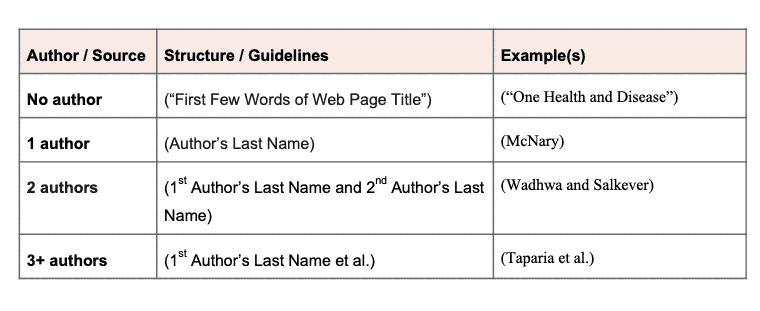
)

MLA citations when there is no author
Published October 22, 2020. Updated August 15, 2021.
Sometimes you may encounter a source that doesn’t have the author’s name listed. The MLA handbook provides different rules for such sources.
For help writing your essay, research paper , or other project, check out these writing tips .
MLA citation for sources that list no authors
When a source has no authors listed use the source’s title in the place of the author’s name. If the title of the source is long, you may use a shortened version.
The title should be italicized for longer works (books, plays, TV shows, etc.) or put in quotation marks for shorter works (articles, interviews, etc.). When in doubt, first figure out how the title is formatted in the works cited list citation (italicized or in quotations) and use that same formatting in the in-text citation.
For the works cited list, you can start the reference with the title of the source when the author’s name is not listed.
Books with no authors listed
In-text citation format and example:
( Title of the book page number)
( Norse Tales of Legends 22)
Works cited list citation template and example:
Title of the book: Subtitle . Publisher, Year.
Norse Tales of Legends , Gods, and Heroes . Longmeadow Press, 1996.
Webpages/websites with no authors listed
In the case of webpages that don’t have any author’s name listed, use the title of the webpage. Place the title in quotation marks and format it in title case. Since it is a webpage and no page numbers are available, no page numbers need to be included with direct quotes.
In-text citation template and example:
(“ Shortened Webpage Title”).
The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models (“5 Things”).
“Title of Web Page.” Title of Website , Publisher, Date published in Day Month Year format, URL.
“5 Things to Know About the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich Mission.” Global Climate Change, California Institute of Technology, 2 Oct. 2020, climate.nasa.gov/news/3028/5-things-to-know-about-the-sentinel-6-michael-freilich-mission/.
Citing works created by a corporate author/organization
It is not necessary that authors must be individual persons. You may also be required to cite works created by a company, government agency, or any kind of organization. In such cases, the entity is listed as the author in the citation.
(Name of the organization page number if available)
(United Nations Children’s Fund)
Name of the organization. Title of the Document. Publisher or Sponsoring Organization, Date of publication or modification date, URL .
United Nations Children’s Fund. Convention on the Rights of the Child Text. UNICEF, 18 Nov. 2002, www.unicef.org/child-rights-convention/convention-text.
However, you may also come across cases where the corporate/organization author and the publisher of the work are the same entity. In such cases, the ‘author’s name’ is skipped, and the entity is listed as the publisher of the work.
The Effects of Ticket Pricing on Arts Attendance Patterns: An Economics Literature Review (2000-2018). National Endowment for the Arts, September 2020.
It is important that you carefully look through the document/source before using the no-author format for citations. You must also give due credit to authors whenever they are listed in the source.
MLA Style Guides
MLA Format: Annotated bibliography | Abstract | Block Quote | Headings | MLA 8 vs. 9 | Outline | Page Numbers | Sample paper | Title page
Citing Sources: In-text citations | Works cited | Footnotes | Citing Multiple Authors | Citing Sources with No Authors | Using et al
MLA Citation Generator: Article | Book | Image | Interview | Journal | Movie | PDF | Textbook | Website | YouTube
Published July 14, 2021.

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation

Thursday, February 23: The Clark Library is closed today.
MLA Style (9th Edition) Citation Guide: Websites
- Introduction to MLA Style
- Journal Articles
- Magazine/Newspaper Articles
- Books & Ebooks
- Government & Legal Documents
- Biblical Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Videos/DVDs/TV Shows
- How to Cite: Other
- 9th Edition Updates
- Additional Help
Table of Contents
Entire website - no separate pages or sections, page or section from a website.
Note: For your Works Cited list, all citations should be double spaced and have a hanging indent.
A "hanging indent" means that each subsequent line after the first line of your citation should be indented by 0.5 inches.
It can sometimes be difficult to find out who the author of a website is. Remember that an author can be a corporation or group, not only a specific person. Author information can sometimes be found under an "About" section on a website.
If there is no known author, start the citation with the title of the website instead.
The best date to use for a website is the date that the content was last updated. Otherwise look for a copyright or original publication date. Unfortunately this information may not be provided or may be hard to find. Often date information is put on the bottom of the pages of a website.
If you do not know the complete date, put as much information as you can find. For example you may have a year but no month or day. If the source does not include a copyright/last modified date, then omit the date and include an access date in your citation instead.
Access Date
Date of access is optional in MLA 8th/9th edition; it is recommended for pages that may change frequently or that do not have a copyright/publication date.
In your works cited list, abbreviate months as follows:
January = Jan. February = Feb. March = Mar. April = Apr. May = May June = June July = July August = Aug. September = Sept. October = Oct. November = Nov. December = Dec.
Spell out months fully in the body of your paper.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed access date.
Works Cited List Example:
Mabillard, Amanda. Shakespeare Online, 29 Dec. 2011, www.shakespeare-online.com. Accessed 6 July 2016.
In-Text Citation Example:
(Author's Last Name)
(Mabillard)
Note: In this example, the name of the organization affiliated with the website is omitted since it is the same as the website title.
Created by an Unknown Author, or the Author is the same as the Website Title/Publisher
"Title of Section." Title of Website, Publisher or Sponsoring Organization, Date of publication or last modified date, URL. Accessed Date Month (abbreviated) Year.
Note: The publisher or sponsoring organization can often be found in a copyright notice at the bottom of the home page or on a page that gives information about the site . If the website publisher is the same as the author and title of the web site , then include only the title of the web site.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview.” WebMD, 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
("Title of Section")
(“Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview”)
Created by a Known Author
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Page or Document." Title of Website, Publisher or Sponsoring Organization, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Date Month (abbreviated) Year.
Morin, Amy. "How to Prevent the Media From Damaging Your Teen's Body Image." Verywell Family, About Inc., 6 Oct. 2019, www.verywellfamily.com/media-and-teens-body-image-2611245. Accessed 1 Nov. 2019.
- << Previous: Government & Legal Documents
- Next: Biblical Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jun 28, 2024 12:34 PM
- URL: https://libguides.up.edu/mla

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): No Author, No Date etc.
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- In-Text Citation
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On this Page
What to do when information is missing, no page numbers, no database name, how to alphabetize titles in works cited list.
If there is no author given, your citation will start with the title of the work. You must put these citations in correct alphabetical order in your Works Cited list.
When putting works in alphabetical order, ignore initial articles such as "the", "a", or "an". For example the title The Best of Canada would be alphabetized as if it started with the word Best instead of the word The.
If the title begins with a number, alphabetize it as if the number was spelled out. For example the title 5 Ways to Succeed in Business would be alphabetized under F as if it had started with the word Five .
For example, this is how the following titles would be alphabetized:
Anthropology in Action [A] The Best of Canada [B... ignore "The"] Easy Plant Care [E] 5 Ways to Succeed in Business [F... 5=Five] A Special Kind of Madness [S... ignore "A"]
If no author or creator is provided, start the citation with the title of the source you are citing instead. Do not use "Anonymous" as the author's name. Use the first one, two, or three main words from the title, in either italics or in "quotation marks" (the same way it is written in your Works Cited list). You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your Works Cited list.
"How to Teach Yourself Guitar." eHow, Demand Media, www.ehow.com/how_5298173_teach-yourself-guitar.html. Accessed 24 June 2016.
In-text citation would be ("How to Teach")
Note : An author/creator won't necessarily be a person's name. It may be an organization or corporation, for example Health Canada or a username on a site such as YouTube. Also, it is possible for the author's name to be written as only initials. If the author is known only by initials, treat the initials as one unit. Use the initials in your in-text citation and list the entry under the first initial in your Works Cited page.
If no date is provided, skip that information in your citation. It is recommended that you add the date you accessed the work at the end of the citation in your Works Cited list. Access date is given by putting the word "Accessed" followed by the date you viewed or accessed the work (format = Day Month (shortened) Year).
Example:
"Audit and Assurance." Chartered Professional Accountants Canada , www.cpacanada.ca/en/business-and-accounting-resources/audit-and-assurance. Accessed 6 Sept. 2019.
Some sources, such as online materials, won't have page numbers provided. If this is the case, leave the page numbers out of the citation. For your in-text citation, just use the author's name or the title of the work if there is no author given. For your Works Cited list, just leave the page number part out.
Williamson, Jennifer. "Canada: Business: Attire." Global Road Warrior, World Trade Press, 2018, www.globalroadwarrior/com/#mode=country®ionId=27&uri=country-content&nid=13.08&key=country-attire. Accessed 17 July 2016.
In-text citation would be (Williamson)
Note If there are no page, chapter, paragraph, or section numbers in the original text, then don't include any. Never count pages or paragraphs yourself .
If you find an article through the search bar on the main library page, you might be unsure which database the article is from, because this searches across many different databases.
You can find the name of the database a few ways:
Method 1. Click on the title of the article in the search results list. This will bring you to a page with a description of the article as well as other useful information. Scroll down to the bottom of this list of information, and you should see "Database" listed near the bottom.
Method 2. You can also find the name of the database in the summary of information just below the title of the article in the search results list. It will look something like this:
| A Cross-National Study of Evolutionary Origins of Gender Shopping Styles: She Gatherer, He Hunter? By: Dennis, Charles; Brakus, J. Joško; Ferrer, Gemma García; McIntyre, Charles; Alamanos, Eleftherios; King, Tamira. Journal of International Marketing. Dec2018, Vol. 26 Issue 4, p38-53. 16p. 1 Diagram, 3 Charts. DOI: 10.1177/1069031X18805505. , Database: Business Source Complete |
Notice the name of the database is listed at the end.
- << Previous: Works Quoted in Another Source
- Next: Works Cited List & Sample Paper >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9
MLA 8 Citation Guide
- TITLE of SOURCE
- TITLE of CONTAINER
- OTHER CONTRIBUTORS
- PUBLICATION DATE
- Works Cited
- Journal Article with One Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3 or more Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three or More Authors
- Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- Reference Work
- Basic Web Page
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government or Agency Document
- YouTube Video
- Electronic Image
- Figures and Charts
- Class Lecture/Notes
- Secondary Sources
Ask Us 24/7

Online help is available anytime via our AskUs 24/7 chat service:
Document from a web site with no author
Name of Organization Title of Web Document. Title of Website, Date if given , URL of specific document . Access date if advisable.
People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals. Animals Used for Food. PETA , 2008 , www.peta.org/issues/animals-used-for-food/
(Name of organization, Page or paragraph number if available)
( People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals )
----------------------------------------------------------------
If, however, there is no specific organization responsible for the web site's content , follow this format:
Title or Appropriate Title of Specific Document . Title of Website, Date if given , URL of the Site. Accessed date as appropriate.
Osteoarthritis Overview . eMedicineHealth.com, 2017, www.emedicinehealth.com/osteoarthritis/article_em.htm#osteoarthritis_overview. Accessed 2 March 2018.
("Title of Specific Document" page or paragraph number if available)
("Osteoarthritis overview")
- When citing sources that you find on the Internet you only need to include a accessdate if the information you use is likely to change over time
- Sometimes websites are missing pieces of information that you would typically use when citing them, like an author or a date. In that case, just adjust citation
Citing Web Resources
Purdue Owl the the Web

- << Previous: Basic Web Page
- Next: Blog post >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 1:47 PM
- URL: https://utica.libguides.com/mla
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Website Citation
How to Cite a Website in MLA
If you are a student faced with creating an MLA website citation for the first time, you may be confused about where to begin. This guide is here to answer all of your questions and take the guesswork out of creating an MLA citation for websites.
All academic fields require students and researchers to document their sources. Those studying the humanities, including fields in language literature, will typically follow MLA format when structuring their papers as well as when documenting sources.
Citing your sources is a necessary part of any research paper or project. This element serves both to give credit to the researchers and authors whose work informed yours, as well as to preserve academic integrity. Any source that provided you with ideas or information that you have included in your work and which are not considered common knowledge must be included, including websites.
The Modern Language Association is not associated with this guide. All of the information, however, is based on the MLA Handbook, Ninth Edition as well as the MLA website, and is presented as guidance for students writing in this style.
If you are looking for help with APA format , our reference library can provide you with guidance for this and more styles .
What You Need
To cite a website, you should have the following information:
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication date,
- Location of the source (such as DOI, URL, or page range).
The Modern Language Association refers to these guidelines as “core elements” on page 105 of the Handbook. If your teacher has asked you to cite your sources in this format, these elements will form the foundation for each MLA website citation included in your MLA Works Cited list, as well as the entries for sources in any other format.
If one of the elements does not apply, students may omit it. Supplemental items may also be included when necessary. In addition to the supplemental details discussed below, a list of additional supplemental components can be found on the MLA website.
If it’s an APA citation website page or an APA reference page you need help with, we have many other resources available for you!
Table of Contents
This guide includes the following sections:
- MLA9 Changes
- Citing websites with an author
- Citing websites with no author
- Citing websites with no formal title
- Citing social media websites
- In-text citations
Changes to MLA Citation for Websites in Ninth Edition
In previous editions, students and researchers creating an MLA website citation were not required to include the URL. However, beginning with MLA 8, it is recommended that you include the URL when creating a citation for a website unless your teacher instructs you otherwise. Even though web pages and URLs can be taken down or changed, it is still possible to learn about the source from the information seen in the URL.
When including URLs in a citation, http:// and https:// should be omitted from the website’s address ( Handbook 195). Additionally, If you are creating a citation that will be read on a digital device, it is helpful to make the URL clickable so that readers can directly access the source themselves.
If the website’s publisher includes a permalink or DOI (Digital Object Identifier), these are preferable as they are not changeable in the same manner as URLs. Whether you include a URL, permalink, or DOI, this information should be included in the location portion of your citation.
Another change that occurred with the eighth edition that impacts how to cite a website in MLA is the removal of the date the website was accessed. While you may still find it useful to include this information or your teacher may request it, it is no longer a mandatory piece of your citation. Should you choose to add this optional information, you may list it after the URL in the following manner:
- Accessed Day Month Year.
- Accessed 2 May 1998.
- Accessed 31 Apr. 2001.
- Accessed 17 Sept. 2010.
For an overview of additional formatting changes in the ninth edition, including resources to help with writing an annotated bibliography , check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s writing and citation guides, and try out our plagiarism checker for help with grammar and to avoid unintentional plagiarism.
MLA 9: Citing Websites With an Author
To make an MLA 9 citation for a website, you will need the following pieces of information:
- author’s name
- title of the article or page
- title of the website
- name of the publisher (Note: Only include the name of the publisher when it differs from the name of the website.)
- date the page or site was published (if available)
Citing a Website in MLA
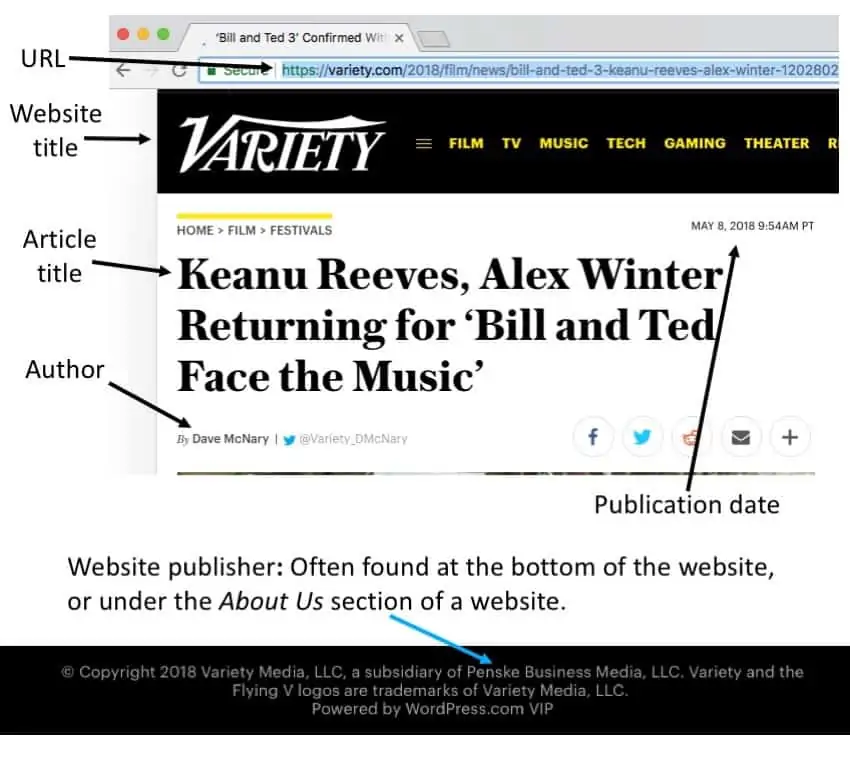
Place the author’s name in reverse order, the last name first, followed by a comma, and then the first name followed by a period. The title of the web page or article is placed in quotation marks, with a period before the end quotation. The title of the website is written in italics followed by a comma. If the name of the publisher differs from the name of the website, include it after the title. Immediately following the publisher is the date that the page or article was published or posted. Finally, end with the URL, permalink, or DOI, followed by a period.
| Works Cited | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of the Article or Individual Page.” , Name of the Publisher, date of publication in day month year format, URL. |
| Example | McNary, Dave. “Keanu Reeves, Alex Winter Returning for ‘Bill and Ted Face the Music.’” , Penske Media Corporation, 8 May 2018, variety.com/2018/film/news/bill-and-ted-3-keanu-reeves-alex-winter-1202802946/. |
View Screenshot | Cite your source
In-text website citation with one author
The in-text citation for a website with an author is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author’s Last Name). |
| Example | (McNary). |
Cite your source
An APA parenthetical citation is similar, except it also includes the year the source was published.
To learn more about formatting MLA in-text & parenthetical citations , be sure to check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s resources and citation guides.
How to cite a website with two authors in MLA 9
According to Section 5.7 of the Handbook , for a website with two authors, place the authors’ names in the same order as the source (similar to an APA citation ). The first name should be formatted in reverse order as was done for a single author. The second name, however, is written as First Name Last Name and is followed by a period, as demonstrated in the template that follows:
| Works Cited | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Last name, First name of Author 1, and First Name Last Name of Author 2. “Title of Web Page.” , Publisher, date published in day month year format, URL. |
| Example | Wadhwa, Vivek, and Alex Salkever. “How Can We Make Technology Healthier for Humans?” , Condé Nast, 26 June 2018, www.wired.com/story/healther-technology-for-humans/. |
In-text website citation with two authors
The in-text citation for a website with two authors should include both authors’ last names, in the order in which they are listed in the source and your works cited:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author #1 and Author #2). |
| Example | (Wadhwa and Salkever). |
How to cite a website with three or more authors in MLA 9
For a source with three or more authors, you should place the authors’ names in the same order as the source. The first name is listed in reverse order and is followed by a comma and et al. Et al is the abbreviation for et alia, a gender-neutral Latin phrase meaning “and others.”
| Works Cited | |
|---|---|
| Structure | First listed author’s Last name, First name, et al. “Title of Web Page.” , Publisher, date published in day month year format, DOI or URL. |
| Example | Marsh, Joanne, et al. “Generating Research Income: Library Involvement in Academic Research.” , vol. 36, no. 113, 18 Dec. 2012, pp. 48-61, https:doi.org/10.29173/lirg539 |
In-text website citation with 3+ authors
The in-text citation for a website with three or more authors should contain only the first author’s last name, followed by et al. ( Handbook 232):
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Last Name 1 et al.). |
| Example | (Marsh et al.). |
Click on this page if you’re looking for information on how to create an APA in-text citation .
MLA 9 Citation for Websites with No Author
Sometimes, websites do not state who wrote the information on the page. When no author is listed, you may omit the author information from the MLA citation for the website and begin, instead, with the title ( Handbook 108).
| Works Cited | |
|---|---|
| Structure | “Title of Web Page.” , Publisher, date published in day month year format, URL. |
| Example | “One Health and Disease: Tick-Borne.” , U.S. Department of the Interior, www.nps.gov/articles/one-health-disease-ticks-borne.htm. |
Note about web pages by organizations/corporations: Often, web pages are published by organizations or corporations with no author indicated. In these cases, you can assume that the publisher also authored the web page (like the example above). Since the author and publisher are the same in these cases, you can skip showing an author and just indicate the organization /corporation as the publisher ( Handbook 119 ).
In-text website citation with no author
The in-text citation for a website without an author is noted with the first noun phrase or words in the title in quotations and parenthesis, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Title of Web Page). |
| Example | (“One Health and Disease”). |
MLA 9 Citation for Websites Without a Formal Title
When citing a web page that does not include a formal title, it is acceptable to include a description of the page. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks. Follow the description with the name of the website.
| Works Cited | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Description of web page. , Publisher, date published in day month year format, URL. |
| Example | General Information on the New York Mets. , The Weissman Center for International Business Baruch College/CUNY, www.baruch.cuny.edu/nycdata/sports/nymets.htm. |
In-text website citation without a title
The in-text citation for a website without a formal title uses a shortened version of the webpage description for the in-text citation. Use the first noun phrase of the description from your Works Cited citation in parenthesis, followed by a period. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Shortened Description of Webpage). |
| Example | (General Information). |
MLA 9 Citation for Social Media Websites
In an increasingly digital world, social media platforms have become one of the most popular sources students turn to when writing a research paper. From Black history facts , to quotes from notable people, such as Martin Luther King and Winston Churchill , social media has become a mega influence in our world.
When citing social media in your work, follow the same format as an MLA citation for a website. Here are some examples of ways you can cite various social media platforms in your work:
How to cite Twitter in MLA 9
Many notable individuals use Twitter as a platform to share intriguing ideas. It’s a shame Twitter was unavailable to long-gone scientists, authors, and presidents such as Albert Einstein , Mark Twain , and Abraham Lincoln . Luckily, we have the Twitter profiles of today’s great minds at our fingertips!
To cite a tweet, you will begin with the account holder’s name and their Twitter handle in square brackets, followed by a period ( Handbook 118). After this, in quotations, you should enter the full text of the tweet, including any hashtags. The publisher, Twitter, is then listed in italics, followed by the date the tweet was posted in day, month, year format. Finally, include a URL to the tweet followed by a period.
| Reference List | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Last name, First name [Username]. “Tweet Message.” date posted, URL. |
| Example | Miranda, Lin-Manuel [@Lin_Manuel]. “Gmorning from a sky still blue above the smoke from a world still full of love and hope beyond the headlines from your own best self, whispering, ‘I’m still here, and it’s never too late to put me to work.’” , 22 June 2018, twitter.com/Lin_Manuel/status/1010165965378719745. |
Note: When the account name and username are similar, the username can be excluded from the citation. For example, if the account’s username was @FirstNameLastName or @OrganizationName.
In-text website citation of a Twitter post
The in-text citation for a Twitter post is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the tweet used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author’s Last Name). |
| Example | (Miranda). |
How to cite Instagram in MLA 9
To cite an Instagram post, begin with the account holder’s name and their username in square brackets. In quotations, list the title of the photo, if it is given. If there is no title, write a brief description of the picture but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. The publisher, Instagram, is then listed in italics. Any other contributors (such as the photographer, if it is not the same as the account holder) are then listed, after which you will add the date the photo was published and the URL.
| Reference List | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Account holder’s Last name, First name [Username]. “Photo Title” or Description. , other contributors, date photo was published, URL. |
| Example | National Geographic [@natgeo]. “Path of the Panther.” , photographed by Carlton Ward, 16 June 2018, www.instagram.com/p/BkFfT9xD6h6/?taken-by=natgeo. |
In-text website citation of an Instagram post
The in-text citation for an Instagram post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Instagram post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author’s Last Name OR Name of Account). |
| Example | (National Geographic). |
How to cite Facebook in MLA 9
To cite a Facebook post, begin with the account holder’s name or username. In quotations, list the title or caption of the post, if it is given. If there is no title or caption, write a brief description of the post, but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. Examples: Image of Malcolm X, or, Muhammed Ali headshot.
The publisher, Facebook, is then listed in italics, after which you will add the date posted and URL.
| Reference List | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Author Last Name, First Name or Account Name. “Title or Caption of the Post” or Description of Post. , day month year of post, URL. |
| Example | GoatsofAnarchy. Loner goats become stallmates and fall in love. , 25 June 2018, www.facebook.com/thegoatsofanarchy/posts/2103455423030332:0. |
In-text website citation of a Facebook post
The in-text citation for a Facebook post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Facebook post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author’s Last Name OR Name of Account). |
| Example | (GoatsofAnarchy). |
Social media and website comments
Citing the comments left on social media or a website begins with the commenter’s name or username. To indicate that you are citing a comment, follow the name with a period and then the words Comment on , followed by the title of the source (for example, the name of the article) in quotation marks. This is then followed by the title of the website in italics, and the publisher, if applicable. The date is then listed, followed by the URL, permalink, or DOI.
| Reference List | |
|---|---|
| Structure | Commenter’s Last Name, First Name or Username. Comment on “Title.” , day month year, URL. |
| Example | Wester, Gary. Comment on “Climate Reality and I are headed to Berlin this June to train leaders who want to help solve the climate crisis.” , 2 May 2018, www.facebook.com/algore/posts/10155643818533865:0. |
In-text citation of a social media comment
The in-text citation for a social media comment is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
| In-text Citation | |
|---|---|
| Structure | (Author’s Last Name). |
| Example | (Wester). |
In-text Citations for Websites
In-text citations generally consist of parentheses and the last names of the authors or the first few words of the web page title.
Since there are no page numbers, unless the web page includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you don’t need to include any additional information.
When you have multiple authors, place them in the same order they are listed in the source.
If what you really need is an APA book citation or a reference for an APA journal , there are more guides on EasyBib.com for you to explore.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Troubleshooting
Solution #1: when and how to reference entire websites versus specific pages in mla.
Reference an entire website when your information comes from multiple pages or if you are describing the entirety of the website. If your information is only from one page, only cite the singular page.
Whole website, author known
- Write the author’s name in last name, first name format with a period following.
- Next, write the name of the website in italics.
- Write the contributing organization’s name with a comma following.
- List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following.
- Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
Works cited example:
Night, Samuel. Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
In-text example:
Whole website, author unknown
- If there is no specific author, begin the citation by writing the website name in italics.
Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
( Food Creations )
Webpage, author known
If information is from only a few pages or the pages cover multiple topics, reference each page
- If an author is named, write the author’s name in last name, first name format.
- If a title is not provided, create your own description of the page.
- List the title of the website in italics with a comma following.
- Write the date that the page was created followed by a comma.
- Lastly, list the URL followed by a period.
Blake, Evan. “Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
Webpage, author unknown
If an author is not named, write the name of the page in quotation marks with a period following.
“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
(“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe”)
Solution #2: Referencing a conversation on social media in MLA
The in-text citation should identify the author and talk about the format (e.g., video, post, image, etc.) in prose.
Lilly West’s photo of traditional Japanese sweets shows an example of nature influencing Japanese design.
The basic structure of a works-cited reference for social media stays the same no matter the format or the social media service (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.). Here are works- cited-list entry guidelines:
- The name is listed in last name, first name format with a period following. If an organization, just write the organization’s name as it’s usually presented.
- If the username is very different from the author’s real name, include it in brackets after the user’s real name but before the period.
- Write the title, post text, or description of the post in quotation marks. End it with a period.
- Write the website name in italics with a comma afterward.
- List the day, month, and year that the post was created followed by a comma.
- List the URL followed by a period. Leave out “https://” and “http://”.
Facebook example:
West, Lily. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Facebook , 30 May 2021, www.facebook.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Twitter reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Twitter, 30 May 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Instagram reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Instagram , 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #3: How to cite a social media post without a title or text
If there is no text or title where the title element usually goes, instead describe the post without quotation marks. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. Photo of traditional Japanese sweets on a green plate. Instagram , photographed by Bethany Lynn, 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #4: How to cite a social media post with a long title or text
If the text is very long, you can shorten it by adding ellipsis at the end of the text. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Nothing is better in life than feeling like all of the effort you’ve invested has finally. . . .” Twitter, 17 Feb. 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
- Works Cited
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated June 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
It’s 100% free to create MLA citations. The EasyBib Citation Generator also supports 7,000+ other citation styles. These other styles—including APA, Chicago, and Harvard—are accessible for anyone with an EasyBib Plus subscription.
No matter what citation style you’re using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.), the EasyBib Citation Generator can help you create the right bibliography quickly.
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Creating an account is not a requirement for generating MLA citations. However, registering for an EasyBib account is free, and an account is how you can save all the citations you create. This can help make it easier to manage your citations and bibliographies.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
It supports MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and over 7,000 total citation styles.
If there is no author, the title becomes the website page’s identifier.
In-text example (no author): ( Honey Bee Medley )
Works cited example (no author): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, 2018, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees.
If there is no publication date, include an accessed date instead.
Works cited example (no author, no date): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
If there is no title, briefly describe the source.
Works cited example (no author, no date, no title): Collage of honey bees. Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
To cite a website that has no page number in MLA, it is important that you know the name of the author, title of the webpage, website, and URL. The templates for an in-text citation and works-cited-list entry of a website that has no page number, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
You can use a time stamp if you are referring to an audio or video. Otherwise, use only the author’s surname.
(Author Surname)
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
Author or Organization Name. “Title of the Webpage.” Website Name . Publication Date, URL.
Dutta, Smita S. “What is Extra Sensory Perception?” Medindia . 16 Nov. 2019, www.medindia.net/patients/patientinfo/extra-sensory-perception.htm#3 .
Abbreviate the month in the date field.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 8 & MLA 9 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, the complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.
What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.
How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
For tables:
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.

Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Guidelines for referring to the works of others in your text using MLA style are covered throughout the MLA Handbook and in chapter 7 of the MLA Style Manual . Both books provide extensive examples, so it's a good idea to consult them if you want to become even more familiar with MLA guidelines or if you have a particular reference question.
Basic in-text citation rules
In MLA Style, referring to the works of others in your text is done using parenthetical citations . This method involves providing relevant source information in parentheses whenever a sentence uses a quotation or paraphrase. Usually, the simplest way to do this is to put all of the source information in parentheses at the end of the sentence (i.e., just before the period). However, as the examples below will illustrate, there are situations where it makes sense to put the parenthetical elsewhere in the sentence, or even to leave information out.
General Guidelines
- The source information required in a parenthetical citation depends (1) upon the source medium (e.g. print, web, DVD) and (2) upon the source’s entry on the Works Cited page.
- Any source information that you provide in-text must correspond to the source information on the Works Cited page. More specifically, whatever signal word or phrase you provide to your readers in the text must be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of the corresponding entry on the Works Cited page.
In-text citations: Author-page style
MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number(s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the sentence itself or in parentheses following the quotation or paraphrase, but the page number(s) should always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence. For example:
Both citations in the examples above, (263) and (Wordsworth 263), tell readers that the information in the sentence can be located on page 263 of a work by an author named Wordsworth. If readers want more information about this source, they can turn to the Works Cited page, where, under the name of Wordsworth, they would find the following information:
Wordsworth, William. Lyrical Ballads . Oxford UP, 1967.
In-text citations for print sources with known author
For print sources like books, magazines, scholarly journal articles, and newspapers, provide a signal word or phrase (usually the author’s last name) and a page number. If you provide the signal word/phrase in the sentence, you do not need to include it in the parenthetical citation.
These examples must correspond to an entry that begins with Burke, which will be the first thing that appears on the left-hand margin of an entry on the Works Cited page:
Burke, Kenneth. Language as Symbolic Action: Essays on Life, Literature, and Method . University of California Press, 1966.
In-text citations for print sources by a corporate author
When a source has a corporate author, it is acceptable to use the name of the corporation followed by the page number for the in-text citation. You should also use abbreviations (e.g., nat'l for national) where appropriate, so as to avoid interrupting the flow of reading with overly long parenthetical citations.
In-text citations for sources with non-standard labeling systems
If a source uses a labeling or numbering system other than page numbers, such as a script or poetry, precede the citation with said label. When citing a poem, for instance, the parenthetical would begin with the word “line”, and then the line number or range. For example, the examination of William Blake’s poem “The Tyger” would be cited as such:
The speaker makes an ardent call for the exploration of the connection between the violence of nature and the divinity of creation. “In what distant deeps or skies. / Burnt the fire of thine eyes," they ask in reference to the tiger as they attempt to reconcile their intimidation with their relationship to creationism (lines 5-6).
Longer labels, such as chapters (ch.) and scenes (sc.), should be abbreviated.
In-text citations for print sources with no known author
When a source has no known author, use a shortened title of the work instead of an author name, following these guidelines.
Place the title in quotation marks if it's a short work (such as an article) or italicize it if it's a longer work (e.g. plays, books, television shows, entire Web sites) and provide a page number if it is available.
Titles longer than a standard noun phrase should be shortened into a noun phrase by excluding articles. For example, To the Lighthouse would be shortened to Lighthouse .
If the title cannot be easily shortened into a noun phrase, the title should be cut after the first clause, phrase, or punctuation:
In this example, since the reader does not know the author of the article, an abbreviated title appears in the parenthetical citation, and the full title of the article appears first at the left-hand margin of its respective entry on the Works Cited page. Thus, the writer includes the title in quotation marks as the signal phrase in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader directly to the source on the Works Cited page. The Works Cited entry appears as follows:
"The Impact of Global Warming in North America." Global Warming: Early Signs . 1999. www.climatehotmap.org/. Accessed 23 Mar. 2009.
If the title of the work begins with a quotation mark, such as a title that refers to another work, that quote or quoted title can be used as the shortened title. The single quotation marks must be included in the parenthetical, rather than the double quotation.
Parenthetical citations and Works Cited pages, used in conjunction, allow readers to know which sources you consulted in writing your essay, so that they can either verify your interpretation of the sources or use them in their own scholarly work.
Author-page citation for classic and literary works with multiple editions
Page numbers are always required, but additional citation information can help literary scholars, who may have a different edition of a classic work, like Marx and Engels's The Communist Manifesto . In such cases, give the page number of your edition (making sure the edition is listed in your Works Cited page, of course) followed by a semicolon, and then the appropriate abbreviations for volume (vol.), book (bk.), part (pt.), chapter (ch.), section (sec.), or paragraph (par.). For example:
Author-page citation for works in an anthology, periodical, or collection
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write something like this:
See also our page on documenting periodicals in the Works Cited .
Citing authors with same last names
Sometimes more information is necessary to identify the source from which a quotation is taken. For instance, if two or more authors have the same last name, provide both authors' first initials (or even the authors' full name if different authors share initials) in your citation. For example:
Citing a work by multiple authors
For a source with two authors, list the authors’ last names in the text or in the parenthetical citation:
Corresponding Works Cited entry:
Best, David, and Sharon Marcus. “Surface Reading: An Introduction.” Representations , vol. 108, no. 1, Fall 2009, pp. 1-21. JSTOR, doi:10.1525/rep.2009.108.1.1
For a source with three or more authors, list only the first author’s last name, and replace the additional names with et al.
Franck, Caroline, et al. “Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic.” American Journal of Preventative Medicine , vol. 45, no. 3, Sept. 2013, pp. 327-333.
Citing multiple works by the same author
If you cite more than one work by an author, include a shortened title for the particular work from which you are quoting to distinguish it from the others. Put short titles of books in italics and short titles of articles in quotation marks.
Citing two articles by the same author :
Citing two books by the same author :
Additionally, if the author's name is not mentioned in the sentence, format your citation with the author's name followed by a comma, followed by a shortened title of the work, and, when appropriate, the page number(s):
Citing multivolume works
If you cite from different volumes of a multivolume work, always include the volume number followed by a colon. Put a space after the colon, then provide the page number(s). (If you only cite from one volume, provide only the page number in parentheses.)
Citing the Bible
In your first parenthetical citation, you want to make clear which Bible you're using (and underline or italicize the title), as each version varies in its translation, followed by book (do not italicize or underline), chapter, and verse. For example:
If future references employ the same edition of the Bible you’re using, list only the book, chapter, and verse in the parenthetical citation:
John of Patmos echoes this passage when describing his vision (Rev. 4.6-8).
Citing indirect sources
Sometimes you may have to use an indirect source. An indirect source is a source cited within another source. For such indirect quotations, use "qtd. in" to indicate the source you actually consulted. For example:
Note that, in most cases, a responsible researcher will attempt to find the original source, rather than citing an indirect source.
Citing transcripts, plays, or screenplays
Sources that take the form of a dialogue involving two or more participants have special guidelines for their quotation and citation. Each line of dialogue should begin with the speaker's name written in all capitals and indented half an inch. A period follows the name (e.g., JAMES.) . After the period, write the dialogue. Each successive line after the first should receive an additional indentation. When another person begins speaking, start a new line with that person's name indented only half an inch. Repeat this pattern each time the speaker changes. You can include stage directions in the quote if they appear in the original source.
Conclude with a parenthetical that explains where to find the excerpt in the source. Usually, the author and title of the source can be given in a signal phrase before quoting the excerpt, so the concluding parenthetical will often just contain location information like page numbers or act/scene indicators.
Here is an example from O'Neill's The Iceman Cometh.
WILLIE. (Pleadingly) Give me a drink, Rocky. Harry said it was all right. God, I need a drink.
ROCKY. Den grab it. It's right under your nose.
WILLIE. (Avidly) Thanks. (He takes the bottle with both twitching hands and tilts it to his lips and gulps down the whiskey in big swallows.) (1.1)
Citing non-print or sources from the Internet
With more and more scholarly work published on the Internet, you may have to cite sources you found in digital environments. While many sources on the Internet should not be used for scholarly work (reference the OWL's Evaluating Sources of Information resource), some Web sources are perfectly acceptable for research. When creating in-text citations for electronic, film, or Internet sources, remember that your citation must reference the source on your Works Cited page.
Sometimes writers are confused with how to craft parenthetical citations for electronic sources because of the absence of page numbers. However, these sorts of entries often do not require a page number in the parenthetical citation. For electronic and Internet sources, follow the following guidelines:
- Include in the text the first item that appears in the Work Cited entry that corresponds to the citation (e.g. author name, article name, website name, film name).
- Do not provide paragraph numbers or page numbers based on your Web browser’s print preview function.
- Unless you must list the Web site name in the signal phrase in order to get the reader to the appropriate entry, do not include URLs in-text. Only provide partial URLs such as when the name of the site includes, for example, a domain name, like CNN.com or Forbes.com, as opposed to writing out http://www.cnn.com or http://www.forbes.com.
Miscellaneous non-print sources
Two types of non-print sources you may encounter are films and lectures/presentations:
In the two examples above “Herzog” (a film’s director) and “Yates” (a presentor) lead the reader to the first item in each citation’s respective entry on the Works Cited page:
Herzog, Werner, dir. Fitzcarraldo . Perf. Klaus Kinski. Filmverlag der Autoren, 1982.
Yates, Jane. "Invention in Rhetoric and Composition." Gaps Addressed: Future Work in Rhetoric and Composition, CCCC, Palmer House Hilton, 2002. Address.
Electronic sources
Electronic sources may include web pages and online news or magazine articles:
In the first example (an online magazine article), the writer has chosen not to include the author name in-text; however, two entries from the same author appear in the Works Cited. Thus, the writer includes both the author’s last name and the article title in the parenthetical citation in order to lead the reader to the appropriate entry on the Works Cited page (see below).
In the second example (a web page), a parenthetical citation is not necessary because the page does not list an author, and the title of the article, “MLA Formatting and Style Guide,” is used as a signal phrase within the sentence. If the title of the article was not named in the sentence, an abbreviated version would appear in a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence. Both corresponding Works Cited entries are as follows:
Taylor, Rumsey. "Fitzcarraldo." Slant , 13 Jun. 2003, www.slantmagazine.com/film/review/fitzcarraldo/. Accessed 29 Sep. 2009.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL , 2 Aug. 2016, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/01/. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Multiple citations
To cite multiple sources in the same parenthetical reference, separate the citations by a semi-colon:
Time-based media sources
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
When a citation is not needed
Common sense and ethics should determine your need for documenting sources. You do not need to give sources for familiar proverbs, well-known quotations, or common knowledge (For example, it is expected that U.S. citizens know that George Washington was the first President.). Remember that citing sources is a rhetorical task, and, as such, can vary based on your audience. If you’re writing for an expert audience of a scholarly journal, for example, you may need to deal with expectations of what constitutes “common knowledge” that differ from common norms.
Other Sources
The MLA Handbook describes how to cite many different kinds of authors and content creators. However, you may occasionally encounter a source or author category that the handbook does not describe, making the best way to proceed can be unclear.
In these cases, it's typically acceptable to apply the general principles of MLA citation to the new kind of source in a way that's consistent and sensible. A good way to do this is to simply use the standard MLA directions for a type of source that resembles the source you want to cite.
You may also want to investigate whether a third-party organization has provided directions for how to cite this kind of source. For example, Norquest College provides guidelines for citing Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers —an author category that does not appear in the MLA Handbook . In cases like this, however, it's a good idea to ask your instructor or supervisor whether using third-party citation guidelines might present problems.
If I have two works with identical titles and no authors in my works-cited list, how do I distinguish between them in my parenthetical citations?
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook . For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
Writers sometimes need to cite anonymous sources with identical titles, such as articles in reference works. Since in MLA style works without authors are cited parenthetically by title, you need to provide additional information in your in-text citation to distinguish the sources.
For example, let’s say you have in your works-cited list two articles without authors titled “Harry Houdini,” one from Encyclopedia.com and one from Wikipedia :
“Harry Houdini.” Encyclopedia.com , 2016, www.encyclopedia.com/ people/literature-and-arts/theater-biographies/harry-houdini. “Harry Houdini.” Wikipedia : The Free Encyclopedia , Wikimedia Foundation, 20 Feb. 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harry_Houdini.
In your parenthetical citations, provide the title of the article and then add in brackets additional information to clarify which source you are using—usually, the first unique piece of information. In this case, that information is the title of the website:
As one source notes, “No one before or since has so completely defined the art of escape as Harry Houdini, magician, actor, and stage personality” (“Harry Houdini” [ Encyclopedia.com ]). Houdini “tried to escape from special handcuffs commissioned by London’s Daily Mirror ,” while the spectators remained “in suspense for an hour” (“Harry Houdini” [ Wikipedia ]).
For more on differentiating between sources with the same title in your in-text citations, see our previous post . For tips on how to distinguish between them when you are discussing the works in your prose, see here .
Scribbr MLA Citation Generator
Accurate MLA citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
Scribbr's MLA Citation Generator for Chrome
Effortlessly cite any page or article directly from your browser with just one click. Our extension simplifies the citation process by automatically retrieving essential details such as the title, author(s), and publication date , ensuring accurate MLA citations in seconds.
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 9 & MLA 8 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Source types | Websites, books, articles |
| 🔎 Autocite | Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN |

Trust in expert-verified MLA citations
Avoid the risk of losing points due to incorrect citations. Our MLA citation experts have meticulously refined our algorithms, ensuring precision and reliability. This dedication has earned us recognition and recommendations from educators worldwide.
Experience distraction-free citation
Focus on your work without interruptions. Our citation generator provides a clean interface, free from distracting video pop-ups and flashing ads. Best of all, it's completely free for everyone.
Features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
MLA 8th & 9th edition
Scribbr's Citation Generator supports both MLA 8 and MLA 9 (as well as APA and Harvard ). No matter what edition you're using, we’ve got you covered!
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr's citation generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Create perfectly formatted MLA Style annotated bibliographies with just a few clicks.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Citation guides
Getting to grips with citation is simple with the help of our highly rated MLA citation guides and videos .
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Missing information
- No page numbers
- Scroll to top
How to cite in MLA format

MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook . You can also use Scribbr’s free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.
An MLA citation has two components:
- In-text citation : Every time you quote or paraphrase a source, you cite the author and the page number in parentheses.
- Works Cited : At the end of your paper, you give a full reference for every source you cited, alphabetized by the author’s last name.
MLA Works Cited list
The list of Works Cited (also known as the bibliography or reference page) gives full details of every source you cited in your text. Each entry is built from nine core elements:
Following this format, you can create a citation for any type of source—for example, a book , journal article , website , or movie . You only include information that’s relevant to the type of source you’re citing.
Missing information in MLA citations
Regardless of the source type, the most important elements of any MLA citation are the author , the source title , and the publication date. If any of these are missing from the source, the Works Cited entry will look slightly different.
| What’s missing? | What to do | Works Cited example |
|---|---|---|
| No author | Start with the source title instead. Alphabetize by the first word (ignoring ). | “Australia fires: ‘Catastrophic’ alerts in South Australia and Victoria.” , 20 Nov. 2019, www.bbc.com/news/world-australia-50483410. |
| No title | Give a brief description of the source. Use sentence case and no italics or quotation marks. | Mackintosh, Charles Rennie. Chair of stained oak. 1897–1900, Victoria and Albert Museum, London. |
| No date | Leave out the publication date. Add the date you accessed the source at the end of the citation. | “Who are Scribbr Editors?” , www.scribbr.com/about-us/editors/. Accessed 10 June 2019. |
MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate MLA citations in seconds
Get started
MLA in-text citations
MLA in-text citations are brief references that direct your reader to the full source entry. You include them every time you quote , block quote , paraphrase or summarize a source.
The in-text citation must match the first word of the Works Cited entry—usually the author’s last name . It also includes a page number or range to help the reader locate the relevant passage.
| Author | What to do | Citation example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | Give the author’s last name. | (Wallace 11–12) |
| 2 authors | Give both author’s last names. | (Wallace and Armstrong 11–12) |
| 3+ authors | Name the first author followed by “et al.” | (Wallace et al. 11–12) |
| Corporate author | If a source was created by an organization other than the publisher, use the organization name as author. | (U.S. Global Change Research Program 22) |
| No author | If the author is the same as the publisher, or if no author is credited, use the source title instead. Format the title the same as in the full Works Cited reference, and shorten if it is more than four words. | (“Australia Fires”) |
| Multiple sources by the same author | Include the title (or a shortened version) after the author’s name in each source citation. | (Morrison, , 73) (Morrison, , 45) |
If you already named the author in your sentence, include only the page number in parentheses:
Sources with no page numbers
If the source has no page numbers, you either use an alternative locator, or leave the page number out of the citation:
| Source type | What to do | Citation example |
|---|---|---|
| Audiovisual source (e.g. a or ) | Give the time range of the relevant section. | (Arnold 03:15–03:21). |
| Source with numbered sections (e.g. an ) | Give a paragraph, section, or chapter number. | (Smith, par. 38) (Rowling, ch. 6) |
| Source with no numbered sections (e.g. a ) | Leave out the page number. | (Barker) |
Tools and resources
Besides the MLA Citation Generator, Scribbr provides many more helpful tools and resources;
- Citation generator : Generate flawless APA , MLA , and Harvard citations in seconds
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect and correct plagiarism with the most accurate plagiarism checker for students
- AI Proofreader : Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Hire a professional editor to improve your writing
- Citation checker : Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Guides and videos : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How can I cite multiple pages from the same site with no author listed in MLA?
I'm writing an MLA paper which in which I need to site 2 pages from https://www.merriam-webster.com . Here are what my citations look like in my works cited page:
"dirigisme". Merriam-Webster Online, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/dirigisme . Accessed 28 February 2020. "fascism". Merriam-Webster Online, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/fascism . Accessed 28 February 2020.
How do I distinguish between these 2 sources while making in-text citations?
- academic-writing
(I have a very similar answer [but not the same] to this for a similar question .)
All of the examples in this answer are taken directly from this link. and this link .
You would just make two separate citations because you are citing two separate articles. However, you should still follow the same format for each of the website citations.
If each of the articles has a date but no author, follow this citation:
MLA website citation with no author
Format: “Title of Article.” Website Name, Day Month Year, URL. Works Cited entry: “US Election 2020: A Guide to the Final Presidential Debate.” BBC News, 21 Oct. 2020, www.bbc.com/news/election-us-2020-54620868 . In-text citation: (“US Election 2020”)
If the articles do not have an author or date, follow this format:
MLA website citation with no author or date
Format: “Title of Article.” Website Name, URL. Accessed Day Month Year. Works Cited entry: “Citing Sources and Referencing.” Scribbr, www.scribbr.com/category/citing-sources . Accessed 16 July 2019. In-text citation: (“Citing Sources”)
But, if the two articles are both written by the same author; you can follow this type of citation:
MLA journal citation: 2 authors
Works Cited: Eve, Martin Paul, and Joe Street. “The Silicon Valley Novel.” Literature & History, vol. 27, no. 1, May 2018, pp. 81-97, doi:10.1177/0306197318755680. In-text citation: (Eve and Street 84)
For more information, check out my answer here , this article , and this article.
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Writing Stack Exchange. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged academic-writing citations mla or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
Hot Network Questions
- How to read chainline specs for crankset and bottom bracket compatibility?
- Is "able to find related code by searching keyword 'MyClass '(variable declaration)" a reason to avoid using auto in c++?
- Are directed graphs with out-degree exactly 2 strongly connected with probability 1?
- Don't make noise. OR Don't make a noise
- Were there any stone vessels made in Paleolithic?
- Measure by mass vs. 'Spooned and Leveled'
- Evil God Challenge: What if an evil god is just trolling humanity and that explains why there's good in the world?
- Source impedance-trace impedance - load termination impedance confusion
- Does it make sense to use a skyhook to launch and deorbit mega-satellite constellations now?
- Why does `p` not put all yanked lines after quitting and reopening Vim?
- Does Justice Sotomayor's "Seal Team 6" example, in and of itself, explicitly give the President the authority to execute opponents? If not, why not?
- What is the purpose of the BJT in this circuit?
- Raid 0+1 Failure Cases Vs. Raid 1+0
- How do I drill a 60cm hole in a tree stump, 4.4 cm wide?
- Is it possible to abstract an ElGamal encryption for EC and Discrete Log by using a Group Law?
- Why didn't Smith give Atlas painkillers during the surgery?
- Can you be charged with breaking and entering if the door was open, and the owner of the property is deceased?
- Handle big vector containing ton of structs
- Transparent Glass Material Eevee Blender version 4.2
- Why is pressure in the outermost layer of a star lower than at its center?
- Who first promoted the idea that the primary purpose of government is to protect its citizens?
- What is meant by "I was blue ribbon" and "I broke my blue ribbon"?
- error when re-applying the permissions script into the original database - sql server
- Major church father / reformer who thought Paul is one of the 24 elders in Rev 4:4 and/or one of the 12 apostles of the Lamb in Rev 21:14
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format | For Students
Starting from when I entered high school, the importance of submitting assignments in a particular format became a top priority. I quickly realized the significance of adhering to these guidelines, as they remained essential throughout my academic journey. You never know when the need for proper formatting will arise. At first, it may seem overwhelming, but in this simple guide, I'll show you how to write an essay in MLA format [For Students].
When is MLA format used?
MLA format is created by the Modern Language Association which is a standardized way to format academic papers and cite sources. It’s mainly used for subjects in the humanities, like literature, philosophy, and the arts. Unlike APA or Chicago formats, which are used for social sciences and history, MLA puts a strong emphasis on the authorship of sources.
Most students will need to use MLA format at some point, especially in humanities courses. It’s essential for essays, research papers, and other assignments in these subjects.
General Guidelines/ Rules of MLA Formatting
The first step to learning how to write an essay in MLA format for students is to get familiar with the general guidelines. It's all about following the rules to get your paper formatted in the MLA style:
Margins and Font:
Set 1-inch margins on all sides.
Choose a readable font such as Times New Roman, 12-point size.
Double-space the entire document, including block quotes (quotes longer than four lines), notes, and the works cited page.
Paragraph Indentation:
Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches (press Tab key once).
Punctuation:
Utilize standard punctuation marks and maintain consistency with punctuation, italics, and quotation marks throughout your paper.
Quotations:
Use double quotation marks (" ") for direct quotes.
For quotes longer than four lines, format as a block quote: start on a new line, indent 0.5 inches from the left margin (without quotation marks), and keep double-spacing.
Here is an essay MLA format template for your reference:
How to Set up MLA Format Essay [Step-by-Step]
So we have seen the general guidelines in the above example and also saw an essay MLA format example/sample showing what our final MLA format will look like. However, going through guidelines is not enough when you're learning how to write an essay in MLA format in Word or PDF format. You need a professional writing software that not only provides the tools but also allows you to use them easily.
Therefore, I will be using WPS Writer as my partner in writing an essay in MLA format, and I would recommend students to download WPS Writer from their website so that you can easily follow this guide. And yes, it is completely free. So let's begin formatting an essay to MLA format in WPS Writer:
1. Page Margins
So the first step is to ensure that our page margins are set to 1 inch on every side. Setting the margins first would help you avoid any formatting errors if you do this at a later stage. To set page margins in WPS Writer:
Step 1: Open WPS Writer and visit the “Page Layout” tab in the toolbar.
Step 2: Find the Page Margin options on the far left of the Page Layout ribbon.
Step 3: Set all the margin fields—top, bottom, left, and right—to 1 inch.
2. Line Spacing
Next, we need to ensure that the line spacing is set to double spacing . This helps improve readability and ensures your paper meets MLA formatting standards. To set double line spacing in WPS Writer:
Step 1: In WPS Writer, go to the “Home” tab in the toolbar.
Step 2: Find and click the “Line Spacing” option in the Home ribbon.
Step 3: In the Line Spacing drop-down, click on More.
Step 4: The Paragraph window will pop up. Visit the Spacing section and in the Line Spacing field, select “Double”.
Step 5: After that, click on OK to exit the Paragraph window.
Note: We can also use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + 2 to quickly change the line spacing to double.
3. Header- In the Upper-Left Corner
After setting the page settings, let's move on to the content of the essay, starting with the header in the following order:
Student's Name
Professor's Name
Course and Course Code
Due Date in the format DD Month, Year
Step 1: Follow the order to enter the header into your essay.
Step 2: To make the Header left aligned, visit the Home tab and then click on the “Align Text Left” icon.
Step 3: After entering the header, make sure the Font is set to "Times New Roman" in the Fonts field in the Home ribbon.
Step 4: After the font, the font size should also be set to "12." Therefore, make the change in the "Font Size" field in the Home ribbon.
4. Last Name & Page Numbers- In the Upper-Right Corner
MLA Format requires a running header that includes your last name along with the page number on the top right corner of every page. Let's see how we can create our running header for the MLA Format:
Step 1: Double-click on the Header area to open the Header/Footer in WPS Writer.
Step 2: Now type your last name and set its alignment to right by clicking on the “Align Text Right” icon in the Home ribbon.
Step 3: To add the page number, click on the "Page Number" option in the Header/Footer ribbon and select the "Header right" option to insert a page number in the right corner.
Once the running header has been added, it is important to set the font size of the running header to 12 and the font to "Times New Roman".
Step 4: Simply select your running header and click on the Home tab.
Step 5: In the Home tab, change the Font to "Times New Roman" in the Fonts field.
Step 6: To change the font size, in the Home ribbon, enter "12" in the Font size field.
The last setting for the running header is to set the header margin to "0.5 inches":
Step 7: Head over to the Header/Footer tab.
Step 8: In the Header/Footer ribbon, enter "0.5 in" in the “Header Height” field to set the header margin to 0.5 inches.
5. Title of Essay- On the Line Below the Date
After the header and running header, let's begin our essay with the title of our essay. Remember the rules:
The title should be center aligned.
The title should not be bolded, italicized, or placed in quotation marks unless it includes the title of a source (e.g., a book or movie title).
Step 1: Insert the title right below the header and visit the Home tab.
Step 2: In the Home ribbon, click on the “Center” icon to center align the title.
6. Headings and Subheadings- Into Sections
Headings and subheadings are important as they give reference to the reader. There are no hard and fast rules for their formatting, except that they need to be center aligned. You can set the font style to bold to help the reader distinguish them.
Step 1: Enter your heading below the title of the essay and visit the Home tab.
Step 2: In the Home ribbon, click on “Center” to align the heading to the center.
Step 3: To change the font style to bold, in the Home ribbon, click on the “Bold” icon right below the font field.
7. In-text Citation
In MLA format, in-text citations use parenthetical references to indicate quotes or ideas from another author. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do in-text citations:
Step 1: When you quote or paraphrase from a source, use the author's last name and the page number where the information is found.
Step 2: After the quote or paraphrase, place the citation in parentheses. The citation should include the author's last name followed by the page number without a comma between them.
Step 3: The parenthetical citation should be placed before the period at the end of the sentence.
8. Works Cited Page
Finally, you will need to cite all the sources you took assistance from in writing your paper. Follow the following steps to understand how to cite your work in MLA format.
Step 1: Use a page break to start a fresh new page with the title "Works Cited." The heading "Works Cited" will follow similar heading guidelines as before.
Step 2: Double-space all entries and do not add extra spaces between entries.
Step 3: Use a hanging indent for each entry. The first line of each citation is flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented by 0.5 inches simply using the “Tab” key..
Step 4: List entries in alphabetical order by the author's last name. If a work has no author, alphabetize it by the first significant word in the title.
Step 5: Format your sources as mentioned below for respective source medium:
Books Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of Publication.
Articles in Journals Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article." Title of Journal, vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
Websites Format: Author's Last Name, First Name (if available). "Title of Webpage." Title of Website, Publisher, Date of Publication, URL.
Bonus Tips: How to Convert Word to PDF without losing Format
Once you finish writing your essay, the next challenge is converting it from Microsoft Word to PDF without losing formatting. This can be frustrating because sometimes the formatting doesn't stay the same.
To avoid this issue, use WPS Office . It offers strong PDF features and keeps APA and MLA formatting intact. On the other hand, Microsoft Word 365, though widely used, may occasionally struggle to keep formatting consistent when converting to PDF. It's important to choose tools that prioritize preserving the look and structure of your academic work.
Here is how you can use WPS PDF to convert your essay documents to PDF without compromising on the quality:
Step 1: On WPS Writer, click on the Menu button on the top left corner of the screen.
Step 2: Now simply click on the “Export to PDF” option in the Menu.
Step 3: The Export to PDF window will open. Here, you can alter a few settings such as the output path. After going through the settings, simply click on Export to PDF to save the essay document as a PDF.
FAQs about writing an essay in MLA format
1. how to cite an image in mla.
To cite an image in MLA style, you need to format the citation based on where the image was viewed. For online images, the citation should follow this structure:
MLA format:
Creator’s last name, First name. “Image Title” or Description of the image. Website Name in italics, Day Month Year, URL.
MLA Works Cited entry:
Smith, Jamie. “Vintage Cars.” Travel With Us, 15 Mar. 2023, www.travelwithus.com/vintage-cars.
MLA in-text citation:
(Smith) Note: If you discover an image through a search engine such as Google, ensure that you credit and link to the website that hosts the image, rather than the search engine.
2. Do I need to include a title page in my MLA essay?
In most instances, an MLA-formatted essay does not necessitate a separate title page unless instructed otherwise by your instructor. Instead, begin your essay with a header and center the title on the subsequent line.
3. How to Cite a Website in MLA?
To cite a website in MLA style, you should include the author’s name (if known), the title of the page in quotation marks, the name of the website in italics, the publication date, and the URL without "https://". If the identity of the author is not known, start with the title of the page. If the publication date is unavailable or if there's a possibility of content modifications, include an access date at the end.
Author’s last name, First name. “Title of Page.” Website Name, Day Month Year, URL.
Adams, John. "Explore with us." Random Discoveries, 15 Sept. 2023, www.randomdiscoveries.com/explore-with-us.
Write Your Essays in Comfort With WPS Office
It’s so easy! The great thing about MLA format is that it’s not vastly different from APA and Chicago formats. There are only a few distinctions, and once you learn how to write an essay in MLA format [For Students], everything will become much easier for your academic life. Also, WPS Office is an incredibly handy tool for students. Not only can you format comfortably, but it’s also designed to be student-friendly, avoiding complex procedures. Simple yet advanced, and best of all, free. Get WPS Office today and write essays with ease and comfort!
- 1. How to Do Hanging Indent in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 2. How to Remove Page Breaks in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 3. How to Use Track Changes in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 4. How to Double Space in Word for Your Essay: A Guide for Students
- 5. How to Make MLA Format Heading and Header in WPS Office (Step-by-Step)
- 6. Top 10 Best Introduce Yourself Essay Sample Words
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
Top of page
Article South Korea: Amendments to Take Effect Addressing Constitutionality of Family Relations Registration Act
Back to Search Results
On July 19, 2024, amendments to South Korea’s Act on Registration of Family Relations enacted to correct provisions found unconstitutional by the Constitutional Court will come into effect.
Act No. 19547 (July 18, 2023) amended the Act on Registration of Family Relations (Act No. 8435, May 17, 2007, as amended) in accordance with a March 2023 decision of the Constitutional Court that found some provisions violated the constitutional rights relating to birth registration of children born out of wedlock. (Constitutional Court of Korea, Affirmation of Nonconformity to the Constitution of the Article 46 (2) of the Act on the Registration, Etc. of Family Relationships , 2021 Hun-Ma975, March 23, 2023 (unofficial translation).)
Background: Constitutional Court Decision
In its March 2023 decision (Constitutional Court of Korea, 2021 Hun-Ma975 , March 23, 2023), the Constitutional Court held that children have a fundamental right under South Korea’s Constitution to have their birth registered immediately after birth. It further ruled that articles 46 (2) and 57(1) & (2) of the Act on Registration of Family Relations violated the Constitution because they did not allow a biological father to report the birth of a child born to a mother married to another man.
The case arose when children born out of wedlock and their biological fathers who were not their mothers’ husbands filed the constitutional complaint that the provisions infringed out-of-wedlock children’s right to be registered immediately after birth and the biological fathers’ rights to custody, freedom of family life, and equality.
The Constitutional Court affirmed that the right of out-of-wedlock children to be registered immediately after birth is a fundamental right based on the Constitution’s article 10 (the personal right to human dignity and worth and the right to pursue happiness), article 34 (1) (the right to a life worthy of human beings), article 34 (4) (the duty of the state to implement policies to enhance the welfare of the young), and article 36 (1) (the guarantee of family life).
The Constitutional Court held that the rights of the out-of-wedlock child complainants to be registered immediately after birth was infringed. The court noted that the legislative objective of these provisions of the act is to ensure birth registration and to provide accurate identification of children as to their biological relationships, nationality, etc. But the court pointed out that the current birth declaration system fails to ensure effective birth registration for children born of a married woman and a man other than her husband. In such cases, under article 46 (1), the married woman and her husband are obligated to register their birth because the child is assumed to have been conceived in wedlock. ( Civil Act , Act No. 471, Feb. 22, 1958, as amended, art. 844 (1).) However, there are circumstances under which the married woman would not report the child’s birth because she does not want to reveal she has committed adultery, and her husband would not report the child’s birth because the child is not his biological child. The court further observed that while under article 46 (3) of the act, a prosecutor or local government may report a birth of the child instead of parents when a child’s welfare could be harmed, it is not mandatory, and it is also difficult for them to find out such circumstances of children.
The Constitutional Court noted that if a mother or her husband does not register an out-of-wedlock childbirth within the reporting period, effective methods for birth registration could include allowing the biological father to register the out-of-wedlock childbirth or imposing an obligation to a medical institution to send relevant data of childbirth for the registration ex officio.
On the other hand, regarding the complaints of their biological fathers who are not their mothers’ husbands, the court held that the provisions do not infringe their constitutional rights. Regarding the right to equality between married mothers of out-of-wedlock children and their biological fathers, the Constitutional Court stated that there is a rational reason for the different treatment, and thus the court found the rights of the complainants who were natural fathers were not infringed.
While finding that the provisions violated the rights of the out-of-wedlock child complainants, the court ordered their continued application until the legislature enacted remedial legislation, which the court said must be done no later than May 31, 2025.
Amendments to Family Relations Registration Act
The amendments in Act No. 19547 address the constitutional infirmities in the Act on Registration of Family Relations identified by the Constitutional Court. The amendments
- allow new forms of verification of a child’s birth to a mother by persons involved in the delivery, by domestic or overseas authorized agencies, or through records of rescue operations or emergency medical services (art. 44(4) 1-3);
- specify the obligation of medical institutions to submit specified birth information into the mother’s medical records (art. 44-3);
- provide for the recording of births ex officio even if the parents do not register the birth (art. 44-4); and
- give local governments the right to request necessary documents for registration of birth (art. 44-5).
Prepared by Inseol Hong, Foreign Law Intern, under the supervision of Sayuri Umeda, Foreign Law Specialist
Law Library of Congress, July 2, 2024
Read more Global Legal Monitor articles .
About this Item
- South Korea: Amendments to Take Effect Addressing Constitutionality of Family Relations Registration Act
Online Format
- Global Legal Monitor (7,687)
- Law Library of Congress (423,221)
- Birth Certificates and Registration
- Children's Rights
- Constitutional Law
- Human Rights and Civil Liberties
- Marriage and Family Status
Jurisdiction
- South Korea
Article Author
- Umeda, Sayuri
Featured in
- About the Law Library | Law Library of Congress | Research Centers
Rights & Access
Publications of the Library of Congress are works of the United States Government as defined in the United States Code 17 U.S.C. §105 and therefore are not subject to copyright and are free to use and reuse. The Library of Congress has no objection to the international use and reuse of Library U.S. Government works on loc.gov . These works are also available for worldwide use and reuse under CC0 1.0 Universal.
More about Copyright and other Restrictions.
For guidance about compiling full citations consult Citing Primary Sources.
Credit Line: Law Library of Congress
Cite This Item
Citations are generated automatically from bibliographic data as a convenience, and may not be complete or accurate.
Chicago citation style:
Umeda, Sayuri. South Korea: Amendments to Take Effect Addressing Constitutionality of Family Relations Registration Act . 2024. Web Page. https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-01/south-korea-amendments-to-take-effect-addressing-constitutionality-of-family-relations-registration-act/.
APA citation style:
Umeda, S. (2024) South Korea: Amendments to Take Effect Addressing Constitutionality of Family Relations Registration Act . [Web Page] Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-01/south-korea-amendments-to-take-effect-addressing-constitutionality-of-family-relations-registration-act/.
MLA citation style:
Umeda, Sayuri. South Korea: Amendments to Take Effect Addressing Constitutionality of Family Relations Registration Act . 2024. Web Page. Retrieved from the Library of Congress, <www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2024-07-01/south-korea-amendments-to-take-effect-addressing-constitutionality-of-family-relations-registration-act/>.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An exception: if a corporate author is also the work's publisher, list that entity as the publisher and skip the "Author" slot: Reading at Risk: A Survey of Literary Reading in America. National Endowment for the Arts, June 2004. Cite these works in your text by title or by corporate author—that is, by the first item in the works-cited ...
Published on July 17, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead.
Create manual citation. A citation on an MLA works cited page usually begins with the last name of the source's author. However, there are times when an author isn't stated. There are also times when instead of an individual, an organization or company is stated as the author. The guidelines below follow rules from the 9th edition of the ...
Here is how to cite a webpage without an author in three of the most popular citation styles: APA 7, MLA 9, and Chicago (17th ed.). APA 7. Reference Entry Template: Title of webpage/article. (Year, Month Date of publication). In Website Name. URL. Reference Entry Example: Giant panda. (2022, June 29).
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook. For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook . If a website has no author or it is unclear what organization produced it, use the title of the site in your in-text citation.
Webpages/websites with no authors listed. In the case of webpages that don't have any author's name listed, use the title of the webpage. Place the title in quotation marks and format it in title case. Since it is a webpage and no page numbers are available, no page numbers need to be included with direct quotes.
Author. It can sometimes be difficult to find out who the author of a website is. Remember that an author can be a corporation or group, not only a specific person. Author information can sometimes be found under an "About" section on a website. If there is no known author, start the citation with the title of the website instead. Date
No Date. If no date is provided, skip that information in your citation. It is recommended that you add the date you accessed the work at the end of the citation in your Works Cited list. Access date is given by putting the word "Accessed" followed by the date you viewed or accessed the work (format = Day Month (shortened) Year). Example:
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
Document from a web site with no author. If no author name is given, but the page is from a domain that includes .org, you may be able to list the name of the organization as the author, like this: Reference list: Name of Organization Title of Web Document. Title of Website, Date if given, URL of specific document. Access date if advisable.
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications) The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any ...
Write the author's name in last name, first name format with a period following. Next, write the name of the website in italics. Write the contributing organization's name with a comma following. List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following. Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
Example of a website citation with two authors in MLA 8 style. If there are more than 2 authors you would simply append 'et al.' after the first one. For example: Casselman, Ben, et. al. "G.D.P. Grew at 4.1% Rate in U.S. in Latest Quarter. Here's What That Means.".
MLA Formatting and Style Guide Overview of how to create MLA in-text citations and reference lists In-Text Citations. Resources on using in-text citations in MLA style. The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Cite your MLA source. Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Set 1 inch page margins. Use double line spacing. Include a ½" indent for new paragraphs. Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page. Center the paper's title.
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA ...
These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author's last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves. Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format: %%Last name of the author, First name of the author. "Source's Title.".
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
Writers sometimes need to cite anonymous sources with identical titles, such as articles in reference works. Since in MLA style works without authors are cited parenthetically by title, you need to provide additional information in your in-text citation to distinguish the sources. For example, let's say you have in your works-cited list two articles without …
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
However, you should still follow the same format for each of the website citations. If each of the articles has a date but no author, follow this citation: MLA website citation with no author. Format: "Title of Article." Website Name, Day Month Year, URL. Works Cited entry: "US Election 2020: A Guide to the Final Presidential Debate."
If a work has no author, alphabetize it by the first significant word in the title. Step 5: Format your sources as mentioned below for respective source medium: Books Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of Publication. Articles in Journals Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article."
On July 19, 2024, amendments to South Korea's Act on Registration of Family Relations enacted to correct provisions found unconstitutional by the Constitutional Court will come into effect.Act No. 19547 (July 18, 2023) amended the Act on Registration of Family Relations (Act No. 8435, May 17, 2007, as amended) in accordance with a March 2023 … Continue reading "South Korea ...