ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
The art of happiness: an explorative study of a contemplative program for subjective well-being.

- 1 Department of Psychology and Cognitive Science, University of Trento, Trento, Italy
- 2 Department of Psychology, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
- 3 Institute Lama Tzong Khapa, Pisa, Italy
In recent decades, psychological research on the effects of mindfulness-based interventions has greatly developed and demonstrated a range of beneficial outcomes in a variety of populations and contexts. Yet, the question of how to foster subjective well-being and happiness remains open. Here, we assessed the effectiveness of an integrated mental training program The Art of Happiness on psychological well-being in a general population. The mental training program was designed to help practitioners develop new ways to nurture their own happiness. This was achieved by seven modules aimed at cultivating positive cognition strategies and behaviors using both formal (i.e., lectures, meditations) and informal practices (i.e., open discussions). The program was conducted over a period of 9 months, also comprising two retreats, one in the middle and one at the end of the course. By using a set of established psychometric tools, we assessed the effects of such a mental training program on several psychological well-being dimensions, taking into account both the longitudinal effects of the course and the short-term effects arising from the intensive retreat experiences. The results showed that several psychological well-being measures gradually increased within participants from the beginning to the end of the course. This was especially true for life satisfaction, self-awareness, and emotional regulation, highlighting both short-term and longitudinal effects of the program. In conclusion, these findings suggest the potential of the mental training program, such as The Art of Happiness , for psychological well-being.

Introduction
People desire many valuable things in their life, but—more than anything else—they want happiness ( Diener, 2000 ). The sense of happiness has been conceptualized as people's experienced well-being in both thoughts and feelings ( Diener, 2000 ; Kahneman and Krueger, 2006 ). Indeed, research on well-being suggests that the resources valued by society, such as mental health ( Koivumaa-Honkanen et al., 2004 ) and a long life ( Danner et al., 2001 ), associate with high happiness levels. Since the earliest studies, subjective well-being has been defined as the way in which individuals experience the quality of their life in three different but interrelated mental aspects: infrequent negative affect, frequent positive affect, and cognitive evaluations of life satisfaction in various domains (physical health, relationships, and work) ( Diener, 1984 , 1994 , 2000 ; Argyle et al., 1999 ; Diener et al., 1999 ; Lyubomksky et al., 2005 ; Pressman and Cohen, 2005 ). A growing body of research has been carried out aimed at identifying the factors that affect happiness, operationalized as subjective well-being. In particular, the construct of happiness is mainly studied within the research fields of positive psychology or contemplative practices, which are grounded in ancient wisdom traditions. Positive psychology has been defined as the “the scientific study of human strengths and virtues” ( Sheldon and King, 2001 ), and it can be traced back to the reflections of Aristotle about different perspectives on well-being ( Ryan and Deci, 2001 ). On the other end, contemplative practices include a great variety of mental exercises, such as mindfulness, which has been conceived as a form of awareness that emerges from experiencing the present moment without judging those experiences ( Kabat-Zinn, 2003 ; Bishop et al., 2004 ). Most of these exercises stem from different Buddhist contemplative traditions such as Vipassana and Mahayana ( Kornfield, 2012 ). Notably, both perspective share the idea of overcoming suffering and achieving happiness ( Seligman, 2002 ). Particularly, Buddhism supports “the cultivation of happiness, genuine inner transformation, deliberately selecting and focusing on positive mental states” ( Lama and Cutler, 2008 ). In addition, mindfulness has been shown to be positively related to happiness ( Shultz and Ryan, 2015 ), contributing to eudemonic and hedonic well-being ( Howell et al., 2011 ).
In fact, although the definition of happiness has a long history and goes back to philosophical arguments and the search for practical wisdom, in modern times, happiness has been equated with hedonism. It relies on the achievement of immediate pleasure, on the absence of negative affect, and on a high degree of satisfaction with one's life ( Argyle et al., 1999 ). Nonetheless, scholars now argue that authentic subjective well-being goes beyond this limited view and support an interpretation of happiness as a eudemonic endeavor ( Ryff, 1989 ; Keyes, 2006 ; Seligman, 2011 ; Hone et al., 2014 ). Within this view, individuals seem to focus more on optimal psychological functioning, living a deeply satisfying life and actualizing their own potential, personal growth, and a sense of autonomy ( Deci and Ryan, 2008 ; Ryff, 2013 ; Vazquez and Hervas, 2013 ; Ivtzan et al., 2016 ). In psychology, such a view finds one of its primary supports in Maslow's (1981) theory of human motivation. Maslow argued that experience of a higher degree of satisfaction derives from a more wholesome life conduct. In Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, once lower and more localized needs are satisfied, the unlimited gratification of needs at the highest level brings people to a full and deep experience of happiness ( Inglehart et al., 2008 ). Consequently, today, several scholars argue that high levels of subjective well-being depend on a multi-dimensional perspective, which encompasses both hedonic and eudemonic components ( Huta and Ryan, 2010 ; Ryff and Boylan, 2016 ). Under a wider perspective, the process of developing well-being reflects the notion that mental health and good functioning are more than a lack of illness ( Keyes, 2005 ). This approach is especially evident if we consider that even the definition of mental health has been re-defined by the World Health Organization (1948) , which conceives health not merely as the absence of illness, but as a whole state of biological, psychological, and social well-being.
To date, evidence exists suggesting that happiness is, in some extent, modulable and trainable. Thus, simple cognitive and behavioral strategies that individuals choose in their lives could enhance happiness ( Lyubomirsky et al., 2005 ; Sin and Lyubomirsky, 2009 ). In the history of psychology, a multitude of clinical treatments have been applied to minimize the symptoms of a variety of conditions that might hamper people from being happy, such as anger, anxiety, and depression (for instance, see Forman et al., 2007 ; Spinhoven et al., 2017 ). In parallel with this view, an alternative—and less developed—perspective found in psychology focuses on the scientific study of individual experiences and positive traits, not for clinical ends, but instead for personal well-being and flourishing (e.g., Fredrickson and Losada, 2005 ; Sin and Lyubomirsky, 2009 ). Yet, the question of exactly how to foster subjective well-being and happiness, given its complexity and importance, remains open to research. Answering this question is of course of pivotal importance, both individually and at the societal level. Positive Psychology Interventions encompass simple, self-administered cognitive behavioral strategies intended to reflect the beliefs and behaviors of individuals and, in response to that, to increase the happiness of the people practicing them ( Sin and Lyubomirsky, 2009 ; Hone et al., 2015 ). Specifically, a series of comprehensive psychological programs to boost happiness exist, such as Fordyce's program ( Fordyce, 1977 ), Well-Being Therapy ( Fava, 1999 ), and Quality of Life Therapy ( Frisch, 2006 ). Similarly, a variety of meditation-based programs aim to develop mindfulness and emotional regulatory skills ( Carmody and Baer, 2008 ; Fredrickson et al., 2008 ; Weytens et al., 2014 ), such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR; Kabat-Zinn, 1990 ) and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT; Teasdale et al., 2000 ). Far from being a mere trend ( De Pisapia and Grecucci, 2017 ), those mindfulness-based interventions have been shown to lead to increased well-being ( Baer et al., 2006 ; Keng et al., 2011 ; Choi et al., 2012 ; Coo and Salanova, 2018 ; Lambert et al., 2019 ) in several domains, such as cognition, consciousness, self, and affective processing ( Raffone and Srinivasan, 2017 ). Typically, mindfulness programs consist of informal and formal practice that educate attention and develop one's capacity to respond to unpredicted and/or negative thoughts and experiences ( Segal and Teasdale, 2002 ). In this context, individuals are gradually introduced to meditation practices, focusing first on the body and their own breath, and later on thoughts and mental states. The effects of these programs encompass positive emotions and reappraisal ( Fredrickson et al., 2008 ; Grecucci et al., 2015 ; Calabrese and Raffone, 2017 ) and satisfaction in life ( Fredrickson et al., 2008 ; Kong et al., 2014 ) and are related to a reduction of emotional reactivity to negative affect, stress ( Arch and Craske, 2006 ; Jha et al., 2017 ), and aggressive behavior ( Fix and Fix, 2013 ). All these effects mediate the relationship between meditation frequency and happiness ( Campos et al., 2016 ). This allows positive psychology interventions to improve subjective well-being and happiness and also reduce depressive symptoms and negative affect along with other psychopathologies ( Seligman, 2002 ; Quoidbach et al., 2015 ). Engaging in mindfulness might enhance in participants the awareness of what is valuable to them ( Shultz and Ryan, 2015 ). This aspect has been related to the growth of self-efficacy and autonomous functioning and is attributable to an enhancement in eudemonic well-being ( Deci and Ryan, 1980 ). Moreover, being aware of the present moment provides a clearer vision of the existing experience, which in turn has been associated with increases in hedonic well-being ( Coo and Salanova, 2018 ). Following these approaches, recent research provides evidence that trainings that encompass both hedonic and eudemonic well-being are correlated with tangible improved health outcomes ( Sin and Lyubomirsky, 2009 ).
Although there is a consistent interest in scientific research on the general topic of happiness, such studies present several limitations. Firstly, most of the research has focused on clinical studies to assess the effectiveness of happiness-based interventions—in line with more traditional psychological research, which is primarily concerned with the study of mental disorders ( Garland et al., 2015 , 2017 ; Groves, 2016 ). Secondly, most of the existing interventions are narrowly focused on the observation of single dimensions (i.e., expressing gratitude or developing emotional regulation skills) ( Boehm et al., 2011 ; Weytens et al., 2014 ). Moreover, typically studies involve brief 1- to 2-week interventions ( Gander et al., 2016 ), in contrast with the view that eudemonia is related to deep and long-lasting aspects of one's personal lifestyle. Furthermore, while the effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapies is well-documented, research that investigates the effects of mindfulness retreats has been lacking, which are characterized by the involvement of more intense practice from days to even years [for meta-analysis and review, see Khoury et al. (2017) , McClintock et al. (2019) , Howarth et al. (2019) ].
In this article, we report the effects on subjective well-being of an integrated mental training program called The Art of Happiness , which was developed and taught by two of the authors (CM for the core course subject matter and NDP for the scientific presentations). The course lasted 9 months and included three different modules (see Methods and Supplementary Material for all details), namely, seven weekends (from Friday evening to Sunday afternoon) dedicated to a wide range of specific topics, two 5-day long retreats, and several free activities at home during the entire period. The course was designed to help practitioners develop new ways to nurture their own happiness, cultivating both self-awareness and their openness to others, thereby fostering their own emotional and social well-being. The basic idea was to let students discover how the union of ancient wisdom and spiritual practices with scientific discoveries from current neuropsychological research can be applied beneficially to their daily lives. This approach and mental training program was inspired by a book of the Fourteenth Dalai Lama Tenzin Gyatso and the psychiatrist Lama and Cutler (2008) . The program rests on the principle that happiness is inextricably linked to the development of inner equilibrium, a kinder and more open perspective of self, others, and the world, with a key role given to several types of meditation practices. Additionally, happiness is viewed as linked to a conceptual understanding of the human mind and brain, as well as their limitations and potentiality, in the light of the most recent scientific discoveries. To this end, several scientific topics and discoveries from neuropsychology were addressed in the program, with a particular focus on cognitive, affective, and social neuroscience. Topics were taught and discussed with language suitable for the general public, in line with several recent books (e.g., Hanson and Mendius, 2011 ; Dorjee, 2013 ; Goleman and Davidson, 2017 ). The aim of this study was to examine how several psychological measures, related to psychological well-being, changed among participants in parallel with course attendance and meditation practices. Given the abovementioned results of the positive effects on well-being ( Baer et al., 2006 ; Fredrickson et al., 2008 ; Keng et al., 2011 ; Choi et al., 2012 ; Kong et al., 2014 ; Coo and Salanova, 2018 ; Lambert et al., 2019 ), we predicted to find a significant increase in the dimensions of life satisfaction, control of anger, and mindfulness abilities. Conversely, we expected to observe a reduction of negative emotions and mental states ( Arch and Craske, 2006 ; Fix and Fix, 2013 ; Jha et al., 2017 )—i.e., stress, anxiety and anger. Moreover, our aim was to explore how those measures changed during the course of the mental training program, considering not only the general effects of the course (longitudinal effects) but also specific effects within each retreat (short-term effects). Our expectation for this study was therefore that the retreats would have had an effect on the psychological dimensions of well-being linked to the emotional states of our participants, while the whole course would have had a greater effect on the traits related to well-being. The conceptual distinction between states and traits was initially introduced in regard to anxiety by Cattell and Scheier (1961) , and then subsequently further elaborated by Spielberger et al. (1983) . When considering a mental construct (e.g., anxiety or anger), we refer to trait as a relatively stable feature, a general behavioral attitude, which reflects the way in which a person tends to perceive stimuli and environmental situations in the long term ( Spielberger et al., 1983 ; Spielberger, 2010 ). For example, subjects with high trait anxiety have indeed anxiety as a habitual way of responding to stimuli and situations. The state, on the other hand, can be defined as a temporary phase within the emotional continuum, which, for example, in anxiety is expressed through a subjective sensation of tension, apprehension, and nervousness, and is associated with activation of the autonomic nervous system in the short term ( Spielberger et al., 1983 ; Saviola et al., 2020 ). Here, in the adopted tests and analyses, we keep the two time scales separated, and we investigate the results with the aim of understanding the effects of the program on states and traits of different emotional and well-being measures. As a first effect of the course, we expect that the retreats affect mostly psychological states (as measured in the comparison of psychological variables between start and end of each retreat), whereas the full course is predicted to affect mainly psychological traits (as measured in the comparison of the psychological variables between start, middle, and end of the entire 9-month period).
Materials and Methods
Participants.
The participants in the mental training program and in the related research were recruited from the Institute Lama Tzong Khapa (Pomaia, Italy) in a 9-month longitudinal study (seven modules and two retreats) on the effects of a program called The Art of Happiness (see Supplementary Material for full details of the program). Twenty-nine participants followed the entire program (there were nine dropouts after the first module). Their mean age was 52.86 years (range = 39–66; SD = 7.61); 72% were female. Participants described themselves as Caucasian, reaching a medium-high scholarly level with 59% of the participants holding an academic degree and 41% holding a high school degree. The participants were not randomly selected, as they were volunteers in the program. Most of them had no serious prior experience of meditation, only basic experience consisting of personal readings or watching video courses on the web, which overall we considered of no impact to the study. The only exclusion criteria were absence of a history of psychiatric or neurological disease, and not being currently on psychoactive medications. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Sapienza University of Rome, and all participants gave written informed consent. The participants did not receive any compensation for participation in the study.
The overall effectiveness of the 9-month training was examined using a within-subjects design, with perceived stress, mindfulness abilities, etc. (Time: pre–mid–end) as the dependent variable. The effectiveness of the retreats was examined using a 2 × 2 factor within-subjects design (condition: pre vs. post; retreat: 1 vs. 2), with the same dependent variables. The specific contemplative techniques that were applied in the program are described in the Supplementary Material , the procedure is described in the Procedure section, and the measurements are described in the Materials section.
Mental Training Program
The program was developed and offered at the Institute Lama Tzong Khapa (Pomaia, Italy). It was one of several courses that are part of the Institute's ongoing programs under the umbrella of “Secular Ethics and Universal Values.” These various programs provide participants with opportunities to discover how the interaction of ancient wisdom and spiritual practices with contemporary knowledge from current scientific research in neuropsychology can be applied extensively and beneficially to improve the quality of their daily lives.
Specifically, The Art of Happiness was a 9-month program, with one program activity each month, either a weekend module or a retreat; there were two retreats—a mid-course retreat and a concluding retreat (for full details on the program, see Supplementary Material ). Each thematic module provided an opportunity to sequentially explore the topics presented in the core course text, The Art of Happiness by the Lama and Cutler (2008) .
In terms of the content of this program, as mentioned above, the material presented and explored has been drawn on the one hand from the teachings of Mahayana Buddhism and Western contemplative traditions, and current scientific research found in neuropsychology on the other hand. On the scientific side, topics included the effects of mental training and meditation, the psychology and neuroscience of well-being and happiness, neuroplasticity, mind–brain–body interactions, different areas of contemplative sciences, the placebo effects, the brain circuits of attention and mind wandering, stress and anxiety, pain and pleasure, positive and negative emotions, desire and addiction, the sense of self, empathy, and compassion (for a full list of the scientific topics, see Supplementary Material ).
The overall approach of the course was one of non-dogmatic exploration. Topics were presented not as undisputed truths, but instead as information to be shared, explored, examined, and possibly verified by one's own experience. Participants were heartily invited to doubt, explore, and test everything that was shared with them, to examine and experience firsthand whether what was being offered has validity or not.
The course was, essentially, an informed and gentle training of the mind, and in particular of emotions, based on the principle that individual well-being is inextricably linked to the development of inner human virtues and strengths, such as emotional balance, inner self-awareness, an open and caring attitude toward self and others, and clarity of mind that can foster a deeper understanding of one's own and others' reality.
The program provided lectures and discussions, readings, and expert videos introducing the material pertinent to each module's topic. Participants engaged with the material through listening, reading, discussing, and questioning. Participants were provided with additional learning opportunities to investigate each topic more deeply, critically, and personally, through the media of meditation, journaling, application to daily life, exercises at home, and contemplative group work with other participants in dyads and triads. Participants were then encouraged to reflect repeatedly on their insights and on their experiences, both successful and not, to apply their newly acquired understandings to their lives, by incorporating a daily reflection practice into their life schedule. The two program retreats also provided intensive contemplative experiences and activities, both individual and in dialogue with others.
On this basis, month after month in different dedicated modules, participants learned new ways to nurture their own happiness, to cultivate their openness to others, to develop their own emotional and social well-being, and to understand some of the scientific discoveries on these topics.
The specific topics addressed in corresponding modules and retreats, each in a different and consecutive month, were as follows: (1) The Purpose of Life: Authentic Happiness; (2) Empathy and Compassion; (3) Transforming Life's Suffering; (4) Working with Disturbing Emotions I: Hate and Anger; first retreat (intermediate); (5) Working with Disturbing Emotions II: The Self Image; (6) Life and Death; (7) Cultivating the Spiritual Dimension of Life: A Meaningful Life; second retreat (final). Full details of the entire program are reported in the Supplementary Material .
Participants were guided in the theory and practice of various contemplative exercises throughout the course pertaining to all the different themes. Recorded versions of all the various meditation exercises were made available to participants, enabling them to repeat these practices at home at their own pace.
Participants were encouraged to enter the program already having gained some basic experience of meditation, but this was not a strict requirement. In fact, not all participants in this experiment actually fulfilled this (only five), although each of the other participants had previous basic experiences of meditation (through personal readings, other video courses, etc.). In spite of this variety, by the end of the 9-month program, all participants were comfortable with contemplative practices in general and more specifically with the idea of maintaining a meditation practice in their daily lives.
During the various Art of Happiness modules, a variety of basic attentional and mindful awareness meditations were practiced in order to enhance attentional skills and cultivate various levels of cognitive, emotional, social, and environmental awareness.
Analytical and reflective contemplations are a form of deconstructive meditation ( Dahl et al., 2015 ), which were applied during the course in different contexts. On the one hand, these types of meditations were applied in the context of heart-opening practices—for example, in the cultivation of gratitude, forgiveness, loving-kindness toward self and others, self-compassion, and compassion for others. Analytical and reflective meditations were also practiced as a learning tool for further familiarization with some of the more philosophical subject matter of the course—engaging in a contemplative analysis of impermanence (for example, contemplating more deeply and personally the transitory nature of one's own body, of one's own emotions and thoughts, as well as of the material phenomena that surround us). These analytical meditations were also accompanied by moments of concentration (sustained attention) at the conclusion of each meditation focusing on what the meditator has learned or understood in the meditative process, in order to stabilize and reinforce those insights more deeply within the individual.
Additional contemplative activities were also included in the program: contemplative art activities, mindful listening, mindful dialogue, and the practice of keeping silence during the retreat. Participants were, in addition, encouraged to keep a journal of their experiences during their Art of Happiness journey, especially in relation to their meditations and the insights and questions that emerged within themselves, in order to enhance their self-awareness and cultivate a deeper understanding of themselves, their inner life and well-being, and their own inner development during the course and afterward.
During the two retreats, the previous topics were explored again (modules 1–4 for the intermediary retreat and modules 5–7 for the final retreat), but without discussing the theoretical aspects (i.e., the neuroscientific and psychological theories), instead only focusing on the contemplative practices, which were practiced extensively for the whole day, both individually and in group activities (for a full list of the contemplative practices and retreat activities, see Supplementary Material ).
We collected data at five-time points, always during the first day (either of the module or the retreat): at baseline (month 1 - T0), at pre (T1) and post (P1) of the mid-course retreat (month 5–Retreat 1), and at pre (T2) and post (R2) of the final retreat (month 9–Retreat 2), as shown in Figure 1 . Participants filled out the questionnaires on paper all together within the rooms of the Institute Lama Tzong Khapa at the beginning of each module or retreat, and at the end of the retreats, with the presence of two researchers. The order of the questionnaires was randomized, per person and each questionnaire session lasted less than an hour.
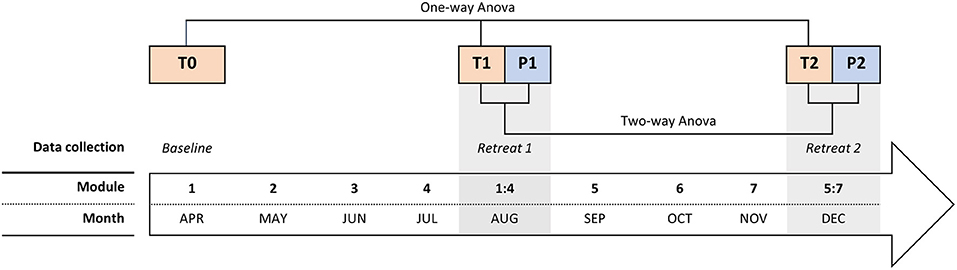
Figure 1 . The timing of the course and the experimental procedure, including the modules, the retreats, and the 5 data collections (from T0 to P2).
The adopted questionnaires were those commonly used in the literature to measure a variety of traits and states linked to well-being. An exhaustive description of the self-reported measures follows below.
Satisfaction With Life Scale (SWLS)
The SWLS ( Diener et al., 1985 ) was developed to represent cognitive judgments of life satisfaction. Participants indicated their agreement in five items with a seven-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree). Scores range from 5 to 35, with higher scores representing higher levels of satisfaction. Internal consistency is very good with Cronbach's α = 0.85 [Italian version of the normative data in Di Fabio and Palazzeschi (2012) ].
Short Version of the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS-10)
The PSS ( Cohen et al., 1983 ) was designed to assess individual perception and reaction to stressful daily-life situations. The questionnaire consists of 10 questions related to the feelings and thoughts of the last month, with a value ranging from 0 (never) to 4 (very often) depending on the severity of the disturbance caused. Scores range from 0 to 40. Higher scores represent higher levels of perceived stress, reflecting the degree to which respondents find their lives unpredictable or overloaded. Cronbach's α ranges from 0.78 to 0.93 [Italian version of the normative data by Mondo et al. (2019) ].
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI)
The STAI ( Spielberger et al., 1983 ) was developed to assess anxiety. It has 40 items, on which respondents evaluate themselves in terms of frequency with a four-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (almost never) to 4 (almost always). The items are grouped in two independent subscales of 20 items each that assess state anxiety, with questions regarding the respondents' feelings at the time of administration, and trait anxiety, with questions that explore how the participant feels habitually. The scores range from 20 to 80. Higher scores reflect higher levels of anxiety. Internal consistency coefficients for the scale ranged from 0.86 to 0.95 [Italian version of the normative data by Spielberger et al. (2012) ].
Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS)
PANAS ( Watson et al., 1988 ) measures two distinct and independent dimensions: positive and negative affect. The questionnaire consists of 20 adjectives, 10 for the positive affect subscale and 10 for the negative affect scale. The positive affect subscale reflects the degree to which a person feels enthusiastic, active, and determined while the negative affect subscale refers to some unpleasant general states such as anger, guilt, and fear. The test presents a five-point Likert scale (1 = very slightly or not at all; 5 = extremely). The alpha reliabilities are acceptably high, ranging from 0.86 to 0.90 for positive affect and from 0.84 to 0.87 for negative affect [Italian version of the normative data by Terracciano et al. (2003) ].
Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire (FFMQ)
The FFMQ ( Baer et al., 2008 ) was developed to assess mindfulness facets through 39 items rated on a five-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (never or very rarely true) to 5 (very often or always true). A total of five subscales are included: attention and observation of one's own thoughts, feelings, perceptions, and emotions ( Observe ); the ability to describe thoughts in words, feelings, perceptions, and emotions ( Describe ); act with awareness, with attention focused and sustained on a task or situation, without mind wandering ( Act-aware ); non-judgmental attitude toward the inner experience ( Non-Judge ); and the tendency to not react and not to reject inner experience ( Non-React ). Normative data of the FFMQ have demonstrated good internal consistency, with Cronbach's α ranging from 0.79 to 0.87 [Italian version by Giovannini et al. (2014) ].
State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory-2 (STAXI-2)
The STAXI-2 ( Spielberger, 1999 ) provides measures to assess the experience, expression, and control of anger. It comprises 57 items rated on a four-point Likert scale, ranging from 0 (not at all) to 3 (very much indeed). Items are grouped by four scales: the first, State Anger scale, refers to the emotional state characterized by subjective feelings and relies on three more subscales: Angry Feelings, Physical Expression of Anger, and Verbal Expression of Anger. The second scale is the Trait Anger and indicates a disposition to perceive various situations as annoying or frustrating with two subscales—Angry Temperament and Angry Reaction. The third and last scales are Anger Expression and Anger Control. These assess anger toward the environment and oneself according to four relatively independent subscales: Anger Expression-OUT, Anger Expression-IN, Anger Control-OUT, and Anger Control-IN. Alpha coefficients STAXI-2 were above 0.84 for all scales and subscales, except for Trait Anger Reaction, which had an alpha coefficient of 0.76 [Italian version by Spielberger (2004) ].
Statistical Analysis
The responses on each questionnaire were scored according to their protocols, which resulted in one score per participant and a time point for each of the 22 scale/subscale questionnaires examined. Missing values (<2%) were imputed using the median. Descriptive statistics for all variables were analyzed and are summarized in Table 1 and in the first panel (column) of Figures 2 – 5 . Prior to conducting primary analyses, the distribution of scores on all the dependent variables was evaluated. Because the data were not normally distributed, we used non-parametric tests. Permutation tests are non-parametric tests as they do not rely on assumptions about the distribution of the data and can be used with different types of scales and with a small sample size.
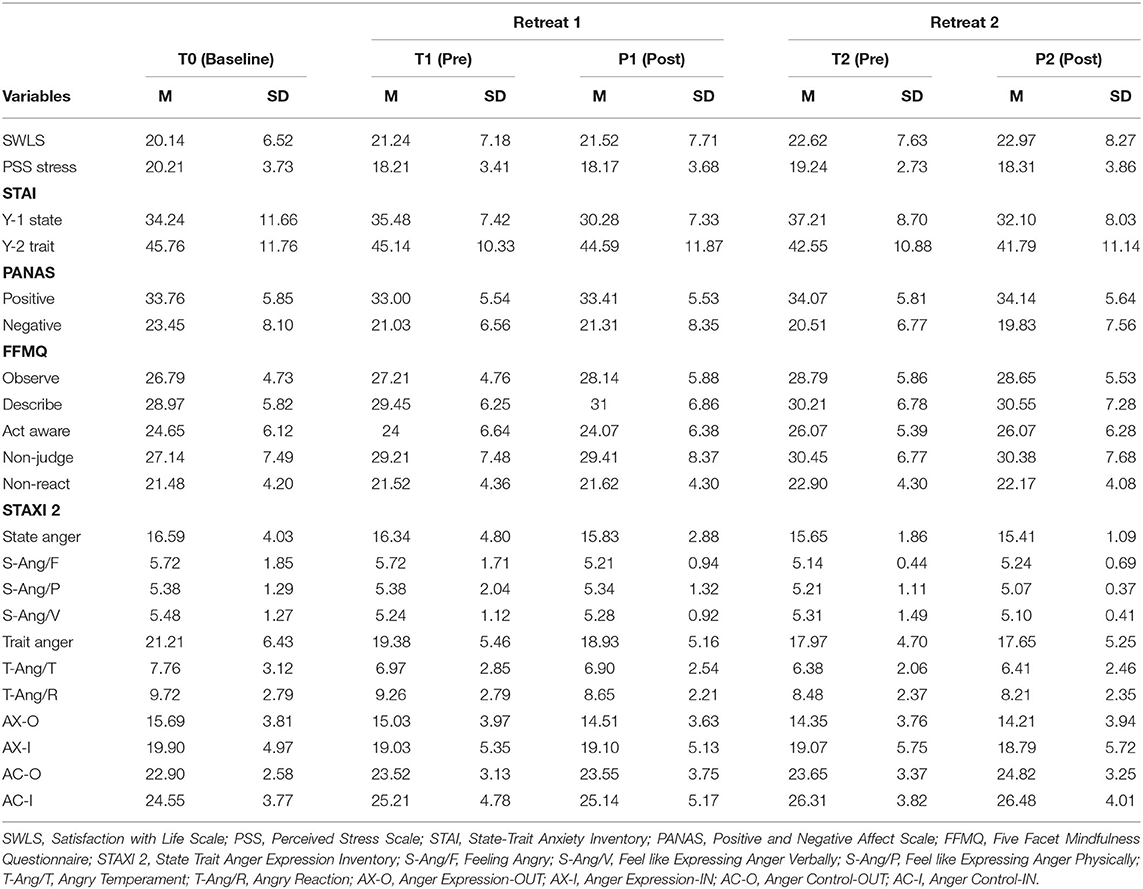
Table 1 . Descriptive statistics of the depended variables among time points.
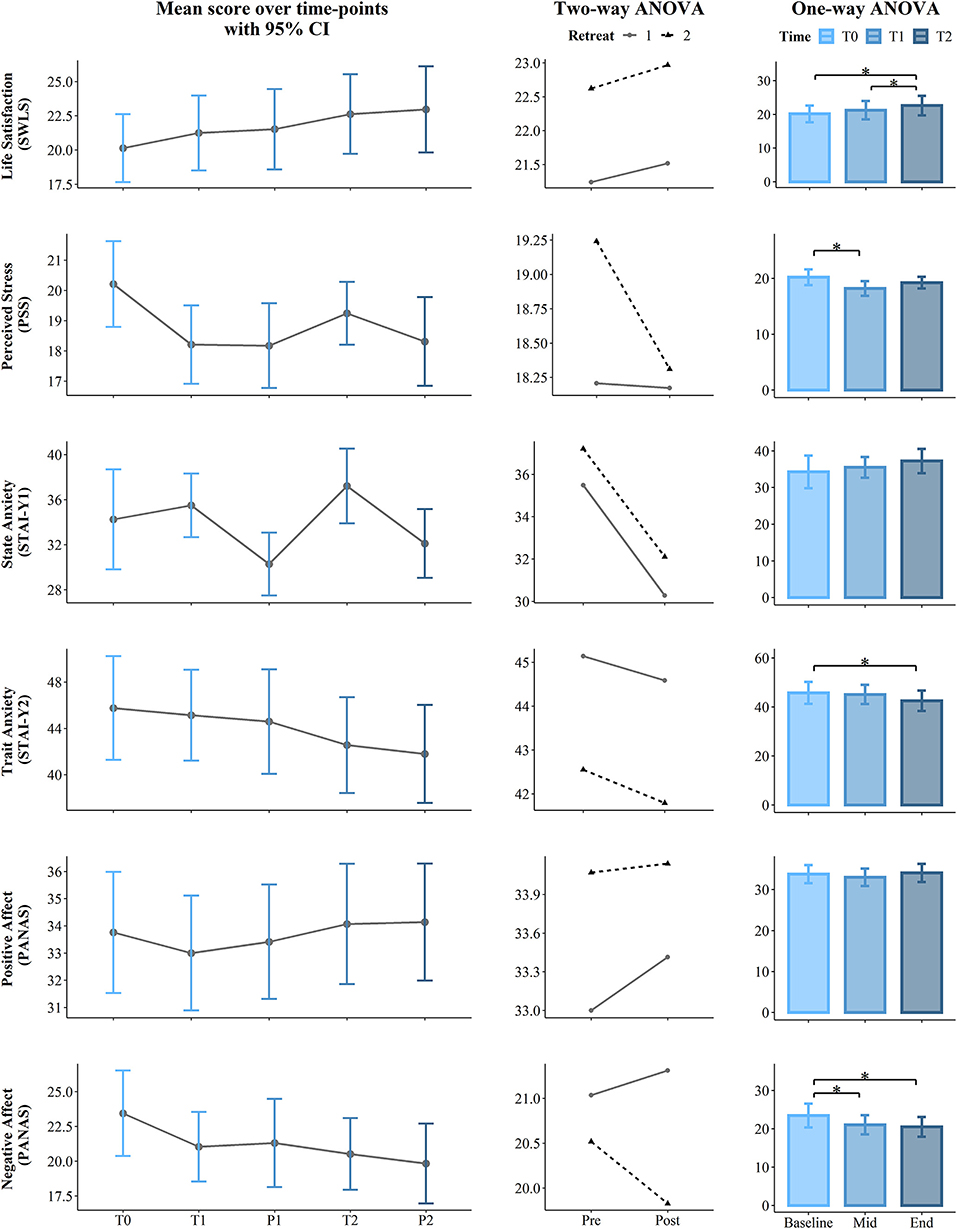
Figure 2 . Results of the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS), Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), State and Trait Anxiety Index (STAI), and Positive and Negative Affect Scales (PANAS). The first (left) panel depicts pooled mean raw data per time point estimating 95% confidence interval. The second (central) panel represents changes in pooled mean ( y -axis) between retreats. The solid line represents retreat 1 and the dotted line denotes retreat 2 derived from the contrasts of the two-way ANOVA. The third (right) panel depicts bar charts representing the changes in mean between the 3 time points derived from the one-way ANOVA. Note that scores are on the y -axis and time is on the x -axis. Time points legend: baseline (month 1—T0), pre (T1), post (P1), mid-course retreat (month 5—retreat 1), pre (T2), and post (R2) of the final retreat (month 9—retreat 2). Statistical significance, * p < 0.05.
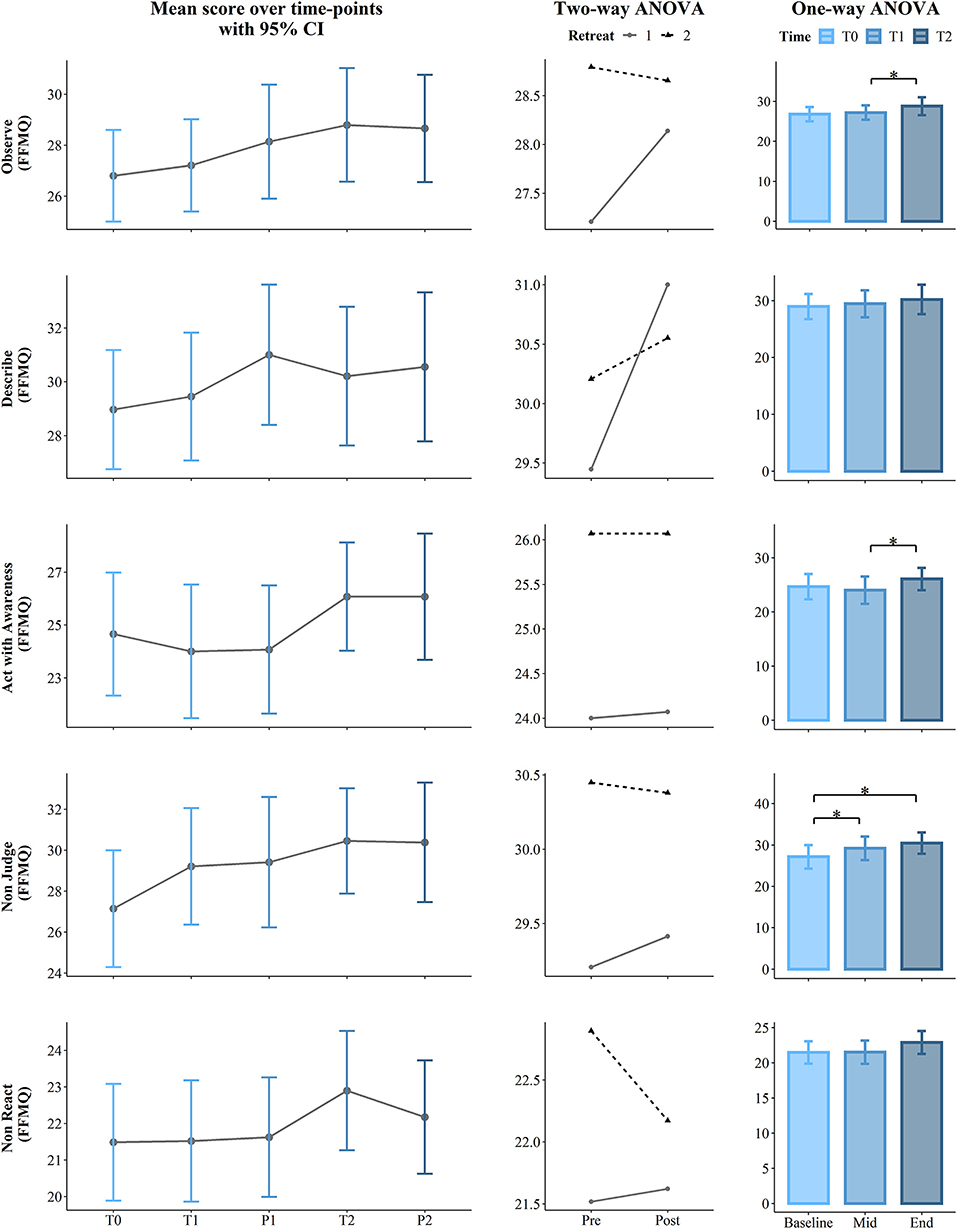
Figure 3 . Results for the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire FFMQ (Observe, Describe, Act with Awareness, Non-judge, and Non-react). The first (left) panel depicts pooled mean raw data per time point estimating 95% confidence interval. The second (central) panel represents changes in pooled mean ( y -axis) between retreats. The solid line represents retreat 1 and the dotted line denotes retreat 2 derived from the contrasts of the two-way ANOVA. The third (right) panel depicts bar charts representing the changes in mean between the 3 time points derived from one-way ANOVA. Note that scores are on the y -axis and time id on the x -axis. Time points legend: baseline (month 1—T0), pre (T1), post (P1), mid-course retreat (month 5—retreat 1), pre (T2), and post (P2) of the final retreat (month 9—retreat 2). Statistical significance, * p < 0.05.
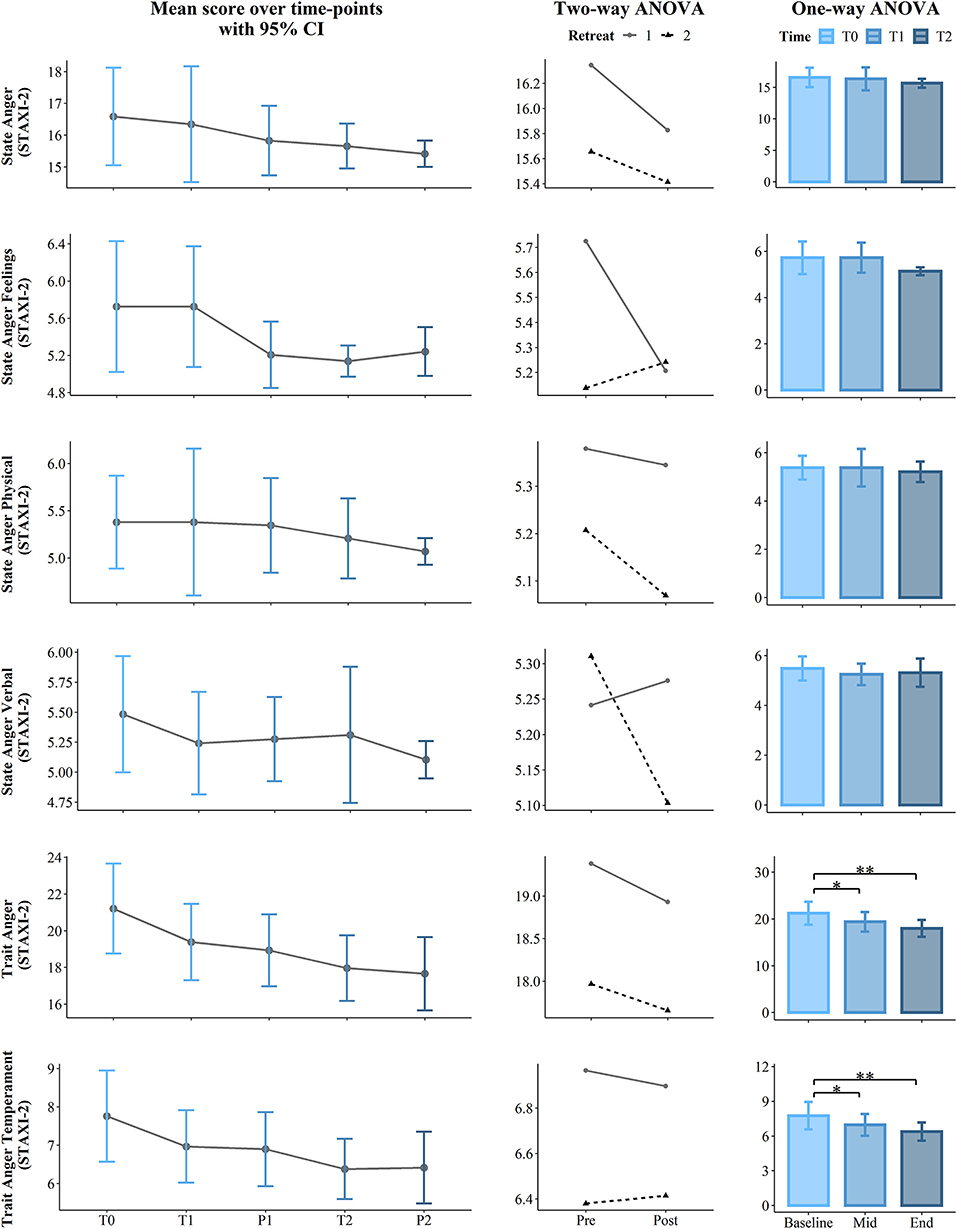
Figure 4 . Results of the first part of the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI-2): State Anger, State Anger Feelings, State Anger Physical, State Anger Verbal, Trait Anger, and Trait Anger Temperament. The first (left) panel depicts pooled mean raw data per time point estimating 95% confidence interval. The second (central) panel represents changes in pooled mean ( y -axis) between retreats. The solid line represents retreat 1 and the dotted line denotes retreat 2 derived from the contrasts of the two-way ANOVA. The third (right) panel depicts bar charts representing the changes in mean between the 3 time points derived from one-way ANOVA. Note that scores are on the y -axis and time is on the x -axis. Time points legend: baseline (month 1—T0), pre (T1), post (P1), mid-course retreat (month 5—retreat 1), pre (T2), and post (R2) of the final retreat (month 9—retreat 2). Statistical significance, ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05.
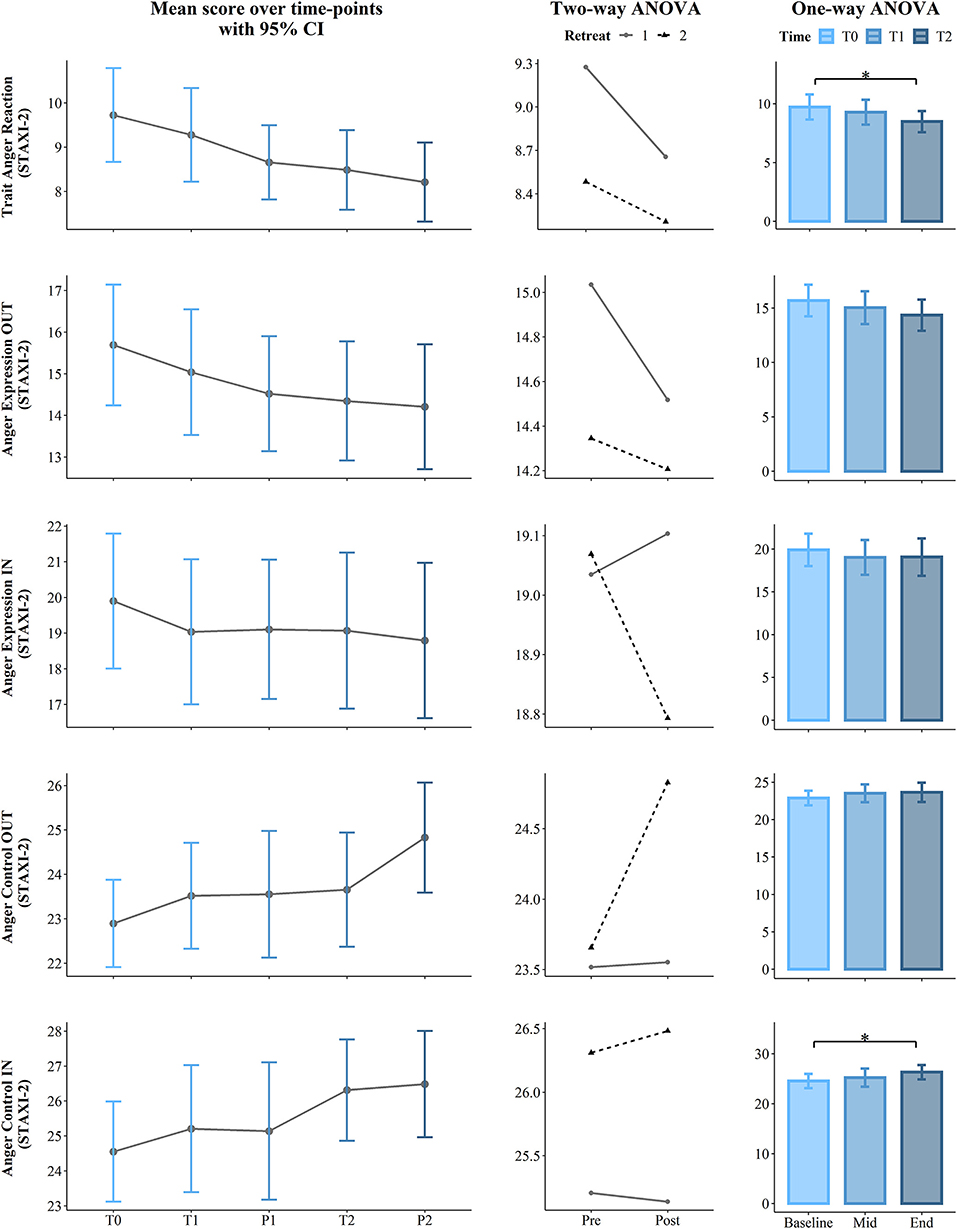
Figure 5 . Results from the second part of the State Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI-2): Trait Anger Reaction, Anger Expression-IN, Anger Expression-OUT, Anger Control-IN, and Anger Control OUT. The first (left) panel depicts pooled mean raw data per time point estimating 95% confidence interval. The second (central) panel represents changes in pooled mean ( y -axis) between retreats. The solid line represents retreat 1 and the dotted line denotes retreat 2 derived from the contrasts of the two-way ANOVA. The third (right) panel depicts bar charts representing the changes in mean between the 3 time points derived from one-way ANOVA. Note that scores are on the y -axis and time is on the x -axis. Time points legend: baseline (month 1—T0), pre (T1), post (P1), mid-course retreat (month 5—Retreat 1), pre (T2), and post (R2) of the final retreat (month 9—Retreat 2). Statistical significance, * p < 0.05.
The longitudinal effects of the program were analyzed to determine whether scores changed between the start, mid-point (5 months), and the end (9 months) of the course. To achieve this, we compared the main effect of the program on the score , considering Time as a unique factor with three levels: at the baseline (T0), at the pre of the mid-retreat (T1), and at the pre of the final retreat (T2). Here, we used a one-way permutation Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance (RM ANOVA) with the aovperm() function from the Permuco package v. 1.0.2 in R ( Frossard and Renaud, 2018 ), which implements a method from Kherad-Pajouh and Renaud (2014) . The difference between the traditional and the permutation ANOVA is that, while the traditional ANOVA tests the equality of the group mean, the permutation version tests the exchangeability of the group observations. In this study, the number of permutations was set to 100,000 and the alpha level was set to 0.05; therefore, the p -value was computed as the ratio between the number of permutation tests that have an F value higher than the critical F value and the number of permutations performed. Effect size estimates were calculated using partial eta squared. Post hoc testing used pairwise permutational t -tests with the “pairwise.perm.t.test” function from the “RVAideMemoire” package in R ( Hervé and Hervé, 2020 ). To account for Type I errors introduced by multiple pairwise tests and Type II errors introduced by small sample size, we applied the false discovery rate (FDR) correction method of Benjamini and Hochberg (1995) and set statistical significance at p = 0.05. Results are summarized in Table 2 and in the third panel (column) of Figures 2 – 5 .
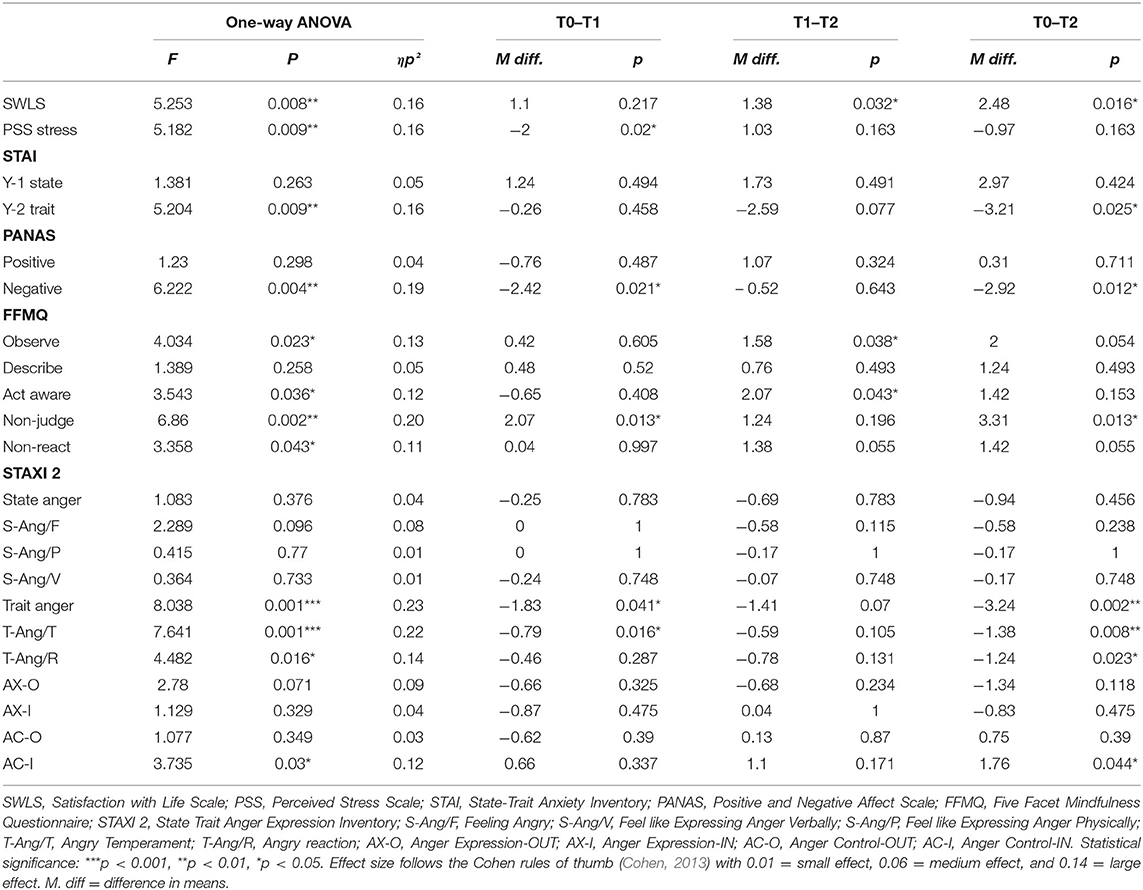
Table 2 . One-way ANOVA and pairwise comparison results with 100,000 permutations.
The short-term effects of the contemplative program on each retreat were analyzed to determine whether scores changed post-retreats and whether these changes occurred in both retreats. Thus, we used a two-way permutation RM ANOVA, with the score of each scale/subscale as the dependent variable and the within-subject factors Retreat (1, 2) and Condition (Pre T1/T2, Post P1/P2) as independent variables. Results are summarized in Table 3 and in the second panel (column) of Figures 2 – 5 .
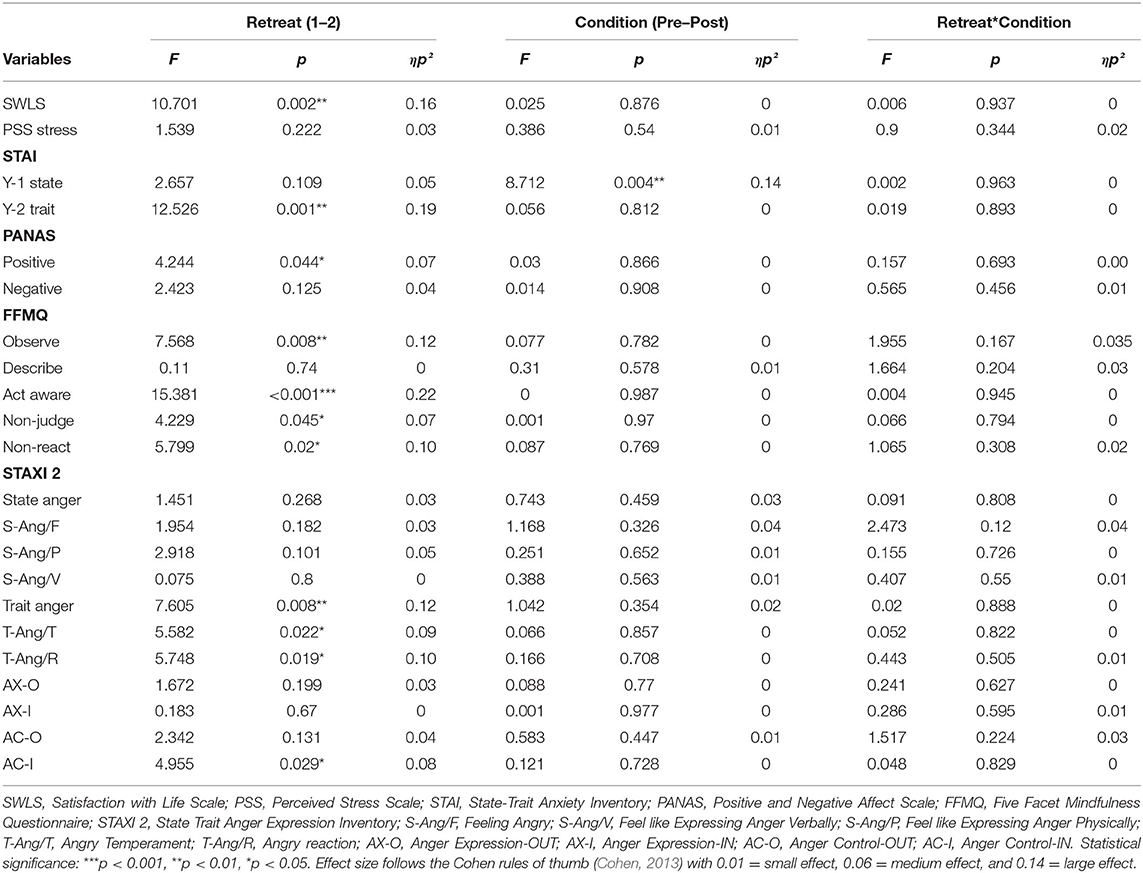
Table 3 . Results of the two-way permutation RM ANOVAs.
In addition, we explored differences attributed to the course and to the retreats using a paired permutation t test with the “perm.t.test()” function in R. We compare those psychological measures at the beginning of the course (T0) with its very end (P2), which coincided with the end of the second retreat. In this way, we illustrate a summary of changes due both to the second retreat and to the whole course. The results are summarized in Table 4 and depicted in a radar plot in Figure 6 .
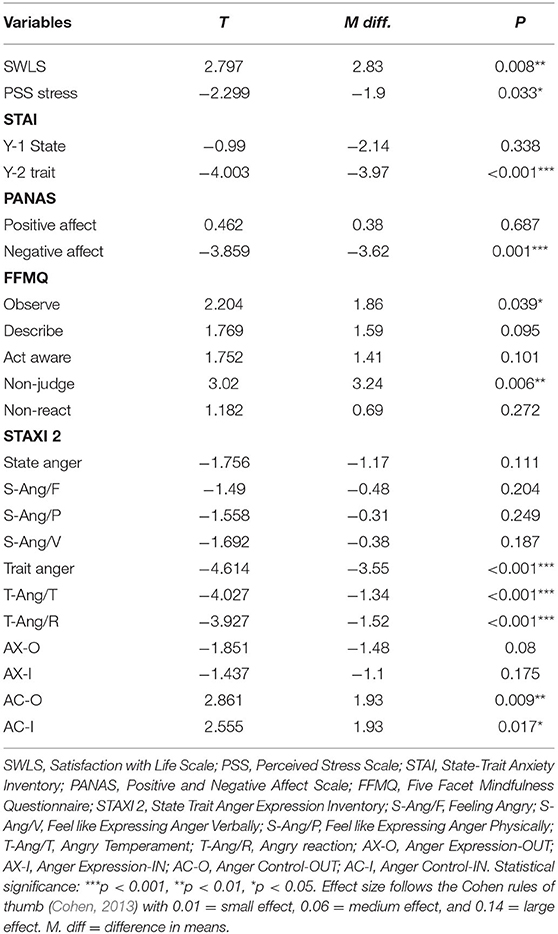
Table 4 . Overall changes between the start (T0) and the end of the course (P2).
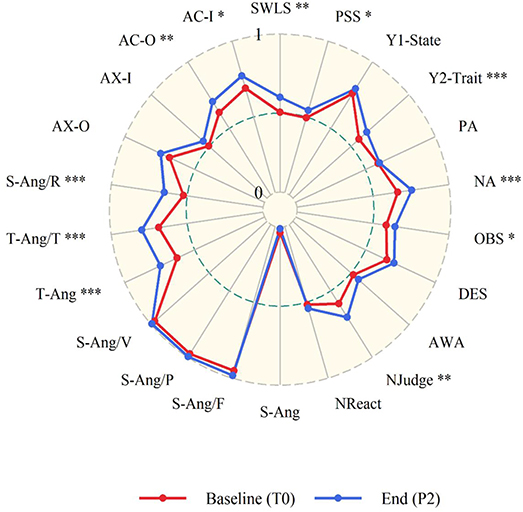
Figure 6 . Results of the permutation t -test between the start and the end of the course. All values ranged from 0 to 1. Variables: SWLS, Satisfaction with Life Scale; S-Ang/F, Feeling Angry; S-Ang/V, Feel like Expressing Anger Verbally; S-Ang/P, Feel like Expressing Anger Physically; T-Ang/T, Angry Temperament; T-Ang/R, Angry reaction; AX-O, Anger Expression-OUT; AX-I, Anger Expression-IN; AC-O, Anger Control-OUT; AC-I, Anger Control-IN; PSS, Perceived Stress Scale; STAI-Y1, State-Trait Anxiety Inventory—State; STAI-Y2, State-Trait Anxiety Inventory—Trait; PA and NA, Positive and Negative Affect Scales, respectively; OBS, Observe; DES, Describe; AWA, Act with awareness, Njudge, Non-judge; NReact, Non-react. To make consistent that an increase of the specific scale corresponds to an improvement in well-being, negative scales were reversed, namely: PSS, STAI-Y1, STAI-Y2, PANAS-NA, S-Ang, S-Ang/F, S-Ang/P, S-Ang/V, T-Ang, T-Ang/T, S-Ang/R, AX-O, AX-I. Concerning the statistical significance, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05.
Effects of the Program
Results from one-way permutation RM ANOVA showed a statistically significant effect of the program on SWLS at the p = 0.008 level over the Time course factor with a large effect size (ηp 2 = 0.16). Post hoc analysis revealed that the SWLS score was significantly higher at T2 with respect to T2 (mean difference = 2.48; p = 0.016). Similarly, SWLS was higher T2 as compared to T1 (mean difference = 1.38; p = 0.032).
Results also provided statistically significant evidence of changes in the PSS over the Time course ( p = 0.009), showing a large effect size (ηp 2 = 0.16). Post-hoc results showed a difference between T0 and T1, revealing that the PSS was significantly lower at T1 (mean difference = −2, p = 0.02).
Results revealed a significant effect of the Time course for Trait Anxiety ( p = 0.009, ηp 2 = 0.16). Post-hoc tests revealed a reduction in Trait Anxiety from the start of the course (T0) to the first day of the second retreat (T2) (M diff. = −3.21, p = 0.25).
Results also showed a significant effect of the Time course for negative affect ( p = 0.004, ηp 2 = 0.19). Post hoc analysis revealed that contemplative practice led to a reduction in negative affect from the baseline (T0) to the first day of the first retreat (T1) (mean difference = −2.42) and between T0 and first day of the second retreat (T2) (mean difference = −2.92), which differed significantly with p = 0.021 and p = 0.012, respectively.
Moreover, a significant effect of the Time course was found for several subscales of the FFMQ. First, the observe scale was found at the p = 0.023 level showing a large effect size (ηp 2 = 0.13). Post-hoc comparisons revealed an increasing capacity to observe one's own thoughts, from the middle of the course (T1) to the first day of the second retreat (T2) (mean difference = 1.58, p = 0.038). Likewise, there was a significant difference for the capacity to Act with Awareness ( p = 0.036, ηp 2 = 0.12). Post hoc comparisons revealed an increased level at T2 as compared to T1 (mean difference = 2.07, p = 0.043). The Time course had a significant effect on the Non-Judge subscale with a large effect size ( p = 0.002, ηp 2 = 0.20). Post hoc analysis indicated a significant increase from T0 to T1 (mean difference = 2.07, p = 0.013), as well as from T0 to T2 (mean difference = 3.31, p = 0.013).
In regard to the STAXI-2, we found Time course significant effects on Trait Anger ( p = 0.001, ηp 2 = 0.23) and its subscales, Trait Anger Temperament ( p = 0.001, ηp 2 = 0.22) and Trait Anger Reaction ( p = 0.016, ηp 2 = 0.14). Post-hoc comparisons revealed a significance difference on the Trait Anger Scale, which decreased from the beginning of the course (T0) to 5 months later (T1) (mean difference = −1.83, p = 0.041) and also from T0 to the end of the course (T2) (mean difference = −3.24, p = 0.002). Similarly, State Anger Temperament significantly decreased from T0 to T1 (mean difference = −0.79, p = 0.016) and from T0 to T2 (mean difference = −1.38, p = 0.008). Additionally, Trait Anger Reaction decreased from T0 to T2 (mean difference = −1.24, p = 0.023). Finally, the longitudinal effect of the course on the STAXI-2 led to significant results in the Anger Control-IN subscale over the Time course ( p = 0.03, ηp 2 = 0.12). Here, post-hoc comparisons showed a statistically significant difference between T0 and T2, which increased (mean difference = 1.76, p =.044). For more details, see Table 2 and the third panel (column) of Figures 2 – 5 .
Effects of the Retreats
Two-way permutation RM ANOVAs showed a significant main effect for Retreat on SWLS ( p = 0.002, ηp 2 = 0.16), Trait Anxiety ( p = 0.001, ηp 2 = 0.19), positive affect ( p = 0.044, ηp 2 = 0.07), Observe ( p = 0.008, ηp 2 = 0.12), Act with awareness ( p ≤ 0.001, ηp 2 = 0.22), Non-Judge ( p = 0.045, ηp 2 =.07), Non-React ( p = 0.02, ηp 2 = 0.10), Trait Anger ( p = 0.008, ηp 2 = 0.12), Trait Anger Temperament ( p = 0.022, ηp 2 = 0.09), Trait Anger Reaction ( p = 0.019, ηp 2 = 0.10), and Anger Control-IN ( p = 0.029, ηp 2 = 0.08). A main effect of the Condition (Pre vs. Post) was found only for the State Anxiety scale with p = 0.004 and a large effect size (ηp 2 = 0.14). Analysis results including F statistics are summarized in Table 3 ; a visual representation of the data is presented in the second panel (column) of Figures 2 – 5 .
Overall Effects of the Course and Retreats
As predicted, permutation t -test analysis revealed that participants increased their reported level of SWLS from the start (T0) to the end (P2) of the course (mean difference = 2.83, p = 0.008). Two subscales from the FFMQ, namely, the capacity to observe one's own thoughts (mean difference = 1.86, p = 0.039) and non-judgmental attitude toward the inner experience (mean difference = 3.24, p = 0.006), also significantly increased from the start to the end of the course. On the other hand, the affect linked to the progression from the start (T0) to the very end of the course (P2) was related to a significant decrease in the negative affect (mean difference = −3.62, p = 0.001). In the same way, the average level of stress of the sample decreased significantly (mean difference = −1.9, p = 0.033) along with a significant decrease of Trait Anxiety (M diff = −3.97, p ≤ 0.001). Participants also decreased on almost all STAXI-2 subscales. Here, the results from permutation paired t -test reveal a significant difference in scores, which decreased from T0 to P2 on all the subscales of Trait Anger (mean difference = −3.55, p ≤ 0.001; Trait Anger Temperament: mean difference = −1.34, p ≤ 0.001; Trait Anger Reaction: mean difference = −1.52, p ≤ 0.001), with an increased value for the subscales Anger Control-OUT (mean difference = 1.93, p ≤ 0.009) and Anger Control-IN (mean difference = 1.93, p = 0.017). For more details, see Table 4 and Figure 6 .
The aim of this study was to examine the effectiveness of an integrated 9-month mental training program called The Art of Happiness , which was developed to increase well-being in a general population. By a range of well-established psychometric assessment tools, we quantified how several psychological well-being variables changed with course attendance. We took into account both the trait effects of the course acting at a long timescale (over the 9-month duration of the full course) and the state effects of intensive retreat experiences acting at a short time scale (over the course of each of the two retreats). Several psychological well-being measures related to states and—more importantly—traits gradually improved as participants progressed from the beginning to the end of the course.
On the one hand, the program produced a significant longitudinal effect (9 months) revealing a progressive increase in the volunteer's levels of life satisfaction and of the capacities to reach non-judgmental mental states, to act with awareness, to non-react to inner experience, and to exercise control over attention to the internal state of anger, in line with other contemplative interventions ( Fredrickson et al., 2008 ; Keng et al., 2011 ; Baer et al., 2012 ; Kong et al., 2014 ). Conversely, after the completion of the program, there were decreases in levels of trait anxiety, trait anger (including both the anger temperament and reaction subscales), and negative affect, showing a progressive reduction during the intervention. These results support prior research that demonstrated the longitudinal positive effects of a multitude of contemplative practices on well-being measures linked to—among others—decreased trait anxiety, trait anger, and negative affect ( Fix and Fix, 2013 ; Khoury et al., 2015 ; Gotink et al., 2016 ). Such findings highlight the gradual development of mental states related to subjective well-being in parallel with ongoing contemplative practices over a time scale of months, with a gradual increase of wholesome mental states, and a gradual decrease of unwholesome mental states. Notably, as in other mindfulness interventions ( Khoury et al., 2015 ; Gotink et al., 2016 ), there was a significant reduction in the level of perceived stress already in the first few months of the program (T0–T1).
Additionally, these results show the specific effects between retreat experiences within the program as an intervention for fostering happiness. Specifically, the retreats had a positive effect on the participants' perceived well-being, which improved between the two retreats (with a 4-month interval). Among other assessed dimensions, between the retreats, there were significantly increased levels of life satisfaction, positive affect, and mindful abilities to act with awareness, to observe, non-react, and non-judge inner experience and the capacity to control anger toward oneself. Conversely, there were significantly lower levels of trait anxiety and trait anger (including both the anger temperament and reaction subscales) between the retreats (over a period of 4 months).
Regarding the very short effects of the course, we highlight significant changes within the first part of the training and prior to the first retreat (T0–T1). Here, some variables related to happiness changed most, suggesting their independence from retreat. Particularly, PSS notably decreased along with negative affect and Trait Anger (the subscale of Angry Temperament), while the capacity of non-judgmental attitude toward the inner experience significantly increased, providing useful information for future interventions.
Moreover, participants' state anxiety significantly decreased in a very short time (5 days), between pre and post of both retreats. These findings are consistent with previous studies, which demonstrated the positive effects of contemplative training and practices on these measures in retreats ( Khoury et al., 2017 ; Howarth et al., 2019 ; McClintock et al., 2019 ). In Figure 6 , we make a general and integrated comparison between the various psychological measures, comparing the very beginning of the course with its very end, which also coincided with the end of the second retreat. In this way, we illustrate both state changes (due to the second retreat) and trait changes (due to the whole course). This representation allows an integrated view of all the changes that took place at different time scales. This graph might suggest that the only measures that did not change significantly from the beginning to the end of the course are those in which the participants already had a score strongly oriented toward well-being, and therefore with little room for a change. Thus, future studies could take into account individual differences when evaluating happiness programs.
Although the present findings are promising, this study presents several limitations that need to be taken into consideration. The two main limitations rely on the absence of a randomized control group and in the fact that participants were self-selected. This lack of verification makes it difficult to determine whether the results are attributable to the program or to other factors, for example, simply arising due to spending time in a happiness-oriented activity. It is also important to note that despite examining several assessments within persons, the sample size was restricted to 29. Furthermore, responses to the questionnaires may have been biased toward the socially desirable response as the course's staff administered them, and another active group could have controlled for these effects. Consequently, it is recommended to conduct future studies with larger samples and a well-designed and controlled trial, in order to achieve more conclusive findings. Another limitation is that, while all the participants attended the whole course with a comparable (coherent) level of commitment to the practices (including the retreats), we did not verify their course-related activity and practices at home, and therefore, we have no way to check whether they actually did the practice activities at home as suggested during the modules.
Possible new directions of exploration of this study concern the age range of the participants, which, in our case, was limited to middle-aged individuals (39–66), and therefore, the effects on younger or older individuals remain currently unexplored. Another interesting direction would be to conduct follow-up measurements to assess the stability of the longitudinal effects months or years after the end of the program. Finally, while well-being and happiness are individual and subjective narratives of one's life as good and happy ( Bauer et al., 2008 ), and therefore self-assessments through questionnaires are a valid and common tool of investigation, in interventions such as The Art of Happiness , it would be appropriate to also explore individual differences, more objective psychophysiological effects, as well as cultural and social aspects influencing the inner model of happiness.
Despite these methodological limitations and still unexplored directions of research, the results described here suggest that The Art of Happiness may be a promising program for fostering well-being in individuals, improving mental health and psychological functioning. Longitudinal integrated contemplative programs with retreats offer a unique opportunity for the intensive development of the inner attitudes related to the capacity to be happy, reducing mental health symptoms and improving a more stable eudemonic well-being in healthy adults.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Nicola De Pisapia, upon reasonable request.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of the Sapienza University of Rome. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
ND, CM, and AR designed the study. ND, CM, LC, and AR collected the data. CR analyzed the data. CR and ND wrote the original draft. All authors edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Institute Lama Tzong Khapa (Pomaia, Italy) for the support in various phases of this experiment. We also wish to express our gratitude to the reviewers for their thoughtful comments and efforts toward improving the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.600982/full#supplementary-material
Arch, J. J., and Craske, M. G. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness: emotion regulation following a focused breathing induction. Behav. Res. Ther. 44, 1849–1858. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2005.12.007
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Argyle, M., Kahneman, D., Diener, E., and Schwarz, N. (1999). Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , eds D. Kahneman, E. Diener, and N. Schwarz. Russell Sage Found.
Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Lykins, E. L. B., and Peters, J. R. (2012). Mindfulness and self-compassion as predictors of psychological wellbeing in long-term meditators and matched nonmeditators. J. Posit. Psychol. 7, 230–238. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2012.674548
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., and Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment 13, 27–45. doi: 10.1177/1073191105283504
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., et al. (2008). Construct validity of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment 15, 329–342. doi: 10.1177/1073191107313003
Bauer, J. J., McAdams, D. P., and Pals, J. L. (2008). Narrative identity and eudaimonic well-being. J. Happiness Stud. 9, 81–104. doi: 10.1007/s10902-006-9021-6
Benjamini, Y., and Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 57, 289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., et al. (2004). Mindfulness: a proposed operational definition. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 11, 230–241. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bph077
Boehm, J. K., Lyubomirsky, S., and Sheldon, K. M. (2011). A longitudinal experimental study comparing the effectiveness of happiness-enhancing strategies in Anglo Americans and Asian Americans. Cogn. Emot. 25, 1263–1272. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2010.541227
Calabrese, L., and Raffone, A. (2017). Gli aspetti della pratica della mindfulness e la centralita ‘della regolazione del se’. G. Ital. di Psicol. 44, 271–274. doi: 10.1421/87330
Campos, D., Cebolla, A., Quero, S., Bretón-López, J., Botella, C., Soler, J., et al. (2016). Meditation and happiness: Mindfulness and self-compassion may mediate the meditation-happiness relationship. Pers. Individ. Dif. 93, 80–85. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.08.040
Carmody, J., and Baer, R. A. (2008). Relationships between mindfulness practice and levels of mindfulness, medical and psychological symptoms and well-being in a mindfulness-based stress reduction program. J. Behav. Med. 31, 23–33. doi: 10.1007/s10865-007-9130-7
Cattell, R. B., and Scheier, I. H. (1961). The Meaning and Measurement of Neuroticism and Anxiety . New York, NY: The Ronald Press Company
Choi, Y., Karremans, J. C., and Barendregt, H. (2012). The happy face of mindfulness: mindfulness meditation is associated with perceptions of happiness as rated by outside observers. J. Posit. Psychol. 7, 30–35. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2011.626788
Cohen, J. (2013). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences . New York, NY: Routledge.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., and Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 24, 385–396. doi: 10.2307/2136404
Coo, C., and Salanova, M. (2018). Mindfulness can make you happy-and-productive: a mindfulness controlled trial and its effects on happiness, work engagement and performance. J. Happiness Stud. 19, 1691–1711. doi: 10.1007/s10902-017-9892-8
Dahl, C. J., Lutz, A., and Davidson, R. J. (2015). Reconstructing and deconstructing the self: cognitive mechanisms in meditation practice. Trends Cogn. Sci. 19, 515–523. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2015.07.001
Danner, D. D., Snowdon, D. A., and Friesen, W. V. (2001). Positive emotions in early life and longevity: findings from the nun study. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 80, 804–813. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.80.5.804
De Pisapia, N., and Grecucci, E. A. (2017). Mindfulness: fashion or revolution? G. Ital. di Psicol. 44, 249–270. doi: 10.1421/87329
CrossRef Full Text
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (1980). Self-determination theory: when mind mediates behavior. J. mind Behav. 1, 33–43.
Deci, E. L., and Ryan, R. M. (2008). Hedonia, eudaimonia, and well-being: an introduction. J. Happiness Stud. 9, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s10902-006-9018-1
Di Fabio, A., and Palazzeschi, L. (2012). The Satisfaction With Life Scale (SWLS): Un contributo alla validazione italiana con lavoratori adulti [The Satisfaction With Life Scale (SWLS): A contribution to Italian validation with adult workers]. Counseling 5, 207–215.
Diener, E. (1984). Subjective well-being. Psychol. Bull . 95, 542–575. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542
Diener, E. (1994). Assessing subjective well-being: progress and opportunities. Soc. Indicat. Res. 31, 103–157.
Diener, E. (2000). Subjective well-being: the science of happiness and a proposal for a national index. Am. Psychol. 55, 34–43. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.34
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsem, R. J., and Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. J. Pers. Assess. 49, 71–75. doi: 10.1207/s15327752jpa4901_13
Diener, E., Suh, E. M., Lucas, R. E., and Smith, H. L. (1999). Subjective well-being: three decades of progress. Psychol. Bull. 125:276. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.125.2.276
Dorjee, D. (2013). Mind, Brain and the Path to Happiness . London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315889580
Fava, G. A. (1999). Well-being therapy: conceptual and technical issues. Psychother. Psychosom. 68, 171–179. doi: 10.1159/000012329
Fix, R. L., and Fix, S. T. (2013). The effects of mindfulness-based treatments for aggression: a critical review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 18, 219–227. doi: 10.1016/j.avb.2012.11.009
Fordyce, M. W. (1977). Development of a program to increase personal happiness. J. Couns. Psychol. 24, 511–521. doi: 10.1037/0022-0167.24.6.511
Forman, E. M., Herbert, J. D., Moitra, E., Yeomans, P. D., and Geller, P. A. (2007). A randomized controlled effectiveness trial of acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive therapy for anxiety and depression. Behav. Modif. 31, 772–799. doi: 10.1177/0145445507302202
Fredrickson, B. L., Cohn, M. A., Coffey, K. A., Pek, J., and Finkel, S. M. (2008). Open hearts build lives: positive emotions, induced through loving-kindness meditation, build consequential personal resources. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 95, 1045–1062. doi: 10.1037/a0013262
Fredrickson, B. L., and Losada, M. F. (2005). Positive affect and the complex dynamics of human flourishing. Am. Psychol. 60, 678–686. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.60.7.678
Frisch, M. B. (2006). Quality of Life Therapy: Applying a Life Satisfaction Approach to Positive Psychology and Cognitive Therapy . New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 535.
Frossard, J., and Renaud, O. (2018). Permuco: Permutation Tests for Regression, (Repeated Measures) ANOVA/ANCOVA and Comparison of Signals. R Package Version 1.0.0.
Gander, F., Proyer, R. T., and Ruch, W. (2016). Positive psychology interventions addressing pleasure, engagement, meaning, positive relationships, and accomplishment increase well-being and ameliorate depressive symptoms: a randomized, placebo-controlled online study. Front. Psychol. 7:686. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00686
Garland, E. L., Geschwind, N., Peeters, F., and Wichers, M. (2015). Mindfulness training promotes upward spirals of positive affect and cognition: multilevel and autoregressive latent trajectory modeling analyses. Front. Psychol. 6:15. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00015
Garland, E. L., Kiken, L. G., Faurot, K., Palsson, O., and Gaylord, S. A. (2017). Upward spirals of mindfulness and reappraisal: testing the mindfulness-to-meaning theory with autoregressive latent trajectory modeling. Cognit. Ther. Res. 41, 381–392. doi: 10.1007/s10608-016-9768-y
Giovannini, C., Giromini, L., Bonalume, L., Tagini, A., Lang, M., and Amadei, G. (2014). The Italian five facet mindfulness questionnaire: a contribution to its validity and reliability. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 36, 415–423. doi: 10.1007/s10862-013-9403-0
Goleman, D., and Davidson, R. (2017). The Science of Meditation: How to Change Your Brain, Mind and Body . New York, NY: Penguin Random House.
Gotink, R. A., Meijboom, R., Vernooij, M. W., Smits, M., and Hunink, M. G. M. (2016). 8-week mindfulness based stress reduction induces brain changes similar to traditional long-term meditation practice – a systematic review. Brain Cogn. 108, 32–41. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2016.07.001
Grecucci, A., De Pisapia, N., Thero, D. K., Paladino, M. P., Venuti, P., and Job, R. (2015). Baseline and strategic effects behind mindful emotion regulation: behavioral and physiological investigation. PLoS ONE 10:e0116541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116541
Groves, P. (2016). Mindfulness in psychiatry–where are we now? BJPsych Bull. 40, 289–292. doi: 10.1192/pb.bp.115.052993
Hanson, R., and Mendius, R. (2011). The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love and Wisdom. Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications Inc. doi: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.1118110
Hervé, M. M., and Hervé, M. M. (2020). Package ‘RVAideMemoire.’
Hone, L. C., Jarden, A., Schofield, G., and Duncan, S. (2014). Measuring flourishing: the impact of operational definitions on the prevalence of high levels of wellbeing. Int. J. Wellbeing 4, 62–90. doi: 10.5502/ijw.v4i1.4
Hone, L. C., Jarden, A., and Schofield, G. M. (2015). An evaluation of positive psychology intervention effectiveness trials using the re-aim framework: a practice-friendly review. J. Posit. Psychol. 10, 303–322. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2014.965267
Howarth, A., Smith, J. G., Perkins-Porras, L., and Ussher, M. (2019). Effects of brief mindfulness-based interventions on health-related outcomes: a systematic review. Mindfulness 10, 1957–1968. doi: 10.1007/s12671-019-01163-1
Howell, A. J., Dopko, R. L., Passmore, H.-A., and Buro, K. (2011). Nature connectedness: associations with well-being and mindfulness. Pers. Individ. Dif. 51, 166–171. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2011.03.037
Huta, V., and Ryan, R. M. (2010). Pursuing pleasure or virtue: the differential and overlapping well-being benefits of hedonic and eudaimonic motives. J. Happiness Stud. 11, 735–762. doi: 10.1007/s10902-009-9171-4
Inglehart, R., Foa, R., Peterson, C., and Welzel, C. (2008). Development, freedom, and rising happiness: a global perspective (1981–2007). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 3, 264–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6924.2008.00078.x
Ivtzan, I., Young, T., Martman, J., Jeffrey, A., Lomas, T., Hart, R., et al. (2016). Integrating mindfulness into positive psychology: a randomised controlled trial of an online positive mindfulness program. Mindfulness 7, 1396–1407. doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0581-1
Jha, A. P., Morrison, A. B., Parker, S. C., and Stanley, E. A. (2017). Practice is protective: mindfulness training promotes cognitive resilience in high-stress cohorts. Mindfulness 8, 46–58. doi: 10.1007/s12671-015-0465-9
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1990). Full Catastrophe Living: The Program of the Stress Reduction Clinic at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center . Available online at: lelandshields.com (accessed October 28, 2019).
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based interventions in context: past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 10, 144–156. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bpg016
Kahneman, D., and Krueger, A. B. (2006). Developments in measurements of subjective well-being. J. Econ. Perspect. 20, 3–24. doi: 10.1257/089533006776526030
Keng, S. L., Smoski, M. J., and Robins, C. J. (2011). Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 31, 1041–1056. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.04.006
Keyes, C. L. M. (2005). Mental illness and/or mental health? Investigating axioms of the complete state model of health. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 73, 539–548. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.73.3.539
Keyes, C. L. M. (2006). Subjective well-being in mental health and human development research worldwide: an introduction. Soc. Indic. Res. 77, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11205-005-5550-3
Kherad-Pajouh, S., and Renaud, O. (2014). A general permutation approach for analyzing repeated measures ANOVA and mixed-model designs. Stat. Pap. 56, 947–967. doi: 10.1007/s00362-014-0617-3
Khoury, B., Knäuper, B., Schlosser, M., Carrière, K., and Chiesa, A. (2017). Effectiveness of traditional meditation retreats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 92, 16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2016.11.006
Khoury, B., Sharma, M., Rush, S. E., and Fournier, C. (2015). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 78, 519–528. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2015.03.009
Koivumaa-Honkanen, H., Kaprio, J., Honkanen, R., Viinamäki, H., and Koskenvuo, M. (2004). Life satisfaction and depression in a 15-year follow-up of healthy adults. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 39, 994–999. doi: 10.1007/s00127-004-0833-6
Kong, F., Wang, X., and Zhao, J. (2014). Dispositional mindfulness and life satisfaction: the role of core self-evaluations. Pers. Individ. Dif. 56, 165–169. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2013.09.002
Kornfield, J. (2012). Teachings of the Buddha . Boston, MA: Shambhala Publications.
Lama, D., and Cutler, H. (2008). The art of happiness: A handbook for living. Penguin.
Lambert, L., Passmore, H. A., and Joshanloo, M. (2019). A positive psychology intervention program in a culturally-diverse university: boosting happiness and reducing fear. J. Happiness Stud. 20, 1141–1162. doi: 10.1007/s10902-018-9993-z
Lyubomirsky, S., King, L., and Diener, E. (2005). The benefits of frequent positive affect: does happiness lead to success? Psychol. Bull. 131, 803–855. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.6.803
Lyubomksky, S., Sheldon, K. M., and Schkade, D. (2005). Pursuing happiness: the architecture of sustainable change. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 9, 111–131. doi: 10.1037/1089-2680.9.2.111
Maslow, A. H. (1981). Motivation and Personality . New York, NY: Harper.
McClintock, A. S., Rodriguez, M. A., and Zerubavel, N. (2019). The effects of mindfulness retreats on the psychological health of non-clinical adults: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness 10, 1443–1454. doi: 10.1007/s12671-019-01123-9
Mondo, M., Sechi, C., and Cabras, C. (2019). Psychometric evaluation of three versions of the Italian perceived stress scale. Curr. Psychol. 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s12144-019-0132-8
Pressman, S. D., and Cohen, S. (2005). Does positive affect influence health? Psychol. Bull. 131, 925. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.131.6.925
Quoidbach, J., Mikolajczak, M., and Gross, J. J. (2015). Positive interventions: an emotion regulation perspective. Psychol. Bull . 141, 655–693. doi: 10.1037/a0038648
Raffone, A., and Srinivasan, N. (2017). Mindfulness and cognitive functions: toward a unifying neurocognitive framework. Mindfulness 8, 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s12671-016-0654-1
Ryan, R. M., and Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: a review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 52, 141–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.141
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 57, 1069–1081. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.57.6.1069
Ryff, C. D. (2013). Psychological well-being revisited: advances in the science and practice of eudaimonia. Psychother. Psychosom. 83, 10–28. doi: 10.1159/000353263
Ryff, C. D., and Boylan, J. M. (2016). “Linking happiness to health: Comparisons between hedonic and eudaimonic well-being,” in Handbook of Research Methods and Applications in Happiness and Quality of Life (Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing Limited).
Saviola, F., Pappaianni, E., Monti, A., Grecucci, A., Jovicich, J., and De Pisapia, N. (2020). Trait and state anxiety are mapped differently in the human brain. Sci. Rep. 10:11112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68008-z
Segal, Z. V., and Teasdale, J. (2002). Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Depression: : A New Approach to Preventing Relapse . New York, NY: The Guilford Press. Guilford Publications.
Seligman, M. E. P. (2002). “Positive psychology, positive prevention, and positive therapy,” in Handbook of Positive Psychology , eds C. R. Snyder and S. J. Lopez (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 3–9.
Seligman, M. E. P. (2011). Flourish: A Visionary New Understanding of Happiness and Well-Being . New York, NY: Free Press.
Sheldon, K. M., and King, L. (2001). Why positive psychology is necessary. Am. Psychol. 56, 216–217. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.56.3.216
Shultz, P. P., and Ryan, R. M. (2015). “The ‘why,’ ‘what,’ and ‘how’ of healthy self-regulation: Mindfulness and well-being from a self-determination theory perspective,” in Handbook of Mindfulness and Self-Regulation (New York, NY: Springer), 81–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2263-5_7
Sin, N. L., and Lyubomirsky, S. (2009). Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J. Clin. Psychol. 65, 467–487. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20593
Spielberger, C. (2004). STAXI-2 State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory-2. Adattamento Italiano a Cura di Anna Laura Comunian. Florence: Giunti OS Organizzazioni speciali.
Spielberger, C. D. (1999). Professional Manual for the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory-2 (STAXI-2). Odessa, FL.
PubMed Abstract
Spielberger, C. D. (2010). State-Trait anger expression inventory. Corsini Encycl. Psychol. 1. doi: 10.1002/9780470479216.corpsy0942
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., Lushene, R., Vagg, P. R., and Jacobs, G. A. (1983). Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory . Palo, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Spielberger, C. D., Pedrabissi, L., and Santinello, M. (2012). STAI State-Trait Anxiety Inventory Forma Y: Manuale. Firenze: Giunti OS Organizzazioni speciali.
Spinhoven, P., Huijbers, M. J., Ormel, J., and Speckens, A. E. M. (2017). Improvement of mindfulness skills during mindfulness-based cognitive therapy predicts long-term reductions of neuroticism in persons with recurrent depression in remission. J. Affect. Disord. 213, 112–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.02.011
Teasdale, J. D., Segal, Z. V., Williams, J. M. G., Ridgewaya, V. A., Soulsby, J. M., and Lau, M. A. (2000). Prevention of relapse/recurrence in major depression by mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 68, 615–623. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.68.4.615
Terracciano, A., McCrae, R. R., and Costa, P. T. (2003). Factorial and construct validity of the Italian positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS). Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 19, 131–141. doi: 10.1027//1015-5759.19.2.131
Vazquez, C., and Hervas, G. (2013). Addressing current challenges in cross-cultural measurement of well-being: the pemberton happiness index. Well Being Cult. 3, 31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4611-4_3
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., and Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 54, 1063–1070. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Weytens, F., Luminet, O., Verhofstadt, L. L., and Mikolajczak, M. (2014). An integrative theory-driven positive emotion regulation intervention. PLoS ONE 9:e95677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095677
World Health Organization (1948). Constitution Basic Documents WHO World Health Organization. World Health Organization, Constitution . Geneva: Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia Globalization.
Keywords: meditation, wisdom, happiness, well–being, mindfulness
Citation: Rastelli C, Calabrese L, Miller C, Raffone A and De Pisapia N (2021) The Art of Happiness: An Explorative Study of a Contemplative Program for Subjective Well-Being. Front. Psychol. 12:600982. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.600982
Received: 31 August 2020; Accepted: 11 January 2021; Published: 11 February 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Rastelli, Calabrese, Miller, Raffone and De Pisapia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nicola De Pisapia, nicola.depisapia@unitn.it
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 20 July 2023
A systematic review of the strength of evidence for the most commonly recommended happiness strategies in mainstream media
- Dunigan Folk ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6728-2776 1 &
- Elizabeth Dunn ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1214-7512 1
Nature Human Behaviour volume 7 , pages 1697–1707 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
9831 Accesses
10 Citations
1541 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Social sciences
We conducted a systematic review of the evidence underlying some of the most widely recommended strategies for increasing happiness. By coding media articles on happiness, we first identified the five most commonly recommended strategies: expressing gratitude, enhancing sociability, exercising, practising mindfulness/meditation and increasing nature exposure. Next, we conducted a systematic search of the published scientific literature. We identified well-powered, pre-registered experiments testing the effects of these strategies on any aspect of subjective wellbeing (that is, positive affect, negative affect and life satisfaction) in non-clinical samples. A total of 57 studies were included. Our review suggests that a strong scientific foundation is lacking for some of the most commonly recommended happiness strategies. As the effectiveness of these strategies remains an open question, there is an urgent need for well-powered, pre-registered studies investigating strategies for promoting happiness.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
111,21 € per year
only 9,27 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Microdosing with psilocybin mushrooms: a double-blind placebo-controlled study
Determinants of behaviour and their efficacy as targets of behavioural change interventions
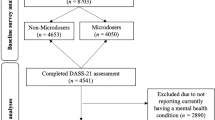
Adults who microdose psychedelics report health related motivations and lower levels of anxiety and depression compared to non-microdosers
Data availability.
The results of the media search are available on the Open Science Framework at https://tinyurl.com/2kkayzh9 .
How to be happy, how to get rich - Explore. Google Trends (2021); https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?geo=CA&q=how to be happy,how to get rich
Nelson, L. D., Simmons, J. & Simonsohn, U. Psychology’s Renaissance. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 69 , 511–534 (2018).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Simmons, J. P., Nelson, L. D. & Simonsohn, U. False-positive psychology: undisclosed flexibility in data collection and analysis allows presenting anything as significant. Psychol. Sci. 22 , 1359–1366 (2011).
Nuzzo, R. Scientific method: statistical errors. Nature 506 , 150–152 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wagenmakers, E.-J., Wetzels, R., Borsboom, D., van der Maas, H. L. J. & Kievit, R. A. An agenda for purely confirmatory research. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 7 , 632–638 (2012).
Nosek, B. A., Ebersole, C. R., DeHaven, A. C. & Mellor, D. T. The preregistration revolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115 , 2600–2606 (2018).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fraley, R. C. & Vazire, S. The N-pact factor: evaluating the quality of empirical journals with respect to sample size and statistical power. PLoS ONE 9 , e109019 (2014).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
John, L. K., Loewenstein, G. & Prelec, D. Measuring the prevalence of questionable research practices with incentives for truth telling. Psychol. Sci. 23 , 524–532 (2012).
Collaboration, O. S. Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science 349 , aac4716 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Wagenmakers, E. J. et al. Registered Replication Report: Strack, Martin, & Stepper (1988). Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 11 , 917–928 (2016).
Myers, D. G. & Diener, E. The scientific pursuit of happiness. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 13 , 218–225 (2018).
Diener, E. et al. Findings all psychologists should know from the new science on subjective well-being. Can. Psychol. 58 , 87–104 (2017).
Hunt, J. T., Howell, A. J. & Passmore, H.-A. In vivo nature exposure as a positive psychological intervention: a review of the impact of nature interventions on wellbeing. Nat. Health https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003154419-12 (2021).
Funder, D. C. et al. Improving the dependability of research in personality and social psychology: recommendations for research and educational practice. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 18 , 3–12 (2014).
Carr, A. et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Posit. Psychol. 16 , 749–769 (2021).
Bolier, L. et al. Positive psychology interventions: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. BMC Public Health 13 , 119 (2013).
Simonsohn, U., Simmons, J. & Nelson, L. D. Above averaging in literature reviews. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 1 , 551–552 (2022).
Kvarven, A., Strømland, E. & Johannesson, M. Comparing meta-analyses and preregistered multiple-laboratory replication projects. Nat. Hum. Behav. 4 , 423–434 (2019).
Richard, F. D., Bond, C. F. & Stokes-Zoota, J. J. One hundred years of social psychology quantitatively described. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 7 , 331–363 (2003).
Diener, E. Subjective well-being. Psychol. Bull. 95 , 542–575 (1984).
Watson, C., Clark, L. A. & Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 54 , 1063–1070 (1988).
Diener, E., Emmons, R., Larsen, R. & Griffin, S. The satisfaction with life scale. J. Pers. Assess. 49 , 71–75 (1985).
Lyubomirsky, S. & Lepper, H. A measure of subjective happiness: preliminary reliability and construct validation. Soc. Indic. Res. 46 , 137–155 (1999).
Diener, E. & Ryan, K. Subjective well-being: a general overview. South Afr. J. Psychol. 39 , 391–406 (2009).
Nelson-Coffey, S. K., Johnson, C. & Coffey, J. K. Safe haven gratitude improves emotions, well-being, and parenting outcomes among parents with high levels of attachment insecurity. J. Posit. Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760.2021.1991454 (2021).
Walsh, L. C., Regan, A., Twenge, J. M. & Lyubomirsky, S. What is the optimal way to give thanks? Comparing the effects of gratitude expressed privately, one-to-one via text, or publicly on social media. Affect. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42761-022-00150-5 (2022).
Atad, O. I. & Russo-Netzer, P. The effect of gratitude on well-being: should we prioritize positivity or meaning? J. Happiness Stud. 23 , 1245–1265 (2022).
Toepfer, S. M., Cichy, K. & Peters, P. Letters of gratitude: further evidence for author benefits. J. Happiness Stud. 13 , 187–201 (2012).
Shin, L. J. et al. Gratitude in collectivist and individualist cultures. J. Posit. Psychol. 15 , 598–604 (2020).
Titova, L., Wagstaff, A. E. & Parks, A. C. Disentangling the effects of gratitude and optimism: a cross-cultural investigation. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 48 , 754–770 (2017).
Walsh, L. C., Regan, A. & Lyubomirsky, S. The role of actors, targets, and witnesses: examining gratitude exchanges in a social context. J. Posit. Psychol. 17 , 233–249 (2022).
Fritz, M. M., Armenta, C. N., Walsh, L. C. & Lyubomirsky, S. Gratitude facilitates healthy eating behavior in adolescents and young adults. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 81 , 4–14 (2019).
Armenta, C. N., Fritz, M. M., Walsh, L. C. & Lyubomirsky, S. Satisfied yet striving: gratitude fosters life satisfaction and improvement motivation in youth. Emotion 22 , 1004–1016 (2020).
Lyubomirsky, S., Dickerhoof, R., Boehm, J. K. & Sheldon, K. M. Becoming happier takes both a will and a proper way: an experimental longitudinal intervention to boost well-being. Emotion 11 , 391–402 (2011).
Oltean, L. E., Miu, A. C., Șoflău, R. & Szentágotai-Tătar, A. Tailoring gratitude interventions. How and for whom do they work? The potential mediating role of reward processing and the moderating role of childhood adversity and trait gratitude. J. Happiness Stud. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-022-00530-5 (2022).
Oishi, S., Koo, M., Lim, N. & Suh, E. M. When gratitude evokes indebtedness. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 11 , 286–303 (2019).
Oliveira, R., Baldé, A., Madeira, M., Ribeiro, T. & Arriaga, P. The impact of writing about gratitude on the intention to engage in prosocial behaviors during the COVID-19 outbreak. Front. Psychol. 12 , https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.588691 (2021).
Layous, K. et al. The proximal experience of gratitude. PLoS ONE 12 , 1–26 (2017).
Asebedo, S. D., Seay, M. C., Little, T. D., Enete, S. & Gray, B. Three good things or three good financial things? Applying a positive psychology intervention to the personal finance domain. J. Posit. Psychol. 16 , 481–491 (2021).
Neumeier, L. M., Brook, L., Ditchburn, G. & Sckopke, P. Delivering your daily dose of well-being to the workplace: a randomized controlled trial of an online well-being programme for employees. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 26 , 555–573 (2017).
Manthey, L., Vehreschild, V. & Renner, K. H. Effectiveness of two cognitive interventions promoting happiness with video-based online instructions. J. Happiness Stud. 17 , 319–339 (2016).
Cunha, L. F., Pellanda, L. C. & Reppold, C. T. Positive psychology and gratitude interventions: a randomized clinical trial. Front. Psychol. 10 , https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00584 (2019).
Regan, A., Walsh, L. C. & Lyubomirsky, S. Are some ways of expressing gratitude more beneficial than others? Results from a randomized controlled experiment. Affect. Sci. 4 , 72–81 (2022).
Layous, K., Kumar, S. A., Arendtson, M. & Najera, A. The effects of rumination, distraction, and gratitude on positive and negative affect. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 124 , 1053–1078 (2022).
Baumeister, R. F. & Leary, M. R. The need to belong: desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychol. Bull. 117 , 497–529 (1995).
Dunbar, R. I. M. & Shultz, S. Evolution in the social brain. Science 317 , 1344–1347 (2007).
Ryan, R. M. & Deci, E. L. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 55 , 68–78 (2000).
Kardas, M., Schroeder, J. & Brien, E. O. Keep talking: (mis)understanding the hedonic trajectory of conversation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. , 123 , 717–740 (2022).
Schroeder, J., Lyons, D. & Epley, N. Hello, stranger? Pleasant conversations are preceded by concerns about starting one. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 151 , 1141–1153 (2022).
Jacques-Hamilton, R., Sun, J. & Smillie, L. D. Costs and benefits of acting extraverted: a randomized controlled trial. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 148 , 1538–1556 (2018).
Margolis, S. & Lyubomirsky, S. Experimental manipulation of extraverted and introverted behavior and its effects on well-being. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 149 , 719–731 (2020).
Gunaydin, G., Oztekin, H., Karabulut, D. H. & Salman-Engin, S. Minimal social interactions with strangers predict greater subjective well-being. J. Happiness Stud. Interdiscip. Forum Subj. Well-Being 22 , 1839–1853 (2021).
Google Scholar
Van Dam, N. T. et al. Mind the hype: a critical evaluation and prescriptive agenda for research on mindfulness and meditation. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 13 , 36–61 (2018).
Kabat-Zinn, J. Mindfulness-based interventions in context: past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 10 , 144–156 (2003).
Brown, K. W. & Ryan, R. M. The benefits of being present: mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 84 , 822–848 (2003).
Noone, C. & Hogan, M. J. A randomised active-controlled trial to examine the effects of an online mindfulness intervention on executive control, critical thinking and key thinking dispositions in a university student sample. BMC Psychol. 6 , 1–18 (2018).
Krick, A. & Felfe, J. Who benefits from mindfulness? The moderating role of personality and social norms for the effectiveness on psychological and physiological outcomes among police officers. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 25 , 99–112 (2019).
De Vibe, M. et al. Mindfulness training for stress management: a randomised controlled study of medical and psychology students. BMC Med. Educ. 13 , 107 (2013).
Solhaug, I. et al. Long-term mental health effects of mindfulness training: a 4-year follow-up study. Mindfulness 10 , 1661–1672 (2019).
Gallegos, A., Hoerger, M., Talbot, N., Moynihan, J. & Duberstein, P. Emotional benefits of mindfulness-based stress reduction in older adults: the moderating roles of age and depressive symptom severity. Aging Ment. Health 17 , 823–829 (2013).
Fredrickson, B., Cohn, M. & Al, E. Open hearts build lives: positive emotions, induced through loving-kindness meditation, build consequential personal resources. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 95 , 1045–1062 (2008).
Pandya, S. P. Meditation program mitigates loneliness and promotes wellbeing, life satisfaction and contentment among retired older adults: a two-year follow-up study in four South Asian cities. Aging Ment. Health 25 , 286–298 (2021).
Bojanowska, A., Kaczmarek, Ł. D., Urbanska, B. & Puchalska, M. Acting on values: a novel intervention enhancing hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. J. Happiness Stud. 23 , 3889–3908 (2022).
Cheung, R. Y. M., Chan, S. K. C., Chui, H., Chan, W. M. & Ngai, S. Y. S. Enhancing parental well-being: initial efficacy of a 21-day online self-help mindfulness-based intervention for parents. Mindfulness 13 , 2812–2826 (2022).
Chen, S. & Jordan, C. H. Incorporating ethics into brief mindfulness practice: effects on well-being and prosocial behavior. Mindfulness 11 , 18–29 (2020).
Rhodes, R. E., Janssen, I., Bredin, S. S. D., Warburton, D. E. R. & Bauman, A. Physical activity: health impact, prevalence, correlates and interventions. Psychol. Health 32 , 942–975 (2017).
Kokkinos, P. Physical activity, health benefits, and mortality risk. ISRN Cardiol. 2012 , 1–14 (2012).
Haskell, W. L., Blair, S. N. & Hill, J. O. Physical activity: health outcomes and importance for public health policy. Prev. Med. 49 , 280–282 (2009).
Matzer, F., Nagele, E., Lerch, N., Vajda, C. & Fazekas, C. Combining walking and relaxation for stress reduction—a randomized cross-over trial in healthy adults. Stress Health 34 , 266–277 (2018).
Bernstein, E. E. & McNally, R. J. Acute aerobic exercise hastens emotional recovery from a subsequent stressor. Health Psychol. 36 , 560–567 (2017).
Miller, J. C. & Krizan, Z. Walking facilitates positive affect (even when expecting the opposite). Emotion 16 , 775–785 (2016).
Bryan, A., Hutchison, K. E., Seals, D. R. & Allen, D. L. A transdisciplinary model integrating genetic, physiological, and psychological correlate of voluntary exercise. Health Psychol. 26 , 30–39 (2007).
Müller, C. et al. Effects of a single physical or mindfulness intervention on mood, attention, and executive functions: results from two randomized controlled studies in university classes. Mindfulness 12 , 1282–1293 (2021).
Steinberg, H. et al. Exercise enhances creativity independently of mood. Br. J. Sports Med. 31 , 240–245 (1997).
Hui, B. P. H., Parma, L., Kogan, A. & Vuillier, L. Hot yoga leads to greater well-being: a six-week experience-sampling RCT in healthy adults. Psychosoc. Inter. 31 , 67–82 (2022).
Brailovskaia, J., Swarlik, V. J., Grethe, G. A., Schillack, H. & Margraf, J. Experimental longitudinal evidence for causal role of social media use and physical activity in COVID-19 burden and mental health. J. Public Health https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01751 (2022).
Tse, M. M. Y., Tang, S. K., Wan, V. T. C. & Vong, S. K. S. The effectiveness of physical exercise training in pain, mobility, and psychological well-being of older persons living in nursing homes. Pain. Manag. Nurs. 15 , 778–788 (2014).
Lai, A. Y. K. et al. A community-based lifestyle-integrated physical activity intervention to enhance physical activity, positive family communication, and perceived health in deprived families: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Front. Public Health 8 , https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00434 (2020).
Sjögren, T. et al. Effects of a physical exercise intervention on subjective physical well-being, psychosocial functioning and general well-being among office workers: a cluster randomized-controlled cross-over design. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 16 , 381–390 (2006).
Courneya, K. S., McNeil, J., O’Reilly, R., Morielli, A. R. & Friedenreich, C. M. Dose–response effects of aerobic exercise on quality of life in postmenopausal women: results from the Breast Cancer and Exercise Trial in Alberta (BETA). Ann. Behav. Med. 51 , 356–364 (2017).
de Kort, Y. A. W., Meijnders, A. L., Sponselee, A. A. G. & IJsselsteijn, W. A. What’s wrong with virtual trees? Restoring from stress in a mediated environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 26 , 309–320 (2006).
Zelenski, J. M., Dopko, R. L. & Capaldi, C. A. Cooperation is in our nature: nature exposure may promote cooperative and environmentally sustainable behavior. J. Environ. Psychol. 42 , 24–31 (2015).
Tyrväinen, L. et al. The influence of urban green environments on stress relief measures: a field experiment. J. Environ. Psychol. 38 , https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.12.005 (2014).
Vert, C. et al. Physical and mental health effects of repeated short walks in a blue space environment: a randomised crossover study. Environ. Res. 188 , 109812 (2020).
Izenstark, D., Ravindran, N., Rodriguez, S. & Devine, N. The affective and conversational benefits of a walk in nature among mother–daughter dyads. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 13 , 299–316 (2021).
Passmore, H. A. & Holder, M. D. Noticing nature: Individual and social benefits of a two-week intervention. J. Posit. Psychol. 12 , 537–546 (2017).
McEwan, K., Richardson, M., Sheffield, D., Ferguson, F. J. & Brindley, P. A smartphone app for improving mental health through connecting with urban nature. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 16 , 1–15 (2019).
Chambers, C. D. Registered reports: a new publishing initiative at Cortex. Cortex https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2012.12.016 (2013).
Tversky, A. & Kahneman, D. Availability: a heuristic for judging frequency and probability. Cogn. Psychol. 5 , 207–232 (1973).
Buettner, D., Nelson, T. & Veenhoven, R. Ways to greater happiness: a Delphi study. J. Happiness Stud. 21 , 2789–2806 (2020).
Yarkoni, T. The generalizability crisis. Behav. Brain Sci. 45 , e1 (2022).
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J. & Norenzayan, A. The weirdest people in the world? Behav. Brain Sci. 33 , 61–83 (2010).
Lyubomirsky, S. & Layous, K. How do simple positive activities increase well-being? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 22 , 57–62 (2013).
Blake, K. R. & Gangestad, S. On attenuated interactions, measurement error, and statistical power: guidelines for social and personality psychologists. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 46 , 1702–1711 (2020).
Wood, A. M. et al. in The Wiley Handbook of Positive Clinical Psychology (eds Wood, A. M. & Johnson, J.) 137–151 (John Wiley & Sons, 2016).
Fritz, M. M. & Lyubomirsky, S. in The Social Psychology of Living Well (eds Forgas, J. P. & Baumeister, R. F.) Chap 7 (Routledge, 2018).
Farias, M., Maraldi, E., Wallenkampf, K. C. & Lucchetti, G. Adverse events in meditation practices and meditation‐based therapies: a systematic review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 142 , 374–393 (2020).
Landis, J. R. & Koch, G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33 , 159 (1977).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Lyubomirsky and H. Passmore for comments on a previous version of this manuscript, and M. Smith for providing guidance on conducting the systematic literature search. We also thank J. Tan, P. Ramachadran, R. Li, R. Kaur, C. Peretz and C. Cardle for assistance with the media and scholarly literature searches. Our work was supported by grant #GR012572 from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC; E.D.) and the SSHRC Doctoral Award #6567 (D.F.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Psychology Department, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
Dunigan Folk & Elizabeth Dunn
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.F. and E.D. both contributed to the conceptualization and writing of the manuscript. D.F. managed the literature review and effect size extraction.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dunigan Folk .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Kirk Brown, Jessie Sun, Katie Hobbs and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplemental Tables 1–6.
Reporting Summary
Peer review file, rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Folk, D., Dunn, E. A systematic review of the strength of evidence for the most commonly recommended happiness strategies in mainstream media. Nat Hum Behav 7 , 1697–1707 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01651-4
Download citation
Received : 04 February 2022
Accepted : 09 June 2023
Published : 20 July 2023
Issue Date : October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-023-01651-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Long-term analysis of a psychoeducational course on university students’ mental well-being.
- Catherine Hobbs
- Sarah Jelbert
Higher Education (2024)
Centenary Personality: Are There Psychological Resources that Distinguish Centenarians?
- Mª Dolores Merino
- Marta Sánchez-Ortega
- Inmaculada Mateo-Rodríguez
Journal of Happiness Studies (2023)
Mindfulness and Happiness
- Bassam Khoury
Mindfulness (2023)
Worker Well-Being: A Continuous Improvement Framework
- Lisa C. Walsh
- Madison Montemayor-Dominguez
- Sonja Lyubomirsky
Applied Research in Quality of Life (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
The relationship between happiness and quality of life: A model for Spanish society
Contributed equally to this work with: Víctor-Raúl López-Ruiz, Nuria Huete-Alcocer, José-Luis Alfaro-Navarro, Domingo Nevado-Peña
Roles Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
Current address: Plaza de la Universidad, Albacete, Spain
Affiliation Department of Spanish and International Economics, Econometrics and History and Economic Institutions, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Albacete, Spain
Roles Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Department of Political Economy and Public Finance, Economic and Business Statistics and Economic Policy, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Albacete, Spain
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Current address: Ronda de Toledo, Ciudad Real, Spain
Affiliation Department Business Administration, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
- Víctor-Raúl López-Ruiz,
- Nuria Huete-Alcocer,
- José-Luis Alfaro-Navarro,
- Domingo Nevado-Peña

- Published: November 3, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528
- Reader Comments
A key goal for society as a whole is the pursuit of well-being, which leads to the happiness of its individual members; as such, it is of critical socioeconomic relevance. In this regard, it is important to study which factors primarily affect the happiness of the population. In principle, these factors are associated with income level and residential and job stability, or more specifically, citizens’ quality of life. This research, which is based on a multidimensional concept of quality of life, uses a regression model to explain the dependence of Spaniards’ happiness on the well-being or quality of life provided by their work, their family situation, their income level and aspects of their place of residence, among other factors. The data were collected through an anonymous survey administered to a representative sample of Spanish citizens. The methodology used approaches the intangible concept of happiness as resulting from different individual and social causes selected from dimensions addressed in the literature, and calculates their effects or importance through regression coefficients. One of the findings is that people with the highest level of well-being or quality of life in the most important dimensions mostly claim to be happy. With respect to gender, it has a significant influence on the dimensions included in the model of citizen happiness and on personal issues. It is also shown that the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic negatively influenced the quality of life of Spanish citizens and therefore their happiness.
Citation: López-Ruiz V-R, Huete-Alcocer N, Alfaro-Navarro J-L, Nevado-Peña D (2021) The relationship between happiness and quality of life: A model for Spanish society. PLoS ONE 16(11): e0259528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528
Editor: Yuriy Bilan, Rzeszow University of Technology: Politechnika Rzeszowska im Ignacego Lukasiewicza, POLAND
Received: May 23, 2021; Accepted: October 20, 2021; Published: November 3, 2021
Copyright: © 2021 López-Ruiz et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: AUTHORS WHO RECEIVED AWARD: ALL AUTHORS. GRANT NUMBER: 2020-GRIN-28711 AND 2021-GRIN-31005 FUNDER: UNIVERSITY OF CASTILLA-LA MANCHA The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Citizen’s quality of life, in an urban and community context, has become a central element of politics in most countries of the European Union [ 1 ]—so much so that it is the subject of extensive debate in different scientific fields. In sociology, quality of life is interpreted as the subjective understanding of well-being taking into account individual needs and perspectives; in economics, it is standard of living; and in medicine, it is the relationship between health and disease, along with the factors that have an impact on a healthy lifestyle. The health factor in quality of life is often elevated above other elements, although the concept of quality of life needs to be understood more broadly [ 2 ].
Life satisfaction is a subjective assessment of quality of life in general and is an indicator of subjective well-being [ 3 , 4 ], which is seen as synonymous with happiness when it refers to how people feel and think about their lives [ 4 , 5 ]. The topics of life satisfaction and happiness are currently attracting a good deal of attention from researchers in social sciences, psychology, philosophy and economics [ 6 ]. Most researchers use the word happiness carefully to convey its particular meaning: being happy is not just about being cheerful; it is a special feeling that is precious and extremely desirable, but difficult to attain [ 2 ]. Much of the research to date has focused on establishing objective methods for analysing quality of life and well-being, relying on geographical and socioeconomic aspects related to quality of life, well-being and happiness, with a particular emphasis on the impact of social and spatial inequalities, and social justice [ 7 ].
At the same time, however, there are many studies that consider more subjective aspects by means of social surveys [ 8 ], with citizens rating their well-being, health, life satisfaction and happiness in general [ 9 ]. Happiness is part of lived experience and everyday life [ 10 ]. However, happiness is also related to other socioeconomic aspects, such as individuals’ job satisfaction, which can have important implications for both individuals and organizations [ 10 , 11 ]. There is evidence that life satisfaction, and therefore happiness, depends on the type of job a person has [ 12 ]. Furthermore, we should take into account the characteristics of urban areas, as they are centres of economic activity and consumption, where a high quality of life can attract human capital and develop aspects that bring about economic growth and foster well-being [ 13 ]. In this vein, [ 14 ] argue that, in order to achieve said growth and ensure people’s subjective well-being, the environmental quality of cities must be improved. In short, happiness directly depends on the different dimensions in which our (multidimensional) quality of life can be observed, fundamentally those relating to workplace and residential environments.
Based on this interpretation, the present study applies a subjective approach to analyse the influence on happiness simultaneously exerted by individuals’ internal features and external factors [ 15 ]. The aim of this study is to gain a better understanding of the influence of certain determinants on the happiness of Spanish citizens, since individuals tend to actively select their place of residence in light of the job opportunities, public goods and services they provide [ 16 ]. Thus, the choice of where to live is associated with an individual’s social and economic prospects [ 17 ] and therefore with his/her pursuit of happiness [ 9 ]. This is what determines the success or failure of cities or municipalities in providing opportunities for residents to attain a comfortable quality of life, with the goal being not only to attract new residents but also to encourage existing ones to stay. This situation calls for certain actions to ensure inhabitants’ satisfaction with life in the city where they live [ 1 ]. Furthermore, working conditions and even the income gained through work are seen as clear assets in a possible model of happiness [ 14 , 18 , 19 ]. Happiness at work, which covers workplace relations and the individual’s self-esteem and assessment of their job, leads to life satisfaction and therefore happiness. But a comprehensive model of happiness must account for the personal issues related to each individual, considered fundamental by [ 20 ], such as personal development, physical and mental conditions, and even spirituality.
In summary, we present a study of Spaniards’ preferences regarding different dimensions of quality of life for achieving happiness, and we also assess differences by gender. Using a survey of this population and a representative sample, we determine the main, significant relationships with the different dimensions, primarily relating to work and the place of residence. To do so, we run a regression model in which happiness is explained by these external or social variables, while the influence of individual’s internal factors is approximated from the error. Due to the time frame of the analysis, we are also able to evaluate the possible effect of the pandemic on quality of life and thus individuals’ happiness. A negative impact will doubtlessly be observed, due to the adverse situation in health, social capital and/or economic factors [ 21 ]. We use a model of happiness in which residential safety, individuals’ family, work and financial situation, their immediate surroundings, care for the environment and the culture and sports on offer all play an important role. The study proposes a conceptualization of the model for measuring happiness; an applied estimation method and the results, analysing differences by gender; and the conclusions drawn. We also examine the relevance of the issues inherent to the individual in this search for happiness, which represents a novel methodological approach.
Background on happiness and development of hypotheses
Since the 1960s, the analysis of people’s quality of life has attracted the attention of researchers from many disciplines. Specifically, in the last decade there has been growing academic interest in quality of life, which in turn has included a series of studies that investigate well-being and happiness [ 22 ], with the latter becoming an important indicator of a country’s development.
It is generally believed that improving national happiness is the ultimate purpose of economic development [ 23 ]. In our case, individual happiness or the quality of life of a society is a key indicator of growth, and is broader and more complex than the aggregate measure of production. Thus, the measurement and analysis of happiness are becoming increasingly important in the social sciences [ 24 ], where there have been numerous attempts to define, measure and analyse subjective measures of happiness from the perspective of different academic disciplines, ranging from neuroscience and psychology to philosophy and economics [ 25 ]. For example [ 26 , 27 ], hold that happiness reveals the individual’s assessment of the general aspects of his/her life and situation, and how much an individual likes the life he/she lives. In this context, the central concept of happiness is the subjective assessment of one’s life, or life satisfaction [ 28 ]; hence [ 29 ], believe that happiness can be measured through “Satisfaction with life in this city”. This way of measuring happiness finds support in the studies of [ 30 – 32 ]. In addition [ 33 ], view happiness as the experience of satisfaction, and this satisfaction can come from everything around a person. Accordingly, the place of residence affects happiness [ 34 ].
The literature review conducted for this research reveals the intermingling of the terms happiness and quality of life, as they are very closely linked; the same happens with happiness and well-being, in the subjective sense, which are considered equivalent concepts [ 35 ]. Nevertheless, there are some studies that make a clear distinction between quality of life and happiness, using elements such as income to measure quality of life [ 36 ]; others use employment [ 18 , 37 ]; or the residential environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure, crime or security, and social belonging [ 38 , 39 ]. In other studies, quality of life is seen as related to more abstract issues such as freedom, human rights and happiness [ 40 ], which makes it difficult to differentiate between quality of life and happiness. But equally we are seeing the emergence of many studies that use social surveys to examine more subjective aspects [ 8 ], with citizens rating their well-being, health, life satisfaction and happiness in general [ 9 ]. Thus, it has been shown that happiness is one of the key factors in subjective well-being and overall life satisfaction [ 5 , 28 , 41 – 43 ], as it is interwoven with and embedded in the cultural context where the individual lives [ 44 ]. As such, the current view of urban, economic and social policy on cities is becoming increasingly important [ 1 ] in determining the happiness of their residents [ 16 , 39 ]. Indeed, people’s place of residence affects every aspect of their day-to-day life and therefore their happiness [ 16 , 45 , 46 ].
In this study, we adopt a subjective approach, based on the idea that Spaniards’ happiness—measured through their response to the statement “I feel satisfied in my place of residence”—depends on different types of factors. These are mostly drawn from the model of the different dimensions of quality of life which [ 47 ] refer to as important areas of life. To that end, we apply the quality of life model proposed by [ 48 ], which takes a subjective, general, multidimensional approach, with some of the characteristics relating to quality of life analysed for Spanish society ( Table 1 ).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528.t001
The influence of the different quality of life factors on a citizen’s happiness calls for a multidimensional approach that allows us to include a set of potential factors. We explore these in depth below, proposing the hypotheses to be tested in this study.
Happiness and the family situation
[ 1 ] demonstrates that household composition and the length of time a family remain living in a city are not associated with satisfaction with life in that place. However, other studies [ 49 ] report that life satisfaction is significantly correlated, albeit weakly, with the family situation, essentially with the composition of the family (parents’ marital status, number of children, etc.). For example, the size of the family unit has a positive impact on individual happiness [ 4 ]. [ 50 ] state that only when families have their first child is a positive effect on their happiness observed. In this vein, researchers such as [ 51 ] indicate that having children is negatively related to subjective well-being, due to the negative impact on financial satisfaction.
Generally speaking, family-related aspects have an influence on happiness, as do demographic factors at the individual level: marital status, education, unemployment, disability, age and sex [ 14 ]. The happiness of older people is more vulnerable when they live alone than when they live with family [ 18 ]. Therefore, we propose the first hypothesis (H1) that a favourable family situation, in which family members are united and support one other, will have a positive effect on the happiness of each individual family member.
Happiness and trust in one’s place of residence
People normally choose to live where they can feel happy with what they do in their daily life, such as their job, have confidence in their surroundings, and enjoy the services on offer that are accessible from their place of residence, such as healthcare and education. In addition to offering competitive opportunities to achieve a better financial situation and thus higher standard of living, the place where a person chooses to live can also influence a person’s happiness and well-being [ 46 ]. The migration flows from rural to urban areas in the last century were primarily motivated by this issue, and it is reflected in the inhabitants of large cities and in cities’ urban planning. In this vein, studies such as that by [ 52 ] claim that urban green spaces in cities help to assure citizens’ happiness by enhancing their physical and mental health. In recent years, changes have been made to global policy with efforts to build more urban green spaces, aimed at creating comfortable living environments and thereby improving quality of life in cities. This has been shown by numerous studies [ 53 , 54 ], which find greater increases in well-being and therefore happiness in cities due to the job opportunities, public goods and services they provide [ 16 ].
This issue, along with the type of urbanization of a city, including streets and buildings, has proven to be equally important for predicting happiness. Thus, we are seeing a shift in subjective well-being with the development of the economy in large cities compared to smaller, rural areas [ 54 ]. Conversely, other studies, such as that by [ 46 ] demonstrate that urban development, in the sense of the choice between rural or urban places of residence, does not directly affect happiness. As such, we propose a second hypothesis (H2), which holds that one’s place of residence (rural or urban), and trust in those surroundings, urban planning and local residents—that is, one’s immediate socio-residential circle—has a direct and positive effect on one’s happiness.
Happiness and the employment situation
Another key factor that exerts an influence on happiness is a person’s employment situation [ 16 , 55 ]. Job satisfaction, broadly referring to the degree to which people like their job [ 56 ] also forms part of this issue. However, little is known about the relationship between happiness and how happy people are with their job [ 11 ]. [ 57 ] report that employees’ orientation to happiness is significant for achieving well-being or happiness at work.
Furthermore, there are studies that differentiate between happiness in one’s personal and professional life. When employees lack support in doing their job, it increases their unhappiness and they end up in a frustrating situation [ 10 ]. But not having a job is also considered a driver of unhappiness, with the unemployed being far less happy than employed people [ 4 , 58 ].
Another aspect to take into account in workers’ happiness is the type of job they do [ 12 ] identify differences in the association between orientations to happiness and life satisfaction across occupation types.
We thus propose the third hypothesis (H3) which posits that working and favourable workplace conditions have a positive and significant effect on an individual’s happiness.
Happiness and the financial situation
Over the past two decades, there has been a marked rise in economic studies of happiness, particularly those related to the effect of income on happiness [ 7 , 8 , 16 , 19 , 38 , 55 , 59 – 61 ]. In economics, happiness is defined as a benefit: a rise in income can increase people’s utility levels, leading to a higher level of happiness [ 4 , 23 ].
Numerous studies have shown that most people with higher income levels have higher subjective well-being, although their happiness increases to a lesser extent [ 58 ]. However, other studies indicate that the impact of the income gap on happiness is unclear [ 23 ]. It could be the case that people with lower incomes have greater future prospects, which would encourage them to work much harder to improve their happiness [ 62 ].
On the other hand, if we focus on the place of residence, distinguishing between urban and rural, studies such as that by [ 23 ] found that the difference in income led to a significant decrease in residents’ subjective well-being. However, income inequality has a greater influence on the happiness of urban residents than on that of residents in rural areas [ 23 ]. As such, a household’s financial situation and the type of community are significantly correlated [ 1 ].
Therefore, the fourth hypothesis (H4) that we propose to examine is whether the financial situation has a significant and positive relationship with happiness, through the effect of subjective social well-being.
Happiness and safety
The socioeconomic and cultural conditions and prospects of an individual’s city and neighbourhood of residence are important [ 1 ]. Inhabitants socioeconomic characteristics play an important role in satisfaction with the neighbourhood, pointing to the critical relevance of policies aimed at strengthening and sustaining local communities [ 3 ].
When citizens assess neighbourhood-related problems, they tend to significantly associate them with their satisfaction with living in that particular area, although such problems are not significant when it comes to their assessment of the city [ 1 ]. However, other studies have found that a positive attitude towards other citizens is positively correlated with the satisfaction of those who live in the city in question [ 63 ], and a positive social attitude towards neighbours is positively related to satisfaction with the neighbourhood [ 64 ] and with the local area [ 65 ]. Moreover, other studies have found that households with children differ from childless households in their perception of satisfaction with the neighbourhood or local area [ 65 ].
According to [ 64 ], a higher income level is associated with higher neighbourhood satisfaction; however, they find no relationship between housing satisfaction and neighbourhood satisfaction. On the other hand, a positive relationship has been found between subjective well-being and home ownership [ 66 ].
In this context, the fifth hypothesis (H5) addresses the existence of a positive and significant relationship between perceived safety in one’s place of residence and the individual’s happiness.
Environment, climate change and happiness
There is limited evidence that momentary happiness is associated with immediate urban environments. [ 67 ] demonstrate that momentary happiness is influenced by immediate microenvironment variables and built environment characteristics, including temperature and noise. Similarly, the relationships between well-being and environmental factors are prompting a growing interest in the fields of psychology, health, conservation and economics [ 67 , 68 ]. However, the lack of attention paid to the city environment points to a need for research to understand how different aspects of the environment impact happiness over a lifetime [ 69 ]. In the same vein, there are reasons to believe that the natural environment is positively related to well-being, health and happiness. Natural environments can increase happiness by facilitating and encouraging—for practical, cultural and/or psychological reasons—behaviour that is physically and mentally beneficial, including physical exercise, recreation, and social interaction; conversely, knowledge of a local environmental problem and its negative effects on human health and the ecosystem could directly reduce levels of happiness [ 68 ].
Thus, citizens’ perceptions of air pollution can influence their happiness [ 70 ]. [ 68 ] provide evidence that citizens are significantly happier outdoors, in any type of green or natural habitat, than in an urban environment. Indeed, some studies have explored how the dissemination of information on air quality in cities positively affects the happiness of citizens and their economic development [ 14 ].
Therefore, we propose a sixth hypothesis (H6) on sustainability, the environment, pollution and the happiness of the individual, positing a positive and significant relationship between happiness and an improvement in the environment and sustainable green policies.
Other factors relating to accessibility, leisure and well-being (public services)
The benefits of leisure experiences (including social, physical, personal and psychological benefits) are among the main factors affecting quality of life [ 71 ]. According to [ 13 ], urban spaces are no longer centred around improving the infrastructure and transport connectivity of large cities; rather, there is a growing focus on other aspects such as economic competitiveness, culture and environmental values. In this regard, studies such as that of [ 69 ] analyze whether the provision of services within cities contributes to the happiness of their residents. Their results show that cities should focus on providing quality services, including good surveillance, schools, access to health services, easy access to transport services and cultural and sporting opportunities. The provision of such services underpins the success or failure of cities to provide opportunities for residents to secure a comfortable quality of life. Thus, there is a close relationship between the progress that is being made in the standard of living and the urbanization of the place of residence. Accordingly, some scholars have concluded that we are happier in cities [ 53 ], as people tend to choose their place of residence according to the job opportunities, goods and public services they provide [ 16 ].
In this regard, the seventh hypothesis (H7) that we propose is a significant and positive relationship between the citizen’s happiness and the range and accessibility of cultural and sports services on offer.
The Covid-19 pandemic and happiness
Happiness and life satisfaction are determined not only by personal aspects and life events, but also by circumstances external to the individual occurring at a certain point in time. In this regard, it can be stated that the Covid-19 pandemic is having a negative impact on multiple aspects of life for people around the world. However, it has been found that asking about the Covid-19 pandemic in surveys leads to positive changes in both momentary happiness and overall happiness with life [ 72 ].
There is a growing number of studies examining the effect of Covid-19 [ 21 ]. The results of some studies indicate that lockdowns have a significant and negative impact on happiness [ 21 ]. However, there are others that report that attitudes towards the Covid-19 pandemic in terms of the credibility of real-time data updates and society’s confidence in the handling of the pandemic are associated with lower levels of depression and higher levels of happiness [ 6 ].
Due to the impact that the pandemic is having on society, including people being confined to their homes, rural areas are offering new possibilities as places to live; indeed, it has been shown that such places are safer than urban localities in times of pandemic [ 73 ]. This represents an opportunity to address the issue of “Empty Spain", as the possibility of working from home can provide a boost to depopulated rural municipalities [ 74 ]. Indeed, a good many jobs can feasibly be done from home and thus from many of these rural areas [ 75 ].
We therefore propose the eighth hypothesis of this research (H8), which posits the existence of a negative and significant relationship between the effects of the pandemic and the happiness of individuals.
All the variables presented above are aimed at assessing quality of life and its influence on the happiness of the individual (Spanish citizen). Of the proposed hypotheses, the first seven posit a positive and significant relationship between the analysed variables and the happiness of the individual. The last hypothesis, relating to the pandemic, posits a negative and significant effect.
Furthermore, there is another set of conditions or variables, which we can identify as personal and inherent to the individual, relating to spirituality and physical and mental health [ 76 ]; these factors shape people’s development and personal growth, their sense of the meaning of life, self-respect and self-esteem, and as such are expected to have a significant influence on their happiness. In this regard, authors such as [ 77 ] develop a theoretical model of quality of life that distinguishes conditions of physical well-being, health and self-esteem within the category of the individual’s internal environment of quality of life. Although such issues are difficult to measure, even by means of an anonymous questionnaire, by running a regression model we can isolate the effects through the error or the variables not explicitly included in the model. By doing so, we can test whether this personal dimension influences the relationship with happiness. Below we explain the proposed method, the specification of the model and the measurement of all of the social and personal effects that allow us to test whether the hypotheses are supported.
Materials and methods
To test the hypotheses on the relationships between quality of life factors and individual happiness, and by extension social happiness, we establish a model for working-age Spanish citizens over 16 years old, with a sample generated through a questionnaire. The model includes the quality of life dimensions selected on the basis of their theoretical relevance and the statistical significance registered by their partial correlation and regression coefficients. Specifically, the equation is specified for each individual surveyed, with the quality of life dimensions that influence their happiness.
The data were collected between 2nd July and 8th September 2020 using an anonymous online questionnaire distributed through mailing lists and social networks. The final sample obtained was composed of 933 responses from across Spain. It should be borne in mind that this period coincides with the tail end of the first wave of the pandemic, which had lasted over three months, and the return to a “new normal” with the 14-day notification rate of new cases per 100 000 inhabitants well below 10 and minimum values for hospitalizations and deaths, according to information from the Ministry of Health. The tabulation method chosen was a 10-point Likert scale measuring citizens’ degree of satisfaction with the different aspects of quality of life and well-being in their places of residence and workplaces (with 1 being “not at all satisfied” and 10 being "very satisfied"), relating to the dimensions of the proposed model of quality of life and happiness. Questions related to Covid-19 and its effect on quality of life were also included.
Once the information had been collected, classified and tabulated, we ran an Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression using EViews 11 software. This type of estimation has been carried out for various quality of life factors, aiming to explain a high proportion of the variance in the dependent variable [ 47 ].
Where the dependent variable is the happiness of individual i (Hpi). The β coefficients indicate the relevance of each independent variable with respect to the happiness of the individual, with the constant term being an autonomous factor of happiness justified by the individual minimum. The relationship is linear and includes a random variable u that captures, in line with our happiness model, the variables referring to the individual’s personal situation that are not incorporated in the quality of life dimensions but that together may be relevant ( Fig 1 ). However, regarding the behaviour of this random variable, it is normally distributed with zero expectation value, are uncorrelated, and with constant variance.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528.g001
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528.t002
The model of citizen happiness therefore incorporates the key factors of citizen quality of life that influence life satisfaction, with the importance of the personal factors determined through the error, or the proportion of variance not explained. That is, the model explicitly analyses the factors related to social behaviour in the residential and labour spheres, including those relating to external circumstances, while personal issues account for the part of the happiness that is inherent to the individual and that cannot be directly quantified but can be measured through the proportion of the variance that is not explained by the model.
Results and discussion
First, Table 2 shows the main descriptive statistics of the variables that have the most significant relationships with the variable Hp for the whole sample, and broken down by gender.
The descriptive analysis of the dependent variable shows that, although there is a gender gap in favour of women, the difference is not significant. However, in the set of independent variables, there are clear differences in favour of men in the work-related issues of income and the assessment of their job, stemming from the gender inequality in the Spanish labour market. Although less significant, in the issues regarding personal relationships with one’s surroundings it is women who register higher average values (av). Regarding the dispersion, measured through the standard deviation (σ) and the coefficient of variation (CV), it is similar for all items, but greater for work-related issues, income and pandemic effects, while the lowest values correspond to the relationship between safety and life satisfaction. The coefficients of variation, means and standard errors for the selected variables can be seen in Table 2 .
By estimating the regression model in Equation 1, which yields the results summarized in Table 3 , we can determine the happiness model for Spanish society in terms of priorities for quality of life. It seems clear that in this model, gender is a determinant of priorities regarding happiness. For men, 55.2% of the variance is explained by these factors, while the corresponding value for women is only 41.5% (values of the coefficient of determination R 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0259528.t003
As a contribution to the scientific understanding of happiness, the following general observations can be made for Spanish citizens: all of the independent variables relating to life satisfaction are significant, as shown by the individual significance values (t-values), and have a direct relationship with happiness. We can thus accept the first seven hypotheses proposed, regarding the family situation (Fm), trust (Tr), the environment (En), culture and sport (CS), safety (Sf), financial situation (In), and job satisfaction, job assessment and working conditions (Hw). The pandemic is not found to be significant, although it has a negative sign. Therefore, H8 is not supported. This may be due to the time when the survey was carried out, despite the fact that the average value for this element in terms of quality of life was 6.9 out of 10. Lastly, regarding the personal issues not analysed in the model, the value of the coefficient of determination indicates that they account for approximately half the effect on the happiness of the Spanish individual in 2020: the R 2 is 0.45 and the residuals meet the requirement of normality (Jarque-Bera test: 124.89, p-value: 0.0000).
Looking closely at the effects, we can see that the most influential variable is the one referring to individuals’ closest circle, the family (Fm). It registers the largest significant effect (t-value 10.5) for both genders, although in this case the β effect is clearly higher in women (0.34 to 0.16 for women and men respectively).
Similarly, the items relating to the environment and sustainability (En) are relevant in all cases, but the effect is somewhat higher for men.
The safety of one’s surroundings, of one’s city, town or neighbourhood (Sf), is another clearly significant variable, but not for the male gender. The situation is reversed when it comes to trust in people, in terms of personal relationships (Tr): in this case, the effect is significant, but if we break it down by gender, it is men for whom the effect is significant, as shown by the t-value. The issues of trust and safety are thus relevant and are one reason why, if we extract the information by the size of the place of residence, the results point to small cities or large towns as being advantageous for attaining a higher quality of life and greater life satisfaction.
Finally, in terms of items regarding the individuals’ surroundings, we see a uniformly significant effect of the culture and sports variable (CS) in all equations.
The variables reflecting the workplace and financial situation merit particular mention, as there is a clear gender gap relating to the labour market. Both the income variable (In) and satisfaction with one’s job and workplace relations (Hw) are favourable for the male gender. For women, they are not significant (t value 0.19).
In summary, in terms of fit, more of the variance of the dependent variable is explained for men (R 2 0.55). The factors driving this relate to both the residential and the workplace environment. In the latter case, the assessment of their job and status at work clearly bring men happiness. However, the female gender is more influenced by the family situation and the safety of their place of residence, although these explain a smaller proportion of the variance (R 2 0.415). As such, individual factors not explicitly incorporated in the model, such as physical, mental and personal development issues, are more important for women’s happiness.
Conclusions
The study of happiness as a variable that is dependent on certain social factors has become critical, even more so in precarious situations such as the one generated by the current Covid-19 pandemic. In this regard, the literature reviewed confirms that the most extensively analysed factors in this relationship are those relating to financial and labour spheres, and to a lesser extent aspects of one’s place of residence.
The model of happiness proposed here is theoretically grounded and empirically tested through regression analysis, and represents a novel contribution to the literature in that it includes both explicit social factors or those relating to interpersonal relationships in one’s place of residence, surroundings and workplace, as well as implicit personal issues, inherent to the individual.
Based on data from a questionnaire, we have been able to quantify the main factors though which Spanish society attains happiness. The regression analysis provides evidence to support the hypotheses that posit the significance of factors such as one’s family situation, trust in neighbours, the safety of the place where one lives, culture, sport, sustainability, an unpolluted environment, and the one’s financial and labour situation. They all exert a positive influence on citizens’ happiness; however, the model reveals a divergence when analysing results by gender.
The gender gap in the Spanish labour market plays a decisive role in the factors relating to quality of life assessment in the happiness model. In particular, job assessment, workplace relations and happiness at work, along with one’s financial situation, are determining factors for men, but do not show the same effect for women.
On the other hand, the pandemic does not show a significant effect on life satisfaction, despite the fact that 80% respondents admitted to feeling affected in their personal, family or work sphere; this may be because the survey was conducted in the summer, when the first three-month wave of the pandemic was coming to an end.
This study opens up new lines of future research that will depend on the availability of information. An in-depth analysis is needed of the longer-term influence that the Covid-19 pandemic has had on these factors, in order to determine whether this situation has changed the key factors for citizen’s happiness, or even their preferences for cities with lower population density. To that end, a survey is currently being prepared to collect a new sample at a different time.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 19. Frey, B.S., What future happiness research?, ed. I.A.M.G.t.t.E.o. Happiness. 2021. 17–27.
- 20. Maslow A.H., Toward a Psychology of Being. New York, Cincinnati. 1962, Toronto: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
- 39. Zhang Y. and Wang P. The Relationship between the Degree of Urban Development and Human Happiness. in 2nd International Conference on Social Science, Public Health and Education (SSPHE 2018). 2019. Atlantis Press.
- 75. Anghel, B., EL TELETRABAJO EN ESPAÑA. p. 20.
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Happiness →

- 01 May 2024
- What Do You Think?
Have You Had Enough?
James Heskett has been asking readers, “What do you think?” for 24 years on a wide variety of management topics. In this farewell column, Heskett reflects on the changing leadership landscape and thanks his readers for consistently weighing in over the years. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 09 Apr 2024
Why Work Rituals Bring Teams Together and Create More Meaning
From weekly lunch dates with colleagues to bedtime stories with children, we often rely on rituals to relax and bond with others. While it may feel awkward to introduce teambuilding rituals in the workplace, the truth is, the practices improve performance, says Michael Norton in his book The Ritual Effect.

- 02 Apr 2024
What's Enough to Make Us Happy?
Experts say happiness is often derived by a combination of good health, financial wellbeing, and solid relationships with family and friends. But are we forgetting to take stock of whether we have enough of these things? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 Mar 2024
Do People Want to Work Anymore?
Surveys indicate that US employee engagement and job satisfaction are down. To what degree are attitudes toward work to blame? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 14 Nov 2023
Do We Underestimate the Importance of Generosity in Leadership?
Management experts applaud leaders who are, among other things, determined, humble, and frugal, but rarely consider whether they are generous. However, executives who share their time, talent, and ideas often give rise to legendary organizations. Does generosity merit further consideration? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 03 Oct 2023
- Research Event
Build the Life You Want: Arthur Brooks and Oprah Winfrey Share Happiness Tips
"Happiness is not a destination. It's a direction." In this video, Arthur C. Brooks and Oprah Winfrey reflect on mistakes, emotions, and contentment, sharing lessons from their new book.

- 12 Sep 2023
Successful, But Still Feel Empty? A Happiness Scholar and Oprah Have Advice for You
So many executives spend decades reaching the pinnacles of their careers only to find themselves unfulfilled at the top. In the book Build the Life You Want, Arthur Brooks and Oprah Winfrey offer high achievers a guide to becoming better leaders—of their lives.

- 28 Aug 2023
- Research & Ideas
The Clock Is Ticking: 3 Ways to Manage Your Time Better
Life is short. Are you using your time wisely? Leslie Perlow, Arthur Brooks, and DJ DiDonna offer time management advice to help you work smarter and live happier.

- 21 Aug 2023
You’re More Than Your Job: 3 Tips for a Healthier Work-Life Balance
Younger workers are rejecting the idea of sticking with one employer for the long haul and are instead finding happiness by job-hopping and creating dramatically different boundaries with work. In a new book, Christina M. Wallace maps out a step-by-step guide to building a flexible and fulfilling life that includes rest, relationships, and a rewarding career.

- 15 Aug 2023
Why Giving to Others Makes Us Happy
Giving to others is also good for the giver. A research paper by Ashley Whillans and colleagues identifies three circumstances in which spending money on other people can boost happiness.

- 14 Feb 2023
When a Vacation Isn’t Enough, a Sabbatical Can Recharge Your Life—and Your Career
Burning out and ready to quit? Consider an extended break instead. Drawing from research inspired by his own 900-mile journey, DJ DiDonna offers practical advice to help people chart a new path through a sabbatical.

- 10 Jan 2023
How to Live Happier in 2023: Diversify Your Social Circle
People need all kinds of relationships to thrive: partners, acquaintances, colleagues, and family. Research by Michael Norton and Alison Wood Brooks offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend from home.

- 29 Sep 2022
Inclusive Leadership Advice: Get Comfortable With the Uncomfortable
People tend to seek sameness, but they can teach themselves to relish in the differences of the human experience. Francesca Gino offers these three principles from improv to anyone who's trying to lead more inclusively.

- 21 Sep 2022
You Don’t Have to Quit Your Job to Find More Meaning in Life
Before you give notice and go on a vision quest, consider this: Fulfillment doesn't require big change, says research by Julian De Freitas and colleagues. In fact, you can find more meaning even in a job you don't love.

- 02 Jun 2022
Blissful Thinking: When It Comes to Finding Happiness, 'Your Dreams Are Liars'
Happiness research is all the rage. Arthur Brooks shares how understanding the origins of joy can improve the way we lead organizations—and our personal lives.

- 25 Jan 2022

More Proof That Money Can Buy Happiness (or a Life with Less Stress)
It's not about the bigger home or the better vacation. Financial stability helps people escape the everyday hassles of life, says research by Jon Jachimowicz. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.

- 29 Nov 2021
How Bonuses Get Employees to Choose Work Over Family
Working late again? Research by Ashley Whillans and colleagues shows how incentive pay encourages workers to think of downtime as wasted time. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 05 Jan 2021
- Cold Call Podcast
Using Behavioral Science to Improve Well-Being for Social Workers
For child and family social workers, coping with the hardships of children and parents is part of the job. But that can cause a lot of stress. Is it possible for financially constrained organizations to improve social workers’ well-being using non-cash rewards, recognition, and other strategies from behavioral science? Assistant Professor Ashley Whillans describes the experience of Chief Executive Michael Sanders’ at the UK’s What Works Centre for Children’s Social Care, as he led a research program aimed at improving the morale of social workers in her case, “The What Works Centre: Using Behavioral Science to Improve Social Worker Well-being.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 05 Oct 2020
Want to Be Happier? Make More Free Time
Enjoying life requires time, but too often we willingly give it away in pursuit of money and career. Ashley Whillans shows how to restore the proper balance. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 21 May 2020
Fighting the COVID Blues: Advice from Business Research
Pandemic uncertainty doesn't have to spell doom. Happiness experts at Harvard Business School offer these research-based strategies for managing stress. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
Sustainable Happiness
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 22 April 2023
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Xavier Landes 7
12 Accesses
Sustainable happiness is a wide concept. It characterizes conditions under which happiness, understood broadly as a mental state, attitude, and functioning, is individually and collectively secured or enhanced in the long run while preserving the natural and social environment. Thus, happiness is sustainable in two ways. First of all, it is sustainable qua happiness, namely, it characterizes situations where the individual or community is flourishing in the long term. Put differently, happiness achievement in the short run does not impair its realization in the future. Second, such happiness spares social and natural resources, namely, it minimally guarantees an equivalent access to these resources for the future generations. In other words, happiness is at least compatible, at best conducive, to sustainability understood as the preservation of economic, social, and environmental resources necessary for the satisfaction of future generations. The assumption of sustainable...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Aristotle. (2009). Nicomachean ethics . Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Centre for Bhutan Studies & GNH Research. (2016). A compass towards a just and harmonious society: 2015 GNH survey report . Thimphu: Centre for Bhutan Studies & GNH Research.
Deaton, A. (2013). The great escape: Health, wealth, and the origins of inequality . Princeton/Oxford: Princeton University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Easterlin, R. A. (1974). Does economic growth improve the human lot? Some empirical evidence. In P. A. David & M. W. Reder (Eds.), Nations and households in economic growth: Essays in honor of Moses Abramovitz (pp. 89–125). New York: Academic Press.
Frank, R. H. (1999). Luxury fever: Why money fails to satisfy in an era of excess . New York: The Free Press.
Haybron, D. (2008). The pursuit of unhappiness: The elusive psychology of well-being . Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press.
Kasser, T. (2002). The high price of materialism . Cambridge, MA/London: The MIT Press.
Layard, R. (2005). Happiness: Lessons from a new science . New York: Penguin Books.
O’Brien, C. (2008). Sustainable happiness: How happiness studies can contribute to a more sustainable future. Canadian Psychology, 49 (4), 289–295.
Article Google Scholar
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2017). Self-determination theory: Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness . New York: The Guilford Press.
Seligman, M. (2002). Authentic happiness . New York: Simon & Schuster.
World Commission on Environment and Development. (1987). Our common future . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stockholm School of Economics in Riga, Riga, Latvia
Xavier Landes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xavier Landes .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
London Metropolitan University, Guildhall Faculty of Business and Law London Metropolitan University, London, UK
Samuel Idowu
Cologne Business School, Ingolstadt, Germany
René Schmidpeter
College of Business, Loyola University New Orleans, New Orleans, LA, USA
Nicholas Capaldi
International Training Centre of the IL, International Labor Organization, Turin, Italy
Liangrong Zu
Department of Economics, Society and Politics, University of Urbino Carlo Bo, Urbino, Italy
Mara Del Baldo
Instituto Politécnico da Guarda, Guarda, Portugal
Section Editor information
Leeeds Business School, Leeds Beckett University, Leeds, UK
Brian T. Jones
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Landes, X. (2023). Sustainable Happiness. In: Idowu, S., Schmidpeter, R., Capaldi, N., Zu, L., Del Baldo, M., Abreu, R. (eds) Encyclopedia of Sustainable Management. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02006-4_633-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02006-4_633-1
Received : 09 April 2020
Accepted : 25 February 2023
Published : 22 April 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-02006-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-02006-4
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Business and Management Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

Happiness in University Students: Personal, Familial, and Social Factors: A Cross-Sectional Questionnaire Survey
Yingying jiang.
1 School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China; nc.ude.usc@gnaijyy (Y.J.); nc.ude.usc@nehcgnij (J.C.); nc.ude.usc@oaimgnefuy (Y.M.)
2 XiangYa School of Public Health, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China; nc.ude.usc@ulnahc
Yufeng Miao
3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong 999077, China; kh.ukh@gyil
Qihong Deng
4 School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
Associated Data
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Happiness is the foundation of a better life and a goal that people pursue; however, happiness levels among university students are low. The purpose of this study is to explore the main factors influencing student happiness. A nationwide cross-sectional study was conducted in China in 2020. Data on student happiness was collected using the Oxford Happiness Questionnaire, and students’ personal, familial, and social information were obtained using another questionnaire. Logistic regression analysis was employed to examine the association between student happiness and these factors in terms of odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). A total of 2186 valid questionnaires were obtained. Firstly, student happiness was found to be associated with personal factors. The results found that happiness was significantly associated with state of health, the adjusted OR (95% CI) = 3.41 (2.01–5.79) for healthy students compared to unhealthy students, and that happiness decreased with the student’s age (OR = 0.79 and 95% CI = 0.63–0.98). Secondly, the research suggested that happiness was associated with familial factors. Both frequent contact with family and a harmonious relationship with parents significantly enhanced happiness with ORs (95% CIs) 1.42 (1.17–1.71) and 2.32 (1.83–2.95), respectively. Thirdly, student happiness was associated with several social factors. Students who performed well academically, who went to sleep early, and who were in a loving relationship were found to be happier than those with poor academic performance, went to sleep late, and who were single, for which the ORs (95% CIs) were, respectively, 1.87 (1.51–2.32), 1.50 (1.24–1.81), and 1.32 (1.09–1.60). The survey identified several key personal, familial, and social factors influencing university student happiness, which can provide an effective measure to improve their happiness.
1. Introduction
Happiness is a subjective index often used to measure quality of life and refers to individual and social well-being [ 1 ]. Many studies have put forward their own views on the definition of happiness [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. For example, Veenhoven (1992) indicated that: “ Happiness is the degree to which a person judges whether his quality of life is satisfactory ” [ 8 ]. In a word, happiness is a subjective and internal emotion, and requires cognition [ 9 , 10 ]. It affects life expectancy, as happier people tend to have healthier and longer lives [ 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Therefore, happiness is not only a goal that people pursue, but also a guide and inexhaustible motivation for people’s behavior [ 14 ]. A large number of studies have shown that happiness is linked to ideals in many fields, from physical health and mental joyfulness to harmonious interpersonal relationships and career success [ 15 ]. According to the recent World Happiness Report, 2019, nearly one in three people are not happy with their lives, with the percentage increasing rapidly over the past decade [ 16 ].
Low levels of happiness among university students have been reported worldwide and have received considerable attention [ 17 ]. A 2017 survey showed that adults aged 18–25 had the highest rate of depression at 13.1 percent, compared with 7.7 percent for those aged 26–49 and 4.7 percent for those aged 50 and above. In addition, the incidence of suicidal thoughts in young people aged 18–25 was twice as high as in other age groups, and the incidence of suicide was 4.5 times higher than in other age groups [ 18 ]. University life is a special period when students start to be independent, but if they are not mature enough to adapt to the changes in their personal lives and studies [ 19 ], this may cause students to be easily stressed [ 20 ]. A previous study reported that about half the number of college students have moderate stress-related mental health problems [ 21 ], and more than 20 percent of college students in China suffer from psychiatric disorders, and this rate has been growing [ 22 , 23 , 24 ]. According to the 2018 National College Health Assessment Survey, 13 percent of college students have suicidal thoughts and about 2 percent have attempted suicide at least once in the past year [ 25 ]. A low level of happiness can have a range of negative consequences: impaired physical and mental health, even severe mental illness or suicide, strained interpersonal relationships, and poor academic performance, all of which will seriously affect their future development and career [ 25 , 26 ]. With increasing numbers of college students worldwide [ 27 ], the low level of happiness experienced by students prompts an urgent need to examine its influencing factors so as to be able to take active and effective measures to improve student happiness.
The origins of happiness are very complicated [ 28 ]. For a long time, the similarity in happiness levels among family members over generations seems to indicate that genetic factors may play an important role in happiness [ 29 , 30 ]. Some common genes or genetic variants associated with happiness have indeed been found [ 31 , 32 , 33 ]. However, there is accumulating evidence that both genetic and non-genetic factors play important roles in the origins of happiness [ 34 ]. In particular, the rapid decline in happiness cannot be explained by genetic change.
Human beings are group-living creatures with an emotional, thinking consciousness, so relevant non-genetic factors can be divided into individual and collective aspects, and previous studies have also confirmed that they are closely related to happiness. As a force for social development and national prosperity, the healthy growth of college students is of great significance. In addition, although there have been many studies on happiness, most of them focused mainly on adults or teenagers [ 35 ]. However, the psychological state of college students is unique as they are at the boundary between adolescence and adulthood, which should be considered separately [ 36 ]. Due to the particularity of college students, their collective life can be further divided into family and society. Therefore, this work focuses on the personal, familial, and social factors that affect happiness in university students, and aims to explore some potential variables that may affect happiness.
First of all, happiness is a subjective measure of a person’s well-being and is significantly associated with personal characteristics. A large number of studies have shown that gender makes a difference in happiness, with females generally being happier than males [ 35 , 37 , 38 ]. Health is also linked to happiness with the rate of happiness being higher in healthy people than in unhealthy people [ 39 , 40 , 41 ]. For students, those with high academic achievement have a higher level of happiness [ 42 , 43 ].
Second, family relationships also play an important role in happiness, as human beings are high-level creatures with an emotional consciousness; therefore, family is the key place where emotions are cultivated [ 44 ]. In particular, the relationship between parents is regarded to be the core of family unity and plays a key role in children’s development [ 45 ]. A recent study found that the main sources of children’s happiness are family relationships [ 46 ].
Third, people are social, and thus social behaviors are also found to be associated with happiness. Studies have shown that good peer relationships [ 46 ], regular physical activity [ 47 , 48 ], regular diet [ 37 , 49 ], and no drug dependence [ 50 ] are positively associated with happiness. However, the widespread use of mobile phones, computers, and other electronic devices has led to a substantial increase in internet addiction and insomnia [ 51 ], which have been found to be strongly negatively associated with happiness levels [ 52 ].
Recently there has been a rapid rise in the suicide rate among young people [ 53 , 54 ] and particularly among college students. The purpose of this study is to explore the main factors influencing student happiness in order to find useful suggestions to improve the quality of their development, and to benefit society and country as well.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. study protocol and participants.
Between January and June 2020, an online questionnaire survey of happiness in university students was conducted in China. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Central South University (Number: XYGW-2020-17). The plan was to conduct surveys in 34 provincial administrative regions, including 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities directly under the central government, and 2 special administrative regions. Each region collected 80 questionnaires, for a total of 2720. Prior to data collection, university students were informed of the nature and objectives of the study. All of the students voluntarily completed an anonymous questionnaire after giving their consent to participate.
In total, 2367 completed questionnaires were received across the country, with a recovery rate of 87.02%. In the questionnaire setting, the current educational background option is included to screen out the questionnaires that do not meet the requirements. In addition, since undergraduate and graduate students are the primary groups in Chinese colleges, it will be more accurate to select college students with this educational background for research, and thus 133 students who did not match those criteria were excluded. Then, 7 students who were of abnormal height (<100 cm or >200 cm) and 6 students of abnormal weight (<30 kg or >200 kg) were excluded. Next, 35 students who did not meet the geographical conditions were excluded, as these conditions may confound the study. Finally, the responses from 2186 valid questionnaires were entered into a database ( Figure 1 ). Of our sample, 52% were male and 48% were female, while 77% were undergraduate students and 23% were graduate students.

Distribution of the surveyed number, and happiness rate ( n , %) among students from universities across China ( n = 2186).
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
The questionnaire was divided into two parts. See the attached table for the contents of the questionnaire ( Table 1 ). The first 15 short surveys collected basic information about the students, which included personal factors ( sex, age, body mass index (BMI), grade , discipline, health ), familial factors ( contact with family, relationship between parents ), and social factors ( living expenses, sleeping habits, exam scores, relationship status ) ( Table 1 ). Corrections between these factors were reported in Table 2 .
Covariate information for the students stratified by happiness in this study ( n = 2186).
The values p < 0.05 were in bold.
Odds ratio (95%CI) of college student happiness for personal factors ( n = 2186).
# Adjusted for all the covariates in Table 1 . * p ≤ 0.05. *** p ≤ 0.001.
As for the measurement of well-being, researchers have proposed a variety of ways, which can be divided into single-item indicators and multi-item indicators. The reliability and accuracy of the former have been questioned in the survey process: researchers cannot estimate the internal consistency of a single indicator [ 55 ], that is, the same subject will have different degrees of well-being results at an interval of one hour in the same test item. In addition, a single-item index cannot capture the multi-dimensional aspects of psychological structure [ 56 ]. Multi-item indicators increase validity through the aggregation of multiple indicators, which has proven to be more reliable in the measurement of well-being.
Furthermore, there are many reliable methods in multi-item measurement, but each method has its own best-use conditions. For example, after consulting the relevant literature of the SWLS questionnaire, it is found that the questionnaire is suitable for different age groups [ 57 ]. An online survey was conducted worldwide in 2018, and multiple linear regression analysis was used to study the influencing factors of dentists’ subjective well-being [ 58 ]. A cross-sectional observational study conducted in 2019 investigated the relationship between migraine patients and life satisfaction through an online questionnaire [ 59 ]. However, this study only looked at college students. After consulting the relevant research on the well-being of college students, it is found that the Oxford well-being questionnaire is in agreement with reality, and is a good metric with which to study the predictive relationship between social media addiction and the well-being of college students [ 60 ].
Furthermore, the Oxford well-being questionnaire items can be easily included in a larger questionnaire in random order and with reversed items in the questionnaire. These changes can reduce the possibility of context and adaptive response and improve the reliability of data [ 61 ]. Moreover, compared with other subjective well-being indicators, SWLS has a weaker correlation with emotion [ 57 ]. Therefore, the Oxford Happiness Questionnaire was used to gather data related to happiness. It is a 29-item measure that utilizes a six-point rating scale of agreement, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 6 (strongly agree) ( Figure 2 ).

Oxford Happiness Questionnaire.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data were entered into Microsoft Excel and were analyzed using SPSS version 16.0 statistical software. We used multiple logistic regression models to analyze the data. Happiness was coded as a dichotomous variable with 1 = “happiness” and 0 = “unhappiness” according to the median score (120). A simple univariate analysis was performed to assess the association between all the covariates and college student happiness to obtain the significant covariates. We then employed simple logistic regression analysis to estimate the crude effect of the personal, familial, and social factors on student happiness. Finally, multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the effects after adjustment for the covariates. The effect was presented as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) and a p -value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The analysis reliability was 0.700, and the analytical validity was 0.958.
Out of the 2186 respondents, 1094 participants (50.0%) reported happiness. The associations between potential factors and student happiness are shown in Table 1 . The prevalence of happiness was higher in females (52.7%), those with standard BMI (51.9%), good health status (51.3%), frequent contact with family (55.0%), and good relations with their parents (54.5%), as well as those having high exam scores (63.7%), going to sleep early (before 24:00) (58.0%), and falling in love (55.4%).
The association between student happiness and their personal factors is shown in Table 2 . The results found happiness was significantly associated with health status, with the adjusted OR (95% CI) = 3.41 (2.01–5.79) for healthy students compared to unhealthy students. In addition, we found that age was negatively associated with happiness, OR (95% CI) = 0.79 (0.63–0.98).
The association between student happiness and familial factors is presented in Table 3 . The results show that both frequent contact with family and a harmonious relationship with parents were positively associated with happiness, with adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of 1.42 (1.17–1.71) and 2.32 (1.83–2.95), respectively.
Odds ratio (95%CI) of college student happiness for family factors ( n = 2186).
# Adjusted for all the covariates in Table 1 . *** p ≤ 0.001.
Student happiness is associated with several social factors ( Table 4 ). Firstly, a higher exam scores significantly enhanced student happiness with adjusted OR (95% CI) = 1.87 (1.51–2.32). Secondly, going to sleep earlier made students happier, the adjusted OR (95% CI) = 1.50 (1.24–1.81), as compared with going to sleep late. Thirdly, relationship status also affected student happiness, as the results found that students who were in a love relationship had significantly higher happiness than single students with adjusted OR = 1.32 (1.09–1.60).
Odds ratio (95%CI) of college student happiness for social factors ( n = 2186).
# Adjusted for all the covariates in Table 1 . ** p ≤ 0.01. *** p ≤ 0.001.
4. Discussion
The nationwide cross-sectional study comprehensively explored factors affecting the happiness of college students in China. The results showed that happiness was significantly associated with a student’s personal, familial, and social factors. Students in good health, with high academic performance, who went to sleep earlier, and who were in a loving relationship, were happier. In addition, those who were in frequent contact with their families or who had a good relationship with their parents, were happier. Since university is a critical period for personal growth, these findings provide guidance for the public and the government to cultivate happiness in university students so as to help their future development.
The survey found that younger students are happier. This is consistent with the globally recognized U-shaped relationship between happiness and age, where happiness decreases with age before the middle age [ 62 ]. A cross-sectional survey of college students in Chile found that age had a negative association with happiness [ 40 ], and another study observed that first- and second-year pharmacy students had higher levels of happiness than third- and fourth-year students [ 63 ]. It also found that healthy students are happier. A cross-sectional study of the World Database on Happiness also shows a consistently positive association between health and happiness [ 64 ] and a study in Thailand found that healthy people are happier and less likely to feel lonely and hopeless [ 41 ].
The results suggested that contact with family and the relationship with parents were significantly associated with student happiness. This is consistent with the widely known attachment theory that individuals have to communicate meaningfully with each other to lead a happy life [ 65 ]. Support from family increases a student’s life satisfaction and provides them with additional emotional help and encouragement, which are conducive to student happiness. Studies have shown that the family environment has a big impact on an individual’s happiness [ 66 ]. A survey of medical students found that those who lived with their families reported significantly higher levels of happiness than those who lived in residence [ 38 ]. The effect that the relationship between parents has on childhood happiness or mental health, has been widely observed [ 45 ]. One study showed that parental conflict can lead to mental illness and lower happiness in Chinese children [ 67 ], while a national cohort study found that parental relationships are linked to children’s depressive symptoms in China [ 68 ]. A retrospective study has also shown that parental relationships are associated with a child’s psychological development, and this is even more important than paying direct attention to the child’s education [ 69 ].
In addition, it observed that doing well in exams had a positive association with happiness, which is consistent with previous research relating grades with happiness. Several cross-sectional studies have found a link between academics and happiness [ 42 , 70 , 71 ] and a longitudinal study suggested there may be a causal relationship between academics and happiness [ 72 ]. What’s more, a survey of college student happiness shows that happiness comes at least in part from academic achievement [ 73 ]. Nevertheless, some surveys found that happiness was not associated with college grade point average [ 74 , 75 , 76 ] and found that happiness has nothing to do with academic performance.
It found that going to sleep early had a significantly positive correlation with happiness. Numerous previous studies support this finding. A cross-sectional study of Japanese students discovered that staying up late was associated with being 1.45 times less happy than going to bed early [ 77 ]. Another study in Japan observed that the levels of subjective happiness were strongly associated with the prevalence of sleep problems, and a linear dose–response relationship was observed between sleep problems and subjective happiness scores [ 35 ]. Another cross-sectional study found that poor sleep efficiency was more prevalent among people who are less happy [ 78 ]. Moreover, an exploratory study using non-contact sheet sensors found that college student happiness was associated with taking a shorter time to fall asleep [ 79 ].
This study showed that students who are in a loving relationship are happier. Separated from their families, they transfer emotion to classmates, friends, and other peers. Once a love relationship is established, this intimate relationship may become an important source of emotional support for college students and improve their sense of identity and happiness. Studies have shown that non-single people are happier than single youth [ 38 , 80 ]. Researchers have also found that non-single college students reported higher levels of life satisfaction and happiness [ 38 , 81 ].
There are many studies on happiness, but the survey of college students is limited [ 35 ]. Further, there are few studies on China’s nationwide college students, such as some for a certain grade [ 60 ], some for a certain region [ 82 ], and more abroad [ 60 ]. This research was conducted in 2020, which investigated college students from all over China.
Some limitations should be acknowledged in this study. Firstly, some possible biases may be present in this study. Participant responses may confound our research because the study was based on self-administered questionnaires. Secondly, it used a cross-sectional survey, which is only able to find associations. Further research needs to use a prospective approach, which records the state of change over time through longitudinal studies to determine the causal relationships. Thirdly, this survey group included only Chinese students, so whether our conclusions are generally applicable remains to be considered. However, given a large number of students in our study and the fact that the happiness of Chinese students has been proved to be relatively stable [ 83 ], the study is still instructive. Moreover, we only considered part of the factors that influence college student happiness, and there are potential variables that are not included. Furthermore, the arrival of COVID-19 brought serious impacts to all walks of life, including people’s physical and mental health. In this study, the unexpected and inevitable lead to a deviation in the survey. However, the research is conducted in the form of an online questionnaire and considering that the sample was of college students, and communication tools such as mobile phones and computers are basically inseparable from students, the impact of the epidemic is not great. On the other hand, the study was carried out from January to June 2020. At this time, college students across the country had gone home because of China’s Spring Festival holiday, and because the epidemic had already caused a shutdown in the first month of the lunar calendar, college students stayed home during the survey period. Finally, and most importantly, the study has not considered the role of the built environment. The indoor, neighborhood, and city-level built environment have an important impact on the happiness of residents [ 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 ]. In addition, urban air pollution lowers Chinese urbanites’ happiness [ 88 ]. Therefore, future happiness research will add more potential variables and external environmental factors.
5. Conclusions
Happiness is more than a transient feeling in life but is also of great importance for the development and future careers of university students, and lasting happiness will especially promote a more productive, cohesive, caring, and sustainable society. This nationwide survey found that student happiness is significantly associated with their personal (health state), familial (contact with family and relation with parents), and social (academic performance, sleep habits, and love) factors. The findings indicate that the decline of student physical fitness levels, the reduced contact with family, and the increased use of electronic products (such as mobile phones and games) that contribute to going to sleep late and contribute to poor academic performance, may be the primary, underlying reasons for the decline in university student happiness in recent years.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.D. and Y.L.; methodology, C.L.; software, J.C. and Y.J.; validation, Y.J.; formal analysis, Y.J.; investigation, C.L., J.C., Y.M. and Y.J.; resources, Q.D. and Y.L.; data curation, Y.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, Q.D., C.L. and Y.J.; supervision, Q.D.; project administration, Y.M.; funding acquisition, Q.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977369, 81861138005 and 42007391) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2021JJ30813).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Central South University (protocol code XYGW-2020-17and date of approval 2020/01/04).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The Science of Happiness in Positive Psychology 101

Whether on a global or an individual level, the pursuit of happiness is one that is gaining traction and scientific recognition.
There are many definitions of happiness, and we will also explore those in this article. For now, we invite you to think of a time when you were happy. Were you alone? With others? Inside? Outside.
At the end of this article, revisit that memory. You may have new insight as to what made that moment “happy,” as well as tips to train your brain towards more happiness.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Happiness & Subjective Wellbeing Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify sources of authentic happiness and strategies to boost wellbeing.
This Article Contains:
A definition of happiness, a look at the science of happiness, the scientific research on happiness at work, 17 interesting facts and findings, a study showing how acts of kindness make us happier, the global pursuit of happiness, measures of happiness, four qualities of life.
- How to Train your Brain for Happiness
A Take-Home Message
In general, happiness is understood as the positive emotions we have in regards to the pleasurable activities we take part in through our daily lives.
Pleasure, comfort, gratitude, hope, and inspiration are examples of positive emotions that increase our happiness and move us to flourish. In scientific literature, happiness is referred to as hedonia (Ryan & Deci, 2001), the presence of positive emotions and the absence of negative emotions.
In a more broad understanding, human wellbeing is made up of both hedonic and Eudaimonic principles, the literature on which is vast and describes our personal meaning and purpose in life (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Research on happiness over the years has found that there are some contributing correlational factors that affect our happiness. These include (Ryan & Deci, 2001):
- Personality Type
- Positive Emotions versus Negative Emotions
- Attitude towards Physical Health
- Social Class and Wealth
- Attachment and Relatedness
- Goals and Self-Efficacy
- Time and Place.
So what is the “ science of happiness? ”
This is one of those times when something is exactly what it sounds like – it’s all about the science behinds what happiness is and how to experience it, what happy people do differently, and what we can do to feel happier.
This focus on happiness is new to the field of psychology; for many decades – basically since the foundation of psychology as a science in the mid- to late-1800s – the focus was on the less pleasant in life. The field focused on pathology, on the worst-scenario cases, on what can go wrong in our lives.
Although there was some attention paid to wellbeing, success, and high functioning, the vast majority of funding and research was dedicated to those who were struggling the most: those with severe mental illness, mental disorders, or those who have survived trauma and tragedy.
While there’s certainly nothing wrong with doing what we can to raise up those who are struggling, there was an unfortunate lack of knowledge about what we can do to bring us all up to a higher level of functioning and happiness.
Positive psychology changed all of that. Suddenly, there was space at the table for a focus on the positive in life, for “ what thoughts, actions, and behaviors make us more productive at work, happier in our relationships, and more fulfilled at the end of the day ” (Happify Daily, n.d.).
The science of happiness has opened our eyes to a plethora of new findings about the sunny side of life.
Current research and studies
For instance, we have learned a lot about what happiness is and what drives us.
Recent studies have shown us that:
- Money can only buy happiness up to about $75,000 – after that, it has no significant effect on our emotional wellbeing (Kahneman & Deaton, 2010).
- Most of our happiness is not determined by our genetics, but by our experiences and our day-to-day lives (Lyubomirsky et al., 2005).
- Trying too hard to find happiness often has the opposite effect and can lead us to be overly selfish (Mauss et al., 2012).
- Pursuing happiness through social means (e.g., spending more time with family and friends) is more likely to be effective than other methods (Rohrer et al., 2018).
- The pursuit of happiness is one place where we should consider ditching the SMART goals; it may be more effective to pursue “vague” happiness goals than more specific ones (Rodas et al., 2018).
- Happiness makes us better citizens – it is a good predictor of civic engagement in the transition to adulthood (Fang et al., 2018).
- Happiness leads to career success, and it doesn’t have to be “natural” happiness – researchers found that “experimentally enhancing” positive emotions also contributed to improved outcomes at work (Walsh et al., 2018).
- There is a linear relationship between religious involvement and happiness. Higher worship service attendance is correlated with more commitment to faith, and commitment to faith is related to greater compassion. Those more compassionate individuals are more likely to provide emotional support to others, and those who provide emotional support to others are more likely to be happy (Krause et al., 2018). It’s a long road, but a direct one!

Download 3 Free Happiness Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to discover authentic happiness and cultivate subjective well-being.
Download 3 Free Happiness Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
There’s been a ton of research on the effects of happiness in the workplace. Much of this is driven by companies who want to find a way to improve productivity, attract new talent, and get a dose of good publicity, all at the same time. After all, who wouldn’t want to do business with and/or work for a company full of happy employees?
Although the jury is still out on exactly how happy employees “should” be for maximum productivity, efficiency, and health, we have learned a few things about the effects of a happy workforce:
- People who are happy with their jobs are less likely to leave their jobs, less likely to be absent, and less likely to engage in counterproductive behaviors at work.
- People who are happy with their jobs are more likely to engage in behavior that contributes to a happy and productive organization, more likely to be physically healthy, and more likely to be mentally healthy.
- Happiness and job performance are related—and the relationship likely works in both directions (e.g., happy people do a better job and people who do a good job are more likely to be happy).
- Unit- or team-level happiness is also linked to positive outcomes, including higher customer satisfaction, profit, productivity, employee turnover, and a safer work environment.
- In general, a happier organization is a more productive and successful organization (Fisher, 2010).
To sum up the findings we have so far, it’s easy to see that happiness at work does matter – for individuals, for teams, and for organizations overall. We don’t have all the answers about exactly how the relationship between happiness and productivity works, but we know that there is a relationship there.
Lately, many human resources managers, executives, and other organizational leaders have decided that knowing there’s a relationship is good enough evidence to establish happiness-boosting practices at work, which means that we have a lot of opportunities to see the impact of greater happiness at work in the future.

Research in this field is booming, and new findings are coming out all the time. Here are a few of the most interesting facts and findings so far:
- Happiness is linked to lower heart rate and blood pressure, as well as healthier heart rate variability.
- Happiness can also act as a barrier between you and germs – happier people are less likely to get sick.
- People who are happier enjoy greater protection against stress and release less of the stress hormone cortisol.
- Happy people tend to experience fewer aches and pains, including dizziness, muscle strain, and heartburn.
- Happiness acts as a protective factor against disease and disability (in general, of course).
- Those who are happiest tend to live significantly longer than those who are not.
- Happiness boosts our immune system, which can help us fight and fend off the common cold.
- Happy people tend to make others happier as well, and vice versa – those who do good, feel good!
- A portion of our happiness is determined by our genetics (but there’s still plenty of room for attitude adjustments and happiness-boosting exercises!).
- Smelling floral scents like roses can make us happier.
- Those who are paid by the hour may be happier than those on salary (however, these findings are limited, so take them with a grain of salt!).
- Relationships are much more conducive to a happy life than money.
- Happier people tend to wear bright colors; it’s not certain which way the relationship works, but it can’t hurt to throw on some brighter hues once in a while—just in case!
- Happiness can help people cope with arthritis and chronic pain better.
- Being outdoors – especially near the water – can make us happier.
- The holidays can be a stressful time, even for the happiest among us – an estimated 44% of women and 31% of men get the “holiday blues.”
- Happiness is contagious! When we spend time around happy people, we’re likely to get a boost of happiness as well.
Newman (2015) is the source for the first six facts and findings, and Florentine (2016) for the latter 11 .

Feeling blue? Treat yourself to a decadent dessert.
Feeling frustrated after an argument with a friend? Skip your workout and have an extra scoop of ice cream.
The message is clear: If you want to feel happy, you should focus on your own wishes and desires. Yet this is not the advice that many people grew up hearing. Indeed, most of the world’s religions (and grandmothers everywhere) have long suggested that people should focus on others first and themselves second.
Psychologists refer to such behavior as prosocial behavior and many recent studies have shown that when people have a prosocial focus, doing kind acts for others, their own happiness increases.
But how does prosocial behavior compare to treating yourself in terms of your happiness? And does treating yourself really make you feel happy?
Nelson et al. (2016) presented their research answering these questions.
Participants were divided into four groups and given new instructions each week for four weeks.
One group was instructed to perform random acts of kindness for themselves (such as going shopping or enjoying a favorite hobby); the second group was instructed to perform acts of kindness for others (such as visiting an elderly relative or helping someone carry groceries); the third group was instructed to perform acts of kindness to improve the world (such as recycling or donating to charity); the fourth group was instructed to keep track of their daily activities.
Each week, the participants reported their activities from the previous week, as well as their experience of positive and negative emotions.
At the beginning, the end, and again two weeks after the four-week period, participants completed a questionnaire to assess their psychological flourishing. As a measure of overall happiness, the questionnaire included questions about psychological, social, and emotional wellbeing .
The Results
The results of the study were striking. Only participants who engaged in prosocial behavior demonstrated improvements in psychological flourishing.
Participants who practiced prosocial behavior demonstrated increases in positive emotions from one week to the next. In turn, these increases in feelings such as happiness, joy, and enjoyment predicted increases in psychological flourishing at the end of the study. In other words, positive emotions appeared to have been a critical ingredient linking prosocial behavior to increases in flourishing.
But what about the people who treated themselves?
They did not show the same increases in positive emotions or psychological flourishing as those who engaged in acts of kindness. In fact, people who treated themselves did not differ in positive emotions, negative emotions, or psychological flourishing over the course of the study compared to those who merely kept track of their daily activities.
This research does not say that we shouldn’t treat ourselves, show ourselves self-love when we need it, or enjoy our relaxation when we have it. However, the results of this study strongly suggest that we are more likely to reach greater levels of happiness when we exhibit prosocial behavior and show others kindness through our actions.

In world economic circles, Richard Easterlin investigated the relationship between money and wellbeing.
The Easterlin paradox—”money does not buy happiness” (Mohun, 2012)—sparked a new wave of thinking about wealth and wellbeing.
In 1972, Bhutan chose to pursue a policy of happiness rather than a focus on economic growth tracked via their gross domestic product (GDPP). Subsequently, this little nation has been among the happiest, ranking amongst nations with far superior wealth (Kelly, 2012).
More global organizations and nations are becoming aware and supportive of the importance of happiness in today’s world. This has lead to The United Nations inviting nations to take part in a happiness survey, resulting in the “ World Happiness Report ,” a basis from which to steer public policy. Learn about the World Happiness Report for 2016 .
The United Nations also established World Happiness Day , March 20 th , which was the result of efforts of the Bhutan Kingdom and their Gross National Happiness initiative (Helliwell et al., 2013).
Organizations such as the New Economic Foundation are playing an influential role as an economic think tank that focuses on steering economic policy and development for the betterment of human wellbeing.
Ruut Veenhoven, a world authority on the scientific study of happiness, was one of the sources of inspiration for the United Nations General Assembly (2013) adopting happiness measures. Veenhoven is a founding member of the World Database of Happiness , which is a comprehensive scientific repository of happiness measures worldwide.
The objective of this organization is to provide a coordinated collection of data, with common interpretation according to a scientifically validated happiness theory, model, and body of research.
At this point, you might be wondering: Is it possible to measure happiness? Many psychologists have devoted their careers to answering this question and in short, the answer is yes.
Happiness can be measured by these three factors: the presence of positive emotions, the absence of negative emotions, and life satisfaction (Ryan & Deci, 2001). It is a uniquely subjective experience, which means that nobody is better at reporting on someone’s happiness than the individuals themselves.
For this reason scales, self-report measures, and questionnaires are the most common formats for measuring happiness. The most recognized examples are the following:
- The PANAS (Positive Affect and Negative Affect Schedule);
- The SWLS (Satisfaction With Life Scale) ;
- The SHS (Subjective Happiness Scale)
However, there are many instruments available to measure happiness that have proven reliable and valid over time (Hefferon & Boniwell, 2011).

Of the four dimensions, satisfaction is our personal subjective measure of happiness as we interpret life as a whole. Veenhoven’s (2010) global research into happiness suggests that happiness is possible for many.
This is an overview of his Four Qualities:
Using Veenhoven’s Four Qualities it is possible to assess the happiness of any country.
Liveability of environment
This dimension includes factors such as law, freedom, schooling, employment, electricity or gas, etc. It is a measurement of how well an environment meets what Maslow proposed as our basic needs (safety, security, shelter, food) (Maslow, 1943).
Life-ability of individuals
The ability of individuals to deal with life is important; both mental and physical health are identified as important factors, together with social values of solidarity, tolerance, and love (Veenhoven, 2010).
Utility of life
In this dimension, Veenhoven (2010) references a higher-order meaning, for example, religious affiliations.
Uchida et al. (2014) found that high levels of national disaster negatively impacted a nation’s level of happiness.
Satisfaction
Happiness is a complex construct that cannot be directly controlled. Through policy and individual and organizational action, one can endeavor to influence and increase happiness (Veenhoven, 2010).
However, happiness is a subjective experience and only once we change the way we perceive the world can we really begin sharing and creating happiness for others.
But is it possible to train yourself to be happier?
The answer is yes!
How to Train Your Brain for Happiness
At birth, our genetics provide us a set point that accounts for some portion of our happiness. Having enough food, shelter, and safety account for another portion.
There’s also quite a bit of happiness that’s entirely up to us (Lyubomirsky et al., 2005).
By training our brain through awareness and exercises to think in a happier, more optimistic, and more resilient way, we can effectively train our brains for happiness.
New discoveries in the field of positive psychology show that physical health, psychological wellbeing, and physiological functioning are all improved by how we learn to “feel good” (Fredrickson, et al., 2000).
What Are The Patterns We Need To “Train Out” of Our Brains?
- Perfectionism – Often confused with conscientiousness, which involves appropriate and tangible expectations, perfectionism involves inappropriate levels of expectations and intangible goals. It often produces problems for adults, adolescents, and children.
- Social comparison – When we compare ourselves to others we often find ourselves lacking. Healthy social comparison is about finding what you admire in others and learning to strive for those qualities. However, the best comparisons we can make are with ourselves. How are you better than you were in the past?
- Materialism – Attaching our happiness to external things and material wealth is dangerous, as we can lose our happiness if our material circumstances change (Carter & Gilovich, 2010).
- Maximizing – Maximizers search for better options even when they are satisfied. This leaves them little time to be present for the good moments in their lives and with very little gratitude (Schwartz et al., 2002).
Misconceptions About Mind Training
Some of the misconceptions about retraining your brain are simply untrue. Here are a few myths that need debunking:
1. We are products of our genetics so we cannot create change in our brains.
Our minds are malleable. Ten years ago we thought brain pathways were set in early childhood. In fact, we now know that there is huge potential for large changes through to your twenties, and neuroplasticity is still changing throughout one’s life.
The myelin sheath that covers your neural pathways gets thicker and stronger the more it is used (think of the plastic protective covering on wires); the more a pathway is used, the stronger the myelin and the faster the neural pathway. Simply put, when you practice feeling grateful, you notice more things to be grateful for.
2. Brain training is brainwashing.
Brainwashing is an involuntary change. If we focus on training our mind to see the glass half full instead of half empty, that is a choice.
3. If we are too happy we run the risk of becoming overly optimistic.
There is no such thing as overly optimistic, and science shows that brain training for positivity includes practices like mindfulness and gratitude. No one has ever overdosed on these habits.
How Is The Brain Wired For Happiness?

Our brains come already designed for happiness. We have caregiving systems in place for eye contact, touch, and vocalizations to let others know we are trustworthy and secure .
Our brains also regulate chemicals like oxytocin.
People who have more oxytocin trust more readily, have increased tendencies towards monogamy, and exhibit more caregiving behavior. These behaviors reduce stress which lowers production of hormones like cortisol and inhibits the cardiovascular response to stress (Kosfeld et al., 2005).
The following TED talk provides an insight into how we can overcome our negative mental patterns:
If happiness has little to do with having too many resources, then it is an inner state that we have the power to cultivate. The above video even offers specific exercises for you to try. Just by doing them, you are actively re-wiring your brain towards calm and happy sensations.
Meanwhile, this TED talk gives a better understanding of how to wire your brain to accept the positivity and happiness in your life:
The negativity bias that Dr. Rick Hanson discusses can help us understand how we can activate and “install” positive thinking as part of our core brain chemistry. If you don’t have a moment to watch either of these videos now, make time for it later—they are rich with relevant data and tips.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
Happiness is the overall subjective experience of our positive emotions. There are many factors which influence our happiness, and ongoing research continues to uncover what makes us happiest.
This global pursuit of happiness has resulted in measures such as the World Happiness Report, while the World Happiness Database is working to collaborate and consolidate the existing happiness pursuits of different nations.
We are living in a time when the conditions for happiness are known. This can be disheartening at times when there is much negativity in the world.
There is, however, good news in this situation: neuroplasticity.
The human brain is wired for happiness and positive connections with others. It is actually possible to experience and learn happiness despite what has been genetically hardwired.
In a world where the focus on happiness is growing and the mirror is turning back towards ourselves, the happiness of the world relies on the happiness within each one of us and how we act, share, and voice the importance of happiness for everyone.
What are the steps you are taking to make yourself and others happier? Let us know by leaving a comment below!
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Happiness Exercises for free .
- Carter, T. J., & Gilovich, T. (2010). The relative relativity of material and experiential purchases. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 98 (1), 146.
- Fang, S., Galambos, N. L., Johnson, M. D., & Krahn, H. J. (2018). Happiness is the way: Paths to civic engagement between young adulthood and midlife. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 42 (4), 425–433.
- Fisher, C. D. (2010). Happiness at work. International Journal of Management Reviews , 12 (4), 384–412.
- Florentine, E. (2016, July 1). 11 Scientific facts about happiness. Bustle . Retrieved from https://www.bustle.com/articles/169675-11-scientific-facts-about-happiness-that-youll-want-to-know.
- Fredrickson, B. L., Mancuso, R. A., Branigan, C., & Tugade, M. M. (2000). The undoing effect of positive emotions . Motivation and Emotion , 24 (4), 237–258.
- Happify Daily. (n.d.). What is the science of happiness? Retrieved from https://www.happify.com/hd/what-is-the-science-of-happiness/.
- Hefferon, K., & Boniwell, I. (2011). Positive psychology: Theory, research, and applications . Open University Press.
- Helliwell, J., Layard, R., & Sachs, J. (2013) . World happiness report 2013. United Nations.
- Kahneman, D., & Deaton, A. (2010). High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional well-being. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences , 107 (38), 16489–16493.
- Kelly, A. (2012) Gross national happiness in Bhutan: the big idea from a tiny state that could change the world. The Guardian . Retrieved from: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/dec/01/bhutan-wealth-happiness-counts?CMP=share_btn_link
- Kosfeld, M., Heinrichs, M., Zak, P. J., Fischbacher, U., & Fehr, E. (2005). Oxytocin increases trust in human s . Nature , 435 (7042), 673–676.
- Krause, N., Ironson, G., & Hill, P. (2018). Religious involvement and happiness: Assessing the mediating role of compassion and helping others. The Journal of Social Psychology , 158 (2), 256–270.
- Lyubomirsky, S., Sheldon, K. M., & Schkade, D. (2005). Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change. Review of General Psychology, 9 (2), 111–131.
- Maguire, E., Gadian, D., Johnsrude, I., Good, C., Ashburne, J., Frackowiak, R., & Frith, C. (2000). Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 97(8), 4398-4403.
- Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation . Psychological Review , 50 (4), 370.
- Mauss, I. B., Savino, N. S., Anderson, C. L., Weisbuch, M., Tamir, M., & Laudenslager, M. L. (2012). The pursuit of happiness can be lonely. Emotion, 12 (5), 908–912.
- Mohun, J. (2012) The economics book . DK.
- Nelson, S. K., Layous, K., Cole, S. W., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2016). Do unto others or treat yourself? The effects of prosocial and self-focused behavior on psychological flourishing. Emotion, 16 (6), 850–861.
- Newman, K. M. (2015, July 28). Six ways happiness is good for your health . Greater Good Magazine . Retrieved from https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/six_ways_happiness_is_good_for_your_health
- Rodas, M. A., Ahluwalia, R., & Olson, N. J. (2018). A path to more enduring happiness: Take a detour from specific emotional goals. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 28 (4), 673–681.
- Rohrer, J. M., Richter, D., Brümmer, M., Wagner, G. G., & Schmukle, S. C. (2018). Successfully striving for happiness: Socially engaged pursuits predict increases in life satisfaction. Association for Psychological Science , 29 (8), 1291–1298.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annual Reviews Psychology, 52 , 141–66.
- Ryff, C. D., & Singer, B. H. (2006). Know Thyself and Become What You Are: A Eudemonic approach to psychological well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies 9:13 -39, 2008.
- Schwartz, B., Ward, A., Monterosso, J., Lyubomirsky, S., White, K., & Lehman, D. R. (2002). Maximizing versus satisficing: Happiness is a matter of choice. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 83 (5), 1178.
- Shapiro, S. L., Carlson, L. E., Astin, J. A., & Freedman, B. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness. Journal of clinical psychology , 62(3), 373-386.
- Sheldon, K. M., & Lyubomirsky, (2006). Achieving Sustainable Gains in Happiness: Change your actions, not your circumstances . Journal of Happiness Studies (2006) 7:55-86.
- Uchida, Y., Takahashi, Y., & Kawahara, K. (2014). Changes in hedonic and eudaimonic well-being after a severe nationwide disaster: The case of the great east Japan earthquake . Journal of Happiness Studies, 15 , 207–221.
- United Nations General Assembly. (2013). Happiness: towards a holistic approach to development. Sixty-seventh session Agenda item 14. Retrieved from http://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/67/697
- Veenhoven, R. (2000). The four qualities of life: Ordering concepts and measures of the good life . Journal of Happiness Studies , 1 , 1–39.
- Veenhoven, R. (2010). Greater happiness for a greater number: Is that possible and desirable? Journal of Happiness Studies , 11 , 605–629.
- Walsh, L. C., Boehm, J. K., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2018). Does happiness promote career success? Revisiting the evidence. Journal of Career Assessment, 26 (2), 199–219.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thank you for this beautiful well written article. I came across it during my research regarding the science of happiness. The beauty in writing this post is the power to influence souls in a positive manner many who you will not meet.
Sending some love and light to you and all those who get to read your blog.
Being in the field of Human Resource for four decades, coming across and dealing with millions of minds, after reading your article, gives a feeling that I have learnt something new today…
Thank you and congratulations for such a informative work.
God bless…
Thank you for your search light into one of the nerve center of our generation. i will like to use part of this in my upcoming book
Hello Katherine, Now reading https://positivepsychology.com/happiness/ Salute to you for enriching us. Nearly hundred of us relatives are creating an audio book for our blind uncle about life skills. Any quote from you that I can add in the document? Will be grateful. regards, Prabodh Sirur
Hi Prabodh,
Wow, that sounds like a lovely gift for your uncle! We actually have a couple of posts containing quotes about happiness, so you may want to take a look at those for some inspiration. You can find those here and here .
Hope this helps, and good luck with the audiobook!
– Nicole | Community Manager
Thanks for your article, I translated this article for a mental health lesson and I really enjoyed this article.
Thank you for this super helpful article!!
Thank You for such an Informative and Detailed Article on Science of Happiness. I am a Budding Happiness Life Coach and stumbled on this Article. This gives me more understanding of Happiness in Scientific way, with your permission, I would like to share my learning in my course. Thank You and looking forward for more such Articles. Thank You and God Bless You
Hi Srinivas, Thank you for your lovely feedback. We’re glad you liked the article. Feel free to share it with others by clicking ‘Yes’ on the ‘Was this article useful to you’ button. From there, a range of sharing options will appear. – Nicole | Community Manager
Thanks, very nice lecture and informative But I wish to know more about role of religious effects on Happiness? another thing is it ok to translate lecture to other language and share it? Regards Dr Eirebi Albogasim
Hi Dr. Albogasim, Thanks for reading. There’s quite a bit of research showing that those who practice religion tend to be happier than the general population ( here’s an article on the topic). And yes, feel free to translate and share the lecture. – Nicole | Community Manager
I stumbled on your article as I am researching on Happiness to publish my 3rd book. Thanks for sharing! A very elaborate and informative article. The “Take home message” is very encouraging. And I vouch for the neuroplasticity of the brain. We can train ourselves to be Happy. Once we change our attitude, it is easy to be Happy. I learnt how to be Happy at the age of 23. Few years back I posted an article sharing my findings on Happiness in this Linked-in forum. Please see the link for the same https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/easy-happy-ramesh-thota-pmp-cqa/ . Appreciate if you can share your views.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Embracing JOMO: Finding Joy in Missing Out
We’ve probably all heard of FOMO, or ‘the fear of missing out’. FOMO is the currency of social media platforms, eager to encourage us to [...]

The True Meaning of Hedonism: A Philosophical Perspective
“If it feels good, do it, you only live once”. Hedonists are always up for a good time and believe the pursuit of pleasure and [...]

Happiness Economics: Can Money Buy Happiness?
Do you ever daydream about winning the lottery? After all, it only costs a small amount, a slight risk, with the possibility of a substantial [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (50)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (43)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Happiness Exercises Pack [PDF]
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Does Happiness Really Mean?
It's not the same for everyone
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell/ Jiaqi Zhou
How to Cultivate Happiness
How to be a happier person.
Happiness is something that people seek to find, yet what defines happiness can vary from one person to the next. Typically, happiness is an emotional state characterized by feelings of joy, satisfaction, contentment, and fulfillment. While happiness has many different definitions, it is often described as involving positive emotions and life satisfaction.
When most people talk about the true meaning of happiness, they might be talking about how they feel in the present moment or referring to a more general sense of how they feel about life overall.
Because happiness tends to be such a broadly defined term, psychologists and other social scientists typically use the term ' subjective well-being ' when they talk about this emotional state. Just as it sounds, subjective well-being tends to focus on an individual's overall personal feelings about their life in the present.
Two key components of happiness (or subjective well-being) are:
- The balance of emotions: Everyone experiences both positive and negative emotions, feelings, and moods. Happiness is generally linked to experiencing more positive feelings than negative ones.
- Life satisfaction: This relates to how satisfied you feel with different areas of your life including your relationships, work, achievements, and other things that you consider important.
Another definition of happiness comes from the ancient philosopher Aristotle, who suggested that happiness is the one human desire, and all other human desires exist as a way to obtain happiness. He believed that there were four levels of happiness: happiness from immediate gratification, from comparison and achievement, from making positive contributions, and from achieving fulfillment.
Happiness, Aristotle suggested, could be achieved through the golden mean, which involves finding a balance between deficiency and excess.
Signs of Happiness
While perceptions of happiness may be different from one person to the next, there are some key signs that psychologists look for when measuring and assessing happiness.
Some key signs of happiness include:
- Feeling like you are living the life you wanted
- Going with the flow and a willingness to take life as it comes
- Feeling that the conditions of your life are good
- Enjoying positive, healthy relationships with other people
- Feeling that you have accomplished (or will accomplish) what you want in life
- Feeling satisfied with your life
- Feeling positive more than negative
- Being open to new ideas and experiences
- Practicing self-care and treating yourself with kindness and compassion
- Experiencing gratitude
- Feeling that you are living life with a sense of meaning and purpose
- Wanting to share your happiness and joy with others
One important thing to remember is that happiness isn't a state of constant euphoria . Instead, happiness is an overall sense of experiencing more positive emotions than negative ones.
Happy people still feel the whole range of human emotions—anger, frustrastion, boredom, loneliness, and even sadness—from time to time. But even when faced with discomfort, they have an underlying sense of optimism that things will get better, that they can deal with what is happening, and that they will be able to feel happy again.
"Even people who have experienced terrible trauma can still also experience happiness," says Hannah Owens, LMSW , "though it is important to recognize that it might be more difficult for them to obtain the balance generally associated with overall happiness, and that their happiness might look very different from others' who have not had to deal with such challenges."
Types of Happiness
There are many different ways of thinking about happiness. For example, the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle made a distinction between two different kinds of happiness: hedonia and eudaimonia.
- Hedonia: Hedonic happiness is derived from pleasure. It is most often associated with doing what feels good, self-care, fulfilling desires, experiencing enjoyment, and feeling a sense of satisfaction.
- Eudaimonia: This type of happiness is derived from seeking virtue and meaning. Important components of eudaimonic well-being including feeling that your life has meaning, value, and purpose. It is associated more with fulfilling responsibilities, investing in long-term goals, concern for the welfare of other people, and living up to personal ideals.
Hedonia and eudemonia are more commonly known today in psychology as pleasure and meaning, respectively. More recently, psychologists have suggested the addition of the third component that relates to engagement . These are feelings of commitment and participation in different areas of life.
Research suggests that happy people tend to rank pretty high on eudaimonic life satisfaction and better than average on their hedonic life satisfaction.
All of these can play an important role in the overall experience of happiness, although the relative value of each can be highly subjective. Some activities may be both pleasurable and meaningful, while others might skew more one way or the other.
For example, volunteering for a cause you believe in might be more meaningful than pleasurable. Watching your favorite tv show, on the other hand, might rank lower in meaning and higher on pleasure.
Some types of happiness that may fall under these three main categories include:
- Joy: A often relatively brief feeling that is felt in the present moment
- Excitement: A happy feeling that involves looking forward to something with positive anticipation
- Gratitude: A positive emotion that involves being thankful and appreciative
- Pride: A feeling of satisfaction in something that you have accomplished
- Optimism: This is a way of looking at life with a positive, upbeat outlook
- Contentment: This type of happiness involves a sense of satisfaction
While some people just tend to be naturally happier, there are things that you can do to cultivate your sense of happiness.
Pursue Intrinsic Goals
Achieving goals that you are intrinsically motivated to pursue, particularly ones that are focused on personal growth and community, can help boost happiness. Research suggests that pursuing these types of intrinsically-motivated goals can increase happiness more than pursuing extrinsic goals like gaining money or status.
Enjoy the Moment
Studies have found that people tend to over earn—they become so focused on accumulating things that they lose track of actually enjoying what they are doing.
So, rather than falling into the trap of mindlessly accumulating to the detriment of your own happiness, focus on practicing gratitude for the things you have and enjoying the process as you go.
Reframe Negative Thoughts
When you find yourself stuck in a pessimistic outlook or experiencing negativity, look for ways that you can reframe your thoughts in a more positive way.
People have a natural negativity bias , or a tendency to pay more attention to bad things than to good things. This can have an impact on everything from how you make decisions to how you form impressions of other people. Discounting the positive—a cognitive distortion where people focus on the negative and ignore the positive—can also contribute to negative thoughts.
Reframing these negative perceptions isn't about ignoring the bad. Instead, it means trying to take a more balanced, realistic look at events. It allows you to notice patterns in your thinking and then challenge negative thoughts.
Avoid Social Comparison
Another way to cultivate happiness and to make sure that you are able to maintain your happiness, Owens says, is to stop comparing yourself to others.
"No two lives are alike, and focusing on what others have is a sure-fire way to feel envy and regret. Focus on the good things in your own life, and you'll be more likely to find contentment in them," she says.
Impact of Happiness
Why is happiness so important? Happiness has been shown to predict positive outcomes in many different areas of life including mental well-being, physical health, and overall longevity.
- Positive emotions increase satisfaction with life.
- Happiness helps people build stronger coping skills and emotional resources.
- Positive emotions are linked to better health and longevity. One study found that people who experienced more positive emotions than negative ones were more likely to have survived over a 13 year period.
- Positive feelings increase resilience. Resilience helps people better manage stress and bounce back better when faced with setbacks. For example, one study found that happier people tend to have lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol and that these benefits tend to persist over time.
- People who report having a positive state of well-being are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors such as eating fruits and vegetables and engaging in regular physical exercise.
- Being happy may make help you get sick less often. Happier mental states are linked to increased immunity.
Some people seem to have a naturally higher baseline for happiness—one large-scale study of more than 2,000 twins suggested that around 50% of overall life satisfaction was due to genetics, 10% to external events, and 40% to individual activities.
So while you might not be able to control what your “base level” of happiness is, there are things that you can do to make your life happier and more fulfilling. Even the happiest of individuals can feel down from time to time and happiness is something that all people need to consciously pursue.
Cultivate Strong Relationships
Social support is an essential part of well-being. Research has found that good social relationships are the strongest predictor of happiness. Having positive and supportive connections with people you care about can provide a buffer against stress, improve your health, and help you become a happier person.
In the Harvard Study of Adult Development, a longitudinal study that looked at participants over 80 years, researchers found that relationships and how happy people are in those relationships strongly impacted overall health.
So if you are trying to improve your happiness, cultivating solid social connections is a great place to start. Consider deepening your existing relationships and explore ways to make new friends.
Get Regular Exercise
Exercise is good for both your body and mind. Physical activity is linked to a range of physical and psychological benefits including improved mood. Numerous studies have shown that regular exercise may play a role in warding off symptoms of depression, but evidence also suggests that it may also help make people happier, too.
In one analysis of past research on the connection between physical activity and happiness, researchers found a consistent positive link.
Even a little bit of exercise produces a happiness boost—people who were physically active for as little as 10 minutes a day or who worked out only once a week had higher levels of happiness than people who never exercised.
Show Gratitude
In one study, participants were asked to engage in a writing exercise for 10 to 20 minutes each night before bed. Some were instructed to write about daily hassles, some about neutral events, and some about things they were grateful for. The results found that people who had written about gratitude had increase positive emotions, increased subjective happiness, and improve life satisfaction.
As the authors of the study suggest, keeping a gratitude list is a relatively easy, affordable, simple, and pleasant way to boost your mood. Try setting aside a few minutes each night to write down or think about things in your life that you are grateful for.
Find a Sense of Purpose
Research has found that people who feel like they have a purpose have better well-being and feel more fulfilled. A sense of purpose involves seeing your life as having goals, direction, and meaning. It may help improve happiness by promoting healthier behaviors.
Some things you can do to help find a sense of purpose include:
- Explore your interests and passions
- Engage in prosocial and altruistic causes
- Work to address injustices
- Look for new things you might want to learn more about
This sense of purpose is influenced by a variety of factors, but it is also something that you can cultivate. It involves finding a goal that you care deeply about that will lead you to engage in productive, positive actions in order to work toward that goal.
Challenges of Finding Happiness
While seeking happiness is important, there are times when the pursuit of life satisfaction falls short. Some challenges to watch for include:
Valuing the Wrong Things
Money may not be able to buy happiness, but there is research that spending money on things like experiences can make you happier than spending it on material possessions.
One study, for example, found that spending money on things that buy time—such as spending money on time-saving services—can increase happiness and life satisfaction.
Rather than overvaluing things such as money, status, or material possessions, pursuing goals that result in more free time or enjoyable experiences may have a higher happiness reward.
Not Seeking Social Support
Social support means having friends and loved ones that you can turn to for support. Research has found that perceived social support plays an important role in subjective well-being. For example, one study found that perceptions of social support were responsible for 43% of a person's level of happiness.
It is important to remember that when it comes to social support, quality is more important than quantity. Having just a few very close and trusted friends will have a greater impact on your overall happiness than having many casual acquaintances.
Thinking of Happiness as an Endpoint
Happiness isn’t a goal that you can simply reach and be done with. It is a constant pursuit that requires continual nurturing and sustenance.
One study found that people who tend to value happiness most also tended to feel the least satisfied with their lives. Essentially, happiness becomes such a lofty goal that it becomes virtually unattainable.
“Valuing happiness could be self-defeating because the more people value happiness, the more likely they will feel disappointed,” suggest the authors of the study.
Perhaps the lesson is to not make something as broadly defined as “happiness” your goal. Instead, focus on building and cultivating the sort of life and relationships that bring fulfillment and satisfaction to your life.
It is also important to consider how you personally define happiness. Happiness is a broad term that means different things to different people. Rather than looking at happiness as an endpoint, it can be more helpful to think about what happiness really means to you and then work on small things that will help you become happier. This can make achieving these goals more manageable and less overwhelming.
History of Happiness
Happiness has long been recognized as a critical part of health and well-being. The "pursuit of happiness" is even given as an inalienable right in the U.S. Declaration of Independence. Our understanding of what will bring happiness, however, has shifted over time.
Psychologists have also proposed a number of different theories to explain how people experience and pursue happiness. These theories include:
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
The hierarchy of needs suggests that people are motivated to pursue increasingly complex needs. Once more basic needs are fulfilled, people are then motivated by more psychological and emotional needs.
At the peak of the hierarchy is the need for self-actualization, or the need to achieve one's full potential. The theory also stresses the importance of peak experiences or transcendent moments in which a person feels deep understanding, happiness, and joy.
Positive Psychology
The pursuit of happiness is central to the field of positive psychology . Psychologists who study positive psychology are interested in learning ways to increase positivity and helping people live happier, more satisfying lives.
Rather than focusing on mental pathologies, the field instead strives to find ways to help people, communities, and societies improve positive emotions and achieve greater happiness.
Finley K, Axner M, Vrooman K, Tse D. Ideal levels of prosocial involvement in relation to momentary affect and eudaimonia: Exploring the golden mean . Innov Aging . 2020;4(Suppl 1):614. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2083
Kringelbach ML, Berridge KC. The neuroscience of happiness and pleasure . Soc Res (New York) . 2010;77(2):659-678.
Panel on Measuring Subjective Well-Being in a Policy-Relevant Framework; Committee on National Statistics; Division on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; National Research Council; Stone AA, Mackie C, editors. Subjective Well-Being: Measuring Happiness, Suffering, and Other Dimensions of Experience [Internet]. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
Lee MA, Kawachi I. The keys to happiness: Associations between personal values regarding core life domains and happiness in South Korea . PLoS One . 2019;14(1):e0209821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0209821
Hsee CK, Zhang J, Cai CF, Zhang S. Overearning . Psychol Sci . 2013;24(6):852-9
Carstensen LL, Turan B, Scheibe S, et al. Emotional experience improves with age: evidence based on over 10 years of experience sampling . Psychol Aging . 2011;26(1):21‐33. doi:10.1037/a0021285
Steptoe A, Wardle J. Positive affect and biological function in everyday life . Neurobiol Aging . 2005;26 Suppl 1:108‐112. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.016
Sapranaviciute-Zabazlajeva L, Luksiene D, Virviciute D, Bobak M, Tamosiunas A. L ink between healthy lifestyle and psychological well-being in Lithuanian adults aged 45-72: a cross-sectional study . BMJ Open . 2017;7(4):e014240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014240
Costanzo ES, Lutgendorf SK, Kohut ML, et al. Mood and cytokine response to influenza virus in older adults . J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci . 2004;59(12):1328‐1333. doi:10.1093/gerona/59.12.1328
Lyubomirsky S, Sheldon KM, Schkade D. Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change . Review of General Psychology. 2005;9 (2):111–131. doi:0.1037/1089-2680.9.2.111
The Harvard Gazette. Good genes are nice, but joy is better .
Zhang Z, Chen W. A systematic review of the relationship between physical activity and happiness . J Happiness Stud 20, 1305–1322 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-018-9976-0
Cunha LF, Pellanda LC, Reppold CT. Positive psychology and gratitude interventions: a randomized clinical trial . Front Psychol . 2019;10:584. Published 2019 Mar 21. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00584
Ryff CD. Psychological well-being revisited: advances in the science and practice of eudaimonia . Psychother Psychosom . 2014;83(1):10‐28. doi:10.1159/000353263
Whillans AV, Dunn EW, Smeets P, Bekkers R, Norton MI. Buying time promotes happiness . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2017;114(32):8523‐8527. doi:10.1073/pnas.1706541114
Gulacti F. The effect of perceived social support on subjective well-being . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2010;2(2):3844-3849. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.602
Mauss IB, Tamir M, Anderson CL, Savino NS. Can seeking happiness make people unhappy? [corrected] Paradoxical effects of valuing happiness [published correction appears in Emotion. 2011 Aug;11(4):767]. Emotion . 2011;11(4):807‐815. doi:10.1037/a0022010
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. People desire many valuable things in their life, but—more than anything else—they want happiness (Diener, 2000).The sense of happiness has been conceptualized as people's experienced well-being in both thoughts and feelings (Diener, 2000; Kahneman and Krueger, 2006).Indeed, research on well-being suggests that the resources valued by society, such as mental health (Koivumaa ...
Introduction. The existing definitions of happiness, subjective well-being, and health related quality of life and the main components assigned to these constructs in the research literature (see Table 1) suggest conceptual overlap between these dimensions (Camfield & Skevington, 2008).Quality of life was defined in the cross-cultural project of the World Health Organization (WHO) as:
Learn how happiness is defined, measured and influenced by various factors from this comprehensive review of research on life satisfaction and subjective well-being.
Happiness is a new concept in positive psychology. Although, everyone uses this concept commonly as a clear concept, it has a complex meaning and composed of several factors. In ease, all effective factors divided into two dimensions: endogenic and exogenic. In spite of the influence of exogenic factors on happiness, endogenic factors form the ...
The international peer-reviewed Journal of Happiness Studies is devoted to theoretical and applied advancements in all areas of well-being research. It covers topics referring to both the hedonic and eudaimonic perspectives characterizing well-being studies. The former includes the investigation of cognitive dimensions such as satisfaction with ...
Ms. Samiksha Bhatt. Assistant Professor, Shri V aishnav Institute of Architecture, SVVV Indore. Abstract. The pursuit to happiness is perhaps as old as the existence of mankind. Mention of ...
happiness is related to feeling right across distinct emotions or whether happiness is related to experiencing certain right emotions more than others. We assessed relations of the absolute discrep-ancies between experienced and desired emotions with greater well-being and depressive symptoms in eight countries around the globe.
A systematic review examines the happiness-promoting strategies most commonly recommended in the media. This review suggests that the scientific evidence underlying some of these strategies, such ...
Abstract and Figures. The (net) happiness (or welfare) of an individual is the excess of her positive affective feelings over negative ones. This subjective definition of happiness is more ...
The psychological constructs in blue (happiness and wellbeing) represent outcome variables that reflect a combination of interacting constituent emotions, feelings, and behaviors, and they are not as well-suited for precise measurement with neuroscience methods, but may be correlated with variables yielded from neuroscientific research. ...
Happiness is a crucial ingredient of human well-being and health (Duckworth, Steen, & Seligman, 2005; Fredrickson, 1998; Lyubomirsky, King, & Diener, 2005) and, therefore, people generally value happiness (Diener, 2000; Myers, 2000).Indeed, in an acknowledgment of its value, the pursuit of happiness was identified as an "inalienable right" in the US Declaration of Independence.
Coping, happiness and ideology. Some suggestions for the application of happiness research in politicological research [Paper presentation]. International Conference "towards the good society: Applying the social sciences," Rotterdam, The Netherlands. (Study AT 1992).
Developing interventions to increase happiness is a major focus of the emerging field of positive psychology. Common beliefs about the need to reduce stress to obtain happiness suggest that stress management activities should be included in these interventions. However, the research on the relationship between positive and negative affect is equivocal. Theoretically, they are conceptualized as ...
A key goal for society as a whole is the pursuit of well-being, which leads to the happiness of its individual members; as such, it is of critical socioeconomic relevance. In this regard, it is important to study which factors primarily affect the happiness of the population. In principle, these factors are associated with income level and residential and job stability, or more specifically ...
By uniquely combining the critical approach of sociology with techniques from other disciplines, the contributors illuminate new approaches to the study of happiness and well-being. 978-1-5292-0615-9. Sociology. In the past, happiness studies has been dominated by the work of philosophers, economists and psychologists, but more recently there ...
New research on happiness from Harvard Business School on issues including spending money on new experiences versus goods, and how and why spending money on others promotes happiness. ... A research paper by Ashley Whillans and colleagues identifies three circumstances in which spending money on other people can boost happiness.
1. Introduction. Research on children's and adolescents' happiness has increased in recent years [] due to the association between happiness and improved physical and mental health [2,3].For the present systematic review, happiness was conceptualized as a relatively stable, positive, and affective trait [4,5], with an emphasis on subjective well-being and general life satisfaction [2,6,7].
The relevance of the topic is related to how happiness impacts employees and organizations. First, there are individual effects directly related to one's personal life, such as income (Diener et al., 2002), higher life expectancy and health (Salas-Vallina et al., 2017), increased career self-awareness, no burnout, and feeling of solidarity (Ozkara San, 2015).
Definition. Sustainable happiness is a wide concept. It characterizes conditions under which happiness, understood broadly as a mental state, attitude, and functioning, is individually and collectively secured or enhanced in the long run while preserving the natural and social environment. Thus, happiness is sustainable in two ways.
When quality aspects of green areas are considered, they are also significantly correlated with happiness. This paper contributes to the knowledge of surrounding greenness and subjective well-being in one of the most urbanized regions in the world and promotes the discussion of well-being policies in urban planning.
1. Introduction. Happiness is a subjective index often used to measure quality of life and refers to individual and social well-being [].Many studies have put forward their own views on the definition of happiness [2,3,4,5,6,7].For example, Veenhoven (1992) indicated that: "Happiness is the degree to which a person judges whether his quality of life is satisfactory" [].
Pleasure, comfort, gratitude, hope, and inspiration are examples of positive emotions that increase our happiness and move us to flourish. In scientific literature, happiness is referred to as hedonia (Ryan & Deci, 2001), the presence of positive emotions and the absence of negative emotions. In a more broad understanding, human wellbeing is ...
History. Happiness is something that people seek to find, yet what defines happiness can vary from one person to the next. Typically, happiness is an emotional state characterized by feelings of joy, satisfaction, contentment, and fulfillment. While happiness has many different definitions, it is often described as involving positive emotions ...