

Essay on Punishment
Students are often asked to write an essay on Punishment in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Punishment
Understanding punishment.
Punishment is a way to correct wrong behavior. It is often used by parents, teachers, or law enforcement officers. It can be in the form of time-out, fines, or even jail time. The main goal is to discourage bad behavior.
Types of Punishment
There are two main types of punishment: physical and non-physical. Physical punishment can be spanking or hitting. Non-physical punishment can be things like taking away privileges. Both types aim to teach a lesson.
Effects of Punishment
Punishment can have different effects. It can stop bad behavior, but it can also cause fear or resentment. It’s important to use punishment wisely and fairly.
Punishment vs Discipline
Punishment and discipline are not the same. Punishment focuses on past wrongs. Discipline focuses on teaching the right behavior for the future. Both are used to guide behavior.
In conclusion, punishment is a tool for correcting behavior. It should be used carefully to teach and guide, not to harm or create fear.
250 Words Essay on Punishment
Punishment is a way people face consequences for their actions. It is a method used by parents, teachers, and the law to teach right from wrong. It helps to maintain order and discipline.
There are two main types of punishment: physical and non-physical. Physical punishment involves causing bodily pain, like a smack. Non-physical punishment can be taking away privileges or giving extra work. Each type has its own effects on the person being punished.
Punishment can have different effects. It might stop bad behavior for a while. But, it can also lead to fear, anger, and resentment. It may not teach the person why their behavior was wrong.
Alternatives to Punishment
Instead of punishment, some people prefer to use positive reinforcement. This means rewarding good behavior. This can encourage the person to behave well, rather than just avoiding punishment.
In the end, the goal of punishment is to help people learn from their mistakes. It’s important to use it wisely and fairly. It should teach a lesson, not cause harm. It’s also good to remember that there are other ways to teach good behavior.
500 Words Essay on Punishment
What is punishment.
Punishment is a penalty given to someone for a mistake or wrongdoing. It is a way to correct wrong behavior. For example, if a child does not do their homework, their teacher might give them extra work as punishment. This is meant to teach the child to do their homework on time in the future.
There are two main types of punishment: physical and non-physical. Physical punishment involves causing pain to the body, like spanking. It is often seen as harsh and is not widely accepted today. Non-physical punishment does not cause physical pain. It involves things like timeouts, grounding, or taking away privileges.
Punishment can have different effects on people. Sometimes, it can help correct bad behavior. A person might think twice about doing something wrong if they know there will be a punishment. But, punishment can also have negative effects. It can cause fear, anger, or resentment. It might not teach the person why their behavior was wrong, only that they should avoid punishment.
There are other ways to correct wrong behavior besides punishment. One way is through positive reinforcement. This means rewarding good behavior instead of punishing bad behavior. For example, a parent might give their child a treat for cleaning their room. This encourages the child to clean their room in the future. Another way is through teaching and communication. This involves explaining why a behavior is wrong and how to behave better.
In conclusion, punishment is a tool used to correct wrong behavior. It comes in different forms and can have different effects. While it can sometimes be effective, there are also other ways to encourage good behavior. It is important to consider the best approach for each situation.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Purple Hibiscus
- Essay on Purpose In Life As A Student
- Essay on Purpose Of Arnis
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.5 The Purposes of Punishment
Learning objective.
- Ascertain the effects of specific and general deterrence, incapacitation, rehabilitation, retribution, and restitution.
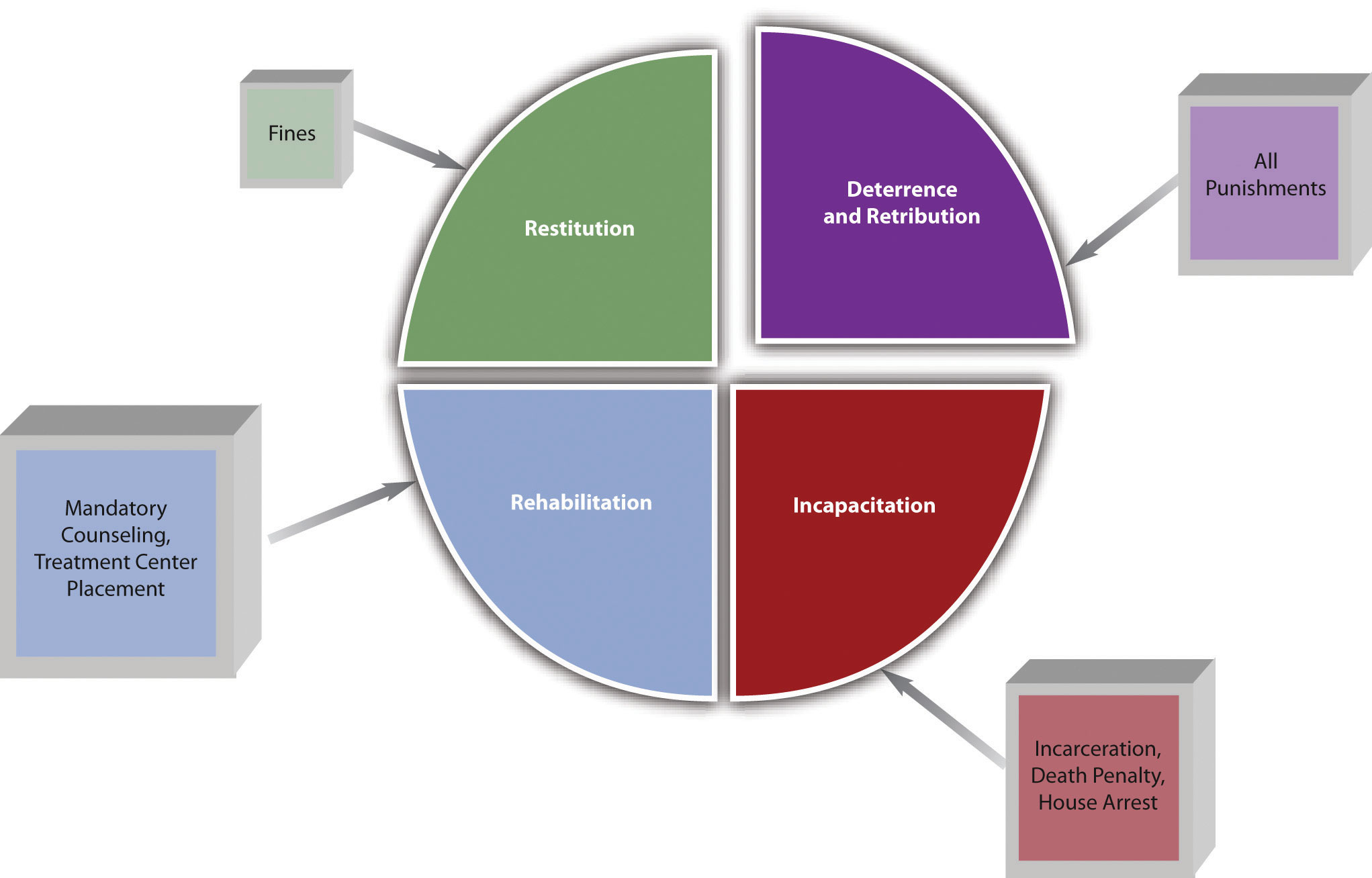
Punishment has five recognized purposes: deterrence , incapacitation , rehabilitation , retribution , and restitution .
Specific and General Deterrence
Deterrence prevents future crime by frightening the defendant or the public . The two types of deterrence are specific and general deterrence . Specific deterrence applies to an individual defendant . When the government punishes an individual defendant, he or she is theoretically less likely to commit another crime because of fear of another similar or worse punishment. General deterrence applies to the public at large. When the public learns of an individual defendant’s punishment, the public is theoretically less likely to commit a crime because of fear of the punishment the defendant experienced. When the public learns, for example, that an individual defendant was severely punished by a sentence of life in prison or the death penalty, this knowledge can inspire a deep fear of criminal prosecution.
Incapacitation
Incapacitation prevents future crime by removing the defendant from society. Examples of incapacitation are incarceration, house arrest, or execution pursuant to the death penalty.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation prevents future crime by altering a defendant’s behavior. Examples of rehabilitation include educational and vocational programs, treatment center placement, and counseling. The court can combine rehabilitation with incarceration or with probation or parole. In some states, for example, nonviolent drug offenders must participate in rehabilitation in combination with probation, rather than submitting to incarceration (Ariz. Rev. Stat., 2010). This lightens the load of jails and prisons while lowering recidivism , which means reoffending.
Retribution
Retribution prevents future crime by removing the desire for personal avengement (in the form of assault, battery, and criminal homicide, for example) against the defendant. When victims or society discover that the defendant has been adequately punished for a crime, they achieve a certain satisfaction that our criminal procedure is working effectively, which enhances faith in law enforcement and our government.
Restitution
Restitution prevents future crime by punishing the defendant financially . Restitution is when the court orders the criminal defendant to pay the victim for any harm and resembles a civil litigation damages award. Restitution can be for physical injuries, loss of property or money, and rarely, emotional distress. It can also be a fine that covers some of the costs of the criminal prosecution and punishment.
Figure 1.4 Different Punishments and Their Purpose
Key Takeaways
- Specific deterrence prevents crime by frightening an individual defendant with punishment. General deterrence prevents crime by frightening the public with the punishment of an individual defendant.
- Incapacitation prevents crime by removing a defendant from society.
- Rehabilitation prevents crime by altering a defendant’s behavior.
- Retribution prevents crime by giving victims or society a feeling of avengement.
- Restitution prevents crime by punishing the defendant financially.
Answer the following questions. Check your answers using the answer key at the end of the chapter.
- What is one difference between criminal victims’ restitution and civil damages?
- Read Campbell v. State , 5 S.W.3d 693 (1999). Why did the defendant in this case claim that the restitution award was too high? Did the Texas Court of Criminal Appeals agree with the defendant’s claim? The case is available at this link: http://scholar.google.com/scholar_case?case=11316909200521760089&hl=en&as_sdt=2&as_vis=1&oi=scholarr .
Ariz. Rev. Stat. §13-901.01, accessed February 15, 2010, http://law.justia.com/arizona/codes/title13/00901-01.html .
Criminal Law Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Punishment - Essay Samples And Topic Ideas For Free
Punishment involves the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual in response to a particular action or behavior. Essays on punishment could explore various theories of punishment, the effectiveness of different forms of punishment, or the ethical considerations surrounding punishment in legal, educational, or societal contexts. We’ve gathered an extensive assortment of free essay samples on the topic of Punishment you can find in Papersowl database. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Cruel Capital Punishment in George Orwell’s Story “A Hanging”
George Orwell’s story “A Hanging” tells readers about a traumatic involvement Orwell had when he was given the opportunity to travel from Europe to participate in the capital punishment of a Hindu male. “I had never realized what it means to destroy a healthy, conscious man.” The effect of reading that line, it really sinks in how distraught Orwell felt. In this essay, Orwell uses a variety of literary elements to create a grave atmosphere and notes the behavior between […]
Is Capital Punishment a Violation of Human Rights
The Eighth Amendment of United States Constitution provides that “excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted.” Numerous Supreme Court Justices have wrestled with the interpretation of the Eighth Amendment and the question of what the Framers really meant by it. Capital Punishment also known as ‘The Death Penalty’ should be abolished because it is inhuman and shows little regard for human life. For years and even today, the idea ‘an eye […]
Dispute Resolution in Criminal Justice
In my class of Sociology of Criminal Justice, we are learning what happened socially in the United States to cause the criminal justice policy to change so dramatically into a punishment policy, where we deliver harsher punishment to individuals to incapacitate and deter them from committing punishment. The class also explores what the aspects are of this punishment policy and what the consequences have been for the past decades from this policy. One particular topic that has stuck with in […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Abolition of Corporal Punishment in Australia
Corporal punishment is the infliction of physical pain as a form of punishment. It often involves the "punisher" and the "punished". The power gap between the two is usually great. In today's society, corporal punishment has been outlawed in several countries. Other countries, however, including Australia still consider it as a form of discipline. Controversies surround this issue. It is unclear why the only people it is legal to smack are the most vulnerable, the children. Corporal punishment is classified […]
Capital Punishment Vs. Juveniles
Many people around the world believe a prison is a safe place for criminals or felons that have committed a crime. Those criminals could have been in jail for many reasons. It could be for murder, kidnapping, burglary, status offenses, or even possession of drugs. Sometimes criminals tend to break out of prison for a sentence of life, because of the attempt. One of the most hated consequences for crimes during trials is the Death Penalty/Capital Punishment. Capital Punishment is […]
Is the Death Penalty “Humane”
What’s the first thing that pops up in your mind when you hear the words Capital Punishment? I’m assuming for most people the first thing that pops up is a criminal sitting on a chair, with all limbs tied down, and some type of mechanism connected to their head. Even though this really isn't the way that it is done, I do not blame people for imagining that type of image because that is how movies usually portray capital punishment. […]
Why Capital Punishment should be Abolished
Capital punishment has been used in the United States for vicious criminals since its inception. It helps in restituting, retribution and incapacitating for crimes like murder, treason and other serious crimes (Kasten 2). Today, the state governments have the responsibility to decide on capital punishment. There are thirty-eight states in the United States that have allowed capital punishment but only seventeen have implemented the punishment on more than two criminals over the twenty years that the law has been in […]
The Problematics of Capital Punishment
Capital punishment is a universal problematic ideology under constant debate. Those that oppose the death penalty often agree that it is immoral for the government to take the life of an individual. They frequently state that the death penalty is a cruel and unusual punishment, but our Constitution would never allow such punishments. It states in the eighth amendment, “Excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted,” (Martin and Jackson) which protects […]
Why the Death Penalty is Unjust
Capital punishment being either a justifiable law, or a horrendous, unjust act can be determined based on the perspective of different worldviews. In a traditional Christian perspective, the word of God given to the world in The Holy Bible should only be abided by. The Holy Bible states that no man (or woman) should shed the blood of another man (or woman). Christians are taught to teach a greater amount of sacrifice for the sake of the Lord. Social justice […]
The Use of Capital Punishment
Capital Punishment is when a person is legally punished for a crime by death. This is a subject that is very controversial and people tend to have a strong opinion of support or opposition on the topic. I support capital punishment for what I believe are many logical and sound reasons. Capital punishment is the most equal discipline for a person who commits murder. Putting someone to death for a terrible crime makes other criminals think twice of doing the […]
Redemption and Capital Punishment
In 2005, a man named Stanley Tookie Williams was sentenced to death by the State of California after being convicted of murdering four people. While waiting for his execution, Williams attempted to make amends by writing children’s books that warned about the dangers of gangs and violence. Because of these acts, many people believed that Williams’ sentence should be reduced to life in prison. The governor of California, Arnold Schwarzenegger, did not believe he truly regretted his actions, due to […]
The Debate of the Death Penalty
Capital punishment is a moral issue that is often scrutinized due to the taking of someone’s life. This is in large part because of the views many have toward the rule of law or an acceptance to the status quo. In order to get a true scope of the death penalty, it is best to address potential biases from a particular ethical viewpoint. By looking at it from several theories of punishment, selecting the most viable theory makes it a […]
My Opinion on the Capital Punishment
I believe the laws of the death penalty can go both ways as of why it should be loosened but retained for serial killers. I think the death penalty should be banned because it's not the best way to punish killers because it doesn’t reduce the crime rate. Not only does it not reduce crime rate but it also isn’t equal throughout the United States because only twenty states have abolished capital punishment. The death penalty cost the United States […]
The Inclusion of Capital Punishment through History
The inclusion of capital punishment as a penalty for criminal behavior has existed from the beginning of civilized society. The practice came to the United States with the first immigrants, was not excluded by the framers of the constitution, and continues to be a form of criminal punishment in thirty states, as well as the United States Government and Military. Despite its long history, capital punishment is controversial because of its extreme nature. As the American population has grown and […]
Should Capital Punishment be Allow in Modern Society
America faces an ethically instilled dilemma on whether or not a convicted criminal of a serious crime should face the ending of his or her life as punishment. Many people argue that this form of compensation is unethical, while others believe that the punishment is justified. This immensely controversial topic leads to many states outlawing the punishment completely, while others severely restrict its boundaries. On the other hand, some legislatures are completely for the punishment. There are two distinct ways […]
The Idea of Capital Punishment
While punishing crimes by death may seem outlandish to most, capital punishment, better known as the death penalty, is still legal in the majority of our states to this day. Surprisingly, studies show that the majority of citizens in the United States still support capital punishment. In my opinion, I believe that the death penalty should be abolished in all states for three reasons: the morals of using such an extreme punishment, the risk of an unfair judgement, and the […]
The Solution to the Death Penalty
There has never been a time when the United States of America was free from criminals indulging in killing, stealing, exploiting people, and even selling illegal items. Naturally, America refuses to tolerate the crimes committed by those who view themselves as above the law. Once these convicts are apprehended, they are brought to justice. In the past, these criminals often faced an ultimate punishment: the death penalty. Mercy was a foreign concept due to their underdeveloped understanding of the value […]
Texas Capital Punishment
The death penalty has existed for centuries. Ancient societies like the Romans to modern day Texans have had their hands filled with this idea. The difference is the methods used to execute its victims; ranging from disturbing impalements to painless deaths by injection. Texas has had its own history of methods, electric chairs, gas chambers, firing squad, death by hanging and now by lethal injection. The question of whether these methods have caused a decrease in crime in the state […]
Corporal Punishment System
When Commiting a crime, there should be levels of seriousness towards it. Some people end up paying for crimes that they probably did not commit in the first place. There is a lot of debate going on about capital punishment, what is capital punishment? Capital punishment is for people who have committed a crime. No matter how little or big the crime is there is always a punishment and this is one of them. Criminals are now walking and surround […]
Why Capital Punishment is Cruel: Argumenatation
Death penalty, or capital punishment, are means of legal punishment that have been continuously analyzed and argued. Some serious criminal offenses are punishable by death (most often violent homicides where the jury determines that the convicted offender lacks remorse). Capital punishment remains controversial and has been outlawed in many countries. Many countries also still allow the death penalty under certain circumstances/when a certain crime is committed. Many states in the United States still allow capital punishment. The majority of the […]
The Abolishment of Capital Punishment
Dating back to the 18th century, the death penalty was a punishment used by many across the world. Currently, the death penalty is legal in 30 states (Gramlich). Since 1976, 1,483 people have been killed as a punishment for their crimes in the United States (Death Penalty Info). The act of killing a human as punishment for a crime that has been committed is justified in a number of ways. One of the main reasons being that if the crime […]
Pro-Death Penalty Argumentation
The death penalty should be considered an essential legal measure since it deters potential criminals. During a presidential debate in 2000, George W. Bush defended the death penalty as ethically and legally acceptable. It guarantees that lawbreakers are punished in a way that contributes to the overall decrease in crime rates. According to Immanuel Kant, a deontologist, governments should adopt laws that penalize individuals who take the lives of others (Chapple et al.). When someone is slain, the killer gets […]
Time to Say Goodbye to Capital Punishment
On May 18, 2017, My aunt, Ebony Archie left her car running to go inside a Kroger grocery store. She went inside the store to get my 6-year-old little cousin, Kingston cupcakes for his graduation from the kindergarten ceremony that was the next day. Kingston was fast asleep on the back seat so she figured why need leave him there since it was a quick stop. While my aunt entered the store there were 3 teenage boys sitting in their […]
Capital Punishment in the State of California
Along with costly trials and imprisonments comes the possibility of wrongfully executing an innocent human being – something of which has unfortunately occurred after past death sentence trials. A wrongful execution can stem anywhere from: inadequate legal representation, police and prosecutorial misconduct to mistaken eyewitness testimonies and racial prejudice or community/political pressures to solve a case. “According to a sweeping new statistical analysis, … the rate of wrongful death sentences in the U.S. is much higher than experts have estimated” […]
Capital Punishment or Permanent Punishment
No two people have the same list of beliefs and opinions. Good luck trying to venture out into the world trying to figure out this complex mind game. Politicians have a 0% chance of having the same views. With, every person does not see eye too eye on literally everything. A debacle that has been expressed year after year between the states, federal government, and even other countries have battled back and forth over this issue. What is the issue […]
Why Capital Punishment is Cruel and Regressive
Capital Punishment is the legally authorized killing someone for committing a heinous crime. This form of punishment is very flawed and should be outlawed for the following reasons: The Death Penalty Models the Behavior it Seeks to Prevent, The death penalty is incompatible with human rights and human dignity/ There is no humane way to kill, The risk of executing innocent people exists in any justice system, and there has been numerous amounts of cases to make Capital Punishment unconstitutional […]
Inappropriate Behavior
The discrimination in the United States that was based on color, religion and race was brought to an end by the Civil Rights Act of 1964 that was amended and given powers to help in the distribution of facilities equally to the citizens. The powers were to help in the reinforcement of the law to help protect the employers from all ways of being discriminated. What civil rights may prohibit Marwan’s conduct with his co-worker? Do those laws apply to […]
Capital Punishment Crime Deterrence
Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Beginning of Capital Punishment The death penalty, also know as capital punishment, is where a criminal is put to death by a governing authority. Capital punishment has been used since ancient times. The earliest sign of capital punishment dates back to the eighteenth century BCE. In ancient Babylon, Greece and Asia capital punishment was used for crimes such as property damage, theft and practicing magic. A code of vengeance between tribal groups, known as the vendetta […]
Crime and Punishment: Women Mental Health in Prison
An unsafe living environment is a risk factor for many future crimes, as young women who run away from home to avoid abuse are more likely to get involved in drug distribution, prostitution and property crime (DeHart, 2008). Drug distribution, prostitution and property crime (such as robbery and theft) become their only source of fast and reliable income while substance abuse is an unfortunate and tragic by-product of the drug trade, as many women self-medicate in an attempt to cope […]
Capital Punishment is Morally Indefensible
The story of one of the most horrific hate crimes of our day came to an end this past Thursday. Or did it? Capital punishment also termed punishment by death was used on John William King by lethal injection for the murder of James Byrd Jr. The family however shared with CNN news reporters as they watched their brother’s murderer be executed, “they believe this was a just punishment, however, they felt nothing, there was no sense of relief."" Understandably […]
Additional Example Essays
- Mental Illness and Gun Control
- War On Drugs and Mass Incarceration
- A Debate on whether Graffiti Is a Form of Art or an Act of Vandalism
- The Negative Impacts of the War on Drugs
- Why Youth Join Gangs?
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
ReviseSociology
A level sociology revision – education, families, research methods, crime and deviance and more!
Sociological Perspectives on Punishment
Last Updated on February 9, 2017 by
One way of controlling and reducing crime is to punish offenders. Given that punishment typically involves restricting people’s freedom and sometimes inflicting harm on people, it requires some justification as a strategy for crime control. Two main justifications exist for punishment: Crime reduction and retribution . These methods link to different penal policies.
One justification for punishing offenders is that it prevents future crimes. This can be done through:
Deterrence – Punishing the individual discourages them from future offending – and others through making an example of them. This relates to Durkheim’s Functionalist Theory that crime and punishment reinforce social regulation , where prison sentence for a crime committed reaffirms the boundaries of acceptable behaviour.
Rehabilitation – The aim is to change offenders’ behaviour through education so they can earn an ‘honest living’ on release
Incapacitation – Removing the capacity for offenders to re-offend through long term prison sentences, cutting of hands, chemical castration or the death penalty.
Retribution
Reducing crime is not the only function of punishment, it also performs a straightforward ‘retributive function’ – in which the criminal is simply punished for harming another person, and the victim gets a sense of satisfaction that the criminal is ‘paying for their crime. This is an expressive rather than an instrumental view of punishment – it expresses society’s outrage at the crime.
Left Realism
Left realists believe that prison alone is an ineffective method at reducing crime. They believe it needs to be combined with the practice of restorative justice …which involves the offender actively doing something to make up for the harm done as a result of their crime. This may involve measures such as reparation, (paying back) mediation, (offender meeting victim) reintegrative ‘shaming’, (facing offenders with the consequences of their actions and family conferencing which seeks to bring offender, victim and members of the community into some form of dialogue and ‘healing’ process. All this is very unlike the anonymous processing and exclusionist shaming of the courts and prison sentences.
Home office research suggests meeting the offender benefits 80% of victims who choose to participate. For some victims it is about forgiveness – letting go of anger in order to move on with their lives. But for many, meeting the offender is about confronting them with the real impact of their crime, asking the questions that never get answered in court, and the hope that – for some offenders at least – understanding the impact of their actions might help to prevent them reoffending.
The research evidence on RJ is stronger than for almost any other criminal justice intervention. Research using randomised control trials ( Home Office/Ministry of Justice seven-year, £7m evaluation of the impact of RJ ) has found that offenders who met their victim compared to those who did not, the frequency of reoffending fell by 27% (ie 27% less crime after RJ). However, at present fewer than 1% of victims of crime have access to a restorative justice process. ( http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/2010/sep/17/restorative-justice-cuts-crime )
According to the Marxist Sociologist David Gordon prison benefits the Capitalist system in three major ways:
- The imprisonment of selected members of the lower classes neutralises opposition to the system, keeping potential revolutionaries from forming together and taking political action.
- The imprisonment of many members of the underclass also sweeps out of sight the ‘worst jetsam of Capitalist society’ such that we cannot see it
- By punishing individuals and making them responsible for their actions, defining these individuals as ‘social failures’ we ignore the failings of the system that lead to the conditions of inequality and poverty that create the conditions which lead to crime. Our attention is diverted away from the immorality and greed of the elite classes.
NB – We are not talking about small numbers here – Focussing on the USA, David Garland argues that we have entered the era of mass incarceration. Approximately 2.3 million people are in jail in the US (about 750/100 000)
Focusing on the UK, the prison population has doubled since 1993 from approximately 40 000 to nearly 90 000 today.
There is evidence to support the Marxist view that it is mainly the marginalised who end up in jail – Looking at stats on prisoners we find that…
• 10% of men and 30% of women have had a previous psychiatric admission to hospital before they come into prison.
• 48% of all prisoners are at, or below, the level expected of an 11 year old in reading, 65% in numeracy and 82% in writing.
• 71% of children in custody have been involved with, or in the care of, social services before entering custody.
NB2 – While Right Realists would claim that locking more people up is a causal factor in the crime rate going down over the last two decades, this claim is challenged. This correlation may be a coincidence – other factors (such as abortion and the rise of ICT meaning more people stay indoors) may also play a role in this).
Interactionism
Once a person is labelled as deviant, it is extremely difficult to remove that label. The deviant person becomes stigmatised as a criminal or deviant and is likely to be considered, and treated, as untrustworthy by others. The deviant individual is then likely to accept the label that has been attached, seeing himself or herself as deviant, and act in a way that fulfils the expectations of that label. Even if the labelled individual does not commit any further deviant acts than the one that caused them to be labelled, getting rid of that label can be very hard and time-consuming. For example, it is usually very difficult for a convicted criminal to find employment after release from prison because of their label as ex-criminal. They have been formally and publicly labelled a wrongdoer and are treated with suspicion likely for the remainder of their lives.
Total Institutions and The Mortification of the Self
Erving Goffman (1961) argued that places such as mental asylums, concentration camps and prisons function as ‘total institutions’ – places which are closed off to the outside world and where inmates’ lives come under the complete control of the institution.
According to Goffman, becoming an inmate in a total institution involves a process of “mortification of the self” – inmates are subjected to degrading and humiliating treatments designed to remove any trace of individual identity. For instance, personal clothing and items are confiscated, inmates are strip searched, their heads are shaved, and they are issued an ID number. The point of such treatment is to mark a clear separation between the inmates’ former selves and their institutional selves. Inmates are constantly under surveillance and they have no privacy. Minute behaviour is observed and assessed, and if necessary, sanctioned.
As a result of having every aspect of their daily lives controlled, inmates effectively lose the ability to construct their own identities and function independently. Rather than making sick people well, asylums make them more insane, and rather rehabilitating, prisons actually make prisoners more criminal.
Post and Late Modernism
In his classic text, entitled ‘discipline and punish’ Michel Foucault’s points out that punishment has changed from being very direct, immediate and physical – involving torture and sometimes death to being more focused on incarceration and rehabilitation. However, although punishment today may be less severe than in the past, the state has expanded its control over its citizens in more subtle ways and ‘invades’ our private lives much more than at it ever used to. This is especially true when you look at the way criminals are treated today. While prisoners are unlikely to be subjected to torture or death (unless you’re Muslim, black or stupid and live in Texas) they are subjected to an ever increasing array of what Foucault calls ‘technologies of surveillance’ – they are kept under surveillance programmes and are expected to reform their behaviour.
Prison is the most obvious example of this – with prisoners under (potential) constant surveillance, while those who avoid prison might have to subject themselves to being tagged, visit probation officers, or turn up to ‘rehabilitation classes’ (such as drug counselling or anger management) all of which involve surveillance and behavioural modification.
Foucault sees the growth of prison as a means of punishment as reflecting the move from sovereign power to disciplinary power – Sovereign power involves direct physical coercion to get people to obey the laws, and under this system punishments are carried out on people’s physical bodies – punishment is harsh – it is a spectacle.
Today, however, political and economic systems are maintained through ‘disciplinary power’ – power is exercised through surveillance – people change their behaviour because they know they are being watched. Prison seams more humane than physical punishment but in reality it is much more invasive as a means of social control.
NB – As with Marxism above, we are talking about huge numbers 7 million people (1/32 of the population) are either in jail, on probation or parole, and Garland uses the concept of Transcarceration to refer to this shift. Certain people move between various state institutions – from care – to prison – to mental hospital – throughout their whole lives, effectively being under constant surveillance by the state.
David Garland – The Punitive State and The Culture of Control
David Garland argues that there has been a relatively recent shift in attitudes towards punishment.
He argues that in the 1950s the state practised ‘penal welfarism’ – in which the criminal justice system did not just try to catch and punish offenders, but also tried to rehabilitate them, so that they could be reintigrated into society
However, since the 1950s individual freedoms have increased, while social bonds have weakened, life is more uncertain and less predictable, and (despite the fact that crime is now decreasing) the public are more worried about crime than ever.
As a result, the state has now abandoned ‘penal welfarism’, it is much less concerned with rehabilitation and reintegration of prisoners, it’s primary concern is now convincing the public that it is taking a tough approach on crime and reassuring communities that something is being done about crime.
Garland argues that we have now moved into a new era in which a ‘punitive state’ enforces a ‘culture of control’ – there are three main ways in which the state now seeks to control crime and punish offenders:
The state increasingly identifies potential groups who are at risk of offending at a young age and take early interventions. This links to the Actuarialism (risk management) strategy referred to in a previous topic.
The state locks increasing amounts of people up, Garland argues we have entered the era of ‘mass incarceration’ and ‘transcarceration’.
Politicians increasingly use the issue of crime control, and ‘being tough on crime’ as a means to win elections – in effect, crime control has become a political tool which politicians use to win power, rather than being about reducing crime perse.
Evaluations of Garland
This is an important contribution in that it draws our attention towards the ‘political nature of crime control – and it helps to explain the increasing prison populations and ‘transcacerated’ population even though crime has been decreasing for decades.
This is a rather cynical theory – Garland seems to be saying that politicians today simply use their ‘tough on crime’ approach to get votes and maintain power, rather than trying to do anything which will really address the underlying causes of crime. Is this really the case?
Michel Foucault would probably argue that this theory is too simplistic in terms of its understanding of political power – it diverts our attention away from other agencies of social control in preventing/ constructing deviance through surveillance.
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from ReviseSociology
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
Should the Death Penalty Be Abolished?
In its last six months, the United States government has put 13 prisoners to death. Do you think capital punishment should end?

By Nicole Daniels
Students in U.S. high schools can get free digital access to The New York Times until Sept. 1, 2021.
In July, the United States carried out its first federal execution in 17 years. Since then, the Trump administration has executed 13 inmates, more than three times as many as the federal government had in the previous six decades.
The death penalty has been abolished in 22 states and 106 countries, yet it is still legal at the federal level in the United States. Does your state or country allow the death penalty?
Do you believe governments should be allowed to execute people who have been convicted of crimes? Is it ever justified, such as for the most heinous crimes? Or are you universally opposed to capital punishment?
In “ ‘Expedited Spree of Executions’ Faced Little Supreme Court Scrutiny ,” Adam Liptak writes about the recent federal executions:
In 2015, a few months before he died, Justice Antonin Scalia said he w o uld not be surprised if the Supreme Court did away with the death penalty. These days, after President Trump’s appointment of three justices, liberal members of the court have lost all hope of abolishing capital punishment. In the face of an extraordinary run of federal executions over the past six months, they have been left to wonder whether the court is prepared to play any role in capital cases beyond hastening executions. Until July, there had been no federal executions in 17 years . Since then, the Trump administration has executed 13 inmates, more than three times as many as the federal government had put to death in the previous six decades.
The article goes on to explain that Justice Stephen G. Breyer issued a dissent on Friday as the Supreme Court cleared the way for the last execution of the Trump era, complaining that it had not sufficiently resolved legal questions that inmates had asked. The article continues:
If Justice Breyer sounded rueful, it was because he had just a few years ago held out hope that the court would reconsider the constitutionality of capital punishment. He had set out his arguments in a major dissent in 2015 , one that must have been on Justice Scalia’s mind when he made his comments a few months later. Justice Breyer wrote in that 46-page dissent that he considered it “highly likely that the death penalty violates the Eighth Amendment,” which bars cruel and unusual punishments. He said that death row exonerations were frequent, that death sentences were imposed arbitrarily and that the capital justice system was marred by racial discrimination. Justice Breyer added that there was little reason to think that the death penalty deterred crime and that long delays between sentences and executions might themselves violate the Eighth Amendment. Most of the country did not use the death penalty, he said, and the United States was an international outlier in embracing it. Justice Ginsburg, who died in September, had joined the dissent. The two other liberals — Justices Sotomayor and Elena Kagan — were undoubtedly sympathetic. And Justice Anthony M. Kennedy, who held the decisive vote in many closely divided cases until his retirement in 2018, had written the majority opinions in several 5-to-4 decisions that imposed limits on the death penalty, including ones barring the execution of juvenile offenders and people convicted of crimes other than murder .
In the July Opinion essay “ The Death Penalty Can Ensure ‘Justice Is Being Done,’ ” Jeffrey A. Rosen, then acting deputy attorney general, makes a legal case for capital punishment:
The death penalty is a difficult issue for many Americans on moral, religious and policy grounds. But as a legal issue, it is straightforward. The United States Constitution expressly contemplates “capital” crimes, and Congress has authorized the death penalty for serious federal offenses since President George Washington signed the Crimes Act of 1790. The American people have repeatedly ratified that decision, including through the Federal Death Penalty Act of 1994 signed by President Bill Clinton, the federal execution of Timothy McVeigh under President George W. Bush and the decision by President Barack Obama’s Justice Department to seek the death penalty against the Boston Marathon bomber and Dylann Roof.
Students, read the entire article , then tell us:
Do you support the use of capital punishment? Or do you think it should be abolished? Why?
Do you think the death penalty serves a necessary purpose, like deterring crime, providing relief for victims’ families or imparting justice? Or is capital punishment “cruel and unusual” and therefore prohibited by the Constitution? Is it morally wrong?
Are there alternatives to the death penalty that you think would be more appropriate? For example, is life in prison without the possibility of parole a sufficient sentence? Or is that still too harsh? What about restorative justice , an approach that “considers harm done and strives for agreement from all concerned — the victims, the offender and the community — on making amends”? What other ideas do you have?
Vast racial disparities in the administration of the death penalty have been found. For example, Black people are overrepresented on death row, and a recent study found that “defendants convicted of killing white victims were executed at a rate 17 times greater than those convicted of killing Black victims.” Does this information change or reinforce your opinion of capital punishment? How so?
The Federal Death Penalty Act prohibits the government from executing an inmate who is mentally disabled; however, in the recent executions of Corey Johnson , Alfred Bourgeois and Lisa Montgomery , their defense teams, families and others argued that they had intellectual disabilities. What role do you think disability or trauma history should play in how someone is punished, or rehabilitated, after committing a crime?
How concerned should we be about wrongfully convicted people being executed? The Innocence Project has proved the innocence of 18 people on death row who were exonerated by DNA testing. Do you have worries about the fair application of the death penalty, or about the possibility of the criminal justice system executing an innocent person?
About Student Opinion
• Find all of our Student Opinion questions in this column . • Have an idea for a Student Opinion question? Tell us about it . • Learn more about how to use our free daily writing prompts for remote learning .
Students 13 and older in the United States and the United Kingdom, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Nicole Daniels joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2019 after working in museum education, curriculum writing and bilingual education. More about Nicole Daniels

1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
Philosophy, One Thousand Words at a Time
Theories of Punishment
Author: Travis Joseph Rodgers Category: Ethics , Social and Political Philosophy Word Count: 995
Criminals are punished with fines, public scorn, imprisonment, death and more.
Philosophical theories of punishment ask what justifies punishment, both in general and what justifies particular punishments. Most theories appeal to punishment’s effects on the future or facts about the past .
This essay reviews these theories.

1. Forward-Looking Theories
According to forward-looking theories of punishment, punishments are justified to the extent that they bring about future good results. Theories differ in terms of what those results are.
1.1. Deterrence Theories
One goal of punishment is to bring about less crime. One way of doing this is by discouraging would-be criminals. Deterrence theories propose that punishments are justified to the degree to which they reduce, or deter , crime by preventing people from committing crimes or discouraging repeat offenses.
To understand how effective a punishment is as a deterrent, we consider the negative consequences for the criminal. If thieves are asked only to return stolen goods, that “punishment” is a very light consequence. Stealing might then be a good gamble: if a thief succeeds, she gets the items; if she is caught, she simply returns them. Fines or imprisonment provides a more effective deterrent and a stronger incentive to not steal.
A punishment’s deterrent force results from the severity of the penalty and the likelihood of punishment. More severe punishments and more effective means of catching and prosecuting criminals increase a punishment’s deterrent effect.
1.2. Rehabilitation Theories
Rather than focusing on reducing crime, rehabilitation theories of punishment focus on making criminals into people who are less likely to commit crimes. [1]
Consider two purse thieves. One steals for excitement. Another steals because of a lack of legitimate job opportunities and a lack of food: this thief feels bad about snatching purses but, nonetheless, he steals.
In the first case, rehabilitation theorists urge trying to improve the person’s character and values. In the second, mandatory job training or education could be part of the punishment. Rehabilitation is often attempted using education, training, medication, and therapy.
1.3. Concerns about Forward-Looking Theories
All forward-looking theories must specify what resources can be used to bring about the desired results. Costly punishments like the death penalty and life imprisonment might be justified if they effectively realize whatever goods the theory aims at: e.g., killing some criminals could most improve the world on some views, and since some wrongdoers might be incapable of rehabilitation, permanently removing them from society might be best. [2]
A problem for forward-looking theories is that the punishments recommended might not seem “proportional” to the crime. Serious crimes might call for light punishments if recidivism – repeat criminal offenses – is unlikely; light crimes might call for brutal punishments if that effectively reduces them. [3] Subjecting criminals, or even innocent people, to extreme punishments to “send a message” or deter others from committing crimes is another potential problem for forward-looking theories. [4]
2. Backward-Looking Theories
Backward-looking theories identify the justification for punishment in some fact about how the to-be punished crime was committed.
Most theories seek a punishment “proportional to” or “fitting” the crime. Retributivist theories see punishment as a “paying back” for the crime committed. Restorative theories seek to return the victim’s status to what it was prior to the crime. Both theories look “backward” to the crime itself to determine an appropriate punishment: retributivists focus on doing harm to the wrongdoer; restorative theories focus on doing good to the crime victim.

2.1. Retributivist Theories
An influential example of retributivism is the lex talionis (the law of retaliation), the view that the crime is to be revisited upon the perpetrator of the crime: we should “reap what we sow.” [5] So, thieves should be deprived of their property, murders should forfeit their own life, and so on.
On this view, punishment is not intended to make the world a better place, to reduce criminality, or to improve the perpetrator. [6] These may sometimes happen, and these may be further goods, but the justification for the punishment is simply that it is what the criminal deserves . That such theories do not aim at making the world an overall better place is sometimes a point of criticism of the theory. Why punish, some ask, if it serves no broader good? One reply is that people, especially criminals, getting what they deserve is its own good.
Some potential problems for retributivism include that some crimes are incapable of being paid back in full: e.g., a mass murderer can be killed only once; a criminal might destroy a unique artifact that no punishment can restore. In other cases, paying the person back with a similar punishment seems morally abhorrent, as in the case of sexual assault.
2.2. Restorative Theories
A second backward-looking theory suggests that the justification for punishment is not to inflict suffering on someone or to create an overall better world but to restore those who were harmed by the crime.
This restorative theory of punishment is backward-looking in that it targets the victim’s situation prior to the crime, by forcing the wrongdoer to help the victim. [7] A punishment, which the wrongdoer is forced to do, is justified to the extent that it restores victims to their standing prior to the crime, e.g., their mental and/or physical state, property restoration, and so on. This may seem more compassionate than retributivism since the goal of these punishments is to make the victim better off, comparatively, and thus the world a better place. [8]
Restorative justice faces a similar retributivist problem of fully “restoring” someone. Some losses cannot be restored (e.g., the losses to murder victims loved ones), and sometimes restoring the harmed individual would require seemingly unjustified offenses (e.g., enslaving a criminal to the victim until a theft is paid back). [9]
3. Conclusion
Some of the elements of these theories of punishment can be combined. We might recommend rehabilitation when possible and deterrence when not possible. We might also recommend restoration in addition to retribution. And forward-looking and backward-looking elements might be balanced against one another, to decrease crime while giving no more punishment than deserved. [10]
[1] An important question about whether a punishment is justified is whether the proposed punishment would be just or unjust . Thus, questions about the justification for punishment lead to fundamental questions about justice in general.
[2] Mill (1868) argues in favor of the death penalty only in cases where rehabilitation is not possible, for instance.
[3] Murray Rothbard (1998) defends a backward-looking, retributivist theory of punishment and challenges forward-looking theories on these and other grounds.
[4] Punishing innocents to decrease criminality in others is often called telishment rather than punishment.
[5] Douglas Husak (1992), Immanuel Kant (1887), and Christopher Heath Wellman (2012) discuss slightly different versions of this kind of theory.
[6] Indeed, Kant (1887) notoriously argues that those who murder must die, and that a society has a duty to execute those who have committed murder, regardless of the consequences for the society.
[7] Murray Rothbard’s (1998) writing in economics explains the “victim’s situation” as their rights. In other words, you must compensate (or restore) a victim for any right you violate.
[8] Some proponents consider restorative justice an alternative to punishment, but note that like other views of punishment, restorative justice involves some “hard treatment” of the wrongdoer and serves to protect rights of individuals and order in society.
[9] Roderick Long, a proponent of restorative justice, raises and attempts to address some of these concerns.
[10] This article focuses on theories of criminal punishment, but these same theory types can be applied to non-criminal cases of punishment as well. For instance, we might view “making a good person” as a desirable future state and then justify punishing a child to the extent that that punishment does the best job of making the child a good or better person. And we might think that boycotting a business owned by a bigot is giving it exactly what it deserves.
Husak, Douglas. 1992. “Why Punish the Deserving.” Nous 26 (4): 447-464.
Kant, Immanuel. 1887. The Philosophy of Law: An Exposition of the Fundamental Principles of Jurisprudence as the Science of Right, trans. W. Hastie (Edinburgh).
Long, Roderick. 1993-94. “Punishment vs. Restitution: A Formulation.” Formulations .
Mill, John Stuart. 1988. “Speech in Favor of Capital Punishment 1868.” The Collected Works of John Stuart Mill, Vol. XXVIII.: Public and Parliamentary Speeches. Eds. John M. Robson and Bruce Kinzer. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1988. pp. 266-273.
Rothbard, Murray. 1998. “Punishment and Proportionality . ” New York University Press, (2 nd edition with an introduction by Hans-Hermann Hoppe); originally published Atlantic Highlands, NJ: Humanities Press, 1982.
Wellman, Christopher Heath. 2012 . “The Rights Forfeiture Theory of Punishment”, Ethics , 122: 371–393.
For Further Reading
Boonin, David. 2008. The Problem of Punishment . Cambridge University Press.
Hart, H.L.A. 1968. Punishment and Responsibility. Oxford University Press.
Related Essays
The Death Penalty by Benjamin S. Yost
Praise and Blame by Daniel Miller
Introduction to Consequentialism by Shane Gronholz
Introduction to Deontology: Kantian Ethics by Andrew Chapman
John Rawls’ ‘A Theory of Justice’ by Ben Davies
Social Contract Theory by David Antonini
Philosophy of Law: An Overview by Mark Satta
Moral Luck by Jonathan Spelman
Hell and Universalism by A.G. Holdier
Pascal’s Wager: A Pragmatic Argument for Belief in God by Liz Jackson
PDF Download
Download this essay in PDF .
About the Author
Travis Joseph Rodgers is Professor of Humanities at Valencia College in Orlando, Florida. He received his Ph.D. in philosophy from Florida State University. His specialties are ethics and ancient philosophy. His research focuses on the question of political legitimacy – that is, under what conditions governments might be justified in forcing someone to do something, applied ethics, and ethical theory. valenciacollege.academia.edu/TravisRodgers
Follow 1000-Word Philosophy on Facebook and Twitter and subscribe to receive email notifications of new essays at 1000WordPhilosophy.com
Share this:, 14 thoughts on “ theories of punishment ”.
- Pingback: Cultural Relativism: Do Cultural Norms Make Actions Right and Wrong? – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Philosophy of Law: An Overview – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Just War Theory – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Pascal’s Wager: A Pragmatic Argument for Belief in God – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Moral Luck – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Free Speech – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Ethics: A Collection of Online Resources and Key Quotes - The Daily Idea
- Pingback: Free Will and Moral Responsibility – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Free Will and Free Choice – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Ethics: A Collection of Online Resources and Key Quotes | The Daily Idea
- Pingback: Hell and Universalism – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Political Philosophy: A Collection of Online Resources and Key Quotes – The Daily Idea
- Pingback: The Death Penalty – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update - Daily Nous
Comments are closed.
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

Punishment and Responsibility: Essays in the Philosophy of Law (2nd edn)
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This classic collection of essays, first published in 1968, has had an enduring impact on academic and public debates about criminal responsibility and criminal punishment. Forty years on, its arguments are as powerful as ever. H. L. A. Hart offers an alternative to retributive thinking about criminal punishment that nevertheless preserves the central distinction between guilt and innocence. He also provides an account of criminal responsibility that links the distinction between guilt and innocence closely to the ideal of the rule of law, and thereby attempts to by-pass unnerving debates about free will and determinism. Always engaged with live issues of law and public policy, Hart makes difficult philosophical puzzles accessible and immediate to a wide range of readers. For this new edition, otherwise a reproduction of the original, John Gardner adds an introduction, which provides a critical engagement with the book's main arguments, and explains the continuing importance of Hart's ideas in spite of the intervening revival of retributive thinking in both academic and policy circles. Unavailable for ten years, the new edition of Punishment and Responsibility makes available again the central text in the field for a new generation of academics, students and professionals engaged in criminal justice and penal policy.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Home — Essay Samples — Law, Crime & Punishment — Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice — Punishment
Essays on Punishment
Compare and contrast punishment and sentencing, juvenile punishment, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
The Four Goals of Punishment
Punishment and rehabilitation in the us: researching their efficiency, rehabilitation of offenders instead of punishment: less eligibility argument, the effectiveness of rehabilitation vs harsh punishment, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
"Frederick Clegg is a Failed Man": Punishments in The Collector
Props, scenery, and punishment in sartre’s no exit, what forms a punishment should take: theoretical analysis, the unethical nature of death penalty: an argumentative perspective, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Why Registering Young Children as Sex Offenders is not a Sollution
Corporal punishment and violent discipline, the influence of corporal punishment on a child, why i support the death penalty in special cases, the greek mythology of the sphinx, discussion of whether juveniles should be tried as adults, an overview of history and definition of mob lynching, critical analysis of the effectiveness of the juvenile justice system, effects of correctional policies and practices in relation to sex offenders, gun violence, perspectives on adolescent sex offender registration policies, how strain leads to crime, personal review of the article regarding to raising the age of responsibility, the threat of organized retail crime and active shooters , the need for strict legal punishment for animal abandonment, ending corporal punishment at school in india, corporal punishment must be abolished, the principle that punishment should fit the crime, ingraham v wright case: a critical analysis, relevant topics.
- Mass Incarceration
- Juvenile Delinquency
- Juvenile Justice System
- Criminal Behavior
- Forensic Science
- Criminology
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Profiling
- Criminal Investigation
- Criminal Justice
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Crime and Punishment, Essay Example
Pages: 1
Words: 301
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Crime is a violent act with an aim of hurting other individual. The aim of a crime is to destabilize the peace and tranquillity of the society. There are various aspects that make up a crime. They include:
- The nature of the crime
- The motive of the crime
- Whether the culprit was caught or not
- The punishment
- The reason of the punishment
- The effectiveness of the punishment
The above aspects are vital in understanding crime and punishment. Crime has origin like any other thing in existence. There are theories that have been brought up to understand crime with an aim of stopping it. These criminals behaviour are known to have been triggered by something to do these acts of violence. There are some French and Italian thinkers who have come up with various schools of thought to understand crime and the motives behind them. These thinkers have been able to understand the minds of criminals. Understanding the minds of the criminals can lead to early prevention of crime (Tonry, 2000).
The punishment for the crimes is something that has evolved through the ages. The punishment was meant to change the behaviour of the perpetrator and was to be fitting to the crime. This is something that initially brought up a lot of problems since the perpetrators came out not reformed. It is something that has changed over the ages as various reformers have come up to change the status quo. These reformers made a significant difference and the change was positive. The main reason for punishment is being achieved now. This is now up for debate since change comes from an individual choice to change their habit and behaviour ( Dostoevsky, 2004).
Tonry H. Michael . (2000). The Handbook of Crime & Punishment . Foster City, CA: Oxford University press.
Dostoevsky F. (2004). Crime and Punishment Enriched Classics . Kentucky: Simon and Schuster.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Elected Representative Letter, Research Paper Example
Synthetic Biology, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

An Essay on Crimes and Punishments
- Cesare Bonesana di Beccaria (author)
- Voltaire (author)
An extremely influential Enlightenment treatise on legal reform in which Beccaria advocates the ending of torture and the death penalty. The book also contains a lengthy commentary by Voltaire which is an indication of high highly French enlightened thinkers regarded the work.
- EBook PDF This text-based PDF or EBook was created from the HTML version of this book and is part of the Portable Library of Liberty.
- ePub ePub standard file for your iPad or any e-reader compatible with that format
- Facsimile PDF This is a facsimile or image-based PDF made from scans of the original book.
- Kindle This is an E-book formatted for Amazon Kindle devices.
An Essay on Crimes and Punishments. By the Marquis Beccaria of Milan. With a Commentary by M. de Voltaire. A New Edition Corrected. (Albany: W.C. Little & Co., 1872).
The text is in the public domain.
- United States
Related Collections:
Excerpts from
An essay on crimes and punishments, by cesare beccaria translated from the italian, 1775 (original published in 1764), introduction, chapter i: of the origin of punishments, chapter ii: of the right to punish, chapter vi: of the proportion between crimes and punishments, chapter xii: of the intent of punishments, chapter xix: of the advantage of immediate punishment, chapter xxvii: of the mildness of punishments.

Arguments for and Against the Death Penalty
Click the buttons below to view arguments and testimony on each topic.
The death penalty deters future murders.
Society has always used punishment to discourage would-be criminals from unlawful action. Since society has the highest interest in preventing murder, it should use the strongest punishment available to deter murder, and that is the death penalty. If murderers are sentenced to death and executed, potential murderers will think twice before killing for fear of losing their own life.
For years, criminologists analyzed murder rates to see if they fluctuated with the likelihood of convicted murderers being executed, but the results were inconclusive. Then in 1973 Isaac Ehrlich employed a new kind of analysis which produced results showing that for every inmate who was executed, 7 lives were spared because others were deterred from committing murder. Similar results have been produced by disciples of Ehrlich in follow-up studies.
Moreover, even if some studies regarding deterrence are inconclusive, that is only because the death penalty is rarely used and takes years before an execution is actually carried out. Punishments which are swift and sure are the best deterrent. The fact that some states or countries which do not use the death penalty have lower murder rates than jurisdictions which do is not evidence of the failure of deterrence. States with high murder rates would have even higher rates if they did not use the death penalty.
Ernest van den Haag, a Professor of Jurisprudence at Fordham University who has studied the question of deterrence closely, wrote: “Even though statistical demonstrations are not conclusive, and perhaps cannot be, capital punishment is likely to deter more than other punishments because people fear death more than anything else. They fear most death deliberately inflicted by law and scheduled by the courts. Whatever people fear most is likely to deter most. Hence, the threat of the death penalty may deter some murderers who otherwise might not have been deterred. And surely the death penalty is the only penalty that could deter prisoners already serving a life sentence and tempted to kill a guard, or offenders about to be arrested and facing a life sentence. Perhaps they will not be deterred. But they would certainly not be deterred by anything else. We owe all the protection we can give to law enforcers exposed to special risks.”
Finally, the death penalty certainly “deters” the murderer who is executed. Strictly speaking, this is a form of incapacitation, similar to the way a robber put in prison is prevented from robbing on the streets. Vicious murderers must be killed to prevent them from murdering again, either in prison, or in society if they should get out. Both as a deterrent and as a form of permanent incapacitation, the death penalty helps to prevent future crime.
Those who believe that deterrence justifies the execution of certain offenders bear the burden of proving that the death penalty is a deterrent. The overwhelming conclusion from years of deterrence studies is that the death penalty is, at best, no more of a deterrent than a sentence of life in prison. The Ehrlich studies have been widely discredited. In fact, some criminologists, such as William Bowers of Northeastern University, maintain that the death penalty has the opposite effect: that is, society is brutalized by the use of the death penalty, and this increases the likelihood of more murder. Even most supporters of the death penalty now place little or no weight on deterrence as a serious justification for its continued use.
States in the United States that do not employ the death penalty generally have lower murder rates than states that do. The same is true when the U.S. is compared to countries similar to it. The U.S., with the death penalty, has a higher murder rate than the countries of Europe or Canada, which do not use the death penalty.
The death penalty is not a deterrent because most people who commit murders either do not expect to be caught or do not carefully weigh the differences between a possible execution and life in prison before they act. Frequently, murders are committed in moments of passion or anger, or by criminals who are substance abusers and acted impulsively. As someone who presided over many of Texas’s executions, former Texas Attorney General Jim Mattox has remarked, “It is my own experience that those executed in Texas were not deterred by the existence of the death penalty law. I think in most cases you’ll find that the murder was committed under severe drug and alcohol abuse.”
There is no conclusive proof that the death penalty acts as a better deterrent than the threat of life imprisonment. A 2012 report released by the prestigious National Research Council of the National Academies and based on a review of more than three decades of research, concluded that studies claiming a deterrent effect on murder rates from the death penalty are fundamentally flawed. A survey of the former and present presidents of the country’s top academic criminological societies found that 84% of these experts rejected the notion that research had demonstrated any deterrent effect from the death penalty .
Once in prison, those serving life sentences often settle into a routine and are less of a threat to commit violence than other prisoners. Moreover, most states now have a sentence of life without parole. Prisoners who are given this sentence will never be released. Thus, the safety of society can be assured without using the death penalty.
Ernest van den Haag Professor of Jurisprudence and Public Policy, Fordham University. Excerpts from ” The Ultimate Punishment: A Defense,” (Harvard Law Review Association, 1986)
“Execution of those who have committed heinous murders may deter only one murder per year. If it does, it seems quite warranted. It is also the only fitting retribution for murder I can think of.”
“Most abolitionists acknowledge that they would continue to favor abolition even if the death penalty were shown to deter more murders than alternatives could deter. Abolitionists appear to value the life of a convicted murderer or, at least, his non-execution, more highly than they value the lives of the innocent victims who might be spared by deterring prospective murderers.
Deterrence is not altogether decisive for me either. I would favor retention of the death penalty as retribution even if it were shown that the threat of execution could not deter prospective murderers not already deterred by the threat of imprisonment. Still, I believe the death penalty, because of its finality, is more feared than imprisonment, and deters some prospective murderers not deterred by the thought of imprisonment. Sparing the lives of even a few prospective victims by deterring their murderers is more important than preserving the lives of convicted murderers because of the possibility, or even the probability, that executing them would not deter others. Whereas the life of the victims who might be saved are valuable, that of the murderer has only negative value, because of his crime. Surely the criminal law is meant to protect the lives of potential victims in preference to those of actual murderers.”
“We threaten punishments in order to deter crime. We impose them not only to make the threats credible but also as retribution (justice) for the crimes that were not deterred. Threats and punishments are necessary to deter and deterrence is a sufficient practical justification for them. Retribution is an independent moral justification. Although penalties can be unwise, repulsive, or inappropriate, and those punished can be pitiable, in a sense the infliction of legal punishment on a guilty person cannot be unjust. By committing the crime, the criminal volunteered to assume the risk of receiving a legal punishment that he could have avoided by not committing the crime. The punishment he suffers is the punishment he voluntarily risked suffering and, therefore, it is no more unjust to him than any other event for which one knowingly volunteers to assume the risk. Thus, the death penalty cannot be unjust to the guilty criminal.”
Full text can be found at PBS.org .
Hugo Adam Bedau (deceased) Austin Fletcher Professor of Philosophy, Tufts University Excerpts from “The Case Against The Death Penalty” (Copyright 1997, American Civil Liberties Union)
“Persons who commit murder and other crimes of personal violence either may or may not premeditate their crimes.
When crime is planned, the criminal ordinarily concentrates on escaping detection, arrest, and conviction. The threat of even the severest punishment will not discourage those who expect to escape detection and arrest. It is impossible to imagine how the threat of any punishment could prevent a crime that is not premeditated….
Most capital crimes are committed in the heat of the moment. Most capital crimes are committed during moments of great emotional stress or under the influence of drugs or alcohol, when logical thinking has been suspended. In such cases, violence is inflicted by persons heedless of the consequences to themselves as well as to others….
If, however, severe punishment can deter crime, then long-term imprisonment is severe enough to deter any rational person from committing a violent crime.
The vast preponderance of the evidence shows that the death penalty is no more effective than imprisonment in deterring murder and that it may even be an incitement to criminal violence. Death-penalty states as a group do not have lower rates of criminal homicide than non-death-penalty states….
On-duty police officers do not suffer a higher rate of criminal assault and homicide in abolitionist states than they do in death-penalty states. Between l973 and l984, for example, lethal assaults against police were not significantly more, or less, frequent in abolitionist states than in death-penalty states. There is ‘no support for the view that the death penalty provides a more effective deterrent to police homicides than alternative sanctions. Not for a single year was evidence found that police are safer in jurisdictions that provide for capital punishment.’ (Bailey and Peterson, Criminology (1987))
Prisoners and prison personnel do not suffer a higher rate of criminal assault and homicide from life-term prisoners in abolition states than they do in death-penalty states. Between 1992 and 1995, 176 inmates were murdered by other prisoners; the vast majority (84%) were killed in death penalty jurisdictions. During the same period about 2% of all assaults on prison staff were committed by inmates in abolition jurisdictions. Evidently, the threat of the death penalty ‘does not even exert an incremental deterrent effect over the threat of a lesser punishment in the abolitionist states.’ (Wolfson, in Bedau, ed., The Death Penalty in America, 3rd ed. (1982))
Actual experience thus establishes beyond a reasonable doubt that the death penalty does not deter murder. No comparable body of evidence contradicts that conclusion.”
Click here for the full text from the ACLU website.
Retribution
A just society requires the taking of a life for a life.
When someone takes a life, the balance of justice is disturbed. Unless that balance is restored, society succumbs to a rule of violence. Only the taking of the murderer’s life restores the balance and allows society to show convincingly that murder is an intolerable crime which will be punished in kind.
Retribution has its basis in religious values, which have historically maintained that it is proper to take an “eye for an eye” and a life for a life.
Although the victim and the victim’s family cannot be restored to the status which preceded the murder, at least an execution brings closure to the murderer’s crime (and closure to the ordeal for the victim’s family) and ensures that the murderer will create no more victims.
For the most cruel and heinous crimes, the ones for which the death penalty is applied, offenders deserve the worst punishment under our system of law, and that is the death penalty. Any lesser punishment would undermine the value society places on protecting lives.
Robert Macy, District Attorney of Oklahoma City, described his concept of the need for retribution in one case: “In 1991, a young mother was rendered helpless and made to watch as her baby was executed. The mother was then mutilated and killed. The killer should not lie in some prison with three meals a day, clean sheets, cable TV, family visits and endless appeals. For justice to prevail, some killers just need to die.”
Retribution is another word for revenge. Although our first instinct may be to inflict immediate pain on someone who wrongs us, the standards of a mature society demand a more measured response.
The emotional impulse for revenge is not a sufficient justification for invoking a system of capital punishment, with all its accompanying problems and risks. Our laws and criminal justice system should lead us to higher principles that demonstrate a complete respect for life, even the life of a murderer. Encouraging our basest motives of revenge, which ends in another killing, extends the chain of violence. Allowing executions sanctions killing as a form of ‘pay-back.’
Many victims’ families denounce the use of the death penalty. Using an execution to try to right the wrong of their loss is an affront to them and only causes more pain. For example, Bud Welch’s daughter, Julie, was killed in the Oklahoma City bombing in 1995. Although his first reaction was to wish that those who committed this terrible crime be killed, he ultimately realized that such killing “is simply vengeance; and it was vengeance that killed Julie…. Vengeance is a strong and natural emotion. But it has no place in our justice system.”
The notion of an eye for an eye, or a life for a life, is a simplistic one which our society has never endorsed. We do not allow torturing the torturer, or raping the rapist. Taking the life of a murderer is a similarly disproportionate punishment, especially in light of the fact that the U.S. executes only a small percentage of those convicted of murder, and these defendants are typically not the worst offenders but merely the ones with the fewest resources to defend themselves.
Louis P. Pojman Author and Professor of Philosophy, U.S. Military Academy. Excerpt from “The Death Penalty: For and Against,” (Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc., 1998)
“[Opponents of the capital punishment often put forth the following argument:] Perhaps the murderer deserves to die, but what authority does the state have to execute him or her? Both the Old and New Testament says, “’Vengeance is mine, I will repay,’ says the Lord” (Prov. 25:21 and Romans 12:19). You need special authority to justify taking the life of a human being.
The objector fails to note that the New Testament passage continues with a support of the right of the state to execute criminals in the name of God: “Let every person be subjected to the governing authorities. For there is no authority except from God, and those that exist have been instituted by God. Therefore he who resists what God has appointed, and those who resist will incur judgment…. If you do wrong, be afraid, for [the authority] does not bear the sword in vain; he is the servant of God to execute his wrath on the wrongdoer” (Romans 13: 1-4). So, according to the Bible, the authority to punish, which presumably includes the death penalty, comes from God.
But we need not appeal to a religious justification for capital punishment. We can site the state’s role in dispensing justice. Just as the state has the authority (and duty) to act justly in allocating scarce resources, in meeting minimal needs of its (deserving) citizens, in defending its citizens from violence and crime, and in not waging unjust wars; so too does it have the authority, flowing from its mission to promote justice and the good of its people, to punish the criminal. If the criminal, as one who has forfeited a right to life, deserves to be executed, especially if it will likely deter would-be murderers, the state has a duty to execute those convicted of first-degree murder.”
National Council of Synagogues and the Bishops’ Committee for Ecumenical and Interreligious Affairs of the National Conference of Catholic Bishops Excerpts from “To End the Death Penalty: A Report of the National Jewish/Catholic Consultation” (December, 1999)
“Some would argue that the death penalty is needed as a means of retributive justice, to balance out the crime with the punishment. This reflects a natural concern of society, and especially of victims and their families. Yet we believe that we are called to seek a higher road even while punishing the guilty, for example through long and in some cases life-long incarceration, so that the healing of all can ultimately take place.
Some would argue that the death penalty will teach society at large the seriousness of crime. Yet we say that teaching people to respond to violence with violence will, again, only breed more violence.
The strongest argument of all [in favor of the death penalty] is the deep pain and grief of the families of victims, and their quite natural desire to see punishment meted out to those who have plunged them into such agony. Yet it is the clear teaching of our traditions that this pain and suffering cannot be healed simply through the retribution of capital punishment or by vengeance. It is a difficult and long process of healing which comes about through personal growth and God’s grace. We agree that much more must be done by the religious community and by society at large to solace and care for the grieving families of the victims of violent crime.
Recent statements of the Reform and Conservative movements in Judaism, and of the U.S. Catholic Conference sum up well the increasingly strong convictions shared by Jews and Catholics…:
‘Respect for all human life and opposition to the violence in our society are at the root of our long-standing opposition (as bishops) to the death penalty. We see the death penalty as perpetuating a cycle of violence and promoting a sense of vengeance in our culture. As we said in Confronting the Culture of Violence: ‘We cannot teach that killing is wrong by killing.’ We oppose capital punishment not just for what it does to those guilty of horrible crimes, but for what it does to all of us as a society. Increasing reliance on the death penalty diminishes all of us and is a sign of growing disrespect for human life. We cannot overcome crime by simply executing criminals, nor can we restore the lives of the innocent by ending the lives of those convicted of their murders. The death penalty offers the tragic illusion that we can defend life by taking life.’1
We affirm that we came to these conclusions because of our shared understanding of the sanctity of human life. We have committed ourselves to work together, and each within our own communities, toward ending the death penalty.” Endnote 1. Statement of the Administrative Committee of the United States Catholic Conference, March 24, 1999.
The risk of executing the innocent precludes the use of the death penalty.
The death penalty alone imposes an irrevocable sentence. Once an inmate is executed, nothing can be done to make amends if a mistake has been made. There is considerable evidence that many mistakes have been made in sentencing people to death. Since 1973, over 180 people have been released from death row after evidence of their innocence emerged. During the same period of time, over 1,500 people have been executed. Thus, for every 8.3 people executed, we have found one person on death row who never should have been convicted. These statistics represent an intolerable risk of executing the innocent. If an automobile manufacturer operated with similar failure rates, it would be run out of business.
Our capital punishment system is unreliable. A study by Columbia University Law School found that two thirds of all capital trials contained serious errors. When the cases were retried, over 80% of the defendants were not sentenced to death and 7% were completely acquitted.
Many of the releases of innocent defendants from death row came about as a result of factors outside of the justice system. Recently, journalism students in Illinois were assigned to investigate the case of a man who was scheduled to be executed, after the system of appeals had rejected his legal claims. The students discovered that one witness had lied at the original trial, and they were able to find another man, who confessed to the crime on videotape and was later convicted of the murder. The innocent man who was released was very fortunate, but he was spared because of the informal efforts of concerned citizens, not because of the justice system.
In other cases, DNA testing has exonerated death row inmates. Here, too, the justice system had concluded that these defendants were guilty and deserving of the death penalty. DNA testing became available only in the early 1990s, due to advancements in science. If this testing had not been discovered until ten years later, many of these inmates would have been executed. And if DNA testing had been applied to earlier cases where inmates were executed in the 1970s and 80s, the odds are high that it would have proven that some of them were innocent as well.
Society takes many risks in which innocent lives can be lost. We build bridges, knowing that statistically some workers will be killed during construction; we take great precautions to reduce the number of unintended fatalities. But wrongful executions are a preventable risk. By substituting a sentence of life without parole, we meet society’s needs of punishment and protection without running the risk of an erroneous and irrevocable punishment.
There is no proof that any innocent person has actually been executed since increased safeguards and appeals were added to our death penalty system in the 1970s. Even if such executions have occurred, they are very rare. Imprisoning innocent people is also wrong, but we cannot empty the prisons because of that minimal risk. If improvements are needed in the system of representation, or in the use of scientific evidence such as DNA testing, then those reforms should be instituted. However, the need for reform is not a reason to abolish the death penalty.
Besides, many of the claims of innocence by those who have been released from death row are actually based on legal technicalities. Just because someone’s conviction is overturned years later and the prosecutor decides not to retry him, does not mean he is actually innocent.
If it can be shown that someone is innocent, surely a governor would grant clemency and spare the person. Hypothetical claims of innocence are usually just delaying tactics to put off the execution as long as possible. Given our thorough system of appeals through numerous state and federal courts, the execution of an innocent individual today is almost impossible. Even the theoretical execution of an innocent person can be justified because the death penalty saves lives by deterring other killings.
Gerald Kogan, Former Florida Supreme Court Chief Justice Excerpts from a speech given in Orlando, Florida, October 23, 1999 “[T]here is no question in my mind, and I can tell you this having seen the dynamics of our criminal justice system over the many years that I have been associated with it, [as] prosecutor, defense attorney, trial judge and Supreme Court Justice, that convinces me that we certainly have, in the past, executed those people who either didn’t fit the criteria for execution in the State of Florida or who, in fact, were, factually, not guilty of the crime for which they have been executed.
“And you can make these statements when you understand the dynamics of the criminal justice system, when you understand how the State makes deals with more culpable defendants in a capital case, offers them light sentences in exchange for their testimony against another participant or, in some cases, in fact, gives them immunity from prosecution so that they can secure their testimony; the use of jailhouse confessions, like people who say, ‘I was in the cell with so-and-so and they confessed to me,’ or using those particular confessions, the validity of which there has been great doubt. And yet, you see the uneven application of the death penalty where, in many instances, those that are the most culpable escape death and those that are the least culpable are victims of the death penalty. These things begin to weigh very heavily upon you. And under our system, this is the system we have. And that is, we are human beings administering an imperfect system.”
“And how about those people who are still sitting on death row today, who may be factually innocent but cannot prove their particular case very simply because there is no DNA evidence in their case that can be used to exonerate them? Of course, in most cases, you’re not going to have that kind of DNA evidence, so there is no way and there is no hope for them to be saved from what may be one of the biggest mistakes that our society can make.”
The entire speech by Justice Kogan is available here.
Paul G. Cassell Associate Professor of Law, University of Utah, College of Law, and former law clerk to Chief Justice Warren E. Burger. Statement before the Committee on the Judiciary, United States House of Representatives, Subcommittee on Civil and Constitutional Rights Concerning Claims of Innocence in Capital Cases (July 23, 1993)
“Given the fallibility of human judgments, the possibility exists that the use of capital punishment may result in the execution of an innocent person. The Senate Judiciary Committee has previously found this risk to be ‘minimal,’ a view shared by numerous scholars. As Justice Powell has noted commenting on the numerous state capital cases that have come before the Supreme Court, the ‘unprecedented safeguards’ already inherent in capital sentencing statutes ‘ensure a degree of care in the imposition of the sentence of death that can only be described as unique.’”
“Our present system of capital punishment limits the ultimate penalty to certain specifically-defined crimes and even then, permit the penalty of death only when the jury finds that the aggravating circumstances in the case outweigh all mitigating circumstances. The system further provides judicial review of capital cases. Finally, before capital sentences are carried out, the governor or other executive official will review the sentence to insure that it is a just one, a determination that undoubtedly considers the evidence of the condemned defendant’s guilt. Once all of those decisionmakers have agreed that a death sentence is appropriate, innocent lives would be lost from failure to impose the sentence.”
“Capital sentences, when carried out, save innocent lives by permanently incapacitating murderers. Some persons who commit capital homicide will slay other innocent persons if given the opportunity to do so. The death penalty is the most effective means of preventing such killers from repeating their crimes. The next most serious penalty, life imprisonment without possibility of parole, prevents murderers from committing some crimes but does not prevent them from murdering in prison.”
“The mistaken release of guilty murderers should be of far greater concern than the speculative and heretofore nonexistent risk of the mistaken execution of an innocent person.”
Full text can be found here.
Arbitrariness & Discrimination
The death penalty is applied unfairly and should not be used.
In practice, the death penalty does not single out the worst offenders. Rather, it selects an arbitrary group based on such irrational factors as the quality of the defense counsel, the county in which the crime was committed, or the race of the defendant or victim.
Almost all defendants facing the death penalty cannot afford their own attorney. Hence, they are dependent on the quality of the lawyers assigned by the state, many of whom lack experience in capital cases or are so underpaid that they fail to investigate the case properly. A poorly represented defendant is much more likely to be convicted and given a death sentence.
With respect to race, studies have repeatedly shown that a death sentence is far more likely where a white person is murdered than where a Black person is murdered. The death penalty is racially divisive because it appears to count white lives as more valuable than Black lives. Since the death penalty was reinstated in 1976, 296 Black defendants have been executed for the murder of a white victim, while only 31 white defendants have been executed for the murder of a Black victim. Such racial disparities have existed over the history of the death penalty and appear to be largely intractable.
It is arbitrary when someone in one county or state receives the death penalty, but someone who commits a comparable crime in another county or state is given a life sentence. Prosecutors have enormous discretion about when to seek the death penalty and when to settle for a plea bargain. Often those who can only afford a minimal defense are selected for the death penalty. Until race and other arbitrary factors, like economics and geography, can be eliminated as a determinant of who lives and who dies, the death penalty must not be used.
Discretion has always been an essential part of our system of justice. No one expects the prosecutor to pursue every possible offense or punishment, nor do we expect the same sentence to be imposed just because two crimes appear similar. Each crime is unique, both because the circumstances of each victim are different and because each defendant is different. The U.S. Supreme Court has held that a mandatory death penalty which applied to everyone convicted of first degree murder would be unconstitutional. Hence, we must give prosecutors and juries some discretion.
In fact, more white people are executed in this country than black people. And even if blacks are disproportionately represented on death row, proportionately blacks commit more murders than whites. Moreover, the Supreme Court has rejected the use of statistical studies which claim racial bias as the sole reason for overturning a death sentence.
Even if the death penalty punishes some while sparing others, it does not follow that everyone should be spared. The guilty should still be punished appropriately, even if some do escape proper punishment unfairly. The death penalty should apply to killers of black people as well as to killers of whites. High paid, skillful lawyers should not be able to get some defendants off on technicalities. The existence of some systemic problems is no reason to abandon the whole death penalty system.
Reverend Jesse L. Jackson, Sr. President and Chief Executive Officer, Rainbow/PUSH Coalition, Inc. Excerpt from “Legal Lynching: Racism, Injustice & the Death Penalty,” (Marlowe & Company, 1996)
“Who receives the death penalty has less to do with the violence of the crime than with the color of the criminal’s skin, or more often, the color of the victim’s skin. Murder — always tragic — seems to be a more heinous and despicable crime in some states than in others. Women who kill and who are killed are judged by different standards than are men who are murderers and victims.
The death penalty is essentially an arbitrary punishment. There are no objective rules or guidelines for when a prosecutor should seek the death penalty, when a jury should recommend it, and when a judge should give it. This lack of objective, measurable standards ensures that the application of the death penalty will be discriminatory against racial, gender, and ethnic groups.
The majority of Americans who support the death penalty believe, or wish to believe, that legitimate factors such as the violence and cruelty with which the crime was committed, a defendant’s culpability or history of violence, and the number of victims involved determine who is sentenced to life in prison and who receives the ultimate punishment. The numbers, however, tell a different story. They confirm the terrible truth that bias and discrimination warp our nation’s judicial system at the very time it matters most — in matters of life and death. The factors that determine who will live and who will die — race, sex, and geography — are the very same ones that blind justice was meant to ignore. This prejudicial distribution should be a moral outrage to every American.”
Justice Lewis Powell United States Supreme Court Justice excerpts from McCleskey v. Kemp, 481 U.S. 279 (1987) (footnotes and citations omitted)
(Mr. McCleskey, a black man, was convicted and sentenced to death in 1978 for killing a white police officer while robbing a store. Mr. McCleskey appealed his conviction and death sentence, claiming racial discrimination in the application of Georgia’s death penalty. He presented statistical analysis showing a pattern of sentencing disparities based primarily on the race of the victim. The analysis indicated that black defendants who killed white victims had the greatest likelihood of receiving the death penalty. Writing the majority opinion for the Supreme Court, Justice Powell held that statistical studies on race by themselves were an insufficient basis for overturning the death penalty.)
“[T]he claim that [t]his sentence rests on the irrelevant factor of race easily could be extended to apply to claims based on unexplained discrepancies that correlate to membership in other minority groups, and even to gender. Similarly, since [this] claim relates to the race of his victim, other claims could apply with equally logical force to statistical disparities that correlate with the race or sex of other actors in the criminal justice system, such as defense attorneys or judges. Also, there is no logical reason that such a claim need be limited to racial or sexual bias. If arbitrary and capricious punishment is the touchstone under the Eighth Amendment, such a claim could — at least in theory — be based upon any arbitrary variable, such as the defendant’s facial characteristics, or the physical attractiveness of the defendant or the victim, that some statistical study indicates may be influential in jury decision making. As these examples illustrate, there is no limiting principle to the type of challenge brought by McCleskey. The Constitution does not require that a State eliminate any demonstrable disparity that correlates with a potentially irrelevant factor in order to operate a criminal justice system that includes capital punishment. As we have stated specifically in the context of capital punishment, the Constitution does not ‘plac[e] totally unrealistic conditions on its use.’ (Gregg v. Georgia)”
The entire decision can be found here.
84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples
If you’ve looked for capital punishment essay topics, you’re in luck! Below, our experts have collected some death penalty title ideas and samples for your paper.
📝 Capital Punishment Essay Writing Tips
✔️ top death penalty title ideas, 🏆 best death penalty essay titles & examples, 💡 most interesting death penalty topics to write about, ❓ capital punishment research questions.
Capital punishment has been a debatable issue for decades. Some people believe that the death penalty plays a crucial role in the criminal justice system, while others think that this procedure is highly unethical.
An essay on capital punishment may be a challenging assignment because students should know much about the subject. Do not worry, we have got you covered! Read this article until the end and learn some important tips on writing capital punishment essays.
Start with choosing the subject for your paper. Here are some capital punishment essay topics that you can use:
- Capital punishment in the media
- Crime and punishment in today’s world: Death penalty
- Capital punishment essay: Arguments against death penalty
- The legal and ethical implications of capital punishment
- Capital punishment should be forbidden: Anti-death penalty arguments
- Why capital punishment may target the poor
- Death penalty: An issue of life and death
Remember that these are just examples of topics and titles for your paper. You can choose any related capital punishment essay titles. Once you have selected a topic of your essay, you can start working on the assignment. Here are the key points you should use to write an outstanding essay:
- Study the subject thoroughly. Use reliable sources to analyze the legal and ethical aspects of the death penalty. Select the sources you will use in the paper and remember that they should be credible.
- A well-developed outline is key. Make sure that your paper includes an introduction, a conclusion, and several body paragraphs.
- If you are not sure about the structure of your paper, check out essays online to see how they are organized. This step can also help you to see whether the selected problem is relevant. Remember that you should avoid copying the information you will find online. Plagiarism will make your essay look unreliable and get you a bad grade.
- Remember that you should present your capital punishment essay thesis in the last sentence of your introductory paragraph. Hint: Start working on your introductory paragraph after you research the subject. It will help you to present the background information correctly.
- Identify the goals of your paper clearly. Do you want to prove your point or provide insight on the issue? Answer these questions before starting to work on your assignment.
- Define capital punishment. You can discuss its legal implications, its prevalence in different countries, and the offenses that can potentially lead to a death penalty.
- When working on an opinion piece, state your viewpoint clearly. Do you think that all countries should legalize death penalties? Do you believe that capital punishment is unethical? Do some offenders deserve a death penalty more than others do? Answer these questions in detail.
- Remember that the purpose of your paper should be to help the reader understand capital punishment better. Your essay should motivate the audience to develop an opinion about the subject.
- Always support your arguments with evidence. Cite articles in an appropriate style (MLA, APA, Harvard, or other). The best type of sources for your paper is peer-reviewed articles and other scholarly publications.
- Restate your arguments and the thesis in a concluding section. Provide a summary of your findings along with recommendations for future research.
Need more ideas for your essay? Check out our free samples on the website!
- Why should the death penalty be abolished?
- What are some unusual punishments for crimes?
- Can the death penalty be compared to killing in cold blood?
- Is life imprisonment more just than the death penalty?
- Reasons to criticize capital punishment in China.
- Analyzing A Descending Spiral by Marc Bookman.
- What are the pros of capital punishment?
- Executing the innocent people: the issue of mistake.
- Abolishing the death penalty in Texas.
- Serial killers sentenced to capital punishment.
- Death Penalty: Utilitarian View on Capital Punishment Another significant benefit offered by the death penalty to the society is that it leads to the permanent incapacitation of the convicted person.
- Capital Punishment in the UK Should be Reintroduced? ‘Capital Punishment’ or the ‘Death Penalty’ is the judicially ordered, lawful infliction of death as a punishment for a serious crime called a ‘capital offence’ or a ‘capital crime.
- Analysis: Speech In Favor of Capital Punishment by John Stuart Mills Mills rightly points out that the very grounds of humanity used to support the removal of the death penalty should also be the ones used to support retaining of the sentence.
- Capital Punishment and Deterrence of Crime For the case of murder or crimes that necessitate capital punishment, the incentive to commit murder is directly related to the uncertainties that punishments for the crime will generate.
- Capital Punishment: Proponents and Opponents Arguements The opponents of capital of capital punishment argue that it is not a just and humane way of punishing heinous criminals in the society because everybody has right to life.
- Capital Punishment: Advantages and Disadvantages This paper examines death penalty from an impartial view by considering disadvantages and advantages of capital punishment in society. Thirdly, Teeters views that death penalty is a retribution action in which a victim is punished […]
- The Death Penalty in the Modern Society The cost of maintenance of the convicted individuals is also one of the reasons that necessitate the death penalty. The reaffirmation of the death penalty is also attributed to the teachings portrayed by most religions.
- Capital Punishment Role in the World However, it is wrong and unjustified because it is inhuman, unfair, violates the human right to life, and it does not aid in reduction of crime.
- Capital Punishment and the Death Penalty Furthermore, the defense and, in the United States, the prosecution has the right of vexatious challenge, which allows it to confront several participants without providing a reason.
- Capital Punishment Is Morally and Legally Wrong The problem of the death penalty is complex and multifaceted. It affects the political, legal, moral, cultural, and other fields of life.
- Justifications for Capital Punishment This statement mostly appeals to a general deterrence argument, as the fear of punishment emerged from showing its implementation, but not from other justifications effects.
- The Significance of Capital Punishment in the UAE Current analysis of the importance of the death penalty worldwide focuses on the advantages and disadvantages of the punishment. The UAE has a mandatory death penalty which is susceptible to the judgment of authorities and […]
- Capital Punishment: Utilitarianism and Retributivism Theories However, to rule out chances of an innocent person being punished, the theory advocates for justice; before punishment is administered, the court should proof beyond reasonable doubt that the accused is guilty.
- Capital Punishment Interpretation and Exceptions Under custody, the law applies to cases in which the conditions of custody are compromised and to situations where the suspect is held unfairly. The suspect responded with a yes and this was used as […]
- Capital Punishment Debates: Death Penalty The capital punishment has been practiced in almost all the societies and all epochs in the development of the mankind. The author educates the society as a whole on litigious issues of the death penalty […]
- Capital Punishment in Florida The system is erroneous and cases that almost end up in the ‘chair’ are overturned contrary to the expectations of the family members of the murdered.
- Capital Punishment: Term Definition In that regard, taking such issues such as euthanasia, abortion and capital punishment, the latter can be considered as the most delicate, especially considering many cases that represent exceptions that are feared to be repeated.
- Capital Punishment – Moral or Immoral? It would not be a futile exercise to interpret capital punishment in the light of religion before proceeding to the subject of my argument. Countries that give importance to such punishments should tone down and […]
- Capital Punishment in the US Analysis Capital Punishment is the lawful infliction of death as a punishment for a major crime. The first argument against Capital Punishment is that it is inhumane.
- An Orwellian Look at Capital Punishment His reaction to the actual hanging of a puny Hindu man borders on a strategy of remaining as a detached viewer and subconsciously, his gorge rises at the thought of a human being with a […]
- Public Opinion on Capital Punishment for Juveniles This essay is a study of the public opinion on Capital Punishment for juveniles, this is a very controversial subject as many people are against Captial punishment, and many are for life imprisonment, capital punishment […]
- Capital Punishment and Race Factor in the US First of all, it is necessary to briefly discuss the history of race in the U.S.to provide a foundation for the bias and explain its causes.
- The Controversy Over Capital Punishment It is as a result of this that he concludes that Ford calls for the execution of capital punishment as a penalty in criminal offences.
- Capital Punishment in Melville’s “Billy Budd, Sailor” One of the reasons for the triumph of Billy Budd, Sailor in America and the United Kingdom, was the precision, with which the author portrayed the historical and cultural context, particularly Melville analyzed both issues […]
- Capital Punishment in Indonesia The government is also known to safeguard the details of capital punishment in the country. The targeted prisoners are “executed in the middle of the night”.
- Capital Punishment, Its Ethics and Infair Justice The main factors leading to differences in stands between the anti-capital punishment and pro-death are the morality and religious issues surrounding the matter.
- Capital Punishment and Unusual Punishment The issue of capital punishment has always been on the radar of the Supreme Court of the United States. The key question that should be answered is the future of capital punishment and unusual punishment […]
- Capital Punishment in United States The most compelling argument in support of capital punishment is that failing to execute murderers may in itself put more lives in danger.
- Debates on Capital Punishment in the US For example, capital punishment is the best punishment for murder because it is equal to the crime. Thirdly, capital punishment is a violation of the human right to life.
- The Ethical and Legal Standards of Capital Punishment This is one of the details that should be considered. This is one of the pitfalls that should be avoided.
- Isolation and Capital Punishments On the other hand, capital punishments such as deaths deprives of people the freedom of life and goes against God’s command which disallows intentional killings of persons, or murder. Similarly, capital punishment in the form […]
- Does the Death Sentence Offer Justice to the Criminal? It is not enough to be locked in prison for ending the life of a fellow human being. Revenge is one of the ways that can be used.
- The Consequences of Capital Punishment The appeals in the death penalty cases are usually many and cause the social costs of the cases to be even more expensive.
- Moral Issue of Capital Punishment Capital punishment is also a form of premeditated death as the action is planned for, does it mean that the state has the right to premeditate deaths for some of its citizens because they are […]
- The Death Penalty Debate in the United States of America The punishment is believed to have been there even at the time of the earlier colonies of the United States; it as well continued to be in force within the states that came to form […]
- Psychological Aspects of Capital Punishment According to research done by Freedman and Hemenway on a group of death row inmates, it was established that almost a two-thirds of the death row inmates are retarded.
- Avoiding of Capital Punishment Capital punishment is also unnecessary since there are better ways of punishing criminals such as life imprisonment to keep the society in order and at peace.
- The Economic Significance of Capital Punishment The survival of any civilization hinges on the establishment of laws and codes of conduct and the subsequent obeying of the same by the society’s members.
- Capital Punishment in Modern American History: Lists of Capital Crimes That Varied From Region to Region Politicians are frequently trying to expand the scope of capital punishment by bringing in a host of crimes under it.”The US public has deep concern over violent crimes due to the cynical manipulation of capital […]
- Analysis of Capital Punishment in the Films Those for the death penalty in the movie are represented by Ramunda who becomes a strong advocate for the death penalty and in many instances, is a counterpart of Cushing.
- Capital Punishment Legislation The main reasons that opponents of the death penalty give for their position are, the fact that the death penalty is inhumane and cruel.
- Capital Punishment as an Option in Maryland Death penalty is the most serious punishment that can be used by the government against people; and even if it costs less then keeping a person in jail till the end of his/her life and […]
- Capital Punishment in Political View This is because quiet a number of the abolitions have been associated with democratic developments in political systems of the countries that have abolished the penalties. Conservatives have in the United States been strongly opposed […]
- Capital Punishment: A Critical Evaluation of Its Appropriateness in Modern Society In line with the above argument, supporters of capital punishment argue that the practice permanently removes thieves, murderers, rapists, and other criminals from the face of society, in the process making it safer for compliant […]
- What Does Capital Punishment Mean in History?
- How Can Death Penalty Prevent Repeat Offenders?
- Why Should Capital Punishment Be Reinstated in Australia?
- How Objective and Justifiable Are Our Reasons for Enforcing the Death Penalty?
- Does Capital Punishment Have a Deterrent Effect?
- How Has the Death Penalty Changed Over Time?
- What Is Wrong With Capital Punishment?
- Should Federal Courts Review State Death Penalty Cases?
- Can Capital Punishment Ever Be Justified?
- Should the Death Penalty Apply to Juvenile Criminals?
- Does the Death Penalty Breach Human Rights?
- Can Capital Punishment Keep Us Safe?
- Should the Death Penalty Be a Part of the System of Justice?
- Does Capital Punishment Equate to Cruel and Unusual Punishment?
- Should the Death Penalty Be Enforced?
- How Does Capital Punishment Affirm Life?
- Should the Death Penalty Be Imposed for Drug Offences?
- Does Capital Punishment Have a Local Deterrent Effect on Homicides?
- Should the Death Penalty Be Mandatory for Homicide?
- How Does Capital Punishment Work in the United States?
- Should the Death Penalty Be Morally Acceptable?
- Does Race Affect the Way of Capital Punishment?
- What Crimes Are Charged With Death Penalty?
- Does the Capital Punishment Have a Role in Civilized Society?
- Why Should Capital Punishment Be Abolished?
- What Effects Does the Death Penalty Cause on Society?
- How Does Legislation Help to Prevent Racial Bias in Death Penalty Convictions?
- Is the Death Penalty Fair?
- Does Jodi Arias Deserve the Death Penalty?
- What Attitudes Might Christians Hold About Capital Punishment?
- Constitution Research Ideas
- Prison Paper Topics
- Euthanasia Titles
- Mass Incarceration Essay Topics
- Crime Ideas
- Murder Questions
- Crime Prevention Research Topics
- Serial Killer Paper Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 22). 84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/capital-punishment-essay-examples/
"84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 22 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/capital-punishment-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples'. 22 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/capital-punishment-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/capital-punishment-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "84 Capital Punishment Essay Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/capital-punishment-essay-examples/.

- Lok Sabha Elections 2024
- Firstpost Defence Summit
- Entertainment
- Web Stories
- First Sports
- Fast and Factual
- Between The Lines
- Firstpost America

Pune Porsche crash: Why teen who killed 2 has been let off with writing an essay while father has been detained
A 17-year-old in Maharashtra’s Pune has been granted bail on the condition that he write a 300-word essay after allegedly driving drunk and killing two people. Two days after the incident, the juvenile’s father was detained as per the Motor Vehicles Act, 2019. The tragedy has sparked outrage, with many slamming the judiciary and the existing traffic laws read more
)
Picture this: you indulge in drink driving, and then allegedly run over two people, killing them. What would be your punishment by law? In case of a 17-year-old in Pune, he was granted bail for the incident on the condition that he writes an essay on the crash and works with the traffic police for 15 days.
While it may sound incredulous and unbelievable, it is, in fact, a shocking truth. A teen in Pune has been let off on bail on the condition that he work with Pune’s Yerwada traffic police, compose an essay on the accident, undergo treatment for alcohol dependency and then submit a report thereafter.
The incident has left many balking at the court’s decision. Pune’s Police has, in fact, said that the teen should be tried as an adult, adding that they would appeal to a higher court now.
And on Tuesday (21 May), the father of the accused teen has been detained in the crime.
We take a closer look at the entire incident, the laws involved and what society has to say about this.
The incident
In the wee hours of Sunday (19 May), Aneesh Awadhiya and his friend Ashwini Koshta, both 24, died when the motorbike they were on was hit by a Porsche allegedly driven by a 17-year-old in the Kalyani Nagar locality of Pune in the western state of Maharashtra. While Ashwini died on the spot, Aneesh was shifted to a city hospital, where he died soon after.
Investigating the matter, the Pune Police then arrested a 17-year-old, who they believed was behind the wheel of the luxury car when it hit the bike. Pune Commissioner of Police Amitesh Kumar said that the minor, belonging to a prominent realtor’s family, was celebrating his Class XII results at a local pub, where he was seen consuming alcohol before the crash.
While he was heading home from the bar, the teen lost control of the car and rammed into a motorcycle at the Kalyani Nagar junction around 2.30 am.
“Upon inquiry, the minor has said his father had handed over the grey Porsche to him despite knowing that he had no driver’s training and did not have a driver’s licence. He has also said his father allowed him to party with his friends and that his father was aware that he was consuming alcohol,” reads the FIR registered by Assistant Police Inspector Vishwanath Todkari at Yerwada Police Station, as per an Indian Express report.
Following the incident, Deputy Commissioner of Pune City Police Vijay Kumar Magar arrested the juvenile, after booking him for rash and negligent driving, as well as causing harm by endangering life or personal safety under IPC sections 304A, 279, 337, 338, and 427, in addition to relevant sections of the Maharashtra Motor Vehicle Act.
Teen granted bail, outrage ensues
After being apprehended, the 17-year-old was produced before the holiday court on Sunday afternoon where authorities sought his custody and permission to try him as an adult. However, the court refused and granted him bail within 14 hours of the crime under certain conditions.
The police stated that bail was granted as the court did not find the crime committed by the juvenile to be serious.
The teen’s lawyer, Prashant Patil, said the court granted bail on certain conditions. First, the teen would have to “work with traffic police of Yerwada for 15 days”. Secondly, he would have to pen a 300-word essay on the ‘effect of road accident and their solution’. As part of his bail conditions, the teen accused would also have to undergo treatment from a doctor to help him quit drinking and “take psychiatric counselling” and submit the report to the court.
After news broke of the bail conditions in the matter, outrage ensued, with many accusing the judge of going soft on the accused. Many expressed their contempt for the system on X; some calling the Indian judiciary “a joke”. Another wrote, “Hope the criminal writes a good essay to impress the honourable judge. Just can’t express how I feel about it.”
Family of the two victims also expressed anger at the court’s decision. Koshta’s family in Jabalpur in Madhya Pradesh said they were dismayed by the bail conditions. “We are in shock,” her uncle Jugal Kishor Koshta told NDTV . “It is condemnable that he should get bail. He and his parents should be investigated.”
Koshta’s other uncle told NDTV , “We want his bail cancelled and he should remain in police custody. Because of him, an innocent girl, who has seen nothing of life, died.”
Awadhiya’s family also echoed similar sentiments. Atmaram Awadhiya, the grandfather, said that the teen should not be granted bail. “Two people have died in this accident. This is completely wrong. We want strict punishment. The bail granted to the accused should be cancelled,” he was quoted as telling NDTV .
The victim’s uncle also chimed in, saying: “The accused, a minor, was drunk and was driving at 240 km per hour. He did not have a driving licence. This is murder, not accident.”
Following the outrage, Maharashtra’s deputy chief minister Devendra Fadnavis reached out to the Pune Police Commissioner Amitesh Kumar and asked him to ensure there was no soft-pedalling against the accused in the Porsche hit-and-run case. And following this, Commissioner Kumar said that they would appeal the order in a higher court. “We will not leave any stone unturned to prove that this is a heinous crime,” he was quoted as telling India Today .
#WATCH | Maharashtra: Visuals of the Porsche car and bike currently at Yerwada Police Station in Pune. Two people were killed when a speeding Porsche car hit them from behind on 19th May. The accused has been granted bail by the Juvenile Justice Board and his father was… https://t.co/HKj8uK4d9q pic.twitter.com/91SeqwfTeN — ANI (@ANI) May 21, 2024
Father detained
On Tuesday (21 May), the Pune Police detained the father of the teen accused from Maharashtra’s Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar, formerly known as Aurangabad, and will bring him back to the city for further probe.
The father, a prominent realtor in Pune, was on the run since the incident. He has now been booked under the provision of sections 75 and 77 of the Juvenile Justice Act on the charges of allowing his minor son to drive the Porsche and consume liquor. Section 75 deals with “wilful neglect of a child, or exposing a child to mental or physical illnesses,” while section 77 deals with supplying a child with intoxicating liquor or drugs.
According to the FIR lodged in connection with the incident, the man, despite knowing his son did not have a valid driving licence, gave him the car, thus endangering the latter’s life, and allowed him to party even as the father knew that he consumes liquor.
Apart from this, the Pune police have arrested Cosie restaurant owner Pralhad Bhutda and manager Sachin Katkar and Hotel Blak manager Sandip Sangle for allegedly serving alcohol to the juvenile, Additional Commissioner of Police (Crime) Shailesh Balkawade said.
What the law says
The accused teen has been charged under Section 304A of the IPC, which deals with causing death by negligence. Moreover, he has been charged with Section 279 of the IPC, which deals with rash driving.
But then why has his father been arrested? As per the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, parents/guardians of juveniles shall be held guilty in case of an offence by a juvenile. The law mandates that a fine of Rs 25,000 with three years’ imprisonment will be imposed and the juvenile will be tried under the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act while the registration of the vehicle will be cancelled.
The law also states that the juvenile shall not be granted a driver’s licence until the minor has attained the age of 25.
This change was introduced after a parliamentary panel had suggested higher penalties for traffic offences. In fact, the panel had recommended treating accidents caused by drink driving as pre-meditated crimes rather than as cases of ‘negligence’.
With inputs from agencies
- climate change
I Hate Summer—and You Should Too

W ake me when it’s over—summer, that is. I know, I know, you just love it: the long days, the warm evenings, the trips to the beach, the afternoons at the ballpark when your favorite team is playing and the pennant race is tightening—and the temperature is skyrocketing, and your skin is blistering, and the beer is $6, and the drive home will be in 88° heat, which is fine if you don’t mind running the air conditioner, except that you’re burning through $4–a-gallon gas, because it’s summer-driving season and the giant oil companies didn’t get to be the giant oil companies without knowing the right time of year to hike their prices.
And that’s hardly all of it. Summertime is the season of horribles, from higher crime rates, to increased warfare, to spikes in asthma, to raging wildfires, to swarms of bugs, to a rise in traffic accidents—and even to a bump in divorces, because how could a 100° heat wave, a busted A.C., and the kids out of school not spell domestic bliss?
What’s more, it’s only getting worse. Last summer was the hottest on record, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the 10 warmest years were all from 2010 to 2022. So with a lousy part of the year becoming lousier still, here, in no particular order, are nine reasons summer is the suckiest season of them all.
Road wrecks
There’s nothing like long days, no school, and lots of teen drivers to make the highways a safe place to be. Not . It’s no coincidence that the Automobile Association of America (AAA) labels the stretch between Memorial Day and Labor Day “the 100 deadliest days.” There are over 11.7 million U.S. drivers between the ages of 15 and 20, and if you know what’s good for you you’ll stay out of their way—especially when they’re out as a group, driving recreationally. “We know that when teens are joyriding as opposed to driving with a specific destination and time in mind, there is a heightened risk,” said Diana Gugliotta, senior manager of public affairs for AAA Northeast, in a statement last year.
Read More : What It's Like To Be Deathly Afraid of Feet
AAA’s numbers back that up. When a teen driver has only other teens in a vehicle, the risk of fatality for the driver and all passengers increases 51%. When at least one passenger is over 35, the overall fatality risk declines 8%. From 2011 to 2020, there were 7,316 deaths in summertime teen-related traffic accidents—nearly half the total of all teen-related traffic accidents for the year.
This means war
Napoleon Bonaparte could tell you a thing or two about what it’s like to pick a fight with Russia in the dead of winter. In 1812, the French army suffered half a million casualties in battles that climaxed in December—a rout that led to Napoleon’s abdication and exile in 1914. Any general worth his steed would prefer to fight in the summer when there’s plenty of light, the roads are clear, and soldiers aren’t bundled up against the cold. As far back as 55 BCE , the Roman army’s “campaigning season” would end when summer wound down and the soldiers would retreat to their winter quarters. It’s probably not a coincidence that World War I began in August 1914, World War II on Sept. 1, 1939, and Nazi Germany’s invasion of Russia in June 1941. More recently , in August 1990, Iraq invaded Kuwait, and in August 1991, the old Soviet Union nearly fell into civil war when communist hardliners tried to oust President Mikhail Gorbachev. America’s 20-year war in Afghanistan typically saw its fiercest fighting in the summer months, and the same is true of the war in Ukraine .
Hot-weather warfare is likely only to get worse. A 2009 paper in PNAS found that rising temperatures exacerbated by climate change could lead to a 54% increase in the risk of civil war in Africa by 2030. A 2011 study in Nature found that warmer weather during El Niño years doubled the risk of civil war in 90 tropical countries and could have accounted for 20% of conflicts around the world over the past half century. Meantime, what’s the season of peace on Earth and goodwill toward men? Wintertime, baby. Wintertime.
Going buggy
Summer advertises itself as the season of birdsong and butterflies. Don’t believe it. It’s the season of pests—particularly ticks, mosquitoes, flies, fleas, bees, and wasps. Ticks, mosquitoes, and fleas in particular can spread diseases that include malaria, yellow fever, Zika, dengue, Lyme, and chikungunya. Bees, wasps, and yellowjackets—with their infernal stings—are similarly creatures of the summer. And you think you know flies? You don’t know flies. There are 110,000 species of them —most more active in hot weather—making up a global population of 17 million flies for every living human. Pssst ! They’ve got us surrounded.
Read More : Long Dismissed, Chronic Lyme Disease Is Finally Getting Its Moment
Season of wheeze
Ah, summer, it takes your breath away. Literally. More than 25 million Americans have asthma, and 4.7 million of them are children— according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). If that means suffering during the temperate months, it’s much worse when the oven that is summer turns the dial up to broil. Heat and humidity constrict and narrow airways , trap ozone, and cause the air to entrain more particulate matter from cars, trucks, and smokestacks. What’s more, stagnant summer air—especially in homes with poor air conditioning or none at all—can exacerbate the presence of mold, dust, and pollen. And then—and stop me if I’ve mentioned this before—climate change is making things more punishing still for people with asthma. A 2023 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency report found that rising temperatures could increase the incidence of childhood asthma by anywhere from 4% to 11%, due partly to worsening pollution and allergies, and the growing problem of wildfire smoke .
Speaking of wildfires…
When it comes to dust, haze, and a mustard-colored sky, Mars has got nothing on Earth—at least during the summer fire season. Last year’s Canadian wildfires , sparked by lightning and fueled by high temperatures and drought, torched more than 71,000 square miles of land in Canada—an area the size of North Dakota—and yellowed out skies in the U.S. from the Midwest to the Northeast to the mid-Atlantic states. But the U.S. is playing with matches too. California’s wildfire season runs from April through October—peaking in the summer—with megadroughts and heat waves driving the flames. Of the state’s 20 largest fires, half occurred from 2017 to 2022. Climate change, of course, plays a regrettable role in all of this.
Crime and punishment
Nothing puts bad guys in a bad mood like hot weather—or so it seems. A 2019 study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that on days with a maximum temperature above 85°F, all crime increases by 2.2% and violent crime by 5.7%. A 2023 study in PLOS One attributed this to what is known as the Theory of Routine Activities, which postulates that for crime to occur, three factors must be present: a motivated offender, a suitable target, and an absence of guards or surveillance. Of these, it is the second one—the suitable target—that is especially common in summer, according to the 2023 study, with greater numbers of people out on the streets.
As for the first variable, a motivated offender, well, even criminals don’t want to be outside commiting a crime in a 20°-below polar vortex. During a particularly deep freeze in 2015, Boston saw a 32% drop in burglaries, a 35% drop in larceny, and 46% drop in vehicle theft. Over the same period, New York City set a modern-day record , going 12 days without a homicide.
Summer’s contribution to violent crime in particular may be due at least in part to the common experience of hot weather leading to hot tempers, with even the most even-keeled people more inclined to blow a seam if they can’t cool off. One 2020 study found that people playing competitive video games in a hot room were more aggressive toward their gaming partner than they were when the room was cooler.
Daylight Saving Time
Don’t get me started on Daylight Saving Time. There is just nothing to like about this spring-forward inanity. For starters, it increases energy consumption (when it was supposed to decrease it) due to greater use of air conditioning. The changes in sleep patterns it causes contribute to heart attack , stroke , inflammation , and suicide , not to mention a 6% increase in fatal traffic accidents due to circadian scrambling and overall sleepiness. Small children and teens suffer particularly when the change in the clocks affects sleep cycles.
Read More : What to Know About the Latest Advances in Managing Severe Asthma
Finally, the atmospherics are all wrong. Nighttime is nighttime, people; the sun is the party guest that won’t go home if it’s still out at 9 p.m. I say send it packing no later than 8 p.m. and then race back to a nice wintertime sundown at cocktail hour. Cheers.
Trouble on the homefront
If you want to stay married, it might be wise to sleep through summer. That’s the finding of a 2016 study out of the University of Washington showing that August, along with March, are the two peak months for divorce in the U.S. The reason in both cases is more or less the same: couples tend to see winter and summer vacations as untouchable family time and, even in highly stressed marriages, will make it a point to hold the ship together for those treasured stretches. Once the good times are over, however, the marriages might be too.
“People tend to face the holidays with rising expectations, despite what disappointments they might have had in years past,” said sociology professor and the study’s co-author Julie Brines, in a statement at the time the research was released. “They’re very symbolically charged moments in time.”
When those expectations are dashed, a bust-up is likelier to follow. And while both early spring and late summer were implicated equally in that study, other research by Stowe Family Law in the U.K. found that September—the tail end of summer—is the peak divorce month on the other side of the pond, with total-immersion family time throwing financial, interpersonal, and other issues into relief.
It kills your skin
No matter how good it might feel to bake in the sun, your skin really, truly does not want a tan. In a rapidly warming world, it should come as no surprise that the sun is murder on your skin—drying it, aging it, cracking it, and much more importantly, leading to cancer. A 2022 paper in the journal Cureus found the highest rates of skin cancer diagnoses occurring from July to October.
Simple steps like wearing sunscreen , avoiding the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., and wearing protective clothing can all help reduce the risk. Sunshine in the winter, of course, can cause similar damage, but in the summer you're out a whole lot more and wearing a whole lot less. That—like summer as a whole—spells trouble.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Happens if Trump Is Convicted ? Your Questions, Answered
- The Deadly Digital Frontiers at the Border
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 31 Most Anticipated Movies of Summer 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Jeffrey Kluger at [email protected]

Cops Say DUI Teen Killed 2. Initial Punishment? An Essay
T here's outrage in India over a teen who cops say killed two people after driving while drunk. The Independent reports that the unnamed 17-year-old from Pune, in the state of Maharashtra, was driving a Porsche before dawn on Sunday when he slammed into a motorbike carrying two 20-something software engineers coming home from a party, according to local authorities.
・ What happened: The teen, said to have been out celebrating results of a test he'd taken, was reportedly speeding at nearly 125mph when he hit the motorbike. After crashing into the motorbike, the teen is said to have hit some nearby railings. The two riders died instantly at the scene, per police.
・ Video: CNN notes that CCTV footage from just minutes before the crash shows a white Porsche racing down a busy road; people can then be seen running toward where the accident took place, though the crash site itself isn't shown in the video.
・ Legalities: The legal age to drive in India is 18, while the legal age to drink in Maharashtra is 25.
・ Charges: The teen was first charged with death by negligence, but that was later upgraded to culpable homicide not amounting to murder, per CBS News . He was also hit with drunk-driving charges.
・ Repercussions: It's not just the nature of the boy's crime that has people outraged—it's the fact that his initial punishment handed down by the Juvenile Justice Board, after being released on bail, included getting treatment and counseling for his drinking, shadowing local police for 15 days, and writing a 300-word essay on road safety.
・ Reaction: "This was a surprising order" doled out by the juvenile board regarding the teen, the son of a well-known real estate mogul, says Maharashtra's deputy chief minister, Devendra Fadnavis, per CNN. He calls it a "heinous crime" that could possibly lead to the boy being charged as an adult (possible under the law if kids older than 16 commit such a "heinous" act).
・ Reaction II: "Why aren't essays assigned to truck drivers or bus drivers?" Rahul Gandhi, leader of the opposition Indian National Congress, gripes. One of the victim's relatives, meanwhile, tells NDTV that the fact the teen received bail almost immediately was "condemnable."
・ Change in plans: After backlash from the public, local cops approached the justice board on Wednesday and asked for the boy's bail to be revoked, and the board agreed, per CBS. The teen will now be sent to a juvenile detention center until at least June 5, and a further probe will determine if he'll be tried as an adult. The teen's father was also arrested for letting his son drive, as were three others who allegedly served the boy booze.
More From Newser
・ This Feather Is Worth 40 Times Its Weight in Gold
・ Palace Gives Update on Princess Kate
・ Billionaire's Attempt to Hide Portrait Blows Up in Her Face
・ His Wine Cellar Was a Mammoth Graveyard
・ Families of Israeli Hostages Share Disturbing Video
This article originally appeared on Newser: Cops Say DUI Teen Killed 2. Initial Punishment? An Essay


Cops Say DUI Teen Killed 2. Initial Punishment? An Essay

- What happened: The teen, said to have been out celebrating results of a test he'd taken, was reportedly speeding at nearly 125mph when he hit the motorbike. After crashing into the motorbike, the teen is said to have hit some nearby railings. The two riders died instantly at the scene, per police.
- Video: CNN notes that CCTV footage from just minutes before the crash shows a white Porsche racing down a busy road; people can then be seen running toward where the accident took place, though the crash site itself isn't shown in the video.
- Legalities: The legal age to drive in India is 18, while the legal age to drink in Maharashtra is 25.
- Charges: The teen was first charged with death by negligence, but that was later upgraded to culpable homicide not amounting to murder, per CBS News . He was also hit with drunk-driving charges.
- Repercussions: It's not just the nature of the boy's crime that has people outraged—it's the fact that his initial punishment handed down by the Juvenile Justice Board, after being released on bail, included getting treatment and counseling for his drinking, shadowing local police for 15 days, and writing a 300-word essay on road safety.
- Reaction: "This was a surprising order" doled out by the juvenile board regarding the teen, the son of a well-known real estate mogul, says Maharashtra's deputy chief minister, Devendra Fadnavis, per CNN. He calls it a "heinous crime" that could possibly lead to the boy being charged as an adult (possible under the law if kids older than 16 commit such a "heinous" act).
- Reaction II: "Why aren't essays assigned to truck drivers or bus drivers?" Rahul Gandhi, leader of the opposition Indian National Congress, gripes. One of the victim's relatives, meanwhile, tells NDTV that the fact the teen received bail almost immediately was "condemnable."
- Change in plans: After backlash from the public, local cops approached the justice board on Wednesday and asked for the boy's bail to be revoked, and the board agreed, per CBS. The teen will now be sent to a juvenile detention center until at least June 5, and a further probe will determine if he'll be tried as an adult. The teen's father was also arrested for letting his son drive, as were three others who allegedly served the boy booze.
- A DuckDuckGo extension in your browser, please access Newser without it: Either by removing it, whitelisting us, or using another browser.
Trump Team Seeks to Block ‘The Apprentice:’ Report
Trump is cranky enough about the forthcoming drama starring sebastian stan that he’s reportedly sicced his attorneys on the proceedings., sean ‘diddy’ combs is ‘incensed’ about cassie video: report, an unnamed “member of his inner circle” was quoted saying, “he insists it doesn’t tell the full story about what happened.”, singapore airlines changes seatbelt rule after deadly flight.
SMOOTHER SKIES
The airline has also changed at least one flight path after one person died and dozens were hospitalized.
George lucas slams ‘all white’ criticisms of star wars.
‘THEY’RE ALL ALIENS!’
The “Star Wars” creator addressed remarks he’s heard over the years that the first six movies lacked diversity.
Iconic ‘doge’ meme dog kabosu dies at 18.
MUCH LIFE, SO AMAZE
The dog behind one of the internet’s earliest and longest-lasting memes lives on in bronze memorials, advertising campaigns, and cryptocurrency.
U.s. fears joint north korea-russia ‘october surprise’: nbc.
PROVOCATION
The White House is increasingly concerned about the military alliance between Putin and Kim, six U.S. officials told NBC News.
Openai ceo altman repeatedly tried to get scarjo: report, he allegedly kept pestering even after she directly told him she didn’t want the gig., kremlin hits back at trump’s wild hostage negotiation claim, “there aren’t any contacts with donald trump,” kremlin spokesman dmitry peskov said thursday., fury after alleged killer teen in india told to write essay as punishment.
‘HEINOUS CRIME’
Night Editor

©AnilDave via Getty Images
Outrage is brewing in India after a teenager was released on bail, handed 15 days of community service and ordered to write an essay about road safety after allegedly killing two people while drunk driving. According to CNN, citing Maharashtra state’s deputy chief minister Devendra Fadnavis, the 17-year-old was allegedly speeding while driving a Porsche when his vehicle hit a motorcycle and killed two people during the crash in the city of Pune. The teen was taken into custody but later released by the Juvenile Justice Board. “The outrage grew after this. According to police, the boy is 17 years and 8 months. This is a heinous crime,” Fadnavis told reporters Tuesday, according to CNN. India’s juvenile laws means a child above 16 could be tried if they allegedly commit a “heinous” crime. “This was a surprising order passed (by the Juvenile Justice Board),” Fadnavis said. CCTV video shared across social media and on local news channels alleged to have been taken just before the crash shows the Porsche speeding along a road seconds before the incident, as people rush to the scene. The crash itself cannot be seen.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In conclusion, punishment is a tool for correcting behavior. It should be used carefully to teach and guide, not to harm or create fear. 250 Words Essay on Punishment Understanding Punishment. Punishment is a way people face consequences for their actions. It is a method used by parents, teachers, and the law to teach right from wrong.
Key Takeaways. Specific deterrence prevents crime by frightening an individual defendant with punishment. General deterrence prevents crime by frightening the public with the punishment of an individual defendant. Incapacitation prevents crime by removing a defendant from society. Rehabilitation prevents crime by altering a defendant's behavior.
The objective is that, the intensity of the punishment should fit the seriousness of the crime. This act of punishment is usually enforced by a sentencing judge whether in the form of a fine, probation or incarceration. One such example is, if an individual is caught stealing a bar. Free Essay: Punishment has been in existence since the early ...
58 essay samples found. Punishment involves the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual in response to a particular action or behavior. Essays on punishment could explore various theories of punishment, the effectiveness of different forms of punishment, or the ethical considerations surrounding punishment ...
punishment, the infliction of some kind of pain or loss upon a person for a misdeed (i.e., the transgression of a law or command). Punishment may take forms ranging from capital punishment, flogging, forced labour, and mutilation of the body to imprisonment and fines.Deferred punishments consist of penalties that are imposed only if an offense is repeated within a specified time.
One way of controlling and reducing crime is to punish offenders. Given that punishment typically involves restricting people's freedom and sometimes inflicting harm on people, it requires some justification as a strategy for crime control. Two main justifications exist for punishment: Crime reduction and retribution. These methods link to different penal policies. Reduction One justification
In the July Opinion essay "The Death Penalty Can Ensure 'Justice Is Being Done,'" Jeffrey A. Rosen, then acting deputy attorney general, makes a legal case for capital punishment:
Most theories appeal to punishment's effects on the future or facts about the past. This essay reviews these theories. 1. Forward-Looking Theories. According to forward-looking theories of punishment, punishments are justified to the extent that they bring about future good results. Theories differ in terms of what those results are.
Abstract. This classic collection of essays, first published in 1968, has had an enduring impact on academic and public debates about criminal responsibility and criminal punishment. Forty years on, its arguments are as powerful as ever. H. L. A. Hart offers an alternative to retributive thinking about criminal punishment that nevertheless ...
Punishment and sentencing are two essential components of the criminal justice system, each serving distinct yet interconnected purposes. While punishment is often viewed as a means of retribution or deterrence, sentencing involves the process of determining the appropriate consequences for criminal behavior. In this essay,...
Punishment Essay Adam P. Rogers Grand Canyon University Gov - 357 Professor Thurtle 11/5/ Introduction When discussing the idea and severity of punishment, it is not a new thing to talk about. The idea of different punishments and how severe those punishments should be is something that is still debated today. What we consider to be "modern ...
Crime is a violent act with an aim of hurting other individual. The aim of a crime is to destabilize the peace and tranquillity of the society. There are various aspects that make up a crime. They include: The nature of the crime. The motive of the crime. Whether the culprit was caught or not. The punishment. The reason of the punishment.
The main character of the novel Crime and Punishment by Dostoyevsky was influenced by the ideas of West European utilitarianism, based on the theories of correct actions and values."New, "strange, unfinished ideas' ' of Western […] We will write. a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts.
An Essay on Crimes and Punishments. Cesare Bonesana di Beccaria (author) Voltaire (author) An extremely influential Enlightenment treatise on legal reform in which Beccaria advocates the ending of torture and the death penalty. The book also contains a lengthy commentary by Voltaire which is an indication of high highly French enlightened ...
This essay remains hugely influential in providing the dominant framework for philosophic theories of punishment, including the death penalty. Hart, H.L.A. "Punishment and the Elimination of Responsibility." Punishment and Responsibility: Essays in the Philosophy of Law. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1968. pp. 158-185. Heyd, David.
An Essay on Crimes and Punishments by Cesare Beccaria translated from the Italian, 1775 (original published in 1764) ... That a punishment may produce the effect required, it is sufficient that the evil it occasions should exceed the good expected from the crime; including in the calculation the certainty of the punishment, and the privation of ...
Punishment Essay Punishment within judicial systems has been around ever since the biblical times. Criminals have always been punishment for their crimes in many ways, the most debated and talked about forms of punishment is the death penalty or also referred to as capital punishment.
The death penalty is applied unfairly and should not be used. Agree. Disagree. Testimony in Opposition to the Death Penalty: Arbitrariness. Testimony in Favor of the Death Penalty: Arbitrariness. The Death Penalty Information Center is a non-profit organization serving the media and the public with analysis and information about capital ...
PDF Cite. In Crime and Punishment, Fyodor Dostoyevsky created an unforgettable novel of haunting intensity. With its sustained focus on the emotions and thoughts of its young protagonist, Rodion ...
The punishment becomes a statement of meaning in an ongoing community conversation. Two additional aspects of restorative justice are particularly relevant to thinking about schools as moral communities. First is the issue of public confidence. There is some research indicating that restorative justice is supported by the general public.
Capital punishment - Arguments, Pros/Cons: Capital punishment has long engendered considerable debate about both its morality and its effect on criminal behaviour. Contemporary arguments for and against capital punishment fall under three general headings: moral, utilitarian, and practical. Supporters of the death penalty believe that those who commit murder, because they have taken the life ...
Capital punishment has been a debatable issue for decades. Some people believe that the death penalty plays a crucial role in the criminal justice system, while others think that this procedure is highly unethical. An essay on capital punishment may be a challenging assignment because students should know much about the subject.
Anger is growing in India after a teenager who allegedly killed two people while drunk driving was ordered to write an essay as punishment, with many demanding a harsher penalty and accusing the ...
Jump to essay-1 U.S. Const. amend. VIII (cruel and unusual punishments [shall not be] inflicted). Jump to essay-2 Gregg v. Georgia, 428 U.S. 153, 174 (1976). See generally Amdt8.4.2 Evolving or Fixed Standard of Cruel and Unusual Punishment. Jump to essay-3 Robinson v. California, ...
A 17-year-old in Maharashtra's Pune has been granted bail on the condition that he write a 300-word essay after allegedly driving drunk and killing two people. Two days after the incident, the juvenile's father was detained as per the Motor Vehicles Act, 2019. The tragedy has sparked outrage, with many slamming the judiciary and the existing traffic laws
A 2022 paper in the journal Cureus found the highest rates of skin cancer diagnoses occurring from July to October. Simple steps like wearing sunscreen, avoiding the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m ...
An Essay. There's outrage in India over a teen who cops say killed two people after driving while drunk. The Independent reports that the unnamed 17-year-old from Pune, in the state of Maharashtra ...
BreadTube is the place for the new wave of creators, journalists and artists making high-quality content that goes against the prevailing winds of the internet.
Posted May 23, 2024 10:00 AM CDT. Stock photo. (Getty Images/Ivan-balvan) There's outrage in India over a teen who cops say killed two people after driving while drunk. The Independent reports ...
Matt Young. Outrage is brewing in India after a teenager was released on bail, handed 15 days of community service and ordered to write an essay about road safety after allegedly killing two ...