

Comparing and Contrasting
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.”
Introduction
In your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them.
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments
Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples:
- Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both.
But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment:
- Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips.
Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projects
Sometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper.
Discovering similarities and differences
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places:
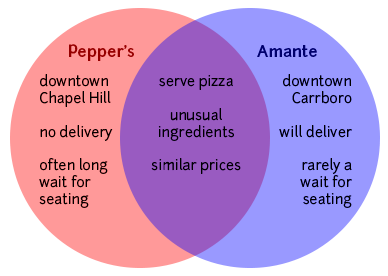
To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered.
Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places:
| Pepper’s | Amante | Papa John’s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | |||
| Price | |||
| Delivery | |||
| Ingredients | |||
| Service | |||
| Seating/eating in | |||
| Coupons |
As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself?
Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location.
Two historical periods or events
- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories
- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art
- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus on
By now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions:
- What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper.
Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems.
Your thesis
The thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.”
Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier:
Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture.
You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage.
Organizing your paper
There are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two:
Subject-by-subject
Begin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion.
The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together.
A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second.
Point-by-point
Rather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants.
If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant.
There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you.
Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper.
Cue words and other tips
To help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions:
- like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these:
- Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Tips for Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay

- 5-minute read
- 19th August 2022
Compare and contrast essays are a specific form of academic essay with unique requirements, so if you’re a student , it’s important that you to know how to write one. Luckily, we’ve pieced together this guide to help you plan, structure, and put together your essay, complete with tips for comparing and contrasting.
Let’s begin.
1. What Is a Compare and Contrast Essay?
As you may have guessed, when writing a compare and contrast essay, you’ll need to do two things:
- Compare the similarities between two or more given subjects.
- Contrast their differences.
Compare and contrast essays are a common essay style because they allow your teacher or lecturer to assess your understanding of two theories, research methods, literary techniques, or other subjects. These subjects are usually related and may sometimes be confused with one another or are in conflict with each other.
By comparing and contrasting the subjects, you can also improve your analysis skills .
Some examples of compare and contrast essay titles include:
Compare and contrast a Shakespearean sonnet with a Petrarchan sonnet. What are the similarities and differences between anabolic and catabolic reactions? How were Nehru’s political beliefs similar to Gandhi’s? How did they differ?
2. Planning a Compare and Contrast Essay
As with any essay, before you begin writing, you should have a plan . In this case, you’ll first need to identify the similarities and differences between your subjects.
You can do this by writing out a list of all the qualities each subject possesses. Then, you can pick out any similar qualities that show up in both lists, and any qualities that are unique to just one of them. If you’re a visual learner, you might want to draw this as a Venn diagram .
Once you have all the similarities and differences prepared, consider which of them will be the most useful to include in your essay. Ask yourself:
- How much can you write about each point?
- What will your conclusion be, and which points support it?
- How will each point fit into your essay’s structure?
To answer that last question, let’s take a look at some ways to structure your essay.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Structuring a Compare and Contrast Essay
Now that you’ve got a plan for your essay, it’s time to organize it. There are three main structures you can follow when writing a compare and contrast essay:
- The block structure: All of the information about one subject (e.g., Shakespearean sonnets) is presented in the first few paragraphs, followed by the subject it’s being compared and contrasted with (e.g., Petrarchan sonnets).
- The alternating structure: One similarity or difference between both subjects (e.g., rhyme scheme) is explored in one paragraph, followed by a paragraph on another similarity or difference (e.g., use of imagery), and so on.
- The similarities and differences structure: All the similarities between both subjects are presented, followed by the differences.
There are benefits to each of these structures. The block structure, for example, can be easier to write, while the alternating structure presents each similarity and difference clearly, and the similarities and differences structure focuses on those points rather than the subjects themselves.
So, when deciding which structure to use, consider what would work best for your essay. If you intend to cover each subject in detail, for example, you might want to choose the block structure.
On the other hand, if you want to emphasize the connections between each subject, the alternating structure might be best.
Finally, if you want to conclude that the subjects are either overwhelmingly similar or different to each other, the similarities and differences structure may work in your favor.
Whichever structure you follow, though, you’ll need to include a strong introduction and conclusion.
Your introduction should:
- Establish the subjects you will be comparing and contrasting.
- Provide some background about their connection (e.g., “Shakespearean and Petrarchan sonnets are poetic forms common in the 14th to 19th centuries”).
- Explain what you aim to achieve with your essay.
Meanwhile, your conclusion should:
- Summarize the main similarities and differences you have identified.
- Make a point regarding the relationship between your subjects.
4. Things to Remember
Here are some important tips to keep in mind when writing your compare and contrast essay:
- Ensure you are comparing or contrasting the same criteria between each subject. For example, it wouldn’t make sense to compare the line length of a Shakespearean sonnet with the rhyme scheme of a Petrarchan sonnet, as these are two separate categories.
- Always address both subjects of your essay in any introductions, conclusions, and topic sentences.
- Use comparison words and phrases such as “similarly,” “like,” and “in the same way” when comparing subjects.
- Use contrast words and phrases such as “in contrast,” “however,” and “whereas” when contrasting subjects.
- As with any essay, make sure to back up any arguments you make with evidence and credible sources .
Expert Academic Proofreading
Once you’ve written your compare and contrast essay, don’t forget to have it proofread. Our dedicated essay editing team is available 24/7 to help polish your paper. Try us out with a free proofreading and editing sample .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Comparing & Contrasting
A compare and contrast paper discusses the similarities and differences between two or more topics. The paper should contain an introduction with a thesis statement, a body where the comparisons and contrasts are discussed, and a conclusion.
Address Both Similarities and Differences
Because this is a compare and contrast paper, both the similarities and differences should be discussed. This will require analysis on your part, as some topics will appear to be quite similar, and you will have to work to find the differing elements.
Make Sure You Have a Clear Thesis Statement
Just like any other essay, a compare and contrast essay needs a thesis statement. The thesis statement should not only tell your reader what you will do, but it should also address the purpose and importance of comparing and contrasting the material.
Use Clear Transitions
Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives.
- Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too
- Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however, although, differs, conversely, rather than.
For more information, check out our transitions page.
Structure Your Paper
Consider how you will present the information. You could present all of the similarities first and then present all of the differences. Or you could go point by point and show the similarity and difference of one point, then the similarity and difference for another point, and so on.
Include Analysis
It is tempting to just provide summary for this type of paper, but analysis will show the importance of the comparisons and contrasts. For instance, if you are comparing two articles on the topic of the nursing shortage, help us understand what this will achieve. Did you find consensus between the articles that will support a certain action step for people in the field? Did you find discrepancies between the two that point to the need for further investigation?
Make Analogous Comparisons
When drawing comparisons or making contrasts, be sure you are dealing with similar aspects of each item. To use an old cliché, are you comparing apples to apples?
- Example of poor comparisons: Kubista studied the effects of a later start time on high school students, but Cook used a mixed methods approach. (This example does not compare similar items. It is not a clear contrast because the sentence does not discuss the same element of the articles. It is like comparing apples to oranges.)
- Example of analogous comparisons: Cook used a mixed methods approach, whereas Kubista used only quantitative methods. (Here, methods are clearly being compared, allowing the reader to understand the distinction.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Developing Arguments
- Next Page: Avoiding Logical Fallacies
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

9 Easy Steps for Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Posted on November 17, 2023 November 17, 2023
Compare and contrast essays are common assignments in middle and high school English classes. They frequently show up in college as well, and while this task may not be explicitly given to professionals, the ability to compare two subjects critically during the writing process is crucial to academics of every age.
Once you master this type of essay , you will see benefits throughout your life. Strong comparison skills will help you write better college entrance essays and argue your point in debates. These skills will improve your test scores and deepen your college papers. Looking professionally, they could aid in easily convincing team members of anything from a new workflow software to a functional coffeemaker to a promotion.
In order to write a good compare and contrast essay , though, you need the ability to formulate a highly-researched and well-structured piece of academic writing . That means understanding the type of essay assigned, familiarizing yourself with this specific writing process , and knowing how to effectively incorporate transition words . It also requires a firm grasp of different styles of citations , in order to lend confidence to your argument and give proper credit to others.
Let’s take a look at what exactly a comparison essay is, what purpose its writing serves, and how to write one in nine easy steps.
What is a Compare and Contrast Essay ?
A compare and contrast essay is exactly what it sounds like. You take two – or sometimes more – items and evaluate the similarities and differences between them. Your paper might tackle any subject, such as science, history, economics, literature, or philosophy.
Comparing essays are different from other types of essays that are commonly assigned in school. For instance, a descriptive essay usually pertains to one subject, book, or idea, exploring it in detail. A persuasive essay, on the other hnad, tries to convince the reader to take one specific course of action.
The main aspect of contrast essay topics is that they consider two subjects or ideas at once. Some of the most common contrast essay examples include comparisons between:
- Exploring two different scientific methods for similarities and differences in approach
- Reading contextually two classic novels from the same time period
- Examining contrasting political systems in the United States or abroad
- Looking at two different cultures to see values and practices they share and, conversely, do not share
- Considering two possible approaches to a moral or logistical problem
- Exploring two methods of farming specifically focusing on productivity, simplicity, and empirical evidence
You could theoretically use this organizational structure to examine two items within the same category for almost any subject.
Purpose of a Compare and Contrast Essay
The purpose of a compare and contrast essay is to point out all the similarities and all differences between two nouns, ideas, et cetera. Considering two ideas fully can naturally transition into an ability to argue for or against a position or stance.
In debate, for example, comparing and contrasting is a critical skill as you must be able to examine the topic from both angles. Obviously, you need to make a case for your own side of the debate, however it is critical you see the other side’s point of view as well. Otherwise, you will find yourself completely unprepared for their arguments. Therefore, comparing the benefits, ideological underpinnings and rhetorical styles that best match both sides of an issue is an excellent lifelong skill.
In literature, you will benefit from the ability to compare two books for themes, writing style, word choice, characterization, and more. Doing so helps you become a better writer yourself, as well as understand the complexity of the human condition.
Knowing how to develop a solid argument, moreover, helps you:
- Deepen your critical thinking skills
- Develop eloquence in your speaking and writing
- Practice using skills such as outlining and reading for clues
- Explore how context changes meaning
Now let’s explore exactly how to write one, step by step.
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
You will complete your compare and contrast essay in three main stages: researching, writing and proofreading. While this might sound like an overly formal approach, it is effective because it allows you to organize your main points ahead of time, using any visual aid you might need to see the similarities and differences.
Once you’ve laid out your points of comparison , you can group them according to likeness. There are two methods for this we will discuss: the alternating method and the block method . These will allow you to craft your main thesis and insert appropriate transitions where needed. Then you’ll add an introduction and conclusion to round out the paper before moving on to proofreading.
Make sure you spend enough time on the research phase. It is tempting to skip over this part and launch into the writing, bypassing the less-exciting step of examining your sources thoroughly. However, this is a good way to miss important points that might reinforce or work against your argument.
Step 1: Conduct Initial Research
Your initial research should answer questions such as:
- What sources will I use (if given a choice by my teacher or professor)? Do I need additional sources to support or strengthen the research from my first ones? Do I have enough information to write the paper?
- Do my subjects have enough in common that comparing and contrasting them will be useful? Apples and oranges might be different, but they are at least both types of fruit; apples and cats aren’t a very useful comparison at all.
- Has anyone else compared these two subjects before? Should I take a look at their work to see what to do/not to do?
Step 2: List Out Similarities & Differences
Next, it’s time to list out what is similar and what is different between your two items. Let’s say you are contrasting two books from the 1800s. The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde by Robert Louis Stevenson and Frankenstein by Mary Shelley are both early examples of science fiction, so they make a good pair.
Start by using a Venn diagram , chart, or another visual tool to make a side by side comparison. You might include setting, plot, characters, year written and year set, mood, themes, tone and appearances throughout later pop culture. Make sure your points of comparison are grouped together so you’re not searching for the corollaries later.
Step 3: Develop a Thesis Statement
Once you have rough compare and contrast sentences written out, you can then craft a topic sentence . This is also known as a thesis or thesis statement , in which you lay out the main argument you will make.
For instance, you might write “While The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde by Robert Louis Stevenson and Frankenstein by Mary Shelley both use elements of speculative fiction and folklore differently, they speak to the same innate fear that our humanity is a fragile thing.” This shows the reader that you are going to share both the differences (the main writing elements) and similarities (themes) in the paragraphs to come.
Having established the case you will make, it is time to turn those rough points and thesis sentences into a fully fleshed-out paper. Let’s move on to the writing.
Step 4: Create an Outline
Armed with your main points , you should now elevate your rough content into an outline. There are two main ways to structure a compare and contrast essay ; the alternating method and the block method .
- Alternating Method : In this method, you alternate between one item and another, back and forth. So in our example, you would first tackle the setting of both books, comparing and contrasting. Next, are the characters, with similarities and differences as well. Work your way down the list, speaking about both subjects in turn. This will buffer your argument throughout.
- Block Method : With this approach, you instead tackle all aspects of one topic in a block , then the other, subject by subject . That means you would address how Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde uses the setting, characters, time period, and so forth completely. Then you move on to do the same with Frankenstein . In the second block, it makes sense to call out the first book repeatedly, but you will save the main thrust of your argument for the conclusion.
Either approach allows you to create a rough outline of your main points , with additional brainstorming when needed. Afterwards, you can begin with the actual fleshing out of the paper.
Step 5: Write the Introduction
Once you have a thesis statement and an essay outline , the actual essay writing becomes much simpler. Start with the introduction, and plan to have the thesis you created at the end of the intro paragraph(s). Lead up to that statement with a brief description of both items you’re comparing (in this case, the two novels), including pertinent subject matter information such as the author, writing periods, and overarching themes.
Step 6: Write the Body Paragraphs
The most important component of your essay structure is the body paragraphs, and standard essay form asks for three paragraphs. If your essay is longer, instead of using a single paragraph for the first subject , second subject and so on, you might use a whole section. Either way, you will use the first body paragraph as a compare and contrast in the alternating method , or a thorough treatment of the first subject overall. Then, you will address the second subject , and so forth.
Step 7: Write the Conclusion
The conclusion should wrap up your essay overall, driving home the main point of your thesis. Be sure to restate it, not verbatim, but quite closely near the top of your concluding paragraph.
Next, it’s time to make sure you don’t have any outstanding errors or plagiarism that might ruin your grade. Always proofread a paper before turning it in to ensure you are submitting your best work.
Step 8: Check for Spelling & Grammar
First, use a spellchecker to catch errors. Most word processing software offers this tool for spelling and grammar. If you take this approach, make sure it is set correctly to your language and dialect, or mistakes will slip through. Alternatively, you can use an online service, which will help take your writing to the next level.
Step 9: Check for Citation Errors
While most students are honorable and do their own work, it is possible to get caught accidentally plagiarizing simply because you do not know the proper citation rules. For instance, you need to source every quote from a novel, even if you are using the same novel repeatedly and have already cited it in your paper . Sadly, even unintentional plagiarism can lead to serious academic and career consequences, so you must be vigilant.
Luckily, that won’t happen if you use a plagiarism checker like Quetext . Not only does it identify where sources are needed, but it will also help you catch instances of similar wording, which might also require a source citation . Overall, it allows you to:
- Verify your writing for originality so you don’t get caught for plagiarism , even while summarizing or paraphrasing
- Flag content in need of citations
- Add in-text MLA/APA/Chicago-style citations where needed
- Create MLA/APA/Chicago Style citations for references page
Understanding the meaning, purpose and benefits of a compare and contrast essay will enable you to tackle them more effectively from now on. This is especially true if you use the nine steps listed above, which will earn you points in both high school and college courses. That is, if you properly check that you have not plagiarized from any of your sources.
Using a plagiarism checker will benefit you not only in academic settings, but also in all instances of future writing. Even unintentional plagiarism can lead to severe negative consequences regardless of your profession or standing. Plagiarism checkers provide a simple way to ensure you have properly cited and paraphrased all your writing, and give you peace of mind before submitting any work.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

How to Use AI to Enhance Your Storytelling Process
- Posted on June 12, 2024

Essential Comma Rules for Business Emails
- Posted on June 7, 2024

How to Write Polished, Professional Emails With AI
- Posted on May 30, 2024

A Safer Learning Environment: The Impact of AI Detection on School Security
- Posted on May 17, 2024

Rethinking Academic Integrity Policies in the AI Era
- Posted on May 10, 2024 May 10, 2024

Jargon Phrases to Avoid in Business Writing
- Posted on May 3, 2024 May 3, 2024

Comparing Two Documents for Plagiarism: Everything You Need to Know
- Posted on April 26, 2024 April 26, 2024

Mastering Tone in Email Communication: A Guide to Professional Correspondence
- Posted on April 17, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
5 Compare and Contrast Essay Examples (Full Text)
A compare and contrast essay selects two or more items that are critically analyzed to demonstrate their differences and similarities. Here is a template for you that provides the general structure:

A range of example essays is presented below.
Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
#1 jean piaget vs lev vygotsky essay.
1480 Words | 5 Pages | 10 References
(Level: University Undergraduate)

Thesis Statement: “This essay will critically examine and compare the developmental theories of Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky, focusing on their differing views on cognitive development in children and their influence on educational psychology, through an exploration of key concepts such as the role of culture and environment, scaffolding, equilibration, and their overall implications for educational practices..”
#2 Democracy vs Authoritarianism Essay

Thesis Statement: “The thesis of this analysis is that, despite the efficiency and control offered by authoritarian regimes, democratic systems, with their emphasis on individual freedoms, participatory governance, and social welfare, present a more balanced and ethically sound approach to governance, better aligned with the ideals of a just and progressive society.”
#3 Apples vs Oranges Essay
1190 Words | 5 Pages | 0 References
(Level: 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade)

Thesis Statement: “While apples and oranges are both popular and nutritious fruits, they differ significantly in their taste profiles, nutritional benefits, cultural symbolism, and culinary applications.”
#4 Nature vs Nurture Essay
1525 Words | 5 Pages | 11 References
(Level: High School and College)

Thesis Statement: “The purpose of this essay is to examine and elucidate the complex and interconnected roles of genetic inheritance (nature) and environmental influences (nurture) in shaping human development across various domains such as physical traits, personality, behavior, intelligence, and abilities.”
#5 Dogs vs Cats Essay
1095 Words | 5 Pages | 7 Bibliographic Sources
(Level: 6th Grade, 7th Grade, 8th Grade)
Thesis Statement: “This essay explores the distinctive characteristics, emotional connections, and lifestyle considerations associated with owning dogs and cats, aiming to illuminate the unique joys and benefits each pet brings to their human companions.”
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
I’ve recorded a full video for you on how to write a compare and contrast essay:
Get the Compare and Contrast Templates with AI Prompts Here
In the video, I outline the steps to writing your essay. Here they are explained below:
1. Essay Planning
First, I recommend using my compare and contrast worksheet, which acts like a Venn Diagram, walking you through the steps of comparing the similarities and differences of the concepts or items you’re comparing.
I recommend selecting 3-5 features that can be compared, as shown in the worksheet:

Grab the Worksheet as Part of the Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack
2. Writing the Essay
Once you’ve completed the worksheet, you’re ready to start writing. Go systematically through each feature you are comparing and discuss the similarities and differences, then make an evaluative statement after showing your depth of knowledge:

Get the Rest of the Premium Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack (With AI Prompts) Here
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Thesis Statement
Compare and contrast thesis statements can either:
- Remain neutral in an expository tone.
- Prosecute an argument about which of the items you’re comparing is overall best.
To write an argumentative thesis statement for a compare and contrast essay, try this AI Prompts:
💡 AI Prompt to Generate Ideas I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that pass a reasonable judgement.
Ready to Write your Essay?

Take action! Choose one of the following options to start writing your compare and contrast essay now:
Read Next: Process Essay Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.7 Comparison and Contrast
Learning objectives.
- Determine the purpose and structure of comparison and contrast in writing.
- Explain organizational methods used when comparing and contrasting.
- Understand how to write a compare-and-contrast essay.
The Purpose of Comparison and Contrast in Writing
Comparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay , then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. The purpose of conducting the comparison or contrast is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities. For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic. Drawing distinctions between elements in a similar category will increase the audience’s understanding of that category, which is the purpose of the compare-and-contrast essay.
Similarly, to focus on comparison, choose two subjects that seem at first to be unrelated. For a comparison essay, you likely would not choose two apples or two oranges because they share so many of the same properties already. Rather, you might try to compare how apples and oranges are quite similar. The more divergent the two subjects initially seem, the more interesting a comparison essay will be.
Writing at Work
Comparing and contrasting is also an evaluative tool. In order to make accurate evaluations about a given topic, you must first know the critical points of similarity and difference. Comparing and contrasting is a primary tool for many workplace assessments. You have likely compared and contrasted yourself to other colleagues. Employee advancements, pay raises, hiring, and firing are typically conducted using comparison and contrast. Comparison and contrast could be used to evaluate companies, departments, or individuals.
Brainstorm an essay that leans toward contrast. Choose one of the following three categories. Pick two examples from each. Then come up with one similarity and three differences between the examples.
- Romantic comedies
- Internet search engines
- Cell phones
Brainstorm an essay that leans toward comparison. Choose one of the following three items. Then come up with one difference and three similarities.
- Department stores and discount retail stores
- Fast food chains and fine dining restaurants
- Dogs and cats
The Structure of a Comparison and Contrast Essay
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader. Take the following thesis as an example that leans more toward contrasting.
Thesis statement: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.
Here the thesis sets up the two subjects to be compared and contrasted (organic versus conventional vegetables), and it makes a claim about the results that might prove useful to the reader.
You may organize compare-and-contrast essays in one of the following two ways:
- According to the subjects themselves, discussing one then the other
- According to individual points, discussing each subject in relation to each point
See Figure 10.1 “Comparison and Contrast Diagram” , which diagrams the ways to organize our organic versus conventional vegetables thesis.
Figure 10.1 Comparison and Contrast Diagram
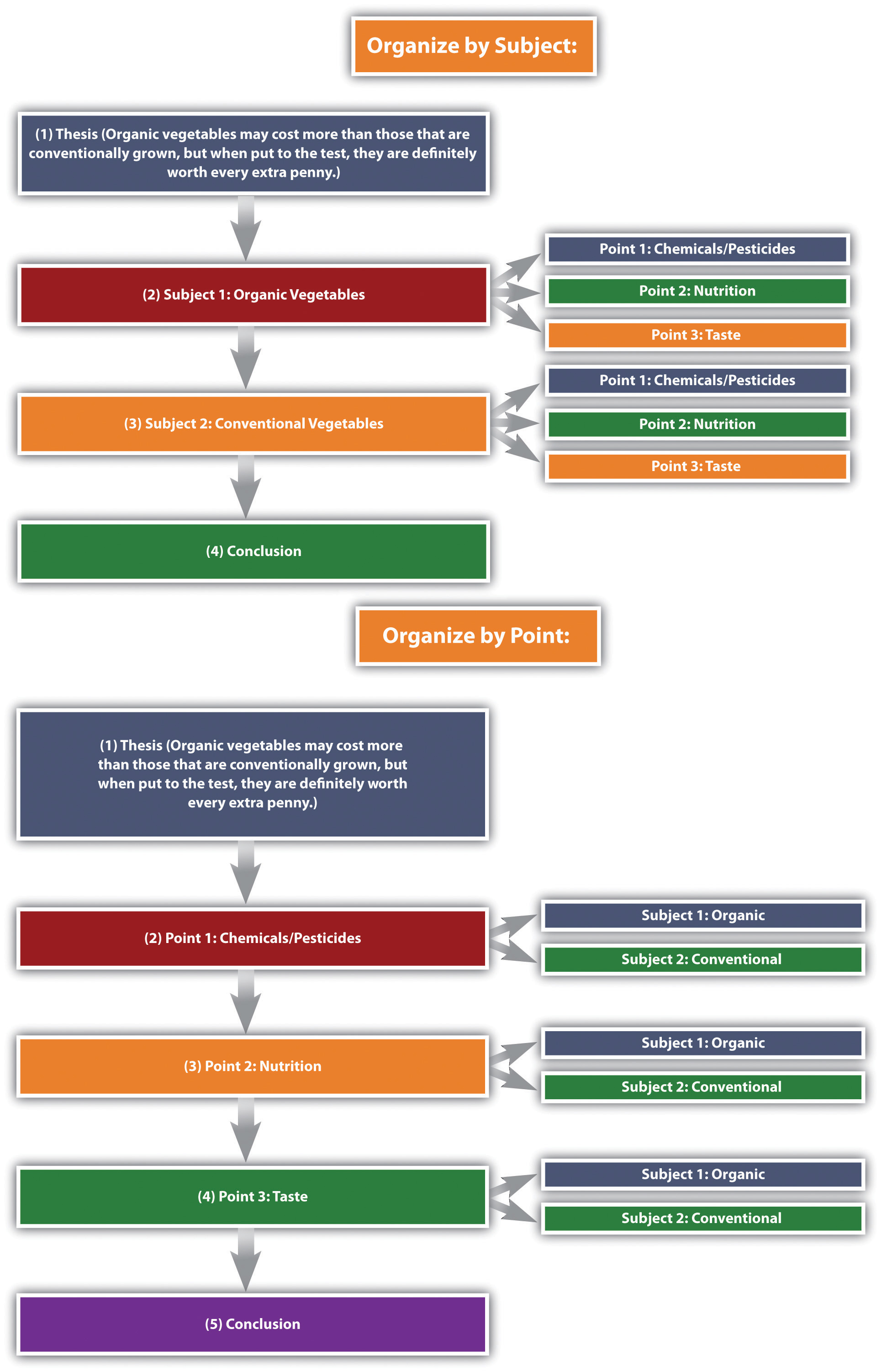
The organizational structure you choose depends on the nature of the topic, your purpose, and your audience.
Given that compare-and-contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is helpful to have some phrases on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis. See Table 10.3 “Phrases of Comparison and Contrast” for examples.
Table 10.3 Phrases of Comparison and Contrast
| Comparison | Contrast |
|---|---|
| one similarity | one difference |
| another similarity | another difference |
| both | conversely |
| like | in contrast |
| likewise | unlike |
| similarly | while |
| in a similar fashion | whereas |
Create an outline for each of the items you chose in Note 10.72 “Exercise 1” and Note 10.73 “Exercise 2” . Use the point-by-point organizing strategy for one of them, and use the subject organizing strategy for the other.
Writing a Comparison and Contrast Essay
First choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so.
The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects.
After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis. See Chapter 15 “Readings: Examples of Essays” to read a sample compare-and-contrast essay.
Many business presentations are conducted using comparison and contrast. The organizing strategies—by subject or individual points—could also be used for organizing a presentation. Keep this in mind as a way of organizing your content the next time you or a colleague have to present something at work.
Choose one of the outlines you created in Note 10.75 “Exercise 3” , and write a full compare-and-contrast essay. Be sure to include an engaging introduction, a clear thesis, well-defined and detailed paragraphs, and a fitting conclusion that ties everything together.

Key Takeaways
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
There are two main organizing strategies for compare-and-contrast essays.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Search form
How to write a compare and contrast essay, by luisa brenton.
As a student, you’ve got to write a lot of different essays and writing assignments, which all have different requirements and expectations. To get the best grade possible, it is important that you understand these differences and make use of them as best you can. In this way, you don’t spend time barking up the wrong tree.
Now, it would be great if we could deal with each and every essay expectations. That would make for a rather unwieldy blog post. So, instead, here we’re going to look at one of the most popular forms, which is the compare and contrast essay.
Recognizing the compare and contrast essay
Often they’re not actually that hard to spot. Some will even have the word ‘compare’ and ‘contrast’ in the title. For example, you might have ‘compare two romantic poets and explore the differences between them’ or ‘contrast the first and the Second World War and the political reasons for them’. Other words that you might see are such words as ‘differences’, ‘similarities’ or other words like that.
But it doesn’t always work out that easily. Sometimes you’re going to find questions that are far more subtle. For example, ‘take a major literary theme and explore how Virginia Wolfe and F Scott Fitzgerald dealt with them’ or ‘How does liberty evolve from the 15 th to the 16 th century?’
Yet, the idea though they might not use the words ‘compare’ and ‘contrast’ you can still find it between the lines.
Representing differences and similarities visually
When you’ve been asked to discuss the similarities or differences between two things (or three) then the best thing you can do is draw a Venn diagram. You know the one I’m talking about – where you draw as many circles as there are concepts (e.g. first world war and second world war) where they each overlap all the other circles?
Then you write the differences in the areas where the circles don’t overlap and the similarities in the areas where they do. In this way, you’ll have an easy time of knowing what the differences and similarities are.
Of course, don’t get carried away. Remember that you’re writing for a specific class, which means that you’re supposed to write about areas that fit within the structure thereof.
One trick that might work if you’re struggling to know what’s relevant is to include another circle in your diagram so that you can write those things that fall within the scope of the class inside of that circle and those that don’t outside of it.
Note that this strategy works a lot better if you’re only asked to compare two things, as when you’re asked to compare more it can get very confusing very quickly as there are just too many circles.
Decide what to write about
The next thing that you’ll need to decide on is what you’re going to include in your essay. The first things to focus on is what is absolutely essential to the argument you’re going to make. These points will need to be included no matter what.
If that alone does not fill up your essay, however, then it’s time to pull out a point system. Give things a score from one to five (or ten, if you’ve got a lot of topics and need the extra differentiation).
Things to base your score on:
- Is it relevant to the class?
- Is it interesting and informative?
- Does it fit into the argument that you’re going to make or is it a tangent?
- Is it a topic that the teacher or professor seems particularly interested in?
- How obvious is it? (The more obvious, the less the need to include it)
Time to formulate your structure
The first thing that you want to do at this point is formulated your thesis. You probably already had a central argument outline above (otherwise you would have struggled to complete the last section) but now it’s time to put it down in words.
Don’t skip this part! Often you can realize where you’re making errors in your reasoning simply by writing down what you’re trying to argue. Also, always answer the most important question of all about your thesis and that is ‘why should I care about this particular question? Why is it relevant?’ That question will need to be answered somewhere in your essay.
That done, it’s time to create a structure. Return to your Venn diagram and take the pieces that you’ve ranked highest (as well as those that you decided are central to the question and your argument) and put them in order.
Make sure you start out with a whopper of an argument – something that’s engaging and interesting so that you draw in the reader. Take your second strongest argument and put it right at the end (this is important due to the peak and end effect, which states that we remember the end of things better than what comes in the middle).
Start writing
Now you’ve got everything worked out, all you’ve got to do is fill in the gaps. Now remember to use clear paragraphs and well-defined sentences. Also, remember to focus on good transitions, so that people can spot when you’re moving on from one area to another.
Now, if this is a struggle, don’t stress out too much. There are plenty of tools available to help you online – from other websites that deal with this kind of thing in more detail, to services that can help you with the process (check out the best sites for writing help).
And remember, if you’re struggling at this point, that doesn’t mean you always will. Essay writing (actually all writing) is something that you get better at over time, particularly if you pay attention to what your professors and teachers are saying and not just the grades they give you.
So with those thoughts, you should be much better prepared to deal with the contrast and comparison essay. Let me know how it goes.
Luisa Brenton is an ex-marketer, present writer, and a future professor at the Chicago University. She has been working as an educational blogger for top websites.You can contact her on Twitter.
One comment on “How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay”
Hi Luisa, I was searching for the tips to write an perfect essay for my college and found this. Thanks for the wonderful tips, will apply it and let you know the results.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
Last Updated: May 12, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 29 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 3,104,012 times.
The purpose of a compare and contrast essay is to analyze the differences and/or the similarities of two distinct subjects. A good compare/contrast essay doesn’t only point out how the subjects are similar or different (or even both!). It uses those points to make a meaningful argument about the subjects. While it can be a little intimidating to approach this type of essay at first, with a little work and practice, you can write a great compare-and-contrast essay!
Formulating Your Argument

- You could pick two subjects that are in the same “category” but have differences that are significant in some way. For example, you could choose “homemade pizza vs. frozen grocery store pizza.”
- You could pick two subjects that don’t appear to have anything in common but that have a surprising similarity. For example, you could choose to compare bats and whales. (One is tiny and flies, and the other is huge and swims, but they both use sonar to hunt.)
- You could pick two subjects that might appear to be the same but are actually different. For example, you could choose "The Hunger Games movie vs. the book."

- For example, ask yourself: What can we learn by thinking about “The Hunger Games” and “Battle Royale” together that we would miss out on if we thought about them separately?
- It can be helpful to consider the “So what?” question when deciding whether your subjects have meaningful comparisons and contrasts to be made. If you say “The Hunger Games and Battle Royale are both similar and different,” and your friend asked you “So what?” what would your answer be? In other words, why bother putting these two things together?

- A “Venn diagram” can often be helpful when brainstorming. This set of overlapping circles can help you visualize where your subjects are similar and where they differ. In the outer edges of the circle, you write what is different; in the overlapping middle area, you write what’s similar. [2] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- You can also just draw out a list of all of the qualities or characteristics of each subject. Once you’ve done that, start looking through the list for traits that both subjects share. Major points of difference are also good to note.

- For example, if you are comparing and contrasting cats and dogs, you might notice that both are common household pets, fairly easy to adopt, and don’t usually have many special care needs. These are points of comparison (ways they are similar).
- You might also note that cats are usually more independent than dogs, that dogs may not provoke allergies as much as cats do, and that cats don’t get as big as many dogs do. These are points of contrast (ways they are different).
- These points of contrast can often be good places to start thinking about your thesis, or argument. Do these differences make one animal a superior type of pet? Or a better pet choice for a specific living situation (e.g., an apartment, a farm, etc.)?

- Show readers why one subject is more desirable than the other. Example: "Cats are better pets than dogs because they require less maintenance, are more independent, and are more adaptable."
- Help readers make a meaningful comparison between two subjects. Example: "New York City and San Francisco are both great cities for young professionals, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, social environment, and living conditions."
- Show readers how two subjects are similar and different. Example: "While both The Catcher in the Rye and To Kill a Mockingbird explore the themes of loss of innocence and the deep bond between siblings, To Kill a Mockingbird is more concerned with racism while The Catcher in the Rye focuses on the prejudices of class."
- In middle school and high school, the standard format for essays is often the “5-paragraph form,” with an introduction, 3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. If your teacher recommends this form, go for it. However, you should be aware that especially in college, teachers and professors tend to want students to break out of this limited mode. Don’t get so locked into having “three main points” that you forget to fully explore your topic.
Organizing Your Essay

- Subject by subject. This organization deals with all of the points about Topic A, then all of the points of Topic B. For example, you could discuss all your points about frozen pizza (in as many paragraphs as necessary), then all your points about homemade pizza. The strength of this form is that you don’t jump back and forth as much between topics, which can help your essay read more smoothly. It can also be helpful if you are using one subject as a “lens” through which to examine the other. The major disadvantage is that the comparisons and contrasts don’t really become evident until much further into the essay, and it can end up reading like a list of “points” rather than a cohesive essay. [4] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Point by point. This type of organization switches back and forth between points. For example, you could first discuss the prices of frozen pizza vs. homemade pizza, then the quality of ingredients, then the convenience factor. The advantage of this form is that it’s very clear what you’re comparing and contrasting. The disadvantage is that you do switch back and forth between topics, so you need to make sure that you use transitions and signposts to lead your reader through your argument.
- Compare then contrast. This organization presents all the comparisons first, then all the contrasts. It’s a pretty common way of organizing an essay, and it can be helpful if you really want to emphasize how your subjects are different. Putting the contrasts last places the emphasis on them. However, it can be more difficult for your readers to immediately see why these two subjects are being contrasted if all the similarities are first.

- Introduction. This paragraph comes first and presents the basic information about the subjects to be compared and contrasted. It should present your thesis and the direction of your essay (i.e., what you will discuss and why your readers should care).
- Body Paragraphs. These are the meat of your essay, where you provide the details and evidence that support your claims. Each different section or body paragraph should tackle a different division of proof. It should provide and analyze evidence in order to connect those proofs to your thesis and support your thesis. Many middle-school and high-school essays may only require three body paragraphs, but use as many as is necessary to fully convey your argument.
- Acknowledgement of Competitive Arguments/Concession. This paragraph acknowledges that other counter-arguments exist, but discusses how those arguments are flawed or do not apply.
- Conclusion. This paragraph summarizes the evidence presented. It will restate the thesis, but usually in a way that offers more information or sophistication than the introduction could. Remember: your audience now has all the information you gave them about why your argument is solid. They don’t need you to just reword your original thesis. Take it to the next level!

- Introduction: state your intent to discuss the differences between camping in the woods or on the beach.
- Body Paragraph 1 (Woods): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 2 (Woods): Types of Activities and Facilities
- Body Paragraph 3 (Beach): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 4 (Beach): Types of Activities and Facilities

- Introduction

- Body Paragraph 1: Similarity between woods and beaches (both are places with a wide variety of things to do)
- Body Paragraph 2: First difference between woods and beaches (they have different climates)
- Body Paragraph 3: Second difference between woods and beaches (there are more easily accessible woods than beaches in most parts of the country)
- Body Paragraph 4: Emphasis on the superiority of the woods to the beach

- Topic sentence: This sentence introduces the main idea and subject of the paragraph. It can also provide a transition from the ideas in the previous paragraph.
- Body: These sentences provide concrete evidence that support the topic sentence and main idea.
- Conclusion: this sentence wraps up the ideas in the paragraph. It may also provide a link to the next paragraph’s ideas.
Putting It All Together

- If you are having trouble finding evidence to support your argument, go back to your original texts and try the brainstorming process again. It could be that your argument is evolving past where it started, which is good! You just need to go back and look for further evidence.

- For example, in a body paragraph about the quality of ingredients in frozen vs. homemade pizza, you could close with an assertion like this: “Because you actively control the quality of the ingredients in pizza you make at home, it can be healthier for you than frozen pizza. It can also let you express your imagination. Pineapple and peanut butter pizza? Go for it! Pickles and parmesan? Do it! Using your own ingredients lets you have fun with your food.” This type of comment helps your reader understand why the ability to choose your own ingredients makes homemade pizza better.

- Reading your essay aloud can also help you find problem spots. Often, when you’re writing you get so used to what you meant to say that you don’t read what you actually said.

- Avoid bias. Don't use overly negative or defamatory language to show why a subject is unfavorable; use solid evidence to prove your points instead.
- Avoid first-person pronouns unless told otherwise. In some cases, your teacher may encourage you to use “I” and “you” in your essay. However, if the assignment or your teacher doesn’t mention it, stick with third-person instead, like “one may see” or “people may enjoy.” This is common practice for formal academic essays.
- Proofread! Spelling and punctuation errors happen to everyone, but not catching them can make you seem lazy. Go over your essay carefully, and ask a friend to help if you’re not confident in your own proofreading skills.
Sample Body Paragraphs

- "When one is deciding whether to go to the beach or the woods, the type of activities that each location offers are an important point to consider. At the beach, one can enjoy the water by swimming, surfing, or even building a sandcastle with a moat that will fill with water. When one is in the woods, one may be able to go fishing or swimming in a nearby lake, or one may not be near water at all. At the beach, one can keep one's kids entertained by burying them in sand or kicking around a soccer ball; if one is in the woods, one can entertain one's kids by showing them different plans or animals. Both the beach and the woods offer a variety of activities for adults and kids alike."

- "The beach has a wonderful climate, many activities, and great facilities for any visitor's everyday use. If a person goes to the beach during the right day or time of year, he or she can enjoy warm, yet refreshing water, a cool breeze, and a relatively hot climate. At the beach, one can go swimming, sunbathe, or build sandcastles. There are also great facilities at the beach, such as a changing room, umbrellas, and conveniently-located restaurants and changing facilities. The climate, activities, and facilities are important points to consider when deciding between the beach and the woods."
Sample Essay Outline

Community Q&A
- Collect your sources. Mark page numbers in books, authors, titles, dates, or other applicable information. This will help you cite your sources later on in the writing process. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 2
- Don't rush through your writing. If you have a deadline, start early. If you rush, the writing won't not be as good as it could be. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Use reputable sources. While Wikipedia may be an easy way to start off, try to go to more specific websites afterwards. Many schools refuse to accept Wikipedia as a valid source of information, and prefer sources with more expertise and credibility. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- If you have external sources, make sure you always cite them. Otherwise, you may be guilty of plagiarism. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/interactives/compcontrast/
About This Article

To write a compare and contrast essay, try organizing your essay so you're comparing and contrasting one aspect of your subjects in each paragraph. Or, if you don't want to jump back and forth between subjects, structure your essay so the first half is about one subject and the second half is about the other. You could also write your essay so the first few paragraphs introduce all of the comparisons and the last few paragraphs introduce all of the contrasts, which can help emphasize your subjects' differences and similarities. To learn how to choose subjects to compare and come up with a thesis statement, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Huma Bukhari
Feb 16, 2019
Did this article help you?
Alain Vilfort
Mar 2, 2017
Aida Mirzaie
Aug 19, 2018
Michaela Mislerov
Apr 2, 2017
Subhashini Gunasekaran
Jul 31, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.2: Comparison and Contrast Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 107769

- Kathryn Crowther et al.
- Georgia Perimeter College via GALILEO Open Learning Materials
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Writing a Comparison-and-Contrast Essay
First, choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so. Be sure to make an argument in your thesis; explain to the reader what’s at stake in analyzing the relationship between your stated subjects.
The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects.
After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis. This conclusion is the “and so” statement for your essay, giving you the place to offer a judgment based on the examination you have just offered.
Sample Comparison-and-Contrast Essays
A South African Storm
By Allison Howard – Peace Corps Volunteer: South Africa (2003-2005)
It’s a Saturday afternoon in January in South Africa. When I begin the 45–minute walk to the shops for groceries, I can hear thunder cracking in the distance up the mountain in Mageobaskloof. But at 4 p.m. the sky is still light and bright and I am sure—famous last words—I will be fine without an umbrella.
Just the basics: eggs, bread, Diet Coke in a bag slung into the crook of my elbow. Halfway from town, two black South African women—domestic workers in the homes of white Afrikaner families—stop me with wide smiles. They know me; I’m the only white person in town who walks everywhere, as they do. They chatter quickly in northern Sotho: “Missus, you must go fast. Pula e tla na! The rain, it comes!” They like me, and it feels very important to me that they do.“Yebo, yebo, mma,” I say—Yes, it’s true—and I hurry along in flip-flops, quickening my pace, feeling good about our brief but neighborly conversation. These are Venda women.
My black South African friends tell me it’s easy to tell a Venda from a Shangaan from a Xhosa from a Pedi. “These ones from Venda, they have wide across the nose and high in the cheekbones,” they say. But I don’t see it; I’m years away from being able to distinguish the nuances of ethnicity. Today, I know these women are Vendas simply because of their clothing: bright stripes of green and yellow and black fabric tied at one shoulder and hanging quite like a sack around their bodies. They’ve already extended a kindness to me by speaking in northern Sotho. It’s not their language but they know I don’t speak a word of Afrikaans (though they don’t understand why; Afrikaans is the language of white people). They know I struggle with Sotho and they’re trying to help me learn. So they speak Sotho to me and they’re delighted and amused by my fumbling responses. And I am, quite simply, delighted by their delight.
The Venda ladies are right: the rain, it comes. Lightly at first, and by habit I begin trotting to hurry my way home. Just a little rain at first and there are plenty of us out in it. I can see others up ahead on the street and others still just leaving the shops to get back before the real rain begins.
The people who are walking along this swath of tar road are black. Black people don’t live in this neighborhood—or in my town at all, for the most part. They work and board here as domestic workers, nannies, gardeners. Their families live in black townships and rural villages—some just outside of my town; others far away, in places like Venda.
Today, we’re walking together in the rain, and I’m quickening my pace because—after all, it’s raining. That’s what you do in the rain. And even though it’s coming down noticeably harder, it’s 80 degrees and I’m not cold, I’m just wet. My hair is stuck to my forehead and my T-shirt is soaked … and I’m the only one running for cover. And I think: So what? It’s just water and in the middle of the January summer, it’s warm, refreshing water. Why run? Why do we run from the rain?
In my life back in the United States, I might run because I was carrying a leather handbag, or because I wore an outfit that shouldn’t get wet. I would run because rain dishevels and messes things up. Mostly though, we run because we just do; it’s a habit. I’ve done it a hundred times: running to my car or the subway station with a newspaper sheltering my head. I have never not quickened my pace in the rain until today.
It took all of my 27 years and a move to Africa, where I don’t have a leather handbag to shelter or a pretty outfit to protect. I’m wearing an old cotton skirt and a T-shirt, and I’m drenched, and I love it. I learn things here in the most ordinary circumstances. And I feel like a smarter, better woman today because I got groceries in the rain.
But on the long walk home, positively soaked and smiling like a fool, I notice a car pulling over and a man yelling in Afrikaans to get in, get in. I look in the direction I’ve come from and several meters behind me is a woman with a baby tied to her back and an elderly man carrying bags, leading a young boy by the hand. On the road ahead, a woman about my age carries a parcel wrapped in plastic, balanced precariously on her head. There are maybe 20 people walking with me in my reverie of rain and they are black. And the man in the car is white and he’s gesturing frantically for me to get in. Why me? Why not the others? Because I’m white and it’s about race. Everything is about race here.
This man in the car is trying to do something kind and neighborly. He wants to help me and his gesture is right, but his instincts are so wrong. How do you resent someone who is, for no benefit of his own, trying to help? But I do. I resent him and I resent the world he lives in that taught him such selective kindness. This whole event unravels in a few seconds’ time. He’s leaned over and opened the car door, urging me in … and I get in. And we speed past my fellow walkers and he drops me at my doorstep before I have time to think of anything besides giving him directions.
It feels like a mistake because I’m ashamed to think what the Venda women would have felt if he’d ignored them and they had watched me climb into that car. In some ways, the whole episode seems absurd. I’m not going to atone for 400 years of South African history by walking with black people in the rain. If I’d refused his ride, he wouldn’t have thought anything besides the fact that I was certifiably crazy. That’s the thing about being here: I’m not going to change anything. But I believe it matters in some infinitesimal way that people like the Venda women, and the dozens of people who may walk alongside me on any given day, know that I’m there. In black South African culture it is polite to greet every person you pass. That’s what they do, so I do it, too. On the occasional morning, someone might greet me as “sesi,” sister. I have to believe that matters; I know it matters to me.
I was disappointed in myself for getting into the car because I acted according to the same habit that makes us think rain an inconvenience. Just as we run from the rain, I hopped into that car because I’m supposed to. Conventionally, it makes sense. But convention compels us to do so many things that don’t make any sense at all. Convention misinforms our instincts. And in a larger sense, it is convention that propels Afrikaner culture anachronistically into the future. Ten years after the supposed end of apartheid, I’m living in a world of institutionalized racism. Convention becomes institution—and it’s oppressive and it’s unjust. I know that if I’m going to make it here for two more years, I need to walk in the rain. It’s a small, wasted gesture, but it’s an uncorrupted instinct that makes me feel human.
So much about living here feels like that fraction of a second when the Afrikaner man was appealing to my conventional sensibilities and the people on the street were appealing to my human instincts. It may feel unnatural to reject those sensibilities just as, at first, it feels unnatural to walk in the rain. But if I lose a hold on my instincts here, I’ll fail myself and I’ll fail to achieve those tiny things that matter so much. It’s simple and it’s small; and it’s everything. Gandhi said, “Be the change you wish to see in the world.” Indeed. Let it rain.
Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington, DC
Both Washington, DC, and London are capital cities of English-speaking countries, and yet they offer vastly different experiences to their residents and visitors. Comparing and contrasting the two cities based on their history, their culture, and their residents show how different and similar the two are.
Both cities are rich in world and national history, though they developed on very different time lines. London, for example, has a history that dates back over two thousand years. It was part of the Roman Empire and known by the similar name, Londinium. It was not only one of the northernmost points of the Roman Empire but also the epicenter of the British Empire where it held significant global influence from the early sixteenth century on through the early twentieth century. Washington, DC, on the other hand, has only formally existed since the late eighteenth century. Though Native Americans inhabited the land several thousand years earlier, and settlers inhabited the land as early as the sixteenth century, the city did not become the capital of the United States until the 1790s. From that point onward to today, however, Washington, DC, has increasingly maintained significant global influence. Even though both cities have different histories, they have both held, and continue to hold, significant social influence in the economic and cultural global spheres.
Both Washington, DC, and London offer a wide array of museums that harbor many of the world’s most prized treasures. While Washington, DC, has the National Gallery of Art and several other Smithsonian galleries, London’s art scene and galleries have a definite edge in this category. From the Tate Modern to the British National Gallery, London’s art ranks among the world’s best. This difference and advantage has much to do with London and Britain’s historical depth compared to that of the United States. London has a much richer past than Washington, DC, and consequently has a lot more material to pull from when arranging its collections. Both cities have thriving theater districts, but again, London wins this comparison, too, both in quantity and quality of theater choices. With regard to other cultural places like restaurants, pubs, and bars, both cities are very comparable. Both have a wide selection of expensive, elegant restaurants as well as a similar amount of global and national chains. While London may be better known for its pubs and taste in beer, DC offers a different bar-going experience. With clubs and pubs that tend to stay open later than their British counterparts, the DC night life tend to be less reserved overall.
Both cities also share and differ in cultural diversity and cost of living. Both cities share a very expensive cost of living—both in terms of housing and shopping. A downtown one-bedroom apartment in DC can easily cost $1,800 per month, and a similar “flat” in London may double that amount. These high costs create socioeconomic disparity among the residents. Although both cities’ residents are predominantly wealthy, both have a significantly large population of poor and homeless. Perhaps the most significant difference between the resident demographics is the racial makeup. Washington, DC, is a “minority majority” city, which means the majority of its citizens are races other than white. In 2009, according to the US Census, 55 percent of DC residents were classified as “Black or African American” and 35 percent of its residents were classified as “white.” London, by contrast, has very few minorities—in 2006, 70 percent of its population was “white,” while only 10 percent was “black.” The racial demographic differences between the cities is drastic.
Even though Washington, DC, and London are major capital cities of English-speaking countries in the Western world, they have many differences along with their similarities. They have vastly different histories, art cultures, and racial demographics, but they remain similar in their cost of living and socioeconomic disparity.
Sample Student Outline
In “Batman: A Hero for Any Time,” Jacob Gallman-Dreiling compares the traditional portrayal of the superhero Batman with the modern version. As you read, look for the comparison and contrast phrases that the author uses to help the reader understand the argument he is making. What kind of organizational structure does the essay follow?
Jacob Gallman-Dreiling
English 1101
16 March 2013
Thesis : Although the framework of the Batman story always remains the same, the character has been re-imagined over time to suit the changing expectations of a hero through his characterization as well as that of those who surround him, both friends and foes.
- Bruce Wayne’s parents are murdered in front of him.
- Bruce Wayne grows up to inherit his parents’ fortune.
- Batman fights crime with the help of Commissioner Gordon and others.
- Batman employs an arsenal of non-lethal weapons to aid him.
- Characters could not use concealed weapons.
- Stories required “morals.”
- Stories could not use kidnapping or excessive violence.
- Stories incorporated elements of science fiction.
- Stories had limitations on the portrayal of female characters.
- Batman’s suits often had ridiculous properties he conveniently prepared for the upcoming mission.
- Batman is haunted by the death of his parents.
- Batman has become a skilled detective and fighter.
- Batman’s suit is more armor than spandex.
- Batman is haunted by his mistakes.
- Batman and Commissioner Gordon conspire to hide the truth about Harvey Dent from the people of Gotham.
- Characters like Ace the Bat-Hound, Bat-Mice, and Batwoman were created to draw in children.
- Issues were built around a villain-of-the-week.
- Dick Grayson grows up and goes to college.
- Batgirl is paralyzed by the Joker.
- Joker is given several conflicting backstories explaining his psychosis.
- Catwoman has changed from a harmless cat-burglar to a reformed prostitute.
Sample Student Essay
Batman: A Hero for Any Time
Few ideas in this world are as timeless as that of a superhero. The ancient Greeks had Odysseus and Hercules. The British have Sherlock Holmes and Allan Quatermain. The Americans developed the modern concept of the superhero with characters like Superman and Spider-Man and created elaborate stories for the origin of their powers, much like the Greeks used when creating their heroes. While the world of superheroes was originally a white man’s club, the creation of Wonder Woman ushered in a new era of diversity. Now men, women, people of color, even those of differing sexual orientations are represented among the ranks of those who fight against evil. Though teams of superheroes like the Justice League of America and the XMen have enduring popularity, few superheroes have captured the imagination like Batman. Created in 1939 by Bob Kane and Bill Finger, a boy orphaned by violence grows to become the Caped Crusader, avenger of the fictional of Gotham. This comic book hero has spurred film, radio, and television adaptations, has spawned action figures and video games, and has maintained an uninterrupted comic book publication, something few other superhero titles can boast. Although the framework of the Batman story always remains the same, the character has been re-imagined over time to suit the changing expectations of a hero through his characterization as well as through the portrayal of those who surround him, both friends and foes.
The basic framework of the Batman story has stayed the same since his debut in May, 1939. At the age of eight, Bruce Wayne, the son of wealthy socialites, witnesses his parents’ murder at the hands of a desperate mugger and swears to avenge their deaths by waging war on all criminals. He grows up to inherit their fortune and the family company, using the money to fund charitable efforts and to reside in stately Wayne Manor. By night, he becomes Batman, ridding the Gotham City streets of menacing foes like the Joker, the Riddler, and Two-Face. He is aided in his fight by his sidekick Robin, Batgirl, and Commissioner Gordon, as well as his butler Alfred Pennyworth. His most enduring love interest is Selina Kyle, who is also known as the notorious cat-burglar, Catwoman. Batman eschews lethal weaponry such as guns, instead preferring to outwit his foes using his intellect to bring them to justice.
While the key details of Batman’s backstory have remained unchanged for almost seventy-five years, his characterization has changed to suit the ever-evolving expectations of a superhero. When the character debuted in the Silver Age of comics—the decades between 1950 and 1970—he was a sunny, pulpy character: he was billed as the “World’s Greatest Detective” and performed as such, while reflecting what is considered to be a more innocent time. His villains were grand, but he outsmarted them using his intelligence and science. The introduction of the Comics Code Authority in 1954 restricted not only the way that stories were presented but also the types of stories that could be presented. For instance, concealed weapons were forbidden, stories were required to have “morals,” and kidnapping and excessive violence were forbidden. As such, Batman’s stories began incorporating elements of science fiction. As the comics demonstrate, Batman famously repels aliens and an island of animatronic dinosaurs during this period. Also, female characters in the Batman stories of this time are poorly treated. The villain Catwoman had to be shelved due to regulations regarding women and violence, while the original Batwoman was brought on as a potential love interest to quiet the growing assertion of conservative culture warriors that Batman and Robin were, in fact, lovers. When this version of Batwoman was deemed unnecessary, she was written out. This period is also famous for Batman having “batsuits” with heretofore unseen special properties, such as fireproofing and thermal heating.
Modern portrayals of Batman show him as a deeply flawed, psychologically scarred hero. During the 1980s the Comics Code’s influence was waning, and writers like Frank Miller took advantage of this to tell brutal, psychological stories. Haunted by the murder of his parents, a modern Batman is dangerous and calculating. He has returned to his roots as a skilled detective and fighter, which has made him suspicious and paranoid. He is often depicted as having calculated how to defeat his allies, should the need arise, with contingency plans for everyone from Robin to Superman. Modern writers have a young Bruce Wayne train as a ninja before returning to Gotham to become Batman, so greater emphasis is placed on his stealth and fighting skills. The batsuit has reflected this change as well, shifting from a cloth/spandex suit to one that is very clearly body armor, built to withstand bullets and knives.
He is also haunted by his mistakes. After the death of Jason Todd, the second sidekick to go by the codename Robin, Batman spirals into anger and depression over not being able to prevent Jason’s death at the hands of the Joker. For the next decade, Jason’s murder haunts Batman alongside that of his parents as his greatest failure. He puts Jason’s costume on display in the Batcave as motivation. In the 2008 Christopher Nolan film The Dark Knight , Batman and Commissioner Gordon conspire to hide the truth of the popular District Attorney Harvey Dent’s descent into madness so that Gotham City will have a symbol of hope. While that decision is for the good of the city, it leads to Bruce Wayne’s reclusion and an eight year hiatus as Batman. Such dark, psychological stories would never have been allowed during the heyday of the Comics Code Authority.
Just as the portrayal of Batman has shifted to meet the current expectations of a superhero, so too have the depictions of the characters around him, both allies and enemies. During the Silver Age, Batman’s associates are, like Batman himself, light-hearted. Characters like Ace the Bat-Hound and the Bat-Mice were introduced to bring in more young readers, though these characters were rarely seen after 1964. Issues were built around a villain-of-the-week who is purely evil and has no outside motivation. These stories also tend to be episodic with no story arcs or even character arcs. The Joker is originally a calculating murderer, but his character becomes a gleeful trickster to comply with the Code.
As readers matured, the creative forces driving the various Batman outlets were able to tell more complex, meaningful stories. Thus, in modern portrayals, Batman’s associates deal with real, lasting consequences and changes. Beginning with Frank Miller’s The Dark Knight comic series, Batman’s friends begin their trials. Dick Grayson, the original Robin, grows up and goes to college, being replaced by the ill-fated Jason Todd. He becomes a hero in his own right, going by the codename Nightwing and becoming the leader of the Teen Titans. In the seminal 1988 graphic novel The Killing Joke , Batgirl is partially paralyzed by the Joker, who shoots her through her spine as part of an effort to drive her father, Commissioner Gordon, insane. This condition lasts until the DC-Universe-wide reboot in 2011, and she is now able to walk and has resumed the mantle of Batgirl. The Joker himself has been given many different backstories, all of them horrific. Filmmakers give a nod to the Joker’s varied backstories in the film The Dark Knight by having the Joker give conflicting accounts of how he received his trademark scars. Catwoman is originally just a bored housewife who turns to crime, but beginning in the 1980s her story retroactively changes to her being a prostitute who turns to burglary to buy freedom for herself and her sister. Once a staunch villain of Batman, this new version of the character is portrayed more as an antihero; though she is not necessarily an upstanding citizen, the new Catwoman will join forces with Batman to fight evil when it suits her. These stories appeal to an audience craving depth and substance to their characters, far different from the Pre-Vietnam War era Batman stories.
While the key details to the Batman story never change, the way the character has been presented has changed over time, as has the way his associated characters have been presented. It is perhaps this adaptability that has allowed Batman to flourish in popularity for almost seventy-five years, with no signs of that popularity waning. As the demographic for Batman’s stories matures, the power wielded by the Comics Code Authority has diminished, making darker, more meaningful stories possible. Previously one dimensional characters were given subtleties and nuances, much in the way modern film versions depict the heroes of old, from Odysseus to Sherlock Holmes. As society’s norms change, this change is reflected in the way films, stories, and comic books depict superheroes. With all the changes occurring in culture worldwide, who knows what the next generation’s Batman will be like?
External Links
“ Disability ” ( https://tinyurl.com/y99te6e2 ) by Nancy Mairs: In “Disability,” writer Nancy Mairs discusses the experience of being a disabled person in a world focused on the able-bodied. It seems to be titled “Hers” but it is the correct essay.
“ Friending, Ancient or Otherwise ” ( https://tinyurl.com/y85u8ae8 ) by Alex Wright: In “Friending, Ancient or Otherwise,” writer Alex Wright explores the evolution and purpose of friendship in the age of social media.
“ Sex, Lies and Conversation: Why Is It So Hard for Men and Women to Talk to Each Other ? ” ( https://tinyurl.com/y95dpehx ) by Deborah Tannen. In this essay, Tannen compares and contrasts conversation styles. You can view the essay here ( https://tinyurl.com/y9vnjqv8 ) also.
Contributors and Attributions
Adapted from Successful College Composition (Crowther et al.) . Sourced from LibreTexts , licensed under CC BY-NC-SA .
Adapted from Let's Get Writing (Browning, DeVries, Boylan, Kurtz and Burton) . Sourced from LibreTexts , licensed under CC BY-NC-SA .
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This section will help you determine the purpose and structure of comparison/contrast in writing.
The Purpose of Compare/Contrast in Writing
Comparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay, then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. The purpose of conducting the comparison or contrast is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities. For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic. Drawing distinctions between elements in a similar category will increase the audience’s understanding of that category, which is the purpose of the compare-and-contrast essay.
Similarly, to focus on comparison, choose two subjects that seem at first to be unrelated. For a comparison essay, you likely would not choose two apples or two oranges because they share so many of the same properties already. Rather, you might try to compare how apples and oranges are quite similar. The more divergent the two subjects initially seem, the more interesting a comparison essay will be.
The Structure of a Compare/Contrast Essay
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader. Take the following thesis as an example that leans more toward contrasting:
Thesis Statement: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.
Here the thesis sets up the two subjects to be compared and contrasted (organic versus conventional vegetables), and it makes a claim about the results that might prove useful to the reader.
You may organize compare-and-contrast essays in one of the following two ways:
- According to the subjects themselves, discussing one then the other
- According to individual points, discussing each subject in relation to each point
The organizational structure you choose depends on the nature of the topic, your purpose, and your audience.
Given that compare-and-contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is helpful to have some phrases on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis.
Phrases of Comparison and Contrast
| one similarity | one difference |
| another similarity | another difference |
| both | conversely |
| like | in contrast |
| likewise | unlike |
| similarly | while |
| in a similar fashion | whereas |
Writing an Compare/Contrast Essay
First choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so.
The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects.
After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis.
Compare/Contrast Essay Example
Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington, DC
By Scott McLean in Writing for Success
Both Washington, DC, and London are capital cities of English-speaking countries, and yet they offer vastly different experiences to their residents and visitors. Comparing and contrasting the two cities based on their history, their culture, and their residents show how different and similar the two are.
Both cities are rich in world and national history, though they developed on very different time lines. London, for example, has a history that dates back over two thousand years. It was part of the Roman Empire and known by the similar name, Londinium. It was not only one of the northernmost points of the Roman Empire but also the epicenter of the British Empire where it held significant global influence from the early sixteenth century on through the early twentieth century. Washington, DC, on the other hand, has only formally existed since the late eighteenth century. Though Native Americans inhabited the land several thousand years earlier, and settlers inhabited the land as early as the sixteenth century, the city did not become the capital of the United States until the 1790s. From that point onward to today, however, Washington, DC, has increasingly maintained significant global influence. Even though both cities have different histories, they have both held, and continue to hold, significant social influence in the economic and cultural global spheres.
Both Washington, DC, and London offer a wide array of museums that harbor many of the world’s most prized treasures. While Washington, DC, has the National Gallery of Art and several other Smithsonian galleries, London’s art scene and galleries have a definite edge in this category. From the Tate Modern to the British National Gallery, London’s art ranks among the world’s best. This difference and advantage has much to do with London and Britain’s historical depth compared to that of the United States. London has a much richer past than Washington, DC, and consequently has a lot more material to pull from when arranging its collections. Both cities have thriving theater districts, but again, London wins this comparison, too, both in quantity and quality of theater choices. With regard to other cultural places like restaurants, pubs, and bars, both cities are very comparable. Both have a wide selection of expensive, elegant restaurants as well as a similar amount of global and national chains. While London may be better known for its pubs and taste in beer, DC offers a different bar-going experience. With clubs and pubs that tend to stay open later than their British counterparts, the DC night life tend to be less reserved overall.
Both cities also share and differ in cultural diversity and cost of living. Both cities share a very expensive cost of living—both in terms of housing and shopping. A downtown one-bedroom apartment in DC can easily cost $1,800 per month, and a similar “flat” in London may double that amount. These high costs create socioeconomic disparity among the residents. Although both cities’ residents are predominantly wealthy, both have a significantly large population of poor and homeless. Perhaps the most significant difference between the resident demographics is the racial makeup. Washington, DC, is a “minority majority” city, which means the majority of its citizens are races other than white. In 2009, according to the US Census, 55 percent of DC residents were classified as “Black or African American” and 35 percent of its residents were classified as “white.” London, by contrast, has very few minorities—in 2006, 70 percent of its population was “white,” while only 10 percent was “black.” The racial demographic differences between the cities is drastic.
Even though Washington, DC, and London are major capital cities of English-speaking countries in the Western world, they have many differences along with their similarities. They have vastly different histories, art cultures, and racial demographics, but they remain similar in their cost of living and socioeconomic disparity.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
- There are two main organizing strategies for compare-and-contrast essays.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Successful Writing. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/successful-writing/s14-07-comparison-and-contrast.html . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Comparing and Contrasting London and Washington, DC. Authored by : Scott McLean. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/successful-writing/s14-07-comparison-and-contrast.html . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Peer Review Checklist
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Effective Thesis Statements
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- How to Write a Summary
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice
101 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
Great Ideas for Essays
- Teaching Resources
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Tips & Strategies
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Curriculum and Instruction, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
Compare and contrast essays are taught in school for many reasons. For one thing, they are relatively easy to teach, understand, and format. Students can typically understand the structure with just a short amount of instruction. In addition, these essays allow students develop critical thinking skills to approach a variety of topics.
Brainstorming Tip
One fun way to get students started brainstorming their compare and contrast essays is to create a Venn diagram , where the overlapping sections of the circle contain similarities and the non-overlapping areas contain the differing traits.
Following is a list of 101 topics for compare and contrast essays that you are welcome to use in your classroom. As you look through the list you will see that some items are academic in nature while others are included for interest-building and fun writing activities.
- Apple vs. Microsoft
- Coke vs. Pepsi
- Renaissance Art vs. Baroque Art
- Antebellum Era vs. Reconstruction Era in American History
- Childhood vs. Adulthood
- Star Wars vs. Star Trek
- Biology vs. Chemistry
- Astrology vs. Astronomy
- American Government vs. British Government (or any world government)
- Fruits vs. Vegetables
- Dogs vs. Cats
- Ego vs. Superego
- Christianity vs. Judaism (or any world religion )
- Republican vs. Democrat
- Monarchy vs. Presidency
- US President vs. UK Prime Minister
- Jazz vs. Classical Music
- Red vs. White (or any two colors)
- Soccer vs. Football
- North vs. South Before the Civil War
- New England Colonies vs. Middle Colonies OR vs. Southern Colonies
- Cash vs. Credit Cards
- Sam vs. Frodo Baggins
- Gandalf vs. Dumbledore
- Fred vs. Shaggy
- Rap vs. Pop
- Articles of Confederation vs. U.S. Constitution
- Henry VIII vs. King Louis XIV
- Stocks vs. Bonds
- Monopolies vs. Oligopolies
- Communism vs. Capitalism
- Socialism vs. Capitalism
- Diesel vs. Petroleum
- Nuclear Power vs. Solar Power
- Saltwater Fish vs. Freshwater Fish
- Squids vs. Octopus
- Mammals vs. Reptiles
- Baleen vs. Toothed Whales
- Seals vs. Sea Lions
- Crocodiles vs. Alligators
- Bats vs. Birds
- Oven vs. Microwave
- Greek vs. Roman Mythology
- Chinese vs. Japanese
- Comedy vs. Drama
- Renting vs. Owning
- Mozart vs. Beethoven
- Online vs. Traditional Education
- North vs. South Pole
- Watercolor vs. Oil
- 1984 vs. Fahrenheit 451
- Emily Dickinson vs. Samuel Taylor Coleridge
- W.E.B. DuBois vs. Booker T. Washington
- Strawberries vs. Apples
- Airplanes vs. Helicopters
- Hitler vs. Napoleon
- Roman Empire vs. British Empire
- Paper vs. Plastic
- Italy vs. Spain
- Baseball vs. Cricket
- Jefferson vs. Adams
- Thoroughbreds vs. Clydesdales
- Spiders vs. Scorpions
- Northern Hemisphere vs. Southern Hemisphere
- Hobbes vs. Locke
- Friends vs. Family
- Dried Fruit vs. Fresh
- Porcelain vs. Glass
- Modern Dance vs. Ballroom Dancing
- American Idol vs. The Voice
- Reality TV vs. Sitcoms
- Picard vs. Kirk
- Books vs. Movies
- Magazines vs. Comic Books
- Antique vs. New
- Public vs. Private Transportation
- Email vs. Letters
- Facebook vs. Twitter
- Coffee vs. an Energy Drink
- Toads vs. Frogs
- Profit vs. Non-Profit
- Boys vs. Girls
- Birds vs. Dinosaurs
- High School vs. College
- Chamberlain vs. Churchill
- Offense vs. Defense
- Jordan vs. Bryant
- Harry vs. Draco
- Roses vs. Carnations
- Poetry vs. Prose
- Fiction vs. Nonfiction
- Lions vs. Tigers
- Vampires vs. Werewolves
- Lollipops vs. popsicles
- Summer vs. Winter
- Recycling vs. Landfill
- Motorcycle vs. Bicycle
- Halogen vs. Incandescent
- Newton vs. Einstein
- . Go on vacation vs. Staycation
- Rock vs. Scissors
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- American English to British English Vocabulary
- Venn Diagrams to Plan Essays and More
- Topical Organization Essay
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- Writing About Literature: Ten Sample Topics for Comparison & Contrast Essays
- Organizing Compare-Contrast Paragraphs
- Comparing and Contrasting in English
- 25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
- Compare-Contrast Prewriting Chart
- Expository Essay Genre With Suggested Prompts
- Comparison in Composition
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
100 Last-Day-of-School Activities Your Students Will Love!
137 Intriguing Cause & Effect Essay Topics for Students
Teach critical thinking, logic, and the art of persuasion.

Cause-and-effect essays aren’t just a way to help students strengthen their writing skills. They’ll also learn critical thinking, logic, and the art of persuasion. In addition, they teach students to demonstrate how one thing directly influences another. Coming up with engaging cause-and-effect essay topics can be challenging, but we have you covered. This list of ideas includes a variety of topics that range from social and cultural movements to mental health and the environment.
Science and Environment Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- Describe the effect of urbanization on the environment.
- What is the impact of air pollution on health?
- What are the causes and consequences of plastics on marine life?
- What is the impact of rising sea temperatures on fish and marine life?
- Describe the impact of human behavior on global warming.

- What is the effect of social media on environmentalism?
- What causes volcanic eruptions?
- What causes trees to die?
- What are the effects of gravity?
- Why are plants green?
- Why do trees shed their leaves?
- What causes a species to become endangered?
- What are some of the causes of animals losing their habitats?
- Describe the effect of overpopulation on the environment.
- What are the effects of famine on human population?
- What are the causes and effects of Antarctica floods?
- What are the effects of pollution on the ocean?
- What effect do cars have on the environment?
- Why is it important to manage wildfires?
- What has been the impact of DNA on crime scene processing?

- What are the impacts of deforestation in Brazil?
- What are the effects of GMO foods on human health?
- What are the impacts of immunizations on human health?
Technology and Social Media Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- What are the effects of social media on adolescent development?
- How does technology affect productivity?
- What are the effects of video games on childhood development?
- How do cell phones affect human relationships?
- What are some reasons a teacher might ban cell phones from class?

- What effects do cell phones have on sleep?
- What effects did the invention of the Internet have on technology?
- What were the origins of cyberbullying?
- What are the effects of tablet use on small children?
- How has online dating changed relationships?
- What makes some people less likely to use social media?
- What are the effects of social media on privacy?
- How does the rise of TikTok affect Facebook and Instagram?
- In what ways could social media lead to extremism?
- What is the impact of social media on the increasing popularity of plastic surgery and other enhancements?

- What are some of the benefits of owning a smartphone and what are some of the drawbacks?
- What has been the impact of online shopping on brick-and-mortar stores?
- What has been the impact of smartphones on marriages and relationships?
- What are the causes and effects of texting while driving?
- What has the rise of “influencers” meant for Hollywood?
- In what ways have photo filters influenced young people’s self-esteem?
Culture and Social Issues Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- What are some of the reasons for substance abuse in young people?
- What are some of the effects of bullying?
- How does economic status affect the quality of health care?
- What are some of the causes of homelessness?
- Explain the effects of ignorance on discrimination.
- What are the impacts of death sentences on social justice?

- How does financial success affect societal privilege?
- What effects does growing up poor have on children?
- In what ways does religion influence society?
- What are the effects of immigration on a host country?
- What are the effects of ageism on job opportunities?
- What is the impact of LGBTQ+ representation in TV and movies?
- What are the effects of school shootings on politics?
- How do school uniforms affect students?
- What are the impacts of high student debt?
- What are the impacts of body shaming on people?
- What were the lasting impacts of the AIDS epidemic on society?

- What impact does banning abortion have in the United States?
- What has been the impact of marriage equality in the United States?
- What are the causes and effects of noise pollution?
- What are the causes and effects of inflation on the economy?
- What are the effects of TV shows on our behavior?
Sports Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- Examine the effects of exercise on mental health.
- What led to baseball being an iconic American sport?
- What drives people to participate in extreme sports?
- In what ways did globalization affect modern sports?
- What were the effects of doping on amateur and professional sports?
- Select a sport and write about the historical factors that led to the popularization of that sport.

- Describe the ways in which youth sports influence a child’s development.
- What were the driving forces behind the first Olympics?
- How can team sports help develop social skills?
- How have e-sports changed the sporting landscape?
- In what ways do race biases influence sports?

- What are the effects of regular workouts on immunity?
- How does participating in sports affect leadership skills?
- In what ways can sports lead to character development?
- What effect does famous athletes’ social commentary have on their fans?
History Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- What are the effects of the war in Syria on the United States?
- What have been the lasting effects of the Civil Rights Movement?
- What were the causes and effects of the attack on Pearl Harbor?
- What led up to the Berlin Wall being torn down and what effects did that have?

- What lasting impact did 9/11 have on modern American society?
- What were the causes of the Salem Witch Trials?
- What was the cultural impact of the Spanish-American War?
- How has globalization led to modern-day slavery?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of the Great Depression on women’s employment?
- How did cartels come into existence? What effect have they had on the United States and Mexico?
- What were the causes and effects of the Women’s Liberation Movement?
- Give an example of colonialism in history and name the resulting impact to the affected society.

- What led to the rise of ISIS and what has the impact been on international security?
- What factors led to the Titanic’s sinking?
- What were the causes and effects of the Vietnam War?
- Choose an American president. What led him to become president and what were the effects of his presidency?
Mental Health Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- How can stress affect the immune system?
- How does social anxiety affect young people?
- How can high academic expectations lead to depression?
- What are the effects of divorce on young people?
- How does service in the armed forces lead to post-traumatic stress disorder?

- What are the effects of mindfulness on mental health?
- Describe the ways in which the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted mental health.
- How does childhood trauma impact childhood development?
- What impact does witnessing violence have on mental health?
- What is behind increasingly high levels of anxiety in modern American society?

- What are the causes and effects of panic attacks?
- What are the causes and consequences of high stress in the workplace?
- What are some of the causes of insomnia and in what ways does it affect mental health?
- What is the impact of staying home for an extended period of time?
Current Events Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- Choose a local public education campaign. What are the effects of that campaign?
- What are the causes and effects of migration?
- What are the causes and effects of terrorist attacks?

- What are the effects of legalizing genetic engineering research?
- How do low voting rates impact elections and government?
- What is the effect of raising the minimum wage?
- What are the effects of globalization on society?
- How does gerrymandering affect election outcomes?
- What are the causes and effects of police brutality?
- What are the causes and effects of political polarization?

- What are the causes and effects of fake news?
- What are the effects of global war on citizens?
- What is the effect of international aid on poverty or health?
- Why do some countries have nuclear weapons, and what does this mean for other countries?
Education Cause & Effect Essay Topics
- What are the effects of teacher quality on student success?
- What are the causes and effects of student loan debt?
- What are the causes and effects of low graduation rates?

- What are the effects of assigning homework?
- What are the causes and effects of school funding disparities?
- What are the causes and effects of the digital divide in education?
- What is the effect of AI on education?
- What are the causes and effects of student burnout?
- Should students be required to study a foreign language in school, and what are the effects of learning a foreign language?

- What effect has the COVID pandemic had on education?
- What are the effects of same-sex classrooms or schools?
What are your best cause-and-effect essay topics for students? Come exchange ideas in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out our list of interesting persuasive essay topics for kids and teens..

You Might Also Like

The Big List of Essay Topics for High School (120+ Ideas!)
Ideas to inspire every young writer! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
College Essay Format: Top Writing and Editing Tips for 2024
A good college essay format, with the right topic, goes beyond describing your academic accomplishments and extracurriculars. Learn how to make your college essay stand out with these tips.
![write a compare and contrast essay for me [Featured image] An aspiring college student works on her college essay with a notebook and laptop.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/4IHXkh2mCduYnwEWif0upB/945c78e704166063f12ea217051b43a1/GettyImages-1270139085.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
You want to stand out in a crowd, particularly when you’re applying to the college of your choice. As part of the application process, many schools ask for an essay to accompany the standard academic and personal information they require.
At its core, your college application essay tells a story that offers admissions officers a glimpse into who you are, beyond your grades, extracurricular activities, and test scores. Your college essay, often called a "personal statement," is your opportunity to reveal your personality and give an idea about the kind of student you'll be in college.
So how should a college essay be formatted? This article covers formatting best practices, how to choose a compelling topic for your essay, and tips to help you craft an essay that captures your reader's attention, clearly communicates its message, and is free from errors.
College essay format best practices
Your personal statement should tell a compelling story that effectively demonstrates your unique values and personality. While the format of your college essay is largely up to you, consequently, it can be helpful to have a sense of how you might format your essay before composing it.
Consider the following college essay format to organize your writing and craft the most compelling story possible.
1. Think about using a title.
A title for your college essay isn't necessary. But, including one could make your essay intriguing to readers. That said, if you're low on word count, skip a title altogether and just jump into your narrative. You can also wait until after you write your essay to decide. It's often easier to come up with a fitting, compelling title after you've told your story.
2. Open with a hook.
Your opening sentence is one of the most important parts of your essay. It's what you'll use to capture the attention of the reader and compel them to continue reading. The start of your essay is your opportunity to make an impactful first impression, so make your opening a good one.
Here are two examples of how you might craft an interesting hook for your essay:
Start in the middle of your story: Call out the most interesting point of your story, and then backtrack from there. For example, "And there I found myself, surrounded by baby sea turtles on the hazy shores of Virginia Beach."
Make a specific generalization: This is a sentence that makes a general statement on what your essay will be about but gives a specific description. An example: "Each year on our family vacation out of the city, I contemplate the meaning of life as we cross the Golden Gate Bridge."
3. Use your introduction to set up your story.
While your hook will spark the reader's curiosity, the rest of your introduction should give them an idea of where you're going with your essay. Set your story up in four to five sentences, making sure to only include information that is absolutely necessary to understand your story.
4. Tell your story in the body of your essay.
The Common Application has a 650 word limit for personal statements. That means, if both your introduction and conclusion are roughly 100 words each, your body will most likely end up being about 450 words. Think of that as three to five paragraphs, with each paragraph having its own main idea or point.
Write in a narrative style—closer to how you might write a short story than an instruction manual. Tell your story in a way that’s logical, clear, and makes sense for what you're trying to convey about yourself.
While you should pay strict attention to using proper grammar and sentence structure, you have the freedom to make your essay a reflection of your personality. If you're a humorous person, use humor. If you're an eternal optimist or love getting into the minute details of life, let that shine through. But, keep in mind that your essay is fundamentally about highlighting the qualities that you'd bring to a college community, so keep your anecdotes focused and on point.
5. Use the conclusion to clarify your essay's core idea.
Finish your story with a conclusion paragraph, where you clarify the value or idea you're trying to convey. What is the main thing you want the college to know about you through this story? Is it what you've learned, a value that's important to you, or what you want to contribute to society? Finally, use the last line of your personal statement to reinforce this central idea, so that your reader leaves with a clear impression about who you are. After the "hook" of your personal statement, the concluding line is the most important of your essay.
How to develop your college essay story
Now that you know how to format your college essay, we'll explore how to develop the story you'll tell in it. Here are some steps to get started:
1. Explore past college essay prompts
Over 900 colleges use Common App essay prompts, which means you may be able to write one essay for several college applications. Some past Common App college essay prompts—which are announced publicly each year—include the following topics:
Share a story about your background, interest, identity, or talent that makes you complete as a person.
Describe a time when you faced a setback, failure, or challenge and what you learned from it.
Tell about a topic, concept, or idea that is so captivating to you that you lose all track of time.
Write about something that someone has done for you that you are grateful for, and how gratitude has motivated or affected you.
These are broad topics that give you the freedom to tell all kinds of different things about yourself. Explore these questions to start brainstorming ideas of stories you may be able to tell about yourself.
There are a lot of potential prompts out there. Some of the other college essay prompts you might encounter include:
Describe a person you admire and how that person has influenced your behavior and thinking.
Why do you want to attend this school?
Describe your creative side.
Name an extracurricular activity that is meaningful to you and how it has impacted your life.
Tell about what you have done to make your community or school a better place.
2. Pick a topic.
Choose a topic that allows you to best highlight what you want the college to know about you. A good start is to list three positive adjectives that describe you. Then, see if you can write two or three real-life examples of each trait that demonstrates that you possess that characteristic.
If you're having trouble coming up with ideas, think about the stories other people tell about you or the positive words they use to describe you. Consider asking people who know you well the following questions:
What do you think sets me apart from others?
What are my strengths?
How would you describe my personality?
What are my quirks?
These ideas can become the inspiration to develop material for a good college essay. You don't have to write about a major life-changing event. It can be a mundane or ordinary situation—like a dinner table conversation, a day at school, or a conversation with a friend. Often, slightly unusual topics are better than typical ones because they hold a reader's attention.
Regardless of the topic you choose, remember that the true topic of your college essay is you, and the purpose of it is to show how you are unique. It highlights an important piece of who you are and where you want to head in life.
3. Consider length.
Consult your college application instructions to see how long your essay should be. Typically, personal statements are between 500 and 650 words long, while supplemental essays are often around 250 to 300 words. Use the required essay length to help you determine what you will share. You won't be able to tell your life story within these few paragraphs, so choose the most impactful examples as your content.
4. Outline your essay.
An outline helps you plan your essay's key points, including its beginning, middle, and end. Use your outline to stay on topic and get the most out of your word count.
The most effective outlines are usually the simplest. For instance, a good story has a beginning, middle, and end. Likewise, your essay will have an introduction, body, and conclusion. Unless the college requests a specific admission essay format, use the format you've been using to write essays in high school that you're likely to be the most comfortable with.
If you're stuck on how to open your essay, write the middle of your story first. Then, go back and write a compelling introduction and a concise conclusion.
Tips for writing your college essay
Your college essay format and writing should be both compelling in clear. So, as you're writing your college essay, keep these tips in mind:
1. Be authentic.
One of the most essential parts of how to format a college application essay is to be authentic. The college wants to know who you are, and they will be reading dozens of essays a day. The best way to make yours stand out is to just be yourself instead of focusing on what you think they want to hear.
Imagine you’re speaking to an actual person as you write. Be honest and accurate, using words you normally use. Your essay is a personal statement, so it should sound natural to the reader—and to you too.
2. Show you can write .
While the most important part of your personal statement is showcasing who you are, you'll also be judged on your writing ability. That's because knowing the fundamental principles of writing is important to college success. Show that you understand the structure of an essay and proper use of the English language.
3. Stay on topic.
If you're using a specific question as your writing prompt, answer the question directly in the opening paragraph. Then, use the rest of the essay to elaborate on your answer. Make good use of your word count limit by being concise and coherent. Stay on topic and refrain from adding any information that doesn't add to the main idea of your essay.
4. Use concrete details to make your story come to life.
Your essay should describe a real-life event that you've experienced. And, to make that experience as vivid as possible for your reader, you'll want to lean into concrete details that effectively convey it through the written word. This adds color and validity to your personal statement. Personal examples will show you embody the characteristics or values you claim to, rather than merely saying you do.
5. Follow directions.
Read and understand the specific instructions set by the college for your essay. Then, review them again before you submit your essay to make sure you've met all of the requirements. Only once you're confident that you've followed them correctly and that your essay is free from any errors should you submit your essay.
How to edit your college essay
Once you've written your essay, you'll want to edit it until you’re satisfied it conveys your message and is free of errors. Let your first draft be as messy or pristine as it comes out. Then, go back later—several times if needed—to clean it up. Ask yourself these questions as you edit your essay:
Is my essay free of grammar, spelling, capitalization, and punctuation errors?
Is it the proper word length assigned by the college?
Have I answered the question in the prompt?
Does the introduction make me want to read more?
Are there any vague statements I can replace with more specific details?
Do any parts drone on or feel boring?
Does it feel too formal?
Are any parts or words repetitive?
Have I misused any words (such as there, their, and they're)?
Are my sentences varied in length?
Have I shared with the college what I most want them to know about me?
It can also be helpful to ask someone you trust to read your essay and give you constructive feedback. This might be a trusted teacher, parent, school counselor, or college student. It's best to choose someone who is familiar with the purpose of a college essay.
Ask them to give feedback about your essay using the same questions as above. But they should never try to rewrite your essay. And never let others edit out your voice. Ask them to focus on grammar and mechanics and to give suggestions on items to add in or leave out.
Above all, ask your guest editor what point they think you were trying to make with your essay. If they get it right, you know you've crafted a college essay that reflects you and your intended message.
PSA: Save your essay drafts!
Instead of writing your essay directly in the online application, draft and save your essay in a document like Google Docs or Word—or start out on paper and pen if that's what you're most comfortable with. That way you can make edits and use helpful online spelling and grammar checkers. And, you won't risk losing your essay if the application times out or you navigate away from it by mistake.
When you copy and paste your essay into the application, make sure your formatting, such as line spacing and bolding for headings, remains intact.
Enhance your writing skills on Coursera
Bring out your best in your college essay with a course in Writing a Personal Essay from Wesleyan University. Learn how to find your voice, structure your essay, choose relevant details, and write in a way that pulls in your readers.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make sure they have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison. 2. Brainstorm key points: Once you have chosen the subjects, brainstorm the key points you want to compare and contrast. These could include characteristics, features, themes, or arguments related to each subject. 3.
4. Provide evidence: Support your comparisons with evidence from the subjects you are analyzing. This could include quotes, statistics, or examples. 5. Use transitions: Transition words and phrases help to guide the reader through your essay and make it easier to follow your arguments. 6. Revise and edit: After you have written your essay, be ...
Making effective comparisons. As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place. For example, you might contrast French ...
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you're considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common.
An academic compare and contrast essay looks at two or more subjects, ideas, people, or objects, compares their likeness, and contrasts their differences. It's an informative essay that provides insights on what is similar and different between the two items. Depending on the essay's instructions, you can focus solely on comparing or ...
Compare and contrast essays examine topics from multiple viewpoints. This kind of essay, often assigned in middle school and high school, teaches students about the analytical writing process and prepares them for more advanced forms of academic writing. Compare and contrast essays are relatively easy to write if you follow a simple step-by-step approach.
Choose a structure for your essay and plan how you will write it. Write up your comparison and use evidence to support your argument. Revise and proofread your essay to make sure it is perfect. For more advice on each stage, check out our guide below. 1. Pick Two Subjects to Compare and Contrast. A compare and contrast assignment will ask you ...
Summarize the main similarities and differences you have identified. Make a point regarding the relationship between your subjects. 4. Things to Remember. Here are some important tips to keep in mind when writing your compare and contrast essay: Ensure you are comparing or contrasting the same criteria between each subject.
Use Clear Transitions. Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives. Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too. Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however ...
There are two main ways to structure a compare and contrast essay; the alternating method and the block method. Alternating Method: In this method, you alternate between one item and another, back and forth. So in our example, you would first tackle the setting of both books, comparing and contrasting.
When writing a compare and contrast essay, it can be helpful to see examples of well-crafted essays that effectively compare and contrast two subjects. Here are a few examples: Example 1: In this essay, we will compare and contrast the themes of love and betrayal in Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" and Emily Bronte's "Wuthering ...
Key Elements of the Compare and Contrast: The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be ...
Write a Compare and Contrast Essay. Before you begin to draft a compare and contrast essay, you should brainstorm by creating a Venn diagram or a chart to list the pros and cons of each subject you are comparing to another. The first paragraph of your compare and contrast essay should contain references to both sides of your comparison.
To write an argumentative thesis statement for a compare and contrast essay, try this AI Prompts: 💡 AI Prompt to Generate Ideas I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that pass a reasonable judgement.
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader.
The first things to focus on is what is absolutely essential to the argument you're going to make. These points will need to be included no matter what. If that alone does not fill up your essay, however, then it's time to pull out a point system. Give things a score from one to five (or ten, if you've got a lot of topics and need the ...
4. Outline your body paragraphs based on point-by-point comparison. This is the more common method used in the comparison and contrast essay. [6] You can write a paragraph about each characteristic of both locations, comparing the locations in the same paragraph.
Writing a Comparison-and-Contrast Essay. First, choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish ...
Compare and Contrast Paragraph—Dogs and Cats. Sample lines: "Researchers have found that dogs have about twice the number of neurons in their cerebral cortexes than what cats have. Specifically, dogs had around 530 million neurons, whereas the domestic cat only had 250 million neurons.
A compare and contrast essay requires deep thought. The considerations you make can deliver great insight about your subject of choice. Here are some tips to help. ... This is maybe the most basic structure for a compare and contrast essay. With this method, you write one body paragraph with all the similarities of your two subjects and one ...
The Structure of a Compare/Contrast Essay. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful ...
127 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics. Crafting a compare and contrast essay is typically much more interesting and fun than working on a dissertation. With this piece of writing, a student gets his chance to be creative. Besides, one doesn't have to re-invent the bicycle: these essays already have a purpose and a topic.
Recycling vs. Landfill. Motorcycle vs. Bicycle. Halogen vs. Incandescent. Newton vs. Einstein. Go on vacation vs. Staycation. Rock vs. Scissors. Cite this Article. These compare and contrast essay topics provide teachers and students with great and fun ideas for home and class work.
The following ideas work well for compare-contrast essays. ( Find 80+ compare-contrast essay topics for all ages here.) Public and private schools. Capitalism vs. communism. Monarchy or democracy. Dogs vs. cats as pets. WeAreTeachers. Paper books or e-books. Two political candidates in a current race.
137 Intriguing Cause & Effect Essay Topics for Students. Teach critical thinking, logic, and the art of persuasion. Cause-and-effect essays aren't just a way to help students strengthen their writing skills. They'll also learn critical thinking, logic, and the art of persuasion. In addition, they teach students to demonstrate how one thing ...
1. Be authentic. One of the most essential parts of how to format a college application essay is to be authentic. The college wants to know who you are, and they will be reading dozens of essays a day. The best way to make yours stand out is to just be yourself instead of focusing on what you think they want to hear.