
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Last modified on: 10 months ago
- Reading Time: 2 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles. Students are suggested to solve the questions by themselves first and then check the answers. This will help students to check their grasp on this particular chapter Triangles.
Case Study Questions:
Questions 1:
ΔABC is an isosceles triangle in which ∠B = ∠C and LM | | BC. If ∠A = 50º.

(i) The quadrilateral LMCB is (A) Trapezium (B) Square (C) rectangle (D) rhombus
(ii) The value of ∠LMC is: (A) 65º (B) 115º (C) 130º (D) 100º
(iii) The value of ∠ALM is: (A) 130º (B) 80º (C) 65º (D) 100º
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics...
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive and reliable study resource and case study questions for class 9 CBSE, myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter. With over 10,000 study notes, solved sample papers and practice questions, it’s got everything you need to ace your exams. Plus, it’s updated regularly to keep you aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus . So why wait? Start your journey to success with myCBSEguide today!
Significance of Mathematics in Class 9
Mathematics is an important subject for students of all ages. It helps students to develop problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, and to think logically and creatively. In addition, mathematics is essential for understanding and using many other subjects, such as science, engineering, and finance.
CBSE Class 9 is an important year for students, as it is the foundation year for the Class 10 board exams. In Class 9, students learn many important concepts in mathematics that will help them to succeed in their board exams and in their future studies. Therefore, it is essential for students to understand and master the concepts taught in Class 9 Mathematics .
Case studies in Class 9 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a detailed analysis of a particular mathematical problem or situation. Case studies are often used to examine the relationship between theory and practice, and to explore the connections between different areas of mathematics. Often, a case study will focus on a single problem or situation and will use a variety of methods to examine it. These methods may include algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Example of Case study questions in Class 9 Mathematics
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has included case study questions in the Class 9 Mathematics paper. This means that Class 9 Mathematics students will have to solve questions based on real-life scenarios. This is a departure from the usual theoretical questions that are asked in Class 9 Mathematics exams.
The following are some examples of case study questions from Class 9 Mathematics:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 1
There is a square park ABCD in the middle of Saket colony in Delhi. Four children Deepak, Ashok, Arjun and Deepa went to play with their balls. The colour of the ball of Ashok, Deepak, Arjun and Deepa are red, blue, yellow and green respectively. All four children roll their ball from centre point O in the direction of XOY, X’OY, X’OY’ and XOY’ . Their balls stopped as shown in the above image.
Answer the following questions:
Answer Key:
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2
- Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure
- The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z
- Suraj was told to mark ∠ AOC as 4y
- Clive Made and angle ∠ COE = 60°
- Peter marked ∠ BOE and ∠ BOD as y and x respectively
Now answer the following questions:
- 2y + z = 90°
- 2y + z = 180°
- 4y + 2z = 120°
- (a) 2y + z = 90°
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 3
- (a) 31.6 m²
- (c) 513.3 m³
- (b) 422.4 m²
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 4
How to Answer Class 9 Mathematics Case study questions
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Students need to be careful while solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study questions. They should not make any assumptions and should always check their answers. If they are stuck on a question, they should take a break and come back to it later. With some practice, the Class 9 Mathematics students will be able to crack case study questions with ease.
Class 9 Mathematics Curriculum at Glance
At the secondary level, the curriculum focuses on improving students’ ability to use Mathematics to solve real-world problems and to study the subject as a separate discipline. Students are expected to learn how to solve issues using algebraic approaches and how to apply their understanding of simple trigonometry to height and distance problems. Experimenting with numbers and geometric forms, making hypotheses, and validating them with more observations are all part of Math learning at this level.
The suggested curriculum covers number systems, algebra, geometry, trigonometry, mensuration, statistics, graphing, and coordinate geometry, among other topics. Math should be taught through activities that include the use of concrete materials, models, patterns, charts, photographs, posters, and other visual aids.
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
Class 9 Mathematics question paper design
The CBSE Class 9 mathematics question paper design is intended to measure students’ grasp of the subject’s fundamental ideas. The paper will put their problem-solving and analytical skills to the test. Class 9 mathematics students are advised to go through the question paper pattern thoroughly before they start preparing for their examinations. This will help them understand the paper better and enable them to score maximum marks. Refer to the given Class 9 Mathematics question paper design.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN (CLASS 9 MATHEMATICS)
Mycbseguide: blessing in disguise.
Class 9 is an important milestone in a student’s life. It is the last year of high school and the last chance to score well in the CBSE board exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect platform for students to get started on their preparations for Class 9 Mathematics. myCBSEguide provides comprehensive study material for all subjects, including practice questions, sample papers, case study questions and mock tests. It also offers tips and tricks on how to score well in exams. myCBSEguide is the perfect door to enter for class 9 CBSE preparations.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
14 thoughts on “CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
This method is not easy for me
aarti and rashika are two classmates. due to exams approaching in some days both decided to study together. during revision hour both find difficulties and they solved each other’s problems. aarti explains simplification of 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator and rashika explains 4+ ?2 simplification of (v10-?5)(v10+ ?5) by using the identity (a – b)(a+b). based on above information, answer the following questions: 1) what is the rationalising factor of the denominator of 2+ ?2 a) 2-?2 b) 2?2 c) 2+ ?2 by rationalising the denominator of aarti got the answer d) a) 4+3?2 b) 3+?2 c) 3-?2 4+ ?2 2+ ?2 d) 2-?3 the identity applied to solve (?10-?5) (v10+ ?5) is a) (a+b)(a – b) = (a – b)² c) (a – b)(a+b) = a² – b² d) (a-b)(a+b)=2(a² + b²) ii) b) (a+b)(a – b) = (a + b
MATHS PAAGAL HAI
All questions was easy but search ? hard questions. These questions was not comparable with cbse. It was totally wastage of time.
Where is search ? bar
maths is love
Can I have more questions without downloading the app.
I love math
Hello l am Devanshu chahal and l am an entorpinior. I am started my card bord business and remanded all the existing things this all possible by math now my business is 120 crore and my business profit is 25 crore in a month. l find the worker team because my business is going well Thanks
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- CBSE Maths Important Questions
- Class 9 Maths
- Chapter 6: Lines Angles

Important Questions CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6-Lines and Angles
CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 (Lines and Angles) Important Questions with solutions are given here, which can be easily accessed. These questions have been prepared by our experts for students of standard 9 to make them prepare for final exam (2022 – 2023) . All the questions are based on CBSE syllabus and taken in reference from NCERT book. Students can do their revision by practising the Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6: Lines and Angles here and score good marks.
To revise the important questions chapter-wise for 9th Maths , reach us at BYJU’S. The chapter lines and angles will consist of topics such as angles formed after the intersection of two lines, linear pair of angles, complementary angles, etc. Let us solve the questions here to understand all the concepts.
Also Check:
- Important 2 Marks Questions for CBSE 9th Maths
- Important 3 Marks Questions for CBSE 9th Maths
- Important 4 Marks Questions for CBSE 9th Maths
Important Questions & Solutions For Class 9 Chapter 6 (Lines and Angles)
Q.1: In the figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40°, find ∠BOE and reflex ∠COE.

From the given figure, we can see;
∠AOC, ∠BOE, ∠COE and ∠COE, ∠BOD, ∠BOE form a straight line each.
So, ∠AOC + ∠BOE +∠COE = ∠COE +∠BOD + ∠BOE = 180°
Now, by substituting the values of ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40° we get:
70° +∠COE = 180°
∠COE = 110°
110° + 40° + ∠BOE = 180°
Q.2: In the Figure, lines XY and MN intersect at O. If ∠POY = 90° and a : b = 2 : 3, find c.

As we know, the sum of the linear pair is always equal to 180°
∠POY + a + b = 180°
Substituting the value of ∠POY = 90° (as given in the question) we get,
a + b = 90°
Now, it is given that a : b = 2 : 3 so,
Let a be 2x and b be 3x.
∴ 2x + 3x = 90°
Solving this we get
So, x = 18°
∴ a = 2 × 18° = 36°
Similarly, b can be calculated and the value will be
b = 3 × 18° = 54°
From the diagram, b + c also forms a straight angle so,
b + c = 180°
=> c + 54° = 180°
Q.3: In the Figure, POQ is a line. Ray OR is perpendicular to line PQ. OS is another ray lying between rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = 1/2(∠QOS – ∠POS).

In the question, it is given that (OR ⊥ PQ) and ∠POQ = 180°
So, ∠POS + ∠ROS + ∠ROQ = 180° (Linear pair of angles)
Now, ∠POS + ∠ROS = 180° – 90° (Since ∠POR = ∠ROQ = 90°)
∴ ∠POS + ∠ROS = 90°
Now, ∠QOS = ∠ROQ + ∠ROS
It is given that ∠ROQ = 90°,
∴ ∠QOS = 90° + ∠ROS
Or, ∠QOS – ∠ROS = 90°
As ∠POS + ∠ROS = 90° and ∠QOS – ∠ROS = 90°, we get
∠POS + ∠ROS = ∠QOS – ∠ROS
=>2 ∠ROS + ∠POS = ∠QOS
Or, ∠ROS = ½ (∠QOS – ∠POS) (Hence proved).
Q.4: It is given that ∠XYZ = 64° and XY is produced to point P. Draw a figure from the given information. If ray YQ bisects ∠ZYP, find ∠XYQ and reflex ∠QYP.

Here, XP is a straight line
So, ∠XYZ +∠ZYP = 180°
substituting the value of ∠XYZ = 64° we get,
64° +∠ZYP = 180°
∴ ∠ZYP = 116°
From the diagram, we also know that ∠ZYP = ∠ZYQ + ∠QYP
Now, as YQ bisects ∠ZYP,
∠ZYQ = ∠QYP
Or, ∠ZYP = 2∠ZYQ
∴ ∠ZYQ = ∠QYP = 58°
Again, ∠XYQ = ∠XYZ + ∠ZYQ
By substituting the value of ∠XYZ = 64° and ∠ZYQ = 58° we get.
∠XYQ = 64° + 58°
Or, ∠XYQ = 122°
Now, reflex ∠QYP = 180° + ∠XYQ
We computed that the value of ∠XYQ = 122°. So,
∠QYP = 180° + 122°
∴ ∠QYP = 302°
Q.5: In the Figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GED = 126°, find ∠AGE, ∠GEF and ∠FGE .

Since AB || CD GE is a transversal.
It is given that ∠GED = 126°
So, ∠GED = ∠AGE = 126° (alternate interior angles)
∠GED = ∠GEF + ∠FED
EF ⊥ CD, ∠FED = 90°
∴ ∠GED = ∠GEF + 90°
Or, ∠GEF = 126° – 90° = 36°
Again, ∠FGE + ∠GED = 180° (Transversal)
Substituting the value of ∠GED = 126° we get,
∠AGE = 126°
∠GEF = 36° and
Q.6: In the Figure, if PQ || ST, ∠PQR = 110° and ∠RST = 130°, find ∠QRS.

First, construct a line XY parallel to PQ.

As we know, the angles on the same side of the transversal are equal to 180°.
So, ∠PQR + ∠QRX = 180°
Or,∠QRX = 180° – 110°
∴ ∠QRX = 70°
∠RST + ∠SRY = 180°
Or, ∠SRY = 180° – 130°
∴ ∠SRY = 50°
Now, for the linear pairs on the line XY-
∠QRX + ∠QRS + ∠SRY = 180°
Substituting their respective values we get,
∠QRS = 180° – 70° – 50°
Or, ∠QRS = 60°
Q.7: In Fig. 6.33, PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Prove that AB || CD.

First, draw two lines BE and CF such that BE ⊥ PQ and CF ⊥ RS.
Now, since PQ || RS,
So, BE || CF

BE and CF are normals between the incident ray and reflected ray.
As we know,
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection (By the law of reflection)
∠1 = ∠2 and
We also know that alternate interior angles are equal.
Here, BE ⊥ CF and the transversal line BC cuts them at B and C.
So, ∠2 = ∠3 (As they are alternate interior angles)
Now, ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠3 + ∠4
Or, ∠ABC = ∠DCB
So, AB ∥ CD (alternate interior angles are equal)
Q.8: In Fig. 6.40, ∠X = 62°, ∠XYZ = 54°. If YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY respectively of Δ XYZ, find ∠OZY and ∠YOZ.

As we know, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is 180°.
So, ∠X +∠XYZ + ∠XZY = 180°
substituting the values as given in the question we get,
62° + 54° + ∠XZY = 180°
Or, ∠XZY = 64°
Now, As we know, ZO is the bisector so,
∠OZY = ½ ∠XZY
∴ ∠OZY = 32°
Similarly, YO is a bisector and so,
∠OYZ = ½ ∠XYZ
Or, ∠OYZ = 27° (As ∠XYZ = 54°)
Now, as the sum of the interior angles of the triangle,
∠OZY +∠OYZ + ∠O = 180°
∠O = 180° – 32° – 27°
Or, ∠O = 121°
Q.9: In the figure, if AB || CD || EF, PQ || RS, ∠RQD = 25° and ∠CQP = 60°, then find ∠QRS.

According to the given figure, we have
AB || CD || EF
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then each pair of alternate exterior angles is equal.
Now, since, PQ || RS
⇒ ∠PQC = ∠BRS
We have ∠PQC = 60°
⇒ ∠BRS = 60° … eq.(i)
We also know that,
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then each pair of alternate interior angles is equal.
Now again, since, AB || CD
⇒ ∠DQR = ∠QRA
We have ∠DQR = 25°
⇒ ∠QRA = 25° … eq.(ii)
Using linear pair axiom,
∠ARS + ∠BRS = 180°
⇒ ∠ARS = 180° – ∠BRS
⇒ ∠ARS = 180° – 60° (From (i), ∠BRS = 60°)
⇒ ∠ARS = 120° … eq.(iii)
Now, ∠QRS = ∠QRA + ∠ARS
From equations (ii) and (iii), we have,
∠QRA = 25° and ∠ARS = 120°
Hence, the above equation can be written as:
∠QRS = 25° + 120°
⇒ ∠QRS = 145°
Video Lesson on Constructing Angles

Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Extra Questions
- If two lines intersect, prove that the vertically opposite angles are equal.
- Bisectors of interior ∠B and exterior ∠ACD of a Δ ABC intersect at the point T.Prove that ∠ BTC = ½ ∠ BAC.
- A transversal intersects two parallel lines. Prove that the bisectors of any pair of corresponding angles so formed are parallel.
- In the figure, OD is the bisector of ∠AOC, OE is the bisector of ∠BOC and OD ⊥ OE. Show that the points A, O and B are collinear.

5. The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 5 : 3: 7. The triangle is
- An acute-angled triangle
- An obtuse-angled triangle
- A right triangle
- An isosceles triangle
6. Can a triangle have all angles less than 60°? Give a reason for your answer.
7. Can a triangle have two obtuse angles? Give the reason for your answer.
8. How many triangles can be drawn having its angles as 45°, 64° and 72°? Give the reason for your answer.
9. How many triangles can be drawn having its angles as 53°, 64° and 63°? Give the reason for your answer.
10. Two distinct points in the plane determine a _________________ line.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
doubt in 7 q. how can you prove that if angle 1 and 2 are equal 3 and four are equal? please tell?
they form a ‘z’ that is the shape of alternate interior angles if you look closely so only we conclude it like it
According to the chapter light angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. So angle 1 is incidence and 2 reflected ray same for 3 and 4
Just like angle 1 and angle 2, angle 3 is incident ray and angle 4 is reflected ray. CF is normal between them. Therefore, by the law of reflection, angle 3 and angle 4 are equal.
it is based on the law of reflection angle i (incident ray) = angle r (reflected ray).
both the angles are equal as it was formed by an incident ray and a reflected ray and both the ray measures the same ,so if
Incident ray is equal ro reflected ray so /_1 + /_2 = /_3 + /_4 another reason is alternate interior angles
It’s given that the day bisects the angle to form 2 angles. So the two angles are equal. Moreover the incident ray is equal to the reflected ray, so the reflected ray is marked as an incident ray once it comes in contact with the other surface. Hope it helped
How do we do the 3rd question??I am having a doubt
∠POS + ∠ROS + ∠ROQ = 180° (Linear pair of angles)
Thanks for the questions. It was very useful.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Are you preparing for your Class 9 Maths board exams and looking for an effective study resource? Well, you’re in luck! In this article, we will provide you with a collection of Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths specifically designed to help you excel in your exams. These questions are carefully curated to cover various mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. So, let’s dive in and explore these valuable resources that will enhance your preparation and boost your confidence.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

CBSE Class 9 Maths Board Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. The CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends.
If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is where you should hang out. CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 will provide you with detailed, latest, comprehensive & confidence-inspiring solutions to the maximum number of Case Study Questions covering all the topics from your NCERT Text Books !
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th – MATHS: Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
Case study questions are a form of examination where students are presented with real-life scenarios that require the application of mathematical concepts to arrive at a solution. These questions are designed to assess students’ problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and understanding of mathematical concepts in practical contexts.
Chapterwise Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths
Case study questions play a crucial role in the field of mathematics education. They provide students with an opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, thereby enhancing their comprehension of mathematical concepts. By engaging with case study questions, students develop the ability to analyze complex problems, make connections between different mathematical concepts, and formulate effective problem-solving strategies.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Number System
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Quadilaterals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Circles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Constructions
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Statistics
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability
The above Case studies for Class 9 Mathematics will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
- Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
- Class 9 Social Science Case Study Questions
How to Approach Case Study Questions
When tackling case study questions, it is essential to adopt a systematic approach. Here are some steps to help you approach and solve these types of questions effectively:
- Read the case study carefully: Understand the given scenario and identify the key information.
- Identify the mathematical concepts involved: Determine the relevant mathematical concepts and formulas applicable to the problem.
- Formulate a plan: Devise a plan or strategy to solve the problem based on the given information and mathematical concepts.
- Solve the problem step by step: Apply the chosen approach and perform calculations or manipulations to arrive at the solution.
- Verify and interpret the results: Ensure the solution aligns with the initial problem and interpret the findings in the context of the case study.
Tips for Solving Case Study Questions
Here are some valuable tips to help you effectively solve case study questions:
- Read the question thoroughly and underline or highlight important information.
- Break down the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
- Visualize the problem using diagrams or charts if applicable.
- Use appropriate mathematical formulas and concepts to solve the problem.
- Show all the steps of your calculations to ensure clarity.
- Check your final answer and review the solution for accuracy and relevance to the case study.
Benefits of Practicing Case Study Questions
Practicing case study questions offers several benefits that can significantly contribute to your mathematical proficiency:
- Enhances critical thinking skills
- Improves problem-solving abilities
- Deepens understanding of mathematical concepts
- Develops analytical reasoning
- Prepares you for real-life applications of mathematics
- Boosts confidence in approaching complex mathematical problems
Case study questions offer a unique opportunity to apply mathematical knowledge in practical scenarios. By practicing these questions, you can enhance your problem-solving abilities, develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts, and boost your confidence for the Class 9 Maths board exams. Remember to approach each question systematically, apply the relevant concepts, and review your solutions for accuracy. Access the PDF resource provided to access a wealth of case study questions and further elevate your preparation.
Q1: Can case study questions help me score better in my Class 9 Maths exams?
Yes, practicing case study questions can significantly improve your problem-solving skills and boost your performance in exams. These questions offer a practical approach to understanding mathematical concepts and their real-life applications.
Q2: Are the case study questions in the PDF resource relevant to the Class 9 Maths syllabus?
Absolutely! The PDF resource contains case study questions that align with the Class 9 Maths syllabus. They cover various topics and concepts included in the curriculum, ensuring comprehensive preparation.
Q3: Are the solutions provided for the case study questions in the PDF resource?
Yes, the PDF resource includes solutions for each case study question. You can refer to these solutions to validate your answers and gain a better understanding of the problem-solving process.

You Might Also Like
Mcq questions of class 9 maths chapter 10 circles with answers, class 9 science case study questions chapter 12 sound, class 9 mcq questions for chapter 9 force and laws of motion with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 6 Class 9 Lines and Angles
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for New NCERT Book - for 2023-24 Edition.
Get NCERT Solutions of all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 6 Class 9 Lines and Angles free at teachoo. Answers to each question has been solved with Video. Theorem videos are also available.
In this chapter, we will learn
- Basic Definitions - Line, Ray, Line Segment, Angles, Types of Angles (Acute, Obtuse, Right, Straight, Reflex), Intersecting Lines, Parallel Lines
- What is Linear Pair of Angles
- Vertically Opposite Angles are equal
- Angles formed by a transversal on parallel lines - Corresponding Angles, Alternate Interior Angles, Alternate Exterior Angles, Interior Angles on the same of transversal. And its properties
- Theorem 6.6 - Lines parallel to the same line are parallel to each other
- Angle Sum Property of Triangle
- Exterior Angle Property of a Triangle
Click on Serial Order Wise, if you want to study from the NCERT Book.
This is useful when you are looking for an answer to a specific question.
click on Concept Wise - the best way to study maths. Each chapter is divided into topics, first the topic is explained. Then, the questions of that topic, from easy to difficult.
Check it out now.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Important Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 6
Home » CBSE » CBSE Important Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 6

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 – Lines and Angles
Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6, Lines And Angles, exposes you to fundamental geometry with a particular emphasis on the characteristics of the angles created when two lines cross one another and when a line intersects two or more parallel lines at different points.
Quick Links
You can prepare for the upcoming board exams and improve your grade in class by using the Chapter 6 Class 9 Mathematics important questions. Extramarks has concentrated on getting you ready for the Class 9 exam using the CBSE curriculum. Your mathematical knowledge will be sharpened by solving these important questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 , which will also help you grasp the topic better.
These important questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 provide a sample of the kinds of questions that are frequently asked in board exams. Learning about these can also give you more assurance as you take the examinations. Students can practice all types of questions from the chapters with the aid of these important questions Class 9 Mathematics chapter 6 .
Extramarks experts have created the important questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 in a well-structured format to offer a variety of potential approaches to solving problems and guarantee a thorough comprehension of the concepts. For their exams, it is advised that the students thoroughly practice all of these solutions. Additionally, it will assist students in laying the groundwork for more challenging courses.
Students are given other online learning resources, like revision notes, sample papers, and previous years question papers in addition to the NCERT Solutions, which are accessible in Extramarks. These materials were created with consideration for the NCERT and CBSE curricula. Additionally, it is suggested that students practice the important CBSE questions in Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 to get a sense of the final exam’s question format.
Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 – With Solutions
The students may easily prepare all the concepts included in the CBSE Syllabus in a much better and more effective method with the help of Extramarks important questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 . These resources include a thorough explanation, key formulas, are also offered to students to assist them in getting a quick review of all the topics.
A few Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 are provided here, along with their answers:
Question 1: If one angle of the triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is
(A) An equilateral triangle
(B) An obtuse triangle
(C) An isosceles triangle
(D) A right triangle
Solution 1: (D) A right triangle
Explanation:
We suppose the angles of △ABC be ∠A, ∠B and ∠C
Given, ∠A= ∠B+∠C …(equation 1)
But, in any △ABC,
Using the angle sum property, we have,
∠A+∠B+∠C=180o …(equation 2)
From equations (eq1) and (eq2), we get
∠A+∠A=180 o
⇒∠A=180 o /2 = 90 o
Thus, we get that the triangle is a right-angled triangle
Question 2. The exterior angle of the triangle is 105°, and its two interior opposite angles are equal. Each of these equal angles is
Solution 2: (B) 52 ½ o
As per the question,
The exterior angle of the triangle will be = 105°
We suppose the two interior opposite angles of the triangle = x
We know that,
The exterior angle of a triangle will be = the sum of interior opposite angles
Thus, we have,
105° = x + x
Question 3: The angles of the triangle are in the ratio 5 : 3: 7. The triangle is
(A) An acute angled triangle
(B) An isosceles triangle
(C) A right triangle
(D) An obtuse-angled of triangle
Solution 3: (A) An acute angled triangle
The angles of the triangle are in the ratio of 5 : 3: 7
Let the ratio 5:3:7 be 5x, 3x and 7x
Using the angle sum property of the triangle,
5x + 3x +7x =180
Putting the value of x, i.e., x = 12, in 5x, 3x and 7x we have,
5x = 5×12 = 60o
3x = 3×12 = 36o
7x = 7×12 = 84o
As all the angles are less than 90o, the triangle will be an acute-angled triangle.
Question 4: In the given figure, if PQ || RS, then find the measure of angle m.
Solution 4:
Here, PQ || RS, PS is a transversal.
⇒ ∠PSR = ∠SPQ = 56°
Also, ∠TRS + m + ∠TSR = 180°
14° + m + 56° = 180°
⇒ m = 180° – 14 – 56 = 110°
Question 5: In Figure, the lines AB and CD intersect at the point O. If ∠AOC +∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40°, find ∠BOE and the reflex ∠COE.
Solution 5:
From the diagram, we have
(∠AOC +∠BOE +∠COE) and (∠COE +∠BOD +∠BOE) forming a straight line.
Then, ∠AOC+∠BOE +∠COE = ∠COE +∠BOD+∠BOE = 180°
Now, by substituting the values of ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40° we have,
∠COE = 110° and ∠BOE = 30°
So, reflex ∠COE = 360o – 110o = 250°
Question 6: In the given figure, POQ is the line. The ray OR is the perpendicular to the line PQ. OS is another ray lying between the rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = 1 2 (∠QOS – ∠POS).
Solution 6:
Given that OR is perpendicular to PQ
⇒ ∠POR = ∠ROQ = 90°
∴ ∠POS + ∠ROS = 90°
⇒ ∠ROS = 90° – ∠POS
Adding ∠ROS to both sides, we have
∠ROS + ∠ROS = (90° + ∠ROS) – ∠POS
⇒ 2∠ROS = ∠QOS – ∠POS
⇒ ∠ROS = 1 2 (∠QOS – ∠POS).
Question 7: In Figure, the lines XY and MN intersect at the point O. If ∠POY = 90° and a: b = 2 : 3, find c.
Solution 7:
We know, the sum of the linear pair is always equal to 180°
∠POY +a +b = 180°
Putting the value of ∠POY = 90° (given in the question), we have,
Now, given, a: b = 2 : 3, so,
We suppose a be 2x, and b be 3x
∴ 2x+3x = 90°
Solving this equation, we get
So, x = 18°
∴ a = 2×18° = 36°
In the similar manner, b can be calculated, and the value will be
b = 3×18° = 54°
From the given diagram, b+c also forms a straight angle, so,
c+54° = 180°
Therefore, c = 126°
Question 8: In the Figure, ∠PQR = ∠PRQ, then prove that ∠PQS = ∠PRT.
Solution 8:
As ST is a straight line so,
∠PQS+∠PQR = 180° (since it is a linear pair) and
∠PRT+∠PRQ = 180° (since it is a linear pair)
Now, ∠PQS + ∠PQR = ∠PRT+∠PRQ = 180°
We know, ∠PQR =∠PRQ (as given in the question)
∠PQS = ∠PRT. (Hence proved).
Question 9: In the Figure, if x+y = w+z, then prove that AOB is a line.
Solution 9:
To prove AOB is a straight line, we will first have to prove that x+y is a linear pair
i.e. x+y = 180°
We know, the angles around a point are 360° so,
x+y+w+z = 360°
In the question, it is given that,
So, (x+y)+(x+y) = 360°
2(x+y) = 360°
∴ (x+y) = 180° (Hence proved).
Question 10: In Figure, POQ is a line. The ray OR is perpendicular to the line PQ. OS is another ray lying between the rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = ½ (∠QOS – ∠POS).
Solution 10:
Given that (OR ⊥ PQ) and ∠POQ = 180°
Thus, ∠POS+∠ROS+∠ROQ = 180°
Now, ∠POS+∠ROS = 180°- 90° (As ∠POR = ∠ROQ = 90°)
Again, ∠QOS = ∠ROQ+∠ROS
Given, ∠ROQ = 90°,
∴ ∠QOS = 90° +∠ROS
Or, ∠QOS – ∠ROS = 90°
As ∠POS + ∠ROS = 90° and ∠QOS – ∠ROS = 90°, we have
∠POS + ∠ROS = ∠QOS – ∠ROS
2 ∠ROS + ∠POS = ∠QOS
Or, ∠ROS = ½ (∠QOS – ∠POS) (Hence proved).
Question 11: In the figure, find the values of x and y and show that AB || CD.
Solution 11:
We know, a linear pair is equal to 180°.
Thus, x+50° = 180°
We also know, vertically opposite angles are equal.
Thus, y = 130°
In the two parallel lines, the alternate interior angles are equal. Here,
x = y = 130°
This proves that the alternate interior angles are equal, and thus, AB || CD.
Question 12: In the given figure, PQ || RS and EF || QS. If ∠PQS = 60°, then find the value of ∠RFE.
Solution 12:
Given PQ || RS
Thus, ∠PQS + ∠QSR = 180°
⇒ 60° + ∠QSR = 180°
⇒ ∠QSR = 120°
Now, EF || QS ⇒ ∠RFE = ∠QSR [corresponding ∠s]
⇒ ∠RFE = 120°
Question 13: In the figure, if AB || CD, CD || EF and y : z = 3 : 7, find x.
Solution 13:
We know, AB || CD and CD||EF
Since the angles on the same side of the transversal line sum up to 180°,
x + y = 180° —–equation (i)
∠O = z (Since corresponding angles)
and, y +∠O = 180° (Since linear pair)
So, y+z = 180°
Now, let y = 3w and thus, z = 7w (As y : z = 3 : 7)
Therefore, 3w+7w = 180°
Or, 10 w = 180°
Thus, w = 18°
Now, y = 3×18° = 54°
and, z = 7×18° = 126°
Now, the angle x can be calculated from equation (i)
Or, x+54° = 180°
Question 14: In the figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GED = 126°, find ∠AGE, ∠GEF and ∠FGE.
Solution 14:
As AB || CD, GE is a transversal.
Given that ∠GED = 126°
So, ∠GED = ∠AGE = 126° (Since they are alternate interior angles)
∠GED = ∠GEF +∠FED
As EF⊥ CD, ∠FED = 90°
∴ ∠GED = ∠GEF + 90°
Or, ∠GEF = 126° – 90° = 36°
Again, ∠FGE +∠GED = 180° (Since transversal)
Substituting the value of ∠GED = 126° we get,
∠AGE = 126°
∠GEF = 36° and
Question 15: In figure, if AB || CD. If ∠ABR = 45° and ∠ROD = 105°, then find ∠ODC.
Solution 15:
Through the point O, we draw a line ‘l’ parallel to AB.
⇒ line I will also be parallel to CD, then
∠1 = 45°[alternate int. angles]
∠1 + ∠2 + 105° = 180° [straight angle]
∠2 = 180° – 105° – 45°
Now, ∠ODC = ∠2 [alternate int. angles]
= ∠ODC = 30°
Question 16: In the figure, if PQ || ST, ∠PQR = 110° and ∠RST = 130°, find ∠QRS.
[Hint: Draw a line parallel to ST through the point R.]
Solution 16:
First, we construct a line XY parallel to PQ.
We know, the angles on the same side of the transversal are equal to 180°.
Thus, ∠PQR+∠QRX = 180°
Or, ∠QRX = 180°-110°
∴ ∠QRX = 70°
In the similar manner,
∠RST +∠SRY = 180°
Or, ∠SRY = 180°- 130°
Therefore, ∠SRY = 50°
Now, from the linear pairs on the line XY-
∠QRX+∠QRS+∠SRY = 180°
Putting the values, we have,
∠QRS = 180° – 70° – 50°
Hence, ∠QRS = 60°
Question 17: In the figure, if AB || CD, ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PRD = 127°, find x and y.
Solution 17:
From the above diagram,
∠APQ = ∠PQR (Since Alternate interior angles)
Now, substituting the value of ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PQR = x, we ,
∠APR = ∠PRD (i.e., alternate interior angles)
Or, ∠APR = 127° (Given ∠PRD = 127°)
∠APR = ∠APQ+∠QPR
Now, substituting the values of ∠QPR = y and ∠APR = 127° we get,
127° = 50°+ y
Or, y = 77°
Thus, the measure of x and y are as follows:
x = 50° and y = 77°
Question 18: In the given figure, p ll q, find the value of x.
Solution 18:
We extend the line p to meet RT at S.
Such that MS || QT
Now, in ARMS, we have
∠RMS = 180° – ∠PMR (Since linear pair]
= 180° – 120°
∠RMS + ∠MSR + ∠SRM = 180° [i.e., by angle sum property of a ∆]
⇒ 60° + ∠MSR + 30o = 180°
⇒ MSR = 90°
Now, PS || QT – ∠MSR = ∠RTQ
⇒ ∠RTQ = x = MSR = 90° (Since corresponding ∠s]
Question 19: In the figure, PQ and RS are the two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Prove that AB || CD.
Solution 19:
Firstly, we draw the two lines, BE and CF, such that BE ⊥ PQ and CF ⊥ RS.
Now, since PQ || RS,
So, BE || CF
The angle of incidence = Angle of reflection (By the law of reflection)
∠1 = ∠2 and
We also know, the alternate interior angles are equal. Here, BE ⊥ CF and the transversal line BC cuts them at points B and C.
So, ∠2 = ∠3 (Since they are alternate interior angles)
Here, ∠1 +∠2 = ∠3 +∠4
Or, ∠ABC = ∠DCB
So, AB || CD (since alternate interior angles are equal)
Question 20: In figure, the sides QP and RQ of ΔPQR are produced to the points S and T, respectively. If ∠SPR = 135° and ∠PQT = 110°, find ∠PRQ.
Solution 20:
Given that TQR is a straight line, and thus, the linear pairs (i.e. ∠TQP and ∠PQR) will add up to 180°
So, ∠TQP +∠PQR = 180°
Now, substituting the value of ∠TQP = 110° we have,
We consider the ΔPQR,
The side QP is extended to the point S, and so ∠SPR forms the exterior angle.
Therefore, ∠SPR (∠SPR = 135°) is equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles. (By triangle property)
Or, ∠PQR +∠PRQ = 135°
Now, substituting the value of ∠PQR = 70° we get,
∠PRQ = 135°-70°
Hence, ∠PRQ = 65°
Question 21: In the figure, ∠X = 62°, ∠XYZ = 54°. If YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY, respectively of Δ XYZ, find ∠OZY and ∠YOZ.
Solution 21:
We know, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is 180
So, ∠X +∠XYZ +∠XZY = 180°
Putting the given values in the question, we have,
62°+54° +∠XZY = 180°
Or, ∠XZY = 64°
Now, we know that ZO is the bisector, so,
∠OZY = ½ ∠XZY
Therefore, ∠OZY = 32°
In the similar manner, YO is a bisector, and so,
∠OYZ = ½ ∠XYZ
Or, ∠OYZ = 27° (As ∠XYZ = 54°)
Now, the sum of the interior angles of the given triangle,
∠OZY +∠OYZ +∠O = 180°
Putting their respective values, we get,
∠O = 180°-32°-27°
Hence, ∠O = 121°
Question 22: In the figure, if AB || DE, ∠BAC = 35° and ∠CDE = 53°, find ∠DCE.
Solution 22:
We know, AE is the transversal since AB || DE
Here ∠BAC and ∠AED are the alternate interior angles.
Hence, ∠BAC = ∠AED
Given, ∠BAC = 35°
Now considering the triangle CDE. We know that the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is 180°.
∴ ∠DCE+∠CED+∠CDE = 180°
Putting the values, we get
∠DCE+35°+53° = 180°
Hence, ∠DCE = 92°
Question 23: To protect the poor people from cold weather, Ram Lal. has given his land to make a shelter home for them. In the given figure, ‘the sides QP and RQ of ∆PQR are produced to points S and T, respectively. If ∠PQT = 110° and ∠SPR = 135°, find the value of ∠PRQ.
Solution 23:
∠SPR + ∠QPR = 180° [i.e., a linear pair]
135° + ∠QPR = 180° [∵ ∠SPR = 135°]
⇒ ∠QPR = 180° – 135° = 45°
In ∆PQR, by the exterior angle property, we have
∠QPR + ∠PRQ = ∠PQT
45° + ∠PRQ = 110°
∠PRQ = 110° – 45° = 65°
Question 24: In the figure, if the lines PQ and RS intersect at point T, in such a way that ∠PRT = 40°, ∠RPT = 95°, and ∠TSQ = 75°, find ∠SQT.
Solution 24:
We consider the triangle PRT.
∠PRT +∠RPT + ∠PTR = 180°
Thus, ∠PTR = 45°
Now, ∠PTR will be equal to ∠STQ as they are the vertically opposite angles.
So, ∠PTR = ∠STQ = 45°
Again, in triangle STQ,
∠TSQ +∠PTR + ∠SQT = 180°
Solving this equation, we get,
74° + 45° + ∠SQT = 180°
Question 25: In the figure, if PQ ⊥ PS, PQ || SR, ∠SQR = 28° and ∠QRT = 65°, then find the values of x and y.
Solution 25:
x +∠SQR = ∠QRT (Because they are alternate angles and QR is the transversal)
Thus, x+28° = 65°
It is also known that the alternate interior angles are the same, and so,
∠QSR = x = 37°
∠QRS +∠QRT = 180° (Since linear pair)
Or, ∠QRS+65° = 180°
So, ∠QRS = 115°
Using the angle sum property in Δ SPQ,
∠SPQ + x + y = 180°
90°+37° + y = 180°
y = 1800 – 1270 = 530
Hence, y = 53°
Question 26: In the figure, the side QR of ΔPQR is produced to a point S. If the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS meet at the point T, then prove that ∠QTR = ½ ∠QPR.
Solution 26:
We consider the ΔPQR. ∠PRS is the exterior angle, and ∠QPR and ∠PQR are the interior angles.
So, ∠PRS = ∠QPR+∠PQR (According to the triangle property)
Or, ∠PRS -∠PQR = ∠QPR ———–equation(i)
Now, considering the ΔQRT,
∠TRS = ∠TQR+∠QTR
Or, ∠QTR = ∠TRS-∠TQR
We know, QT and RT bisect ∠PQR and ∠PRS, respectively.
So, ∠PRS = 2 ∠TRS and ∠PQR = 2∠TQR
Here, ∠QTR = ½ ∠PRS – ½∠PQR
Or, ∠QTR = ½ (∠PRS -∠PQR)
From equation (i), we know, ∠PRS -∠PQR = ∠QPR
Therefore, ∠QTR = ½ ∠QPR (hence proved).
Question 27: For what value of x + y in the figure will ABC be a line? Justify the answer.
Solution 27:
The value of x + y should be 180o for ABC to be a line.
Justification:
From the figure, we can state that,
BD is a ray intersecting AB and BC at point B, which implies
and, ∠DBC = x
If a ray stands on the line, then sum of the two adjacent angles formed will be 180°.
⇒ If the sum of the two adjacent angles is 180°, then a ray stands on the line.
So, for ABC to be a line,
Then, the sum of ∠ABD and ∠DBC should be equal to 180°.
⇒ ∠ABD + ∠DBC = 180°
⇒ x + y = 180°
Thus, the value of x + y should be equal to 180° for ABC to be a line.
Question 28: Can a triangle have all angles less than 60°? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 28:
No. A triangle cannot have all the angles less than 60°
As per the angle sum property,
We know the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle should be = 180°.
We suppose all the angles are 60o,
Then we get, 60o + 60o + 60o = 180o.
Now, considering angles less than 60o,
We suppose 59o to be the highest natural number, less than 60o.
Then we get,
59 o +59 o + 59 o = 177 o ≠ 180 o
Thus, we can say that if all the angles are less than 60o, the measure of the angles won’t be satisfying the angle sum property.
Therefore, a triangle cannot have all the angles less than 60o.
Question 29: Can a triangle have two obtuse angles? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 29:
No. A triangle cannot have two obtuse angles.
According to the angle sum property,
We know, the sum of all the interior angles of the triangle should be = 180o.
An obtuse angle is one with a value greater than 90° but less than 180°.
We consider the two angles to be equal to the lowest natural number greater than 90o, i.e., 91o.
If the triangle has two obtuse angles, then there are two angles that would be at least 91° each.
By adding the two angles, we get
Sum of the two angles = 91° + 91°
⇒ Sum of the two angles = 182°
The sum of the two angles already exceeds the sum of the three angles of the triangle, even before taking into consideration the third angle.
Thus, a triangle cannot have two obtuse angles.
Question 30: How many triangles can be drawn having angles as 45°, 64° ,and 72°? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 30:
No such triangle can be drawn having its angles 45°, 64° and 72°.
We know the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle should be = 180o.
But, as per the question,
We have the angles as 45°, 64° and 72°.
Sum of these angles is = 45° + 64° + 72°
= 181 o , which is greater than 180o.
So, the angles do not satisfy the angle sum property of a triangle.
Therefore, no triangle can be drawn having angles 45°, 64° and 72°.
Question 31: How many triangles can be drawn having their angles as 53°, 64° and 63°? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 31:
Infinitely many triangles can be drawn having angles as 53°, 64° and 63°.
We know the sum of all the interior angles of the triangle should be = 180o.
We have the angles as 53°, 64°, and 63°.
Sum of these angles = 53° + 64° + 63°
Thus, the angles satisfies the angle sum property of the triangle.
Therefore, infinitely many triangles may be drawn, having their angles as 53°, 64° and 63°.
Question 32: In the figure, OD is the bisector of ∠AOC, and OE is the bisector of ∠BOC and OD ⊥ OE. Show that points A, O and B are collinear.
Solution 32:
According to the question,
In the figure,
OD and OE are the bisectors of ∠AOC and ∠BOC.
To prove: The points A, O and B are collinear.
i.e., AOB is a straight line.
As OD and OE bisect angles ∠AOC and ∠BOC, respectively.
∠AOC = 2∠DOC …(equation 1)
And ∠COB = 2∠COE …(equation 2)
Adding (equation 1) and (equation 2), we have,
∠AOC = ∠COB = 2∠DOC + 2∠COE
∠AOC +∠COB = 2(∠DOC +∠COE)
∠AOC + ∠COB = 2∠DOE
Since OD⊥OE
∠AOC +∠COB = 2×90o
∠AOC +∠COB =180o
So, ∠AOC + ∠COB form a linear pair.
Thus, AOB is a straight line.
Therefore, the points A, O and B are collinear.
Question 33: In the figure, OP bisects ∠BOC and OQ bisects ∠AOC. Prove that ∠POQ = 90°
Solution 33:
∵ OP bisects ∠BOC
∴ ∠BOP = ∠POC = x (say)
Also, OQ bisects. ∠AOC
∠AOQ = ∠COQ = y (say) .
∵ Ray OC stands on ∠AOB
∴ ∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° [linear pair]
⇒ ∠AOQ + ∠QOC + ∠COP + ∠POB = 180°
⇒ y + y + x + x = 180°.
⇒ 2x + 2y = 180°
⇒ x + y = 90°
Now, ∠POQ = ∠POC + ∠COQ
= x + y = 90°
Question 34: In the figure, ∠1 = 60° and ∠6 = 120°. Show that the lines m and n are parallel.
Solution 34:
We have from figure ∠1 = 60° and ∠6 = 120°
As, ∠1 = 60° and ∠6 = 120°
Here, ∠1 = ∠3 [i.e.,vertically opposite angles]
∠3 = ∠1 = 60°
Now, ∠3 + ∠6 = 60° + 120°
⇒ ∠3 + ∠6 = 180°
If the sum of the two interior angles on the same side of l is 180°, then the lines are parallel.
Therefore, m || n
Question 35: AP and BQ are the bisectors of the two alternate interior angles which are formed by the intersection of the transversal t with the parallel lines l and m (figure). Show that AP || BQ.
Solution 35:
l || m and t is the transversal
∠MAB = ∠SBA [alternate angles]
⇒ ½ ∠MAB = ½ ∠SBA
⇒ ∠PAB = ∠QBA
But, ∠2 and ∠3 are alternate angles.
Hence, AP||BQ.
Question 36: If in the Figure, the bisectors AP and BQ of the alternate interior angles are parallel, then show that l || m.
Solution 36:
AP is the bisector of ∠MAB
BQ is the bisector of ∠SBA.
Given: AP||BQ.
So ∠2 = ∠3 [Alternate angles]
⇒ ∠2 + ∠2 = ∠3 +∠3
From the figure, we have ∠1= ∠2and ∠3 = ∠4
⇒ ∠1+ ∠2 = ∠3 +∠4
⇒ ∠MAB = ∠SBA
But we also know that these are the alternate angles.
Therefore, the lines l and m are parallel, i.e., l ||m.
Question 37: In the figure, BA || ED and BC || EF. Show that ∠ABC = ∠DEF [Hint: Produce DE to intersect BC at P (say)].
Solution 37:
Construction:
We extend DE to intersect BC at point P.
Given that EF||BC and DP are transversal,
∠DEF = ∠DPC …(equation 1) [Since corresponding angles]
Also given, AB||DP and BC is a transversal,
∠DPC = ∠ABC …(equation 2) [Since Corresponding angles]
From (equation 1) and (equation 2), we get
∠ABC = ∠DEF
Hence, Proved.
Question 38: In the given figure, AB || CD, ∠FAE = 90°, ∠AFE = 40°, find ∠ECD.
Solution 38:
external ∠FEB = ∠A + F
= 90° + 40° = 130°
As AB || CD
Therefore, ∠ECD = FEB = 130°
Hence, ∠ECD = 130°.
Question 39: If the two lines intersect each other, prove that the vertically opposite angles are equal.
Solution 39:
AB and CD intersect each other at the point O.
We suppose the two pairs of vertically opposite angles be,
1st pair – ∠AOC and ∠BOD
2nd pair – ∠AOD and ∠BOC
The vertically opposite angles are equal,
i.e., ∠AOC = ∠BOD, and ∠AOD = ∠BOC
The ray AO stands on the line CD.
If a ray lies on the line, then the sum of the adjacent angles is equal to 180°.
⇒ ∠AOC + ∠AOD = 180° (i.e., By linear pair axiom) … equation (i)
In the similar manner, the ray DO lies on the line AOB.
⇒ ∠AOD + ∠BOD = 180° (i.e.,By linear pair axiom) … equation (ii)
From equations (i) and (ii),
∠AOC + ∠AOD = ∠AOD + ∠BOD
⇒ ∠AOC = ∠BOD – – – – equation (iii)
In the similar manner, the ray BO lies on the line COD.
⇒ ∠DOB + ∠COB = 180° (By using linear pair axiom) – – – – equation (iv)
Also, the ray CO is lying on the line AOB.
⇒ ∠COB + ∠AOC = 180° (By using linear pair axiom) – – – – equation (v)
From equations (iv) and (v),
∠DOB + ∠COB = ∠COB + ∠AOC
⇒ ∠DOB = ∠AOC – – – – equation (vi)
Therefore, from equation (iii) and equation (vi),
∠AOC = ∠BOD, and ∠DOB = ∠AOC
Thus, we get vertically opposite angles are equal.
Hence Proved.
Question 40: Bisectors of the interior ∠B and the exterior ∠ACD of a Δ ABC intersect at point T.
Prove that ∠ BTC = ½ ∠ BAC.
Solution 40:
Given: In△ ABC, we produce BC to D and the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACD meet at point T.
∠BTC = ½ ∠BAC
In △ABC, ∠ACD is an exterior angle.
The exterior angle of the triangle is equal to the sum of two opposite angles,
∠ACD = ∠ABC + ∠CAB
Now, dividing the L.H.S and R.H.S by 2,
⇒ ½ ∠ACD = ½ ∠CAB + ½ ∠ABC
⇒ ∠TCD = ½ ∠CAB + ½ ∠ABC …equation (1)
[∵CT is the bisector of ∠ACD⇒ ½ ∠ACD = ∠TCD]
Then in △ BTC,
∠TCD = ∠BTC +∠CBT
⇒ ∠TCD = ∠BTC + ½ ∠ABC …(2)
[∵BT is bisector of △ ABC ⇒∠CBT = ½ ∠ABC ]
From equations (1) and (2),
½ ∠CAB + ½ ∠ABC = ∠BTC + ½ ∠ABC
⇒ ½ ∠CAB = ∠BTC or ½ ∠BAC = ∠BTC
Hence, proved.
Question 41: A transversal intersects the two parallel lines. Prove that the bisectors of any pair of the corresponding angles so formed are parallel.
Solution 41:
We suppose,
EF be the transversal that passes through the two parallel lines at the point P and Q, respectively.
PR and QS are the bisectors of ∠EPB and ∠PQD.
We know, corresponding angles of the parallel lines are equal,
So, ∠EPB = ∠PQD
½ ∠EPB = ½ ∠PQD
∠EPR = ∠PQS
But we also know that they are the corresponding angles of PR and QS
Since the corresponding angles are equal,
Question 42: The lines AB and CD intersect at the point O. If ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40°, find ∠BOE and the reflex ∠COE.
Solution 42:
∠AOC, ∠BOE, ∠COE and ∠COE, ∠BOD, ∠BOE form a straight line each.
Thus, ∠AOC + ∠BOE +∠COE = ∠COE +∠BOD + ∠BOE = 180°
Here, by putting the values of ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40° we get:
70° +∠COE = 180°
∠COE = 110°
110° + 40° + ∠BOE = 180°
Question 43: The lines XY and MN intersect at O. If ∠POY = 90° and a: b = 2 : 3, find c.
Solution 43:
We know, the sum of a linear pair is always equal to 180°
∠POY + a + b = 180°
Substitutg the value of ∠POY = 90° (as given), we get,
a + b = 90°
Now, we know from the question a: b = 2 : 3, so,
We suppose a be 2x, and b be 3x.
∴ 2x + 3x = 90°
By solving the equation, we get
∴ a = 2 × 18° = 36°
b = 3 × 18° = 54°
Here, b + c also forms a straight angle, so,
b + c = 180°
=> c + 54° = 180°
Question 44: Given, POQ is a line. The ray OR is perpendicular to the line PQ. OS is another ray lying between the rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = 1/2(∠QOS – ∠POS).
Solution 44:
Given in the question that (OR ⊥ PQ) and ∠POQ = 180°
So, ∠POS + ∠ROS + ∠ROQ = 180° (Since linear pair of angles)
Now, ∠POS + ∠ROS = 180° – 90° (As ∠POR = ∠ROQ = 90°)
Now, ∠QOS = ∠ROQ + ∠ROS
Again, given ∠ROQ = 90°,
Therefore, ∠QOS = 90° + ∠ROS
Since ∠POS + ∠ROS = 90° and ∠QOS – ∠ROS = 90°, we get
=>2 ∠ROS + ∠POS = ∠QOS
Question 45: If AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GED = 126°, find the value of ∠AGE, ∠GEF and ∠FGE.
Solution 45:
Since AB || CD GE is a transversal.
It is given that ∠GED = 126°
So, ∠GED = ∠AGE = 126° (alternate interior angles)
∠GED = ∠GEF + ∠FED
EF ⊥ CD, ∠FED = 90°
Again, ∠FGE + ∠GED = 180° (Since it is the transversal)
Question 46: If ∠X = 62°, ∠XYZ = 54°. If YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY, respectively of Δ XYZ, find ∠OZY and ∠YOZ.
Solution 46:
We know, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is 180°.
Then, ∠X +∠XYZ + ∠XZY = 180°
Substituting the values given in the equation we get,
62° + 54° + ∠XZY = 180°
Now, ZO is the bisector, so,
∴ ∠OZY = 32°
In the similar manner, YO is the bisector, and thus,
Now, as the sum of interior angles of the triangle,
So, ∠OZY +∠OYZ + ∠O = 180°
∠O = 180° – 32° – 27°
Or, ∠O = 121°
Question 47: If AB || CD || EF, PQ || RS, ∠RQD = 25° and ∠CQP = 60°, then find the value of ∠QRS.
Solution 47:
AB || CD || EF
If the transversal intersects the two parallel lines, then each pair of the alternate exterior angles are equal.
Now, as PQ || RS
⇒ ∠PQC = ∠BRS
We have ∠PQC = 60°
⇒ ∠BRS = 60° … equation (i)
If the transversal intersects the two parallel lines, then each pair of the alternate interior angles is equal.
Now, since AB || CD
⇒ ∠DQR = ∠QRA
We have ∠DQR = 25°
⇒ ∠QRA = 25° … equation (ii)
By using the linear pair axiom,
∠ARS + ∠BRS = 180°
⇒ ∠ARS = 180° – ∠BRS
⇒ ∠ARS = 180° – 60° (From equation (i), ∠BRS = 60°)
⇒ ∠ARS = 120° … equation (iii)
Now, ∠QRS = ∠QRA + ∠ARS
From equations (ii) and (iii), we have,
∠QRA = 25° and ∠ARS = 120°
Hence, the above equation can be written as:
∠QRS = 25° + 120°
⇒ ∠QRS = 145°
Question 48: If an angle is half of its complementary angle, then find its degree measure.
Solution 48:
We suppose that the required angle be x
∴ Its complement = 90° – x
Now, according to the given statement, we obtain
x = 1 2 (90° – x)
⇒ 2x = 90° – x
Hence, the required angle is 30°.
Question 49: The two complementary angles are in the ratio of 1: 5. Find the measures of the angles.
Solution 49:
We suppose that the two complementary angles be x and 5x.
∴ x + 5x = 90°
Hence, the two complementary angles are 15° and 5 × 15°, i.e., 15° and 75°.
Question 50: If an angle is 14 o more than its complement, then find its measure.
Solution 50:
Let the required angle be x
x = 90° – x + 14°
⇒ 2x = 104°
Hence, the required angle is 52 o .
Question 51: If AB || EF and EF || CD, then find the value of x.
Solution 51:
Since EF || CD ∴ y + 150° = 180°
⇒ y = 180° – 150° = 30°
Now, ∠BCD = ∠ABC
x + y = 70°
x + 30 = 70
⇒ x = 70° – 30° = 40°
Hence, the value of x is 40°.
Question 52: In the given figure, the lines AB and CD intersect at O. Find the value of x.
Solution 52:
Here, the lines AB and CD intersect at O.
∴ ∠AOD and ∠BOD form a linear pair
⇒ ∠AOD + ∠BOD = 180°
⇒ 7x + 5x = 180°
⇒ 12x = 180°
Question 53: In the given figure, if x°, y° and z° are the exterior angles of ∆ABC, then find the value of x° + y° + z°.
Solution 53:
We know that an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two opposite interior angles.
⇒ x° = ∠1 + ∠3
⇒ y° = ∠2 + ∠1
⇒ z° = ∠3 + ∠2
Adding all these, we have
x° + y° + z° = 2(∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3)
Question 54: In figure., AD and CE are the angle bisectors of ∠A and ∠C, respectively. If ∠ABC = 90°, then find ∠AOC.
Solution 54:
∵ AD and CE are the bisectors of ∠A and ∠C
∠OAC = 1 2 ∠A and
∠OCA 1 2 ∠C
∠OAC + ∠OCA = 1 2 (∠A + ∠C)
= 1 2 (180 0 – ∠B) [ Since, ∠A + ∠B +∠C = 180 0 ]
= 1 2 (180 0 – 90 0 ) [Since, ∠ABC = 90 0 ]
= 1 2 x 90 0 = 45 0
∠AOC + ∠OAC + ∠OCA = 180°
⇒ ∠AOC + 45o = 180°
⇒ ∠AOC = 180° – 45° = 135°.
Question 55: In the given figure, prove that m || n.
Solution 55:
ext. ∠BDM = ∠C + ∠B
= 38° + 25° = 63°
Now, ∠LAD = ∠MDB = 63°
But these are corresponding angles. Hence,
Question 56: In the given figure, two straight lines, PQ and RS, intersect each other at O. If ∠POT = 75°, find the values of a, b, and c.
Solution 56:
Here, 4b + 75° + b = 180° [since a straight angle]
5b = 180° – 75° = 105°
b – 105∘ 5 = 21°
Therefore, a = 4b = 4 × 21° = 84° (i.e., vertically opp. ∠s]
Again, 2c + a = 180° [Since, a linear pair]
⇒ 2c + 84° = 180°
⇒ c = 96° 2 = 48°
Therefore, the values of a, b and c are a = 84°, b = 21° and c = 48°.
Question 57: In the figure, ∠X = 72°, ∠XZY = 46°. If YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY, respectively ∆XYZ, find ∠OYZ and ∠YOZ.
Solution 57:
In ∆XYZ, we have
∠X + XY + ∠Z = 180°
⇒ ∠Y + ∠Z = 180° – ∠X
⇒ ∠Y + ∠Z = 180° – 72°
⇒ Y + ∠Z = 108°
⇒ 1 2 ∠Y + 1 2 ∠Z = 1 2 × 108°
∠OYZ + ∠OZY = 54°
[∵ YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY]
⇒ ∠OYZ + 1 2 × 46° = 54°
∠OYZ + 23° = 54°
⇒ ∠OYZ = 54 0 – 23° = 31°
Again, in ∆YOZ, we have
∠YOZ = 180° – (∠OYZ + ∠OZY)
= 180° – (31° + 23°) 180° – 54° = 126°
Question 58: Prove that if the two lines intersect each other, then the bisectors of the vertically opposite angles are in the same line.
Solution 58:
Let AB and CD be the two intersecting lines intersecting each other at the point O.
OP and OQ are the bisectors of ∠AOD and ∠BOC.
∴ ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠3 = ∠4 …equation (i)
Now, ∠AOC = ∠BOD [vertically opp. ∠s] ……equation (ii)
⇒ ∠1 + ∠AOC + ∠3 = ∠2 + ∠BOD + ∠4 [adding equation (i) and (ii)]
Also, ∠1 + ∠AOC + ∠3 + ∠2 + ∠BOD + ∠4 = 360° (Since ∠s at a point are 360°]
⇒ ∠1 + ∠AOC + ∠3 + ∠1 + ∠AOC + ∠3 = 360° [by using equation (i), (ii)]
⇒ ∠1 + ∠AOC + ∠3 = 180°
or ∠2 + ∠BOD + ∠4 = 180°
Therefore, OP and OQ are in the same line.
Question 59: In the given figure, AB || CD and EF || DG, find ∠GDH, ∠AED and ∠DEF.
Solution 59:
As AB || CD and HE is the transversal.
∴ ∠AED = ∠CDH = 40° [i.e., corresponding ∠s]
Now, ∠AED + ∠DEF + ∠FEB = 180° [since a straight ∠]
40° + CDEF + 45° = 180°
∠DEF = 180° – 45 – 40 = 95°
Again, given, EF || DG and HE is the transversal.
∴ ∠GDH = ∠DEF = 95° [i.e., corresponding ∠s]
Therefore, ∠GDH = 95°, ∠AED = 40° and ∠DEF = 95°
Question 60: In the figure, DE || QR and AP and BP are the bisectors of ∠EAB and ∠RBA, respectively. Find ∠APB.
Solution 60:
Here, AP and BP are the bisectors of ∠EAB and ∠RBA, respectively.
⇒ ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠3 = ∠4
Since DE || QR and the transversal n intersects DE and QR at A and B, respectively.
⇒ ∠EAB + ∠RBA = 180°
[Since co-interior angles are supplementary]
⇒ (∠1 + ∠2) + (∠3 + ∠4) = 180°
⇒ (∠1 + ∠1) + (∠3 + ∠3) = 180° (using equation (i)
⇒ 2(∠1 + ∠3) = 180°
⇒ ∠1 + ∠3 = 90°
Now, in ∆ABP, by angle sum property, we have
∠ABP + ∠BAP + ∠APB = 180°
⇒ ∠3 + ∠1 + ∠APB = 180°
⇒ 90° + ∠APB = 180°
⇒ ∠APB = 90°
Question 61: If the two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then prove that the bisectors of any of the two corresponding angles are parallel.
Solution 61:
Given: AB || CD and the transversal PQ meet these lines at E and F, respectively. EG and FH are
the bisectors of pair of the corresponding angles ∠PEB and ∠EFD.
To Prove: EG || FH
∵ EG and FH are the bisectors of ∠PEB, respectively.
∠PEG = 1 2 ∠PEB ………equation (i)
And, ∠EFH = 1 2 ∠EFD …..equation (ii)
Since, AB || CD and PQ is a transversal
Therefore, ∠PEB = ∠EFD
1 2 ∠PEB = 1 2 ∠EFD
∠PEG = ∠EFH
Which are the corresponding angles of EG and FH ∴ EG || FH.
Question 62: In the given figure, m and n are the two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other. Show that the incident rays CA is parallel to the reflected ray BD.
Solution 62:
Let the normals at A and B meet at point P.
Since the mirrors are perpendicular to each other, therefore, BP || OA and AP || OB.
Thus, BP ⊥ PA, i.e., ∠BPA = 90°
Therefore, ∠3 + ∠2 = 90° [by angle sum property] …equation (i)
Also, ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠4 = ∠3 [Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection]
Thus, ∠1 + ∠4 = 90° [from equations (i)) …(ii]
Adding equation (i) and (ii), we have
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 = 180°
i.e., ∠CAB + ∠DBA = 180°
Hence, CA || BD
Question 63: If the two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, prove that the bisectors of two pairs of the interior angles form a rectangle.
Solution 63:
Given: AB || CD and the transversal EF cut them at P and Q, respectively and the bisectors of
the pair of interior angles form a quadrilateral PRQS.
To Prove: PRQS is a rectangle.
Proof: Since PS, QR, QS and PR are the bisectors of angles
∠BPQ, ∠CQP, ∠DQP and ∠APQ, respectively.
∴∠1 = 1 2 ∠BPQ, ∠2 = 1 2 ∠CQP,
∠3 = 1 2 ∠DQP and ∠4 = 1 2 ∠APQ
Now, AB || CD and EF is the transversal
∴ ∠BPQ = ∠CQP
⇒ ∠1 = ∠2 (∵∠1 = 1 2 ∠BPQ and ∠2 = 1 2 ∠QP)
But these are the pairs of alternate interior angles of PS and QR
In the similar manner, we can prove ∠3 = ∠4 = QS || PR
∴ PRQS is the parallelogram.
Further ∠1 + ∠3 = 1 2 ∠BPQ + 1 2 ∠DQP = 1 2 (∠BPQ + ∠DQP)
= 1 2 × 180° = 90° (Since ∠BPQ + ∠DQP = 180°)
∴ In ∆PSQ, we have ∠PSQ = 180° – (∠1 + ∠3) = 180° – 90° = 90°
Therefore, PRRS is the parallelogram whose one angle ∠PSQ = 90°.
Hence, PRQS is a rectangle.
Question 64: If in ∆ABC, the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at point O. Prove that ∠BOC = 90° + 1 2 ∠ A.
Solution 64:
We suppose ∠B = 2x and ∠C = 2y
∵OB and OC bisect ∠B and ∠C, respectively.
∠OBC = 1 2 ∠B = 1 2 × 2x = x
and ∠OCB = 1 2 ∠C = 1 2 × 2y = y
Now, in ∆BOC, we have
∠BOC + ∠OBC + ∠OCB = 180°
⇒ ∠BOC + x + y = 180°
⇒ ∠BOC = 180° – (x + y)
Again, in ∆ABC, we have
∠A + 2B + C = 180°
⇒ ∠A + 2x + 2y = 180°
⇒ 2(x + y) = 1 2 (180° – ∠A)
⇒ x + y = 90° – 1 2 ∠A …..equation (ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we have
∠BOC = 180° – (90° – 1 2 ∠A) = 90° + 1 2 ∠A
Question 65: In the figure, if I || m and ∠1 = (2x + y)°, ∠4 = (x + 2y)° and ∠6 = (3y + 20)°. Find ∠7 and ∠8.
Solution 65:
Here, ∠1 and ∠4 form a linear pair
∠1 + ∠4 = 180°
(2x + y)° + (x + 2y)° = 180°
3(x + y)° = 180°
As I || m and n is a transversal
(x + 2y)° = (3y + 20)°
2x = 80 = x = 40
From (i), we have
40 + y = 60 ⇒ y = 20
Now, ∠1 = (2 x 40 + 20)° = 100°
∠4 = (40 + 2 x 20)° = 80°
∠8 = ∠4 = 80° [corresponding ∠s]
∠1 = ∠3 = 100° [vertically opp. ∠s]
∠7 = ∠3 = 100° [corresponding ∠s]
Hence, ∠7 = 100° and ∠8 = 80°
Question 66: In the given figure, if PQ ⊥ PS, PQ || SR, ∠SQR = 28o and ∠QRT = 65°. Find the values of x, y and z.
Solution 66:
Here, PQ || SR.
⇒ ∠PQR = ∠QRT
⇒ x + 28° = 65°
⇒ x = 65° – 28° = 37°
Now, in ∆SPQ, ∠P = 90°
∴ ∠P + x + y = 180° [i.e.,angle sum property]
∴ 90° + 37° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 180° – 90° – 37° = 53°
Now, ∠SRQ + ∠QRT = 180° [linear pair]
z + 65° = 180°
z = 180° – 65° = 115°
Question 67: In the figure, AP and DP are bisectors of two adjacent angles, A and D, of a quadrilateral ABCD. Prove that 2∠APD = ∠B + ∠C.
Solution 67:
In quadrilateral ABCD, we have
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
1 2 ∠A + 1 2 ∠B + 1 2 ∠C + 1 2 ∠D = 1 2 X360 0
1 2 ∠A + 1 2 ∠D = 180 0 – + 1 2 (∠B + ∠C)
As, AP and DP are the bisectors of ∠A and ∠D.
Therefore, ∠PAD = 1 2 ∠A
and, ∠PDA = 1 2 ∠D
Now, ∠PAD + ∠PDA = 180 0 – 1 2 (∠B + ∠C) (i)
In APD, we have,
∠APD + ∠PAD + ∠PDA = 180 0
∠APD + 180 0 – 1 2 (∠B + ∠C) = 180 0 [ Using (i)]
∠APD = 1 2 (∠B + ∠C)
2 ∠APD = (∠B + ∠C)
Question 68: In the figure, PS is the bisector of ∠QPR; PT ⊥ RQ and Q > R. Show that ∠TPS = 1 2 (∠Q – ∠R).
Solution 68:
As PS is the bisector of ∠QPR
∴∠QPS = ∠RPS = x (suppose)
In ∆PRT, we have
∠PRT + ∠PTR + ∠RPT = 180°
⇒ ∠PRT + 90° + ∠RPT = 180°
⇒ ∠PRT + ∠RPS + ∠TPS = 90°
⇒ ∠PRT + x + ∠TPS = 90°
⇒ ∠PRT or ∠R = 90° – ∠TPS – x
Again in ΔΡQT, we have
∠PQT + ∠PTQ + ∠QPT = 180°
⇒ ∠PQT + 90° + ∠QPT = 180°
⇒ ∠PQT + ∠QPS – TPS = 90°
⇒ ∠PQT + x – ∠TPS = 90° [Since ∠QPS = x]
⇒ ∠PQT or ∠Q = 90° + ∠TPS – x …equation (ii)
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we get
⇒ ∠Q – ∠R = (90° + ∠TPS – x) – 190° – ∠TPS – x)
⇒ ∠Q – ∠R = 90° + ∠TPS – X – 90° + ∠TPS + x
⇒ 2∠TPS = 2Q- ∠R
⇒ ∠TPS = 1 2 (Q – ∠R)
Question 69: In a triangle, if ∠A = 2∠B = 6∠C, find the measures of ∠A, ∠B and ∠C, also find the value of ∠A+2∠B 3∠C .
Solution 69:
We consider ∠A = 2∠B = 6∠C = x
2∠B = x = ∠B = 1 2
6 ∠ C = x ∠C = x 6
We know that ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180 0
[ using angle sum property of a ]
x + x 2 + x 6 = 180 0
6x + 3x + x = 180 0 x 6
10x = 1080 0 x = 108 0
x = ∠A = 108 0
Also, ∠B = x 2 = 108 2 = 54 0
∠C = x 6 = 108 6 = 18 0
Thus, ∠A = 108 0 , ∠B = 54 0 , ∠C = 18 0
Now, ∠A + 2∠B 3∠C = 108 + 108 3 x 18 = 216 54 = 4 0
Question 70: Students in a school are preparing banners for a rally. The parallel lines I and m are cut by the transversal t. If ∠4 = ∠5 and ∠6 = ∠7, what is the measure of angle 8?
Solution 70:
Here, given, ∠4 = ∠5 and ∠6 = ∠7
Now, I || m and t is the transversal
∴ ∠4 + ∠5 + ∠6 + ∠7 = 180° [Since co-interior angles are supplementary]
∠5 + ∠5 + ∠6 + ∠6 = 180° [using equation (i)]
2(∠5 + ∠6) = 180°
∠5 + ∠6 = 90°
We know, the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is 180°
∴ ∠8 + ∠5 + ∠6 = 180°
⇒ ∠8 + 90° = 180° [using (ii)]
⇒ ∠8 = 180° – 90° = 90°
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6
The chapter on Lines and Angles is divided into two sections; the first section teaches students about lines, while the second section teaches them about various angles. It’s crucial to master the principles of lines and angles in order to comprehend geometry in classes 9th and 10th.
Below are a few benefits for students to practise from our set of Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6:
- It is a one-stop solution, meaning students will get questions from many different sources. Consequently, they will save time during preparation by gathering the questions and responses in advance.
- A team of expert Mathematics teachers reviews and verifies the questions and answers before providing them to the students. So we have lakhs of students who have trusted Extramarks teaching resources.
- After studying the updated CBSE curriculum, experienced Mathematics teachers have created these solutions. So they adhere to the latest NCERT guidelines.
- Since every question and answer is created with the exam in mind, students can confidently approach exams and overcome exam anxiety.
Be in touch with us at Extramarks to get the important exam questions for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics, all chapters, with solutions. Use the additional questions offered here by clicking on the links below to practise your revision.
- CBSE revision notes
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- CBSE extra questions and solutions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 In a PQR, if 2P = 3Q = 2R, find the measures of P, Q and R.
Marks: 4 Ans
We know that the sum of angles of a triangle is 180. P + Q + R = 180 o … i Given, 2 P = 3 Q = 2 R P = 3 2 Q And, R = 3 2 Q By putting the values of P and R in i , we get 3 2 Q + Q + 3 2 Q = 180 8 2 Q = 180 Q = 360 8 = 45 P = 3 2 Q = 3 2 — 45 = 67 . 5 And, R = 3 2 Q = 3 2 — 45 = 67 . 5 Hence, the measures of P , Q and R are 67 . 5 , 45 and 67 . 5 respectively.

Marks: 3 Ans

Marks: 2 Ans
Given, PQ RS As SQ is transversal y = 46 ° [Alternate interior angles] Again, as SP PQ SPQ = 90 ° In SPQ, x + 90 ° + 46 ° = 180 o [Sum of angles of a triangle is 180 o ] x = 44 ° Hence, in the given figure, x = 44 ° and y = 46 °
Q.4 If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of other two, show that the triangle is right-angled-triangle.
Marks: 1 Ans
Let x, y and z be three angles of a ABC. We know that the sum of angles of a triangle is 180 ° x + y + z = 180 ° (i) As per the given condition Let x = y + z y + z + y + z = 180 ° 2(y + z) = 180 ° y + z = 90 ° x = 180 ° – 90 ° = 90 ° [From (i)] ABC is a right-angled-triangle

Please register to view this section
Faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. how can i learn class 9 mathematics chapter 6 in a fast and efficient way.
Solving important questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 is the greatest technique for mastering the chapters of Class 9 Math. There are several questions in it that are crucial for the exams. These solved questions are meant to help students understand the steps that must be taken while addressing complex questions Additionally, it improves analytical and logical thinking skills, which are important for performing well in exams.
2. Should I daily solve the questions from the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Mathematics?
Students are strongly encouraged to solve Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 important questions every day because Mathematics is a subject that benefits from regular practice. Students who follow this advice will feel quite confident when taking exams and can easily answer challenging questions.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 6 lines and angles| pdf download.

- Exercise 6.1 Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 6.2 Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 6.3 Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapters:
How many exercises in chapter 6 lines and angles, if the supplement of an angle is 4 times of its complement, find the angle., what is the measure of an angle whose measure is 32° less than its supplement, angles ∠p and 100° form a linear pair. what is the measure of ∠p, contact form.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles PDF
Selfstudys is an educational website that has taken the initiative to help all the students score good marks in their exams. They provide various study materials, conduct tests, and also help the students to check their Solutions which helps them give them a brief idea. One of the critical study materials is NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles, which allows the students to understand the topic deeply. Our subject matter experts at Selfstudys who have been in the field of education for quite some time have developed the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions after devoting their time and energy. They have included all the topics which not only make the student confident before the exam but also help them score good marks in the exams. These Solutions are also created as per the latest curriculum of the CBSE which also keeps the students updated about the latest syllabus.
Each and every solution is included in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles, be it easy or advanced. This helps the students to get an idea about all the types of questions which can help them in improving their scores. Scoring good marks in exams is a relatively easy task if a student chooses to study from the correct study materials. Apart from the normal questions, the students will also get an idea about the most common questions that have a higher chance of appearing in the exam.
The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions is created in an easy language which makes it easier for the students to learn them. Our subject matter experts are aware of the learning power of each and every student this is the reason why they have developed these Solutions in the most straightforward language possible.
Maths Class 9 Chapter 6 Lines and Angles PDF NCERT Solutions PDF
From the official website of Selftstudys, all the students can download the Maths Class 9 Chapter 6 Lines and Angles PDF NCERT Solutions. As they are created by the subject matter experts in PDF Format, it is very easy to access and download. They can also be downloaded on mobile phones and can be shared with a single click.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions Exercise Wise
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Exercise Wise provides the Solutions exercise-wise provided in the NCERT Maths textbook for Class 9. These Solutions cover various maths topics and concepts. By going through these Solutions, students can clarify their doubts, understand the concepts thoroughly, and develop a strong foundation in mathematics. These Solutions also help in improving various skills and one of them is problem-solving skills and analytical skills. It also helps the students prepare for their final exams. These Maths Class 9 Chapter 6 Lines and Angles PDF NCERT Solutions Exercise Wise is a very important study material for students who want to score good marks in the subject.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Formula Wise
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles is a very important study material for all students seeking a comprehensive understanding of maths concepts and topics. Developed formula-wise, these Solutions provide step-by-step explanations and examples to help the students understand the concepts easily. By studying the formulas and solving the problems, students can enhance various skills which include problem-solving skills, and develop a strong foundation in maths, preparing them for higher grades and competitive exams. The formula-wise approach makes learning more systematic and allows students to grasp maths concepts effectively.
How to Download the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions?
There are a total of 5-6 steps that students can follow to download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles:
- Visit the official website of Selfstudys i.e. Selfstudys.com.
- Once the website is completely loaded, you need to click on the three lines which you will find on the upper left side. Following that, you have to click on the ‘NCERT Books and Solutions’ column.
- After clicking on the option of ‘NCERT Books and Solutions’, a new list will open where you need to select the option of ‘NCERT Solutions’.
- Following that, you will be redirected to a page where you need to select the class and the subject for which you want to download the NCERT Solutions.
- In this case, you need to select Class 9 and the subject Maths to download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles.
What are the Features of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles?
There are many features of the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions which can be very beneficial for all the students. The most important features include:
- Well-Explained: The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles are written in a well-detailed way which helps the students to understand each and every concept without any confusion. This also helps the students to be confident even before sitting for the exam which can increase the chance of students to do well in their exams.
- Helps the students to find their mistakes: The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles helps the students to find their mistakes as the students can go through them after finding their mistakes which can help them in knowing where they need to put more effort in order to improve their scores.
- Error-free Solutions: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions are prepared by subject matter experts, ensuring accuracy and authenticity in them. Students can rely on these Solutions to check their own answers and gain confidence in their understanding of the maths concepts.
- Clarity and simplicity: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions are written in clear and simple language, making them easy to understand for students. They aim to present the concepts and Solutions in a concise and straightforward manner to promote effective learning.
- Step-by-step Solutions: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions offer step-by-step explanations of all the Solutions. This helps students follow a sequence of steps and understand the process of arriving at the correct answers.
- Illustrations and examples: The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles consists of illustrations and examples to clarify the concepts further. These examples help students enhance various skills and one of them is problem-solving skills.
What are the Benefits of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles?
The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions has several benefits to offer to the students. Some of the most important of them are:
- Conceptual understanding: The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles provides a comprehensive explanation of the concepts covered in Chapter 6 Lines and Angles. They help students develop a strong conceptual understanding of various maths concepts.
- Accuracy: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions are prepared by subject matter experts, ensuring accuracy and correctness. They provide clear and step-by-step explanations, making it easier for students to grasp the concepts and solve problems correctly.
- Time management: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions include various time management techniques and strategies which can be a complete game changer for all the students. By following the step-by-step Solutions, students can learn how to manage their time effectively during exams and solve problems more efficiently.
- Self-assessment: The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles allows students to self-assess their progress and performance. By comparing their Solutions with the provided Solutions, students can identify their strengths and weaknesses, and work on improving their understanding of the concepts.
- Increases Confidence: Regular practicing of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles helps the students to increase their confidence which can help them to score good marks in their exams.
- Helps in clearing doubts: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions helps all the students to clear all their doubts while studying them. If a student comes across a hard question, they can refer to these Solutions to understand the correct approach and clear all their doubts.
What are the tips to study from the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions?
There are various tips that can help the students to study effectively from the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles:
- Read the chapter thoroughly: Begin by reading the chapter from your NCERT textbook to get to know about the concepts and topics covered. Look at the explanations, examples, and details provided in the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions.
- Understand the concepts: Before going through the Solutions, ensure you have a clear understanding of the concepts and definitions discussed in the chapter. If you come across any terms which you are not aware of, you can refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles.
- Use the Solutions as a guide: The Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions acts as a guide to help you understand the step-by-step process of solving problems. Instead of simply copying the Solutions, aim to understand each step and the reasoning behind it. This will enhance your problem-solving skills.
- Compare your Solutions: After attempting the exercise questions, compare your answers with the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles. Analyze any differences and identify any mistakes or errors you made. This will allow you to learn from your mistakes and improve your problem-solving approach.
- Do regular practice of the Solutions: To strengthen your understanding and skills, practice regularly with the exercises and additional practice questions provided in the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions. The more you practice, the better you'll become at applying the concepts and solving problems.
What Are the Methods To Study From NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles?
Studying for the exam requires focus and concentration. Below we will discuss various methods of how students can study for an Exam with the help of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles:
- Read the Solutions: Start by reading the Maths Class 9 Chapter 6 Lines and Angles PDF NCERT Solutions as it can be a complete game changer for them. It can help the students in scoring good marks in the exams. Reading the Solutions on a regular basis will help the students to stick the concepts in their minds.
- Understand the NCERT Solutions: After reading the Solutions, all the students should understand the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions thoroughly as it helps to create a base for all the students. It can help them to strengthen their concepts which helps them to score good marks in exams. Students can understand all the concepts with in-depth knowledge.
- Practice the questions regularly: It is advisable for all the students to regularly practice the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles as it helps the students to get familiar with all the concepts and also stick the concepts in their minds.
- Identify your strengths and weaknesses: All the students should identify their strengths and weaknesses while solving the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles and work on them as it will help them to know where they are lacking behind. This increases their chances of scoring well in the exams.
- Stay Relaxed: This is the most important method of studying the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Miscellaneous Solutions and all the students should follow it. They should stay relaxed and not panic while going through the NCERT Solutions as being panicked affects their preparation.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

CBSE Important Questions for Class 9 Maths pdf
Important questions for class 9 maths chapter-6 lines and angles.
- Active page
Jul 21, 2022, 16:45 IST
CBSE Important Questions for class 9 maths chapter-6 Lines and Angles
Find below Important questions of class 9 maths of chapter-Lines and Angles prepared by academic team of Entrancei. All important questions of chapter Lines and Angles class 9 maths are uploaded in pdf form with detail step by step solutions.
Do solve NCERT questions and for reference use NCERT solutions for class 9 prepared by Entrancei team. For additional information related to the subject you can check the Maths Formula section.
Download free pdf for CBSE Important Questions for class 9 maths chapter Lines and Angles
Related link.
- chapter-1 Number Systems
- Chapter-2 Polynomials
- Chapter-3 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter-4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- chapter-5 Introduction to Euclids Geometry
- chapter-6 Lines and Angles
- chapter-7 Triangles
- Chapter-8 Quadrilaterals
- Chapter-9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Chapter-10 Circles
- Chapter-13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter-14 Statistics
- Chapter-15 Probability
- Chapter-12 Heron’s Formula
- chapter-11 Constructions
Talk to Our counsellor

Test: Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions - EmSAT Achieve MCQ
10 questions mcq test - test: lines & angles- case based type questions, direction: bse stands for a disease called bovine spongiform encephalopathy. “bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. this disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.” a farmer has a field abcd formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. his four cows suffering from bse. thus, he tied them at four corners of the field abcd. q. if ∠bac = 30°, find ∠acd..

Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.” A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD. Q. ∠ABC + ∠BCD = 180° as :
- A. Corresponding angles are supplementary.
- B. Alternate interior angles are supplementary.
- C. Alternate exterior angles are supplementary.
- D. Angles on the same side of a transversal are supplementary.
Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.” A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD. Q. If cow at C and cow at D is 2 km apart, then what is the distance between cow at A and cow at B?
So, AB = CD
Given, distance between cow at C and cow at D = CD = 2 km
⇒ AB = 2 km
Hence distance between cow at A and cow at B is 2 km.
Direction: BSE stands for a disease called Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. “Bovine” means that the disease affects cows, “spongiform” refers to the way the brain from a sick cow looks spongy under a microscope, and “encephalopathy” indicates that it is a disease of the brain. This disease is commonly called “mad cow disease.”

A farmer has a field ABCD formed by two pair of parallel roads as shown below in which l ||m and p || q. His four cows suffering from BSE. Thus, he tied them at four corners of the field ABCD.
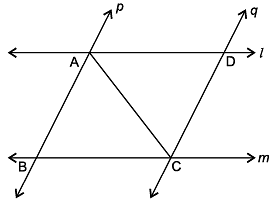
Q. If ∠B = 45°, then ∠D = _________ .
(opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal)

Q. If we join BD such that BD meet AC at O and ∠BOC = 30°, then what is the measure of ∠AOD?
(vertically opposite angles are equal)
Direction: A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflective surface.
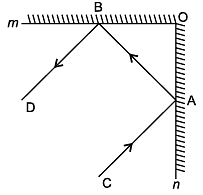
An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. In figure, m and n are two plane mirrors perpendicular to each other.
Q. Parallel lines :
- A. meet at a point
- B. never meet
- C. sometimes meet
- D. meet at right angle
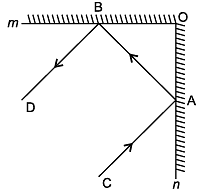
Q. If BO = 3 cm, AB = 5 cm then, AO =
So, AO is perpendicular to BO.
Thus, triangle AOB is a right-angled triangle.
OA 2 + OB 2 = AB 2
OA 2 + 3 2 = 5 2
OA 2 + 9 = 25
OA 2 = 25 – 9 = 16
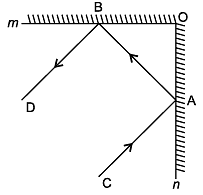
Q. Which statement is incorrect ?
- A. Corresponding angles formed at corresponding corners.
- B. Alternate interior angles are equal
- C. Angles on the same side of the transversal are complementary
- D. Vertically opposite angles are equal
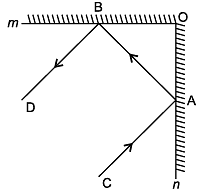
Q. ∠DBA + ∠BAC
Therefore, they are supplementary.
Hence, ∠DBA + ∠BAC = 180°
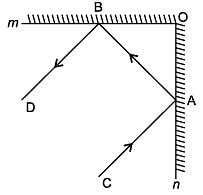
Q. Incident ray CA is :
- A. parallel to AB
- B. perpendicular to BD
- C. parallel to BD
- D. perpendicular to AO
As mirrors are perpendicular to each other, therefore, BP || OA and AP || OB.
So, BP ⊥ PA, i.e., ∠ BPA = 90°
Therefore, ∠ 3 + ∠ 2 = 90° (Angle sum property) (1)
Also, ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠4 = ∠3 (Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection)
Therefore, ∠1 + ∠4 = 90° [From (1)] (2) Adding (1) and (2), we have
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 = 180°
i.e., ∠CAB + ∠DBA = 180°
Hence, CA || BD
Top Courses for EmSAT Achieve

Important Questions for Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions
Lines & angles- case based type questions mcqs with answers, online tests for lines & angles- case based type questions, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles. Here we are providing case study questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles. Students are suggested to solve the questions by themselves first and then check the answers. This will help students to check their grasp on this particular chapter Triangles. Case Study ...
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2. Read the Source/Text given below and answer any four questions: Maths teacher draws a straight line AB shown on the blackboard as per the following figure. Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure. The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z.
Introduction of CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in English is available as part of our Class 9 preparation & CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in Hindi for Class 9 courses. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 (Lines and Angles) Important Questions with solutions are given here, which can be easily accessed. These questions have been prepared by our experts for students of standard 9 to make them prepare for final exam (2022 - 2023).All the questions are based on CBSE syllabus and taken in reference from NCERT book. Students can do their revision by practising the ...
Case study questions lines and angles class 9 chapter 6 is discussed here.Case study question based on lines and angles, alternate interior angles, correspon...
CBSE Class 9 Maths Board Exam will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs.The CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Question Bank on Case Studies, provided in this article, can be very helpful to understand the new format of questions. Share this link with your friends. If you want to want to prepare all the tough, tricky & difficult questions for your upcoming exams, this is ...
Worried about how to Solve the Lines and Angles - Case-Based MCQ Questions? from CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 (1st & 2nd Term Exam) (Board Exam 2021 - 2022) ...
Check it out now. Updated forNew NCERT Book -for 2023-24 Edition.Get NCERT Solutions of all exercise questions and examples of Chapter 6 Class 9 Lines and Angles free at teachoo. Answers to each question has been solved with Video. Theorem videos are also available.In this chapter, we will learnBasic Definitions- Lin.
Solution: Let the angles of a triangle be 2x, 3x and 4x. Since sum of all angles of a triangle is 180°. ∴ 2x + 3x + 4x = 180°. ∴ The required three angles are 2 × 20° = 40°, 3 × 20° = 60° and 4 × 20° = 80°. Question 9. A triangle ABC is right angled at A. L is a point on BC such that AL ⊥ BC.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Ex 6.1. In figure, lines AB and CD intersect at 0. If ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD = 40°, find ∠BOE and reflex ∠COE. Thus, ∠BOE = 30° and reflex ∠COE = 250°. Ex 6.1 Class 9 Maths Question 2. In figure, lines XY and MN intersect at 0. If ∠POY = 90° , and a : b = 2 : ...
Lines and Angles - Competency Based Questions. Select the number of questions for the test: 5. 10. Strengthen your understanding of Lines and Angles in CBSE Class 9 Maths through competency based questions. Acquire in-depth knowledge and improve problem-solving abilities with comprehensive solutions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English; NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi; NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Sanskrit; NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Foundation of IT; CBSE Sample Papers. Previous Year Question Papers; CBSE Topper Answer Sheet; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10; Solved CBSE ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths CBSE Chapter 6: Get free access to Lines And Angles Class 9 Solutions which includes all the exercises with solved solutions. Visit TopperLearning now!
A few Important Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 6 are provided here, along with their answers: Question 1: If one angle of the triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is. (A) An equilateral triangle. (B) An obtuse triangle. (C) An isosceles triangle. (D) A right triangle.
Three exercises are given in Chapter 6 Lines and Angles NCERT Solutions which will improve your knowledge of Geometry. Every students must try to solve each questions given in the exercise that is why we have also provided exercise wise solutions of every problem that you can find below. Exercise 6.1 Chapter 6 Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions.
c. 3 + 4 = 100°. d. 280°. 16. Read the Source/Text given below and answer any four questions: [4] Once 4 students from class IX F were selected for plantation of flower plants in the school garden. The selected students were Pankaj, Raju, Deepak and Renu. As shown PQ and MN are the parallel lines of the plants.
Question 1. If an angle is half of its complementary angle, then find its degree measure. Hence, the required angle is 30°. Question 2. The two complementary angles are in the ratio 1 : 5. Find the measures of the angles. Let the two complementary angles be x and 5x. Hence, the two complementary angles are 15° and 5 × 15° i.e., 15° and 75°.
Also, you can complete the class 9 Lines and Angles worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 9 Maths Important Questions with these class 9 notes. However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Lines and Angles to get all the answers.
There are a total of 5-6 steps that students can follow to download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles: Visit the official website of Selfstudys i.e. Selfstudys.com. Once the website is completely loaded, you need to click on the three lines which you will find on the upper left side.
All important questions of chapter Lines and Angles class 9 maths are uploaded in pdf form with detail step by step solutions. Do solve NCERT questions and for reference use NCERT solutions for class 9 prepared by Entrancei team. For additional information related to the subject you can check the Maths Formula section.
The Test: Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions questions and answers have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus.The Test: Lines & Angles- Case Based Type Questions MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test ...
MCQs from CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 6: Lines and Angles. 1. Intersecting lines cut each other at: a) One point. b) Two points. c) Three points. d) Null. Answer/Explanation. 2.
Lines and Angles Class 9 MCQs Questions with Answers. Question 1. In ΔABC, ∠A = 50° and the external bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O as shown in figure. The measure of ∠BOC is. Question 2. Question 3. Reference Angle Calculator tool helps in finding a reference angle for degrees and radians. Question 4.