- Skip to search box
- Skip to main content

Princeton University Library
Literature mapping.
- Manual Mapping
- Connected Papers
- Open Knowledge Maps
Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit creates citation maps as well as networks of recommended articles based on user provided collections of articles. You can get article and collaborator recommendations, set alerts, and share collections. User account required for use, but always free.
- Import collection from Zotero or build a new collection using Pubmed ID, DOI, or keyword search.
- Literature maps include network view and timeline view.
- << Previous: Open Knowledge Maps
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 3:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.princeton.edu/litmapping
Literature Mapping Tools
Research rabbit.
- Connected Papers
- Library Subscriptions
- A.I. Glossary
- Need Assistance?
Related Guides
- Altmetrics by Sabine Lanteri Last Updated Apr 5, 2024 171 views this year
- Citation Management Tools by Dianna McKellar Last Updated Feb 27, 2024 1039 views this year
- Copyright Basics by Paige Morgan Last Updated Mar 20, 2024 301 views this year
- Open Access by Jessica Deshaies Last Updated May 29, 2024 875 views this year
- Research Methods by Alison Wessel Last Updated Aug 21, 2023 1929 views this year
Research Rabbit originally was known for its data visualizations which allow you to see connections between academic papers and authors. It has expanded its offerings to include a function that recommends papers based on your research interests and collaborative/sharing functions. You can upload papers and use DOIs and PMIDs to locate and add papers. Recommendations appear to be citation based but there is not an explanation of that function from the company.
Notes: From our own testing, the network and citations shown are not always related: we uploaded a digital scholarship article and it connected to other authors with the same last name, in completely different research fields, and included more general articles like about the philosophy of education.
Data sources: Research Rabbit was originally based on Microsoft Academic Graph which was retired December 31, 2021. It is unclear what data sources Research Rabbit is pulling from at this time.
- << Previous: Elicit
- Next: Connected Papers >>
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 1:40 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/litmap
- My Playlists
- Media Upload
- How To Use Media Hopper Create
- How To Use Media Hopper Create In Learn
- Creative Commons
- All Channels
How to Create a Literature Review Outline with Research Rabbit | Research Rabbit Tutorial
Related media.

Literature Discovery through Citation Chaining and Mapping: Research Rabbit
- PowerSearch
- Google Scholar
- Article Databases
- Scite, Semantic Scholar, Dimensions, Lens
- Connected Papers
Research Rabbit
- Comparison of Mapping Tools
Research Rabbit helps you find papers based on one or a set of seed papers or a research topic by keywords.
- Find " Similar Work "
- Find " Earlier Work " - all references
- Find " Later Work " - all citations (citing articles)
- Explore " These authors " - refine your search to specific authors' works
- Explore " Suggested authors " - expand your search to related authors' works
Research Rabbit is "forever free for researchers".
Research Rabbit - Tutorial (18min)
Navigating Research Rabbit for the first time can be a bit frustrating. Watch the tutorial below to learn some helpful tips!
Helpful tutorials & guides:
- Research Rabbit Youtube channel
- ResearchRabbit: Uplift Your Research Adventure Down the Rabbit Hole (HKUST Library, Dec 2021)
- ResearchRabbit is out of beta- my review of this new literature mapping tool (Aaron Tay, Aug 2021)
How to Read the "Map"
- Category : treat it like folders, e.g. broader subjects
- Collection: subfolders, e.g. topics
- Each node: one paper
- Node size: no. of citations
- Green : papers in the Collection
- Blue : paper recommendations
- << Previous: Litmaps
- Next: Undermind >>
- Last Updated: May 19, 2024 7:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hkust.edu.hk/citation-chaining
A new literature mapping tool - ResearchRabbit
By Aaron Tay, Lead, Data Services
One of the challenges of doing literature review is that you are constantly switching between different modes of searching and browsing. You may find some relevant papers via keyword searching or stumble upon some via Wikipedia or at a conference, which leads you to look at the references or citations of that paper, which may lead you to spot interesting authors that you decide to check out their publications, which leads to more citation mining…. and before you know it you might be lost.
It often feels like you are tumbling down the rabbit hole, as each relevant paper you find opens up yet more avenues to explore and the possibilities seem endless.
What if a tool existed that helped you with doing all this in a seamless way and as a bonus provided quick visualisations to help you decide which direction you might want to go when exploring the literature “forest”?
A new literature mapping tool - ResearchRabbit aims to do this.
Adding relevant papers to start into ResearchRabbit
Like other tools similar to this (see earlier Research Radar piece) , you start off by adding one or several relevant papers you already know into a “collection”. You can add specific papers by title or unique IDs (DOIS/PMIDs) or even import references from most reference managers using BibReX or RIS format.
Don’t have any papers to start off with? You can also search by keywords by clicking “Add by Search” using different search engines.
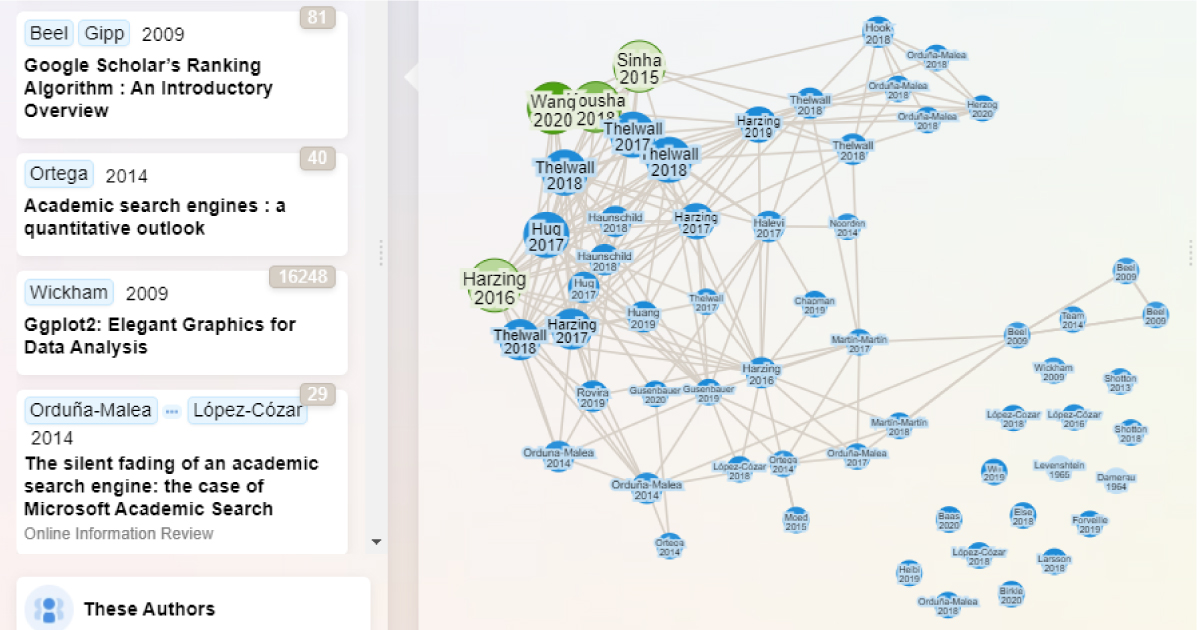
Once you have added one or more papers into the collection, this is where the fun starts.
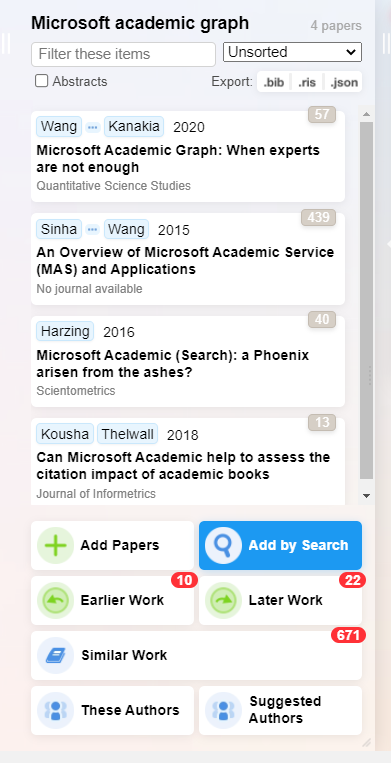
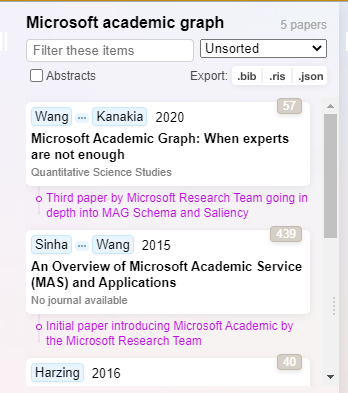
Say we pick one paper - Hazing & Alakangas (2017) to focus on, clicking on it gives us options including
- “All References” (show all papers that reference selected paper)
- “All citations” (show all papers that cite selected paper)
- “Similar Work” (show “similar papers” to selected paper that you might be interested in)
- “These Authors” (show all authors of selected paper) “Suggested Authors”(show suggested authors that you might be interested in)
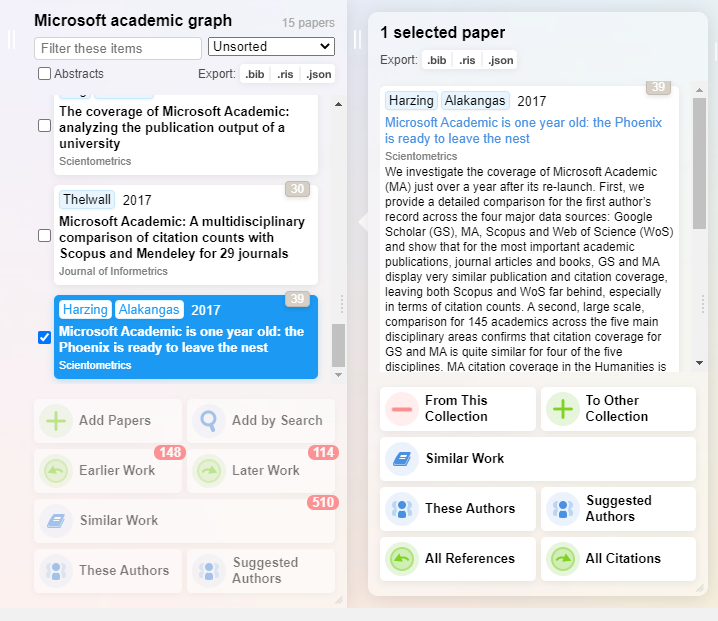
Let’s say we want to look for potential papers to add to our collection by looking at references of Hazing & Alakangas (2017). Clicking on “All citations” will generate 30 papers that are referenced by that paper known to Research Rabbit in a new column titled “All Citations”.
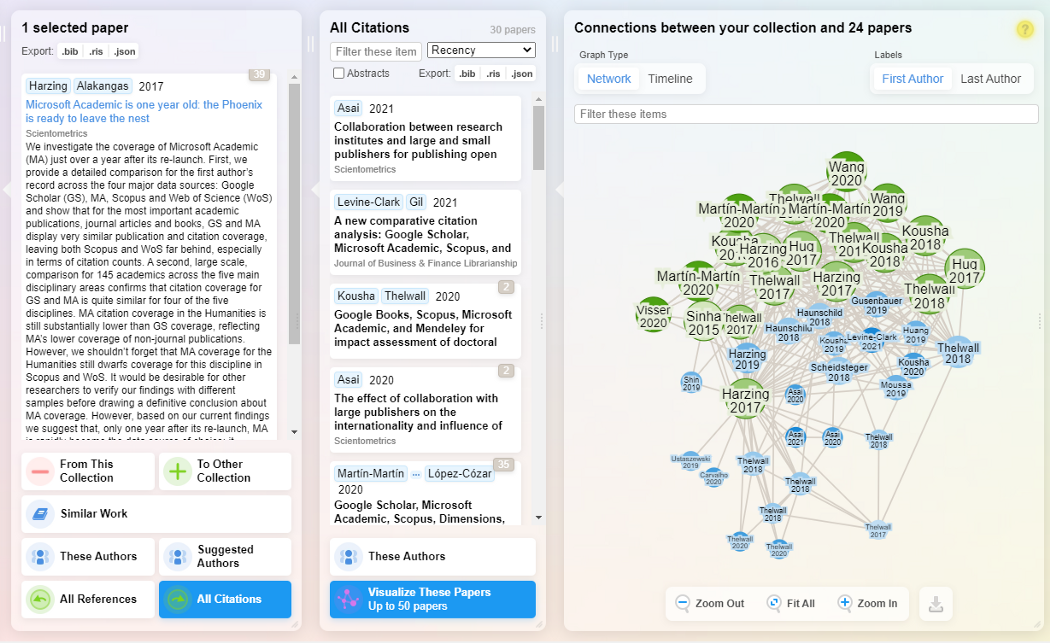
You also get a visualisation graph which each paper represented by a node and links between them represent citations. More importantly, papers that are already in your collection are coloured in green and those which are not are in blue.
This helps you see how connected the papers you are currently considering with those already in your collection.
If any of the papers listed in this new column are of interest, you can drag them to your collection or click on them and select “To this collection”.
From here, you can repeat this process, and select one of these papers and click on say “All references” to generate yet another column of papers that are references of that paper and continue drilling down further.
But instead, let’s try clicking on one of the paper’s- Kousha & Thelwall (2020) and let’s say we are interested in the authors of these papers and we want to see what else they have written.
We can select the paper, select “these authors” and for the selected author, we can click on “Published work”.
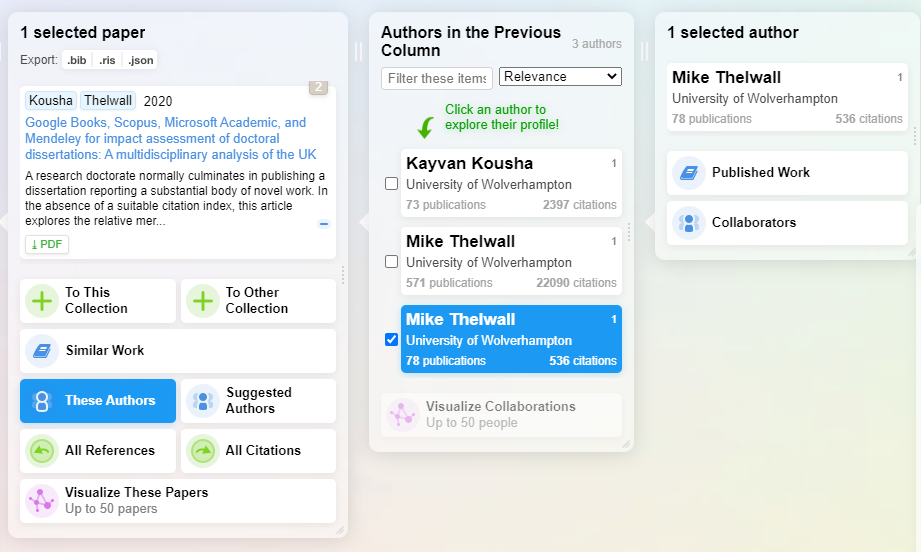
This will generate as you probably expected yet another new column of papers and the same visualisation you have seen earlier.
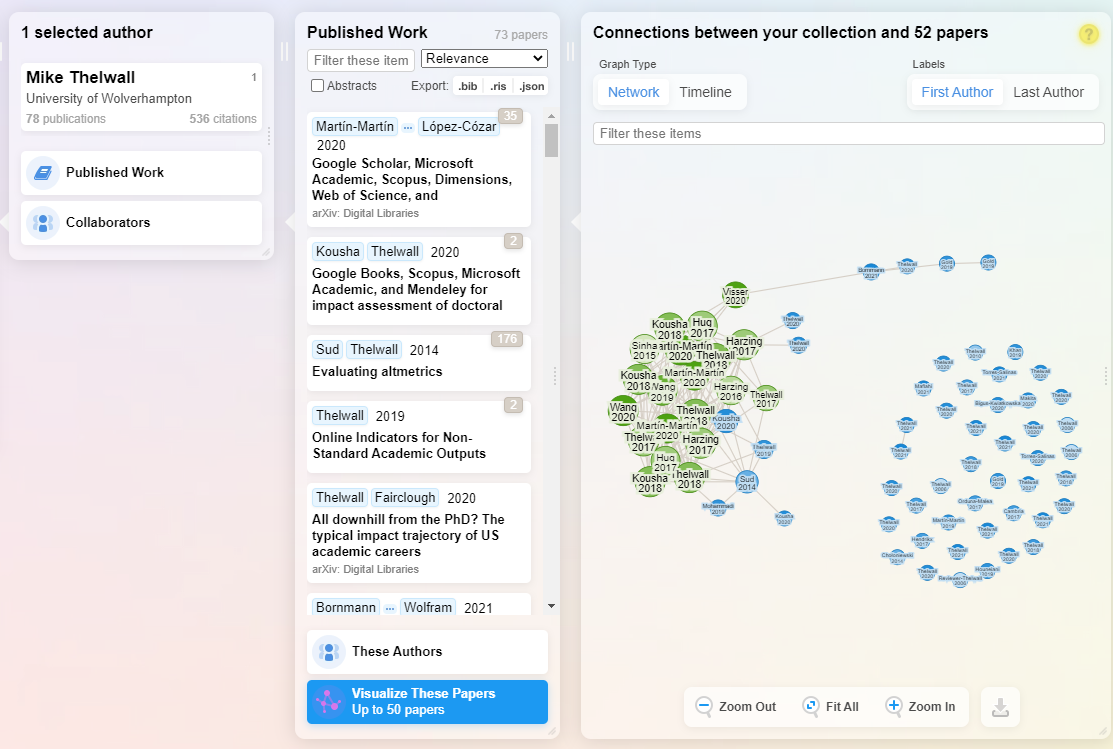
Finally, clicking on “Suggested authors” will prompt Research Rabbit to produce a new column of suggested authors as well as visualisation. This time, the visualisation will be a co-authorship graph showing which authors have co-authored together.
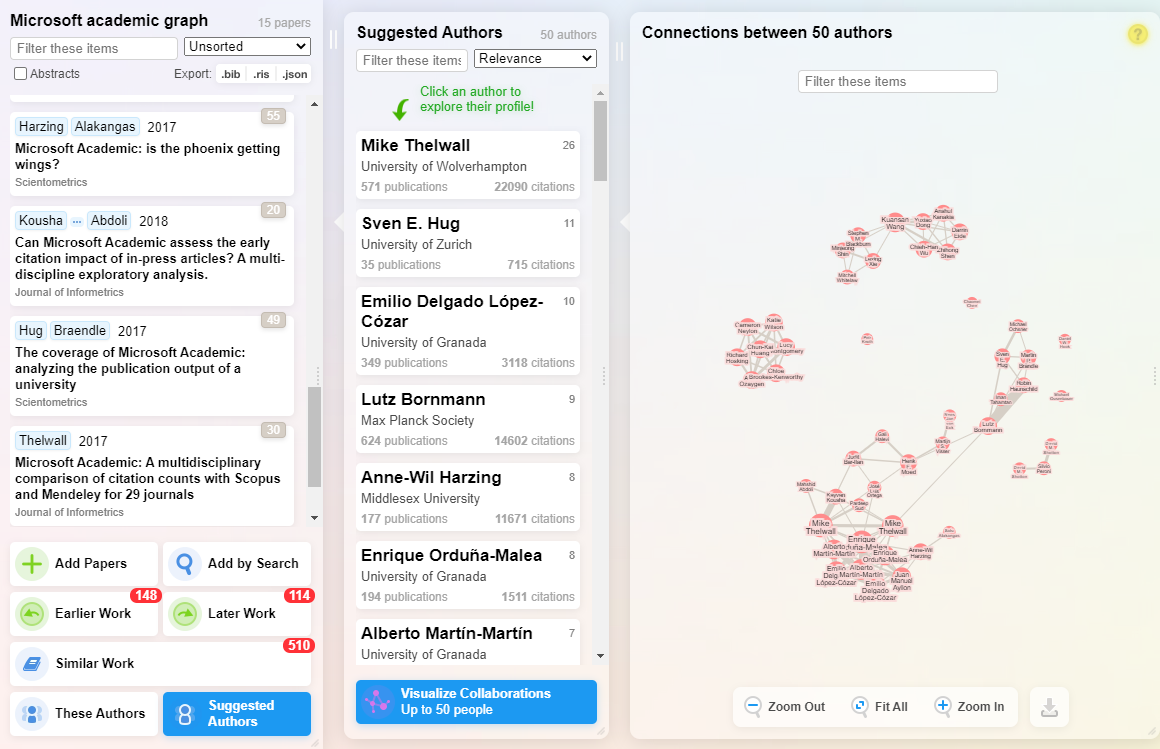
This allows you to tell which suggested authors have worked together before helping you detect possible clusters of research.
As you add more papers to the collection, you will be given options like “Similar paper”, “Later work”, “Earlier work” that are recommendations based on multiple papers in the collection. Clicking on them will give you the same panels as seen earlier.

Like most similar tools, ResearchRabbit allows you to export what you have found in your collection to reference managers via RIS, Bibtex files. You will get weekly updates as the algorithm finds new papers that might be of interest.
ResearchRabbit also promotes collaboration. You can share collection with other users in either read-only mode, or allow them to add papers.
ResearchRabbit allows you to add notes, which can be helpful if you have collaborators adding to the collection.
Good literature review involves the use of a combination of techniques such as keyword searching, using relevant papers as seeds to find more related papers by either looking at citations, references or works by relevant authors and to repeat iteratively until you have exhausted the possibilities. Research Rabbit reduces the friction of doing such steps and allows you to navigate the landscape with visualisation graphs to quickly populate your collection with relevant papers.
How does Research Rabbit compare to the other 3 tools mentioned in the earlier Research Radar piece on tools to help with literature mapping ?
It’s still early days, but in terms of simplicity, low effort investment , one shot tool , this librarian feels Connected Papers is still the one to the beat, as in my experience it works very well with just one paper. In comparison while ResearchRabbit can work with one paper, it starts to really shine when you have more papers to your collection.
ResearchRabbit has a higher learning curve due to the variety of options available, however, if you are in the market for a tool that allows you to do intensive custom literature review and are willing to spend the time, ResearchRabbit is a very promising tool, once you get the hang of it.
Do note that like all the other literature mapping tools reviewed , the quality of ResearchRabbit recommendations depends heavily on the metadata available (title, abstract, citations) from the index used. For example, the tool may not have information (or have incomplete information due to extraction errors) on the references of a paper and relying on it to drill down to references could mean missing relevant references you might discover if you have done so by hand.
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Publication Research Help
- Research Rabbit & Elicit
Publication Research Help: Research Rabbit & Elicit
- Peer Reviewed Architecture Journals
- Peer Reviewed Planning Journals
- Creating an ORCID iD
- Google Scholar Profile

Research Rabbit
ResearchRabbit is a free online “citation-based literature mapping tool." It is a visual literature review software mapping tool that is similar to Spotify. The tool connects your research interests to related articles and authors.
Intro video
Research Rabbit pdf guide from The Learning Centre
- Step by step guide to Research Rabbit Created by the Learning Centre, James Cook University
AI Research Assistant Elicit
The AI Research Assistant Elicit uses language models to help you automate research workflows, like parts of literature review.
Elicit can find relevant papers without perfect keyword match, summarize takeaways from the paper specific to your question, and extract key information from the papers. While answering questions with research is the main focus of Elicit, there are also other research tasks that help with brainstorming, summarization, and text classification.
Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers’ workflows. Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review. If you ask a question, Elicit will show relevant papers and summaries of key information about those papers in an easy-to-use table.
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How to use Elicit - YouTube videos
- << Previous: Google Scholar Profile
Something went wrong when searching for seed articles. Please try again soon.
No articles were found for that search term.
Author, year The title of the article goes here
LITERATURE REVIEW SOFTWARE FOR BETTER RESEARCH
“Litmaps is a game changer for finding novel literature... it has been invaluable for my productivity.... I also got my PhD student to use it and they also found it invaluable, finding several gaps they missed”
Varun Venkatesh
Austin Health, Australia

As a full-time researcher, Litmaps has become an indispensable tool in my arsenal. The Seed Maps and Discover features of Litmaps have transformed my literature review process, streamlining the identification of key citations while revealing previously overlooked relevant literature, ensuring no crucial connection goes unnoticed. A true game-changer indeed!
Ritwik Pandey
Doctoral Research Scholar – Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning

Using Litmaps for my research papers has significantly improved my workflow. Typically, I start with a single paper related to my topic. Whenever I find an interesting work, I add it to my search. From there, I can quickly cover my entire Related Work section.
David Fischer
Research Associate – University of Applied Sciences Kempten
“It's nice to get a quick overview of related literature. Really easy to use, and it helps getting on top of the often complicated structures of referencing”
Christoph Ludwig
Technische Universität Dresden, Germany
“This has helped me so much in researching the literature. Currently, I am beginning to investigate new fields and this has helped me hugely”
Aran Warren
Canterbury University, NZ
“I can’t live without you anymore! I also recommend you to my students.”
Professor at The Chinese University of Hong Kong
“Seeing my literature list as a network enhances my thinking process!”
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
“Incredibly useful tool to get to know more literature, and to gain insight in existing research”
KU Leuven, Belgium
“As a student just venturing into the world of lit reviews, this is a tool that is outstanding and helping me find deeper results for my work.”
Franklin Jeffers
South Oregon University, USA
“Any researcher could use it! The paper recommendations are great for anyone and everyone”
Swansea University, Wales
“This tool really helped me to create good bibtex references for my research papers”
Ali Mohammed-Djafari
Director of Research at LSS-CNRS, France
“Litmaps is extremely helpful with my research. It helps me organize each one of my projects and see how they relate to each other, as well as to keep up to date on publications done in my field”
Daniel Fuller
Clarkson University, USA
As a person who is an early researcher and identifies as dyslexic, I can say that having research articles laid out in the date vs cite graph format is much more approachable than looking at a standard database interface. I feel that the maps Litmaps offers lower the barrier of entry for researchers by giving them the connections between articles spaced out visually. This helps me orientate where a paper is in the history of a field. Thus, new researchers can look at one of Litmap's "seed maps" and have the same information as hours of digging through a database.
Baylor Fain
Postdoctoral Associate – University of Florida

We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Penn State University Libraries
Generative ai: chatgpt and beyond.
- Comparing LLMs
- Google Gemini
- Perplexity.ai
- ResearchRabbit
- Citing LLMs
- Resources for Instructors
Find out more about ResearchRabbit
- Step by step guide to Research Rabbit Created by the Learning Centre, James Cook University
- Research Rabbit Tips and Tricks Lots of tips, including importing to reference managers
What is ResearchRabbit?
ResearchRabbit is a free online “citation-based literature mapping tool." It is a visual literature review software mapping tool that is similar to Spotify. The tool connects your research interests to related articles and authors.
The tool allows users to create collections based on their research focus. You can start by looking up a title, DOI, PMID, or keywords, find the paper in the results, and add it to your collection. You can expand the details of the paper by displaying the paper's abstract and comments you've written. From there, selecting a paper will allow you to explore similar papers, references in your original paper, and citations in your original paper. You can also explore additional works by the paper's author and suggested authors, as well as linked content.
The unique map feature allows you to visualise the relationship between papers, represented as circles on the map. Research Rabbit will draw connections between papers that reference each other, as well as colour code them. Papers come in three colours: green, which are the papers in your collection; and blue, the papers that Research Rabbit recommends. The colour shading is dictated by the level of information the site has on the paper: the darker the circle, the more information Research Rabbit has access to. When circles are completely white, then the site has no information on them. Exploring papers through the map can lead you into further and more specific research, essentially taking you "down the rabbit hole".
ResearchRabbit Tutorial
This is an overview of Research Rabbit by Roman Koshykar from Rochester Institute of Technology.
- << Previous: Scite.ai
- Next: Citing LLMs >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 9:36 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/LLMs
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Animals (Basel)
- PMC10135268

Feeding, Nutrition and Rearing Systems of the Rabbit
1. introduction.
During the last years, several issues have contributed to a progressive decline in rabbit meat consumption in the European Union, including consumers’ concerns for animal welfare, the unsuitable presentation of the end product, an increased popularity of rabbits as pet animals, high production costs (aggravated by the ongoing geopolitical crises), and criticism about the environmental sustainability of rabbit farms [ 1 ]. Therefore, the rabbit sector is looking for sustainable solutions to limit the use of antimicrobials, improve the health and welfare of animals, and reduce the environmental impact of farms. Progress in genetics, breeding management, and feeding techniques have enhanced health conditions and feed efficiency in rabbit production; however, further improvements are required to guarantee the economic sustainability of rabbit farms [ 2 , 3 ].
This Special Issue of Animals collects research papers and literature reviews on genetic, feeding, and nutritional strategies for improving health, feed efficiency, and meat quality in growing rabbits. Innovative techniques for the determination of nutrients use efficiency have also been investigated.
2. Recent Advances in Rabbit Production in This Special Issue
The microbiota hosted in the gastrointestinal tract of the rabbit is involved in several crucial roles, including the regulation of digestive processes, stimulation of the immune response, and contrasts to biotic and abiotic stresses. According to the available information, the use of probiotics in growing rabbits can positively affect intestinal morphology, modulate the composition of gastrointestinal microbiota, and reduce mortality and morbidity rates [ 4 ]. Some benefits on growth performance and digestive and feed efficiency have also been reported. Studies on this topic are particularly relevant to provide socially and environmentally friendly alternatives to the use of antimicrobials and to improve profitability in rabbit production. However, further research efforts are required to develop suitable technologies for the dietary supplementation of probiotics that need to reach the target site of action to exert their beneficial effects [ 4 ].
In a recent study, dietary supplementation with lysozyme has been effective in enhancing rabbits’ growth, caecal fermentation, blood lipid profile, and antioxidant status [ 5 ]. Furthermore, alternative ingredients such as Moringa oleifera leaves have been tested in the diets of growing rabbits, with positive effects on growth, feed conversion ratio, antioxidant status, and meat fatty acids profile [ 6 ]. Testing alternative feedstocks is particularly important to sustain the expansion of the rabbit industry in developing countries where conventional raw materials are less available or not available at all. In addition, M. oleifera leaves are rich in essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that can improve the nutritional profile of rabbit meat [ 6 ].
The use of high-energy diets in the post-weaning period, provided that minimal insoluble fibre contents are guaranteed, has proven to be a viable strategy to improve feed conversion ratio and reduce feeding costs in rabbit production [ 7 ]. The use of fatty ingredients such as soybean oil is a common strategy to increase the digestible energy content of diets. Nonetheless, recent findings have shown that lard and palm kernel oil may be valuable alternative sources of fat as they have been associated with reduced mortality in growing rabbits [ 8 ]. An increase in dietary fat content can also be useful to improve nitrogen use efficiency and limit nitrogen excretion in growing rabbits [ 8 ]. Moreover, when diets are supplemented with essential amino acids according to the current recommendations, dietary crude protein levels can be reduced without affecting the growth and feed efficiency of high-producing fattening rabbits [ 7 ]. On the other hand, a low-quality protein (i.e., protein with an unbalanced amino acid profile) in the diet negatively affects productive and reproductive traits, and increases nitrogen excretion. Thus, the development of tools for an early detection of poor nutrients use efficiency is fundamental to improve the environmental sustainability of rabbit farms. Urea nitrogen seems to be an appropriate indicator of amino acid imbalance in monogastric animals, including rabbits [ 9 ]. Furthermore, bioelectrical impedance has been proposed as a non-invasive method to estimate in vivo carcass composition and to determine the nutrient retention and overall energy and nitrogen retention efficiencies of fattening rabbits [ 10 ]; however, more studies on these topics are required.
Genetic selection can be applied not only to optimize the growth performance and feed efficiency of growing rabbits but also to create lines with different meat attributes, such as fat lines to provide greater amounts of healthy fatty acids, and lean lines to provide lean meat for everyday consumption. A divergent selection for total body-fat content measured by computed tomography has been effective in creating two rabbit populations (fat and lean) for different production purposes [ 11 ]. This study will support the adoption of genetic selection programs aimed at diversifying rabbit production in terms of carcass and meat composition according to consumer demands.
3. Conclusions
The future of the rabbit sector depends on its capability to address the ongoing global challenges and offer safe, highly nutritional, and environmentally and ethically sustainable products at affordable prices. Each of the research topics published in this Special Issue has significantly contributed to increasing the state of knowledge on rabbit genetics, feeding, and nutrition, opening innovative routes that should be explored to enhance sustainability in rabbit production.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
who ResearchRabbit. "The best thing is that you don't have to go through all the struggle to figure out what words are required for your research and you can just sit back put a link of paper that you already have and start reading." - A Happy Rabbit. "Having papers suggested that are both earlier and later than those already on my list, as ...
Drilling down to individual papers from research rabbit. As you can see from the image above, as you drill down to Hazing & Alakangas (2017), ResearchRabbit will create a column to the right of ...
Based on those papers, ResearchRabbit generates a network of "recommended papers"! 🙌 3. If any recommended papers are relevant, add those to your project 4. ResearchRabbit then generates even better recommendations - like a "feedback loop"! 🤯 5. Finally, save your project 💾 so ResearchRabbit can send updates when relevant ...
Use Research Rabbit to plan your literature review outline!Check Out Research Rabbit: https://www.researchrabbit.ai/Get the Scientific Research paper Checkli...
Discover the 4 steps to using Research Rabbit to discover relevant papers without stress in less than 10 minutes!Get the 30-day Research Jumpstart Guide: htt...
Explore Research Rabbit, the premier AI tool for research, offering an effortless literature review experience. Dive into this tutorial review to discover it...
The most powerful discovery app ever built for researchers!
Research Rabbit creates citation maps as well as networks of recommended articles based on user provided collections of articles. You can get article and collaborator recommendations, set alerts, and share collections. User account required for use, but always free. Import collection from Zotero or build a new collection using Pubmed ID, DOI ...
Research Rabbit. Research Rabbit originally was known for its data visualizations which allow you to see connections between academic papers and authors. It has expanded its offerings to include a function that recommends papers based on your research interests and collaborative/sharing functions. You can upload papers and use DOIs and PMIDs to ...
It often feels like tumbling down the rabbit hole, as each relevant paper that is found opens up yet more avenues to explore and dig out the endless possibilities. Research Rabbit is a new literature mapping tool that helps with doing all this complex literature review in a seamless way and provide quick visualizations to help in exploring the ...
There is no additional charge to you. Timecodes 00:00 How to use research rabbit to outline your literature review 00:08 Create a Review Collection 01:25 Add specific papers to Collection 03:06 Expand Collection Using Network Analysis 05:24 Determine Literature Review Themes 07:18 Organizing Your Literature Review Outline
Research Rabbit Youtube channel; ResearchRabbit: Uplift Your Research Adventure Down the Rabbit Hole (HKUST Library, Dec 2021) ResearchRabbit is out of beta- my review of this new literature mapping tool (Aaron Tay, Aug 2021)
Good literature review involves the use of a combination of techniques such as keyword searching, using relevant papers as seeds to find more related papers by either looking at citations, references or works by relevant authors and to repeat iteratively until you have exhausted the possibilities. ... Research Rabbit reduces the friction of ...
The AI Research Assistant Elicit uses language models to help you automate research workflows, like parts of literature review. Elicit can find relevant papers without perfect keyword match, summarize takeaways from the paper specific to your question, and extract key information from the papers. While answering questions with research is the ...
This video will help you unravel the mysteries of Research Rabbit, a free tool designed to simplify and enhance the research process for academics, students,...
Research Rabbit can help you in the prewriting stage. The visualization features can give ideas on how to organize your literature review section in your research article. For example, if you would like to organize your literature review section in themes, you may
essay, minor project, or literature review. The concept is simple: you start by using one or more papers (called seed papers), and the app will find more papers relevant to the topic of interest (which is dictated by the seed pa pers you previously selected). The tool is designed to support your research without you switching between searching ...
Literature Review. Research Rabbit is a new and innovative tool designed to help students with their literature reviews for their dissertations. It is a free, web-based platform that provides interactive conceptual maps and streamlines the research process. This makes it easier for students to access and organize the vast amount of information ...
So, if real-time collaboration over a literature review is needed, SciSpace comes up short. Research Rabbit facilitates more lightweight sharing and coordination around the collection of research content. However, a structured comparative analysis is better achieved by exporting literature review workspaces. 6.
The Seed Maps and Discover features of Litmaps have transformed my literature review process, streamlining the identification of key citations while revealing previously overlooked relevant literature, ensuring no crucial connection goes unnoticed. A true game-changer indeed! Ritwik Pandey.
ResearchRabbit is a free online "citation-based literature mapping tool." It is a visual literature review software mapping tool that is similar to Spotify. The tool connects your research interests to related articles and authors. The tool allows users to create collections based on their research focus. You can start by looking up a title ...
#literaturereview #research #artificialintelligence
Temporomandibular disorders (TMDs) are a heterogeneous group of musculoskeletal and neuromuscular conditions involving the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), masticatory muscles, and associated structures. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as a promising therapy for TMJ repair. This systematic review aims to consolidate findings from the preclinical animal studies evaluating MSC ...
This Special Issue of Animals collects research papers and literature reviews on genetic, feeding, and nutritional strategies for improving health, feed efficiency, and meat quality in growing rabbits. Innovative techniques for the determination of nutrients use efficiency have also been investigated. Go to: 2.