
What Are Some of the Current Challenges in Quality Education?
Around the world, millions of children face significant barriers to receiving the quality education they deserve — from overcrowded classrooms to undertrained teachers; from lack of access for students with disabilities to gender inequity; from the massive impact of pandemic-related school closures to lack of family support for education .
Time in School Doesn’t Equal Time Spent Learning
In Rwanda, where these obstacles are the reality for many children, a student can expect to complete roughly 6.9 years of school by the time they turn 18. However, when this figure is adjusted to factor in what they have learned, this actually only equates to 3.9 years (Source: Human Capital Index 2020 ). This is why Wellspring focuses not only on ensuring that children have access to school — an area in which great progress has been made in Rwanda — but on building the capacity of teachers and leaders to provide children with a quality education .
Ill-Equipped Teachers
There is a great need for teachers to be equipped with skills that improve the quality of students’ learning, and this is particularly true in this season of mass teacher recruitment. Alongside the building of thousands of new classrooms across Rwanda, over 20,000+ new teachers have been recruited, many of whom have no background as educators. Wellspring has had a key role to play in developing resources and providing support that will set these new educators up for success.
Language Barriers in Teaching and Learning
Another challenge faced by teachers and students alike is the requirement that lessons are taught in English, rather than in Kinywarwanda — the native tongue of most teachers and students in Rwanda . This presents a significant obstacle to teaching and learning, and a great deal of support is needed to ensure that lessons are being absorbed and understood.
Prioritizing Pre-Primary
There is an increasing awareness too of the importance of quality education at the pre-primary level, and this is leading Wellspring to engage more intentionally and strategically in early childhood education. The challenge is that access to, and enrolment in, pre-primary education remains low in Rwanda. The Rwandan government is proactively promoting greater enrolment to ensure that young children are as ready as they can be for their formal primary and secondary education.
The Road Ahead
This pursuit of quality education for every child —which is also the focus of UN Sustainable Development Goal 4 —and work towards removing the obstacles children face in accessing this kind of education is worth our investment and will make a difference for generations to come. This takes capacity-building work at the grassroots level and advocacy work at the systemic level, and Wellspring is privileged to play a part in both.
Other Foundational Pieces
We are sharing these Foundational Pieces to help you learn more about who we are and what we do.

What do we mean by Quality Education?

What are Barriers to Girls’ Education?

Why Does Education Matter?
This site belongs to UNESCO's International Institute for Educational Planning

IIEP Learning Portal

Search form
- issue briefs
- Monitor learning
Using data to improve the quality of education
There is a worldwide concern that learning outcomes have not kept pace with the expansion of education. The extent of the learning deficit is largely unknown because many countries have few systematic data on who is learning and who is not. Learning assessments provide data on the status of learning, which can be used to monitor the quality of systems and student learning outcomes. Regular monitoring can reveal changes over time in response to interventions to improve student outcomes, providing feedback and additional data for decision-making.
Learning data, in conjunction with other dimensions of quality such as context, teaching and learning environment, and learner characteristics can reveal the factors that most affect learning outcomes. By revealing gaps in student achievement and service provision, data can be used to identify those groups that are being underserved and are underperforming. Once identified, such inequities can be addressed.
Data can be used to hold the system accountable for the use of resources by showing whether increased public investment in education has resulted in measurable gains in student achievement. Although direct accountability for results rests mainly with the school, the enabling policy and practice environment is the responsibility of decision-makers at all administrative levels.
Which actor needs which type of data?
Data-driven decisions to improve learning are taken at each level of the system. The specificity of the data decreases from school to national level and the time lag between data collection and application increases. Decisions concerning individual students, classes, and schools are made locally, where raw data are produced. System-wide decisions based on aggregated data are made nationally.
Classroom teachers
Classroom teachers manage the teaching and learning process. They monitor students’ learning by informal means, such as quizzes and games, and formative tests. Teachers use the data to assess a student’s performance, strengths, weaknesses, and progress. Additional information on an individual student’s background allows the teacher to diagnose possible causes of poor performance and apply remedies. The data can also be used for self-evaluation to identify where teachers could improve their pedagogy or classroom management.
Head teachers
Head teachers assess the school’s overall performance. They examine student achievement and attainment, staff performance, and use of school resources. Head teachers set and monitor school practices, programmes, and policies. They need raw achievement data, information on teachers’ classroom practices and contribution to student outcomes, and on their own performance as rated by supervisors.
Parents and communities
Parents and communities require information on students’ achievement, including their strengths and weaknesses, and any behavioural issues. They are concerned about public examination results, since performance determines their children’s progress to further education or employment. Parents and school staff can discuss and agree an agenda for action to support student needs. Parents can support school improvement through parent-teacher associations and school boards.
District and provincial level actors
District level actors have responsibility for oversight of the management and quality of schools in the district. They collect and aggregate school data on student attendance and achievement, teacher attrition and absenteeism, and resources. They play an important role in the identification of the resource needs of schools, in monitoring standards and recommending improvement measures.
Provincial level administrators, coordinators, and supervisors make decisions based on evidence of an issue serious enough, or an opportunity good enough, to warrant commitment of time and provincial resources. Their focus is on how to plan and use interventions to provide large groups of schools with the resources and expertise to set up and evaluate their education programmes and, guided by evaluation results, to adopt procedures to improve effectiveness.
National level officials
National level officials make broad policy decisions on links between government directives and the plans and resources needed to comply with those directives. They need substantial system-wide information on current student outcomes and associated factors, together with data on long-term trends. These are collected and collated to provide the basis for decisions on the whole or on a major part of the education system. Data sources include EMIS, national examination results, and learning assessments.
What information can the data provide and how can it be used?
Learning data, augmented with background data, provide information on how well students are learning, what factors are associated with achievement, and which groups perform poorly. This information can be used for system analysis, improved resource allocation, agenda setting or during the policy-cycle.
Education system analysis
Education systems may be analyzed in terms of:
- What students are learning;
- Whether what they learn responds to parents’, community, and country needs and aspirations (relevance);
- How well resources are used to produce results (internal efficiency);
- What the main factors influencing learning are; and
- Which aspects of the system require improvement.
If the data show some groups’ learning outcomes are low due to their location, ethnicity, religion, or disability, measures can be taken to provide additional resources, such as teachers or books, aimed at improving their achievement.
Improved resource allocation
The data may reveal issues with the provision and use of resources. School infrastructure, availability of instructional materials, and the use of instructional time influence learning outcomes. Improved instructional materials with information on their use may contribute to better achievement.
Agenda setting and policy-making
According to Clarke (2017), there are differences between countries at different income levels in the focus of their policy and design. Generally, high-income countries with established assessment programmes use data for sector-wide reforms or a programme of interventions aimed at improving learning outcomes. Low-income countries that are beginning to use the programmes tend to identify a few separate issues, such as resource allocation or teacher qualifications, as responsible for poor achievement. Resulting policies include a few discrete interventions.
Data analysis can identify areas that require improvement, from which agenda for action can be designed. For example, Meckes and Carrasco found that in Chile, publication of the correlation between students’ socio-economic status and their achievement prompted demands for policies to address equity issues (Raudonyte, 2019).
Seychelles’ use of SACMEQ findings in 2000 provides an example of using assessment results for policy formulation. SACMEQ data indicated large differences in learning outcomes among pupils in the same school, attributable to a long-established practice of streaming by ability from Grade 1. By Grade 6 the learning achievement between girls and boys had widened to such an extent that there were more girls in the elite class and more boys in the inferior class. Effective communication channels, an enabling political context, and effective dialogue among actors contributed to the decision to adopt a de-streaming policy (Leste 2005 quoted in Raudonyte, 2019).
The regular collection of learning and other related data to monitor policy implementation can inform on the status of planned activities, reveal implementation challenges, pinpoint early indications of impact, and suggest modifications to adjust shortcomings. For example, the Learn to Read initiative in Madhya Pradesh was monitored on a monthly basis through standardized tests to detect shortcomings and adjust implementation (Tobin et al., 2015).
National assessments can be used to gauge the impact of policy on learning outcomes and to provide feedback to address shortcomings. In theory, there should be a seamless progression from testing through agenda setting, policy formulation, implementation, and monitoring and evaluation based on more testing. In practice, such a feedback mechanism is often less well organized. This may be due, among other things, to lack of experience with using assessments, weak technical capacity, poor coordination between assessment and decision-making bodies, and funding shortfalls.
Challenges to data use
For data to be used effectively they must be actionable, available to all who are in a position to act and presented in an appropriate form for each group of stakeholders. Barriers to data use include the following:
Data availability
Inadequate funding of an assessment programme can mean the programme cannot be completed. Delays in analysis can prevent data from being released in a timely manner. Results may be withheld if they are below expectations. Findings may be dismissed if they do not respond to the needs of the system, or are not actionable or linked to viable policy options.
Access problems
Data access problems include: a failure to communicate results to both the public and those who are in a position to act; results retained within a ministry of education to restrict their use by other stakeholders and prevent the media and public from lobbying for action; the content and format of the reports may not be suited to some or all target groups, who need a variety of data and presentation modes.
Quality issues
Issues with the design, relevance, and credibility of the assessment programme can lead to data being withheld or ignored. Real or perceived deficiencies in assessment instrumentation, sampling and analysis can raise validity and relevance issues. Occasional or ill-designed assessments mean that skills and content are not comparable over time. Caution is needed when developing policy messages based on assessment results without an analysis of supplementary data.
Limited capacity and skills to assess and use the data
Ministries of education may lack experience with national assessments, have poorly established decision-making procedures and low technical capacity. Technical personnel may lack expertise in assessment design, in-depth data analysis, and interpretation. This may result in recommendations being superficial and uninformative. Policy-makers may not understand the implications of the assessment or may not focus on the analysis due to time constraints. Data collection, analysis, availability, and use may be adversely affected by funding constraints.
Political climate
Conflict and political unrest may impact assessment implementation. Political sensitivities due to low levels of achievement can prevent data use. There may be a lack of political will to act on a recommendation.
Minimizing the challenges
Credibility and acceptability issues can be addressed by involving all relevant stakeholders in the design and implementation of an assessment. The assessment team should have the technical competence to design, administer the assessment and analyze results. Ongoing technical training of existing and potential staff is necessary to ensure quality and to allow for attrition.
Building local capacity or establishing a regional coordinating body are possibilities. Both options require substantial investment in capacity building that could be costly and time-consuming.
Judicious use of media channels at all stages of the assessment including dissemination of results, and regular stakeholder discussions will ensure the public are kept informed. Distribution will be facilitated if there is a budget for dissemination, a dissemination plan and if the reports prepared are tailored to different users’ needs.
Existing structures, policy-making and decision-making processes within ministries can also be a barrier to data use. In order to adapt to a data-driven decision-making culture, ministries of education may need to restructure and redefine the roles and responsibilities within the organization. Links among staff and with relevant outside institutions need to be established and sustained.
Australia. Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. 2018. ‘ Education learning and development module: Learning assessment ’ . Canberra: DFAT.
Best, M.; Knight, P.; Lietz, P.; Lockwood, C.; Nugroho, D.; Tobin, M. 2013. The impact of national and international assessment programmes on education policy, particularly policies regarding resource allocation and teaching and learning practices in developing countries. Final report. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London.
Birdsall, N.; Bruns, B.; Madan, J. 2016. Learning data for better policy: A global agenda. Washington, DC: Center for Global Development.
Clarke, P. 2017. ‘ Making use of assessments for creating stronger education systems and improving teaching and learning’ . Paper commissioned for the 2017/18 Global Education Monitoring Report, Accountability in education: Meeting our commitments. Paris: UNESCO.
Custer, S.; King, E. M.; Atinc, T. M.; Read, L.; Sethi, T. 2018. Towards data driven education systems: Insights into using information to measure results and manage change . Washington, DC: Center for Universal Education at Brookings/AidData.
De Chaisemartin, T.; Schwanter, U. 2017. Ensuring learning data matters . IIEP-UNESCO Learning Portal.
Mählck, L.; Ross, K. N. 1990. Planning the quality of education: The collection and use of data for informed decision-making . Paris: IIEP-UNESCO.
Postlethwaite, T. N., Kellaghan, T. 2008. National assessments of educational achievement . Paris: IIEP-UNESCO.
Raudonyte, I.2019. Use of learning assessment data in education policy-making . Paris: IIEP-UNESCO.
Ross, K. N. 1997. ‘Research and policy: a complex mix’. In: IIEP Newsletter , 15 (1), pp. 1-–4.
Saito, M. 2015. The use of learning assessments in policy and planning. IIEP-UNESCO Learning Portal.
Tobin, M.; Lietz, P.; Nugroho, D.; Vivekanandan, R.; Nyamkhuu, T. 2015. Using large-scale assessments of students’ learning to inform education policy. Insights from the Asia-Pacific region . Melbourne/ Bangkok: ACER/ UNESCO.
UNESCO; IIEP Pôle de Dakar; World Bank; UNICEF. 2014. Education sector analysis methodological guidelines. Vol. 1: Sector-wide analysis, with emphasis on primary and secondary education . Dakar: UNESCO. IIEP Pôle de Dakar.
UNESCO Office Bangkok and Regional Bureau for Education in Asia and the Pacific. 2013. The use of student assessment for policy and learning improvement . Bangkok: UNESCO Office Bangkok.
UNESCO Office Bangkok and Regional Bureau for Education in Asia and the Pacific. 2017. Analyzing and utilizing data for better learning outcomes . Paris/ Bangkok: UNESCO/ UNESCO Office Bangkok.
UNESCO Office Bangkok and Regional Bureau for Education in Asia and the Pacific. 2017. Large-scale assessment data and learning outcomes: Linking assessments to evidence-based policy making and improved learning . Bangkok: UNESCO Office Bangkok.
UNESCO-UIS. 2018. SDG 4 data digest: Data to nurture learning . Montreal: UIS.
Willms, J. D. 2018. Learning divides: Using data to inform educational policy . Information Paper No. 54. Montreal: UIS.
Related information
- The use of learning assessment data
- Quality of education
Newly Launched - World's Most Advanced AI Powered Platform to Generate Stunning Presentations that are Editable in PowerPoint

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

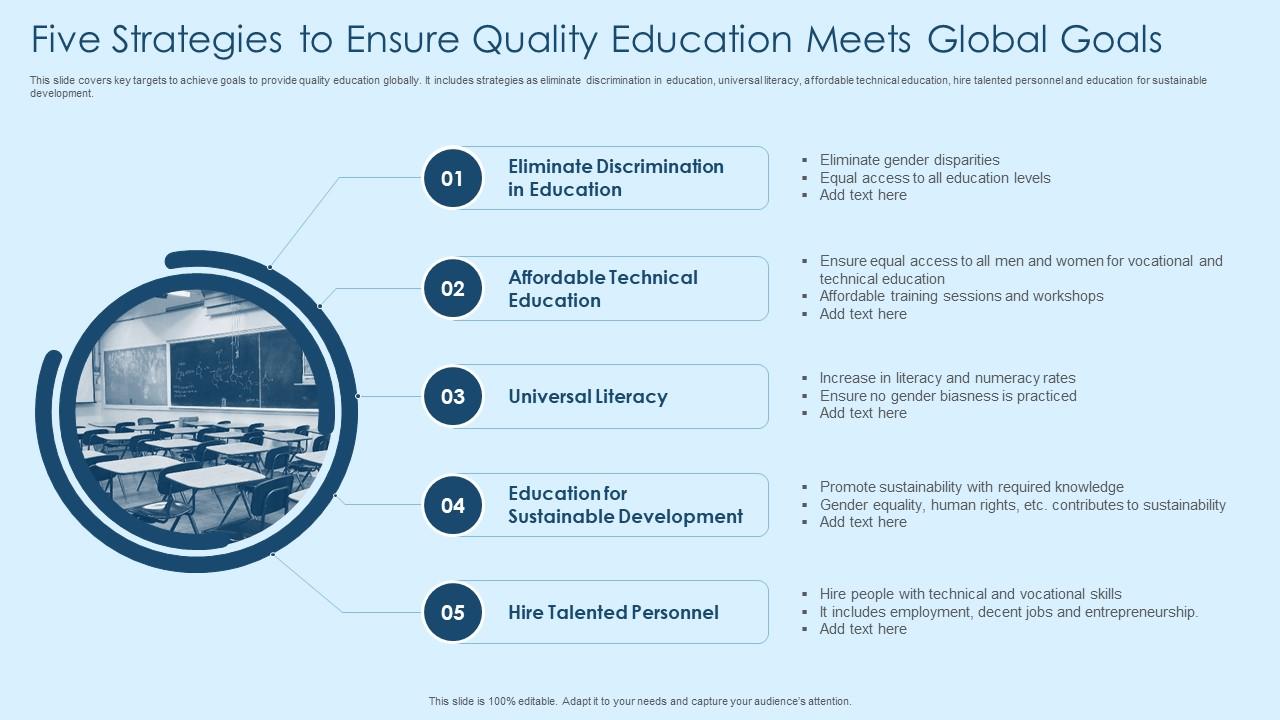
Five Strategies To Ensure Quality Education Meets Global Goals
This slide covers key targets to achieve goals to provide quality education globally. It includes strategies as eliminate discrimination in education, universal literacy, affordable technical education, hire talented personnel and education for sustainable development.
- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.

PowerPoint presentation slides
This slide covers key targets to achieve goals to provide quality education globally. It includes strategies as eliminate discrimination in education, universal literacy, affordable technical education, hire talented personnel and education for sustainable development. Presenting our set of slides with name Five Strategies To Ensure Quality Education Meets Global Goals. This exhibits information on five stages of the process. This is an easy-to-edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Universal Literacy, Hire Talented Personnel, Affordable Technical Education.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Diagrams , Business , Marketing , Planning , Icons , Business Slides , Flat Designs , Linear Process Diagrams , Process Management
- Universal Literacy ,
- Hire Talented Personnel ,
- Affordable Technical Education
Five Strategies To Ensure Quality Education Meets Global Goals with all 6 slides:
Use our Five Strategies To Ensure Quality Education Meets Global Goals to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Ratings and Reviews
by Chas Kelly
August 18, 2022
by Doyle Andrews
August 17, 2022

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

QUALITY CONCERN TO TEACHER EDUCATION

Related Papers
Dr Yashpal D Netragaonkar
"Quality Teachers for Quality Education and many events are taking place around the world to promote that ideal from the grassroots on up to the highest levels of government" — UNESCO Quality in systems improvement is an unending Journey. It needs deliberate and persistent attempt is an systematic way. Quality does not comes by chance. It is a continuous process. It comes through strategies of better Human Resource Development. It comes by comparison preferably with the best. It comes when everyone works in a right way
International Journal of Advanced Education and Research
Dr. Amitesh Kumar Singh
Quality has become the global perspective in each field of development. Quality is defined as delighting the customer by continuous meeting and improving upon agreed requirement. India is a developing country in the world and providing the mass education at elementary and higher education. Teacher education system is an important vehicle to improve the quality of education. Therefore, teacher preparation needs to give more thinking into the different roles a teacher needs to meet the new challenges in the information society. After Independent the emerging socioeconomic and political situations influenced the national scenario of Teacher Education. The Government of India setup different Committees and Commissions for addressing to the specific issues of Teacher Education. A large number of teachers were found untrained and attempt was made to clear the backlog. The main concerns of teacher education were pertaining to both quality and quantity.
Umakant Devaramani
Education is the most important and power full instrument invented by humankind to shape and mould he in a desirable manner. The history of the world proves that education has been the root cause for any change, which takes place in social, cultural, spiritual, political, and economic aspect of human life. In present, education has become one of the necessities of human life, like food, clothing, and shelter. Therefore, we can say that life is education and education is life. The Kothari Commission (1664-66) remarks, "The destiny of India is being shaped in its classrooms." No doubt, education plays a sig nificant role in nation's development but the quality of education is greatly determined by the quality of teachers. In this era of globalization and technological revolution, education is considered as a first step for every human activity. It plays a vital role in Innovations and best practices towards quality education and the development human capital and is linke...
International Research Journal Commerce arts science
The quest for quality has been the major concern of the entire human civilization. What is quality? Whenever quality in education is discussed it may be important to reflect on, what is understood by the term quality. Many educators, researchers and politicians have tried to define this term and a number of different definitions can be found in the literature. One almost classical definition is the way in which Coombs (1985) described quality in his book “The World Crises in Education: The View from the Eighties”: “Qualitative dimensions means much more than the quality of education as customarily defined and judged by student learning achievements, in terms of traditional curriculum and standards. Quality pertains to the relevance of what is taught and learned - to how well it fits the present and future needs of the particular learners. It also refers to significant changes in the educational system itself, in the cultural and political environment.” (Coombs, 1985, p. 105)
Asia-Pacific Journal of Teacher Education
Parlo Singh
Journal of Education for Teaching
Ayesha Rabadi-Raol
Wydawnictwo FRSE
Dr.SHAZLI KHAN
There is a growing concern of assuring quality at all levels of education in the present educational scenario. The quality of education we provide to our children depends on the quality of education of teacher we inject into the education system, which in turn depends on the quality of teacher education programme. Quality is not just the quantum of knowledge imparted to students but also the effectiveness with which they are able to apply that knowledge in meeting the challenges of tomorrow. Quality in teacher education programme also depends on the quality of teaching. For this there is an urgent review of curriculum of teacher education programme. The quality of pre-service and in-service education needs to be upgraded. It has been rightly said by the Education Commission (1964-66) that, “ Of all the different factors which influence the quality of education and its contribution to national development, the quality, competence and character of teachers are undoubtedly the most sig...
Rafeedali Elassery E
RELATED PAPERS
Kelechi Mezieobi
Ester Ogena
REV-2011 Conference Proceedings , pp. 273-277
Jalobeanu Mihai-Stanislav
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Eric Quainoo Jnr
International Journal of Indian Psychology
Ankit Chauhan
National Academy of Education
Suzanne Wilson
Djamaludin Ancok , Neila Ramdhani
International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Literature (IMPACT: IJRHAL)
Hari Krishnan
Irene Manning
Scholarly Research Journal
Scholarly R E S E A R C H Journals
MGES Journals
Keshav Prasad Bhattarai
Review of Economics and Development Studies
Mohammad Nabi
Dr PRATIBHA PATANKAR
Alina Roscan
Iflah sultan
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Djamaludin Ancok
RCEP Working Paper
Regional Center for Educational Planning (RCEP) - UNESCO
Research Paradigms for Sustainable Development in Education
jagannath Dange , Siddaraju Siddu
UPA National E-JOURNAL Vol.3.April 2017 ISSN 2455-4375
Dr. K J SIBI
Carol O. Ezeugbor
Dr. Carol O Ezeugbor
Rafiq Jaffer
ELT Journal
Ronald White
Sahat Maruli
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Quality Management In Education:
Oct 06, 2014
340 likes | 676 Views
Quality Management In Education:. Dr. Manish Semwal. Institutional Organizational Structure. THE Management. ____________________________________________________________________________. Principal Education ’ s Quality Assurance HR/ Teachers training/ Publishing. Bursar
Share Presentation
- quality management
- improvement actions
- related quality service
- giving quality global education

Presentation Transcript
Quality Management In Education: Dr. Manish Semwal
Institutional Organizational Structure THE Management ____________________________________________________________________________ • Principal • Education’s Quality • Assurance • HR/ Teachers training/ Publishing • Bursar • Maintenance • Food Court • Cleaning Finance Controller Security Transportation _________________________________________________ VP ss IBDPC MYPC MYPS PYPC PYPS UNC __________________________________________________. Faculties HODS
Mapping: Total Staff
Infrastructure
Quality Objectives • Maintain and improve the standards of world education, QMS and EMS • Achieve full compliance with applicable quality requirements. • Invest in specific Educational Projects to enhance quality of education. • Improve communications, trust, and relationships with stakeholders on quality management and education. • Make school as a learning community based on open standards, suggestions and improvements by stakeholders and affiliated organization for giving quality global education. • Assist local schools network with their present global educational support and responsibilities through the provision of support and sharing to meet the more complex educational needs, • Organize various educational & environmental activities, action plan and awareness program related to quality education and environmental conservation.
A Systemic Model of Education Axis of Processes Main Processes: Quality global education, Managerial Processes: strategic mng, quality mng, resource mng, performance mng, information mng, etc. Support Processes: maintenance, acquisitions, investments Axis of Needs/Requirements Knowledge Needs: competence, innovation, assistance in solving specific problems of stakeholders Axis of Services/ product Study Programs, Teaching- learning resources Counseling Contracts Axis of Furnishing Organization Human resources, infrastructure, information System and managerial mechanisms
The Methodology Legal/Official Aims: to create an adequate international and national framework meant to improve the quality of education in Indonesia and its compatibility with the International standards of performance. • Three fundamental domains of organization and functioning in GMIS are taken into consideration in insuring the quality of education: • Institutional Capacity • Educational Efficiency (projection of objectives and results, and organization of the framework of learning accomplishment ) • Quality Management centered upon those strategies, structures, techniques and operations enabling the GMIS to demonstrate that it evaluates its performances of quality insurance and improvement, and its systems of information demonstrate the results of the learning and research processes.
A Systemic Approach of Educational ProgramsPlanning – Implementation- evaluation Requirements of Competence Geographical Area Specific Domain Technology, Management, Tendencies Evaluation Study Programme Offers Human and Technical Capability Policies and Mechanisms of Leadership (Planning, Control, Improvement Requirements of Competence Evaluation Specific Requirements of Competence Capability Leadership System Specific Competences Specifications and Requirements for the Teaching and Learning Process Evaluation Specifications (Ed. Plans, Analytical Programms), and Requirements Leadership System Specific Competences Evaluation
Development Plan and strategies • Process improvement actions • Quality Management system and improvement actions • Service improvement actions with QMS Compliances • Communication focus • Record maintenance
Process applied to enhance quality • Target Mapping. • Awareness and involvements. • Data collection and trend analysis • Audits for improvements • Communication Activities • Review Performance of Staff • Corrective action plan
Category of Output quality Review A = Category of Related Quality management System : - Adequacy of Work Instruction & Procedure. - Implementation of Work Instruction & Procedure. B = Category of Related Quality service to stakeholders:- - Dimension. - Appearance. - Electrical characteristic/function. C = Category of Related to Resource . - Employee needed. - Employee competence - Support facilities. - Financial Needed.
Achievement Criteria of Output 1 = Poor If Achievement 0 % ~ 69% 2 = Fair If Achievement 70% ~ 89% 3 = Satisfy If Achievement 90% ~ 100%
Aspect Evaluation Total Output (Achievement) :A = Related of Quality Management System Achievement : 2.8 (Satisfy)B = Related of Quality services to Customer Requirement Achievement : 2.3 (Fair) C = Related of Resources Achievement : 2.2 (Fair)Conclusion : School get Grade Satisfy for Related Management System, and Fair for Related to Services & Related to Resources.
Example of Recommendation and suggestions
1. Audit Result X = Dominant factor of problem in each input. - = No problem in each input,
2. Customer Feedback
3. Process Performance and Service Conformity(Quality Objective/Target) Provide good quality service which meet with stakeholders specification and requirements and obtained legislation
4. Corrective & Preventive Action Status. None is identified in internal audit
5. Follow up Last Management Review
6. Internal & External Change in scope of QMS
Complaint Mapping and Improvement Example: July 10 2013
Complaint Areas
Overall Review Performance of faculty and staff (1-3) Example: End of Term- May 2013
Overall Performance Rating of Teachers and Staff
Enriching school QualityExample: First term 2013
Recent Achievements
- More by User

Quality Systems and Risk Management (Q9 & Q10)
Quality Systems and Risk Management (Q9 & Q10) Advisory Committee of the Office of Pharmaceutical Science, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, USFDA October 5, 2006 Frederick Razzaghi CHPA Agenda Introduction Quality Risk Management Q9 Relation of Q9 to Q10 The guidance Next step
1.72k views • 41 slides

Data Quality Management Control Program
Data Quality Management Control Program. Chief, Data Quality Section, PASBA May 2009 . Overview. Regulatory Guidance Program Management Organizational Factors System Inputs, Processes, and Outputs CHCS ADM MEPRS/EAS TPOCS MEWACS.
1.15k views • 71 slides

The Importance of Education Quality
The Importance of Education Quality. Ariel Fiszbein Chief Economist, Human Development Network World Bank Brussels, June 24, 2008. 1. Education quality is about children learning. It’s about children learning.
1.36k views • 29 slides

STOCK MANAGEMENT
STOCK MANAGEMENT. W. Frank Dell II, CMC September, 2003. AGENDA. INTRODUCTION DEPARTMENT / CATEGORY / ITEM REPLENISHMENT PROMOTING. Objectives. Introduce stock organization and management Present the science of buying Identify promotion management. Retail Strategy. Product Quality.
1.1k views • 64 slides

Chapter 8 Quality Management
Chapter 8 Quality Management. Total Quality Management Defined Quality Specifications and Costs Six Sigma Quality and Tools External Benchmarking ISO 9000 Service Quality Measurement. OBJECTIVES . Total Quality Management (TQM).
1.02k views • 44 slides

TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT: TQM Origins, Evolution & key elements
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT: TQM Origins, Evolution & key elements. What is Quality?. Quality is “fitness for use” (Joseph Juran) Quality is “conformance to requirements” (Philip B. Crosby)
1.7k views • 36 slides

Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition
Chapter 8: Project Quality Management. Information Technology Project Management, Fourth Edition. Learning Objectives. Understand the importance of project quality management for information technology products and services.
1.66k views • 96 slides

Introduction- Laboratory Quality Management System
Introduction- Laboratory Quality Management System. At the end of this activity, participants will be able to: Explain the importance of a quality management system List the quality system essential elements Describe the history of development of quality principles
8.88k views • 41 slides

Managing Quality
Managing Quality. 6. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10e Principles of Operations Management, 8e PowerPoint slides by Jeff Heyl. Quality and Strategy.
1.07k views • 65 slides

Chapter 9. TQM & Quality Tools. Quality and Total Quality Management. Quality is the ability of a product or service to consistently meet or exceed customer expectations.
1.34k views • 74 slides

Managing Quality. 6. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10e Principles of Operations Management, 8e PowerPoint slides by Jeff Heyl. Outline. Defining Quality Implications of Quality Ethics and Quality Management Total Quality Management
1.33k views • 56 slides

INNOVATIVE QUALITY TQM – LEAN MANAGEMENT – SIX SIGMA Day 1 Developed by Olga Trofymova, PhD
INNOVATIVE QUALITY TQM – LEAN MANAGEMENT – SIX SIGMA Day 1 Developed by Olga Trofymova, PhD. Olga Trofymova. Director of the Quality Centre, Kharkov, Ukraine. Trainer and consultant for SME with 10-years experience. Associated professor at National Aerospace University.
911 views • 76 slides

Quality assurance and Quality control in medical radiography
Quality assurance and Quality control in medical radiography. Topic 2. Departmental standards for radiographic image quality QA/QC group establishment Quality Management. Objectives. Diagnostic procedure chain.
7.59k views • 37 slides

“People, Process and Technology…” Data Quality Management Control Program
COMPOSITE HEALTH CARE SYSTEM. “People, Process and Technology…” Data Quality Management Control Program TRICARE Data Quality Course January 2012. Agenda. Part 1 – CHCS – Essential Elements… Information Resources Data Quality Building Blocks CHCS Support for Data Quality
932 views • 67 slides

STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT
STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT. Quality. Fitness for use, acceptable standard Based on needs, expectations and customer requests. Types of Quality. Quality of design Quality of conformance Quality of performance. Quality of Design.
3.18k views • 84 slides

Quality management
Slovak University of Technology Faculty of Material Science and Technology in Trnava. Quality management. Definition of Quality. What is the quality ? Quality is conformance to requirements Other definitions: Quality is fitness for use Quality is meeting customer expectations.
3.23k views • 205 slides

Quality and Quality Management
Quality and Quality Management. Report in Production Management. Maria Ella T. Betos Katherine J. Erfe. Discussion Proper:. Quality, Quality Management and Quality Tools Total Quality Management and Quality Management System (TQM and QMS) Focus of Quality Management – Customers
1.66k views • 36 slides

Personal Financial Management Seminar
Personal Financial Management Seminar. Office of Frank M. Pees Standing Chapter 13 Trustee. Debtor Education. Personal Financial Management. Meets post-filing financial education requirement. Must show ID and sign-in and sign-out to receive certificate.
1.15k views • 77 slides

Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management. Chapter 16. What is Quality?. Quality means user satisfaction: that goods or services satisfy the needs and expectations of the user. Quality and Product Policy. Established by management Product planning wants and needs of the marketplace
1.5k views • 101 slides

Total Quality Management and Cost of Quality
Total Quality Management and Cost of Quality. Evsevios Hadjicostas. The International Quality movement. Operator Quality Control Foreman Quality Control Full-time Inspectors Statistical Quality Control Total Quality Control Total Quality Management. Total Quality Management.
1.95k views • 67 slides

Environmental Engineering Management (EEM 690)
Lecture 5. - Water Quality and IWRM - Soil and groundwater pollution and control. Environmental Engineering Management (EEM 690). FAISAL ANWAR. Water Quality Management: Rules and Regulations. Drinking Water: Australian Drinking Water Quality Guideline or WHO guideline
1.32k views • 85 slides

Quality Management “ It costs a lot to produce a bad product. ” Norman Augustine
Quality Management “ It costs a lot to produce a bad product. ” Norman Augustine. Cost of quality. Prevention costs Appraisal costs Internal failure costs External failure costs Opportunity costs. What is quality management all about?.
1.02k views • 62 slides
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- My Wish List
- Compare Products
- Presentations
Quality Education
You must be logged in to download this file*
item details (7 Editable Slides)
(7 Editable Slides)
Related Products
Get your hands on our high-quality Quality Education PowerPoint template to describe the type of education that aims to improve the social, logical, physical, and overall development of students. These engaging graphics will give your slideshow an extra boost of creativity and style.
Educators, psychologists, and online tutors can utilize these impressive PowerPoint slides to communicate the goals, purpose, and factors of quality education. You can also highlight the approaches that help improve the quality of education to enhance the social and literacy skills of students.
Sizing Charts
| Size | XS | S | S | M | M | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | 32 | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 |
| UK | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| US | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Bust | 79.5cm / 31" | 82cm / 32" | 84.5cm / 33" | 89.5cm / 35" | 94.5cm / 37" | 99.5cm / 39" |
| Waist | 61.5cm / 24" | 64cm / 25" | 66.5cm / 26" | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" |
| Hip | 86.5cm / 34" | 89cm / 35" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" |
| Size | XS | S | M | L | XL | XXL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK/US | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 44 |
| Neck | 37cm / 14.5" | 38cm /15" | 39.5cm / 15.5" | 41cm / 16" | 42cm / 16.5" | 43cm / 17" |
| Chest | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" | 111.5cm / 44" |
| Waist | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" |
| Seat | 90cm / 35.4" | 95cm / 37.4" | 100cm / 39.4" | 105cm / 41.3" | 110cm / 43.3" | 115cm / 45.3" |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
He defined it as education that supports individual learning needs, is locally relevant, and prepares students for the future. It involves teaching methods like interactive lectures, group projects, and role-playing to develop skills like critical thinking. Quality education also emphasizes reflective teaching where teachers evaluate their own ...
These slides are about Quality Education, this presentation will help you to find the factors, dimensions and approaches of quality education, and will make you aware of issues and problems which are affecting the quality of education. 1 of 47. Download now. Quality Education - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Jun 24, 2015 • Download as PPT, PDF •. Engage with the ongoing quality assessment debate at national level, building on an understanding of core principles in quality management and with due reference to the interests of those with a stake in HE quality. Gwen?
S. Sanaullah Madni. (1) The document discusses key elements of quality education, including the teacher and teaching methods, educational content, learning environment, school management and policies, parent involvement, and standards assessment. (2) It defines quality as the standard or degree of excellence of something and notes that ...
It begins by defining quality in the context of education and tracing the origins and evolution of the concept of quality from industry to education. It then identifies and describes major internal and external factors that can affect quality, including teaching/learning environments, teachers/learners, community/parents, and curriculum.
Quality of education. Jul 2, 2016 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 0 likes • 271 views. AI-enhanced description. R. Rachana Gaddale. This document discusses issues with the Indian education system and competitive exams. It argues that the current system focuses too much on rote learning and testing knowledge, rather than teaching skills.
Quality is the distinguishing characteristic guiding students and higher education institutions when receiving and providing higher education. 4. Definitions in Quality Assurance QUALITY Fitness for purpose' - Juran Conformance to requirements' - Crosby An educational definition is that of an ongoing process ensuring the delivery of ...
Challenges discussed include technology issues, student and faculty abilities, and retaining students online. Benefits include flexibility, convenience, and developing technology skills. Student feedback provides mixed views, with some praising flexibility while others prefer face-to-face interaction. In conclusion, the author believes online ...
This is the presentation used in a Conversation Club class about "Quality Education", the lesson plan that complete it can also be found in this profile. Slideshow view. Download now. Download to read offline. Quality education presentation - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
There is an increasing awareness too of the importance of quality education at the pre-primary level, and this is leading Wellspring to engage more intentionally and strategically in early childhood education. The challenge is that access to, and enrolment in, pre-primary education remains low in Rwanda. The Rwandan government is proactively ...
TQM in Education Crosby's model • Focus on the quality of the teaching system you use to educate them. • Consider every component of the system and find the causes for examination failures and eliminate them at source. • The system will then produce students who pass their examinations automatically.
Presentation Transcript. Quality in Education Shelley O'Grady, M.S. Assistant Professor Biotechnology Department, Austin Community College [email protected]. Acknowledgements • This work was sponsored by South-Central Region of Bio-link • Developing a quality system is a *team* effort Contributors: • Bio-link • Linnea Fletcher ...
Data-driven decisions to improve learning are taken at each level of the system. The specificity of the data decreases from school to national level and the time lag between data collection and application increases. Decisions concerning individual students, classes, and schools are made locally, where raw data are produced.
Enhancing Access and Quality in Tertiary Education: New Challenges and Opportunities Washington DC, 2 February 2006. the future of tertiary education?. are tertiary education systems ready?. outline of the presentation. changing education & training needs. 837 views • 71 slides.
Features of these PowerPoint presentation slides: This slide covers key targets to achieve goals to provide quality education globally. It includes strategies as eliminate discrimination in education, universal literacy, affordable technical education, hire talented personnel and education for sustainable development.
Presentation Transcript. Quality Education Collected and presented by ELT. Supervisor Mr. Ashraf Adli. Introduction In all aspects of the school and its surrounding education community, the rights of the whole child, and all children, to survival, protection, development and participation are at the centre.
This study assesses the development and practice of QA in institutions of higher learnings (IHLs) in Ghana. The mixed research method was used to collect data from staff and officers of institutions of higher learning who are directly involved ensuring quality in the institutions. Six (6) IHLs participated in this study.
• Education on quality, where quality is a topic in edu-cation services. This involves studying, promoting, and evaluating different approaches for teach-ing, training, and learning quality principles, approaches, and tools. • Quality of education, where quality and quality improvement methods are applied to education sys-
India is a developing country in the world and providing the mass education at elementary and higher education. Teacher education system is an important vehicle to improve the quality of education. Therefore, teacher preparation needs to give more thinking into the different roles a teacher needs to meet the new challenges in the information ...
The Role of Technology in Education: Benefits, Challenges, and Impact on Students In today's rapidly evolving world, technology has become a crucial aspect of education, shaping the way students learn and preparing them for future careers. Importance of Technology in Education: Technology is not just a crisis-management tool; it is a powerful educational asset.
Focusing on quality education for enhanced social inclusion implies identifying strategies for overcoming or eliminating the barriers to full participation in quality education for individuals and groups which experience discrimination, marginalisation and exclusion or which are particularly vulnerable. 3 Castel, R. (1991) « De l'indigence ...
Quality Objectives • Maintain and improve the standards of world education, QMS and EMS • Achieve full compliance with applicable quality requirements. • Invest in specific Educational Projects to enhance quality of education. • Improve communications, trust, and relationships with stakeholders on quality management and education.
Educators, psychologists, and online tutors can utilize these impressive PowerPoint slides to communicate the goals, purpose, and factors of quality education. You can also highlight the approaches that help improve the quality of education to enhance the social and literacy skills of students.