- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Business Education
- Business Law
- Business Policy and Strategy
- Entrepreneurship
- Human Resource Management
- Information Systems
- International Business
- Negotiations and Bargaining
- Operations Management
- Organization Theory
- Organizational Behavior
- Problem Solving and Creativity
- Research Methods
- Social Issues
- Technology and Innovation Management
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter

Article contents
Qualitative designs and methodologies for business, management, and organizational research.
- Robert P. Gephart Robert P. Gephart Alberta School of Business, University of Alberta
- and Rohny Saylors Rohny Saylors Carson College of Business, Washington State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190224851.013.230
- Published online: 28 September 2020
Qualitative research designs provide future-oriented plans for undertaking research. Designs should describe how to effectively address and answer a specific research question using qualitative data and qualitative analysis techniques. Designs connect research objectives to observations, data, methods, interpretations, and research outcomes. Qualitative research designs focus initially on collecting data to provide a naturalistic view of social phenomena and understand the meaning the social world holds from the point of view of social actors in real settings. The outcomes of qualitative research designs are situated narratives of peoples’ activities in real settings, reasoned explanations of behavior, discoveries of new phenomena, and creating and testing of theories.
A three-level framework can be used to describe the layers of qualitative research design and conceptualize its multifaceted nature. Note, however, that qualitative research is a flexible and not fixed process, unlike conventional positivist research designs that are unchanged after data collection commences. Flexibility provides qualitative research with the capacity to alter foci during the research process and make new and emerging discoveries.
The first or methods layer of the research design process uses social science methods to rigorously describe organizational phenomena and provide evidence that is useful for explaining phenomena and developing theory. Description is done using empirical research methods for data collection including case studies, interviews, participant observation, ethnography, and collection of texts, records, and documents.
The second or methodological layer of research design offers three formal logical strategies to analyze data and address research questions: (a) induction to answer descriptive “what” questions; (b) deduction and hypothesis testing to address theory oriented “why” questions; and (c) abduction to understand questions about what, how, and why phenomena occur.
The third or social science paradigm layer of research design is formed by broad social science traditions and approaches that reflect distinct theoretical epistemologies—theories of knowledge—and diverse empirical research practices. These perspectives include positivism, interpretive induction, and interpretive abduction (interpretive science). There are also scholarly research perspectives that reflect on and challenge or seek to change management thinking and practice, rather than producing rigorous empirical research or evidence based findings. These perspectives include critical research, postmodern research, and organization development.
Three additional issues are important to future qualitative research designs. First, there is renewed interest in the value of covert research undertaken without the informed consent of participants. Second, there is an ongoing discussion of the best style to use for reporting qualitative research. Third, there are new ways to integrate qualitative and quantitative data. These are needed to better address the interplay of qualitative and quantitative phenomena that are both found in everyday discourse, a phenomenon that has been overlooked.
- qualitative methods
- research design
- methods and methodologies
- interpretive induction
- interpretive science
- critical theory
- postmodernism
- organization development
Introduction
Qualitative research uses linguistic symbols and stories to describe and understand actual behavior in real settings (Denzin & Lincoln, 1994 ). Understanding requires describing “specific instances of social phenomena” (Van Maanen, 1998 , p. xi) to determine what this behavior means to lay participants and to scientific researchers. This process produces “narratives-non-fiction division that link events to events in storied or dramatic fashion” to uncover broad social science principles at work in specific cases (p. xii).
A research design and/or proposal is often created at the outset of research to act as a guide. But qualitative research is not a rule-governed process and “no one knows” the rules to write memorable and publishable qualitative research (Van Maanen, 1998 , p. xxv). Thus qualitative research “is anything but standardized, or, more tellingly, impersonal” (p. xi). Design is emergent and is often created as it is being done.
Qualitative research is also complex. This complexity is addressed by providing a framework with three distinct layers of knowledge creation resources that are assembled during qualitative research: the methods layer, the logic layer, and the paradigmatic layer. Research methods are addressed first because “there is no necessary connection between research strategies and methods of data collection and analysis” (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 227). Research methods (e.g., interviews) must be adapted for use with the specific logical strategies and paradigmatic assumptions in mind.
The first, or methods, layer uses qualitative methods to “collect data.” That is, to observe phenomena and record written descriptions of observations, often through field notes. Established methods for description include participant and non-participant observation, ethnography, focus groups, individual interviews, and collection of documentary data. The article explains how established methods have been adapted and used to answer a range of qualitative research questions.
The second, or logic, layer involves selecting a research strategy—a “logic, or set of procedures, for answering research questions” (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 18). Research strategies link research objectives, data collection methods, and logics of analysis. The three logical strategies used in qualitative organizational research are inductive logic, deductive logic and abductive logic (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 79). 1 Each logical strategy makes distinct assumptions about the nature of knowledge (epistemology), the nature of being (ontology), and how logical strategies and assumptions are used in data collection and analysis. The task is to describe important methods suitable for each logical strategy, factors to consider when selecting methods (Blaikie, 2010 ), and illustrates how data collection and analysis methods are adapted to ensure for consistency with specific logics and paradigms.
The third, or paradigms, layer of research design addresses broad frameworks and scholarly traditions for understanding research findings. Commitment to a paradigm or research tradition entails commitments to theories, research strategies, and methods. Three paradigms that do empirical research and seek scientific knowledge are addressed first: positivism, interpretive induction, and interpretive abduction. Then, three scholarly and humanist approaches that critique conventional research and practice to encourage organizational change are discussed: critical theory and research, postmodern perspectives, and organization development (OD). Paradigms or traditions provide broad scholarly contexts that make specific studies comprehensible and meaningful. Lack of grounding in an intellectual tradition limits the ability of research to contribute: contributions always relate to advancing the state of knowledge in specific unfolding research traditions that also set norms for assessing research quality. The six research designs are explained to show how consistency in design levels can be achieved for each of the different paradigms. Further, qualitative research designs must balance the need for a clear plan to achieve goals with the need for adaptability and flexibility to incorporate insights and overcome obstacles that emerge during research.
Our general goal has been to provide a practical guide to inspire and assist readers to better understand, design, implement, and publish qualitative research. We conclude by addressing future challenges and trends in qualitative research.
The Substance of Research Design
A research design is a written text that can be prepared prior to the start of a research project (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 4) and shared or used as “a private working document.” Figure 1 depicts the elements of a qualitative research design and research process. Interest in a topic or problem leads researchers to pose questions and select relevant research methods to fulfill research purposes. Implementation of the methods requires use of logical strategies in conjunction with paradigms of research to specify concepts, theories, and models. The outcomes, depending on decisions made during research, are scientific knowledge, scholarly (non-scientific) knowledge, or applied knowledge useful for practice.
Figure 1. Elements of qualitative research design.
Research designs describe a problem or research question and explain how to use specific qualitative methods to collect and analyze qualitative data that answer a research question. The purposes of design are to describe and justify the decisions made during the research process and to explain how the research outcomes can be produced. Designs are thus future-oriented plans that specify research activities, connect activities to research goals and objectives, and explain how to interpret the research outcomes using paradigms and theories.
In contrast, a research proposal is “a public document that is used to obtain necessary approvals for a research proposal to proceed” (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 4). Research designs are often prepared prior to creating a research proposal, and research proposals often require the inclusion of research designs. Proposals also require greater formality when they are the basis for a legal contract between a researcher and a funding agency. Thus, designs and proposals are mutually relevant and have considerable overlap but are addressed to different audiences. Table 1 provides the specific features of designs and proposals. This discussion focuses on designs.
Table 1. Decisions Necessitated by Research Designs and Proposals
Source: Based on Blaikie ( 2010 ), pp. 12–34.
The “real starting point” for a research design (or proposal) is “the formulation of the research question” (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 17). There are three types of research questions: “what” questions seek descriptions; “why” questions seek answers and understanding; and “how” questions address conditions where certain events occur, underlying mechanisms, and conditions necessary for change interventions (p. 17). It is useful to start with research questions rather than goals, and to explain what the research is intended to achieve (p. 17) in a technical way.
The process of finding a topic and formulating a useful research question requires several considerations (Silverman, 2014 , pp. 31–33, 34–40). Researchers must avoid settings where data collection will be difficult (pp. 31–32); specify an appropriate scope for the topic—neither too wide or too narrow—that can be addressed (pp. 35–36); fit research questions into a relevant theory (p. 39); find the appropriate level of theory to address (p. 42); select appropriate designs and research methods (pp. 42–44); ensure the volume of data can be handled (p. 48); and do an effective literature review (p. 48).
A literature review is an important way to link the proposed research to current knowledge in the field, and to explain what was previously known or what theory suggests to be the case (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 17). Research questions can used to bound and frame the literature review while the literature review often inspires research questions. The review may also provide bases for creating new hypotheses and for answering some of the initial research questions (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 18).
Layers of Research Design
There are three layers of research design. The first layer focuses on research methods for collecting data. The second layer focuses on the logical frameworks used for analyzing data. The third layer focuses on the paradigm used to create a coherent worldview from research methods and logical frameworks.
Layer One: Design as Research Methods
Qualitative research addresses the meanings people have for phenomena. It collects narratives of organizational activity, uses analytical induction to create coherent representations of the truths and meanings in organizational contexts, and then creates explanations of this conduct and its prevalence (Van Maanan, 1998 , pp. xi–xii). Thus qualitative research involves “doing research with words” (Gephart, 2013 , title) in order to describe the linguistic symbols and stories that members use in specific settings.
There are four general methods for collecting qualitative data and creating qualitative descriptions (see Table 2 ). The in-depth case study approach provides a history of an event or phenomenon over time using multiple data sources. Observational strategies use the researcher to observe and describe behavior in actual settings. Interview strategies use a format where a researcher asks questions of an informant. And documentary research collects texts, documents, official records, photographs, and videos as data—formally written or visually recorded evidence that can be replayed and reviewed (Creswell, 2014 , p. 190). These methods are adapted to fit the needs of specific projects.
Table 2. Qualitative Data Collection Methods
The in-depth case study method.
The in-depth case study is a key strategy for qualitative research (Piekkari & Welch, 2012 ). It was the most common qualitative method used during the formative years of the field, from 1956 to 1965 , when 48% of qualitative papers published in the Administrative Science Quarterly used the case study method (Van Maanen, 1998 , p. xix). The case design uses one or more data collection strategies to describe in detail how a single event or phenomenon, selected by a researcher, has changed over time. This provides an understanding of the processes that underlie changes to the phenomenon. In-depth case study methods use observations, documents, records, and interviews that describe the events in the case unfolded and their implications. Case studies contextualize phenomena by studying them in actual situations. They provide rich insights into multiple dimensions of a single phenomenon (Campbell, 1975 ); offer empirical insights into what, how, and why questions related to phenomena; and assist in the creation of robust theory by providing diverse data collected over time (Gephart & Richardson, 2008 , p. 36).
Maniha and Perrow ( 1965 ) provide an example of a case study concerned with organizational goal displacement, an important issue in early organizational theorizing that proposed organizations emerge from rational goals. Organizational rationality was becoming questioned at the time that the authors studied a Youth Commission with nine members in a city of 70,000 persons (Maniha & Perrow, 1965 ). The organization’s activities were reconstructed from interviews with principals and stakeholders of the organization, minutes from Youth Commission meetings, documents, letters, and newspaper accounts (Maniha & Perrow, 1965 ).
The account that emerged from the data analysis is a history of how a “reluctant organization” with “no goals to guide it” was used by other aggressive organizations for their own ends. It ultimately created its own mission (Maniha & Perrow, 1965 ). Thus, an organization that initially lacked rational goals developed a mission through the irrational process of goal slippage or displacement. This finding challenged prevailing thinking at the time.
Observational Strategies
Observational strategies involve a researcher present in a situation who observes and records, the activities and conversations that occur in the setting, usually in written field notes. The three observational strategies in Table 2 —participant observation, ethnography, and systematic self-observation—differ in terms of the role of the researcher and in the data collection approach.
Participant observation . This is one of the earliest qualitative methods (McCall & Simmons, 1969 ). One gains access to a setting and an informant holding an appropriate social role, for example, client, customer, volunteer, or researcher. One then observes and records what occurs in the setting using field notes. Many features or topics in a setting can become a focus for participant observers. And observations can be conducted using continuum of different roles from the complete participant, observer as participant, and participant observer, to the complete observer who observes without participation (Creswell, 2014 , Table 9.2, p. 191).
Ethnography . An ethnography is “a written representation of culture” (Van Maanen, 1988 ) produced after extended participation in a culture. Ethnography is a form of participant observation that focuses on the cultural aspects of the group or organization under study (Van Maanen, 1988 , 2010 ). It involves prolonged and close contact with group members in a role where the observer becomes an apprentice to an informant to learn about a culture (Agar, 1980 ; McCurdy, Spradley, & Shandy, 2005 ; Spradley, 1979 ).
Ethnography produces fine-grained descriptions of a micro-culture, based on in-depth cultural participation (McCurdy et al., 2005 ; Spradley, 1979 , 2016 ). Ethnographic observations seek to capture cultural members’ worldviews (see Perlow, 1997 ; Van Maanen, 1988 ; Watson, 1994 ). Ethnographic techniques for interviewing informants have been refined into an integrated developmental research strategy—“the ethno-semantic method”—for undertaking qualitative research (Spradley, 1979 , 2016 ; Van Maanen, 1981 ). The ethnosemantic method uses a structured approach to uncover and confirm key cultural features, themes, and cultural reasoning processes (McCurdy et al., 2005 , Table 3 ; Spradley, 1979 ).
Systematic Self-Observation . Systematic self-observation (SSO) involves “training informants to observe and record a selected feature of their own everyday experience” (Rodrigues & Ryave, 2002 , p. 2; Rodriguez, Ryave, & Tracewell, 1998 ). Once aware that they are experiencing the target phenomenon, informants “immediately write a field report on their observation” (Rodrigues & Ryave, 2002 , p. 2) describing what was said and done, and providing background information on the context, thoughts, emotions, and relationships of people involved. SSO generates high-quality field notes that provide accurate descriptions of informants’ experiences (pp. 4–5). SSO allows informants to directly provide descriptions of their personal experiences including difficult to capture emotions.
Interview Strategies
Interviews are conversations between researchers and research participants—termed “subjects” in positivist research and informants in “interpretive research.” Interviews can be conducted as individual face-to-face interactions (Creswell, 2014 , p. 190) or by telephone, email, or through computer-based media. Two broad types of interview strategies are (a) the individual interview and (b) the group interview or focus group (Morgan, 1997 ). Interviews elicit informants’ insights into their culture and background information, and obtain answers and opinions. Interviews typically address topics and issues that occur outside the interview setting and at previous times. Interview data are thus reconstructions or undocumented descriptions of action in past settings (Creswell, 2014 , p. 191) that provide descriptions that are less accurate and valid descriptions than direct, real-time observations of settings.
Structured and unstructured interviews. Structured interviews pose a standardized set of fixed, closed-ended questions (Easterby-Smith, Thorpe, & Jackson, 2012 ) to respondents whose responses are recorded as factual information. Responses may be forced choice or open ended. However, most qualitative research uses unstructured or partially structured interviews that pose open-ended questions in a flexible order that can be adapted. Unstructured interviews allow for detailed responses and clarification of statements (Easterby-Smith et al., 2012 ; McLeod, 2014 )and the content and format can be tailored to the needs and assumptions of specific research projects (Gephart & Richardson, 2008 , p. 40).
The informant interview (Spradley, 1979 ) poses questions to informants to elicit and clarify background information about their culture, and to validate ethnographic observations. In interviews, informants teach the researcher their culture (Spradley, 1979 , pp. 24–39). The informant interview is part of a developmental research sequence (McCurdy et al., 2005 ; Spradley, 1979 ) that begins with broad “grand tour” questions that ask an informant to describe an important domain in their culture. The questions later narrow to focus on details of cultural domains and members’ folk concepts. This process uncovers semantic relationships among concepts of members and deeper cultural themes (McCurdy et al., 2005 ; Spradley, 1979 ).
The long interview (McCracken, 1988 ) involves a lengthy, quasi-structured interview sessions with informants to acquire rapid and efficient access to cultural themes and issues in a group. Long interviews differ ethnographic interviews by using a “more efficient and less obtrusive format” (p. 7). This creates a “sharply focused, rapid and highly intense interview process” that avoids indeterminate and redundant questions and pre-empts the need for observation or involvement in a culture. There are four stages in the long interview: (a) review literature to uncover analytical categories and design the interview; (b) review cultural categories to prepare the interview guide; (c) construct the questionnaire; and (d) analyze data to discover analytical categories (p. 30, fig. 1 ).
The active interview is a dynamic process where the researcher and informant co-construct and negotiate interview responses (Holstein & Gubrium, 1995 ). The goal is to uncover the subjective meanings that informants hold for phenomenon, and to understand how meaning is produced through communication. The active approach is common in interpretive, critical, and postmodern research that assumes a negotiated order. For example, Richardson and McKenna ( 2000 ) explored how ex-patriate British faculty members themselves interpreted and explained their expatriate experience. The researchers viewed the interview setting as one where the researchers and informants negotiated meanings between themselves, rather than a setting where prepared questions and answers were shared.
Documentary, Photographic, and Video Records as Data
Documents, records, artifacts, photographs, and video recordings are physically enduring forms of data that are separable from their producers and provide mute evidence with no inherent meaning until they are read, written about, and discussed (Hodder, 1994 , p. 393). Records (e.g., marriage certificate) attest to a formal transaction, are associated with formal governmental institutions, and may have legally restricted access. In contrast, documents are texts prepared for personal reasons with fewer legal restrictions but greater need for contextual interpretation. Several approaches to documentary and textual data analysis have been developed (see Table 3 ). Documents that researchers have found useful to collect include public documents and minutes of meetings; detailed transcripts of public hearings; corporate and government press releases; annual reports and financial documents; private documents such as diaries of informants; and news media reports.
Photographs and videos are useful for capturing “accurate” visual images of physical phenomena (Ray & Smith, 2012 ) that can be repeatedly reexamined and used as evidence to substantiate research claims (LeBaron, Jarzabkowski, Pratt, & Fetzer, 2018 ). Photos taken from different positions in space may also reveal different features of phenomena. Videos show movement and reveal activities as processes unfolding over time and space. Both photos and videos integrate and display the spatiotemporal contexts of action.
Layer Two: Design as Logical Frameworks
The second research design layer links data collection and analysis methods (Tables 2 and 3 ) to three logics of enquiry that answer specific questions: inductive, deductive, and abductive logical strategies (see Table 4 ). Each logical strategy focuses on producing different types of knowledge using distinctive research principles, processes, and types of research questions they can address.
Table 3. Data Analysis and Integrated Data Collection and Analysis Strategies
Table 4. logical strategies for answering qualitative research questions with evidence.
Based in part on Blaikie ( 1993 ), ch. 5 & 6; Blaikie ( 2010 ), p. 84, table 4.1
The Inductive Strategy
Induction is the scientific method for many scholars (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 134), and an essential logic for qualitative management research (Pratt, 2009 , p. 856). Inductive strategies ask “what” questions to explore a domain to discover unknown features of a phenomenon (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 83). There are four stages to the inductive strategy: (a) observe and record all facts without selection or anticipating their importance; (b) analyze, compare, and classify facts without employing hypotheses; (c) develop generalizations inductively based on the analyses; and (d) subject generalizations to further testing (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 137).
Inductive research assumes a real world outside human thought that can be directly sensed and described (Blaikie, 2010 ). Principles of inductive research reflect a realist and objectivist ontology. The selection, definition, and measurement of characteristics to be studied are developed from an objective, scientific point of view. Facts about organizational features need to be obtained using unbiased measurement. Further, the elimination method is used to find “the characteristics present in all the positive cases, which are absent in all the negative cases, and which vary in appropriate degrees” (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 135). This requires data collection methods that provide unbiased evidence of the objective facts without pre-supposing their importance.
Induction can establish limited generalizations about phenomena based solely on the observations collected. Generalizations need to be based on the entire sample of data, not on selected observations from large data sets, to establish their validity. The scope of generalization is limited to the sample of data itself. Induction creates evidence to increase our confidence in a conclusion, but the conclusions do not logically follow from premises (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 164). Indeed, inferences from induction cannot be extended beyond the original set of observations and no logical or formal process exists to establish the universality of inferences.
Key data collection methods for inductive designs include observational strategies that allow the researcher to view behavior without making a priori hypotheses, to describe behavior that occurs “naturally” in settings, and to record non-impressionistic descriptions of behavior. Interviews can also elicit descriptions of settings and behavior for inductive qualitative research. Data analysis methods need to describe actual interactions in real settings including discourse among members. These methods include ethnosemantic analysis to uncover key terms and validate actual meanings used by members; analyses of conversational practices that show how meaning is negotiated through sequential turn taking in discourse; and grounded theory-based concept coding and theory development that use the constant comparative method.
Facts or descriptions of events can be compared to one another and generalizations can be made about the world using induction (Blaikie, 2010 ). Outcomes from inductive analysis include descriptions of features in a limited domain of social action that are inferred to exist in other similar settings. Propositions and broader insights can be developed inductively from these descriptions.
The Deductive Strategy
Deductive logic (Blaikie, 1993 , 2010 ) addresses “why” questions to explain associations between concepts that represent phenomena of interest. Researchers can use induction, abduction, or any means, to develop then test the hypotheses to see if they are valid. Hypotheses that are not rejected are temporarily corroborated. The outcomes from deduction are tested hypotheses. Researchers can thus be very creative in hypothesis construction but they cannot discover new phenomena with deduction that is based only on phenomena known in advance (Blaikie, 2010 ). And there is also no purely logical or mechanical process to establish “the validity of [inductively constructed] universal statements from a set of singular statements” from which deductive hypotheses were formed (Hempel, 1966 , p. 15 cited in Blaikie, 1993 , p. 140).
The deductive strategy uses a realist and objectivist ontology and imitates natural science methods. Useful data collection methods include observation, interviewing, and collection of documents that contain facts. Deduction addresses the assumedly objective features of settings and interactions. Appropriate data analysis methods include content coding to identify different types, features, and frequencies of observed phenomena; grounded theory coding and analytical induction to create categories in data, determine how categories are interrelated, and induce theory from observations; and pattern recognition to compare current data to prior models and samples. Content analysis and non-parametric statistics can be used to quantify qualitative data and make it more amenable to analysis, although quantitative analysis of qualitative data is not, strictly speaking, qualitative research (Gephart, 2004 ).
The Abductive Strategy
Abduction is “the process used to produce social scientific accounts of social life by drawing on the concepts and meanings used by social actors, and the activities in which they engage” (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 176). Abductive reasoning assumes that the socially meaningful world is the world experienced by members. The first abductive task is to discover the insider view that is basic to the actions of social actors (p. 176) by uncovering the subjective meanings held by social actors. Subjective meaning (Schutz, 1973a , 1973b ) refers to the meaning that actions hold for the actors themselves and that they can express verbally. Subjective meaning is not inexpressible ideas locked in one’s mind. Abduction starts with lay descriptions of social life, then moves to technical, scientific descriptions of social life (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 177) (see Table 4 ). Abduction answers “what” questions with induction, why questions with deduction, and “how” questions with hypothesized processes that explain how, and under what conditions, phenomena occur. Abduction involves making a logical leap that infers an explanatory process to explain an outcome in an oscillating logic. Deductive, inductive, and inferential processes move recursively from actors’ accounts to social science accounts and back again in abduction (Gephart, 2018 ). This process enables all theory and second-order scientific concepts to be grounded in actors’ first-order meanings.
The abductive strategy contains four layers: (a) everyday concepts and meanings of actors, used for (b) social interaction, from which (c) actors provide accounts, from which (d) social scientific descriptions are made, or theories are generated and applied, to interpret phenomena (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 177). The multifaceted research process, described in Table 4 , requires locating and comprehending members’ important everyday concepts and theories before observing or creating disruptions that force members to explain the unstated knowledge behind their action. The researcher then integrates members’ first-order concepts into a general, second-order scientific theory that makes first-order understandings recoverable.
Abduction emerged from Weber’s interpretive sociology ( 1978 ) and Peirce’s ( 1936 ) philosophy. But Alfred Schutz ( 1973a , 1973b ) is the contemporary scholar who did the most to extend our understanding of abduction, although he never used the term “abduction” (Blaikie, 1993 , 2010 ; Gephart, 2018 ). Schutz conceived abduction as an approach to verifiable interpretive knowledge that is scientific and rigorous (Blaikie, 1993 ; Gephart, 2018 ). Abduction is appropriate for research that seeks to go beyond description to explanation and prediction (Blaikie, 1993 , p. 163) and discovery (Gephart, 2018 ). It employs an interpretive ontology (Schutz, 1973a , 1973b ) and social constructionist epistemology (Berger & Luckmann, 1966 ), using qualitative methods to discover “why people do what they do” (Blaikie, 1993 ).
Dynamic data collection methods are needed for abductive research to capture descriptions of interactions in actual settings and their meanings to members. Observational and interview approaches that elicit members’ concepts and theories are particularly relevant to abductive understanding (see Table 2 ). Data analysis methods must analyze situated, first-order (common sense) discourse as it unfolds in real settings and then systematically develop second-order concepts or theories from data. Relevant approaches to produce and validate findings include ethnography, ethnomethodology, and grounded theorizing (see Table 3 ). The combination of what, why, and how questions used in abduction produces a broader understanding of phenomena than do what and why deductive and inductive questions.
Layer Three: Paradigms of Research
Scholarly paradigms integrate methods, logics, and intellectual worldviews into coherent theoretical perspectives and form the most abstract level of research design. Six paradigms are widely used in management research (Burrell & Morgan, 1979 ; Cunliffe, 2011 ; Gephart, 2004 , 2013 ; Gephart & Richardson, 2008 ; Hassard, 1993 ). The first three perspectives—positivism, interpretive induction, and interpretive abduction—build on logics of design and seek to produce rigorous empirical research that constitutes evidence (see Table 5 ). Three additional perspectives pursue philosophical, critical, and practical knowledge: critical theory, postmodernism, and organization development (see Table 6 ). Tables 5 and 6 describe important features of each research design to show similarities and differences in the processes through which theoretical meaning is bestowed on research results in management and organization studies.
Table 5. Paradigms, Logical Strategies, and Methodologies for Empirical Research
Sources: Based on and adapted and extended from Blaikie ( 1993 , pp. 137, 145, & 152); Blaikie ( 2010 , Table 4.1, p. 84); Gephart ( 2013 , Table 9.1, p. 291) and Gephart ( 2018 , Table 3.1, pp. 38–39).
Table 6. Alternative Paradigms, Logical Strategies, and Methodologies
Based in part on Gephart ( 2004 , 2013 , 2018 ).
The Positivist Approach
The qualitative positivist approach makes assumptions equivalent to those of quantitative research (Gephart, 2004 , 2018 ). It assumes the world is objectively describable and comprehensible using inductive and deductive logics. And rigor is important and achieved by reliability, validity, and generalizability of findings (Kirk & Miller, 1986 ; Malterud, 2001 ). Qualitative positivism mimics natural science logics and methods using data recorded as words and talk rather than numerals.
Positivist research (Bitektine, 2008 ; Su, 2018 ) starts with a hypothesis. This can, but need not, be based in data or inductive theory. The research process, aimed at publication in peer-reviewed journals, requires researchers to (a) identify variables to measure, (b) develop operational definitions of the variables, (c) measure (describe) the variables and their inter-relationships, (d) pose hypotheses to test relationships among variables, then (e) compare observations to hypotheses for testing (Blaikie, 2010 ). When data are consistent with theory, theory passes the test. Otherwise the theory fails. This theory is also assessed for its logical correctness and value for knowledge. The positivist approach can assess deductive and inductive generalizations and provide evidence concerning why something occurs—if proposed hypotheses are not rejected.
Positivists view qualitative research as highly subject to biases that must be prevented to ensure rigor, and 23 methodological steps are recommended to enhance rigor and prevent bias (Gibbert & Ruigrok, 2010 , p. 720). Replicability is another concern because methodology descriptions in qualitative publications “insufficiently describe” how methods are used (Lee, Mitchell, & Sablynski, 1999 , p. 182) and thereby prevent replication. To ensure replicability, a qualitative “article’s description of the method must be sufficiently detailed to allow a reader . . . to replicate that reported study either in a hypothetical or actual manner.”
Qualitative research allows positivists to observe naturally unfolding behavior in real settings and allow “the real world” of work to inform research and theory (Locke & Golden-Biddle, 2004 ). Encounters with the actual world provide insights into meaning construction by members that cannot be captured with outsider (etic) approaches. For example, past quantitative research provided inconsistent findings on the importance of pre- and post-recruitment screening interviews for job choices of recruits. A deeper investigation was thus designed to examine how recruitment impacts job selection (Rynes, Bretz, & Gerhart, 1991 ). To do so, students undergoing recruitment were asked to “tell us in their own words” how their recruiting and decision processes unfolded (Rynes et al., 1991 , p. 399). Using qualitative evidence, the researchers found that, in contrast to quantitative findings, “people do make choices based on how they are treated” (p. 509), and the choices impact recruitment outcomes. Rich descriptions of actual behavior can disconfirm quantitative findings and produce new findings that move the field forward.
An important limitation of positivism is its common emphasis on outsiders’ or scientific observers’ objective conceptions of the world. This limits the attention positivist research gives to members’ knowledge and allows positivist research to impose outsiders’ meanings on members’ everyday behavior, leading to a lack of understanding of what the behavior means to members. Another limitation is that no formal, logical, or proven techniques exist to assess the strength of “relationships” among qualitative variables, although such assessments can be formally done using well-formed quantitative data and techniques. Thus, qualitative positivists often provide ambiguous or inexplicit quantitative depictions of variable relations (e.g., “strong relationship”). Alternatively, the analysts quantify qualitative data by assigning numeric codes to categories (Greckhamer, Misngyi, Elms, & Lacey, 2008 ), using non-parametric statistics, or quantitative content analysis (Sonpar & Golden-Biddle, 2008 ) to create numerals that depict associations among variables.
An illustrative example of positivist research . Cole ( 1985 ) studied why and how organizations change their working structures from bureaucratic forms to small, self-supervised work teams that allow for worker participation in shop floor activities. Cole found that existing research on workplace change focused on the micropolitical level of organizations. He hypothesized that knowledge could be advanced differently, by examining the macropolitical change in industries or nations. Next, a testable conclusion was deduced: a macro analysis of the politics of change can better predict the success of work team implementation, measured as the spread of small group work structures, than an examination of the micropolitics of small groups ( 1985 ). Three settings were selected for the research: Japan, Sweden, and the United States. Japanese data were collected from company visits and interviews with employment officials and union leaders. Swedish documentary data on semiautonomous work groups were used and supplemented by interviews at Volvo and Saab, and prior field research in Sweden. U.S. data were collected through direct observations and a survey of early quality circle adopters.
Extensive change was observed in Sweden and Japan but changes to small work groups were limited in the United States (Cole, 1985 ). This conclusion was verified using records of the experiences of the three nations in work reform, compared across four dimensions: timing and scope of changes, managerial incentives to innovate, characteristics of mobilization, and political dimensions of change. Data revealed the United States had piecemeal experimentation and resistance to reform through the 1970s; diffusion emerged in Japan in the early 1960s and became extensive; and Swedish workplace reform started in the 1960s and was widely and rapidly diffused.
Cole then answered the questions of “why” and “how” the change occurred in some countries but not others. Regarding why Japanese and Swedish managers were motivated to introduce workplace change due to perceived managerial problems and the changing national labor market. Differences in the political processes also influenced change. Management, labor, and government interest in workplace change was evident in Japan and Sweden but not in the United States where widespread resistance occurred. As to how, the change occurred through macropolitical processes (Cole, 1985 , p. 120), specifically, the commitment of the national business leadership to the change and whether or not the change was contested or uncontested by labor impacted the adoption of change. Organizational change usually occurs through broad macropolitical processes, hence “the importance of macro-political variables in explaining these outcomes” (p. 122).
Interpretive Induction
Two streams of qualitative research claim the label of “interpretive research” in management and organization studies. The first stream, interpretive induction, emphasizes induction as its primary logical strategy (e.g., Locke, 2001 , 2002 ; Pratt, 2009 ). It assumes a “real world” that is inherently objective but interpreted through subjective lenses, hence different people can perceive or report different things. This research is interpretive because it addresses the meanings and interpretations people give to organizational phenomena, and how this meaning is provided and used. Interpretive induction contributes to scientific knowledge by providing empirical descriptions, generalizations, and low-level theories about specific contexts based on thick descriptions of members’ settings and interactions (first-order understandings) as data.
The interpretive induction paradigm addresses “what” questions that describe and explain the existence and features of phenomena. It seeks to uncover the subjective, personal knowledge that subjects have of the objective world and does so by creating descriptive accounts of the activities of organizational members. Interpretive induction creates inductive theories based on limited samples that provide low-scope, abstract theory. Limitations (Table 5 ) include the fact that inductive generalizations are limited to the sample used for induction and need to be subjected to additional tests and comparisons for substantiation. Second, research reports often fail to provide details to allow replication of the research. Third, formal methods for assessing the accuracy and validity of results and findings are limited. Fourth, while many features of scientific research are evident in interpretive induction research, the research moves closer to humanistic knowledge than to science when the basic assumptions of inductive analysis are relaxed—a common occurrence.
An illustrative example of interpretive induction research . Adler and Adler ( 1988 , 1998 ) undertook a five-year participant-observation study of a college basketball program (Adler, 1998 , p. 32). They sought to “examine the development of intense loyalty in one organization.” Intense loyalty evokes “devotional commitment of . . . (organizational) members through a subordination that sometime borders on subservience” (p. 32). The goal was to “describe and analyze the structural factors that emerged as most related” to intense loyalty (p. 32).
The researchers divided their roles. Peter Adler was the active observer and “expert” who undertook direct observations while providing counsel to players (p. 33). Patricia Adler took the peripheral role of “wife” and debriefed the observer. Two research questions were posed: (a) “what” kinds of organizational characteristics foster intense loyalty? (b) “how” do organizations with intense loyalty differ structurally from those that lack intense loyalty?
The first design stage (Table 5 ) recorded unbiased observations in extensive field notes. Detailed “life history” accounts were obtained from 38 team members interviewed (Adler & Adler, 1998 , p. 33). Then analytical induction and the constant comparative method (Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ) were used to classify and compare observations (p. 33). Once patterns emerged, informants were questioned about variations in patterns (p. 34) to develop “total patterns” (p. 34) reflecting the collective belief system of the group. This process required a “careful and rigorous means of data collection and analysis” that was “designed to maximize both the reliability and validity of our findings” (p. 34). The study found five conceptual elements were essential to the development of intense loyalty: domination, identification, commitment, integration, and goal alignment (p. 35).
The “what” question was answered by inducing a generalization (stage 3): paternalistic organizations with charismatic leadership seek people who “fit” the organization’s style and these people require extensive socialization to foster intense loyalty. This description contrasts with rational bureaucratic organizations that seek people who fit specific, generally known job descriptions and require limited socialization (p. 46). The “how” question is answered by inductive creation of another generalization: organizations that control the extra-organizational activities of members are more likely to evoke intense loyalty by forcing members to subordinate all other interests to those of the organization (p. 46).
The Interpretive Abduction Approach
The second stream of interpretive research—interpretive abduction—produces scientific knowledge using qualitative methods (Gephart, 2018 ). The approach assumes that commonsense knowledge is foundational to how actors know the world. Abductive theory is scientifically built from, and refers to, everyday life meanings, in contrast to positivist and interpretive induction research that omits concern with the worldview of members. Further, interpretive abduction produces second-order or scientific theory and concepts from members’ first-order commonsense concepts and meanings (Gephart, 2018 , p. 34; Schutz, 1973a , 1973b ).
The research process, detailed in Table 5 (process and stages), focuses on collecting thick descriptive data on organizations, identifying and interpreting first-order lay concepts, and creating abstract second-order technical constructs of science. The second-order concepts describe the first-order principles and terms social actors use to organize their experience. They compose scientific concepts that form a theoretical system to objectively describe, predict, and explain social organization (Gephart, 2018 , p. 35). This requires researchers to understand the subjective view of the social actors they study, and to develop second-order theory based on actors’ subjective meanings. Subjective meaning can be shared with others through language use and communication and is not private knowledge.
A central analytical task for interpretive abduction is creating second-order, ideal-type models of social roles, motives, and interactions that describe the behavioral trajectories of typical actors. Ideal-type models can be objectively compared to one another and are the special devices that social science requires to address differences between social phenomena and natural phenomena (Schutz, 1973a , 1973b ). The models, once built, are refined to preserve actors’ subjective meanings, to be logically consistent, and to present human action from the actor’s point of view. Researchers can then vary and compare the models to observe the different outcomes that emerge. Scientific descriptions can then be produced, and theories can be created. Interpretive abduction (Gephart, 2018 , p. 35) allows one to addresses what, why, and how questions in a holistic manner, to describe relationships among scientific constructs, and to produce “empirically ascertainable” and verifiable relations among concepts (Schutz, 1973b , p. 65) that are logical, hold practical meaning to lay actors, and provide abstract, objective meaning to interpretive scientists (Gephart, 2018 , p. 35). Abduction produces knowledge about socially shared realities by observing interactions, uncovering members’ first-order meanings, and then developing technical second-order or scientific accounts from lay accounts.
Interpretive abduction (Gephart, 2018 ) uses well-developed methods to create, refine, test, and verify second-order models, and it provides well-developed tools to support technical, second-level analyses. Research using the interpretive abduction approach includes a study of how technology change impacts sales automobile practices (Barley, 2015 ) and an investigation study of how abduction was used to develop new prescription drugs (Dunne & Dougherty, 2016 ).
An illustrative example of the interpretive abduction approach . Perlow ( 1997 ) studied time management among software engineers facing a product launch deadline. Past research verified the widespread belief that long working hours for staff are necessary for organizational success. This belief has adversely impacted work life and led to the concept of a “time bind” faced by professionals (Hochschild, 1997 ). One research question that subsequently emerged was, “what underlies ‘the time bind’ experienced by engineers who face constant deadlines and work interruptions?” (Perlow, 1997 , p. xvii). This is an inductive question about the causes and consequences of long working hours not answered in prior research that is hard to address using induction or deduction. Perlow then explored assumption underlying the hypothesis, supported by lay knowledge and management literature, that even if long working hours cause professionals to destroy their life style, long work hours “further the goals of our organizations” and “maximize the corporation’s bottom line” (Perlow, 1997 , p. 2).
The research commenced (Table 5 , step 1) when Perlow gained access to “Ditto,” a leader in implementing flexible work policies (Perlow, 1997 , p. 141) and spent nine months doing participant observation four days a week. Perlow collected descriptive data by walking around to observe and converse with people, attended meetings and social events, interviewed engineers at work and home and spouses at home, asked participants to record activities they undertook on selected working days (Perlow, 1997 , p. 143), and made “thousands of pages of field notes” (p. 146) to uncover trade-offs between work and home life.
Perlow ( 1997 , pp. 146–147) analyzed first-order concepts uncovered through his observations and interviews from 17 stories he wrote for each individual he had studied. The stories described workstyles, family lives, and traits of individuals; provided objective accounts of subjective meanings each held for work and home; offered background information; and highlighted first-order concepts. Similarities and differences in informant accounts were explored with an empirically grounded scheme for coding observations into categories using grounded theory processes (Gioia, Corley, & Hamilton, 2012 ). The process allowed Perlow to find key themes in stories that show work patterns and perceptions of the requirements of work success, and to create ideal-type models of workers (step 3). Five stories were selected for detailed analysis because they reveal important themes Perlow ( 1997 , p. 147). For example, second-order, ideal-type models of different “roles” were constructed in step 3 including the “organizational superstar” (pp. 15–21) and “ideal female employee” (pp. 22–32) based on first-order accounts of members. The second-order ideal-type scientific models were refined to include typical motives. The models were compared to one another (step 4) to describe and understand how the actions of these employee types differed from other employee types and how these variations produced different outcomes for each trajectory of action (steps 4 and 5).
Perlow ( 1997 ) found that constant help-seeking led engineers to interrupt other engineers to get solutions to problems. This observation led to the abductively developed hypothesis that interruptions create a time crisis atmosphere for engineers. Perlow ( 1997 ) then created a testable, second-order ideal-type (scientific) model of “the vicious working cycle” (p. 96), developed from first-order data, that explains the productivity problems that the firm (and other research and development firms)—commonly face. Specifically, time pressure → crisis mentality → individual heroics → constant interruptions of others’ work to get help → negative consequences for individual → negative consequences for the organization.
Perlow ( 1997 ) then tested the abductive hypothesis that the vicious work cycle caused productivity problems (stage 5). To do so, the vicious work cycle was transformed into a virtuous cycle using scheduling quiet times to prevent work interruptions: relaxed work atmosphere → individuals focus on own work completion → few interruptions → positive consequences for individual and organization. To test the hypothesis, an experiment was conducted (research process 2 in Table 5 ) with engineers given scheduled quiet times each morning with no interruptions. The experiment was successful: the project deadline was met. The hypothesis about work interruptions and the false belief that long hours are needed for success were supported (design stage 6). Unfortunately, the change was not sustained and engineers reverted to work interruptions when the experiment ended.
There are three additional qualitative approaches used in management research that pursue objectives other than producing empirical findings and developing or testing theories. These include critical theory and research, postmodernism, and change intervention research (see Table 6 ).
The Critical Theory and Research Approach
The term “critical” has many meanings including (a) critiques oriented to uncovering ideological manifestations in social relations (Gephart, 2013 , p. 284); (b) critiques of underlying assumptions of theories; and (c) critique as self-reflection that reflexively encapsulates the investigator (Morrow, 1994 , p. 9). Critical theory and critical management studies bring these conceptions of critical to bear on organizations and employees.
Critical theory and research extend the theories Karl Marx, and the Frankfurt School in Germany (Gephart & Kulicki, 2008 ; Gephart & Pitter, 1995 ; Habermas, 1973 , 1979 ; Morrow, 1994 ; Offe, 1984 , 1985 ). Critical theory and research assume that social science research differs from natural science research because social facts are human creations and social phenomena cannot be controlled as readily as natural phenomena (Gephart, 2013 , p. 284; Morrow, 1994 , p. 9). As a result, critical theory often uses a historical approach to explore issues that arise from the fundamental contradictions of capitalism. Critical research explores ongoing changes within capitalist societies and organizations, and analyzes the objective structures that constrain human imagination and action (Morrow, 1994 ). It seeks to uncover the contradictions of advanced capitalism that emerge from the fundamental contradiction of capitalism: owners of capital have the right to appropriate the surplus value created by workers. This basic contradiction produces further contradictions that become sources of workplace oppression and resistance that create labor issues. Thus contradictions reveal how power creates consciousness (Poutanen & Kovalainen, 2010 ). Critical reflection is used to de-reify taken-for-granted structures that create power inequities and to motivate resistance and critique and escape from dominant structures (see Table 6 ).
Critical management studies build on critical theory in sociology. It seeks to transform management and provide alternatives to mainstream theory (Adler, Forbes, & Willmott, 2007 ). The focus is “the social injustice and environmental destruction of the broader social and economic systems” served by conventional, capitalist managers (Adler et al., 2007 , p. 118). Critical management research examines “the systemic corrosion of moral responsibility when any concern for people or for the environment . . . requires justification in terms of its contribution to profitable growth” (p. 4). Critical management studies goes beyond scientific skepticism to undertake a radical critique of socially divisive and environmentally destructive patterns and structures (Adler et al., 2007 , p. 119). These studies use critical reflexivity to uncover reified capitalist structures that allow certain groups to dominate others. Critical reflection is used to de-reify and challenge the facts of social life that are seen as immutable and inevitable (Gephart & Richardson, 2008 , p. 34). The combination of dialogical inquiry, critical reflection, and a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods and data are common in this research (Gephart, 2013 , p. 285). Some researchers use deductive logics to build falsifiable theories while other researchers do grounded theory building (Blaikie, 2010 ). Validity of critical research is assessed as the capability the research has to produce critical reflexivity that comprehends dominant ideologies and transforms repressive structures into democratic processes and institutions (Gephart & Richardson, 2008 ).
An illustrative example of critical research . Barker ( 1998 , p. 130) studied “concertive control” in self-managed work teams in a small manufacturing firm. Concertive control refers to how workers collaborate to engage in self-control. Barker sought to understand how control practices in the self-managed team setting, established to allow workers greater control over their work, differed from previous bureaucratic processes. Interviews, observations, and documents were used as data sources. The resultant description of work activities and control shows that rather than allowing workers greater control, the control process enacted by workers themselves became stronger: “The iron cage becomes stronger” and almost invisible “to the workers it incarcerates” (Barker, 1998 , p. 155). This study shows how traditional participant observation methods can be used to uncover and contest reified structures and taken-for-granted truths, and to reveal the hidden managerial interests served.
Postmodern Perspectives
The postmodern perspective (Boje, Gephart, & Thatchenkery, 1996 ) is based in philosophy, the humanities, and literary criticism. Postmodernism, as an era, refers to the historical stage following modernity that evidences a new cultural worldview and style of intellectual production (Boje et al., 1996 ; Jameson, 1991 ; Rosenau, 1992 ). Postmodernism offers a humanistic approach to reconceptualize our experience of the social world in an era where it is impossible to establish any foundational underpinnings for knowledge. The postmodern perspective assumes that realities are contradictory in nature and value-laden (Gephart & Richardson, 2008 ; Rosenau, 1992 , p. 6). It addresses the values and contradictions of contemporary settings, how hidden power operates, and how people are categorized (Gephart, 2013 ). Postmodernism also challenges the idea that scientific research is value free, and asks “whose values are served by research?”
Postmodern essays depart from concerns with systematic, replicable research methods and designs (Calas, 1987 ). They seek instead to explore the values and contradictions of contemporary organizational life (Gephart, 2013 , p. 289). Research reports have the character of essays that seek to reconceptualize how people experience the world (Martin, 1990 ; Rosenau, 1992 ) and to disrupt this experience by producing “reading effects” that unsettle a community (Calas & Smircich, 1991 ).
Postmodernism examines intertextual relations—how texts become embedded in other texts—rather than causal relations. It assumes there are no singular realities or truths, only multiple realities and multiple truths, none of which are superior to other truths (Gephart, 2013 ). Truth is conceived as the outcome of language use in a context where power relations and multiple realities exist.
From a methodological view, postmodern research tends to focus on discourse: texts and talk. Data collection (in so far as it occurs) focuses on records of discourse—texts of spoken and written verbal communication (Fairclough, 1992 ). Use of formal or official records including recordings, texts and transcripts is common. Analytically, scholars tend to use critical discourse analysis (Fairclough, 1992 ), narrative analysis (Czarniawska, 1998 ; Ganzin, Gephart, & Suddaby, 2014 ), rhetorical analysis (Culler, 1982 ; Gephart, 1988 ; McCloskey, 1984 ) and deconstruction (Calais & Smircich, 1991 ; Gephart, 1988 ; Kilduff, 1993 ; Martin, 1990 ) to understand how categories are shaped through language use and come to privilege or subordinate individuals.
Postmodernism challenges models of knowledge production by showing how political discourses produce totalizing categories, showing how categorization is a tool for social control, and attempting to create opportunities for alternative representations of the world. It thus provides a means to uncover and expose discursive features of domination, subordination, and resistance in society (Locke & Golden-Biddle, 2004 ).
An illustrative example of postmodern research . Martin ( 1990 ) deconstructed a conference speech by a company president. The president was so “deeply concerned” about employee well-being and involvement at work that he encouraged a woman manager “to have her Caesarian yesterday” so she could participate in an upcoming product launch. Martin deconstructs the story to reveal the suppression of gender conflict in the dialogue and how this allows gender conflict and subjugation to continue. This research established the existence of important domains of organizational life, such as tacit gender conflict, that have not been adequately addressed and explored the power dynamics therein.
The Organization Development Approach
OD involves a planned and systematic diagnosis and intervention into an organizational system, supported by top management, with the intent of improving the organization’s effectiveness (Beckhard, 1969 ; Palmer, Dunford, & Buchanan, 2017 , p. 282). OD research (termed “clinical research” by Schein, 1987 ) is concerned with changing attitudes and behaviors to instantiate fundamental values in organizations. OD research often follows the general process of action research (Lalonde, 2019 ) that involves working with actors in an organization to help improve the organization. OD research involves a set of stages the OD practitioner (the leader of the intervention) uses: (a) problem identification; (b) consultation between OD practitioner and client; (c) data collection and problem diagnosis; (d) feedback; (e) joint problem diagnosis; (f) joint action planning; (g) change actions; and (h) further data gathering to move recursively to a refined step 1.
An illustrative example of the organization development approach . Numerous OD techniques exist to help organizations change (Palmer et al., 2017 ). The OD approach is illustrated here by the socioeconomic approach to management (SEAM) (Buono & Savall, 2007 ; Savall, 2007 ). SEAM provides a scientific approach to organizational intervention consulting that integrates qualitative information on work practices and employee and customer needs (socio) with quantitative and financial performance measures (economics). The socioeconomic intervention process commences by uncovering dysfunctions that require attention in an organization. SEAM assumes that organizations produce both (a) explicit benefits and costs and (b) hidden benefits and costs. Hidden costs refer to economic implications of organizational dysfunctions (Worley, Zardet, Bonnet, & Savall, 2015 , pp. 28–29). These include problems in working conditions; work organization; communication, co-ordination, and co-operation; time management; integrated training; and strategy implementation (Savall, Zardet, & Bonnet, 2008 , p. 33). Explicit costs are emphasized in management decision-making but hidden costs are ignored. Yet hidden costs from dysfunctions often greatly outstrip explicit costs.
For example, a fishing company sought to protect its market share by reducing the price and quality of products, leading to the purchase of poor-quality fish (Savall et al., 2008 , pp. 31–32). This reduced visible costs by €500,000. However, some customers stopped purchasing because of the lower-quality product, producing a loss of sales of €4,000,000 in revenue or an overall drop in economic performance of €3,500,000. The managers then changed their strategy to focus on health and quality. They implemented the SEAM approach, assessed the negative impact of the hidden costs on value added and revenue received, and purchased higher-quality fish. Visible costs (expenses) increased by €1,000,000 due to the higher cost for a better-quality product, but the improved quality (performance) cut the hidden costs by increasing loyalty and increased sales by €5,000,000 leaving an increased profit of €4,000,000.
SEAM allows organizations to uncover hidden costs in their operations and to convert these costs into value-added human potential through a process termed “qualimetrics.” Qualimetrics assesses the nature of hidden costs and organizational dysfunctions, develops estimates of the frequencies and amounts of hidden costs in specific organizational domains, and develops actions to reduce the hidden costs and thereby release additional value added for the organization (Savall & Zardet, 2011 ). The qualimetric process is participative and involves researchers who use observations, interviews and focus groups of employees to (a) describe, qualitatively, the dysfunctions experienced at work (qualitative data); (b) estimate the frequencies with which dysfunctions occur (quantitative data); and (c) estimate the costs of each dysfunction (financial data). Then, strategic change actions are developed to (a) identify ways to reduce or overcome the dysfunction, (b) estimate how frequently the dysfunction can be remedied, and (c) estimate the overall net costs of removing the hidden costs to enhance value added. The economic balance is then assessed for changes to transform the hidden costs into value added.
OD research creates actionable knowledge from practice (Lalonde, 2019 ). OD intervention consultants use multistep processes to change organizations that are flexible practices not fixed research designs. OD plays an important role in developing evidence-based practices to improve organizational functioning and performance. Worley et al. ( 2015 ) provide a detailed example of the large-scale implementation of the SEAM OD approach in a large, international firm.
Here we discuss implication of qualitative research designs for covert research, reporting qualitative work and novel integrations of qualitative and quantitative work.
Covert Research
University ethics boards require researchers who undertake research with human participants to obtain informed consent from the participants. Consent requires that all participants must be informed of details of the research procedure in which they will be involved and any risks of participation. Researchers must protect subjects’ identities, offer safeguards to limit risks, and insure informant anonymity. This consent must be obtained in the form of a signed agreement from the participant, obtained prior to the commencement of research observations (McCurdy et al., 2005 , pp. 29–32).
Covert research that fails to fully disclose research purposes or practices to participants, or that is otherwise deceptive by design or tacit practice, has long been considered “suspect” in the field (Graham, 1995 ; Roulet, Gill, Stenger, & Gill, 2017 ). This is changing. Research methodologists have shown that the over/covert dimension is a continuum, not a dichotomy, and that unintended covert elements occur in many situations (Roulet et al., 2017 ). Thus all qualitative observation involves some degree of deception due practical constraints on doing observations since it is difficult to do fully overt research, particularly in observational contexts with many people, and to gain advance consent from everyone in the organization one might encounter.
There are compelling benefits to covert research. It can provide insights not possible if subjects are fully informed of the nature or existence of the research. For example, the year-long, covert observational study of an asylum as a “total institution” (Goffman, 1961 ) showed how ineffective the treatment of mental illness was at the time. This opened the field of mental health to social science research (Roulet et al., 2017 , p. 493). Covert research can also provide access to institutions that researchers would otherwise be excluded from, including secretive and secret organizations (p. 492). This could allow researchers to collect data as an insider and to better see and experience the world from members’ perspective. It could also reduce “researcher demand effects” that occur when informants obscure their normal behavior to conform to research expectations. Thus, the inclusion of covert research data collection in research designs and proposals is an emerging trend and realistic possibility. Ethics applications can be developed that allow for aspects of covert research, and observations in many public settings do not require informed consent.
The Appropriate Style for Reporting Qualitative Work
The appropriate style for reporting qualitative research has become an issue of concern. For example, editors of the influential Academy of Management Journal have noted the emergence of an “AMJ style” for qualitative work (Bansal & Corley, 2011 , p. 234). They suggest that all qualitative work should use this style so that qualitative research can “benefit” from: “decades of refinement in the style of quantitative work.” The argument is that most scholars can assess the empirical and theoretical contributions of quantitative work but find it difficult to do so for qualitative research. It is easier for quantitatively trained editors and scholars “to spot the contribution of qualitative work that mimics the style of quantitative research.” Further, “the majority of papers submitted to . . . AMJ tend to subscribe to the paradigm of normal science that aims to find relationships among valid constructs that can be replicated by anyone” (Bansal, Smith, & Vaara, 2018 , p. 1193). These recommendations appear to explicitly encourage the reporting of qualitative results as if they were quantitatively produced and interpreted and highlights the advantage of conformity to the prevailing positivist perspective to gain publication in AMJ.
Yet AMJ editors have also called for researchers to “ensure that the research questions, data, and analysis are internally consistent ” (Bansal et al., 2018 , p. 1193) and to “Be authentic , detailed and clear in argumentation” (emphasis added) (Bansal et al., 2018 , p. 1193). These calls for consistency appear to be inconsistent with suggestions to present all qualitative research using a style that mimics quantitative, positivist research. Adopting the quantitative or positivist style for all qualitative reports may also confuse scholars, limit research quality, and hamper efforts to produce innovative, non-positivist research. This article provides six qualitative research designs to ensure a range of qualitative research publications are internally consistent in methods, logics, paradigmatic commitments, and writing styles. These designs provide alternatives to positivist mimicry in non-positivist scholarly texts.
Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Research in New Ways
Qualitative research often omits consideration of the naturally occurring uses of numbers and statistics in everyday discourse. And quantitative researchers tend to ignore qualitative evidence such as stories and discourse. Yet knowledge production processes in society “rely on experts and laypeople and, in so doing, make use of both statistics and stories in their attempt to represent and understand social reality” (Ainsworth & Hardy, 2012 , p. 1649). Numbers and statistics are often used in stories to create legitimacy, and stories provide meaning to numbers (Gephart, 1988 ). Hence stories and statistics cannot be separated in processes of knowledge production (Ainsworth & Hardy, 2012 , p. 1697). The lack of attention to the role of quantification in everyday life means a huge domain of organizational discourse—all talk that uses numbers, quantities, and statistics—is largely unexplored in organizational research.
Qualitative research has, however, begun to study how words and numbers are mutually used for organizational storytelling (Ainsworth & Hardy, 2012 ; Gephart, 2016 ). This focus offers the opportunity to develop research designs to explore qualitative features and processes involved in quantitative phenomena such as financial crises (Gephart, 2016 ), to address how stories and numbers need to work together to create legitimate knowledge (Ainsworth & Hardy, 2012 ), and to show how statistics are used rhetorically to convince others of truths in organizational research (Gephart, 1988 ).
Ethnostatistics (Gephart, 1988 ; Gephart & Saylors, 2019 ) provides one example of how to integrate qualitative and quantitative research. Ethnostatistics examines how statistics are constructed and used by professionals. It explores how statistics are constructed in real settings, how violations of technical assumptions impact statistical outcomes, and how statistics are used rhetorically to convince others of the truth of research outcomes. Ethnostatistics has been used to reinterpret data from four celebrated network studies that themselves were reanalyzed (Kilduff & Oh, 2006 ). The ethnostatistical reanalyses revealed how ad hoc practices, including judgment calls and the imputation of new data into old data set for reanalysis, transformed the focus of network research from diffusion models to structural equivalence models.
Another innovative study uses a Bayesian ethnostatistical approach to understand how the pressure to produce sophisticated and increasingly complex theoretical narratives for causal models has impacted the quantitative knowledge generated in top journals (Saylors & Trafimow, 2020 ). The use of complex causal models has increased substantially over time due to a qualitative and untested belief that complex models are true. Yet statistically speaking, as the number of variables in a model increase, the likelihood the model is true rapidly decreases (Saylors & Trafimow, 2020 , p. 3).
The authors test the previously untested (qualitative) belief that complex causal models can be true. They found that “the joint probability of a six variable model is about 3.5%” (Saylors & Trafimow, 2020 , p. 1). They conclude that “much of the knowledge generated in top journals is likely false” hence “not reporting a (prior) belief in a complex model” should be relegated to the set of questionable research practices. This study shows how qualitative research that explores the lay theories and beliefs of statisticians and quantitative researchers can challenge and disrupt conventions in quantitative research, improve quantitative practices, and contribute qualitative foundations to quantitative research. Ethnostatistics thus opens the qualitative foundations of quantitative research to critical qualitative analyses.
The six qualitative research design processes discussed in this article are evident in scholarly research on organizations and management and provide distinct qualitative research designs and approaches to use. Qualitative research can provide research insights from several theoretical perspectives, using well-developed methods to produce scientific and scholarly insights into management and organizations. These approaches and designs can also inform management practice by creating actionable knowledge. The intended contribution of this article is to describe these well-developed methods, articulate key practices, and display core research designs. The hope is both to better equip researchers to do qualitative research, and to inspire them to do so.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance of Karen Lund at The University of Alberta for carefully preparing Figure 1 . Thanks also to Beverly Zubot for close reading of the manuscript and helpful suggestions.
- Adler, P. A. , & Adler, P. (1988). Intense loyalty in organizations: A case study of college athletics. Administrative Science Quarterly , 401–417.
- Adler, P. A. , & Adler, P. (1998). Intense loyalty in organizations: A case study of college athletics. In J. Van Maanen (Ed.), Qualitative studies of organizations (pp. 31–50). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Adler, P. S. , Forbes, L. C. , & Willmott, H. (2007). Critical management studies. Academy of Management Annals , 1 (1), 119–180.
- Agar, M. H. (1980). The professional stranger: An informal introduction to ethnography . New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Ainsworth, S. , & Hardy, C. (2012). Subjects of inquiry: Statistics, stories, and the production of knowledge. Organization Studies , 33 (12), 1693–1714.
- Akeson, C. (2005). Getting the truth: The police detective and the art of interviewing. In D. W. McCurdy , J. P. Spradley , & D. J. Shandy (Eds.), The cultural experience: Ethnography in complex society (2nd ed., pp. 103–111). Long Grove, IL: Waveland Press.
- Avenier, M.-J. , & Thomas, C. (2015). Finding one’s way around various methodological guidelines for doing rigorous case studies: A comparison of four epistemological frameworks. Systèmes d’information & Management , 20 (1), 61–98.
- Bansal, P. , & Corley, K. (2011). From the editors—The coming of age for qualitative research: Embracing the diversity of qualitative methods. Academy of Management Journal , 54 (2), 233–237.
- Bansal, P. , Smith, W. K. , & Vaara, E. (2018). From the editors: New ways of seeing through qualitative research. Academy of Management Journal , 61 (4), 1189–1195.
- Barker, J. R. (1993). Tightening the iron cage: Concertive control in self-managing teams. Administrative Science Quarterly , 38 (3), 408–437.
- Barker, J. (1998). Tightening the iron cage: Concertive control in self-managing teams. In J. Van Maanen (Ed.), Qualitative studies of organizations (pp. 126–158). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Barley, S. R. (2015). Why the internet makes buying a car less loathsome: How technologies change role relations. Academy of Management Discoveries , 1 (1), 31–60.
- Beckhard, R. (1969). Organization development: Strategies and models . Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Berger, P. L. , & Luckmann, T. (1966). The social construction of reality: A treatise in the sociology of knowledge . New York, NY: Doubleday.
- Bhaskar, R. (1978). A realist theory of science . Sussex: Harvester Press; Atlantic Highlands, NJ: Humanities Press.
- Bitektine, A. (2008). Prospective case study design: Qualitative method for deductive theory testing. Organizational Research Methods , 11 (1), 160–180.
- Blaikie, N. (1993). Approaches to social enquiry (1st ed.). Cambridge, UK: Polity Press.
- Blaikie, N. (2010). Designing social research: The logic of anticipation (2nd ed.). Cambridge, UK: Polity Press.
- Boje, D. M. (2001). Narrative methods for organizational and communication research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Boje, D. M. (2008). Storytelling organizations . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Boje, D. M. , Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Thatchenkery, T. J. (Eds.). (1996). Postmodern management and organization theory . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Boje, D. M. , & Saylors, R. (2014). Quantum storytelling: An ontological perspective on process. In F. Cooren , E. Vaara , A. Langley , & H. Tsoukas (Eds.), Language and communication at work: Discourse, narrativity, and organizing (pp. 197–217). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Buono, A. F. , & Savall, H. (Eds.). (2007). Socio-economic intervention in organizations: The intervener-researcher and the SEAM approach to organizational analysis . Charlotte, NC: Information Age.
- Burrell, G. , & Morgan, G. (1979). Sociological paradigms and organisational analysis: Elements of the sociology of corporate life . London, UK: Heinemann.
- Calás, M. B. (1987). Organizational science/fiction: The postmodern in the management disciplines (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
- Calás, M. B. , & Smircich, L. (1991). Voicing seduction to silence leadership. Organization Studies , 12 (4), 567–601.
- Campbell, D. T. (1975). Degrees of freedom and the case study. Comparative Political Studies , 8 (2), 178–193.
- Cicourel, A. V. (1980). Three models of discourse analysis: The role of social structure. Discourse Processes , 3 (2), 101–132.
- Cole, R. E. (1985). The macropolitics of organizational change: A comparative analysis of the spread of small-group activities. Administrative Science Quarterly , 30 (4), 560–585.
- Coulon, A. (1995). Ethnomethodology . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Culler, J. (1982). On deconstruction: Theory and criticism after structuralism . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Cummings, T. G. , & Worley, C. G. (2015). Organization development and change (10th ed.). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
- Cunliffe, A. L. (2010). Retelling tales of the field: In search of organizational ethnography 20 years on. Organizational Research Methods , 13 (2), 224–239.
- Cunliffe, A. L. (2011). Crafting qualitative research: Morgan and Smircich 30 years on. Organizational Research Methods , 14 (4), 647–673.
- Czarniawska, B. (1998). A narrative approach to organization studies . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- de Rond, M. , & Tuncalp, D. (2017). Where the wild things are: How dreams can help identify countertransference in organizational research. Organizational Research Methods , 20 (3), 413–437.
- Denzin, N. K. , & Lincoln, Y. S. (1994). Introduction: Entering the field of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (1st ed., pp. 1–7). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Dunne, D. D. , & Dougherty, D. (2016). Abductive reasoning: How innovators navigate in the labyrinth of complex innovation. Organization Studies , 37 (2), 131–159.
- Duriau, V. J. , Reger, R. K. , & Pfarrer, M. D. (2007). A content analysis of the content analysis literature in organization studies: Research themes, data sources, and methodological refinements. Organizational Research Methods , 10 (1), 5–34.
- Dutton, J. E. , Workman, K. M. , & Hardin, A. E. (2014). Compassion at work. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior , 1 (1), 277–304.
- Easterby-Smith, M. , Thorpe, R. , & Jackson, P. (2012). Management research (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Fairclough, N. (1992). Discourse and social change . Cambridge, UK: Polity Press.
- Ganzin, M. , Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Suddaby, R. (2014). Narrative and the construction of myths in organizations. In F. Cooren , E. Vaara , A. Langley , & H. Tsoukas (Eds.), Language and communication at work: Discourse, narrativity, and organizing (pp. 219–260). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Garfinkel, H. (1964). Studies of the routine grounds of everyday activities. Social Problems , 11 (3), 225–250.
- Garfinkel, H. (1967). Studies in ethnomethodology . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (1978). Status degradation and organizational succession: An ethnomethodological approach. Administrative Science Quarterly , 23 (4), 553–581.
- Gephart, R. P. (1986). Deconstructing the defense for quantification in social science: A content analysis of journal articles on the parametric strategy. Qualitative Sociology , 9 (2), 126–144.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (1988). Ethnostatistics: Qualitative foundations for quantitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (1993). The textual approach: Risk and blame in disaster sensemaking. Academy of Management Journal , 36 (6), 1465–1514.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (1997). Hazardous measures: An interpretive textual analysis of quantitative sensemaking during crises. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 18 (S1), 583–622.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (2004). From the editors: Qualitative research and the Academy of Management Journal . Academy of Management Journal , 47 (4), 454–462.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (2013). Doing research with words: Qualitative methodologies and industrial/organizational psychology. In J. M. Cortina & R. S. Landis (Eds.), Modern research methods for the study of behavior in organizations (pp. 265–317). New York, NY: Routledge.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (2016). Counter-narration with numbers: Understanding the interplay of words and numerals in fiscal storytelling. European Journal of Cross-Cultural Competence and Management , 4 (1), 21–40.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. (2018). Qualitative research as interpretive social science. In C. Cassell , A. L. Cunliffe , & G. Grandy (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative business and management research methods: History and traditions (pp. 33–53). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Kulicki, M. (2008). Environmental ethics and business: Toward a Habermasian perspective. In D. M. Boje (Ed.), Critical theory ethics for business and public administration (pp. 373–393). Charlotte, NC: Information Age.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Pitter, R. (1995). Textual analysis in technology research: An investigation of the management of technology risk. Technology Studies , 2 (2), 325–354.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Richardson, J. (2008). Qualitative research methodologies and international human resource management. In M. M. Harris (Ed.), Handbook of research in international human resource management (pp. 29–52). New York, NY: Erlbaum.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. , & Saylors, R. (2019). Ethnostatistics . In P. Atkinson , S. Delamont , A. Cernat , J. W. Sakshaug , & R. A. Williams (Eds.), SAGE research methods foundations . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gephart, R. P., Jr. , Topal, C. , & Zhang, Z. (2010). Future-oriented sensemaking: Temporalities and institutional legitimation. In T. Hernes & S. Maitlis (Eds.), Process, sensemaking, & organizing (pp. 275–311). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Gibbert, M. , & Ruigrok, W. (2010). The “what” and “how” of case study rigor: Three strategies based on published work. Organizational Research Methods , 13 (4), 710–737.
- Gill, G. J. (2017). Dynamics of democratization: Elites, civil society and the transition process . New York, NY: Macmillan International Higher Education.
- Gioia, D. A. , Corley, K. G. , & Hamilton, A. L. (2012). Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research: Notes on the Gioia methodology. Organizational Research Methods , 16 (1), 15–31.
- Glaser, B. G. , & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Chicago, IL: Aldine.
- Goffman, E. (1961). Asylums: Essays on the social situation of mental patients and other inmates . New York, NY: Anchor Books.
- Graham, L. (1995). On the line at Subaru-Isuzu: The Japanese model and the American worker . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Greckhamer, T. , Misangyi, V. F. , Elms, H. , & Lacey, R. (2008). Using qualitative comparative analysis in strategic management research: An examination of combinations of industry, corporate, and business-unit effects. Organizational Research Methods , 11 (4), 695–726.
- Greenwood, M. , Jack, G. , & Haylock, B. (2019). Toward a methodology for analyzing visual rhetoric in corporate reports. Organizational Research Methods , 22 (3), 798–827.
- Habermas, J. (1973). Legitimation crisis ( T. McCarthy , Trans.). Frankfurt, Germany: Suhrkamp Verlag.
- Habermas, J. (1979). Communication and the evolution of society ( T. McCarthy , Trans.). Boston, MA: Beacon Press.
- Hansen, H. , & Trank, C. Q. (2016). This is going to hurt: Compassionate research methods. Organizational Research Methods , 19 (3), 352–375.
- Hassard, J. (1993). Sociology and organization theory: Positivism, paradigms and postmodernity . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Hempel, C. (1966). Philosophy of natural science . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Hochschild, A. R. (1997). The time bind: When work becomes home and home becomes work . New York, NY: Metropolitan Books.
- Hodder, I. (1994). The interpretation of documents and material culture. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (1st ed., pp. 393–402). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Holstein, J. A. , & Gubrium, J. F. (1995). The active interview . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Jameson, F. (1991). Postmodernism, or, the cultural logic of late capitalism . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Kelle, U. (Ed.). (1995). Computer-aided qualitative data analysis: Theory, methods and practice . London, UK: SAGE.
- Kilduff, M. (1993). Deconstructing organizations. Academy of Management Review , 18 (1), 13–31.
- Kilduff, M. , & Oh, H. (2006). Deconstructing diffusion: An ethnostatistical examination of Medical Innovation network data reanalyses. Organizational Research Methods , 9 (4), 432–455.
- Kirk, J. , & Miller, M. L. (1986). Reliability and validity in qualitative research . Beverly Hills, CA: SAGE.
- Lalonde, C. (2019). The development of actionable knowledge in crisis management. In R. P. Gephart, Jr. , C. C. Miller , & K. Svedberg Helgesson (Eds.), The Routledge companion to risk, crisis and emergency management (pp. 431–446). New York, NY: Routledge.
- LeBaron, C. , Jarzabkowski, P. , Pratt, M. G. , & Fetzer, G. (2018). An introduction to video methods in organizational research. Organizational Research Methods , 21 (2), 239–260.
- Lee, T. W. , & Mitchell, T. R. (1994). An alternative approach: The unfolding model of voluntary employee turnover. Academy of Management Review , 19 (1), 51–89.
- Lee, T. W. , Mitchell, T. R. , & Sablynski, C. J. (1999). Qualitative research in organizational and vocational psychology, 1979–1999. Journal of Vocational Behavior , 55 (2), 161–187.
- Lee, T. W. , Mitchell, T. R. , Wise, L. , & Fireman, S. (1996). An unfolding model of voluntary employee turnover. Academy of Management Journal , 39 (1), 5–36.
- Locke, K. (2001). Grounded theory in management research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Locke, K. (2002). The grounded theory approach to qualitative research. In F. Drasgow & N. Schmitt (Eds.), Measuring and analyzing behavior in organizations: Advances in measurement and data analysis (pp. 17–43). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
- Locke, K. , & Golden-Biddle, K. (2004). An introduction to qualitative research: Its potential for industrial and organizational psychology. In S. G. Rogelberg (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in industrial and organizational psychology (pp. 99–118). Oxford, UK: Blackwell.
- Malterud, K. (2001). Qualitative research: Standards, challenges, and guidelines. The Lancet , 358 (9280), 483–488.
- Maniha, J. , & Perrow, C. (1965). The reluctant organization and the aggressive environment. Administrative Science Quarterly , 10 (2), 238–257.
- Martin, J. (1990). Deconstructing organizational taboos: The suppression of gender conflict in organizations. Organization Science , 1 (4), 339–359.
- McCall, G. J. , & Simmons, J. L. (1969). (Eds.). Issues in participant observation: A text and reader . Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- McCloskey, H. J. (1984). Ecological ethics and politics .Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield
- McCloskey, D. N. (1985). The rhetoric of economics (1st ed.). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
- McCracken, G. (1988). The long interview . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- McCurdy, D. , Spradley, J. , & Shandy, D. (2005). The cultural experience: Ethnography in complex society (2nd ed.). Long Grove, IL: Waveland Press.
- McLeod, S. A. (2014, February 5). The interview research method . Simply Psychology.
- Mills, A. J. , Durepos, G. , & Wiebe, E. (Eds.). (2010). Encyclopedia of case study research (Vol. 1). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Morgan, D. L. (1997). Focus groups as qualitative research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Morrow, R. A. (with Brown, D. D. ). (1994). Critical theory and methodology (1st ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Offe, C. (1984). Das Wachstum der Dienstleistungsarbeit: Vier soziologische Erklärungsansätze. In C. Offe (Ed.), Arbeitsgeselleschaft. Strukturprobleme und Zukunftsperspektiven (pp. 291–319). Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Campus Verlag.
- Offe, C. (1985). New social movements: Challenging the boundaries of institutional politics. Social Research , 52 (4), 817–868.
- Palmer, I. , Dunford, R. , & Buchanan, D. A. (2017). Managing organizational change: A multiple perspectives approach (3rd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
- Perlow, L. A. (1997). Finding time: How corporations, individuals, and families can benefit from new work practices . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Piekkari, R. , & Welch, C. (2012). Pluralism in international business and international management research: Making the case. In R. Piekkari & C. Welch (Eds.), Rethinking the case study in international business and management research (pp. 3–23). Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
- Peirce, C. S. (1936). The Collected Papers . Eds. Charles Hartshorne and Paul Weiss . Cambridge M.A.: Harvard University Press.
- Pollach, I. (2012). Taming textual data: The contribution of corpus linguistics to computer-aided text analysis. Organizational Research Methods , 15 (2), 263–287.
- Poutanen, S. , & Kovalainen, A. (2010). Critical theory. In A. J. Mills , G. Durepos , & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of case study research (Vol. 1, pp. 260–264). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Pratt, M. G. (2009). For the lack of a boilerplate: Tips on writing up (and reviewing) qualitative research. Academy of Management Journal , 52 (5), 856–862.
- Ray, J. L. , & Smith, A. D. (2012). Using photographs to research organizations: Evidence, considerations, and application in a field study. Organizational Research Methods , 15 (2), 288–315.
- Richardson, J. , & McKenna, S. (2000). Metaphorical “types” and human resource management: Self-selecting expatriates. Industrial and Commercial Training , 32 (6), 209–218.
- Rodriguez, N. , & Ryave, A. (2002). Systematic self-observation . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Rodriguez, N. , Ryave, A. , & Tracewell, J. (1998). Withholding compliments in everyday life and the covert management of disaffiliation. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography , 27 (3), 323–345.
- Rosenau, P. M. (1992). Post-modernism and the social sciences: Insights, inroads, and intrusions . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Rosile, G. A. , Boje, D. M. , Carlon, D. M. , Downs, A. , & Saylors, R. (2013). Storytelling diamond: An antenarrative integration of the six facets of storytelling in organization research design. Organizational Research Methods , 16 (4), 557–580.
- Roulet, T. J. , Gill, M. J. , Stenger, S. , & Gill, D. J. (2017). Reconsidering the value of covert research: The role of ambiguous consent in participant observation. Organizational Research Methods , 20 (3), 487–517.
- Rynes, S. L. , Bretz, R. D. , & Gerhart, B. (1991). The importance of recruitment in job choice: A different way of looking. Personnel Psychology , 44 (3), 487–521.
- Savall, H. (2007). ISEOR’s socio-economic method: A case of scientific consultancy. In A. F. Buono & H. Savall (Eds.), Socio-economic intervention in organizations: The intervener-researcher and the SEAM approach to organizational analysis (pp. 1–31). Charlotte, NC: Information Age.
- Savall, H. , & Zardet, V. (2011). The qualimetrics approach: Observing the complex object . Charlotte, NC: Information Age.
- Savall, H. , Zardet, V. , & Bonnet, M. (2008). Releasing the untapped potential of enterprises through socio-economic management . Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Organization.
- Saylors, R. , & Trafimow, D. (2020). Why the increasing use of complex causal models is a problem: On the danger sophisticated theoretical narratives pose to truth . Organizational Research Methods , 1094428119893452.
- Schein, E. H. (1987). The clinical perspective in fieldwork . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Schutz, A. (1973a). Common-sense and scientific interpretation of human action. In M. Natanson (Ed.), Collected papers, volume I: The problem of social reality (pp. 3–47). The Hague, The Netherlands: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Schutz, A. (1973b). Concept and theory formation in the social sciences. In M. Natanson (Ed.), Collected papers, volume I: The problem of social reality (pp. 48–66). The Hague, The Netherlands: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Silverman, D. (2014). Interpreting qualitative data (5th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Smith, A. (2015). What grounded theory is . . . Organizational Research Methods , 18 (4), 578–580.
- Sonpar, K. , & Golden-Biddle, K. (2008). Using content analysis to elaborate adolescent theories of organization. Organizational Research Methods , 11 (4), 795–814.
- Spradley, J. P. (1979). The ethnographic interview . Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Spradley, J. P. (2016). Participant observation . Long Grove, IL: Waveland Press.
- Stake, R. E. (2005). Qualitative case studies. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed., pp. 443–466). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Su, N. (2018). Positivist qualitative methods. In C. Cassell , A. L. Cunliffe , & G. Grandy (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative business and management research methods: History and traditions (pp. 17–32). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Van Maanen, J. (1973). Observations on the making of policemen. Human Organization , 32 (4), 407–418.
- Van Maanen, J. (1981, March). Fieldwork on the beat: An informal introduction to organizational ethnography . Paper presented at the workshop on Innovations in Methodology for Organizational Research, Center for Creative Leadership, Greensboro, NC.
- Van Maanen, J. (1988). Tales of the field: On writing ethnography . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Van Maanen, J. (1998). Different strokes: Qualitative research on the Administrative Science Quarterly from 1956 to 1996. In J. Van Maanen (Ed.), Qualitative studies of organizations (pp. ix–xxxii). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Van Maanen, J. (2010). A song for my supper: More tales of the field. Organizational Research Methods , 13 (2), 240–255.
- Walsh, I. , Holton, J. A. , Bailyn, L. , Fernandez, W. , Levina, N. , & Glaser, B. (2015). What grounded theory is . . . A critically reflective conversation among scholars. Organizational Research Methods , 18 (4), 581–599.
- Watson, T. J. (1994) . In search of management: Culture, chaos, and control in managerial work . London, UK: Routledge.
- Weber, M. (1978). Economy and society: An outline of interpretive sociology . Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Whittle, A. (2018). Ethnomethodology. In C. Cassell , A. L. Cunliffe , & G. Grandy (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative business and management research methods: History and traditions (pp. 217–232). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Worley, C. G. , Zardet, V. , Bonnet, M. , & Savall, A. (2015). Becoming agile: How the SEAM approach to management builds adaptability . Hoboken, NJ: Jossey-Bass.
- Yan, A. , & Gray, B. (1994). Bargaining power, management control, and performance in United States-China joint ventures: A comparative case study. Academy of Management Journal , 37 (6), 1478–1517.
- Ybema, S. , Yanow, D. , Wels, H. , & Kamsteeg, F. (2009). Organizational ethnography: Studying the complexity of everyday life . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
1. The fourth logic is retroduction. This refers to the process of building hypothetical models of structures and mechanisms that are assumed to produce empirical phenomena. It is the primary logic used in the critical realist approach to scientific research (Avenier & Thomas, 2015 ; Bhaskar, 1978 ). Retroduction requires the use of inductive or abductive strategies to discover the mechanisms that explain regularities (Blaikie, 2010 , p. 87). There is no evident logic for discovering mechanisms and this requires disciplined scientific thinking aided by creative imagination, intuition, and guesswork (Blaikie, 2010 ). Retroduction is likr deduction in asking “what” questions and differs from abduction because it produces explanations rather than understanding, causes rather than reasons, and hypothetical conceptual mechanisms rather than descriptions of behavioral processes as outcomes. Retroduction is becoming important in the field but has not as yet been extensively used in management and organization studies (for examples of uses, see Avenier & Thomas, 2015 ); hence, we do not address it at length in this article.
Related Articles
- Agency Theory in Business and Management Research
- Assessing the State of Top Management Teams Research
- Case Study Research: A State-of-the-Art Perspective
- Advances in Team Creativity Research
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Business and Management. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 03 June 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|195.158.225.244]
- 195.158.225.244
Character limit 500 /500

Chapter 1. Introduction
“Science is in danger, and for that reason it is becoming dangerous” -Pierre Bourdieu, Science of Science and Reflexivity
Why an Open Access Textbook on Qualitative Research Methods?
I have been teaching qualitative research methods to both undergraduates and graduate students for many years. Although there are some excellent textbooks out there, they are often costly, and none of them, to my mind, properly introduces qualitative research methods to the beginning student (whether undergraduate or graduate student). In contrast, this open-access textbook is designed as a (free) true introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access more advanced instruction.
Textbooks are typically arranged in one of two ways: (1) by technique (each chapter covers one method used in qualitative research); or (2) by process (chapters advance from research design through publication). But both of these approaches are necessary for the beginner student. This textbook will have sections dedicated to the process as well as the techniques of qualitative research. This is a true “comprehensive” book for the beginning student. In addition to covering techniques of data collection and data analysis, it provides a road map of how to get started and how to keep going and where to go for advanced instruction. It covers aspects of research design and research communication as well as methods employed. Along the way, it includes examples from many different disciplines in the social sciences.
The primary goal has been to create a useful, accessible, engaging textbook for use across many disciplines. And, let’s face it. Textbooks can be boring. I hope readers find this to be a little different. I have tried to write in a practical and forthright manner, with many lively examples and references to good and intellectually creative qualitative research. Woven throughout the text are short textual asides (in colored textboxes) by professional (academic) qualitative researchers in various disciplines. These short accounts by practitioners should help inspire students. So, let’s begin!
What is Research?
When we use the word research , what exactly do we mean by that? This is one of those words that everyone thinks they understand, but it is worth beginning this textbook with a short explanation. We use the term to refer to “empirical research,” which is actually a historically specific approach to understanding the world around us. Think about how you know things about the world. [1] You might know your mother loves you because she’s told you she does. Or because that is what “mothers” do by tradition. Or you might know because you’ve looked for evidence that she does, like taking care of you when you are sick or reading to you in bed or working two jobs so you can have the things you need to do OK in life. Maybe it seems churlish to look for evidence; you just take it “on faith” that you are loved.
Only one of the above comes close to what we mean by research. Empirical research is research (investigation) based on evidence. Conclusions can then be drawn from observable data. This observable data can also be “tested” or checked. If the data cannot be tested, that is a good indication that we are not doing research. Note that we can never “prove” conclusively, through observable data, that our mothers love us. We might have some “disconfirming evidence” (that time she didn’t show up to your graduation, for example) that could push you to question an original hypothesis , but no amount of “confirming evidence” will ever allow us to say with 100% certainty, “my mother loves me.” Faith and tradition and authority work differently. Our knowledge can be 100% certain using each of those alternative methods of knowledge, but our certainty in those cases will not be based on facts or evidence.
For many periods of history, those in power have been nervous about “science” because it uses evidence and facts as the primary source of understanding the world, and facts can be at odds with what power or authority or tradition want you to believe. That is why I say that scientific empirical research is a historically specific approach to understand the world. You are in college or university now partly to learn how to engage in this historically specific approach.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries in Europe, there was a newfound respect for empirical research, some of which was seriously challenging to the established church. Using observations and testing them, scientists found that the earth was not at the center of the universe, for example, but rather that it was but one planet of many which circled the sun. [2] For the next two centuries, the science of astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry emerged and became disciplines taught in universities. All used the scientific method of observation and testing to advance knowledge. Knowledge about people , however, and social institutions, however, was still left to faith, tradition, and authority. Historians and philosophers and poets wrote about the human condition, but none of them used research to do so. [3]
It was not until the nineteenth century that “social science” really emerged, using the scientific method (empirical observation) to understand people and social institutions. New fields of sociology, economics, political science, and anthropology emerged. The first sociologists, people like Auguste Comte and Karl Marx, sought specifically to apply the scientific method of research to understand society, Engels famously claiming that Marx had done for the social world what Darwin did for the natural world, tracings its laws of development. Today we tend to take for granted the naturalness of science here, but it is actually a pretty recent and radical development.
To return to the question, “does your mother love you?” Well, this is actually not really how a researcher would frame the question, as it is too specific to your case. It doesn’t tell us much about the world at large, even if it does tell us something about you and your relationship with your mother. A social science researcher might ask, “do mothers love their children?” Or maybe they would be more interested in how this loving relationship might change over time (e.g., “do mothers love their children more now than they did in the 18th century when so many children died before reaching adulthood?”) or perhaps they might be interested in measuring quality of love across cultures or time periods, or even establishing “what love looks like” using the mother/child relationship as a site of exploration. All of these make good research questions because we can use observable data to answer them.
What is Qualitative Research?
“All we know is how to learn. How to study, how to listen, how to talk, how to tell. If we don’t tell the world, we don’t know the world. We’re lost in it, we die.” -Ursula LeGuin, The Telling
At its simplest, qualitative research is research about the social world that does not use numbers in its analyses. All those who fear statistics can breathe a sigh of relief – there are no mathematical formulae or regression models in this book! But this definition is less about what qualitative research can be and more about what it is not. To be honest, any simple statement will fail to capture the power and depth of qualitative research. One way of contrasting qualitative research to quantitative research is to note that the focus of qualitative research is less about explaining and predicting relationships between variables and more about understanding the social world. To use our mother love example, the question about “what love looks like” is a good question for the qualitative researcher while all questions measuring love or comparing incidences of love (both of which require measurement) are good questions for quantitative researchers. Patton writes,
Qualitative data describe. They take us, as readers, into the time and place of the observation so that we know what it was like to have been there. They capture and communicate someone else’s experience of the world in his or her own words. Qualitative data tell a story. ( Patton 2002:47 )
Qualitative researchers are asking different questions about the world than their quantitative colleagues. Even when researchers are employed in “mixed methods” research ( both quantitative and qualitative), they are using different methods to address different questions of the study. I do a lot of research about first-generation and working-college college students. Where a quantitative researcher might ask, how many first-generation college students graduate from college within four years? Or does first-generation college status predict high student debt loads? A qualitative researcher might ask, how does the college experience differ for first-generation college students? What is it like to carry a lot of debt, and how does this impact the ability to complete college on time? Both sets of questions are important, but they can only be answered using specific tools tailored to those questions. For the former, you need large numbers to make adequate comparisons. For the latter, you need to talk to people, find out what they are thinking and feeling, and try to inhabit their shoes for a little while so you can make sense of their experiences and beliefs.
Examples of Qualitative Research
You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research “in the field.” A good qualitative researcher will present the product of their hours of work in such a way that it seems natural, even obvious, to the reader. Because we are trying to convey what it is like answers, qualitative research is often presented as stories – stories about how people live their lives, go to work, raise their children, interact with one another. In some ways, this can seem like reading particularly insightful novels. But, unlike novels, there are very specific rules and guidelines that qualitative researchers follow to ensure that the “story” they are telling is accurate , a truthful rendition of what life is like for the people being studied. Most of this textbook will be spent conveying those rules and guidelines. Let’s take a look, first, however, at three examples of what the end product looks like. I have chosen these three examples to showcase very different approaches to qualitative research, and I will return to these five examples throughout the book. They were all published as whole books (not chapters or articles), and they are worth the long read, if you have the time. I will also provide some information on how these books came to be and the length of time it takes to get them into book version. It is important you know about this process, and the rest of this textbook will help explain why it takes so long to conduct good qualitative research!
Example 1 : The End Game (ethnography + interviews)
Corey Abramson is a sociologist who teaches at the University of Arizona. In 2015 he published The End Game: How Inequality Shapes our Final Years ( 2015 ). This book was based on the research he did for his dissertation at the University of California-Berkeley in 2012. Actually, the dissertation was completed in 2012 but the work that was produced that took several years. The dissertation was entitled, “This is How We Live, This is How We Die: Social Stratification, Aging, and Health in Urban America” ( 2012 ). You can see how the book version, which was written for a more general audience, has a more engaging sound to it, but that the dissertation version, which is what academic faculty read and evaluate, has a more descriptive title. You can read the title and know that this is a study about aging and health and that the focus is going to be inequality and that the context (place) is going to be “urban America.” It’s a study about “how” people do something – in this case, how they deal with aging and death. This is the very first sentence of the dissertation, “From our first breath in the hospital to the day we die, we live in a society characterized by unequal opportunities for maintaining health and taking care of ourselves when ill. These disparities reflect persistent racial, socio-economic, and gender-based inequalities and contribute to their persistence over time” ( 1 ). What follows is a truthful account of how that is so.
Cory Abramson spent three years conducting his research in four different urban neighborhoods. We call the type of research he conducted “comparative ethnographic” because he designed his study to compare groups of seniors as they went about their everyday business. It’s comparative because he is comparing different groups (based on race, class, gender) and ethnographic because he is studying the culture/way of life of a group. [4] He had an educated guess, rooted in what previous research had shown and what social theory would suggest, that people’s experiences of aging differ by race, class, and gender. So, he set up a research design that would allow him to observe differences. He chose two primarily middle-class (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly White) and two primarily poor neighborhoods (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly African American). He hung out in senior centers and other places seniors congregated, watched them as they took the bus to get prescriptions filled, sat in doctor’s offices with them, and listened to their conversations with each other. He also conducted more formal conversations, what we call in-depth interviews, with sixty seniors from each of the four neighborhoods. As with a lot of fieldwork , as he got closer to the people involved, he both expanded and deepened his reach –
By the end of the project, I expanded my pool of general observations to include various settings frequented by seniors: apartment building common rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, pharmacies, senior centers, bars, parks, corner stores, shopping centers, pool halls, hair salons, coffee shops, and discount stores. Over the course of the three years of fieldwork, I observed hundreds of elders, and developed close relationships with a number of them. ( 2012:10 )
When Abramson rewrote the dissertation for a general audience and published his book in 2015, it got a lot of attention. It is a beautifully written book and it provided insight into a common human experience that we surprisingly know very little about. It won the Outstanding Publication Award by the American Sociological Association Section on Aging and the Life Course and was featured in the New York Times . The book was about aging, and specifically how inequality shapes the aging process, but it was also about much more than that. It helped show how inequality affects people’s everyday lives. For example, by observing the difficulties the poor had in setting up appointments and getting to them using public transportation and then being made to wait to see a doctor, sometimes in standing-room-only situations, when they are unwell, and then being treated dismissively by hospital staff, Abramson allowed readers to feel the material reality of being poor in the US. Comparing these examples with seniors with adequate supplemental insurance who have the resources to hire car services or have others assist them in arranging care when they need it, jolts the reader to understand and appreciate the difference money makes in the lives and circumstances of us all, and in a way that is different than simply reading a statistic (“80% of the poor do not keep regular doctor’s appointments”) does. Qualitative research can reach into spaces and places that often go unexamined and then reports back to the rest of us what it is like in those spaces and places.
Example 2: Racing for Innocence (Interviews + Content Analysis + Fictional Stories)
Jennifer Pierce is a Professor of American Studies at the University of Minnesota. Trained as a sociologist, she has written a number of books about gender, race, and power. Her very first book, Gender Trials: Emotional Lives in Contemporary Law Firms, published in 1995, is a brilliant look at gender dynamics within two law firms. Pierce was a participant observer, working as a paralegal, and she observed how female lawyers and female paralegals struggled to obtain parity with their male colleagues.
Fifteen years later, she reexamined the context of the law firm to include an examination of racial dynamics, particularly how elite white men working in these spaces created and maintained a culture that made it difficult for both female attorneys and attorneys of color to thrive. Her book, Racing for Innocence: Whiteness, Gender, and the Backlash Against Affirmative Action , published in 2012, is an interesting and creative blending of interviews with attorneys, content analyses of popular films during this period, and fictional accounts of racial discrimination and sexual harassment. The law firm she chose to study had come under an affirmative action order and was in the process of implementing equitable policies and programs. She wanted to understand how recipients of white privilege (the elite white male attorneys) come to deny the role they play in reproducing inequality. Through interviews with attorneys who were present both before and during the affirmative action order, she creates a historical record of the “bad behavior” that necessitated new policies and procedures, but also, and more importantly , probed the participants ’ understanding of this behavior. It should come as no surprise that most (but not all) of the white male attorneys saw little need for change, and that almost everyone else had accounts that were different if not sometimes downright harrowing.
I’ve used Pierce’s book in my qualitative research methods courses as an example of an interesting blend of techniques and presentation styles. My students often have a very difficult time with the fictional accounts she includes. But they serve an important communicative purpose here. They are her attempts at presenting “both sides” to an objective reality – something happens (Pierce writes this something so it is very clear what it is), and the two participants to the thing that happened have very different understandings of what this means. By including these stories, Pierce presents one of her key findings – people remember things differently and these different memories tend to support their own ideological positions. I wonder what Pierce would have written had she studied the murder of George Floyd or the storming of the US Capitol on January 6 or any number of other historic events whose observers and participants record very different happenings.
This is not to say that qualitative researchers write fictional accounts. In fact, the use of fiction in our work remains controversial. When used, it must be clearly identified as a presentation device, as Pierce did. I include Racing for Innocence here as an example of the multiple uses of methods and techniques and the way that these work together to produce better understandings by us, the readers, of what Pierce studied. We readers come away with a better grasp of how and why advantaged people understate their own involvement in situations and structures that advantage them. This is normal human behavior , in other words. This case may have been about elite white men in law firms, but the general insights here can be transposed to other settings. Indeed, Pierce argues that more research needs to be done about the role elites play in the reproduction of inequality in the workplace in general.
Example 3: Amplified Advantage (Mixed Methods: Survey Interviews + Focus Groups + Archives)
The final example comes from my own work with college students, particularly the ways in which class background affects the experience of college and outcomes for graduates. I include it here as an example of mixed methods, and for the use of supplementary archival research. I’ve done a lot of research over the years on first-generation, low-income, and working-class college students. I am curious (and skeptical) about the possibility of social mobility today, particularly with the rising cost of college and growing inequality in general. As one of the few people in my family to go to college, I didn’t grow up with a lot of examples of what college was like or how to make the most of it. And when I entered graduate school, I realized with dismay that there were very few people like me there. I worried about becoming too different from my family and friends back home. And I wasn’t at all sure that I would ever be able to pay back the huge load of debt I was taking on. And so I wrote my dissertation and first two books about working-class college students. These books focused on experiences in college and the difficulties of navigating between family and school ( Hurst 2010a, 2012 ). But even after all that research, I kept coming back to wondering if working-class students who made it through college had an equal chance at finding good jobs and happy lives,
What happens to students after college? Do working-class students fare as well as their peers? I knew from my own experience that barriers continued through graduate school and beyond, and that my debtload was higher than that of my peers, constraining some of the choices I made when I graduated. To answer these questions, I designed a study of students attending small liberal arts colleges, the type of college that tried to equalize the experience of students by requiring all students to live on campus and offering small classes with lots of interaction with faculty. These private colleges tend to have more money and resources so they can provide financial aid to low-income students. They also attract some very wealthy students. Because they enroll students across the class spectrum, I would be able to draw comparisons. I ended up spending about four years collecting data, both a survey of more than 2000 students (which formed the basis for quantitative analyses) and qualitative data collection (interviews, focus groups, archival research, and participant observation). This is what we call a “mixed methods” approach because we use both quantitative and qualitative data. The survey gave me a large enough number of students that I could make comparisons of the how many kind, and to be able to say with some authority that there were in fact significant differences in experience and outcome by class (e.g., wealthier students earned more money and had little debt; working-class students often found jobs that were not in their chosen careers and were very affected by debt, upper-middle-class students were more likely to go to graduate school). But the survey analyses could not explain why these differences existed. For that, I needed to talk to people and ask them about their motivations and aspirations. I needed to understand their perceptions of the world, and it is very hard to do this through a survey.
By interviewing students and recent graduates, I was able to discern particular patterns and pathways through college and beyond. Specifically, I identified three versions of gameplay. Upper-middle-class students, whose parents were themselves professionals (academics, lawyers, managers of non-profits), saw college as the first stage of their education and took classes and declared majors that would prepare them for graduate school. They also spent a lot of time building their resumes, taking advantage of opportunities to help professors with their research, or study abroad. This helped them gain admission to highly-ranked graduate schools and interesting jobs in the public sector. In contrast, upper-class students, whose parents were wealthy and more likely to be engaged in business (as CEOs or other high-level directors), prioritized building social capital. They did this by joining fraternities and sororities and playing club sports. This helped them when they graduated as they called on friends and parents of friends to find them well-paying jobs. Finally, low-income, first-generation, and working-class students were often adrift. They took the classes that were recommended to them but without the knowledge of how to connect them to life beyond college. They spent time working and studying rather than partying or building their resumes. All three sets of students thought they were “doing college” the right way, the way that one was supposed to do college. But these three versions of gameplay led to distinct outcomes that advantaged some students over others. I titled my work “Amplified Advantage” to highlight this process.
These three examples, Cory Abramson’s The End Game , Jennifer Peirce’s Racing for Innocence, and my own Amplified Advantage, demonstrate the range of approaches and tools available to the qualitative researcher. They also help explain why qualitative research is so important. Numbers can tell us some things about the world, but they cannot get at the hearts and minds, motivations and beliefs of the people who make up the social worlds we inhabit. For that, we need tools that allow us to listen and make sense of what people tell us and show us. That is what good qualitative research offers us.
How Is This Book Organized?
This textbook is organized as a comprehensive introduction to the use of qualitative research methods. The first half covers general topics (e.g., approaches to qualitative research, ethics) and research design (necessary steps for building a successful qualitative research study). The second half reviews various data collection and data analysis techniques. Of course, building a successful qualitative research study requires some knowledge of data collection and data analysis so the chapters in the first half and the chapters in the second half should be read in conversation with each other. That said, each chapter can be read on its own for assistance with a particular narrow topic. In addition to the chapters, a helpful glossary can be found in the back of the book. Rummage around in the text as needed.
Chapter Descriptions
Chapter 2 provides an overview of the Research Design Process. How does one begin a study? What is an appropriate research question? How is the study to be done – with what methods ? Involving what people and sites? Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
Chapter 3 describes and explains various ways of knowing the (social) world. What is it possible for us to know about how other people think or why they behave the way they do? What does it mean to say something is a “fact” or that it is “well-known” and understood? Qualitative researchers are particularly interested in these questions because of the types of research questions we are interested in answering (the how questions rather than the how many questions of quantitative research). Qualitative researchers have adopted various epistemological approaches. Chapter 3 will explore these approaches, highlighting interpretivist approaches that acknowledge the subjective aspect of reality – in other words, reality and knowledge are not objective but rather influenced by (interpreted through) people.
Chapter 4 focuses on the practical matter of developing a research question and finding the right approach to data collection. In any given study (think of Cory Abramson’s study of aging, for example), there may be years of collected data, thousands of observations , hundreds of pages of notes to read and review and make sense of. If all you had was a general interest area (“aging”), it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to make sense of all of that data. The research question provides a helpful lens to refine and clarify (and simplify) everything you find and collect. For that reason, it is important to pull out that lens (articulate the research question) before you get started. In the case of the aging study, Cory Abramson was interested in how inequalities affected understandings and responses to aging. It is for this reason he designed a study that would allow him to compare different groups of seniors (some middle-class, some poor). Inevitably, he saw much more in the three years in the field than what made it into his book (or dissertation), but he was able to narrow down the complexity of the social world to provide us with this rich account linked to the original research question. Developing a good research question is thus crucial to effective design and a successful outcome. Chapter 4 will provide pointers on how to do this. Chapter 4 also provides an overview of general approaches taken to doing qualitative research and various “traditions of inquiry.”
Chapter 5 explores sampling . After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (Observations? Interviews?), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview , the sample should follow the research question and research design. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. Chapter 5 explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Chapter 6 addresses the importance of reflexivity in qualitative research. Related to epistemological issues of how we know anything about the social world, qualitative researchers understand that we the researchers can never be truly neutral or outside the study we are conducting. As observers, we see things that make sense to us and may entirely miss what is either too obvious to note or too different to comprehend. As interviewers, as much as we would like to ask questions neutrally and remain in the background, interviews are a form of conversation, and the persons we interview are responding to us . Therefore, it is important to reflect upon our social positions and the knowledges and expectations we bring to our work and to work through any blind spots that we may have. Chapter 6 provides some examples of reflexivity in practice and exercises for thinking through one’s own biases.
Chapter 7 is a very important chapter and should not be overlooked. As a practical matter, it should also be read closely with chapters 6 and 8. Because qualitative researchers deal with people and the social world, it is imperative they develop and adhere to a strong ethical code for conducting research in a way that does not harm. There are legal requirements and guidelines for doing so (see chapter 8), but these requirements should not be considered synonymous with the ethical code required of us. Each researcher must constantly interrogate every aspect of their research, from research question to design to sample through analysis and presentation, to ensure that a minimum of harm (ideally, zero harm) is caused. Because each research project is unique, the standards of care for each study are unique. Part of being a professional researcher is carrying this code in one’s heart, being constantly attentive to what is required under particular circumstances. Chapter 7 provides various research scenarios and asks readers to weigh in on the suitability and appropriateness of the research. If done in a class setting, it will become obvious fairly quickly that there are often no absolutely correct answers, as different people find different aspects of the scenarios of greatest importance. Minimizing the harm in one area may require possible harm in another. Being attentive to all the ethical aspects of one’s research and making the best judgments one can, clearly and consciously, is an integral part of being a good researcher.
Chapter 8 , best to be read in conjunction with chapter 7, explains the role and importance of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) . Under federal guidelines, an IRB is an appropriately constituted group that has been formally designated to review and monitor research involving human subjects . Every institution that receives funding from the federal government has an IRB. IRBs have the authority to approve, require modifications to (to secure approval), or disapprove research. This group review serves an important role in the protection of the rights and welfare of human research subjects. Chapter 8 reviews the history of IRBs and the work they do but also argues that IRBs’ review of qualitative research is often both over-inclusive and under-inclusive. Some aspects of qualitative research are not well understood by IRBs, given that they were developed to prevent abuses in biomedical research. Thus, it is important not to rely on IRBs to identify all the potential ethical issues that emerge in our research (see chapter 7).
Chapter 9 provides help for getting started on formulating a research question based on gaps in the pre-existing literature. Research is conducted as part of a community, even if particular studies are done by single individuals (or small teams). What any of us finds and reports back becomes part of a much larger body of knowledge. Thus, it is important that we look at the larger body of knowledge before we actually start our bit to see how we can best contribute. When I first began interviewing working-class college students, there was only one other similar study I could find, and it hadn’t been published (it was a dissertation of students from poor backgrounds). But there had been a lot published by professors who had grown up working class and made it through college despite the odds. These accounts by “working-class academics” became an important inspiration for my study and helped me frame the questions I asked the students I interviewed. Chapter 9 will provide some pointers on how to search for relevant literature and how to use this to refine your research question.
Chapter 10 serves as a bridge between the two parts of the textbook, by introducing techniques of data collection. Qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection – for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Techniques can be effectively combined, depending on the research question and the aims and goals of the study. Chapter 10 provides a general overview of all the various techniques and how they can be combined.
The second part of the textbook moves into the doing part of qualitative research once the research question has been articulated and the study designed. Chapters 11 through 17 cover various data collection techniques and approaches. Chapters 18 and 19 provide a very simple overview of basic data analysis. Chapter 20 covers communication of the data to various audiences, and in various formats.
Chapter 11 begins our overview of data collection techniques with a focus on interviewing , the true heart of qualitative research. This technique can serve as the primary and exclusive form of data collection, or it can be used to supplement other forms (observation, archival). An interview is distinct from a survey, where questions are asked in a specific order and often with a range of predetermined responses available. Interviews can be conversational and unstructured or, more conventionally, semistructured , where a general set of interview questions “guides” the conversation. Chapter 11 covers the basics of interviews: how to create interview guides, how many people to interview, where to conduct the interview, what to watch out for (how to prepare against things going wrong), and how to get the most out of your interviews.
Chapter 12 covers an important variant of interviewing, the focus group. Focus groups are semistructured interviews with a group of people moderated by a facilitator (the researcher or researcher’s assistant). Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are best used to collect data on a specific topic that is non-personal and shared among the group. For example, asking a group of college students about a common experience such as taking classes by remote delivery during the pandemic year of 2020. Chapter 12 covers the basics of focus groups: when to use them, how to create interview guides for them, and how to run them effectively.
Chapter 13 moves away from interviewing to the second major form of data collection unique to qualitative researchers – observation . Qualitative research that employs observation can best be understood as falling on a continuum of “fly on the wall” observation (e.g., observing how strangers interact in a doctor’s waiting room) to “participant” observation, where the researcher is also an active participant of the activity being observed. For example, an activist in the Black Lives Matter movement might want to study the movement, using her inside position to gain access to observe key meetings and interactions. Chapter 13 covers the basics of participant observation studies: advantages and disadvantages, gaining access, ethical concerns related to insider/outsider status and entanglement, and recording techniques.
Chapter 14 takes a closer look at “deep ethnography” – immersion in the field of a particularly long duration for the purpose of gaining a deeper understanding and appreciation of a particular culture or social world. Clifford Geertz called this “deep hanging out.” Whereas participant observation is often combined with semistructured interview techniques, deep ethnography’s commitment to “living the life” or experiencing the situation as it really is demands more conversational and natural interactions with people. These interactions and conversations may take place over months or even years. As can be expected, there are some costs to this technique, as well as some very large rewards when done competently. Chapter 14 provides some examples of deep ethnographies that will inspire some beginning researchers and intimidate others.
Chapter 15 moves in the opposite direction of deep ethnography, a technique that is the least positivist of all those discussed here, to mixed methods , a set of techniques that is arguably the most positivist . A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative data collection and quantitative data collection, commonly by combining a survey that is analyzed statistically (e.g., cross-tabs or regression analyses of large number probability samples) with semi-structured interviews. Although it is somewhat unconventional to discuss mixed methods in textbooks on qualitative research, I think it is important to recognize this often-employed approach here. There are several advantages and some disadvantages to taking this route. Chapter 16 will describe those advantages and disadvantages and provide some particular guidance on how to design a mixed methods study for maximum effectiveness.
Chapter 16 covers data collection that does not involve live human subjects at all – archival and historical research (chapter 17 will also cover data that does not involve interacting with human subjects). Sometimes people are unavailable to us, either because they do not wish to be interviewed or observed (as is the case with many “elites”) or because they are too far away, in both place and time. Fortunately, humans leave many traces and we can often answer questions we have by examining those traces. Special collections and archives can be goldmines for social science research. This chapter will explain how to access these places, for what purposes, and how to begin to make sense of what you find.
Chapter 17 covers another data collection area that does not involve face-to-face interaction with humans: content analysis . Although content analysis may be understood more properly as a data analysis technique, the term is often used for the entire approach, which will be the case here. Content analysis involves interpreting meaning from a body of text. This body of text might be something found in historical records (see chapter 16) or something collected by the researcher, as in the case of comment posts on a popular blog post. I once used the stories told by student loan debtors on the website studentloanjustice.org as the content I analyzed. Content analysis is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest. In other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis.
Where chapter 17 has pushed us towards data analysis, chapters 18 and 19 are all about what to do with the data collected, whether that data be in the form of interview transcripts or fieldnotes from observations. Chapter 18 introduces the basics of coding , the iterative process of assigning meaning to the data in order to both simplify and identify patterns. What is a code and how does it work? What are the different ways of coding data, and when should you use them? What is a codebook, and why do you need one? What does the process of data analysis look like?
Chapter 19 goes further into detail on codes and how to use them, particularly the later stages of coding in which our codes are refined, simplified, combined, and organized. These later rounds of coding are essential to getting the most out of the data we’ve collected. As students are often overwhelmed with the amount of data (a corpus of interview transcripts typically runs into the hundreds of pages; fieldnotes can easily top that), this chapter will also address time management and provide suggestions for dealing with chaos and reminders that feeling overwhelmed at the analysis stage is part of the process. By the end of the chapter, you should understand how “findings” are actually found.
The book concludes with a chapter dedicated to the effective presentation of data results. Chapter 20 covers the many ways that researchers communicate their studies to various audiences (academic, personal, political), what elements must be included in these various publications, and the hallmarks of excellent qualitative research that various audiences will be expecting. Because qualitative researchers are motivated by understanding and conveying meaning , effective communication is not only an essential skill but a fundamental facet of the entire research project. Ethnographers must be able to convey a certain sense of verisimilitude , the appearance of true reality. Those employing interviews must faithfully depict the key meanings of the people they interviewed in a way that rings true to those people, even if the end result surprises them. And all researchers must strive for clarity in their publications so that various audiences can understand what was found and why it is important.
The book concludes with a short chapter ( chapter 21 ) discussing the value of qualitative research. At the very end of this book, you will find a glossary of terms. I recommend you make frequent use of the glossary and add to each entry as you find examples. Although the entries are meant to be simple and clear, you may also want to paraphrase the definition—make it “make sense” to you, in other words. In addition to the standard reference list (all works cited here), you will find various recommendations for further reading at the end of many chapters. Some of these recommendations will be examples of excellent qualitative research, indicated with an asterisk (*) at the end of the entry. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. A good example of qualitative research can teach you more about conducting research than any textbook can (this one included). I highly recommend you select one to three examples from these lists and read them along with the textbook.
A final note on the choice of examples – you will note that many of the examples used in the text come from research on college students. This is for two reasons. First, as most of my research falls in this area, I am most familiar with this literature and have contacts with those who do research here and can call upon them to share their stories with you. Second, and more importantly, my hope is that this textbook reaches a wide audience of beginning researchers who study widely and deeply across the range of what can be known about the social world (from marine resources management to public policy to nursing to political science to sexuality studies and beyond). It is sometimes difficult to find examples that speak to all those research interests, however. A focus on college students is something that all readers can understand and, hopefully, appreciate, as we are all now or have been at some point a college student.
Recommended Reading: Other Qualitative Research Textbooks
I’ve included a brief list of some of my favorite qualitative research textbooks and guidebooks if you need more than what you will find in this introductory text. For each, I’ve also indicated if these are for “beginning” or “advanced” (graduate-level) readers. Many of these books have several editions that do not significantly vary; the edition recommended is merely the edition I have used in teaching and to whose page numbers any specific references made in the text agree.
Barbour, Rosaline. 2014. Introducing Qualitative Research: A Student’s Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A good introduction to qualitative research, with abundant examples (often from the discipline of health care) and clear definitions. Includes quick summaries at the ends of each chapter. However, some US students might find the British context distracting and can be a bit advanced in some places. Beginning .
Bloomberg, Linda Dale, and Marie F. Volpe. 2012. Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Specifically designed to guide graduate students through the research process. Advanced .
Creswell, John W., and Cheryl Poth. 2018 Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Traditions . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a classic and one of the go-to books I used myself as a graduate student. One of the best things about this text is its clear presentation of five distinct traditions in qualitative research. Despite the title, this reasonably sized book is about more than research design, including both data analysis and how to write about qualitative research. Advanced .
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. A readable and personal account of conducting qualitative research by an eminent sociologist, with a heavy emphasis on the kinds of participant-observation research conducted by the author. Despite its reader-friendliness, this is really a book targeted to graduate students learning the craft. Advanced .
Lune, Howard, and Bruce L. Berg. 2018. 9th edition. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences. Pearson . Although a good introduction to qualitative methods, the authors favor symbolic interactionist and dramaturgical approaches, which limits the appeal primarily to sociologists. Beginning .
Marshall, Catherine, and Gretchen B. Rossman. 2016. 6th edition. Designing Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Very readable and accessible guide to research design by two educational scholars. Although the presentation is sometimes fairly dry, personal vignettes and illustrations enliven the text. Beginning .
Maxwell, Joseph A. 2013. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced .
Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a comprehensive text that served as my “go-to” reference when I was a graduate student. It is particularly helpful for those involved in program evaluation and other forms of evaluation studies and uses examples from a wide range of disciplines. Advanced .
Rubin, Ashley T. 2021. Rocking Qualitative Social Science: An Irreverent Guide to Rigorous Research. Stanford : Stanford University Press. A delightful and personal read. Rubin uses rock climbing as an extended metaphor for learning how to conduct qualitative research. A bit slanted toward ethnographic and archival methods of data collection, with frequent examples from her own studies in criminology. Beginning .
Weis, Lois, and Michelle Fine. 2000. Speed Bumps: A Student-Friendly Guide to Qualitative Research . New York: Teachers College Press. Readable and accessibly written in a quasi-conversational style. Particularly strong in its discussion of ethical issues throughout the qualitative research process. Not comprehensive, however, and very much tied to ethnographic research. Although designed for graduate students, this is a recommended read for students of all levels. Beginning .
Patton’s Ten Suggestions for Doing Qualitative Research
The following ten suggestions were made by Michael Quinn Patton in his massive textbooks Qualitative Research and Evaluations Methods . This book is highly recommended for those of you who want more than an introduction to qualitative methods. It is the book I relied on heavily when I was a graduate student, although it is much easier to “dip into” when necessary than to read through as a whole. Patton is asked for “just one bit of advice” for a graduate student considering using qualitative research methods for their dissertation. Here are his top ten responses, in short form, heavily paraphrased, and with additional comments and emphases from me:
- Make sure that a qualitative approach fits the research question. The following are the kinds of questions that call out for qualitative methods or where qualitative methods are particularly appropriate: questions about people’s experiences or how they make sense of those experiences; studying a person in their natural environment; researching a phenomenon so unknown that it would be impossible to study it with standardized instruments or other forms of quantitative data collection.
- Study qualitative research by going to the original sources for the design and analysis appropriate to the particular approach you want to take (e.g., read Glaser and Straus if you are using grounded theory )
- Find a dissertation adviser who understands or at least who will support your use of qualitative research methods. You are asking for trouble if your entire committee is populated by quantitative researchers, even if they are all very knowledgeable about the subject or focus of your study (maybe even more so if they are!)
- Really work on design. Doing qualitative research effectively takes a lot of planning. Even if things are more flexible than in quantitative research, a good design is absolutely essential when starting out.
- Practice data collection techniques, particularly interviewing and observing. There is definitely a set of learned skills here! Do not expect your first interview to be perfect. You will continue to grow as a researcher the more interviews you conduct, and you will probably come to understand yourself a bit more in the process, too. This is not easy, despite what others who don’t work with qualitative methods may assume (and tell you!)
- Have a plan for analysis before you begin data collection. This is often a requirement in IRB protocols , although you can get away with writing something fairly simple. And even if you are taking an approach, such as grounded theory, that pushes you to remain fairly open-minded during the data collection process, you still want to know what you will be doing with all the data collected – creating a codebook? Writing analytical memos? Comparing cases? Having a plan in hand will also help prevent you from collecting too much extraneous data.
- Be prepared to confront controversies both within the qualitative research community and between qualitative research and quantitative research. Don’t be naïve about this – qualitative research, particularly some approaches, will be derided by many more “positivist” researchers and audiences. For example, is an “n” of 1 really sufficient? Yes! But not everyone will agree.
- Do not make the mistake of using qualitative research methods because someone told you it was easier, or because you are intimidated by the math required of statistical analyses. Qualitative research is difficult in its own way (and many would claim much more time-consuming than quantitative research). Do it because you are convinced it is right for your goals, aims, and research questions.
- Find a good support network. This could be a research mentor, or it could be a group of friends or colleagues who are also using qualitative research, or it could be just someone who will listen to you work through all of the issues you will confront out in the field and during the writing process. Even though qualitative research often involves human subjects, it can be pretty lonely. A lot of times you will feel like you are working without a net. You have to create one for yourself. Take care of yourself.
- And, finally, in the words of Patton, “Prepare to be changed. Looking deeply at other people’s lives will force you to look deeply at yourself.”
- We will actually spend an entire chapter ( chapter 3 ) looking at this question in much more detail! ↵
- Note that this might have been news to Europeans at the time, but many other societies around the world had also come to this conclusion through observation. There is often a tendency to equate “the scientific revolution” with the European world in which it took place, but this is somewhat misleading. ↵
- Historians are a special case here. Historians have scrupulously and rigorously investigated the social world, but not for the purpose of understanding general laws about how things work, which is the point of scientific empirical research. History is often referred to as an idiographic field of study, meaning that it studies things that happened or are happening in themselves and not for general observations or conclusions. ↵
- Don’t worry, we’ll spend more time later in this book unpacking the meaning of ethnography and other terms that are important here. Note the available glossary ↵
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
In contrast to methodology, methods are more simply the practices and tools used to collect and analyze data. Examples of common methods in qualitative research are interviews , observations , and documentary analysis . One’s methodology should connect to one’s choice of methods, of course, but they are distinguishable terms. See also methodology .
A proposed explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation. The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative research. Even when qualitative researchers offer possible explanations in advance of conducting research, they will tend to not use the word “hypothesis” as it conjures up the kind of positivist research they are not conducting.
The foundational question to be addressed by the research study. This will form the anchor of the research design, collection, and analysis. Note that in qualitative research, the research question may, and probably will, alter or develop during the course of the research.
An approach to research that collects and analyzes numerical data for the purpose of finding patterns and averages, making predictions, testing causal relationships, and generalizing results to wider populations. Contrast with qualitative research .
Data collection that takes place in real-world settings, referred to as “the field;” a key component of much Grounded Theory and ethnographic research. Patton ( 2002 ) calls fieldwork “the central activity of qualitative inquiry” where “‘going into the field’ means having direct and personal contact with people under study in their own environments – getting close to people and situations being studied to personally understand the realities of minutiae of daily life” (48).
The people who are the subjects of a qualitative study. In interview-based studies, they may be the respondents to the interviewer; for purposes of IRBs, they are often referred to as the human subjects of the research.
The branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. For researchers, it is important to recognize and adopt one of the many distinguishing epistemological perspectives as part of our understanding of what questions research can address or fully answer. See, e.g., constructivism , subjectivism, and objectivism .
An approach that refutes the possibility of neutrality in social science research. All research is “guided by a set of beliefs and feelings about the world and how it should be understood and studied” (Denzin and Lincoln 2005: 13). In contrast to positivism , interpretivism recognizes the social constructedness of reality, and researchers adopting this approach focus on capturing interpretations and understandings people have about the world rather than “the world” as it is (which is a chimera).
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Research based on data collected and analyzed by the research (in contrast to secondary “library” research).
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The practice of being conscious of and reflective upon one’s own social location and presence when conducting research. Because qualitative research often requires interaction with live humans, failing to take into account how one’s presence and prior expectations and social location affect the data collected and how analyzed may limit the reliability of the findings. This remains true even when dealing with historical archives and other content. Who we are matters when asking questions about how people experience the world because we, too, are a part of that world.
The science and practice of right conduct; in research, it is also the delineation of moral obligations towards research participants, communities to which we belong, and communities in which we conduct our research.
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Research, according to US federal guidelines, that involves “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research: (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or (2) Obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.”
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
A method of observational data collection taking place in a natural setting; a form of fieldwork . The term encompasses a continuum of relative participation by the researcher (from full participant to “fly-on-the-wall” observer). This is also sometimes referred to as ethnography , although the latter is characterized by a greater focus on the culture under observation.
A research design that employs both quantitative and qualitative methods, as in the case of a survey supplemented by interviews.
An epistemological perspective that posits the existence of reality through sensory experience similar to empiricism but goes further in denying any non-sensory basis of thought or consciousness. In the social sciences, the term has roots in the proto-sociologist August Comte, who believed he could discern “laws” of society similar to the laws of natural science (e.g., gravity). The term has come to mean the kinds of measurable and verifiable science conducted by quantitative researchers and is thus used pejoratively by some qualitative researchers interested in interpretation, consciousness, and human understanding. Calling someone a “positivist” is often intended as an insult. See also empiricism and objectivism.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
A word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data (Saldaña 2021:5).
Usually a verbatim written record of an interview or focus group discussion.
The primary form of data for fieldwork , participant observation , and ethnography . These notes, taken by the researcher either during the course of fieldwork or at day’s end, should include as many details as possible on what was observed and what was said. They should include clear identifiers of date, time, setting, and names (or identifying characteristics) of participants.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
A detailed description of any proposed research that involves human subjects for review by IRB. The protocol serves as the recipe for the conduct of the research activity. It includes the scientific rationale to justify the conduct of the study, the information necessary to conduct the study, the plan for managing and analyzing the data, and a discussion of the research ethical issues relevant to the research. Protocols for qualitative research often include interview guides, all documents related to recruitment, informed consent forms, very clear guidelines on the safekeeping of materials collected, and plans for de-identifying transcripts or other data that include personal identifying information.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 31 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Business Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Business research: definition, types & methods.
10 min read What is business research and why does it matter? Here are some of the ways business research can be helpful to your company, whichever method you choose to carry it out.
What is business research?
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad – it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels. Or it could involve sizing up the competition through competitor research.
Often when carrying out business research, companies are looking at their own data, sourced from their employees, their customers and their business records. However, business researchers can go beyond their own company in order to collect relevant information and understand patterns that may help leaders make informed decisions. For example, a business may carry out ethnographic research where the participants are studied in the context of their everyday lives, rather than just in their role as consumer, or look at secondary data sources such as open access public records and empirical research carried out in academic studies.
There is also a body of knowledge about business in general that can be mined for business research purposes. For example organizational theory and general studies on consumer behavior.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
Why is business research important?
We live in a time of high speed technological progress and hyper-connectedness. Customers have an entire market at their fingertips and can easily switch brands if a competitor is offering something better than you are. At the same time, the world of business has evolved to the point of near-saturation. It’s hard to think of a need that hasn’t been addressed by someone’s innovative product or service.
The combination of ease of switching, high consumer awareness and a super-evolved marketplace crowded with companies and their offerings means that businesses must do whatever they can to find and maintain an edge. Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market.
Thanks to the standard of modern business research tools and methods, it’s now possible for business analysts to track the intricate relationships between competitors, financial markets, social trends, geopolitical changes, world events, and more.
Find out how to conduct your own market research and make use of existing market research data with our Ultimate guide to market research
Types of business research
Business research methods vary widely, but they can be grouped into two broad categories – qualitative research and quantitative research .
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people’s thoughts, feelings and opinions. It relies heavily on the observations of researchers, who collect data from a relatively small number of participants – often through direct interactions.
Qualitative research interviews take place one-on-one between a researcher and participant. In a business context, the participant might be a customer, a supplier, an employee or other stakeholder. Using open-ended questions , the researcher conducts the interview in either a structured or unstructured format. Structured interviews stick closely to a question list and scripted phrases, while unstructured interviews are more conversational and exploratory. As well as listening to the participant’s responses, the interviewer will observe non-verbal information such as posture, tone of voice and facial expression.
Focus groups
Like the qualitative interview, a focus group is a form of business research that uses direct interaction between the researcher and participants to collect data. In focus groups , a small number of participants (usually around 10) take part in a group discussion led by a researcher who acts as moderator. The researcher asks questions and takes note of the responses, as in a qualitative research interview. Sampling for focus groups is usually purposive rather than random, so that the group members represent varied points of view.
Observational studies
In an observational study, the researcher may not directly interact with participants at all, but will pay attention to practical situations, such as a busy sales floor full of potential customers, or a conference for some relevant business activity. They will hear people speak and watch their interactions , then record relevant data such as behavior patterns that relate to the subject they are interested in. Observational studies can be classified as a type of ethnographic research. They can be used to gain insight about a company’s target audience in their everyday lives, or study employee behaviors in actual business situations.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive design of research where one observes peoples’ behavior in their natural environment. Ethnography was most commonly found in the anthropology field and is now practices across a wide range of social sciences.
Ehnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use.
The ethnographic research process is a popular methodology used in the software development lifecycle. It helps create better UI/UX flow based on the real needs of the end-users.
If you truly want to understand your customers’ needs, wants, desires, pain-points “walking a mile” in their shoes enables this. Ethnographic research is this deeply rooted part of research where you truly learn your targe audiences’ problem to craft the perfect solution.
Case study research
A case study is a detailed piece of research that provides in depth knowledge about a specific person, place or organization. In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new theories about how businesses operate. Proponents of case study research feel that it adds significant value in making theoretical and empirical advances. However its detractors point out that it can be time consuming and expensive, requiring highly skilled researchers to carry it out.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding the patterns and relationships that emerge from mass data – for example by analyzing the material posted on social media platforms, or via surveys of the target audience. Data collected through quantitative methods is empirical in nature and can be analyzed using statistical techniques. Unlike qualitative approaches, a quantitative research method is usually reliant on finding the right sample size, as this will determine whether the results are representative. These are just a few methods – there are many more.
Surveys are one of the most effective ways to conduct business research. They use a highly structured questionnaire which is distributed to participants, typically online (although in the past, face to face and telephone surveys were widely used). The questions are predominantly closed-ended, limiting the range of responses so that they can be grouped and analyzed at scale using statistical tools. However surveys can also be used to get a better understanding of the pain points customers face by providing open field responses where they can express themselves in their own words. Both types of data can be captured on the same questionnaire, which offers efficiency of time and cost to the researcher.
Correlational research
Correlational research looks at the relationship between two entities, neither of which are manipulated by the researcher. For example, this might be the in-store sales of a certain product line and the proportion of female customers subscribed to a mailing list. Using statistical analysis methods, researchers can determine the strength of the correlation and even discover intricate relationships between the two variables. Compared with simple observation and intuition, correlation may identify further information about business activity and its impact, pointing the way towards potential improvements and more revenue.
Experimental research
It may sound like something that is strictly for scientists, but experimental research is used by both businesses and scholars alike. When conducted as part of the business intelligence process, experimental research is used to test different tactics to see which ones are most successful – for example one marketing approach versus another. In the simplest form of experimental research, the researcher identifies a dependent variable and an independent variable. The hypothesis is that the independent variable has no effect on the dependent variable, and the researcher will change the independent one to test this assumption. In a business context, the hypothesis might be that price has no relationship to customer satisfaction. The researcher manipulates the price and observes the C-Sat scores to see if there’s an effect.
The best tools for business research
You can make the business research process much quicker and more efficient by selecting the right tools. Business research methods like surveys and interviews demand tools and technologies that can store vast quantities of data while making them easy to access and navigate. If your system can also carry out statistical analysis, and provide predictive recommendations to help you with your business decisions, so much the better.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
Qualitative Research in Business and Management
- Michael D Myers - University of Auckland, New Zealand
- Description
This accessible and expansive, yet remarkably concise textbook is designed to help readers with their research project. As well as guiding them through the key methods of collecting and analysing qualitative data, this book provides invaluable information on writing up their research and how to get published.
Now in its third edition, Qualitative Research in Business and Management has been fully updated to include a range of recent examples of aspects of qualitative research in action, and a new look at the methods and ethics of using social media data.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
Supplements
The online resources featured are further reading, weblinks and powerpoint slides.
Qualitative Research in Business and Management is an accessible and well-structured introduction in qualitative research. Myers clearly explains the main concepts and principles of qualitative research, illustrating them with recent examples from top journals. Being concise and comprehensive, I consider this the best textbook in the field.
Perfect for Dissertation support
Great book, well written
This is one of few books on qualitative research method in business. The coverage is extensive. It includes both the design and data analysis of qualitative research. Although the author is a scholar in information systems, he managed to include all the business and management sub-areas in the book. The explanation is also very easy to follow.
A good book to invite students to prepare for theses using qualitative methods. The book covers the essential in an abordable way.
a useful text aimed at Business and management students which will provide a useful source of advice and guidance as well as introducing the basics.
Well explained qualitative research concepts and the exercise sections are useful.
Currently this book is still in the university (building). Due to Covid 19 I was not able to collect it.
It is a clear and concise volume that summarises many of the issues my students face in conducting their qualitative research.
Preview this book
For instructors, select a purchasing option, related products.

Qualitative Research : Definition
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use in-depth studies of the social world to analyze how and why groups think and act in particular ways (for instance, case studies of the experiences that shape political views).
Events and Workshops
- Introduction to NVivo Have you just collected your data and wondered what to do next? Come join us for an introductory session on utilizing NVivo to support your analytical process. This session will only cover features of the software and how to import your records. Please feel free to attend any of the following sessions below: April 25th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125 May 9th, 2024 12:30 pm - 1:45 pm Green Library - SVA Conference Room 125
- Next: Choose an approach >>
- Choose an approach
- Find studies
- Learn methods
- Getting Started
- Get software
- Get data for secondary analysis
- Network with researchers

- Last Updated: May 23, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stanford.edu/qualitative_research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Qualitative Research Methods

Ethnographic Research -Types, Methods and Guide

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a standalone study, purely relying on qualitative data, or part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and applications of qualitative research.
Qualitative research, at its core, asks open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers, such as "how" and "why." [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions, qualitative research design is often not linear like quantitative design. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be complex to capture accurately and quantitatively. In contrast, a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a particular time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify, and it is essential to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore "compete" against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each other, qualitative and quantitative work are neither necessarily opposites, nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites and certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated.
Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design originates in social and cultural anthropology and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc, through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded theory
Grounded Theory is the "generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior." [5] Unlike quantitative research, which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and, therefore, lends itself to research aimed at social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is the "study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular.” [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are pretty similar, but the differences can be seen upon careful examination. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the individual's perspective. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the "lived experiences" of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way from their perspective. Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources. In contrast, Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomenon from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called a "thick" or "rich" description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of "thick" description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, hoping to create a cohesive story or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be "opportunities for innovation." [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards underpinning different research approaches. Essentially, research paradigms are the "worldviews" that inform research. [4] It is valuable for qualitative and quantitative researchers to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontologies and epistemologies. Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality,” whereas epistemology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of knowledge" that inform researchers' work. [2] It is essential to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a complete understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, researchers must understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist versus postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we must discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social and natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in their research. It stems from positivist ontology, that there is an objective reality that exists that is wholly independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained, but could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world,” and therefore, postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are also constructivist, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but instead that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. "Constructivism contends that individuals' views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality.” [6] constructivist thought focuses on how "reality" is not a fixed certainty and how experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike positivist views, that there is not necessarily an "objective"reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and our world are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have. It can even change the role of the researchers. [2] For example, is the researcher an "objective" observer, such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the study undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research and reflect on their positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale for being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques, including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic, and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one-on-one and appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be participant-observers to share the experiences of the subject or non-participants or detached observers.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or the participants' environment, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed, which may then be coded manually or using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results could also be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
The healthcare team can use two reporting standards to standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a more comprehensive range of qualitative research. [13]
Applications
Many times, a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis, which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data to better understand what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative techniques can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research, researchers can explore poorly studied subjects with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual actions, and social science research.
An excellent qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected that will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because, often, the information sought is not well categorized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of why teens start to smoke and factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered "cool," and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current nonsmokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the survey results to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the primary factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the primary factor that contributed to teens starting smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on keeping teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly in the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure to smoke. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and sees that the smokers tend to hang out in a shady, overgrown area of the park. The researcher notes that smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park, where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk populations their perceptions of the changes and what factors are still at play, and quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community and the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or combined with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation not only to help generate hypotheses that can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research allows researchers to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many ways, including the evaluation criteria. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. Credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability are the correlating concepts in qualitative research. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept on the left and the qualitative concept on the right:
- Internal validity: Credibility
- External validity: Transferability
- Reliability: Dependability
- Objectivity: Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid, qualitative researchers should ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple data collection methods to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable if we interviewed the magician, backstage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews and surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: A peer can review results to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
A "thick" or "rich" description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research, whereas an indicator such as an audit trail might help evaluate the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description: This is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was conducted. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original information records should also be kept (eg, surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should consider is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. Suppose a researcher wanted to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tell the employees they will watch them to see what factors affect employee theft. In that case, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being protected.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens unconsciously for the participant, so it is essential to eliminate or limit the transmission of the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in contrived scenarios with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative or quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research is not an island apart from quantitative research but an integral part of research methods to understand the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is essential for all healthcare team members as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members, including social workers, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research, including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, healthcare team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Rizvi A, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [ 2014] Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics Peterson K, McCleery E. 2014 May
- Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. [Campbell Syst Rev. 2021] Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Mugellini G, Della Bella S, Colagrossi M, Isenring GL, Killias M. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun; 17(2):e1173. Epub 2021 May 24.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
6 Qualitative data examples for thorough market researchers
Types of qualitative data in market research, 6 qualitative data examples, get nuanced insights from qualitative market research.
There are plenty of ways to gather consumer insights for fresh campaigns and better products, but qualitative research is up there with the best sources of insight.
This guide is packed with examples of how to turn qualitative data into actionable insights, to spark your creativity and sharpen your research strategy. You’ll see how qualitative data, especially through surveys, opens doors to deeper understanding by inviting consumers to share their experiences and thoughts freely, in their own words — and how qualitative data can transform your brand.
Before we dig into some examples of how qualitative data can empower your teams to make focused, confident and quick decisions on anything from product to marketing, let’s go back to basics. We can categorize qualitative data into roughly three categories: binary, nominal and ordinal data. Here’s how each of them is used in qualitative data analysis.
Binary data
Binary data represents a choice between two distinct options, like ‘yes’ or ‘no’. In market research, this type of qualitative data is useful for filtering responses or making clear distinctions in consumer preferences.
Binary data in qualitative research is great for straightforward insights, but has its limits. Here’s a quick guide on when to use it and when to opt for qualitative data that is more detailed:
Binary data is great for:
- Quick Yes/No questions : like “Have you used our app? Yes or No.”
- Initial screening : to quickly sort participants for further studies.
- Clear-cut answers : absolute factors, such as ownership or usage.
Avoid binary data for:
- Understanding motivations : it lacks the depth to explore why behind actions.
- Measuring intensity : can’t show how much someone likes or uses something.
- Detail needed for product development : misses the nuanced feedback necessary for innovations.

Nominal data
Nominal data categorizes responses without implying any order. For example, when survey respondents choose their favorite brand from a list, the data collected is nominal, offering insights into brand preferences among different demographics.
Some other examples of qualitative data that can be qualified as nominal are asking participants to name their primary information source about products in categories like social media, friends, or online reviews. Or in focus groups, discussing brand perceptions could classify brands into categories such as luxury, budget-friendly, or eco-conscious, based on participant descriptions.
Nominal data is great for:
- Categorizing responses : such as types of consumer complaints (product quality, customer service, delivery issues).
- Identifying preferences : like favorite product categories (beverages, electronics, apparel).
- Segmentation : grouping participants based on attributes (first-time buyers, loyal customers).
Nominal data is not for:
- Measuring quantities : it can’t quantify how much more one category is preferred over another.
- Ordering or ranking responses : it doesn’t indicate which category is higher or lower in any hierarchy.
- Detailed behavioral analysis : While it can group behaviors, it doesn’t delve into the frequency or intensity of those behaviors.

Ordinal data
Ordinal data introduces a sense of order, ranking preferences or satisfaction levels. In qualitative analysis, it’s particularly useful for understanding how consumers prioritize features or products, giving researchers a clearer picture of market trends.
Other examples of qualitative data analyses that use ordinal data, are for instance a study on consumer preferences for coffee flavors, participants might rank flavors in order of preference, providing insights into flavor trends. You can also get ordinal data from focus groups on things like customer satisfaction surveys or app usability, by asking users to rate their ease of use or happiness on an ordinal scale.
Ordinal data is great for:
- Ranking preferences : asking participants to rank product features from most to least important.
- Measuring satisfaction levels : using scales like “very satisfied,” “satisfied,” “neutral,” “dissatisfied,” “very dissatisfied.”
- Assessing Agreement : with statements on a scale from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.”
Ordinal data is not for:
- Quantifying differences : it doesn’t show how much more one rank is preferred over another, just the order.
- Precise measurements : can’t specify the exact degree of satisfaction or agreement, only relative positions.

This mix of qualitative and quantitative data will give you a well-rounded view of participant attitudes and preferences.
The things you can do with qualitative data are endless. But this article shouldn’t turn into a work of literature, so we’ll highlight six ways to collect qualitative data and give you examples of how to use these qualitative research methods to get actionable results.

How to get qual insights with Attest
You can get to the heart of what your target customers think, with reliable qualitative insights from Attest Video Responses
1. Highlighting brand loyalty drivers with open-ended surveys and questionnaires
Open-ended surveys and questionnaires are great at finding out what makes customers choose and stick with a brand. Here’s why this qualitative data analysis tool is so good for gathering qualitative data on things like brand loyalty and customer experience:
Straight from the source
Open-ended survey responses show the actual thoughts and feelings of your target audience in their own words, while still giving you structure in your data analysis.
Understanding ‘why’
Numbers can show us how many customers are loyal; open-ended survey responses explain why they are. You can also easily add thematic analysis to the mix by counting certain keywords or phrases.
Guiding decisions
The insights from these surveys can help a brand decide where to focus its efforts, from making sure their marketing highlights what customers love most to improving parts of their product.
Surveys are one of the most versatile and efficient qualitative data collection methods out there. We want to bring the power of qualitative data analysis to every business and make it easy to gather qualitative data from the people who matter most to your brand. Check out our survey templates to hit the ground running. And you’re not limited to textual data as your only data source — we also enable you to gather video responses to get additional context from non verbal cues and more.

2. Trend identification with observation notes
Observation notes are a powerful qualitative data analysis tool for spotting trends as they naturally unfold in real-world settings. Here’s why they’re particularly valuable insights and effective for identifying new trends:
Real behavior
Observing people directly shows us how they actually interact with products or services, not just how they say they do. This can highlight emerging trends in consumer behavior or preferences before people can even put into words what they are doing and why.
Immediate insights
By watching how people engage with different products, we can quickly spot patterns or changes in behavior. This immediate feedback is invaluable for catching trends as they start.
Context matters
Observations give you context. You can see not just what people do, but where and how they do it. This context can be key to understanding why a trend is taking off.
Unprompted reactions
Since people don’t know they’re being observed for these purposes, their actions are genuine. This leads to authentic insights about what’s really catching on.
3. Understanding consumer sentiments through semi-structured interviews
Semi-structured interviews for qualitative data analysis are an effective method for data analysts to get a deep understanding of consumer sentiments. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to gather in-depth insights. Here’s why they’re particularly useful for this type of research question:
Personal connection
These interviews create a space for a real conversation, allowing consumers to share their feelings, experiences, and opinions about a brand or product in a more personal setting.
Flexibility
The format lets the interviewer explore interesting points that come up during the conversation, diving deeper into unexpected areas of discussion. This flexibility uncovers richer insights than strictly structured interviews.
Depth of understanding
By engaging in detailed discussions, brands can understand not just what consumers think but why they think that way and what stations their train of thought passes by.
Structure and surprise
Semi-structured interviews can be tailored to explore specific areas of interest while still allowing for new insights to emerge.
4. Using focus groups for informing market entry strategies
Using a focus group to inform market entry strategies provides a dynamic way to discover your potential customers’ needs, preferences, and perceptions before launching a product or entering a new market. Here’s how focus groups can be particularly effective for this kind of research goal:
Real conversations
Focus groups allow for real-time, interactive discussions, giving you a front-row seat to hear what your potential customers think and feel about your product or service idea.
Diverse Perspectives
By bringing together people from various backgrounds, a focus group can offer a wide range of views and insights, highlighting different consumer needs and contextual information that you might miss out on in a survey.
Spotting opportunities and challenges
The dynamic nature of focus groups can help uncover unique market opportunities or potential challenges that might not be evident through other research methods, like cultural nuances.
Testing ideas
A focus group is a great way to test and compare reactions to different market entry strategies, from pricing models to distribution channels, providing clear direction on what approach might work best.
5. Case studies to gain a nuanced understanding of consumers on a broad level
Case studies in qualitative research zoom in on specific stories from customers or groups using a product or service, great for gaining a nuanced understanding of consumers at a broad level. Here’s why case studies are a particularly effective qualitative data analysis tool for this type of research goal:
In-depth analysis
Case studies can provide a 360-degree look at the consumer experience, from initial awareness to post-purchase feelings.
This depth of insight reveals not just what consumers do, but why they do it, uncovering motivations, influences, and decision-making processes.
Longitudinal insight
Case studies can track changes in consumer behavior or satisfaction over time, offering a dynamic view of how perceptions evolve.
This longitudinal perspective is crucial for giving context to the lifecycle of consumer engagement with a brand.
Storytelling power
The narrative nature of case studies — when done right — makes them powerful tools for communicating complex consumer insights in an accessible and engaging way, which can be especially useful for internal strategy discussions or external marketing communications.
6. Driving product development with diary studies
Diary studies are a unique qualitative research method that involves participants recording their thoughts, experiences, or behaviors over a period of time, related to using a product or service. This qualitative data analysis method is especially valuable for driving product development for several reasons:
Real-time insights
Diary studies capture real-time user experiences and feedback as they interact with a product in their daily lives.
This ongoing documentation provides a raw, unfiltered view of how a product fits into the user’s routine, highlighting usability issues or unmet needs that might not be captured in a one-time survey or interview.
Realistic user journey mapping
By analyzing diary entries, you can map out the entire user journey, identifying critical touch points where users feel delighted, frustrated, or indifferent.
This then enables you to implement targeted improvements and innovations at the moments that matter most.
Identifying patterns
Over the course of a diary study, patterns in behavior, preferences, and challenges can emerge, which is great for thematic analysis.
It can guide product developers to prioritize features or fixes that will have the most significant impact on user satisfaction, which is especially great if they don’t know what areas to focus on first.
Qualitative research brings your consumers’ voices directly to your strategy table. The examples we’ve explored show how qualitative data analysis methods like surveys, interviews, and case studies illuminate the ‘why’ behind consumer choices, guiding more informed decisions. Using these insights means crafting products and messages that resonate deeply, ensuring your brand not only meets but exceeds consumer expectations.

Customer Research Manager
Related articles
Making it personal – using tech to build connections with consumers | diageo, panel discussion – future-proofing your brand with consumer insights, attest product release: multi-market | attest’s alyssa stringer, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
The use of evidence to guide decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic: divergent perspectives from a qualitative case study in British Columbia, Canada
- Laura Jane Brubacher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2806-9539 1 , 2 ,
- Chris Y. Lovato 1 ,
- Veena Sriram 1 , 3 ,
- Michael Cheng 1 &
- Peter Berman 1
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 66 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The challenges of evidence-informed decision-making in a public health emergency have never been so notable as during the COVID-19 pandemic. Questions about the decision-making process, including what forms of evidence were used, and how evidence informed—or did not inform—policy have been debated.
We examined decision-makers' observations on evidence-use in early COVID-19 policy-making in British Columbia (BC), Canada through a qualitative case study. From July 2021- January 2022, we conducted 18 semi-structured key informant interviews with BC elected officials, provincial and regional-level health officials, and civil society actors involved in the public health response. The questions focused on: (1) the use of evidence in policy-making; (2) the interface between researchers and policy-makers; and (3) key challenges perceived by respondents as barriers to applying evidence to COVID-19 policy decisions. Data were analyzed thematically, using a constant comparative method. Framework analysis was also employed to generate analytic insights across stakeholder perspectives.
Overall, while many actors’ impressions were that BC's early COVID-19 policy response was evidence-informed, an overarching theme was a lack of clarity and uncertainty as to what evidence was used and how it flowed into decision-making processes. Perspectives diverged on the relationship between 'government' and public health expertise, and whether or not public health actors had an independent voice in articulating evidence to inform pandemic governance. Respondents perceived a lack of coordination and continuity across data sources, and a lack of explicit guidelines on evidence-use in the decision-making process, which resulted in a sense of fragmentation. The tension between the processes involved in research and the need for rapid decision-making was perceived as a barrier to using evidence to inform policy.
Conclusions
Areas to be considered in planning for future emergencies include: information flow between policy-makers and researchers, coordination of data collection and use, and transparency as to how decisions are made—all of which reflect a need to improve communication. Based on our findings, clear mechanisms and processes for channeling varied forms of evidence into decision-making need to be identified, and doing so will strengthen preparedness for future public health crises.
Peer Review reports
The challenges of evidence-informed decision-making Footnote 1 in a public health emergency have never been so salient as during the COVID-19 pandemic, given its unprecedented scale, rapidly evolving virology, and multitude of global information systems to gather, synthesize, and disseminate evidence on the SARS-CoV-2 virus and associated public health and social measures [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, rapid decision-making became central for governments globally as they grappled with crucial decisions for which there was limited evidence. Critical questions exist, in looking retrospectively at these decision-making processes and with an eye to strengthening future preparedness: Were decisions informed by 'evidence'? What forms of evidence were used, and how, by decision-makers? [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Scientific evidence, including primary research, epidemiologic research, and knowledge synthesis, is one among multiple competing influences that inform decision-making processes in an outbreak such as COVID-19 [ 7 ]. Indeed, the use of multiple forms of evidence has been particularly notable as it applies to COVID-19 policy-making. Emerging research has also documented the important influence of ‘non-scientific’ evidence such as specialized expertise and experience, contextual information, and level of available resources [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the politics of evidence-use in policy-making [ 11 ]; what evidence is used and how can be unclear, and shaped by political bias [ 4 , 5 ]. Moreover, while many governments have established scientific advisory boards, the perspectives of these advisors were reportedly largely absent from COVID-19 policy processes [ 6 ]. How evidence and public health policy interface—and intersect—is a complex question, particularly in the dynamic context of a public health emergency.
Within Canada, a hallmark of the public health system and endorsed by government is evidence-informed decision-making [ 12 ]. In British Columbia (BC), Canada, during the early phases of COVID-19 (March—June 2020), provincial public health communication focused primarily on voluntary compliance with recommended public health and social measures, and on supporting those most affected by the pandemic. Later, the response shifted from voluntary compliance to mandatory enforceable government orders [ 13 ]. Like many other jurisdictions, the government’s public messaging in BC asserted that the province took an approach to managing the COVID-19 pandemic and developing related policy that was based on scientific evidence, specifically. For example, in March 2021, in announcing changes to vaccination plans, Dr. Bonnie Henry, the Provincial Health Officer, stated, " This is science in action " [ 14 ]. As a public health expert with scientific voice, the Provincial Health Officer has been empowered to speak on behalf of the BC government across the COVID-19 pandemic progression. While this suggests BC is a jurisdiction which has institutionalized scientifically-informed decision-making as a core tenet of effective public health crisis response, it remains unclear as to whether BC’s COVID-19 response could, in fact, be considered evidence-informed—particularly from the perspectives of those involved in pandemic decision-making and action. Moreover, if evidence-informed, what types of evidence were utilized and through what mechanisms, how did this evidence shape decision-making, and what challenges existed in moving evidence to policy and praxis in BC’s COVID-19 response?
The objectives of this study were: (1) to explore and characterize the perspectives of BC actors involved in the COVID-19 response with respect to evidence-use in COVID-19 decision-making; and (2) to identify opportunities for and barriers to evidence-informed decision-making in BC’s COVID-19 response, and more broadly. This inquiry may contribute to identifying opportunities for further strengthening the synthesis and application of evidence (considered broadly) to public health policy and decision-making, particularly in the context of future public health emergencies, both in British Columbia and other jurisdictions.
Study context
This qualitative study was conducted in the province of British Columbia (BC), Canada, a jurisdiction with a population of approximately five million people [ 15 ]. Within BC’s health sector, key actors involved in the policy response to COVID-19 included: elected officials, the BC Government’s Ministry of Health (MOH), the Provincial Health Services Authority (PHSA), Footnote 2 the Office of the Provincial Health Officer (PHO), Footnote 3 the BC Centre for Disease Control (BCCDC), Footnote 4 and Medical Health Officers (MHOs) and Chief MHOs at regional and local levels.
Health research infrastructure within the province includes Michael Smith Health Research BC [ 16 ] and multiple post-secondary research and education institutions (e.g., The University of British Columbia). Unlike other provincial (e.g., Ontario) and international (e.g., UK) jurisdictions, BC did not establish an independent, formal scientific advisory panel or separate organizational structure for public health intelligence in COVID-19. That said, a Strategic Research Advisory Council was established, reporting to the MOH and PHO, to identify COVID-19 research gaps and commission needed research for use within the COVID-19 response [ 17 ].
This research was part of a multidisciplinary UBC case study investigating the upstream determinants of the COVID-19 response in British Columbia, particularly related to institutions, politics, and organizations and how these interfaced with, and affected, pandemic governance [ 18 ]. Ethics approval for this study was provided by the University of British Columbia (UBC)’s Institutional Research Ethics Board (Certificate #: H20-02136).
Data collection
From July 2021 to January 2022, 18 semi-structured key informant interviews were conducted with BC elected officials, provincial and regional-level health officials, and civil society actors (e.g., within non-profit research organizations, unions) (Table 1 ). Initially, respondents were purposively sampled, based on their involvement in the COVID-19 response and their positioning within the health system organizational structure. Snowball sampling was used to identify additional respondents, with the intent of representing a range of organizational roles and actor perspectives. Participants were recruited via email invitation and provided written informed consent to participate.
Interviews were conducted virtually using Zoom® videoconferencing, with the exception of one hybrid in-person/Zoom® interview. Each interview was approximately one hour in duration. One to two research team members led each interview. The full interview protocol focused on actors’ descriptions of decision-making processes across the COVID-19 pandemic progression, from January 2020 to the date of the interviews, and they were asked to identify key decision points (e.g., emergency declaration, business closures) [see Additional File 1 for the full semi-structured interview guide]. For this study, we used a subset of interview questions focused on evidence-use in the decision-making process, and the organizational structures or actors involved, in BC's early COVID-19 pandemic response (March–August 2020). Questions were adapted to be relevant to a respondent’s expertise and particular involvement in the response. ‘Evidence’ was left undefined and considered broadly by the research team (i.e., both ‘scientific’/research-based and ‘non-scientific’ inputs) within interview questions, and therefore at the discretion of the participant as to what inputs they perceived and described as ‘evidence’ that informed or did not inform pandemic decision-making. Interviews were audio-recorded over Zoom® with permission and transcribed using NVivo Release 1.5© software. Each transcript was then manually verified for accuracy by 1–2 members of the research team.
Data analysis
An inductive thematic analysis was conducted, using a constant comparative method, to explore points of divergence and convergence across interviews and stakeholder perspectives [ 19 ]. Transcripts were inductively coded in NVivo Release 1.5© software, which was used to further organize and consolidate codes, generate a parsimonious codebook to fit the data, and retrieve interview excerpts [ 20 ]. Framework analysis was also employed as an additional method for generating analytic insights across stakeholder perspectives and contributed to refining the overall coding [ 21 ]. Triangulation across respondents and analytic methods, as well as team collaboration in reviewing and refining the codebook, contributed to validity of the analysis [ 22 ].
How did evidence inform early COVID-19 policy-making in BC?
Decision-makers described their perceptions on the use of evidence in policy-making; the interface between researchers and policy-makers; and specific barriers to evidence-use in policy-making within BC’s COVID-19 response. In discussing the use of evidence, respondents focused on ‘scientific’ evidence; however, they noted a lack of clarity as to how and what evidence flowed into decision-making. They also acknowledged that ‘scientific’ evidence was one of multiple factors influencing decisions. The themes described below reflect the narrative underlying their perspectives.
Perceptions of evidence-use
Multiple provincial actors generally expressed confidence or had an overall impression that decisions were evidence-based (IDI5,9), stating definitively that, "I don’t think there was a decision we made that wasn’t evidence-informed" (IDI9) and that "the science became a driver of decisions that were made" (IDI5). However, at the regional health authority level, one actor voiced skepticism that policy decisions were consistently informed by scientific evidence specifically, stating, "a lot of decisions [the PHO] made were in contrast to science and then shifted to be by the science" ( IDI6). The evolving nature of the available evidence and scientific understanding of the virus throughout the pandemic was acknowledged. For instance, one actor stated that, "I’ll say the response has been driven by the science; the science has been changing…from what I’ve seen, [it] has been a very science-based response" (IDI3).
Some actors narrowed in on certain policy decisions they believed were or were not evidence-informed. Policy decisions in 2020 that actors believed were directly informed by scientific data included the early decision to restrict informal, household gatherings; to keep schools open for in-person learning; to implement a business safety plan requirement across the province; and to delay the second vaccine dose for maximum efficacy. One provincial public health actor noted that an early 2020 decision made, within local jurisdictions, to close playgrounds was not based on scientific evidence. Further, the decision prompted public health decision-makers to centralize some decision-making to the provincial level, to address decisions being made 'on the ground' that were not based on scientific evidence (IDI16). Similarly, they added that the policy decision to require masking in schools was not based on scientific evidence; rather, "it's policy informed by the noise of your community." As parents and other groups within the community pushed for masking, this was "a policy decision to help schools stay open."
Early in the pandemic response, case data in local jurisdictions were reportedly used for monitoring and planning. These "numerator data" (IDI1), for instance case or hospitalization counts, were identified as being the primary mode of evidence used to inform decisions related to the implementation or easing of public health and social measures. The ability to generate epidemiological count data early in the pandemic due to efficient scaling up of PCR testing for COVID-19 was noted as a key advantage (IDI16). As the pandemic evolved in 2020, however, perspectives diverged in relation to the type of data that decision-makers relied on. For example, it was noted that BCCDC administered an online, voluntary survey to monitor unintended consequences of public health and social measures and inform targeted interventions. Opinions varied on whether this evidence was successfully applied in decision-making. One respondent emphasized this lack of application of evidence and perceived that public health orders were not informed by the level and type of evidence available, beyond case counts: "[In] a communicable disease crisis like a pandemic, the collateral impact slash damage is important and if you're going to be a public health institute, you actually have to bring those to the front, not just count cases" (IDI1).
There also existed some uncertainty and a perceived lack of transparency or clarity as to how or whether data analytic ‘entities’, such as BCCDC or research institutions, fed directly into decision-making. As a research actor shared, "I’m not sure that I know quite what all those channels really look like…I’m sure that there’s a lot of improvement that could be driven in terms of how we bring strong evidence to actual policy and practice" (IDI14). Another actor explicitly named the way information flowed into decision-making in the province as "organic" (IDI7). They also noted the lack of a formal, independent science advisory panel for BC’s COVID-19 response, which existed in other provincial and international jurisdictions. Relatedly, one regional health authority actor perceived that the committee that was convened to advise the province on research, and established for the purpose of applying research to the COVID-19 response, "should have focused more on knowledge translation, but too much time was spent commissioning research and asking what kinds of questions we needed to ask rather than looking at what was happening in other jurisdictions" (IDI6). Overall, multiple actors noted a lack of clarity around application of evidence and who is responsible for ensuring evidence is applied. As a BCCDC actor expressed, in relation to how to prevent transmission of COVID-19:
We probably knew most of the things that we needed to know about May of last year [2020]. So, to me, it’s not even what evidence you need to know about, but who’s responsible for making sure that you actually apply the evidence to the intervention? Because so many of our interventions have been driven by peer pressure and public expectation rather than what we know to be the case [scientifically] (IDI1).
Some described the significance of predictive disease modelling to understand the COVID-19 trajectory and inform decisions, as well as to demonstrate to the public the effectiveness of particular measures, which "help[ed] sustain our response" (IDI2). Others, however, perceived that "mathematical models were vastly overused [and] overvalued in decision-making around this pandemic" (IDI1) and that modellers stepped outside their realm of expertise in providing models and policy recommendations through the public media.
Overall, while many actors’ impressions were that the response was evidence-informed, an overarching theme was a lack of clarity and uncertainty with respect to how evidence actually flowed into decision-making processes, as well as what specific evidence was used and how. Participants noted various mechanisms created or already in place prior to COVID-19 that fed data into, and facilitated, decision-making. There was an acknowledgement that multiple forms of evidence—including scientific data, data on public perceptions, as well as public pressure—appeared to have influenced decision-making.
Interface between researchers and policy-makers
There was a general sense that the Ministry supported the use of scientific and research-based evidence specifically. Some actors identified particular Ministry personnel as being especially amenable to research and focused on data to inform decisions and implementation. More broadly, the government-research interface was characterized by one actor as an amicable one, a "research-friendly government", and that the Ministry of Health (MOH), specifically, has a research strategy whereby, "it’s literally within their bureaucracy to become a more evidence-informed organization" (IDI11). The MOH was noted to have funded a research network intended to channel evidence into health policy and practice, and which reported to the research side of the MOH.
Other actors perceived relatively limited engagement with the broader scientific community. Some perceived an overreliance on 'in-house expertise' or a "we can do that [ourselves] mentality" within government that precluded academic researchers’ involvement, as well as a sense of "not really always wanting to engage with academics to answer policy questions because they don’t necessarily see the value that comes" (IDI14). With respect to the role of research, an actor stated:
There needs to be a provincial dialogue around what evidence is and how it gets situated, because there’s been some tension around evidence being produced and not used or at least not used in the way that researchers think that it should be (IDI11).
Those involved in data analytics within the MOH acknowledged a challenge in making epidemiological data available to academic researchers, because "at the time, you’re just trying to get decisions made" (IDI7). Relatedly, a research actor described the rapid instigation of COVID-19 research and pivoting of academic research programs to respond to the pandemic, but perceived a slow uptake of these research efforts from the MOH and PHSA for decision-making and action. Nevertheless, they too acknowledged the challenge of using research evidence, specifically, in an evolving and dynamic pandemic:
I think we’ve got to be realistic about what research in a pandemic situation can realistically contribute within very short timelines. I mean, some of these decisions have to be made very quickly...they were intuitive decisions, I think some of them, rather than necessarily evidence-based decisions (IDI14).
Relatedly, perspectives diverged on the relationship between 'government' and public health expertise, and whether or not public health actors had an independent voice in articulating evidence to inform governance during the pandemic. Largely from Ministry stakeholders, and those within the PHSA, the impressions were that Ministry actors were relying on public health advice and scientific expertise. As one actor articulated, "[the] government actually respected and acknowledged and supported public health expertise" (IDI9). Others emphasized a "trust of the people who understood the problem" (IDI3)—namely, those within public health—and perceived that public health experts were enabled "to take a lead role in the health system, over politics" (IDI12). This perspective was not as widely held by those in the public health sector, as one public health actor expressed, "politicians and bureaucrats waded into public health practice in a way that I don't think was appropriate" and that, "in the context of a pandemic, it’s actually relatively challenging to bring true expert advice because there’s too many right now. Suddenly, everybody’s a public health expert, but especially bureaucrats and politicians." They went on to share that the independence of public health to speak and act—and for politicians to accept independent public health advice—needs to be protected and institutionalized as "core to good governance" (IDI1). Relatedly, an elected official linked this to the absence of a formal, independent science table to advise government and stated that, "I think we should have one established permanently. I think we need to recognize that politicians aren't always the best at discerning scientific evidence and how that should play into decision-making" (IDI15).
These results highlight the divergent perspectives participants had as to the interface between research and policy-making and a lack of understanding regarding process and roles.
Challenges in applying evidence to policy decisions
Perspectives converged with respect to the existence of numerous challenges with and barriers to applying evidence to health policy and decision-making. These related to the quality and breadth of available data, both in terms of absence and abundance. For instance, as one public health actor noted in relation to health policy-making, "you never have enough information. You always have an information shortage, so you're trying to make the best decisions you can in the absence of usually really clear information" (IDI8). On the other hand, as evidence emerged en masse across jurisdictions in the pandemic, there were challenges with synthesizing evidence in a timely fashion for 'real-time' decision-making. A regional health authority actor highlighted this challenge early in the COVID-19 pandemic and perceived that there was not a provincial group bringing new synthesized information to decision-makers on a daily basis (IDI6). Other challenges related to the complexity of the political-public health interface with respect to data and scientific expertise, which "gets debated and needs to be digested by the political process. And then decisions are made" (IDI5). This actor further expressed that debate among experts needs to be balanced with efficient crisis response, that one has to "cut the debate short. For the sake of expediency, you need to react."
It was observed that, in BC’s COVID-19 response, data was gathered from multiple sources with differing data collection procedures, and sometimes with conflicting results—for instance, 'health system data' analyzed by the PHSA and 'public health data' analyzed by the BCCDC. This was observed to present challenges from a political perspective in discerning "who’s actually getting the 'right' answers" (IDI7). An added layer of complexity was reportedly rooted in how to communicate such evidence to the public and "public trust in the numbers" (IDI7), particularly as public understanding of what evidence is, how it is developed, and why it changes, can influence public perceptions of governance.
Finally, as one actor from within the research sector noted, organizationally and governance-wise, the system was "not very well set up to actually use research evidence…if we need to do better at using evidence in practice, we need to fix some of those things. And we actually know what a lot of those things are." For example , "there’s no science framework for how organizations work within that" and " governments shy away from setting science policy " (IDI11). This challenge was framed as having a macro-level dimension, as higher-level leadership structures were observed to not incentivize the development and effective use of research among constituent organizations, and also micro-level implications. From their perspective, researchers will struggle without such policy frameworks to obtain necessary data-sharing agreements with health authorities, nor will they be able to successfully navigate other barriers to conducting action-oriented research that informs policy and practice.
Similarly, a research actor perceived that the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted pre-existing fragmentation, "a pretty disjointed sort of enterprise" in how research is organized in the province:
I think pandemics need strong leadership and I think pandemic research response needed probably stronger leadership than it had. And I think that’s to do with [how] no one really knew who was in charge because no one really was given the role of being truly in charge of the research response (IDI14).
This individual underscored that, at the time of the interview, there were nearly 600 separate research projects being conducted in BC that focused on COVID-19. From their perspective, this reflected the need for more centralized direction to provide leadership, coordinate research efforts, and catalyze collaborations.
Overall, respondents perceived a lack of coordination and continuity across data sources, and a lack of explicit guidelines on evidence-use in the decision-making process, which resulted in a sense of fragmentation. The tension between the processes involved in research and the need for rapid decision-making was perceived as a barrier to using evidence to inform policy.
This study explored the use of evidence to inform early COVID-19 decision-making within British Columbia, Canada, from the perspectives of decision-makers themselves. Findings underscore the complexity of synthesizing and applying evidence (i.e., ‘scientific’ or research-based evidence most commonly discussed) to support public health policy in 'real-time', particularly in the context of public health crisis response. Despite a substantial and long-established literature on evidence-based clinical decision-making [ 23 , 24 ], understanding is more limited as to how public health crisis decision-making can be evidence-informed or evidence-based. By contributing to a growing global scholarship of retrospective examinations of COVID-19 decision-making processes [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ], our study aimed to broaden this understanding and, thus, support the strengthening of public health emergency preparedness in Canada, and globally.
Specifically, based on our findings on evidence-based public health practice, we found that decision-makers clearly emphasized ‘evidence-based’ or ‘evidence-informed’ as meaning ‘scientific’ evidence. They acknowledged other forms of evidence such as professional expertise and contextual information as influencing factors. We identified four key points related to the process of evidence-use in BC's COVID-19 decision-making, with broader implications as well:
Role Differences: The tensions we observed primarily related to a lack of clarity among the various agencies involved as to their respective roles and responsibilities in a public health emergency, a finding that aligns with research on evidence-use in prior pandemics in Canada [ 29 ]. Relatedly, scientists and policy-makers experienced challenges with communication and information-flow between one another and the public, which may reflect their different values and standards, framing of issues and goals, and language [ 30 ].
Barriers to Evidence-Use: Coordination and consistency in how data are collected across jurisdictions reportedly impeded efficiency and timeliness of decision-making. Lancaster and Rhodes (2020) suggest that evidence itself should be treated as a process, rather than a commodity, in evidence-based practice [ 31 ]. Thus, shifting the dialogue from 'barriers to evidence use' to an approach that fosters dialogue across different forms of evidence and different actors in the process may be beneficial.
Use of Evidence in Public Health versus Medicine: Evidence-based public health can be conflated with the concept of evidence-based medicine, though these are distinct in the type of information that needs to be considered. While ‘research evidence’ was the primary type of evidence used, other important types of evidence informed policy decisions in the COVID-19 public health emergency—for example, previous experience, public values, and preferences. This concurs with Brownson’s (2009) framework of factors driving decision-making in evidence-based public health [ 32 ]. Namely, that a balance between multiple factors, situated in particular environmental and organizational context, shapes decision-making: 1) best available research evidence; 2) clients'/population characteristics, state, needs, values, and preferences; and 3) resources, including a practitioner’s expertise. Thus, any evaluation of evidence-use in public health policy must take into consideration this multiplicity of factors at play, and draw on frameworks specific to public health [ 33 ]. Moreover, public health decision-making requires much more attention to behavioural factors and non-clinical impacts, which is distinct from the largely biology-focused lens of evidence-based medicine.
Transparency: Many participants emphasized a lack of explanation about why certain decisions were made and a lack of understanding about who was involved in decisions and how those decisions were made. This point was confirmed by a recent report on lessons learned in BC during the COVID-19 pandemic in which the authors describe " the desire to know more about the reasons why decisions were taken " as a " recurring theme " (13:66). These findings point to a need for clear and transparent mechanisms for channeling evidence, irrespective of the form used, into public health crisis decision-making.
Our findings also pointed to challenges associated with the infrastructure for utilizing research evidence in BC policy-making, specifically a need for more centralized authority on the research side of the public health emergency response to avoid duplication of efforts and more effectively synthesize findings for efficient use. Yet, as a participant questioned, what is the realistic role of research in a public health crisis response? Generally, most evidence used to inform crisis response measures is local epidemiological data or modelling data [ 7 ]. As corroborated by our findings, challenges exist in coordinating data collection and synthesis of these local data across jurisdictions to inform 'real-time' decision-making, let alone to feed into primary research studies [ 34 ].
On the other hand, as was the case in the COVID-19 pandemic, a 'high noise' research environment soon became another challenge as data became available to researchers. Various mechanisms have been established to try and address these challenges amid the COVID-19 pandemic, both to synthesize scientific evidence globally and to create channels for research evidence to support timely decision-making. For instance: 1) research networks and collaborations are working to coordinate research efforts (e.g., COVID-END network [ 35 ]); 2) independent research panels or committees within jurisdictions provide scientific advice to inform decision-making; and 3) research foundations, funding agencies, and platforms for knowledge mobilization (e.g., academic journals) continue to streamline funding through targeted calls for COVID-19 research grant proposals, or for publication of COVID-19 research articles. While our findings describe the varied forms of evidence used in COVID-19 policy-making—beyond scientific evidence—they also point to the opportunity for further investments in infrastructure that coordinates, streamlines, and strengthens collaborations between health researchers and decision-makers that results in timely uptake of results into policy decisions.
Finally, in considering these findings, it is important to note the study's scope and limitations: We focused on evidence use in a single public health emergency, in a single province. Future research could expand this inquiry to a multi-site analysis of evidence-use in pandemic policy-making, with an eye to synthesizing lessons learned and best practices. Additionally, our sample of participants included only one elected official, so perspectives were limited from this type of role. The majority of participants were health officials who primarily referred to and discussed evidence as ‘scientific’ or research-based evidence. Further work could explore the facilitators and barriers to evidence-use from the perspectives of elected officials and Ministry personnel, particularly with respect to the forms of evidence—considered broadly—and other varied inputs, that shape decision-making in the public sphere. This could include a more in-depth examination of policy implementation and how the potential societal consequences of implementation factor into public health decision-making.
We found that the policy decisions made during the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic were perceived by actors in BC's response as informed by—not always based on—scientific evidence, specifically; however, decision-makers also considered other contextual factors and drew on prior pandemic-related experience to inform decision-making, as is common in evidence-based public health practice [ 32 ]. The respondents' experiences point to specific areas that need to be considered in planning for future public health emergencies, including information flow between policy-makers and researchers, coordination in how data are collected, and transparency in how decisions are made—all of which reflect a need to improve communication. Furthermore, shifting the discourse from evidence as a commodity to evidence-use as a process will be helpful in addressing barriers to evidence-use, as well as increasing understanding about the public health decision-making process as distinct from clinical medicine. Finally, there is a critical need for clear mechanisms that channel evidence (whether ‘scientific’, research-based, or otherwise) into health crisis decision-making, including identifying and communicating the decision-making process to those producing and synthesizing evidence. The COVID-19 pandemic experience is an opportunity to reflect on what needs to be done to guild our public health systems for the future [ 36 , 37 ]. Understanding and responding to the complexities of decision-making as we move forward, particularly with respect to the synthesis and use of evidence, can contribute to strengthening preparedness for future public health emergencies.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are not publicly available to maintain the confidentiality of research participants.
The terms 'evidence-informed' and 'evidence-based' decision-making are used throughout this paper, though are distinct. The term 'evidence-informed' suggests that evidence is used and considered, though not necessarily solely determinative in decision-making [ 38 ].
The Provincial Health Services Authority (PHSA) works with the Ministry of Health (MOH) and regional health authorities to oversee the coordination and delivery of programs.
The Office of the Provincial Health Officer (PHO) has binding legal authority in the case of an emergency, and responsibility to monitor the health of BC’s population and provide independent advice to Ministers and public offices on public health issues.
The British Columbia Centre for Disease Control (BCCDC) is a program of the PHSA and provides provincial and national disease surveillance, detection, treatment, prevention, and consultation.
Abbreviations
British Columbia
British Columbia Centre for Disease Control
Coronavirus Disease 2019
Medical Health Officer
Ministry of Health
Provincial Health Officer
Provincial Health Services Authority
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus—2
University of British Columbia
Rubin O, Errett NA, Upshur R, Baekkeskov E. The challenges facing evidence-based decision making in the initial response to COVID-19. Scand J Public Health. 2021;49(7):790–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Williams GA, Ulla Díez SM, Figueras J, Lessof S, Ulla SM. Translating evidence into policy during the COVID-19 pandemic: bridging science and policy (and politics). Eurohealth (Lond). 2020;26(2):29–48.
Google Scholar
Vickery J, Atkinson P, Lin L, Rubin O, Upshur R, Yeoh EK, et al. Challenges to evidence-informed decision-making in the context of pandemics: qualitative study of COVID-19 policy advisor perspectives. BMJ Glob Heal. 2022;7(4):1–10.
Piper J, Gomis B, Lee K. “Guided by science and evidence”? The politics of border management in Canada’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Polit Sci. 2022;4
Cairney P. The UK government’s COVID-19 policy: what does “Guided by the science” mean in practice? Front Polit Sci. 2021;3(March):1–14.
Colman E, Wanat M, Goossens H, Tonkin-Crine S, Anthierens S. Following the science? Views from scientists on government advisory boards during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative interview study in five European countries. BMJ Glob Heal. 2021;6(9):1–11.
Salajan A, Tsolova S, Ciotti M, Suk JE. To what extent does evidence support decision making during infectious disease outbreaks? A scoping literature review. Evid Policy. 2020;16(3):453–75.
Article Google Scholar
Cairney P. The UK government’s COVID-19 policy: assessing evidence-informed policy analysis in real time. Br Polit. 2021;16(1):90–116.
Lancaster K, Rhodes T, Rosengarten M. Making evidence and policy in public health emergencies: lessons from COVID-19 for adaptive evidence-making and intervention. Evid Policy. 2020;16(3):477–90.
Yang K. What can COVID-19 tell us about evidence-based management? Am Rev Public Adm. 2020;50(6–7):706–12.
Parkhurst J. The politics of evidence: from evidence-based policy to the good governance of evidence. Abingdon: Routledge; 2017.
Office of the Prime Minister. Minister of Health Mandate Letter [Internet]. 2021. https://pm.gc.ca/en/mandate-letters/2021/12/16/minister-health-mandate-letter
de Faye B, Perrin D, Trumpy C. COVID-19 lessons learned review: Final report. Victoria, BC; 2022.
First Nations Health Authority. Evolving vaccination plans is science in action: Dr. Bonnie Henry. First Nations Health Authority. 2021.
BC Stats. 2021 Sub-provincial population estimates highlights. Vol. 2021. Victoria, BC; 2022.
Michael Smith Health Research BC [Internet]. 2023. healthresearchbc.ca. Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Michael Smith Health Research BC. SRAC [Internet]. 2023. https://healthresearchbc.ca/strategic-provincial-advisory-committee-srac/ . Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Brubacher LJ, Hasan MZ, Sriram V, Keidar S, Wu A, Cheng M, et al. Investigating the influence of institutions, politics, organizations, and governance on the COVID-19 response in British Columbia, Canada: a jurisdictional case study protocol. Heal Res Policy Syst. 2022;20(1):1–10.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
DeCuir-Gunby JT, Marshall PL, McCulloch AW. Developing and using a codebook for the analysis of interview data: an example from a professional development research project. Field Methods. 2011;23(2):136–55.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(117):1–8.
Creswell JW, Miller DL. Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory Pract. 2000;39(3):124–30.
Sackett D. How to read clinical journals: I. Why to read them and how to start reading them critically. Can Med Assoc J. 1981;1245:555–8.
Evidence Based Medicine Working Group. Evidence-based medicine: a new approach to teaching the practice of medicine. JAMA Netw. 1992;268(17):2420–5.
Allin S, Fitzpatrick T, Marchildon GP, Quesnel-Vallée A. The federal government and Canada’s COVID-19 responses: from “we’re ready, we’re prepared” to “fires are burning.” Heal Econ Policy Law. 2022;17(1):76–94.
Bollyky TJ, Hulland EN, Barber RM, Collins JK, Kiernan S, Moses M, et al. Pandemic preparedness and COVID-19: an exploratory analysis of infection and fatality rates, and contextual factors associated with preparedness in 177 countries, from Jan 1, 2020, to Sept 30, 2021. Lancet. 2022;6736(22):1–24.
Kuhlmann S, Hellström M, Ramberg U, Reiter R. Tracing divergence in crisis governance: responses to the COVID-19 pandemic in France, Germany and Sweden compared. Int Rev Adm Sci. 2021;87(3):556–75.
Haldane V, De Foo C, Abdalla SM, Jung AS, Tan M, Wu S, et al. Health systems resilience in managing the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from 28 countries. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):964–80.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rosella LC, Wilson K, Crowcroft NS, Chu A, Upshur R, Willison D, et al. Pandemic H1N1 in Canada and the use of evidence in developing public health policies—a policy analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2013;83:1–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Saner M. A map of the interface between science & policy. Ottawa, Ontario; 2007. Report No.: January 1.
Lancaster K, Rhodes T. What prevents health policy being “evidence-based”? New ways to think about evidence, policy and interventions in health. Br Med Bull. 2020;135(1):38–49.
Brownson RC, Fielding JE, Maylahn CM. Evidence-based public health: a fundamental concept for public health practice. Annu Rev Public Health. 2009;30:175–201.
Rychetnik L, Frommer M, Hawe P, Shiell A. Criteria for evaluating evidence on public health interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2002;56:119–27.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Khan Y, Brown A, Shannon T, Gibson J, Généreux M, Henry B, et al. Public health emergency preparedness: a framework to promote resilience. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):1–16.
COVID-19 Evidence Network to Support Decision-Making. COVID-END [Internet]. 2023. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/networks/covid-end . Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Moving forward from the COVID-19 pandemic: 10 opportunities for strengthening Canada’s public health systems. 2022.
Di Ruggiero E, Bhatia D, Umar I, Arpin E, Champagne C, Clavier C, et al. Governing for the public’s health: Governance options for a strengthened and renewed public health system in Canada. 2022.
Adjoa Kumah E, McSherry R, Bettany-Saltikov J, Hamilton S, Hogg J, Whittaker V, et al. Evidence-informed practice versus evidence-based practice educational interventions for improving knowledge, attitudes, understanding, and behavior toward the application of evidence into practice: a comprehensive systematic review of undergraduate studen. Campbell Syst Rev. 2019;15(e1015):1–19.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our gratitude to current and former members of the University of British Columbia Working Group on Health Systems Response to COVID-19 who contributed to various aspects of this study, including Shelly Keidar, Kristina Jenei, Sydney Whiteford, Dr. Md Zabir Hasan, Dr. David M. Patrick, Dr. Maxwell Cameron, Mahrukh Zahid, Dr. Yoel Kornreich, Dr. Tammi Whelan, Austin Wu, Shivangi Khanna, and Candice Ruck.
Financial support for this work was generously provided by the University of British Columbia's Faculty of Medicine (Grant No. GR004683) and Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies (Grant No. GR016648), as well as a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant (Grant No. GR019157). These funding bodies were not involved in the design of the study, the collection, analysis or interpretation of data, or in the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Population and Public Health, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Laura Jane Brubacher, Chris Y. Lovato, Veena Sriram, Michael Cheng & Peter Berman
School of Public Health Sciences, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Canada
Laura Jane Brubacher
School of Public Policy and Global Affairs, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Veena Sriram
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CYL, PB, and VS obtained funding for and designed the study. LJB, MC, and PB conducted data collection. LJB and VS analyzed the qualitative data. CYL and LJB collaboratively wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Laura Jane Brubacher .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This case study received the approval of the UBC Behavioural Research Ethics Board (Certificate # H20-02136). Participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Semi-structured interview guide [* = questions used for this specific study]
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Brubacher, L.J., Lovato, C.Y., Sriram, V. et al. The use of evidence to guide decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic: divergent perspectives from a qualitative case study in British Columbia, Canada. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01146-2
Download citation
Received : 08 February 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01146-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Decision-making
- Public health
- Policy-making
- Qualitative
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Background of the Study in Qualitative Research
Ai generator.
Introduction The transition to inclusive education in mainstream schools has raised important questions about the experiences of students with disabilities. This qualitative study explores the experiences and challenges faced by these students in inclusive educational settings.
Contextual Framework Inclusive education aims to integrate all students, regardless of their abilities, into mainstream classrooms. Historically, students with disabilities were often placed in separate schools or classes. Theories of inclusive education, social integration, and equity in education provide a basis for understanding the current shift towards inclusivity.
Literature Review Previous research highlights both the benefits and challenges of inclusive education. Studies show that inclusive settings can promote social interaction and reduce stigmatization. However, they also reveal significant challenges, such as inadequate teacher training, lack of resources, and peer bullying. Despite these findings, there is limited qualitative research that captures the personal experiences and perspectives of students with disabilities in inclusive settings.
Rationale Understanding the lived experiences of students with disabilities in inclusive settings is crucial for developing effective educational practices and policies. This study aims to fill the gap by providing in-depth insights into their daily experiences, challenges, and coping strategies.
Objectives and Research Questions
- To explore the personal experiences of students with disabilities in inclusive classrooms.
- What are the main challenges faced by these students in inclusive educational settings?
- How do students with disabilities perceive their interactions with peers and teachers?
- What strategies do students with disabilities use to navigate inclusive classrooms?
Conclusion The background of the study highlights the importance of examining the experiences of students with disabilities in inclusive educational settings. By providing rich, qualitative data, this research aims to inform better practices and policies to support the successful inclusion of all students in mainstream schools.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Offering extended use of the contraceptive implant via an implementation science framework: a qualitative study of clinicians’ perceived barriers and facilitators
- Nicole Rigler 1 ,
- Gennifer Kully 2 , 3 ,
- Marisa C. Hildebrand 2 ,
- Sarah Averbach 2 , 3 &
- Sheila K. Mody 2
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 697 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The etonogestrel contraceptive implant is currently approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention of pregnancy up to 3 years. However, studies that suggest efficacy up to 5 years. There is little information on the prevalence of extended use and the factors that influence clinicians in offering extended use. We investigated clinician perspectives on the barriers and facilitators to offering extended use of the contraceptive implant.
Using the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), we conducted semi-structured qualitative interviews. Participants were recruited from a nationwide survey study of reproductive health clinicians on their knowledge and perspective of extended use of the contraceptive implant. To optimize the diversity of perspectives, we purposefully sampled participants from this study. We used content analysis and consensual qualitative research methods to inform our coding and data analysis. Themes arose deductively and inductively.
We interviewed 20 clinicians including advance practice clinicians, family medicine physicians, obstetrician/gynecologist and complex family planning sub-specialists. Themes regarding barriers and facilitators to extended use of the contraceptive implant emerged. Barriers included the FDA approval for 3 years and clinician concern about liability in the context of off-label use of the contraceptive implant. Educational materials and a champion of extended use were facilitators.
Conclusions
There is opportunity to expand access to extended use of the contraceptive implant by developing educational materials for clinicians and patients, identifying a champion of extended use, and providing information on extended use prior to replacement appointments at 3 years.
Peer Review reports
The etonogestrel contraceptive implant is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for 3 years of continuous use for the prevention of pregnancy [ 1 ]. However, there is evidence to support its use for up to 5 years while maintaining a low risk of pregnancy [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. The off-label use of the contraceptive implant past its FDA-approved duration and up to 5 years is known as extended use. Importantly, the FDA supports off-label use of marketed drugs and medical devices so long as there is strong relevant published evidence [ 5 ]. Off-label use such as extended use of the contraceptive implant is common with many other reproductive devices and medications, including misoprostol for labor induction, the copper intrauterine device (IUD) for emergency contraception, and, prior to its recent FDA-approval for extended use, the 52 mg levonorgestrel (LNG) IUD for pregnancy prevention. The 52 mg LNG IUD was previously FDA-approved for 5 years, however strong published evidence demonstrated longer efficacy up to 8 years, leading clinicians to counsel on extended use and eventually contributing to updated federal guidelines [ 6 , 7 ].
Though there are clinicians who counsel patients on extended use of the contraceptive implant, many patients still undergo implant replacement after only 3 years of use [ 8 , 9 ]. Continuation rates of the contraceptive implant after 1 and 2 years of use is estimated to be at 81.7% and 68.7%, with the most common reason for early discontinuation prior to 3 years being changes to bleeding pattern [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Ali et al. report the most common reasons that patients decided to stop implant use in years 4 and 5: unspecified personal reasons, desired fertility, bleeding problems, and other medical reasons [ 4 ]. Additionally, a recent nationwide, web-based survey amongst a diverse group of reproductive health clinicians investigated the barriers and facilitators regarding extended use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years [ 14 ]. The most common barriers found in the study were provider concerns about pregnancy risk and the current FDA approval for only 3 years of use. The key facilitators included strong published evidence supporting extended use and patient and clinician education on extended use. Other than these studies, the patient and clinician factors that facilitate and hinder widespread implementation of extended use of the contraceptive implant have not been explored.
Increasing implementation of extended use of the contraceptive implant across practice settings may decrease unnecessary procedures, devices, healthcare visits, and could improve access to, and satisfaction with, the contraceptive implant. Long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) methods such as the contraceptive implant and LNG IUD have significantly higher continuation and approval rates and are more efficacious at preventing pregnancy than non-LARC methods such as oral contraceptive pills and depot medroxyprogesterone acetate injection [ 12 , 15 , [ 16 ]. Given the continued high rates of unintended pregnancies in the United States and the consequential increase in healthcare costs and poor outcomes secondary to pregnancy complications, efficacious pregnancy prevention is an important public health objective and cost-saving measure [ 17 ].
Using a qualitative approach guided by an implementation science framework, the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR), [ 18 ] we sought to explore clinician perspectives on extended use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years as well as the perceived barriers and facilitators for clinicians to offer extended use.
We conducted semi-structured interviews with 20 clinicians including obstetrics and gynecology generalists, family medicine physicians, complex family planning sub-specialists, and advanced practice clinicians. We recruited interview participants from a nationwide, web-based survey that assessed the prevalence of extended use of the contraceptive implant [ 17 ]. This study recruited respondents through email listservs for the Fellowship in Complex Family Planning, the Ryan Residency Training in Family Planning Program, women’s health nurse practitioners, and family medicine physicians, as well as private social media groups for obstetrician-gynecologists. The total reach of the survey was unknown, however, the study had a survey completion rate of 66.6% ( n = 300/450). Of the 300 completed surveys, 290 respondents indicated their interest in being interviewed (96.7%).
Among the survey respondents, we invited 24 clinicians to participate in interviews, yielding an 83.3% response rate. We selectively recruited interview participants to enrich our sample, specifically focusing on clinician type, practice setting, and region of practice within the United States (U.S.). We also selected interview participants based on whether they always, sometimes, or never counsel on extended use to investigate a broad range of perspectives. For this study, offering extended use is defined as counseling on use past the current FDA-approved duration of 3 years and up to 5 years of use. Offering extended use can occur at any clinical encounter, including insertion appointments, replacement and removal appointments at or before 3 years, and general reproductive health appointments. Clinicians who always offer extended use were defined as those who counsel on extended use to patients who are considering or currently have the contraceptive implant. Clinicians who sometimes offer extended use were defined as those who counsel on extended use, but only to particular patients based on patient-specific factors such as body mass index or insurance coverage. Clinicians who never offer extended use were defined as those who never counsel on use of the contraceptive implant past 3 years of use.
The interview guide was created utilizing an implementation science framework that identifies factors for effectively enacting interventions [ 18 ]. The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) is organized into 5 major domains: characteristics of the intervention, individual characteristics, inner setting, outer setting, and the process of implementation. The first domain, intervention characteristics, relates to the inherent qualities of the intervention, such as pharmacologic properties and side effects of the contraceptive implant when used up to 5 years. Individual characteristics relates to the roles and characteristics of individual patients and clinicians interacting with the intervention, such as educational background and type of insurance coverage. The inner setting domain assesses the internal setting in which an intervention will be implemented (i.e., clinic type, culture, and policies). The broader context in which an intervention will be implemented, including national policies and social norms is evaluated within the outer setting domain. Finally, the process of implementation domain explores the activities and strategies used to implement the intervention, such as educational materials or clinician and staff trainings on extended use.
We designed the interview guide around these specific domains with questions that aimed to identify targeted strategies to support successful implementation. The complete interview guide is in Appendix A . The interview guide was designed with input from clinicians who regularly prescribe contraception, including extended use of the contraceptive implant, as well as CFIR and implementation science experts. The Human Research Protection Program at our institution approved the study.
A single research team member conducted semi-structured interviews via secure video conference between July and August 2021. Interview participants provided informed consent. All participants were asked a full set of open-ended questions based on the interview guide, with focused follow-up questions to further investigate potential themes or to clarify points. All interviews were audio recorded, then transcribed. For data analysis, we used a content analysis approach to identify concepts and patterns within the dataset [ 19 ]. Themes arose deductively and inductively, with deductive themes identified from the CFIR domains and inductive themes arising from interview insights. Consensual qualitative research methods informed both our data analysis and coding process [ 20 ]. Three authors were involved in the thematic coding of the transcripts. Initially, 5 transcripts were independently coded then checked for inter-coder reliability. Any disagreements were discussed, and a consensus was achieved. The remaining transcripts were then coded by one of the three authors. Once all interviews were coded, major themes and representative quotes were identified. The research team utilized ATLAS.ti for analysis [ 21 ].
Between July and August 2021, we interviewed 20 clinicians from a variety of clinical settings, regions, and women’s health professions, achieving the intended diversity of perspectives (Table 1 ). Among participants, 7 (35.0%) always, 8 (40.0%) sometimes, 5 (25.0%) never offer extended use of the contraceptive implant (Table 2 ).
Characteristics of the intervention
We found that changes to bleeding pattern in or after the third year of use was a barrier to clinicians offering extended use of the contraceptive implant. The participants in this study noted that perceived increases in the irregularity or frequency of a patient’s bleeding makes extended use of the implant difficult for patients to accept. One clinician noticed that some patients correlate changes in their bleeding pattern with a perceived decrease in the efficacy of their implant:
"People who do start noticing changes in bleeding pattern […] [and] associating that with, ‘Oh, my implant is wearing out or becoming expired. I need to get this changed out."
-Complex Family Planning Specialist, Southwest, Academic Setting, sometimes offers extended use
The same clinician discussed that more research on bleeding patterns in the extended use period and potential treatments for implant-associated irregularities could be a facilitator of extended use:
"For bleeding, I think it would be awesome if there is a research study, looking at use of OCPs [oral contraceptive pills] to manage bleeding near the end of the use of an implant or near that three-year mark,, […] So that we could give people… Honestly, either a natural history or a, ‘Here’s how you can manage that if you do want to keep using your implant longer.’"
- Complex Family Planning Specialist, Southwest, Academic Setting, sometimes offers extended use
Information on the bleeding pattern in years 4 and 5 of use and how clinicians can address irregular bleeding during implant use may increase acceptability of extended use.
Individual characteristics
We found that insurance impacts whether a clinician offers extended use:
"I do sometimes have patients saying, ‘I might be changing jobs or I’m going to be turning 27 or whatever.’ And so insurance is a barrier and so they’re like, ‘I want the new one while I still have this insurance.’"
- Family Medicine Physician, Midwest, Community Setting, sometimes offers extended use
Many participants agreed with this concept and stated that acceptability of extended use depends on a patient’s perception of their future insurance status. Clinicians observed that if a patient believes they will have coverage for a replacement or removal in the future, they are more likely to pursue extended use of their implant. Conversely, one clinician discussed how lack of current insurance coverage could be a facilitator of extended use:
"So, I would generally offer extended use to people that didn’t have insurance and would have to self-pay. I would like go through the data with them so they wouldn’t have to pay like $1,000 to get a new implant because it could work another year, or people that were concerned about changing side effects at that time."
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist, Southwest, Academic Setting, sometimes offers extended use
Overall, clinicians perceived that patients’ concerns about current and future insurance coverage may affect acceptance of extended use.
Inner setting
This study found that having a champion of extended use at a clinician’s home or affiliate institution was a facilitator of extended use. Most clinicians in the study stated that it is or would be helpful to have someone who worked with them clinically that was knowledgeable on the data about extended use. When asked which factor would promote extended use of the implant the most, this clinician stated:
"…having a champion who is really ready to present the evidence, because the evidence can be there, but people don’t have time to read it. If it’s not brought to them, they’re not really going to know about it."
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist, West Coast, Community Setting, does not offer extended use
Potential champions identified were physicians, nurses, medical directors, or other clinicians in leadership positions, but participants generally believed that the position should be held by someone who is passionate about contraception, highly familiar with the specific setting, and knowledgeable about the clinical studies on extended use.
A barrier noted by a few participants was the effect of discordant counseling by different clinicians, sometimes within the same clinic, on acceptability of extended use:
"I mean, I guess like getting everyone on the same page, like in your practice can be a barrier. Especially in the practice I’ve been at, which like I said was in a state that was very litigious, so people weren’t always willing to like go outside guidelines that were… So getting your whole group on the same page so patients get like a more consistent message."
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist, Southwest, Academic Setting, sometimes offers extended use.
Participants discussed that it is important for clinician teams to relay a cohesive message to patients, especially in settings where patients may see multiple clinicians for their contraceptive care.
Outer setting
Lack of FDA approval for extended use was identified as barrier by many clinicians, and some clinicians counseled patients only on the FDA-approved duration of the contraceptive implant:
"So, generally in our practice we don’t really talk about extended use. We say this is FDA approved for three years."
- Advanced Practice Clinician, Southeast, Community Setting, sometimes offers extended use.
Even clinicians who do offer extended use of the implant noted that off-label use can be confusing to patients, making it difficult to counsel on extended use:
"So I have patients all the time, who’ll say, ‘Well, what do you mean I can keep X, Y or Z in for an extra year?’ And I’ll say, ‘We have big studies that tell us that this is an okay thing to do.’ But that just feels weird. People don’t necessarily understand the role of the FDA or sort of how it works. And so it’s something like extended use just might be a really such a foreign concept. Right? It’s so far outside. But I think that there are also, there are lay outlets that cover this stuff. So it’s not that it’s impossible to access. It’s just that the patient has to be interested just like the provider has to be interested."
- Complex Family Planning Specialist, East Coast, Academic Setting, sometimes offers extended use.
Clinicians also observed that certain clinics must follow official guidelines without the flexibility to offer extended use, regardless of a clinician’s perspective or willingness to counsel on extended use. Interestingly, patient confusion as well as mistrust of the healthcare system may impact patient acceptability of extended use in the context of a three-year FDA-approved duration:
"The other thing is the FDA approval because the box says three years, but then like I tell people, you can take it out in five years. And then they don’t believe… Like who is right. Is it my doctor who’s getting in front of me right or the box, right?"
- Family Medicine Physician, West Coast, Community Setting, always offers extended use.
This clinician noted that a disconnect between a clinician’s counseling and prescription information may lead patients to be confused about the recommendation for extended use.
Another barrier mentioned by a few participants was provider concern about liability in the event of an unintended pregnancy. Participants discussed fear of both legal and interpersonal repercussions of unintended pregnancy after counseling on off-label use of a contraceptive device:
"Even though there’s a slim chance that a patient would get pregnant on Nexplanon [the contraceptive implant], I feel like if we were to say, ‘Yeah, you can use it beyond the four years,’ and they come up and they get pregnant, they’re that 1% chance that gets pregnant, I feel like there could be a little bit of blame laid on us if we were to tell them that they’re able to it beyond the three years when the label doesn’t say that yet."
- Advanced Practice Clinician, Southeast, Private Practice, does not offer extended use.
Some participants felt that they would “have no ground to stand on” in the event of a lawsuit (OBGYN Physician, Midwest, Private Practice), making them concerned about the possibility of increased liability in counseling on off-label use without FDA approval.
Interestingly, multiple clinicians also discussed abortion restrictions in the United States as influencing patients in their decision to pursue extended use or not:
"In the past four years [2017–2021] have also had a lot of patients express concern about the administration. And so wanting to kind of be as current as they can be with their devices and so potentially exchanging them sooner than they need."
- Complex Family Planning Specialist, West Coast, Academic Setting, always offers extended use.
Clinicians observed that patients are noticing and reacting to abortion restrictions when making their contraceptive decisions, which may impact the widespread implementation of extended use.
Process of implementation
Many clinicians reported that a barrier to implementing extended use was patient preference for removal when they are already in clinic for a scheduled removal or replacement procedure, regardless of being counseled on extended use at that time:
“’Oh, I’m already here. I’m approved. Let’s just go ahead and get it done.’ So there’s probably not a whole lot you can do about that either, once they’re already in the clinic, and have their mind set on it.”
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist, Southeast, Academic Setting, does not offer extended use.
Many participants in this study noted that patients have made logistical arrangements prior to their appointments including paid time off, childcare, or prior authorization. It can be difficult for clinicians to offer extended use within this context, therefore counseling is better done prior to a patient coming in for a replacement appointment.
A perceived facilitator of extended use that was mentioned often was clear, concise clinician educational services or materials that illustrates existing data on efficacy and risks. Clinicians believed that this education could be in the form of continued medical education, targeted trainings, or written summaries of relevant studies, data, and recommendations. One consistency across interviews was that education on extended use must be integrated into regular practice and be easily understood by busy clinicians:
"I think that when we get a pamphlet or a brochure or a one page, something that just has everything condensed so it’s a really quick, oh, okay, this is something that we can be offering patients. And these are the reasons why it would be a benefit to them, and these are the patients that maybe would fall out of not offering this to. I think because of how busy we are, that’s the best way for us to make change."
- Advanced Practice Clinician, Southwest, Academic Setting, does not offer extended use.
Participants reported that these resources should be widely distributed beyond the complex family planning and obstetrician-gynecology community to increase accessibility to extended use.
Another potential facilitator identified was effective patient educational materials such as flyers that state the 5-year efficacy of the contraceptive implant, though producing these might require FDA approval. Participants in this study report that patients rely on clinicians to provide information on the efficacy and duration of their contraceptive implant. However, it is difficult for patients to accept extended use when there are inconsistencies across multiple sources of information:
"I mean, if online, there was information where it said you can keep it in for three to five years and they’re able to back that up. You know, people like to do their own research. I think that would be helpful, versus it says everywhere three, three, three, three, three, and then you’re the only person telling them something different, then it’s a little more tricky."
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist, West Coast, Community Setting, does not offer extended use.
Overall, participants in this study expressed that it would be helpful to have easily understood information for clinicians and patients that explained the evidence for extended use.
Our results demonstrate that there is an opportunity to increase widespread implementation of extended use through multiple interventions. Clinicians reported that patients prefer to have their implants replaced when they are already in clinic for the procedure. Therefore, intervening prior to replacement appointments at 3 years in the form of telemedicine visits or notifications from scheduling staff may make extended use of the contraceptive implant more acceptable to patients. Further, clinician and patient education on extended use that is easily understood and widely disseminated would likely increase use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years.
The implementation of extended use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years likely decreases healthcare costs secondary to fewer procedures and unintended pregnancies, and expands reproductive choices for patients seeking contraception. It has been found that clinicians who offer extended use state that most of their patients accept extended use when it is offered [ 14 ]. However, the reasons why a patient may or may not accept extended use are unclear, but may include changes in bleeding and concerns about use past the FDA-approved duration. Research on bleeding patterns in the extended use period may facilitate counseling and give patients a better expectation of possible changes they may see in years 4 and 5. Additionally, research on the patient perspective and acceptability of using the contraceptive implant past its FDA-approved timeframe is needed.
This study focused on clinicians and their perspectives on extended use. However, it is important to note that patients may be fully informed about extended use and choose to replace their implant at or before 3 years of duration. All discussions regarding contraception, including extended use of the implant, should always occur within a patient-centered and shared decision-making model. Widespread offering of extended use may allow for more patients to make fully informed decisions about the duration and use of their contraceptive devices, therefore expanding reproductive choice and agency in addition to potentially sparing patients from unnecessary procedures and extra healthcare costs.
Interestingly, although there are data to reflect high implant efficacy in years 4 and 5, [ 2 , 3 , 4 ] some participants in this study believe there is increased liability in counseling on off-label use without FDA approval. Importantly, off-label use is common among reproductive clinicians and is protected by the FDA if there is strong published evidence supporting off label use [ 5 ]. Additionally, the Society of Family Planning supports extended use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years [ 22 ]. The FDA requires implant training for clinicians before they can insert or remove the implant. This training includes the FDA product labeling indicating the maximum duration of use for pregnancy prevention as three years [ 1 ]. It is possible that clinician training and product labels that advertise a 3-year duration dissuade clinicians from offering extended use of the contraceptive implant due to concerns about legal repercussions in the event of an unintended pregnancy with extended use. Therefore, organization- or systems-level guidelines, policy changes, and trainings in support of extended use may allow clinicians to feel comfortable offering off-label use of the implant. Additionally, FDA approval of the contraceptive implant to 5 years would likely greatly facilitate implementation of extended use.
Changing the FDA label to reflect extended use can be expensive, and contraceptive companies may not be incentivized to change the label. However, increasing the FDA approval of the contraceptive implant would allow for companies to have a longer-acting contraceptive device that is more directly comparable to other LARC devices such as the 52 mg LNG IUD that can be used for up to 8 years. If FDA approval for 5 years of use were to occur, it is not known if the barriers described in this study would continue to apply. However, it is likely that the facilitators of extended use from this study would support implementation of extended use irrespective of the federally approved duration.
One strength of the study is the national sample and the diversity of clinician types and settings. There is also representation of clinicians who consistently offer extended use and those who do not offer extended use. Another strength of this study is that it was designed utilizing a framework focusing on implementation, thus yielding results that can be used to create effective interventions.
Limitations of this study include the small sample size and selection bias from recruiting from a prior study that utilized listservs and social media. Additionally, we recruited from a population that was specifically interested in family planning and identified mostly as Caucasian and female. Because of this, our results may not be generalizable to the national population of clinicians who offer contraceptive implant services. However, our direct selection of participants who only sometimes or do not offer extended use allowed us to hear diverse perspectives regardless of prior knowledge or interest in extended use. Another limitation is that we did not ask advanced practice clinicians what their specific training was (i.e., nurse practitioner or physician’s assistant). As the training for advanced practice clinicians can vary greatly, our results may not be generalizable to all advanced practice clinicians.
In conclusion, this study describes the barriers and facilitators to widespread implementation of extended use of the contraceptive implant. These results offer new perspectives and potential strategies to increase widespread implementation of extended use of the contraceptive implant up to 5 years of use. Based on our findings, there is opportunity to expand access to extended use by developing educational materials for clinicians and patients, identifying a champion of extended use, and counseling on extended use prior to removal appointments at 3 years. Of note, these results should be viewed in the context of recent policy access issues regarding reproductive health and used to support patient-centered contraceptive choices, regardless of a patient’s decision to extend use of their contraceptive implant up to 5 years. It is important that clinicians and patients utilize shared decision making when discussing extended use of the contraceptive implant.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to being stored in a private, HIPAA-compliant database, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
Food and Drug Administration
CoIntrauterine device
- Long-acting reversible contraception
Levonorgestrel
Obstetrician-Gynecologist
United States
Nexplanon® Prescribing Information. Organon. 2021. https://www.organon.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/n/nexplanon/nexplanon_pi.pdf . Accessed 20 Feb 2023.
McNicholas C, Swor E, Wan L, Peipert JF. Prolonged use of the etonogestrel implant and levonorgestrel intrauterine device: 2 years beyond food and drug administration-approved duration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216(6):586e.
Article Google Scholar
McNicholas C, Maddipati R, Zhao Q, Swor E, Peipert JF. Use of the etonogestrel implant and levonorgestrel intrauterine device beyond the U.S. food and drug administration-approved duration. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125(3):599–604. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000000690 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ali M, Akin A, Bahamondes L, Brache V, Habib N, Landoulsi S, Hubacher D, WHO study group on subdermal contraceptive implants for women. Extended use up to 5 years of the etonogestrel-releasing subdermal contraceptive implant: comparison to levonorgestrel-releasing subdermal implant. Hum Reprod. 2016;31(11):2491–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dew222 .
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (1998). Off-label and investigational use of marketed drugs, biologics, and medical devices: guidance for institutional review boards and clinical investigators . Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/label-and-investigational-use-marketed-drugs-biologics-and-medical-devices . Accessed 20 Dec 2022.
Jensen JT, Lukkari-Lax E, Schulze A, Wahdan Y, Serrani M, Kroll R. Contraceptive efficacy and safety of the 52-mg levonorgestrel intrauterine system for up to 8 years: findings from the mirena extension trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227(6):873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022.09.007 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
O’Dwyer MC. Contraceptive Efficacy of the Mirena Intrauterine System Through 8 Years of Use. NEJM Journal Watch. Retrieved from https://www.jwatch.org/na55371/2022/10/04/contraceptive-efficacy-mirena-intrauterine-system-through . Accessed 7 Mar 2024.
Teunissen AM, Grimm B, Roumen FJ. Continuation rates of the subdermal contraceptive Implanon(®) and associated influencing factors. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2014;19(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.3109/13625187.2013.862231 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Moray KV, Chaurasia H, Sachin O, Joshi B. A systematic review on clinical effectiveness, side-effect profile and meta-analysis on continuation rate of etonogestrel contraceptive implant. Reprod Health. 2021;18(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-01054-y .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Blumenthal PD, Gemzell-Danielsson K, Marintcheva-Petrova M. Tolerability and clinical safety of implanon. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2008;13(Suppl 1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/13625180801960012 .
Mansour D, Korver T, Marintcheva-Petrova M, Fraser IS. The effects of implanon on menstrual bleeding patterns. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2008;13(Suppl 1):13–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/13625180801959931 .
Diedrich JT, Zhao Q, Madden T, Secura GM, Peipert JF. Three-year continuation of reversible contraception. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213(5):e6621-6628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2015.08.001 .
Funk S, Miller MM, Mishell DR Jr, Archer DF, Poindexter A, Schmidt J, Zampaglione E, Implanon US Study Group. Safety and efficacy of implanon, a single-rod implantable contraceptive containing etonogestrel. Contraception. 2005;71(5):319–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2004.11.007 .
Rigler N, Averbach S, Sandoval S, Meurice M, Hildebrand M, Mody SK. Barriers and facilitators of extended use of the contraceptive arm implants: a cross-sectional survey of clinicians. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;139:4S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000826380.60071.b8 .
Hubacher D, Spector H, Monteith C, Chen PL. Not seeking yet trying long-acting reversible contraception: a 24-month randomized trial on continuation, unintended pregnancy and satisfaction. Contraception. 2018;97(6):524–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2018.02.001 .
Winner B, Peipert JF, Zhao Q, Buckel C, Madden T, Allsworth JE, Secura GM. Effectiveness of long-acting reversible contraception. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(21):1998–2007. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1110855 .
Monea E, Thomas A. Unintended pregnancy and taxpayer spending. Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2011;43(2):88–93. https://doi.org/10.1363/4308811 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
CFIR Research Team-Center for Clinical Management Research. The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research: Constructs. 2023. https://cfirguide.org/constructs/ . Accessed 24 Jan 2023.
Forman J, Damschroder LJ. Qualitative content analysis. In: Jacoby L, Siminoff L, editors. Empirical research for bioethics: A primer, vol. 11. Oxford: Elsevier Publishing; 2008. p. 39–62.
Chapter Google Scholar
Hill CE, Knox S, Thompson BJ, Williams EN, Hess SA. Consensual qualitative research: an update. J Couns Psychol. 2005;52:1–25.
Soratto J, Pires DEP, Friese S. Thematic content analysis using ATLAS.ti software: potentialities for researchs in health. Rev Bras Enferm. 2020;73(3):e20190250. https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2019-0250 .
Dethier D, Qasba N, Kaneshiro B. Society of family planning clinical recommendation: extended use of long-acting reversible contraception. Contraception. 2022;113:13–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2022.06.003 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants in this study.
This study was funded by Organon (Study #201908). The funder had no role in the study design, analysis, or interpretation of findings.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Medicine, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA
Nicole Rigler
Division of Complex Family Planning, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences, University of California San Diego, 9300 Campus Point Dr. MC 7433, La Jolla, San Diego, CA, USA
Gennifer Kully, Marisa C. Hildebrand, Sarah Averbach & Sheila K. Mody
Center on Gender Equity and Health, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA
Gennifer Kully & Sarah Averbach
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SM is the principal investigator and lead data analysis, including qualitative coding, and dissemination of findings. She was also involved in study design and participant recruitment. NR was the primary interviewer and was involved in study design, recruitment, data management, data analysis, and dissemination of findings. GK and MH were involved with study design, recruitment, coordination of the study, IRB documentation, data analysis, and dissemination of findings. SA was involved with study design and dissemination of findings. All authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sheila K. Mody .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at University of California, San Diego (Study #201908). All participants gave written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
S.M. is a consultant for Bayer and Merck. She has grant funding from Organon and receives authorship royalties from UpToDate. S.A. has served as a consultant for Bayer on immediate postpartum IUD use. The remaining authors report no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rigler, N., Kully, G., Hildebrand, M.C. et al. Offering extended use of the contraceptive implant via an implementation science framework: a qualitative study of clinicians’ perceived barriers and facilitators. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 697 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10991-4
Download citation
Received : 19 December 2023
Accepted : 15 April 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10991-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Contraceptive implant
- Long-acting contraception
- Extended use
- Contraceptive access
- Implementation science
- Consolidated framework for implementation research
- Off-label use
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2024
Patient experiences: a qualitative systematic review of chemotherapy adherence
- Amineh Rashidi 1 ,
- Susma Thapa 1 ,
- Wasana Sandamali Kahawaththa Palliya Guruge 1 &
- Shubhpreet Kaur 1
BMC Cancer volume 24 , Article number: 658 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
122 Accesses
Metrics details
Adherence to chemotherapy treatment is recognized as a crucial health concern, especially in managing cancer patients. Chemotherapy presents challenges for patients, as it can lead to potential side effects that may adversely affect their mobility and overall function. Patients may sometimes neglect to communicate these side effects to health professionals, which can impact treatment management and leave their unresolved needs unaddressed. However, there is limited understanding of how patients’ experiences contribute to improving adherence to chemotherapy treatment and the provision of appropriate support. Therefore, gaining insights into patients’ experiences is crucial for enhancing the accompaniment and support provided during chemotherapy.
This review synthesizes qualitative literature on chemotherapy adherence within the context of patients’ experiences. Data were collected from Medline, Web of Science, CINAHL, PsychINFO, Embase, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library, systematically searched from 2006 to 2023. Keywords and MeSH terms were utilized to identify relevant research published in English. Thirteen articles were included in this review. Five key themes were synthesized from the findings, including positive outlook, receiving support, side effects, concerns about efficacy, and unmet information needs. The review underscores the importance for healthcare providers, particularly nurses, to focus on providing comprehensive information about chemotherapy treatment to patients. Adopting recommended strategies may assist patients in clinical practice settings in enhancing adherence to chemotherapy treatment and improving health outcomes for individuals living with cancer.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Cancer can affect anyone and is recognized as a chronic disease characterized by abnormal cell multiplication in the body [ 1 ]. While cancer is prevalent worldwide, approximately 70% of cancer-related deaths occur in low- to middle-income nations [ 1 ]. Disparities in cancer outcomes are primarily attributed to variations in the accessibility of comprehensive diagnosis and treatment among countries [ 1 , 2 ]. Cancer treatment comes in various forms; however, chemotherapy is the most widely used approach [ 3 ]. Patients undergoing chemotherapy experience both disease-related and treatment-related adverse effects, significantly impacting their quality of life [ 4 ]. Despite these challenges, many cancer patients adhere to treatment in the hope of survival [ 5 ]. However, some studies have shown that concerns about treatment efficacy may hinder treatment adherence [ 6 ]. Adherence is defined as “the extent to which a person’s behaviour aligns with the recommendations of healthcare providers“ [ 7 ]. Additionally, treatment adherence is influenced by the information provided by healthcare professionals following a cancer diagnosis [ 8 ]. Patient experiences suggest that the decision to adhere to treatment is often influenced by personal factors, with family support playing a crucial role [ 8 ]. Furthermore, providing adequate information about chemotherapy, including its benefits and consequences, can help individuals living with cancer gain a better understanding of the advantages associated with adhering to chemotherapy treatment [ 9 ].
Recognizing the importance of adhering to chemotherapy treatment and understanding the impact of individual experiences of chemotherapy adherence would aid in identifying determinants of adherence and non-adherence that are modifiable through effective interventions [ 10 ]. Recently, systematic reviews have focused on experiences and adherence in breast cancer [ 11 ], self-management of chemotherapy in cancer patients [ 12 ], and the influence of medication side effects on adherence [ 13 ]. However, these reviews were narrow in scope, and to date, no review has integrated the findings of qualitative studies designed to explore both positive and negative experiences regarding chemotherapy treatment adherence. This review aims to synthesize the qualitative literature on chemotherapy adherence within the context of patients’ experiences.
This review was conducted in accordance with the Joanna Briggs Institute [ 14 ] guidelines for systemic review involving meta-aggregation. This review was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42021270459).
Search methods
The searches for peer reviewed publications in English from January 2006-September 2023 were conducted by using keywords, medical subject headings (MeSH) terms and Boolean operators ‘AND’ and ‘OR’, which are presented in the table in Appendix 1 . The searches were performed in a systematic manner in core databases such including Embase, Medline, PsycINFO, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Scopus and the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI). The search strategy was developed from keywords and medical subject headings (MeSH) terms. Librarian’s support and advice were sought in forming of the search strategies.
Study selection and inclusion criteria
The systematic search was conducted on each database and all articles were exported to Endnote and duplicates records were removed. Then, title and abstract of the full text was screened by two independent reviewers against the inclusion criteria. For this review, populations were patients aged 18 and over with cancer, the phenomenon of interest was experiences on chemotherapy adherence and context was considered as hospitals, communities, rehabilitation centres, outpatient clinics, and residential aged care. All peer-reviewed qualitative study design were also considered for inclusion. Studies included in this review were classified as primary research, published in English since 2006, some intervention implemented to improve adherence to treatment. This review excluded any studies that related to with cancer and mental health condition, animal studies and grey literature.
Quality appraisal and data extraction
The JBI Qualitative Assessment and Review Instrument for qualitative studies was used to assess the methodological quality of the included studies, which was conducted by the primary and second reviewers independently. There was no disagreement between the reviews. The qualitative data on objectives, study population, context, study methods, and the phenomena of interest and findings form the included studies were extracted.
Data synthesis
The meta-aggregation approach was used to combine the results with similar meaning. The primary and secondary reviewers created categories based on the meanings and concept. These categories were supported by direct quotations from participants. The findings were assess based on three levels of evidence, including unequivocal, credible, and unsupported [ 15 , 16 ]. Findings with no quotation were not considered for synthesis in this review. The categories and findings were also discussed by the third and fourth reviewers until a consensus was reached. The review was approved by the Edith Cowan University Human Research Ethics Committee (2021–02896).
Study inclusion
A total of 4145 records were identified through a systematic search. Duplicates ( n = 647) were excluded. Two independent reviewers conducted screening process. The remaining articles ( n = 3498) were examined for title and abstract screening. Then, the full text screening conducted, yielded 13 articles to be included in the final synthesis see Appendix 2 .
Methodological quality of included studies
All included qualitative studies scored between 7 and 9, which is displayed in Appendix 3 . The congruity between the research methodology and the research question or objectives, followed by applying appropriate data collection and data analysis were observed in all included studies. Only one study [ 17 ] indicated the researcher’s statement regarding cultural or theoretical perspectives. Three studies [ 18 , 19 , 20 ] identified the influence of the researcher on the research and vice-versa.
Characteristics of included studies
Most of studies conducted semi-structured and in-depth interviews, one study used narrative stories [ 19 ], one study used focus group discussion [ 21 ], and one study combined focus group and interview [ 22 ] to collect data. All studies conducted outpatient’s clinic, community, or hospital settings [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 ]. The study characteristics presented in Appendix 4 .
Review findings
Eighteen findings were extracted and synthesised into five categories: positive outlook, support, side effects, concern about efficacy and unmet information needs.
Positive outlook
Five studies discussed the link between positivity and hope and chemotherapy adherence [ 19 , 20 , 23 , 27 , 28 ]. Five studies commented that feeling positive and avoid the negativity and worry could encourage people to adhere in their mindset chemotherapy: “ I think the main thing for me was just keeping a positive attitude and not worrying, not letting myself worry about it ” [ 20 ]. Participants also considered the positive thoughts as a coping mechanism, that would help them to adhere and complete chemotherapy: “ I’m just real positive on how everything is going. I’m confident in the chemo, and I’m hoping to get out of her soon ” [ 23 ]. Viewing chemotherapy as part of their treatment regimen and having awareness of negative consequences of non-adherence to chemotherapy encouraged them to adhere chemotherapy: “ If I do not take medicine, I do not think I will be able to live ” [ 28 ]. Adhering chemotherapy was described as a survivor tool which helped people to control cancer-related symptoms: “ it is what is going to restore me. If it wasn’t this treatment, maybe I wasn’t here talking to you. So, I have to focus in what he is going to give me, life !” [ 27 ]. Similarly, people accepted the medical facts and prevent their life from worsening; “ without the treatment, it goes the wrong way. It is hard, but I have accepted it from the beginning, yes. This is how it is. I cannot do anything about it. Just have to accept it ” [ 19 ].
Finding from six studies contributed to this category [ 20 , 21 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 29 ]. Providing support from families and friends most important to the people. Receiving support from family members enhanced a sense responsibility towards their families, as they believed to survive for their family even if suffered: “ yes, I just thought that if something comes back again and I say no, then I have to look my family and friends in the eye and say I could have prevented it, perhaps. Now, if something comes back again, I can say I did everything I could. Cancer is bad enough without someone saying: It’s your own fault!!” [ 29 ]. Also, emotional support from family was described as important in helping and meeting their needs, and through facilitation helped people to adhere chemotherapy: “ people who genuinely mean the support that they’re giving […] just the pure joy on my daughter’s face for helping me. she was there day and night for me if I needed it, and that I think is the main thing not to have someone begrudgingly looking after you ” [ 20 ]. Another study discussed the role family, friends and social media as the best source of support during their treatment to adhere and continue “ I have tons of friends on Facebook, believe it or not, and it’s amazing how many people are supportive in that way, you know, just sending get-well wishes. I can’t imagine going through this like 10 years ago whenever stuff like that wasn’t around ” [ 23 ]. Receiving support from social workers was particularly helpful during chemotherapy in encouraging adherence to the chemotherapy: “ the social worker told me that love is courage. That was a huge encouragement, and I began to encourage myself ” [ 25 ].
Side effects
Findings from five studies informed this category [ 17 , 21 , 22 , 25 , 26 ]. Physical side effects were described by some as the most unpleasure experience: “ the side effects were very uncomfortable. I felt pain, fatigue, nausea, and dizziness that limited my daily activities. Sometimes, I was thinking about not keeping to my chemotherapy schedule due to those side effect ” [ 17 ]. The impact of side effects affected peoples’ ability to maintain their independence and self-care: “ I couldn’t walk because I didn’t have the energy, but I wouldn’t have dared to go out because the diarrhoea was so bad. Sometimes I couldn’t even get to the toilet; that’s very embarrassing because you feel like you’re a baby ” [ 26 ]. Some perceived that this resulted in being unable to perform independently: “ I was incredibly weak and then you still have to do things and you can’t manage it ” [ 22 ]. These side effect also decreased their quality of life “ I felt nauseated whenever I smelled food. I simply had no appetite when food was placed in front of me. I lost my sense of taste. Food had no taste anymore ” [ 25 ]. Although, the side effects impacted on patients´ leisure and free-time activities, they continued to undertake treatment: “ I had to give up doing the things I liked the most, such as going for walks or going to the beach. Routines, daily life in general were affected ” [ 21 ].
Concern about efficacy
Findings form four studies informed this category [ 17 , 18 , 24 , 28 ]. Although being concerned about the efficacy of the chemotherapy and whether or not chemotherapy treatment would be successful, one participant who undertook treatment described: “the efficacy is not so great. It is said to expect about 10% improvement, but I assume that it declines over time ” [ 28 ]. People were worried that such treatment could not cure their cancer and that their body suffered more due to the disease: “ I was really worried about my treatment effectiveness, and I will die shortly ” [ 17 ]. There were doubts expressed about remaining the cancer in the body after chemotherapy: “ there’s always sort of hidden worries in there that whilst they’re not actually taking the tumour away, then you’re wondering whether it’s getting bigger or what’s happening to it, whether it’s spreading or whatever, you know ” [ 24 ]. Uncertainty around the outcome of such treatment, or whether recovering from cancer or not was described as: “it makes you feel confused. You don’t know whether you are going to get better or else whether the illness is going to drag along further” [ 18 ].
Unmet information needs
Five studies contributed to this category [ 17 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 26 ]. The need for adequate information to assimilate information and provide more clarity when discussing complex information were described. Providing information from clinicians was described as minimal: “they explain everything to you and show you the statistics, then you’re supposed to take it all on-board. You could probably go a little bit slower with the different kinds of chemo and grappling with these statistics” [ 26 ]. People also used the internet search to gain information about their cancer or treatments, “I’ve done it (consult google), but I stopped right away because there’s so much information and you don’t know whether it’s true or not ” [ 21 ]. The need to receive from their clinicians to obtain clearer information was described as” I look a lot of stuff up online because it is not explained to me by the team here at the hospital ” [ 23 ]. Feeling overwhelmed with the volume of information could inhibit people to gain a better understanding of chemotherapy treatment and its relevant information: “ you don’t absorb everything that’s being said and an awful lot of information is given to you ” [ 22 ]. People stated that the need to know more information about their cancer, as they were never dared to ask from their clinicians: “ I am a low educated person and come from a rural area; I just follow the doctor’s advice for my health, and I do not dare to ask anything” [ 17 ].
The purpose of this review was to explore patient’s experiences about the chemotherapy adherence. After finalizing the searches, thirteen papers were included in this review that met the inclusion criteria.
The findings of the present review suggest that social support is a crucial element in people’s positive experiences of adhering to chemotherapy. Such support can lead to positive outcomes by providing consistent and timely assistance from family members or healthcare professionals, who play vital roles in maintaining chemotherapy adherence [ 30 ]. Consistent with our study, previous research has highlighted the significant role of family members in offering emotional and physical support, which helps individuals cope better with chemotherapy treatment [ 31 , 32 ]. However, while receiving support from family members reinforces individuals’ sense of responsibility in managing their treatment and their family, it also instils a desire to survive cancer and undergo chemotherapy. One study found that assuming self-responsibility empowers patients undergoing chemotherapy, as they feel a sense of control over their therapy and are less dependent on family members or healthcare professionals [ 33 ]. A qualitative systematic review reported that support from family members enables patients to become more proactive and effective in adhering to their treatment plan [ 34 ]. This review highlights the importance of maintaining a positive outlook and rational beliefs as essential components of chemotherapy adherence. Positive thinking helps individuals recognize their role in chemotherapy treatment and cope more effectively with their illness by accepting it as part of their treatment regimen and viewing it as a tool for survival. This finding is supported by previous studies indicating that positivity and positive affirmations play critical roles in helping individuals adapt to their reality and construct attitudes conducive to chemotherapy adherence [ 35 , 36 ]. Similarly, maintaining a positive mindset can foster more favourable thoughts regarding chemotherapy adherence, ultimately enhancing adherence and overall well-being [ 37 ].
This review identified side effects as a significant negative aspect of the chemotherapy experience, with individuals expressing concerns about how these side effects affected their ability to perform personal self-care tasks and maintain independent living in their daily lives. Previous studies have shown that participants with a history of chemotherapy drug side effects were less likely to adhere to their treatment regimen due to worsening symptoms, which increased the burden of medication side effects [ 38 , 39 ]. For instance, cancer patients who experienced minimal side effects from chemotherapy were at least 3.5 times more likely to adhere to their treatment plan compared to those who experienced side effects [ 40 ]. Despite experiencing side effects, patients were generally willing to accept and adhere to their treatment program, although one study in this review indicated that side effects made some patients unable to maintain treatment adherence. Side effects also decreased quality of life and imposed restrictions on lifestyle, as seen in another study where adverse effects limited individuals in fulfilling daily commitments and returning to normal levels of functioning [ 41 ]. Additionally, unmet needs regarding information on patients’ needs and expectations were common. Healthcare professionals were considered the most important source of information, followed by consultation with the internet. Providing information from healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, can support patients effectively and reinforce treatment adherence [ 42 , 43 ]. Chemotherapy patients often preferred to base their decisions on the recommendations of their care providers and required adequate information retention. Related studies have highlighted that unmet needs among cancer patients are known factors associated with chemotherapy adherence, emphasizing the importance of providing precise information and delivering it by healthcare professionals to improve adherence [ 44 , 45 ]. Doubts about the efficacy of chemotherapy treatment, as the disease may remain latent, were considered negative experiences. Despite these doubts, patients continued their treatment, echoing findings from a study where doubts regarding efficacy were identified as a main concern for chemotherapy adherence. Further research is needed to understand how doubts about treatment efficacy can still encourage patients to adhere to chemotherapy treatment.
Strengths and limitation
The strength of this review lies in its comprehensive search strategy across databases to select appropriate articles. Additionally, the use of JBI guidelines provided a comprehensive and rigorous methodological approach in conducting this review. However, the exclusion of non-English studies, quantitative studies, and studies involving adolescents and children may limit the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, this review focuses solely on chemotherapy treatment and does not encompass other types of cancer treatment.
Conclusion and practical implications
Based on the discussion of the findings, it is evident that maintaining a positive mentality and receiving social support can enhance chemotherapy adherence. Conversely, experiencing treatment side effects, concerns about efficacy, and unmet information needs may lead to lower adherence. These findings present an opportunity for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, to develop standardized approaches aimed at facilitating chemotherapy treatment adherence, with a focus on providing comprehensive information. By assessing patients’ needs, healthcare professionals can tailor approaches to promote chemotherapy adherence and improve the survival rates of people living with cancer. Raising awareness and providing education about cancer and chemotherapy treatment can enhance patients’ understanding of the disease and its treatment options. Utilizing videos and reading materials in outpatient clinics and pharmacy settings can broaden the reach of educational efforts. Policy makers and healthcare providers can collaborate to develop sustainable patient education models to optimize patient outcomes in the context of cancer care. A deeper understanding of individual processes related to chemotherapy adherence is necessary to plan the implementation of interventions effectively. Further research examining the experiences of both adherent and non-adherent patients is essential to gain a comprehensive understanding of this topic.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. on our submission system as well.
World Health Organization. Cancer 2021 [ https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer .
Klapheke A, Yap SA, Pan K, Cress RDDHSDCA. Sociodemographic disparities in chemotherapy treatment and impact on survival among patients with metastatic bladder cancer. Urologic Oncology: Seminars Original Investigations. 2018;36(6):19–308.
Article Google Scholar
Moth EB, Kiely BE, Naganathan V, Martin A, Blinman P. How do oncologists make decisions about chemotherapy for their older patients with cancer? A survey of Australian oncologists. Support Care Cancer. 2018;26(2):451–60.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Khamboon T, Pakanta I. Intervention for symptom cluster management of fatigue, loss of appetite, and anxiety among patients with lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Asia-Pacific J Oncol Nurs. 2021;8(3):267–75.
Garcia ACM, Camargos Junior JB, Sarto KK, Silva Marcelo CAd, Paiva EMC, Nogueira DA, Mills J. Quality of life, self-compassion and mindfulness in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2021;51:N.PAG-N.PAG.
Horne R, Chapman SCE, Parham R, Freemantle N, Forbes A, Cooper V. Understanding patients’ adherence-related beliefs about Medicines prescribed for long-term conditions: a Meta-Analytic Review of the necessity-concerns Framework. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12):e80633.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
WHO. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organisation; 2003.
Google Scholar
Warby A, Dhillon HM, Kao S, Vardy JL. A survey of patient and caregiver experience with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Support Care Cancer. 2019;27(12):4675–86.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Arunachalam SS, Shetty AP, Panniyadi N, Meena C, Kumari J, Rani B, et al. Study on knowledge of chemotherapy’s adverse effects and their self-care ability to manage - the cancer survivors impact. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 2021;11:100765.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Nizet P, Touchefeu Y, Pecout S, Cauchin E, Beaudouin E, Mayol S, et al. Exploring the factors influencing adherence to oral anticancer drugs in patients with digestive cancer: a qualitative study. Support Care Cancer. 2022;30(3):2591–604.
Clancy C, Lynch J, Oconnor P, Dowling M. Breast cancer patients’ experiences of adherence and persistence to oral endocrine therapy: a qualitative evidence synthesis. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2020;44.
Magalhães B, Fernandes C, Lima L, Martinez-Galiano JM, Santos C. Cancer patients’ experiences on self-management of chemotherapy treatment-related symptoms: A systematic review and thematic synthesis. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2020;49.
Peddie N, Agnew S, Crawford M, Dixon D, MacPherson I, Fleming L. The impact of medication side effects on adherence and persistence to hormone therapy in breast cancer survivors: a qualitative systematic review and thematic synthesis. Breast. 2021;58:147–59.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ: Br Med J. 2009;339(7716):332–6.
Joanna Briggs Institute. The Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools for use in JBI systematic reviews. Checklist for qualitative research. 2017.
Zachary M, Kylie P, Craig L, Edoardo A, Alan P. Establishing confidence in the output of qualitative research synthesis: the ConQual approach. BMC Med Res Methodol [Internet]. 2014;14(1):108.
Iskandarsyah A, de Klerk C, Suardi DR, Soemitro MP, Sadarjoen SS, Passchier J. Psychosocial and cultural reasons for Delay in seeking help and Nonadherence to treatment in Indonesian women with breast Cancer: a qualitative study. Health Psychol. 2014;33(3):214–21.
Chircop D, Scerri J. The lived experience of patients with Non-hodgkin’s lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2018;35:117–21.
Kvåle K, Synnes O. Living with life-prolonging chemotherapy—control and meaning‐making in the tension between life and death. Eur J Cancer Care. 2018;27(1):1.
Staneva AA, Beesley VL, Niranjan N, Gibson AF, Rowlands I, Webb PM. I wasn’t gonna let it stop me: exploring women’s experiences of getting through chemotherapy for ovarian cancer. Cancer Nurs. 2019;42(2):E31–8.
Talens A, Guilabert M, Lumbreras B, Aznar MT, López-Pintor E. Medication Experience and Adherence to Oral Chemotherapy: A Qualitative Study of Patients’ and Health Professionals’ Perspectives. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8).
Dumas L, Lidington E, Appadu L, Jupp P, Husson O, Banerjee S, et al. Exploring older women’s attitudes to and experience of treatment for advanced ovarian cancer: a qualitative phenomenological study. Cancers. 2021;13(6):1207.
Albrecht TA, Keim-Malpass J, Boyiadzis M, Rosenzweig M. Psychosocial experiences of young adults diagnosed with acute leukemia during hospitalization for induction chemotherapy treatment. J Hospice Palliat Nurs. 2019;21(2):167–73.
Beaver K, Williamson S, Briggs J. Exploring patient experiences of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2016;20:77–86.
Chou J-F, Lu YY. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy: the lived experiences of Taiwanese patients with ovarian cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2019;23(6):E100–6.
Farrell C, Heaven C. Understanding the impact of chemotherapy on dignity for older people and their partners. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2018;36:82–8.
Wakiuchi J, Silva Marcon S, de Oliveira DC, Aparecida Sales C. Rebuilding subjectivity from the experience of cancer and its treatment. Revista Brasileira De Enfermagem. 2019;72(1):125–33.
Yagasaki K, Komatsu H, Takahashi T. Inner conflict in patients receiving oral anticancer agents: a qualitative study. BMJ Open [Internet]. 2015; 5(4).
Gassmann C, Kolbe N, Brenner A. Experiences and coping strategies of oncology patients undergoing oral chemotherapy: first steps of a grounded theory study. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2016;23:106–14.
Tang GX, Yan PP, Yan CL, Fu B, Zhu SJ, Zhou LQ, et al. Determinants of suicidal ideation in gynecological cancer patients. Psycho-oncology. 2016;25(1):97–103.
Oven Ustaalioglu B, Acar E, Caliskan M. The predictive factors for perceived social support among cancer patients and caregiver burden of their family caregivers in Turkish population. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2018;22(1):63–9.
Levkovich I, Cohen M, Karkabi K. The experience of fatigue in breast Cancer patients 1–12 Month Post-chemotherapy: a qualitative study. Behav Med. 2019;45(1):7–18.
Simchowitz B, Shiman L, Spencer J, Brouillard D, Gross A, Connor M, Weingart SN. Perceptions and experiences of patients receiving oral chemotherapy. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2010;14(4):447–53.
Rashidi A, Kaistha P, Whitehead L, Robinson S. Factors that influence adherence to treatment plans amongst people living with cardiovascular disease: a review of published qualitative research studies. Int J Nurs Stud 2020;110(103727).
Aydogan U, Doganer YC, Komurcu S, Ozturk B, Ozet A, Saglam K. Coping attitudes of cancer patients and their caregivers and quality of life of caregivers. Indian J Palliat Care. 2016;22(2):150–6.
Langford DJ, Morgan S, Cooper B, Paul S, Kober K, Wright F, et al. Association of personality profiles with coping and adjustment to cancer among patients undergoing chemotherapy. Psycho-oncology. 2020;29(6):1060–7.
Jamie MJ, Pensak NA, Sporn NJ, MacDonald JJ, Lennes IT, Safren SA et al. Treatment satisfaction and adherence to oral chemotherapy in patients with Cancer. J Oncol Pract. 2017;13(2).
Tsai Y-F, Huang W-C, Cho S-F, Hsiao H-H, Liu Y-C, Lin S-F, et al. Side effects and medication adherence of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in Taiwan. Medicine. 2018;97(26):415.
D S, M P, G R, S H. Importance of medication adherence and factors affecting it. IP Int J Compr Adv Pharmacolog. 2020;3(2):69–77.
Bekalu YE, Wudu MA, Gashu AW. Adherence to Chemotherapy and Associated factors among patients with Cancer in Amhara Region, Northeastern Ethiopia, 2022. A cross-sectional study. Cancer Control. 2023;30.
Hsu H-C, Liou W-S, Chiang A-J, Tsai S-Y, Jeang S-R, Wu S-L, et al. Longitudinal perceptions of the side effects of chemotherapy in patients with gynecological cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2017;25(11):3457–64.
Gow K, Rashidi A, Whithead L. Factors influencing medication adherence among adults living with diabetes and comorbidities: a qualitative systematic review. Curr Diab Rep. 2023:1–7.
Rashidi A, Whitehead L, Kaistha P. Nurses’ perceptions of factors influencing treatment engagement among patients with cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review. BMC Nurs. 2021;20(1):251.
Zebrack BJ, Block R, Hayes-Lattin B, Embry L, Aguilar C, Meeske KA, et al. Psychosocial service use and unmet need among recently diagnosed adolescent and young adult cancer patients. Cancer. 2013;119(1):201–14.
Timmers L, Boons CCLM, van den Verbrugghe M, Van Hecke A, Hugtenburg JG. Supporting adherence to oral anticancer agents: clinical practice and clues to improve care provided by physicians, nurse practitioners, nurses and pharmacists. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1).
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing and Midwifery, Edith Cowan University, 270 Joondalup Drive, Joondalup, Perth, WA, 6027, Australia
Amineh Rashidi, Susma Thapa, Wasana Sandamali Kahawaththa Palliya Guruge & Shubhpreet Kaur
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
First author (AR) and second author (ST) conceived the review and the second author oversight for all stages of the review provided by the second author. All authors (AR), (ST), (WG) and (SK) undertook the literature search. Data extraction, screening the included papers and quality appraisal were undertaken by all authors (AR), (ST), (WG) and (SK). First and second authors (AR) and (ST) analysed the data and wrote the first draft of the manuscript and revised the manuscript and all authors (AR), (ST), (WG) and (SK) approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Amineh Rashidi .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The review was approved by the Edith Cowan University Human Research Ethics Committee (2021–02896). A proposal for the systematic review was assessed by the Edith Cowan University Human Research Ethics Committee and deemed not appropriate for full ethical review. However, a Data Management Plan (2021-02896-RASHIDI) was approved and monitored as part of this procedure. Raw data was extracted from the published manuscripts and authors could not identify individual participants during or after this process.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, supplementary material 4, supplementary material 5, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rashidi, A., Thapa, S., Kahawaththa Palliya Guruge, W. et al. Patient experiences: a qualitative systematic review of chemotherapy adherence. BMC Cancer 24 , 658 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-024-12353-z
Download citation
Received : 17 November 2023
Accepted : 07 May 2024
Published : 30 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-024-12353-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Chemotherapy treatment
- Medication adherence
- Qualitative research
- Patients experiences
ISSN: 1471-2407
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Qualitative research for international business
- Perspective
- Published: 15 June 2011
- Volume 42 , pages 582–590, ( 2011 )
Cite this article

- Yves Doz 1
13k Accesses
324 Citations
Explore all metrics
Qualitative research in international business has been rare, the main research streams of the field relying more on quantitative methods. This paper first outlines why qualitative research has been scant. It then presents areas, such as theory building, where qualitative research could make a substantial contribution. Third, it reviews approaches to high standards of qualitative research and criteria for evaluating qualitative research. Finally, some possible research areas where qualitative research might prove fruitful are suggested.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Putting qualitative international business research in context(s)

A Reviewer’s Perspective: Which Mistakes Do Authors Often Make in Qualitative International Business Research?
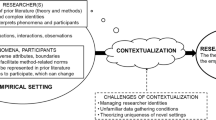
Something borrowed, something new: Challenges in using qualitative methods to study under-researched international business phenomena
A parallel may be drawn here with the transitory role of the “International Division” in US multinational companies: when the attention of the business divisions was primarily home-centric (US-centric) international divisions provided a countervailing power, bringing management attention to international markets. Once a company internationalized, international divisions were disbanded, business divisions became “global”, but attention often remained or reverted to being home-centric.
Of course, the boundaries between qualitative and quantitative research can at times be fuzzy, for instance around text analysis or in quantitative analysis of case data, such as in the chronology of events.
Christopher Bartlett is one of the very few researchers in IB to have explicitly combined the development of research cases and teaching cases in a joint effort. For instance, cumulatively, the whole stream of cases on Procter and Gamble he wrote over a number of years constitutes a set of very insightful snapshots of the internationalization process of a major multinational (P&G, Vizir, Ariel Ultra, SKII). Together with Sumantra Ghoshal, who was the theory builder where Bartlett was the empiricist, they contributed significantly to our understanding of multinational companies.
The risk of communicating evidence via teaching cases is obvious: under the appearance of a story a teaching case usually contains a strong theoretical or conceptual hidden structure it is designed to surface, illustrate and communicate in a pedagogical process.
One cannot help but recall a revealing anecdote. American researchers studying the aircraft industry had a long day of hard research interviews in a windowless meeting room at Boeing, surviving on coffee and snacks. The same research team, upon flying to Toulouse, France, to meet Airbus management, was taken directly to a three star restaurant around noon and treated to a lavish lunch. Finally, around four in the afternoon, one of the researchers asked the seniormost Airbus executive about going to his office and having the interview, to which the befuddled executives retorted “Oh, we had quite a long interview over lunch, didn't we? Let me take you back to the airport”. At that point the researchers deeply regretted having exchanged opening their note pads for several glasses of wine! Their memory was blurry.
Aguilar, F. J. 1973. Daag Europe, Harvard Business School Case 9-374-037.
Aharoni, Y. 1966. The foreign investment decision process. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Google Scholar
Allison, G. 1971. Essence of decision: Explaining the Cuban missile crisis. Boston, MA: Little Brown.
Axelrod, R. 1984. The evolution of cooperation. New York: Basic Books.
Axelrod, R. 1997. The complexity of cooperation: Agent-based models of competition and collaboration. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Bartlett, C. 1979. Multinational structural evolution: The changing decision environment in international divisions, Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, Harvard Business School, Boston, MA.
Bartlett, C., & Ghoshal, S. 1989. Managing across borders. Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press.
Bower, J. L. 1970. Managing the resource allocation process: A study of corporate planning and investment. Boston, MA, Harvard Business School Press.
Brannen, M. Y., & Peterson, M. 2009. Merging without alienating: Interventions promoting cross-cultural organizational integration and their limitations. Journal of International Business Studies, 40 (3): 468–489.
Article Google Scholar
Brown, S., & Eisenhardt, K. 1997. The art of continuous change: Linking complexity theory and time-paced evolution in relentlessly shifting organizations. Administrative Science Quarterly, 42 (1): 1–34.
Buckley, P. J. 2002. Is the international business research agenda running out of steam? Journal of International Business Studies, 33 (2): 365–373.
Buckley, P. J., & Casson, M. C. 2009. The internalisation theory of the multinational enterprise: A review of the progress of a research agenda after 30 years. Journal of International Business Studies, 40 (9): 1563–1580.
Buckley, P. J., & Lessard, D. R. 2005. Regaining the edge for international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 36 (6): 595–599.
Burgelman, R. 1994. Fading memories: A process theory of strategic business exit in dynamic environments. Administrative Science Quarterly, 39 (1): 24–56.
Chandler, A. 1962. Strategy and structure: Chapters in the history of industrial enterprise. Boston, MA: MIT Press.
Cheng, J. L. C. 2007. Critical issues in international management research: An agenda for future advancement. European Journal of International Management, 1 (1/2): 23–38.
Christensen, C. 1997. The innovators’ dilemma: When new technologies cause great firms to fail. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
DiMaggio, P. 1995. Comments on “what theory is not”. Administrative Science Quarterly, 40 (3): 391–397.
Dore, 1973. British factory-Japanese factory: The origins of national diversity in industrial relations. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Doz, Y. 1976. National policies and multinational management, Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Harvard Business School, Boston, MA.
Doz, Y. 2004. Toward a managerial theory of the MNC. Advances in International Management, 16: 3–30.
Doz, Y., & Prahalad, C. K. 1991. Managing DMNCs: A search for a new paradigm. Strategic Management Journal, 12 (S1): 145–164.
Dubois, A., & Gibbert, M. 2010. From complexity to transparency: Managing the interplay between theory, method and empirical phenomena in IMM case studies. Industrial Marketing Management, 38 (1): 129–136.
Eisenhardt, K. 1989. Building theories from case study research. Academy of Management Review, 14 (4): 532–550.
Ghoshal, S., & Bartlett, C. 1994. Linking organizational context and managerial action: The dimensions of quality of management. Strategic Management Journal, 15 (S2): 91–112.
Gibbert, M., & Ruigrok, W. 2010. The “what” and “how” of case study rigor: Three strategies based on published work. Organizational Research Methods, 13 (4): 710–737.
Gibbert, M., Ruigrok, W., & Wicki, B. 2008. What passes as a rigorous case study? Strategic Management Journal, 29 (13): 1465–1474.
Glaser, B., & Strauss, A. 1967. The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Chicago, IL: Aldine Transaction.
Gray, B. 1989. Collaborating: Finding common ground for multiparty problems. San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass Business and Management Series.
Johanson, J., & Vahlne, J.-E. 1977. The internationalization process of the firm: A model of Knowledge development and increasing foreign market commitments. Journal of International Business Studies, 8 (1): 23–32.
Kogut, B., & Zander, U. 1993. Knowledge of the firm and the evolutionary theory of the multinational corporation. Journal of International Business Studies, 24 (4): 625–645.
Mintzberg, H., & Waters, J. 1985. Of strategies, deliberate and emergent. Strategic Management Journal, 6 (3): 257–272.
Peng, M. 2004. Identifying the big question in international business research. Journal of Business Studies, 35 (2): 99–108.
Pettigrew, A. 1973. The politics of organizational decision-making. London: Tavistock Press.
Piekkari, R., & Welch, C. (Eds) 2010. Rethinking the case study in international business research. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar.
Piekkari, R., Welch, C., & Paavilainen, E. 2009. The case study as disciplinary convention: Evidence from international business journals. Organizational Research Methods, 12 (3): 567–589.
Poole, M., Van de Ven, A., Dooley, K., & Holmes, M. 2000. Organizational change and innovation processes: Theory and methods for research. New York: Oxford University Press.
Prahalad, C. K. 1975. The strategic process in a multinational corporation, Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation, Harvard Business School, Boston, MA.
Pratt, M. 2009. For the lack of a boilerplate: Tips on writing up (and reviewing) qualitative research. Academy of Management Journal, 52 (5): 856–862.
Quinn, J. B. 1980. Strategies for change: Logical incrementalism. Homewood, IL: Irwin Press.
Rangan, S. 2009. The influence of macro structure on the foreign market performance of transnational firms: The value of IGO connections, export dependence, and immigration links. Administrative Science Quarterly, 54 (2): 229–267.
Siggelkow, N. 2007. Persuasion with case studies. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (1): 20–24.
Thomas, D., Brannen, M. Y., & Garcia, D. 2010. Bicultural individuals and intercultural effectiveness. European Journal of Cross-cultural Competence and Management, 1 (4): 315–333.
Van de Ven, A. 2007. Engaged scholarship: A guide for organizational and social research. New York: Oxford University Press.
Van Maanen, J. 1988. Tales from the field: On writing ethnography. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Weick, K. 1989. Theory construction as disciplined imagination. Academy of Management Review, 14 (4): 516–531.
Weick, K. 1993. The collapse of sensemaking in organizations: The Mann Gulch disaster. Administrative Science Quarterly, 38 (4): 628–652.
Weick, K. 2007. The generative properties of richness. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (1): 14–19.
Wilkins, M. 1970. The emergence of multinational enterprise: American business abroad from the colonial era to 1914. Boston, MA: Harvard University Press.
Wilkins, M. 1974. The maturing of multinational enterprise: American business abroad from 1914 to 1970. Boston, MA: Harvard University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Wilkins, M. 1997. The conceptual domain of international business inquiry. In B. Tyne & D. Nigh (Eds), International business: An emerging vision. Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press.
Yin, R. K. 1989. Case study research: Design and methods (applied social research methods). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Yin, R. K. 1994. Case study research: Design and methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
INSEAD, Boulevard de Constance, Fontainebleau Cedex, France
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Additional information
Accepted by Rosalie Tung, Area Editor, 24 February 2011. This paper was single-blind reviewed. It has been with the author for one revision .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Doz, Y. Qualitative research for international business. J Int Bus Stud 42 , 582–590 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2011.18
Download citation
Received : 29 October 2010
Revised : 24 February 2011
Accepted : 24 February 2011
Published : 15 June 2011
Issue Date : 01 June 2011
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2011.18
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- research methods
- theory building
- qualitative research
- international business research agenda
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
The factors of job crafting in emergency nurses: regression models versus qualitative comparative analysis
- Yu Wang 2 ,
- Qiaofang Yang 2 ,
- Luwen Wang 3 ,
- Qingwei Zhang 2 &
- Yingli Li 1
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 369 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Job crafting is defined as a series of proactive behaviors exhibited by employees in order to balance work resources and needs, which has a significant positive impact on the nurses. It is necessary to find the core factors that influence the job crafting, as emergency nurses deal with the most complex tasks, so as to improve their job satisfaction.
To investigate the core factors of job crafting among emergency nurses.
A cross-sectional design was used in the study. A total of 255 nurses were recruited from two hospitals in Zhengzhou and Shenzhen, China in December 2021. 255 nurses completed an online questionnaire. Hierarchical regression models and fsQCA models were used to explore the factors influencing job crafting among emergency nurses and helped us to identify core factors.
The hierarchical regression model and the fsQCA model found that the occupational benefit, psychological empowerment, and research experience were the core factors affecting their job crafting. Job involvement was not significant in the regression model, but the QCA model indicated that it needs to be combined with other factors to impact on job crafting. The QCA model uncovered seven key conditional configurations that led to high and low job crafting among emergency nurses, explaining 80.0% of the results for high job crafting and 82.6% of the results for the low job crafting, respectively.
Conclusions
The results of this study provide valuable insights into the job crafting experienced by emergency nurses. Junior emergency nurses should be granted a high level of psychological empowerment without assigning them overly complex tasks, such as research tasks, as these challenges can stop their job crafting. Intermediate and senior emergency nurses, on the other hand, can be assigned research tasks coupled with high psychological empowerment to enhance their job crafting.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
As diseases become more complex and technology evolves rapidly, nursing work is changing, which has posed new tasks and demands for the nurses these days. It was noted that employees should work stepwise in the traditional human resource management system. However, in recent years, researchers have encouraged employees to change their jobs in line with the reality of their work. ‘Job crafting’ is an employee-focused approach to job redesigning [ 1 ].Job crafting is defined as a series of proactive behaviors exhibited by employees in order to balance work resources and needs, with the aim of aligning their work with their own preferences, motivations, and passions [ 2 ].YEPES-BALDÓ surveyed 530 Spanish nurses and found that the job crafting score was 3.17 ± 0.66 [ 3 ]. BAGHDADI conducted a survey among 594 nurses in Saudi Arabia, reporting the job crafting score was 3.54 ± 0.50 [ 4 ]. In summary, it is observed that there are variations in the level of job crafting among nurses, which is generally at a moderate level.
Wrzesniewski first proposed job crafting, suggesting that employees could engage in job crafting in three dimensions: cognitive, task, and relational [ 1 ]. Job demand-resource was further integrated by Tims and Bakker, and it suggested that all working conditions can be classified as job demands or resources [ 5 , 6 ], which includes four dimensions: reducing hindering job demands, increasing challenging job demands, increasing structural job resources and increasing social job resources. Promoting-focused job crafting has been shown to be positively related to job involvement and satisfaction, and negatively related to burnout, depression, and illness [ 7 , 8 ]. Furthermore, studies conducted in the field of career development have shown that promotion-focused job crafting is positively related to career competency and career promotion [ 9 ]. Emergency nurses encounter more complex clinical environments and problems than other departments. The emergency department serves as the first line of defense in hospitals to save patients’ lives. However, it is also the department where adverse events such as nurse-patient disputes and complaints are most likely to occur. According to reports, emergency nurses experience higher occupational stress than other departments, which can lead to dissatisfaction with nursing work among nurses, and even turnout [ 10 ]. This, in turn, will result in a shortage of emergency nurses, further increasing the occupational stress on those remaining in the emergency department. Furthermore, nurses face additional research tasks and pressures in addition to solving clinical problems in China. So, we defined emergency nurse’s hindering and challenging demands as a research experience, professional position, number of night shifts, etc.
Autonomy is an important work feature, as it can be associated with a better capacity to handle stress [ 6 ]. Structural and psychological empowerment are two categories of authority that can give nurses some autonomy at work. Psychological empowerment as an extension of structural empowerment, focuses on the internal feelings of an individual toward organizational empowerment. Spritzer defined psychological empowerment as a sense of control over one’s work environment, which includes the dimensions of impact, meaning, competence, and self-determination [ 11 ]. Increased psychological empowerment of nurse has been shown to lead to job satisfaction and more positive organizational behavior [ 12 ]. The sense of control over their work behaviors can be increased if nurses have a stronger psychological empowerment. They feel more confident acquiring the required knowledge and skills to do their job, and also have a greater perception of their impact on organizational management, decision-making, and performance [ 13 ]. This helps nurses take the initiative toward rebuilding the organizational relationships and actively redesigning work content to address the challenges on the job [ 14 ]. Therefore, we defined the work resources as the level of psychological empowerment given to nurses by their organizations.
Occupational benefits are internal, personal motivators that nurses blend with their good work experiences and cognitive assessments [ 15 ]. It can also result in greater job satisfaction, the promotion of creative behavior, and a reduction in burnout and turnover intentions [ 16 ]. Occupational benefits reflect how satisfied employees are with the organization’s management, which has a significant impact on whether or not they want to stay. According to the JD-R theory, nurses’ job crafting has resulted in favorable occupational benefits for them. Emergency nurses are often faced with critically ill patients, and their nursing work demands a high level of expertise. Correspondingly, the rehabilitation of patients can bring them a sense of accomplishment and self-worth, providing a strong sense of occupational benefits [ 17 ]. In order to continually obtain this feeling, emergency nurses may engage in job crafting to reshape their work.Their practice reflects how they view the rewards and advantages of their profession, which supports their involvement in their work.
Job involvement, as a type of work commitment, is the psychological recognition of an individual’s work. It is more linked with the satisfaction of internal needs.From the perspective of an organization, Pfeffe stated that job involvement is crucial for motivating employees [ 18 ]. However, there is a disagreement at the moment on whether or not job involvement affects individual performance [ 19 ]. On the other hand, some studies have shown that job involvement is the only variable associated with the nurses’ intention to continue working in their current position, not withstanding their work environment [ 20 ]. When demands exceed resources, employees feel immense pressure, leading to negative emotions and affecting job involvement [ 21 ]. Thus, this suggests that work involvement may arise from job crafting. From this, we hypothesized that emergency nurses with high levels of job involvement may pay more attention to the details of work, which in turn identifies work processes or tasks that need to be improved and triggers job crafting. Therefore, it is worth to be further analyzed whether job involvement would have an impact on job crafting.
Due to the growing complexity of the nurses’ work, one antecedent variable cannot fully explain the causes of the findings. Regression model could only examine the net effect of one of the independent variables on outcomes rather than exploring complex causal relationships between the antecedent variables [ 22 ]. The configuration theory is based on the idea of sets, as it allows the analysis of configuration effects generated by multiple conditional variables of the organization’s management [ 23 ]. This study used both regression modeling and fsQCA modeling. fsQCA adds depth by showing complex paths to job crafting, where variables can combine differently to explain outcomes. Even non-significant regression variables can impact job crafting in fsQCA. Combining both methods gives a comprehensive view of why emergency nurses reshape their work, revealing intrinsic motivations. Therefore, the aim of our study is to explore the core factors influencing job crafting in emergency nurses through a hierarchical regression model and fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis.
A convenience sampling method was applied in the study, an online questionnaire was sent to the emergency nurses through a mobile program in the cities of Shenzhen and Zhengzhou, China, in March 2023. The inclusion criteria were: working in the emergency department; working for more than 1 year; voluntary participation, and informed consent. The exclusion criteria were: trainee nurses, vacation nurses. Based on sample size estimation principles, this study calculated the required sample size to be 5–10 times the number of independent variables. We calculated a required sample of 110–220, given 22 independent variables. Considering a 20% invalid questionnaire rate, we distributed 280 questionnaires.
Instruments
General information questionnaire.
The general information questionnaire was designed by the researcher and includes gender, age, monthly income, etc.
Perceived occupational benefits Questionnaire[ 24 ]
The questionnaire contains 5 dimensions and 29 items. The questionnaire had a 5-point Likert scale, with 1 indicating “strongly disagree” and 5 indicating “strongly agree”. No reverse scoring items were available for the scale. The scores represented the nurses’ perception of professional benefits along with a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.96 in the study.
Job crafting Scale[ 2 ]
With 21 items, the scale is scored on a 5-point Likert scale. Here, higher scores indicate better job crafting. The scale comprises four dimensions: increasing structural work resources, increasing social work resources, increasing challenging work demands, and decreasing hindering work demands. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is 0.93 in the study.
Psychological empowerment Scale[ 25 ]
This scale includes 4 dimensions: work meaning, autonomy, self-efficacy, and work influence. Each dimension has 3 items under it, totaling 12 items. The 5-point Likert scale is used, where a higher total score indicates a higher degree of PE. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of this scale was tested to be 0.94.
Job involvement Scale[ 26 ]
The scale consists of 10 items on a 5-point Likert scale, with items 2 and 7 being reverse-scored. The level of score indicates the extent of job involvement. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the scale in the study was tested to be 0.82.
Date collection
Researchers contacted nursing management personnel from various hospitals to obtain their consent and support. Nurses were informed about the research objectives, significance, and principles of anonymity and then shared the questionnaire links to those who agreed to participate. The survey was set up through a survey platform, and to ensure quality, all questions were mandatory. Each nurse gets the link via WeChat and is limited to one response. After the survey concluded, a total of 280 questionnaires were collected. Among them, those questionnaires with identical responses for all items and completion times less than 3 min were excluded. Ultimately, 255 questionnaires were valid, resulting in an effective response rate of 91.07%.
SPSS 24.0 software was used to analyze the data; it was described using frequencies, percentages, or means ± standard deviations, depending on the data type. Comparisons between groups were analyzed using independent samples t-test or one-way ANOVA with a test level of α = 0.05. The paper looks at the amount of variance explained by demographic factors on Job crafting(R 2 ) in the one-way analysis of the first level of the hierarchical regression model. In the second level of the hierarchical regression model, other factors that may affect job crafting are integrated to observe the amount of variance explained variance (ΔR 2 ).
Qualitative comparative analysis (QCA ) is a new method for analysing complex causal relationships in histological problems based on Boolean algebra and set theory.QCA is a new method that combines quantitative and qualitative analysis, providing strong support for studying the configuration problem. Based on variable type, QCA is divided into csQCA, mvQCA, and fsQCA. fsQCA has been selected in this paper to analyze the configuration effects of job crafting factors among emergency nurses. QCA requires the calibration of the original data into the set. Calibration is the process of assigning sets to cases. Sociodemographic variables that were meaningful for univariate analysis were included in the analysis of the fsQCA model. In this case (Research experience: 0 = None; 1 = have), (Professional Position: 0 = Advanced; 0.5 = Intermediate; 1 = Junior). The fuzzy set requires setting three critical values according to the theoretical or conceptual settings: fully affiliated, crossover, and fully unaffiliated, and with the affiliation of the transformed set between 0 and 1. For the continuous variables, the 0.05th, 0.5th and 0.95th percentile of the data were taken and substituted into the Calibrate function (x, fully in, crossover, fully out).It was analyzed whether the antecedent variable was necessary for job crafting in emergency nurses before the sufficient analysis. If the antecedent variable was greater than 0.9 [ 27 ], it was considered necessary. A truth table for sufficient analysis was constructed using fsQCA 3.0, with consistency set to 0.8 and frequency set to 1. If variables appear in both parsimonious and intermediate solutions, they are called core conditions. If they only appear in intermediate solutions, they are called edge conditions [ 28 ].
Descriptive and univariate analysis
A total of 255 nurses were included, of which 228 (89.4%) were female and up to 209 (82.0%) had no research experience. The results demonstrated that research experience and job position were considered influential variables for job crafting among emergency nurses. Also, the differences were all statistically significant ( p < 0.05), as seen in Table 1 .
Hierarchical regression models
A variance variation of 0.047 was obtained after entering the sociodemographic factors into the regression model, with significance in the one-way analysis. In the paper, it was shown that nurses with no research experience had a lower job crafting than nurses with research experience( P <0.05) In the second step, three psychological variables were added, and it was found that a variance variation of 0.283 was obtained. The significant variables were research experience (β=-0.135, p < 0.05), perceived occupational benefits (β = 0.177, p < 0.05), and psychological empowerment (β = 0.317, p < 0.001), as can be seen in Table 2 .
Necessary analysis
The consistency score was considered necessary for evaluating whether the antecedent variable was available as the outcome variable. The consistency score is similar to the significance of the coefficient in a regression model. It represents the extent to which the outcome has to rely on the antecedent variable. In this study, no variable existed as a necessary condition since none of the antecedent variables reached 0.9. Refer to Table 3 for details.
Sufficient analysis
Six conditional configurations that generated high job crafting and six conditional configurations that generated low job crafting were analyzed together. The twelve configurations were sufficient conditions to constitute high and low job crafting for the emergency nurses. The overall solution coverage of high and low job crafting was 0.800 and 0.826, as seen in Table 4 . This shows that the twelve configurations explain 80% of the results for high job crafting and 82.6% for low. The paper remove unique coverage of less than 0.1 for the configuration because it was hard to cover 10% of the samples. Three configurations of high job crafting and four configurations of low job crafting for emergency nurses are obtained.The raw coverage of H1 was 0.106 in the high job crafting configuration, which meant that this configuration could explain 10.6% of the sample.Among the low job crafting configurations, it was found that L2 had the highest raw coverage. The configurations are elaborated as follows: ① H1: high psychological empowerment + high job involvement + junior professional position + no research experience. ② H2: high psychological empowerment + high job involvement + have research experience. ③ H3:high job involvement + high perceived occupational benefits + senior professional position + no research experience. ④ L1: low perceived occupational benefits + senior professional position + no research experience. ⑤ L2: low psychological empowerment + senior professional position + no research experience. ⑥ L3: high job involvement + senior professional position + low perceived occupational benefits. ⑦ L4: low job involvement + senior professional position + research experience.The most relevant pathway or combination to explain low job crafting was L2 (raw coverage = 0.038; consistency = 0.879), which explained 64.3% of the cases. The most relevant pathway or combination to explain high job crafting was H1 (raw coverage = 0.106; consistency = 0.798), which explained 60.1% of the cases.Refer to Table 4 for details.
Discussions
This study explored the effects of sociodemographic variables, psychological empowerment, occupational benefits, and job involvement, on job crafting among the emergency nurses. The majority of existing studies have concentrated on linear regression models. This neglects the complement of other methods, like the fsQCA model [ 29 ]. The study overlooked the synergy between factors if the researcher focuses only on regression models. In helping the researcher to construct intervention plans, the fsQCA models with different pathways formed by the synergy between factors are particularly important [ 30 ]. Regression models indicated that research experience, psychological empowerment and occupational benefits were associated with job crafting, which is consistent with existing research [ 31 ]. Based on the results of the fsQCA analysis, no necessary conditions for job crafting were found. In terms of the sufficiency analysis, it was found that H1 has the highest coverage, explaining 10.6% of cases after comparing the raw coverage of the three configurations that stimulate high job crafting among emergency nurses. This suggested that the majority of emergency nurses who exhibit high job crafting are influenced by the conditions present in H1, and psychological empowerment is the core condition. For the four paths of the low job crafting, L2 has the highest raw coverage. This indicated that nurses with junior professional position and no research experience who lack sufficient psychological empowerment are unlikely to engage in job crafting. Once again, psychological empowerment emerges as a core condition in this path, reinforcing the results obtained through regression analysis.
We can discuss the professional position and research experience from “increasing the challenging work demands” and “lessening hindering work demands”, based on the job crafting theory [ 6 ]. Since junior emergency nurses were newly exposed to clinical nursing work along with the special characteristics of emergency nursing, they faced higher work stress when addressing clinical problems that were primarily acute and serious. The problems mentioned above can also serve as a cause of stress that constantly reduces self-efficacy in the emergency care process. Additionally, the junior emergency nurses lack knowledge and experience in nursing research when they were students, and the research ability of nurses working in clinical settings is low in China [ 32 ]. Most nurses are under pressure to perform the job guided by the goal of job position improvement [ 33 ], and the inner drive to explore and solve research problems was insufficient [ 34 ]. If the nurses were assigned to research work by the organization, the work demands would inevitably exceed their abilities, leading to work hindrances. Junior nurses experience less pressure about job position improvement, and they may be fearful of research work. This may create defensive job crafting by lessening hindering work demands. Although this helps them to accomplish their clinical goals, it may reduce their work motivation and job involvement. The second dimension of job crafting is about increasing the challenging work demands. It has been revealed that a lack of challenging work may lead to absences and job dissatisfaction. Research tasks, as a challenge, may lead to the creation of job crafting for advanced practice nurses. By expanding task boundaries and increasing challenging work demands, the nurses have contributed to the organization. It was shown that challenge demands were associated with goal achievement and work motivation [ 6 ]. The H2, with research experience as a core condition, confirmed that the high job crafting was associated with the individuals’ promotion of “challenge demands”.
The high level of psychological empowerment in nurses was a core condition that influenced the level of job crafting on both core configurations (H1&L2). From regression models, it was also seen that psychological empowerment was a core element affecting job crafting (β = 0.317, p < 0.001). This means that the job crafting gradually increased with the psychological empowerment. The self-determination theory suggests that autonomous motivational orientation, as opposed to control motivational orientation, would be more beneficial in addressing the basic psychological needs. A high level of psychological empowerment as a variable of autonomous motivational orientation could enhance individual job performance and job ability [ 35 ]. The resource conservation theory states that employees can experience higher psychological security as they sense higher levels of psychological empowerment through a cycle of resource loss and gain spirals. These positive job resources assist them in conserving and building more resources to cope with the prospect of poor career outcomes and job demands [ 36 ], which precisely confirm the findings of this paper.
In the emergency departments, nurses face a large number of job challenges on a daily basis. The ability of nurses to cope better with these challenges is closely related to perceived occupational benefits. Emergency nurses who perceive high levels of empowerment were better able to respond to the work challenges [ 37 ]. With increased resources for employees to do their jobs, a positive impact was bound to be seen on their psychological empowerment [ 14 ]. By acquiring and conserving resources, nurses are most likely to achieve the most appropriate match between people and job demands. Nurses who are motivated and empowered can develop more job crafting [ 38 ]. If this goal is achieved, it would increase nurses’ satisfaction and thus would promote job crafting resulting in a virtuous circle. To summarize, the results of both the QCA and the regression model demonstrated that the psychological empowerment was a core condition that influenced job crafting among the emergency nurses. From H1, H2 and L2, it can also be proved that high psychological empowerment was the core condition for a high job crafting, regardless of whether or not they had done clinical research work.
The identification with one’s job based on its potential to meet one’s needs and expectations is called job involvement. The job involvement has been mentioned in the literature as a reason why nurses feel so committed to their jobs [ 39 ]. Nurses with a high level of job involvement deliberately consider their work an important part of their lives. Whether or not they can feel good about themselves is closely related to their personal work. Thus, a healthy management structure should consider job involvement as an important predictor of organizational productivity. This attitude of nurses toward their jobs should be promoted [ 20 ]. However, the regression model shows that job involvement does not influence job crafting. Meanwhile, the H1-H3 all indicated that job involvement was an impact on job crafting, and two of these paths indicated that job involvement was a core condition for a high job crafting. Job involvement is influenced by the worker’s identification with the job they are doing. This is, in turn, derived from whether the job can meet the needs of the worker or not. This means that once a nurse has job involvement, a balance between job resources and demands can be reached and the nurse’s job crafting would be suspended. The QCA model revealed that job involvement may need to have an impact on job crafting in conjunction with the other factors. Several studies have also shown that job involvement is correlated with psychological empowerment [ 40 ]. The impact of nurses’ job involvement on their job crafting needs to be further explored.
The occupational benefits of nurses is a cognitive assessment of their feelings about the content of their work, which comes from their internal traits and the external work environment [ 41 ]. Job crafting is a positive behavior for individuals to balance job demands and resources. It can help individuals use available job resources to cope with the stress of job demands and achieve higher levels of job performance [ 42 ]. It enables the nurses to perceive occupational benefits. The H3 demonstrated that both the occupational benefits and the job involvement must be maintained at high levels for junior emergency nurses to lead to a high job crafting. The existence of a low occupational benefits and job involvement will inevitably lead to low job crafting, as seen from L3 and L4. When junior emergency nurses perceive occupational benefits, it may lead to more job autonomy which results in increased psychological recognition of their work [ 43 ]. High levels of job involvement allow nurses to be fully immersed in their work, improving efficiency and quality. With increased efficiency and quality, nurses can obtain more job performance and achievement, in turn bringing them stronger occupational benefits.
Limitations
Although the study obtained some results that could be effective in improving the job crafting for the emergency nurses, the limitations of the study are as follows. First, this cross-sectional survey was conducted with emergency nurses in China, which may limit the extension of these results to other regions. And convenient sampling techniques and the non-calculated sample size of the study limits the generalizability. Secondly, the cross-sectional study does not allow for the detection of possible changes in the levels of job crafting in each participant over time. Lastly, the data were collected from participants using self-report measures, and thus may not reflect their true feelings.
Implications for the profession
The findings of the paper provided two important insights for motivating job crafting in emergency nurses. Firstly, we recognized challenge demands have a significant contribution to job crafting. As such, nursing managers in emergency departments should assign nurses challenging tasks, such as participating in nursing research. These challenges not only stimulate nurses’ potential but also foster their personal growth. However, it’s crucial to align these challenging work demands with commensurate rewards, such as promotion in position, bonus allocation, etc. Meanwhile, it is necessary to give adequate psychological empowerment and cultivate a proper understanding of challenge demands such as research tasks to inspire job crafting in the nurses. This approach will encourage nurses to more actively engage in job crafting, continually improving their work efficiency. Secondly, emergency nursing managers should should carry out a layered method and focus on the main job demands of the nurses at different levels. Junior nurses experience more difficulty in facing the challenges brought by clinical work, which may not deal with the busy and ever-changing work of the emergency department. Thus, special attention should be paid to their psychological endurance and work stress to prevent job burnout and turnover when assigning research or other challenging tasks to them. For senior nurses, management should provide more psychological empowerment, making them feel trusted and respected by the organization. An organization that meets the staff needs and promotes staff development on priority allows nurses to perceive occupational benefits, enhances their sense of emotional belonging, and lastly, boosts the job crafting with a rise in job involvement [ 44 ]. Nurses will be more proactive in participating in work planning and implementation, actively adjusting and optimizing work processes to better meet the various challenges in the emergency department.
The study explored various influencing factors on the job crafting of emergency nurses through hierarchical regression and fsQCA models. Both the models have demonstrated that research experience, psychological empowerment, and occupational benefits were predictors of job crafting, along with high levels of psychological empowerment being the core condition on the higher paths (H1 & S2). Based on research findings, junior emergency nurses should be granted a high level of psychological empowerment without assigning them overly complex tasks, such as research tasks, as these challenges can stop their job crafting. Intermediate and senior emergency nurses, on the other hand, can be assigned research tasks coupled with high psychological empowerment to enhance their job crafting.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Wrzesniewski A, Dutton JE. Crafting a job: revisioning employees as active crafters of their work. Acad Manage Rev. 2001;26(2):179.
Article Google Scholar
Tims M, Bakker AB, Derks D. Development and validation of the job crafting scale. J VOCAT BEHAV. 2012;80(1):173–86.
Yepes-Baldó M, Romeo M, Westerberg K, Nordin M. Job Crafting, Employee Well-being, and Quality of Care. WESTERN J NURS RES. 2018;40(1):52–66.
Baghdadi NA, Farghaly Abd EL, Aliem SM, Alsayed SK. The relationship between nurses’ job crafting behaviours and their work engagement. J NURS MANAGE. 2021;29(2):214–9.
Bakker AB, Demerouti E. Job demands–resources theory: taking stock and looking forward. J OCCUP HEALTH PSYCH. 2017;22(3):273–85.
Tims M, Bakker AB. Job crafting: towards a new model of individual job redesign. SA J IND PSYCHOL 2010, 36(2).
Rudolph CW, Katz IM, Lavigne KN, Zacher H. Job crafting: a meta-analysis of relationships with individual differences, job characteristics, and work outcomes. J VOCAT BEHAV. 2017;102:112–38.
Lichtenthaler PW, Fischbach A. A meta-analysis on promotion- and prevention-focused job crafting. EUR J WORK ORGAN PSY. 2019;28(1):30–50.
Akkermans J, Tims M. Crafting your Career: how Career competencies relate to Career Success via Job crafting. Appl Psychol. 2017;66(1):168–95.
Yinghao Z, Dan Z, Qi L, Yu W, Xiaoying W, Ao F, Lin Z. A cross-sectional study of clinical emergency department nurses’ occupational stress, job involvement and team resilience. INT EMERG NURS. 2023;69:101299.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Spreitzer GM. PSYCHOLOGICAL, EMPOWERMENT IN THE WORKPLACE: DIMENSIONS, MEASUREMENT AND VALIDATION. ACAD MANAGE J. 1995;38(5):1442–65.
Jafari F, Salari N, Hosseinian-Far A, Abdi A, Ezatizadeh N. Predicting positive organizational behavior based on structural and psychological empowerment among nurses. COST EFFECT RESOUR A. 2021;19(1):38.
Hatamian P, Farsani MA. Predicting Job Satisfaction Based on Personality Traits and Psychological Empowerment in Employed Middle-Aged and Elderly People. Sālmand 2019, 13(4):418–427.
Matsuo M. Personal growth initiative as a predictor of psychological empowerment: the mediating role of job crafting. HUM RESOUR DEV Q. 2019;30(3):343–60.
Hu Y, Hu J, Li L, Zhao B, Liu X, Li F. Development and preliminary validation of a brief nurses’ perceived professional benefit questionnaire (NPPBQ). BMC MED RES METHODOL. 2020;20(1):18.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhan T, Li H, Ding X. Can social support enhance sense of coherence and perceived professional benefits among Chinese registered nurses? A mediation model. J NURS MANAGE. 2020;28(3):488–94.
Mollanazari M, Shams Z. The Influence of Professional Identity and Outcome Knowledge on Professional Judgment. 2017.
Paullay IM, Alliger GM, Stone-Romero EF. Construct validation of two instruments designed to measure job involvement and work centrality. J APPL PSYCHOL. 1994;79(2):224–8.
Zhang B, Chen JZ. The Summary of Work Engagement,Job involvement and Job Embeddedness. East China Economic Manage 2009.
Nylen-Eriksen M, Grov EK, Bjornnes AK. Nurses’ job involvement and association with continuing current position-A descriptive comparative study. J CLIN NURS. 2020;29(13–14):2699–709.
Jiang D, Ning L, Liu T, Zhang Y, Liu Q. Job demands-resources, job crafting and work engagement of tobacco retailers. FRONT PUBLIC HEALTH 2022, 10.
Furnari S, Crilly D, Misangyi VF, Greckhamer T, Fiss PC, Aguilera RV. Capturing Causal Complexity: Heuristics for Configurational Theorizing. ACAD MANAGE REV. 2020;46(4):778–99.
Rihoux B, Ragin CC. Configurational comparative methods: qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) and related techniques : Configurational comparative methods.
Jing H, Xiaohong L. Establishment of a questionnaire of nurses’ perceived professional benefits: reliability and validity assessment. Nurs J Chin People’s Liberation army. 2013;22(30):1–5.
Google Scholar
Chaoping L, Xiaoxuan L, Kan S, Xuefeng C. Psychological empowerment: measurement and its effect on emplpyee work attitude in China. ACTA PSYCHOL SIN. 2006;1(38):99–106.
Kanungo RN. Measurement of job and work involvement. J APPL PSYCHOL. 1982;67(3):341–9.
Ming Z, Du Y. Qualitative comparative analysis(QCA) in management and organization research: position, tactics and directions. Chin J Manage. 2019;16(09):1312–23.
Fernandez-Garcia D, Moreno-Latorre E, Gimenez-Espert M, Prado-Gasco V. Satisfaction with the clinical practice among nursing students using regression models and qualitative comparative analysis. NURS EDUC TODAY. 2021;100:104861.
Gimenez-Espert M, Valero-Moreno S, Prado-Gasco VJ. Evaluation of emotional skills in nursing using regression and QCA models: a transversal study. NURS EDUC TODAY. 2019;74:31–7.
Mei S, Lv J, Ren H, Guo X, Meng C, Fei J, Yuan T, Yue J, Gao R, Song Q, et al. Lifestyle behaviors and depressive symptoms in Chinese adolescents using regression and fsQCA models. FRONT PUBLIC HEALTH. 2022;10:825176.
Harbridge R, Ivanitskaya L, Spreitzer G, Boscart V. Psychological empowerment and job crafting among registered nurses working in public health: a quantitative study. APPL NURS RES. 2023;69:151649.
Wang M, Xie R, Lu Q, Ou J, Gao L. Determinants of research ability among nurses in a tertiary hospital in China: a cross-sectional survey. J Educational Res Reviews. 2019;7(10):206–12.
Gao L, Lu Q, Hou X, Ou J, Wang M. Effectiveness of a nursing innovation workshop at enhancing nurses’ innovation abilities: a quasi-experimental study. NURS OPEN. 2022;9(1):418–27.
Chun T, Shizhe L, Wenrui L, Xiangqun M, Abdi A. Current situation and influencing factors of scientific research innovation activities of professionals in disease control and prevention institutions in Jiangxi Province. Mod Prev Medicin. 2022;49(06):1148–52.
Deci EL, Olafsen AH, Ryan RM. Self-determination theory in Work organizations: the state of a science. ANNU REV ORGAN PSYCH. 2017;4(1):19–43.
Zhou H, Chen J. How does psychological empowerment prevent emotional exhaustion? Psychological safety and Organizational Embeddedness as mediators. FRONT PSYCHOL. 2021;12:546687.
Boudrias JS, Morin AJ, Brodeur MM. Role of psychological empowerment in the reduction of burnout in Canadian healthcare workers. NURS HEALTH SCI. 2012;14(1):8–17.
Miller ML. Relationships Between Job Design, Job Crafting, Idiosyncratic Deals, and Psychological Empowerments. Dissertations & Theses - Gradworks 2015.
Abd-El AS, Abou HE. The relationship between transformational Leadership practices of First-Line nurse managers and nurses’ organizational resilience and job involvement: a structural equation Model. WORLDV EVID-BASED NU. 2021;18(5):273–82.
Faulkner J, Laschinger H. The effects of structural and psychological empowerment on perceived respect in acute care nurses. J NURS MANAGE. 2008;16(2):214–21.
Zhou H, Zhu Y, Zhang X, Peng J, Li Q, Wang X, Wang L, Cai X, Lan L. Psychological capital and Perceived Professional benefits: testing the Mediating role of perceived nursing work environment among Chinese nurses. J PSYCHOSOC NURS MEN. 2018;56(4):38–47.
Hui C, Hui Y. Application progress on job demand-resources model in the field of nursing. Chin Evidence-Based Nurs. 2021;7(16):2181–5.
Jinxia J, Haiyan S, Zhu X, Meimei T. Perspectives of professional benefits among emergency nurses: a qualitative study. J Nurs Sci. 2020;35(11):63–5.
Clegg C, Spencer C. A circular and dynamic model of the process of job design. J OCCUP ORGAN PSYCH. 2007;80(2):321–39.
Download references
This work was supported by grants from Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Project(LHGJ20200109);and Jiaxing University Research Fund (CD70522005).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Medicine, Jiaxing University, Jiaxing, China
Department of Nursing, Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Yu Wang, Qiaofang Yang & Qingwei Zhang
Heart Failure Ward, Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Yu Wang : Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation). Development or design of methodology; creation of models. Qiaofang Yang : Provision of study materials, participants, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools. Luwen Wang : Visualization, Investigation. Qingwei Zhang: Application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data, and acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication. Yingli Li : Writing- Reviewing and Editing, and Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yingli Li .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This research focuses on nursing management. The Ethics Committee of Fuwai Central China Cardiovascular Hospital has verified that no approval from the Research Ethic Committee is necessary. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations(Declaration of Helsinki).The objective of the study was communicated to the participants, and informed consent was obtained prior to data collection. To safeguard the confidentiality of the participants, personal identifiers were not included in the data collection format.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wang, Y., Yang, Q., Wang, L. et al. The factors of job crafting in emergency nurses: regression models versus qualitative comparative analysis. BMC Nurs 23 , 369 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02035-3
Download citation
Received : 25 August 2023
Accepted : 21 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02035-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Job crafting
- Emergency nurses
- Hierarchical regression model
- fsQCA model
- Configuration
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Case study method is the most widely used method in academia for researchers interested in qualitative research (Baskarada, 2014).Research students select the case study as a method without understanding array of factors that can affect the outcome of their research.
Qualitative research designs focus initially on collecting data to provide a naturalistic view of social phenomena and understand the meaning the social world holds from the point of view of social actors in real settings. ... In R. Piekkari & C. Welch (Eds.), Rethinking the case study in international business and management research (pp. 3 ...
Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Business and Management Research Methods provides a state-of-the-art overview of qualitative research methods in the business and management field.. The Handbook celebrates the diversity of the field by drawing from a wide range of traditions and by bringing together a number of leading international researchers engaged in studying a variety of topics through ...
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history. Qualitative research question examples
Qualitative research is a 'big tent' that encompasses various schools of thoughts. There is a general consensus that qualitative research is best used to answer why and howresearch questions, but not how much or to what extent questions. The word 'how can Footnote 5 ' is also frequently used in the research question of a qualitative research; this typically requires open-ended vs ...
Second Edition. This pragmatic, applied textbook showcases the potential and impact of qualitative research in business and management. Using case studies and a global approach it provides you with an overview of the philosophies, methodologies and methods you will need to research in this field. Demystifying the whole process, it walks you ...
Qualitative research methods. Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people's thoughts, feelings and opinions. ... In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new ...
Qualitative research seeks to gain insights and understand people's experiences and perspectives by studying social organizations and human behavior. Data in qualitative studies focuses on people's beliefs and emotional responses. Qualitative data is especially helpful when a company wants to know how customers feel about a product or ...
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
Qualitative Research in Business and Management. This accessible and expansive, yet remarkably concise textbook is designed to help readers with their research project. As well as guiding them through the key methods of collecting and analysing qualitative data, this book provides invaluable information on writing up their research and how to ...
Qualitative research is the naturalistic study of social meanings and processes, using interviews, observations, and the analysis of texts and images. In contrast to quantitative researchers, whose statistical methods enable broad generalizations about populations (for example, comparisons of the percentages of U.S. demographic groups who vote in particular ways), qualitative researchers use ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
1 Often begins with a single case, chosen because of its convenience or interest. 2 Often studies phenomena in the contexts in which they arise through observation and/or recording or the analysis of printed and Internet material. 3 Hypotheses are often generated from the analysis rather than stated at the outset.
Course Description. This doctoral level course examines the qualitative method used in business research, with a focus on five qualitative designs: narrative, phenomenological, grounded theory, ethnographic, and case study. Underpinning philosophical assumptions are presented in context with the selected qualitative designs.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences ...
Diary studies are a unique qualitative research method that involves participants recording their thoughts, experiences, or behaviors over a period of time, related to using a product or service. This qualitative data analysis method is especially valuable for driving product development for several reasons: Real-time insights
The course aims to foster an understanding of how qualitative inquiry adds depth and nuance to our comprehension of individual and collective human experiences. It addresses the common critiques of qualitative research and introduces the four trustworthiness criteria that researchers use in evaluating the soundness of a given qualitative study ...
Study context. This qualitative study was conducted in the province of British Columbia (BC), Canada, a jurisdiction with a population of approximately five million people [].Within BC's health sector, key actors involved in the policy response to COVID-19 included: elected officials, the BC Government's Ministry of Health (MOH), the Provincial Health Services Authority (PHSA), Footnote 2 ...
This qualitative study explores the experiences and challenges faced by these students in inclusive educational settings. Contextual Framework Inclusive education aims to integrate all students, regardless of their abilities, into mainstream classrooms. Historically, students with disabilities were often placed in separate schools or classes.
The etonogestrel contraceptive implant is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for 3 years of continuous use for the prevention of pregnancy [].However, there is evidence to support its use for up to 5 years while maintaining a low risk of pregnancy [2,3,4].The off-label use of the contraceptive implant past its FDA-approved duration and up to 5 years is known as ...
Methodological quality of included studies. All included qualitative studies scored between 7 and 9, which is displayed in Appendix 3. The congruity between the research methodology and the research question or objectives, followed by applying appropriate data collection and data analysis were observed in all included studies.
Qualitative research in international business has been rare, the main research streams of the field relying more on quantitative methods. This paper first outlines why qualitative research has been scant. It then presents areas, such as theory building, where qualitative research could make a substantial contribution. Third, it reviews approaches to high standards of qualitative research and ...
The rigor of the research is fundamentally based on the clear sample rationale and the triangulation of researchers during the data analysis . For the processing and organization of the data, we used MAXQDA software. The study findings were reported according to the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) . 2.5.
Qualitative comparative analysis (QCA ) is a new method for analysing complex causal relationships in histological problems based on Boolean algebra and set theory.QCA is a new method that combines quantitative and qualitative analysis, providing strong support for studying the configuration problem.