanding behavior and experiences.
- Relevant Events: Identify any significant life events, experiences, or transitions that might have had an impact on the subject's psychology and behavior.
- Psychological Factors: Assess the subject's psychological profile, including personality traits, cognitive abilities, and emotional well-being, if applicable.
- Social and Environmental Factors: Consider the subject's social and environmental context, including relationships, living conditions, and cultural influences.
Step 4: Detailing the Subject's Challenges
While writing a psychology case study, it is crucial to provide a thorough description of the subject's symptoms or the challenges they are facing. This step allows you to dive deeper into the specific issues that are the focus of your study, providing clarity and context for your readers.
To effectively describe the subject's symptoms or challenges, consider the following from our psychology essay writing service :
- Symptomatology: Enumerate the symptoms, behaviors, or conditions that the subject is experiencing. This could include emotional states, cognitive patterns, or any psychological distress.
- Onset and Duration: Specify when the symptoms or challenges began and how long they have persisted. This timeline can offer insights into the progression of the issue.
- Impact: Discuss the impact of these symptoms on the subject's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Consider their functional impairment and how it relates to the observed issues.
- Relevant Diagnoses: If applicable, mention any psychological or psychiatric diagnoses that have been made in relation to the subject's symptoms. This information can shed light on the clinical context of the case.
Step 5: Analyzing Data and Establishing a Diagnosis
Once you have gathered all the necessary information and described the subject's symptoms or challenges, the next critical step is to analyze the data and, if applicable, establish a diagnosis.
To effectively analyze the data and potentially make a diagnosis:
- Data Synthesis: Organize and synthesize the collected data, bringing together all the relevant information in a coherent and structured manner.
- Pattern Recognition: Identify patterns, themes, and connections within the data. Look for recurring behaviors, triggers, or factors that might contribute to the observed symptoms or challenges.
- Comparison with Diagnostic Criteria: If the study involves diagnosing a psychological condition, compare the subject's symptoms and experiences with established diagnostic criteria, such as those found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
- Professional Consultation: It is advisable to consult with qualified professionals, such as clinical psychologists or psychiatrists, to ensure that the diagnosis, if applicable, is accurate and well-informed.
- Thorough Assessment: Ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the data, considering all possible factors and nuances before reaching any conclusions.
Step 6: Choosing an Intervention Strategy
Choosing an appropriate intervention approach is a pivotal phase in case study psychology, especially if your subject's case involves therapeutic considerations. Here's how to navigate this step effectively:
- Review Findings: Revisit the data and analysis you've conducted to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject's symptoms, challenges, and needs.
- Consultation: If you're not a qualified mental health professional, it's advisable to consult with experts in the field, such as clinical psychologists or psychiatrists. They can offer valuable insights and recommendations for treatment.
- Tailored Approach: Select a treatment approach that is tailored to the subject's specific needs and diagnosis, if applicable. This could involve psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of interventions.
- Goal Setting: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the chosen treatment approach. What do you hope to achieve, and how will progress be measured?
- Informed Consent: If the subject is involved in the decision-making process, ensure they provide informed consent and are fully aware of the chosen treatment's details, potential benefits, and risks.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Once the treatment plan is established, put it into action and closely monitor the subject's progress. Make necessary adjustments based on their responses and evolving needs.
- Ethical Considerations: Be mindful of ethical standards and maintain the subject's confidentiality and well-being throughout the treatment process.
Step 7: Explaining Treatment Objectives and Procedures
In the final phases of your psychology case study, it's essential to provide a clear and detailed description of the treatment goals and processes that have been implemented. This step ensures that your readers understand the therapeutic journey and its intended outcomes.
Here's how to effectively describe treatment goals and processes:
- Specific Goals: Outline the specific goals of the chosen treatment approach. What are you aiming to achieve in terms of the subject's well-being, symptom reduction, or overall improvement?
- Interventions: Describe the therapeutic interventions that have been employed, including psychotherapeutic techniques, medications, or other strategies. Explain how these interventions are intended to address the subject's challenges.
- Timelines: Specify the expected timeline for achieving treatment goals. This may include short-term and long-term objectives, as well as milestones for assessing progress.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Discuss the methods used to monitor and evaluate the subject's response to treatment. How are you measuring progress or setbacks, and how frequently are assessments conducted?
- Adjustments: Explain how the treatment plan is adaptable as you would in a persuasive essay . If modifications to the goals or interventions are required, clarify the decision-making process for making such adjustments.
- Collaboration: If relevant, highlight any collaboration with other professionals involved in the subject's care, emphasizing a multidisciplinary approach for comprehensive treatment.
- Patient Involvement: If the subject is actively engaged in their treatment, detail their role, responsibilities, and any tools or resources provided to support their participation.
Step 8: Crafting the Discussion and Concluding Remarks
In the final phase of your psychology case study, the discussion section is where you interpret the findings, reflect on the significance of your study, and offer insights into the broader implications of the case. Here's how to effectively write this section:
- Interpretation: Begin by interpreting the data and analysis you've presented in your case study. What do the findings reveal about the subject's psychology, behavior, or experiences?
- Relevance to Research Questions: Discuss how your findings align with or deviate from the initial research questions or hypotheses you set out to investigate.
- Comparison with Literature: Compare your findings with existing literature and research in the field of psychology. Highlight any consistencies or disparities and explain their significance.
- Clinical Considerations: If your case study has clinical or practical relevance, address the implications for therapeutic approaches, interventions, or clinical practices.
- Generalizability: Evaluate the extent to which the insights from your case study can be generalized to a broader population or other similar cases.
- Strengths and Limitations: Be candid about the strengths and limitations of your case study. Acknowledge any constraints or biases and explain how they might have influenced the results.
- Future Research Directions: Suggest areas for future research or additional case studies that could build on your findings and deepen our understanding of the subject matter.
- Conclusion: Summarize the key takeaways from your case study and provide a concise conclusion that encapsulates the main findings and their significance.
5 Helpful Tips for Crafting a Psychology Case Study
Much like learning how to write a synthesis essay , writing a compelling case study involves careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some essential guidelines to help you in the process:
- Consider Cultural Sensitivity: Recognize the importance of cultural diversity and sensitivity in your case study. Take into account the cultural background of your subject and its potential impact on their behavior and experiences.
- Use Clear Citations: Properly cite all sources, including previous research, theories, and relevant literature. Accurate citations lend credibility to your case study and acknowledge the work of others.
- Engage in Peer Discussion: Engage in discussions with peers or colleagues in the field throughout the case study process. Collaborative brainstorming and sharing insights can lead to a more well-rounded study.
- Be Mindful of Ethics: Continuously monitor and reassess the ethical considerations of your case study, especially when it involves sensitive topics or individuals. Prioritize the well-being and rights of your participants.
- Practice Patience and Persistence: Case studies can be time-consuming and may encounter setbacks. Exercise patience and persistence to ensure the quality and comprehensiveness of your research.
Case Study Psychology Example
In this psychology case study example, we delve into a compelling story that serves as a window into the fascinating realm of psychological research, offering valuable insights and practical applications.
Final Outlook
As we conclude this comprehensive writing guide on how to write a psychology case study, remember that every case holds a unique story waiting to be unraveled. The art of crafting a compelling case study lies in your hands, offering a window into the intricate world of the human mind. We encourage you to embark on your own investigative journeys, armed with the knowledge and skills acquired here, to contribute to the ever-evolving landscape of psychology.
Ready to Unravel the Mysteries of the Human Mind?
Our team of psychologists and researchers is adept at transforming complex concepts into engaging stories, ensuring that when you request us to ' write my case study for me ,' your unique vision is effectively brought to life.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Project Types We Cover
- Admissions Essay
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Research Paper
- Book Reviews
- Personal Statement
- Ph.D Dissertation
- Proofreading
Academic Fields & Subjects
- Programming
- Computer Science
- Other projects we help with
- Our Experts
- Plagiarism Checker
- Writing Tips
Psychology Case Study: Guide to Follow
By: Henrique Bertulino

If you’re studying psychology at the college or university, you’ll most likely deal with such an assignment as the case study . It is a common task for schools that combine theoretical education with the practice one. On the one hand, it requires a lot of time and effort, so many students don’t appreciate such assignments. On the other hand, it helps you develop the necessary skills to build a successful career.
Assignment Purposes
Cognitive-behavioral, psychoanalytic, interpretative phenomenological analysis, grounded theory, advantages of case studies, disadvantages of case studies, types of psychology case studies, quantitative research, qualitative research, identifying the key issues, describing the solution, where to look for information, college student with a sleep disorder, jill price's amazing memory abilities, the woman with suicidal thoughts, tell a story, use appropriate language, approach it as a challenge, don’t be biased, seek for help.
One thing you should understand is that there is nothing impossible. You may have never heard about this assignment before, but once you finish this article, you’ll be able to come up with a perfect paper. Or at least you’ll know that you may count on our support whenever you need it. If you don’t have enough time or desire to submit the case study on yourself, just rely on our professional authors.
What is The Psychology Case Study?
Let’s start with a case study definition . It is an in-depth investigation of an individual, group of people, community, or event. Typically, psychologists gather data from different sources and use some other methods for this purpose. This one is often used in clinical cases when it is not practical or even possible to conduct lab research.
Speaking about students, you may deal with real individuals, imagined individuals, characters from books, movies, TV shows, etc. It depends on the features of your educational program, as well as on your knowledge and experience. For example, first-year students may not be allowed to be real psychology patients. They can only observe the process and make notes. But if you have a particular background, you can define diagnosis and suggest your treatment.
Most students learn better from examples than from theoretical material. The real world is often different from the class, so case studies are a beneficial technique.
Case studies are used not in psychology only, they are also common for medical schools, law schools, business schools, etc. They can be used anywhere if the professors want students to apply their knowledge to real situations. Most case tasks require researchers to provide a solution to problems that can arise in their work routine. There is no one correct answer because different psychologists have different methods, strategies, approaches. The main objective is to teach bachelors of science how they can develop an action plan and decide.
Psychological Approaches You May Use
Using this approach, you focus on the person as a whole. It means you should look at one’s behavior not only as a therapist but through the eyes of the subject you study as well. This approach helps to evolve and put a treatment plan into place due to the patient’s self-image and feelings.
This approach is suitable for patients with mood, eating, and other disorders, e.g., schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Working on a case, the future therapist should consider the patient’s habits, thoughts, beliefs. Sometimes it is necessary to observe patient behavior during a particular period to understand how one reacts to different events, interacts with other people, etc.
Sigmund Freud developed this approach. He championed that the mind is often unconscious, and this part affects people’s behavior.
Adherents of this theory focus on individuals or groups of people and analyze how they make sense of some events and their personal significance.
Using this approach, you should first collect the data about the subject or events you study, and only then you integrate them into broader categories. Then you’re looking for a relationship between them to understand the issues better and develop a treatment.
The case method has a lot of advantages, both for instructors and students. It is an excellent opportunity to engage the class in real projects by abstracting from the theoretical questions. This assignment develops your skills in:
- Problem-understanding and solving;
- Analytical thinking;
- Research methods using;
- Handling with ambiguities;
- Stress resistance.
The huge advantage is that students find case studies exciting. They spend years in the classroom, and now they have an opportunity to touch the real psychologist’s daily routine. It is a perfect chance to show yourself, to do something creative, and make your suggestions.
Although case studies have enough advantages, there are some limitations as well. Firstly, this tool lacks scientific rigor. You can’t use raw data only, and your subjective feeling may affect the final result. It is also challenging to replicate. Because you deal with a particular person or a group, other students may not receive the same effect as the other community even if one is using the same tools. A lot of things depend on your interpretation, not on the data as it is.
Besides, case studies take a lot of time and effort since you can’t just sit in front of your laptop working on the project. You need to meet people, communicate with them, to analyze a lot of information. And the last task is to prepare a well-structured text to organize your thoughts and provide the main insights.
These disadvantages show that case studies can’t be used as only a psychological approach. However, they are still handy for the community and educational purposes as well.
2 Essential Methods of Case Study
There are two main methods that you may use to submit a piece:
- The prospective one is when you observe a person or a group of people to determine outcomes. For example, you want to understand how the disease progresses and gather a group to watch over it.
- The retrospective tool is the one where you look at historical information. It means that you start with an outcome, e.g., a disease. You work your way backward to analyze the person’s life and determine risk factors that may affect the illnesses’ development.
- Collective. Using this type, you study the behavior of the group of people in a particular setting.
- Descriptive. It goes about observing the subjects and comparing them to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory. This case paper type is often used for causal investigations. You study factors that may cause some things you’re interested in.
- Exploratory. If you’re going to conduct further and more in-depth research, you use the exploratory case study to start with. It helps you to gather more data before you state your research questions and hypotheses.
- Instrumental. It occurs when the person or group allows you to understand more than what was initially apparent.
- Intrinsic. You may use this type when you have a personal interest in the case. For example, when you observe your relatives contribute to the psychological theory development.
4 Steps You Need to Write a Psychology Case Study
Working on your student’s assignments, try to understand your next steps. It will show you how much time you should devote to and where to start.
Before you start working on an assignment, you should construct an efficient methodology. You need to know how to gather the data, answer the research issue, and find trustworthy sources.
Defining the best strategy, you should think about these questions:
- What issue do you want to address in your case study?
- Who is your target audience?
- Are you going to study an individual, a group, an organization?
- Do you have a particular period to explore? Is this the current state? Maybe you want to explore some events that have changed over time?
- Where is your research issue taking place?
You should know that there are two main types of research methods. You can follow one of them to prepare your psychology case study.
This type is focused more on quantity than on quality. You gather data and present it in the form of hard cold facts, stats analysis, numbers. This research approach requires you to deploy math frameworks to question the data quantity. There are also several sub-methods you may follow:
- Survey. Researchers utilize polls of questions, questionnaires, interviews to understand how subjects behave in particular situations. You may use chat, email, phone, and other ways to conduct a successful survey.
- Correlation. This quantitative research type is intended to test and analyze two variables and their interconnection. You may use it to understand an occurrence.
- Experiment. This type is a platform for many studies. You have hypotheses, and you need to confirm it or to refute it.
The qualitative research has another direction. Your task is not just to provide the data you’ve gathered. You need to present it in detail. Your text will include reviews, interviews, opinions, and other sources you may use to support evidence.
There are also some sub-methods future psychologists should be familiar with:
- Ethnographic. Working on research, you explore the particular culture, its features. Is there any motivation to keep it going? How this community affects the participants?
- Grounded theory. This type is quite different from other research models. You already have data on a particular topic, and now you need to move towards developing the new concept.
- Case study. Researchers define one target and focus on it. They collect data using various resources, including literature, concepts, theories, interviews, etc.
As you can see, the case study itself is a qualitative research tool. However, you may gather and analyze data using quantitative methods as well.
One of the essential steps of writing a case study is to explain the issue you’re going to research. It defines the purpose of the whole project and the scenario you’ll follow along the way.
If you can see various issues or challenges, write all of them down. Your task is to assess them and identify the most important ones. Try to describe each of them in a couple of sentences, providing their effect and consequences. You will see what matters and what you are interested in. Further, working on the issue, you should also explain the reasons for its occurrence. Remember that you have to address these issues within the real-life context.
The next step important for a good grade is the description of the possible solution. Now you know the roots and causes of the problem, so it's time to think about the hypotheses you had and their results. What worked out? What not? You should provide a detailed description to fulfill the purpose.
It is not enough just to write about the solution. A good case is intended to teach people something, to give them knowledge and insights. If you know the causes and reasons of the research issue, you should write about them. Other researchers may use your data for their projects. Besides, you need the analysis to understand your strong and weak sides. Working on this section, you’ll see that some explanations are evidence-based, while others are just your assumptions.
There are a lot of various sources that you can use to gather data about a person or a group. You can use one of these essential sources:
- Archival records. You can use archives to find necessary name lists, survey records, census records, etc.
- Documents. It goes about administrative notes, newspaper articles, letters, and other papers.
- Interviews. It is one of the essential sources to gather information about individuals or groups. You can communicate with subjects, using different psychology questions to ask , such as survey-type or open-ended questions.
- Direct observation. Researchers observe the subject in different settings, often in a natural one.
- Participant observation. You can gather information serving as a participant in different events, observing the actions and outcomes.
- Physical artifacts. You observe the subject in any way you may find tools, instruments, objects, and other artifacts useful for your research.
Ensure your sources are trustworthy because you can’t just copy information from the Facebook post or the email subscription. It is vital to use authorized journals, official notes, observations, and so on. Ask your professor where you can find the necessary information. One may provide you with access to secured databases.
Psychology's Famous Case Studies to Get Inspired By
A simple case search will help you find the most famous case studies that affected psychology as a science and provided researchers with powerful insights. We’ve compiled a list with some interesting cases for your inspiration.
Gerry was a regular 21-year-old college student with an outstanding academic performance. Everything was okay until Geery realized that he can’t sleep as usual. Thoughts did not leave his head during the nights. Suddenly Gerry began demanding his friends’ attention regardless of the time at the watch. He’d always been respectful, so such behavior wasn’t normal at all. But the further the worse. A couple of days later, the student said that his roommates were spying on him.
After visiting the counselor, Gerry was diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy helped him to prevent relapse.
Jill Price has a diagnosis that many people could dream of. She has hyperthymesia, in other words, an incredible memory that stores many details of her life. Jill can easily remember what her dinner was like 20 years ago. But if you are in a hurry to learn how to acquire such a superpower, we will disappoint you. The patient did not feel happy at all. In addition to important information and pleasant moments in life, she remembers all the derogatory remarks and traumatic events in the smallest detail.
Jill Price is 54 years old now, and she is still involved in psychological case studies that try to understand her brain's characteristics. The gathered evidence points to a rare offshoot of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Jessica worked in a large hospital as a medical resident. She woke up on the wrong side of the evil one day, but she couldn’t shake it. Her favorite job seemed stupid and useless, and the previously responsible Jessica began to ignore her shifts simply. She has similar problems at home with her husband and children. One day she even found herself wishing she was dead. These thoughts appeared in her head more often, but the woman continued to convince her husband that nothing was wrong. Fortunately, she worked in a hospital, so her coworkers understood that it was not. They convinced their colleague to seek help. Jessica was diagnosed with a major depressive disorder.
A Fem More Case Study Tips to Succeed
Of course, the case study is primarily a psychology task that requires particular knowledge and experience. However, the final result depends on your writing skills, as well. And if you know how to write an essay , it will simplify the whole process. The case study also has a particular structure, requires you to formulate thoughts clear and understandable, attract readers’ attention in the introduction, and provide evidence-based facts. Here are some tips that will help you to come up with a great case study!
Though the case study is an academic assignment, it is a paper about someone’s life. And life is always a story. Think about the paper’s scenario using these questions:
- When has everything started?
- What were the first events?
- How the patient felt?
- What was the reaction of the surrounding?
- Were there some confusing, funny, exciting events?
- How did one ask for help?
- What was the reason for conducting this study?
- How have you developed the solution?
- What are your significant insights?
Reading case study examples , you’ll see that they keep you on your toes. It is almost a book or a TV show, just for psychologists.
Writing a case study, you should consider your target audience all the time. If it is just an academic assignment, you may use the terms and expressions you use in the class. However, if you want to publish your paper, it is crucial to think about readers who are not as familiar with psychology science as you’re. When you’re writing that the patient has bipolar disorder, explain what it means. You can create a particular chapter with definitions and explanations, or use them exactly in the text. Is it dangerous? Which symptoms it has? Imagine that your readers know nothing and use appropriate language to explain your data.
The case study is a common task for different majors, not psychology only. For example, students who are pursuing a business degree, deal with it as well. Of course, they work under other circumstances, but the final goal is to understand the causes and reasons for some events.
You may take their approach to succeed with your paper. Imagine that you have some business goals, and your work defines whether you’ll get the profit. If you come up with a perfect solution, describing the case study, your readers will benefit from the job you’ve done.
Working with people, it is not so easy to forget about your emotions and personal opinion. Most psychologists have feelings for their patients, but particular ethical norms are developed to regulate the behavior.
As a student, you may have some difficulties with the moving part of the case study. Your work not with an object, but with a real person. It is vital to stay professional in the paper, to show evidence-based facts only, without biased content. Consult your professor or discuss this issue with fellow students if you need any advice.
In samples that we’ve used above, people asked for professional help since they could not solve the problem independently. You may find yourself in a similar situation when you have many assignments on different subjects and don’t know how to cope with all of them. You can always hire a professional author who will help you organize your thoughts in a structured paper or provide you with a custom case study. Use this opportunity to free yourself time and to impress your professor! And if you need to buy psychology paper online — you know where to go!
User ratings:
User ratings is 4.7 stars.
4.7 /5 ( 101 Votes)

Head of Customer Success
I'm a medical doctor and brand manager. The process of getting into Med school and studying at it made me learn and apply many strategies to keep my productivity high while spending less time and effort. As a working student, I had to figure out how to study smarter, not harder. During this period, my interest in neurology and psychiatry, as well as my aspiration to help others, intensified. At Studybay, I use my knowledge, skills, and experience to develop helpful solutions for students and make their study paths more productive and fun.
Add Your Comment
We are very interested to know your opinion

Upgrade your writing skills!
Try our AI essay writer from Studybay today!

A case study is a research method that extensively explores a particular subject, situation, or individual through in-depth analysis, often to gain insights into real-world phenomena or complex issues. It involves the comprehensive examination of multiple data sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, to provide a rich and holistic understanding of the subject under investigation.
Case studies are conducted to:
- Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon
- Explore unique or atypical situations
- Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context
- Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research
- Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving
A typical case study consists of the following components:
- Introduction: Provides a brief background and context for the study, including the purpose and research questions.
- Case Description: Describes the subject of the case study, including its relevant characteristics, settings, and participants.
- Data Collection: Details the methods used to gather data, such as interviews, observations, surveys, or document analysis.
- Data Analysis: Explains the techniques employed to analyze the collected data and derive meaningful insights.
- Findings: Presents the key discoveries and outcomes of the case study in a logical and organized manner.
- Discussion: Interprets the findings, relates them to existing theories or frameworks, discusses their implications, and addresses any limitations.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the main findings, highlights the significance of the research, and suggests potential avenues for future investigations.
Case studies offer several benefits, including:
- Providing a deep understanding of complex and context-dependent phenomena
- Generating detailed and rich qualitative data
- Allowing researchers to explore multiple perspectives and factors influencing the subject
- Offering practical insights for professionals and practitioners
- Allowing for the examination of rare or unique occurrences that cannot be replicated in experimental settings
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Writing A Case Study
Case Study Examples
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
15 min read
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
It’s no surprise that writing a case study is one of the most challenging academic tasks for students. You’re definitely not alone here!
Most people don't realize that there are specific guidelines to follow when writing a case study. If you don't know where to start, it's easy to get overwhelmed and give up before you even begin.
Don't worry! Let us help you out!
We've collected over 25 free case study examples with solutions just for you. These samples with solutions will help you win over your panel and score high marks on your case studies.
So, what are you waiting for? Let's dive in and learn the secrets to writing a successful case study.
- 1. An Overview of Case Studies
- 2. Case Study Examples for Students
- 3. Business Case Study Examples
- 4. Medical Case Study Examples
- 5. Psychology Case Study Examples
- 6. Sales Case Study Examples
- 7. Interview Case Study Examples
- 8. Marketing Case Study Examples
- 9. Tips to Write a Good Case Study
An Overview of Case Studies
A case study is a research method used to study a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves analyzing and interpreting data from a variety of sources to gain insight into the subject being studied.
Case studies are often used in psychology, business, and education to explore complicated problems and find solutions. They usually have detailed descriptions of the subject, background info, and an analysis of the main issues.
The goal of a case study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Typically, case studies can be divided into three parts, challenges, solutions, and results.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is:
Case Study Sample PDF
How to Write a Case Study Examples
Learn how to write a case study with the help of our comprehensive case study guide.
Case Study Examples for Students
Quite often, students are asked to present case studies in their academic journeys. The reason instructors assign case studies is for students to sharpen their critical analysis skills, understand how companies make profits, etc.
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students:
|
Case Study Example in Software Engineering
Qualitative Research Case Study Sample
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
Social Work Case Study Example
Ethical Case Study
Case Study Example PDF
These examples can guide you on how to structure and format your own case studies.
Struggling with formatting your case study? Check this case study format guide and perfect your document’s structure today.
Business Case Study Examples
A business case study examines a business’s specific challenge or goal and how it should be solved. Business case studies usually focus on several details related to the initial challenge and proposed solution.
To help you out, here are some samples so you can create case studies that are related to businesses:
|
|
Here are some more business case study examples:
Business Case Studies PDF
Business Case Studies Example
Typically, a business case study discovers one of your customer's stories and how you solved a problem for them. It allows your prospects to see how your solutions address their needs.
Medical Case Study Examples
Medical case studies are an essential part of medical education. They help students to understand how to diagnose and treat patients.
Here are some medical case study examples to help you.
Medical Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Example
Want to understand the various types of case studies? Check out our types of case study blog to select the perfect type.
Psychology Case Study Examples
Case studies are a great way of investigating individuals with psychological abnormalities. This is why it is a very common assignment in psychology courses.
By examining all the aspects of your subject’s life, you discover the possible causes of exhibiting such behavior.
For your help, here are some interesting psychology case study examples:
Psychology Case Study Example
Mental Health Case Study Example
Sales Case Study Examples
Case studies are important tools for sales teams’ performance improvement. By examining sales successes, teams can gain insights into effective strategies and create action plans to employ similar tactics.
By researching case studies of successful sales campaigns, sales teams can more accurately identify challenges and develop solutions.
Sales Case Study Example
Interview Case Study Examples
Interview case studies provide businesses with invaluable information. This data allows them to make informed decisions related to certain markets or subjects.
Interview Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Examples
Marketing case studies are real-life stories that showcase how a business solves a problem. They typically discuss how a business achieves a goal using a specific marketing strategy or tactic.
They typically describe a challenge faced by a business, the solution implemented, and the results achieved.
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like.
: ABC Solutions, a leading provider of tech products and services.
Engaging and informative content highlighting products and services. Incorporating real-world examples to showcase the impact of ABC Solutions. Utilizing analytics to refine content strategies. Aligning content with customer needs and pain points. Content marketing efforts led to a significant boost in brand visibility. Compelling narratives highlighting how products and services transformed businesses.
|
Here are some more popular marketing studies that show how companies use case studies as a means of marketing and promotion:
“Chevrolet Discover the Unexpected” by Carol H. Williams
This case study explores Chevrolet's “ DTU Journalism Fellows ” program. The case study uses the initials “DTU” to generate interest and encourage readers to learn more.
Multiple types of media, such as images and videos, are used to explain the challenges faced. The case study concludes with an overview of the achievements that were met.
Key points from the case study include:
- Using a well-known brand name in the title can create interest.
- Combining different media types, such as headings, images, and videos, can help engage readers and make the content more memorable.
- Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
“The Met” by Fantasy
“ The Met ” by Fantasy is a fictional redesign of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, created by the design studio Fantasy. The case study clearly and simply showcases the museum's website redesign.
The Met emphasizes the website’s features and interface by showcasing each section of the interface individually, allowing the readers to concentrate on the significant elements.
For those who prefer text, each feature includes an objective description. The case study also includes a “Contact Us” call-to-action at the bottom of the page, inviting visitors to contact the company.
Key points from this “The Met” include:
- Keeping the case study simple and clean can help readers focus on the most important aspects.
- Presenting the features and solutions with a visual showcase can be more effective than writing a lot of text.
- Including a clear call-to-action at the end of the case study can encourage visitors to contact the company for more information.
“Better Experiences for All” by Herman Miller
Herman Miller's minimalist approach to furniture design translates to their case study, “ Better Experiences for All ”, for a Dubai hospital. The page features a captivating video with closed-captioning and expandable text for accessibility.
The case study presents a wealth of information in a concise format, enabling users to grasp the complexities of the strategy with ease. It concludes with a client testimonial and a list of furniture items purchased from the brand.
Key points from the “Better Experiences” include:
- Make sure your case study is user-friendly by including accessibility features like closed captioning and expandable text.
- Include a list of products that were used in the project to guide potential customers.
“NetApp” by Evisort
Evisort's case study on “ NetApp ” stands out for its informative and compelling approach. The study begins with a client-centric overview of NetApp, strategically directing attention to the client rather than the company or team involved.
The case study incorporates client quotes and explores NetApp’s challenges during COVID-19. Evisort showcases its value as a client partner by showing how its services supported NetApp through difficult times.
- Provide an overview of the company in the client’s words, and put focus on the customer.
- Highlight how your services can help clients during challenging times.
- Make your case study accessible by providing it in various formats.
“Red Sox Season Campaign,” by CTP Boston
The “ Red Sox Season Campaign ” showcases a perfect blend of different media, such as video, text, and images. Upon visiting the page, the video plays automatically, there are videos of Red Sox players, their images, and print ads that can be enlarged with a click.
The page features an intuitive design and invites viewers to appreciate CTP's well-rounded campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team. There’s also a CTA that prompts viewers to learn how CTP can create a similar campaign for their brand.
Some key points to take away from the “Red Sox Season Campaign”:
- Including a variety of media such as video, images, and text can make your case study more engaging and compelling.
- Include a call-to-action at the end of your study that encourages viewers to take the next step towards becoming a customer or prospect.
“Airbnb + Zendesk” by Zendesk
The case study by Zendesk, titled “ Airbnb + Zendesk : Building a powerful solution together,” showcases a true partnership between Airbnb and Zendesk.
The article begins with an intriguing opening statement, “Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend,” and uses stunning images of beautiful Airbnb locations to captivate readers.
Instead of solely highlighting Zendesk's product, the case study is crafted to tell a good story and highlight Airbnb's service in detail. This strategy makes the case study more authentic and relatable.
Some key points to take away from this case study are:
- Use client's offerings' images rather than just screenshots of your own product or service.
- To begin the case study, it is recommended to include a distinct CTA. For instance, Zendesk presents two alternatives, namely to initiate a trial or seek a solution.
“Influencer Marketing” by Trend and WarbyParker
The case study "Influencer Marketing" by Trend and Warby Parker highlights the potential of influencer content marketing, even when working with a limited budget.
The “Wearing Warby” campaign involved influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses during their daily activities, providing a glimpse of the brand's products in use.
This strategy enhanced the brand's relatability with influencers' followers. While not detailing specific tactics, the case study effectively illustrates the impact of third-person case studies in showcasing campaign results.
Key points to take away from this case study are:
- Influencer marketing can be effective even with a limited budget.
- Showcasing products being used in everyday life can make a brand more approachable and relatable.
- Third-person case studies can be useful in highlighting the success of a campaign.
Marketing Case Study Template
Marketing Case Study Example
Now that you have read multiple case study examples, hop on to our tips.
Tips to Write a Good Case Study
Here are some note-worthy tips to craft a winning case study
- Define the purpose of the case study This will help you to focus on the most important aspects of the case. The case study objective helps to ensure that your finished product is concise and to the point.
- Choose a real-life example. One of the best ways to write a successful case study is to choose a real-life example. This will give your readers a chance to see how the concepts apply in a real-world setting.
- Keep it brief. This means that you should only include information that is directly relevant to your topic and avoid adding unnecessary details.
- Use strong evidence. To make your case study convincing, you will need to use strong evidence. This can include statistics, data from research studies, or quotes from experts in the field.
- Edit and proofread your work. Before you submit your case study, be sure to edit and proofread your work carefully. This will help to ensure that there are no errors and that your paper is clear and concise.
There you go!
We’re sure that now you have secrets to writing a great case study at your fingertips! This blog teaches the key guidelines of various case studies with samples. So grab your pen and start crafting a winning case study right away!
Having said that, we do understand that some of you might be having a hard time writing compelling case studies.
But worry not! Our expert case study writing service is here to take all your case-writing blues away!
With 100% thorough research guaranteed, our online essay service can craft an amazing case study within 24 hours!
So why delay? Let us help you shine in the eyes of your instructor!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
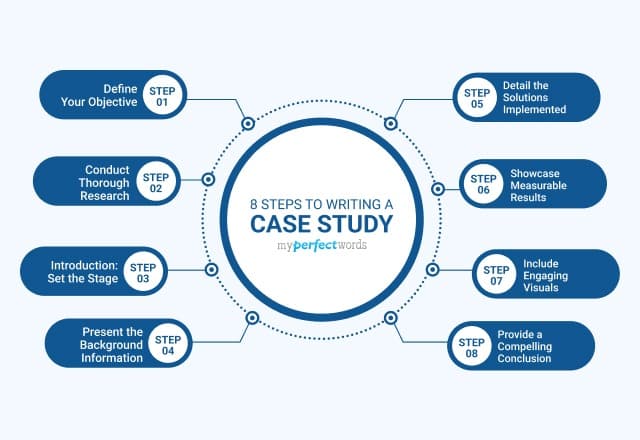
Psychology Case Study Examples
- For those experiencing suicidal thoughts, please contact the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988
- For those experiencing abuse, please contact the Domestic Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-SAFE (7233)
- For those experiencing substance use, please contact SAMHSA National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357
Experiments are often used to help researchers understand how the human mind works. There have been many famous examples in psychology over the years. Some have shown how phenomena like memory and personality work. Others have been disproven over time. Understanding the study design, data, content, and analytical approach of case studies is important to verifying the validity of each study.
In considering case studies, researchers continuously test and reevaluate the conclusions made by past psychologists to continue offering the most up-to-date and effective care to modern clients. Prospective case studies are continually being developed based on previous findings and multiple case studies done in one area can lend credence to the findings. Learning about the famous psychology case studies can help you understand how research continues to shape what psychologists know about the human experience and mind.
Examples of the most famous case study in psychology
Hundreds of thousands of case studies have been done in psychology, and narrowing a list of the most ground-breaking studies can be challenging. However, the following seven case studies present findings that have defied expectations, achieved positive outcomes for humanity, and launched further research into existing knowledge gaps within the niche.

Phineas Gage
The case of Phineas Gage is perhaps the most cited study in psychology. This famous case study showed how different areas of the brain affect personality and cognitive ability. While working as a construction foreman on a railroad, Phineas Gage was involved in an accident in which a rod was pushed through his cheek and brain. He survived, but because of the accident, both his personality and his ability to learn new skills were affected.
Although the case is frequently cited and referenced in psychology, relatively little information about Gage's life before and after the accident is known. Researchers have discovered that the last two decades of his life were spent in his original job, which may have been unlikely to have been possible if the extent of his injuries were as severe as initially believed. Still, his case was a starting point for psychology research on how memory and personality work in the brain, and it is a seminal study for that reason.
Genie the "feral child"
Although an outdated term, "feral children" referred to children raised without human interaction, often due to abuse or neglect. One famous case study of a neglected child was done with a child known as Genie. She was raised in a single bedroom with little human interaction. She never gained the cognitive ability of an average adult, even though she was found at age 13. Later in life, she regressed and stopped speaking altogether. Her case has been studied extensively by psychologists who want to understand how enculturation affects cognitive development. It's one of many cognitive psychology examples that have had an impact on this field.
Henry Molaison
The case study of Henry Molaison has helped psychologists understand memory. It is one of the most famous case studies in neuroscience. Henry Molaison was in a childhood accident that left him with debilitating seizures. Doctors could stop the seizures by removing slivers of his brain's hippocampus, though they did not fully understand what they were doing at the time. As a result, scientists learned how important the hippocampus is to forming long-term memories. After the surgery, Molaison could no longer form long-term memories, and his short-term memory was brief. The case study started further research into memory and the brain.
Jill Price had one of a few documented cases of hyperthymesia, a term for an overactive memory that allowed her to remember such mundane things as what she had for dinner on an average day in August 20th years previously. Her case study was used as a jumping-off point to research how memory works and why some people have exceptional memories.
However, through more research, it was discovered that her overall memory was not exceptional. Rather, she only remembered details of her own life. She was diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), with memories being part of her obsession. This case study is still relevant because it has helped modern psychologists understand how mental illness affects memory.
In the John/Joan case study , a reputable sexologist tested his theory that nurture, not nature, determined gender. The case study has been cited extensively and laid the groundwork for other research into gender identity. However, the case study was not legitimate. In this study, Dr. John Money performed surgery on an infant whose genitals were damaged during circumcision.
The boy was raised as a girl; however, he never identified as female and eventually underwent gender-affirming surgery as an adult. Because Dr. Money didn't follow up with the patient appropriately and did not report adverse findings, the case study is still often cited as successful.
Anna O. was the pseudonym given to a German woman who was one of the first to undergo psychoanalysis. Her case inspired many of the theories of Freud and other prominent psychologists of the time. It was determined at the time that Anna's symptoms of depression were eliminated through talk therapy. More recently, it has been suggested that Anna O. had another illness, such as epilepsy, from which she may have recovered during the therapy. This case study is still cited as a reason psychologists believe that psychotherapy, or talk therapy, can be helpful to many patients.
Victor the "wild boy" of Aveyron
Another study done on a child that had grown up without parents was done with a boy named "Victor" who had been found wandering in the wilderness and was thought to have been living alone for years. The boy could not speak, use the bathroom, or connect with others. However, through the study of his condition, he was able to learn bathroom habits, how to dress, writing, and primary language. Psychologists today speculate that he may have been autistic.
Ethical concerns for doing a case study
When case studies are flawed through not having enough information or having the wrong information, they can be harmful. Valuable research hours and other resources can be wasted while theories are used for inappropriate treatment. Case studies can therefore cause as much harm as benefit, and psychologists are often careful about how and when they are used.
Those who are not psychologists and are interacting with studies can also practice caution. Psychologists and doctors often disagree on how case studies should be applied. In addition, people without education in psychology may struggle to know whether a case study is built on a faulty premise or misinformation. It can also be possible to generalize case studies to situations they do not apply. If you think a case study might apply to your case or that of a loved one, consider asking a therapist for guidance.
Case studies are descriptions of real people. The individuals in the studies are studied intensively and often written about in medical journals and textbooks. While some clients may be comfortable being studied for science, others may not have consented due to the inability or lack of consent laws at the time. In addition, some subjects may not have been treated with dignity and respect.
When considering case study content and findings from psychology, it can be helpful to think of the cases as stories of real individuals. When you strip away the science and look at the case as a whole person in a unique situation, you may get more out of the study than if you look at it as research that proves a theory.
Therapeutic implications of a case study
Case examples are sometimes used in therapy to determine the best course of treatment. If a typical case study from psychology aligns with your situation, your therapist may use the treatment methods outlined in the study. Psychiatrists and other mental health professionals also use case examples to understand mental illness and its treatment.
Researchers have reviewed the role of case studies in counseling and psychotherapy. In one study, the authors discussed how reading case studies benefits therapists, providing a conceptual guide for clinical work and an understanding of the theory behind the practice. They also stressed the importance of teaching psychotherapy trainees to do better case study research. They encouraged practitioners to publish more case studies documenting the methods they use in their practice.
How a case study is used in counseling
If you want to meet with a psychologist, counseling may benefit you. Therapists often use theories behind popular case studies and can discuss their implications with you. In addition, you may be able to participate in case studies in your area, as psychologists and psychiatrists often perform clinical trials to understand treatments on a deeper level.
Online therapy can also be beneficial if you cannot find a therapist in your area. Through a platform like BetterHelp, you can get matched with a provider meeting your needs and choose between phone, video, or live chat sessions. When experiencing symptoms of a mental health condition, it can sometimes be hard to leave home for therapy. You can use many online therapy platforms from the comfort and safe space of your own home.
Therapy is a personal experience; not everyone will go into it seeking the same outcomes. Keeping this in mind may ensure you get the most out of online therapy, regardless of your specific goals. If you're interested in learning more about the effectiveness of online therapy, you can look into various clinical studies that have shown it can be as effective, if not more effective, than in-person options.
BetterHelp therapist reviews
“Amanda provides an excellent balance of warmth, accountability, and reliability. She keeps you on-topic while actively listening and providing guidance as needed. Her credentials and expertise are well applied to our sessions and I am so grateful for her.”
“She’s been amazing, helped me process my feelings and work on the things I needed to heal to grow stronger and be content with my life. She was available every day, I managed to connect with her deeply, she was supportive. I never expected to meet someone who’d have such a big positive effect on my life. I want to continue my journey with her and I trust the lessons I’ve learned from her will continue to be useful for my present and future.”
Therapy Is Personal
For more information about BetterHelp as a company, find us on:
- RAINN (Rape, Abuse, and Incest National Network) - 1-800-656-4673
- The National Suicide Prevention Lifeline - 1-800-273-8255
- National Domestic Violence Hotline - 1-800-799-7233
- NAMI Helpline (National Alliance on Mental Illness) - 1-800-950-6264
- SAMHSA (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration) SAMHSA Facebook , SAMHSA Twitter , SAMHSA LinkedIn
- Mental Health America, MHA Twitter , MHA Facebook , MHA Instagram , MHA Pinterest , MHA LinkedIn
- WebMD, WebMD Facebook , WebMD Twitter , WebMD Pinterest , WebMD LinkedIn
- NIMH (National Institute of Mental Health), NIMH Facebook , NIMH Twitter, NIMH YouTube , NIMH LinkedIn
- APA (American Psychiatric Association), APA Twitter , APA Facebook , APA LinkedIn , APA Instagram
Get help now:
- Emergency: 911
- National Domestic Violence Hotline: 1- 800-799-7233
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 1-800-273-TALK (8255)
- National Hopeline Network: 1-800-SUICIDE (784-2433)
- Crisis Text Line: Text “DESERVE” TO 741-741
- Lifeline Crisis Chat (Online live messaging): https://suicidepreventionlifeline.org/chat/
- Self-Harm Hotline: 1-800-DONT CUT (366-8288)
- Family Violence Helpline: 1-800-996-6228
- Planned Parenthood Hotline: 1-800-230-PLAN (7526)
- American Association of Poison Control Centers: 1-800-222-1222
- National Council on Alcoholism & Drug Dependency Hope Line: 1-800-622-2255
- National Crisis Line - Anorexia and Bulimia: 1-800-233-4357
- LGBTQ+ Hotline: 1-888-843-4564
- TREVOR Crisis Hotline: 1-866-488-7386
- AIDS Crisis Line: 1-800-221-7044
- Veterans Crisis Line: https://www.veteranscrisisline.net
- TransLifeline: https://www.translifeline.org - 877-565-8860 APA Youtube
- Suicide Prevention Wiki: http://suicideprevention.wikia.com
- Color Psychology: What Does Your Favorite Color Say About You?
- Meaningful Facts About Love
- The Four Goals Of Therapy: What Are They?
- Can Therapy Answer The Question: Why Do We Dream?
- What Is The "Learned Helplessness" Definition?
- What Is Rationalization Therapy And How Can I Benefit from It?
- The Complete Guide To Positive Therapy And How It Can Help You
- Mary Calkins And Her Career In Therapy - A Case Study
- The Psychology Behind What Causes Deja Vu
- Defining Closure Therapy - A Case Study
- Sense Of Entitlement - A Case Study
- Careers In Therapy - A Case Study
- Edward Thorndike And His Influence - A Case Study
- Is Autonomy Therapy A Thing And How Can I Benefit?
- The Use Of The Rorschach Inkblot Test
- The Case For Aaron Beck Theory And His Contribution
- Amazing Podcasts You Need In Your Library
- The Case For Reliability Therapy
- Understanding Imprinting Therapy
- How Can Career Counseling Help Me?
- The Benefits Of Family Counseling
- How To Know When You Or Your Family Need Counseling Services
- Counseling For Couples - How Does Couples Therapy Work?
- Finding The Best Premarital Counseling 2020: What Is Premarital Counseling And Why You Should Do It?
- Counseling For Couples As Part Of A Healthy Relationship
- Starting Off On The Right Foot: Pre Marriage Counseling
- The Benefits Of Online Mental Health Counseling
- A Guide To Affordable Counseling
- Parent Counseling: Parent-Child Conflict: Win-Win
- Facing Life Squarely With The Help Of Personal Counseling
- Is Phone Counseling/Therapy Appropriate?
- Can Text Counseling Help Someone?
- Couples Therapy: How Much Does Couple Counseling Cost?
- When Counseling For Depression Is Necessary
- Couple Counseling Online Techniques
- Reasons To Use E-Counseling
- Get Telephone Counseling When And Where You Need It
- Most Recommended Premarital Counseling Books
- What Are The Most Common And Effective Couple Counseling Techniques?
- What Is Divorce Counseling And Is It Right For You?
- What Is Affect? Psychology And The Expression Of Emotions Medically reviewed by Julie Dodson , MA
- What Is Developmental Psychology? Definition And Importance Medically reviewed by Laura Angers Maddox , NCC, LPC
- Psychologists
- Relationships and Relations
- The Big Think Interview
- Your Brain on Money
- Explore the Library
- Will true AI turn against us?
- Do we have free will?
- Why are there conspiracy theories?
- Is religion helping or hurting us?
- Are we alone in the universe?
- Should we trust science?
- Michio Kaku
- Neil deGrasse Tyson
- Michelle Thaller
- Steven Pinker
- Ray Kurzweil
- Cornel West
- Helen Fisher
- Smart Skills
- High Culture
- The Present
- Hard Science
- Special Issues
- Starts With A Bang
- Perception Box
- Strange Maps
- The Learning Curve
- Everyday Philosophy
- Free Newsletters
- Memberships
Psychology’s 10 greatest case studies – digested

These ten characters have all had a huge influence on psychology and their stories continue to intrigue each new generation of students. What’s particularly fascinating is that many of their stories continue to evolve – new evidence comes to light, or new technologies are brought to bear, changing how the cases are interpreted and understood. What many of these 10 also have in common is that they speak to some of the perennial debates in psychology, about personality and identity, nature and nurture, and the links between mind and body.
Phineas Gage
One day in 1848 in Central Vermont, Phineas Gage was tamping explosives into the ground to prepare the way for a new railway line when he had a terrible accident. The detonation went off prematurely, and his tamping iron shot into his face, through his brain, and out the top of his head.
Remarkably Gage survived, although his friends and family reportedly felt he was changed so profoundly (becoming listless and aggressive) that “he was no longer Gage.” There the story used to rest – a classic example of frontal brain damage affecting personality. However, recent years have seen a drastic reevaluation of Gage’s story in light of new evidence. It’s now believed that he underwent significant rehabilitation and in fact began work as a horse carriage driver in Chile. A simulation of his injuries suggested much of his right frontal cortex was likely spared, and photographic evidence has been unearthed showing a post-accident dapper Gage. Not that you’ll find this revised account in many psychology textbooks: a recent analysis showed that few of them have kept up to date with the new evidence.
Henry Gustav Molaison (known for years as H.M. in the literature to protect his privacy), who died in 2008, developed severe amnesia at age 27 after undergoing brain surgery as a form of treatment for the epilepsy he’d suffered since childhood. He was subsequently the focus of study by over 100 psychologists and neuroscientists and he’s been mentioned in over 12,000 journal articles! Molaison’s surgery involved the removal of large parts of the hippocampus on both sides of his brain and the result was that he was almost entirely unable to store any new information in long-term memory (there were some exceptions – for example, after 1963 he was aware that a US president had been assassinated in Dallas). The extremity of Molaison’s deficits was a surprise to experts of the day because many of them believed that memory was distributed throughout the cerebral cortex. Today, Molaison’s legacy lives on: his brain was carefully sliced and preserved and turned into a 3D digital atlas and his life story is reportedly due to be turned into a feature film based on the book researcher Suzanne Corkin wrote about him: Permanent Present Tense, The Man With No Memory and What He Taught The World .
Victor Leborgne (nickname “Tan”)
The fact that, in most people, language function is served predominantly by the left frontal cortex has today almost become common knowledge, at least among psych students. However, back in the early nineteenth century, the consensus view was that language function (like memory, see entry for H.M.) was distributed through the brain. An eighteenth century patient who helped change that was Victor Leborgne, a Frenchman who was nicknamed “Tan” because that was the only sound he could utter (besides the expletive phrase “sacre nom de Dieu”). In 1861, aged 51, Leborgne was referred to the renowned neurologist Paul Broca, but died soon after. Broca examined Leborgne’s brain and noticed a lesion in his left frontal lobe – a segment of tissue now known as Broca’s area. Given Leborgne’s impaired speech but intact comprehension, Broca concluded that this area of the brain was responsible for speech production and he set about persuading his peers of this fact – now recognised as a key moment in psychology’s history. For decades little was known about Leborgne, besides his important contribution to science. However, in a paper published in 2013, Cezary Domanski at Maria Curie-Sklodowska University in Poland uncovered new biographical details, including the possibility that Leborgne muttered the word “Tan” because his birthplace of Moret, home to several tanneries.
Wild Boy of Aveyron
The “Wild boy of Aveyron” – named Victor by the physician Jean-Marc Itard – was found emerging from Aveyron forest in South West France in 1800, aged 11 or 12, where’s it’s thought he had been living in the wild for several years. For psychologists and philosophers, Victor became a kind of “natural experiment” into the question of nature and nurture. How would he be affected by the lack of human input early in his life? Those who hoped Victor would support the notion of the “noble savage” uncorrupted by modern civilisation were largely disappointed: the boy was dirty and dishevelled, defecated where he stood and apparently motivated largely by hunger. Victor acquired celebrity status after he was transported to Paris and Itard began a mission to teach and socialise the “feral child”. This programme met with mixed success: Victor never learned to speak fluently, but he dressed, learned civil toilet habits, could write a few letters and acquired some very basic language comprehension. Autism expert Uta Frith believes Victor may have been abandoned because he was autistic, but she acknowledges we will never know the truth of his background. Victor’s story inspired the 2004 novel The Wild Boy and was dramatised in the 1970 French film The Wild Child .
Nicknamed ‘Kim-puter’ by his friends, Peek who died in 2010 aged 58, was the inspiration for Dustin Hoffman’s autistic savant character in the multi-Oscar-winning film Rain Man . Before that movie, which was released in 1988, few people had heard of autism, so Peek via the film can be credited with helping to raise the profile of the condition. Arguably though, the film also helped spread the popular misconception that giftedness is a hallmark of autism (in one notable scene, Hoffman’s character deduces in an instant the precise number of cocktail sticks – 246 – that a waitress drops on the floor). Peek himself was actually a non-autistic savant, born with brain abnormalities including a malformed cerebellum and an absent corpus callosum (the massive bundle of tissue that usually connects the two hemispheres). His savant skills were astonishing and included calendar calculation, as well as an encyclopaedic knowledge of history, literature, classical music, US zip codes and travel routes. It was estimated that he read more than 12,000 books in his life time, all of them committed to flawless memory. Although outgoing and sociable, Peek had coordination problems and struggled with abstract or conceptual thinking.
“Anna O.” is the pseudonym for Bertha Pappenheim, a pioneering German Jewish feminist and social worker who died in 1936 aged 77. As Anna O. she is known as one of the first ever patients to undergo psychoanalysis and her case inspired much of Freud’s thinking on mental illness. Pappenheim first came to the attention of another psychoanalyst, Joseph Breuer, in 1880 when he was called to her house in Vienna where she was lying in bed, almost entirely paralysed. Her other symptoms include hallucinations, personality changes and rambling speech, but doctors could find no physical cause. For 18 months, Breuer visited her almost daily and talked to her about her thoughts and feelings, including her grief for her father, and the more she talked, the more her symptoms seemed to fade – this was apparently one of the first ever instances of psychoanalysis or “the talking cure”, although the degree of Breuer’s success has been disputed and some historians allege that Pappenheim did have an organic illness, such as epilepsy. Although Freud never met Pappenheim, he wrote about her case, including the notion that she had a hysterical pregnancy, although this too is disputed. The latter part of Pappenheim’s life in Germany post 1888 is as remarkable as her time as Anna O. She became a prolific writer and social pioneer, including authoring stories, plays, and translating seminal texts, and she founded social clubs for Jewish women, worked in orphanages and founded the German Federation of Jewish Women.
Kitty Genovese
Sadly, it is not really Kitty Genovese the person who has become one of psychology’s classic case studies, but rather the terrible fate that befell her. In 1964 in New York, Genovese was returning home from her job as a bar maid when she was attacked and eventually murdered by Winston Mosely. What made this tragedy so influential to psychology was that it inspired research into what became known as the Bystander Phenomenon – the now well-established finding that our sense of individual responsibility is diluted by the presence of other people. According to folklore, 38 people watched Genovese’s demise yet not one of them did anything to help, apparently a terrible real life instance of the Bystander Effect. However, the story doesn’t end there because historians have since established the reality was much more complicated – at least two people did try to summon help, and actually there was only one witness the second and fatal attack. While the main principle of the Bystander Effect has stood the test of time, modern psychology’s understanding of the way it works has become a lot more nuanced. For example, there’s evidence that in some situations people are more likely to act when they’re part of a larger group, such as when they and the other group members all belong to the same social category (such as all being women) as the victim.
Little Albert
“Little Albert” was the nickname that the pioneering behaviourist psychologist John Watson gave to an 11-month-old baby, in whom, with his colleague and future wife Rosalind Rayner, he deliberately attempted to instill certain fears through a process of conditioning. The research, which was of dubious scientific quality, was conducted in 1920 and has become notorious for being so unethical (such a procedure would never be given approval in modern university settings). Interest in Little Albert has reignited in recent years as an academic quarrel has erupted over his true identity. A group led by Hall Beck at Appalachian University announced in 2011 that they thought Little Albert was actually Douglas Merritte, the son of a wet nurse at John Hopkins University where Watson and Rayner were based. According to this sad account, Little Albert was neurologically impaired, compounding the unethical nature of the Watson/Rayner research, and he died aged six of hydrocephalus (fluid on the brain). However, this account was challenged by a different group of scholars led by Russell Powell at MacEwan University in 2014. They established that Little Albert was more likely William A Barger (recorded in his medical file as Albert Barger), the son of a different wet nurse. Earlier this year, textbook writer Richard Griggs weighed up all the evidence and concluded that the Barger story is the more credible, which would mean that Little Albert in fact died 2007 aged 87.
Chris Sizemore
Chris Costner Sizemore is one of the most famous patients to be given the controversial diagnosis of multiple personality disorder, known today as dissociative identity disorder. Sizemore’s alter egos apparently included Eve White, Eve Black, Jane and many others. By some accounts, Sizemore expressed these personalities as a coping mechanism in the face of traumas she experienced in childhood, including seeing her mother badly injured and a man sawn in half at a lumber mill. In recent years, Sizemore has described how her alter egos have been combined into one united personality for many decades, but she still sees different aspects of her past as belonging to her different personalities. For example, she has stated that her husband was married to Eve White (not her), and that Eve White is the mother of her first daughter. Her story was turned into a movie in 1957 called The Three Faces of Eve (based on a book of the same name written by her psychiatrists). Joanne Woodward won the best actress Oscar for portraying Sizemore and her various personalities in this film. Sizemore published her autobiography in 1977 called I’m Eve . In 2009, she appeared on the BBC’s Hard Talk interview show.
David Reimer
One of the most famous patients in psychology, Reimer lost his penis in a botched circumcision operation when he was just 8 months old. His parents were subsequently advised by psychologist John Money to raise Reimer as a girl, “Brenda”, and for him to undergo further surgery and hormone treatment to assist his gender reassignment.
Money initially described the experiment (no one had tried anything like this before) as a huge success that appeared to support his belief in the important role of socialisation, rather than innate factors, in children’s gender identity. In fact, the reassignment was seriously problematic and Reimer’s boyishness was never far beneath the surface. When he was aged 14, Reimer was told the truth about his past and set about reversing the gender reassignment process to become male again. He later campaigned against other children with genital injuries being gender reassigned in the way that he had been. His story was turned into the book As Nature Made Him, The Boy Who Was Raised As A Girl by John Colapinto, and he is the subject of two BBC Horizon documentaries. Tragically, Reimer took his own life in 2004, aged just 38.
Christian Jarrett ( @Psych_Writer ) is Editor of BPS Research Digest
This article was originally published on BPS Research Digest . Read the original article .


Sign up for your FREE e-newsletter
You’ll regularly recieve powerful strategies for personal development, tips to improve the growth of your counselling practice, the latest industry news and much more.
We’ll keep your information private and never sell, rent, trade or share it with any other organisation. And you can cancel anytime.
Counselling Case Study: Relationship Problems
Mark is 28 and has been married to Sarah for six years. He works for his uncle and they regularly stay back after work to chat. Sarah has threatened to leave him if he does not spend more time with her, but when they are together, they spend most of the time arguing, so he avoids her even more. He loves her, but is finding it hard to put up with her moods. The last few weeks, he has been getting really stressed out and is having trouble sleeping. He’s made a few mistakes at work and his uncle has warned him to pick up his act.
This study deals with the first two of five sessions. The professional counsellor will be using an integrative approach, incorporating Person Centred and Behavioural Therapy techniques in the first session, moving to a Solution Focused approach in the second session. For ease of writing the Professional Counsellor is abbreviated to “C”.
After leaving school at 17, Mark completed a mechanic apprenticeship at a service station owned by his uncle and has worked there ever since. His father died from a heart attack when Mark was six years old and his uncle, who never married, has been a significant influence in his life. He is the youngest of three children, and the only boy in the family. One sister (Anne) is happily married with two children and the other (Erin) is single and works overseas. Mark and his mother have a close relationship, and he was living at home until his marriage.
Some of Mark’s friends are not married and say he was a fool for ‘getting tied down’ so young. Mark used to think that they were just jealous because Sarah is such a ‘knockout’, but lately he has started to wonder if they were right. In the last couple of months, Sarah has been less concerned about her appearance and Mark has commented on this to her. Sarah had been looking for work, but doesn’t seem to do much of anything now.
Three months ago, Sarah found out she can’t have children. According to Mark, she hadn’t spoken about wanting kids so he guessed it wasn’t a big deal to her. When she told him, Mark had joked that at least they wouldn’t have to go into debt to educate them. He thought humour was the best way to go, because he had never been very good at heavy stuff. Sarah had just looked at him and didn’t respond. He asked if she wanted to go out to a movie that night, and she had started to shout at him that he didn’t care about anyone but himself. At that point, he walked out and went to see his brother-in-law, Joe and sister, Anne.
Since then, he and Sarah hardly spoke and when they did it often turned into an argument that ended with Sarah going into the bedroom, slamming the door and crying. Mark usually walked out and drove over to Joe’s place. When Anne tried to talk to Sarah about it, Sarah got angry and told Anne to keep out of it, after all what would she know about it. She had her kids. Joe and Anne had kept their distance since then. Mark talked to his mother, but she said that this was something he and Anne had to work out together. It was she who suggested that Mark come to see C.
Session One
When Mark arrived for the first session, he seemed agitated. C spent some time developing rapport, and eventually Mark seemed to relax a bit. C described the structure of the counselling session, checked if that was ok with Mark, then asked how C could help him.
Mark: “I really wanted Sarah to come; my wife, but she said that I need to sort myself out. I have to tell you, I don’t think counselling is really for men. Women are the ones that like to talk for hours about their problems. I only came here because she insisted and I don’t want her to walk out on me.”
C: “Your marriage is important to you.”
Mark: “Yeah, sure. We’ve had fights before, but they weren’t anything major. And we always made up pretty quickly. But this is different. It seems like whatever I say is wrong, you know? Lately, I haven’t been able to concentrate properly at work and I wake up a lot through the night. I’m feeling really tired and I wish Sarah would get off my case.”
C used encouragers while Mark described what had been happening over the past few months. When he had finished ventilating his immediate concerns, C, moving into Behavioural techniques, summarized and asked Mark to decide what issue he wanted to deal with first. “Mark, you have discussed a number of issues: you are concerned that communication between you and Sarah has been reduced to mostly arguments; you’re unsure how to deal with the fact that Sarah cannot have children; you want to improve your relationship with Sarah; you are worried that Sarah might leave you, and you are feeling very stressed out. What area would you like to work on first?”
Mark: “I just want her to talk to me without arguing. All this is making it really hard for me to concentrate at work, you know.”
C: “Sounds like two goals there, to reduce your stress and to improve communication between Sarah and yourself.”
M: “Yeah, I guess so. If she would just talk to me instead of crying.”
C used open questions and reflections to encourage Mark to look at his feelings. “How do you feel when she goes into the bedroom and starts crying?” Mark: “Well, she’s never been a crier, and I don’t know what to say to her. If I mention not having children, she will probably cry even more.”
C: “So you feel confused about what to do, and anxious that you may upset her even more.”
Mark: “Yes, I just can’t seem to think straight sometimes. Like, I want things to be the way they were, but it’s just getting worse.”
C informed Mark about the use of relaxation techniques to reduce his stress and checked out if he would like to give it a try. “Mark, you appear to be having difficulty coping because you are feeling very stressed. I believe that learning relaxation techniques would decrease the level of stress and help you think more clearly. How does this sound to you?”
Mark: “I’m not into that chanting stuff if that’s what you mean.”
C explained that there are many forms of relaxation and described the deep breathing and muscle tensing method; Mark agreed to do this for 10 minutes twice a day.
As the first session drew to a close, C reviewed the relaxation technique and asked Mark to practise it as often as possible. A second appointment was arranged for the following week.
At the next session, C asked Mark how the relaxation exercise had helped. “I forget to do it some mornings, so I did it for twenty minutes at night instead. I told Sarah what I’m doing and she just leaves me to it. Not sure if it’s making any difference but I’ll keep doing it. It’s nice to have twenty minutes of peace and quiet.” At this point, C moved into a Solution Focused approach.
C congratulated Mark on commencing the relaxation practice, then checked out if it was okay to ask him some different types of questions. Mark agreed and C asked a miracle question. “Imagine that you wake up tomorrow and a miracle has happened. Your problem has been solved. What would other people notice about you that would indicate things are different?”
Mark looked at C, who waited in silence. Eventually Mark responded. “Ok, they would see me and Sarah talking a lot more, without arguing.”
C: “What else would they notice about you?”
Mark: “I would probably be spending more time at home. You know, not staying back so late at work.”
C: “What would they notice that was different about Sarah?”
Mark: “That’s easy. She wouldn’t be crying and yelling all the time.”
C: “So what would she be doing instead?”
Mark: “I guess she would be talking to me, and smiling.”
After spending some time exploring what would be different if the miracle happened, C asked Mark what he had tried in the past to improve communication. Mark revealed that he bought Sarah some flowers and a box of chocolates (his uncle’s suggestion) but it hadn’t really made any difference. C complimented Mark on his efforts and continued with an exception question.
“Can you think of a recent occasion, when you would have expected a quarrel to start and it didn’t?”
Mark furrowed his brow and appeared to be thinking deeply for some time. C waited in silence. Finally, Mark answered. “Actually, about a week ago, I was a bit late home from work and I was expecting another tongue-lashing, but it never came.”
C asked Mark what was different about that night.
Mark: “Well, Sarah was happier.”
C: “How did you know she was happier?”
Mark: “She talked to me, you know, just talked about something she had seen on the telly or something like that.”
C: “And how was that for you, Mark?”
Mark: “Not bad. Actually, it wasn’t too shabby. We did get to chat, and we haven’t done that for ages.”
C: “Can you explain, “Wasn’t too shabby”; I haven’t heard that term before?”
Mark: “Oh, it means it was all good, you know, it was okay.”
C: “So you came home and chatted with Sarah over a cuppa and you found that wasn’t too shabby?” Both smiled
Mark: “I really liked it. I remember thinking I would have come home earlier if I had known it was going to be like that.”
C: “If I was to ask Sarah what was different about that night, what do you think she would say?”
Mark: “Boy, this is getting weird.”
Mark: “Let’s see. She would probably say, “He actually sat and had a cup of coffee with me, instead of just flopping in front of the telly. She’s always griping about that.”
At the appropriate time, C called for a break. “I’d like to take a break and give us both time to consider all the things we’ve talked about. After that, I will give you some feedback.” After the break C summarized what had been discussed and complimented Mark on the work he had put into exploring his problems. He seemed less stressed and had shown that he was committed to improving his relationship with Sarah.
Counselling continued for another three sessions, by which time Mark’s stress had reduced considerably, he was coming home from work earlier and making an effort to talk more to Sarah. The arguments were less frequent and not so heated.
Session Summary
The Person Centred approach allows the client to take the lead and discuss issues as they see them. This encourages the client to talk openly, which was especially useful in this instance since the client showed a reluctance to do so at first.
The Behavioural technique of goal setting is used to clarify what the client wants to achieve out of the sessions.
Solution Focused Therapy, this approach acknowledges that the client has the ability to solve his own problem.
Miracle questions assist the client to examine how they and others would be behaving if the problem were already dealt with. This helps the client to look at their current behaviour and see what they can do to bring about the required change. Exploring what the client has tried in the past highlights that the client is committed to solving the problem. Exception questions help the client to see that there are times when the problem does not occur, and that they have contributed to that situation. This shows the client that they have control over the problem.
Clarifying client’s words, eg. “Not too shabby” shows respect for the client’s language and emphasises that the client is the expert.
Author: Jan McIntyre
Related Case Studies: A Case of Acceptance and Letting Go , A Case of Stress , A Case of Using Logical Consequences
- April 16, 2007
- Case Study , Person-centred , Solution-focused
- Case Studies , Relationship & Families
Comments: 1
Thank you! Very well explained. How to build rapport so that client loosens up.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Topics for Psychology Case Studies
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Ridofranz / Getty Images
In one of your psychology classes, you might be asked to write a case study of an individual. What exactly is a case study? A case study is an in-depth psychological investigation of a single person or a group of people.
Case studies are commonly used in medicine and psychology. For example, these studies often focus on people with an illness (for example, one that is rare) or people with experiences that cannot be replicated in a lab.
Here are some ideas and inspiration to help you come up with a fascinating psychological case study.
What Should Your Case Study Be About?
Your instructor will give you directions and guidelines for your case study project. Make sure you have their permission to go ahead with your subject before you get started.
The format of your case study may vary depending on the class requirements and your instructor's expectations. Most psychological case studies include a detailed background of the person, a description of the problem the person is facing, a diagnosis, and a description of an intervention using one or more therapeutic approaches.
The first step in writing a case study is to select a subject. You might be allowed to conduct a case study on a volunteer or someone you know in real life, such as a friend or family member.
However, your instructor may prefer that you select a less personal subject, such as an individual from history, a famous literary figure, or even a fictional character.
Psychology Case Study Ideas
Want to find an interesting subject for your case study? Here are just a few ideas that might inspire you.
A Pioneering Psychologist
Famous or exceptional people can make great case study topics. There are plenty of fascinating figures in the history of psychology who would be interesting subjects for a case study.
Here are some of the most well-known thinkers in psychology whose interesting lives could make a great case study:
- Sigmund Freud
- Harry Harlow
- Mary Ainsworth
- Erik Erikson
- Ivan Pavlov
- Jean Piaget
- Abraham Maslow
- William James
- B. F. Skinner
Examining these individuals’ upbringings, experiences, and lives can provide insight into how they developed their theories and approached the study of psychology.
A Famous Patient in Psychology
The best-known people in psychology aren’t always professionals. The people that psychologists have worked with are among some of the most fascinating people in the history of psychology.
Here are a few examples of famous psychology patients who would make great case studies:
- Anna O. (Bertha Pappenheim)
- Phineas Gage
- Genie (Susan Wiley)
- Kitty Genovese
- Little Albert
- David Reimer
- Chris Costner Sizemore (Eve White/Eve Black)
- Dora (Ida Bauer)
- Patient H.M. (Henry Molaison)
By taking a closer look at the lives of these psychology patients, you can gain greater insight into their experiences. You’ll also get to see how diagnosis and treatment were different in the past compared to today.
A Historical Figure
Historical figures—famous and infamous—can be excellent subjects for case studies. Here are just a few influential people from history that you might consider doing a case study on:
- Eleanor Roosevelt
- George Washington
- Abraham Lincoln
- Elizabeth I
- Margaret Thatcher
- Walt Disney
- Benjamin Franklin
- Charles Darwin
- Howard Hughes
- Catherine the Great
- Pablo Picasso
- Vincent van Gogh
- Edvard Munch
- Marilyn Monroe
- Andy Warhol
- Salvador Dali
You’ll need to do a lot of reading and research on your chosen subject's life to figure out why they became influential forces in history. When thinking about their psychology, you’ll also want to consider what life was like in the times that they lived.
A Fictional Character or a Literary Figure
Your instructor might allow you to take a more fun approach to a case study by doing a deep dive into the psychology of a fictional character.
Here are a few examples of fictional characters who could make great case studies:
- Macbeth/Lady Macbeth
- Romeo/Juliet
- Sherlock Holmes
- Norman Bates
- Elizabeth Bennet/Fitzwilliam Darcy
- Katniss Everdeen
- Harry Potter/Hermione Granger/Ron Weasley/Severus Snape
- Batman/The Joker
- Atticus Finch
- Mrs. Dalloway
- Dexter Morgan
- Hannibal Lecter/Clarice Starling
- Fox Mulder/Dana Scully
- Forrest Gump
- Patrick Bateman
- Anakin Skywalker/Darth Vader
- Ellen Ripley
- Michael Corleone
- Randle McMurphy/Nurse Ratched
- Miss Havisham
The people who bring characters to life on the page can also be fascinating. Here are some literary figures who could be interesting case studies:
- Shakespeare
- Virginia Woolf
- Jane Austen
- Stephen King
- Emily Dickinson
- Sylvia Plath
- JRR Tolkien
- Louisa May Alcott
- Edgar Allan Poe
- Charles Dickens
- Ernest Hemingway
- F. Scott Fitzgerald
- George Orwell
- Maya Angelou
- Kurt Vonnegut
- Agatha Christie
- Toni Morrison
- Daphne du Maurier
- Franz Kafka
- Herman Melville
Can I Write About Someone I Know?
Your instructor may allow you to write your case study on a person that you know. However, you might need to get special permission from your school's Institutional Review Board to do a psychological case study on a real person.
You might not be able to use the person’s real name, though. Even if it’s not required, you may want to use a pseudonym for them to make sure that their identity and privacy are protected.
To do a case study on a real person you know, you’ll need to interview them and possibly talk to other people who know them well, like friends and family.
If you choose to do a case study on a real person, make sure that you fully understand the ethics and best practices, especially informed consent. Work closely with your instructor throughout your project to ensure that you’re following all the rules and handling the project professionally.
APA. Guidelines for submitting case reports .
American Psychological Association. Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct, including 2010 and 2016 amendments .
Rolls, G. (2019). Classic Case Studies in Psychology: Fourth Edition . United Kingdom: Taylor & Francis.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
5 Fascinating Clinical Psychology Case Studies

If you pursue work as a clinical psychologist, you’ll be able to make a major difference in people’s lives. In most cases, these psychologists are the first practitioners to recognize and diagnose mental health disorders. Many clinical psychologists also practice “talk therapy,” where they talk through issues with patients and help them develop better coping mechanisms. But what’s it really like to work in clinical psychology? Take a look at each case study psychology below to get an idea.
A Day in the Life of a Clinical Psychologist
As you might be able to tell from the name, a clinical psychologist applies psychology knowledge in a clinical setting. Using their knowledge of different mental disorders and how they present, clinical psychologists help patients identify and then treat mental health disorders. They also can help patients work through psychological issues even if no disorder is present.
However, it’s important to note that clinical psychologists do not prescribe medication. Often, once a clinical psychologist makes a diagnosis that requires medication, they will refer a patient to a psychiatrist. The psychiatrist handles the medication, but a clinical psychologist will often help a patient manage some of their symptoms through some form of talk therapy. In the case of some complex disorders, a psychologist may be able to coordinate with the patient’s psychiatrist in order to ensure the best care possible.
Some people believe that talk therapy is just a patient talking while the psychologist listens. However, this couldn’t be further from the truth. Clinical psychologists are tasked with assessing each patient and developing an individualized treatment plan. Often, that plan includes delving into the patient’s issues and helping them understand their roots. From there, the psychologist can help the patient develop healthier coping mechanisms for dealing with those issues.
Usually, clinical psychologists primarily work with patients on an individual basis. They do this either as part of a group practice or in private practice. Sometimes, they may teach classes, although this usually isn’t the bulk of their workload. Clinical psychologists often will conduct and publish research that sometimes involves case studies of patients.
Becoming a Clinical Psychologist

To become a clinical psychologist, you will need to pursue a doctoral degree. Most clinical psychologists have either a Ph.D. or a PsyD, though the Ph.D. is more common in the field and will usually afford you more career opportunities. PsyD programs tend to accept more applicants than Ph.D. programs. A PsyD degree places more focus on applying concepts of psychology to the clinical setting. A Ph.D. program certainly applies concepts of psychology as well, but it has much more of a focus on research than PsyD programs do.
Regardless of which program you choose, becoming a clinical psychologist involves a considerable time commitment. The first step is obtaining a four-year bachelor’s degree. From there, some candidates pursue a master’s degree, while others go straight into a Ph.D. training program.
Most PsyD programs take four to five years to complete, while most Ph.D. programs take between five and seven years. In the case of a Ph.D., graduates will need to complete a residency program much like medical doctors. Residency programs usually last about one to three years. During that time, new psychologists are overseen by an experienced psychologist. Upon completion of the residency, a clinical psychologist must also take and pass a licensure exam in order to practice in their state. Most states will also allow you to obtain different certifications in specialized areas.
As you can see, the decision to become a clinical psychologist isn’t one to make on a whim. Usually, though, you’ll be able to get a sense of the field from the undergraduate courses you take early on.
What’s a Case Study?
In a moment, we’ll take you through five interesting case studies from real clinical psychologists. But what exactly is a case study?
Simply put, a case study is a very detailed account of an individual patient’s case. (The case studies below are abbreviated versions of case studies.) Psychologists usually keep notes on all patients, but a case study is much more formal. Each study is an in-depth exploration of a patient’s disorder, and it usually contains information on the patient’s personal history as well as how their disorder presents. Most case studies also have information on treatments that have worked (and those that have not worked) for a given patient.
So why is a single case study valuable, especially when most studies survey larger groups of patients? For one, case studies are extremely valuable in the case of rare conditions. With very rare mental health disorders, it can be near-impossible to find larger studies. With case studies, it’s still possible to get an accurate picture of the disorder and what it looks like in different patients.
Case studies can also help future clinical psychologists to sharpen their diagnostic skills. In a broader study, you might learn about some of the common symptoms of a diagnose. But individual patients have their own quirks, and the same disorder can look different from patient to patient. Reading case studies can be a great way to see how different mental health issues can look in different people.
Lastly, case studies can be useful in supporting or refuting existing research. In some cases, they may point to issues that need to be researched further.
To really start to get a sense of what it’s like to be a clinical psychologist, check out these five interesting case studies reported by actual clinicians:
Wishing for Death

Even if you seem to have a promising future, it’s still possible to deal with severe depression. This is what happened to Jessica, a woman who had successfully completed medical school and obtained a residency at a large hospital. In Jessica’s case, her mental state declined seemingly overnight; she awoke one day feeling especially sad. But instead of lifting, that sadness continued and even worsened.
As is the case with many people with depression, Jessica lost interest in things she had previously enjoyed. She stopped having sex with her husband and even found interacting with her children to be a chore. She even found that her job was in jeopardy, as she stopped caring about work and began missing shifts.
Featured Programs
Often, people suffering from severe depression will consider suicide. Some will go as far as making and going through with suicide plans. Jessica wasn’t considering or fantasizing about suicide. But she did begin to wish she was dead, and these thoughts slowly became all-consuming. Despite feeling drained from her low mood, Jessica still had trouble sleeping at night. This is when her thoughts of death were at their worst.
Jessica continued to insist that nothing was wrong. But her coworkers at the hospital saw that something was off. Jessica wasn’t being lazy or slacking for no reason; it was clear her mental health was suffering. Her colleagues were able to convince Jessica to see a mental health professional. She was diagnosed with major depressive disorder, a mental health disorder that causes severe and persistent sadness and loss of interest.
College Struggles
Many mental health issues present themselves when people are college-aged, and this is what happened to Gerry, a 21-year-old college student who got good grades. Gerry got along well with his friends and roommates until he started having trouble sleeping. At night, his thoughts began to race and felt as though they were spinning out of control.
But that wasn’t all. Gerry was usually a kind and mild-mannered person, but he began calling his friends at all hours of the night, becoming angry if they didn’t give him the attention he wanted. Within a few days, Gerry started to believe his roommates were spying on him. He told them as much. Instead of writing it off as simply a quirk, his friends became very concerned. They talked to Gerry and explained the strange changes they’d been seeing in his behavior. Ultimately, they were able to convince Gerry to seek mental health help.
After talking with a clinician, Gerry was ultimately diagnosed with bipolar disorder. It can be an intimidating diagnosis to receive, but Gerry was referred to a psychiatrist who could work with him to find the right medication. The combination of medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy helped him to return back to his normal self.
A Case of Obsession

Plenty of people are fastidious about certain things, but one salesman took it a little too far. The salesman was having trouble leaving his house on time to get to work because he had an overwhelming and obsessive need to follow a set of rituals. Many of them were about securing the home. It started with double-checking and triple-checking that doors were locked.
The salesman also became incredibly worried about the electrical wiring in the home. He began to obsess over whether it would cause an electrical fire. If he didn’t complete the various rituals he felt compelled to do, the man believed he would experience bad luck.
Once he saw a psychologist, the man was diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Since this disorder involves holding onto irrational beliefs, cognitive-behavioral therapy is essential. The man’s psychologist worked with him through therapy and helped him to manage and then overcome his obsessive thoughts. Ultimately, the salesman was able to get back to a much more normal life.
Unexpected Panic
Panic disorders and anxiety disorders can seem to poison your life. That’s what it felt like for one forest ranger. Up until his mid-30s, he didn’t suffer from more than normal anxiety. But one day, while standing in line at the grocery store, he suddenly felt an overwhelming wave of panic. His heart rate went up and he started sweating. The panic attack was so bad that the forest ranger thought he would pass out, so he abandoned his shopping cart and returned to the car.
Naturally, the forest ranger didn’t want the same thing to happen again. Because that first panic attack had occurred in a grocery store, he began avoiding supermarkets. But that didn’t help for long. He began to experience intense anxiety in many areas of his life. His symptoms were so severe that his family life began to suffer, so he sought help.
The forest ranger saw a psychologist and was diagnosed with an anxiety disorder. Though some people with anxiety disorders benefit from medication, the forest ranger was able to work through and manage his symptoms through cognitive behavioral therapy.
Bizarre Behaviors
Most severe mental disorders don’t start in childhood. When they do appear, these disorders often involve someone who previously seemed outwardly normal suddenly exhibiting strange behaviors. This is what happened to a 21-year-old business student. He suddenly began becoming agitated for no ostensible reason. During his bouts of agitation, other people heard him whispering angrily to himself.
The young man’s friends and family were very concerned, but they were unable to reach him by phone. He explained that aliens had placed a chip in his brain and that it would explode if he answered his phone.
Sometimes, symptoms like those the young man had can be caused or made worse by abusing alcohol or drugs. However, the young man didn’t abuse either. A family history of mental illness can sometimes be a risk factor, and the man did say he had an aunt who had been treated at psychiatric hospitals several times.
Thanks in part to the concern of his friends and family, the young man talked to a psychologist and gave a detailed account of his symptoms. He was diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia. This is a difficult diagnosis to receive. But as the young man found, schizophrenia is possible to manage with good care. The young man’s psychologist was able to continue therapy, and he was also referred to a psychiatrist for help with medication. Often, for those diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia, a combination of therapy and the right medications can effectively manage symptoms.
Each case study psychology above is just a short introduction to the types of cases you may encounter working as a clinical psychologist. And when working in the field, you’ll be asked to write your own case studies, too. While in school, you’ll learn the correct way to write case studies and how sharing case studies with other psychologists can help the field grow as a whole. Hopefully, these case studies have also shed some light on one of the best parts of working as a clinical psychologist — you can help people confront and work through mental health challenges and work toward healthier, happier lives.
Related Resources:
- Top 10 Most Affordable Online Master’s in Clinical Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 6 Most Affordable Online PhD/PsyD Programs in Clinical Psychology
- What Does a Clinical Psychologist Do?
- 5 Career Settings for a Clinical Psychologist
- 5 Differences Between Clinical and Developmental Psychology
- 5 Differences Between Social Psychology and Clinical Psychology
- 5 Highest Paying Careers in Clinical Psychology
- 5 Internship Opportunities in Clinical Psychology
- 5 Podcasts for Clinical Psychology
- 5 Reasons to Become a Clinical Psychologist
- 5 TED Talks on Clinical Psychology
- 5 Websites for Clinical Psychologists
- Online Clinical Psychology Degree
- Can Clinical Psychologists Prescribe Medication?
- What are the Differences Between a Clinical Psychologist and a Counselor?
- What is Clinical Psychology?
- What is the Employment Outlook for Clinical Psychologists?
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. Marriage and Family Counseling Programs
- Top 5 Online Doctorate in Educational Psychology
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. in Industrial and Organizational Psychology Programs
- Top 10 Online Master’s in Forensic Psychology
- 10 Most Affordable Counseling Psychology Online Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Industrial Organizational Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Developmental Psychology Online Programs
- 15 Most Affordable Online Sport Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable School Psychology Online Degree Programs
- Top 50 Online Psychology Master’s Degree Programs
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Educational Psychology
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Industrial/Organizational Psychology
- Top 10 Most Affordable Online Master’s in Clinical Psychology Degree Programs
- 50 Great Small Colleges for a Bachelor’s in Psychology
- 50 Most Innovative University Psychology Departments
- The 30 Most Influential Cognitive Psychologists Alive Today
- Top 30 Affordable Online Psychology Degree Programs
- 30 Most Influential Neuroscientists
- Top 40 Websites for Psychology Students and Professionals
- Top 30 Psychology Blogs
- 25 Celebrities With Animal Phobias
- Your Phobias Illustrated (Infographic)
- 15 Inspiring TED Talks on Overcoming Challenges
- The 25 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History
- 20 Most Unethical Experiments in Psychology
- 10 Fascinating Facts About the Psychology of Color
- 15 Scariest Mental Disorders of All Time
- 15 Things to Know About Mental Disorders in Animals
- 13 Most Deranged Serial Killers of All Time

Site Information
- About Online Psychology Degree Guide
Not Just a Boring Worksheet: New Interactive Case Studies for Abnormal Psychology
How do you teach your students about the diagnostic process? Do you have them read a case study? Do you show them a quick video in class?
Do you ever get the sense that they're not really engaged in the case studies you give them?
With the new McGraw-Hill Interactive Case Studies, your students are involved in the diagnostic process, developing empathy and critical thinking skills as they work their way through 12 differential diagnoses.
What did our student reviewers have to say about the Interactive Case Studies?
"You get to apply what you know, or think you know. It helped me piece together the whole puzzle." – Student at the University of Georgia
"It's very interactive. You have to think about what you're doing." – Student at Prairie View A&M University
"It felt like a game… more interesting than reading the text." – Student at University of Nebraska – Omaha
"Cool activity… I would choose it over boring homework." – Student at San Jose State University
Our instructor reviewers were on board, too, agreeing that students would learn much more from the case studies and enjoy them much more than a worksheet.
Let's take a peek at the Interactive Case Studies!
At the beginning of the case, students are introduced to the practitioner they will be working with. The practitioner guides the student throughout the case, providing background, conducting the client interview, and discussing possible diagnoses based on the presenting case.

As students observe the client interview, they are presented with a series of glowing objects, which – when clicked – provide background information about the client that cannot necessarily be obtained from the interview. Examples include medical records and interviews with family.
At three checkpoints during the case, students are asked to decide which information from the interview is more relevant to making a diagnosis, and which information is less relevant.
Throughout the case, students have access to an interactive continuum to see the range of behavior for the particular disorder, from functional to dysfunctional. The continuum indicates the behaviors students should pay attention to, while also conveying the idea that behavior is on a continuum and that a diagnosis is never black and white.
At the conclusion of the interview, students are asked to match the information in their notebook (which is populated at each of the three checkpoints) to the symptoms of the disorder.
After performing this exercise, students are asked to select whether they believe the client has one of two presented disorders (or no disorder). The practitioner then makes a diagnosis, provides feedback to the student, and offers an overview of their treatment plan for the client.
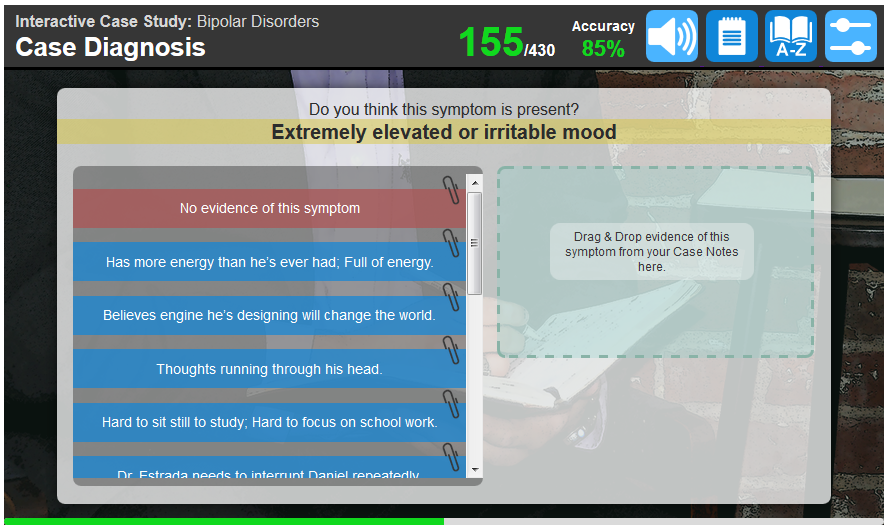
The Interactive Case Studies are live for fall classes, and are assignable and assessable within Connect.
Which disorders are covered by the Interactive Case Studies?
There are 12 case studies, covering the following disorders and groups of disorders:
- Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders
- Psychotic Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder
- Depressive Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Eating Disorders
- Substance-Related Disorders
- Conduct and Impulse Control Disorders
- Somatic Symptom Disorders
- Gender Dysphoria and Transvestic Disorder
- Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Attending a conference?
Checkout if mcgraw hill will be in attendance:.
Writing: Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Error goes here
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
New User? Start Here
Psychology Case Study Examples With Solutions
Hire one of our psychologists for unique solutions.
What Are Psychology Case Study Examples For Students?
We know how difficult it is to get good psychology case study examples with solutions. Here we have listed psychology case study analysis examples which will help students get an idea of the kind of topics they should frame:-
- The pattern of anger which follows from parents to children
- Significant factors for the development of social anxiety
- How therapy psychologically helps a person
- Connection of finances and mental wellbeing
- Should critical thinking be introduced in classes in school?
- The negative impact of horror movies and stories on children
- Obsession issues related to gambling
These are some of the vital psychology case studies examples for students. If you need psychology case study examples with solutions, then get our psychology case study help online. Click on the button below to get our help today.
How To Write A Case Study Psychology?
Case studies are elaborate work which needs a lot of research, patience, and flair in writing. Like every other case study, the process of writing case studies in psychology is similar. Yet here we are going to break down the steps for how to write a case study in psychology:-
Choose a topic
Picking a vital psychology case study topic is highly important. Unfortunately, most students pick up bland topics that are of no interest to the readers and the professor. Instead, go through psychology case study analysis examples to pick out good topics which are new and less talked about.
Do your research
The next tip is to do thorough research. Look for offline and online sources in case study psychology topics to gather the best facts.
Build a structure
Building accurate structure in the case study is very important. Every case study follows a specific format. If you are unaware, look through papers of experts in case study of psychology to get an idea of structure building.
Discuss the problems
Every psychology paper has one main problem that needs to be discussed. Even in your case study of psychology do not forget to discuss the main problem. First, state the roots of the problem for your audience to be aware of your topic.
State remedies
Of course, the next step is to state the solutions to the problems. Stating down the issues only is not the correct format. The next step is to lay down all the essential ways out of the problem.
Finally, the last step is to conclude your paper. A reasonable conclusion can have a long-lasting effect on getting readers to finish the article on a clear note. Therefore, write a rational decision which adds clarity to the topic.
These are the perfect steps to writing a good case study in psychology. But, of course, we know saying is easier than done. So if you are facing any problem with it, get our psychology case study help online, where professionals frame the best paper for you. Above are the top steps for how to write psychology case study.
How Does A Case Study Research Method Work?
The process of case study in psychology research is very intense. Although the research process might not seem to be very different. Yet here we are stating the tips on how to research for a psychology case study analysis example:-
1) Online sources ( websites, pdfs, etc.)
2) Offline sources (books, journals, news)
3) Interviews
These are some of the standard case study research methods. Apart from this, there are tons of other research methods, but these are the most common. However, these can be very difficult for beginner students, so we offer online psychology case study help. So connect with us today to get the help you need for your psychology case study.
Click To Connect
What Are The Types Of Psychology Case Study?
Numerous students tend to say, ‘I need exceptional psychology case study examples with solutions’ when they cannot develop a profound knowledge of the different types of psychology case studies and how to approach them in an accurate manner. However, you can prevent this situation from becoming a reality by opting for our quality psychology case study help services.
Here are certain types of psychological case studies enlisted by our stalwarts that you must know to revamp your psychology case study game by notches-
Collective Case Study
Collective case studies in psychology involve studying a group of individuals. Psychologists might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For instance, psychologists can explore how to access resources in a community that has hugely impacted the collective mental well-being of those living there.
Descriptive Case Study
According to our prolific stalwarts who cater to requests like ‘how to write a psychology case study’, descriptive case studies involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information collected is compared to the pre-existing theory.
Explanatory Case Study
In psychology, explanatory case studies are often used to conduct casual investigations. In other words, psychologists are interested in looking at the crucial factors that may have changed certain things to occur. The aim of these types of case studies aims to answer 'how' or 'why' questions with little control on behalf of the researcher over the occurrence of events. This kind of case study focuses on phenomena within the context of real-life situations.
Exploratory Case Study
Psychology exploratory case studies are sometimes used as a prelude to conducting extensive and in-depth research. This enables psychologists to collect more information before developing the research questions and hypotheses.
Instrumental Case Study
Instrumental case studies occur when an individual or a group allows researchers to comprehend more than what is initially obvious to observers. It is the study of a case to provide insight into a specific issue, redraw generalisations, or build theory. In the instrumental case study, one needs to research the case to facilitate the understanding of something else.
Intrinsic Case Study
An intrinsic case study of a case (like the person, specific group, occupation, department, or company) where the case itself is of primary interest in the exploration. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are brilliant examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
Now, if you are unable to comprehend these kinds of psychology case studies successfully, availing our psychology case study solutions will be the wisest choice for your career. We also conduct comprehensive study sessions and offer remarkable psychology case study examples with solutions that will help you get back on track right away.
What Are The Different Psychology Case Study Formats Available To Us?
Although case study is a single term, there are many different psychological case study formats. Here are some of the significant case study formats in psychology:-
Illustrative case study
An illustrative case study is a descriptive kind of case study which offers a lot of information on the main subject. If you are poor in writing and researching, you can get our online case study in psychology as we provide the best illustrative case study.
Cumulative case study
A cumulative case study is used for qualitative works mainly. However, it can also be used to compare subjects to put across an idea of a point.
Exploratory case study
Explanatory case studies are the ones which are written to set the base on the main topic. This is like a preliminary search that gives light background information on the main subject before getting onto the main idea.
These are some of the significant psychological case study formats. Apart from these, there are numerous other case study format psychology which exists. If you are facing a problem with any of them, then get our Psychology case study service today with us.
Hire Experts
Psychology Case Study Topics Covered By Our Case Study Experts
The various psychology case study topics are sure to give nightmares to students. The crucial theories, various concepts, and the right methods to incorporate are not a cup of tea for every student. Taking psychology case study help from us will aid you in deciphering the exact intricacies of the field.
Your psychology case studies will exhibit sheer brilliance if we have written them for you. So, put an end to all your concerns about writing a challenging paper and avail our psychology case study services from us. The breadth of our expertise range across the following trending and popular psychology case study topics-
- Impacts of distance learning and how it impacts social interaction
- Relationship between social development and the ageing process
- Ways poor early childhood development affects emotions effectively
- Can lack of social cognition lead to frontal brain damage?
- Impact of autism on young children
- Ways people encounter postpartum depression
- How memory loss can be recovered
- Ways ADHD impact our development and growth
- Impact of gender roles
- Ways judgment influences us
- Ageing and adulthood
- Five development stages of a child
- Ways short-term memory changes as a person grow
- Ways parental development impacts child development.
- Mood freezing and its implications
- Lack of sleep and its impact on memory
- The ethical question of having your clients as friends on social media
- Committing a crime as a way of justifying the past trauma
- Causes of Alzheimer’s disease
- The adult content in cartoon anime
- Role of therapists
- Anxiety disorders among male and female adults
- Controlling chronic pain through psychology
- Impact of abusive relationships
- Effects of insomnia
If you need a psychology case study on a topic that is not listed above, do not panic. Our stalwarts of psychology case study services have decades of in-hand knowledge and experience in handling any topics. If you aim to score high GPAs without putting your hand into the arduous task, connect with our psychology case study stalwarts immediately.
What Are The Benefits Of Using MyAssignmentHelp As Your Online Psychology Case Study Service?
Students can find many psychology case study help services online, so what makes us the best Psychology case study service? The perks we provide are a lot more than others, which is why students keep us as their top priority. Here is a list of our excellent benefits which makes us the best in the industry:-
Top-quality papers
Getting top-quality papers from a trusted Psychology case study service is the intention when students avail psychology case study help services. We have qualified and experienced professionals in our psychology case study help services who craft the most insightful papers on psychology.
Authentic assignments
Our psychology assignments are crafted by excellent experts in our psychology case study help services. We never provide plagiarized works. Get 100% original papers from us.
On-time submission
Need a good case study on psychology within deadlines? Don’t worry as we can provide excellent papers even within 24 hours. Get our psychology case study help services as we have never missed an assignment deadline.
Free revisions
Not satisfied with the paper we have written? Don't worry, as our online psychology case study help services offer free revisions. Furthermore, we do not charge any extra cost for modifying our paper.
Free sample papers
Our psychology case study help services also provide free sample papers. These free psychology case studies can help students understand the concept and use it as a study guide.
24/7 assistance
Experts in our Psychology case study service are available 24/7. We are here to listen to any queries of our students and resolve them. Be it morning or night, there has been no time when students could not reach out to us.
Monetary perks
Our Psychology case study service online provides all these features at a nominal rate. On top of that, we offer discounts and offers. Our Psychology case study service also contributes to refer and earn policy and sign-up bonus, which can help reduce the prices even more.
These are some of the perks which make our Psychology case Study Service the best. Students who get our online psychology case study help services always receive the best merit. So connect with us today to get the help you need and get over your psychology case study worries.
Other Case Study Services Covered By Myassignmenthelp.Com
| Business law case study | Case Study Help | Employee Case Study | |
| Zara SWOT and PESTLE Analysis | Walmart Case Study | Case Study Assignment | Gillette Case Study |
| Internet marketing | Toyota case study | Zara Case Study | Accounting Case Study |
Most Popular Questions Searched By Students
Q.1 what is a case study psychology.
Case studies are well-written papers on any topic. For example, a case study on psychology is writing excellent essays based on the subject. You can get our psychology case study help online to receive incredible pieces on any psychology topic. You can also get psychology case study examples with solutions by well educated case study experts.
Q.2 How to write a psychology case study
To write a good psychology case study, you must first pick a topic and then research it. After this, start framing the structure as per deadlines, and finally, do not forget to proofread after completing the entire writing process. You can also get psychology case study examples for students by top case study experts
Q.3 Why Is Case Study Used In Psychology? What Is A Case Study?
A case study is used in psychology to discuss important topics that are less discussed. It also highlights important events and brings them under people's notice. A case study is a kind of assignment written to talk about any topic in detail. Visit us for how to write psychology case study.
Q.4 What Are The Benefits Of A Case Study In Psychology?
There are many benefits of case studies in psychology. Some of them are pouring light on an important topic, providing insightful or new information with an existing topic, and talking about less discussed problems.
Q.5 Can Someone Write A Case Study On Psychology For Me?
You can trust our service if you are looking for a reliable Psychology case study service. We have top experts in our Psychology case study service online. They are all qualified and experienced, so they write full-class papers based on the topic at affordable prices.
TO DOWNLOAD " Company Law Case Studies
The best expert top experts.
Masters in Account...
I am thorough with the changing financial scenario in US and the factors behind it. I am also updated with the changing ...
MS in Computer Sci...
I boast excellent observation and analysis skills. I am excellently thorough with the subject knowing all the aspects, a...
I took a MBA degre...
Along with an in-depth knowledge in marketing I am also skilled in composing assignments especially case studies with pr...
Msc in Nursing fro...
I am in this field for 15 years, which helps me come up with unique topics and cases for students’ papers. I have comp...
MS in Statistics...
I am skilled in creative writing to craft any kind of assignment especially essays, thesis and dissertations of any kind...
MS in Biology...
I am skilled to do research to find proper content for research papers, thesis and dissertation. I give only verified co...
M.sc in Electronic...
Allotting responsibilities and giving directions on achieving the targets within the team. Excellent research and creati...
myCBSEguide
- Class 12 Psychology Case...
Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Are you having trouble preparing for the CBSE Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions? Are you looking for a wide range of Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions? Then you’ve landed in the right place. Students can explore Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions to assist them in answering a range of questions concerning the case study.
Other ed-tech sites may provide limited study material for Class 12 Psychology students, but myCBSEguide has a variety of questions that cover all aspects of Class 12 Psychology including case study questions. Class 12 Psychology questions are designed to help students understand and retain the material covered. In addition, myCBSEguide also offers practice tests and sample papers to help students prepare for Class 12 Psychology exams.
All About Class 12 Psychology Case Study
What is a case study.
A case study is a scenario in a specific professional environment that students must analyze and answer based on specific questions provided about the circumstance. In many cases, the scenario or case study includes a variety of concerns or problems that must be addressed in a professional setting.
Case Study Questions in Class 12 Psychology
Class 12 Psychology Case-Based Questions are a new feature to the exam. Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions are easy to comprehend and will help you get good grades. You may also get free access to the most recent NCERT textbooks for Class 12 Psychology and all other subjects on myCBSEguide, which had been designed in accordance with the most recent Class 12 CBSE/NCERT Psychology curriculum and examination pattern.
Sample Case Study Questions in Class 12 Psychology
Below are some examples of Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions. These Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions will be extremely beneficial in preparing for the upcoming Class 12 Psychology exams. Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions are created by qualified teachers using the most recent CBSE/NCERT syllabus and books for the current academic year. If you revise your Class 12 Psychology exams and class tests on a regular basis, you will be able to achieve higher marks.
Class 12 Psychology Case Study Question 1
Read the case given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option: This is a story of three students Ruby, Radhika and Shankar who were enrolled in an Undergraduate Psychology Program in a University. Ruby was the admission officer’s dream. She was selected for the program as she had perfect entrance test scores, outstanding grades and excellent letters of recommendation. But when it was time for Ruby to start coming up with ideas of her own, she disappointed her professors. On the other hand, Radhika did not meet the admission officer’s expectations. She had good grades but low entrance exam scores. However, her letters of recommendation described her as a creative young woman. She could design and implement research work with minimal guidance at college. Shankar ranked somewhere in between the two students. He was satisfactory on almost every traditional measure of success. But rather than falling somewhere in the middle of his class at college, Shankar proved to be an outstanding student. His strength lay in the ability to not only adapt well to the demands of his new environment but also to modify the environment to suit his needs.
Identify the theory of intelligence which best explains the intelligence of all the three students in the story:
- One Factor Theory
- Theory of Primary Mental Abilities
- Hierarchical Model of Intelligence
- Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
Identify the type of intelligence Ruby possesses.
- Componential
- Experiential
Which of the following statement is NOT TRUE about Radhika’s intelligence?
- People high on this quickly find out which information is crucial in a given situation.
- It is also called experiential intelligence.
- It involves modifying the environment to suit the needs.
- It reflects in creative performances.
Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reasoning (R). Read the statements and choose the appropriate option. Assertion (A): Shankar is not high in contextual intelligence. Reason (R): Shankar was good at adapting well to the demands of his new environment and modifying the environment to suit his needs. Options:
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is true, but R is false.
- A is false, but R is true.
Out of the three students mentioned in the story, who are/is more likely to be a successful entrepreneur?
- Radhika and Shankar
- Ruby and Radhika
Identify the three components of intelligence that Ruby is high on
- Knowledge acquisition, Meta, creativity
- Knowledge acquisition, Meta, performance
- Knowledge acquisition, Meta, planning
- Planning, performance, adaptability
Class 12 Psychology Case Study Question 2
Refer to the picture given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option:
Which type of personality assessment is being depicted in the above picture?
- Projective Technique
- Psychometric Tests
- Behavioural Analysis
- Self-report Measures
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of this test?
- It reveals the unconscious mind.
- It can be conducted only on an individual basis.
- Its interpretation is objective.
- The stimuli are unstructured.
Identify the name of the test from the options given below.
- Thematic Appreciation Test
- Thematic Apperception Test
- Theatre Apperception Test
- Theatre Appreciation Test
Which of the following statements are NOT true of this test? i. In the first phase, called performance proper, the subjects are shown the cards and are asked to tell what they see in each of them. ii. The second phase is called inquiry. iii. Each picture card depicts one or more people in a variety of situations. iv. The subject is asked to tell a story describing the situation presented in the picture. Choose the correct option:
Which of the following is NOT a drawback of this test?
- It requires sophisticated skills and specialised training
- It has problems associated with reliability of scoring
- It has problems associated with validity of interpretations
- It is an indirect measure of assessment.
Identify the stimuli that are used in such kinds of tests as given in the above picture.
- Picture cards
NOTE- The following questions are for the Visually Impaired Candidates in lieu of questions 55 to 60. Answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
Nafisa feels that she is liked by her peers in class. This reflects that she ________.
- is high on self-efficacy
- is high on social self-esteem
- possesses a high IQ
- is an introvert
Discrepancy between the real self and ideal self often results in ________.
- self-actualisation
- self-regulation
- unhappiness and dissatisfaction
- intrapsychic conflicts
If an individual is fat, soft and round along with a temperament that is relaxed and sociable, then he/she is said to have the characteristics of an:
Gurmeet was given a personality test to assess how he expresses aggression in the face of a frustrating situation. Identify the test most suitable for this.
- Rosenzweig Picture Frustration test
- Eysenck Personality questionnaire
- 16 Personality Factors Test
According to Karen Horney the origin of maladjustment can be traced to ________.
- the inferiority feelings of childhood.
- basic anxiety resulting from disturbed interpersonal relations.
- overindulgence of the child at early stages of development.
- failure to deal with intrapsychic conflicts.
An individual’s sole concern with the satisfaction of ________ needs would reduce him/her to the level of animals.
- belongingness
Class 12 Psychology Case Study Question 3
Read the case given below and answer the questions
Mental health professionals have attempted to understand psychological disorders using different approaches through the ages. Today, we have sophisticated facilities and hospitals dedicated to the treatment of the mentally ill. While studying the history of psychological disorders it is interesting to note that some practices from ancient times are still in use. Take the case of Lakshmi and her daughter, Maya. Maya exhibits abnormal behaviours and Lakshmi believes that this is because of evil spirits that have possessed her. She has been taking her daughter to a self-proclaimed healer, who uses counter-magic and prayer to cure her. Stigma and lack of awareness prevents Lakshmi from using the modern facilities and hospitals that provide quality mental health care. On the other hand, when young Rita reported seeing people and hearing voices, mental health professionals at a modern facility were able to understand her hallucinations using a convergence of three approaches. Psychologists use official manuals like the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – 5th Edition (DSM-5) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) to indicate presence or absence of disorders. Today there is increased compassion for people who suffer from disorders and a lot of emphasis is placed on providing community care.
- Identify the method used by the healer to cure Maya’s illness. How does this theory from ancient times explain Maya’s treatment?
- Which approach do you think would best explain Rita’s treatment? How do you think DSM – 5 and ICD -10 help mental health professionals in indicating the presence or absence of disorders?
Class 12 Psychology syllabus at a glance
Class 12 Psychology students must have a better comprehension of Class 12 Psychology New curriculum in order to have a positive impression of the exam pattern and marking scheme. By studying the CBSE Class 12 Syllabus, students will learn the unit names, chapters within each unit, and sub-topics. Let’s have a look at the Class 12 Psychology Syllabus, which contains the topics that will be covered in the CBSE test framework.
CBSE Class – 12 Psychology (Code No. 037) Syllabus
Course Structure
| I | Variations in Psychological Attributes | 30 | 13 |
| II | Self and Personality | 32 | 13 |
| III | Meeting Life Challenges | 23 | 9 |
| IV | Psychological Disorders | 30 | 12 |
| V | Therapeutic Approaches | 25 | 9 |
| VI | Attitude and Social Cognition | 16 | 8 |
| VII | Social Influence and Group Processes | 14 | 6 |
Benefits of Solving Class 12 Psychology Case Study Question
- You will be able to locate significant case study problems in your class quizzes and examinations because we offer the best collection of Class 12 Psychology case study questions 2. You’ll be able to go over all of the crucial and challenging themes from your CBSE Class 12 Psychology textbooks again.
- Answers to all Class 12 Psychology case study questions have been supplied.
- Class 12 Psychology Students in Class will be able to download all Psychology chapter-by-chapter assignments and worksheets in PDF format.
- Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions will aid in the enhancement and improvement of topic understanding, resulting in higher exam scores.
myCBSEguide: The best platform for Class 12 Psychology
myCBSEguide is the best platform for Class 12 Psychology students. It offers a wide range of resources that are not only helpful for academic purposes but also for personal development. The platform provides access to a variety of online courses, mock tests, and practice materials that can help Class 12 Psychology students ace their exams. Additionally, the forum on the website is a great place to interact with other students and get insights into different aspects of the subject. Overall, myCBSEguide is an invaluable resource for anyone pursuing Class 12 Psychology.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
4 thoughts on “Class 12 Psychology Case Study Questions”
where are the answers? atleast give answers with the questions so we can know our mistakes
No answers ?.
teri behen ko naman
Dude what about the answers?
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Filter by Keywords
10 Case Study Examples to Inspire Your Marketing Efforts
Sudarshan Somanathan
Head of Content
June 20, 2024
When your prospects are nearing a decision in their buyer’s journey, a strong case study can sway them your way. After all, everyone, even corporate decision-makers, loves a good story.
That’s why having satisfied customers showcase your strengths is more impactful than any self-promotion. It boosts credibility and earns you valuable recognition when potential customers come across these case studies.
No matter what you offer, case studies work because they build trust. They showcase real-life success stories , their detailed analysis proving your expertise and the quality of your products or services.
That’s why they’re crucial for organizational growth.
Intrigued? Read on to explore the different types of case studies, their practical applications, and some marketing case study examples.
By the end of this blog post, you will also have learned how to write a case study using a case study template. ✍️
Understanding Case Studies
1. illustrative case studies, 2. exploratory case studies, 3. descriptive case studies, 4. cumulative case studies, 5. critical instance case studies, 6. instrumental case studies, 1. lucanet and hubspot, 2. cartoon network and clickup , 3. callingly and zapier , 4. philips and github , 5. google ads and samsung, 6. movingwaldo and mailchimp, 7. shutterstock and workday, 8. pidilite and salesforce , 9. sentinelone and storylane , 10. benchling and airtable , stage 1: research and preparation, stage 2: producing the case study, use the clickup case study template.
A case study is a detailed study of how your product or service has helped past customers.
It acts as a track record of your company’s association with past customers and an insight into how they benefitted from your product offerings.
You can think of case studies as story-telling based on real-world data and results.
Potential customers trust them because of their attention to detail in describing exactly how you delivered results for past customers. And if the past customer is someone they know or identify with, acquiring their trust is far easier.
According to the Content Marketing Institute, 73% of marketers use case studies , as they are proven tactics to drive sales.
These studies are tailored to various industries, from business and marketing to psychology, technology, and healthcare.
Creating compelling business case studies requires precision and clarity, like drafting a professional document. That’s where creative brief templates come in handy. They provide a structured framework to outline key details and create case study examples that resonate with your target audience.
Types of Case Studies
Knowing the distinct kinds of case studies will help you use the best combination to influence your potential customers. We’ll also cover a few case study examples later on so you can see the different ways in which you or your marketing team can create your own case studies.
While one type of case study may help customers solve a business problem through a product/solution, others may be more suited for studying a specific event or business phenomenon.
Let’s explore the commonly used types and case study examples.
Illustrative case studies describe a particular situation, phenomenon, or event. They use two or more instances to show just what a situation is like . The aim is to provide context, make the unfamiliar more accessible, and provide a real-world context for abstract concepts or theories.
For instance, SaaS case study examples highlight how a software solution significantly improved a client’s sales and efficiency.
Lids, a leading sports apparel retailer, has experienced rapid growth in recent years. To manage this growth effectively, Lids implemented ClickUp , a project management platform, to expedite workflows, save time, streamline administration, and improve results.
With ClickUp, our teams are more collaborative, efficient and we’re all more on-top of our work. It has made the way we work so much better.
The case study demonstrates how integrating a robust project management platform like ClickUp can streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and support substantial organizational growth.
Exploratory case studies are conducted before a large-scale investigation to help pinpoint research questions and methods for a more extensive study.
These are often used when there is limited prior knowledge or existing theories about the subject. They are more frequently employed in social science disciplines.
For example, a research case study investigates the link between mental health disorders and social media usage in younger populations.
Researchers conducted a systematic review focusing on the impact of social media use on mental health . The study aimed to provide insights for future mental health strategies by analyzing the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes.
Utilizing research plan templates can help structure such investigations, ensuring an in-depth analysis and data collection and analysis efficiency.
A descriptive case study starts with a descriptive theory as a foundation. It then attempts to find connections between the subject of discussion and the theory. These case studies rely on detailed qualitative data analysis to develop an argument.
Let’s consider a descriptive case study example on the usage of technology in classrooms focused on an elementary school in a suburban district during the 2011-2012 academic year.
This compelling case study highlights the importance of detailed, qualitative data in developing its argument.
A cumulative case study collects information from various sources to summarize past studies without increasing costs or time. It aims to aggregate data from multiple sources to draw broader conclusions.
For example, a case study on the impact of climate change on the Indian coastline aggregates data from various sources to provide a comprehensive summary of past research.
It highlights that climate change and climate variability pose significant challenges to this ecosystem.
Critical instance case studies focus on a unique or critical event to learn more about its causes and consequences. They are often used to investigate rare or significant events.
For instance, Blackboard utilized Amazon EC2 Spot Instances to scale its virtual classroom solution amidst the COVID-19 pandemic.
This case study demonstrates how Blackboard effectively managed a staggering 4,800% surge in video conferencing usage while optimizing costs and enhancing performance.
Instrumental case studies use a specific case to generate insights into a broader issue or to refine a theoretical explanation. They are more frequently used to explore complex concepts or theories.
The story of Accenture’s Global SAP System serves as an instrumental case study example.
It uses Accenture’s journey to create a unified SAP system to generate strategic insights into broader issues related to aligning business and IT strategies, standardizing business processes, and establishing global governance structures.
10 Case Study Examples for Different Use Cases
Exploring a variety of case study examples can help you understand the nuances of their formatting, data presentation, and brand positioning. Here are ten case study examples to inspire you.

LucaNet is an international finance company that provides performance management solutions. With a global customer base, it wanted to opt for automated, personalized marketing in addition to handling complex lead management.
HubSpot helped LucaNet automate its global marketing operations and bring all customer data into a centralized hub.
What do we like best about this case study presentation? HubSpot immediately showcases its key achievements at the top and provides compelling data on time savings, lead generation, and increase in MQLs.
✔️Takeaway : Highlight your measurable impact to showcase your ability to deliver tangible outcomes.

Cartoon Network’s social media team struggled with managing complicated workflows across different project management tools.
ClickUp provided them with a unified platform to execute their social media management needs and ensure all team members are on the same page.
ClickUp’s case study of Cartoon Network is a good example of the appropriate use of supporting visuals. Rather than simply stating that ClickUp’s flexible views improved Cartoon Network’s project management, it demonstrates them in practical use.
✔️Takeaway : Create separate sections highlighting your client’s problem and the benefits offered by your solution in bullet points. The usage of supporting visuals is a major plus.

Callingly noticed that Zapier customers tend to get more value from their platform. To capitalize on this, they wanted to educate their customers on how to use Zapier effectively.
Callingly embedded Zapier into its app, allowing customers to discover, create, and edit Zaps directly within the platform. This integration aims to give customers more control over their workflows and automate tasks seamlessly.
The integration makes it easier for customers to discover and use Zapier, reducing the need for customers to switch between platforms or manually set up Zaps.
This makes for one of the brilliant business case study examples, thoughtfully capturing how the company helped Callingly through compelling video demonstrations.
Their ‘why’ and ‘how’ sections are particularly impressive.
✔️Takeaway : Use impactful videos to engage users and educate customers on how your product works and help clients achieve impressive results.

GitHub’s case study of Philips concisely lists the customer’s problems, solutions, and products right on top for readers prone to TL; DR. It introduces the customer before presenting figures on how collaborating with GitHub helps Philips centralize their codebase.
You’ll also find excerpts from conversations with several Philips employees, including the principal engineer and the program director, who elaborate on their need for software and how GitHub assisted.
This case study example isn’t limited to products and solutions—it’s about listening to customers and providing real-world value.
✔️Takeaway : Having a well-written case study summary helps. Real conversations with customers and end-users can add interesting detail and value to otherwise serious (and sometimes boring) textual documents.

Google’s case study of Samsung is well-documented. It elaborately covers how Samsung utilized Performance Max, a goal-based campaign that lets advertisers access their advertising campaign across all of Google’s products from a single interface.
What we like about the case study example is how it is a potential guide for newer businesses to experiment with Performance Max for their own ad campaigns.
As with all of Google’s UI, the case study is minimalistic and straightforward. Yet, it leaves you wanting to experiment and try things out yourself.
✔️Takeaway : A good case study and a how-to guide don’t always need to be different. Great case studies don’t just make a point; they compel readers to take action and see the results for themselves.

Mailchimp’s case study is a detailed report on how MovingWaldo leveraged features like email and marketing automation, segmentation, A/B testing, and email marketing. It addresses the ‘how’, ‘why’, and ‘when.’
The case study page provides specific dates detailing when MovingWaldo implemented solutions and began observing their impact. They have also posted a short video describing the process, which breaks the monotony of reading long documents.
Another highlight is a brief section detailing the future course of action, conveying that the journey of success is ongoing with additional feature enhancements. The case study transcends from being an account of the past to offering insights for the future.
✔️Takeaway : Specificity, such as adding exact dates, helps strengthen your case studies. Video and other multimedia content can take it up a notch.

Workday offers glimpses of its case studies, letting you choose between reading the story or watching the video.
The case study begins with a powerful quote from the customer that demonstrates the impact of the solution. It then provides a brief description of the success metrics and highlights the core impact of the integration.
It addresses Shutterstock’s pain points, such as diverse data sources, team members, and workflows, and showcases Workday’s effectiveness in countering those.
While Workday keeps the case study short, it includes all the key details to educate the customer about the implementation. This is a great example of crafting a brief yet powerful case study.
✔️Takeaway : Short case studies are effective when well written because they pack a punch and tell a compelling story. Utilizing relevant quotes is also helpful.

In this case study example, Salesforce brings out its value with the opening lines. It then lists each point of impact created by the software integration and explains its process.
One of the best things about this case study is its organization (value summarized upfront) and thorough explanation of Pidilite’s challenges and how they were solved.
They also feature a ‘what next’ section detailing the next steps Pidilite plans to take in its collaboration with Salesforce, implying that they continue providing value to the customer.
✔️Takeaway : End your case study with a brief overview of your future collaboration plans with your customer. This tells your readers that the collaboration is ongoing and that you aim to keep improving your services to add value.

This case study example is an excellent showcase of customer success. What stands out is the use of a tabular format to list different use cases of Storylane’s software and provide a before-and-after for each use case.
The table works well to summarize key achievements in a way that’s easy on the eye. The ‘Before’ column details the company’s pain points, and the ‘After’ column highlights the results that were brought about once Storylane entered the picture.
✔️Takeaway : Using ‘before’ and ‘after’ succinctly in your case studies helps drive impact and make your case studies stand out.

We liked this case study example because it simply explains how Airtable assists Benchling in prioritizing collaboration and addressing customer needs.
It explains the functioning of the biology-first platform in a way that helps even non-technical readers understand the context.
The case study ends with an insight into Airtable and Benchling’s future collaboration plans, indicating that more is to come in the years ahead.
✔️Takeaway : Write a case study using simple language so customers can easily understand the product and software integration.
How to Create Your Own Case Study
We hope these case study examples have inspired you to portray your success over the years with some fantastic case studies.
While you may have ideas, feeling stuck with the marketing planning process is natural.
Here’s how you can create your own case study in six easy steps. We’ll divide the process into two stages, research and prep, and production.
- Choose the customer: First, choose a customer willing to share their story and provide a testimonial and results. It’s important to choose a customer who has experienced significant benefits from your product or service since this will make your case study more compelling
Pro Tip: Not sure how to write an effective outreach email to enlist customer support for your case study program? Take help from ClickUp Brain’ s AI Writer to write persuasive copy. Moreover, you can email your customers directly from ClickUp!
- Outline the customer’s journey: Detail the customer’s journey from start to finish, including their actions before, during, and after using your services
Pro Tip: Storyboard your case study with your team using collaborative ClickUp Whiteboards . Once you’re happy with the outcome, create a ClickUp Task directly from the whiteboard. Assign it to the relevant owners, add tags for easy filtering, and use ClickUp Brain to generate sub-tasks and a brief task description automatically.

- Collect data: Gather quantitative and qualitative data on the company’s performance after using your services. This could include metrics like increased sales, improved efficiency, or higher customer satisfaction
- Draft the case study: Begin writing the case study by introducing the company and providing background information. Next, discuss the challenges they faced before using your product or service. Then, detail the solution you provided and how it was implemented. Finally, showcase the results and benefits the customer experienced after using your product or service, using the data you collected to support these points
Pro Tip: Brainstorm possible case study formats and outlines with ClickUp Brain, your creative partner in this endeavor.
- Get approval from the customer: Once you’ve drafted the case study, share it with the customer for their feedback and approval. This ensures that all the information is accurate and that the customer is comfortable with how their story is presented. It also provides an opportunity to make any necessary revisions
Pro Tip: Create a shareable case study in ClickUp Docs and share it with your customer in a single click for approval

- Publish and promote: After obtaining the customer’s approval, publish the case study on your website, blog, or other relevant platforms. Promote it through various channels such as social media, email newsletters, and sales presentations
Pro Tip: When your case study is ready to be distributed, add the relevant owners for social media and email distribution by simply mentioning them in a task comment
Instead of the process we just outlined, you can also use ClickUp’s free case study templates to plan, structure, and execute your case studies to maximize the efficiency of your content marketing efforts.
With ClickUp’s Case Study Template , you can:
- Gather data from distinct sources to analyze it and identify key takeaways
- Craft compelling stories using an organized template to drive real impact
- Collect ideas and note testimonials from clients to showcase real-life results
- Create a visual journey of the customer’s software integration steps
- Monitor and analyze the case study’s engagement
- Collaborate with marketing team members to create the case study together
ClickUp helps marketing teams optimize the entire process of writing a case study, from collecting data to finally sending customers an email for approval.
Craft Effective Case Studies with ClickUp
Case studies are an excellent way to build trust with prospective clients and provide evidence for your claims. They exemplify how your products and services have aided others in reaching their business and marketing goals . Studying popular case study examples can help you ideate and find the perfect format for your own customer stories.
Collaborative work management platforms like ClickUp can help you plan and execute your case study project with ease. Draft customer success case studies showcasing results effectively using ClickUp’s Case Study Template. It not only provides you with a rough layout but also improves team collaboration, helps maintain consistency with the format, collects data, and much more.
Use the integrated AI assistant, ClickUp Brain, to generate outlines, write catchy copy, and brainstorm ideas. Put your case story together, along with the relevant links, images, and rich formatting, in ClickUp Docs and share it with stakeholders for input and approval.
Sign up for ClickUp today to create the most impactful marketing case studies to attain your marketing goals.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
One notable example is Freud's study on Little Hans. This case study explored a 5-year-old boy's fear of horses and related it back to Freud's theories about psychosexual stages. Another classic example is Genie Wiley (a pseudonym), a feral child who was subjected to severe social isolation during her early years.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Sara, a 35-year-old married female. Sara was referred to treatment after having a stillbirth. Sara showed symptoms of grief, or complicated bereavement, and was diagnosed with major depression, recurrent. The clinician recommended interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) for a duration of 12 weeks. Bleiberg, K.L., & Markowitz, J.C. (2008).
6. Stanford Prison Experiment. One of the most controversial and widely-cited studies in psychology is the Stanford Prison Experiment, conducted by Philip Zimbardo at the basement of the Stanford psychology building in 1971. The hypothesis was that abusive behavior in prisons is influenced by the personality traits of the prisoners and prison ...
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
Sample #3: Conceptualization in a family therapy case. This 45-year-old African-American woman was initially referred for individual therapy for "rapid mood swings" and a tendency to become embroiled in family conflicts. Several sessions of family therapy also appear indicated, and her psychiatrist concurs.
Step 1: Gathering Information for Subject Profiling. To create a comprehensive psychology case study, the first crucial step is gathering all the necessary information to build a detailed profile of your subject. This profile forms the backbone of your study, offering a deeper understanding of the individual or situation you're examining.
Here are four tips to consider while writing a psychology case study: Remember to use the rules of APA formatting. Use fictitious names instead of referring to the patient as a client. Refer to previous case studies to understand how to format and stylize your study. Proofread and revise your report before submitting it.
Advantages of Case Studies. The case method has a lot of advantages, both for instructors and students. It is an excellent opportunity to engage the class in real projects by abstracting from the theoretical questions. This assignment develops your skills in: Problem-understanding and solving;
Purpose. Case studies are conducted to: Investigate a specific problem, event, or phenomenon. Explore unique or atypical situations. Examine the complexities and intricacies of a subject in its natural context. Develop theories, propositions, or hypotheses for further research. Gain practical insights for decision-making or problem-solving.
Example of Case Study Suitable for Students. Title: Energy Efficiency Upgrade: A Case Study of GreenTech Office. Introduction: GreenTech Office embarked on an energy efficiency upgrade to reduce its environmental impact. This case study delves into the facts and figures behind the initiative's success.
The case of Phineas Gage is perhaps the most cited study in psychology. This famous case study showed how different areas of the brain affect personality and cognitive ability. While working as a construction foreman on a railroad, Phineas Gage was involved in an accident in which a rod was pushed through his cheek and brain.
Psychology's 10 greatest case studies - digested. These ten characters have all had a huge influence on psychology. Their stories continue to intrigue those interested in personality and ...
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Clinical psychology—Case studies. 2. Psychotherapy—Case studies. I. O'Donohue, William T. II. Lilienfeld, Scott O., 1960- RC467.C367 2013 616.89—dc23 2012024765 ISBN 978--19-973366-8 1 3 5 7 9 8 6 4 2 Printed in the United States of America e erpafpr ed- oni ac.
This study deals with the first two of five sessions. The professional counsellor will be using an integrative approach, incorporating Person Centred and Behavioural Therapy techniques in the first session, moving to a Solution Focused approach in the second session. For ease of writing the Professional Counsellor is abbreviated to "C".
"For example, a subject during a trance is told that he will poke the fire in six minutes after waking. On being waked he has no memory of Early Investigations into Psychological Oddities CASE STUDY 1 Directions: Read the following case study, then answer the questions that follow. (continued)
A case study is an in-depth psychological investigation of a single person or a group of people. Case studies are commonly used in medicine and psychology. For example, these studies often focus on people with an illness (for example, one that is rare) or people with experiences that cannot be replicated in a lab.
A Case of Obsession. Plenty of people are fastidious about certain things, but one salesman took it a little too far. The salesman was having trouble leaving his house on time to get to work because he had an overwhelming and obsessive need to follow a set of rituals. Many of them were about securing the home.
There are 12 case studies, covering the following disorders and groups of disorders: Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders. Psychotic Disorders. Bipolar Disorder. Depressive Disorders. Anxiety Disorders. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders. Eating Disorders. Substance-Related Disorders.
You can also get psychology case study examples with solutions by well educated case study experts. Q.2 How to write a psychology case study. To write a good psychology case study, you must first pick a topic and then research it. After this, start framing the structure as per deadlines, and finally, do not forget to proofread after completing ...
Psychology case studies/real life examples/theories. Term. 1 / 16. Case study of Phineas Gage (Damasio 1992) Click the card to flip 👆. Definition. 1 / 16. After a tamping rod shot through his left frontal lobe, Gage became aggressive, childlike, and lacked normal social behavior. Indicates functions of reasoning and inhibition localized to ...
Class 12 Psychology Case Study Question 1. Read the case given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option: This is a story of three students Ruby, Radhika and Shankar who were enrolled in an Undergraduate Psychology Program in a University. Ruby was the admission officer's dream. She was selected for the program as ...
For example, a case study on the impact of climate change on the Indian coastline aggregates data from various sources to provide a comprehensive summary of past research. It highlights that climate change and climate variability pose significant challenges to this ecosystem. 5. Critical instance case studies.