Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction, case study:1.
If less is the refractive index then less will be the bending or medium is rarer and velocity of light will be more in that medium. Like the refractive index of air is found to be 1.0003 and that of water is found to be 1.33. And hence water is more denser than air, air is rarer medium as compared to water. Thus, velocity of light in air medium is greater than velocity of light in water medium.
Absolute Refractive index= (speed of light in air)/(speed of light in medium) = c/v

Case study: 2
1/v + 1/u = 1/f
Similarly in case of lenses, lens formula is given by
Thus, P = 1/f
4) If the magnification produced is negative then the image formed is real. And if the magnification produced is positive then the image formed is virtual.
Case study:3
3) Concave mirror is called as converging mirror while convex mirror is called as diverging mirror.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, ncert class 7 mathematics fifth chapter lines and angles exercise 5.1, 5.2 solutions, andhra pradesh scert class 7 biology chapter 1 solutions, assam scert class 8 history and political science chapter 2 solutions, the ghost brahman class 11 long questions for semester 2.
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 1st Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 2nd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 3rd Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 4th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 5th Standard - CVBHSS Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject light reflection and refraction case study questions with solution 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
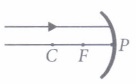
The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror. Inner part works as a concave mirror and the outer bulging part acts as a convex mirror. The center of the reflecting surface of a mirror is called pole and the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is formed is called radius of curvature. (i) When a concave mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the name given to the distance between the mirror and carbon paper?
(ii) The distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between
(iii) The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. The radius of curvature is
(iv) The normal at any point on the mirror passes through
(v) In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor's head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object. (i) When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror. (v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
The relation between distance of an object from the mirror (u), distance of image from the mirror (v) and the focal length (F) is called mirror formula. This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object. The size of image formed by a spherical mirror depends on the position of the object from the mirror. The image formed by a spherical mirror can be bigger than the object, equal to the object or smaller than the object. The size of the image relative to the object is given by the linear magnification (m). Thus, the magnification is given by the ratio of height of image to the height of object. If magnification is negative, image is real and if it is positive, image is virtual. (i) What is the position of an image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 em from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
(iii) If the magnification of an image is -2, the characteristic of image will be
(iv) The mirror formula holds for
(v) A parallel beam of light is made to fall on a concave mirror. An image is formed at a distance of7.5 from the mirror. The focal length of the mirror is
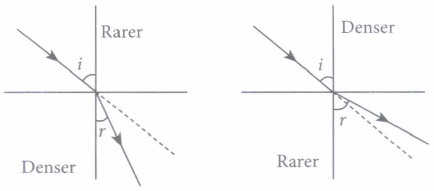
(ii) A ray of light passes from a medium A to another medium B. No bending of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium B at an angle of
(iii) When light passes from one medium to another, the frequency of light
(iv) When light passes from glass to water, the speed of light
(v) The bottom of pool filled with water appears to be ______ due to refraction of light
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject light reflection and refraction case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
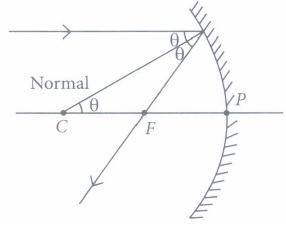
(i) (d) : When an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the..image is formed at infinity. (ii) (d) : When a light ray parallel to the principal axis is incident on a concave mirror, it passes through the principal focus after reflection. Therefore, figure D is correct. (iii) (a) : If m is negative, the image will be real and inverted. (iv) (d) (v) (b): The distance of object from mirror = \(\infty\) Using, \(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\) \(\frac{1}{\infty}-\left(-\frac{1}{7.5}\right)=\frac{1}{f}\) f = 7.5 cm
(i) (a): When, a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends towards the normal. (ii) (c): No bending of light occurs when light is incident normally or perpendicularly on a boundary of two media since angle of incidence and angle of refraction both are zero. (iii) (c): When light goes from one medium to other medium, its frequency does not change (iv) (a): The speed to light increases when light passes from glass to water as water is optically rarer medium. (v) (a): The bottom of a pool of water appears to be less deep than it actually is due to refraction.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Please refer to Chapter 1 Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Light Reflection and Refraction
Case/Passage – 1 A 5.0 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm.
Question: What is the power of the used lens? (a) + 5 D (b) – 5 D (c) + 0.5 D (d) – 0.5 D
Question: What is the distance of image from the pole of lens? (a) v = 60 cm (b) v = – 60 cm (c) v = 30 cm (d) v = –30 cm
Case/Passage – 2
Light travels through a vacuum at a speed c = 3 × 108 m/s. It can also travel through many materials, such as air, water and glass. Atoms in the material absorb, reemit and scatter the light, however. Therefore, light travels through the material at a speed that is less than c, the actual speed depending on the nature of the material. To describe the extent to which the speed of light in a material medium differs from that in a vacuum, we use a parameter called the index of refraction (or refractive index).
Question: Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to
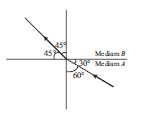
medium B. Retractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is (a) √3/2 (b)√2/3 (c)√1/2 (d) √2
Question:The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students shown as A, B, C and D in the figure. Which one of them is correct?

(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Question: A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown
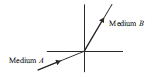
in the figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be (a) greater than unity (b) less than unity (c) equal to unity (d) zero
Question: You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most? (a) Kerosene (b) Water (c) Mustard oil (d) Glycerine
Question: A ray of light is incident in medium 1 on a surface that separates medium 1 from medium 2. Let v1 and v2 represent the velocity of light in medium 1 and medium 2 respectively. Also let n12 and n21 represent the refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 and refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1, respectively. If i and r denote the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, then- (a) sin i/sin r = n 21 V 1 /V 2 (b) sin i/sin r = n 21 V 2 /V 1 (c) sin i/sin r = n 12 V 1 /V 2 (d) sin i/sin r = n 12 V 2 /V 1
Case/Passage – 3 Inside a substance such as glass or water, light travels more slowly than it does in a vacuum. If c denotes the speed of light in a vacuum and v denotes its speed through some other substance, then v = c/n where n is a constant called the index of refraction. To good approximation, a substance’s index of refraction does not depend on the wavelength of light. For instance, when red and blue light waves enter water, they both slow down by about the same amount. More precise measurements, however, reveal that n varies with wavelength. Table presents some indices of refraction of Custon glass, for different wavelengths of visible light. A nanometer (nm) is 10– 9 meters. In a vacuum, light travels as c = 3.0 × 10 8 m/s

Question: Inside Custon glass (a) Orange light travels faster than yellow light (b) Yellow light travels faster than orange light (c) Orange and Yellow light travels equally fast (d) We cannot determine which color of light travels faster
Question: Which of the following phenomena happens because n varies with wavelength (a) A lens focuses light (b) A prism breaks sunlight into different colors (c) Total internal reflections ensures that light travels down a fiber optic cable (d) Light rays entering a pond change direction at the pond’s surface
Question: For blue-green of wavelength 520 nm, the index of refraction of Custon glass is probably closest to (a) 1.49 (b) 1.50 (c) 1.51 (d) 1.52

Related Posts

CBSE Class 10 English Nelson Mandela Long Walk to Freedom Summary

Democracy and Diversity Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

CBSE Class 10 English Bholi Summary

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Light Reflection and Refraction.
Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Light Reflection and Refraction with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Light Reflection and Refraction. Here are the features of case based questions on Light Reflection and Refraction are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Light Reflection and Refraction
How to Download Light Reflection and Refraction Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on-screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as a doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose, etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified images of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it can form a small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
| (a) larger than the object | (b) smaller than the object |
| (c) same size as that of the object | (d) highly enlarged. |
Answer: (c) same size as that of the object
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
| (a) plane | (b) concave |
| (c) convex | (d) either plane or convex. |
Answer: (d): The image is erect in a plane mirror and also in a convex mirror, for all positions of the object.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
| (a) Plane, convex and concave | (b) Convex, concave and plane |
| (c) Concave, plane and convex | (d) Convex, plane and concave |
Answer: (c) : As the image of head is bigger, the upper portion of magic mirror is concave. The middle portion of the image is of same size, so, middle portion of magic mirror is plane. Now, the image of legs looks smaller, therefore, the lower portion of magic mirror is convex.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
Answer: (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 2:
The lenses form different types of images when objects are placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical center of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and the optical center of the convex lens, an erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also, the size of the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect, and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
Answer: (a) at focus
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
Answer: (b) virtual and inverted
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
Answer: (c) highly magnified
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
Answer: (b) at 2 F on the other side
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Answer: (a) anywhere between centre and infinity
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams .
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on-screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as a doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose, etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified images of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it can form a small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
| (a) larger than the object | (b) smaller than the object |
| (c) same size as that of the object | (d) highly enlarged. |
Answer: (c) same size as that of the object
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
| (a) plane | (b) concave |
| (c) convex | (d) either plane or convex. |
Answer: (d): The image is erect in a plane mirror and also in a convex mirror, for all positions of the object.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
| (a) Plane, convex and concave | (b) Convex, concave and plane |
| (c) Concave, plane and convex | (d) Convex, plane and concave |
Answer: (c) : As the image of head is bigger, the upper portion of magic mirror is concave. The middle portion of the image is of same size, so, middle portion of magic mirror is plane. Now, the image of legs looks smaller, therefore, the lower portion of magic mirror is convex.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
Answer: (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 2:
The lenses form different types of images when objects are placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical center of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and the optical center of the convex lens, an erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also, the size of the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect, and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
Answer: (a) at focus
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
Answer: (b) virtual and inverted
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
Answer: (c) highly magnified
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
Answer: (b) at 2 F on the other side
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Answer: (a) anywhere between centre and infinity
Case Study 3: Light reflection and refraction are fundamental phenomena that occur when light interacts with surfaces and passes through different mediums. Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface. The laws of reflection state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane. Refraction, on the other hand, is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another with a different optical density. The bending of light is governed by Snell’s law, which states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of media. The concepts of reflection and refraction help us understand various optical phenomena, such as the formation of images by mirrors and lenses, the dispersion of light, and the phenomenon of total internal reflection.
What is reflection? a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface c) The formation of images by mirrors and lenses d) The dispersion of light Answer: b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface
What do the laws of reflection state? a) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection b) The incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane c) The angle of incidence, angle of reflection, and normal form a right triangle d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
What is refraction? a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface c) The formation of images by mirrors and lenses d) The dispersion of light Answer: a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another
What law governs the bending of light during refraction? a) Law of reflection b) Snell’s law c) Newton’s law d) Coulomb’s law Answer: b) Snell’s law
What optical phenomena can be explained using the concepts of reflection and refraction? a) Formation of images by mirrors and lenses b) Dispersion of light c) Total internal reflection d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

Class 10 Social Science Topper’s Answer Sheet Latest PDF Download FREE
Extra questions of class 10 social studies history chapter 1 the rise of nationalism in europe pdf download.

CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 – Constructions MCQ Quiz
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
James Dyson Award
Sanskriti university, srm university.
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- Short Videos
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023
Cbse class 10 physics chapter 10 important questions and answers : get the important questions with answers for cbse class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction. use these along with other cbse resources to score good marks..

CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 10 Important Questions and Answers: In this article we are going to cover the Multiple Choice Questions, Very Short Answer Questions, Short Answer Questions, Case Study Questions, Long Answer Questions and even Assertion Reason questions that are important for CBSE Class 10 Science Board Examination 2023. These questions are from the tenth chapter of the third unit of the syllabus - Natural Phenomena.
The answers to the questions are also available. Scroll down to the end of the questions to check your answers.
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Multiple choice questions.
Q.1. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that the size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Q.2. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror islikely to be
(a) Plane
(b) Concave
(c) Convex
(d) Either plane or convex
Q.3. You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
(a) Kerosene
(b) Water
(c) Mustard oil
(d) Glycerine
Q.4. As light travels from a rarer to a denser medium it will have
(a) Increased velocity
(b) Decreased velocity
(c) Decreased wavelength
(d) both (b) and (c)
Q.5. How will the image formed by a convex lens be affected if the upper half of the lens is wrapped with a black paper?
(a) The size of the image is reduced to one-half.
(b) The upper half of the image will be absent.
(c) The brightness of the image is reduced.
(d) There will be no effect
Q.6. The velocity of light is maximum in a medium of
(a) glass
(b) water
(c) vacuum
(d) diamond
Q.7. A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using:
(a) a concave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as plane mirror
8. A student conducts an activity using a flask of height 15 cm and a concave mirror. He finds that the image formed is 45 cm in height. What is the magnification of the image?
(a) 45 times
(b) 1/ 45 times
(c) 1/ 3 times
(d) 3 times
Q.9. A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Q.10.. A student conducts an experiment using a convex lens of focal length 20 cm and an object of height 15 cm. He placed the object at 25 cm from the lens. Can the image be formed on a screen?
(a) yes, because a real image will be formed
(b) no, because a virtual image will be formed
(c) yes, because an erect image will be formed
ASSERTION AND REASON
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a
statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Q.1. Assertion: A ray incident along normal to the mirror retraces its path.
Reason: In reflection, angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
2. Assertion: A convex lens is made of two different materials. A point object is placed on the principal axis. The number of images formed by the lens will be two.
Reason :The image formed by convex lens is always virtual.
Q.3. Assertion: When a concave mirror is held in water, its focal length will decrease.
Reason: The focal length of a concave mirror depends on the density the medium in Which it is placed.
Q.4. Assertion: Full length image of a distant object, such as a tall building, can be seen in a convex mirror.
Reason: A convex mirror has a greater focal length than a concave mirror of the same aperture.
Q.5. Assertion: Higher is the refractive index of the medium, lesser is the velocity of light in that medium.
Case Study Based Questions
Q.1. Light is a form of energy which induces sensation of vision to our eyes. It becomes visible when it bounces off on surfaces and hits our eyes. The phenomenon of bouncing back of light rays in the same medium on striking a smooth surface is called reflection of light. If parallel beam of incident rays remains parallel even after reflection and goes only in one direction is known as regular reflection. It takes place mostly in plane mirrors or highly polished metal surfaces. The mirror outside the driver side of a vehicle is usually a spherical mirror and printed on such a mirror is usually the warning "vehicles in this mirror are closer than they appear."
a) Plane mirror
(b) Concave mirror
(c) Convex mirror
(d) Magic mirror
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror can be
(b) Concave
(c) convex
(iv) If an object is placed at 10 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, then find the position of image.
(a) 4 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 12.5 cm
(v) The focal length of mirror is 12 cm. The radius of curvature is
(a) 12 cm
(c) 20 cm
Q.2. We know that lenses form different types of images when objects are kept at varying positions. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the objectis placed between the focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed. As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the sizeof the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted. A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
i. The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(b) at 2F
(c) at optical center
(d) betweenFand 2F
ii. When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
(d) real and erect
iii. The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
(c) small
(d) same as that of object
iv. When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(a) at F
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
Q.3. The refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum is called the absolute refractive index of the medium. It is given by, μ = sin i/sinr
i) How is absolute refractive index related to speed of light?
(a)μ = C/vm
(c)μ=Vm
(ii) In which of the materials given in the above table, light travels fastest?
(a) A
(c) C
(iii) The speed of light in air is 3x108 ms-1 and that in medium A is 2.5 x 10 ms-1. The refractive index of A will be
(a) 1.2
(c)4.5
(iv) When light travels from air to glass,
(a) angle of incidence > angle of refraction
(b) angle of incidence < angle of refraction
(c) angle of incidence = angle of refraction
(d) Can't say
(v) The refractive index of P with respect to Qis 2. Find the refractive index of Q with respect to P.
(a) 0.5
(c) 2
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (2 marks)
Q.1. If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
Q.2. State the two laws of reflection of light.
Q.3. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Q.4. A fish under water is viewing obliquely a fisherman standing on the bank of lake.Does the man look taller or shorter?
Q.5. Which phenomenon occurs when light falls on
(a) highly polished surface
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (3 MARKS)
Q.1. A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Q.2. (a) Water has refractive index 1.33 and alcohol has refractive index 1.36. Which of the two medium is optically denser? Give reason for your answer.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light passing obliquely from water to alcohol.
(c) State the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction in the above case.
Q.3. Three mirrors, one plane, one concave and one convex are lying on the table. identify them without touching them or using any other apparatus or device?
Q.4. A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in closed contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of the combination.
Q.5. An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius ofcurvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror
Q.6. A convex lens of focal length 2.0 m can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (4 MARKS)
Q.1. (i) A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
(ii) A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Q.2. (a) A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image formed.
Answers to Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Unit III: Natural Phenomena
Answer- (b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer- (d) Either plane or convex
Answer- (d) Glycerine
Answer- (b) Decreased velocity
Answer- (c) The brightness of the image is reduced.
Answer- (c) vacuum
Answer- (b) a convex mirror
Answer- (d) 3 times
Answer- (d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
(d)No because the image is
Answer- (a)
Answer- (c)
Answer- (d)
Reason: Refractive index of a medium is inversely proportional to the velocity of light.
Case Study Based Questions:
(i) Which type of mirror is used outside the driver's side of a vehicle?
(iii) If an object is placed at 10 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, then find the position of image.
(iv) The focal length of the mirror is 12 cm. The radius of curvature is
Q.2. We know that lenses form different types of images when objects are kept at varying positions. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed. As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the sizeof the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted. A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
i The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(d) between Fand 2F
ii When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
iii The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is
iv When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(a)at F
Answer- If the image formed by a spherical mirror is always erect and diminished then it is convex mirror.
Laws of reflection of light states that
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Q.3. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a
medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Answer- (a) Laws of refraction of light:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media.
This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
sini/sinr = constant,
where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
This constant value is called refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first when the light travels from first medium to second medium.
⇒ constant = n21 = v1/v2 ∴sini/sinr = v1/v2
If n is the absolute refractive index of the medium, c is the velocity of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in a given medium, then n = c/v.
Ans. As light travels from rarer to denser medium, it bends towards normal and appears to come from greater height. Therefore, to fish under water, man looks taller.
(b) a transparent medium?
Ans. (a) Reflection of light.
Answer- Given f = -20 cm v = -30 cm, u = ?
Using 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
1/u = 1/f – 1/v = 1/(−20) – /(−30) = (−3+2)/60
⇒ u = -60 cm
∴ Object placed at 60 cm from the mirror.
Also magnification, m = h′/h = −v/u
⇒ h’ = −(−30)/−60 × 4 = -2 cm
∴ The size of the image is 2 cm.
Answer- (a) Here, alcohol is optically denser medium as its refractive index is higher than that of water. When we compare the two media, the one with larger refractive index is called the optically denser medium than the other as the speed of light is lower in this medium.
(b) Since light is travelling from water (rarer medium) to alcohol (denser medium), it slows down and bends towards the normal.
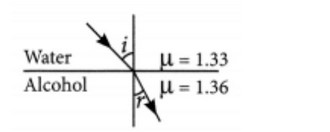
where i = angle of incidence and r = angle of refraction.
(c) According to Snell’s law,
sini/sinr=μalcohol /μwater =1.36/1.33 = 1.0225
∴ sin i = 1.0225 × sin r
Ans. Plane mirror produces the image of same size. Concave mirror produced the magnified image while the convex mirror will produce a diminished image
f1=25cm=0.25 m
f2= -10cm= - 0.1m
Power of convex lens, P1 = 1/f1=1/0.25=+4D
Power of concave lens, P2 = 1/f2=1/ - 0.1m=-10D
power of combination, P = P1 +P2 = 4D – 10D = -6D
Ans: Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror.Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are:
(i) Virtual
(iii) Enlarged
(iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Ans: Yes, it is correct. If the object is placed within 2.0 m from the lens in the it forms magnified virtuaL image Between 2 m and 4 m it will form a real inverted and magnified image.
Q.7. “The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -3”. List all information youobtain from this statement about the mirror/ image.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS

(b) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing object distance, image distance and focal length in the above case.
Answer- (a) Given, h = 5 cm, f = 20 cm, u = -30 cm
Using lens formula, 1/v – 1/u = 1/f
1/v=1/u+1/f=1/(−30)+1/20=(−2+3)/60=1/60
⇒ v = 60 cm
Now, magnification, m = h′/h = v/u
⇒ h’ = v/u × h = 60/(−30) × 5 = -10 cm
Hence, the image formed at 60 cm, which is real and magnified.
|
|
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- SSC CGL 2024 Notification
- UPSC Question Paper 2024
- UPSC Exam Analysis 2024
- Manabadi AP TET Results 2024
- UPSC Prelims Cut Off 2024
- Bihar BEd Admit Card 2024
- Rajasthan BSTC Admit Card 2024
- APSC SO Result 2024
- APSC SO Admit Card 2024
- UPSC CSE Admit Card 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
Latest Education News
UP Cabinet's Decision: Tata Sons to Build ₹650 Crore 'Museum of Temples' in Ayodhya
China's Chang'e-6 Makes History with Moon's Far Side Samples; What Did They Discover?
AKTU Result 2024 OUT at aktu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Semester UG Marksheet PDF
Parliament to Witness India's First Lok Sabha Speaker Elections; Know Every Angle on Matter
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Can You Spot The Whale Among Elephants In 8 Seconds?
Personality Test: Your Standing Position Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
Only eagle eyes can spot 0 among O’s in 5 seconds!
SAMS Odisha Merit List 2024 OUT: Download SAMS Odisha +3 Selection List PDF at samsodisha.gov.in
Find the Animal Weights: A Fun Brain Teaser That'll Test Your Logic in 25 Seconds
UP BEd Result 2024 OUT: यूपी बीएड जेईई रिजल्ट bujhansi.ac.in पर जारी, अलीगढ़ के मनोज ने किया टॉप, ये रहा Direct Link
MJPRU Result 2024 OUT at mjpruiums.in; Download UG and PG ODD Semester Marksheet
Only the sharpest pair of eyes can spot the cherry in the forest in 6 seconds!
UKPSC Cut Off 2024: Check Category-Wise Previous Year Cutoff Marks
DRDO Recruitment 2024: डीआरडीओ में विभिन्न पदों पर निकली भर्ती, जानें डिटेल्स
Durg University Result 2024 OUT at durguniversity.ac.in: Direct Link to Download UG, PG Marksheet
T20 World Cup 2024 Semi Final Schedule: भारत बनाम इंग्लैंड, दक्षिण अफ्रीका बनाम अफगानिस्तान, किसे मिलेगा फाइनल का टिकट
ANU Result 2024 OUT at nagarjunauniversity.co.in: Direct Link to Download UG, PG Marksheet
Only genius eyes can find 3 differences between the coffee table pictures in 8 seconds!
RSMSSB Junior Accountant Result 2024: आज जारी हो सकता है जूनियर अकाउंटेंट परीक्षा का परिणाम
PRSU Result 2024 OUT at prsu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Class 10 Science
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection And Refraction
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction
Ncert solutions class 10 science chapter 10 – cbse free pdf download.
* According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction is structured in a way to present a comprehensible coverage of scientific topics related to our daily life. Basic science has been laid out to students with no sharp divisions in disciplines such as Physics, Chemistry and Biology. NCERT is accepted and recommended throughout schools in the nation. Following are a few reasons to rely on NCERT Solutions :
- The tricky questions inserted between chapters force students to think out of the box and apply the concepts learned in the chapter.
- NCERT Solutions provide you with detailed solutions to the chapter questions that help you fetch marks in the CBSE exams.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter – 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Download most important questions for class 10 science chapter – 10 light reflection and refraction.
NCERT Solutions are popular among students, especially for Science and Mathematics. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 – Light Reflection and Refraction provided here consists of well-explained solutions to all the questions asked in the textbook. Get your hands on the comprehensive NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction, here, for free!
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science – Light Reflection and Refraction
Questions Page: 168
1. Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is called the principal focus of the concave mirror.
2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Radius of curvature (R) = 20 cm
Radius of curvature of the spherical mirror = 2 × Focal length (f)
f= R/2 = 20 / 2 = 10
Therefore, the focal length of the spherical mirror is 10 cm.
3. Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
The mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object is a Concave Mirror.
4. Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
A convex mirror is preferred as a rear-view mirror in cars and vehicles as it gives a wider field of view, which helps the driver see most of the traffic behind him. Convex mirrors always form an erect, virtual, and diminished image of the objects placed in front of it.
Page No: 171
1. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Radius of curvature (R) = 32 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length (f)
f = R/2 = 32/2 = 16
Therefore, the focal length of the given convex mirror is 16 cm.
2. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Magnification produced by a spherical mirror:
Object distance (u) = – 10 cm
v = 3 × (- 10) = – 30 cm
Therefore, the negative sign indicates that an inverted image is formed in front of the given concave mirror at a distance of 30 cm.
Page No: 176
1. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
The light ray bends towards the normal. When a light ray enters from an optically rarer medium (which has a low refractive index) to an optically denser medium (which has a high refractive index), its speed slows down and bends towards the normal. As water is optically denser than air, a ray of light entering from air into water will bend towards the normal.
2. Light enters from air to glass, having a refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 10 8 ms -1 .
Refractive index of a medium (nm) = Speed of light in vacuum/Speed of light in the medium
Speed of light in vacuum (c) = 3 × 10 8 m/s
Refractive index of glass (ng) = 1.50
Speed of light in the glass (v) = Speed of light in vacuum/ Refractive index of glass
=3 × 10 8 /1.50 = 2x 10 8 ms -1 .
3. Find out, from the table, the medium having the highest optical density. Also, find the medium with the lowest optical density.
|
|
| ||
| 1.0003 | Canada Balsam | 1.53 | |
| 1.31 | – | – | |
| 1.33 | Rock salt | 1.54 | |
| 1.36 | – | – | |
| 1.44 | Carbon disulphide | 1.63 | |
|
| 1.46 | Dense flint glass | 1.65 |
| 1.47 | Ruby | 1.71 | |
| 1.50 | Sapphire | 1.77 | |
|
| 1.52 | Diamond | 2.42 |
Lowest optical density = Air
Highest optical density = Diamond
The optical density of a medium is directly related to its refractive index. A medium with the highest refractive index will have the highest optical density and vice-versa.
It can be observed from the table that air and diamond, respectively have the lowest and highest refractive index. Hence, air has the lowest optical density and diamond has the highest optical density.
4. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given in the table.
Light travels faster in water as compared to kerosene & turpentine, as the refractive index of water is lower than that of kerosene and turpentine. The speed of light is inversely proportional to the refractive index.
5. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
A diamond has a refractive index of 2.42, which means that the speed of light in a diamond will reduce by a factor of 2.42 as compared to its speed in the air.
In other words, the speed of light in a diamond is 1/2.42 times the speed of light in a vacuum.
Page No: 184
1. Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
Dioptre is the SI unit of power of lens is denoted by the letter D. 1 dioptre can be defined as the power of a lens of focal length 1 metre.
2. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
The position of the image should be at 2F since the image is real and the same size.
It is given that the image of the needle is formed at a distance of 50 cm from the convex lens. Therefore, the needle is placed in front of the lens at a distance of 50 cm.
Object distance (u) = – 50 cm
Image distance, (v) = 50 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula,
3. Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
The focal length of the concave lens (f) = 2 m
Power of lens (P) = 1/f = 1/ (-2) = -0.5D
Page No: 185
1. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(c) Plastic
Answer –
(d) Clay cannot be used to make a lens because if the lens is made up of clay, the light rays cannot pass through it
2. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
(d) The position of the object should be between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
3. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
(b) The object should be placed at twice the focal length
4. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
(a) Both are likely to be concave.
Page No: 186
5. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(b) concave
(d) either plane or convex
(d) The mirrors are likely to be either plane or convex
6. Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm can be used while reading small letters found in a dictionary
7. We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Range of the distance of the object = 0 to 15 cm from the pole of the mirror.
Nature of the image = virtual, erect, and larger than the object.
8. Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
(c) Solar furnace
Support your answer with a reason.
(a) Concave Mirror: Concave mirrors can produce a powerful parallel beam of light when the light source is placed at their principal focus.
(b) Convex Mirror: Because of its largest field of view.
(c) Concave Mirror: Because it concentrates the parallel rays of the sun at a principal focus.
9. One-half of a convex lens is covered with black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Yes, it will produce a complete image of the object, as shown in the figure. This can be verified experimentally by observing the image of a distant object, like a tree on a screen, when the lower half of the lens is covered with black paper. However, the intensity or brightness of the image will reduce.
10. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
Height of the object, h 0 = 5 cm
Distance of the object from converging lens, u = -25 cm
Focal length of a converging lens, f = 10 cm
Using the lens formula,
Thus, the image is inverted and formed at a distance of 16.7 cm behind the lens and measures 3.3 cm. The ray diagram is shown below.

11. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Focal length of concave lens (OF 1 ), f = – 15 cm
Image distance, v= – 10 cm
The negative value of u indicates that the object is placed 30 cm in front of the lens. This is shown in the following ray diagram.

12. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Focal length of convex mirror (f) = +15 cm
According to the mirror formula,
The image is located at a distance of 6 cm from the mirror on the other side of the mirror.
The positive and a value of less than 1 magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual, erect, and diminished.
13. The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
The positive sign means an image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect. Since the magnification is 1, it means that the size of the image is equal to the size of the object.
14. An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Object distance (u) = – 20 cm
Object height (h) = 5 cm
Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 × Focal length

The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect.
Hence, the image formed is erect, virtual, and smaller in size.
15. An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed so that a sharply focused image can be obtained? Find the size and nature of the image.
Object distance (u) = – 27 cm
Object height (h) = 7 cm
Focal length (f) = – 18 cm

The negative value of image height indicates that the image formed is inverted.
16. Find the focal length of a lens of power -2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
Power of lens (P) = 1/f
f = -1/2 = -0.5 m
A concave lens has a negative focal length. Therefore, it is a concave lens.
17. A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
f = 1/1.5 = 10/15 = 0.66 m
A convex lens has a positive focal length. Therefore, it is a convex lens or a converging lens.

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 10 – Light Reflection and Refraction
Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction are one of the important chapters in Class 10 Science, and the expected marks weightage of the chapter, according to the latest marking scheme is 7 marks. In Chapter 10 of Class 10 Science, students will get well-versed in light phenomena such as refraction and reflection. One will learn about spherical mirrors, image formation and to draw ray diagrams.
Topics covered in this chapter:
- Reflection of Light
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
- Representation of Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors Using Ray Diagram – 4 Questions (2 short, 2 long)
- Mirror Formula and Magnification – 2 Questions (2 Numerical)
- Refraction of Light – 5 Questions (1 numerical, 2 Long answers and 1 Short answer)
- Power of Lens – 3 Questions (2 Short answers and 1 numerical)
Have you ever wondered what makes things visible to us? The answer to the question is light. During the day, it is sunlight that helps us see objects. When light falls on an object, it reflects. This reflected ray, when received by our eyes, helps us see things. Numerous wonderful phenomena are associated with light, such as the formation of the rainbow, of stars, and many more. In Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction of Class 10 Science, let us study the phenomena of refraction and reflection using straight-line propagation of light. We shall also try to understand the reflection of light by spherical mirrors in this chapter using the NCERT Solutions from BYJU’S.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 – Light Reflection and Refraction:
- Provides comprehensive answers to all the questions asked in the chapter
- The language used is lucid and can be understood by all
- The information provided is genuine and appropriate
- These solutions can be referred for CBSE exams, Olympiads and other competitive exams
- Concise answers are provided to help students understand better
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Is the byju’s ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 10 available in pdf format, what are the uses of referring to byju’s ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 10, what are the topics covered in the ncert solutions for class 10 science light reflection and refraction, and how many questions are present under each of them, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is very helpful for me . Nice learning platform 🥰😍😘
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Case Based Questions - Light Reflection and Refraction
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
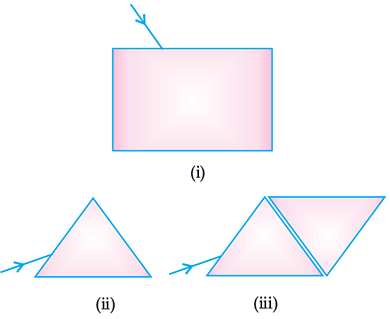
Correct Answer is Option (b) In rectangular glass slab the ray undergoes only refraction and emerges out parallel. In a prism the emerging ray is not parallel but split due to change in wavelength of different colour of light. The shape of the glass slab with two prisms up and down splits light but recombines it into one.
Question 2: The light changes its path as its medium changes. Which of the following is incorrect statement. (a) Speed of light is different in different media. (b) Light changes its path because light only travels in straight line. (c) Speed of light is dependent on medium through which it is passing. (d) The light chooses the path with minimum time, as it changes its medium.
Correct Answer is Option (b) Light changes its path because light only travels in straight line.
Question 3: Light travel fastest in: (a) Air (b) Vacuum (c) Glass (d) diamond
Correct Answer is Option (b) Light travels faster in vacuum than any other medium. This is because there is no obstruction in vacuum for the propagation of light and thus, the refractive index of vacuum is the lowest.
An object is kept at a distance of 18 cm, 20 cm, 22 cm and 30 cm, from a lens of power + 5D. Question 4: The focal length of the given lens is: (a) 0.2 cm (b) 20 cm (c) 5cm (d) 0.5 cm
Correct Answer is Option (b) P = 1/f, f = 100/5 = 20 cm
Question 5: In which case or cases would you get a magnified image? (a) 18cm (b) 20cm (c) 22cm (d) All the above
Correct Answer is Option (d) An object at 18 cm, 22 cm, and 30 cm, the image can be magnified.
Question 6: The power of a lens of focal length 1 metre is called as: (a) Refractive index (b) 1 dioptre (c) Speed of light (d) Wavelength
Correct Answer is Option (b) The power of a lens whose focal length is one metre is dioptre .
Question 7: Name the lens/mirror used in film projectors and telescopes: (a) Convex lens (b) Concave lens (c) Convex mirror (d) Concave mirror
Correct Answer is Option (a) Convex lens used in film projectors and telescopes, where the distance between the eye's lens and retina is too short, as a result of which the focal point lies behind the retina. Eyeglasses with convex lenses increase refraction, and accordingly reduce the focal length.
Question 8: Which of the magnified image can we get on a screen? (a) At 18 cm (b) At 18 cm and 22 cm (c) At 20 cm and 22 cm (d) At 22 and 30 cm
Correct Answer is Option (d) At 22 cm and 30 cm, image can be obtained on a screen.
| |67 docs|58 tests |
Top Courses for Class 10
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Case Based Questions - Light Reflection and Refraction
| 1. What is light reflection? |
| 2. What is light refraction? |
| 3. How does reflection of light occur? |
| 4. What are the laws of reflection? |
| 5. How does refraction of light occur? |
| Rating | |
Sample Paper
Important questions, study material, previous year questions with solutions, objective type questions, past year papers, viva questions, extra questions, practice quizzes, video lectures, mock tests for examination, semester notes, shortcuts and tricks.

Case Based Type Practice Questions: Light- Reflection & Refraction Free PDF Download
Importance of case based type practice questions: light- reflection & refraction, case based type practice questions: light- reflection & refraction notes, case based type practice questions: light- reflection & refraction class 10, study case based type practice questions: light- reflection & refraction on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 10 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 – PDF
1. What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and why?
Answer: The magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors is 1 as the size of the image is equal to the size of object.
2. An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 15 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
Answer: (a) The image of given object formed by the given concave lens is (i) virtual, (ii) erect, (iii) diminished in size, and (iv) is formed on same side of lens at a distance less than 15 cm from the lens.
3. Write two different uses of concave mirror.
Answer: (i) In solar furnace (ii) In shaving mirror.
4. Define power of a lens.
Answer: The ability of lens to converge or diverge the ray of light is called power of lens. It is equal to the reciprocal of focal length, i.e., P = 1/f
5. Name the mirror that is used by a dentist in examining teeth.
Answer: Dentist uses a concave mirror to See large images of the teeth of patients.
6. What is lateral displacement of a light ray passing through a glass slab?
Answer: The shifting of the light ray sideways (though in the direction of original ray) on emergence from a rectangular glass slab is called “lateral displacement”.
7. Define power of a lens and write its SI unit.
Answer: Reciprocal of focal length of a lens, expressed in metre, is called the power of that lens. Its SI unit is 1 dioptre (1 D), where 1 D = 1 m -1 .
8. Name the lens which can be used as a magnifying glass.
Answer: A convex lens can be used as a magnifying glass so as to form magnified image of a tiny object placed near it.
9. Which type of lens has a negative power?
Answer: A concave (diverging) lens has a negative power.
10. What is the difference between virtual image of an object formed by a convex lens and that formed by a concave lens?
Answer: ‘Virtual image formed by a convex lens is always magnified but that formed by a concave lens is diminished one.
11. During its passage from one medium to another, where does a light ray change its path?
Answer: During its passage from one medium to another a light ray changes its path at the boundary face separating the two media.
12. The power of a lens is + 5 D. Find its focal length in metres.
Answer: Focal length, f = 1/P = +1/5 m = 0.2m
13. What is the difference between virtual images produced by concave, plane and convex mirrors?
Answer: The virtual image formed by concave mirror is magnified, that produced by plane mirror is of the same size and that by a convex mirror is diminished.
14. For driving a car what type of mirror would you prefer to see the traffic at your back and why? Explain why it is preferred over a plane mirror?
Answer: A convex mirror is used to see the traffic at the back. It is because a convex mirror always forms an erect though diminished image of the object. It has a wider field of view. So, we will be able to much larger at the back than a plane mirror while driving the car.
15. An erect image three times the size of the object is formed with a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. What is the position of the image?
Answer: For an erect image, magnification is positive. Thus, m = 3 for an erect image three times the size of the object.

16. Discuss the position and nature of the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is moved from infinity towards the pole of mirror.
Answer: As the object is moved from infinity towards the pole of a concave mirror, the image formed starts shifting from the focus of the mirror towards infinity.
When the object is at infinity, the image is formed at the focus or in the focal plane. As the object is shifted, the image is formed between the focus and the centre of curvature, then at the centre of curvature, then beyond the centre of curvature, then at infinity and finally the image is formed behind the mirror.
17. Find the position, nature and size of the image of an object 3 cm high place at a distance of 9 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm.

18. With the help of ray diagrams, show the formation of image of an object by a concave mirror. When it is placed: (i) beyond the centre of curvature (ii) at the centre of curvature.
Answer: (i) When object is beyond the centre of curvature
(ii) When the object is at the centre of curvature
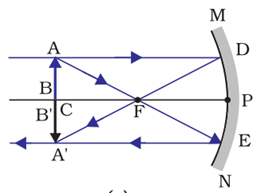
19. A student, holding a mirror in his hand, directed the reflecting surface of the mirror towards the sun. He then directed the reflected light on to a sheet of paper held close to the mirror. (a) What should he do to burn the paper? (b) Which type of mirror does he use? (c) Will he be able to determine the approximate value of focal length of this mirror from this activity? Give reason and draw ray diagram to justify your answer in this case.
Answer: (a) The student should adjust the distance between the mirror and the paper so that solar rays are sharply focussed on the paper. (b) The mirror is a concave mirror. (c) The student can find the approximate focal length by measuring the distance between the paper and the mirror.
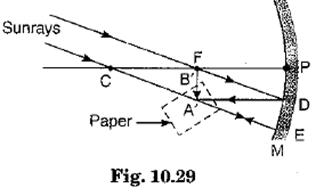
As shown in Fig. 10.29, parallel rays from the sun are focussed on the paper at point A’ in focal plane of mirror such that PB’ = f.
20. A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Answer: Given, focal length of concave mirror f = — 20 cm, height of object h o = + 4 cm and distance of image v = 30 cm. Following two cases may arise here:
Case I: If the image formed is real then v = — 30 cm
So, from mirror formula we have
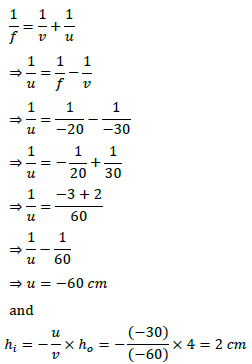
So, the object be placed 60 cm in front of mirror and image is an inverted image of size 2 cm.
Case II: If the image formed is virtual then v = + 30 cm and now
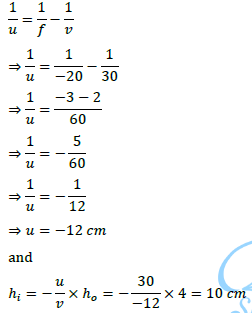
So, the object is placed at 12 cm in front of mirror and image is an erect image of height 10 cm.
21. A 10 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 12 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 18 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image.
Answer: As per question f = + 12 cm, u = – 18 cm and h o = + 10 cm As per lens law, we have
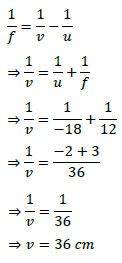
The image is formed on opposite side of lens at a distance of 36 cm from it. The image is a real and inverted image.
Moreover, magnification
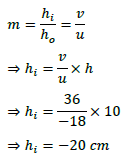
So, the size of image is 20 cm tall and is formed below the principal axis.
22. A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find the (i) position, (ii) nature, and (iii) size of the image formed. [CBSE 2004, 2006, 2014, 2019]
Answer: Here h o = + 5 cm, f= + 20 cm, u = – 30 cm (i) Using lens formula we have
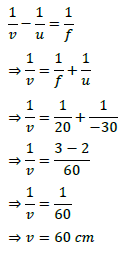
(ii) +ve sign of v means that image is being formed on the other side of lens i.e., the image is a real image.
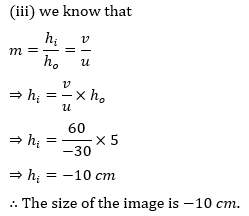
23. A real image, 2/3 rd of the size of an object, is formed by a convex lens when the 3 object is at a distance of 12 cm from it. Find the focal length of the lens.

24. Draw a ray diagram to show refraction through a rectangular glass slab. How is the emergent ray related to incident ray? What is its lateral displacement?
Answer: A ray diagram showing refraction through a rectangular glass slab has been shown in adjoining Fig. 10.32.
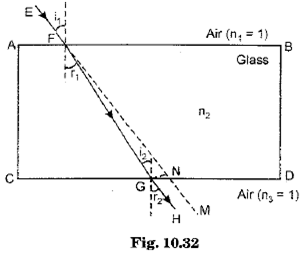
The emergent ray GH is exactly parallel to the incident ray EFNM. It means that ∠r 2 = ∠i 1 . However, the emergent ray is laterally (side ways) displaced as compared to the original path of light ray. In ray diagram, the lateral displacement is GN. Its value increases on increasing the width of glass slab.
25. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Answer: Two basic laws of refraction of light are: (i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the separating surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. (ii) The ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction (r) is a constant. It is known as Snell’s law. Thus, according to Snell’s law
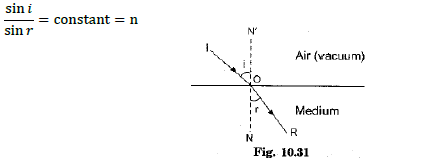
Generally, the constant n is known as the absolute refractive index of given medium. Thus, absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of sine of angle of incidence of a light ray in air (or vacuum) to the sine of angle of refraction of the ray in given medium. Absolute refractive index of a medium is a unitless quantity and its value is one or greater than one In terms of speed of fight, the absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as:
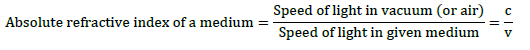
26. What is meant by power of a lens? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of – 20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens.

27. What is meant by power of a lens? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of -20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens.
Answer: Power of a Lens: The ability of a lens to converge or diverge the ray of light after refraction, is called power (P) of the lens. It is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length, i.e. P = 1/f. The SI unit of power of a lens is ‘dioptre’. A lens of focal length 100 cm has a power of 1 dioptre = 1 m -1 . Given: f A = + 40 cm = 0.4 m, f B = -20 cm
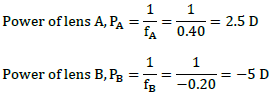
Hence, the nature of lens A is convex with power + 2.5D and lens B is concave with power -5D.
28. What is mean by power of lens? You have three lenses L 1 , L 2 and L 3 of power +10 D, +5 D and – 10 D respectively. State the nature and focal length of each lens. Explain which of the three lenses will from a virtual and magnified image of an object placed at 15 cm from the lens. Draw the ray diagram in support of your answer.
Answer: Power of lens: It is the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays after refraction through a spherical lens is called power of lens. It is the reciprocal of its focal length.

When object is placed between focus and optical centre of convex lens, virtual erect and magnified image is formed on the same side of the lens. Hence, for the object distance of 15 cm, lens L 2 will form the same.
29. We wish to obtain an equal sized inverted image of a candle flame on a screen kept at distance of 4 m from the candle flame. (a) Name the type of lens that should be used. (b) What should be the focal length of the lens and at what distance from the candle flame the lens be placed. (c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer: (a) Convex lens. (b) 2F = 4 ⇒ f = 2 m Distance of candle flame from the lens = 4 m.
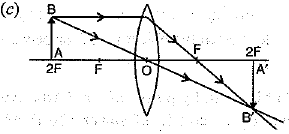
30. If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Answer: Only a convex mirror always form an erect and diminished image behind the mirror between its pole and focus point for all positions of the object placed in front of the mirror.
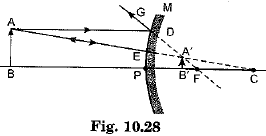
A ray diagram showing the image formation of an object AB is shown here. A convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it gives erect and diminished images of vehicles coming from behind. As a result, it helps the driver in having a much wider field of view.
31. An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
Answer: Here distance of object u = – 15 cm, height of object h o = + 4 cm and the focal length of concave mirror f = – 10 cm.
As per mirror formula we have

32. The magnification of an image formed by a lens is -1. If the distance of the image from the optical centre of the lens is 25 cm, where is the object placed? Find the nature and focal length of the lens. If the object is displaced 15 cm towards the optical centre of the lens, where would the image be formed? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.

Thus, the positive focal length shows that the given lens is a convex lens of focal length 12.5 cm. If the object is now displaced 15 cm towards the optical centre of the lens i.e, object is now placed at a distance of 25 – 15 = 10 cm from the optical centre. Therefore u = – 10 cm, and f = +12.5 cm.
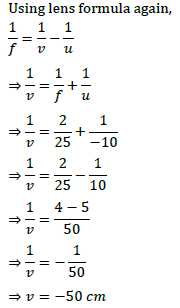
So, in this case, virtual image is formed on the same side of the object at a distance of 50 cm from the optical centre of the lens as shown in figure
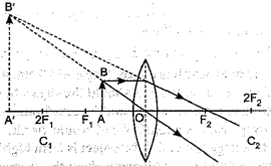
33. If the image formed by a lens for all positions of an object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what is the nature of this lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. If the numerical value of the power of this lens is 10 D, what is its focal length in the Cartesian system?
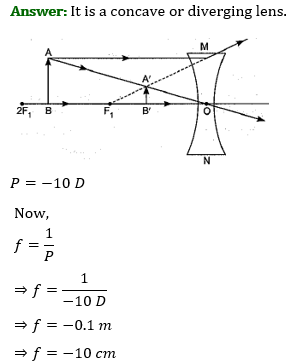
34. Define the term magnification as referred to spherical mirrors. If a concave mirror forms a real image 40 cm from the mirror, when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from its pole, find the focal length of the mirror.
Answer: Magnification of spherical mirror (m): It is equal to the ratio of size (height) of the image to the size (height) of the object. Thus,
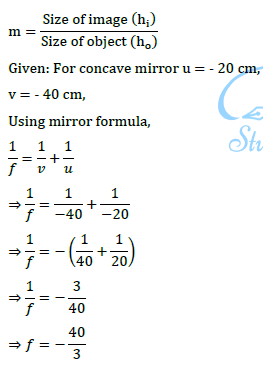
35. State Snell’s law of refraction of light. Express it mathematically. Write the relationship between absolute refractive index of a medium and speed of light in vacuum.

36. Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a (i) concave mirror (ii) convex mirror.
Answer: Ray diagrams have been shown in following Figs. 10.11(a) and (b) respectively.
37. Complete the following diagram [Fig. 10.12]
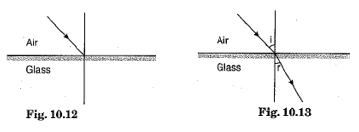
Answer: The completed diagram is as given above in Fig. 10.13.
38. Define optical centre of a spherical lens.
Answer: Optical centre of a spherical lens is a point on its principal axis, a ray of light passing through which goes undeviated along its path after refraction.
39. Draw the following diagram [Fig. 10.22], in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror, on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case.
Answer: The diagrams have been drawn and path of rays after reflection have been shown:
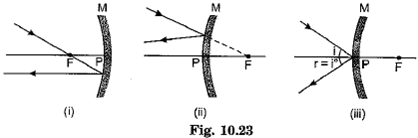
40. State two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of a given object. List two differences between the two images.
Answer: Two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image are : (i) When an object is placed between focus point F and centre of curvature C of the mirror. For this position the image is real, inverted and magnified, and the image is formed beyond centre of curvature of the mirror. (ii) When an object is placed between pole P and focus point F of the mirror. For this position the image is virtual, erect and magnified and the image is formed behind the mirror.
41. It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm. (i) What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror? (ii) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (iii) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also to justify your answer.
Answer: It is given that focal length of concave mirror is 12 cm. (i) To obtain an erect image of an object by this mirror, the object should be placed in front of the mirror between its pole and focus point, that is |u| < 12 cm.
(ii) The image is larger than the object. The ray diagram has been shown in Fig. 10.25.
(iii) If object be placed at 24 cm in front of the mirror then it means that the object is situated at the centre of curvature [ ∵ | u | = 24 cm = 2f – 2 x 12 cm = R ] C of the given mirror. Hence as shown in Fig. 10.24 the real, inverted image of same size is formed at centre of curvature C itself [ |v| = 24 cm].
42. (a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus. (b) In the above ray diagram mark the object-distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or -ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
Answer: (a) The ray diagram is as shown in Fig. 10.37.
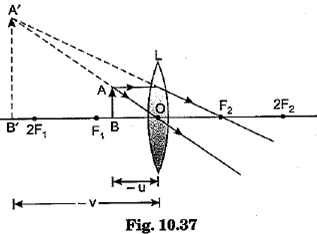
(b) The object distance ‘u’, the image distance ‘v’ and the focal length ‘f’ of the convex lens are correlated as per relation:
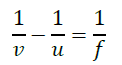
While applying this formula we must specify +ve or -ve signs of u, v and f as per new Cartesian sign convention being followed.
43. Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real, and inverted image of magnification -1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
Answer: Here u = – 20 cm and magnification m = – 1 for real and inverted image ∵ m = v/u, hence v = mu = (-1) × (-20) = + 20 cm

44. A divergent lens has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance should an object of height 4 cm from the optical centre of the lens be placed so that its image is formed 10 cm away from the lens. Find the size of the image also. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in above situation.
Answer: Here focal length of given divergent (concave) lens f = – 20 cm, height of the object h = + 4 cm and distance of image from the lens v = 10 cm. As the image formed by a concave lens is always virtual and erect, hence as per sign convention u = – 10 cm.
As per lens formula we have
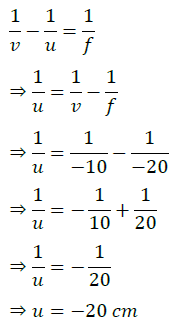
Thus, the object is placed at a distance 20 cm from the lens. Moreover
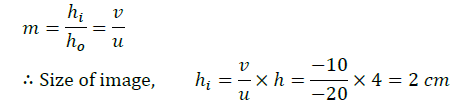
A ray diagram to show the formation of image is given here in Fig. 10.39.
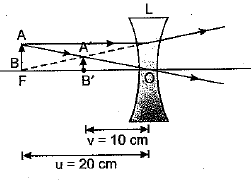
45. The image of an object formed by a mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -1. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Where would the image be if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror? State reason and also draw ray diagram for the new position of the object to justify your answer.
Answer: Given: Magnification of spherical mirror = -1, Image distance, v = -40 cm Magnification,
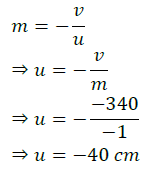
Therefore, the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm in front of the spherical mirror.
Case I: when u = -40 cm and v = -40 cm, Using mirror formula, we get
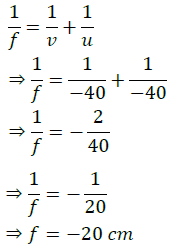
Hence the focal length of the mirror is 20 cm, and the negative focal length shows that it is a concave mirror. The new position of the object when it moves 20 cm towards the concave mirror, u’ = – (40 – 20) = -20 cm. Case II: u’ = – 20 cm, f = – 20 cm, v =?
From mirror formula,
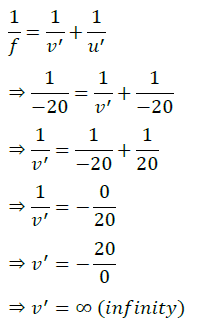
Thus, the image is formed at infinity. Hence when the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror, a real, inverted and highly enlarged image is formed at infinity.
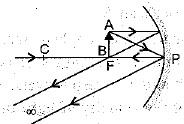
46. If the image formed by mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual and diminished, state the type of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Where are such mirrors commonly used and why?
Answer: Convex Mirror
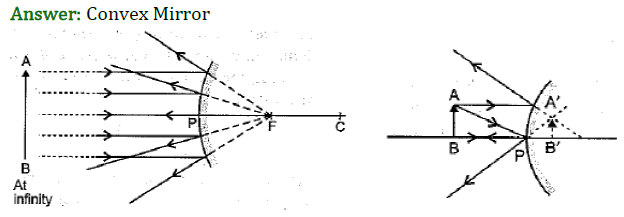
A convex mirror is commonly used as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because it always produces a virtual and erect image whose size is smaller than the object. Therefore, it enables the driver to see a wide field of view of the traffic behind the vehicle in a small mirror. 47. If the image formed by a lens for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual, erect and diminished, state the type of the lens. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. If the numerical value of focal length of such a lens is 20 cm, find its power in new cartesian sign conventions.
Answer: Concave lens (i) When an object is placed at infinity. (ii) When an object is placed between F 1 and 2F 1
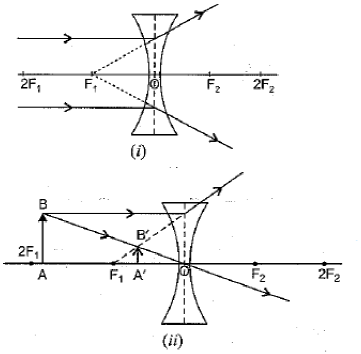
Thus, from the above figures, it is clear that whatever be the position of the object in front of a concave lens, the image formed is always virtual, erect and diminished. The power of the given lens is calculated as
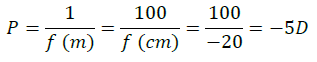
48. To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
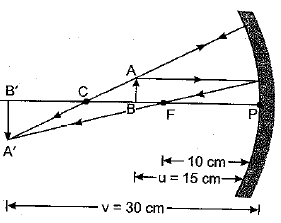
Answer: The position of the image formed by a spherical mirror can be found by considering following two rays: (i) The ray incident parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, passes through the principal focus of a concave mirror. (ii) A ray passing through the centre of curvature in a concave mirror after reflection, retraces its path.
The image formation is shown in the above figure. Here for every 5 cm distance we have 1 cm in the ray diagram. Here AB is the object and ATT is the real and inverted image formed on the basis of above mentioned two rays. Actual measurement shows that the image is formed 30 cm in front of the concave mirror i.e., v = 30 cm.
49. (a) Define optical centre of a lens. What happens when a ray of light passes through the optical centre of lens? (b) Define principal focus and focal length of a lens. Draw ray diagram to show the position of principal focus of a lens.
Answer: (a) The optical centre of a thin lens is a point on its principal axis, a ray of light passing through which goes straight without any bending (or deviation). In Fig. 10.33, the point O is the optical centre.
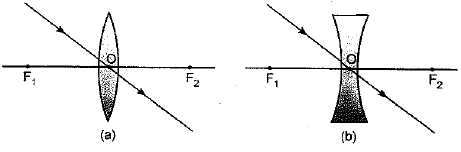
(b) Principal focus of a lens is a point where a light beam incident parallel to the principal axis of the lens, after refraction, actually converges to (in case of a convex lens) or diverges from (in case of a concave lens). Since, a lens has two refracting surfaces, a lens has two principal foci. F 1 and F 2 on either side of lens.
The distance of principal focus of a lens from its optical centre is called its focal length f. Thus, f = OF 1 = OF 2 .
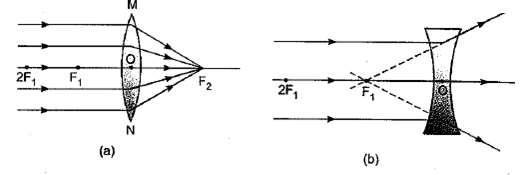
50. A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 80 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the candle flame at a distance of 20 cm from its pole. (i) Which type of mirror should the student use? (ii) Find the magnification of the image produced. (iii) Find the distance between the object and its image. (iv) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case and mark the distance between the object and its image.
Answer: (i) Concave mirror, as it forms a real image on the same side of the mirror.
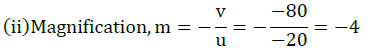
(iii) Distance between the object and its image = 80 – 20 = 60 cm
(iv) The focal length of the concave mirror is given by
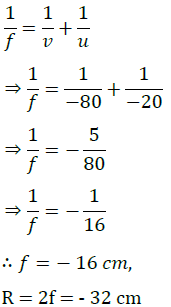
Since u = – 20 cm, it implies that the object lies between F and C, so image is formed beyond the centre of curvature as shown below:
The image is real, inverted and enlarged.
51. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray in each of the following cases. A ray of light incident on a convex mirror. (a) strikes at its pole making an angle θ from the principal axis. (b) is directed towards its principal focus. (c) is parallel to its principal axis.
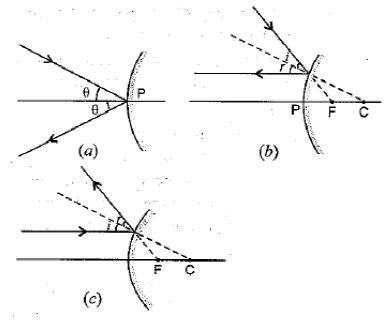
52. An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image.
Answer: Given: h o = + 5 cm, f = – 10 cm, u = – 20 cm, v = ?, h i =?
Using lens formula, web have
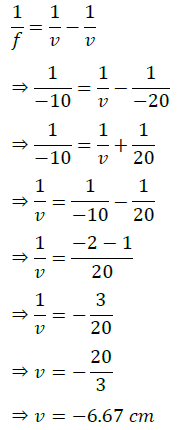
So, the image is formed on the same side of the object at a distance of 6.67 cm. The negative sign indicates that the image is virtual. Also |u|< |u| so the image is diminished.
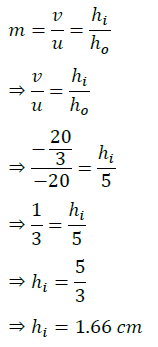
So, the image is virtual, erect, diminished and of size 1.66 cm.
53. An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. (i) Use lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens. (ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case. (iii) Draw ray diagram to justify your answer of part (ii).
Answer: Given u = – 60 cm, f = – 30 cm (i) Using lens formula,
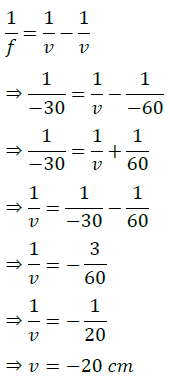
(ii) Nature of image: Virtual Position of image: Between optical centre and focus of concave lens. Size of image: Smaller than the object using
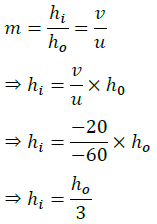
So, size of image is one third of the object. Erect/inverted: Erect image
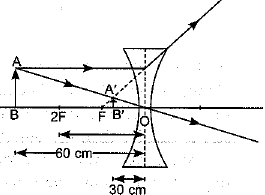
54. (a) List four characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed between its optical centre and principal focus. (b) Size of the image of an object by a concave lens of focal length 20 cm is observed to be reduced to 1/3 rd of its size. Find the distance of the object from the lens.
Answer: (a) When an object is placed between the optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged. Moreover, the image is formed on the same side of lens behind the object.
(b) Here magnification of given concave lens m = +1/3 and focal length of lens f = – 20 cm. As per relation m = v/u for a lens, we get
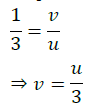
Therefore, as per sign convention followed, both u and v are -ve.
Using lens formula we have
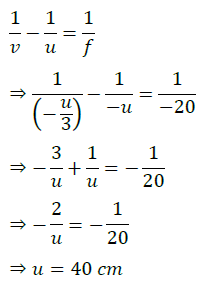
So, the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the lens.
55. (a) What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror. (b) The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is+3. Analyse this value and state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this cased (c) An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Write four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
Answer: (a) Two rays are required.
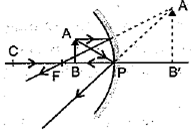
(b) The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +3. It shows that the size of image is three times the size of object, image is virtual and erect and formed behind the mirror. Hence
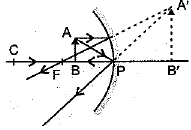
(i) the mirror is a concave mirror, and (ii) the object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror.
(c) The four characteristics of the image formed by the convex mirror are virtual, erect, diminished and laterally inverted.
56. (a) To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror. (b) A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object?
Answer: (a) Rays which are chosen to construct a ray diagram for reflection are: O’) A ray parallel to the principal axis and a ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. Path of these light rays after reflection: (i) It will pass through the principal focus of a concave mirror (ii) It gets reflected back along the same path. When an object is placed between the pole and the principal focus of a concave mirror, a virtual, erect and enlarged image is formed behind the concave mirror as shown in the figure.
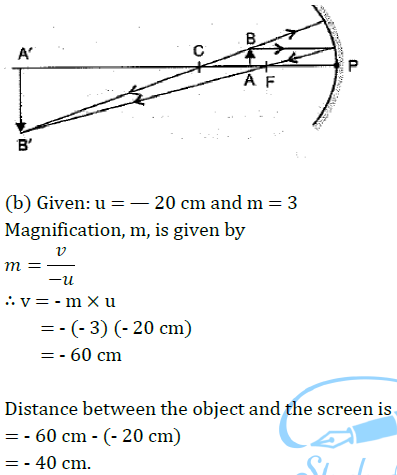
57. (a) If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always diminished, erect and virtual, state the type of the mirror and also draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Write one use such mirrors are put to and why? (b) Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirrors. Find the nature and focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm.
Answer: (a) Convex (diverging) mirror view mirror.
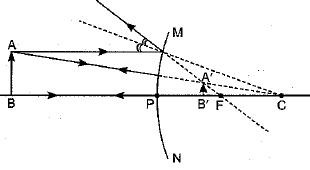
Reason: (i) It always produces a virtual and erect image. (ii) The size of image formed is smaller than the object.
Therefore, it enables the driver to see a wide field view of the traffic behind the vehicle in a small mirror. (b) Radius of Curvature: The separation between the pole and the centre of curvature or the radius of the hollow sphere, of which the mirror is a part, is called radius of curvature (R), i.e., PC = R.
Since focal length of the mirror is +24 cm. It indicates that nature of the given spherical mirror is convex/diverging mirror. As R = 2f = 24 cm Therefore, f = +12 cm 58. (a) Draw labelled ray diagrams for each of the following cases to show the position, nature and size of the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed. (i) between its optical centre (O) and principal focus (F) (ii) between F and 2 F (b) How will the nature and size of the image formed in the above two cases, (i) and (ii) change, if the convex lens is replaced by a concave lens of same focal length?
Answer: A convex lens of focal length ‘f’ can form (i) a magnified and erect image only when the object is placed between its focus ‘F’ and optical centre ‘O’ of the lens.
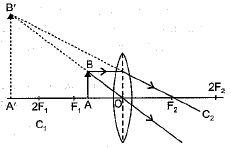
(ii) a magnified and inverted image when an object is placed in the following positions: Between F 1 and 2F 1
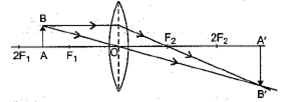
(b) Whatever be the position of object as given in case (i) and (ii), the image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, erect and diminished. 59. State the laws that are followed when light is reflected by spherical mirrors. Daw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed infront of a convex mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed. Briefly explain one use of convex mirror.
Answer: The two laws of reflection of light are: (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. (ii) The incident ray, the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence and the reflected ray from that point, all lie in the same plane. (i) Image formed is behind the mirror between pole (P) and focus (F). (ii) Virtual, erect and diminished image is formed.
(ii) Rear-view mirror of vehicles: Convex mirror Convex mirror is used because it always produces a virtual and erect image whose size is smaller than the object. Therefore, it enables the driver to see wide field view of the traffic behind the vehicle in a small mirror.

Notes of Ch 10 Light – Reflection| Class 10th Science
Study material and notes of ch 10 light – reflection class 10th science.

| Formed when light rays actually meet. | Formed when light rays appear to meet. |
| Can be obtained on screen. | Can’t be obtained on screen. |
| Inverted | Erect |
| Example: image formed on cinema screen and formed by concave mirror. | Example: image formed by plane mirror or convex mirror. |

Contact Form
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions with Answers Science Chapter 10
July 19, 2022 by Bhagya
We have given these Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction to solve different types of questions in the exam. Previous Year Questions & Important Questions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Science Chapter 10 will help the students to score good marks in the board examination.
Important Questions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Question 1. The laws of reflection hold true for (a) plane mirrors only (b) concave mirrors only (c) convex mirrors only (d) all reflecting surface Answer: (d) The laws of reflection holds true for all reflecting surface.
Question 2. List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors. (Delhi 2015, AI2011) Answer: Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are (i) imagedistanceissameasthatofobjectdistance (ii) image formed is virtual and erect (iii) image formed is of the same size as that of the object (iv) image formed is laterally inverted (left appears right and right appears left).
Question 3. State the two laws of reflection of light. (Delhi 2011) Answer: Laws of reflection of light states that (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. (ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Question 4. When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is (a) real (b) inverted (c) virtual and inverted (d) virtual and erect (2020) Answer: (d) When an object is placed between the principal focus and pole of a concave mirror, an enlarged virtual and erect image is formed behind the mirror.
Question 5. What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and why? (Delhi 2015) Answer: Magnification of images formed by plane mirrors is unity because for plane mirrors, the size of the image formed is equal to that of the object.
Question 8. An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Write four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Four characteristics of the image formed by the given convex mirror are : (i) Virtual (ii) Erect (iii) Diminished (iv) Image is always formed behind the mirror between pole and focus.
Question 9. An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror. Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are: (i) Virtual (ii) Erect (iii) Enlarged (iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Question 11. Name the type of mirrors used in the design of solar furnaces. Explain how high temperature is achieved by this device. (AI 2016) Answer: Concave mirrors are used in the designing of solar furnaces. When a solar furnace is placed at the focus of a large concave mirror, it focuses a parallel beam of light on the furnace. Therefore, a high temperature is attained at the point after some time.
Question 12. “The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -3”. List four informations you obtain from this statement about the mirror/ image. (AI 2016) Answer: Negative sign of magnification indicates that the image is real and inverted. Since the image is real and inverted, the mirror is concave and magnification of -3 indicates that the image is magnified.
Question 16. List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors. (Delhi 2015) Answer: Refer to answer 8
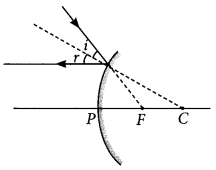
Question 18. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror, Mark on it the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. (Delhi 2014) Answer: Refer to answer 6
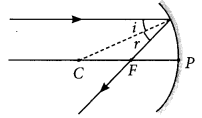
Question 20. List two possible ways in which a concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. State the difference if any between these two images. (AI2014) Answer: A concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object when object is placed: (1) In between its pole and its focus (2) In between its focus and its centre of curvature. Difference,between these two images: The image produced in first case will be virtual and erect. The image produced in second case will be real and inverted.
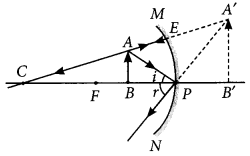
Question 27. A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed. (AI 2019) Answer: Given f = -20 cm v = -30 cm u = ? Using \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -20 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { -3+2 }{ 60 }\) ⇒ u = -60 cm ∴ Object placed at 60 cm from the mirror. Also magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ h’ = \(\frac { -(-30) }{ -60 }\) × 4 = -2 cm ∴ The size of the image is 2 cm.
Question 28. The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted. (Delhi 2017) Given: Object distance, u = – 30 cm, image size, h’ = ? Image distance, v = – 60 cm, Object size ,h = 2.4 cm, Focal length, f = ? Using mirror formula, \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \quad \text { or } \quad \frac{1}{f}=\frac{-1-2}{60}=\frac{-3}{60}=-\frac{1}{20}\) or f = – 20 cm Hence, focal length is 20 cm Also, magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) or, m = \(\frac { (-60)}{ (-30) }\) = -2 or \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = -2 h’ = – 2 × 2.4 = – 4.8 cm As the image formed is real, therefore the mirror is concave. The height of the image is 4.8 cm. The image formed is enlarged and inverted.
Question 29. An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image. (Delhi 2017) Answer: Given : object distance, u = -15 cm, object height, h = 4 cm, focal length f = -10 cm; Image distance, v = ? Using mirror formula, \(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{(-15)}=\frac{1}{-10} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{10}\) or \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{10-15}{150}=\frac{-5}{150}=\frac{-1}{30}\) or v = -30 In order to obtain a sharp image of the object on the screen, screen should be placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror. Also, magnification, m = \(\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{-v}{u}\) or \(\frac{h^{\prime}}{4}=-\frac{(-30)}{(-15)}\) or h’ = \(\frac { -(30)×4 }{ (15) }\) = -2 × 4 or h’ = -8 cm Thus, the height of the image is 8 cm.
Question 32. The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and its magnification is -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror. (AI 2016) Answer: Since the image formed is real and inverted, the mirror is concave. Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ -2 = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ v = 2u Now, if v = – 30 cm then u = – 15 cm As focal length of the mirror is f = \(\frac{u v}{u+v}=\frac{-15 \times-30}{-15-30}=f=\frac{450}{-45}\) = -10 cm If the object is shifted 10 cm towards the mirror, then the object is between principal focus and the optical centre and the image formed will be virtual and erect.
Question 33. If the image formed by mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual and diminished, state the type of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Where are such mirrors commonly used and why? (Foreign 2016, AI 2015) Answer: Refer to answer 7. Convex mirrors are widely used as rear view mirrors in cars, motorcycles etc. It produces an erect image that is smaller in size than the object hence giving a wide view.
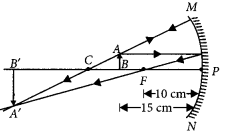
Question 36. A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror. (a) Write the type of mirror. (b) Find the distance of the image from the object. (c) What is the focal length of the mirror? (d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014, AI 2014) Answer: (a) Concave mirror (b) Magnification, m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) or v = u ∴ Distance of the image from the object is, v – u = 0 (c) As the image is formed at centre of curvature i.e., v = R. ∴ focal length of the mirror, f = \(\frac { -50 }{ 2 }\) = -25 cm (d) Refer to answer 23(ii).
Question 37. A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror. (i) Write type of mirror. (ii) What is the nature of the image formed? (iii) How far is the object located from the mirror? (iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014) Answer: (i) This is a concave mirror. (ii) The image is real and inverted and of same size. (iii) As m = – 1 ∴ m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ u = v Hence, object is located at centre of curvature i.e., at distance of 40 cm from the pole of the mirror, (iv) Refer to answer 23(ii).
Question 38. A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror. (i) Write the type of mirror in this case. (ii) What is the focal length of the mirror? (iii) What is the nature of the images formed? (iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014) Answer: (i) The mirror is concave mirror. (ii) Distance the image from the mirror = – 30 cm Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) Here m = – 1 and v = – 30 cm -1 = –\(\frac { (-30) }{ u }\) ∴ u = – 30 cm As v = u, object is placed at centre of curvature. Therefore, focal length of the mirror, f = \(\frac { -30 }{ 2 }\) = – 15 cm (iii) Image formed is real and inverted and of the same size of the object. (iv) Refer to answer 23(ii).
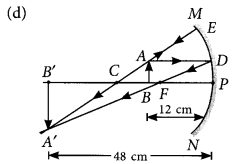
Question 41. A student wants to obtain an erect image of a candle flame using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Foreign 2014) Answer: To obtain an erect image of an object, the object should be placed in between pole and focus. Range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror is in between 15 cm. Nature of the image = Virtual and erect Size of the image = Enlarged For ray diagram, refer to answer 40.
Question 42. A student has a concave mirror of 20 cm focal length and he wants to see an erect image of his face in the mirror. What should be the range of distance of the mirror from his face? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2014) Answer: Focal length of a concave mirror = 20 cm Range will be in between 20 cm. Nature of the image = Virtual and erect Size of the image = Enlarged For ray diagram, refer to answer 40.
Question 43. Mention the types of mirrors used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) shaving mirrors. List two reasons to justify your answer in each case. (Delhi 2013, Delhi 2012) Answer: (i) Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror because (a) it gives erect image. (b) it gives diminished image thus provides wider view of traffic behind the vehicle. (ii) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror because (a) it gives erect image when mirror is close to the face. (b) it gives enlarged image of the face so that a person can shave safely.
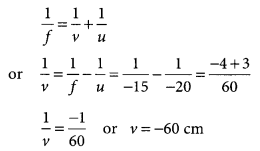
Question 45. To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror. (AI2012) Answer: A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of a convex mirror.
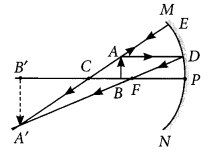
Question 46. State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirrors, in motorcycles. Give reason to justify your answer in each case. (AI 2012) Answer: (i) Concave mirrors are used in headlights of cars to get powerful beams of light. (ii) Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors of vehicle to get a wider field of view and and erect image of traffic behind.
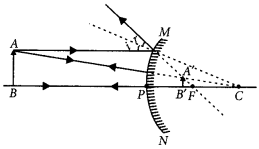
Question 51. (a) A security mirror used in a big showroom has radius of curvature 5 m. If a customer is standing at a distance of 20 m from the cash counter, find the position, nature and size of the image formed in the security mirror. (b) Neha visited a dentist in his clinic. She observed that the dentist was holding an instrument fitted with a mirror. State the nature of this mirror and reason for its use in the instrument used by dentist. (2020) Answer: (a) Given radius of curvature of the mirror, R = 5 m ∴ Focal length, f = R/2 = 2.5 m (convex mirror) and u = -20 m From mirror formula, \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \text { or } \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}\) = \(\frac{1}{2.5}-\frac{1}{-20}=\frac{-20-2.5}{-20 \times 2.5}\) ∴ v = 2.22 m Thus, the image is formed 2.22 m behind the mirror. The image is diminished, virtual and erect.
(b) Concave mirrors are used by dentist. Dentist use it as it is a converging mirror and when used at close range forms a highly enlarged, virtual and erect image of the object.
Question 52. (a) To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror. (b) A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the objects placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object? (Delhi 2017) Answer: (a) Two lights rays whose path of reflection are priorly known are : (i) When the incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, it gets reflected in the same path. (ii) When the ray is incident obliquely to the principal axis, towards the pole of mirror, it gets reflected back by making equal angles with the principal axis (laws of reflections).
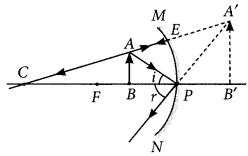
(b) Given : Magnification, m = – 3 Object distance, u = – 20 cm Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) or -3 = \(\frac { -v }{ -20 }\) or v = -60 cm The screen is placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from the pole. Thus, the screen is placed 40 cm (= 60 cm – 20 cm) away from the object.
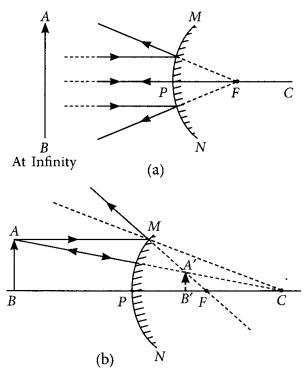
Use of Convex Mirrors Convex mirrors are commonly used as rear-view (wing) mirrors in vehicles because they always give an erect, though diminished image. Also, they have a wider field of view as they are curved outwards. Thus, convex mirrors enable the driver to view a large area.
(b) Radius of Curvature: The radius of the sphere of which the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror forms a part, is called the radius of curvature of the mirror. It is represented by the letter R. ∵ The radius of curvature is equal to twice the focal length. ∴ R = 2f If R = +24 cm ∴ f = \(\frac { R }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 2 }\) = 12 cm Since the radius of curvature is positive, the mirror is convex mirror. Hence the nature of the image is virtual and erect.
Question 55. It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm. (i) What should be the range of distance of a , object placed in front of the mirror? (ii) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (iii) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also to justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams. (AI2016) Answer: Given : focal length of the concave mirror f = 12 cm (i) If the object is placed between the pole and focus of the concave mirror, then the image formed is virtual and erect. Iheretore, the range of distance of the object should be 0 < u <. 12 cm.
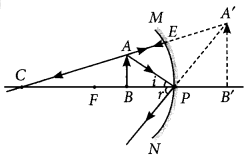
Question 56. Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distances of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. By giving reason, answer the following: (a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification -1. (b) Out of the three mirrors, identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/make up. (c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm. (Foreign 2016) Answer: Given f a = 10 cm, f b = 15 cm, f c = 20 cm u a = 10 cm, u b = 20 cm, u c = 30 cm
(a) Magnification of -1 implies that size of image is same as that of object or image is formed at the same distance as of the object. This is the case when the object distance, u = 2f, i.e., when the object is at the centre of the curvature. For f a , u b and for f b , u c , we get magnification – 1.
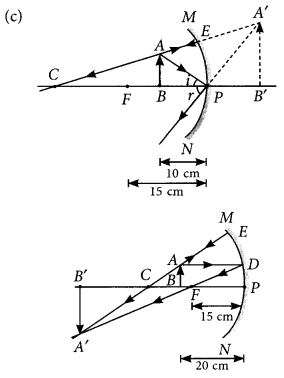
Question 59. Define the following terms in case of a concave mirror: (a) Pole (b) Radius of curvature (c) Principal axis (d) Principal focus Suppose you want to observe an erect image of a candle flame using a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. State the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror. List two other characteristics of the observed image. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (Delhi 2013) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 54(a) (i). (b) Refer to answer 53(b). (c) Refer to answer 54(a) (iii). (d) Refer to answer 54(a) (iv).
If we want to get an erect image of a candle flame using concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, then we must place the object between a pole and focus of the mirror. If u is the image distance, then 0 < u < 20 cm
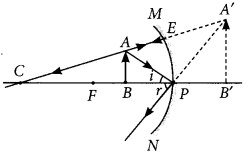
Question 61. List the new Cartesian sign convention for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions for calculating the focal length and nature of a spherical mirror which forms a 1/3 times magnified virtual image of an object placed 18 cm in front of it. (AI 2012) Answer: Refer to answer 60. Given that m = +\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) (virtual image), u = -18 cm Magnification, m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -18 }\) ⇒ v = 6 cm mirror formula \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 3-1 }{ 18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ f = 9 cm As the value of focal length is positive, the mirror used is convex mirror.
Question 62. Name the type of mirror used in the following situations (i) Headlights of a car (ii) Rear-view mirror of vehicle (iii) Solar furnace Support your answer with reason. (Foreign 2012) Answer: (i) Refer to answer 46(i). (ii) Refer to answer 46(ii). (iii) Concave mirrors are used in solar furnaces to concentrate sunlight to produce heat.
Question 63. What is meant by power of a lens? (Delhi 2015) Answer: Power is the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens. It is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length. i.e., P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) Question 64. An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens. (AI2017) Answer: Given : Object distance, u = – 15 cm Focal length, f = + 20 cm Using lens formula, As |u| < |f| The object is placed between F and optical centre of lens. Thus, the four characteristics of the image formed by the convex lens are: (i) Erect (ii) Virtual (iii) Enlarged image, (iv) Image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Question 65. What is meant by power of a lens? What does its sign (+ve or -ve) indicate? State its S.I. unit related to focal length of a lens. (Delhi 2016) Answer: Refer to answer 63. Positive sign (+) of power indicates that lens is convex and negative sign (-) of power indicates that lens is concave. If focal length (f) is expressed in metres, then, power is expressed in dioptres. The SI unit of power is dioptre. Thus, 1 dioptre is the power of lens whose focal length is 1 metre. 1 D = 1 m -1
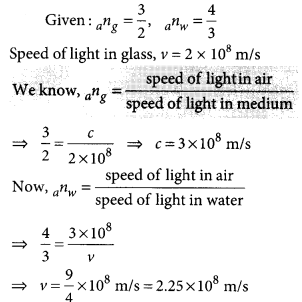
Question 72. The refractive index of a medium V with respect to a medium ‘y’ is 2/3 and the refractive index of medium ‘y’ with respect to medium ‘z’ is 4/3. Find the refractive index of medium ‘z with respect to medium V. If the speed of light in medium ‘x’ is 3 × 10 8 m s -1 , calculate the speed of light in medium ‘y’. (2020) Answer: Given, refractive index of medium x with respect to y, y µx = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) Refractive index of medium y with respect to z, z µy = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) ∴ Refractive index of medium x with respect to z, z µx = y µx . z µy = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) × \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 9 }\) ∴ Refractive index of medium z with respect to x, x µy = \(\frac { 1 }{ ^zµ_x }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 8 }\)
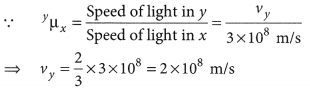
Question 74. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vaccum. (2018) Answer: (a) Laws of refraction of light: (i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. (ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction. \(\frac { sin i }{ sin r }\) = constant, where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction. This constant value is called refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first when the light travels from first medium to second medium. ⇒ constant = n 21 = \(\frac { v_1 }{ v_2 }\) ∴\(\frac { sin i }{ sin r }\) = \(\frac { v_1 }{ v_2 }\) If n is the absolute refractive index of the medium, c is the velocity of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in a given medium, then n = cl v.
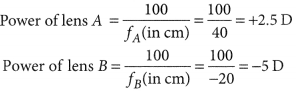
Question 77. (a) Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by a ray of light while passing through the slab. (b) If the refractive index of glass for light going from air to glass is 3/2, find the refractive index of air for light going from glass to air. (Delhi 2016) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 68. (b) Refractive index of glass w.r.t air is 3 g n a = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) Now, refractive index of air w.r.t glass will be a n g = \(\frac { 1 }{ _gn_a }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ (3/2) }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
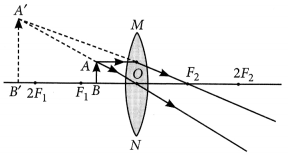
Question 84. An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. (Delhi 2013) Answer: Focal length of given concave lens, f= – 5 cm Distance, u = -10 cm, object size, h = 6 cm Image distance, v = ? Using lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{-5}+\frac{1}{-10}=\frac{-3}{10}\) v = –\(\frac { 10 }{ u }\) = -3.33 cm So, the image is located 3.33 cm from the lens. Magnification (m) of lens is given by m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac{-\frac{10}{3}}{-10}=\frac{1}{3}\) = 0.33 m is positive implies that image is virtual and erect. Also, magnitude of m is less than one implies that image is diminished. Since m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ 6 }\) or h’ = 2 cm
Question 87. What is understood by lateral displacement of light? Illustrate it with the help of a diagram. List any two factors on which the lateral displacement in a particular substance depends. (Foreign 2011) Answer: When a ray of light is incident obliquely on a parallel sided glass slab, the emergent ray shifts laterally. The perpendicular distance between the direction of the incident ray and emergent ray is called lateral shift. Diagram : Refer to answer 68. Tire factors on which the lateral displacement depends are: (i) thickness of the refracting material. (ii) the refractive index of the material.
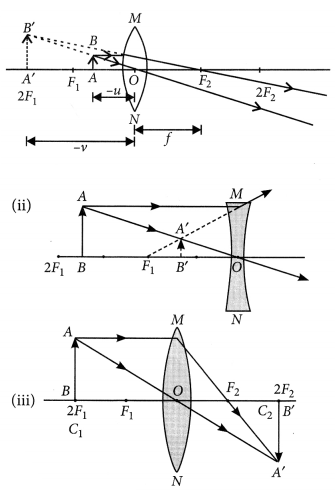
In case (i), the magnification, m is given by, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -u }\) = positive i.e., the image formed virtual and erect. In case (ii), the magnification, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -u }\) = positive i.e., the image formed is virtual and erect.
Question 89. (a) Define the following terms : (i) Power of lens (ii) Principal focus of a concave mirror (b) Write the relationship among the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f) of a (i) Spherical lens (ii) Spherical mirror (c) An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from optical centre of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (2020) Answer: (a) (i) Refer to answer 63. (ii) Refer to answer 54(a)(iv). (b) (i) for a spherical lens, according to lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) where f is the focal length of the lens, v is the image distance and u is the object distance.
(ii) For a spherical mirror, according to mirror formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) where f is the focal length of the mirror, v is the image distance and u is the object distance.
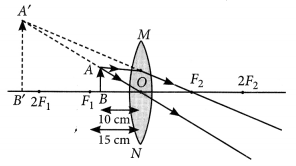
Question 93. Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follows, without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object distance u (cm) | Image distance v (cm) |
| 1 | -90 | + 18 |
| 2 | -60 | + 20 |
| 3 | -30 | + 30 |
| 4 | -20 | + 60 |
| 5 | – 18 | + 90 |
| 6 | – 10 | + 100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer. (b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion? (c) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and the approximate value of magnification. (Delhi 2017) Answer: (a) When an object placed at 2F from a convex lens, then its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. Thus from S. No.(3) we can say that. f = v/2 ⇒ f = \(\frac {30}{ 2 }\) = + 15 cm Thus, the focal length is + 15 cm.
(b) In this case S.No. (6) is incorrect as the object distance is between focus and pole, for such case, the image formed is virtual and on the same side as the object, hence image distance is negative.
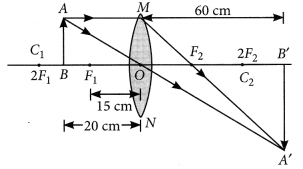
Question 94. Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations.
| S. No. | Object Distance w(cm) | Image Distance v(cm) |
| 1 | -100 | +25 |
| 2 | -60 | +30 |
| 3 | -40 | +40 |
| 4 | -30 | +60 |
| 5 | -25 | +100 |
| 6 | -15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer. (b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion? (c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification. (AI 2017) Answer: (a) When an object is placed at 2F from the convex lens, then its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. Thus from S.No. (3), we can say that ∴ f = \(\frac {v}{ 2 }\) = \(\frac {40}{ 2 }\) = 20 cm
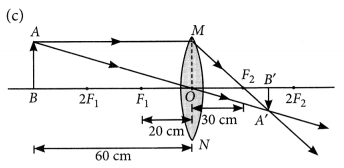
Question 95. (a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus. (b) In the above ray diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper sign (+ve or -ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case. (c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification -1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre. (Delhi 2016) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 88(i). (b) The lens formula is given as \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) (c) Magnification of the lens is given by m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = \(\frac { -v }{ 20 }\) [u = -20 cm] ∴ v = 20 cm As v = u then ∴ f = \(\frac { 20 }{ 2 }\) cm = 10 cm = 0.1 m Power of the lens, P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f(in m) }\) D = \(\frac { 1}{ 0.1 }\) D = 10 D
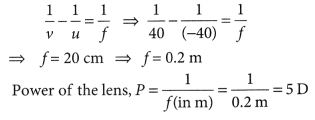
Given that h = 4 cm, u = -20 cm, f = -10 cm Lens formula: \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ (-20) }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ (-10) }\) or \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{-1}{10}-\frac{1}{20}=\frac{-2-1}{20}=\frac{-3}{20}\) or v = \(\frac { -20 }{ 3 }\) cm
Question 102. The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed on the other side of the lens at a distance of 60 cm from the optical centre of the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 3 cm, find the height of its image. (Delhi 2015) Answer: Given that u = -30 cm, v = 60 cm, h = 3 cm Lens Formula: \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ 60 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ (-30) }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac{1+2}{60}=\frac{1}{f}=\frac{3}{60}=\frac{1}{20}\) or f = 20 cm As focal length is positive, hence lens is convex lens. Magnification, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) ∴ \(\frac { 60 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ 3 }\) or h’ = \(\frac { -60×3 }{ 30 }\) = -6 cm ⇒ The height of image is 6 cm and negative sign shows that the image is real and inverted.
Question 103. (a) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum. (b) The absolute refractive indices of two media A and B are 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. If the speed of light in medium B is 2 × 10 8 m/s, calculate the speed of light in (i) vacuum (ii) medium A (Delhi 2015) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 74. (b) Given that n A = 2.0, n A = 1.5, v A = 2 × 10 8 m/s
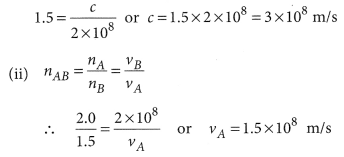
Question 107. (a) Explain the following terms related to spherical lenses: (i) optical centre (ii) centres of curvature (iii) principal axis (iv) aperture (v) principal focus (vi) focal length (b) A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance should the object be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens. (AI 2014) Answer: (a) (i) Optical centre : The centre point of a lens is known as the optical centre. It always lies inside the lens. A light beam passing through the optical centre without any deviation. (ii) Centre of curvature : It is defined as the centre of the sphere of which the lens is originally a part of. Because the spherical lens consists of two spherical surfaces, the lens has two centre of curvature. (iii) Principal axis : A straight line passing through the optical centre and principal focus of a spherical lens. This line is called the principal axis. (iv) Aperture : The diameter of the reflecting surface of spherical lens is called its aperture. (v) Principal focus : A number of rays parallel to the principal axis are falling on a lens. These rays, after refraction from the lens, are appearing to converge to or diverge from a point on the principal axis. This point on the principal axis is called the principal focus of the lens. (vi) Focal length: The distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of a spherical lens is called the focal length. It is represented by the letter f.
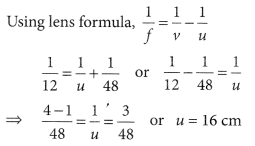
Question 108. (i) Explain the following terms related to spherical lenses (a) Centres of curvature (b) Principal axis (c) Optical centre (d) Principal focus (ii) At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm, should a 6 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at 15 cm from the lens? Also determine the size of the image formed. (AI 2014) Answer: (i) Refer to answer 107(a). (ii) Refer to answer 99.
Question 109. What is meant by power of a lens? Name and define its S.I. unit. One student uses a lens of focal length +50 cm and another of -50 cm. State the nature and find the power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will always give a virtual and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object? (Foreign 2014) Answer: Refer to answer 65. A convex lens has the focal length +50 cm. ∴ power = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { +100 }{ 50 }\) = +2 D A concave lens has the focal length -50 cm. ∴ power = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { -100 }{ 50 }\) = -2 D Concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
Question 110. (a) State the laws of refraction of light. Give an expression to relate the absolute refractive index of a medium with speed of light in vacuum. (b) The refractive indices of water and glass with respect to air are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 10 8 m s -1 , find the speed of light in (i) air, (ii) water. (Delhi 2013) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 74. (b) Refer to answer 66.
Question 111. The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 45 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 90 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2 cm, find the height of its image. (Delhi 2012) Answer: Given that u = -45 cm, v = +90 cm, h = 2 cm (as the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and hence image is formed by convex lens on the other side of the lens). Type of the lens used : Convex lens Lens formula \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ∴ \(\frac{1}{90}-\frac{1}{(-45)}=\frac{1}{f}=\frac{3}{90}\) or f = 30 cm Focal length, f = 30 cm Magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ∴ \(\frac { h’ }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 90 }{ -45 }\) or h’ = -4 cm ⇒ height of image = 4 cm (inverted)
Question 112. State the law of refraction of light that defines the refractive index of a medium with respect to the other. Express it mathematically. How is reffactive index of any medium ‘A’ with respect to a medium ‘B’ related to the speed of propagation of light in two media A and A? State the name of this constant when one medium is vacuum or air. The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to vacuum are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 10 8 m/s, find the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water. (Delhi 2012) Answer: Refer to answer 74 and 66.
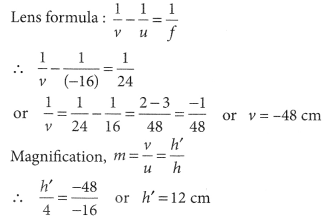
Question 116. (a) What is meant by ‘power of a lens?’ (b) State and define the S.I unit of power of a lens. (c) A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in close contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of this combination. (AI 2011) Answer: (a) Refer to answer 63. (b) Refer to answer 65. (c) Power of convex lens of focal length 25 cm is p 1 = \(\frac { 100 }{ 25(in m) }\) = 4 D Power of concave lens of focal length 10 cm is 100 p 2 = \(\frac { 100 }{ -10(in m) }\) = -10 D ∴ Power of the combination = P = P 1 + P 2 ∴ P = 4 – 10 = -6D
Question 117. (a) Under what condition with a glass lens placed in a transparent liquid become invisible. (b) Describe and illustrate with a diagram, how we should arrange two converging lenses so that a parallel beam of light entering one lens emerges as a parallel beam after passing through the second lens. (c) An object is placed at a distance of 3 cm from a concave lens of focal length 12 cm. Find the (i) position and (ii) nature of the image formed. (Foreign 2011) Answer: (a) If the refractive index of glass lens is equal to the refractive index of liquid then the glass lens placed in a transparent liquid will become invisible.
(ii) Using magnification formula, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -2.4 }{ -3 }\) = + 0.8 Since m is +ve and magnitude of m is less than 1, so the image formed is virtual and diminished.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 PDF Download
Here, we have provided CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10. Students can view these CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction before exams for better understanding of the chapter.
April 10, 2024

Table of Contents
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10: You can find the notes for Grade 10 Science’s NCERT-based notes in Chapter 10 here. By studying for the exams in advance, these notes will help students ace their exams. The Science NCERT Notes for Class 10 in this chapter, provided by us, can help students with all of their conceptual issues and doubts.
These NCERT Notes have been prepared by experts using the most recent revision of the CBSE syllabus to assist students in Class 10 in adequately preparing for their examinations.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 Overview
Students learn about the processes of light reflection and refraction utilising the straight-line propagation of light in Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes
Additionally, natural visual phenomena are investigated. The chapter discusses spherical mirrors’ ability to reflect light, allowing for an examination of their practical applications.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 PDF
Get the Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction notes here. Candidates who are determined to pass the Class 10 exam with a high score should review the notes in this article.
The link to the Class 10 Science Notes on the topic of Light Reflection and Refraction is provided below.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10
One type of energy that gives us the ability to perceive things is light. Light originates from a source, reflects off of objects that our eyes detect, and is then processed by our brain to allow us to see.
According to Maxwell’s theory, waves made up of electric and magnetic fields travel at the speed of light. As a result, Maxwell postulated that electromagnetic waves carry light, indicating that light is a type of radiation.
Nature of Light
Light behaves as a:
- ray, e.g. reflection
- wave, e.g. interference and diffraction
- particle, e.g. photoelectric effect
In quantum physics, the idea of wave-particle duality states that light can behave like a particle or like a wave, depending on the situation.
If light were thought of as a wave, phenomena like diffraction, polarisation, and interference could be explained. One way to explain a phenomenon such as the photoelectric effect is to assume that light is made up of particles known as photons.
Laws of Reflection
Light incident on the surface separating two media.
Light moves in one of two ways when it moves between media:
- gets absorbed (absorption)
- bounces back (reflection)
- passes through or bends (refraction)
A plane mirror reflects the majority of incident light, with the remaining portion being absorbed by the medium.
Characteristics of Light
The formula for the speed of light is c=λμ, where λ stands for wavelength and μ for frequency. The constant speed of light is 2.998×108m/s, or around 3.0×108m/s.
Reflection of Light by Other Media
Regular light reflection results from a medium with a well-polished surface free of flaws. Take a plane mirror, for instance. Even yet, the surface still absorbs some light.
The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane. Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection [ ∠ i = ∠ r ]
Fermat’s Principle
The least-time principle states that light always chooses the fastest route between any two points, even if it’s not the shortest one. Fermat’s principle of least time can be used to support the law of reflection [−i=−r] and the rectilinear propagation of light.
Applications of Fermat’s Principle
Fermat’s Principle allows us to make several observations that will be helpful as we go more into the field of geometric optics:
Light beams in a homogenous medium are rectilinear. That is, light moves in a straight line through any medium where the index of refraction is constant. An angle of incidence and reflection on a surface are equal. The Law of Reflection is this.
Example of Fermat’s Principle
One illustration of this phenomenon is Mirage. On occasion, we may perceive water on the route, but upon arrival, we find that it is dry. The light from the sky that is reflected on the road is what we see.
Since it is colder higher up, the air is much hotter just over the road. Because hot air is thinner and expands faster than cool air, the speed of light decreases less.
Image Formation by a Plane Mirror
A planar mirror always creates an erect, imaginary picture. Both the image and the object are equally spaced from the mirror.
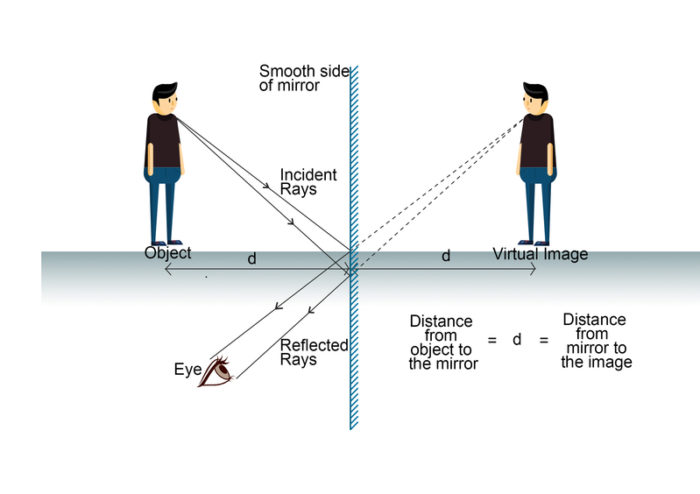
Characteristics of Images
Pictures can be virtual or actual, upright or upside down, and enlarged or smaller. The actual convergence of light beams creates a real image. An apparent convergence of light beams that are diverging is called a virtual picture. An image is said to be either inverted or upright depending on whether it is generated upside down. Magnified refers to a picture generated that is larger than the object. It is diminished if the produced picture is smaller than the object.
Rules of Ray Diagram for Representation of Images Formed
When a ray strikes the concave spherical mirror while traveling through the center of curvature, it retraces its route. The focus or focal point is traversed by rays that are parallel to the primary axis.
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
The ray diagrams for the special two rays can be used to find the image created for objects at different places. The concave mirror is shown in the following table.

Properties of Concave mirror

Mirror Formula and Magnification
| 1/v + 1/u = 1/f |
where “u” stands for object distance, “v” for image distance, and “f” for the spherical mirror’s focal length—which is determined by how similar the triangles are—are all expressed.
The ratio of the image height to the object height is the magnification that a spherical mirror produces. Typically, it is shown as’m’.
Sign Convention for Ray Diagram
The coordinate system’s positive x and y axes represent distances, while the negative x and y axes represent distances.
Remember that the pole (P) is the origin. In most cases, an object’s height is measured as positive when it is above the principal axis, while an image’s height is measured as negative when it is below the principal axis.
Refraction Through a Glass Slab and Refractive Index
Not always is the shortest path the fastest. Since light travels at the fastest possible speed, it bends when it passes through different materials. Refraction is the term used to describe the phenomena of light bending in a different medium.

Laws of Refraction
At the point of incidence, the incident ray, refracted ray, and normal to the interface of two transparent media all lie in the same plane. For a given pair of media and a given colour of light, the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is constant. Snell’s law of refraction is another name for this law.
Refractive Index
The refractive index measures how much light bends when it passes through different materials. The ratio of the speeds in the two media determines this. The amount of bending increases with the ratio.
In addition, it is the constant ratio between the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction for each given pair of media. It is indicated by:
n = sin∠i/sin∠r = speed of light in medium 1/speed of light in medium2.
The relative refractive index is the product of the speed of monochromatic light in the substance of interest and the speed of light in a vacuum. In mathematical notation, it is expressed as:
where v is the light’s velocity within that specific medium, c is the light’s velocity in a vacuum, and n is the medium’s refractive index.
Image Formation by Spherical Lenses
A convex lens’s ability to generate images is displayed in the table below.

Sign Convention for Reflection by Spherical Mirror
The item is positioned with the mirror on the left.

The mirror’s pole is the starting point for all measurements of lengths parallel to the major axis.
All distances measured along the X-axis and in the direction of the incident ray are considered positive, whereas all distances measured along the X-axis and in the opposite direction of the incident ray are considered negative.
Measurements of distance above and perpendicular to the primary axis are interpreted as positive.
Measurements taken below and perpendicular to the primary axis are interpreted as negative.
Power of a Lens
A lens’s power is equal to 1/f (in metres), which is the reciprocal of its focal length. The dioptre (D) is the SI unit of power for a lens.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 FAQs
When a ray of light approaches a smooth polished surface and the light ray bounces back, it is called the reflection of light. The incident light ray that land on the surface is reflected off the surface. The ray that bounces back is called the reflected ray.
Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that allows the human eye to see or makes objects visible. It is also defined as visible radiation to the human eye. Photons, which are tiny packets of energy, are found in light.
“The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media”.

RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Quadrilaterals
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World

.st1{display:none} Related Articles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals
- JKBOSE 11th Result 2024 Expected to be OUT Soon Check Date
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Harmful Microorganisms: Introduction, Types, FAQs
- Gymnosperms: Introduction, Characteristics, Classification, Life Cycle
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Exercise 1.1 Real Numbers
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Polynomials
- RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Exercise 2.1 Polynomials
- HBSE Compartment Admit Card 2024 OUT Download Link Here
- CGBSE 12th Revaluation Result 2024 OUT @cgbse.nic.in Download Now

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
CBSE Class 10 Important Questions on Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction 2024-25
- Class 10 Important Question
- Chapter 10: Light Reflection And Refraction

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-10 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
The concept of light, reflection, and refraction is quite fascinating for the students of Class 10. In the previous classes, students have learned a lot of new things related to these two natural phenomena occurring with light. In Class 10, they will advance to a new level of concepts related to reflection and refraction. The textbook explains the concepts pretty well. Students will need more Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions with answers to prepare for the exams.
By studying the Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions, you will develop your concept for this chapter in a better way. In fact, your answering skills will also increase considerably. Check out how the expert teachers at Vedantu have answered the Light Class 10 Important Questions niftily. Download the PDF and follow the format of answering questions as shown by the experts to score more. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions, they can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 |
|
2 | Chapter 2 |
|
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 |
|
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 | Light Reflection and Refraction |
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 |
|
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
16 | Chapter 16 |
|

Related Chapters
Important Topics under CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction
The following list of important topics covered under the chapter on Light Reflection and Refraction has been provided for students so that they can take a glance at the major concepts and read them through before diving into the important questions.
Reflection of Light
Spherical Mirrors
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
Sign Convention for Spherical Mirrors
Mirror Formula and Magnification
Refraction of Light
Refraction through a Rectangular Glass Slab
Refractive Index
Refraction by Spherical Lenses
Image Formation by Lenses and Their Ray Diagrams
Sign Convention for Spherical Lenses
Lens Formula and Magnification
Power of a Lens

Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. A convex lens has a focal length of \[10\] cm. At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it forms a real and inverted image $20$ cm. away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if the object is $2$ cm high? With the help of a ray, the diagram shows the formation of the image by the lens in this case?
Ans: Given, the focal length of the convex lens,
$\Rightarrow f=+10$ cm
Also, given the image formed is real and inverted with the image distance as $20$ cm.
$\Rightarrow v=+20$ cm
From the lens formula, we have:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{-1}{20}$
$\Rightarrow u=-20$ cm.
$\therefore $ The object is placed at a distance of $20$ cm.
Magnification is given as,
$\Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{v}{u}$
$\Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{20}{\left( -20 \right)}$
$\Rightarrow m=+1$
Also, magnification is given by, $m=\dfrac{Height\text{ of the image}}{Height\text{ of the object}}$.
$\therefore m=\dfrac{Height\text{ of the image}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{Height\text{ of the image}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow Height\text{ of the image}=2$ cm.
Thus, the image is of the same size as that of the object and it is real and inverted.
The ray diagram representing the formation of the image by the lens in this case is:
It is observed that the image is formed at $2{F_2}$ with the object placed at $2{F_1}$.
2. Draw a ray diagram to show the use of a convex lens for the formation of images having the following characteristics.
a. Real & inverted and diminished
Ans: A ray diagram representing a real & inverted and diminished image is given below.
b. Virtual, erect & magnified.
Ans: A ray diagram representing a virtual, erect, and magnified image is given below.
3. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of $50$ cm. from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of objects? Also, find the power of the lens.
Ans: Given, the image is real and inverted at a distance of $50$ cm.
$\Rightarrow v=+50$ cm
Also given, Height of image $=$ Height of object
We know, magnification is given as,
$\therefore -\dfrac{v}{u}=\dfrac{Height\text{ of the image}}{Height\text{ of the object}}$
Since, Height of image $=$ Height of object and $v=+50$ cm
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{50}{u}=1$
$\Rightarrow u=-50$ cm
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{50}-\dfrac{1}{-50}$
$\Rightarrow f=25$ cm
$\Rightarrow f=0.25$ m
The power of a lens is given by,
$\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{1}{f}$
$\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{1}{0.25}$ m
$\Rightarrow P=+4$ D
4. One-half of a convex lens is covered with black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answers experimentally. Explain your observations.
Ans: If we cover one-half of a convex lens with black paper it is observed that it produces a complete image of the object.
Representing the given situation with a ray diagram.
Adjust the position of the burning candle such that its image is formed on the screen placed on the other side of the lens.
We get a full image of the burning candle on the screen.
Thus, from the above observation, we conclude that the formation of an image does not depend on the length of the lens, but the brightness of the image formed on the screen depends since the number of rays passing through the lens gets reduced on covering half the lens with black paper.
5. An object $5$ cm in length is held $25$ cm away from a converging lens of focal length $10$ cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size, and nature of the image formed.
Ans: Given focal length of the lens, $f=+10$ cm.
Object distance from the converging lens is given to be $25$ cm and the height of the object ($ho$) is given to be $5$ cm.
$\Rightarrow u=-25$ cm
$\Rightarrow ho=5$ cm
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-25}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{25}-\dfrac{1}{10}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{50}{3}$ cm
$\Rightarrow v=16.7$ cm
Thus, we conclude that the image formed is real and inverted and is formed at a distance of $16.7$ cm on the other side of the lens.
Also, magnification is given by, $m=\dfrac{Height\text{ of the image}}{Height\text{ of the object}}=\dfrac{hi}{ho}$.
$\therefore -\dfrac{v}{u}=\dfrac{hi}{ho}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{16.7}{-25}=\dfrac{hi}{5}$
$\Rightarrow hi=-\dfrac{10}{3}$ cm
Hence, the image is diminished.
The ray diagram representing the above situation is drawn below.
6. A convex lens of focal length $15$ cm formed an image $10$ cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Ans: Given focal length of the lens, $f=15$ cm.
Image distance from the converging lens is given to be $10$ cm.
$\Rightarrow v=-10$ cm
We observe that the image distance is less than the focal length, hence the image formed would be virtual and erect.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{15}=\dfrac{1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}=-\dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{15}$
$\Rightarrow u=-6$ cm
Light: Reflection and Refraction - Important Questions and Solutions Summary
light rays, mirrors, lenses, prisms, etc., is the advanced version of what you As mentioned earlier, the chapter related to light, reflection, and refraction of have studied in the previous classes. In Class 10, you will have to focus on the theoretical part, as well as, the use of these theories to answer questions.
After you have completed answering the basic questions in the exercise, you might need a question bank to learn more about this chapter. This is where Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions with Answers can be used perfectly. These questions will intellectually challenge your knowledge and foundation of concepts based on this topic. You can answer on your own and check whether you know the right answer or not.
Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Important Questions have been developed by the expert teachers to provide a strong idea of how questions are set in the exams. All these questions are developed to define how theoretical concepts are used to solve conceptual problems. You will gain a better insight into the chapters and strengthen your foundation accordingly.
Benefits of Studying the CBSE Class 10 Important Questions on Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction
The Important Questions for Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction have been developed based on the basic and advanced concepts you have learned in your science textbook. Let us check the benefits of studying these questions first.
Thinking Out of the Box
The Important Questions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 is the ultimate suggestion for the upcoming board exam. You can study these questions, prepare their answers on your own, and compare them with the solution provided. This will help you to understand how efficiently you have studied the chapter. Light Class 10 Important Questions have been developed to help you think out of the box. In most cases, the thoughts of the students remain stuck in the exercises of the textbook. These questions will help them think out of the box and challenge their intellect.
Getting to Know Possible Important Questions of Chapter 10 Class 10 Science
By studying Class 10th Science Chapter 10 Important Questions , you will get to know possible questions that might come in the board exams. All these questions are developed by experienced science teachers. They are well-aware of the type of questions asked in the CBSE exam . Hence, studying these questions will help you learn about different modes and patterns.
Making Concepts Easier to Understand
The Important Questions for Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction have simple explanations. All the concepts in this chapter will be exceptionally simplified and utilized to answer these important questions. Hence, the students will get another way to learn how to use the textbook concepts to solve challenging questions in the exams.
Efficient Answering Methods
The Ch 10 Science Class 10 Important Questions will also come with a proper solution. The solutions will have the perfect answers to all these important questions. You will get another set of questions and answers to follow and find out the best approaches to score well in the exams. These approaches are simplified and designed by following the CBSE guidelines .
Mastering Solving Numerical Questions
This chapter poses a challenge in the form of numerical questions related to mirrors and lenses. These problems are based on a set of formulas related to the focal distance, object distance, and image distance of lenses and mirrors. By using Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions and Solutions, you can master using the formula in different aspects without committing mistakes.
You can download Chapter 10 Science Class 10 Important Questions and solutions in PDF format and study them offline. Get this extra set of questions and use them as a reference to clear your concepts of this crucial chapter.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Study Materials |
|
|
|
|
|

FAQs on CBSE Class 10 Important Questions on Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction 2024-25
1. Why Should You Prefer Vedantu for Important Questions of Light Class 10?
The teachers of Vedantu have formulated the best possible questions of Class 10 Light for the students to follow. The answers are simple and follow the CBSE guidelines. You can rest be assured that you will get the best-quality questions and answers to study.
2. Why Should You Study Light Reflection and Refraction Important Questions?
By studying the Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions, you will get a good idea of what questions are asked in the board exam. Follow the answering style and score more in the main exam.
3. What are the important topics covered in the CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction?
The following are the important topics covered in the Chapter on Light Reflection and Refraction:
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light- Reflection and Refraction Study Notes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 22 Minutes
What is Light ???
Light is the form of energy that enables us to see., properties of light.
• Electromagnetic wave, so does not require any medium to travel. • Light tends to travel in straight line. • Light has dual nature i.e., wave as well as particle. • Light casts shadow. • Speed of light is maximum in vacuum. Its value is 3 × 10^8 m/s. • When light falls on a surface, following may happen : (a) Reflection (b) Refraction (c) Absorption
Bouncing back of light when it strikes on a polished surface like mirror.
Laws of Reflection :
(1) Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. (2) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.

It is a point where atleast two light rays actually meet or appear to meet.

Image Formed by Plane Mirror:

Characteristics of Image:
(i) Virtual and erect. (ii) Size of image is equal to the size of object. (iii) Image is formed as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. (iv) Laterally inverted.
Lateral Inversion :
The right side of the object appears left side of the image and vice-versa.
Application of lateral inversion :
The word AMBULANCE is written as so that it can be read correctly in rear view mirror of vehicles going in front of it.
Spherical Mirrors : Mirrors whose reflecting surface is curved.

• Reflecting surface is curved outwards.
• Diverging mirror
For Concave Mirror:
• Reflecting surface is curved inwards.

• Principal axis : The line joining the pole and center of curvature. • Pole (P) : The centre of the spherical mirror. • Aperture (MN) : It is the effective diameter of the spherical mirror. • Center of Curvature (C) : The centre of the hollow glass sphere of which the mirror was a part. • Radius of Curvature (R) : The distance between the pole and the centre of curvature. • Focus (F) : The point on principal axis where all the parallel light rays actually meet or appear to meet after reflection. • Focal length (f) : The distance between the pole and the focus.
Relationship between focal length and radius of curvature:
Rules for making ray diagrams by concave mirror:.

Ray diagrams for images formed by concave mirror
(i) When object is at infinity :

Image Position − At ‘F’ Nature – Real, inverted Size – Point sized or highly diminished
(ii) When object is beyond ‘C’

Image Position – Between ‘F’ and ‘C’ Nature – Real, inverted Size – Diminished
(iii) When object is at ‘C’

Image Position – At ‘C’ Nature – Real, inverted Size – Same size as that of object
(iv) When object is placed between ‘F’ and ‘C’

Image Position – Beyond ‘C’ Nature – Real, inverted Size – Enlarged
(v) When object is placed at ‘F’

Image Position – At Infinity Nature – Real, inverted Size – Highly enlarged
(vi) When object is between ‘P’ and ‘F’

Position – Behind the mirror Nature – Virtual, erect Size – Enlarged
Uses of Concave Mirror:
(i) Used in torches, search lights and vehicles headlights to get powerful parallel beam of light.

(ii) Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see large image of teeth of patients. (Teeth have to be placed between pole and focus).

(iii) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror to see a larger image of the face. (iv) Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnace.
Rule for image formation by Convex Mirror:

Ray diagrams of images formed by convex mirror:
(i) When object is placed at infinity :

Image Position − At ‘F’ Nature – Virtual, erect Size – Point sized
(ii) When object is placed between pole and infinity

Image Position – Between ‘P’ and ‘F’ Nature – Virtual, erect Size – Diminished
• A full length image of a tall building/tree can be seen in a small convex mirror.
Uses of Convex Mirror:
(i) Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles because
(a) they always give an erect though diminished image. (b) they have a wider field of view as they are curved outwards.

(ii) Convex mirrors are used at blind turns and on points of merging traffic to facilitate vision of both side traffic. (iii) Used in shops as security mirror.
Sign Convention for Reflection by Spherical Mirror Or New Cartesian Sign Convention
(i) The object is placed to the left of the mirror.
(ii) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
(iii) All distances measured in the direction of incident ray (along + X-axis) are taken as positive and those measured against the direction of incident ray (along – X-axis) are taken as negative.
(iv) Distance measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis are taken as positive.
(v) Distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis are taken as negative.

• Object distance = ‘u’ is always negative. • Focal length of concave mirror = Negative • Focal length of convex mirror = Positive
Mirror Formula :

Magnification of Spherical Mirrors:
It is the ratio of height of the image to the height of the object.

- If ‘m’ is negative, image is real.
- If ‘m’ is positive, image is virtual.
- If hi = ho then m = 1, i.e., image is equal to object.
- If hi > hi then m > 1 i.e., image is enlarged.
- If hi < ho then m < 1 i.e., image is diminished.
Note: (1) Magnification of plane mirror is always + 1. ‘+’ sign indicates virtual image. ‘1’ indicates that image is equal to object’s size. (2) If ‘m’ is ‘+ve’ and less than 1, it is a convex mirror . (3) If ‘m’ is ‘+ve’ and more than 1, it is a concave mirror . (4) If ‘m’ is ‘-ve’, it is a concave mirror .
Check Your Knowledge
1. Magnification of plane mirror is + 1. What does it indicate ?
2. A real image, 1/5th size of object is formed at a distance of 18 cm from a mirror. What is the nature of the mirror ? Calculate its focal length.
3. Name the type of mirror used in the following and reason for using it : (a) Solar furnace (b) Rear view mirror in a vehicle
4. What should be the position of the object, when a concave mirror is used : (a) as a shaving mirror ? (b) in torches as reflecting mirror ?
5. (a) Define principal focus of a spherical mirror. (b) For what position of the object does a concave mirror form a real, inverted and diminished image of the object ? Draw the ray diagram. (c) An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 6 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Find the position of the image.
6. For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal to size of object ?
7. Identify the nature of mirror and mention two characteristics of image formed when magnification m = + 6.
8. Suggest a method to find approximate focal length of a concave mirror.
9. Draw ray diagram when : (a) object is placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror. (b) object is placed at infinity from a convex mirror.
10. Name the type of spherical mirror which (a) has positive focal length. (b) always forms a virtual image.
Bending of light when it enters obliquely from one transparent medium to another.
Speed of light is maximum in vacuum. It is 3 × 10^8 m/s. • Cause of refraction : Change in speed of light.
(i) The bottom of swimming pool appears higher.
(ii) A pencil partially immersed in water appears to be bent at the interface of water and air.

(iii) Lemons placed in a glass tumbler appear bigger.
(iv) Letters of a book appear to be raised when seen through a glass slab.
Refraction through glass slab:

Laws of Refraction:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) Snell’s law : The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for a light of given colour and for a given pair of media.

Refractive index (n) : The ratio of speed of light in vaccum or air to the speed of light in a medium is called refractive index.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
1 thought on “ Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light- Reflection and Refraction Study Notes ”
- Pingback: Science (CBSE Class 10) – Sanjeet's Edublog
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
Light Reflection and Refraction CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter 10
Laws of reflection.
The angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection
Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
Spherical Mirrors
Most common type of curved mirrors are spherical mirrors. Mirrors in which reflecting surface are spherical in shape, is known as spherical mirrors. Reflecting surface of a mirror can be curved inwards or curved outwards. The one which is curved inward is known as concave mirror and the one which curved outwards is known as convex mirror.

Fig.1. Spherical mirrors
Some Important Terms
Pole- The centre of the reflecting surface in a spherical mirror is a pole. It is represented by P.
Centre of curvature- Reflecting surface in a spherical mirror has a centre, this is known as centre of curvature. Centre of curvature in convex mirror lies behind the mirror whereas in concave mirror, it lies in front of the mirror.
Radius of curvature- The radius of the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror is known as radius of curvature. It is represented by R.
Principal axis- Straight line passing through the pole and centre of curvature in a spherical mirror is known as principal axis.
Principal focus- The reflected rays appear to come from a point on the principal axis, this is known as principal focus.
Focal length- The distance between the pole and the principal focus in a spherical mirror is known as focal length and it is represented by f.
Aperture- The diameter of the reflecting surface is defined as aperture.
Note: Radius of curvature is twice the focal length (R=2f).

Fig.2. Image showing pole, principal axis, centre of curvature, aperture and principal focus in concave mirror
Representations of the images formed by Spherical Mirrors using Ray Diagrams
We draw the ray diagram to locate the image of an object formed. The intersection point of at least two reflected will give the position of image of the point object. The two rays that can be used to draw the ray diagram are-
A ray parallel to the principal axis should pass through the focus after reflection in case of concave mirror, or appear to diverge in case of convex mirror.

A ray passing through the focus of the concave mirror or directed towards the focus in case of convex mirror, should appear parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
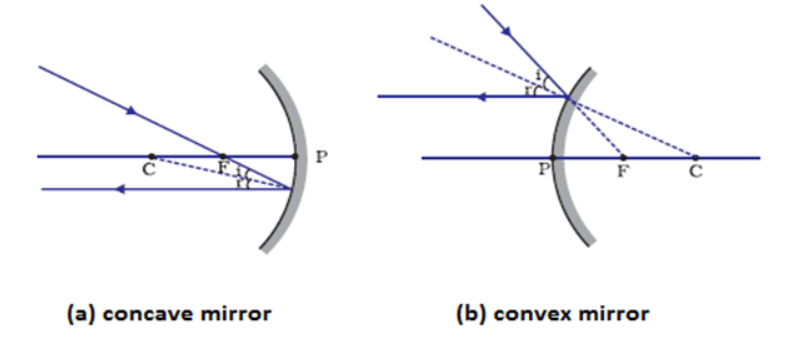
A ray which is passing through the centre of curvature in a concave mirror or directed in case of convex mirror, should reflect along the same path.

A ray when incident obliquely to principal axis on a concave or convex mirror is also reflected obliquely.

Image formation by Concave Mirror

Fig. 3. Ray diagram for the image formation by concave mirror
| At infinity | At the focus F | Highly diminished | Real and inverted |
| Beyond C | Between F and C | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At C | At C | Same size | Real and inverted |
| Between C and F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real and inverted |
| At F | At infinity | Highly enlarged | Real and inverted |
| Between P and F | Behind the mirror | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |
Table.1. Nature, relative size and position of the image formed by concave mirror
Position, nature, and the size of the image formed by a concave mirror is dependent on the position of the object in relation to P, C and F. Image formed can be real or virtual. The image can also be magnified, diminished or even of the same size.
Uses of Concave Mirror
Used in search lights, torches, head lights of the vehicles. Also used in shaving mirrors. Used by dentists also to see larger image of the teeth. Other use in solar furnaces.
Image formation by Convex Mirror
Two positions of the object are considered while understanding the image formed by convex mirror. Either the object should be at infinity or at finite distance from the mirror. Formation of the image by the convex mirror are as follows-

Fig. 5. Ray diagram for the image formation by convex mirror
| At infinity | At the focus F, behind the mirror | Highly diminished | Virtual and erect |
| Between infinity and the pole P of the mirror | Between P and F, behind the mirror | Diminished | Virtual and erect |
Table.2. Nature, relative size and position of the image formed by convex mirror
Uses of Convex Mirror
They are used as rear-view mirrors. They are used to see the traffic behind. They are preferred as they give erect but diminished image.
Sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors
New cartesian sign convention is used to give sign convention used for spherical mirrors. The conventions are as follows-
1. The object is always placed to the left of the mirror.
2. All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
3. All the distances measured to the right of the origin (along + x-axis) are taken as positive while those measured to the left of the origin (along – x-axis) are taken as negative.
4. Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along + y-axis) will be taken as positive.
5. Distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis (along –y-axis) will be taken as negative.
Mirror formula and magnification

The distance of the object from its pole is known as object distance (u), whereas distance from the pole of the mirror is known as image distance (v). The mirror formula is given by-

It is applicable for spherical mirrors in all positions of the object.
Magnification
It is defined as relative extent to which an object is magnified in comparison to its object size.

Where m is the magnification, h o is the height of the object and h i is the height of the image. However, it is to be taken as negative for real images. A negative sign in the value of magnification indicates that the nature of the image is real. A positive sign in the value of the magnification indicates the virtual nature of the image.
Refraction of light
Bending of the light rays as it passes from one medium to another medium is known as refraction of light.
Laws of Refraction
Incident ray, refracted ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is constant. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.

Refractive Index
When light passes from one medium to another medium, it changes its direction. The extent to which the direction changes is expressed in terms of refractive index. The value of refractive index is dependent on the speed of light in two media. v 1 is the speed of light in medium 1 and v 2 is the speed of light in medium 2. The refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is represented as n 21 .

If medium 1 is vacuum or air, then the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to vacuum is known as absolute refractive index of the medium.

Where c is the speed of light in air, v is the speed of light in other medium and n m is the refractive index of the medium.
Refraction by Spherical Lenses
Lenses are defined as transparent materials which are bounded by two surfaces, out of which one or both can be spherical. When both the two spherical surfaces bulge outwards, it is known as convex lens. They converge the light rays. When the two spherical surfaces bulge inwards, they are known as concave lens. They are known as diverging lens. The centre of these spherical surfaces is known as centre of curvature, represented by C.
Any imaginary straight line passing through the centre of curvature of a lens is known as principal axis. The centre point is known as optical centre. The effective diameter of the spherical lens is known as aperture.
Image formation by lenses
Nature, relative size, and position of the image formed by convex lens are given below in the form of table-
|
|
|
|
|
| At infinity | At focus F | Highly diminished | Real and inverted |
| Beyond 2F | Between F and 2F | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At 2F | At 2F | Same size | Real and inverted |
| Between F and 2F | Beyond 2F | Enlarged | Real and inverted |
| At focus F | At infinity | Infinitely large | Real and inverted |
| Between focus F and optical centre O | On the same side of the lens as the object | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |
Image formation in Lenses using Ray Diagrams
Rules for drawing the ray diagrams are as follows-
1. A ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis will pass through the principal focus after refraction from the convex lens.

2. A ray of light passing through principal focus, will emerge parallel to principal axis after refraction from the convex lens.

3. A light ray passing through optical centre will emerge out without any deviation.

Image formed by the Convex Lens for various positions of the object

Image formed by the Concave Lens

Sign convention for Spherical Lenses
Sign convention are used as similar for spherical mirrors. But the focal length of a convex lens is positive and that of concave lens in negative.
Lens formula and magnification
The lens formula is given as

Where, u is object distance, v is image distance and f is focal length.
The ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object is defined as magnification.
Magnification is represented by m, h 0 is the height of the object and h i is the height of the image.

Power of a Lens
The degree of convergence or divergence of light rays is expressed in terms of power. So, the reciprocal of focal length is known as its power. It is represented by letter P. The power is given by-
The SI unit of power is dioptre. It is represented by D. Power of concave lens is negative and power of convex lens is positive.
You Might Like to Refer:
Neet coaching | CBSE Online Class 10 | cbse study material for class 12
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution
Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Our Environment CBSE Class 10 Science Revision...
Management of Natural Resources CBSE Class 10...
Electricity CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes...
Acid Bases and Salts CBSE Class 10 Science...
Metals and Non Metals CBSE Class 10 Science Notes...
Carbon and its Compounds CBSE Class 10 Science...
Revision Notes on Control and Coordination...
Revision Notes on Chemical Reactions and Equations...
Revision Notes on Sources of Energy The largest...
Heredity and Evolution CBSE Class 10 Science...
Periodic Classification of Elements CBSE Class 10...
How Do Organisms Reproduce CBSE Class 10 Science...
Revision Notes on Magnetic Effect of Electric...
Life Processes CBSE Class 10 Science Revision...
Human Eye and Colourful World CBSE Class 10...

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction

Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Updated for 2024-25
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 are available to download. Light Reflection and Refraction is organized in such a way that it covers a wide range of scientific topics that are relevant to our daily lives. Students have been taught basic science with no clear distinctions between areas such as physics, chemistry, and biology. NCERT is widely used and recommended in schools around the country. The following are some of the benefits of using NCERT Solutions :
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
- The challenging questions interspersed between chapters encourage students to think outside the box and apply what they’ve learned in the chapter.
- NCERT Solutions give you complete answers to chapter questions that will help you pass the CBSE Term I exams.
Class 10 Science ch light NCERT solution are widely used by students, particularly in Science and Mathematics. Here you will find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 – Light Reflection and Refraction , which includes well-explained answers to all of the questions from the textbook. Get the whole NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction for free right here!
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 CBSE Free PDF Download
Download the Class 10 Science ch light NCERT solution in a free PDF format now and boost your understanding and performance in the subject. In this you will get light reflection and refraction class 10 questions and answers pdf which you can use offline.
Download PDF for Free. Study without Internet (Offline)
Grade --- Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Class 6 Class 7 Class 8 Class 9 Class 10 Class 11 Class 12
Target Exam JEE NEET CBSE
Preferred time slot for the call --- 9 am 10 am 11 am 12 pm 1 pm 2 pm 3 pm 4 pm 5 pm 6 pm 7 pm 8pm 9 pm 10pm
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Are you a Sri Chaitanya student? No Yes

Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Question Answer
Here are all the to class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction question answer improve your understanding:
Class 10 Science Ch Light EXERCISES Question Answers Page No. 168
1. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(c) Plastic
Ans. (d) Clay
Reason: Clay is not a suitable material for making lenses due to its properties. Lenses are typically made from materials like glass, plastic, or even water, but clay lacks the necessary optical characteristics required for lens functionality.
2. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Ans. (c) Beyond the centre of curvature
Reason: When the image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect, and larger than the object, the object must be positioned beyond the centre of curvature. This specific positioning results in the described characteristics of the image formed by the concave mirror.
3. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
Ans. (b) At twice the focal length
Reason: To obtain a real image of the size of the object with a convex lens, the object should be placed at twice the focal length of the lens. This positioning results in the formation of a real image that is the same size as the object.
4. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Ans. (c) the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex
Reason: Given that the focal length is negative (-15 cm), the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex. This is because the sign convention for focal length distinguishes between concave (negative focal length) and convex (positive focal length) mirrors and lenses.
5. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(b) concave
(d) either plane or convex
Ans. (a) plane
Reason: If your image appears erect regardless of the distance from the mirror, the mirror is likely to be a plane mirror. Plane mirrors always produce virtual and erect images of objects.
6. Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Ans. (c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
Reason: To read small letters found in a dictionary, a convex lens with a shorter focal length (5 cm) would be preferred. A shorter focal length lens provides greater magnification, making it easier to read small letters with clarity.
7. We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
8. Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
(c) Solar furnace
Support your answer with a reason.
(a) Headlights of a car – Concave mirror
Concave mirrors are used in the headlights of cars because they can focus the light from the bulb into a parallel beam, providing better illumination of the road ahead. The bulb is placed at the focus of the concave mirror.
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle – Convex mirror
Convex mirrors are used as side/rear-view mirrors in vehicles. They provide a wider field of view, allowing the driver to see more of the traffic behind them. Convex mirrors form virtual, erect, and diminished images, which is desirable for rear-view mirrors.
(c) Solar furnace – Concave mirror
Concave mirrors are used in solar furnaces to concentrate the sun’s rays onto a small area, creating a high-temperature focal point. The parallel rays from the sun are reflected and focused by the concave mirror, heating up the solar furnace placed at the focus.
9. One-half of a convex lens is covered with black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
No, a convex lens with one-half covered by black paper will not produce a complete image of the object. This can be verified experimentally by placing such a lens in front of an object and observing the image formed on a screen.
When one-half of a convex lens is covered, only the uncovered portion of the lens can refract light and contribute to the formation of the image. The covered portion blocks the light rays passing through it, resulting in an incomplete or partial image.
Experimentally, you will observe that the image formed is cut off on one side, corresponding to the covered portion of the lens. The image will appear as a semicircle or a partial image of the object.
10. An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
Position of the image: 16.67 cm on the opposite side of the lens.
Size of the image: 3.33 cm (inverted).
Nature of the image: Real and inverted.
The lens formula is 1/f = 1/u – 1/v
- Object distance (u) = -25 cm (object distance is negative as per the sign convention)
- Focal length (f) = +10 cm (focal length is positive for a converging lens)
- Object height (h o ) = 5 cm
Using the lens formula:
1/v = 1/f + 1/u
1/v = 1/10 + 1/-25
v = 16.67 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed on the opposite side of the lens.
Calculate the magnification (m):
m = h i /h 0 = v/u
m = 16.67/-25
The negative sign indicates that the image is inverted.
Determine the image height (h i ):
h i = m × h 0
h i = -0.67 × 5 = -3.33 cm
11. A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
12. An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
13. The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
14. An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
15. An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed so that a sharply focused image can be obtained? Find the size and nature of the image.
16. Find the focal length of a lens of power -2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
17. A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
NCERT Exemplar Answers key for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 also are accessible.
Class 10 Science 10th Chapter CBSE Notes
Chapter 10 – Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
10th Chapter One of the most essential chapters in Class 10 Science is Light Reflection and Refraction, which is worth 7 points according to the most recent grading scheme. Students will learn about light phenomena such as refraction and reflection in Chapter 10 of Class 10 Science. Spherical mirrors, image creation, and how to make ray diagrams will all be covered.
Important Topics Covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light: Reflection and Refraction
Understanding these concepts is crucial as they form the basis of many optical devices and natural phenomena. Here are the important topics covered in Class 10 Science Chapter 10:
Reflection of Light:
- Laws of reflection
- Types of mirrors (plane, concave, convex)
- Image formation by mirrors
- Sign convention for spherical mirrors
- Mirror formula and magnification
Refraction of Light:
- Laws of refraction
- Refractive index
- Refraction through a rectangular glass slab
- Total internal reflection
- Refraction by spherical lenses
- Image formation by lenses and their ray diagrams
- Sign convention for spherical lenses
- Lens formula and magnification
- Power of a lens
Optical Phenomena:
- Reflection and refraction of light in nature
- Optical instruments (e.g., microscope, telescope)
- Applications of mirrors and lenses in everyday life
Have you ever pondered what allows us to see things? The response to the question is simple. During the day, sunlight assists us in seeing items. Light reflects as it strikes an object. When this reflected ray reaches our eyes, it aids our vision. Light is responsible for many spectacular events, including the development of the rainbow, stars, and many others. Let us investigate the phenomena of refraction and reflection using straight-line light propagation in Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. In this chapter, we’ll use the NCERT Solutions from INFINITY LEARN to try to comprehend how spherical mirrors reflect light.

Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light: Reflection and Refraction
- Provides thorough answers to all of the chapter’s questions.
- The material presented is authentic and suitable, and the language used is clear and understandable to all.
- For CBSE exams, Olympiads, and other competitive exams, these solutions can be used.
- Concise responses are offered to assist pupils in better understanding.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light
What topics are covered in ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 10.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 cover topics like the laws of reflection and refraction, image formation by mirrors and lenses, refraction through a glass slab, and practical applications of these concepts in optical devices.
How can NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 help in exam preparation?
The NCERT Solutions provide detailed, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions, helping students understand complex concepts and practice problem-solving techniques, which are crucial for performing well in exams.
Where can I download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10?
You can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 from various educational websites and platforms that offer free PDF downloads, ensuring you have easy access to study materials anytime.
Are the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 useful for understanding image formation by lenses and mirrors?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 include comprehensive explanations and ray diagrams for image formation by both concave and convex lenses and mirrors, aiding in a clear understanding of these concepts.
Do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 include numerical problems?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 include solved numerical problems related to reflection and refraction, mirror and lens formulas, and magnification, helping students practice and master these important calculations.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Please select class

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v). The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations.
Contents. Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Case study:1 Case study: 2 Case study:3. At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror.
Answer. Case/Passage - 3. Inside a substance such as glass or water, light travels more slowly than it does in a vacuum. If c denotes the speed of light in a vacuum and v denotes its speed through some other substance, then v = c/n where n is a constant called the index of refraction. To good approximation, a substance's index of refraction ...
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the ...
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the ...
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS. Q.1. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - CBSE Free PDF Download *According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction is structured in a way to present a comprehensible coverage of scientific topics related to our daily life. Basic science has been laid out to students with ...
Answer Key 10.6. 5 Passages. 25 questions. Download case study question pdfs for CBSE Class 10th Maths, CBSE Class 10th English, CBSE Class 10th Sciece, CBSE Class 10th SST. As the CBSE 10th Term-1 Board Exams are approaching fast, you can use these worksheets for FREE for practice by students for the new case study formats for CBSE introduced ...
rarer medium whereas in which the speed of light is less is optically denser medium. Whenever light goes from one medium to another. the frequency Of light does not change however, speed and wavelength change. It concluded that change in speed of light is the basic cause of refraction. (i) When light travels from air to glass, the ray Of light ...
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Case Based Questions - Light Reflection and Refraction - Class 10 ... Students of Class 10 can study Case Based Type Practice Questions: Light- Reflection & Refraction alongwith tests & analysis from the EduRev app, which will help them while preparing for their exam. ...
Answer: Two basic laws of refraction of light are: (i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the separating surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. (ii) The ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction (r) is a constant. It is known as Snell's law.
Study Material and Notes of Ch 10 Light - Reflection Class 10th Science. → Light is the form of energy that provides sensation of vision. → Some common phenomena associated with lights are image formation by mirrors, the twinkling of stars, the beautiful colours of a rainbow, bending of light by a medium and so on.
Spherical Mirrors. Refraction Of Light. Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
The speed of light in vacuum is 3×108 m/s. Solution : Speed of light in vacuum (c) = 3 x 10 8 m/s. Refractive index = c/v. Speed of light in glass = 3 x 10 8 m/s/ 1.50. = 2 x 10 8 m/s. 9. Find out, from Table (10.3), the medium having highest optical density. Also, find the medium with lowest optical density.
Question 3. State the two laws of reflection of light. (Delhi 2011) Answer: Laws of reflection of light states that. (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. (ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane. Question 4.
Students learn about the processes of light reflection and refraction utilising the straight-line propagation of light in Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light. CBSE Class 10 Science Notes. Additionally, natural visual phenomena are investigated. The chapter discusses spherical mirrors' ability to reflect light, allowing for an examination of ...
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction. Long Answer Questions (5 Marks) 1. A convex lens has a focal length of \[10\] cm. At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it forms a real and inverted image $20$ cm. away from the lens?
Speed of light is maximum in vacuum. It is 3 × 10^8 m/s. • Cause of refraction : Change in speed of light. (i) The bottom of swimming pool appears higher. (ii) A pencil partially immersed in water appears to be bent at the interface of water and air. (iii) Lemons placed in a glass tumbler appear bigger.
Get Revision Notes of Class 10th Science Chapter 10 Light- reflection and refraction to score good marks in your Exams. Our notes of Chapter 10 Light- reflection and refraction are prepared by Science experts in an easy to remember format, covering all syllabus of CBSE, KVPY, NTSE, Olympiads, NCERT & other Competitive Exams.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 CBSE Free PDF Download. Download the Class 10 Science ch light NCERT solution in a free PDF format now and boost your understanding and performance in the subject. In this you will get light reflection and refraction class 10 questions and answers pdf which you can use offline.