Know Your Terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics
May 1, 2014
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Whether you’re new to rubrics, or you just don’t know their formal names, it may be time for a primer on rubric terminology.
So let’s talk about rubrics for a few minutes. What we’re going to do here is describe two frequently used kinds of rubrics, holistic and analytic , plus a less common one called the single-point rubric (my favorite, for the record). For each one, we’ll look at an example and explore its pros and cons.

Holistic Rubrics
A holistic rubric is the most general kind. It lists three to five levels of performance, along with a broad description of the characteristics that define each level. The levels can be labeled with numbers (such as 1 through 4), letters (such as A through F) or words (such as Beginning through Exemplary ). What each level is called isn’t what makes the rubric holistic — it’s the way the characteristics are all lumped together.
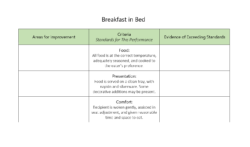
Suppose you’re an unusually demanding person. You want your loved ones to know what you expect if they should ever make you breakfast in bed. So you give them this holistic rubric:
When your breakfast is done, you simply gather your loved ones and say, “I’m sorry my darlings, but that breakfast was just a 2. Try harder next time.”
The main advantage of a holistic rubric is that it’s easy on the teacher — in the short run, anyway. Creating a holistic rubric takes less time than the others, and grading with one is faster, too. You just look over an assignment and give one holistic score to the whole thing.
The main disadvantage of a holistic rubric is that it doesn’t provide targeted feedback to students , which means they’re unlikely to learn much from the assignment. Although many holistic rubrics list specific characteristics for each level, the teacher gives only one score, without breaking it down into separate qualities. This often leads the student to approach the teacher and ask, “Why did you give me a 2?” If the teacher is the explaining kind, he will spend a few minutes breaking down the score. If not, he’ll say something like, “Read the rubric.” Then the student has to guess which factors had the biggest influence on her score. For a student who really tries hard, it can be heartbreaking to have no idea what she’s doing wrong.
Holistic rubrics are most useful in cases when there’s no time (or need, though that’s hard to imagine) for specific feedback. You see them in standardized testing — the essay portion of the SAT is scored with a 0-6 holistic rubric. When hundreds of thousands of essays have to be graded quickly, and by total strangers who have no time to provide feedback, a holistic rubric comes in handy.
Analytic Rubrics
An analytic rubric breaks down the characteristics of an assignment into parts, allowing the scorer to itemize and define exactly what aspects are strong, and which ones need improvement.
So for the breakfast in bed example, an analytic rubric would look like this:
In this case, you’d give your loved ones a separate score for each category. They might get a 3 on Presentation , but a 2 on Food and just a 1 on Comfort . To make feedback even more targeted, you could also highlight specific phrases in the rubric, like, “the recipient is crowded during the meal” to indicate exactly what went wrong.
This is where we see the main advantage of the analytic rubric: It gives students a clearer picture of why they got the score they got. It is also good for the teacher, because it gives her the ability to justify a score on paper, without having to explain everything in a later conversation.
Analytic rubrics have two significant disadvantages , however: (1) Creating them takes a lot of time . Writing up descriptors of satisfactory work — completing the “3” column in this rubric, for example — is enough of a challenge on its own. But to have to define all the ways the work could go wrong, and all the ways it could exceed expectations, is a big, big task. And once all that work is done, (2) students won’t necessarily read the whole thing. Facing a 36-cell table crammed with 8-point font is enough to send most students straight into a nap. And that means they won’t clearly understand what’s expected of them.
Still, analytic rubrics are useful when you want to cover all your bases, and you’re willing to put in the time to really get clear on exactly what every level of performance looks like.
Single-Point Rubrics
A single-point rubric is a lot like an analytic rubric, because it breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria. What makes it different is that it only describes the criteria for proficiency ; it does not attempt to list all the ways a student could fall short, nor does it specify how a student could exceed expectations.
A single-point rubric for breakfast in bed would look like this:
Notice that the language in the “Criteria” column is exactly the same as the “3” column in the analytic rubric. When your loved ones receive this rubric, it will include your written comments on one or both sides of each category, telling them exactly how they fell short (“runny eggs,” for example) and how they excelled (“vase of flowers”). Just like with the analytic rubric, if a target was simply met, you can just highlight the appropriate phrase in the center column.
If you’ve never used a single-point rubric, it’s worth a try. In 2010, Jarene Fluckiger studied a collection of teacher action research studies on the use of single-point rubrics. She found that student achievement increased with the use of these rubrics, especially when students helped create them and used them to self-assess their work.
The single-point rubric has several advantages : (1) It contains far less language than the analytic rubric, which means students are more likely to read it and it will take less time to create , while still providing rich detail about what’s expected. (2) Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended . When using full analytic rubrics, I often find that students do things that are not described on the rubric, but still depart from expectations. Because I can’t find the right language to highlight, I find myself hand-writing justifications for a score in whatever space I can find. This is frustrating, time-consuming and messy. With a single-point rubric, there’s no attempt to predict all the ways a student might go wrong. Similarly, the undefined “Advanced” column places no limits on how students might stretch themselves. “If the highest level is already prescribed then creativity may be limited to that pre-determined level,” says Fluckiger. “Students may surprise us if we leave quality open-ended.”
The main disadvantage of single-point rubrics is that using them requires more writing on the teacher’s part. If a student has fallen short in many areas, completing that left-hand column will take more time than simply highlighting a pre-written analytic rubric.
Need Ready-Made Rubrics?
My Rubric Pack gives you four different designs in Microsoft Word and Google Docs formats. It also comes with video tutorials to show you how to customize them for any need, plus a Teacher’s Manual to help you understand the pros and cons of each style. Check it out here:

Fluckiger, J. (2010). Single point rubric: A tool for responsible student self-assessment. Teacher Education Faculty Publications. Paper 5. Retrieved April 25, 2014 from http://digitalcommons.unomaha.edu/tedfacpub/5 .
Mertler, C. A. (2001). Designing scoring rubrics for your classroom. Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 7(25). Retrieved April 30, 2014 from http://PAREonline.net/getvn.asp?v=7&n=25 .
Know Your Terms is my effort to build a user-friendly knowledge base of terms every educator should know. New items will be added on an ongoing basis. If you heard some term at a PD and didn’t want to admit you didn’t know what it meant, send it to me via the contact form and I’ll research it for you.
What to Read Next
Categories: Instruction , Learning Theory
Tags: assessment , college teaching , Grades 3-5 , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , Grades K-2 , know your terms , rubrics
69 Comments
Jen, This is an awesome, thoughtful post and idea. I’m using this in my class with a final project the kids are turning in this morning. I’m excited about the clarity with which I can evaluate their projects.
I’m so glad to hear it. If you’re willing to share what you made and tell me how it all went later on, I would be thrilled to hear it.
So appreciated! These practical, detailed applications are helpful! Mahalo from Kauai, Hi.
Rubrics are great tools for making expectations explicit. Thanks for this post which gives me some vocabulary to discuss rubrics. Though, I could use some resources on rubric scoring, b/c I see a lot of teachers simply adding up the number of squares and having that be the total point value of an assignment, which leads to incorrect grades on assignments. I’ve found some converters, but haven’t found a resource that has the math broken out.
Thanks for the feedback, Jeremey! You are not the first person to request a clearer breakdown on the math for this rubric (or others), and you’re right, teachers definitely have different approaches to this. I have some good ideas on this, so I will plan a post on it for the near future.
Did you do a post regarding grading a single rubric?
Yup! Here’s Meet the Single Point Rubric . You might also be interested in How To Turn Rubric Scores into Grades . Hope this helps!
Really rubric is a very useful tool when assessing students in class
There is no such thing as an appropriate converter. Levels are levels and points and percentages are points and percentages and never the twain should meet.
(I’m very late to the discussion.)
Years ago, Ken O’Connor was the person who turned my grading around. For that reason, I would be against using the “0-80%” or “0-80 points” piece. O’Connor is very clear about how grades below 50 ruin a grade average.
I would love to be able to grade with standards only, but what I do instead, to fit into our district grading software, is to grade by standards (using letters, where “proficient” is a “B”), and the traditional letters are equal to 95/85/75/65/55. That gives kids a chance if they ever somehow earn only a F. It doesn’t kill the rest of their grade.
(I forgot to say that I absolutely love the one-column rubric. It is going to be a huge help to me this year.)
This post was so helpful! I am struggling right now with assigning Habits of Work grades to my Spanish students in middle and high school. I was using an analytic rubric for both my assessment and the students’ self-assessment, but it’s possible the quantity of words was exacerbating the problem of students scoring themselves in the best column out of reflex or habit. I’m going to try a single-point rubric to see if that can lead us to some more reflective thought.
This website was very helpful. Thank you.
LOVELY post. So didactic and useful. After reading some quite dense posts on rubrics, I’ve enjoyed this a lot. You have now convinced me to use rubrics! THANK YOU Jenny and CONGRATS!!!
SINGLE-POINT rubrics
I have not seen or heard of single point rubrics. I’m really excited to try that out. Less wordy and easier for students to see what is expected of them and get meaningful feedback.
Oooh! I never thought I’d like a post on rubrics, but this was awesome! Thanks for your great explanations. I’m currently working my way through your Teacher’s Guide to Tech/Jumpstart program and I wanted to take a minute and tell you how much I appreciate your site and podcasts too. Everything is so concise, interesting and helpful!
Sariah, thank you!! I haven’t gotten a ton of feedback on the JumpStart program, so it’s really nice to hear that! Let me know if you have any questions!
I am Master of Mathematics Education student and I am busy compiling my assignments on rubrics. Your notes are well explained and straight to the point. However, my Professor have instructed as to look up on primarily rubrics and multi-trait rubrics that i seems not to get. Do you care to differentiate them for me? Thank you.
Hi Martha. I was not familiar with those two terms, so I did a bit of reading in this post: http://carla.umn.edu/assessment/vac/improvement/p_5.html It seems to me that a primary trait rubric focuses on a single, somewhat broad description of how well the student achieved a certain goal. Multi-trait rubrics allow teachers to assess a task on a variety of descriptors. To me, the primary trait seems very much like the holistic rubric, and the multi-trait rubric seems a lot like an analytic rubric. If anyone else reading this knows the finer points of the differences among these four, I would love to hear them!
How to better calculate a grade with a rubric. Please see: http://tinypic.com/r/2dl6d5c/9 .
Thank you so much for this humorous and informative approach to rubrics. It seems to me that the single-point rubric, which I agree makes the most sense for assignment specific rubrics, is really just a clear set of assignment instructions / expectations with the addition of over/under columns to make it rubric-ish.
I love to have students help create rubrics. By the end of the year, we often create the entire rubric together as a class, but often I allow them to start by assigning one “open” section that they think I should grade on for which I help them write “exceeds, meets, doesn’t meet” standards. Then we move on to them assigning points for each standard that I’ve written (this is fascinating for me to see what they weight more heavily), and finally on to writing their own categories for which I write the standards, and then we reverse so that I write the categories and they write the standards. I give a lot of writing and speaking assignments and they really like being involved in how and what and how much we grade. (I never find they are too easy on themselves, either.) I love the single-point rubric especially for assignments I come up with off the cuff and don’t have time to write an elaborate rubric for!
If you’re moving away from traditional grades, the single-point rubric is a perfect instrument for delivering specific feedback.
This is a great site and I really liked the one example used with the multiple rubric styles so we could really understand the difference in them. I am confused about the difference between a Single Point rubric and a Primary Trait rubric. You didn’t mention the Primary Trait rubric so I am wondering if they are the same. Thank you, Karen
Thanks for writing in and for your kind words! I work for Cult of Pedagogy, and in answering your question, I started scrolling myself. Jenn responded to another reader, and I think you might find her response helpful as well as the link:
http://carla.umn.edu/assessment/vac/improvement/p_5.html
“It seems to me that a primary trait rubric focuses on a single, somewhat broad description of how well the student achieved a certain goal. Multi-trait rubrics allow teachers to assess a task on a variety of descriptors. To me, the primary trait seems very much like the holistic rubric, and the multi-trait rubric seems a lot like an analytic rubric.”
Hope this helps!
I do a sort of analytic + single point. I don’t include lots of writing on an analytic rubric. I give them the thick descriptions printed out earlier and I go over them (so each category actually does have detailed descriptions), but the rubric I mark is made up of lots of space and numbers 1-10. I keep it to ten categories. I leave lots of space for comments and comment on every category (even if it’s just one word). I conference with each student briefly when I hand back the rubrics. Each student is given two attempts – first for feedback, second for growth and a final score. (I taught high school theatre, so this method worked the best for me.)
Jen, Thank you for succinctly explaining the types of rubrics and THANK YOU for the free downloadable templates. I will share them with my education senior students!!! AWEsome work you have done.
You are very welcome, Alberta!
Dear Jennifer,
Thank you for the detailed information. I have been using single point rubrics from last year and I love them, but do you think we should give students a checklist as well? If so, what should it look like? I don’t want to kill their creativity, though.
I think the rubric can contain a checklist if you want students to include specific things in their end product, or you could do a separate checklist, then add something like “all items from checklist are included” in your rubric language. There is definitely a gray area here: Defining requirements too narrowly could stifle creativity, but it’s also important to be clear about expectations.
I have been working on a variation of the single-point rubric that I think might be even more useful for communicating expectations and feedback to students. Check it out here: https://docs.google.com/document/d/12JBIcpjeDYuTbQhEgJg2LKC5YPMDwTcIYCtl6jSGTeE/edit?usp=sharing
Really appreciate this post! Thank you. I have used the analytic approach, but I can really see the benefits of a single-point system. Thanks for your clear explanation.
Saying that ‘analytical’ rubrics are difficult and time consuming to write is true, but is also a cop-out. Taking the time to clearly define and articulate student behaviours at each level promotes student independence and self-assessment, and results in better outcomes. The fact that students have departed from what’s written on your rubric suggests that either the assessment wasn’t explained well enough or the rubric itself is of poor quality.
The analytical rubrics provided here fall well short of quality rubric standards. I would suggest reading Patrick griffin’s Assessment for Teaching, and visit the ReliableRubrics websites for good examples.
Thanks for the book and website suggestions, Martin. I do think it’s possible to construct a clear 4-column analytical rubric, but I have rarely seen one that manages to cover all the bases. The ones that DO cover every possible outcome are often insanely long. I’m thinking of some I got in grad school that were–I kid you not–several pages long and written in 9-point font. Despite the fact that I am a diligent student, even I got to the point where I threw in the towel and stopped reading the whole thing. Instead, I just gave my attention to the “3” and “4” columns. I’m guessing that other students do the same thing. If our goal is to have students understand what’s being asked of them and to pay attention to the details, why spend so much time on defining what NOT to do?
Thank you Jennifer, I have shared this with fellow colleagues in Costa Rica. I know this will be of great use!!
Thank you for this work. Your site has been very helfpul to me.
Thank you so much Jennifer! You seem to be an expert in making rubrics! I really appreciate the simplicity of the delivery of your thoughts about rubrics. I just want to ask if there is such a rubric for a cooperative activity? I am Geraldine, by the way, and me and my classmates are planning to conduct cooperative listening activities among Grade 8 students. We are having a hard time looking for a rubric that will assess their outputs as a group. Can you suggest one? Your response will be of great help. Thank you so much. May God bless you more and always!
Hi Geraldine, I work with Cult of Pedagogy and although we can’t think of anything specific to what you’re looking for, I’m thinking you might want to check out our Assessment & Feedback Pinterest board — there are a ton or resources that might help you create a rubric that would be specific to your needs. The most important thing is to identify what you want students to be able to do in the end. For example: listen to others with eye contact. (Be sure to check out Understanding by Design .) Then you can choose a rubric structure that will best fit your needs and provide effective feedback. Other than that, you might be able to find some great ideas through a Google search.
Well, thank you so much! May God bless you!
Great information. Can you tell me how you come to a total/final score on an analytic rubric if the student receives a variety of scores in the different categories? Thanks.
This is a great question! I’d check out Jenn’s post, Speed Up Grading with Rubric Codes . Even if you don’t use the codes, you’ll see in the video how an overall score can be given to a paper, even when scores in indivual categories vary. Basically the overall score reflects where most criteria have been met, along with supportive feedback. Hope this helps!
I loved the all of the rubrics you created for “Breakfast In Bed”. Your topic was an awesome analogy for teacher created tasks. I personally prefer the analytic rubric because I believe it gives the most accurate feedback to the student. If you feel more information is needed, you could expand the categories in the rubric, for example in this case, you could add a column called “sensory enhancements” , such as music or table setting. If you want to add a more personal comment you can always add it in the margin.
This issue has always frustrated me. I have recently been a HUGE proponent of holistic rubrics, but I do see the disadvantage of the feedback issue. For my first time teaching college composition, I used analytic rubrics–and hated them. It wasn’t the making rubrics that was time consuming, but determining how to break up the points and how to assign earned points for a paper. I would score a paper, add up all the points, and realized the paper got a B when, in reality, I knew it was a C-level paper. So I would erase and recalculate until I got the points I thought were more accurate. It took FOREVER!!! After some research, I decided to move to a holistic rubric, and it made grading way faster, but more importantly, I thought the numerical grade was much more accurate and consistent. (Score 6 would get a 95, 5 would be 85, etc., and I would give + or – for 3 more or less points). For feedback, I would annotate and underline/circle the parts of the criteria that they struggled in or did well in and left an end comment. And while I had them turn in a draft that I would give feedback on, I didn’t use the rubric for the draft feedback. Just comments on the paper.
I’m willing to try to single-point, but to get to that final numerical grade (since a no-grade classroom isn’t allowed, unfortunately) you’d still have to break down the points arbitrarily like an analytic rubric. Who’s to say that “structure” should be 30 points while “grammar” should be 10? What’s the actual difference between a 40/50 in “analysis” and a 42/50? My grading PTSD is resurfacing just thinking about grading essays that way. But at the same time, I also don’t like the limited feedback of the holistic rubric.
This is a link to a site where you can download a PDF that talks about a lot of composition issues, but pages 74-76 is about rubrics. Curious to know everyone’s thoughts. https://community.macmillan.com/docs/DOC-1593
Thank you so much 🙂 I learned a lot from this kind of Rubrics 🙂 (y)
Thank you very much for the breakdown of the the types of rubrics. This was very informational!
Thank you for the fantastic article. I came here from the Single Point Rubric post, and I feel so much better equipped to grade my next assignment. Thank you again!
Radhika, Yay! We are glad you found what you needed for your next assignment!
Jennifer, the clear, concise explanations of three types of rubrics are very refreshing. I teach a course called “Assessment and Measurement” to pre-service teachers and I introduce the analytic and holistic rubrics for them to use in performance assessments. The pre-service teachers spend a lot of time with just the language they want to use and, although I think rubrics are the path to more accuracy in grading, I find the idea is overwhelming to novice teachers. May I share this with my students? Of course giving you due credit. This is excellent.
Hi Hazel! Thanks for the positive feedback. You are welcome to share this post with your students!
Thank you! Your picture at the very beginning (and your examples) made the difference between holistic and analytical instantly click for me! Also, I have never heard of single point rubrics before, so I am excited to try them out this fall with an assignment or two that I think they would go perfectly with! Lastly, thanks for the templates!
I’ve been using rubrics for a long time. I started with the most complex, comprehensive things you cannot even imagine. It drove the kids crazy, and me too. Now I teach English to adults (as a 2nd or nth language) and I write much simpler rubrics. But they still have too much information. You are brilliant here with the single point rubric. What do you need to do to get it right? Write in the ways they didn’t match it, which is what you need to do anyways. I’m changing immediately to single point rubrics. I’ll also read your other posting about single point rubrics to see if you have any other ideas. I just met your blog this week (Online Global Academy) and will return, I’m sure. Many thanks. Lee
This is great to hear, Lee! Thanks for sharing.
I’ve always used rubrics but especially appreciate the single point rubric.
Hi My name is Andrena Weir, I work at the American School of Marrakech. Thank you so much for your information. As a Physical Ed teacher these rubrics are great. I like the one column rubric. I feel I spent too much time grading in ways that consume too much time. This is so much appreciated. I need someone like you to be in-contact with if I’m struggling to retrieve new Ideas. Thank you so very much, have the best day.
How about this type of rubric. Al the benefits of analytic but without the verbiage.
The food is raw/burned under/over cooked perfectly cooked
The tray is missing missing some items complete and utensils are dirty clean well presented
You get the idea
e.g. For Maths projects
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/19MXAjBdiEHXwuxg0w7NkRIKuc4X7VNj1qOE74o_vNss/edit?usp=sharing
The blog destroyed my formatting.
The food is || raw/burned || under/over cooked || perfectly cooked
The tray is || missing || missing some items || complete and utensils are || dirty || clean || well presented
or check the linked example
I use rubrics with most of my practical assignments and yes they are very time consuming. After reading this post I’m very excited to try the single-point rubric. Most of the time my students just want to know what is needed. This way they can identify what I want them to be able to do. Thanks so much for this information about rubrics.
So glad this was helpful, Amy! I’ll be sure to let Jenn know.
Want to use analytical rubric
Thanks so much for all of the information. This is great to have as a resource!
I’ve never heard of a single-point rubric before but I love the idea! Your article totally spoke my language and touched on all of my concerns. Thanks for the tips!
Hi, Jennifer, I always come away with actionable tips. I am a faculty developer and Instructional Coach. Rubrics pose challenges for teachers, novice and seasoned alike, so thank you for these discussions to shine a light on rubrics, good and bad.
Meg, I am glad this post was helpful for you in your role! I will be sure to pass on your comments to Jenn.
Being in a rubricade, a crusade of rubrics, against the powers that might be from my school… I’m glad to read what you’ve made.
Neither the academic coordinator nor the headmaster seems to know anything about having more than four levels of achievement. Nothing about having single point rubrics or the ones needed for my laboratory reports which go up to 7 with numbers not correlative.
I’m a high (and middle) school natural sciences teacher, my specialty field is physics.
The rubric in question (rejected by my superiors) has been developped since my first days in the classroom, about 2 thousand eleven. I’ve been modifying it from time to time according to the new breakthroughs experienced in practice.
Maybe your really nice webpage will help me out in going past this nonsense.
Thanks a lot!
Glad you found this helpful!
A holistic rubric is only easier if the faculty are just slapping grades on assignments, which they shouldn’t be doing with any rubric, including a very detailed analytic one. There should be summary comments that explain how the student’s specific response to the assignment meets the descriptor for each score level and then suggestions for what they could do to improve (even if they got an A).
Thanks for your comment- as Jenn mentions in the post, holistic rubrics are limited in their space for feedback. Many teachers prefer the Single Point Rubric for personalized feedback. If the point of rubrics is to set students up with their next steps, this is one you might want to try!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.
How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Fall 2022)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper, single-point rubric, more examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Analytic Rubrics
The who, what, why, where, when, and how of an analytic rubrics.
WHO : Analytic rubrics are for you and your students .
WHAT : An analytic rubric is a scoring tool that helps you identify the criteria that are relevant to the assessment and learning objectives. It is divided into components of the assignment contains a detailed description that clearly states the performance levels (unacceptable to acceptable) and allows you to assign points/grades/levels based on the students’ performance.
WHY: Rubrics help guide students when completing their assignments by giving the guidelines to follow. Students also know what you are looking for in an assignment, and this leads to fewer questions and more time engaged in the assessment and knowledge attainment. Rubrics help you or your assistant grade assignments objectively from the first submission to the last. Rubrics returned to students with the assignment, give the students basic feedback by selecting the correct criteria they met.
WHERE: Create a paper rubric or use the Canvas interactive grading rubric. Learn more about using Canvas Rubrics by selecting the following link https://guides.instructure.com/m/4152/l/724129-how-do-i-add-a-rubric-to-an-assignment
WHEN : Share the analytic rubric before the assessment to share the criteria they must meet and to help guide them when completing the assignment. After the assignment has been completed, return the marked rubric with the assignment as a form of feedback.
HOW: Watch the following video on Analytic Rubrics.
Optional Handouts: Blank rubric for the session (1)
Rubric Design Activity
Teaching Online: Course Design, Delivery, and Teaching Presence Copyright © by Analisa McMillan. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Rubric Design
Main navigation, articulating your assessment values.
Reading, commenting on, and then assigning a grade to a piece of student writing requires intense attention and difficult judgment calls. Some faculty dread “the stack.” Students may share the faculty’s dim view of writing assessment, perceiving it as highly subjective. They wonder why one faculty member values evidence and correctness before all else, while another seeks a vaguely defined originality.
Writing rubrics can help address the concerns of both faculty and students by making writing assessment more efficient, consistent, and public. Whether it is called a grading rubric, a grading sheet, or a scoring guide, a writing assignment rubric lists criteria by which the writing is graded.
Why create a writing rubric?
- It makes your tacit rhetorical knowledge explicit
- It articulates community- and discipline-specific standards of excellence
- It links the grade you give the assignment to the criteria
- It can make your grading more efficient, consistent, and fair as you can read and comment with your criteria in mind
- It can help you reverse engineer your course: once you have the rubrics created, you can align your readings, activities, and lectures with the rubrics to set your students up for success
- It can help your students produce writing that you look forward to reading
How to create a writing rubric
Create a rubric at the same time you create the assignment. It will help you explain to the students what your goals are for the assignment.
- Consider your purpose: do you need a rubric that addresses the standards for all the writing in the course? Or do you need to address the writing requirements and standards for just one assignment? Task-specific rubrics are written to help teachers assess individual assignments or genres, whereas generic rubrics are written to help teachers assess multiple assignments.
- Begin by listing the important qualities of the writing that will be produced in response to a particular assignment. It may be helpful to have several examples of excellent versions of the assignment in front of you: what writing elements do they all have in common? Among other things, these may include features of the argument, such as a main claim or thesis; use and presentation of sources, including visuals; and formatting guidelines such as the requirement of a works cited.
- Then consider how the criteria will be weighted in grading. Perhaps all criteria are equally important, or perhaps there are two or three that all students must achieve to earn a passing grade. Decide what best fits the class and requirements of the assignment.
Consider involving students in Steps 2 and 3. A class session devoted to developing a rubric can provoke many important discussions about the ways the features of the language serve the purpose of the writing. And when students themselves work to describe the writing they are expected to produce, they are more likely to achieve it.
At this point, you will need to decide if you want to create a holistic or an analytic rubric. There is much debate about these two approaches to assessment.
Comparing Holistic and Analytic Rubrics
Holistic scoring .
Holistic scoring aims to rate overall proficiency in a given student writing sample. It is often used in large-scale writing program assessment and impromptu classroom writing for diagnostic purposes.
General tenets to holistic scoring:
- Responding to drafts is part of evaluation
- Responses do not focus on grammar and mechanics during drafting and there is little correction
- Marginal comments are kept to 2-3 per page with summative comments at end
- End commentary attends to students’ overall performance across learning objectives as articulated in the assignment
- Response language aims to foster students’ self-assessment
Holistic rubrics emphasize what students do well and generally increase efficiency; they may also be more valid because scoring includes authentic, personal reaction of the reader. But holistic sores won’t tell a student how they’ve progressed relative to previous assignments and may be rater-dependent, reducing reliability. (For a summary of advantages and disadvantages of holistic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 116.)
Here is an example of a partial holistic rubric:
Summary meets all the criteria. The writer understands the article thoroughly. The main points in the article appear in the summary with all main points proportionately developed. The summary should be as comprehensive as possible and should be as comprehensive as possible and should read smoothly, with appropriate transitions between ideas. Sentences should be clear, without vagueness or ambiguity and without grammatical or mechanical errors.
A complete holistic rubric for a research paper (authored by Jonah Willihnganz) can be downloaded here.
Analytic Scoring
Analytic scoring makes explicit the contribution to the final grade of each element of writing. For example, an instructor may choose to give 30 points for an essay whose ideas are sufficiently complex, that marshals good reasons in support of a thesis, and whose argument is logical; and 20 points for well-constructed sentences and careful copy editing.
General tenets to analytic scoring:
- Reflect emphases in your teaching and communicate the learning goals for the course
- Emphasize student performance across criterion, which are established as central to the assignment in advance, usually on an assignment sheet
- Typically take a quantitative approach, providing a scaled set of points for each criterion
- Make the analytic framework available to students before they write
Advantages of an analytic rubric include ease of training raters and improved reliability. Meanwhile, writers often can more easily diagnose the strengths and weaknesses of their work. But analytic rubrics can be time-consuming to produce, and raters may judge the writing holistically anyway. Moreover, many readers believe that writing traits cannot be separated. (For a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of analytic scoring, see Becker, 2011, p. 115.)
For example, a partial analytic rubric for a single trait, “addresses a significant issue”:
- Excellent: Elegantly establishes the current problem, why it matters, to whom
- Above Average: Identifies the problem; explains why it matters and to whom
- Competent: Describes topic but relevance unclear or cursory
- Developing: Unclear issue and relevance
A complete analytic rubric for a research paper can be downloaded here. In WIM courses, this language should be revised to name specific disciplinary conventions.
Whichever type of rubric you write, your goal is to avoid pushing students into prescriptive formulas and limiting thinking (e.g., “each paragraph has five sentences”). By carefully describing the writing you want to read, you give students a clear target, and, as Ed White puts it, “describe the ongoing work of the class” (75).
Writing rubrics contribute meaningfully to the teaching of writing. Think of them as a coaching aide. In class and in conferences, you can use the language of the rubric to help you move past generic statements about what makes good writing good to statements about what constitutes success on the assignment and in the genre or discourse community. The rubric articulates what you are asking students to produce on the page; once that work is accomplished, you can turn your attention to explaining how students can achieve it.
Works Cited
Becker, Anthony. “Examining Rubrics Used to Measure Writing Performance in U.S. Intensive English Programs.” The CATESOL Journal 22.1 (2010/2011):113-30. Web.
White, Edward M. Teaching and Assessing Writing . Proquest Info and Learning, 1985. Print.
Further Resources
CCCC Committee on Assessment. “Writing Assessment: A Position Statement.” November 2006 (Revised March 2009). Conference on College Composition and Communication. Web.
Gallagher, Chris W. “Assess Locally, Validate Globally: Heuristics for Validating Local Writing Assessments.” Writing Program Administration 34.1 (2010): 10-32. Web.
Huot, Brian. (Re)Articulating Writing Assessment for Teaching and Learning. Logan: Utah State UP, 2002. Print.
Kelly-Reilly, Diane, and Peggy O’Neil, eds. Journal of Writing Assessment. Web.
McKee, Heidi A., and Dànielle Nicole DeVoss DeVoss, Eds. Digital Writing Assessment & Evaluation. Logan, UT: Computers and Composition Digital Press/Utah State University Press, 2013. Web.
O’Neill, Peggy, Cindy Moore, and Brian Huot. A Guide to College Writing Assessment . Logan: Utah State UP, 2009. Print.
Sommers, Nancy. Responding to Student Writers . Macmillan Higher Education, 2013.
Straub, Richard. “Responding, Really Responding to Other Students’ Writing.” The Subject is Writing: Essays by Teachers and Students. Ed. Wendy Bishop. Boynton/Cook, 1999. Web.
White, Edward M., and Cassie A. Wright. Assigning, Responding, Evaluating: A Writing Teacher’s Guide . 5th ed. Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2015. Print.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, sat essay rubric: full analysis and writing strategies.

We're about to dive deep into the details of that least beloved* of SAT sections, the SAT essay . Prepare for a discussion of the SAT essay rubric and how the SAT essay is graded based on that. I'll break down what each item on the rubric means and what you need to do to meet those requirements.
On the SAT, the last section you'll encounter is the (optional) essay. You have 50 minutes to read a passage, analyze the author's argument, and write an essay. If you don’t write on the assignment, plagiarize, or don't use your own original work, you'll get a 0 on your essay. Otherwise, your essay scoring is done by two graders - each one grades you on a scale of 1-4 in Reading, Analysis, and Writing, for a total essay score out of 8 in each of those three areas . But how do these graders assign your writing a numerical grade? By using an essay scoring guide, or rubric.
*may not actually be the least belovèd.
Feature image credit: Day 148: the end of time by Bruce Guenter , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped from original.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
While most colleges had already made SAT Essay scores optional, this move by the College Board means no colleges now require the SAT Essay. It will also likely lead to additional college application changes such not looking at essay scores at all for the SAT or ACT, as well as potentially requiring additional writing samples for placement.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
The Complete SAT Essay Grading Rubric: Item-by-Item Breakdown
Based on the CollegeBoard’s stated Reading, Analysis, and Writing criteria, I've created the below charts (for easier comparison across score points). For the purpose of going deeper into just what the SAT is looking for in your essay, I've then broken down each category further (with examples).
The information in all three charts is taken from the College Board site .
The biggest change to the SAT essay (and the thing that really distinguishes it from the ACT essay) is that you are required to read and analyze a text , then write about your analysis of the author's argument in your essay. Your "Reading" grade on the SAT essay reflects how well you were able to demonstrate your understanding of the text and the author's argument in your essay.
You'll need to show your understanding of the text on two different levels: the surface level of getting your facts right and the deeper level of getting the relationship of the details and the central ideas right.
Surface Level: Factual Accuracy
One of the most important ways you can show you've actually read the passage is making sure you stick to what is said in the text . If you’re writing about things the author didn’t say, or things that contradict other things the author said, your argument will be fundamentally flawed.
For instance, take this quotation from a (made-up) passage about why a hot dog is not a sandwich:
“The fact that you can’t, or wouldn’t, cut a hot dog in half and eat it that way, proves that a hot dog is once and for all NOT a sandwich”
Here's an example of a factually inaccurate paraphrasing of this quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are often served cut in half, this makes them different from sandwiches.
The paraphrase contradicts the passage, and so would negatively affect your reading score. Now let's look at an accurate paraphrasing of the quotation:
The author builds his argument by discussing how, since hot-dogs are never served cut in half, they are therefore different from sandwiches.
It's also important to be faithful to the text when you're using direct quotations from the passage. Misquoting or badly paraphrasing the author’s words weakens your essay, because the evidence you’re using to support your points is faulty.
Higher Level: Understanding of Central Ideas
The next step beyond being factually accurate about the passage is showing that you understand the central ideas of the text and how details of the passage relate back to this central idea.
Why does this matter? In order to be able to explain why the author is persuasive, you need to be able to explain the structure of the argument. And you can’t deconstruct the author's argument if you don’t understand the central idea of the passage and how the details relate to it.
Here's an example of a statement about our fictional "hot dogs are sandwiches" passage that shows understanding of the central idea of the passage:
Hodgman’s third primary defense of why hot dogs are not sandwiches is that a hot dog is not a subset of any other type of food. He uses the analogy of asking the question “is cereal milk a broth, sauce, or gravy?” to show that making such a comparison between hot dogs and sandwiches is patently illogical.
The above statement takes one step beyond merely being factually accurate to explain the relation between different parts of the passage (in this case, the relation between the "what is cereal milk?" analogy and the hot dog/sandwich debate).
Of course, if you want to score well in all three essay areas, you’ll need to do more in your essay than merely summarizing the author’s argument. This leads directly into the next grading area of the SAT Essay.
The items covered under this criterion are the most important when it comes to writing a strong essay. You can use well-spelled vocabulary in sentences with varied structure all you want, but if you don't analyze the author's argument, demonstrate critical thinking, and support your position, you will not get a high Analysis score .
Because this category is so important, I've broken it down even further into its two different (but equally important) component parts to make sure everything is as clearly explained as possible.
Part I: Critical Thinking (Logic)
Critical thinking, also known as critical reasoning, also known as logic, is the skill that SAT essay graders are really looking to see displayed in the essay. You need to be able to evaluate and analyze the claim put forward in the prompt. This is where a lot of students may get tripped up, because they think “oh, well, if I can just write a lot, then I’ll do well.” While there is some truth to the assertion that longer essays tend to score higher , if you don’t display critical thinking you won’t be able to get a top score on your essay.
What do I mean by critical thinking? Let's take the previous prompt example:
Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.
An answer to this prompt that does not display critical thinking (and would fall into a 1 or 2 on the rubric) would be something like:
The author argues that hot dogs aren’t sandwiches, which is persuasive to the reader.
While this does evaluate the prompt (by providing a statement that the author's claim "is persuasive to the reader"), there is no corresponding analysis. An answer to this prompt that displays critical thinking (and would net a higher score on the rubric) could be something like this:
The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches. Because the readers will readily believe the first part of the analogy is true, they will be more likely to accept that the second part (that hot dogs aren't sandwiches) is true as well.
See the difference? Critical thinking involves reasoning your way through a situation (analysis) as well as making a judgement (evaluation) . On the SAT essay, however, you can’t just stop at abstract critical reasoning - analysis involves one more crucial step...
Part II: Examples, Reasons, and Other Evidence (Support)
The other piece of the puzzle (apparently this is a tiny puzzle) is making sure you are able to back up your point of view and critical thinking with concrete evidence . The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses “ relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim(s) or point(s) made. ” This means you can’t just stick to abstract reasoning like this:
That explanation is a good starting point, but if you don't back up your point of view with quoted or paraphrased information from the text to support your discussion of the way the author builds his/her argument, you will not be able to get above a 3 on the Analysis portion of the essay (and possibly the Reading portion as well, if you don't show you've read the passage). Let's take a look of an example of how you might support an interpretation of the author's effect on the reader using facts from the passage :
The author’s reference to the Biblical story about King Solomon elevates the debate about hot dogs from a petty squabble between friends to a life-or-death disagreement. The reader cannot help but see the parallels between the two situations and thus find themselves agreeing with the author on this point.
Does the author's reference to King Solomon actually "elevate the debate," causing the reader to agree with the author? From the sentences above, it certainly seems plausible that it might. While your facts do need to be correct, you get a little more leeway with your interpretations of how the author’s persuasive techniques might affect the audience. As long as you can make a convincing argument for the effect a technique the author uses might have on the reader, you’ll be good.

Say whaaat?! #tbt by tradlands , used under CC BY 2.0 /Cropped and color-adjusted from original.
Did I just blow your mind? Read more about the secrets the SAT doesn’t want you to know in this article .
Your Writing score on the SAT essay is not just a reflection of your grasp of the conventions of written English (although it is that as well). You'll also need to be focused, organized, and precise.
Because there's a lot of different factors that go into calculating your Writing score, I've divided the discussion of this rubric area into five separate items:
Precise Central Claim
Organization, vocab and word choice, sentence structure, grammar, etc..
One of the most basic rules of the SAT essay is that you need to express a clear opinion on the "assignment" (the prompt) . While in school (and everywhere else in life, pretty much) you’re encouraged to take into account all sides of a topic, it behooves you to NOT do this on the SAT essay. Why? Because you only have 50 minutes to read the passage, analyze the author's argument, and write the essay, there's no way you can discuss every single way in which the author builds his/her argument, every single detail of the passage, or a nuanced argument about what works and what doesn't work.
Instead, I recommend focusing your discussion on a few key ways the author is successful in persuading his/her audience of his/her claim.
Let’s go back to the assignment we've been using as an example throughout this article:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich."
Your instinct (trained from many years of schooling) might be to answer:
"There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument."
This is a nice, vague statement that leaves you a lot of wiggle room. If you disagree with the author, it's also a way of avoiding having to say that the author is persuasive. Don't fall into this trap! You do not necessarily have to agree with the author's claim in order to analyze how the author persuades his/her readers that the claim is true.
Here's an example of a precise central claim about the example assignment:
The author effectively builds his argument that hot dogs are not sandwiches by using logic, allusions to history and mythology, and factual evidence.
In contrast to the vague claim that "There are a variety of ways in which the author builds his argument," this thesis both specifies what the author's argument is and the ways in which he builds the argument (that you'll be discussing in the essay).
While it's extremely important to make sure your essay has a clear point of view, strong critical reasoning, and support for your position, that's not enough to get you a top score. You need to make sure that your essay "demonstrates a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas both within paragraphs and throughout the essay."
What does this mean? Part of the way you can make sure your essay is "well organized" has to do with following standard essay construction points. Don't write your essay in one huge paragraph; instead, include an introduction (with your thesis stating your point of view), body paragraphs (one for each example, usually), and a conclusion. This structure might seem boring, but it really works to keep your essay organized, and the more clearly organized your essay is, the easier it will be for the essay grader to understand your critical reasoning.
The second part of this criteria has to do with keeping your essay focused, making sure it contains "a deliberate and highly effective progression of ideas." You can't just say "well, I have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, so I guess my essay is organized" and expect to get a 4/4 on your essay. You need to make sure that each paragraph is also organized . Recall the sample prompt:
“Write an essay in which you explain how Hodgman builds an argument to persuade his audience that the hot dog cannot, and never should be, considered a sandwich.”
And our hypothetical thesis:
Let's say that you're writing the paragraph about the author's use of logic to persuade his reader that hot dogs aren't sandwiches. You should NOT just list ways that the author is logical in support of his claim, then explain why logic in general is an effective persuasive device. While your points might all be valid, your essay would be better served by connecting each instance of logic in the passage with an explanation of how that example of logic persuades the reader to agree with the author.
Above all, it is imperative that you make your thesis (your central claim) clear in the opening paragraph of your essay - this helps the grader keep track of your argument. There's no reason you’d want to make following your reasoning more difficult for the person grading your essay (unless you’re cranky and don’t want to do well on the essay. Listen, I don’t want to tell you how to live your life).
In your essay, you should use a wide array of vocabulary (and use it correctly). An essay that scores a 4 in Writing on the grading rubric “demonstrates a consistent use of precise word choice.”
You’re allowed a few errors, even on a 4-scoring essay, so you can sometimes get away with misusing a word or two. In general, though, it’s best to stick to using words you are certain you not only know the meaning of, but also know how to use. If you’ve been studying up on vocab, make sure you practice using the words you’ve learned in sentences, and have those sentences checked by someone who is good at writing (in English), before you use those words in an SAT essay.
Creating elegant, non-awkward sentences is the thing I struggle most with under time pressure. For instance, here’s my first try at the previous sentence: “Making sure a sentence structure makes sense is the thing that I have the most problems with when I’m writing in a short amount of time” (hahaha NOPE - way too convoluted and wordy, self). As another example, take a look at these two excerpts from the hypothetical essay discussing how the author persuaded his readers that a hot dog is not a sandwich:
Score of 2: "The author makes his point by critiquing the argument against him. The author pointed out the logical fallacy of saying a hot dog was a sandwich because it was meat "sandwiched" between two breads. The author thus persuades the reader his point makes sense to be agreed with and convinces them."
The above sentences lack variety in structure (they all begin with the words "the author"), and the last sentence has serious flaws in its structure (it makes no sense).
Score of 4: "The author's rigorous examination of his opponent's position invites the reader, too, to consider this issue seriously. By laying out his reasoning, step by step, Hodgman makes it easy for the reader to follow along with his train of thought and arrive at the same destination that he has. This destination is Hodgman's claim that a hot dog is not a sandwich."
The above sentences demonstrate variety in sentence structure (they don't all begin with the same word and don't have the same underlying structure) that presumably forward the point of the essay.
In general, if you're doing well in all the other Writing areas, your sentence structures will also naturally vary. If you're really worried that your sentences are not varied enough, however, my advice for working on "demonstrating meaningful variety in sentence structure" (without ending up with terribly worded sentences) is twofold:
- Read over what you’ve written before you hand it in and change any wordings that seem awkward, clunky, or just plain incorrect.
- As you’re doing practice essays, have a friend, family member, or teacher who is good at (English) writing look over your essays and point out any issues that arise.
This part of the Writing grade is all about the nitty gritty details of writing: grammar, punctuation, and spelling . It's rare that an essay with serious flaws in this area can score a 4/4 in Reading, Analysis, or Writing, because such persistent errors often "interfere with meaning" (that is, persistent errors make it difficult for the grader to understand what you're trying to get across).
On the other hand, if they occur in small quantities, grammar/punctuation/spelling errors are also the things that are most likely to be overlooked. If two essays are otherwise of equal quality, but one writer misspells "definitely" as "definately" and the other writer fails to explain how one of her examples supports her thesis, the first writer will receive a higher essay score. It's only when poor grammar, use of punctuation, and spelling start to make it difficult to understand your essay that the graders start penalizing you.
My advice for working on this rubric area is the same advice as for sentence structure: look over what you’ve written to double check for mistakes, and ask someone who’s good at writing to look over your practice essays and point out your errors. If you're really struggling with spelling, simply typing up your (handwritten) essay into a program like Microsoft Word and running spellcheck can alert you to problems. We've also got a great set of articles up on our blog about SAT Writing questions that may help you better understand any grammatical errors you are making.
How Do I Use The SAT Essay Grading Rubric?
Now that you understand the SAT essay rubric, how can you use it in your SAT prep? There are a couple of different ways.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Shape Your Essays
Since you know what the SAT is looking for in an essay, you can now use that knowledge to guide what you write about in your essays!
A tale from my youth: when I was preparing to take the SAT for the first time, I did not really know what the essay was looking for, and assumed that since I was a good writer, I’d be fine.
Not true! The most important part of the SAT essay is using specific examples from the passage and explaining how they convince the reader of the author's point. By reading this article and realizing there's more to the essay than "being a strong writer," you’re already doing better than high school me.

Change the object in that girl’s left hand from a mirror to a textbook and you have a pretty good sketch of what my junior year of high school looked like.
Use The SAT Essay Rubric To...Grade Your Practice Essays
The SAT can’t exactly give you an answer key to the essay. Even when an example of an essay that scored a particular score is provided, that essay will probably use different examples than you did, make different arguments, maybe even argue different interpretations of the text...making it difficult to compare the two. The SAT essay rubric is the next best thing to an answer key for the essay - use it as a lens through which to view and assess your essay.
Of course, you don’t have the time to become an expert SAT essay grader - that’s not your job. You just have to apply the rubric as best as you can to your essays and work on fixing your weak areas . For the sentence structure, grammar, usage, and mechanics stuff I highly recommend asking a friend, teacher, or family member who is really good at (English) writing to take a look over your practice essays and point out the mistakes.
If you really want custom feedback on your practice essays from experienced essay graders, may I also suggest the PrepScholar test prep platform ? I manage the essay grading and so happen to know quite a bit about the essay part of this platform, which gives you both an essay grade and custom feedback for each essay you complete. Learn more about how it all works here .
What’s Next?
Are you so excited by this article that you want to read even more articles on the SAT essay? Of course you are. Don't worry, I’ve got you covered. Learn how to write an SAT essay step-by-step and read about the 6 types of SAT essay prompts .
Want to go even more in depth with the SAT essay? We have a complete list of past SAT essay prompts as well as tips and strategies for how to get a 12 on the SAT essay .
Still not satisfied? Maybe a five-day free trial of our very own PrepScholar test prep platform (which includes essay practice and feedback) is just what you need.
Trying to figure out whether the old or new SAT essay is better for you? Take a look at our article on the new SAT essay assignment to find out!
Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Units and Programs
Make a Gift
- Student Resources
- Faculty Resources
- Teaching Assistants
- Undergraduate Assistants
Jester Center Room A115 201 E 21st St. Austin, Texas 78712 512-471-4421
Analytical Rubric
from John Bean, Engaging Ideas
Scoring Guide for Essays
Quality of ideas: ____ points.
Range and depth of argument; logic of argument; quality of research or original thought; appropriate sense of complexity of the topic; appropriate awareness of opposing views.
Organization & Development: ____ points
Effective title; clarity of thesis statement; logical and clear arrangement of ideas; effective use of transitions; unity and coherence of paragraphs; good development of ideas through supporting detail and evidence.
Clarity & Style: _____ points
Ease of readability; appropriate voice, tone, and style for assignment; clarity of sentence structure; gracefulness of sentence structure; appropriate variety and maturity of sentence structure.
Sentence Structure & Mechanics: _____ points
Grammatically correct sentences; absence of comma splices, run-ons, fragments; absence of usage and grammatical errors; accurate spelling; careful proofreading; attractive and appropriate manuscript form.

- Gradebook App
- Student Reports
- Training & Consulting
- Literacy Booster Offer
- Subscription Pricing
- Professional Development
- Our Mission
- Case Studies
- Privacy Policy & Terms of Service
- Review Mode

5 Analytic Rubric Examples for High School
Analytic rubrics are one of the best ways to assess students. While holistic rubrics are a great way to highlight success and what students have done well, analytic rubrics are much more comprehensive. In this post, we’re going to highlight 5 analytic rubric examples for high school.
Make Student Assessment Simple – Try SUPERRUBRIC Today
What is an analytic rubric.
Analytic rubrics are assessment resources that assess students across specific criteria. In an analytic rubric, each section of the rubric has an independent score.
For example… in an essay, you might score the student’s ability to summarize, use vocabulary, connect ideas – etc. Each section or criteria of the rubric will have an independent score which is totalled up at the end to provide a comprehensive grade.
With analytic rubrics, the combination of multiple criteria that determine both strengths and areas for growth creates a grade that is comprehensive and helps the student to understand where they were successful and what they might need help developing.
Let’s take a look at some of the most common advantages and disadvantages of analytic rubrics.
Advantages of Analytic Rubrics
- Comprehensive assessment
- Assessment of multiple categories/criteria
- Simple to understand
Disadvantages of Analytic Rubrics
- Can take longer to use (if online tools are not utilized)
- They also highlight areas for growth (weaknesses)
Now that we understand what an analytic rubric is, let’s take a look at 5 pre-built rubrics that can be accessed in our rubric maker .
1. Book Report Rubric

Default Assessment Criteria: Book Summary, Critical assessment of text, presentation of ideas, use of language and conventions, word choice.
Use the Book Report Rubric Maker – Click here.
2. Discussion Forum Rubric

Default Assessment Criteria: primary content contribution, Critical engagement, frequency, use of language and conventions, formatting and referencing.
Analytic Discussion Forum Rubric – Click here.
3. Essay Rubric

Default Assessment Criteria: Content and clarity, thematic organization & thesis, formatting and referencing, use of language and conventions, perspective.
Use the Essay Rubric Maker – Click here.
4. Research Paper Rubric

Perhaps one of the most important writing tasks for students who are entering post-secondary studies; a research paper is essential. Our research paper rubric is based on an analytical design that highlights the most important criteria for developing a well written paper.
Default Assessment Criteria: Content and focus, purpose integration, formatting and referencing, use of language and conventions, word choice.
Analytic Research Paper Rubric – Click here.
5. Reading Response Rubric

One of the most common types of assignments in class – assessing a reading response could help your students to better understand how they should be engaging with material in class.
Default Assessment Criteria: Understanding and reflection, depth of connections, use of language and conventions, word choice, formatting and referencing.
Use the Reading Response Rubric Maker – Click here.
Recent Posts
How a literacy rubric will maximize student success, report card writing made simple.
- Executive Functioning Rubrics are a Game Changer
The Teacher’s Guide to Mastering Orthographic Mapping
- Can Rubrics Help with Executive Functioning Skills?
Recent Comments
- 5 Reasons Teachers Love Analytical Rubrics - SUPERRUBRIC - SUPERRUBRIC.COM on 3 Rubrics for Elementary Reading & Writing
- A WordPress Commenter on Discussion Forum Rubric – Free Rubric Maker
Trending Now
- Book Report Rubric – Free Rubric Maker September 19, 2022
- A Teacher’s Guide to a Short Story Writing Rubric October 29, 2023
- Mastering The Rubric for Book Report: Your Comprehensive Guide July 13, 2023
Recently Posted
- How A Literacy Rubric Will Maximize Student Success May 20, 2024

You must log in to post a comment.
© 2024 SUPERRUBRIC.COM.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
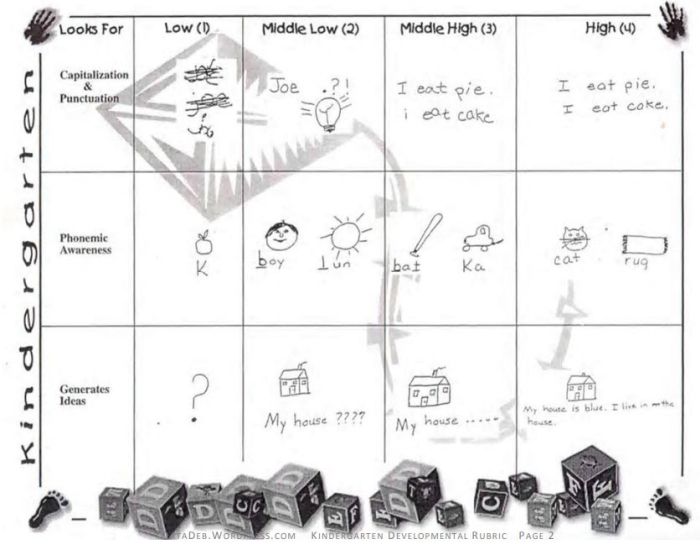
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.
Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
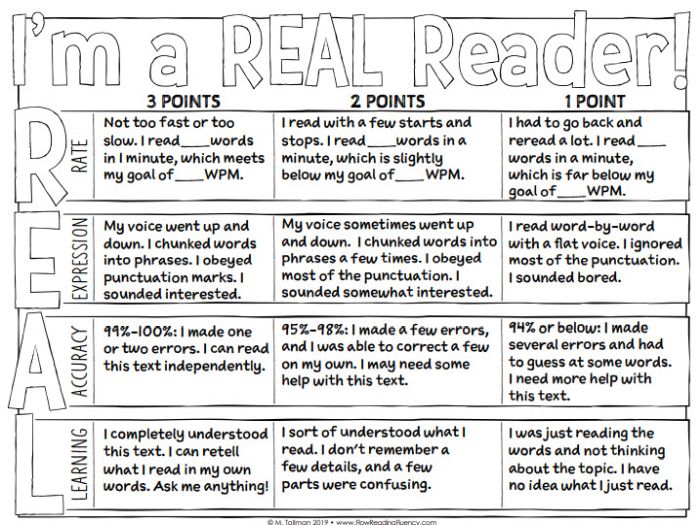
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
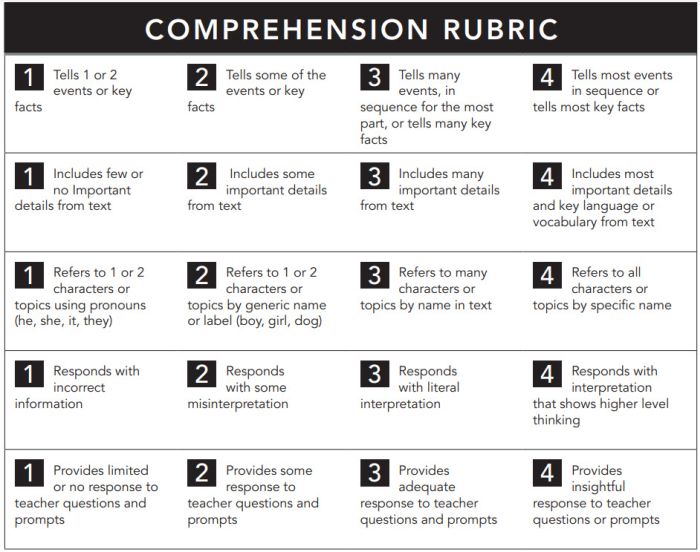
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
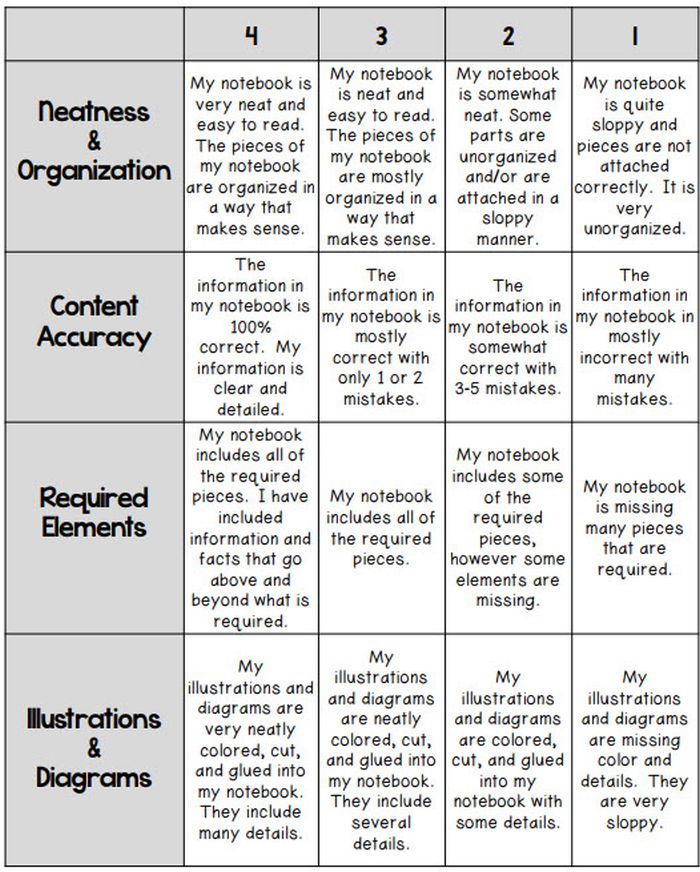
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
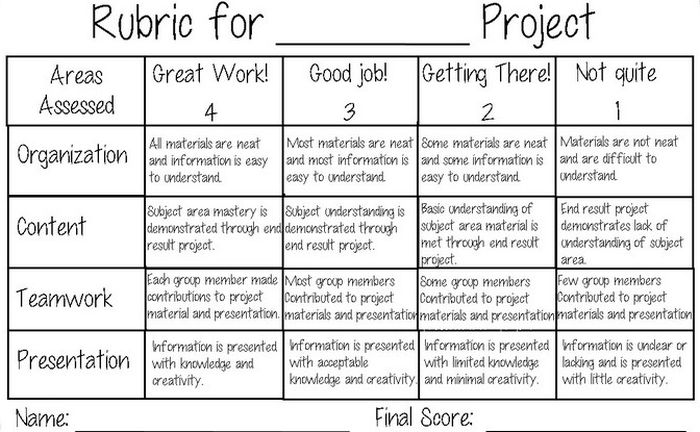
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
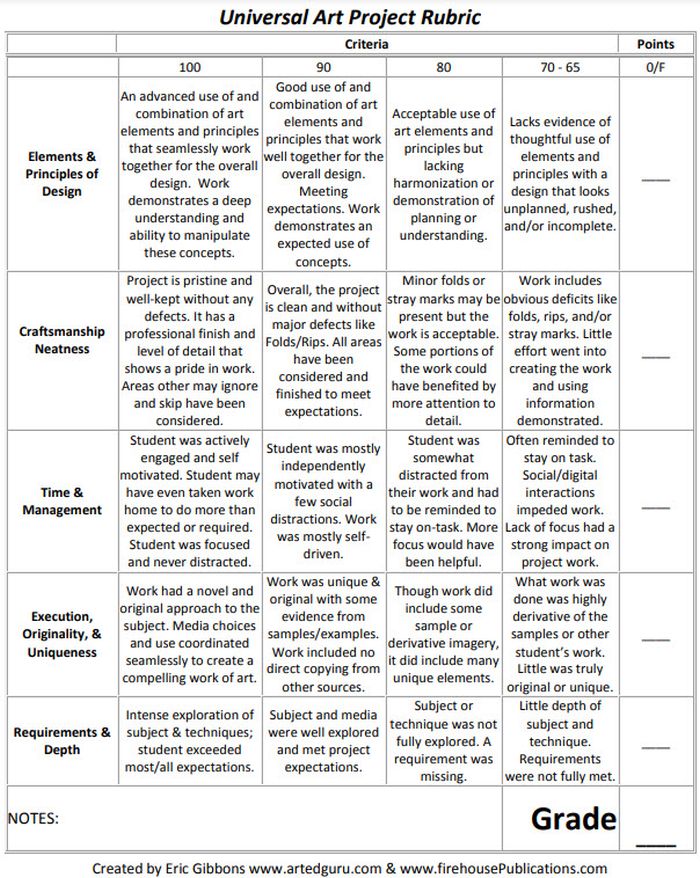
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
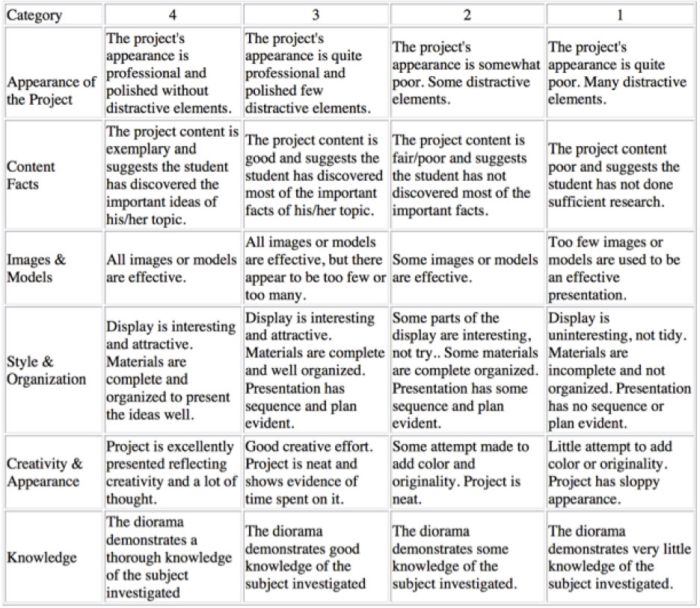
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com

Oral Presentation Rubric
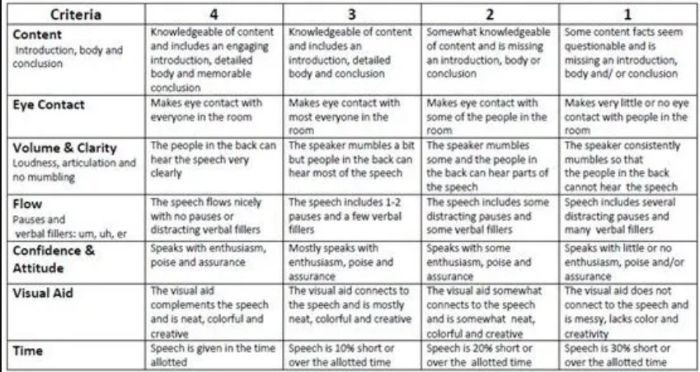
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
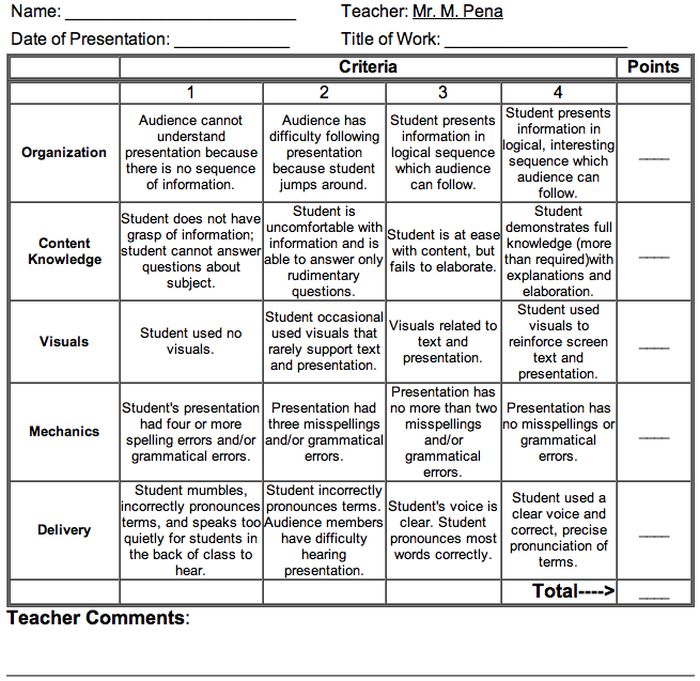
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
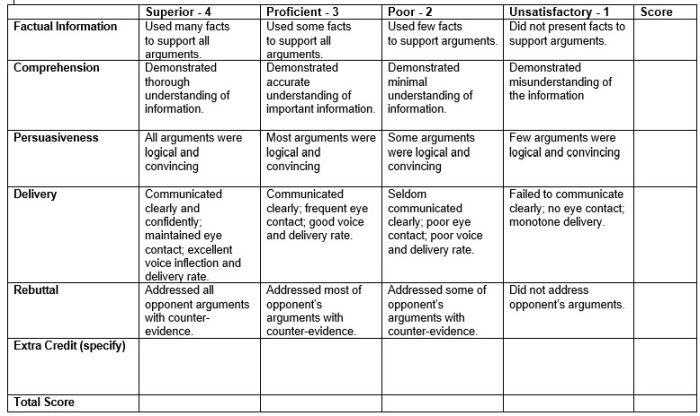
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
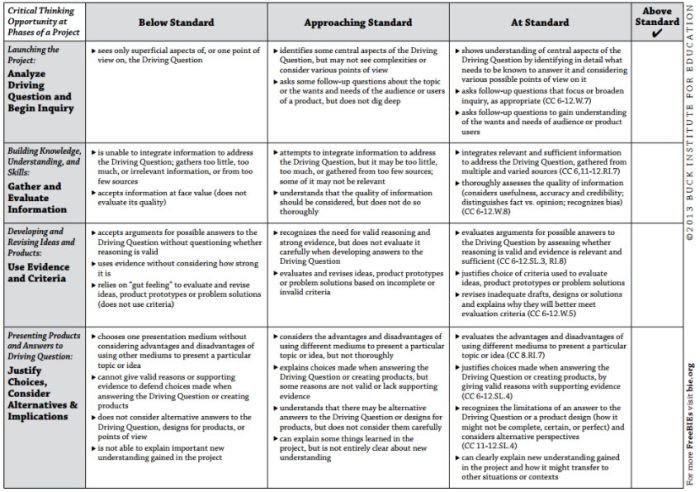
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..

You Might Also Like

20 Useful Digital Assessment Tools for Teachers (Formative, Summative, and More)
Knowledge checks, quizzes and tests, peer evals, and more! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Essay Rubric: Basic Guidelines and Sample Template
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 1293 words
- Icon Clock 7 min read
Lectures and tutors provide specific requirements for students to meet when writing essays. Basically, an essay rubric helps tutors to analyze the quality of articles written by students. In this case, useful rubrics make the analysis process simple for lecturers as they focus on specific concepts related to the writing process. Also, an essay rubric list and organize all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use an essay rubric to enhance their writing skills by examining various requirements. Then, different types of essay rubrics vary from one educational level to another. For example, Master’s and Ph.D. essay rubrics focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school essay rubrics examine basic writing concepts. In turn, a sample template of a high school rubric in this article can help students to evaluate their papers before submitting them to their teachers.
General Aspects of an Essay Rubric
An essay rubric refers to the way how teachers assess student’s composition writing skills and abilities. Basically, an essay rubric provides specific criteria to grade assignments. In this case, teachers use essay rubrics to save time when evaluating and grading various papers. Hence, learners must use an essay rubric effectively to achieve desired goals and grades.

General Assessment Table for an Essay Rubric
1. organization.
Excellent/8 points: The essay contains stiff topic sentences and a controlled organization.
Very Good/6 points: The essay contains a logical and appropriate organization. The writer uses clear topic sentences.
Average/4 points: The essay contains a logical and appropriate organization. The writer uses clear topic sentences.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The essay has an inconsistent organization.
Unacceptable/0 points: The essay shows the absence of a planned organization.
Grade: ___ .
Excellent/8 points: The essay shows the absence of a planned organization.
Very Good/6 points: The paper contains precise and varied sentence structures and word choices.
Average/4 points: The paper follows a limited but mostly correct sentence structure. There are different sentence structures and word choices.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The paper contains several awkward and unclear sentences. There are some problems with word choices.
Unacceptable/0 points: The writer does not contain apparent control over sentence structures and word choice.
Excellent/8 points: The content appears sophisticated and contains well-developed ideas.
Very Good/6 points: The essay content appears illustrative and balanced.
Average/4 points: The essay contains unbalanced content that requires more analysis.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The essay contains a lot of research information without analysis or commentary.
Unacceptable/0 points: The essay lacks relevant content and does not fit the thesis statement. Essay rubric rules are not followed.
Excellent/8 points: The essay contains a clearly stated and focused thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: The written piece comprises a clearly stated argument. However, the focus would have been sharper.
Average/4 points: The thesis phrasing sounds simple and lacks complexity. The writer does not word the thesis correctly.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The thesis statement requires a clear objective and does not fit the theme in the content of the essay.
Unacceptable/0 points: The thesis is not evident in the introduction.
Excellent/8 points: The essay is clear and focused. The work holds the reader’s attention. Besides, the relevant details and quotes enrich the thesis statement.
Very Good/6 points: The essay is mostly focused and contains a few useful details and quotes.
Average/4 points: The writer begins the work by defining the topic. However, the development of ideas appears general.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The author fails to define the topic well, or the writer focuses on several issues.
Unacceptable/0 points: The essay lacks a clear sense of a purpose or thesis statement. Readers have to make suggestions based on sketchy or missing ideas to understand the intended meaning. Essay rubric requirements are missed.
6. Sentence Fluency
Excellent/8 points: The essay has a natural flow, rhythm, and cadence. The sentences are well built and have a wide-ranging and robust structure that enhances reading.
Very Good/6 points: The ideas mostly flow and motivate a compelling reading.
Average/4 points: The text hums along with a balanced beat but tends to be more businesslike than musical. Besides, the flow of ideas tends to become more mechanical than fluid.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The essay appears irregular and hard to read.
Unacceptable/0 points: Readers have to go through the essay several times to give this paper a fair interpretive reading.
7. Conventions
Excellent/8 points: The student demonstrates proper use of standard writing conventions, like spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. The student uses protocols in a way that improves the readability of the essay.
Very Good/6 points: The student demonstrates proper writing conventions and uses them correctly. One can read the essay with ease, and errors are rare. Few touch-ups can make the composition ready for publishing.
Average/4 points: The writer shows reasonable control over a short range of standard writing rules. The writer handles all the conventions and enhances readability. The errors in the essay tend to distract and impair legibility.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The writer makes an effort to use various conventions, including spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar usage, and paragraphing. The essay contains multiple errors.
Unacceptable/0 points: The author makes repetitive errors in spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, and paragraphing. Some mistakes distract readers and make it hard to understand the concepts. Essay rubric rules are not covered.
8. Presentation
Excellent/8 points: The form and presentation of the text enhance the readability of the essay and the flow of ideas.
Very Good/6 points: The format has few mistakes and is easy to read.
Average/4 points: The writer’s message is understandable in this format.
Needs Improvement/2 points: The writer’s message is only comprehensible infrequently, and the paper appears disorganized.
Unacceptable/0 points: Readers receive a distorted message due to difficulties connecting to the presentation of the text.
Final Grade: ___ .
Grading Scheme for an Essay Rubric:
- A+ = 60+ points
- A = 55-59 points
- A- = 50-54 points
- B+ = 45-49 points
- B = 40-44 points
- B- = 35-39 points
- C+ = 30-34 points
- C = 25-29 points
- C- = 20-24 points
- D = 10-19 points
- F = less than 9 points
Basic Differences in Education Levels and Essay Rubrics
The quality of essays changes at different education levels. For instance, college students must write miscellaneous papers when compared to high school learners. In this case, an essay rubric will change for these different education levels. For example, university and college essays should have a debatable thesis statement with varying points of view. However, high school essays should have simple phrases as thesis statements. Then, other requirements in an essay rubric will be more straightforward for high school students. For master’s and Ph.D. essays, the criteria presented in an essay rubric should focus on examining the paper’s complexity. In turn, compositions for these two categories should have thesis statements that demonstrate a detailed analysis of defined topics that advance knowledge in a specific area of study.
Summing Up on an Essay Rubric
Essay rubrics help teachers, instructors, professors, and tutors to analyze the quality of essays written by students. Basically, an essay rubric makes the analysis process simple for lecturers. Essay rubrics list and organize all of the criteria into one convenient paper. In other instances, students use the essay rubrics to improve their writing skills. However, they vary from one educational level to the other. Master’s and Ph.D. essay rubrics focus on examining complex thesis statements and other writing mechanics. However, high school essay rubrics examine basic writing concepts. The following are some of the tips that one must consider when preparing a rubric.
- contain all writing mechanics that relate to essay writing;
- cover different requirements and their relevant grades;
- follow clear and understandable statements.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Newspaper Article in APA 7 With Examples
- 12 October 2020

How to Write a "Who Am I" Essay: Free Tips With Examples
- 10 October 2020

- Basics for GSIs
- Advancing Your Skills
Examples of Rubric Creation
Creating a rubric takes time and requires thought and experimentation. Here you can see the steps used to create two kinds of rubric: one for problems in a physics exam for a small, upper-division physics course, and another for an essay assignment in a large, lower-division sociology course.
Physics Problems
In STEM disciplines (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), assignments tend to be analytical and problem-based. Holistic rubrics can be an efficient, consistent, and fair way to grade a problem set. An analytical rubric often gives a more clear picture of what a student should direct their future learning efforts on. Since holistic rubrics try to label overall understanding, they can lead to more regrade requests when compared to analytical rubric with more explicit criteria. When starting to grade a problem, it is important to think about the relevant conceptual ingredients in the solution. Then look at a sample of student work to get a feel for student mistakes. Decide what rubric you will use (e.g., holistic or analytic, and how many points). Apply the holistic rubric by marking comments and sorting the students’ assignments into stacks (e.g., five stacks if using a five-point scale). Finally, check the stacks for consistency and mark the scores. The following is a sample homework problem from a UC Berkeley Physics Department undergraduate course in mechanics.
Homework Problem
Learning objective.
Solve for position and speed along a projectile’s trajectory.
Desired Traits: Conceptual Elements Needed for the Solution
- Decompose motion into vertical and horizontal axes.
- Identify that the maximum height occurs when the vertical velocity is 0.
- Apply kinematics equation with g as the acceleration to solve for the time and height.
- Evaluate the numerical expression.
A note on analytic rubrics: If you decide you feel more comfortable grading with an analytic rubric, you can assign a point value to each concept. The drawback to this method is that it can sometimes unfairly penalize a student who has a good understanding of the problem but makes a lot of minor errors. Because the analytic method tends to have many more parts, the method can take quite a bit more time to apply. In the end, your analytic rubric should give results that agree with the common-sense assessment of how well the student understood the problem. This sense is well captured by the holistic method.
Holistic Rubric
A holistic rubric, closely based on a rubric by Bruce Birkett and Andrew Elby:
[a] This policy especially makes sense on exam problems, for which students are under time pressure and are more likely to make harmless algebraic mistakes. It would also be reasonable to have stricter standards for homework problems.
Analytic Rubric
The following is an analytic rubric that takes the desired traits of the solution and assigns point values to each of the components. Note that the relative point values should reflect the importance in the overall problem. For example, the steps of the problem solving should be worth more than the final numerical value of the solution. This rubric also provides clarity for where students are lacking in their current understanding of the problem.
Try to avoid penalizing multiple times for the same mistake by choosing your evaluation criteria to be related to distinct learning outcomes. In designing your rubric, you can decide how finely to evaluate each component. Having more possible point values on your rubric can give more detailed feedback on a student’s performance, though it typically takes more time for the grader to assess.
Of course, problems can, and often do, feature the use of multiple learning outcomes in tandem. When a mistake could be assigned to multiple criteria, it is advisable to check that the overall problem grade is reasonable with the student’s mastery of the problem. Not having to decide how particular mistakes should be deducted from the analytic rubric is one advantage of the holistic rubric. When designing problems, it can be very beneficial for students not to have problems with several subparts that rely on prior answers. These tend to disproportionately skew the grades of students who miss an ingredient early on. When possible, consider making independent problems for testing different learning outcomes.
Sociology Research Paper
An introductory-level, large-lecture course is a difficult setting for managing a student research assignment. With the assistance of an instructional support team that included a GSI teaching consultant and a UC Berkeley librarian [b] , sociology lecturer Mary Kelsey developed the following assignment:
This was a lengthy and complex assignment worth a substantial portion of the course grade. Since the class was very large, the instructor wanted to minimize the effort it would take her GSIs to grade the papers in a manner consistent with the assignment’s learning objectives. For these reasons Dr. Kelsey and the instructional team gave a lot of forethought to crafting a detailed grading rubric.
Desired Traits
- Use and interpretation of data
- Reflection on personal experiences
- Application of course readings and materials
- Organization, writing, and mechanics
For this assignment, the instructional team decided to grade each trait individually because there seemed to be too many independent variables to grade holistically. They could have used a five-point scale, a three-point scale, or a descriptive analytic scale. The choice depended on the complexity of the assignment and the kind of information they wanted to convey to students about their work.
Below are three of the analytic rubrics they considered for the Argument trait and a holistic rubric for all the traits together. Lastly you will find the entire analytic rubric, for all five desired traits, that was finally used for the assignment. Which would you choose, and why?
Five-Point Scale
Three-point scale, simplified three-point scale, numbers replaced with descriptive terms.
For some assignments, you may choose to use a holistic rubric, or one scale for the whole assignment. This type of rubric is particularly useful when the variables you want to assess just cannot be usefully separated. We chose not to use a holistic rubric for this assignment because we wanted to be able to grade each trait separately, but we’ve completed a holistic version here for comparative purposes.
Final Analytic Rubric
This is the rubric the instructor finally decided to use. It rates five major traits, each on a five-point scale. This allowed for fine but clear distinctions in evaluating the students’ final papers.
[b] These materials were developed during UC Berkeley’s 2005–2006 Mellon Library/Faculty Fellowship for Undergraduate Research program. Members of the instructional team who worked with Lecturer Kelsey in developing the grading rubric included Susan Haskell-Khan, a GSI Center teaching consultant and doctoral candidate in history, and Sarah McDaniel, a teaching librarian with the Doe/Moffitt Libraries.

TeachOnline@UW: Rubrics – Advantages and Best Practices
Types of Rubrics
Analytic rubrics.
Analytic Rubrics feature a grid of “criteria” (columns) and “levels” of achievement (rows). The instructor assigns points or weights to particular criteria, and then evaluates student performance in each area. This is useful in providing feedback on areas of strength and weakness. Because of this, analytic rubrics take more time to develop than a holistic rubric. See example of an analytic rubric.
Analytic rubrics are particularly useful for problem-solving or application assessments because a rubric can list a different category for each component of the assessment that needs to be included, thereby accounting for the complexity of the task. For example, a rubric for a research paper could include categories for organization, writing, argument, sources cited, depth of content knowledge, and more. A rubric for a presentation could include categories related to style, organization, language, content, etc. Students benefit from receiving rubrics because they learn about their relative strengths and weaknesses.
What are the advantages of using an analytic rubric? Evaluate the following statements.
Holistic rubrics.
Holistic Rubrics describe characteristics of each level of performance for an assignment or activity overall (e.g. characteristics of an excellent research paper). See an example of a holistic rubric.
Holistic rubrics are best to use when there is no single correct answer or response and the focus is on overall quality, proficiency, or understanding of a specific content or skills.
What are the advantages of using a holistic rubric? Evaluate the following statements.
You want to assign a score based on an overall judgement of your students’ work. Would you choose an analytic rubric or a holistic rubric?
You want to assign points based on achievement level for several criteria. would you choose an analytic or a holistic rubric.
Rubrics: Advantages and Best Practices Copyright © by Karen Skibba. All Rights Reserved.
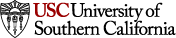
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Short essay question rubric
Short essay question rubric
Sample grading rubric an instructor can use to assess students’ work on short essay questions.
Download this file
Download this file [62.00 KB]
Back to Resources Page
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Foreign Language Rubrics: A Guide to Writing Analytic and Holistic Rubrics
Rubrics give us measurable objectives. Plus, they can be transformed into reliable teaching and learning tools for you and your students.
If you’ve ever felt lost when grading a fistful of short essays, maybe you’ve been missing a rubric in your life!
For essay writing, general participation or even role-play activities, just about every aspect of your class can be assessed with rubrics.
In this post, we’ll look at basic types of rubrics, how they’re structured, how to write expectations and assign assessment values. Finally, I’ll leave you a bonus of a couple of rubrics for really challenging class activities and tasks.
The 2 Main Types of Rubrics: Analytic and Holistic
Analytic rubrics, holistic rubrics, how to write effective foreign language rubrics, 1. start with basic rubric structure, 2. decide on your expectations, 3. choose your assessment values, 4. use your foreign language rubrics to teach and assess, 5. follow useful examples of foreign language rubrics.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)

An analytic rubric looks at the details of the task being assessed.
An analytic rubric focuses on specifics. In the case of writing, for example, you might look at specifics such as grammar, vocabulary use, sentence structure, composition, main ideas and cohesion.
In an oral presentation, you may be looking at body language, vocal expression, pronunciation, as well as introduction, logical argument and conclusion.
For these types of presentations, it may be useful to have students imitate the intonation of the spoken language. This can be based off of clips they’ve seen from actual native speakers of the language.
Holistic rubrics take a few steps back and are a more general, global look at the task. You’ll be assessing overall accomplishment rather than the details that make up the accomplishment.
Say you have an essay that uses persuasive language well, despite some grammar or vocabulary issues. You may consider such an essay better, in certain circumstances, than an essay that’s grammatically correct but doesn’t persuade or has little content value.
Watching a role-play that entertains, that’s generally understood by all and demonstrates the hard work put in by the participants can often lead you to overlook sentence fragments, poorly-conjugated verbs or pronunciation issues, depending on what you’re assessing.

While being creative is fashionable in modern foreign language teaching, creating a rubric will actually begin with a pretty standard format . This format simplifies the seemingly complex task of assessing a task.
Before you even begin brainstorming content, you’ll want to lay out a chart. Flip a Word document into landscape mode and lay out a basic chart with four or five columns and the same number of rows. You can always add an extra row or column later if you want to add something.
It’s a good idea to set the first row and first column in centered bold type. These will be the title cells, and having them in bold helps you to visually recognize your criteria.
Each row in your chart will be titled with the general area or objective that you’ll be assessing.
For example, if you’re grading essays, you might title each of your rows as:
- Vocabulary use
- Overall composition
Keep these titles short and sweet. They represent the main teaching points or objectives you have had in mind while preparing your classes.
Title each column with a “value” of performance, using either a descriptive adjective, such as “excellent” or “good,” or a number, or a combination of both.
This type of scheme is an expansion on the “right/wrong” answer scenario in a normal test. Instead of simply identifying right or wrong, you’re looking at a specific aspect and judging if it’s “excellent,” “good” or “needs work.” If we combine the example rows for an essay rubric in the previous section with these, we’ll get something like this:
We’ll look a bit more closely at these row and column titles in a moment.
Now it’s time to fill in the cells. This is where you’ll explain what you mean when you think the student’s grammar is “excellent” or when their composition is simply “good” with specific expectation statements . Let’s take a look at how to write those.
An expectation is the performance you want from your student when they’re performing the task you’ve assigned to them. You’re not looking for errors they make but rather concentrating on how well they’re doing.
When creating your expectations, use as few words as possible. It’s best to limit yourself to one sentence. Instead of:
The student will be able to use vocabulary learned in previous classes, conjugating verbs correctly according to person and time, adding appropriate suffixes and prefixes and respecting correct word order, while using the most recent vocabulary learned in class in the correct fashion….
Your expectation should read:
Vocabulary is used appropriately, taking advantage of previously and recently studied words, their forms and conjugations.
You’re looking for expectations that focus your attention. While assessing a student with a rubric, you’ll ask yourself the simple, yes/no question: Did the student meet with these expectations?
Though you want your expectations to be concisely worded, you also want them to be understandable, both for you and your students. If you use words like “appropriately,” make sure you have a clear idea what you mean:
- Is the use appropriate to the context ?
- Is it appropriate to the student’s proficiency ?
- Is it appropriate for the task ?
If you’re writing an analytic rubric for a specific task (for example, writing an essay with past tense verb forms) you might want to be a bit more specific:
- Past tense verb forms are used correctly nine out of ten times .
- They’re used correctly six out of ten.
- They’re used correctly three out of ten.
Each expectation will be slipped into the appropriate (there’s that word again!) assessment/value column. A student who achieves 9/10 will get a different score than one who only gets 3/10. How do you assign the value? By using the assessment values .
These will be the titles you put at the head of each of your columns. Yes, we talked about these earlier—suggesting language like “needs work,” “good” and “excellent.” This will guide you when you’re explaining what you expect from your students at each level of performance.
Using words
Placing descriptive adjectives as titles for columns is a good place to start. You’re teaching language, after all, so assigning values like “excellent,” “above average,” “good,” and “needs work” helps you communicate your assessments to your students.
The adjectives you choose should be encouraging, though. “Needs work” obviously sounds much better than “poor” or “unsatisfactory.” You may need to include a “task not completed” category for those few times that a student just doesn’t even come close to making the grade.
Using adjectives isn’t always useful, though, when calculating an overall grade for the activity. That’s where adding numbers comes in very handy.
Using numbers
Seems like a no-brainer, yet sometimes we all need to be reminded. Numbers don’t lie. They’re clean and clear and easy to understand.
2 + 2 always equals 4!
Assign basic numerical values to each of your expectations. The basic number scale will be easy to design. If a higher number is what you choose to represent better performance (that’s the standard way to go) and you have four performance levels to assign, then:
- Excellent = 4 points
- Above average = 3 points
- Satisfactory = 2 points
- Needs work = 1 point
What do you do, though, if one objective, like grammar or main ideas, is more important to the overall score? This problem is solved by weighing each objective.
Weighing importance
Let’s use essay writing as an example and say that the aspects you want to assess include:
- Grammar and vocabulary
- Sentence structure
- Composition
Now, if your objective is to assess how well students have used the passive voice and the vocabulary related to a theme you’ve recently taught, you may consider “grammar and vocabulary” to be more important than the overall composition.
On the other hand, you may have just given a lesson on correct essay composition and opinion expression, so you want to concentrate on what they have to say and how they’ve presented their thoughts.
In either scenario, you’ll assign a “weight” to each of these aspects or goals. In the first case, “grammar and vocabulary” may have a weight of 2 while the remaining aspects have no additional weight assigned. In the second example, both “composition” and “content” will carry a weight number while the remaining goals do not.
When calculating the score, you simply multiply the basic value by the weight number and note the result as the assessment score for that aspect. So, “grammar” performed at an “excellent” level is equal to 4 (the excellent score) × 2 (the weight of the “grammar and vocabulary” category), which naturally is 8.
Assigning final scores
Finally, once you’ve assessed, given feedback and recorded the numerical scores, you’ll need to give those total scores a value.
You’ll begin by calculating the total highest score. In the first example above, that would be (Excellent = 4):
- Grammar and vocabulary 4 × 2 = 8
- Sentence structure 4
- Composition 4
Total possible score: 20 points.
Now divide that total score by the total number of assessment levels: 20 / 4 = 5.
So, for each increment of 5 points you can reassign your descriptive adjectives:
- 16-20 = Excellent
- 11-15 = Above average
- 6-10 = Satisfactory
- 1-5 = Needs work
Wed your rubric to your class plan
Your rubric is more than a guide for scoring your students’ activities. Combined with your day-to-day planning, it should be a basic guide for you in teaching.
Imagine that you’ve spent a week explaining and doing exercises with your students on the subjunctive in Spanish. You’ve taught:
- the construction of the verb form,
- the situations in which it’s used,
- the meaning behind its use in speaking Spanish.
Students have done homework and now you’re ready to evaluate their understanding. In a short role-play exercise, your rubric might read:
- Construction : Students have correctly conjugated the main verb.
- Situations : Students have recognized subjunctive triggers ( ojalá , espero que , etc).
- Meaning : Students have chosen subjunctive use in appropriate situations.
If you keep your rubric in mind while teaching, your teaching will also include what you expect your students to get out of the lectures, exercises and practice. When it’s time to assess them, they’ll know that you’ll be looking out for those same aspects.
Expose the rubric to students
Share those expectations with your students. Many of the concepts we teach in language class are generalizations of language: the subjunctive, the passive voice, modal verbs. We sometimes teach these general concepts without letting our students know “what will be on the test” until right before that test.
Before launching a unit on any language aspect, give your students the rubric you’ll be using to assess them. With this tool, they can focus on details and actively prepare themselves.
Students can use your rubric as a self-assessment tool. If you use clear, understandable, descriptive adjectives for assessment, you can create a “scorecard” for students to use when observing group activities, like role-plays or presentations. Peer assessment is helpful, since students often share the same issues in language class, at times understanding one another better than their teacher.
Strive for fairness
As language teachers, we’ve all had to correct essays. I’ll bet the following situation has happened to you:
The scenario:
You’ve asked your students to write an essay on global warming. You’ve given them some texts to read, perhaps you’ve watched “An Uncomfortable Truth” together in class. Your instructions may be “Write an essay on global warming. Please include one argument for and against the concept. Word count should be between 200 and 500 words.”
The conflict:
The next day, you have 20 essays on your desk. You read the first one, it’s pretty good, content is fine, 254 words, grammar a bit sketchy here and there, a little repetitive. You give it an “excellent.”
The next two or three are pretty easy as well. A couple are similar to that first one, a couple are really wanting some work. Then you come to one that makes you realize that all the previous ones share the same issue: No one has used proper paragraph structure, it’s all one block of text. So, you have to go back to the first one again and mark it down because you really expect paragraphs.
Or you may notice that all of your students are all incorrectly using the same verb structure. You marked down for this error on that first essay, but now you have to go back and be more fair because you’ve realized that maybe you failed in getting the idea across to almost all of your students.
The problem:
Grading in this fashion, you end up assessing the class as a group rather than looking at the work of each student. You haven’t clearly defined your expectations beforehand and you’re allowing each new essay to alter your assessment. Though you may recognize areas where you need to improve as a teacher, you’re not assessing each student as an individual.
The solution:
With a clear set of expectations to apply to each individual before you, you’ll fairly apply those expectations to each student. If you expect students to manipulate that verb form correctly, if you have that in mind from the beginning, if you have informed your students that you expect this from them, each essay you read will pass through that filter, with a simple yes/no answer to the question: “Did they meet my expectations?”
The expectations listed in the following examples will probably fall into the assessment column with the highest value. You’ll work down from these, lowering your expectations to each of the values you consider appropriate for the assessment.
Role-play rubrics
For role-play assessment, the value titles can be excellent/good/needs work or 3/2/1. Remember to use clear adjectives if you’re handing out self-assessment scorecards to students observing the scene.
Analytic grammar/vocabulary use rubric
- Students have used the recently-taught grammar appropriately in their scene.
- Students have employed vocabulary specific to the subject of their scene.
- Word forms (verb conjugation, etc) have been used correctly.
Holistic performance/participation rubric
- Students have quickly outlined the scene and assigned roles and sentences.
- Once a basic script is decided, students have concentrated on rehearsing, with only minor changes to their script.
- Time limits and participation equality have been respected.
- Focus language has been used appropriately.
- The scene was well-organized and entertaining.
Critical writing rubrics
Assessment values for writing might include a tick-off list of number of deviations from your expectations. For example, you may want to assess grammar as: 1 or less errors = excellent; 2 to 3 errors = good; 4 or more = needs work.
Analytic composition/grammar/communication of ideas rubric
- Main ideas : The student has correctly identified the main idea and discussed the pros and cons involved.
- Composition : The student has used the basic essay format taught in class: introduction, development, conclusion, with appropriate paragraph structure and formatting.
- Coherence : Ideas have been presented in a logical fashion, using transitional words and devices previously taught in class, without reverting to simple “and” and “but” use.
- Vocabulary : Words have been correctly used (including word form) and repetition has been limited.
- Grammar : Basic, previously learned sentence structure has been used, while newly taught focus structure has been appropriately included in the writing.
Holistic comprehension/analysis/explanation rubric
- The student has understood and applied teacher instructions fully in composing the essay.
- Source material has been understood and appropriately cited and addressed in the essay.
- Basic composition/grammar/punctuation rules have been respected; handwriting is clear and easy to read.
- The student has communicated his/her ideas or opinions clearly and persuasively.
Behavior rubric
Behavior is something we usually overlook until inappropriate behavior gets in the way of a pleasant and organized classroom. The best assessment values for behavior usually look like the “three strikes you’re out” baseball rule or the “yellow card/red card” rules of soccer.
Analytic “does homework/arrives on time/respects peers” rubric
- The student presents neatly done homework when due.
- The student is punctual for class.
- The student follows classroom rules: having materials, raising hand to speak, etc.
- The student is respectful and helpful to his/her peers during class.
- The student actively and willingly participates in all classroom activities.
Holistic classroom behavior analysis rubric
- Classroom rules are understood and followed.
- Activities are enjoyed and actively carried out by all.
- Self and group evaluations are constructive.
- A positive attitude is shared by students and teacher for learning.
Rubrics can be the key to effective assessment of your students, making your job as a teacher much easier, since you’ll know from the outset what you’re looking for and can easily identify whether or not students have met expectations stemming from your objectives as a teacher.
They also become an active self-assessment and teaching tool when they’re shared with your students and you encourage them to use them on a regular basis. Students appreciate knowing what’s expected of them and are open and encouraged by the recognition, both by the teacher and by their peers, that they have achieved those goals.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


Rhetorical Essay
Rhetorical essay generator.

In the realm of persuasive writing, rhetorical essays stand as powerful demonstrations of linguistic artistry. By employing a variety of literary devices, carefully selected words, and strategic communication techniques, these essays are designed to sway the minds and emotions of readers. Delving into the heart of rhetoric, this article will delve into the essence of rhetorical essays, guiding you through their creation while offering illuminating examples and practical tips. Whether you’re a seasoned writer or new to the craft, understanding the dynamics of a rhetorical essay can enhance your ability to communicate effectively and convincingly.
1. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Template

- Google Docs
2. Rhetorical Essay Outline

Size: 345 KB
3. Structure of Rhetorical Analysis Essay
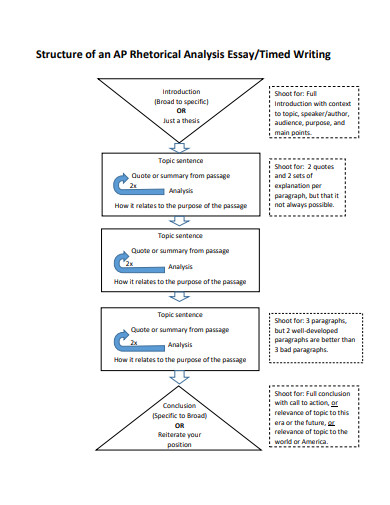
Size: 315 KB
4. Rhetorical Analysis Thesis Statement Essay

Size: 342 KB
5. Editable Rhetorical Essay
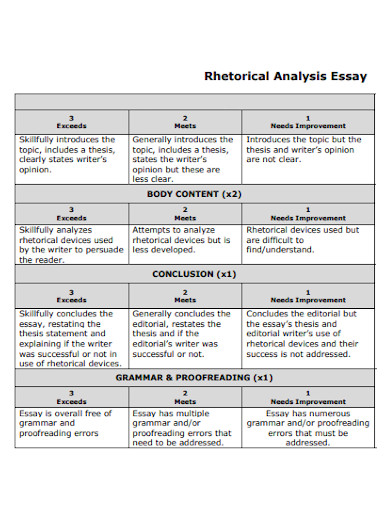
Size: 133 KB
6. Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline

Size: 60 KB
7. Sample Rhetorical Essay

Size: 341 KB
8. Rhetorical Essay Template
Size: 77 KB
9. Rhetorical Essay Ethos

Size: 544 KB
10. Rhetorical Essay Layout

Size: 424 KB
11. Rhetorical Essay Paper

Size: 666 KB
12. Organizing and Outlining Rhetorical Essay

Size: 23 KB
13. Rhetorical Essay Rubric
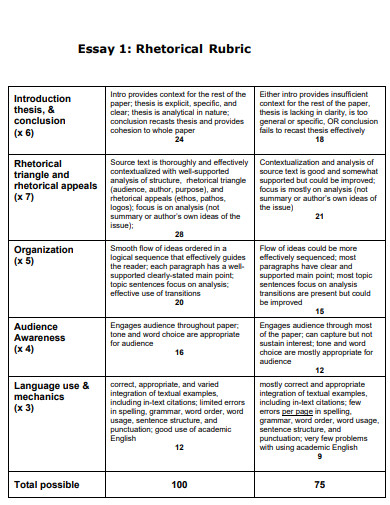
Size: 10 KB
14. Rhetorical Grading Essay
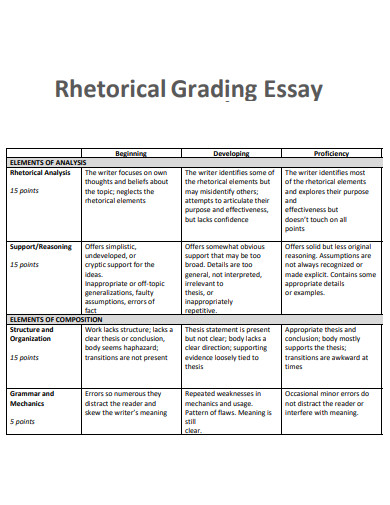
Size: 134 KB
15. Rhetorical Essay Informative Writing
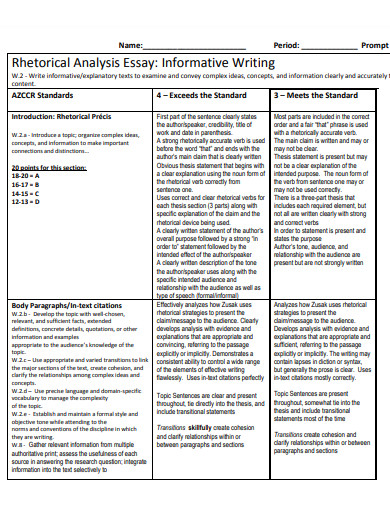
Size: 350 KB
16. Simple Rhetorical Essay

Size: 35 KB
17. Critical Rhetorical Essay

Size: 61 KB
18. Research Rhetorical Essay

Size: 112 KB
19. Rhetorical Essay Reference

Size: 174 KB
20. Rhetorical Essay Worksheet

Size: 303 KB
21. Rhetorical Essay on Gender Equality

Size: 224 KB
22. Formal Rhetorical Essay

Size: 82 KB
23. Rhetorical Essay Format

Size: 128 KB
24. Professional Rhetorical Essay

Size: 26 KB
What is a Rhetorical Essay?
A rhetorical essay is a unique form of discourse that employs persuasive techniques to communicate a particular message or viewpoint. This literary device operates by leveraging linguistic elements to convince an audience of the validity of a certain argument or perspective. Unlike traditional essays that primarily focus on information and analysis, rhetorical essays emphasize the art of persuasion. By dissecting the behaviors of words, examining their impact within a specific context , and avoiding clichés , a rhetorical essay creates an objective and compelling narrative that leaves a lasting impression.
How to write a Rhetorical Essay
Creating a compelling rhetorical essay requires a meticulous approach that blends creativity with strategic communication. To navigate this intricate process, let’s break it down into several key steps that will help you weave together a convincing and impactful piece.
Step 1: Choosing a Subject and Objectives
Begin by selecting a topic that resonates with your audience and aligns with your objectives. Consider the behaviors you intend to evoke and the elements you wish to emphasize. Craft an overarching objective that defines the purpose of your essay, whether it’s to inform, persuade, or provoke thought.
Step 2: Mastering Language and Syntax
Leverage the power of verbs , adjectives, and proper nouns to create a vivid and captivating narrative. Use observation to your advantage, painting a detailed picture that engages your readers’ senses. Employ simple sentences to convey your ideas clearly and concisely, ensuring that your message remains accessible.
Step 3: Employing Rhetorical Devices
Rhetorical essays thrive on the skillful use of literary devices . Incorporate metaphors, similes, and analogies to add depth and resonance to your arguments. Harness the strength of repetition and parallelism to reinforce key points and create a rhythmic flow that captivates your audience.
Step 4: Structuring for Impact
Organize your essay with a clear structure that guides your readers through a logical progression of ideas. Begin with a strong introduction that sets the tone and context, followed by well-organized body paragraphs that present evidence, analysis, and persuasive elements. Conclude with a compelling ending that reinforces your main points and leaves a lasting impression.
What is the most important element of a successful rhetorical essay?
The choice and skillful implementation of rhetorical devices, such as metaphors and analogies, can significantly enhance the impact of your essay.
Can I use humor in a rhetorical essay?
Yes, humor can be a powerful tool in persuasion, but ensure it aligns with your objective and doesn’t undermine the seriousness of your message.
How do I avoid sounding manipulative in my rhetorical essay?
Focus on transparency and authenticity. Present your arguments with integrity and provide solid evidence to support your claims, avoiding any overt manipulation.
In the realm of persuasive writing, rhetorical essays serve as a testament to the power of words. By delving into the behaviors of language, harnessing the art of rhetoric, and crafting a narrative that engages and convinces, you can create essays that leave a lasting impact. So, whether you’re aiming to provoke thought, inspire action, or challenge perceptions, remember that a well-crafted rhetorical essay can be your most potent tool in the realm of written persuasion.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a rhetorical essay analyzing the speech given by Martin Luther King Jr.,
Examine the use of ethos, pathos, and logos in a popular advertisement of your choice in a rhetorical essay.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
You see them in standardized testing — the essay portion of the SAT is scored with a 0-6 holistic rubric. When hundreds of thousands of essays have to be graded quickly, and by total strangers who have no time to provide feedback, a holistic rubric comes in handy. ... So for the breakfast in bed example, an analytic rubric would look like ...
You might Google, "Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level" and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. ... Examples Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper. Above Average (4) Sufficient (3) Developing (2) Needs improvement (1)
Analytic Rubric Samples . Writing - This rubric could be used to assess a third grade student's personal narrative or fiction story. 1 - Needs Improvement . ... - This sample rubric could be used to assess a student's lab report from a scientific investigation. 1 - Needs Improvement . 2 - Fair . 3 - Good . 4 - Excellent .
Analytic Rubrics The WHO, WHAT, WHY, WHERE, WHEN, and HOW of an Analytic Rubrics. WHO: Analytic rubrics are for you and your students.. WHAT: An analytic rubric is a scoring tool that helps you identify the criteria that are relevant to the assessment and learning objectives.It is divided into components of the assignment contains a detailed description that clearly states the performance ...
Essay Rubric Directions: Your essay will be graded based on this rubric. Consequently, use this rubric as a guide when writing your essay and check it again before you submit your essay. Traits 4 3 2 1 Focus & Details There is one clear, well-focused topic. Main ideas are clear and are well supported by detailed and accurate information.
Logical, compelling progression of ideas in essay;clear structure which enhances and showcases the central idea or theme and moves the reader through the text. Organization flows so smoothly the reader hardly thinks about it. Effective, mature, graceful transitions exist throughout the essay.
For example, an instructor may choose to give 30 points for an essay whose ideas are sufficiently complex, that marshals good reasons in support of a thesis, and whose argument is logical; and 20 points for well-constructed sentences and careful copy editing. ... For example, a partial analytic rubric for a single trait, "addresses a ...
Analytic Rubric for Scoring Persuasive Writing (ENG 10) Ideas 4 3 2 1 A main idea is distinct and is developed through vivid and relevant details. A main idea is clear and is developed through relevant details. A main idea is evident and is somewhat developed through details, some of which may be irrelevant.
Body. The body of your essay is not limited to three points, as shown above, but three is typically considered the minimum for a good analysis. To make your analysis more compelling, present your points and arguments in a "strong, stronger, strongest" format. main point #1 - a strong point. strong supporting evidence #1.
Rubric Used for Grading an Analytical Essay (Sociology) (This rubric was developed by Pablo Gaston and relies on the example rubrics presented by the GSI ... more examples. Evidence advances the argument, but it may not be sufficient. Potential counter-arguments are accounted for, but may not be
The SAT essay rubric says that the best (that is, 4-scoring) essay uses " relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for claim (s) or point (s) made. " This means you can't just stick to abstract reasoning like this: The author uses analogies to hammer home his point that hot dogs are not sandwiches.
Scoring Guide for Essays h3. Quality of Ideas: ____ points Range and depth of argument; logic of argument; quality of research or original thought; appropriate sense of complexity of the topic; appropriate awareness of opposing views. h3. Organization & Development: ____ points Effective title; clarity of thesis statement; logical and clear.
Essay repeats and summarizes basic, correct information, but does not link readings to evidence and does not consider alternative perspectives or connections between ideas. Essay displays an understanding of the required readings and underlying concepts including correct use of terminology and proper citation. Essay displays excellent
In an analytic rubric, each section of the rubric has an independent score. For example… in an essay, you might score the student's ability to summarize, use vocabulary, connect ideas - etc. Each section or criteria of the rubric will have an independent score which is totalled up at the end to provide a comprehensive grade.
Analytic Rubric. Source: University of Nebraska. Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. ... This example for essay writing ...
AP English Language Scoring Rubric, Free-Response Question 1-3 | SG 1 Scoring Rubric for Question 1: Synthesis Essay 6 points Reporting Category Scoring Criteria Row A Thesis (0-1 points) 4.B 0 points For any of the following: • There is no defensible thesis. • The intended thesis only restates the prompt.
Sample Directed Self-Placement Analytic Rubric. The Directed Self-Placement for Writing for First-Year Students (DSP) gives incoming students a chance to learn about the types of academic writing most often assigned and valued at the University of Michigan. It asks students to read an article, write an evidence-based argument in response to the ...
Essay Rubric: Basic Guidelines and Sample Template. Lectures and tutors provide specific requirements for students to meet when writing essays. Basically, an essay rubric helps tutors to analyze the quality of articles written by students. In this case, useful rubrics make the analysis process simple for lecturers as they focus on specific ...
Examples of Rubric Creation. Creating a rubric takes time and requires thought and experimentation. Here you can see the steps used to create two kinds of rubric: one for problems in a physics exam for a small, upper-division physics course, and another for an essay assignment in a large, lower-division sociology course.
See example of an analytic rubric. Analytic rubrics are particularly useful for problem-solving or application assessments because a rubric can list a different category for each component of the assessment that needs to be included, thereby accounting for the complexity of the task. For example, a rubric for a research paper could include ...
Office of the Provost 3601 Watt Way, GFS 227 University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-1691 [email protected] (213) 740-3959. Contact Us
the validity of these rubrics (Green & Hawkey, 2002). Secondly, existing holistic rubrics (e.g. Angeli & Valanides, 2009; Welch, Hieb, & Graham, 2015) cannot provide an accurate picture of a student's critical thinking ability in argumentative essays. It is the nature of a holistic rubric to grant a single score to illustrate a comprehensive
An analytic rubric looks at the details of the task being assessed. An analytic rubric focuses on specifics. In the case of writing, for example, you might look at specifics such as grammar, vocabulary use, sentence structure, composition, main ideas and cohesion. ... Let's use essay writing as an example and say that the aspects you want to ...
draft rubric provides a baseline fo r structure, organization, and standard s while promoting an expectation for alteration. An example project for this path . Students read through the draft rubric in groups identifying the key terms as well as those terms that are unclear. Then, each group makes revisions to the rubric as they see fit. The
Step 3: Employing Rhetorical Devices. Rhetorical essays thrive on the skillful use of literary devices. Incorporate metaphors, similes, and analogies to add depth and resonance to your arguments. Harness the strength of repetition and parallelism to reinforce key points and create a rhythmic flow that captivates your audience.