- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
4 Ways to Develop Your Strategic Thinking Skills

- 10 Sep 2020
Think back to the last time you participated in a strategic planning meeting for your organization. You were likely presented with a challenge to solve or goal to achieve.
Do you remember your contributions during that meeting? Did you offer compelling ideas and plot a course of action, or find it difficult to think strategically and develop a solution? Did you have a good idea, but struggle to communicate it in a logical way? Were you an active participant in the conversation, or did others helm it?
Strategic thinking skills are among the most highly sought-after management competencies. Why? Because employees capable of thinking critically, logically, and strategically can have a tremendous impact on a business’s trajectory.
If you want to improve your strategic thinking skills, the good news is that, with the right mindset and practice, you can.
Here are four ways to improve your strategy skills , so the next time you’re involved in a strategic planning meeting, you can ensure your contributions are noticed.
Access your free e-book today.
What Are Strategic Thinking Skills?
Strategic thinking skills are any skills that enable you to use critical thinking to solve complex problems and plan for the future. These skills are essential to accomplish business objectives, overcome obstacles, and address challenges—particularly if they’re projected to take weeks, months, or even years to achieve.
Strategic thinking skills include:
- Analytical skills: To ideate a strategy that helps your organization reach its objectives, you must be capable of analyzing a variety of inputs—from financial statements and KPIs , to market conditions, emerging business trends, and internal resource allocation. This initial analysis is crucial to creating a strategy that aligns with the current reality facing your organization.
- Communication skills: Putting a strategy into place for your company, regardless of its size, requires solid communication skills . The ability to communicate complex ideas, collaborate with internal and external stakeholders, build consensus, and ensure everyone is aligned and working toward shared goals are all central to strategic thinking.
- Problem-solving skills: Strategic planning is often used to solve problems or address challenges, such as missed financial targets, inefficient workflows, or an emerging competitor. Implementing a strategy that addresses the central challenge you face requires you to first understand the problem and its potential solutions. From there, you can craft a strategy that solves it.
- Planning and management skills: Strategy isn’t just about thinking of a solution—it involves implementation, too. Once data has been analyzed, the problem is understood, and a solution has been identified, you need strong planning and management skills to bring everything together.
How to Improve Your Strategic Thinking Skills
1. ask strategic questions.
If you want to improve your strategic thinking skills, one of the simplest things you can do is ask more strategic questions. Doing so allows you to exercise your planning skills, become adept at spotting opportunities, and develop a more strategic mindset you can leverage throughout your career.
According to the Harvard Business School Online course Disruptive Strategy , strategic questions can relate to a challenge, opportunity, or ambiguity you face in your current situation, whether personal or professional. They might, for instance, relate to launching a new business or product, beating a competitor, or structuring your organization for innovation.
It’s also important that your questions apply to your role and responsibilities so you can act on them.
Some examples of strategic questions you might ask include:
- How can we strategically position ourselves to enter a new market?
- What’s the direction for growth for each of our products or services?
- Where will the organization's growth come from in the next five years, and how does it compare with where growth has historically come from?
- How should the organization respond to the threat presented by potentially disruptive competitors ?
2. Observe and Reflect
In addition to asking strategic questions, you need to answer and address them skillfully. One of the most effective ways of accomplishing this is to observe and reflect on your current situation, ensuring any strategy you conceive is grounded in facts.
For example, imagine that the business you work for has begun losing market share for one of its products among its traditional customers. At the same time, it’s gained market share from an entirely new customer base. It’s easy to assume why this might be happening, but doing so can lead you down the wrong path at a critical moment in your organization’s existence.
Instead of blindly following an assumption, gather as much information as possible to use when crafting your strategy. For example, this might include conducting user interviews with new customers to identify the different jobs they hire your product to perform.
Understanding why new customers are attracted to your product can enable you to tailor your marketing strategy and product development to better embrace their needs .
3. Consider Opposing Ideas
Once you’ve landed on a strategy that can help your organization reach its goals, question your assumptions, and put your hypothesis through rigorous testing. By doing so, you can ensure you’re not overlooking another possibility.
Playing devil’s advocate with your ideas can allow you to preemptively identify weaknesses in your argument, and equip you to defend your strategy when others ask questions. It can also help you sharpen the logic skills you need to communicate and execute your strategy.
To develop this skill, get in the habit of questioning yourself any time you’re about to make an assertion. Should you consider a different perspective? Is there another possibility you may have overlooked?
4. Embrace Formal Training
By practicing the methods described above, you can improve your strategic thinking skills at your own pace. However, there are other learning options you can pursue.
If you need to quickly ramp up your strategy skills—to address a pressing need your organization is facing, position yourself for a new role, or finally launch your own business—formal training might be your best option.
For example, by enrolling in the online course Disruptive Strategy , you can discover how to make innovation a reality for your organization. Over six weeks, you’ll learn about the jobs to be done framework and disruptive innovation theory, and build skills to identify and execute high-level strategy.

Cultivating a Strategic Mindset
Whether in the long- or short-term, a strategic mindset can be developed through self-exploration, critical questioning, and formal training.
The advantage of having a strategic mindset is learning how to think rather than what to think. Although you might not always have the right answers, strategic thinking skills can empower you to spot new opportunities, address emerging challenges, and plan for future success.
Are you looking to develop a strategic mindset? Explore our portfolio of online strategy courses and download the free flowchart to determine which is the best fit for you and your goals.

About the Author
- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
Strategic Thinking Definition, Skills, Examples, and Steps
Published: 29 January, 2024
Social Share:

Welcome to Digital Leadership, where we are committed to harnessing emerging technologies and innovative business models to better serve customers. As experts in innovation and digital transformation, our mission is to guide organizations in creating value for all stakeholders, supporting them from strategic conceptualization to effective execution. The ability to think strategically is a cornerstone for success, strategic thinking centres on discovering and cultivating distinctive opportunities to enhance organizational value.
Digital Leadership’s expertise in strategy and execution, invites business entrepreneurs to delve deeper into the realms of strategic thinking for enduring success. We provide Strategic Management Consulting services to empower businesses to elevate their strategic acumen and navigate the complex landscape of value creation . Through collaborative initiatives, we guide organizations in unlocking unique opportunities and ensuring enduring success in today’s dynamic business environment.

Find out how we can help you
Corporate training, innovation consulting and much more.
This article delves into the intricacies of strategic thinking , outlining its definition, key characteristics, and its vital role in both leadership and business. We will explore the steps to develop strategic thinking skills and provide real-life examples to illustrate its application. As we navigate through this exploration, we will differentiate strategic thinking from strategic planning and highlight its significance in digital transformation strategy.
What is Strategic Thinking?
Strategic thinking is centred on identifying and cultivating distinctive opportunities that can generate value for your organization. It asserts that even non-statistically significant data in various forms deserves thorough consideration to inform decisions about the future. It is a multifaceted concept that goes beyond mere planning. It involves the ability to analyze situations, anticipate future trends, and make informed decisions that contribute to an organization’s long-term success.

Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete Business Model Canvas Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
The UNITE Perspectives On Strategy – A Framework For Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is a crucial element of effective leadership, involving the ability to envision and plan for the future while navigating the complexities of the present. It goes beyond day-to-day tasks, focusing on long-term business goals and adapting to dynamic environments. Strategic thinking and strategic planning, while interconnected, serve distinct roles in organizational development and decision-making. Strategic thinking is a continuous and dynamic mental activity that envisions the future, identifies opportunities, and fosters innovation. It emphasizes creativity, adaptability, and a proactive mindset, laying the conceptual foundation for an organization’s direction.
Strategic planning is a systematic process that translates strategic thinking into actionable plans. It involves setting specific goals, defining measurable objectives, and outlining the steps and resources needed for implementation. While strategic thinking explores possibilities and challenges assumptions, strategic planning focuses on specific actions, resource allocation, and timelines. Strategic thinking is future-oriented and adaptable, providing the vision upon which strategic planning builds the roadmap for organizational development. Both are essential components, working collaboratively to navigate the complexities of the business landscape.
At Digital Leadership, strategic thinking is perceived as the art of proactively shaping an organization’s future. This involves anticipating challenges, recognizing opportunities, and aligning resources effectively. To delve deeper into the intricacies of strategic thinking and its role in crafting innovative business strategies , explore the insights provided in our book, “How to Create Innovation.” It serves as a comprehensive guide, offering valuable perspectives on navigating the dynamic landscape of strategic decision-making and fostering a culture of innovation within your organization.

The Only Book On Innovation You’ll Ever Need
+FREE access to 50+ complimentary download packages covering the details with plenty of helpful background information
Strategic Thinking Skills
Enhancing strategic thinking skills is crucial for effective decision-making and leadership. Here are key skills compiled from various sources:
- Active Listening: Engage attentively to comprehend diverse perspectives.
- Analytical Skills: Utilize data and insights to make informed decisions.
- Implement the Plan: Execute strategies efficiently to achieve business goals.
- Observing and Seeking Trends: Stay vigilant to identify emerging patterns and trends.
- Question Everything: Foster a questioning mindset to challenge assumptions.
- Strategic Thinking: Cultivate the ability to envision and plan for the future.
- Understand the Consequences: Evaluate potential outcomes and impacts.
- Articulate Your Goals Clearly: Clearly express your objectives for better alignment.
- Being Creative: Embrace creativity to generate innovative solutions.
- Communicate Clearly: Convey ideas and strategies with clarity.
- Consider Opposing Ideas: Encourage diverse viewpoints for comprehensive decision-making.
- Critical Thinking: Assess information objectively to make well-founded decisions.
- Get Other Perspectives: Seek input from different sources to broaden your understanding.
- Learn and Improve: Embrace a continuous learning mindset for personal and professional growth.
- Vision and Purpose: Align decisions with a clear vision and overarching purpose.
- Prioritization: Effectively prioritize tasks and goals based on strategic importance.
- Adaptability: Be flexible and adapt strategies to changing circumstances.
- Ask Strategic Questions: Pose insightful questions to deepen strategic insights.
- Be Aware of Bias: Recognize and mitigate personal biases in decision-making.
- Analysis: Break down complex situations into manageable components for analysis.
- Scenario Planning: Anticipate potential scenarios and plan accordingly.
These skills collectively contribute to developing a robust strategic thinking mindset, essential for navigating complex business landscapes.
How to Develop Strategic Thinking Skills
Acquiring the art of strategic thinking is a developed skill, not an innate talent. This section outlines practical steps to guide individuals in enhancing their strategic thinking skills . Tailored for aspiring strategic thinkers and leaders, these steps offer valuable insights to successfully navigate the complexities of the business landscape.
(1) Pose Thoughtful Queries for Strategic Insights
Challenge conventional wisdom by formulating insightful questions that stimulate critical thinking, fostering a deeper understanding of issues and encouraging innovative solutions.
(2) Observe, Reflect, and Stay Informed
Allocate time to observe industry trends and changes, reflecting on these observations to gain valuable insights that inform strategic decisions.
(3) Embrace Diverse Perspectives Through Opposing Ideas
Foster a culture that values diverse viewpoints, actively seeking and considering opposing ideas to formulate well-rounded and robust strategic plans.
(4) Invest in Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Systematically refine strategic thinking skills through continuous learning. Enroll in courses, workshops, or programs dedicated to enhancing strategic thinking.
(5) Master Your Organization and Industry Dynamics
Acquire in-depth knowledge of your organization, industry, and market sector to make informed strategic decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of internal and external factors.
(6) Prioritize Strategic Thinking with Dedicated Time
Schedule specific time slots for focused strategic thinking in your routine. Utilize this time to address fundamental questions about your organization’s direction, challenges, and opportunities.
(7) Effectively Communicate Strategic Insights to Influence
Cultivate strong communication skills to articulate strategic insights clearly. Effective communication is pivotal for gaining support and buy-in for proposed strategic initiatives.
By systematically incorporating these steps into your professional journey, you actively develop and refine your strategic thinking skills. This intentional approach empowers you to confidently navigate the complexities of strategic decision-making.
Strategic Thinking Examples
Strategic thinking manifests in various scenarios, demonstrating its impact on organizational success. Below are real-life examples showcasing how strategic thinking has influenced key decisions and outcomes:
- Distinguish between urgent and important tasks to allocate resources efficiently and achieve optimal outcomes.
- Strategically allocate resources based on the prioritization of tasks, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
- Systematically analyze customer feedback to identify trends and insights, informing strategic decisions for product enhancements and customer satisfaction.
- Develop a strategic roadmap by setting both long-term and short-term business goals aligned with the organization’s overarching vision.
- Utilize past sales data to derive insights, identify patterns, and inform strategic decisions for future product development and market positioning.
- Conduct thorough market analysis to identify gaps and opportunities, allowing for strategic entry or expansion into specific market segments.
- Evaluate the alignment between products and market demands, ensuring a strategic fit that resonates with the target audience.
- Develop and implement a deliberate brand positioning strategy that aligns with market trends, consumer preferences, and organizational values.
These examples showcase how strategic thinking is applied across various facets of business operations. By integrating these practices, organizations can foster a strategic mindset, leading to informed decision-making and sustainable success.
In a real-world scenario, imagine a tech company facing fierce market competition and disruptive technological shifts. A strategic thinker in the managerial role would first pinpoint the challenges: intense competition and the impact of tech disruptions. By actively analyzing industry trends and asking crucial questions, such as how to stand out in a crowded market, strategic thinking takes shape.
Encouraging team discussions to gather diverse perspectives ensures a comprehensive understanding of potential strategies. Crafting innovative solutions collaboratively, like exploring unique product features or strategic partnerships, follows. Proactively anticipating future challenges and formulating contingency plans showcase the hands-on nature of strategic thinking.
Effective communication of the strategic vision is crucial. Aligning stakeholders, fostering commitment to the plan, and conveying a well-defined vision are integral. This example highlights that strategic thinking is not just theory; it’s a practical skill with tangible outcomes in navigating complex business landscapes.
What is Strategic Thinking in Leadership
Strategic thinking in leadership goes beyond day-to-day decision-making; it involves a comprehensive approach to envisioning and navigating an organization’s future. It’s the capability of leaders to analyze the current landscape, anticipate future challenges and opportunities, and formulate innovative strategies to drive the organization toward success. Here’s a deeper exploration of what strategic thinking entails in leadership:
- Visionary Leadership: Strategic thinking leaders possess a visionary outlook, setting a clear and inspiring direction for the organization’s future.
- Long-Term Planning: Instead of focusing solely on immediate concerns, strategic leaders plan for the long term, considering sustainable growth and evolution.
- Adaptability: Leaders who think strategically are adaptable, and ready to adjust strategies in response to changing circumstances and market dynamics.
- Risk Management: They evaluate risks meticulously, making calculated decisions that balance potential rewards with potential pitfalls.
- Innovation Advocacy: Encouraging innovation is a key aspect. Strategic leaders foster a culture where novel ideas are valued, leading to continuous improvement.
- Decision-Making: Strategic thinking leaders make decisions based on a holistic understanding of the organization’s goals, industry trends, and competitive landscape.
- Collaborative Approach: They understand the importance of collaboration, seeking input from diverse teams to enhance the quality of strategic decisions.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is paramount. Leaders articulate the strategic vision in a way that inspires and aligns the entire organization.
- Alignment with Values: Strategic leaders ensure that strategic initiatives align with the organization’s core values and mission.
- Continuous Learning: Leaders committed to strategic thinking engage in continuous learning, staying informed about industry advancements and emerging trends.
In essence, strategic thinking in leadership is about proactively shaping the organization’s future, and making informed choices that lead to sustained success and relevance in a dynamic business environment.
Key Characteristics of Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is a multifaceted skill encompassing various key characteristics that contribute to its effectiveness. These attributes set strategic thinkers apart and form the foundation for navigating complex business landscapes. Here are the key characteristics of strategic thinking:
- Forward-Thinking: Strategic thinkers have a future-oriented mindset, anticipating trends, challenges, and opportunities to proactively shape the organization’s destiny.
- Analytical Acumen: The ability to analyze vast amounts of information, discern patterns, and derive meaningful insights is crucial for strategic thinking.
- Innovative Vision: Strategic thinkers embrace innovation, seeking novel solutions and envisioning possibilities that disrupt conventional norms.
- Adaptability: Recognizing the dynamic nature of the business environment, strategic thinkers are adaptable and agile in responding to changes and uncertainties.
- Holistic Perspective: They consider the bigger picture, understanding the interconnectedness of various elements within and outside the organization.
- Risk Assessment: Strategic thinkers evaluate risks objectively, weighing potential rewards against potential drawbacks and making informed decisions.
- Long-Term Orientation: Rather than focusing solely on short-term gains, strategic thinkers prioritize long-term objectives and sustainable growth.
- Open-Mindedness: Embracing diverse perspectives and being receptive to new ideas fosters a climate of creativity and robust strategic planning.
- Effective Communication: Strategic thinkers communicate their vision and plans clearly, ensuring alignment and understanding throughout the organization.
- Results-Driven: Ultimately, strategic thinkers are driven by results, aiming to create lasting value and impact for the organization’s stakeholders.
These key characteristics collectively empower individuals to think strategically, guiding organizations toward success in today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape.
Strategic Thinking in Business
Strategic thinking in the realm of business is a dynamic and critical process that involves the exploration and refinement of existing business models . This approach entails a comprehensive evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses inherent in the current model. By strategically thinking, businesses can foster innovation, identify new revenue streams , optimise operational processes, and adjust to the evolving demands of the market. This strategic perspective is essential for staying competitive and ensuring long-term success in the business landscape.
Applying Strategic Thinking to Business Models
Strategic thinking serves as a catalyst for transforming and optimizing traditional business models. This process entails a meticulous examination of the current model, pinpointing both its strengths and weaknesses. Through strategic thinking, businesses can unleash innovation by exploring novel revenue streams, refining operational processes, and adapting to the ever-changing landscape of market demands. This application of strategic thinking is instrumental in steering businesses towards resilience, growth, and sustained success.
The Business Model Canvas becomes a crucial tool in the strategic thinking process. It provides a visual framework for understanding, designing, and reinventing business models. By leveraging the canvas, organizations gain insights into key components such as value proposition , customer segments, channels , and cost structures. This clarity enhances strategic decision-making and fosters a more agile and adaptive business model.
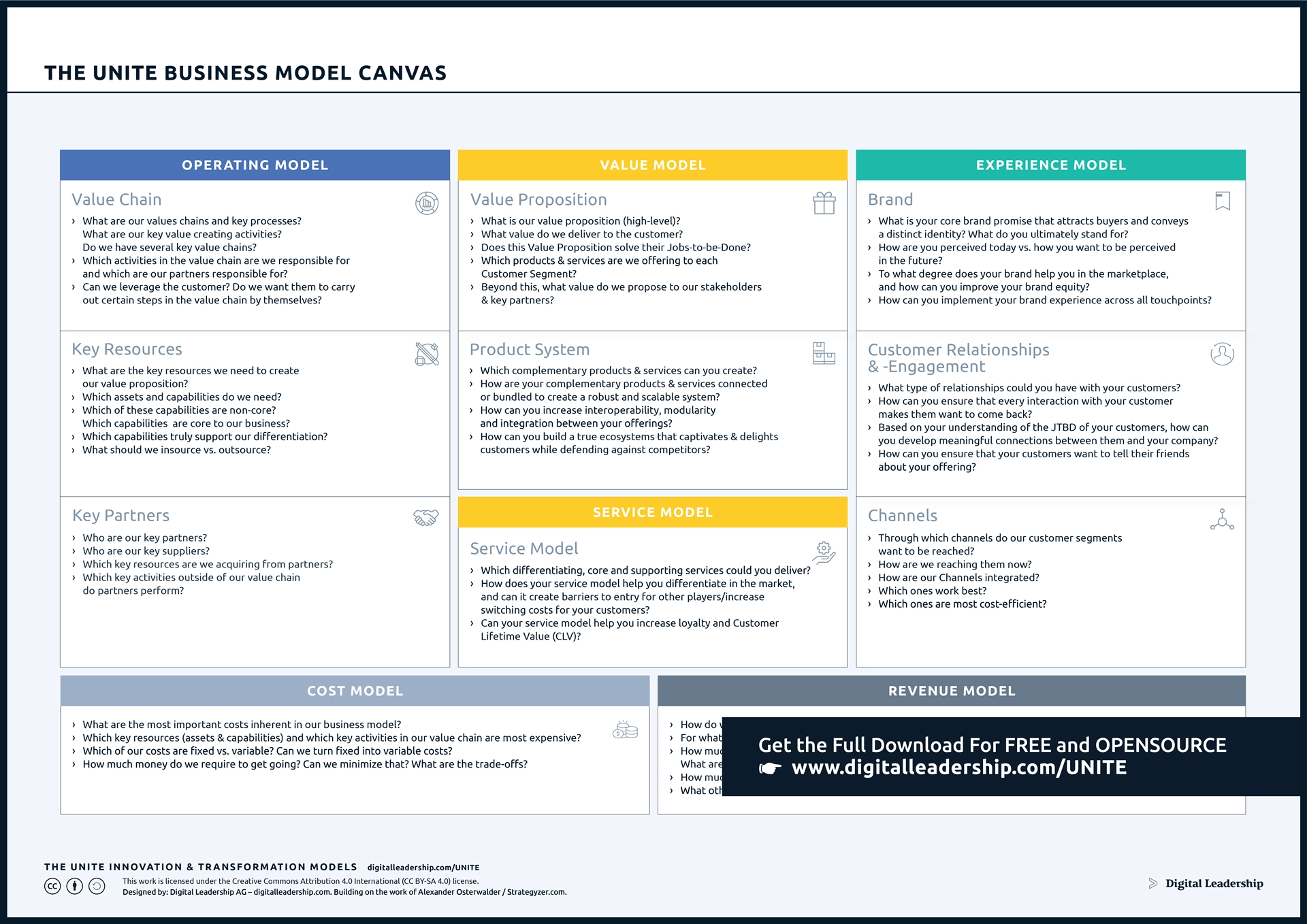
The UNITE Business Model Canvas
The significance of strategic thinking in digital transformation.
In digital transformation, strategic thinking holds immense significance. It serves as the guiding force that shapes and directs the course of digital initiatives. It ensures a holistic approach, considering not only technological aspects but also the broader implications on business models, processes, and customer experiences. By strategically navigating the complexities of the digital transformation strategy , organizations can leverage emerging technologies effectively, enhance operational efficiency, and stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape. The application of strategic thinking becomes a linchpin for organizations aiming to achieve meaningful and sustainable digital transformation outcomes.
Real-Life Examples of Strategic Thinking in Business
To illustrate the tangible impact of strategic thinking, let’s delve into real-life examples where organizations successfully applied this approach to achieve remarkable outcomes.
- Apple Inc.: Apple’s strategic thinking is evident in its continuous innovation and product development. The introduction of the iPod, iPhone, and iPad showcased a forward-thinking approach that revolutionized the consumer electronics industry.
- Amazon: Amazon’s strategic thinking is exemplified in its customer-centric model and diversification. The company started as an online bookstore and strategically expanded into diverse product categories, cloud services (AWS), and even original content creation.
- Tesla: Tesla’s strategic thinking is embodied in its pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. The decision to focus on electric vehicles, solar energy, and energy storage reflects a long-term vision that goes beyond automotive manufacturing.
- Netflix: Netflix’s strategic thinking is evident in its shift from a DVD rental service to a global streaming platform. Embracing digital disruption, Netflix strategically invested in original content creation, transforming the entertainment industry.
- Google: Google’s strategic thinking is showcased in its commitment to innovation. From dominating the search engine market, Google expanded into diverse areas such as online advertising, mobile operating systems (Android), and artificial intelligence.
Differentiating Strategic Thinking from Other Types of Thinking
Thinking is a multifaceted cognitive process that varies across different contexts and objectives. Let’s delve into the distinctions between strategic thinking and other types of thinking:
- Strategic Thinking: Involves envisioning the future, identifying opportunities, and devising plans to achieve long-term goals.
- Critical Thinking: Focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and forming judgments about information or situations, emphasizing logical reasoning.
- Strategic Thinking: Emphasizes planning and decision-making for achieving organizational objectives, often involving a systematic approach.
- Creative Thinking: Involves generating novel ideas, solutions, or approaches, fostering innovation and unconventional thoughts.
- Strategic Thinking: Encompasses a holistic view, considering the overall direction and positioning of the organization.
- Analytical Thinking: Concentrates on breaking down complex problems into smaller components for in-depth examination and understanding.
- Strategic Thinking: Primarily concerned with defining goals, formulating plans, and aligning resources to achieve a predefined vision.
- Design Thinking: Centers around a human-centric approach, empathizing with end-users, and iteratively prototyping solutions for complex problems.
- Strategic Thinking: Focuses on organizational strategy, often involving hierarchical planning and coordination.
- Systems Thinking: Considers the interrelated components and relationships within a system, emphasizing holistic understanding and feedback loops.
- Strategic Thinking: Involves dynamic, adaptive, and non-linear planning, considering various scenarios and external influences.
- Linear Thinking: Follows a sequential and step-by-step approach to problem-solving without necessarily accounting for broader systemic factors.
- Strategic Thinking: Concentrates on forward-looking planning, often in a structured manner, to gain a competitive advantage.
- Lateral Thinking: Encourages unconventional and creative approaches to problem-solving, challenging traditional thought patterns.
Understanding these differences is crucial as it highlights the versatility of thinking processes and underscores the need for a well-rounded cognitive toolkit, incorporating strategic thinking when long-term planning and vision are paramount.
In conclusion, strategic thinking is the compass that guides businesses through the complexities of today’s ever-evolving landscape. By developing and nurturing strategic thinking skills , organizations can pave the way for sustained success and create value for everyone they serve. At Digital Leadership, we are passionate about empowering organizations to embrace strategic thinking. If you’re ready to elevate your strategic approach, contact us today for a transformative journey from strategy to execution.
Related Posts
Continuous improvement steps for enhancing digital leadership.
In digital leadership, organizations must not only keep up with industry trends1
Recent Posts

Examples and Types of Effective Functional Level Strategy for Business Support
A key objective of any business strategy is to improve operational efficiencies...

The Three Levels of Strategy: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, and Functional Strategy
Understanding the intricate levels of strategy is crucial for any organization aiming...
- FREE LIVE TRAINING
How To Overcome The 90% Failure Rate in Innovation
Learn the winning formula from over 80+ successful innovation projects
SAVE MY FREE SPOT NOW

Register For Your FREE Innovation WorkShop Seat Now!
Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator and best-selling author.

Expert tactics to boost your innovation odds.
Insights on capturing customer needs for innovation.
Tools that turn your ideas into triumphs.
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Last one step
Help us better understand our innovation Show members
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
Already have an account? Log in
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.
Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.
Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.
You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review

Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Strategic Thinking: Because Good Ideas Can Come From Anywhere

As part of our update to the Harvard ManageMentor Strategic Thinking topic, we asked Mason Weintraub, Director of Digital Engagement at Oxfam America, about the importance of strategic thinking. Here’s what Mason had to say:
I often think I’m expected to have all the answers about what to do with digital strategy. But the reality is that I lead a very talented team, and one of the ideas that we have tried to engender on the team is that good ideas can come from anywhere.
“Good ideas can come from anywhere.” Most of us recognize the wisdom embedded in that statement, yet we still see strategy as the realm of our organization’s senior leaders. That may be because of our tendency to equate strategic thinking with strategic planning. Although these practices are related and equally necessary for organizational success, they are actually quite distinct.
Strategic planning vs. strategic thinking
In strategic planning, leaders gather data and decide on the path the organization will take to achieve its goals. With strategic thinking, employees at all levels and in all functions continually scan for new ways to contribute to the organization’s success. They apply those insights as they carry out organizational priorities and provide input to the overall strategy. In this way, strategic thinking is part of everyone’s job – whatever their role or level of responsibility.
Why is this ability to think strategically especially important now? Today’s organizations are more dispersed and less hierarchical than ever before. With the pace of change continuing to rise, it’s no longer feasible for people to wait for “orders from above.” All employees must keep an eye on the future, not just react to what’s happening in the present. They need to look beyond their functional areas to become aware of the bigger context in which they operate. And they have to be agile learners who identify opportunities by challenging their own and their team’s assumptions about how things work in their organization and industry.
Becoming a strategic thinker
With strategic thinking taking on even greater importance in organizations, we’ve made key updates to the Harvard ManageMentor Strategic Thinking topic. The content we’ve added is geared to helping people boost their productivity and effectiveness by making strategic thinking a habit, and includes practical ways that enable them to do so.
One practice is simply making the time to think strategically – something that’s not always easy in today’s fast-paced business settings. Another involves inviting dissent on your team. To make strategic decisions, you need people on all sides of an issue to speak their minds. By letting team members know that speaking up is an important part of their jobs, you free them to provide important input.
Other strategic thinking practices are useful for training yourself to see opportunities and threats well before they happen. For example, most of us are comfortable using convergent thinking – analysis, logic, and reasoning – to come up with the “best” option from a set of choices. We tend to be less adept at divergent thinking, which involves generating lots of ideas with the goal of finding innovative solutions. This isn’t an either-or process: When you first diverge as a team to generate ideas and then converge on a path forward, you improve your ability to design and implement strategic actions.
Don’t let the future surprise you
The future will undoubtedly look a lot different from today. No one can predict tomorrow, but by identifying different scenarios, you and members of your team stretch your thinking about what opportunities and threats might emerge, how they might impact your organization, and what you can do about them. You learn to enact truly meaningful change rather than make incremental improvements. And it all begins with strategic thinking.
How do you foster strategic thinking throughout your organization?
Janice Molloy is a content researcher with Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Strategic Leadership: The Essential Skills
- Paul J. H. Schoemaker,
- Steve Krupp,
- Samantha Howland
The storied British banker and financier Nathan Rothschild noted that great fortunes are made when cannonballs fall in the harbor, not when violins play in the ballroom. Rothschild understood that the more unpredictable the environment, the greater the opportunity—if you have the leadership skills to capitalize on it. Through research at the Wharton School and […]
Reprint: R1301L
The more uncertain your environment, the greater the opportunity—if you have the leadership skills to capitalize on it. Research at the Wharton School and at the authors’ consulting firm, involving more than 20,000 executives to date, has identified six skills that, when mastered and used in concert, allow leaders to think strategically and navigate the unknown effectively. They are the abilities to anticipate, challenge, interpret, decide, align, and learn. This article describes the six skills in detail and includes a self-assessment that will enable you to identify the ones that most need your attention. The authors have found that strength in one skill cannot easily compensate for a deficit in another. An adaptive strategic leader has learned to apply all six at once.
The storied British banker and financier Nathan Rothschild noted that great fortunes are made when cannonballs fall in the harbor, not when violins play in the ballroom. Rothschild understood that the more unpredictable the environment, the greater the opportunity—if you have the leadership skills to capitalize on it. Through research at the Wharton School and at our consulting firm involving more than 20,000 executives to date, we have identified six skills that, when mastered and used in concert, allow leaders to think strategically and navigate the unknown effectively: the abilities to anticipate, challenge, interpret, decide, align, and learn. Each has received attention in the leadership literature, but usually in isolation and seldom in the special context of high stakes and deep uncertainty that can make or break both companies and careers. This article describes the six skills in detail. An adaptive strategic leader—someone who is both resolute and flexible, persistent in the face of setbacks but also able to react strategically to environmental shifts—has learned to apply all six at once.
- PS Paul J. H. Schoemaker is the former research director of the Wharton School’s Mack Institute and a coauthor of Peripheral Vision (Harvard Business Review Press, 2006). He served as an adviser to the Good Judgment Project.
- SK Steve Krupp is Senior Managing Partner at Decision Strategies International, Inc.
- SH Samantha Howland , a senior managing partner at DSI, leads its Executive and Leadership Development Practice.
Partner Center

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Strategic Thinking? A Complete Guide
Explore our blog on What is Strategic Thinking and learn how to make informed decisions and identify opportunities and threats to set achievable goals. Understand the fundamentals and key elements that underpin this cognitive skill. Discover the benefits of Strategic Thinking and learn how to cultivate it.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Business Communication Course
- Dealing with Difficult People
- Sentiment Analysis Training

It is not just a buzzword, or a fancy phrase thrown around in the business world. It is a crucial skill that can be applied in various aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional endeavours. So, to step on the ladder to success, it is crucial to understand the concept in detail. Further, this blog will delve deeper into What is Strategic Thinking by exploring its definition, key elements, benefits, and practical tips to develop and enhance this skillset.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Strategic Thinking
2) Benefits of Strategic Thinking
3) Key elements of Strategic Thinking
4) How to improve Strategic Thinking Skills?
5) Conclusion
Understanding What is Strategic Thinking
Strategic Thinking stands as a keystone of intentional and rational thought processes essential for navigating the complexities of business, team dynamics, or individual endeavours. It encompasses a deliberate analysis of critical factors and variables influencing long-term success. This multifaceted approach entails careful consideration of present circumstances and envisioning future scenarios, anticipating potential threats, and identifying lucrative opportunities.
Central to Strategic Thinking is the proactive identification and mitigation of risks while capitalising on emerging prospects. Individuals and organisations can navigate uncertainties with agility and resilience by cultivating a strategic mindset.Moreover, Strategic Thinking extends beyond mere planning; it requires a synthesis of research, analytical acumen, and creative problem-solving. It demands an openness to new ideas and a willingness to challenge conventional wisdom, fostering an environment conducive to innovation and growth. Influential strategic thinkers possess strong communication and leadership skills, enabling them to articulate visions, mobilise resources, and inspire action.
Strategic Thinking is not limited to top-level executives or leaders. It is a skill that can benefit anyone looking to make better decisions and achieve desired outcomes in both personal and professional settings. It can be a powerful tool whether you're an entrepreneur aiming to grow your business, a student planning your academic path, or even an individual seeking personal growth.

Why is Strategic Thinking important?
Strategic Thinking is indispensable for achieving long-term success, fostering adaptability, mitigating risks, identifying opportunities, optimising resources, solving problems, making sound decisions, and cultivating effective Leadership.
It serves as a guiding compass for individuals and organisations navigating the complexities of an ever-changing world. Strategic Thinking holds paramount importance in various aspects of life, business, and organisational management due to several key reasons:
1) Adaptability: Strategic Thinking enables individuals and organisations to anticipate and respond effectively to shifts in the external environment, whether technological advancements, market trends, or regulatory changes.
2) Risk mitigation: Strategic Thinking involves proactively assessing potential risks and vulnerabilities. By identifying threats early on, individuals and organisations can implement measures to mitigate risks, safeguarding against potential disruptions and setbacks.
3) Problem-solving: Strategic Thinking equips individuals with the analytical skills and creative mindset necessary for effective problem-solving. By approaching challenges strategically, individuals can identify root causes, explore alternative solutions, and implement strategic interventions to address complex issues.
4) Decision-making: Strategic Thinking provides a structured framework for decision-making. By weighing the potential outcomes and consequences of different courses of action, individuals can make informed decisions that align with overarching objectives and priorities.
5) Leadership development: Strategic Thinking is a hallmark trait of influential leaders. By cultivating Strategic Thinking skills, individuals can inspire and motivate others, foster innovation, and navigate organisational challenges confidently and clearly.
Learn how to spot opportunities, think systematically and understand the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix with Strategic Planning And Thinking Training .
Benefits of Strategic Thinking
Strategic Thinking is a skill that offers a multitude of benefits, empowering individuals to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve their goals. Here's how it helps individuals:
Enhanced decision-making
Strategic Thinking equips individuals with a structured approach to decision-making. By considering various factors, analysing data, and anticipating future outcomes, Strategic Thinkers are better positioned to make informed and effective decisions. This ability to evaluate options and weigh potential risks leads to more favourable outcomes and minimises the likelihood of costly mistakes.
Improved problem-solving
It goes beyond addressing immediate problems and focuses on long-term solutions. It encourages individuals to identify the root causes of challenges and develop comprehensive strategies to overcome them. By employing a systematic and forward-thinking approach, Strategic Thinkers can find innovative solutions that address underlying issues, leading to more sustainable resolutions.
Goal alignment and focus
Strategic Thinking helps individuals align their actions and decisions with their overall goals. By considering the bigger picture and evaluating how different choices contribute to their desired outcomes, Strategic Thinkers can focus and prioritise tasks that truly matter. This clarity of purpose enables individuals to allocate their time and resources efficiently, resulting in increased productivity and progress towards their objectives.
Anticipation of trends and opportunities
Strategic thinkers have an innate ability to anticipate emerging trends and identify opportunities before others do. They can proactively leverage favourable trends and capitalise on emerging opportunities by staying informed, analysing market dynamics, and considering the future landscape. This foresight enables Strategic Thinkers to stay one step ahead of the competition and make timely moves that drive success.
Effective resource management
Strategic Thinking involves assessing available resources and optimising their utilisation. By considering the strengths and limitations of resources, Strategic Thinkers can allocate them strategically to achieve maximum impact. This efficient resource management ensures that individuals make the most of their time, money, and other assets, resulting in greater efficiency and effectiveness in their endeavours.

Adaptability
In a dynamic and rapidly evolving world, adaptability is crucial for success. Strategic Thinking cultivates a mindset that embraces change and encourages individuals to be flexible in their approaches. By anticipating and embracing change, Strategic thinkers can navigate uncertainties, adapt their strategies, and seize opportunities that arise from shifting circumstances.
Learn how to maintain and strengthen client and business relationships with the Building Business Relationships Training .
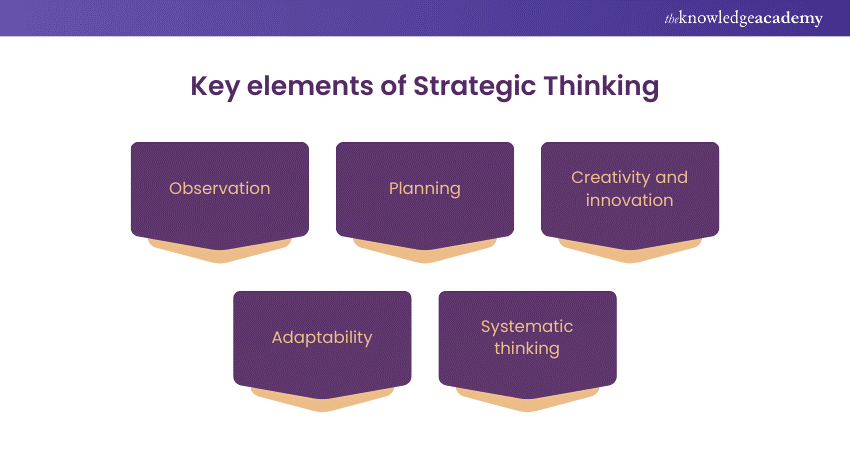
Key elements of Strategic Thinking
Observation
Strategic Thinking hinges on discerning pertinent information and assimilating it effectively. Observation, therefore, plays a pivotal role as it furnishes strategic thinkers with the insights crucial for informed decisions and meticulous planning. The accumulation and analysis of relevant data serve as the bedrock upon which strategic plans are built.
Planning, a cornerstone of Strategic Thinking, entails a multidimensional approach. It requires a deep understanding of prevailing circumstances, organisational imperatives, and insights from observation and analysis. Strategic planners adeptly delineate achievable objectives, charting a course of action while anticipating potential challenges and opportunities.
Extensive research, including competitor analysis, is often integral to planning, enabling informed decision-making and proactive adaptation to market dynamics. Strategic planning is a comprehensive endeavour analysing insights, objectives, and resources to chart a path toward organisational success.
Creativity and innovation
It encourages creative and innovative approaches to problem-solving. It involves thinking outside the box, generating fresh ideas, and exploring unconventional solutions. By embracing creativity, Strategic Thinkers can uncover new opportunities, challenge existing norms, and find unique ways to achieve their objectives.
Adaptability
Strategic Thinking requires adapting and adjusting plans based on changing circumstances. It involves being open to new information, embracing alternative perspectives, and being willing to revise strategies when necessary. Adaptability allows Strategic thinkers to navigate uncertainties and seize emerging opportunities, ensuring they stay on the right path towards their goals.
Systematic thinking
Strategic thinkers understand that actions and decisions have ripple effects across interconnected systems. They consider the broader ecosystem in which they operate and analyse how different variables interact. By taking a systematic thinking approach, Strategic thinkers can identify leverage points, understand interdependencies, and make holistic decisions that address multiple aspects of a situation.
Embrace and hone your creativity with Creative Writing Training - join today!
How to improve Strategic Thinking skills?
Strategic Thinking is important for success in today's dynamic and competitive world. It involves analysing complex situations, anticipating future trends, and making effective action plans. Fortunately, Strategic Thinking Skills can be used and developed over time through deliberate practice and a focus on continuous improvement. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to enhance your Strategic Thinking abilities:
Cultivate curiosity and open-mindedness:
Strategic Thinking begins with a curious and open mindset. Foster a habit of questioning assumptions, exploring alternative perspectives, and seeking new information. Embrace diverse viewpoints and be receptive to feedback and constructive criticism. Cultivating curiosity helps expand your mental horizons and lets you see possibilities beyond the obvious.
Develop a big-picture perspective:
Influential strategic thinkers have a knack for seeing the forest for the trees. Develop the ability to zoom out and analyse situations from a broader perspective. Consider the long-term implications of decisions and actions and strive to understand how different variables interconnect. This holistic view allows you to identify patterns, trends, and potential opportunities or disadvantages that may not be immediately apparent.
Enhance analytical skills
Analytical thinking is fundamental to strategic decision-making. Sharpen your analytical skills by practising critical thinking, problem-solving, and data analysis. Learn to evaluate information objectively, identify critical insights, and draw logical conclusions. Use tools such as SWOT analysis, scenario planning, and risk assessment to assess situations comprehensively and make informed decisions.
Foster creative problem-solving
Strategic Thinking often requires thinking outside the box and finding innovative solutions to complex challenges. Cultivate your creativity by brainstorming, lateral thinking exercises, and mind mapping. Encourage experimentation and take failure as an opportunity for learning and growth. By fostering a culture of creativity, you'll be better equipped to generate novel ideas and approaches.
Practice systems thinking
Develop a “systems thinking” mindset by recognising the interconnectedness of various components within a system. Understand how changes in one aspect of the system can affect the entire system. Use causal loop diagrams, flowcharts, and other tools to visualise relationships and feedback loops. Systems thinking allows you to anticipate the unintended consequences of decisions and develop more robust strategies.
Cultivate strategic agility
Adaptability and flexibility are essential for strategic success in today's fast-paced world. Cultivate strategic agility by embracing change, staying abreast of emerging trends, and adjusting your plans accordingly. Be willing to pivot and course-correct based on new information or shifting circumstances. Develop resilience to navigate uncertainty and thrive in dynamic environments.
Seek feedback and continuous learning
Feedback is invaluable for improving Strategic Thinking skills. Actively seek input from peers, mentors, and stakeholders to understand different perspectives and identify blind spots. Be open to constructive criticism and use it as an opportunity for self-reflection and growth. Additionally, commit to continuous learning by staying updated on industry trends, best practices, and new technologies.
Practice strategic decision-making
Finally, practice your Strategic Thinking skills by making strategic decisions in both professional and personal contexts. Start with small-scale decisions and gradually tackle more complex challenges. Evaluate the outcomes of your choices, reflect on lessons learned, and refine your approach over time. By embracing strategic decision-making as a habit, you'll strengthen your Strategic Thinking muscle and become more adept at navigating uncertainty and driving success.
Conclusion
We hope that after reading this blog, you have understood What is Strategic Thinking and its significance. It is not just a skill reserved for top-level executives; it is a valuable skill anyone can develop and apply in various aspects of life. It involves analysing situations, making long-term decisions, and connecting the dots to achieve desired outcomes. With this skill as your guiding compass, you can navigate complexities and unlock endless possibilities for success and personal fulfillment.
Improve personal and business skills that will help you think strategically and navigate the world of business with our Personal Development Training courses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Strategic Thinking is pivotal in leadership and career growth, guiding decisions towards long-term objectives. It fosters innovation, problem-solving, and adaptability, essential for navigating complexities and driving success in dynamic environments.
Industries like technology, finance, healthcare, and consulting heavily rely on Strategic Thinking. Strategic planning ensures a competitive edge in rapidly evolving sectors, such as tech, where innovation is critical. Similarly, in finance and healthcare, navigating regulatory landscapes demands strategic foresight.
The Knowledge Academy enhances global learning with a vast selection of over 30,000 online courses, accessible in more than 490 locations across 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Our diverse Online Course Catalogue covers 17 essential categories, complemented by a wealth of free educational Online Resources . These resources include up-to-date News , informative Blogs, tutorial videos, interactive webinars, and collections of Interview Questions. Furthermore, professionals looking for personalised education can take advantage of TKA's customisable Course Bundles , crafted to enrich and optimise the learning journey.
The Knowledge Academy's Knowledge Pass , a flexible prepaid voucher system, offers the freedom to join in courses over a 12-month period. Start your limitless learning adventure with us and embrace education that knows no bounds.
Discover an array of Personal Development Courses at The Knowledge Academy, featuring specialised Organisational Skills, Emotional Intelligence Training, Time Management Training, etc. Designed for different skill levels, our courses provide the necessary technical expertise to learn What is Emotional Resilience .
Whether you're starting out or looking to upgrade your Skills, immerse yourself in our Business Skills Blog for further understanding and expertise. Embark on a journey with us to elevate your Personal Development Skills!
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 20th Sep 2024
Fri 1st Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

8 Step Strategic Thinking Process To Develop A Strategic Mindset
What is strategic thinking, 8 step strategic thinking process, benefits of being a strategic thinker, what is a strategic mindset, how can managers develop a strategic mindset.
Other Related Blogs
- Define the goal: The first step in the strategic thinking process is to define the goal or objective that you want to achieve. This should clearly and clearly state what you want to accomplish.
- Gather information: Once you have defined your goal, you must gather information to help you make informed decisions. This may involve researching the market, analyzing data, and gathering stakeholder feedback .
- Analyze the situation: After gathering information, the next step is to analyze the situation. This involves identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) that may impact the success of your plan.
- Develop a strategy: Based on the analysis, you can develop a strategy that outlines the steps you need to take to achieve your goal. Your strategy should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) .
- Implement the plan: Once you have developed your strategy, you must implement it. This involves allocating resources, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities to individuals or teams.
- Monitor progress: As you implement your plan, it is essential to monitor progress regularly. This allows you to identify any issues or challenges and adjust as needed.
- Evaluate outcomes: After implementing your plan, you should evaluate the outcomes to determine whether you achieved your goal. This can involve analyzing data, gathering feedback, and assessing the impact of your plan on stakeholders.
- Learn and improve: A step that continuously keeps happening in strategic thinking process includes learning from your experience and using the insights gained to improve future plans is essential. This involves identifying what worked well and did not and adjusting your approach as needed.
- Better decision-making: Strategic thinkers can analyze situations and identify the best action, leading to better decision-making and outcomes.
- Improved problem-solving: Strategic thinkers are skilled at identifying problems, developing solutions, and implementing strategies to solve complex issues.
- Increased innovation: Strategic thinkers are creative and innovative, constantly exploring new ideas and approaches to improve performance and achieve goals .
- More decisive leadership: Strategic thinkers can see the big picture and develop a clear vision, which can help them inspire and motivate others to achieve shared objectives.
- Better resource management: Strategic thinkers are adept at managing time, money, and people, to achieve desired outcomes efficiently and effectively.
- Enhanced adaptability: Strategic thinkers can anticipate and respond to changes in the environment, enabling them to adapt quickly and effectively to new situations.
- Top 12 Succession Planning Questions To Find The Potential Successors
- Training for Conflict Management Made Easy for Managers 5 Easy Steps
- The silent manipulation: Exposing workplace gaslighting and its effects
- How To Develop Integrity In The Workplace? 5 Proven Tips
- 10 Successful Workplace Delegation Examples for Managers
- Training In House Excellence: Empowering Your Team Members from Within
- 8 Fun Ways to Celebrate Goals Accomplishment with Your Team
- Becoming an Effective Employee Relations Manager: 5 Skills You Need
- How To Find An Executive Coach? A 5 Step Guide For Managers
- From Good to Great: Enhancing Customer Service Skills for Lasting Impressions
- Big-picture thinking: Strategic thinkers can see the big picture and consider all the factors that may impact the success of a plan. They analyze data, assess risks, and consider different scenarios before making decisions.
- Creativity and innovation: Strategic thinkers are creative and innovative, constantly seeking new and better ways to achieve their goals. They are not afraid to take risks and experiment with different approaches.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Strategic thinkers can adapt quickly to changing circumstances and adjust their plans accordingly. They are comfortable with ambiguity and uncertainty and can pivot their strategies as needed.
- Focus on outcomes: Strategic thinkers focus on outcomes and results rather than just completing tasks. They are driven by a desire to achieve specific goals and are willing to put in the effort required to achieve them.
- Collaborative mindset: Strategic thinkers understand that achieving success requires collaboration and teamwork. They can work with others to achieve shared objectives and are skilled at building relationships and partnerships.
- Focus on the big picture: Managers should develop the ability to see beyond day-to-day operations and focus on the bigger picture. They should consider how today’s decisions will impact the organization’s long-term goals.
- Embrace change: A strategic mindset requires managers to be comfortable with change and uncertainty. Therefore, managers should be open to new ideas and be willing to adapt their approach to changing circumstances.
- Analyze data: To make informed decisions, managers need to be able to analyze data and identify trends. They should understand the organization’s key performance indicators (KPIs) and use data to guide their decisions.
- Develop a vision: A strategic mindset requires managers to have a clear vision for the organization’s future. Managers should be able to articulate their vision and communicate it effectively to their team .
- Build a strong team: Strategic thinking is a collaborative process. Therefore, managers should build a strong team that includes individuals with diverse skills and perspectives.
- Be proactive: A strategic mindset requires managers to be proactive rather than reactive. Managers should anticipate potential challenges and opportunities and take action to address them before they become problems.
- Learn continuously: A strategic mindset requires managers to be lifelong learners. Therefore, managers should be open to new ideas and actively seek opportunities to develop new skills and knowledge.
- Seek feedback: To develop a strategic mindset, managers should seek feedback from their team, colleagues, and stakeholders. They should be open to constructive criticism and use it to improve their approach.
Develop the growth mindset to create ambitious strategies!
Download the free growth mindset toolkit for managers to get started today.
Download Now
What are the 6 Ps of strategic thinking?
What is the mindset of a strategic leader, what are the steps of the strategic thinking process.

Strategic Thinking Training For Leaders Simplified
10 best strategic thinking coaches to speed up your growth, 5 powerful skills to become an exceptional business leadership coach, 8 strategic thinking examples to help you succeed.
- Coaching Skills Training
- Coaching TIPS²™
- Continuous Improvement Coaching
- Courageous Conversations Workshop
- Executive Coaching Program
- Feedback 360
- Safety Coaching
- Sales Coaching Training Program
- Free Consultation
- Applied Strategic Thinking®
- Strategic Leadership Course
- Strategic Teaming
- Strategy Development Processes and Services
- Communication Training for Managers
- Conflict and Collaboration
- Confronting Racism Workshop
- Delegation & Accountability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Workshop
- Flexible Leadership
- Leading Change
- Leading Groups to Solutions
- Leading Innovation
- Mid-Level Management Training
- Qualities of Leadership
- Bottom Line Leadership
- Customized Leadership Development Programs
- Leadership Development Program Design
- Mini-MBA & Operational Finance
- Problem Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace
- Transition to Leadership
- Virtual Leadership
- High-Performance Teamwork
- Leadership Team Alignment Workshop
- Orienteering
- Corporate Outdoor Training and Team Building
- Retreats for Teams
- Innovation Skills Training
- Personal Impact Workshop
- Supervisor Training Programs
- Customization of CMOE’s Learning Library
- Full Curriculum Development and Design
- Learning & Development Advisory Services
- Bottom Line Leadership Training
- Consulting Services
- Leadership Retreats
- Learning and Development Consulting Services
- Needs Analysis and Organization Assessments
- Transformation & Change Solutions
- Facilitator Training Workshop
- Empathic Leadership
- Supervisor Development Series
- All Courses
- Digital Learning
- Books and Publications
- Assessments and Surveys
- Clients Served
- History and Experience
- Meet the CMOE Team
- Testimonials
- Articles & Tools
- Scenario Templates
- Certified Partners
- Event Resources
- Industry Insights
- Resource Library
- Video Library
- News and Events
- Professional Accreditation and Continuing Education Units
- Surveys & Assessments
- Strategic Thinking
- 360-Degree Leadership Assessment
- Adaptive Communication
- Adaptive Leadership
- Authentic Leadership Style
- Boundary Spanning Leadership
- Business Change Strategies
- Business-Strategy Principles
- Capacity Building
- Cascading Strategy
- Change Management
- Charismatic Leadership
- Coaching Framework
- Coaching in the Workplace
- Coaching Leadership Style
- Collaborative Coaching
- Competency Assessment
- Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
- Core Competence
- Corporate Strategic Planning
- Crisis Leadership
- Critical Success Factors
- DEI in the Workplace
- Directive Leader
- Empathetic Leadership Definition
- Horizontal Leadership
- Inclusive Leadership
- Innovation Strategy
- Leadership Assessment
- Leadership Competency Framework
- Leadership Model
- Management Succession Planning
- Operational Excellence
- Organizational Alignment
- Participative Leadership Style
- Performance Deficiency Coaching
- Persuasive Leadership Style
- Problem Solving in Business
- Servant Leadership Style
- Strategic Agility
- Strategic Alignment
- Strategic Audit
- Strategic Framework
- Strategic Initiatives: Examples and Development
- Strategic Management
- Strategic Mindset Competency
- Strategy Committee
- Strategy Issues
- Strategy Maps
- Supportive Leadership Style: Definition and Qualities
- Team Building Interventions
- Team Environment
- Team Performance Assessment
- Teamwork Atmosphere
- Total Employee Involvement
- Training Needs Analysis (TNA) Definition
- Transformational Leadership
- Visionary Leadership Style
What is Strategic Thinking?
Strategic thinking is simply an intentional and rational thought process that focuses on the analysis of critical factors and variables that will influence the long-term success of a business, a team, or an individual.
Strategic thinking includes careful and deliberate anticipation of threats and vulnerabilities to guard against and opportunities to pursue. Ultimately strategic thinking and analysis lead to a clear set of goals, plans, and new ideas required to survive and thrive in a competitive, changing environment. This sort of thinking must account for economic realities, market forces, and available resources.
Strategic thinking requires research, analytical thinking, innovation, problem-solving skills, communication and leadership skills, and decisiveness.
Why is Strategic Thinking Important?
The competitive landscape can change quickly for any organization. New trends may emerge quickly and require you to take advantage of them or fall behind. By incorporating everyday strategic thinking into your work and life routines, you will become more skilled at anticipating, forecasting, and capitalizing on opportunities.
On an individual level, thinking strategically allows you to make a greater contribution in your role, become more essential to your organization, and prove that you’re ready to control greater resources.
What is Strategic Thinking in Business?
During an organization’s annual strategic planning process, leaders often compile, analyze, and synthesize external and internal data and ideas to develop its strategic intent and build a strategic narrative. This document will guide the company into the future for a defined period of time. Leaders then choose and plan specific actions that will accomplish these strategic initiatives.
Businesses also need to schedule a time for strategic thinking and reviews throughout the year. Leadership teams should periodically examine their strategic initiatives to ensure execution is taking place, review, and sustain the effort across the organization.
What is Strategic Thinking in Leadership?
Business leaders and stakeholders use strategic thinking and analysis to decide what product mix they’ll offer, what competitive landscape to compete in (or not compete in), and how limited resources will be allocated such as time, employees, and capital. They must decide how to best structure enroll others to achieve important objectives and to avoid putting resources at unnecessary risk of loss.
What are the Components of Strategic Thinking?
If you’re working on your company’s strategy, you’ll need to engage in analysis, problem-solving, decision making, and leading through change.
As you create a strategic direction or plan, you’ll analyze:
- Business opportunities and vulnerabilities
- Feasible of each idea or risk
- The costs associated with each move you are considering
- The likelihood that various tactics will be effective
- Methods of aligning objectives with the overall plan
- The effects of competitors, suppliers, customers, and new substitutes might have on your strategic plans
As you discover obstacles during the planning process, you’ll problem-solve by:
- Gathering relevant information about the problem
- Clearly defining the problem from a strategic point of view
- Brainstorming possible solutions
- Imagining further challenges and how to overcome them
- Delegating assignments of various parts of this strategy to key associates
Strategic thinking requires agility and decisiveness in choosing a plan and sticking with it. However, you have to be aware of new, more promising opportunities. It is a balancing act between consistency and flexibility. You and your team will:
- Make sure decisions are well-informed by thorough research
- Choose objectives and accompanying metrics
- Prioritize objectives
- Follow a standard decision-making process
- Build consensus, when necessary
During strategic planning, you will need to communicate ideas to your staff and gather feedback from them. You’ll then utilize effective channels to communicate a compelling vision of the completed plan to all employees and keep them focused on their contribution to the plan.
How to Improve Strategic Thinking Skills
There are five steps to improving your strategic thinking skills:
1) Set aside time to reflect and plan for the future, identify trends, prioritize tasks, and determine where to allocate resources
2) Uncover your own biases so you can think more clearly about strategy
3) Listen to subject matter experts and opinion leaders in your organization to obtain higher quality information you can use in your strategic thinking
4) Learn to ask good questions to uncover better options and plans—questions such as “Is this idea from a credible source?” and “Is this idea logical?”
5) Explore all the consequences of different strategies and directions
Get more details by reading CMOE’s article, “5 Ways To Improve Your Strategic Thinking Skills Today.”
Books on Strategic Thinking
To develop strategic thinking on your own, consider studying the following books:
Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge in Business, Politics, and Everyday Life : This strategy classic came out in 1991. It’s a great introduction to practical ideas for using good strategic plans to outmaneuver your competition.
Ahead of the Curve: CMOE’s research-based books and publications can help employees at all levels develop better strategic thinking skills and perform more like a leader.
How to Teach Strategic Thinking
Attending a quality workshop is a quick way to improve your strategic thinking skills or to help your employees develop them through strategic thinking exercises. Rather than simply discussing skills, the goal of instruction should be to help you immediately apply strategic thinking to your unique job role.
Strategic thinking is taught best when a workshop is led by experienced facilitators. They should give you feedback as you develop a plan that you can take back to your job and implement right away. Strategic thinking training will help you see how you can improve your organization.
The workshop should:
- Identify learning goals and desired outcomes
- Include pre-reading material of both classic and contemporary articles on strategy
- An opportunity to review, discuss, and clarify best practices, frameworks, and actionable tools and concepts.
- Simulations or learning labs that allow people to practice strategic thinking skills immediately
- Debrief and review simulation or learning lab results and highlights strategic success factors that work. Mistakes and failures are important to learn from and provide insights and discoveries.
- An accurate assessment of your unique mix of existing strategic thinking skills and areas where gaps exist.
- Support and provide guidance in creating a customized and strategic plan that you can immediately apply to your work.
As with any skill, you’ll improve at strategic thinking the more you practice it and the more experience you gain. It’s definitely worth the time and effort; importantly, strategic thinking distinguishes mediocre businesses and workers from those that excel.
Clients We’ve Worked With
Contact form.
Need More Information? Please fill out the following form and we will be in contact with you with more information.
" * " indicates required fields
As Featured In:
The Better Business Bureau has determined that CMOE meets accreditation standards. These standards verify that CMOE’s product quality and competence enhance customer trust and confidence.
©2024 Center for Management & Organization Effectiveness. All rights reserved.
- What is i-nexus
- Why i-nexus
- Strategy Execution
- Hoshin Kanri
- Operational excellence
- Case studies
- i-nexus reviews
- Strategy execution guide
- Hoshin Kanri guide
- Operational excellence guide
- Book a demo
- Demo on-demand
- Plan to practice
- Buy or build
- Customer success overview
- Customer success journey
- Customer services
- Customer support
- News & Press
Why critical thinking is crucial for strategic planning and execution
From paper exercise to deployment reality - the critical thinking process behind deploying your strategy is crucial to your success. today we’re examining the five-step critical thinking process to laying out a high-quality, focused, measurable, and realistic annual strategic plan..
Written by: James Milsom, Head of Marketing
Regardless of the Strategy Execution methodology applied, being successful in the modern era of strategic management is through effective planning, implementation, execution and measurement of efforts.
However, between the planning and implementation phase there is a juncture of grave importance – where we define three-five year strategic objectives and segment these into annual breakthroughs.
Doing so is not a simple tick box exercise of rinsing and repeating what you do on a daily basis, perhaps with a slight increment of measurement attached.
Instead, it requires your leaders and supporting stakeholders to think critically.
Going beyond the realm of the possible and into, quite frankly, the unknown to your business can be daunting.
However, it is only through aiming for performance levels out of your existing reach that you can develop improvements, embed those into your daily management, and succeed in Strategy Execution Management.
Today’s overview looks at the critical thinking required to turn your strategy from a paper exercise into a deployed reality, tips on the five steps you must complete to achieve a new level of thinking for your strategy, and the reasons why you’ll conclude that is paramount to your success.
When should you plan?
To begin, we are often asked when you should begin strategic planning.
This is wholly dependent on your business norms, but typically the strategic planning process should start halfway through the calendar year (or your financial year).
Then, after three-four months of planning you can define your level 1 Hoshin (your three-five year plan), and after than level 2.
All in, the process will take half a year.
To learn about the different levels of deployment, be sure to watch our accompanying webinar.
And then, at the end of year you will be well placed to communicate the next year's improvement priorities, the level 1 and 2 plans, and action plans in place to convert these into reality
The following considers developing your annual strategic plan from level 0 – the top level of your organization.

The five steps of annual strategic planning
What you want to achieve will be set out in your three-five-year strategic plan, which is naturally linked to your business policy and the voice of the customer.
This must then be translated into annual breakthroughs in your second step – bitesize chunks of initiatives to be tackled each year.
The aim at the second step should be to front-end load a set of annual objectives, with the logic being that the majority of the value is to be secured in the first year.
This is because as you move into the second and third years it becomes tougher to achieve the objectives which are set.
The mountain of objectives
Those objectives set in the first year will be foundational in nature, therefore you are, to consider a metaphor, at the start of the mountain.
The opening terrain is less treacherous than say the mid-way point and then the peak. Your strategic plan should aim to navigate half of the mountain of objectives, successfully, in the first year.
The mindset is one where you do not hesitate and push actions to a tomorrow and beyond. The time to act is now.
Naturally, the more success garnered at the beginning of your strategy, commitment and engagement levels will be higher moving into year two and so on.
Processes are embedded and the actions become standardized ways of working for your organization, meaning that you continue to reap the rewards of the first year well into the future.
Your objectives must have a ‘from’ and a ‘to’ involved. Here are some examples:
- We will improve our defect rate on wireless handsets from 3 Sigma to 4.3 Sigma
- We will increase on time deliveries from 92% to 70%
- We will reduce our packaging costs by 25%
- We will grow our market share in wearables from 12.3% to 19%.
Checklist for designing annual breakthrough objectives
Use this 10-item check list to review your annual goals:
- Does it identify how far to improve in the first-year in order to hit the three-five year breakthrough objective?
- Does it divide the three-five-year breakthrough into annual amounts?
- Does it quantify the first-year goal?
- Is it a stretch goal?
- When we accomplish the annual objective, does the customer benefit?
- Will it provide significant competitive advantage?
- Does it require multi-functional involvement?
- Will it result in a new standard and / or system?
- Is the answer to 'how do I do it?' unknown?
- Have you checked that no problems exist in the other areas that need to be fixed first?
It is not enough to simply re-write your existing goals – it must stretch your business beyond its existing levels of performance.
Remember, if it does not do this, or the above answers aren’t yes, this is not an annual objective which supports your strategic plan.
Now you must switch gears to consider how you can take annual breakthrough goals and convert them into tangible action plans .
Action plans are a crucial step in strategic implementation, involving stakeholders and teams in defining the steps which must be taken to achieve improvement priorities.
Improvement priorities are the drivers you’ve identified which, likely in the form of a process, can create sustainable results.
They are, indeed, not short-term tasks. Instead they are focused on the voice of the customer and their needs.
Fine tuning your thinking
How you identify improvement priorities can be as simple as fine-tuning your critical thinking.
For example, if you were asked to improve sales for the business, that is a vague, if not frustrating task to be set, immediately failing our criteria for the priority to be focused and long-term.
However, if you were asked to identify what process are preventing you from entering what we perceive to be our most valuable new markets, that gives you a focus.
From there you would incorporate techniques such as value stream mapping and the 5 whys to reach your conclusions and form priorities.
But remember, don’t take on too many priorities. A priority is not a priority when everything else is a priority.
Additionally, if you cannot easily communicate and measure the top-level improvement priorities to your business, then you must re-evaluate your priorities.
Through critical thinking you will be in a position where you know, with confidence, what you can do to enable your business to reach its annual breakthrough objectives.
Checklist for defining annual improvement priorities
Use this seven-item check list to review your priorities:
- Does it lead to creation of a sustainable process?
- Does it lead to creation of a result-oriented process?
- Does it meet current, latent or emerging customer needs?
- Is it easy to communicate?
- Does it demonstrate a simple flow of logic?
- Is it measurable, but not a measure itself?
- Does it exceed budget targets?
The end-result must be a clear set of priorities that are targeted for improvement, putting you beyond your existing performance.
If it does not, or fails to exceed your budget targets, this is daily management, not breakthrough activity.
4) How Much
Moving into the how-much category we start to turn our attention to measuring the effectiveness of processes. This relates to target setting.
Improvement priorities will guide you as to how you can achieve breakthrough change. Target will tell you how much you must improve by and by what date.
Targets within a Hoshin context are known as Targets To Improve. Their structure is:
From X To Y By 123
The value of target setting
Having identified the processes that are worth improving, a measurement system must be put into place to gauge efficacy, otherwise you will be unclear as to your abilities against set targets.
A sound, working knowledge of statistical control is beneficial here as you can set out and manage expectations of performance based on your previous analysis.
To learn more about statistical control, read our Six Sigma overview .
Examples of Targets To Improve
- We will decrease churn rate from 14.5% to 11% by August
- We will reduce our cost per acquisition from $445 to $380 by September
- We will decrease product defects from 15% by 10% by November
- We will double sales growth in the wearables market from £3.3M to £6.6M by December
In any case, it is highly recommended you measure what matters to your customers, link it to the process and the improvement priority in question.
Checklist for setting Targets To Improve
Use this seven-item check list to set effective targets:
- Does it track progress towards full implementation of the improvement priority?
- Can it be broken down into at least monthly progress increments?
- Does it track progress towards achieving the annual objectives?
- Does it show when the improvement priority has an impact on the annual objectives?
- Does it measure results, rather than action plan milestones?
- Is it easy to calculate and communicate?
To track your targets it is recommended that you adopt something similar to Hoshin Kanri’s Bowling Chart.
To learn more about the power of the Bowling Chart, click here for our overview .
This is absolutely unique to your business, culture and policy.
You must, at this stage, know what resources and people are needed to achieve your annual objectives and improvement priorities.
Ask yourself, who will deliver the results you need, most effectively?
How to know who to involve
In terms of achieving a sense of who should be involved, consider approaching the analysis with this in mind:
- Establish which resources are required on daily management activities (operational / business as usual)
- You are investing in improving a process in one year and the moment after that your process becomes standard value delivery. It is not a project.
- Which resources (human, systems and material) have the greatest influence or opportunity to impact the improvement priority and targets to improve?
- The largest sum or most available resources do not necessarily correlate to having the greatest impact
- These are not necessarily the resources that keep operations running each day, instead they are the talents, thinkers and doers who are best placed to help you realize a step change in performance this year.
- This will, naturally, involve crossing organizational boundaries and challenge existing siloes – be wary of the role of culture here .
Translating this into a systematic view of what resource is needed in which area can be achieved through a planning system such as the Hoshin X-Matrix .
Whether you name this view your policy deployment matrix, strategy matrix or Hoshin X-Matrix, it is a narrative of what your business will achieve, how far they will go, how it will be achieved, how much resource is needed to do this, and who is involved.
From here primary and secondary responsibility will be assigned to leaders (via a dot on the matrix – these people own the objective.
The end result is a total view, whether on a company, site / plant and division level of the deployment strategy and plan.
But be mindful, the further layers you create, the more administration involved, and thus fatigue and disengagement with the strategy.
Is critical thinking important for Strategy Execution Management?
Critical thinking is paramount to your strategy’s success.
Without establishing objectives, prioritizing processes to improve, setting targets (and measuring them), all the while securing the right resources to do this, you may wonder how businesses achieve their strategic goals.
It is with great effort and alarming failure rates.
Challenging your thought processes and your strategy, and more importantly, customers will reap the rewards.
What will your next steps be in Strategy Execution Management?
Click here to visit our strategy execution knowledge hub , filled with content to support you in embracing the 'no normal' of strategy in the 2020s and beyond, or explore these recommendations:
- Strat to Action – Developing a countermeasure culture : Watch our on-demand presentation of how you can guide your business towards using data and countermeasures to drive strategic success.
- How AI and machine-assisted learning will help your Strategy Execution : As Artificial Intelligence becomes a mainstay in our lives, read how AI and machine-assisted learning will evolve to support your Strategy Execution.
- Download our Key to Strategy Execution eBook : Read how companies like Danaher and HP have mastered Strategy Execution Management and what you can learn from them.
About the author
James Milsom is Head of Marketing at i-nexus. James has wide-ranging experience in markets such as telecommunications, energy, education, and software.
As Head of Marketing, his drive is to raise awareness and understanding of the challenges facing enterprises in delivering strategic objectives and transformation amidst changing markets and the obstacles traditional tools and methods present leaders. If you’d like to talk more about Strategy Execution, reach out to James on [email protected] or connect with him on LinkedIn for the latest insights.

A beginner's guide to Gantt charts

Why you should use the x matrix strategic planning tool

Danaher, Ingersoll Rand, and Xerox: Hoshin Kanri case studies
A strategic management process: the role of decision-making style and organisational performance
Journal of Work-Applied Management
ISSN : 2205-2062
Article publication date: 16 February 2023
Issue publication date: 24 April 2023
The purpose of this paper is to present a conceptual framework for integrating strategic thinking factors, organisational performance and the decision-making process.
Design/methodology/approach
The methodology involves a synthesis of literature and proposes a framework that explores the relationship between strategic thinking enabling factors, organisational performance and the moderating effect of decision-making styles.
The framework includes strategic thinking enabling factors (systems perspective, focused intent, intelligent opportunism, thinking in time and hypothesis-driven analysis), organisational performance and the moderating effect of decision-making styles (intuitive and rational).
Research limitations/implications
This research results in a conceptual model only; it remains to be tested in actual practice. The expanded conceptual framework can serve as a basis for future empirical research and provide insights to practitioners into how to strengthen policy development in a strategic planning process.
Originality/value
A paradigm shift in the literature proves that strategic management and decision-making styles are vital in determining organisational performance. This paper highlights the importance of decision-making styles and develops a framework for strategic management by analysing the existing strategic management literature.
- Strategic management
- Intuitive decision-making
- Rational decision-making
- Strategic thinking process
- Organisational performance
Sinnaiah, T. , Adam, S. and Mahadi, B. (2023), "A strategic management process: the role of decision-making style and organisational performance", Journal of Work-Applied Management , Vol. 15 No. 1, pp. 37-50. https://doi.org/10.1108/JWAM-10-2022-0074
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2023, Tamilarasu Sinnaiah, Sabrinah Adam and Batiah Mahadi
Published in Journal of Work-Applied Management . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
Managers are appointed to achieve the organisation's objectives and goals. As these objectives gradually increase with competition, managers must become strategic thinkers with excellent decision-making skills. The strategy towards the organisational outcome highlighted in this section has been widely debated among academic scholars and practitioners. Organisational strategies are essential in sustaining an organisation's competitive advantage to face a complex and uncertain future.
Effective strategic management frameworks enable managers to focus on the complex issues that must be prioritised to hasten decision-making processes ( Dlamini et al. , 2020 ). Whilst enabling managers important to make the decisions needed to direct the organisational effort towards overcoming specific issues ( Wang et al. , 2021 ). The organisation's effectiveness in addressing critical issues with solutions that best fit the current environmental factors will ensure the vitality and image of the organisation. Strategic management is pertinent to manage the organisation in a continuous, systematic manner.
The first segment of strategic management is the effective action programs chosen to reach these goals and objectives.
The second segment is the resource allocation pattern that relates the organisation to its environment.
Moreover, strategic management is defined as translating the thinking process into an action plan that benefits the organisation to sustain its competitive advantages. Strategy also can be categorised as strategic thinking and strategic planning. Strategy is also the commitment of the top-level management to attaining outcomes aligned with the organisation's strategic objectives. Strategy can be realised when there is consistent outcomes or patterns over the years. Therefore, strategy is planning for the future or determining patterns based on consistent outcomes. Organisations must develop plans and also evolve patterns derived from previous organisational outcomes. These phases can be explained as intended strategy and realised strategy.
The effectiveness of the strategies employed can indicate the organisation's performance in achieving its objectives and goals. Organisations need to measure the outcome of the strategies employed by having measurable objectives that will enhance the employees' commitment towards achieving the goals. Conversely, organisational learning and financial measures such as organisational profitability can also benchmark organisational performance. The responsiveness of organisational performance has a direct relationship and is influenced by management efforts to emphasise leadership within the organisational structure. This is done by observing the support and strategies utilised by managers to achieve the objectives and goals. This paper aims to enhance an understanding of strategic management processes involving decision-making styles towards organisational performance. First, this paper highlights strategic management's operational and theoretical approach towards organisational performance. Moreover, this study enhances the result of previous literature on strategic enablers by explaining the effort involving decision-making to strengthen the organisational structure, particularly the decision-making styles (intuitive and rational), that moderates the relationship between the strategic thinking process and organisational performances ( Ritter, 2014 ).
Academic scholars and practitioners have highlighted the importance of strategic management in measuring organisational performance in terms of innovation, entrepreneurship, technology, knowledge, economics, healthcare and organisational performance ( Adam et al ., 2018 , 2020 ; Alosani et al. , 2020 ). Conversely, there is a knowledge gap on the effective judgement practices of strategic management enablers and organisational performance during decision-making ( Abuhjeeleh et al ., 2018 ; Acciarini et al. , 2021 ; Elrehail et al ., 2020 ; Nguyen, 2020 ). This paper analyses the relationship between strategic management and organisational performance and suggests a framework to elucidate the relationship variables such as moderators, rational and intuitive decision-making styles.
2. Literature review
Strategic management is applying strategic decisions towards the organisational vision to achieve strategic competitiveness and sustain competitive advantages ( Alosani et al. , 2020 ; Rodrigues and Franco, 2019 ). Strategic management is a cognitive impairment of structuring the internal capabilities to fulfil external demands and involves plans, patterns, positions, perspectives and plots ( Mintzberg et al ., 2020 ). Strategic management is the managerial discourse involving a framework of the decision-making process, which highlights how the strategy process is formulated in organisations, acknowledging the cognitive management structure of the organisations. Additionally, the organisation's members need to respond effectually to the decisions made by the management and cooperate to ensure that the organisational vision is reached, given that this will affect the organisational adaptability, legitimacy and performance ( Johnsen, 2015 ). Organisations must be aware of the uncertain environments that can influence their welfare.
Consequently, the strategic management process can be reflected in two directions: strategic planning and strategic thinking. Strategic planning emphasises formulating strategies or disciplined efforts to produce strategic decisions to achieve the organisation's objectives ( Bryson, 2018 ). Strategic planning also can be reflected as a system that enhances the decision-making process among the members of an organisation. The strategic management process needs to be fulfilling for the organisation to sustain its competitive advantages. Moreover, strategic thinking is creative, disruptive, future-focused and experimental and often contradicts traditional notions of strategic planning ( Liedtka, 2000 ). Strategic planning is the principal element of the strategic management process involving resource management, implementation, control and evaluation of strategies ( Poister et al ., 2010 ). Strategic planning focuses on formalising existing strategies and employing creativity to enhance perspectives ( Mintzberg et al ., 2020 ). The uncertainties of environments and conflicting perspectives can be evaluated and addressed using strategic thinking as a part of the organisational decision-making process ( Chin et al ., 2018 ). Studies by Goldman et al . (2015) indicated that organisational members are not actively involved during the strategic decision-making process, leading to the decline in the organisation's performance.
The importance of the strategic decision-making process towards organisational performance was emphasised by Steptoe‐Warren et al. (2011) . The research suggested that evaluating, identifying and validating the process will enhance the strategic thinking process to positively impact performance ( Norzailan et al ., 2016 ). Moreover, strategic thinking plays a vital role in analysing the external factors influencing the process. If the organisational members take it lightly, it will lead to perception deficiencies ( Kızıloglu and Serinkan, 2015 ). Additionally, the study highlighted that strategic planning occurs after strategic thinking ( Alatailat et al ., 2019 ; Bonn, 2001 ; Mintzberg, 1994 ). Consequently, this study will focus on strategic thinking as the fundamental phase in the strategic management process.
A conceptual framework that highlights the management principles among the business process in delivering effective solutions for problems is shown in Figure 1 .
3. Strategic management
Strategic management is defined as a framework for achieving success, and it is pivotal for organisations to achieve their objectives and continuously perform better ( Elliott et al ., 2020 ). Additionally, strategic management is a continuous process of looking for a better action plan to ensure the organisation's competitiveness.
3.1 Strategic thinking
The most challenging issue an organisation faces is awareness of the strategic vision and missions, available resources and identifying opportunities for growth within the organisation ( Bryson, 2018 ). Therefore, strategic thinking is a vital element in the chain of processes, which must be carried out effectively and systematically ( Sahay, 2019 ). Nevertheless, organisations need to be aware that strategic thinking can fail miserly if the decision-makers do not realise the strategic enablers or the factors responsible for the effective strategic thinking process. Strategic enablers influence the thoughts and decision process of the organisational members ( Goldman et al ., 2015 ). Therefore, strategic enablers will lead the organisation's members towards idea growth and personal development, while strategic thinkers expedite the organisational performances ( Alatailat et al ., 2019 ).
Individuals involved in the organisational structure utilise their experiences and thought processes in managing conflicts to enhance strategic thinking ( Alaarj et al ., 2016 ). Strategy managers or thinkers recognise the relationship between business responsibilities and departments and organisations and their business stakeholders ( Cabral et al. , 2019 ). This relationship is known as “system thinking”, where an organisation explores the structure reflected in the action and environment that causes the incident. Additionally, the direction or the organisational destiny is a type of strategic intent utilised to help achieve the business objectives. This occurs when all the employees can concentrate on their purpose until it is achievable.
Strategic intent is pertinent in increasing competitive advantages and improving organisational performance ( Chen et al ., 2015 ). Intelligent firms must be considered before becoming competitive to ensure the organisation can create intelligent opportunities to lead the business emerging strategies towards their vision ( Alaarj et al ., 2016 ). Conversely, the organisation should integrate previous events with the current situation to achieve and align with the organisation's objectives. This is vital for organisations to connect to the past and present environment to envision the firms and prepare for any internal or external challenges in their business ( Abubakar et al ., 2019 ). A hypothesis-driven analysis is the core element in the strategic thinking process to gather relevant information regarding the business. Therefore, the challenges faced must be transformed into a hypothesis-driven analysis to understand better the measures needed to be taken by the stakeholders to improve the organisational performances.
3.2 Decision-making style
The role of managers within an organisation must be elucidated to help enhance the decision-making process to create competitive advantages for the organisation ( Dionisio, 2017 ). Moreover, Porter (1990) emphasised the differences between competitive strategy and competitors. Decision-making styles also play a vital role in formalising the strategic decision procedure and can be defined as a habitual or formal response pattern taken by managers when there is an incident ( Kulcsár et al ., 2020 ). According to Acciarini et al. (2021) , decision-making styles are directly related to cognitive styles involved in the strategic thinking process. Decision-making style, which can be both at individual and team levels, can be classified into intuition and rationality ( Dayan and Di Benedetto, 2011 ; Dayan and Elbanna, 2011 ; Giermindl et al ., 2022 ; Luan et al ., 2019 ; Sukhov et al ., 2021 ). Therefore, the author highlighted that cognitive styles could be divided into two different categories: “feeling as information evaluators”, where managers actively gather information intuitively, and “thinking as information evaluators”, where managers systematically collect information ( Behling et al ., 1980 ). Alternatively, decision-making styles can be considered intuitive and rational information gathering and evaluating styles ( Calabretta et al ., 2017 ).
The intuitive decision-making style can be defined as the episodes of uncertainty patterns of action imposed by managers or the decision-makers based on the current situation. In addition, intuitive decision-makers must be aware of current issues and relate the relationship between cognitive schemes with holistic thinking to resolve problems ( Calabretta et al ., 2017 ). It is also believed that the intuitive decision-making process can be influenced by a sudden awareness of information ( Zhu et al ., 2017 ). Decision-makers can determine solutions without fully understanding or realising the extent of information available. Studies agree that the intuitive decision-making process can occur when unsorted information is restructured into an organised pattern of action that transforms into a conscious solution ( Zander et al ., 2016 ). Furthermore, the intuition organisations performance is enhanced when decision-makers utilise the intuition decision-making style when there is no access or relevant analytical data to support them in making strategic decisions that align with the organisation's objectives ( Temprano-García et al ., 2018 ). Conversely, intuition decision-making also contributes positively to the organisations performance when the issues are resolved quickly despite limited resources or knowledge on the current issues.
Studies by Sauter (1999) emphasised that intuition decision-making or illumination is a sudden awareness of information where the decision-makers are unaware of fundamental facts or information. The author also highlighted several ways to establish the intuitive decision-making process. First, detection is an intuition where decision-makers think of several different situations rather than focusing on the current issue ( Kolbe et al. , 2020 ). Working on current strategic issues will enable managers to comprehend related information to help solve the issue by connecting facts or elements that previously did not relate to each other ( Temprano-García et al ., 2018 ). Another form of intuition is evaluation, where the solution appears as an available option creating a sense of certainty or vague feelings towards the analytical data ( Hodgetts et al ., 2017 ).
Conversely, the intuition decision-making process can also be hypothesised as an explicit and implicit decision-making style ( Tabesh and Vera, 2020 ), where explicit decision utilises feelings or emotion and implicit decisions refer to the experience of the relevant situation ( Bhat et al ., 2021 ; Remmers et al ., 2016 ). Moreover, intuitive decision-making styles also utilise the subconscious processing of verbalised and nonverbalised facts or information ( Tabesh and Vera, 2020 ). A recent study suggests that intuitive decision-making aided managers in enhancing the strategic decision towards the organisation's performance ( Francioni and Clark, 2020 ).
Rational decision-making involves several solutions that will be analysed based on the issues and the relevance of this information towards the current problem before implementing the final decision ( Temprano-García et al ., 2018 ). The structured information consisting of conscious thinking must be evaluated critically ( Acciarini et al. , 2021 ). In addition, the rational decision-making process will enhance the effectiveness of the decision by structuring the decision criteria by highlighting and evaluating the alternatives individually ( Fitzgerald et al ., 2017 ). The decision-makers or the managers who utilise rational decision-making styles are more likely to be vigilant and organised about available information during decision-making ( Zhu et al ., 2021 ).
3.3 Organisational performance
For five decades, organisational performance has been widely researched by academic scholars and business practitioners ( Adam et al ., 2018 ). Organisational performance has been analysed in terms of normative and descriptive explanations in strategic planning research for continuous improvement in managing organisational performance ( Buddika et al ., 2016 ). Organisational performance can be explained by describing how things happen without judging good or bad. Alternatively, the organisational performance also can be elucidated by an evaluation in terms of performance against a benchmarked alternative or standard or by a descriptive statement explaining how the situation occurs without judgement ( Camilleri, 2021 ). Even though most research is done on the continuous improvements of organisational performance, practitioners still have many arguments and discussions on the terminology and conceptual bases to determine organisational performance ( Sarraf and Nejad, 2020 ).
Organisational performance can be reflected based on the results of the organisation's common objectives, given that the methods implemented are coherently used. Consequently, the performance processes' flow or the input resources can be critically analysed ( Tsai et al ., 2020 ). The effectiveness of organisational performance is influenced by the process implemented and can be measured by the achievements. Furthermore, organisational performance is defined as analysing the series of improvements to achieve organisational objectives. Generally, various factors can be associated with organisational performance, such as organisational structures, conflict, cross-cultural and social influences ( Sinnaiah et al. , 2023 ).
Performance measurement is a systematic series to identify the effectiveness and efficiency of people's behaviour to perform to their utmost abilities. Adam et al . (2018) described performance measurement as a unit, department or business process. Therefore, it is conceptualised that there is a structural relationship between organisational performance and performance measurement. Moreover, performance measurement requires substantive and relevant restructuring of input resources and processes to be aligned with the current system to increase productivity level or performance. Failure to analyse the performance measures will weaken the organisational strength and drain the organisation's efforts ( Alosani et al. , 2020 ). Thus, strategic thinking can be a highly effective performance measure for organisations.
4. Propositions
4.1 strategic thinking process and performance.
Strategic thinking is a structured assessment of analysing and synthesising information, intensively assessing the current situation and initiating new ideas or best available options to achieve strategic objectives ( Dhir and Dhir, 2020 ). An organisation's success depends on strategic thinking as it will enhance a decision-maker's skills, abilities and knowledge and help sustain competitiveness in uncertain environments ( Dhir et al ., 2021 ). Consequently, the process of strategic thinking is crucial for any organisation to successfully achieve and survive in the market for a more extended period. Decision-makers need to be effective and cognisant of the business opportunities that arise from innovating new ideas to enhance the strategic portfolio of organisations ( Bryson et al ., 2018 ).
Strategic thinking process will positively influence organisational performance.
4.2 Rational decision-making style, strategic thinking process and performance
In evaluating an organisation's performance and the uncertainties of the environment that influences the complexities in achieving positive growth for the organisation successfully, managers must have decision-making skills that utilise strategic thinking processes. Moreover, managers must be responsible for making fast and effective solutions by analysing, evaluating and prioritising available information to overcome strategic issues and obtain positive results ( Acciarini et al. , 2021 ). According to Calabretta et al . (2017) , there is a positive correlation between the strategic thinking process and decision-making style. Decision-making styles have the same structure as strategic thinking, which involves different levels, such as organisation or individuals.
Rational decision-making will moderate the relationship between the strategic thinking process and organisational performance.
4.3 Intuitive decision-making style, strategic thinking process and performance
Several studies highlight the roles of the strategic thinking process among managers within the boundaries of our cognitive capacities ( Kaufmann et al ., 2017 ) and postulate that mental flexibility can influence it ( Barlach and Plonski, 2021 ). Studies also emphasise that managers or decision-makers often utilise intuition during challenging situations, which is expected compared to the rational way of analysing the issues ( Kaufmann et al ., 2017 ). This intuition process can be a two-fold construct consisting of experience-based and emotionally affected situations. Additionally, this can involve a complex process of information affected by new cues towards previous experiences stored in their memory and transform it into subconscious action in the decision-making process ( Stanczyk et al ., 2015 ). Based on the study done by Simon (1976) , academic scholars and practitioners emphasised that managers are highly keen on inner feelings or gut feelings involving strategic decisions when faced with competitive issues ( Al-Jaifi and Al-Rassas, 2019 ; Bozhinov et al ., 2021 ; Palaniappan, 2017 ). The decision-making process utilising intuition uses available information, which might not have been available in the past, to quicken the process of decision-making. It is also important to realise that decision-making depends on the issues faced by the organisations, and not all issues require a rational decision-making style. For specific issues, managers might only need relevant information, deliberation and formal procedures to derive effective solutions for the organisation compared to instances where the managers are not bounded by any set of procedures or rules to solve the issue.
Therefore, strategic thinking is a process of synthesis, and based on intuitive decision-making style, where the outcome is an integrated perspective of the enterprise, managers can utilise intuition decision-making style to arrive at a solution with complete freedom and flexibility towards the organisational performance. The decision-makers attempt to be involved in the decision-making process while being aware of the current issues and having a sense of relationship among the cognitive schemas with the approach of holistic thinking to determine the solution to the problem ( Khemka and Hickson, 2021 ). It is clear that the intuitive decision-making process would include the issues faced by the organisation in analysing the issues and synthesis ( Zhu et al ., 2017 ) although all the processes occur under the sense of relationship or perception. It is also believed that the intuitive decision-making process could be influenced by the decision-makers upon the sudden awareness of information ( Peng et al ., 2020 ), whereby the decision-makers could propose a solution without the understanding or realisation of why the facts are present.
Intuitive decision-making will moderate the relationship between the strategic thinking process and organisational performance.
5. Discussion and conclusion
This paper reviews strategic management involving the strategic thinking process, organisational performance and decision-making styles with extant empirical work transforming into propositions, with the ultimate goal being to integrate the strategic management process into a systematised and approachable process that needs a fast response. Strategic management plays a vital role in aligning the standard repertoire of an organisation's strategic thinking. Moreover, managers must realise that strategic thinking has a unique process that depends on the situation. The thinking process should be aligned with the specific scenarios to ensure the best solution can be implemented. To sustain competitive advantage, managers should be effectively involved in the strategic thinking process to positively impact their organisations ( Bryson et al ., 2018 ).
The importance of strategic thinking enablers (systems perspective, focused intent, intelligent opportunism, thinking in time and hypothesis-driven analysis) was emphasised in the strategic thinking process and organisational performance. The systems perspective exposes the importance of organisations understanding the relationship between functions and departments internally and externally. Furthermore, organisations need to consider the functional, business and organisation strategies towards a highly competitive environment ( Buddika et al ., 2016 ). Consequently, these systems perspectives will help organisations manage interactions effectively across all departments to enhance productivity. Focus on intent will guide the organisations towards achieving strategic objectives and resisting eccentricity ( Bromiley and Rau, 2015 ). Focus intent will positively aid organisations to be more competitive in the long run as the managers realise the sense of discovery in managing strategic objectives. Therefore, it will improve the performance and consciously push the organisation towards innovation by eliminating limitations and becoming high achievers. Conversely, intelligent opportunism will enhance the strategic objectives by creating new opportunities to be more competitive although the strategies do not align with the current vision of the organisation. This is where intelligent opportunism will play an essential role at the managerial level of the organisation to effectively communicate and measure organisational performances ( Camilleri, 2021 ).
Emerging strategies will boost the organisation's motivation and productivity and should be carefully evaluated from time to time as the future of the organisations might be projected based on the past performance. Therefore, the importance of swift thinking permits the strategic managers to purposefully analyse the mission and vision of the organisation over time. The right action at the right time will help the organisations sustain competitively and save the organisations from self-destruction by limiting the positive changes made to help improve the organisation's performance ( Adam et al ., 2018 ).
Maintaining the balance between thinking creation and cognitive processing ( Calabretta et al ., 2017 ) and enhancing organisational performance (education, financial, creative, innovation, e-commerce and quality) is a challenge faced when creating effective management strategies ( Adam et al ., 2018 ; Al-Jaifi and Al-Rassas, 2019 ; Alharbi et al ., 2019 ; Arvis et al ., 2018 ). In addition, based on previous theoretical perspectives, most of the research scenarios will be based on the governance mechanisms of management and the policy development impacts on organisational performance ( Abubakar et al ., 2019 ). Therefore, based on extensive empirical and conceptual research, strategic thinking processes positively contribute to measuring organisational performance. Based on previous research, this study infers that cognitive development plays an effective role in the segregation of control between strategic thinking, which serves as a barrier to becoming more competitive and innovative in the long run ( Adam et al ., 2018 ). In addition, this happens among employees and directly impacts the quality of the organisational harmonies, such as mutual respect, trust and welfare of the employees. A cognitive processing environment is the use of intuition and rationality in decision-making with equal importance. The managers utilise intuition decision-making styles to resolve unrelated information received. During the strategic thinking process, the managers will receive unsorted information without processed knowledge which will be later organised into sorted knowledge using intuition styles ( Zander et al ., 2016 ). However, the rational decision-making style focuses more on the analytical procedure to conclude an issue the organisation faces. This helps the managers build confidence in the solution by eliminating uncertainty during decision-making ( Zhu et al ., 2021 ). Moreover, managers will only accept solutions with clear and less ambiguous information (rational) compared to managers utilising a more subconscious style (intuition) when formulating solutions. Consequently, there will be conflict in the decision-making process within the organisations.
According to Boamah et al. (2022) , the effectiveness of decision-making styles can differ according to the situation and the dependents. Alternatively, both decision-making styles were highlighted as an alternative way of generating a problem–solution approach within organisations ( Kolbe et al. , 2020 ; Stanczyk et al ., 2015 ). This study argues that both decision-making styles have equal importance in resolving problem–solution approaches and can be a harmonious process to achieve an effective performance measure. This argument is supported by Acciarini et al. (2021) , Tabesh and Vera (2020) . Therefore, this study concludes that both decision-making styles (rational and intuition) positively impact the strategic thinking process and organisational performance. Based on the framework in Figure 1 , the proposed framework highlights the missing sections of cognitive processing among businesses when delivering effective solutions for a complex problem. Organisations have only emphasised human capital and treated it as a scarce resource that will determine the organisation's performance. This study proposed that future strategic management researchers should explore the thinking process literature's core principles to investigate policy development further. Future research should transform these academic initiatives into empirical research by implementing this proposed model.
Conceptual framework
Competing interests: The authors reported no competing interests.
Abubakar , A.M. , Elrehail , H. , Alatailat , M.A. and Elçi , A. ( 2019 ), “ Knowledge management, decision-making style and organizational performance ”, Journal of Innovation and Knowledge , Vol. 4 No. 2 , pp. 104 - 114 , available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2017.07.003
Abuhjeeleh , M. , Elrehail , H. and Harazneh , I. ( 2018 ), “ The experiential image of North Cyprus destination as perceived by German tourists ”, Journal for Global Business Advancement , Vol. 11 No. 5 , pp. 630 - 649 .
Adam , A. , Lindahl , G. and Leiringer , R. ( 2020 ), “ The dynamic capabilities of public construction clients in the healthcare sector ”, International Journal of Managing Projects in Business , Vol. 13 No. 1 , pp. 153 - 171 .
Adam , S. , Mahadi , B. and Rahman , A.P.A. ( 2018 ), “ The effect of enterpreneurial orientation towards organizational performance of E-business in Malaysia ”, International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Management Practices , Vol. 1 No. 2 , pp. 12 - 21 .
Acciarini , C. , Brunetta , F. and Boccardelli , P. ( 2021 ), “ Cognitive biases and decision-making strategies in times of change: a systematic literature review ”, Management Decision , Vol. 59 No. 3 , pp. 638 - 652 .
Al-Jaifi , H.A. and Al-Rassas , A.H. ( 2019 ), “ The financing decision puzzle of technology-based firms: evidence from Malaysia ”, International Journal of Business and Globalisation , Vol. 22 No. 2 , pp. 225 - 239 .
Alaarj , S. , Abidin-Mohamed , Z. and Bustamam , U.S.B.A. ( 2016 ), “ Mediating role of trust on the effects of knowledge management capabilities on organizational performance ”, Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 235 , pp. 729 - 738 .
Alatailat , M. , Elrehail , H. and Emeagwali , O.L. ( 2019 ), “ High performance work practices, organizational performance and strategic thinking ”, International Journal of Organizational Analysis , Vol. 27 No. 3 , pp. 370 - 395 .
Alharbi , M. , Dowling , P.J. and Bhatti , M.I. ( 2019 ), “ Strategic planning practices in the telecommunications industry: evidence from Saudi Arabia ”, Review of International Business and Strategy , Vol. 29 No. 4 , pp. 269 - 285 .
Alosani , M.S. , Yusoff , R. and Al-Dhaafri , H. ( 2020 ), “ The effect of innovation and strategic planning on enhancing organizational performance of Dubai Police ”, Innovation and Management Review , Vol. 17 No. 1 , pp. 2 - 24 .
Arvis , J.-F. , Ojala , L. , Wiederer , C. , Shepherd , B. , Raj , A. , Dairabayeva , K. and Kiiski , T. ( 2018 ), Connecting to Compete 2018: Trade Logistics in the Global Economy , World Bank , Washington, DC .
Bamel , N. , Dhir , S. and Sushil , S. ( 2019 ), “ Inter-partner dynamics and joint venture competitiveness: a fuzzy TISM approach ”, Benchmarking: An International Journal , Vol. 26 No. 1 , pp. 97 - 116 .
Barlach , L. and Plonski , G.A. ( 2021 ), “ The Einstellung effect, mental rigidity and decision-making in startup accelerators ”, Innovation and Management Review , Vol. 18 No. 3 , pp. 276 - 291 .
Behling , O. , Gifford , W.E. and Tolliver , J.M. ( 1980 ), “ Effects of grouping information on decision making under risk ”, Decision Sciences , Vol. 11 No. 2 , pp. 272 - 283 .
Bellé , N. , Cantarelli , P. and Belardinelli , P. ( 2018 ), “ Prospect theory goes public: experimental evidence on cognitive biases in public policy and management decisions ”, Public Administration Review , Vol. 78 No. 6 , pp. 828 - 840 .
Bhat , A. , Mahajan , V. and Wolfe , N. ( 2021 ), “ Implicit bias in stroke care: a recurring old problem in the rising incidence of young stroke ”, Journal of Clinical Neuroscience , Vol. 85 , pp. 27 - 35 .
Boamah , F.A. , Zhang , J. , Wen , D. , Sherani , M. , Hayat , A. and Horbanenko , O. ( 2022 ), “ Enablers of knowledge management: practical research-based in the construction industry ”, International Journal of Innovation Science , Vol. 14 No. 1 , pp. 121 - 137 .
Bonn , I. ( 2001 ), “ Developing strategic thinking as a core competency ”, Management Decision , Vol. 39 No. 1 , pp. 63 - 71 .
Bozhinov , V. , Joecks , J. and Scharfenkamp , K. ( 2021 ), “ Gender spillovers from supervisory boards to management boards ”, Managerial and Decision Economics , Vol. 42 No. 5 , pp. 1317 - 1331 .
Bromiley , P. and Rau , D. ( 2015 ), “ Operations management and the resource based view: another view ”, Journal of Operations Management , Vol. 41 No. 1 , pp. 95 - 106 .
Bruine de Bruin , W. , Parker , A.M. and Fischhoff , B. ( 2020 ), “ Decision-making competence: more than intelligence? ”, Current Directions in Psychological Science , Vol. 29 No. 2 , pp. 186 - 192 .
Bryson , J.M. ( 2018 ), Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement , John Wiley & Sons , Hoboken, NJ .
Bryson , J.M. , Edwards , L.H. and Van Slyke , D.M. ( 2018 ), “ Getting strategic about strategic planning research ”, Public Management Review , Routledge , Vol. 20 , pp. 317 - 339 .
Buddika , S.I. , Palitha , J.N. and Peter , G.N. ( 2016 ), “ Operationalising performance measurement dimensions for the Australasian nonprofit healthcare sector ”, The TQM Journal , Emerald Group Publishing , Vol. 28 , pp. 954 - 973 .
Cabral , S. , Mahoney , J.T. , McGahan , A.M. and Potoski , M. ( 2019 ), “ Value creation and value appropriation in public and nonprofit organizations ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 40 No. 4 , pp. 465 - 475 .
Calabretta , G. , Gemser , G. and Wijnberg , N.M. ( 2017 ), “ The interplay between intuition and rationality in strategic decision making: a paradox perspective ”, Organization Studies , Vol. 38 Nos 3-4 , pp. 365 - 401 .
Camilleri , M.A. ( 2021 ), “ Using the balanced scorecard as a performance management tool in higher education ”, Management in Education , Vol. 35 No. 1 , pp. 10 - 21 .
Chen , Y.-M. , Liu , H.-H. , Ni , Y.-T. and Wu , M.-F. ( 2015 ), “ A rational normative model of international expansion: strategic intent perspective, market positions, and founder CEOs/family-successor CEOs ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 68 No. 7 , pp. 1539 - 1543 , available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.01.048
Chin , T. , Rowley , C. , Redding , G. and Wang , S. ( 2018 ), “ Chinese strategic thinking on competitive conflict: insights from Yin-Yang harmony cognition ”, International Journal of Conflict Management , Vol. 29 No. 5 , pp. 683 - 704 .
Dayan , M. and Di Benedetto , C.A. ( 2011 ), “ Team intuition as a continuum construct and new product creativity: the role of environmental turbulence, team experience, and stress ”, Research Policy , Vol. 40 No. 2 , pp. 276 - 286 .
Dayan , M. and Elbanna , S. ( 2011 ), “ Antecedents of team intuition and its impact on the success of new product development projects ”, Journal of Product Innovation Management , Vol. 28 s1 , pp. 159 - 174 .
Deslatte , A. ( 2020 ), “ Positivity and negativity dominance in citizen assessments of intergovernmental sustainability performance ”, Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory , Vol. 30 No. 4 , pp. 563 - 578 .
Dhir , S. and Dhir , S. ( 2020 ), “ Modeling of strategic thinking enablers: a modified total interpretive structural modeling (TISM) and MICMAC approach ”, International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management , Vol. 11 No. 1 , pp. 175 - 188 .
Dhir , S. and Dutta , T. ( 2020 ), “ Linking supervisor-support, person-job fit and person-organization fit to company value ”, Journal of Indian Business Research , Vol. 12 No. 4 , pp. 549 - 561 .
Dhir , S. , Rajan , R. , Ongsakul , V. , Owusu , R.A. and Ahmed , Z.U. ( 2021 ), “ Critical success factors determining performance of cross-border acquisition: evidence from the African telecom market ”, Thunderbird International Business Review , Vol. 63 No. 1 , pp. 43 - 61 .
Dionisio , M.A. ( 2017 ), “ Strategic thinking: the role in successful management ”, Journal of Management Research , Vol. 9 No. 4 , pp. 44 - 57 .
Dlamini , N. , Mazenda , A. , Masiya , T. and Nhede , N.T. ( 2020 ), “ Challenges to strategic planning in public institutions: a study of the Department of Telecommunications and Postal Services, South Africa ”, International Journal of Public Leadership , Vol. 16 No. 1 , pp. 109 - 124 .
Elliott , G. , Day , M. and Lichtenstein , S. ( 2020 ), “ Strategic planning activity, middle manager divergent thinking, external stakeholder salience, and organizational performance: a study of English and Welsh police forces ”, Public Management Review , Taylor & Francis , Vol. 22 , pp. 1581 - 1602 .
Elrehail , H. , Harazneh , I. , Abuhjeeleh , M. , Alzghoul , A. , Alnajdawi , S. and Ibrahim , H.M.H. ( 2020 ), “ Employee satisfaction, human resource management practices and competitive advantage ”, European Journal of Management and Business Economics , Vol. 29 No. 2 , pp. 125 - 149 , doi: 10.1108/EJMBE-01-2019-0001 .
Fitzgerald , D.R. , Mohammed , S. and Kremer , G.O. ( 2017 ), “ Differences in the way we decide: the effect of decision style diversity on process conflict in design teams ”, Personality and Individual Differences , Vol. 104 , pp. 339 - 344 .
Francioni , B. and Clark , K.D. ( 2020 ), “ The mediating role of speed in the global sourcing decision process ”, Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management , Vol. 26 No. 2 , 100609 .
George , B. ( 2021 ), “ Successful strategic plan implementation in public organizations: connecting people, process, and plan (3Ps) ”, Public Administration Review , Vol. 81 No. 4 , pp. 793 - 798 .
Giermindl , L.M. , Strich , F. , Christ , O. , Leicht-Deobald , U. and Redzepi , A. ( 2022 ), “ The dark sides of people analytics: reviewing the perils for organisations and employees ”, European Journal of Information Systems , Vol. 31 No. 3 , pp. 410 - 435 .
Goldman , E.F. , Scott , A.R. and Follman , J.M. ( 2015 ), “ Organizational practices to develop strategic thinking ”, Journal of Strategy and Management , Vol. 8 No. 2 , pp. 155 - 175 .
Hamidullah , M.F. , Riccucci , N.M. and Lee , I.P. ( 2021 ), “ Citizens' perceptions of closing the gender pay gap: an experimental study ”, Public Management Review , Vol. 23 No. 7 , pp. 1032 - 1055 .
Hodgetts , H.M. , Vachon , F. , Chamberland , C. and Tremblay , S. ( 2017 ), “ See No evil: cognitive challenges of security surveillance and monitoring ”, Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 230 - 243 , available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmac.2017.05.001
Hodgkinson , G.P. and Sadler-Smith , E. ( 2018 ), “ The dynamics of intuition and analysis in managerial and organizational decision making ”, Academy of Management Perspectives , Vol. 32 No. 4 , pp. 473 - 492 .
Johnsen , Å. ( 2015 ), “ Strategic management thinking and practice in the public sector: a strategic planning for all seasons? ”, Financial Accountability and Management , Vol. 31 No. 3 , pp. 243 - 268 .
Kaufmann , L. , Wagner , C.M. and Carter , C.R. ( 2017 ), “ Individual modes and patterns of rational and intuitive decision-making by purchasing managers ”, Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management , Vol. 23 No. 2 , pp. 82 - 93 .
Khemka , I. and Hickson , L. ( 2021 ), “ Strategy-based interventions for effective interpersonal decision making ”, Decision Making by Individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities , Springer , pp. 519 - 540 .
Kızıloglu , M. and Serinkan , C. ( 2015 ), “ Perception of strategical management in textile sector ”, Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences , Vol. 207 , pp. 306 - 314 .
Kolbe , L.M. , Bossink , B. and de Man , A.-P. ( 2020 ), “ Contingent use of rational, intuitive and political decision-making in R&D ”, Management Decision , Vol. 58 No. 6 , pp. 997 - 1020 .
Kulcsár , V. , Dobrean , A. and Gati , I. ( 2020 ), “ Challenges and difficulties in career decision making: their causes, and their effects on the process and the decision ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 116 , 103346 , available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2019.103346
Liedtka , J. ( 2000 ), “ Strategic planning as a contributor to strategic change: a generative model ”, European Management Journal , Elsevier , Vol. 18 , pp. 195 - 206 .
Luan , S. , Reb , J. and Gigerenzer , G. ( 2019 ), “ Ecological rationality: fast-and-frugal heuristics for managerial decision making under uncertainty ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 62 No. 6 , pp. 1735 - 1759 .
Mintzberg , H. ( 1994 ), “ The fall and rise of strategic planning ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 72 No. 1 , pp. 107 - 114 .
Mintzberg , H. , Ahlstrand , B. and Lampel , J.B. ( 2020 ), Strategy Safari , Pearson , London .
Nagtegaal , R. , Tummers , L. , Noordegraaf , M. and Bekkers , V. ( 2020 ), “ Designing to debias: measuring and reducing public managers' anchoring bias ”, Public Administration Review , Vol. 80 No. 4 , pp. 565 - 576 .
Nguyen , T.-M. ( 2020 ), “ Do extrinsic motivation and organisational culture additively strengthen intrinsic motivation in online knowledge sharing? ”, VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems , Vol. 50 No. 1 , pp. 75 - 93 , doi: 10.1108/VJIKMS-02-2019-0019 .
Norzailan , Z. , Yusof , S.M. and Othman , R. ( 2016 ), “ Developing strategic leadership competencies ”, Journal of Advanced Management Science , Vol. 4 No. 1 , pp. 66 - 71 .
Palaniappan , G. ( 2017 ), “ Determinants of corporate financial performance relating to board characteristics of corporate governance in Indian manufacturing industry: an empirical study ”, European Journal of Management and Business Economics , Vol. 26 No. 1 , pp. 67 - 85 .
Parker , A.M. , Bruine de Bruin , W. , Fischhoff , B. and Weller , J. ( 2018 ), “ Robustness of decision-making competence: evidence from two measures and an 11-year longitudinal study ”, Journal of Behavioral Decision Making , Vol. 31 No. 3 , pp. 380 - 391 .
Peng , J. , Ren , L. , Yang , N. , Zhao , L. , Fang , P. and Shao , Y. ( 2020 ), “ The network structure of decision-making competence in Chinese adults ”, Frontiers in Psychology , Vol. 11 , p. 2411 .
Poister , T.H. , Pitts , D.W. and Hamilton Edwards , L. ( 2010 ), “ Strategic management research in the public sector: a review, synthesis, and future directions ”, The American Review of Public Administration , SAGE Publications Sage CA , Los Angeles, CA , Vol. 40 , pp. 522 - 545 .
Porter , M.E. ( 1990 ), “ The competitive advantage of nations ”, Harvard Business Review , Cambridge, Massachusetts , Vol. 68 , pp. 73 - 93 .
Remmers , C. , Topolinski , S. and Koole , S.L. ( 2016 ), “ Why being mindful may have more benefits than you realize: mindfulness improves both explicit and implicit mood regulation ”, Mindfulness , Vol. 7 No. 4 , pp. 829 - 837 .
Ritter , S.M. ( 2014 ), “ Creativity—the unconscious foundations of the incubation period ”, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 10 .
Rodrigues and Franco ( 2019 ), “ The corporate sustainability strategy in organisations: a systematic review and future directions ”, Sustainability , Vol. 11 No. 22 , p. 6214 .
Sahay , A. ( 2019 ), “ Strategic thinking: my encounter ”, IBA Journal of Management and Leadership , Vol. 10 No. 2 , pp. 7 - 14 .
Sarraf , F. and Nejad , S.H. ( 2020 ), “ Improving performance evaluation based on balanced scorecard with grey relational analysis and data envelopment analysis approaches: case study in water and wastewater companies ”, Evaluation and Program Planning , Vol. 79 , 101762 .
Sauter , V.L. ( 1999 ), “ Intuitive decision-making ”, Communications of the ACM , Vol. 42 No. 6 , pp. 109 - 115 .
Simon , H.A. ( 1976 ), “ From substantive to procedural rationality ”, 25 Years of Economic Theory , Springer , Boston, MA , pp. 65 - 86 .
Sinnaiah , T. , Adam , S. and Mahadi , B. ( 2023 ), “ Conflict resolution styles and organisational performance: the mediating role of cultural factor ”, IJARBSS , Vol. 13 No. 1 , pp. 1027 - 1037 .
Stanczyk , A. , Foerstl , K. , Busse , C. and Blome , C. ( 2015 ), “ Global sourcing decision-making processes: politics, intuition, and procedural rationality ”, Journal of Business Logistics , Vol. 36 No. 2 , pp. 160 - 181 .
Steptoe‐Warren , G. , Howat , D. and Hume , I. ( 2011 ), “ Strategic thinking and decision making: literature review ”, Journal of Strategy and Management , Vol. 4 No. 3 , pp. 238 - 250 .
Sukhov , A. , Sihvonen , A. , Netz , J. , Magnusson , P. and Olsson , L.E. ( 2021 ), “ How experts screen ideas: the complex interplay of intuition, analysis and sensemaking ”, Journal of Product Innovation Management , Vol. 38 No. 2 , pp. 248 - 270 .
Supramaniam , S. and Singaravelloo , K. ( 2020 ), “ Emotional intelligence, job satisfaction and organisational performance in the Malaysian public administration ”, Institutions and Economies , Vol. 12 No. 1 , pp. 77 - 98 .
Tabesh , P. and Vera , D.M. ( 2020 ), “ Top managers' improvisational decision-making in crisis: a paradox perspective ”, Management Decision , Vol. 58 No. 10 , pp. 2235 - 2256 , doi: 10.1108/MD-08-2020-1060 .
Temprano-García , V. , Rodríguez-Escudero , A.I. and Rodríguez-Pinto , J. ( 2018 ), “ Brand deletion: how the decision-making approach affects deletion success ”, BRQ Business Research Quarterly , Vol. 21 No. 2 , pp. 69 - 83 .
Tsai , F.M. , Bui , T.-D. , Tseng , M.-L. , Wu , K.-J. and Chiu , A.S. ( 2020 ), “ A performance assessment approach for integrated solid waste management using a sustainable balanced scorecard approach ”, Journal of Cleaner Production , Vol. 251 , 119740 .
Wang , T. , Wu , J. , Gu , J. and Hu , L. ( 2021 ), “ Impact of open innovation on organizational performance in different conflict management styles: based on resource dependence theory ”, International Journal of Conflict Management , Vol. 32 No. 2 , pp. 199 - 222 .
Zander , T. , Horr , N.K. , Bolte , A. and Volz , K.G. ( 2016 ), “ Intuitive decision making as a gradual process: investigating semantic intuition-based and priming-based decisions with fMRI ”, Brain and Behavior , Vol. 6 No. 1 , e00420 .
Zhu , Y. , Ritter , S.M. , Müller , B.C. and Dijksterhuis , A. ( 2017 ), “ Creativity: intuitive processing outperforms deliberative processing in creative idea selection ”, Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , Vol. 73 , pp. 180 - 188 .
Zhu , X.S. , Wolfson , M.A. , Dalal , D.K. and Mathieu , J.E. ( 2021 ), “ Team decision making: the dynamic effects of team decision style composition and performance via decision strategy ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 47 No. 5 , pp. 1281 - 1304 .
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the administration of Azman Hashim International Business School, Block T08, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor, for providing the facilities and the PhD Scholar room during this research.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

Career Tips , Choosing a Job , Getting a Job
What is Strategic Management? How Does it Ensure Business Success?
Updated: April 22, 2024
Published: April 19, 2024

To get ahead, corporations are emphasizing strategic management skills as they hire for leadership positions. Whether you are focused on finance, marketing, research and development, or operations, chances are good that you will be called upon to strategically manage projects or processes.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at strategic management, including the steps in the process, the benefits and pitfalls, and how you can become a strategy manager.

What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a comprehensive process that aligns a company’s strategic direction with its operational activities, ensuring it can navigate competitive markets successfully and achieve long-term success.
The main purpose of strategic management is to guide an organization in meeting its goals and objectives through the efficient use of resources. The process includes the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of an organization’s resources and capabilities. As changes or challenges arise – both internally and externally – a strategic manager will implement solutions to effectively adapt business activities. More simply put, strategic management ensures that all employees within a company are focused on the same goals.
Strategic management theory is the process an organization uses to accomplish strategic management and typically involves five steps: goal setting, analysis, strategy formation, strategy implementation, and strategy monitoring.
Goal Setting
It involves establishing clear objectives for the organization, including defining its vision, mission, and overall strategic goals.
It involves gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data about the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats. This phase often results in a SWOT analysis.
Strategy Formation
It involves developing strategic options based on the results of the analysis phase, and then selecting the most appropriate strategies to pursue.
Strategy Implementation
It involves executing the chosen strategies by allocating resources, developing programs, and making necessary adjustments.
Strategy Monitoring
It involves continuously evaluating and controlling the strategic process to ensure the organization remains on track toward its goals, adjusting as needed based on performance and environmental changes.
Applying Strategic Management
Although strategic management should always be used to guide operations, it can be particularly useful during key moments, including periods of significant growth, market change, and future planning. By keeping long-range success in the foreground, strategic management can ensure employees focus on areas most likely to achieve management’s desired outcomes.
The benefits of strategic management are numerous and can significantly impact an organization’s success. They include:
Improved Decision Making
Strategic management provides a framework for making informed decisions by evaluating the internal and external environments of the organization.
Increased Efficiency
By aligning resources with strategic objectives, organizations can operate more efficiently.
Better Coordination Between Departments
Strategic management ensures that all departments work towards common goals, enhancing coordination and reducing conflict.
Financial Benefits
Strategic management leads to improved financial health via liquidity monitoring, revenue generation, profitability management, and solvency planning.
Setting a Clear Direction
By setting a clear direction for the future, strategic management ensures that employees and management are aligned toward achieving the organization’s goals.
Competitive Advantage
Strategic management is crucial for maintaining and achieving a competitive advantage in the market.
As you can see, strategic management is not just about planning; it’s also about adapting to changes, making informed decisions, and ensuring that an organization remains relevant and competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
What Skills are Important for Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a multifaceted discipline that requires a range of skills from leaders and managers. Central is the ability to negotiate, find common ground, and achieve buy-in across diverse stakeholder groups. These skills are essential for unifying different viewpoints and agendas to move the company forward.
Effective delegation is also a cornerstone of strategic management, allowing for the efficient distribution of tasks. In addition, communication skills play a pivotal role. Leaders should be able to impart information clearly and use active listening skills, both key traits of emotional intelligence . The goal is to inspire confidence within your team and among stakeholders.
Finally, strategic management is underpinned by the ability to think strategically. Leaders with critical thinking and problem-solving skills are better able to anticipate future trends, recognize potential issues and opportunities, and craft appropriate solutions.
Together, these skills facilitate the development and implementation of strategic goals, ensuring organizations are well-positioned to navigate complex environments and achieve sustainable success.

How to Become a Strategic Manager?
To become a strategic manager, a solid educational background is typically required. Typically, strategic management roles require at least a bachelor’s degree in a field of study like business administration, finance, economics, or a similar discipline.
Moreover, some positions may look for candidates with more advanced degrees, like a Master’s in Business Administration (MBA) or related areas. This advanced education can provide deeper insights into business strategies, leadership, and organizational management.
UoPeople offers a variety of educational options for aspiring strategic leaders. Both the Associate and Bachelor degrees in business administration focus on the core competencies of leadership, while our Master’s of Business Administration is well-known to help advance your career .
UoPeople’s tuition-free model allows us to offer students an affordable solution to earning a quality business degree. In addition, our classes are all taught online and are asynchronous, making us perfect for adult students balancing career and family lives along with academic goals. UoPeople courses can be completed on your own schedule and in a matter of months.
If you don’t want to undertake a degree program, UoPeople also offers convenient certificate programs that are perfect for adult workers looking to upskill. In particular, our Certificate in Strategy gives students a solid foundation in strategic business methods, business management, accounting, marketing, and economic theory in as little as four months.
Furthermore, combining a bachelor’s or master’s degree with several years of practical experience in business or strategy roles can significantly enhance a candidate’s qualifications for becoming a strategy manager.
Also useful are less formal leadership training programs, workshops, seminars, and conferences that focus on key competencies like strategic thinking, communication, and change management. Additionally, finding a mentor within your company can also be beneficial, especially for someone working in a strategic management role. By working closely with your mentor, you can learn what techniques are the most successful within your business environment.
Strategic management is critical to the operation and profitability of any organization. Because it is so integral to long-term financial success, many corporations are now prioritizing strategic management skills when they are making hiring decisions. For this reason, upskilling in strategic management is currently one of the most popular paths to career advancement.
To deliver on their goals, companies use strategic management continuously. Therefore, there will always be opportunities for strategic managers in the workforce. By keeping a keen eye on how a company’s operations are aligned with its goals, strategic managers can guide their companies to success.
Related Articles
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Strategic Management?
- How It Worls
- The 5 Phases
- Strategic Management FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Alex Dos Diaz
Strategic management is the management of an organization’s resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
Strategic management involves setting objectives, analyzing the competitive environment, analyzing the internal organization, evaluating strategies, and ensuring that management rolls out the strategies across the organization .
Key Takeaways
- Companies, universities, nonprofits, and other organizations can use strategic management as a way to make goals and meet objectives.
- Flexible companies may find it easier to make changes to their structure and plans, while inflexible companies may chafe at a changing environment.
- A strategic manager may oversee strategic management plans and devise ways for organizations to meet their benchmark goals.
Understanding Strategic Management
Strategic management is divided into several schools of thought. A prescriptive approach to strategic management outlines how strategies should be developed, while a descriptive approach focuses on how strategies should be put into practice. These schools differ on whether strategies are developed through an analytic process, in which all threats and opportunities are accounted for, or are more like general guiding principles to be applied.
Business culture , the skills and competencies of employees, and organizational structure are all important factors that influence how an organization can achieve its stated objectives. Inflexible companies may find it difficult to succeed in a changing business environment. Creating a barrier between the development of strategies and their implementation can make it difficult for managers to determine whether objectives have been efficiently met.
While an organization’s upper management is ultimately responsible for its strategy , the strategies are often sparked by actions and ideas from lower-level managers and employees. An organization may have several employees devoted to strategy, rather than relying solely on the chief executive officer ( CEO ) for guidance.
Because of this reality, organizational leaders focus on learning from past strategies and examining the environment at large. The collective knowledge is then used to develop future strategies and to guide the behavior of employees to ensure that the entire organization is moving forward. For these reasons, effective strategic management requires both an inward and outward perspective.
Strategic management extends to internal and external communication practices as well as to tracking, which ensures that the company meets goals as defined in its strategic management plan.
The 5 Phases of Strategic Management
Strategic management involves managing an organization's resources, analyzing internal and external forces, and developing strategies to realize goals and objectives. There are five key phases that can help businesses execute their strategies.
- An organization must first establish clear, realistic goals. Its goals should answer what the company wants to achieve and why. Once set, the company can then identify the objectives, or how the goals will be reached. During this phase, the company can articulate its vision and long and short-term goals.
- Organizations must then be able to examine, understand, and codify what internal and external forces affect their business and goals, as well as what it needs to remain competitive. Analytical tools, such as SWOT analysis, are helpful during this phase.
- Based on the results of the analysis, the company can then develop its strategy, outlining how the company will achieve its goals and how. In this phase, the company will identify the needed people, technology, and other resources; how these resources will be allocated to fulfill tasks, and what performance metrics are needed to measure success. It is also critical to gain buy-in from stakeholders and business leaders.
- Once the strategies are defined, it is time for execution. The strategy is taken from planning to implementation. During this phase, the allocated resources are placed into action based on their roles and responsibilities.
- The final stage of strategic management is to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented strategies using defined metrics. The company will also visit whether ineffective strategies should be replaced with more viable ones. The company should continue to monitor the business landscape and internal operations, as well as maintain strategies that have proven effective.
Example of Strategic Management
For example, a for-profit technical college wishes to increase new student enrollment and enrolled student graduation rates over the next three years. The purpose is to make the college known as the best buy for a student's money among five for-profit technical colleges in the region, with a goal of increasing revenue.
In that case, strategic management means ensuring the school has funds to create high-tech classrooms and hire the most qualified instructors. The college also invests in marketing and recruitment and implements student retention strategies. The college’s leadership assesses whether its goals have been achieved on a periodic basis.
Why Is Strategic Management Important?
Helping their company find ways to be more competitive is the purpose of strategic management. To that end, putting strategic management plans into practice is the most important aspect of the planning itself. Plans in practice involve identifying benchmarks, realigning resources—financial and human—and putting leadership resources in place to oversee the creation, sale, and deployment of products and services.
In business, strategic management is important because it allows a company to analyze areas for operational improvement. In many cases, they can follow either an analytical process, which identifies potential threats and opportunities, or simply follow general guidelines. Given the structure of the organization, a company may choose to follow either a prescriptive or descriptive approach to strategic management. Under a prescriptive model, strategies are outlined for development and execution. By contrast, a descriptive approach describes how a company can develop these strategies.
Strategic management is the process of setting goals, procedures, and objectives in order to make a company or organization more competitive. Typically, strategic management looks at effectively deploying staff and resources to achieve these goals. Often, strategic management includes strategy evaluation, internal organization analysis, and strategy execution throughout the company.
What Is an Example of Strategic Management?
Consider a large company that wants to achieve more ambitious online sales rates. To meet these goals, the company will develop a strategy, communicate this strategy, apply it across various units and departments in the organization, integrate this with employee goals, and execute accordingly. If an effective strategy is applied, ideally, it will help the company achieve its targets through a single, coordinated process.
What Are the Key Elements of Strategic Management?
Strategic management is not a one-size-fits-all strategy. However, there are key elements that are found to be critical. These include goal setting, industry and organizational analyses, strategy formation, strategy implementation; and the measurement, monitoring, and controlling of strategies.
Strategic management is the assembling and management of resources to achieve a company's goals and objectives. Although it is often segmented into either prescriptive or descriptive schools of thought, many businesses subscribe to a combined philosophy, defining how a strategy should be developed and how the strategies will be employed. Strategic management helps companies set goals, gain a competitive edge, better manage their resources, and more. There is not one prescription for all. Companies must create and adapt a strategic management process that works best for their company and those they serve. Strategic management does not end with the successful implementation of strategies; it continues for the life of the business.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/project-management.asp-Final-0c4cd7f77aad40228e7311783c27f728.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

COMMENTS
Summary. Developing your strategic thinking skills isn't enough to get you promoted. In order to advance in your career, you need to demonstrate them. Leaders want to know what you think, and ...
Additionally, Critical Thinking is crucial for making informed decisions in real time and solving specific problems effectively. In contrast, Strategic Thinking takes a broader and more long-term perspective. It considers the larger context, trends, and potential future scenarios.
1. Ask Strategic Questions. If you want to improve your strategic thinking skills, one of the simplest things you can do is ask more strategic questions. Doing so allows you to exercise your planning skills, become adept at spotting opportunities, and develop a more strategic mindset you can leverage throughout your career.
In the late 1970s, Fred Gluck led an effort to revitalize McKinsey's thinking on strategy while, in parallel, Tom Peters and Robert Waterman were leading a similar effort to reinvent the Firm's thinking on organization. The first published product of Gluck's strategy initiative was a 1978 staff paper, "The evolution of strategic management."
Strategic thinking in the realm of business is a dynamic and critical process that involves the exploration and refinement of existing business models. This approach entails a comprehensive evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses inherent in the current model.
Strategic planning vs. strategic thinking. In strategic planning, leaders gather data and decide on the path the organization will take to achieve its goals. With strategic thinking, employees at all levels and in all functions continually scan for new ways to contribute to the organization's success. They apply those insights as they carry ...
Through research at the Wharton School and at our consulting firm involving more than 20,000 executives to date, we have identified six skills that, when mastered and used in concert, allow ...
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to form reasoned judgments or decisions. It goes beyond simply accepting information at face value and instead requires individuals to actively engage with and question the content, considering its reliability, relevance, and implications.
Strategic Thinking stands as a keystone of intentional and rational thought processes essential for navigating the complexities of business, team dynamics, or individual endeavours. It encompasses a deliberate analysis of critical factors and variables influencing long-term success.
rising in sophistication from simple year-to-year budgeting to strategic manage-ment, in which strategic planning and everyday management are inextricably intertwined. But the power of the article comes from the authors' insights into the true nature of strategy and what constitutes high-quality strategic thinking. The article is
Strategic management is the process of defining and implementing procedures and objectives that set a company apart from its competition. Strategic management is also a skill that can be developed as someone gains experience and adopts a strategic mindset. It is considered part of business acumen and can also apply to fields like non-profit ...
Strategic thinking is a thought process focused on analyzing critical factors or variables that may influence the long-term success of a business, team, or individual. It involves planning, seeing the big picture, and putting thought into action to gain a competitive advantage in the industry.
What is Strategic Thinking? Strategic thinking is simply an intentional and rational thought process that focuses on the analysis of critical factors and variables that will influence the long-term success of a business, a team, or an individual. Strategic thinking includes careful and deliberate anticipation of threats and vulnerabilities to ...
Strategic thinking is an intentional process easily lost amid the pressures of operational decision-making and tactical leadership. This paper helps project managers step back from the trees to see the forest and lays the foundation for better strategic thinking within project teams, departments, and overall organizations through changing focus ...
Strategic thinking is a mental or thinking process applied by an individual in the context of achieving a goal or set of goals. As a cognitive activity, it produces thought.. When applied in an organizational strategic management process, strategic thinking involves the generation and application of unique business insights and opportunities intended to create competitive advantage for a firm ...
Strategic Thinking: 5 Characteristics of Strategic Thinkers. Strategic thinkers excel at problem-solving, decision-making, and developing realistic action plans to achieve specific goals.
This skill takes them from executing to thinking and planning. Critical thinkers are good strategic planners because of the following three reasons: 1. Ask strategic questions. This can only ...
Critical thinking is paramount to your strategy's success. Without establishing objectives, prioritizing processes to improve, setting targets (and measuring them), all the while securing the right resources to do this, you may wonder how businesses achieve their strategic goals. It is with great effort and alarming failure rates.
Strategic management is defined as a framework for achieving success, and it is pivotal for organisations to achieve their objectives and continuously perform better (Elliott et al., 2020). Additionally, strategic management is a continuous process of looking for a better action plan to ensure the organisation's competitiveness.
Critical thinking is an essential skill in strategy for effective problem-solving. It allows you to objectively analyze information, predict potential outcomes, and make decisions that can lead to ...
Strategic management is a multifaceted discipline that requires a range of skills from leaders and managers. Central is the ability to negotiate, find common ground, and achieve buy-in across diverse stakeholder groups. These skills are essential for unifying different viewpoints and agendas to move the company forward.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Strategic management is the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis and assessment of all that is necessary for an organization to meet its goals and objectives.
Strategic management is the management of an organization's resources to achieve its goals and objectives. Strategic management involves setting objectives, analyzing the competitive environment ...
"Nurturing Roots, Growing Futures: Combining Policies and Partnerships for Urban Resilience and Transformation"