Learn Computer Science
Explore the World Of Computer Science


Computer Bus
Data bus | address bus | control bus, bus architecture | bus width | bus speed, introduction to computer bus.
The Computer Bus is a communication link used in a computer system to send data, addresses , control signals, and power to various hardware components in a computer system.
The computer buses are used to connect the various hardware components that are part of the computer system. In simple terms, the computer buses are electrical wires that connect the various hardware components in a computer system . The computer bus carries the data , control signals , memory addresses, and power supply to these components.
The buses act as a shared communication channel, allowing various hardware components, such as the CPU (Central Processing Unit), main memory RAM modules, storage devices, input/output devices, and expansion cards, to interact and transfer data with each other.
The computer system makes use of different types of buses, such as data buses, address buses, and control buses.
What Is Computer Bus ?
The primary purpose of a computer bus is to provide a standardized method for components to communicate with each other. By using a bus, various devices can interact and transfer information without the need for custom connections or protocols for each individual component.
Different types of busses are used in the computer. Computer buses can vary in terms of their speed, width, and protocols depending on the specific requirements of the system. Advancements in technology have led to the development of faster and more efficient bus architectures, allowing for increased data transfer rates and improved overall system performance.
In summary, computer buses provide a crucial communication infrastructure within a computer system, enabling the exchange of data and signals between different hardware components. Bus architecture plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation and coordination of various components in a computer system.
In this article, we are going to study in detail what computer buses are, the computer system bus architecture , types of buses , technical features, and functions of computer buses.
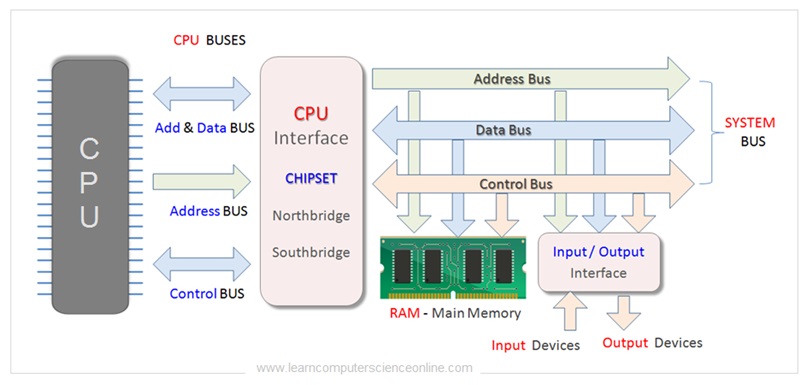
Computer Buses And Functions
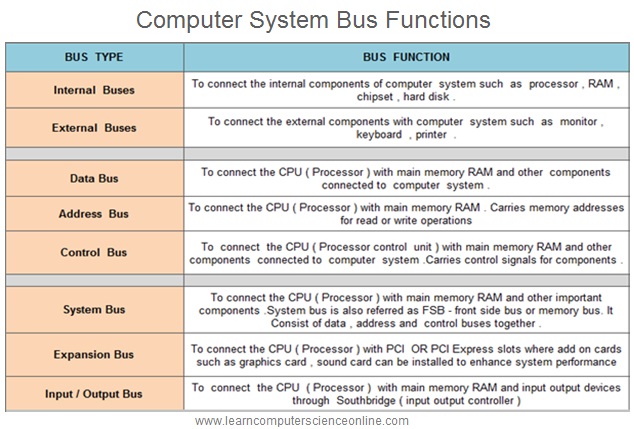
Buses are typically categorized based on their functionality and the type of data they carry. Here are some common types of computer buses that are important part of computer architecture :
Table Of Contents
What is data bus , what is address bus , computer bus functions, motherboard bus architecture, types of computer buses, what is control bus , what is system bus , bus width and bus speed, what is expansion bus .

The computer system consist of number of internal and external components . These components are physically interconnected and communicate with each other through a network of wires running across the computer system. These wires are referred as computer buses. The buses are essential to the functioning of the computer system.
A computer bus is a communication pathway that allows various components within a computer system to transfer data and signals between each other. It serves as a wired physical connection or set of wires running across connecting various system components.
Computer buses enable the transfer and exchange of information, such as commands, addresses, signals, and data, between the different hardware components in a computer. Computer system makes use of different types of busses as per the system architecture.
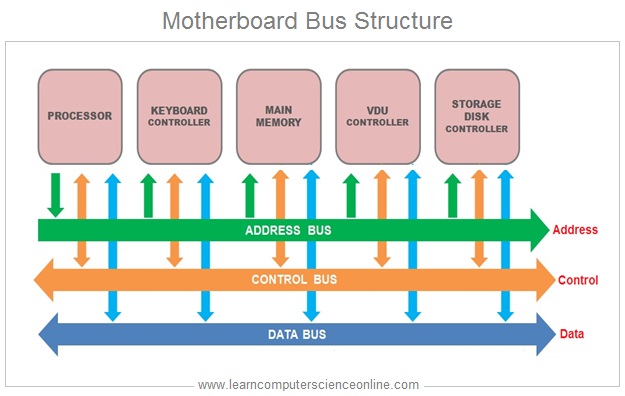
The computer buses can be in the form of wired cables or electrical wires embedded in the computer motherboard PCB ( Printed Circuit Board ) visible on the rear side of motherboard .
It is important for computer science professional to study the computer system bus architecture , technical features of these buses such as bus width and bus speed and its overall impact on the system performance.
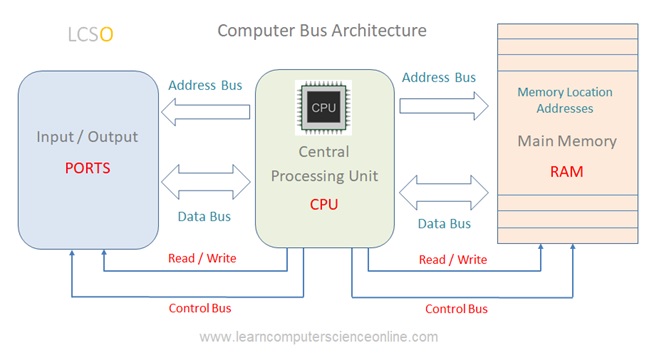
A bus is a common communication pathway used in a computer system through which information flows from one computer component to another.
The computer bus system is a network of buses which physically connect all the components with wires ( actual bus wires OR circuit wires on the motherboard ) .
The bus system consist of different types of buses depending upon the components being connected and the function assigned to the bus .
A bus can consist of set of wires grouped together as connection wire or a printed circuit boards which carry the data and other commands ( instructions ) from the CPU to the memory and to various other components connected to the system.
The bus performance is an important parameter to access the computer system performance . The bus width and the bus speed affects the system performance .
Cable Buses

Motherboard Buses

The data bus is a bidirectional bus and can carry the data in both the direction along the data bus. For example , the CPU can send the data to be stored into the RAM .
Similarly, the CPU can also perform the fetch operation for retrieving the data from the specific memory location.
The computer bus system makes use of different types of buses depending upon the purpose and the function of the bus.
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of number of factors . These factors include :
- Components being connected . ( CPU , RAM , Input And Output Devices ).
- Type of Data being Transmitted ( Data , Address , Control Signals ) .
- Location of the components ( Internal bus And External bus ).
- Connectivity with the CPU chipset ( Through Northbridge Or Through Southbridge )
Bus Types On the Data Being Transmitted
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of type of the data being transmitted as :
1. Data Bus , 2. Address Bus , 3. Control Bus.
Computer Bus Types
Bus Types Based On the Components Being Connected
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of type of the components being connected as :
1. System Bus , 2. Expansion Bus , 3. Input And Output Bus.
Bus Types Based On The Location Of Components
The computer system buses can be classified on the basis of location of the component being connected as :
1. Internal Bus , 2. External Bus
In computer architecture , the data bus is a wired connection dedicated for the transmitting the data between the CPU , peripheral devices and other hardware components . The data bus is a part of the system bus in addition to address bus and the control bus.
A data bus has many different features , but one of the most important feature is the bus width . The width of a data bus refers to the number of bits ( electrical wires ) that the bus can carry at a time.
For example , a 16 Bit wide data bus can carry 16 bits of data simultaneously between the CPU and the system component such as main memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ).
The Common data bus widths include 8 bit , 16 bit , 32 bit and 64 bit . The wider the bus width , faster would be the data flow on the data bus and thus better system performance.
Bus Architecture
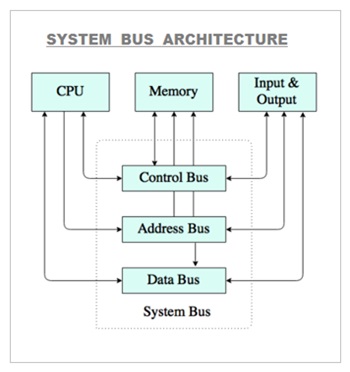
Control Bus
The CPU ( Microprocessor ) contains a control unit which controls the functioning of all other components connected to the computer system. The control bus is used to transfer the control signals from one component to another component .
A control bus is a computer bus that is used by the CPU to communicate with the devices that are connected to the computer system. These devices are connected with the help of cables and printed circuits board such as motherboard .
The Control Bus is a part of System Bus in addition to Data Bus and Address Bus.
The Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) transmits different types of control signals to the system components. The devices also communicate with CPU by transmitting the control signals using the control bus.
The control bus is a bidirectional and assists the CPU in synchronizing control signals to the internal components and the external devices connected to the system.
The control bus transmits the control signals such as device interrupt signal , byte enable signal , memory read or write signals and status signals.
How CPU Works ?
Address bus, what is a address bus .
The computer program consist of number of program instructions. These instructions direct the CPU to perform desired operation.
The operating system loads the program instructions and the data into the main memory . The CPU executes the program instructions one-by-one by fetching the program instructions from the main memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ) .
In order to perform the memory read or write operation from the main memory RAM , the CPU sends either read or write control signal on the control bus and address of the memory location along the “Address Bus” from where the operation is to be performed .
The address bus is a part of the “System Bus” along with the data bus and the control bus which we have discussed .

What Is A System Bus ?
A System Bus is the main bus which contains Data Bus , Address Bus And Control Bus.
The System bus in computer system connects number of vital internal hardware components placed on the motherboard .
These hardware components mainly include CPU , motherboard , Internal add on cards such as Graphic card , Sound card , Network card , RAM ( Main Memory ) and the internal hard disk .
A system bus is a set of parallel wires which connects the two or more independent major internal components of a computer system. The System bus transfers data , memory addresses and device control instructions.
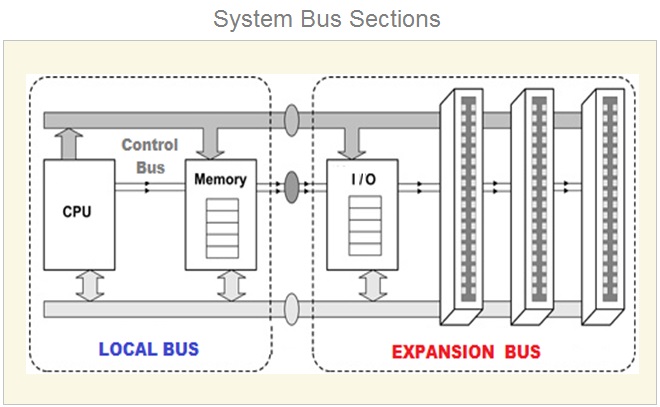
What Are The Functions Of The Computer Bus ?
The computer bus system makes use of different types of buses . Each of these bus is assigned to carry specific type of signal and data depending upon its function.
- Data Sharing .
- Control Signals
- Providing Power to Components .
- Sharing The System Time .
Internal Bus
The internal buses connect the various internal system components such as microprocessor ( CPU ) , RAM ( main memory ) , Chipset ( North Bridge And South Bridge ) and disk memory ( Hard Disk ) .
External Bus
The external bus connects the various external system components such as monitor , keyboard , printer , external hard disk and other components externally connected to the system.
The system bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) and main system memory RAM . The system bus is also referred as FSB ( Front Side Bus ) or memory bus. It consist of data bus , address bus and control bus.
Expansion Bus
The expansion bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) and PCI OR PCI Express slots on the motherboard .
The PCI And PCI Express slots are used to connect the add on cards such as graphics card and sound card . These cards are installed to enhance the system performance.
Input And Output Bus
The input and output bus connects the most important internal system components such as Microprocessor ( CPU ) , main system memory RAM and the input / output devises through input and output controller south bridge .
Computer Bus And System Performance
Computer bus width and bus speed.
A bus is a information highway over which information flows and wider the bus , the more information can flow over the channel .
And therefore , a compatible bus width and bus speed is important for the optimal performance of the two most vital system components which includes Central Processing Unit ( CPU ) and main system memory RAM .
This is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic . whereas , a single lane road can carry less number of cars as compared to a multi lane road .
The computer system at the hardware level understands only binary 0 ( zero ) and 1 ( one ) . And therefore , all computer programs are compiled to convert into machine code instructions in binary which computer CPU can decode and execute.
The bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1 BIT ( Binary 0 OR 1 ) at a time . Therefore , a bus consist of a group of cables so that a group of bits can be sent at a time through these buses .
Why Computer Bus Use Binary ?
What is bus width .
The size of a bus is measured in terms number of Bits it can transmit at a time . Each wire can transmit one bit thus more number of wires in the bus can transmit more bits at a time . This number of wires in bus is referred as Bus Width.
The Bus width is an important measure because it determines how much data can be transmitted at one time. For example, a 16 Bits bus can transmit 16 bits of data and a 32 Bit Bus can transmit 32 bits of data at a time.
The bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1 BIT ( Binary 0 OR 1 ) at a time . Therefore a bus consist of a group of cables so that a group of bits can be sent through the bus .
This is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic .
What Is Bus Speed ?
The Bus performance is important for optimal CPU performance . The Bus performance is measured on two factors ( Bus Width And Bus Speed ) .
The bus speed is another important parameter for the bus performance . The bus speed is defined by its frequency expressed in Hertz .
The bus frequency is the number of data packets sent or received per second. Each time that data is sent or received , It is called as one cycle.
The bus speed is generally referred to the FSB – Front Side Bus speed . The Front Side Bus connects the CPU to the memory controller chip North-bridge .
What Is Bus Bandwidth ?
Let us summarize the bus width and the bus speed using the highway analogy. If the bus width is the number of lanes available for the traffic and the bus speed is how fast the vehicles are moving on each of these lanes.
The bandwidth is the product of Bus Width And Bus Speed and reflects the amount of traffic that the channel can convey per second.
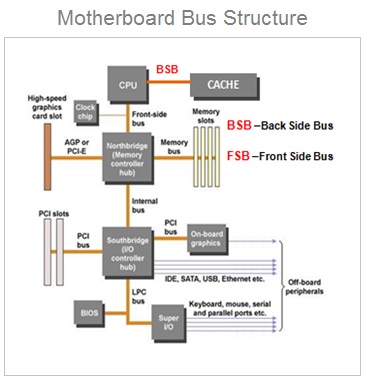
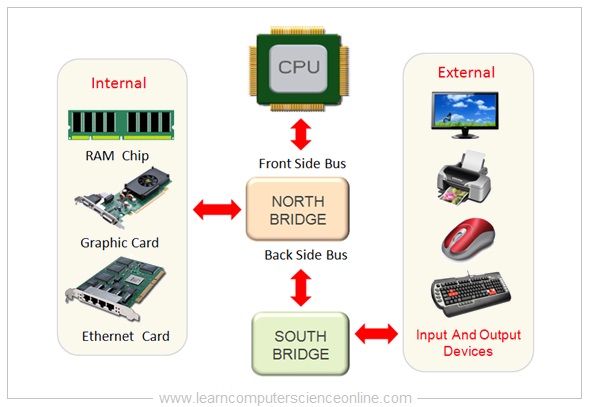
The CPU is connected to the internal system components ( RAM , Graphics Card Network card ) and external peripheral devices ( Monitor , Printer , Mouse , Keyboard ) by using device controller circuits placed on the motherboard .
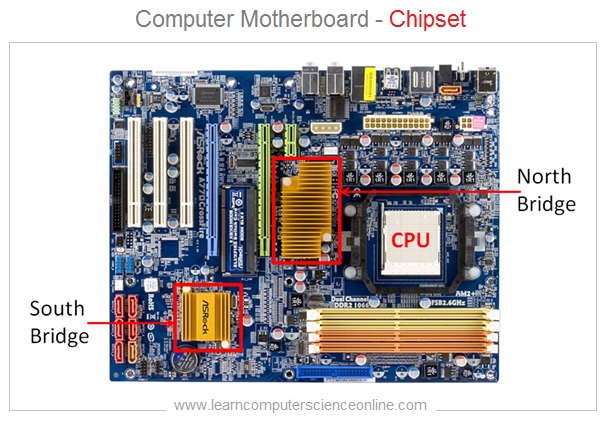
All the device controller chips are now integrated into only two controller chips called chip-set . The chip-set consist of two prominently visible IC Chips called North-bridge and South-bridge placed on the motherboard .
Computer Motherboard Chipset
The memory controller chip North-bridge and input / output controller chip South-bridge circuits are placed on the motherboard.
The internal components ( CPU , main memory RAM , Graphics Card ) are connected through North Bridge.
And other peripheral devices ( Display monitor , printer , keyboard , mouse ) are connected through the input & output controller chip South Bridge.
All these components are connected by using the system of bus wires which essentially carries three different types of information :
1. Memory Addresses , 2. Control Instructions And 3. Data.
1. Memory Addresses.
2. control instructions., chipset north bridge and south bridge.
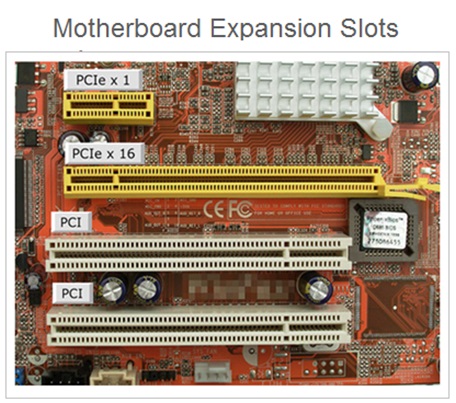
What Is Expansion Bus?
The performance features and functionality of a computer system can be extended by adding an additional cards such as graphics card Or sound card.
The expansion slots are the ports located on the motherboard of a computer system in which an expansion cards can be installed . The user can use these slots to insert additional expansion cards as per the functional requirements .
An expansion bus is a group of wires OR PCB used to connect with the expansion slots on the motherboard. These expansion slots are used for installing the expansion cards .
Expansion Slots
Front And Back Side Bus
Front Side Bus
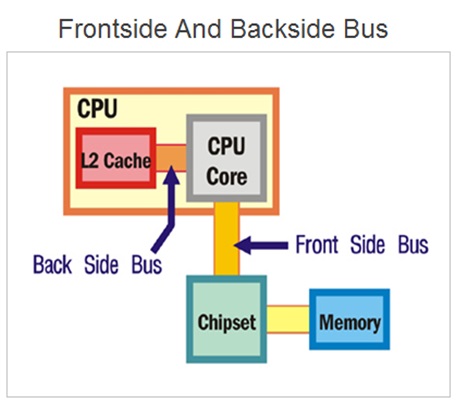
What is front side bus ( fsb ) .
The front side bus ( FSB ) represents one of the most important communication bus that connects some of the most vital components of the system. And hence , the FSB is also referred as system bus .
The front side bus connects the computers central processing unit ( CPU ) with the main system memory RAM . The FSB also connects PCI slots and DIMM slots on the motherboard with the processor socket .
And therefore , the FSB is an important communication bus that connects some of the most important components such as CPU , main memory RAM , graphics card and other components connected through PSI slots.

Chipset Architecture - Front Side Bus ( FSB )
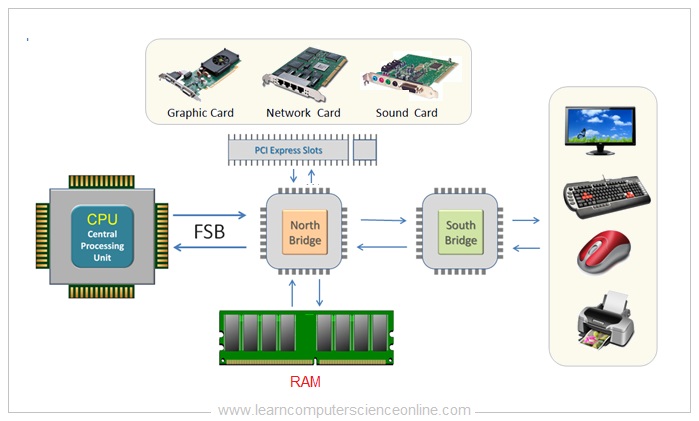
These components are connected using the FSB through one of the memory controller chip called the north bridge . The motherboard chip set consist of two controller chips.
The front side bus is present on the motherboard embedded as a printed circuit board ( PCB ) wired connections running across the motherboard PCB .
The FSB speed is considered as an important parameter that significantly affect the CPU performance . The FSB speed is measured in Megahertz ( MHz ).
The FSB speed is generally ranges between 66 MHz to 800 Mhz. It can also be expressed as a ratio to CPU speed.
RAM Standards - Front Side Bus ( FSB ) Speed
The front side bus ( FSB ) is bi-directional bus . The FSB is used to by the CPU to either receive or send the data from various components connected to the CPU.
The CPU frequently communicates with system main memory RAM and other devices during the program execution. And therefore , the FSB speed matters for the CPU performance.
Join The Best Seller
Computer Science Online Course
Learn computer science and programming fundamentals.
This is the most comprehensive and unique Computer Science And Programming Fundamentals course Online which will give you in depth understanding of most important fundamental concepts in computer science And Programming .

Other Related Topics
Computer organization and architecture.

What Is Control Unit ?

What Is Central Processing Unit ?

What Are CPU Registers ?
Introduction To Computer System

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Computer Notes
- Computer Fundamental
- Computer Memory
- DBMS Tutorial
- Operating System
- Computer Networking
- C Programming
- C++ Programming
- Java Programming
- C# Programming
- SQL Tutorial
- Management Tutorial
- Computer Graphics
- Compiler Design
- Style Sheet
- JavaScript Tutorial
- Html Tutorial
- Wordpress Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- PHP Tutorial
- JSP Tutorial
- AngularJS Tutorial
- Data Structures
- E Commerce Tutorial
- Visual Basic
- Structs2 Tutorial
- Digital Electronics
- Internet Terms
- Servlet Tutorial
- Software Engineering
- Interviews Questions
- Basic Terms
- Troubleshooting
Header Right
What is bus | types of computer bus.
By Dinesh Thakur
What is Computer Bus: The electrically conducting path along which data is transmitted inside any digital electronic device. A Computer bus consists of a set of parallel conductors, which may be conventional wires, copper tracks on a PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD, or microscopic aluminum trails on the surface of a silicon chip. Each wire carries just one bit, so the number of wires determines the largest data WORD the bus can transmit: a bus with eight wires can carry only 8-bit data words, and hence defines the device as an 8-bit device.
A computer bus normally has a single word memory circuit called a LATCH attached to either end, which briefly stores the word being transmitted and ensures that each bit has settled to its intended state before its value is transmitted.
The Computer bus helps the various parts of the PC communicate . If there was no bus, you would have an unwieldy number of wires connecting every part to every other part. It would be like having separate wiring for every light bulb and socket in your house.
We’ll be covering the following topics in this tutorial:
Types of Computer Bus
There are a variety of buses found inside the computer.
D ata Bus : The data bus allows data to travel back and forth between the microprocessor ( CPU ) and memory (RAM).
A ddress Bus : The address bus carries information about the location of data in memory.
C ontrol Bus : The control bus carries the control signals that make sure everything is flowing smoothly from place to place.
E xpansion Bus: If your computer has expansion slots, there’s an expansion bus. Messages and information pass between your computer and the add-in boards you plug in over the expansion bus.
Although this is a bit confusing, these different buses are sometimes together called simply “the bus.” A user can think of the computer’s “bus” as one unit made up of three parts: data, address, and control, even though the three electrical pathways do not run along each other (and therefore don’t really form a single “unit”) within the computer.
There are different sizes, or widths of data buses found in computers today. A data bus’ width is measured by the number of bits that can travel on it at once. The speed at which its bus can transmit words, that is, its bus BANDWIDTH, crucially determines the speed of any digital device. One way to make a bus faster is to increase its width;
for example a 16-bit bus can transmit two 8-bit words at once, ‘side-by-side’, and so carries 8-bit data twice as fast as an 8-bit bus can. A computer’s CPU will typically contain several buses, often of differing widths, that connect its various subunits. It is common for modern CPUs to use on-chip buses that are wider than the bus they use to communicate with external devices such as memory, and the speed difference between on- and off-chip operations must then be bridged by keeping a reservoir of temporary data in a CACHE. For example many of the Pentium class of processors use 256 bits for their fastest on-chip buses, but only 64 bits for external links.
An 8-bit bus carries data along 8 parallel lines. A 16-bit bus, also called ISA (Industry Standard Architecture), carries data along 16 lines. A 32-bit bus, classified as EISA (Enhanced Industry Standard Architecture) or MCA ( Micro Channel Architecture ), can carry data along 32 lines.
The speed at which buses conduct signals is measured in megahertz (Mhz). Typical PCs today run at speeds between 20 and 65Mhz. Also see CPU, Expansion Card, Memory, Motherboard, RAM, ROM, and System Unit.
How Does Computer Bus Work?
A bus transfers electrical signals from one place to another. An actual bus appears as an endless amount of etched copper circuits on the motherboard’s surface. The bus is connected to the CPU through the Bus Interface Unit.
Data travels between the CPU and memory along the data bus. The location (address) of that data is carried along the address bus. A clock signal which keeps everything in synch travels along the control bus.
The clock acts like a traffic light for all the PC’s components; the “green light” goes on with each clock tick. A PC’s clock can “tick” anywhere from 20 to 65 million times per second, which makes it seem like a computer is really fast. But since each task (such as saving a file) is made up of several programmed instructions, and each of those instructions takes several clock cycles to carry out, a person sometimes has to sit and wait for the computer to catch up.
You’ll also like:
- What is Bus Topology? Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Network
- Types of Computer Networks
- Types of Computer Memory
- what is processor in computer? Types of Microprocessor
- What is ISA Bus?

Dinesh Thakur is a Freelance Writer who helps different clients from all over the globe. Dinesh has written over 500+ blogs, 30+ eBooks, and 10000+ Posts for all types of clients.
For any type of query or something that you think is missing, please feel free to Contact us .
Basic Course
- Database System
- Management System
- Electronic Commerce
Programming
- Structured Query (SQL)
- Java Servlet
World Wide Web
- Java Script
- HTML Language
- Cascading Style Sheet
- Java Server Pages

DEV Community
Posted on Oct 9
Understanding the Computer Bus: The Backbone of Digital Communication
Welcome to the next installment of our series on building a 6502 processor simulation in C++. Before diving into the coding, it’s crucial to understand the foundational concepts of computer architecture and organization. In this article, we’ll explore the computer bus — a fundamental component that enables communication between various parts of a computer system.
Understanding how a bus works will not only help you in simulating the 6502 processor but also deepen your knowledge of how modern computers operate. Let’s get started!
What Is a Bus?
In computing, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer or between computers. Think of it as a shared highway that connects different parts of the computer, such as the CPU, memory, and input/output (I/O) devices, allowing them to communicate with each other.
Key Characteristics :
- Shared Transmission Medium : Multiple devices are connected to the same bus and share the communication pathways.
- Multiple Communication Lines : A bus consists of multiple lines (wires or traces on a circuit board), each capable of transmitting binary data (0s and 1s).
- System Integration : Buses are integral to the computer’s architecture, facilitating data transfer across various levels of the system hierarchy.
Bus Structure: The Three Functional Groups
A typical bus comprises around 50 to 100 separate lines, which can be classified into three main functional groups:
- Data Lines (Data Bus)
- Address Lines (Address Bus)
- Control Lines (Control Bus)

Let’s delve into each of these groups to understand their roles.
1. Data Lines (Data Bus)
Purpose : Transfer actual data between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.
- Bidirectional Communication : Data can flow in both directions—reading from memory or writing to it.
- Width Determines Throughput : Common widths are 8, 16, 32, or 64 bits, affecting how much data can be transferred at once.
- Collectively Known As : Data Bus.
Example : When you save a document, the CPU sends data through the data bus to the storage device.
2. Address Lines (Address Bus)
Purpose : Carry the addresses of memory locations or I/O ports where data is to be read from or written to.
- Unidirectional Communication : Typically, addresses flow from the CPU to memory/I/O devices.
- Determines Addressable Memory Space : The number of lines affects how much memory the system can address (e.g., 16, 20, 24 bits).
- Collectively Known As : Address Bus.
Example : To read a value from memory, the CPU places the address of that memory location on the address bus.
3. Control Lines (Control Bus)
Purpose : Transmit control signals used to manage and coordinate various operations within the computer.
- Control Signals : Include read/write commands, interrupt requests, clock signals, and bus arbitration signals.
- Directionality : Can be unidirectional or bidirectional, depending on the specific control signal.
- Collectively Known As : Control Bus.
Typical Control Signals :
- Memory Read : Indicates a read operation from memory.
- Memory Write : Indicates a write operation to memory.
- I/O Read/Write : Similar signals for I/O devices.
- Bus Request/Grant : Manage bus access among multiple devices.
Example : When the CPU wants to write data to memory, it sends a “Memory Write” signal over the control bus.
How Does a Bus Operate?
Understanding the bus operation is crucial for grasping how data moves within a computer system.
Basic Operation Steps :
- Bus Access Request : A device (e.g., CPU) requests control of the bus if it’s shared among multiple devices.
- Address Placement : The device places the address of the target location on the address bus.
- Control Signal Transmission : Appropriate control signals are sent over the control bus to specify the operation type (read/write).
- Data Transfer : Data is transferred over the data bus between devices.
- Bus Release : The device releases control of the bus after the operation is complete.
Example Scenario :
CPU Reads Data from Memory:
- CPU requests bus access.
- Places the memory address on the address bus.
- Sends a “Memory Read” signal on the control bus.
- Memory places the requested data on the data bus.
- CPU reads the data from the data bus.
- Bus is released for other devices to use.
Types of Buses
Computers use various types of buses to handle different communication needs. Here are some of the most common ones:
1. System Bus
Definition : Connects the major components of a computer system, such as the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.
- Components : Combines the data bus, address bus, and control bus.
- Function : Facilitates data transfer among the core components.
- Also Known As : Front-Side Bus.
2. Peripheral Bus (I/O Bus / External Bus)
Definition : Connects peripheral devices to the CPU and memory.
- Purpose : Handles communication with external devices like printers, storage drives, and network cards.
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) : Connects high-speed devices; allows for expansion cards.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) : Connects a wide array of devices; supports plug-and-play and hot-swapping.
Key Points :
- Expansion Slots : PCI devices are typically added via expansion slots on the motherboard.
- Data Transfer Rates : Peripheral buses have varying speeds, with USB 3.0 offering up to 5 Gbps.
3. Local Bus
Definition : Connects internal components at high speeds, often used for graphics and memory.
- ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) : An older standard for connecting low-speed devices.
- MCA (Micro Channel Architecture) : An IBM proprietary bus with improved performance over ISA.
- EISA (Extended ISA) : Extended the ISA bus to 32 bits, allowing for better performance.
- Specialized Roles : Often used in situations where higher performance is needed within the system, such as video rendering.
4. High-Speed Bus
Definition : Designed to support high-capacity and high-speed I/O devices.
Purpose : Connects devices that require rapid data transfer, like high-speed storage and network interfaces.
- PCI Express (PCIe) : A high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard.
- AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) : Designed specifically for graphics cards (now largely replaced by PCIe).
- FireWire (IEEE 1394) : Used for high-speed multimedia devices.
Increased Bandwidth : Supports the demands of modern high-performance devices. Point-to-Point Connections : Reduces bottlenecks by providing dedicated pathways.
CPU Writes Data to a Peripheral Device
- Bus Request : The CPU gains control of the system bus.
- Address Placement : The CPU places the address of the peripheral device on the address bus.
- Control Signal : The CPU sends an “I/O Write” signal over the control bus.
- Data Transmission : The CPU sends the data over the data bus to the peripheral.
- Peripheral Response : The peripheral receives the data and acknowledges the operation.
- Bus Release : The CPU releases the bus for other devices to use.
Key Takeaways :
Synchronization : Control signals ensure that devices are synchronized during data transfer. Resource Sharing : The bus allows multiple devices to share the same communication pathways efficiently.
The computer bus is the lifeline of digital communication within a computer system. It connects all the critical components, allowing them to work together seamlessly.
By understanding the data, address, and control buses, and the different types of buses used in computer systems, you’re better equipped to tackle complex topics in computer architecture and to implement accurate simulations.
- Bidirectional : Capable of transmitting data in both directions.
- Unidirectional : Transmits data in only one direction.
- Bus Width : The number of bits that can be transmitted simultaneously.
- Bus Mastering : A feature that allows a device connected to the bus to initiate transactions.
- Arbitration : The process of managing access to the bus when multiple devices need to use it.
By mastering the concept of the computer bus, you’re building a solid foundation that will support your journey into more advanced topics in computer architecture and processor simulation. Happy studies!
Top comments (0)
Templates let you quickly answer FAQs or store snippets for re-use.
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink .
Hide child comments as well
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse

Minecraft: A Janela para a POO
Mr Punk da Silva - Sep 6

What is Clean Architecture: Part 12-Creating, Updating, and Deleting Entities Using Commands
mohamed Tayel - Sep 5
What is Clean Architecture: Part 11-Organizing the Code Using Features

Modular Architecture for Scalable Frontend Development
Amirreza salimi - Sep 5

We're a place where coders share, stay up-to-date and grow their careers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A computer bus is a communication system within a computer or between computers that transfers data between different components. The purpose of buses is to …
An expansion bus is a computer bus which moves information between the internal hardware of a computer system (including the CPU and RAM) and peripheral devices. It is a collection of wires, connectors, form factors and …
An address bus is a computer bus architecture used to transfer data between devices that are identified by the hardware address of the physical memory which is stored in the form of binary numbers to enable the data bus to access …
What is Computer Bus: The electrically conducting path along which data is transmitted inside any digital electronic device. A Computer bus consists of a set of parallel conductors, which …
In this article, we’ll explore the computer bus — a fundamental component that enables communication between various parts of a computer system. Understanding how a …
The electrically conducting path along which data is transmitted inside any digital electronic device. A Computer bus consists of a set of parallel conductors, which may be conventional wires, copper tracks on a PRINTED …