CIPD 5CO01 Assignment Example | Organizational Performance and Culture in Practice
Get Custom CIPD Assignment from Reliable Writers that Offer CIPD level 3 Assignment help

CIPD 5CO01 Organizational Performance and Culture in Practice
Executive Summary
This paper examines many facets of an organization’s strategic planning. The report is divided into six distinct sections. The first section discusses organisational structure and how the many parts of an organisation work together to achieve a shared objective, as well as providing examples of hierarchical and functional organisational structures. The second section addresses the connection between organisational strategy and revenue and products. The third component consists of an external examination of the case study organisation, BMC, utilising the PESTLE analysis tool, as well as the results of this analysis. The fourth section investigates existing difficulties and their root causes, identifying critical priorities that impact product/service delivery.
The fifth section explains how people practises may have an impact on organisational systems and structures, hence affecting the successful employment, management, and development of people, while the final chapter examines how technology affects people, work, and working practises.
Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of two types of organisation structures, including the reasons underpinning them. (AC 1.1)
An organisational structure is the method in which the many components of an organisation work together to achieve a shared objective (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). Hierarchical and functional organisational structures are examples of organisational structures (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). It is a pyramidal organisation in which the chain of command descends hierarchically from the top, often from the management to the other individuals. Hierarchical organisational structure is most suitable for large corporations and organisations, as it relies on a chain of command to provide varying levels of control (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). The organisational aim is achieved by the management’s clear communication and flow of commands to subordinates. This is more suitable for corporations like Apple Inc. and Horton Corporation. These two companies produce a radically superior product that is in high demand in many nations.
BMC’ follows an Heirachical Organisational culture
Hierarchical organisational structure possesses both advantages and disadvantages. Hierarchical organisational structure is advantageous due to its capacity to define power and responsibility levels more precisely (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). Second, it displays the reporting structure so that there are no disputes in the chain of command. Thirdly, it stimulates employees’ professional advancement, which is clearly specified (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). In addition, it provides each employee with their degree of specialisation inside the firm, enabling them to achieve the required improvements. It also fosters camaraderie among colleagues within the same department. Due to its bureaucratic manner of leadership, this organisational structure is criticised for its potential to stifle innovation as well as significant transformations (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). Second, it may induce employees to operate in the department’s best interest at the detriment of the corporation as a whole (Lee & Edmondson, 2017). Thirdly, it may make employees feel they have less ownership and that they cannot openly communicate their thoughts without going via their immediate managers (Lee & Edmondson, 2017).
Apples’s Functional Organisational Culture
The functional organisational structure is a management strategy in which the company is subdivided into smaller groups based on functional areas such as IT, department, and marketing (Awa, 2016). This organisational structure is better suitable for businesses with a diverse product portfolio. For example, it is applicable to goods with six organised product categories, such as energy, capital, housing, healthcare, and transportation (Awa, 2016). When items are increasingly technical and require higher specialised expertise, this approach divisions are effective. A functional compartmentalization also enables for increased efficiency by grouping together individuals with similar skills and expertise (Awa, 2016). Through cross-functional communication, it becomes feasible to relate to the organization’s overarching mission (Awa, 2016). Without effective communication channels, a functional organisational structure might inhibit the achievement of corporate goals. In addition, it obscures the company’s procedures and plans for various markets or products (Awa, 2016).
Analyse connections between organisational strategy, products, services and customers. (AC 1.2)
An organisational strategy is an executable corporate management plan. The strategy includes price models, marketing methods, branding techniques, and an evaluation of the competition. There are several techniques a business may employ to link its products, services, and income. The first strategy involves budgeting. Budgeting is justified since it serves as the key function connection between a strategy plan and an operation plan. By matching the budget with the business’s goods, the organisation is able to have more realistic revenue forecast. Budgeting also assists in determining the volume of output and forecasting expenditures. However, this strategy is based on estimates rather than real numbers. Consequently, variations may impact the outputs (Baruah & Ward, 2015).
The allocation of resources is a second technique. The distribution of resources necessitates the creation of an operating plan outlining the responsibilities and proper utilisation of resources and equipments. A strategic strategy is regarded realisable if sufficient resources are allocated to provide particular products and services (Baruah & Ward, 2015). If specific equipment is not allocated, it indicates that the corporation has no intention of assigning its goods. This technique is advantageous since it is directly related to the plan (Baruah & Ward, 2015).
In addition to aligning organisational strategy with goods and revenue, workforce planning and performance management is another way. Workforce planning is a basic business procedure that helps to connect the organization’s shifting demands with its strategy (Baruah & Ward, 2015). It focuses on the ongoing improvement of the workforce to fulfill the consumers’ ever-changing demands. It also assists in addressing organisational demands and hence achieves revenue objectives (Somerville et al., 2015). This strategy offers the benefit of correlating expenditures and revenues. In addition, it motivates people to strive towards the achievement of individual and organisational objectives.
Analyse a range of External Factors and Trends Currently Impacting Organisations. Identify Organisational Priorities Arising from the Factors and Trends Analysed. (AC 1.3)
BMC has just bought a culinary establishment in the city of Manchester. As a result, the organisation may be impacted by the numerous external elements that influence the industry. During the COVID-19 pandemic, when negative impacts are still being observed in the business, this is increasingly evident. Using the PESTLE analysis tool, an examination of external influences was conducted:
There is an ongoing trend defined by greater food regulation to comply with the Food and Drug Administration’s ever-evolving safety rules (Trott & Simms, 2017). This is accompanied by the high expense of adhering to quality principles and by high product pricing. Different governments have engaged in a comprehensive examination of the reactions and seriousness of other nations’ pandemic responses (Trott & Simms, 2017). This has the effect of restricting the flow of people and products to certain nations, so impacting business.
The COVID-19 epidemic has caused a significant fall in the economic propensity of the world’s leading nations. This is evidenced by weak market performance, high unemployment and inflation rates, and exchange rate swings. As a result of these tendencies, market performance and product sales are bad (Trott & Simms, 2017). In addition, BMC and other organisations may have a worker shortage owing to the danger of getting the virus and the movement limitations.
As individuals continue to consider the impact of the food they consume on their health, there is a rise in health consciousness. Dietary limitations are a further challenge for the food sector. The effect of health and dietary constraints on the type of food that BMC would provide for its clients, which should be predicated on these principles, is significant (Trott & Simms, 2017). In addition, as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic, there is an upsurge in both panic and prejudice.
Technological
The Corona virus has expanded the use of technology and home-based employment. As a result, BMC may be needed to make investments in technical tools such as robots. However, this tendency has severe consequences, since it may reduce employee productivity (Trott & Simms, 2017). In addition, some organisational functions, such as food manufacturing, cannot be performed distant from the company’s location.
Environmental
BMC should consider the influence of its actions on the environment when conducting business. This is evaluated based on the carbon footprint and the water footprint. As a result, the corporation may be impacted by their substantial expenditures in renewable energy and water saving techniques (Trott & Simms, 2017).
Legal
In the food business, BMC should take into account the ongoing development of higher safety regulations. Additionally, the business should examine the trade tariffs and rules between the United Kingdom and other countries.
Integrating the fragmented pieces of data and knowledge and understanding could be achieved. This makes the propensity of primary data collection methods through surveys, interviews, observations, feedback and statistical data more important. In the workplace or HR analytics, the people analytics process is enabled by technology to apply statistical methods to interpret people data in the HR process by keeping human capital, HR systems, and organizational performance in mind.
*Examples of information are used by professionals:
– Employees contacts.
– Investigation record.
– Time and attendance.
Assess the Scale of Technology within Organisations and How it Impacts work (AC 1.4)
As the organisation continues to expand, a number of issues impact product and service delivery. Uncertainties such as the one generated by the COVID-19 pandemic and technology are two examples of current concerns that influence enterprises. Uncertainty surrounds economic development, credit and capital market performance, as well as new rules, competition, and technological upheavals (Lastauskas & Nguyen, 2021).
Technology is an additional concern that might have an impact on the business. Other organisations that have continued to use technology have boosted their product and service offerings on the market, resulting in heightened competitiveness and heightened product and service availability in the contemporary day (Lastauskas & Nguyen, 2021). In light of this, technology/innovation becomes a crucial concern for any firm seeking to capitalise on the present economic trend. This was especially evident during the COVID-19 epidemic, when businesses utilised technology as a means of facilitating operations (Lastauskas & Nguyen, 2021). Indeed, many firms have embraced remote and flexible employment arrangements. However, the use of technology has also highlighted the need to address the influence on employee productivity, work-life balance, employee engagement, and employee health.
Adoption of technology and workforce planning are important priorities and issues that may impact product and service delivery as well as practice and solutions. From the research, it is clear that technology is a crucial topic that must be examined by every firm that wishes to remain competitive in the present era (CIPD.org, 2020). In the present day, technology is seen as a vital resource. Despite the hazards involved with technology, there are various possibilities that develop as a result of it (CIPD.org, 2020). AI has being utilised to enhance both customer service and automated decision support.
Other 5CO01 CIPD 5CO01 Organizational Performance and Culture in Practice Topics
- Drawing on your reading, explain one theory or model which examines organisational culture AND interpret one theory or model which examines human behaviour. (AC 2.1)
- Assess how people practices impact on organisational culture and behaviour, drawing on examples to support your arguments. (AC 2.2)
- Many organisations have managed considerable change in recent years. CIPD’s report, People Profession 2030: a collective view of future trends (2020) identifies ‘internal change’ as a key future trend.
- Explain different approaches to managing change (AC 2.3)
- Discuss models for how change is experienced. (AC 2.4)
- CIPD’s Good Work Index provides an annual benchmark of job quality. Data is gathered on seven dimensions of good work, including ‘health and wellbeing’. Assess the importance of wellbeing at work and factors which impact wellbeing. (AC 2.5)
- Discuss the links between the employee lifecycle and different people practice roles. (AC 3.1)
- Analyse how people practice connects with other areas of an organisation and supports wider people and organisational strategies. (AC 3.2)
- People professionals provide a service to internal customers but to truly add value, people professions need to understand their customer’s needs. Discuss processes for consulting and engaging with internal customers to understand their needs. (AC 3.3)
Don’t compromise on quality. Our CIPD Assignments help can service all your Assignment Perfectly.
References
Bryson, A., Forth, J., & Stokes, L. (2017). Does employees’ subjective well-being affect workplace performance?. Human relations, 70(8), 1017-1037.
Cassidy, A. (2016). A practical guide to information systems strategic planning. NY: CRC press.
Cattermole, G. (2019). Developing the employee lifecycle to keep top talent. Strategic HR Review
Kirton, G. (2020). Diversity and inclusion in a changing world of work. In The future of work and employment. NY: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Őnday, Ő. (2016). Classical to modern organization theory. International Journal of Business and Management Review, 4(2), 15-59.
Sundaram, R., Ziade, D., & Quinn, D. (2020). Drivers of Change: An Examination of Factors That Prompt Managers to Enforce Changes in Business. International Journal of Management, 11(5).
Yao, T., Qiu, Q., & Wei, Y. (2019). Retaining hotel employees as internal customers: Effect of organizational commitment on attitudinal and behavioral loyalty of employees. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 76, 1-8.
Money Back Guarantee
24/7 Customer support
Guaranteed A or B Grade
Achieve more in less time
Related Services
- CIPD 5CO01 Business, culture, and cha nge in context
- CIPD 5CO02 Principles of analytics
- CIPD 5CO03 Core behaviors for people professionals
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress

- CIPD Level 3 Course
- CIPD Level 5
- CIPD Level 7 Courses
- ILM Assignment Help
- CMI Assignment Help
5CO01 Assignment Guideline Task Two
- November 12, 2021
- Posted by: admin
- Category: CIPD Level 5
5CO01 Organisational performance and culture in practice
Students pursuing 5CO01 must submit a presentation package for assignment two, in which they will provide an assessment of each learning criteria. To better understand the learning concepts, students are also required to refer to the cast study from BMC. Listed below are the questions for this unit; AC 2.1 Principles and models of organisational and human behaviour that demonstrate how individuals, groups, and teams contribute to the success of an organisation
Students will discuss the following theories of human behaviour:
- According to Belbin theory, there are five roles on the Belbin team: resource investigator, implementer, coordinator, plant, team worker, specialist, shaper, monitor, evaluator, and finisher.
- Model of group development based on Tuckman (identifies five stages in the development of a group, including formation, norming, storming, performing, and adjournment).
Students may add theories about motivation such as;-
- In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs ( five levels of human motivation: physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualisation needs), the physiological needs are placed at the top.
- Motivation theory of Hertzberg (two-factor theory explaining motivator factors and hygiene factors)
Theories of organisational behaviour include the following:
- Theories of leadership
- Theories of systems
- Alternative collegial models
Students should explain how the theories mentioned above influence each employee individually, how they influence people working in groups or teams, and how they affect the overall organisation. In A.C.2.2 , we examine the drivers of change in organisations, along with at least two established models explaining how people might experience change.
This lesson will teach students how to identify internal and external drivers of change. Organisational change of products, financial crisis, complaints from the organisation’s stakeholders, such as customers, and workplace accidents are examples of internal change drivers. In PESTLE analysis, external change drivers are identified in terms of politics, economics, social, technology, law, and the environment. The students are also required to identify and explain two types of change models;
- The 8-step change model of Kotter
- The Kubler-Ross curve
- Lewin’s three-stage model of change
- Adams and Spencer’s seven-step model
A.C. 2.3 Positive steps you can take to increase diversity and inclusion in your work, and the negative results of not taking these steps
https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/relations/diversity/factsheet to explain the benefits of diversity and inclusion at work and the impact on organisation success. A.C. 2.4 Based on your experience and current good practice theories, describe the positive and negative ways that people practices can affect the business culture and behaviour of the organisation
Students must understand that people practices can positively and negatively affect organisational culture and behaviour. In evaluating these aspects, the people professionals should look at the following points:-
- Motivation levels
- Beliefs and values at work
- Openness and trust
- Employees’ perceptions
- Students should focus on analysing models such as;-
- Handy’s 4 Cultural types
- Role-modelling
- Stewardship concept
A.C. 2.5 Assessment of the significance of well-being in the workplace and identifying factors affecting well-being that can impact physically, psychologically, and relationships, thus affecting health, commitment, and performance.
Refer to these resources for students https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/well-being/factsheet for insight on the issue of well-being at work. Several factors contribute to employee well-being, and students should explain them. These factors include employee mental health status and stress management. Additionally, the students should explain the significance of employee well-being for an organisation and individuals. Considerations, in this case, include the following:-
- Workplace absenteeism is reduced
- Retention of employees and reduced turnover
- Healthy workplaces that focus on employee inclusion and growth.
- Engagement, motivation, and morale of employees increased.
In A.C.3.1 , you evaluate your working experience and how it illustrates and demonstrates the employee lifecycle concept and principles.
The students will be identifying concepts in the employee life cycle and evaluating the activities that human resource professionals perform at each stage. These stages are:-
- Onboarding/Induction
- Employee development
- Employee retention/exit
Students should consider themselves professionals and search for examples of the activities they engage in at the identified stages from the organisations they work for or are familiar with. If possible, students may consider using first-person language in their examples to demonstrate their involvement and their organisation’s ability to complete the identified activities. A.C 3.2 Building strategic and operational links and supporting people practice with other functions of the organisation
The students evaluate the people practice concept and compare it to the strategic organisational functions organised by senior management. Additionally, they evaluate the partnership between people practices and business operations functions. Last but not least, a link between people practices and organisational services is provided to help identify the best support system for enhancing organisational success. A.C. 3.4 Principles of interacting with internal customers to determine their needs
Potential candidates, organisational managers, and employees are examples of internal customers. These customers can be engaged in a variety of ways, including;-
- Joint consultations
- Needs analysis
- Stakeholder analysis
A.C 3.5 Components of project planning strategies that ensure projects are performed according to customer requirements
Students should think of a project that they have been a part of within a company or organisation. Students should explain the phases of project management, including the following:
- Project conception
- Project development
- Project realisation
- Project termination.
The students also identify strategies for improving the delivery of the project. Among the approaches are:
- Communication between all stakeholders
- Monitoring project activities with leadership involvement
- Participation of leadership in evaluating project success and lessons learned.
Calculate the price of your order

- +44 2871140060

- Terms of Service
5co01 organisational performance and culture in practice
- October 13, 2022
- Posted by: Fletcher Samuel
- Category: CIPD Level 5

5CO01 is a unit that provides insights into the relationships between an organisation’s organisational structure and its commercial factors. It describes all of the modes and factors involved in delivering organisational change and performance. Learners must comprehend the organisational structures associated with:
- Importance of having a business strategy and planning in the digital environment
- Employee well-being is influenced by an appreciative culture.
Learning objectives
Learners will be able to develop skills in the following areas:
- The relationship that exists between organizational structure, strategy, and the physical business environment.
- Analyze the factors and mode of external operations in order to assess an organization’s challenges and priorities.
- Explain theories and human behaviors in an organization, as well as the factors that cause change.
- Consider how to capitalize on diversity and inclusion to foster a positive culture.
- Examine the connection between an employee’s lifecycle and their job. Examine how people use organizational strategies to promote internal needs and achieve organizational goals.
The connection between organisational structure, strategies and physical environment
Learners will gain an understanding of how to assess the strengths and weaknesses of various organizational structures and why they should be supported. Different types of organizations have different products, services, and customers. They gain knowledge about evaluating the connections between organizational strategy, revenue generation methods, products, services, and customers. This can be accomplished by analyzing how external circumstances and business environments shape corporate organizational strategies, organizational perception and performance, strategy establishment and implementation, revenue-generating mode and methods of formulating strategies, and the concept of how to integrate strategies both horizontally and vertically.
Learners describe the mode and factors that have an impact on the external organization. This can be accomplished by employing reliable methods for analyzing legal regulations, the significance of the organizational lifecycle, and the market. Analyzing external factors influences organizational competitiveness and government policies. International and global factors, as well as international bodies, influence organizational decisions. When attempting to understand an organization’s external environment, demographics, social and technological insights, the importance of technology, and how trends affect an organization’s priorities are all important factors to consider.
Learners examine current organizational priorities, issues, and root causes. Organizational construction, differences in work sessions, and new products and services are examples of such priorities and issues. Other issues include working in a remote location, business expansion, financial targets, customer initiatives, reorganization, technology development, labor shortages, new product development, skill shortages, and restructuring.
The unit explains how people’s behaviors affect an organization’s structures and systems. It examines how people professionals can influence organizational structure and systems such as strategic influence, business partnerships, and organizational arrangement, staff capability, talent management, and identifying organizational priorities.
The unit evaluates the level of technology in an organization and how it affects work. Analyzing the functioning equipment, updating work systems in an organization, work systems, technology implementation across an organization, level of technological support, and organization technology spend can all be used to assess the level of technology.
Organisational culture and actual outlook of the way people behave at work
Learners gain understanding of how to interpret people’s and organizations’ behaviors. This can be accomplished by examining how people and organizations behave. For example, the model of behavior in team performance is evaluated in order to comprehend the organizational culture. System theories, nudge theory, and high-performance organizational theory are models that effectively explain different workplace cultures. Leadership and management, group dynamics, organizational support, and motivational theory all attempt to explain human and organizational behavior.
Learners assess the factors that drive change and how those changes are felt. There are several change management approaches, including Lewin’s three-step change model, Kotter’s eight-stage model, planned model of change, drivers of change, environmental model of change, and levers for change.
The unit describes how diversity and inclusion are implemented in the workplace to foster a positive culture. The concepts of diversity and inclusion are well defined while also outlining current diversity and inclusion legislation. The unit sheds light on the impact of culture in the absence of diversity and inclusion. Learners gain proficiency in assessing organizational culture and theory models, assessing the stages of culture in an organization, and outlining cultural classifications. Fair processes and policies, shared skills and knowledge, employee engagement, voice and involvement, shared beliefs, and organizational learning all contribute to a positive culture.
The impact of people practices on organizational culture and behavior determines how people behave at work. This can be determined by observing how much people practice influences people’s behavior. People can be champions for better work and better working lives, for example, by modeling their behavior through role models and policies. Furthermore, beliefs and values, trust, motivation when someone is rewarded, people attitudes toward provisions and learning, and the value an organization places on employees all influence the potential for impact.
The unit investigates the significance of employee well-being at work as well as the factors that influence well-being. This can be accomplished by assessing how employee well-being affects employee engagement, purpose at work and job satisfaction, motivation, physical and mental health, resilience, and self-status. These are all associated with: psychological work-life balance and family challenges; motivation, for example, expectancy theory, where employees put forth effort to perform in order to be rewarded; employee commitment level and issues arising from this such as punctuality, absenteeism, efficiency and capability, relationships stress and conflicts.
How people practice contributes to attaining organisational goals and objectives.
The unit assesses the overview of people’s practice roles at each stage of the lifecycle and how they progressively evolve while providing a firm evaluation of the relationship between employee lifecycle and work-life. Attraction, recruitment, induction, engagement, succession, exit, and post-employment connections are all components of the employee lifecycle.
People practices are related to organizational areas, such as helping others and implementing organizational strategies. This is accomplished by evaluating the links between specific areas of people practice such as human resources, learning and development, and other organizational aspects. The links between some regions of people practice and function making strategies, the links between people practices and organizational functions, the services provided by some regions of people practice and their support in an organization, and the methods by which strategies for people practice are acquired, employees, and organizational support
The unit outlines the current themes that define how people practice carrying out their work in specific areas. This is significant in terms of providing a solution to work challenges encountered in various work settings and environments. Learners examine how current insights shape people’s work in the internal and external environments.
Students will examine the processes of consulting and engaging with internal clients to better understand their needs. This is accomplished by conducting a consultation process to understand how people practices work on internal customer needs, caring out stakeholder analysis, conducting consultation and communication processes, and conducting an activity need analysis.
Learners will have the opportunity to discuss the critical components of project planning strategies that ensure project completion while meeting the needs of the customers. These components include planning, such as setting goals, milestones, assessing risks, gathering resources, costs, and interrelationships; project management, such as conception, development, realisation, and termination; and developing strategies to assist a project in meeting its requirements. For example, the leadership will communicate with stakeholders on a regular basis and will engage in activities that aid in monitoring and evaluation.
AC 1.1 Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of different types of organisation structures including the reasons underpinning them.
Prior to assessing the benefits and drawbacks of various organizational structures, it is critical to understand the concept and its application in the organization. Structure of the organization According to Maduenyi et al. (2015), organizational structure refers to how different organizational activities are carried out in order to achieve the firm’s goals and objectives. These activities may include enforcing the rules and assigning individual responsibilities. Organizational structure also includes how information flows between different levels of the organization. Flat and hierarchical structures are both common.
Hierarchical: This structure is described as a pyramid, with clear authority and levels within the company. Except for the chief executive officer, every individual in the company who follows this structure is a subordinate to another (CEO). Figure 1 illustrates an example of such a structure.
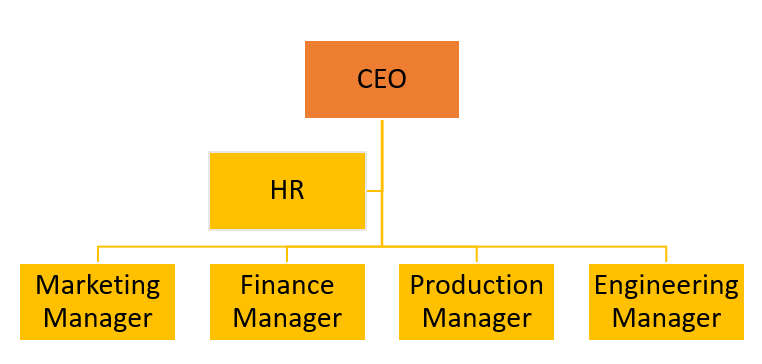
A flat organizational structure is in contrast to a hierarchical one. There are few or no levels between the leadership and management and the employees, as the name implies. This structure is distinguished by less supervision and employee involvement in decision making.
Table 1 summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of the two structures.
AC 1.2 Analyse connections between organisational strategy, revenue generation, products, services and outcomes.
Organizational strategy refers to the actions and activities that a company plans to take in order to achieve its goals and objectives. These actions constitute the strategic plan and necessitate extensive participation from all organizational departments and levels. According to Katuse (2021), organizational strategy is based on several factors such as resources, organizational goals, innovation, and employee learning and development. Corporate, business, and functional strategies are the three types of organizational strategies.
- Organisational Strategy and Revenue
The connection between strategy and revenue generation is centered on how businesses adapt to changes and establish priorities and directions. Outlining the business direction is part of organizational strategy. This ensures that the company meets its goals and maintains its competitiveness, as evidenced by high revenue. Furthermore, an organizational strategy ensures that the firm’s approaches and products are in line with the needs of its customers. This increases the firm’s market share, which increases revenue.
- Organisational Strategy and Products, Services, and Outcomes
The development of an organizational strategy entails the creation of a plan that ensures the firm adapts to current market trends and dynamics. Changing customer needs and preferences are among these trends. This implies the need for a wide range of products and services that not only meet the needs of customers but also align with future trends. For example, in the banking sector, the majority of companies are currently focusing on implementing information and communication technology (ICT) to improve service delivery. These approaches serve as the foundation for achieving business objectives. Another aspect of organizational strategy is the simplification and clarification of decision-making processes, which is critical in increasing profits and achieving the firm’s vision and goals. An effective organizational strategy is aligned with the goals and objectives of the company and ensures that all key performance indicators (KPIs) are met.
Did you enjoy our articles?
Click the order button below to get a high-quality paper.
You can talk to the writer using our messaging system and keep track of how your assignment is going.
AC 1.3 Analyse external factors and trends impacting organisations.
Ac 1.4 assess current organisational priorities and the associated issues and causes., ac 1.5 explain how people practices impact on organisational systems and structures., ac 1.6 evaluate the scale of technology within organisations and how it impacts work., ac 3.3 discuss key themes that currently shape the work of an area of people practice and how these impact on the provision of people solutions., video summary.
- CIPD, 2020. Organisation design. CIPD Factsheet. Available [online] at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/design-factsheet# [Accessed December 26, 2021].
- Katuse, P., 2021. Employee Perceptions on Organisational Strategy Implementation in Covid 19 Era. Indian Journal of Economics and Business , 20 (3).
- Maduenyi, S., Oke, A.O., Fadeyi, O. and Ajagbe, A.M., 2015. Impact of organisational structure on organisational performance.
Related Articles:
- CIPD LEVEL 5
Comments are closed.
Our writing service is available in the UK, USA, Ireland, Canada, Australia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and other countries around the world.


5CO01 Assignment Guideline Task One
Introduction.
Students will be required to provide a formal business report of approximately 2500words. The following is a guide to answering the 5CO01 assignment Task One Questions.
AC 1.1 An evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages of two different types of organisational structures – BMC’s structure and another of your choice
Students will explain BMC’s Hierarchical organisational structure. Decisions at BMC are centralised at the top. Students will explain the advantages and disadvantages of hierarchical structures, and relate this with BMC’s operations. Advantages of hierarchical structures relate to clear line of authority and chain of command. Disadvantages are that it enhance centralisation of power and creates communication barrier.
Students will then differentiate Hierarchical structure with another form structure either functional, horizontal or divisional structures. Students may refer to the structure in the organisation where they work from and will explain the advantages and disadvantages of the organisational structure and then link the structure to the organisation’s purpose.
Starbuck’s Coffee has a functional structure with different departments operating to complete different job functions such as HR, Marketing and Finance. Advantages include specialisation, accountability and clarity of employee roles and responsibilities. Disadvantages include challenges related to employee collaboration, lack of good co-ordination and ineffective flow of information.
AC 1.2 An analysis of the connections between organisational strategy, products & services, customers and revenue generation.
Students will identify how organisational goals link to organisational products and services, the target for the sale of the products to enhance organisational survival and growth.
Students will explain how organisational strategies link to customers, with the aim of meeting customer’s needs and establishing customer loyalty.
Students will explain how organisational strategies link to revenue generation to enhance organisational growth and survival, as well as management of risks.
Example: Students will explain how BMC’s strategic goal is linked to the sale of different food products and the customers in Manchester and other locations as well. Students may refer to OGSM Model while answering this question.
1.3 An analysis of the external factors and trends that are impacting or are likely to impact BMC’s future strategic direction
Students answer this question by considering the analysis models such as PESTLE, STEEPLE, SWOT, BCG or Porter’s Five Forces Model.
From the models, students identify external factors that may affect BMC operations in Manchester.
Example: PESTLE analysis tool evaluates the following elements:- Political (tariffs, political stability), Economic (Covid-19 pandemic, economic growth or decline), Social (lifestyle, culture and norms), Technological (Artificial intelligence, social media), Legal (Employment regulations, labour market laws) and Environmental (Sustainability, green policies, CSR). Refer to https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/pestle-analysis-factsheet . Students should then consider how these factors impact the business and HR operations at BMC.
Examples of external trends that may BMC business include:- Flexible working hours and employee demographics.
1.4 An assessment of two current strategic priorities for BMC and what has caused them
The strategic priorities that BMC should consider include organisation restructuring, new product or service development, new technology developments, new staff and customer initiatives and skills shortage among others.
3.1 A critical evaluation of the relationship between the employee lifecycle and your work (or potential work) as a people professional
The students will identify employee life cycle concepts and evaluate activities that people professionals engage in at the different stages. Stages of employee lifecycle include;-
- Recruitment
- Induction/onboarding
- Employee development
- Employee retention
Students should consider themselves people professionals and seek to find out the activities they engage in at the identified stages, with examples from the organisations they work with or are familiar with.
While giving examples, students may consider using first-person language to show their involvement and their organisation’s capability in completing the identified activities.
3.3 Explanation of two key themes that are currently impacting people practice and shaping how your area of people practice supports the organisation
The impact that the issues have on people practices and solutions are analysed to help shape the area of work among the people and in the organisation. Themes moulding people practices include employee mental well-being, globalisation, new technology, flexible working and nationalisation.
Example: Students discuss issues affecting BMC operations, such as failure of the business to consider people and their well-being, thus resulting to low levels of employee satisfaction and employee turnover. Impact to people practice is that employees become demotivated and thus fail to perform. Solutions would be to develop strategies effective to retain employees through effective workforce planning. Expected positive outcomes would be increased productivity and performance, recruitment of qualified personnel or experts to carry out different organisation roles and responsibilities.
1.5 An assessment of how people practices can impact on organisational systems and structures
Organisational systems can be closed or open. Students differentiate between the open and closed systems.
Students will explain how people practices can affect effective employment.
Students will explain how people practices can affect and improve people management.
Students will explain how people practices can affect development among people in organisations.
The students should provide a paragraph of the potential impacts that organisational structures and systems have on employee recruitment, talent management and priorities in the organisation.
3.2 An assessment of how the BMC People Practice Team: connects with and could support the two strategic priorities at point 4 above
Students evaluate the people practice concept and link them to strategic organisational functions organised by senior management. In addition, the students evaluate people practices’ partnerships to business operations functions. Finally, a link between people practices and organisation services to enhance success is provided to identify with the best support system to enhance organisational success.
3.4 An assessment of how the BMC People Practice Team: would consult with relevant parties to clearly understand needs for this.
Examples of parties that BMC practice team would consult include the organisational internal customers such as managers, employees and potential candidates. Various ways of engaging and consulting with these parties include;-
- Joint consultations
- Needs analysis
- Stakeholder analysis
3.5 An assessment of how the BMC People Practice Team: would plan relevant projects and ensure they were delivered in line with requirements.
Students should think of a project that they have been part of within an organisation. they should consider key components in the project, among them being the project goals and milestones, costs, risks, resources, times and team members’ roles and responsibilities.
The students should explain the project management stages that include;-
- Project conception
- Project development
- Project realisation
- Project termination.
Students also identify approaches effective to enhancing the delivery of the project. Some of the approaches include;-
- Effective communication among all stakeholders
- Leadership involvement in monitoring project activities
- Leadership involvement in evaluating project success and lessons learnt from completing the project.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- CIPD LEVEL 3
- CIPD LEVEL 5
- CIPD Level 5_New Brief
- CIPD LEVEL 7
Latest Posts
Quick links.
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Terms of Service
Terms - Privacy Policy & Safety
© 2021 All Rights Reserved

Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice (5CO01)
This unit examines the connections between organisational structure and the wider world of work in a commercial context. It highlights the factors and trends, including the digital environment, that impact on business strategy and workforce planning, recognising the influence of culture, employee well-being and behaviour in delivering change and organisational performance.

Unit details
- Specialist unit
What will you learn
You will learn about the connections between organisational structure, strategy and the business operating environment. You will analyse external factors and trends and assess organisational priorities and issues, including the scale of technology within organisations. You will also interpret theories and models of organisational and human behaviour and the drivers for change. In addition, you will examine how to build diversity and inclusion that aims to promote a positive culture. Finally, you will evaluate the relationship between the employee lifecycle and your work and how people practice connects and supports wider people and organisational strategies, focusing on how to support internal customer needs and ensure that business goals and objectives are delivered in line with customer requirements.
This unit is suitable for persons who:
are aspiring to, or embarking on, a career in people management
are working in a people practice role and wish to contribute their knowledge and skills to help shape organisational value
are working towards or working in a people manager role
Learning outcomes
On completion of this unit, learners will:
Understand the connections between organisational structure, strategy and the business operating environment.
Understand organisational culture and theoretical perspectives on how people behave at work.
Understand how people practice supports the achievement of business goals and objectives.
Our Price Match Guarantee on like for like CIPD courses means you will never pay more when you study with us.

Can’t wait to get started? Speak to us now about taking the next step in your career
Other units.

Evidence-Based Practice
Professional behaviours and valuing people, supporting self-directed and social learning.

- Tutoring Coming Soon
5CO02 Assignment Example
- December 19, 2021
- Posted by: Harry King
- Category: CIPD Level 5

Task One: Briefing Paper
You have been asked to prepare a briefing paper that is to be given to people practitioners at a regional event, to share insights and good practice. The paper needs to provide understanding of approaches that can be taken to support effective critical thinking and decision-making within the HR remit.
Your Briefing Paper needs to:
- provide an evaluation of the concept of evidence-based practice and assess how evidence- based practice approaches can be used to support sound decision-making and judgments for people practitioners across a range of people practices and organisational issues. (1.1)
- evaluate two micro and two macro analysis tools or methods that can be used in people practice to explore an organisation’s micro and macro environment, and how those identified might be applied to diagnose future issues, challenges and opportunities. (1.2)
- explain the principles of critical thinking and give examples of how you apply these yourself when relating to your own and others’ ideas, to assist objective and rationale debate. (1.3)
- assess at least two different ethical theories and perspectives and explain how an understanding of these can be used to inform and influence effective decision-making. (1.4)
- explain a range of decision-making approaches that could be used to identify possible solutions to a specific issue relating to people practice. (2.3)
- as a worked example to illustrate the points made in 2.3, take this same people practice issue, explain the relevant evidence that you have reviewed, and use one or more decision- making tools to determine a recommended course of action, explaining the rationale for that decision and identifying the benefits, risks and financial implications of the suggested solution. (2.2 & 4)
- compare and contrast a range of different ways and approaches that are used to measure financial and non-financial performance within organisations. (3.1)
It is essential that you refer to academic concepts, theories and professional practice for the tasks to ensure that your work is supported by analysis. Please ensure that any references and sources drawn upon are acknowledged correctly and supported by a bibliography.
Task two: Data analysis and review
In preparing for the forthcoming department heads meeting your manager has asked you to prepare a range of information and interpretations for use at the meeting. Below are two sets of data that have been collected by a 360-degree review for Department ‘A’. Table 1, is the feedback that has been elicited from employees on their line-managers and table 2 is from the customers that use the services and goods from Department A.
Use one analytical tool to review the two data sets to reveal any themes, patterns and trends (2.1).
- From this analysis, graphically present your findings using three or more different methods (3.3).
- Identify the key systems and data used within effective people practices, to give insights by measuring work and people performance (3.2)
- Explain how people practices add value in an organisation and identify methods that might be used to measure the impact of people practices (3.4)
The annual performance reviews for Department ‘A’ last year were scored using a ratings scale from 6 = high performer to 1= low performer.
Any employee scoring 4 and above received a £400.00 bonus in their monthly pay. The budget allocation per department for bonuses last year was £75,000.
Figures from Department ‘A’ for last year were:
- 112 employees received a score of 6
- 98 employees received a score of 5
- 35 employees received a score of 4
- 43 employees received a score of 3 or below
- Using a variety of measurement tools and techniques and the data provided in tables 1, 2 & 3, explain the likely impact and value of these aspects of people practice currently in place in Department ‘A’. What other people practice measures might usefully be employed in Department ‘A’? (3.4)
AC 1.1 provide an evaluation of the concept of evidence-based practice.
Evidence-based HR practice involves making a better decision and informing actions that have the desired outcome (Young, 2020). The concept of evidence-based practice entails finding solutions and approaches to dealing with people management practice based on a strong empirical basis. It is the process through which a decision is evaluated against data in an organisation. The evidence-based approach utilises critical thinking skills and the available evidence to decide on specific HR issues. According to Young (2020), a good decision-making process is based on critical thinking and drawing from the available evidence. Evidence-based decisions are more likely to result in the desired outcomes that will have a long-term impact on organisations practices.
Evidence-based practice also utilises different models of the decision-making process, such as the rational model. This model involves the use of factual information and step by step procedures to arrive at a decision (Uzonwanne, 2016). The figure below summarises the rational decision-making model.
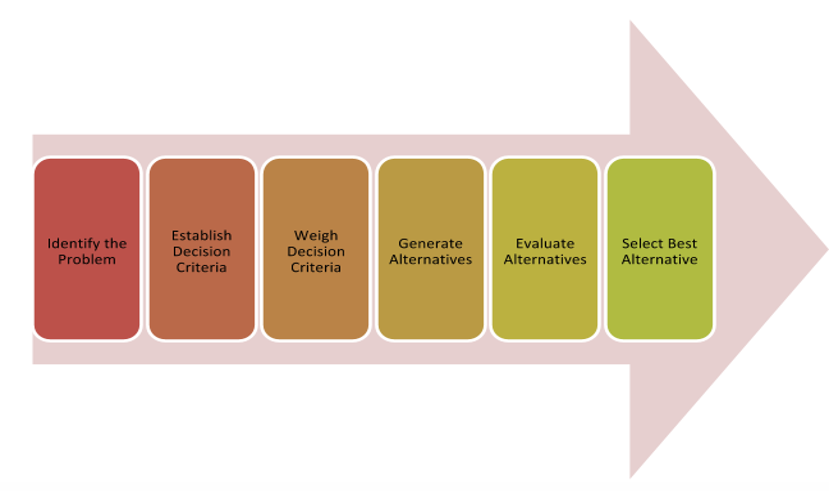
How evidence-based approaches can be used to support sound decision-making and judgments
Evidence-based approaches are essential for supporting sound decision making because they reduce errors caused by judgements. Biased and unreliable management decisions are common in the absence of evidence. Managers are susceptible to bias and errors in their decision making when they base the decisions on previous experiences or popular management decisions. In an article published at the Center for Evidence-Based Management (CEBM), all individuals at all employment levels need to use the best available evidence when making decisions. Using evidence-based decisions is considered to be morally right (Rousseau et al., 2004).
An evidence-based approach can also be used to support sound decision making and judgement at an organisational level by increasing the accountability levels. Most of the decision made by managers have a positive or negative impact on the general organisational performance. Assessing the reliability and validity of evidence not only benefits individuals but also the organisation. This approach ensures that a manager takes the best available decision and can support the decisions with organisational data, professional expertise or insights from scientific research when called to justify the decision.
AC 1.2 Evaluate micro and macro analysis tools that can be used in people practice to explore an organisation’s micro and macro environment and how those identified might be applied to diagnose future issues, challenges and opportunities.
All organisations are affected by either internal or external factors. These factors are part of the general organisational environment, and they should be analysed to establish their impacts on the business. There is a range of tools used in people practice, and they include strategic reviews, future states analysis, SWOT analysis, Ansoff matrix, Fishbone analysis, among others. Analysis methods that can be used to assess an organisation’s micro and macro environments include observations, interviews, job analysis, work sampling and use of questionnaires.
An organisation’s micro-environment refers to the immediate factors or environment that comprises suppliers, customers, competitors and stakeholders (Summer, 2019). They are internal factors that are likely to impact an organisation. Micro-environments can be assessed using the microanalysis tools such as porter’s five forces analytical tool. Macro-environment, on the other side, refers to the more general factors influencing businesses (Summer, 2019). Macro- environments are external factors that impact an organisation’s activities and productivity, but that organisation has no control over it. The macro-environment factors include economic issues, political forces, technological advancements, natural and physical occurrences, and legal factors. An example of a tool used for the analysis of macro-environment factor is the PESTLE analysis tool.
The SWOT analysis tool evaluates both internal and external factors that can influence an organisation. SWOT stands for strength, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. While strengths and weaknesses focus on internal organisational aspects, threats and opportunities focus on external issues that can impact an organisation. The SWOT tool is simple to use and can be used in organisations making an entrance into new markets.
Porter’s five analysis tool was developed by Michael Porter to assess and evaluate the competitive strength of a business (Bruijl, 2018). The model is built on five principles that can be used to assess microenvironments within an organisation. Michael Porter described the five forces: Buyers bargaining power, the threat of entry, suppliers bargaining power, competition from rivalries, and threats by substitutes. Figure 1 below gives a summary of the five forces.
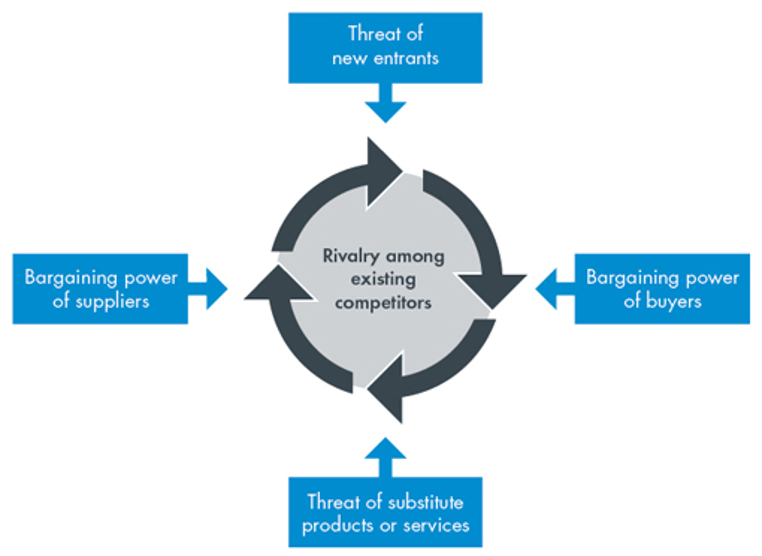
As the acronym suggests, the PESTLE analysis analyses the political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors (Downey, 2007). Trade regulations and policies, and diplomatic tensions are some of the political factors likely to impact an organisation’s performance. It is essential to understand that organisations in the UK are governed by policies and regulations formulated by trade unions and other regulatory bodies. Therefore, the HR department must ensure that an organisation is compliant with all the regulations. HR should also be constantly updated on changes in regulations that are likely to impact an organisation.
One of the biggest external influences for any business is the state of the economy. HR should monitor the shifts in economic trends resulting from changes in global financial status. Economic factors such as inflation, demand and supply, interest rates and exchange rates have direct impacts on organisations. HR should notify the management of the existing economic trends to prepare them for any economic changes. Socially, an organisations performance can be affected by the availability of the workforce. It is HR’s responsibility to come up with a recruiting strategy that will attract the best talent to perform organisational duties. Technological factors include impacts of acquiring new technology, which may result in downsizing or recruiting a skilled workforce. HR is responsible for advising the management on the necessary changes that would make the technological changes beneficial to the organisation and retain a workforce that has adequate knowledge of the technological changes.
Legal factors comprise rules and regulations impacting people practice. HR practitioners should ensure that the organisation is compliant and the existing policies and procedures are compliant with the country’s regulatory standards (Friedman, 2013). The last ‘E’ of the PESTLE tool represents environmental factors, which refer to an all-natural occurring element that may influence people practice. The global market is stimulated to align with the sustainable development goals. It is the HR’s duty to ensure that the organisation is compliant and has environmental sustainability policies incorporated in its daily operations.
AC 1.3. Explain the principles of critical thinking and give examples of how you apply these yourself when relating to your own and others’ ideas to assist objective and rational debate.
Critical thinking is a skill that enables people to think well and reflect on ideas, opinions and arguments objectively (Howlett and Coburn, 2019). It involves objectively analysing and evaluating people practice issues to form a judgement. Based on the definition, various critical thinking principles are based on rational, unbiased analysis evaluation of factual information and sceptical analysis. Objective, rational thinking relates to being logically correct. This principle allows for the differentiation between issues and statements that are logically true or false. Walters adds that rational, objective thinking utilises logic and other cognitive acts such as imagination, creativity, and insights.
In people practice, various principles of critical thinking can be applied to different situations. When applying critical thinking to the decision-making process, HR practitioners must ensure that they understand the issue and differentiate between facts and opinions. Evidence-based decisions are based on the critical thinking principle of validity of evidence to eliminate bias.
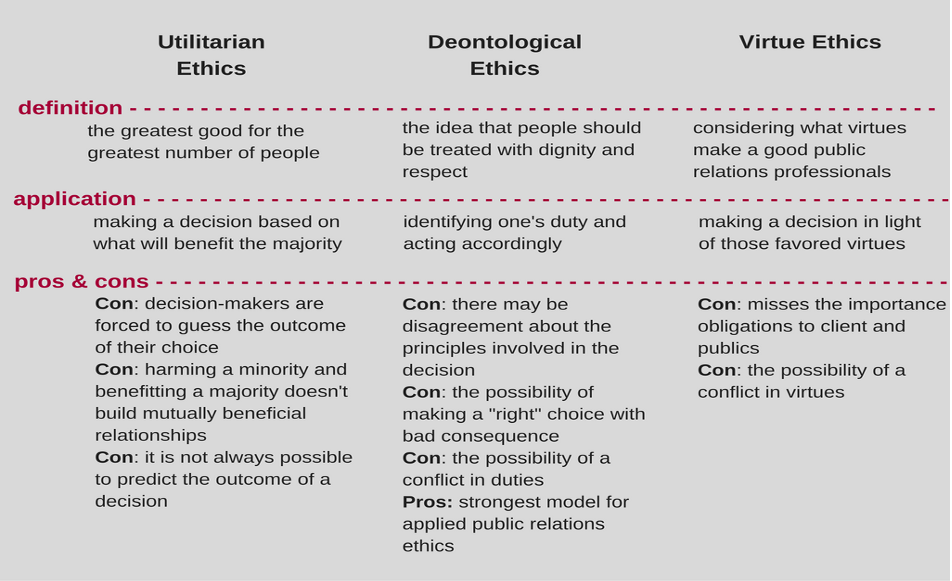
AC 1.4 Assess at least two different ethical theories and perspectives.
Utilitarianism ethical theory is used to determine right from wrong by focusing on the outcome (Driver, 2009). It is one of the most commonly used persuasive methods to normative ethics. This theory is based on the consequence, and it suggests that the most ethical choice is the one that will produce the greatest good. This theory can be used to inform and influence effective decision making when the decision made will result in a positive outcome for most employees or organisation at large. To illustrate this, Covid 19 pandemic has impacted many organisations and thus necessitated cheap labour. HR practitioners are faced with the dilemma of laying off employees and employees new employees at a cheaper cost. While this may not be ethically right, it will benefit organisational sustainability, especially for businesses affected by the pandemic. This theory does not account for justice or any individual rights.
Kantianism or Kant’s moral theory, on the other hand, believes that certain actions are prohibited even if the consequence is happiness. It is an example of a deontological moral theory whose principle is not on the consequence of the action but on individual moral duty (Anscombe, 2005). The theory is based on an individual’s ability to act according to the categorical moral imperatives, which are universal. This theory suggests that decisions should be made based on the moral obligation to individuals and society. Thus the decision will be ethically correct (Chonko, 2012).
Use of Theories to inform and influence effective decision-making.
The decision making theories have a significant influence on the decision-making process. Sound ethical decisions need to be sensitive to good ethical practices. While the theories are divided into three frameworks, HR should be responsible for most ethical obligations in an organisation. The ethical frameworks built around ethical theories include the consequentialist framework, the duty framework and the virtue framework. Using the three frameworks to analyse a situation before making a decision allows the decision-maker to have a clearer perspective of the issue and thus come up with a sound decision sensitive to ethical implications and parties involved (Bonde and Firenze, 2011). The figure below gives a summary of different ethical theories, including their advantages and disadvantages.
AC 2.3 Explain a range of decision-making approaches that could be used to identify possible solutions to a specific issue relating to people practice
HR practitioners play a critical role in the decision-making process of an organisation. Based on HR practitioners’ different functions, different decision-making approaches could be used to find possible solutions for various problems. Some of the decision making processes used by HR include the best fit, future pacing, problem-outcome frame, action learning approaches and de Bono (Six Thinking hats). While one process can be used to solve various HR problems, different issues may require different decision-making approaches.
De Bono (six thinking hats) is a decision-making approach that Edward De Bono developed in 1985. It is a good decision-making approach for group discussions and personal thinking because it involves a combined parallel process. Each of the six hats is metaphors for six different ways of thinking. Mentally wearing different thinking hats results in people looking at problems differently and coming up with different solutions—the six different mind frames as elaborated by Edwards different shapes of the hat and different colours. The white colour represents decisions based on facts. The red colour represents decisions based on emotions. Black represents judgmental decisions, yellow positive view or decisions based on a positive perspective, green decisions based on creativity and blue are thinking decisions (Mulder, 2019). Managers and HR practitioners can switch from one hat to another during a decision making process. The thinking hats are essential for helping people think more deeply concerning specific issues and come up with informed decisions.
Framing problems and outcome is another decision-making approach that can be used to identify the various solution to people specific problems. Framing comprises a schema of interpretations that different individuals depend on to understand and respond to situations. Different diagnosis and framing of problems may result in difficulties when solving the problems. It is essential for HR practitioners to frame their organisational problems to achieve the desired outcome accurately. For example, turnover in an organisation may be framed as an individual problem, an HR problem or a management problem, depending on how it is evaluated.
AC 2.4 As a worked example to illustrate the points made in 2.3, take the same people to practice issues, explain the relevant evidence that you have reviewed and use one or more decision-making tools
Decision making in people practice is continuous throughout the employees’ lifecycle in an organisation. One issue in people practice that requires effective decision making is compensation. Increasing employee compensation is a decision that should be thought through because there are various factors that influence the decision. While performance analysis is essential for determining compensation, other factors such as minimum wage, external markets and industrial payment rates are other factors that should be considered.
Attracting and retaining talent is a people specific area that may face various challenges. Competition for the most talented and qualified employees is evident in both public and private industries. Recruiting a sustainable workforce is essential for effective organisational performance and sustainability. However, competitive wages and rewards may influence turnover and the loss of the best talent pool. The HR is tasked with tough decisions on the best approaches to enhance retention and attract the best talent pool during recruitment. The framing-outcome approach of decision making can be utilised to solve retention and recruitment challenges. The HR can identify specific issues causing turnover, ranging from salaries and wages, organisational culture to the need for career growth. Framing the cause of the problem will enable HR to develop a solution that will result in the desired outcome.
AC 3.1 Appraise different ways organisations measure financial and non-financial performance.
Good performance management is critical for an organisation’s success (Gifford, 2020). Performance management aims at monitoring, maintaining and improving employee performance and aligning them to organisational objectives. However, there are different ways through which organisations can measure their performance. Monitoring performance is essential for the decision-making process as it forms part of the evidence-based practice in people management.
Performance in an organisation can be measured by the use of financial and non-financial indicators. Financial indicators include revenues, gross and net profits, cash flows, return on investments, and productivity. Gross and net profit margins are profitability ratios used to identify a company’s profitability. The working capital is the measure of the available operating liquidity used to fund the daily operations. Cash flow is a financial indicator that indicates the amount of money a business has as a result of its operations. Operating cash flow is often found in the cash flow statements.
Non-financial performance indicators include customer feedback, legal compliance, sector ratings, employee feedback, among others. Customer feedback and customer retention are essential non-financial performance indicators because they directly impact customer retention. Customer retention is as necessary as customer attraction. Retention is essential for establishing the number of customers that are satisfied with a particular product or service, while feedback enables an organisation to identify areas for improvement. Human capital can also be used to measure organisational performance. Based on the employee survey, an organisation can establish its performance based on the skilled employees’ ratio against unskilled labour.
The primary advantage of using non-financial measures is that they result in better compliance with long-term corporate strategy. Non-financial measures take into account different intangible assets and provide adequate information on various operations’ effectiveness (Ahrens and Chapman, 2007). The disadvantages of no-financial measures are that they are expensive to conduct and can consume a lot of time. The advantages of using financial measures are that they are accurate and can be easily monitored. The disadvantage is that they are short –term in nature and are not effective for long term strategic planning.
TASK TWO: DATA ANALYSIS AND REVIEW
AC 2.1 Use one analytical tool to review the two data sets to reveal any themes, patterns and trends.
There are various HR analytical tools that can be used to assess and evaluate data. This section utilised Microsoft excel to conduct a data analysis of the provided information. Graph 1 below is a summary of feedback obtained from employees on their line managers. Of the 256 respondents 250 disagreed that line managers delegated authority, 245 were of the opinion that line managers do not communicate reasons for change and decisions. Two hundred nineteen respondents said that the line managers were not approachable. The three categories mentioned above had the highest numbers of respondents giving a negative review concerning their line managers. As indicated in graph 1 below, the highest number of respondents disagreed with the most positive attributes that were accorded to their line managers.
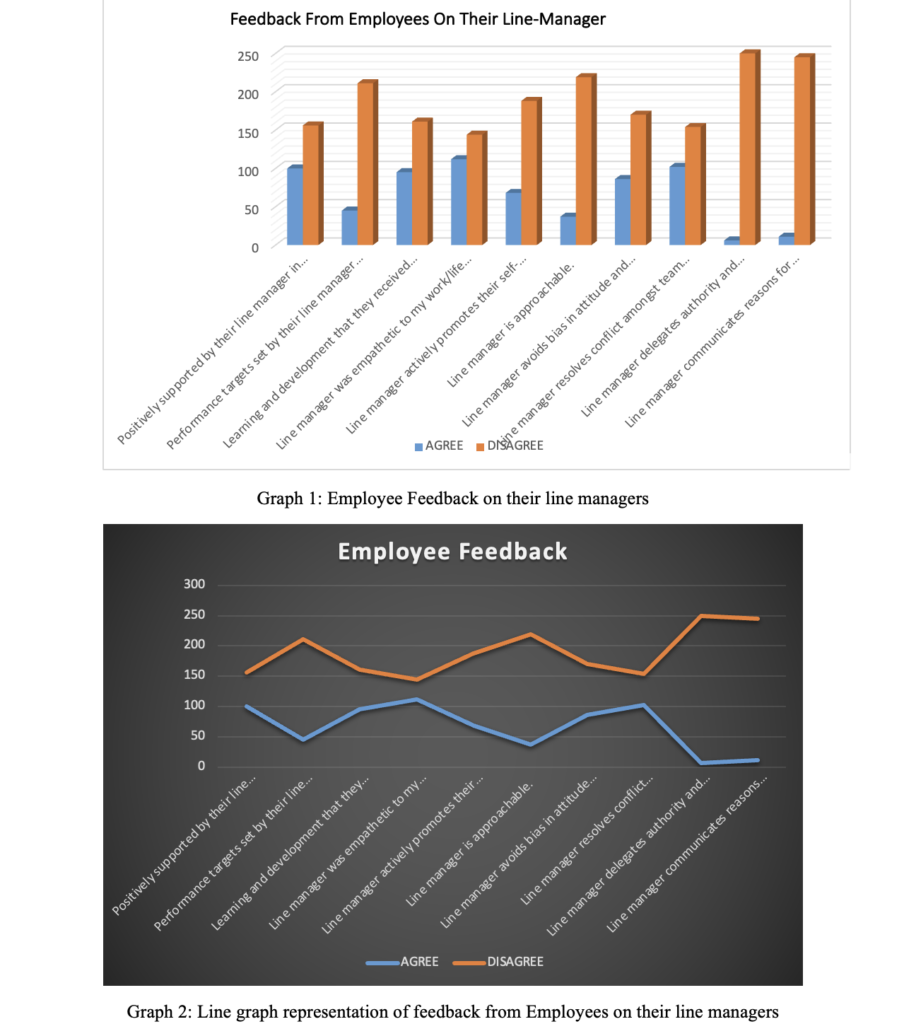
A pie chart representation of data is a circular graph, as shown above. The slices of the pie represent variables that, when combined, should produce the total number. For example, the total number of employees who responded to questions was 256. On the issue of support by line managers, 156 employees disagreed, and 100 agreed. The graph above provides a visual representation of this information in percentile. Pie charts are easy to read and understand. They also visually represent data as part a fractional part of the whole.
Analysis of Employee Feedback
Of the 145 responses from customers, 143 respondents agreed that the products’ packaging was good and acceptable in protecting the goods. One hundred forty-two customers had issues with how their initial enquiries were handled; 114 felt that the range of goods and products was insufficient to meet their needs
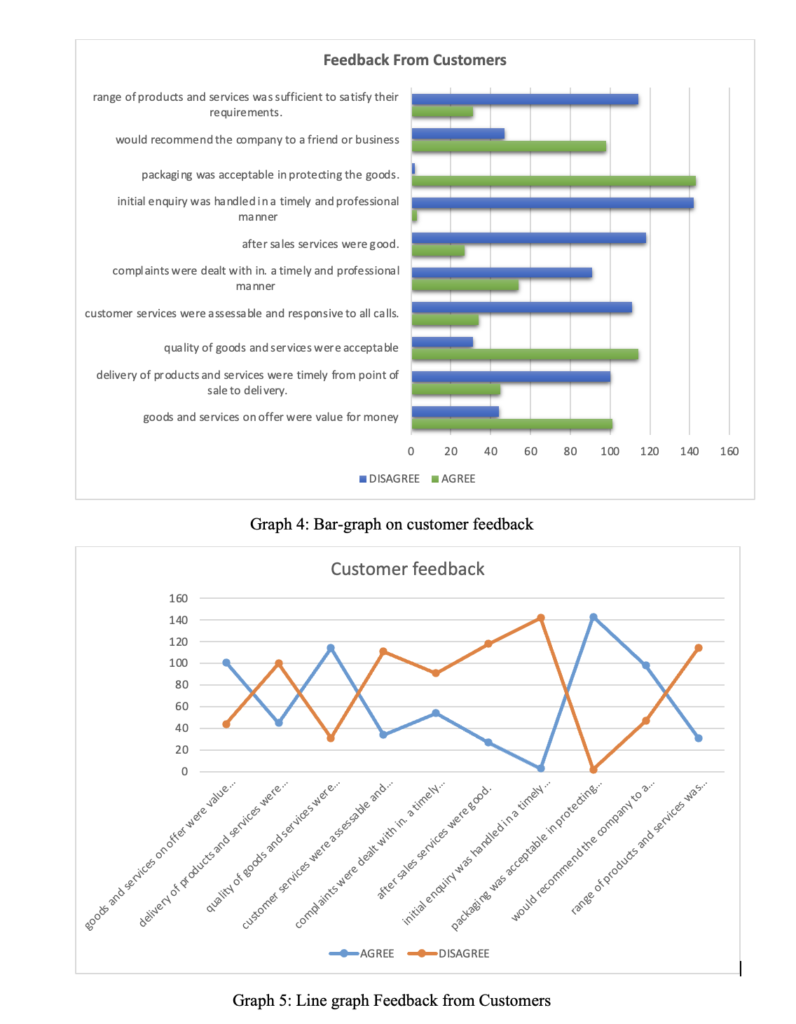
The general trend implied by the data collected indicates a performance gap between employees and their line managers. The gap impacts performance, as evidenced by customer feedback. Based on the findings, line managers need to incorporate employees in their decision-making process. Line managers should also promote a positive organisational culture where employees feel valued and appreciated.
AC 3.2 Identify the critical systems and data used within effective people practices to give insights by measuring work and people performance.
According to CIPD (2020), people data and analytics can help HR and other managers in an organisation to solve business problems and make decisions. There are different types of data that are effective for measuring and giving insight into people practice. Qualitative data contains information on the human observation of behaviours, habits, skills and other employee factors that may influence performance. This data offers an in-depth understanding of issues and descriptive information using words to express various issues. Qualitative data can be used to measure work and people performance by utilising tools such as brainstorming, surveys and interviews. Qualitative data on employee turnover can be obtained in brainstorming sessions or through exit interviews.
Quantitative data, on the other hand, uses numbers and figures to illustrate performance. While quantitative data may be more specific and dependable, it is short term in nature. Quantitative data can be used to establish and keep records of weekly work hours, retention rates, number of employees and their age. This data can be collected by various HR analytical software’s that analyse the information.
AC 3.4 Explain how people practices add value in an organisation and identify methods that might be used to measure the impact of people practices.
The creation of value in an organisation may be influenced by the need to grow and expand, return on investment, or satisfy customer’s needs (Payal Sondhi, 2018). Creating value can be achieved by effectively utilising human potential. The primary objective of good people management practices is to create value for the organisation and its employees as well as the surrounding community. Value creation can be based on income earned or the development of a sense of purpose for the employees. The value created for the society could be attained as sustainability and high-quality life. Organisations capture the value they would like to attain in the organisations mission and strategy. Real business value is captured in drivers that impact an organisation’s business objectives (Brugman and Dijk, 2020).
Other than 360 feedback, some other methods and tools can be used to measure the impact and value of people practice. Measuring value and impact is essential for ensuring that business objectives are being achieved. It can also ensure that there are people who practice contribution in an organisation, justify spending on various functions of HR, continuously improve people practice and identify organisational needs and gaps left to enable informed business decisions.
The cost-benefit analysis tool is essential for analysing the decision that should be implemented and should be foregone. It is the process that sums up potential rewards expected from an action then subtracts the total cost associated with that action (Hayes And Anderson, 2021). For example, all employees whose performance was considered high received a bonus of £400.00. According to the statistical data provided, a total of 245 employees are entitled to bonus payments. Therefore, the total amount of money that the company would spend on bonus is £ 98,000.00. However, the allocated budget was £75,000.00. If all employees received the bonus, the organisation would have spent £23,000.00 more than the intended amount.
Based on the cost-benefit analysis of the situation, the bonus amount should be reduced to fit the set budget. Alternatively, other reward packages, both intrinsic and extrinsic, can be used to reward high performing employees. The company can also enhance its performance by rewarding employees with a high five and six score. By doing so, employees with a score of five might enhance their performance, which influences organisational performance.
Return on investment is a measuring tool that can be used to measure the probability of gaining a return from a particular investment. ROI is a ratio that compares gains and losses in relation to cost. ROI is used for the evaluation of potential returns from an investment. In the case above, the return would be a loss because the allocated budget was exceeded. ROI is expressed as a percentage because it becomes easier to understand.
Ahrens, T. and Chapman, C.S. (2007) Management accounting as practice. Accounting, Organizations and Society , 32(1-2), pp.1–27.
Anscombe, E. (2005) Kantian Ethics . [online] Csus.edu. Available at: https://www.csus.edu/indiv/g/gaskilld/ethics/kantian%20ethics.htm [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Bonde, S. and Firenze, P. (2011) A Framework for Making Ethical Decisions | Science and Technology Studies . [online] Brown University. Available at: https://www.brown.edu/academics/science-and-technology-studies/framework-making-ethical-decisions [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Brugman, T. and Dijk, R. van (2020) Creating Value With Fact-Based HR . [online] AIHR Analytics. Available at: https://www.analyticsinhr.com/blog/creating-value-fact-based-hr/ [Accessed 11 Apr. 2021].
Bruijl, G.H.Th. (2018) The Relevance of Porter’s Five Forces in Today’s Innovative and Changing Business Environment. SSRN Electronic Journal , [online] 1(1). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326026986_The_Relevance_of_Porter’s_Five_Forces_in_Today’s_Innovative_and_Changing_Business_Environment [Accessed 9 Apr. 2021].
Chonko, L. (2012). Ethical Theories . [online] . Available at: https://www.dsef.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/EthicalTheories.pdf [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
CIPD (2020) People Data & Scientific Evidence . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/analytics#gref [Accessed 11 Apr. 2021].
Downey, J. (2007) Strategic Analysis Tools Topic Gateway Series Strategic Analysis Tools Topic Gateway Series No. 34 . [online] . Available at: https://www.cimaglobal.com/Documents/ImportedDocuments/cid_tg_strategic_analysis_tools_nov07.pdf.pdf [Accessed 9 Apr. 2021].
Driver, J. (2009) The History of Utilitarianism . [online] Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/utilitarianism-history/ [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Friedman, E. (2019) 4 External Factors That Affect Human Resource Management . [online] Workology. Available at: https://workology.com/4-external-factors-that-affect-human-resource-management/ [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Gifford, J. (2020) Performance Management | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/performance/factsheet#gref [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Hayes, A. and Anderson, S. (2021) Cost Benefit Analysis | Better Evaluation . [online] Betterevaluation.org. Available at: https://www.betterevaluation.org/en/evaluation-options/CostBenefitAnalysis [Accessed 11 Apr. 2021].
Howlett, W. and Coburn, T. (2019) Critical thinking | Podcast . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/podcasts/critical-thinking#gref [Accessed 9 Apr. 2021].
Lumenlearning.com. (2019) Rational Decision Making vs. Other Types of Decision Making | Principles of Management . [online] Available at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-principlesofmanagement/chapter/rational-decision-making-vs-other-types-of-decision-making/ [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Mulder, P. (2019) Six Thinking Hats by Edward De Bono, a decision making tool | ToolsHero . [online] ToolsHero. Available at: https://www.toolshero.com/decision-making/six-thinking-hats-de-bono/ [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Payal Sondhi (2018) 5 Important Guidelines to Increase HR Values In Your Organization . [online] Entrepreneur. Available at: https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/312696 [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Rousseau, D., Bantz, C., Garman, A., Goodman, P., Griffin, R., Hinings, B., Hirsch, P., Mccarthy, S., Rynes, S., Weingart, L. and Zanardelli, J. (2004) Academy of Management Review. Walshe & Rundall , [online] 31(2), pp.256–269. Available at: https://cebma.org/wp-content/uploads/Rousseau-Is-there-such-thing-as-evidence-based-management.pdf [Accessed 10 Apr. 2021].
Summer (2019) Understanding Of Micro And Macro Factors That Affect Your Business . [online] Mageplaza. Available at: https://www.mageplaza.com/blog/micro-and-macro-factors-affect-your-business.html [Accessed 9 Apr. 2021].
Uzonwanne, F.C. (2016) Rational Model of Decision Making. Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance , pp.1–6.
www.pagecentertraining.psu.edu. (2020). Ethical Theories . [online] Available at: https://www.pagecentertraining.psu.edu/public-relations-ethics/introduction-to-public-relations-ethics/lesson-1/ethical-theories/ [Accessed 11 Apr. 2021].
Young, J. (2020) Evidence-based Practice for Effective Decision-Making | Factsheets . [online] CIPD. Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/analytics/evidence-based-practice-factsheet#gref [Accessed 11 Mar. 2021].
Bibliography
Armstrong, M. (2020) Armstrong’s handbook of strategic human resource management. 7th ed. London: Kogan Page.
Walters, Kerry (1994) Re-Thinking Reason. Albany: State University of New York Press. pp. 181–98.
Choose Your Writer

CIPD Level 5 Assignments Answer Sample for UK Students
Solved cipd level 5 assignments answers, cipd level 5hrd assignment example uk: contemporary developments in human resource development, cipd level 5hr03 assignment example uk: reward for performance & contribution, cipd level 5hr02 talent management & workforce planning assignment example, uk, cipd level 5hr01 assignment example: employment relationship management, cipd 5co03 professional behaviours and valuing people assignment example, uk, 5co02 evidence-based practice cipd level 5 assignment example, uk, cipd 5co01 organizational performance and culture in practice assignment example uk.

Get Free Assignment Quote
Enter Discount Code If You Have, Else Leave Blank

Documentation
3co01 assignment examples.
- Task Two – Self Reflective Journal
- Task One. Presentation Pack (1,000 words)
3CO02 Assignment Examples
- TASK 2: DATA ANALYSIS
- Task 1: Evidence-based Practice Presenation
3CO03 Assignment Examples
- 3CO03 - Core behaviours for people professionals
3CO04 Assignment Examples
- TASK FIVE - FACT SHEET
- TASK FOUR - BRIEFING PAPER
- TASK THREE - GUIDANCE DOCUMENT
- TASK TWO - SIMULATED INTERVIEW
- TASK ONE - BRIEFING PAPER
5CO01 Assignment Examples
- 5CO01: Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice
5CO02 Assignment Example
5co03 assignment examples.
- 5CO03 – Professional Behaviours and Valuing People
5HR01 Assignment Example
5hr02 assignment examples.
- Workforce Planning and Recruitment Pack
5HR03 Assignment Examples
5os02 assignment example, 7co01 assignment example.
- Question 15
- Question 12
7CO02 Assignment Example
- Question 11
7CO03 Assignment Example
5co01 – organisational performance and culture in practice unit guide.
- 1. Unit Aims and Outcomes
Advanced Diploma in Strategic People Management


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5CO01 Assignment Example , 5CO01 Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice covers all areas and questions in this unit. ... Task Two - Presentation Pack. The CEO has also asked you to prepare a presentation to the managers prior to their formal Strategic Management Planning meeting to position them for their meeting. The focus is to ...
(AC 2.2) Many organisations have managed considerable change in recent years. CIPD's report, People Profession 2030: a collective view of future trends (2020) identifies 'internal change' as a key future trend. Explain different approaches to managing change (AC 2.3) Discuss models for how change is experienced. (AC 2.4)
Explain Edgar Schein's model of organisational culture and explain one theory or model which examines human behaviour. (AC 2.1) Assess how people practices in your organisation (or one with which you are familiar) impact both on organisational culture and behaviour, drawing on examples to support your arguments. (AC 2.2)
View 5co01-task-two.docx from BUSINESS 613 at Kisii University. 5CO01 Organisational performance and culture in practice Learner Assessment Brief Task Two Assessment ID / CIPD_5CO01_21_01 Level ... on each slide. For example (AC 2.1, AC 2.2) etc.: an explanation of the principles of ... View Assignment Brief - 5CO01 TASK ONE.docx from LAW 342 ...
5. Explain Edgar Schein's model of organisational culture and explain one theory or model which examines human behaviour. (AC 2.1) 6. Assess how people practices in your organisation (or one with which you are familiar) impact both on organisational culture and behaviour, drawing on examples to support your arguments. (AC 2.2) 7.
Students pursuing 5CO01 must submit a presentation package for assignment two, in which they will provide an assessment of each learning criteria. To better understand the learning concepts, students are also required to refer to the cast study from BMC. Listed below are the questions for this unit;
AC 1.2 Connections Between Organisational Strategy, Products, Services and Customers; AC 1.3 External Factors and Trends and their Influence on Organisational Priorities; AC 1.4: The Scale of Technology within Organisations and its Impact on Work; AC 2.1 Theory/Model of Organisational Culture and Theory/Model of Human Behaviour
Task 2 - Presentation Pack Assessment criteria Evidenced Y/N Evidence reference 2.1 Interpret theories and models which examine organisational and human behaviour. 2.2 Evaluate the drivers for change and basic models for how these changes are experienced. 2.3 Explain how to build diversity and inclusion into your work in order to build a
5CO01 is a unit that provides insights into the relationships between an organisation's organisational structure and its commercial factors. It describes all of the modes and factors involved in delivering organisational change and performance. Learners must comprehend the organisational structures associated with:
5CO01 Assignment Examples. 5CO01: Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice. ... People advancing their work assignments while carrying a high sense of clarity may allow the company to decide most appropriate roles to advance them. It is possible for an organization to temporarily fill a vacant position with an inhouse employees as the ...
5CO01 Organisational performance and culture in practice. Students pursuing 5CO01 are expected to provide a presentation pack for assignment two, where they will provide an assessment for every learning criteria. The students are also expected to refer to the cast study from BMC to provide a good understanding of the learning concepts.
2 5CO01 Organisational performance and culture in practice This unit assignment explores the connections between organisational structure and the wider world of work in a commercial context. It highlights the factors and trends, including the digital ... drawing on examples to support your arguments. (AC 2.2) 7. Peter Cheese, current CEO of ...
Introduction. Students will be required to provide a formal business report of approximately 2500words. The following is a guide to answering the 5CO01 assignment Task One Questions. AC 1.1 An evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages of two different types of organisational structures - BMC's structure and another of your choice.
5co01 Assessment Briefing Notes Oct 21 v1 - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. CIPD
I've had some draft feedback from ICS on the 3 criteria I submitted and got a general note about including organisational examples and I'm really struggling with it. For example AC 1.2 (connecting strategy to products, services and customers). My own organisation is public sector so the focus on products, services and customers isn't really a ...
Contents CIPD Assignment Information 1 Task 1 2 Front Cover 3 Contents 4 Executive Summary 5 Introduction 6 Main Body AC 1.1 - An evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages of two 7 different types of organisational structures - BMC's structure and one other AC 1.2 - An analysis of the connections between organisational strategy, 8 products & services, customers, and revenue generation ...
2 CIPD 5CO01 Task 2: Understand organisational culture and theoretical perspectives on how people behave at work. 2.1 2.1 Explain theories and models which examine organisational and human behaviour. 2.2 2.2 Assess how people practices impact on organisational culture and behaviour. 2.3 2.3 Explain different approaches to managing change.
Estimated reading: 0 minutes 1708 views. 5CO01: Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice. 5CO01 Assignment Examples - Previous 3CO04 Assignment Examples Next - 5CO01 Assignment Examples 5CO02 Assignment Example.
It highlights the factors and trends, including the digital environment, that impact on business strategy and workforce planning, recognising the influence of culture, employee well-being and behaviour in delivering change and organisational performance. EnquireBook this unit. Unit details. Specialist unit. Level 5. 7 credits. What will you learn.
5CO01 - Assessment Brief - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document is a learner assessment brief for an associate diploma program. It provides guidance and requirements for two tasks assessing the student's understanding of organizational performance, culture, and people management. For the first task, the student must write a formal report ...
AC 2.4 As a worked example to illustrate the points made in 2.3, take the same people to practice issues, explain the relevant evidence that you have reviewed and use one or more decision-making tools. Decision making in people practice is continuous throughout the employees' lifecycle in an organisation.
CIPD 5CO01 Organizational Performance and Culture in Practice Assignment Example UK. While learning and understanding the organizational performance, its culture is significant to understand first since the performance and culture affect each other. This module will provide in-depth k. Read More >>. CIPD Level 5 Assignments | 1 st Apr 2021.
Task Two - Self Reflective Journal ; Task One. Presentation Pack (1,000 words) View Details . 3CO02 Assignment Examples . TASK 2: DATA ANALYSIS ... 5CO01 Assignment Examples . 5CO01: Organisational Performance and Culture in Practice ; View Details ...