Essay on Global Warming – Causes and Solutions
500+ words essay on global warming.
Global Warming is a term almost everyone is familiar with. But, its meaning is still not clear to most of us. So, Global warming refers to the gradual rise in the overall temperature of the atmosphere of the Earth. There are various activities taking place which have been increasing the temperature gradually. Global warming is melting our ice glaciers rapidly. This is extremely harmful to the earth as well as humans. It is quite challenging to control global warming; however, it is not unmanageable. The first step in solving any problem is identifying the cause of the problem. Therefore, we need to first understand the causes of global warming that will help us proceed further in solving it. In this essay on Global Warming, we will see the causes and solutions of Global Warming.


Causes of Global Warming
Global warming has become a grave problem which needs undivided attention. It is not happening because of a single cause but several causes. These causes are both natural as well as manmade. The natural causes include the release of greenhouses gases which are not able to escape from earth, causing the temperature to increase.
Get English Important Questions here
Further, volcanic eruptions are also responsible for global warming. That is to say, these eruptions release tons of carbon dioxide which contributes to global warming. Similarly, methane is also one big issue responsible for global warming.

So, when one of the biggest sources of absorption of carbon dioxide will only disappear, there will be nothing left to regulate the gas. Thus, it will result in global warming. Steps must be taken immediately to stop global warming and make the earth better again.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Global Warming Solutions
As stated earlier, it might be challenging but it is not entirely impossible. Global warming can be stopped when combined efforts are put in. For that, individuals and governments, both have to take steps towards achieving it. We must begin with the reduction of greenhouse gas.
Furthermore, they need to monitor the consumption of gasoline. Switch to a hybrid car and reduce the release of carbon dioxide. Moreover, citizens can choose public transport or carpool together. Subsequently, recycling must also be encouraged.
Read Global Warming Speech here
For instance, when you go shopping, carry your own cloth bag. Another step you can take is to limit the use of electricity which will prevent the release of carbon dioxide. On the government’s part, they must regulate industrial waste and ban them from emitting harmful gases in the air. Deforestation must be stopped immediately and planting of trees must be encouraged.
In short, all of us must realize the fact that our earth is not well. It needs to treatment and we can help it heal. The present generation must take up the responsibility of stopping global warming in order to prevent the suffering of future generations. Therefore, every little step, no matter how small carries a lot of weight and is quite significant in stopping global warming.
हिंदी में ग्लोबल वार्मिंग पर निबंध यहाँ पढ़ें
FAQs on Global Warming
Q.1 List the causes of Global Warming.
A.1 There are various causes of global warming both natural and manmade. The natural one includes a greenhouse gas, volcanic eruption, methane gas and more. Next up, manmade causes are deforestation, mining, cattle rearing, fossil fuel burning and more.
Q.2 How can one stop Global Warming?
A.2 Global warming can be stopped by a joint effort by the individuals and the government. Deforestation must be banned and trees should be planted more. The use of automobiles must be limited and recycling must be encouraged.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


The Causes of Climate Change
Human activities are driving the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century.

- The greenhouse effect is essential to life on Earth, but human-made emissions in the atmosphere are trapping and slowing heat loss to space.
- Five key greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapor.
- While the Sun has played a role in past climate changes, the evidence shows the current warming cannot be explained by the Sun.
Increasing Greenhouses Gases Are Warming the Planet
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20 th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
Life on Earth depends on energy coming from the Sun. About half the light energy reaching Earth's atmosphere passes through the air and clouds to the surface, where it is absorbed and radiated in the form of infrared heat. About 90% of this heat is then absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-radiated, slowing heat loss to space.
Four Major Gases That Contribute to the Greenhouse Effect
Carbon dioxide.
A vital component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is released through natural processes (like volcanic eruptions) and through human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
Like many atmospheric gases, methane comes from both natural and human-caused sources. Methane comes from plant-matter breakdown in wetlands and is also released from landfills and rice farming. Livestock animals emit methane from their digestion and manure. Leaks from fossil fuel production and transportation are another major source of methane, and natural gas is 70% to 90% methane.
Nitrous Oxide
A potent greenhouse gas produced by farming practices, nitrous oxide is released during commercial and organic fertilizer production and use. Nitrous oxide also comes from burning fossil fuels and burning vegetation and has increased by 18% in the last 100 years.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
These chemical compounds do not exist in nature – they are entirely of industrial origin. They were used as refrigerants, solvents (a substance that dissolves others), and spray can propellants.
FORCING: Something acting upon Earth's climate that causes a change in how energy flows through it (such as long-lasting, heat-trapping gases - also known as greenhouse gases). These gases slow outgoing heat in the atmosphere and cause the planet to warm.

Another Gas That Contributes to the Greenhouse Effect:
Water vapor.
Water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, but because the warming ocean increases the amount of it in our atmosphere, it is not a direct cause of climate change. Credit: John Fowler on Unsplash
FEEDBACKS: A process where something is either amplified or reduced as time goes on, such as water vapor increasing as Earth warms leading to even more warming.

Human Activity Is the Cause of Increased Greenhouse Gas Concentrations
Over the last century, burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). This increase happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO 2 . To a lesser extent, clearing of land for agriculture, industry, and other human activities has increased concentrations of greenhouse gases.
The industrial activities that our modern civilization depends upon have raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels by nearly 50% since 1750 2 . This increase is due to human activities, because scientists can see a distinctive isotopic fingerprint in the atmosphere.
In its Sixth Assessment Report, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, composed of scientific experts from countries all over the world, concluded that it is unequivocal that the increase of CO 2 , methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere over the industrial era is the result of human activities and that human influence is the principal driver of many changes observed across the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere.
"Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact."

Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The panel's AR6 Working Group I (WGI) Summary for Policymakers report is online at https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ .
Evidence Shows That Current Global Warming Cannot Be Explained by Solar Irradiance
Scientists use a metric called Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) to measure the changes in energy the Earth receives from the Sun. TSI incorporates the 11-year solar cycle and solar flares/storms from the Sun's surface.
Studies show that solar variability has played a role in past climate changes. For example, a decrease in solar activity coupled with increased volcanic activity helped trigger the Little Ice Age.
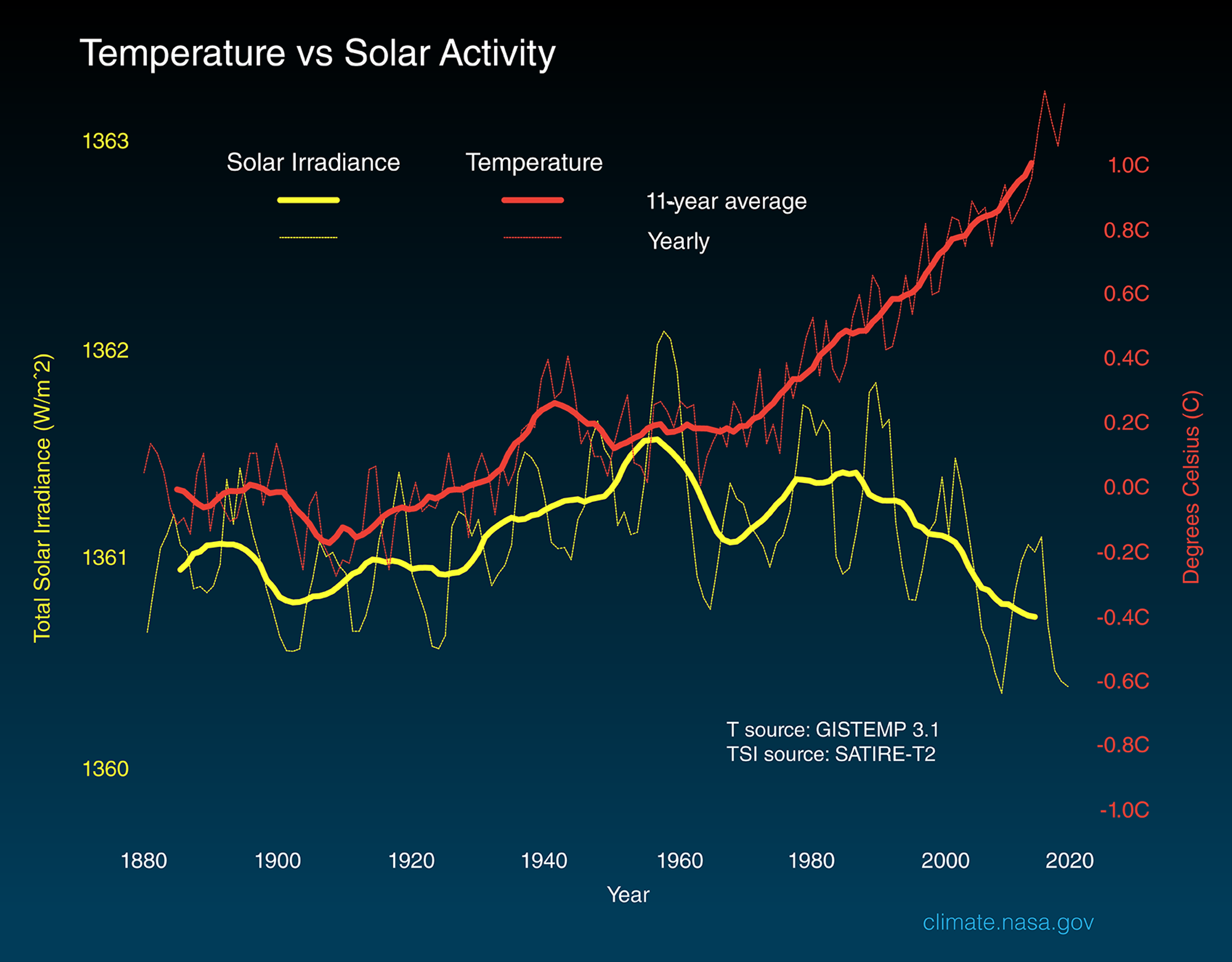
But several lines of evidence show that current global warming cannot be explained by changes in energy from the Sun:
- Since 1750, the average amount of energy from the Sun either remained constant or decreased slightly 3 .
- If a more active Sun caused the warming, scientists would expect warmer temperatures in all layers of the atmosphere. Instead, they have observed a cooling in the upper atmosphere and a warming at the surface and lower parts of the atmosphere. That's because greenhouse gases are slowing heat loss from the lower atmosphere.
- Climate models that include solar irradiance changes can’t reproduce the observed temperature trend over the past century or more without including a rise in greenhouse gases.
1. IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Summary for Policy Makers, Sections A, “ The Current State of the Climate ”
IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Technical Summary, Sections TS.1.2, TS.2.1 and TS.3.1
2. P. Friedlingstein, et al., 2022: “Global Carbon Budget 2022”, Earth System Science Data ( 11 Nov 2022): 4811–4900. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-4811-2022
3. IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, “ Solar and Orbital Forcing ” IPCC 6 th Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 7, Sections 7.3.4.4, 7.3.5.2, Figure 7.6, “ Solar ” M. Lockwood and W.T. Ball, Placing limits on long-term variations in quiet-Sun irradiance and their contribution to total solar irradiance and solar radiative forcing of climate,” Proceedings of the Royal Society A , 476, issue 2228 (24 June 2020): https://doi 10.1098/rspa.2020.0077
Header image credit: Pixabay/stevepb Four Major Gases image credit: Adobe Stock/Ilya Glovatskiy
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth


- ENVIRONMENT
How global warming is disrupting life on Earth
The signs of global warming are everywhere, and are more complex than just climbing temperatures.
Our planet is getting hotter. Since the Industrial Revolution—an event that spurred the use of fossil fuels in everything from power plants to transportation—Earth has warmed by 1 degree Celsius, about 2 degrees Fahrenheit.
That may sound insignificant, but 2023 was the hottest year on record , and all 10 of the hottest years on record have occurred in the past decade. A reconstruction of Earth's average temperature over the past 485 million years showed that when the planet warms, catastrophic weather and mass extinctions follow. At no point in the period of Earth's history examined, the study notes, have temperatures warmed as quickly as they're warming now.
Global warming and climate change are often used interchangeably as synonyms, but scientists prefer to use “climate change” when describing the complex shifts now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems.
Climate change encompasses not only rising average temperatures but also natural disasters, shifting wildlife habitats, rising seas , and a range of other impacts. All of these changes are emerging as humans continue to add heat-trapping greenhouse gases , like carbon dioxide and methane, to the atmosphere.

What causes global warming?
When fossil fuel emissions are pumped into the atmosphere, they change the chemistry of our atmosphere, allowing sunlight to reach the Earth but preventing heat from being released into space. This keeps Earth warm, like a greenhouse, and this warming is known as the greenhouse effect .
Carbon dioxide is the most commonly found greenhouse gas and about 75 percent of all the climate warming pollution in the atmosphere. This gas is a product of producing and burning oil, gas, and coal. About a quarter of Carbon dioxide also results from land cleared for timber or agriculture.
Methane is another common greenhouse gas. Although it makes up only about 16 percent of emissions, it's roughly 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide and dissipates more quickly. That means methane can cause a large spark in warming, but ending methane pollution can also quickly limit the amount of atmospheric warming. Sources of this gas include agriculture (mostly livestock), leaks from oil and gas production, and waste from landfills.
What are the effects of global warming?
One of the most concerning impacts of global warming is the effect warmer temperatures will have on Earth's polar regions and mountain glaciers. The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the planet. This warming reduces critical ice habitat and it disrupts the flow of the jet stream, creating more unpredictable weather patterns around the globe.
( Learn more about the jet stream. )
A warmer planet doesn't just raise temperatures. Precipitation is becoming more extreme as the planet heats. For every degree your thermometer rises, the air holds about seven percent more moisture. This increase in moisture in the atmosphere can produce flash floods, more destructive hurricanes, and even paradoxically, stronger snow storms.
The world's leading scientists regularly gather to review the latest research on how the planet is changing. The results of this review is synthesized in regularly published reports known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports.
A recent report outlines how disruptive a global rise in temperature can be:
- Coral reefs are now a highly endangered ecosystem. When corals face environmental stress, such as high heat, they expel their colorful algae and turn a ghostly white, an effect known as coral bleaching . In this weakened state, they more easily die.
- Trees are increasingly dying from drought , and this mass mortality is reshaping forest ecosystems.
- Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are making wildfires more common and more widespread. Research shows they're even moving into the eastern U.S. where fires have historically been less common.
- Hurricanes are growing more destructive and dumping more rain, an effect that will result in more damage. Some scientists say we even need to be preparing for Cat 6 storms . (The current ranking system ends at Cat 5.)
How can we limit global warming?
Limiting the rising in global warming is theoretically achievable, but politically, socially, and economically difficult.
Those same sources of greenhouse gas emissions must be limited to reduce warming. For example, oil and gas used to generate electricity or power industrial manufacturing will need to be replaced by net zero emission technology like wind and solar power. Transportation, another major source of emissions, will need to integrate more electric vehicles, public transportation, and innovative urban design, such as safe bike lanes and walkable cities.
( Learn more about solutions to limit global warming. )
One global warming solution that was once considered far fetched is now being taken more seriously: geoengineering. This type of technology relies on manipulating the Earth's atmosphere to physically block the warming rays of the sun or by sucking carbon dioxide straight out of the sky.
Restoring nature may also help limit warming. Trees, oceans, wetlands, and other ecosystems help absorb excess carbon—but when they're lost, so too is their potential to fight climate change.
Ultimately, we'll need to adapt to warming temperatures, building homes to withstand sea level rise for example, or more efficiently cooling homes during heat waves.
LIMITED TIME OFFER
Related topics.
- CLIMATE CHANGE
- ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION
- POLAR REGIONS
You May Also Like

Listen to 30 years of climate change transformed into haunting music

How warm oceans supercharge deadly hurricanes

Can energy harnessed from Earth’s interior help power the world?

Why all life on Earth depends on trees

Pizzlies, grolars, and narlugas: Why we may soon see more Arctic hybrids
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
view all topics > Climate change
Humans are causing global warming

COMMENTS
This article provides an overview of the scientific background related to the subject of global warming. It considers the causes of rising near-surface air temperatures, the influencing factors, the process of climate research and forecasting, and the possible …
Q.1 List the causes of Global Warming. A.1 There are various causes of global warming both natural and manmade. The natural one includes a greenhouse gas, volcanic eruption, methane gas and more.
Climate Change. The Causes of Climate Change. Human activities are driving the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century. En español. Takeaways. The greenhouse effect is essential to life on Earth, but human …
Causes of global warming, explained. Human activity is driving climate change, including global temperature rise. January 17, 2019. • 4 min read. The average temperature of the Earth is...
Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all...
What causes global warming? When fossil fuel emissions are pumped into the atmosphere, they change the chemistry of our atmosphere, allowing sunlight to reach the Earth but preventing heat from...
Scientists know that the warming climate is caused by human activities because: They understand how heat-trapping gases like carbon dioxide work in the atmosphere. They know why those gases are increasing in …
anthropogenic climate change. global cooling. (Show more) News •. Scientists say the slime in your dishwasher could unlock a solution to global warming • Oct. 23, 2024, 4:25 …
more frequent and intense extreme weather. sea level rise. food and water scarcity. stress on human health and increase in disease. economic damage. national security threats. migration …