Ten of our favourite early years problem-solving activities

A lot of the time when we hear the term ‘problem-solving’, our brain jumps back to the tricky maths teasers from our school days, and we immediately recoil a little. However, problem-solving is much more than number conundrums.
Problem-solving is a key part of early years development and can support learning across many of the My First Five Years streams. The skill of problem-solving starts developing very early in a child's life and stems from the knowledge of the world that they are constantly building.[1]. For instance, your baby may cry when hungry as they know that crying gets the attention of an adult who can feed them.
Problem-solving is a part of everyday life for children, from being a baby through to their future adulthood. When children learn how to solve problems, it can support them in building resilience, self-confidence and self-esteem. Taking part in problem-solving activities with others can also help children develop social skills, communication and relationships.[2]
Psychologist Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development also focuses on the importance of problem-solving for early childhood development. In each developmental stage of his theory, the psychologist emphasised the importance of play-based learning for young children when it comes to problem-solving, and in turn building skills across the spectrum.[3]


Supporting problem-solving
When thinking about problem-solving activities for your child, it can be difficult to know where to begin.
To keep children engaged, enabling them to take the lead and follow their interests, is key. Play-based, hands-on learning makes acquiring new skills more interesting and memorable for young children.[4]
Many activities can support children when developing their problem-solving abilities – the possibilities are wide open. When considering which problem-solving activities are the most effective, it is also important to consider how they can be adapted to multiple interests, abilities and how accessible they are when it comes to using resources and materials.
To help you out, here are ten of My First Five Years’ favourite problem-solving activities that you can try with your child.
1) Den-building
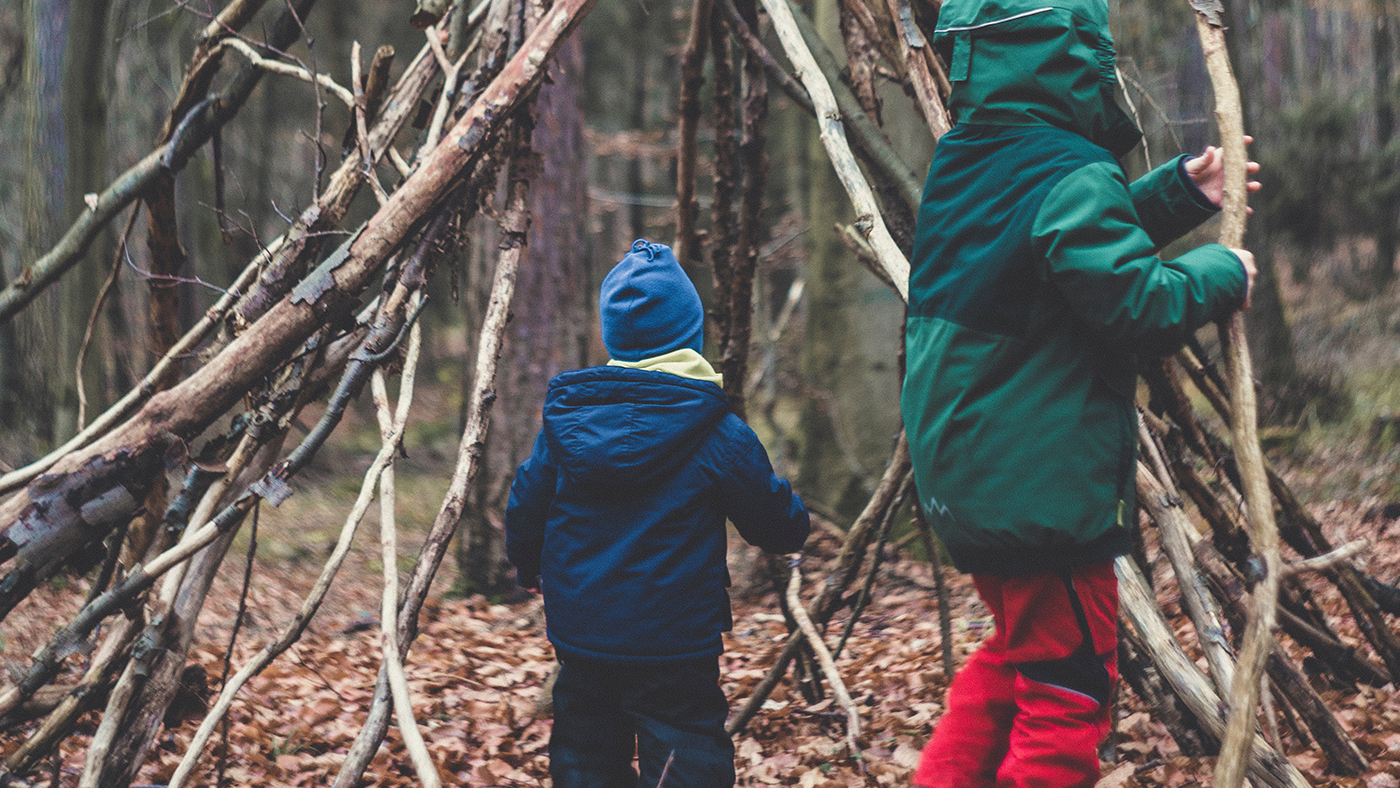

Den-building is brilliant for problem-solving as it requires creative and critical-thinking, foresight, and planning. It is also a wonderful way to promote sustained shared thinking with your child. Sustained shared thinking is a way of working together that encourages individuals to evaluate the problem that they are working on and is focused on collaboration, using experiences and prior knowledge.[5]
When building a den with your child, encourage your child to take the lead. You could provide materials such as boxes and blankets, or you could even ask your child to decide what materials you need before starting, encouraging them to plan out their work. Den-building can also be done both indoors and outdoors and with children from a young age. You may find that people have already started creating these in your local woodland that you can add to, adapt, or just enjoy!
2) Cooking and baking

Cooking and baking are not only fun activities, but they also focus on mathematical problem-solving. To bring problem-solving into a cooking and baking activity, you can ask your child to count out simple measurements, for instance, cups of flour or sugar. Activities like cooking or baking are great for children to be able to take ownership of what is happening; encourage them to choose what you will make and allow them to do all the elements themselves.
What’s great about cooking is it really doesn't matter how it turns out! Problems can arise often in cooking or baking, for example, the mixture may turn out too dry, you may be an ingredient short, or your cakes might not rise how you expected them to. If this is the case, talk to your child about what might have gone wrong and how you can rectify it next time! Then when they come to do it again, they can use their prior knowledge to help them.
3) Playing with patterns

Patterns are a great activity for mathematical problem-solving. You can create patterns of any objects that you can find! For example, with pieces of fruit, pebbles from the garden, building blocks or even snacks! You could encourage your child to continue patterns, fill in the missing pieces or even create their own for you to solve problems with as they grow more confident.
4) Sorting and categorising
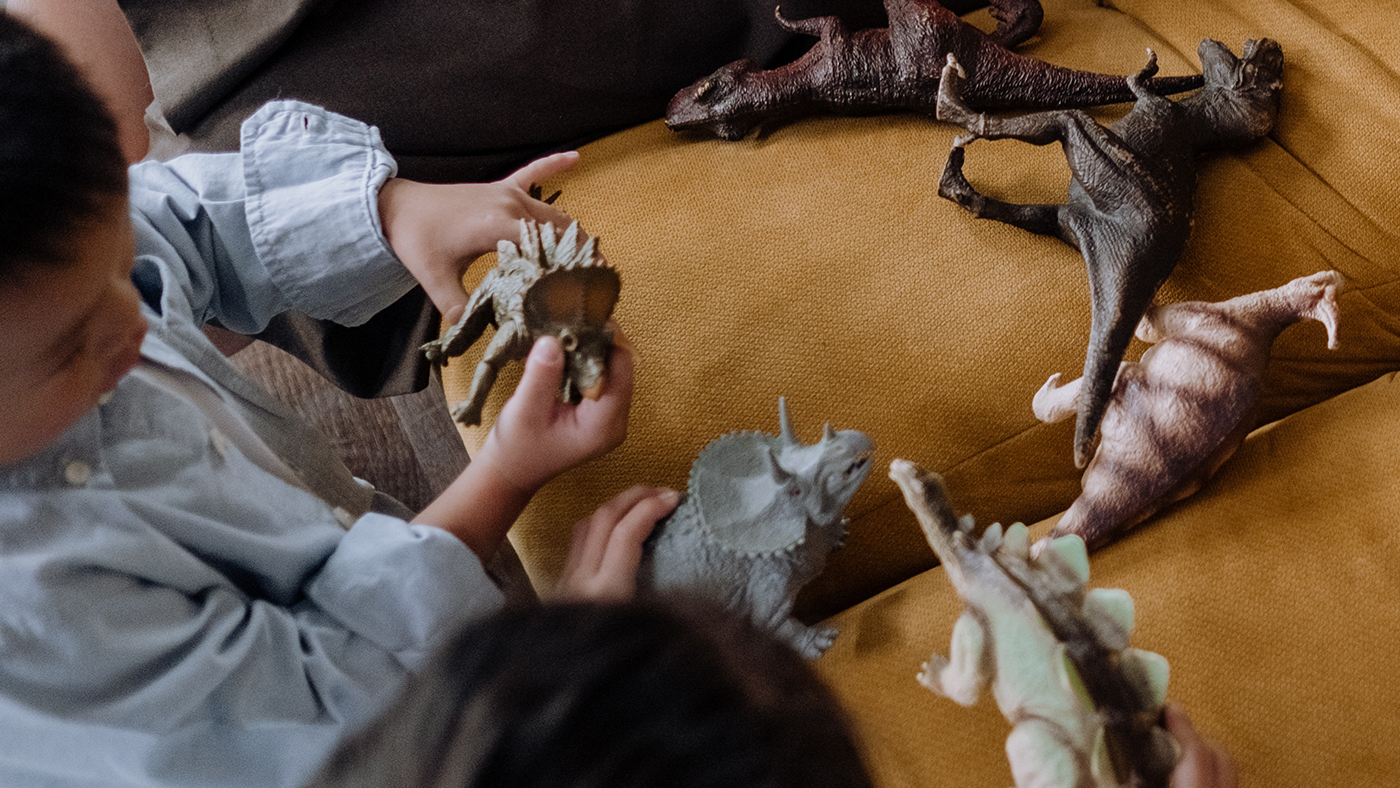

Sorting and categorising objects is an activity that supports children in mathematical problem - solving and can be easily adapted to individual children’s abilities . You could encourage your child to sort by shape, size, colour, or better yet , their interests . For example, if they are a dinosaur enthusiast, they could classify them by wh ich is their favourite or least favourite , or order them by the size of their feet. They may even find enjoyment in helping you with daily sorting such as recycling or washing!

Puzzles are a fun resource that can be used with children from a very young age. There are a wide variety of puzzles for children to access , such as chunky wooden puzzles or traditional shape sorters. When playing with puzzles, children will have to use their prior knowledge and experience of shape, space and measure whil e also experimenting with different angles and placements. They will use trial and error to find the best way to complete the puzzle and then will use this knowledge in future attempts.
6) Ice rescue
As well as being a great problem-solving activity, ice rescue enables children to explore seasonal changes, temperatures and develop their fine and gross motor skills using tools. To play ice rescue, freeze toys inside ice overnight. This could be in cake moulds or small bowls. Use toys that will motivate your child, for instance, their favourite small figurines.
Once frozen, place your blocks of ice in a big bowl or tray, and encourage your child to think about how they can get the items out. You could provide tools, or even get your child to find tools themselves.
7) Obstacle courses

Obstacle courses are versatile and can be made with a wide variety of resources. When setting up an obstacle course for your child, try to include sections where your child will have to stop and think about how they will have to adapt their body to move through it , for example, something that they must climb over or under, or a section where they have to move differently. You could even include them in trying to create the obstacle course and allow them to make it the most challenging they can.
8) Filling, emptying and investigation

Many children enjoy filling and emptying during play. Investigating this way helps children to get a sense of size, capacity and explore predicting and estimation. For instance, if your child likes playing with sand, you could ask them to guess how many scoops they will need to fill a container, or if they like water play you could challenge them to find a way to move the water between two containers as quickly as possible , or from one tray to another.
9) Story problems
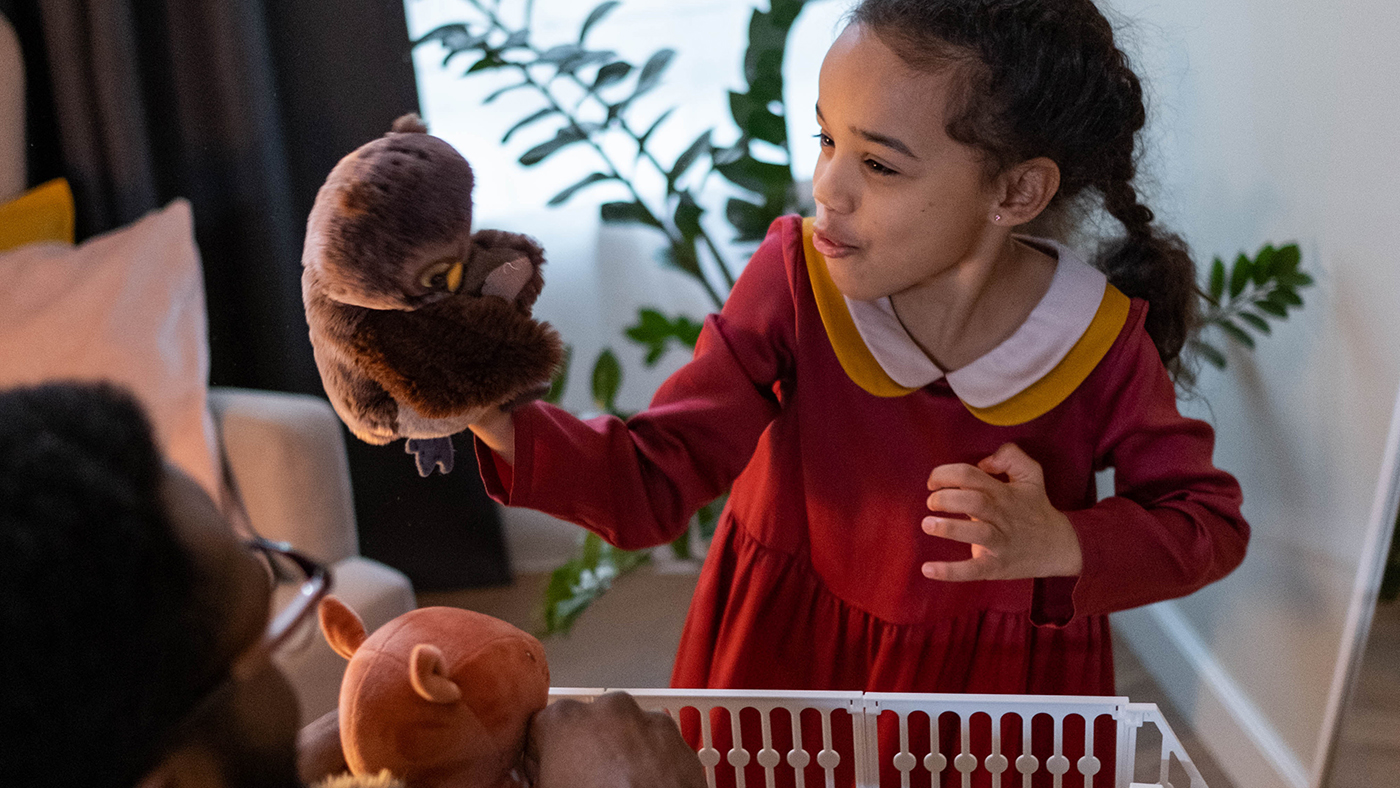

Stories are an effective way of introducing problem-solving and they can be a highly engaging way to promote creative and critical-thinking. You could use familiar or traditional stories to help scaffold play opportunities for your child. For example, you could try building a house for the three little pigs that cannot be knocked over. You could test out different methods using materials that you can find around your home.
If you are feeling creative, you could also make up a little story using your child’s favourite toys. An example of this could be figuring out how to share food between their favourite teddies during a picnic and making sure that everyone gets enough.
10) Playing with loose parts or open-ended resources
Natural materials such as leaves, conkers, sticks, acorns, and pinecones are all brilliant open-ended play opportunities (if supervised). You can also use household objects like bottle caps, curtain rings, tubes, tins, boxes, buttons etcetera in this sort of play. All it requires is a tray of different objects that you've collected and time to explore them. Your child will have to think creatively about how to utilise the objects and in doing so will be challenging their cognitive capacity by problem-solving to achieve the desired outcomes.
References
[1] Rachel Keen. (2011). The Development of Problem Solving in Young Children: A Critical Cognitive Skill. Available: https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev.psych.031809.130730#_i22 .
[2] Sheila Ebbutt. (2009). EYFS best practice - All about ... problem-solving . Available: https://www.nurseryworld.co.uk/features/article/eyfs-best-practice-all-about-problem-solving .
[3] Piaget, J. (1983). Piaget's Theory. In P. Mussen (ed). Handbook of Child Psychology. 4th edition. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley.
[4] Unicef. (2018). Learning Through Play. Available: https://www.unicef.org/sites/default/files/2018-12/UNICEF-Lego-Foundation-Learning-through-Play.pd .
[5] Kathy Sylva, Edward Melhuish, Pam Sammons, Iram Siraj-Blatchford and Brenda Taggar. (2004). The Effective Provision of Pre-School Education (EPPE) Project: Findings from Pre-school to end of Key Stage1. Available: https://dera.ioe.ac.uk/8543/7/SSU-SF-2004-01.pdf .
T&C's | Privacy Policy | Cookies
© Copyright 2023 - My First Five Years Ltd.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- Administration for Children & Families
- Upcoming Events
Teacher Time
- Open an Email-sharing interface
- Open to Share on Facebook
- Open to Share on Twitter
- Open to Share on Pinterest
- Open to Share on LinkedIn
Prefill your email content below, and then select your email client to send the message.
Recipient e-mail address:
Send your message using:
Problem-solving and Relationship Skills in Preschool
Woman: Places, everyone. Are the lights ready? Three, two, one.
Saameh Solaimani: Hi, everyone. I'm Saameh Solaimani. Welcome to "Teacher Time.” Thank you so much for being here with us today.
Gail Joseph: Hi, everyone. I'm Gail Joseph, and I'm so excited to be joining you on "Teacher Time" today. Now, Saameh, I always think it's better when we start with a song, so shall we?
All: [Singing] "Teacher Time.” "Teacher Time.” "Teacher Time.” "Teacher Time.” "Teacher Time.” "Teacher Time."
Gail: Here we are. I love your puppet moves. You've got some really good moves.
Saameh: Thank you. I worked hard on this.
Gail: Well, hi, everyone, and welcome to our third preschool episode of "Teacher Time" this program year. I'm Gail Joseph.
Saameh: I'm Saameh Solaimani, and we're from the National Center on Early Childhood Development, Teaching and Learning.
Gail: We are so excited to have you here with us today. We have been focusing on positive behavior supports this season of "Teacher Time.” Hopefully, you've joined us for some of the previous episodes. So far, we've talked about the importance of relationships and how to support emotional literacy. And today, we're going to be focusing on problem-solving and relationships, and friendship skills in preschool.
I want to draw your attention to the viewer's guide. I've printed mine out here. It's beautiful. You can find it in the resource widget. If you haven't looked at our viewer's guide for a while, I strongly encourage you to. This season, our viewer's guide is a viewer's guide for birth to five, including specific age group information for infants and toddlers and preschool children. It is packed with information about development, about teaching practices. There are quick tips in here. There are reminders. There are things you can cut out and post and put up in your learning space. There are spaces for notetaking.
On the last page is just an extensive resource list that you are going to love. You can download the guide and use it throughout our time together for taking notes, for reflecting, planning how you might use some of the "Teacher Time" practices we're going to talk about in your own settings. And please share your viewer's guide with colleagues. Also, we want your ideas in the next issue of "Teacher Time.” You can see on the back that we ask you to submit some of your own strategies and tips, and then you'll be published in the "Teacher Time" viewer's guide.
Saameh: That would be awesome. We always love to hear from you. Thank you so much, Gail. During our time together, we're going to be discussing teaching practices that support positive behavior. We're going to take some time to promote your wellness with our It's All About You segment. We're going to connect effective practice to brain development in our new segment, which some of you may have seen in our last episode's Neuroscience Nook.
We're going to discuss small change, big impact, and in our focus on equity segments, individualized strategies that build a sense of belonging and promote social and emotional skills with all children, including children who have a variety of learning characteristics. And we're going to wrap up our time together, as we always do, with our BookCASE, where we connect our topic to books that you can share with children and families.
Gail: We love the BookCASE and our "Teacher Time" librarian. Like we do at the beginning of most "Teacher Times," we want to check in with how you're feeling, such an important thing to do periodically throughout the day. Look at our "Teacher Time" feeling tree, find a feeling creature. They all have little numbers on them.
And post in the Q&A which number creature you most relate to at the moment and why. We want to hear from you. We have our amazing Q&A team there, ready to see your input. I'm going to go ahead and start. Now, every time I look at — what I love about our little "Teacher Time" tree here is that I always think a little bit differently about how these creatures are feeling, which is fun. It helps children do that, too.
Saameh: Right.
Gail: I think the little guy that is swinging from the tree there. I'm just pretty excited to be here. I've been on some travel. I'm excited to be back with you and back with our "Teacher Time" viewership. How are you feeling, Saameh?
Saameh: I actually was thinking about this. And I think number 12, sitting on the leaf, surrounded by friends, by community, by all of you. Yeah, I'm feeling very part of this learning community.
Gail: I love it. And our viewers are checking in. Five, a rough week. Some weeks are like that. I hope it gets better for you, Amy. We've got a 12. Somebody is feeling like you. One, five. Our viewers are all over the tree, checking in. I feel like number five, pretty rough afternoon. My goodness. We hope that spending some time today thinking about your own professional development might feel a little bit uplifting for you. But we definitely know how it feels when you're not having a great week, too. Just hanging in there. Thank you so much for sharing.
Saameh: Yes, yes.
Gail: Thank you. Keep it going. Keep it going.
Saameh: We're very excited to be focusing on positive behavior supports this season, as you know. And social and emotional development. As you may know, is one of the domains in the Head Start ELOF, which stands for Early Learning Outcomes Framework. The practical strategies we're going to be discussing today are going to be focusing on the relationships with other children subdomain of social and emotional development. And you can see that highlighted here.
Gail: I love that. Now, like we said last month, this season of "Teacher Time" is focused on working our way through the Pyramid Model. Some of you might be really familiar with the Pyramid Model. Maybe your program is participating in a pyramid training. But if you're not familiar with it, the Pyramid Model is really a model or a framework of positive behavioral support for proactively addressing the social and emotional development. And for preventing and addressing challenging behaviors of young children. The framework offers a continuum of evidence-based teaching practices that are organized into four levels of support. And you can see those there.
At the foundation, it's all about nurturing and responsive relationships. Not only between the teacher, the educator, and the children but between children and between educators. It's all about these relationships. And we want them to be nurturing and responsive no matter what relationship they're in. That's the foundation. The next are high-quality supportive environments. How can we create both the physical and temporal structure of the environment to support positive behavior?
Then we level up and go to social and emotional teaching strategies. That's where we're at right now, is going to dig into some of those social and emotional teaching strategies. Then at the very top, when all of the bottom three pieces are in place, there might still be some children that have some behaviors that could require a little bit more intensive intervention. And we're going to talk about that in May. Be sure to come back.
But if you want to learn more about the Pyramid Model, you can check out the resource list in the back of your viewer's guide for a lot more information about it. Now, we would love to hear what strategies and practices you have in place to support young children's problem-solving and their friendship skills with children that you're working with.
Go ahead and start entering those in the Q&A. And our Q&A team, we've got, like, the star Q&A team today. They're going to start sending those out, too. We're going to be tracking them, but they're also going to be sent out so other people can see them as well when you share what strategies you're using. We always learn so much from our viewers. And there's always something that we're, like, a gem out there in how you're supporting young children's problem-solving.
Saameh: Such a wealth of resources out there.
Gail: Absolutely. Now, as a reminder, positive behavioral support, or sometimes called PBS, sometimes you might hear it called PBIS. Sometimes you might even hear it called a multi-tiered system of support. But positive behavioral support is a positive and proactive approach to preventing and addressing challenging behavior. It focuses on using very intentional teaching strategies to proactively, that's such a big part of it, proactively build all social and emotional skills. And today we're specifically thinking about building problem-solving skills and relationship skills for young children. Now, positive behavioral support recognizes that all behavior communicates a message or a need. And some behaviors, as they're trying to get their needs across, we might find challenging.
Once an educator understands the meaning, what is the message that the child is trying to send with their behavior? What's the meaning? They want something. They want to get away from something. They're not sure how to play with their friends, but they're trying in the way that they can. Once you know what the meaning of that challenging behavior is, then we can figure out how to teach the child a more effective way to communicate their needs and problem-solve with support.
Saameh: So important to keep in mind. Now what we're going to do is we're going to turn our attention to you in our All About You segment. We know that we do our best caregiving and teaching when we feel well ourselves. Engaging in self-care practices can help educators build greater social and emotional capacity to work through problem-solving together. And our ability to support children with problem-solving and relationship skills starts with our ability to center ourselves by noticing and observing what's happening with as little judgment as possible.
We can help young children work through challenges with peers from a more grounded, soft, and objective place, naming what we see happening calmly without so many of the other things going on when we're feeling stressed and overwhelmed. What we're going to do is a little body scan. Before we can support the children in our care with problem-solving and relationship skills, it's important to find ways to regulate our own feelings throughout the day.
Taking a minute to do something like a body scan like we have here to notice what's happening in our own bodies is softening in the moment. We can slow down and center ourselves throughout the day. This practice supports our own well-being first, enabling us to hold a non-judgmental space, as we were saying, respond intentionally to children's cues, behaviors, and communications as we support them in building healthy relationships with each other.
Here we go. Start with a deep breath. Okay, I noticed as I was saying that I was holding my breath. Breathe. Okay, so we're going to start in a seated position or laying down, whatever is comfortable for you. And now you can bring your attention to your body, and you can close your eyes if that's comfortable for you. And you can notice your body wherever you are.
As you exhale, you have a sense of relaxing, and you can notice your feet or body on the floor. You can notice your back against the chair or maybe on the floor. Bring your attention into your stomach area. If it feels tight, let it soften. Notice your hands, arms, shoulders, and let them be soft. Let your jaw and facial muscles be soft. Notice your whole body present, and take one more deep breath. Okay.
Okay, we would love to hear how you were feeling during that or feel now or after the body scan. What do you notice? And let's see. And I noticed like I was saying, that I was holding my breath.
Gail: I feel like we should do that right before "Teacher Time.” It would be really helpful.
Saameh: That's right.
Gail: I felt so calm and centered.
Saameh: We'd love to hear from you how that experience was. Thank you so much for taking the time to take time for yourself. Calm. Self-aware. Conscious. More relaxed.
Gail: It doesn't take very long too, and I know that when I was teaching on a regular basis, just having those moments where I could just feel that tension in my body, and it just takes a moment to take a breath before I interact.
Saameh: It is amazing how much one minute of breathing can do. Yes. It’s not something that requires a lot of time, which I know we don't necessarily have as teachers sometimes.
Social competencies like self-regulation, empathy, perspective-taking, and problem-solving skills are key to foundational healthy social-emotional development. And these include positive interactions and friendships and relationships between peers, as we know. Educators can help children learn the skills necessary to develop healthy peer relationships and find ways to work through social conflicts with adult support.
And that's where we come in. And teaching and modeling problem-solving skills early on with preschool children builds a foundation of problem-solving and relationship skills that most children can access with adult support and start to use independently as they continue to develop. The more we can support young children in developing problem-solving skills in their learning environments, the less we'll see some of those challenging behaviors that oftentimes arise from not having the resources, the tools to work through the problem as they come up, which they will because that's life.
It's important to note that there might be some children in your care who don't readily learn these skills through foundational teaching strategies. This might include children with disabilities or suspected delays. It's important to be aware of the progress for all children and use more individualized practices to work on these skills with children who need a little more support. That’s what we'll be doing today, sharing some strategies to do just that.
Gail: Some key ideas and practices for supporting problem-solving and peer relationship skills with preschool children are the first little slide that you see there or picture that you see there is about promoting healthy relationships. Preschoolers are increasingly interested, as our viewers know, in developing friendships with one or two preferred peers, like we see in the photo on the left. They're able to engage in group play and independently initiate interactions with peers, which is so fun to see develop.
Preschoolers might suggest something to do, like let's play a restaurant or let's build a swimming pool for our animals together or join in an existing activity. Hey, can I play too? Educators can support preschoolers in promoting healthy friendships in quite a few ways that I'm sure our viewers are already doing. But just to name a few, one is that you can help children plan what and how they will play together.
One thing that I always like to, I'm going to go off for a moment, is that one thing that I think about a lot as a preschool teacher is thinking about materials and resources and activities that require two children to play together so that you set the stage for children to interact with each other. Things like those teeter-totters or rowboats in classrooms is just one obvious idea that takes two children.
Another thing is providing suggestions for initiating interactions with other children. And a quick tip there too is right before children go to play, if there's a child that you think could use a little bit more support, is to do a little priming and say, “hey, point to two or three things that you could play with a friend,” and you'll see that they can increase their initiations with other children.
Then, encouraging children to consider other ideas. I don't know if anybody out there is a big puppet user, but I used a lot of puppets when I was teaching at Head Start, and this was a great way to model like at a circle time, model with a puppet and other children role-play how I could consider somebody else's idea. Lots of ways to do that.
Saameh: This is a great time for us to pause and think about what value do I place on peer relationships, and how do I expect peers to act with each other? Sort of that, taking a moment to think about our own ideas because we're subjective beings, and we have our own experiences. It's really important to just take a moment. And awareness of our responses to these questions is supportive of our equitable practice. I do have to say I love what you said about puppets, and we're going to be seeing a little bit of puppet work later on in our episode today. I am also a fan of puppets.
As you see, the second photo you see is representing teaching problem-solving steps, which is so important. Preschoolers are willing to try different strategies to solve problems and show flexibility in their actions and behavior, and they can plan ways to solve a problem and evaluate solutions with our support. In a minute, we're going to hear from Dr. Angel Fettig, Professor of Early Childhood Education at the University of Washington, who will share strategies to support problem-solving in preschool classrooms. She's going to talk about the steps.
Gail: That's great. Of course, another way that we can support children, which you probably feel like you're doing all the time, is teaching problem-solving in the moment. One is to proactively teach, which we're going to hear about strategies for doing that. But the other thing is then supporting that problem-solving as it occurs in the moment. There are a few steps that educators can do to work through that. One is anticipating that social conflicts are going to happen, and you try and anticipate it before they happen.
You might notice a child that's coming into the classroom or into the learning setting feeling a little bit tired, maybe something upsetting happened before, maybe you have some communication with the family and understand that something troubling has just happened at home, and the child is coming into the space. Maybe they're not usually having a difficult time with problem-solving, but today they might be.
But another thing that you can do is anticipate, did you introduce a new toy into your learning space? Maybe you introduced some new props in the dramatic play area, and you know that a lot of children are going to want to use them. You're anticipating that probably in that space, there's going to be a little bit more need to support problem-solving in the moment. You want to anticipate social conflicts before they happen.
Another thing that's so important is being close and helping children manage their feelings. If I'm anticipating that there might be some problem, maybe an individual child might need some more support, or there's an area in the classroom that I think, oh, I'm probably going to want to be close there, is to get close because children will, as they get excited or upset, that fight or flight comes in. You want to be there to support them to help remember some of the problem-solving steps that you've provided.
Now, providing support and reminders of problem-solving steps would be next. I'm going to be close with them, and then I'm going to provide support, and that support could be verbal like I could remind them of the problem-solving steps. It can also be visual, and we're going to talk about some of the visual supports you can have in your classrooms.
Some people in our Q&A have already talked about ways that they've used visuals with problem-solving solution kits, et cetera. We can encourage children to generate and evaluate multiple solutions. I'm going to say that this is really where it's at for preschool children, is to encourage them to generate as many different solutions to a problem as they can. When children have a restricted number of solutions they can try, they're bound to run out of things that are working for them. We want to encourage them to keep being really creative and generating so many different solutions.
Last but not least, when children do problem-solving, find some way to celebrate that. It might be a thumbs-up. It might be a high-five. It might be with a super friend cape or with some other type of big celebration because this is hard work, and it's really hard work when you're a young child just figuring it out. We want to make sure that we're celebrating that. We're going to remember that we always want to individualize the strategies that we're going to use to provide support based on the skills of the children that you're supporting.
Some children might need some additional amount of language that needs to be modified. Some children might need visual cues or gestures paired with verbal language. Some children might need some specific feedback on the consequences to help them learn the effect of their behavior on the environment. Stay tuned for BASICS where we're going to share about some more strategies for providing feedback.
Saameh: I love that. I love what you said about anticipation. I think it goes such a long way. Also, what you were saying about problem-solving and the children coming up with the solutions, generating the solutions, and I keep thinking about how problem-solving is also play in a way.
Gail: Yeah.
Saameh: It's exploration. It's play. In a way, it's fun. It's not necessarily a negative thing. Sometimes we think problem as negative, and it doesn't have to be.
Gail: It can be like a fun challenge. I would support children, and I'd say, “are they making it tough on you?”
Saameh: Exactly.
Gail: And they'd be like, yeah. But then they'd be encouraged to keep going. Sometimes I'd say, let me look. Let me look. I think you've got more solutions in there. I'd peer into their ear, and they'd think that was really fun. You can just really be fun and encourage them to be creative and think of more solutions.
Saameh: I love that one. We’re going to hear from Dr. Angel Fettig, who we were talking about earlier, as she discusses strategies to teach problem-solving skills.
[Video begins]
Angel Fettig: I think in early childhood settings, I think the best thing is to think about simple steps to teach kids. So simple, concrete strategies they can use in the setting. My favorite is to really think about the four-step problem-solving technique. Step one is, what's my problem? Really being able to know that there's a problem here, and this is the problem. Being able to identify it.
Angel: And then step two is helping them brainstorm. What are some things I can do to solve this problem? Guiding them in understanding, How do you brainstorm for solutions?
Gail: Okay.
Angel: And then the next step, step three, is to think about evaluating the solutions you came up with. Do I think using this step is going to be fair for my friends? Is it a safe solution?
Gail: Right.
Angel: Am I going to feel good? Is my friend going to feel good?
Angel: And then step four is guiding them to try it out.
Angel: You try it, see if it works.
Angel: If it doesn't work, then encourage them to try a different strategy, try a different skill. Those are the four steps. And it's really important that we teach those steps systematically and with visuals, just like how we will typically teach any content in early childhood classrooms.
Angel: I think as early childhood educators, we need to plan these into our curriculum in teaching problem-solving skills.
Gail: Great.
[Video ends]
Saameh: So wonderful. As we saw, Dr. Fettig outlines four important steps to go through with preschool children to help teach problem-solving skills. First of all, helping children identify what the problem is in the first place. Next, inviting children to generate and evaluate multiple solutions through brainstorming, as you were sharing, Gail, and then evaluate the solutions. How are these solutions working out? Lastly, we can help children select a solution and try it out and see how it works. We'd love to hear from you in the chat. What are some ways that you support problem-solving with children in your care? Please share in the chat.
As you're doing that, I wanted to share something I remember being surprised to learn early on in my career as an early childhood educator. It was just, like, what a big part of our job supporting children and problem-solving is. It's a huge part. I mean, it was most of the day. It was really doing that, and I was in for a surprise. But, getting down on the children's level, taking the time to be present and understand what's happening, how we can support children to work through the problem in that moment, which I'm sure you all experience many times a day. And the solution kit. We will be talking about that.
Gail: That's right. Owl's Pals, that's a great social and emotional curriculum. I see that one coming up. Tucker the Turtle, we know about that. That's a great one. Trying to hang in there. Sarah, yes, that is so important. It's just that trying to hang in there, taking those deep breaths, getting centered, and getting back into it and knowing that this is part of the job.
Saameh: It truly is.
Gail: What a great job it is to help build this, like, social and emotional foundation for young children so that when they're entering into even larger group settings, they're going to be really successful. Yes, trying to hang in there but knowing you've got a great purpose.
Saameh: Absolutely. What we're going to do now is we're going to take another moment to pause and reflect, a reflective moment, on questions that will support equitable teaching practices. We're going to invite you to reflect on the following questions. How do I expect peers to act with each other? How do I feel about conflict? Do I listen openly to all children when there is a problem? To just take a moment and think about those things. We're going to revisit these questions in our Focus on Equity segment. We thought it would be nice this time to weave throughout.
Gail: I love it. Those are such good questions. I'm just thinking about it myself, like, what was I expecting?
Saameh: Right. Now for our Neuroscience Nook segment. Research tells us that the early years are foundational for brain development. And adults play an important role in supporting healthy brain development connections and architecture.
In this segment, our Neuroscience Nook, we are excited to connect this research to everyday teaching practices. I'm going to just take a moment for this side note. As questions are coming up for you, we want to hear them. Please put them in the Q&A or post them in the "Teacher Time" Community in MyPeers. Just wanted to say that.
What we're going to do is we're going to shift our focus. We're going to talk a little bit about executive functioning, which is a very important brain function. The prefrontal cortex begins to develop very early in life. This area of the brain is responsible for what are called executive functioning skills, which some of you may have heard of. They're essential for development of strong and healthy relationships.
This is a really great graphic here, as you can see. It includes what are some of the main functions of executive functioning and executive functioning skills. What are they? Attention, that would be being able to stay focused on a task. Working memory, which is being able to remember rules and procedures. Self-regulation and the ability to control impulses.
Right there, you can see how important that would be for developing strong and healthy relationships. Organization, things like switching between tasks, that would be called flexible thinking. Problem-solving, planning, behavior, decision-making, and motivation. As you can see, hopefully, you're convinced that executive functioning skills are very important indeed. You can see how all these skills are important.
Gail: Absolutely.
Saameh: Also are interrelated in a lot of ways. What we can do is help young children start to develop these critical relationship building and problem-solving skills. I know what all of you are doing every day, through responsive caregiving and effective teaching practices that are responsive to an individual child's needs. In our most recent episodes of "Teacher Time," those were building relationships and emotional literacy in preschool, we've talked about ways that you can support executive functioning through things like serve and return, and the flipping your lid, the hand model.
Gail: Yes, I remember.
Saameh: Yes. From Dr. Dan Siegel. I practiced that a lot before, by the way.
Gail: Yeah, it was good.
Saameh: We also encourage you to look back at the last two viewers guides, that would be building relationships with children, birth through five, and emotional literacy with children, birth through five, to see more about the importance of nurturing and responsive relationships on the developing brain. What we're going to do is we're going to hear — now we're going to hear from Dr. Juliet Taylor, as she describes the development of executive function.
Juliet Taylor: I'm going to show you a graphic of how executive function develops over time. Here's sort of a graphic representation. And one thing to point out is that we are not born with executive function skills in place. We're born with the potential to develop them, or not, depending on our experiences, our neurophysiology, and the interactions between those things.
This graph shows that on the horizontal axis you can see this is ages birth to 80, and notice that there's not an even distribution between the ages. And that is because there are particular peaks in executive function development. You can see skill proficiency on the vertical axis. And I'm going to highlight a couple of areas where you see tremendous growth in executive function skills, and that is really in the preschool ages, between three to five, and then in early adolescence to early adulthood, there's another spike in development.
The foundations of executive function are laid down in the earliest months and years of life, and that really happens through basic sort of serve and return, it's sometimes called, or those basic interactions between child and adult that happen over and over and over again. And that spike really does happen in the preschool years after children have verbal language.
Saameh: As you can see, that graphic, it's just so helpful to see the development pattern. And we see that we aren't born with executive function. We are, however, born with the potential to develop them, and why our support as educators is so important. We know that the foundation of executive function skills are laid down in the first months and years of life. And what we heard and saw, the yellow highlight, is a spike in executive function development between three and five years old after many children have developed verbal language.
Gail: I love that, and I saw the other spike was like that, like, early or later teen years.
Saameh: I noticed that.
Gail: I've got two of those at home. I feel like I see that on a regular basis. Yeah, very true.
Saameh: It resonates.
Gail: It really resonates, both as a preschool teacher and as a mom of adolescents. That's so great. And, like, looked like some declines as we get older. It's not fun.
Saameh: A little less fun.
Gail: We're going to get to the "Teacher Time" BASICS, and we're going to talk about how we can use BASICS to support problem-solving and relationship skills. If you haven't joined us before, let's just go through really quickly what BASICS is. It's an acronym that helps us remember some really powerful teacher-child or adult-child interaction moves that we can make that can support children's growth and development in any area.
The "Teacher Time" BASICS are B is for behavioral expectations in advance. It is always helpful to tell a young child what you're expecting from them before you start a new activity. A is for attending to and encouraging positive behavior, which is so relevant to the topics that we're talking about now. S is for scaffolding with cues and prompts.
Those can be verbal cues, visual cues. You're going to see some of that today. Increasing engagement is the I. C is for creating and adding challenge. Young children grow when we add some challenge to, whether it's intellectual challenge or social and emotional challenge, that creates some growth for young children. And S is for that specific feedback.
If you've joined us for other webinars, you know that we only take two of these letters to focus on. It's too much to do all of them in one episode. We've focused on different letters at different episodes. You'll see that if you want to go back and look at some prior episodes. You'll see some of the other letters.
But today we're going to focus on the C and the S, create or add challenge, and the second S, which is about providing specific feedback to support problem-solving and relationship skills. We're going to jump to it. We're going to start with creating or adding challenge. This is one of my favorite things.
One fun way that we can create or add challenge to problem-solving and relationship skills is to create a friendship kit and invite children to use it when they notice that another child is upset. You can see on the screen that the friendship kit can have lots of little things in it. Really it could be like a shoebox. It could be a file folder. It could be any way that you can contain it. It could be a lovely basket.
But the idea is that in this friendship kit, there are things like maybe a pack of tissue if somebody is crying. Maybe there's a soft toy for someone to cuddle with if they're feeling like they're missing somebody. Maybe there's a pack of bandages to not only help with a small cut, but maybe if your feelings are hurt. We've had children also apply bandage. Very sweet. A sheet of stickers. Maybe a sticker would help someone.
There can be visual support cards of simple problem-solving solutions and things that you can do when a friend is in duress. Things like giving a gentle hug. Maybe saying, I'm sorry. That is certainly a challenge that we offer to young children is to provide a genuine apology, which is a great repair strategy for them to learn. That's one thing. I'd be curious to see if people are using friendship kits. You can enter that into the Q&A.
I've had lots of lovely experiences in my classroom with these friendship kits where children go to them when another child is upset. I had one experience. Well, I'll tell that story in a little bit. But they're just such great, lovely stories about how young children will use it. It's just like a physical reminder of what it takes to develop those special friendships. Now, there's another way that we can create or add challenges. Thank you for advancing that. That was a nice thing to do from our friendship kit.
Gail: Thanks for advancing the slide.
Saameh: Of course.
Gail: Is to actually create a problem-solving solution kit or problem-solving basket. We have already had viewers tell us that they're using these out and about. You'll see lots of resources for supporting those in your viewer's guide. But this is to add a bunch of visuals about supporting problem-solving. Remember we said that one of the more difficult things for young children to do is to generate multiple solutions that are different from each other.
I do always remember when I started doing a lot of social and emotional development, problem-solving in a classroom, in my preschool classroom, I had a student in there, a child in my classroom named Freddy. I loved that. It was the only Freddy I've ever had. Freddy ran up to me on the playground and he said, "Teacher Gail, I've got a problem.” I was like, "Perfect, so excited about this problem.” I said, "What is it?” "Jordan took the ball and won't give it back.”
Now, that is a real problem that happens on a regular basis in preschool classrooms. I said, "Well, what solutions did you try?” Because we were working on solutions. He said, "I tried five.” I was so excited because that's a lot. I said, "What were they?” He said, "I said, 'Please, please, please.'"
One of the things that this problem-solving basket or solution kit can provide for young children are different solutions. You want children to understand that it's not just trying the same solution over and over again or louder. But it is actually trying different solutions, like wait and take turns, hardest solution. I think to try, make another choice, play together. We could ask an adult if it becomes a big problem.
Gail: Just take a break. Lots of things that can be in there. And check your viewer's guide out because there's lots of visuals that you could cut out and use in your own classrooms and learning settings. We're on to the next. We are going to watch one of our favorite teachers ever. Teacher Heather is going to introduce the problem-solving solution basket to preschoolers in her care. And just pay attention. What do you notice? Share those in chat as you take a look.
Heather: We've been working really hard with the problem-solving basket. I think I'm ready. I'm still mad, but I'm ready. I'm going to use that problem-solving basket you guys told me about. Is that a good idea?
Child: Yeah.
Heather: No, no, no. We got it right here. Remember, guys, we planned it this time. Oh, Eddie, hey, I just happen to have it right here. OK, wait. Here's my mad card because I need to breathe some more. I feel better now. I'm going to get one of those books you guys told me about. Teacher, will you help me? I will. It's hard for Eddie to hold the book, huh? I'm going to find an idea because that's what you guys told me last time. Find an idea in my book. And I don't have to read it, right? We have to look at it, right, Marilyn, because there's pictures, right? Pictures for Eddie. Oh, yeah, I remember. We've been practicing a long time, ever since we started school. Okay, here we go. Sharon, can I trade a block with you? Say no.
Heather: Uh-oh, she said no. I'm so disappointed. I don't know how to fix this. What should we help Eddie say? Hey, Eddie, you know what? Our class does something funny when we feel disappointed. You guys want to help him again? Ready? We say, oh, pickle. And then we try another idea. I'm going to try another idea from a different book because that book didn't have the idea I wanted. Let me see. I'm going to share. Jocelyn, can I have one of your blocks? Great, great, great. Sharon, say yes this time. Can I give you this block and you give me back my three blocks?
Saameh: Love it.
Gail: So great. Oh, pickles.
Saameh: I told you about the puppets.
Gail: Yes, exactly.
Saameh: The puppets showed up.
Gail: Exactly. Puppets are so great for supporting and role-playing social and emotional problems because you can control their —
Saameh: Totally.
Gail: I mean, in a helpful way. You can control what they're saying and experiencing, and the children can help the puppet out. It's really great.
Saameh: I love that.
Gail: She does a great job of that, and our viewers agree. They are commenting that they're loving that, and hopefully we'll share that video with others.
Saameh: I just love that. It's sort of just a way of children stepping outside of the scene and being able to see what's happening.
Gail: It’s like a little fishbowl in a way.
Saameh: When you're in it, you're feeling so many feelings, so many things happening, it's hard to use those executive functioning skills around it. You're actually developing those executive functioning skills when you're like, okay, I wonder how I can support these puppets and planning and working it out and da-da-da. It's really wonderful. It's a great way. Very powerful.
Gail: Yes. Huge puppet family.
Saameh: Yes, we can do so much.
Gail: We're going to have to have a whole episode on puppets.
Saameh: Puppet Time. Yeah, both you and I. Great. We have our S now from our BASICS, and that is specific feedback. Providing specific feedback is another way educators can support problem-solving and relationship skills, and that's naming and acknowledging when we see a child engaging and building relationships. It's really important to be specific about what you see, and we have some examples here.
Like, you're helping me put Natalie's coat on, or I saw you get a tissue for Kai, which was so kind. And I can see that you were both feeling frustrated, and let's get the solution kit and get some ideas of how we might solve the problem. Noticing and acknowledging goes a long way. It's I see you, I hear you, and right there you have buy-in. It's like, OK, let's work together. I think all of us, children, and adults alike.
Educators can provide specific feedback to a child when they see them taking turns, sharing, trying to solve problems, or helping a friend. I can see you being a helpful friend and working with Isaiah to get his mat set up for nap time. That's probably a typical one. Nap time is a big one. Setting up for nap time is a big one. That itself is a whole thing. A lot of ripe opportunities for problem-solving.
Saameh: Providing specific feedback is also a helpful teaching tool. And we might provide feedback on how to be a friend or how to solve a problem, like another one that resonates with me. I hear that you would all like a turn on the tire swing.
Gail: Oh, yes.
Saameh: Many opportunities for problem-solving with a tire swing. Very popular tire swing. Let's try using the sand timer to make sure everyone gets a turn. Or I can see that you're both feeling frustrated. Okay, we talked about this one. Let's get the solution kit. Get some ideas how we might solve the problem. Offer specific ideas of what the child might do next. Remember that how feedback is given, including what you say, how you say it, it should really be individualized to meet the learning characteristics and temperament of each child. It's not just like one size fits all model.
Gail: Absolutely. I think like the key word is the specific here in specific feedback. Because I noticed all the examples that you gave, it wasn't like, a good job. It was really specific and it didn't even have to have a praise statement. It really could just be like saying what you noticed. You got a tissue for Kai. That was so kind.
It's just labeling the behavior that they're doing can be enough to provide them specific feedback that like, wow, that was important enough for my teacher to say or my educational support person to say. Then that specific feedback about like, let's try something new. Let's try something a little bit different. Also, very helpful. It's so great.
Saameh: Yeah.
Gail: I just think it's like the S in there is really important, that specific part. I really love that. Specific. It's almost more important than the praise is the specific sort of I see you.
Saameh: Because empty praise is not necessarily the most helpful.
Gail: Yeah. That's another whole thing that we're going to talk about.
Saameh: At some point.
Gail: But we are so excited that we're going to check back into Teacher Heather's classroom and see how she provides specific feedback while helping two children solve problems. See if maybe a few know this, some of that specific feedback that she's providing.
Heather: Uh-oh. Amy and Jami, what's the problem? You're getting it to make the fort. And it looks like Amy's holding it, too. Thanks, Elina, for moving so I could get up. What are we going to do about it? You both want the same block? What are we going to do about it? How are we going to fix the problem? I'm going to hold the block for a minute while you guys help figure it out. What's your idea? You want to play with it over there. Should we find out what Jami's idea was? What was your idea, Jami? Oh, and she thinks she needs it for that building. You both need this block for two different buildings.
Do you want to look for an idea in the basket? Grab the book. See what you can come up with. There's another one over there, right? I think Amy's got the book. What are we going to do? She's looking. Let's play together. That would be building the same building together. Take a break. You just take a break from building. Wait until she's done. One more minute. She would have it for a minute and then you would have it for a minute.
You build with something else. Maybe next time. Talk to me. Elina dropped it in there. Playing together. You would build it together. Do you want to build together, Jami? Look, Amy's talking to you. Sorry, I just said it and Amy was saying it. Sorry about that, Amy. Here. Amy, you're going to help Jami build her tower. Excellent. You guys are expert problem solvers.
Gail: So great.
Saameh: Live in action.
Gail: And people are providing some feedback on that as well. I mean, she does such a great job of providing that specific feedback along the way.
Saameh: Absolutely.
Gail: Along the way, absolutely.
Saameh: We are ready to move on to our Small Change, Big Impact segment. Small Change, Big Impact, where we share how small adjustments to the way we set up our learning environment, modify our curriculum, or engage with children can make a big difference for a child's learning.
We know that children vary in their learning characteristics and how they engage with the people and materials in their learning environments. These small changes, also known as curriculum modifications, are made based on the individual needs of the child to help promote their engagement and participation. We know that when children are more engaged, they have more opportunities to learn.
Some children might need more highly individualized teaching to help them learn problem-solving, such as embedded teaching or intensive individualized teaching, making curriculum modifications based on a child's individual learning needs. This can be a great place to start to support engagement.
Gail: Absolutely. And today we are focusing on using social stories. I would be so excited to hear how our viewers are using social stories. I imagine that some people are already using these. But for those of you who might not be familiar with social stories, they are a great little curriculum modification, or not little, because they actually take a little bit of time to put in place. But they are there to support a child who might have some more specific or individualized needs to navigate a social situation or just providing them with a little bit more information as to how to navigate a social situation or a change.
These are written from a child's perspective. And this is very individualized. They have the child's picture in them often. The child's name is used in them. The social story highlights and clearly describes to a child what the most important aspects of the social situation are, like what the appropriate behavior expectations are in that situation, how people, including the child, might be feeling or what they might be thinking about in that social situation.
Social stories, hard to say, sometimes social stories can help increase a child's understanding of a social situation. It can help prepare them to use that new focus skill or focus behavior that's going to help them navigate the situation as successfully as possible. They are very effective in introducing many types of new skills and behaviors to children that might need that, again, more focused and turning the volume up, as I like to think about it, on some of the social atmosphere that might be going on for a child to help them learn.
There is a great video, if you haven't seen it yet, because we've actually shown it before. But if you haven't seen it yet, there's a great video on "Teacher Time" Community in MyPeers about how to make and how to use social stories for teaching purposes. We are going to show a video of one preschool educator using a social story to support a child in the learning environment. As we watch, share what you notice about what the teacher is using, how they're using the social story, or anything else that you notice in the Q&A.
Teacher: Andy. Andy, not a big deal, okay?
[Children shouting indistinctly]
All right, Andy, check it out. You need to keep your hands and legs to yourself.
Andy: [Inaudible]
Teacher: And a calm voice.
Andy: It's too hard.
Teacher: Can you show me a calm voice like this? Hmm? Let's do one more.
Andy: I need some help.
Teacher: Look, Andy.
Teacher: If my friends do something I don't like, I can say, "Please.”
Andy: Please.
Teacher: "Stop.”
Andy: Stop.
Teacher: And get a teacher to help me.
Teacher: Well, what do you need help with, Andy?
Andy: That.
Teacher: You can use a calm voice and say, "Please stop.”
Andy: Please stop!
Teacher: This is what we're good at, right, David?
Gail: Well, I love that. That is a real situation. There's a busy, bustling classroom going on, and that teacher still has enough organizational support going on in that classroom to be able to go over and individualize the support for that young child. They are going through a social story, which the child is referencing with the teacher support, but eventually I think the child's able to use it independently on their own.
Again, if you want to know how to create social stories, or if you want some links to social stories, check out your viewer's guide. We've got lots of links to some social stories that you can use, such as using one for Tucker Turtle. There's also that video in MyPeers about how to get those set up.
Saameh: I see somebody in the chat who speaks so much to the relationship that the child has with the teacher, which, yes, as we can see how important that is to starting out, really building that relationship so the child is trusting the teacher to support.
Gail: Absolutely. And Roxanne's comment about being very calm and listening to the child, right, it just takes me back to what you had us do at the beginning. It takes a moment.
Gail: You have to be mindful as an educator to be like, OK, there's a lot going on in the classroom. This child is really needing my support. Taking a deep breath and then walking them through it.
Gail: It's great so that you can stay calm and support them. I love it
Saameh: Very important. Throughout this webinar, as you've noticed, we have been discussing ways to foster social emotional skills for all children. Today in our Focus on Equity segment, we're going to be using our equity lens to take a closer look at implicit bias and how it impacts how we interact with children and support them in building problem-solving and relationship skills.
The value that we place on peer relationships and the way we go about building and maintaining them are influenced by our families, our culture, our community, and our experiences. And sometimes subtle biases can interfere with our ability to support and partner with children and their families with an open mind. Uncovering these biases takes time and reflection.
What you may have noticed is that we paused and we took those reflective moments throughout this webinar today for reflective practice and starting to think about the following questions. These are ones that we've gone through today here at the webinar. What value do I place on peer relationships? How do I expect peers to act with each other? How do I feel about conflict? Do I listen openly to all children when there is a problem? Is there a child that I am more likely to make negative assumptions about when a problem involves that child?
It's really to take a moment to reflect on these things throughout our day or week or in certain situations. It can be really helpful to ask a friend, colleague, or coach to video record you during a time of day where there tends to be more conflict between children and then to watch that video and notice how you respond and interact with each child involved in a conflict. This is interesting because it reminds me of a puppet thing again. It's like taking a step outside and looking at yourself from the outside.
Saameh: It's kind of hard to see your own back is what somebody told me before.
Saameh: This is a way of doing that.
Saameh: And does every child receive the support and instruction they need?
Gail: That's right.
Saameh: We're going to wrap up with our BookCASE. This month, Dr. Gail Joseph had the chance to meet with our "Teacher Time" Librarian, Emily Small.
Saameh: I'm so excited to hear about the books this month.
Gail: I got to go to the library. It's pretty fun.
Saameh: Oh, nice. Let's watch them make the CASE.
Gail: Hi, everyone. It's time for one of our favorite segments, The BookCASE. And how lucky are we to have our very own "Teacher Time" Librarian, Emily Small.
Emily Small: Thanks for having me back.
Gail: We're so excited. This is just such a treat. Emily has brought a collection of fabulous books for us to talk about. And she’s going to make the CASE for one of them. If you're new to "Teacher Time," let me just remind you what the CASE is.
The CASE really stands for an acronym for four strategies that are really helpful to help you maximize the learning you can get from children's books. C is for connect. We want to think about how we can connect the content or the characters or the story of the book to one of the ELOF outcomes. And the A is for advanced vocabulary.
We know that children love big words and finding big words in books is a great strategy to help support their growing vocabulary. S is to support their active engagement with the book reading. And E is to extend the learning beyond the book. Finding ways that you can keep that magic of the book alive. With that, tell us about the books you have.
Emily: The first one we have is "Luli and the Language of Tea.” This book just came out in 2022. It is probably one of my favorites. It features some children that don't know each other because their families are going to an English language learning class. I also feel like we don't see that very often in picture books.
Gail: I've never seen it.
Emily: Luli is trying to connect with the other children in the space. And she discovers that tea is all a part of their culture. They have a tea party. It's just a great way for kids to learn that you are connected to others. And you just have to find that connection piece.
Gail: Love that. And the illustrations look amazing.
Emily: Yes.
Gail: So engaging.
Emily: We have "Amy Wu and the Warm Welcome.” This is the third one in the "Amy Wu" series. Highly recommend them all. There's a new child in Amy's class who doesn't speak English. And Amy really wants him to feel welcome. You see the steps she takes to help the child feel welcome in class. It's a really great story.
Gail: Again, illustrations are beautiful. I don't even know this book and I want to read it.
Emily: Yes, I love how bright the colors are. Just like, yes, it draws you in immediately. We have "I Forgive Alex: A Simple Story About Understanding.” This is a wordless picture book. Wordless books are fantastic to use for all families, but especially ones where English may not be their home language because anyone can tell a story in any language with a wordless book.
Gail: That is such a great strategy to bring in.
Emily: Yeah. I'll show you some of the photos. But basically it's a story of a child that accidentally ruins another child's artwork. It's just an accident and then the steps that are taken to rekindle that friendship.
Gail: It's such a beautiful story and I love it. Without words, but you can still tell the story.
Emily: And for the CASE, we have "The Little Book of Friendship.” This book is tiny but has so much great stuff in it.
Emily: For the connection, it has really good concrete examples of how to be a good friend, how to make a friend, and then it even addresses when you're not getting along with your friends and those challenges that come up.
Gail: Which happens. A lot.
Emily: Yes, yes.
Gail: Great. Emily, for our A, our advanced vocabulary, we see words like bloom, grumpy, amazing, complimenting. We've got a lot of good emotion words.
Emily: For our supporting engagement, this book asks a lot of questions. It would be great for people to pause while they're reading, maybe write them down so kids can reference them later.
Gail: Great strategy.
Emily: Then for our extend the learning, at the beginning it talks about making a friendship garden. And you could make a friendship garden in your classroom where they all work together to build a garden. Also taking photos of your own children in the classroom so that kids can reference back to them, maybe in a photo album or posting when they're having a hard time with friends.
Gail: Such a great way to make the CASE for this book, "The Little Book of Friendship.” We hope you will find all these books at your local library.
Gail: And bring them into your classroom.
Emily: Yeah.
Gail: Thanks for being with us.
Emily: Thanks for having me.
Saameh: Awesome. That was wonderful.
Gail: It was so fun to be in our "Teacher Time" Library.
Saameh: Thank you. That's about all we have time for today.
Gail: That's it.
Saameh: And thank you so much for joining us. Join us again next month for Responding to Challenging Behavior with Infants and Toddlers. And again in May for with Preschoolers. And bye for now. Thank you so much for being here with us.
Gail: See you on MyPeers. Take care.
Children are born ready to solve problems, and they rely on supportive relationships to learn how to recognize problems and find solutions. Problem-solving involves patience, persistence, and creativity from both the child and the adults in their lives. As preschool children explore their world and engage in play with peers, challenges and conflicts provide opportunities to learn and grow. Discuss practical strategies to foster problem-solving and relationship-building skills in preschoolers.
Note: The evaluation, certificate, and engagement tools mentioned in the video were for the participants of the live webinar and are no longer available. For information about webinars that will be broadcast live soon, visit the Upcoming Events section.
Video Attachments
- Webinar Slides (611.22 KB)
- Viewer's Guide (1.31 MB)
Resource Type: Video
National Centers: Early Childhood Development, Teaching and Learning
Age Group: Preschoolers
Audience: Teachers and Caregivers
Series: Teacher Time
Last Updated: September 26, 2023
- Privacy Policy
- Freedom of Information Act
- Accessibility
- Disclaimers
- Vulnerability Disclosure Policy
- Viewers & Players
- Teaching & Learning
- Early Years
Problem-solving in early maths: 3 simple teaching tips

E d has made an enclosure for dinosaurs using four wooden blocks. He wants to make sure the dinosaurs can’t escape.
“Interesting, I can see the dinosaurs are all locked inside the enclosure,” says Ed’s teacher, “but the tyrannosaurus rex is very tall. I think it would be able to climb out? Is there something you could do to stop him escaping?”
Ed fetches four more blocks and stacks them on top of his enclosure, making it taller.
“Good thinking, Ed,” says the teacher, “but we can still see his head, so it might need to be taller. There are no more long blocks for you to use. I wonder what you could use instead?”
“I think lots of these shorter ones might fit on the top,” says Ed.
- What would “phonics for maths” look like?
- Is this the “right” way to teach early maths?
- How to develop number sense
There are frequent opportunities for mathematical problem-solving throughout a typical day in an early years setting. But how can we ensure that we maximise their impact when they arise?
The Education Endowment Foundation’s Early Years Evidence Store identifies approaches that educators can use to support young children’s early maths learning and development, while providing a summary of the evidence behind each approach.
Created as part of the EEF’s work supporting the Department for Education’s Stronger Practice Hubs, the store has been co-developed by researchers and educators.
The newly published Early Mathematics theme recommends five approaches for supporting children’s maths development:
- Teaching the association between number and quantity.
- Promoting fluency with numbers and sequences.
- Teaching problem-solving skills for maths.
- Teaching and modelling how to make comparisons and connections.
- Facilitating mathematical language.
If we look at the third approach, teaching problem-solving skills for maths, this covers how we teach children to apply purposeful thinking, communicate their ideas and use manipulatives to solve problems.
Strategies for teaching early mathematical problem-solving skills
Evidence and experience tell us that explicitly teaching problem-solving skills can be effective when combined with other approaches, especially when matched to children’s level of development.
A multi-pronged approach is particularly important for children from lower-income families or those at greater risk of not meeting expected levels of development. Sequencing learning and breaking tasks down, as well as modelling problem-solving strategies, can also help to improve outcomes.
But what does that look like in practice?
1. Thinking aloud
In the example at the start of this article, Ed’s teacher models her mathematical thinking aloud, encouraging Ed to do the same. Deliberate modelling, meanwhile, provides opportunities for the teacher to suggest additional challenges for Ed’s play in manageable chunks.
2. Modelling using representations to solve a mathematical problem
Educators can encourage children to use representations in different contexts to scaffold understanding.
This could be through using drawings, fingers or objects, such as pinecones or cubes. For example:
Ben is playing with a friend in the mud kitchen. They plan to make “fir cakes” for the teddy bears they have set up on the picnic bench.
Their teacher asks them how many cakes they will make. Ben tells her, “Four, so there is one each.” Andrea encourages Ben to use his fingers to check this, as she points to each teddy.
The teacher counts aloud as Ben lifts each finger, stopping at five.
“I need five cakes then,” Ben says.
“Yes,” the teacher agrees, “you need one more cake, and then there is one for each teddy”.
3. Reminding
Educators can prompt children to remember and apply a previous strategy to solve a mathematical problem. For example:
During welcome time, the teacher asks the class how they can find out how many children are here today, using their self-registration board.
“We can count them,” says Amrita.
“Yes, you are right; we can count the children. Is there a way we can do it that helps us count them correctly?”
The children aren’t sure, so the teacher reminds them: “If we move the photos one by one into the basket as we count, it’ll make sure we only count each photo once.”
Amrita then moves the photos one at a time into the basket as the children count in chorus to work out how many children are at nursery today.
Lauren Grocott is an early years specialist for the Education Endowment Foundation (EEF)
For more examples of how to teach problem-solving, including narration and using mistakes as teaching and learning opportunities, visit the Early Maths theme of the Early Years Evidence Store
You need a Tes subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content:.
- Unlimited access to all Tes magazine content
- Exclusive subscriber-only stories
- Award-winning email newsletters
Already a subscriber? Log in
You need a subscription to read this article
Subscribe now to read this article and get other subscriber-only content, including:.
topics in this article

Early Years Guide
Introduction.
The first few years of a child’s life are especially important for mathematics development . For many education experts, no other group represents a greater opportunity to improve mathematical standards than children in the early years.
The more grounded in mathematical concepts young children become, the better their later outcomes. Conversely, research shows that children who start behind in mathematics tend to stay behind throughout their educational journey.
On this page, we’ll examine:
- What do we mean by Early Years?
- What does learning look like in the Early Years?
- Why is Cognitive Load Theory so important?
- What mastery strategies are available for Early Years?
What do we mean when we talk about Early Years?
The UK government published the Statutory Framework for the early years foundation stage in March 2017. It sets standards for the learning, development and care of children from birth to five years old.
Areas of learning
The EYFS framework outlines seven areas of learning :
- Communication and language
- Physical development
- Personal, social and emotional development
- Mathematics
- Understanding the world
- Expressive art and design
Mathematics in EYFS
In the context of mathematics, the framework says children must be given opportunities to develop their skills in the following areas:
- Understanding and using numbers
- Calculating simple addition and subtraction problems
- Describing shapes, spaces, and measure
Revised guidance
The DfE published revised guidance in March 2021 to take effect in September 2021.
The mathematics component now incorporates many elements of the mastery approach.
Specifically, the revised framework says:
Children should be able to count confidently, develop a deep understanding of the numbers to 10, the relationships between them and the patterns within those numbers.
By providing frequent and varied opportunities to build and apply this understanding — such as using manipulatives, including small pebbles and tens frames for organising counting — children will develop a secure base of knowledge and vocabulary from which mastery of mathematics is built.
In addition, it is important that the curriculum includes rich opportunities for children to develop their spatial reasoning skills across all areas of mathematics including shape, space and measures.
It is important that children develop positive attitudes and interests in mathematics, look for patterns and relationships, spot connections, ‘have a go’, talk to adults and peers about what they notice and not be afraid to make mistakes.
Early Learning Goals
The latest framework has the following early learning goals for mathematics:
Children at the expected level of development will:
- Have a deep understanding of number to 10, including the composition of each number
- Subitise (recognise quantities without counting) up to five
- Automatically recall (without reference to rhymes, counting or other aids) number bonds up to five (including subtraction facts) and some number bonds to 10, including double facts
Numerical patterns
- Verbally count beyond 20, recognising the pattern of the counting system
- Compare quantities up to 10 in different contexts, recognising when one quantity is greater than, less than or the same as the other quantity
- Explore and represent patterns within numbers up to 10, including evens and odds, double facts and how quantities can be distributed equally
Reception class is the first year at primary school in England, generally for children ages four to five. Unlike every other school year, it’s not compulsory for children to attend Reception, though it’s a good way to introduce them to life at school.
Multi-academy trusts
Looking for impactful maths provision across your multi-academy trust?

Learning in the early years
The first few years of a child’s life are especially important for mathematics development , says the National Center for Excellence in the Teaching of Mathematics.
Research shows that early mathematical knowledge predicts later reading ability and general education and social progress.
As young as eight months old, children are developing an awareness of number names , and include these in their speech, as soon as they begin to talk. As children listen to the talk around them, they are introduced to numbers through opportunities that occur in everyday life, and experience a variety of number rhymes. This supports their growing knowledge of number names.
According to the NCETM, there are:
Six key areas of mathematical learning
Cardinality and counting, composition.
- Shape and Space
Looking briefly at each in turn:
When children understand the cardinality of numbers , they know what the numbers mean in terms of knowing how many things they refer to.
Comparing numbers involves knowing which numbers are worth more or less than each other.
Learning to ‘see’ a whole number and its parts at the same time is a key development in children’s number understanding.
Developing an awareness of pattern helps young children to notice and understand mathematical relationships.
Shape and space
Mathematically, the areas of shape and space are about developing visualising skills and understanding relationships, such as the effects of movement and combining shapes
Measuring in mathematics is based on the idea of using numbers of units in order to compare attributes , such as length or capacity.
Learning to count in the early years is a fundamental skill and key to mastering mathematical concepts in the future, but there’s more to it than you might think, says Sabrina Pinnock, a primary school teacher in Yorkshire.
According to researchers Rochel Gelman and C.R. Gallistel, these are the steps needed to successfully count :
- The one-to-one principle: children must name each object they count and understand there are two groups: the one that has been counted and the one that hasn’t yet been counted
- The stable order principle: children must know how to count in the right order
- The cardinal principle: children need to understand the last number in the set is the total amount
- Counting anything: children need to realise that anything can be counted, not just objects that can be touched, but also things like claps and jumps
- Order of counting doesn’t matter: children need to understand that the order of counting in the set is irrelevant and will still lead to the same amount
Assessing children to find out which step they are struggling with is key to helping them overcome difficulties and become confident counters.

How do children develop counting skills?
Very young children start to count spontaneously and later begin to refine their skills by pointing their finger at the objects they are counting.
They will often try to get all the names of the numbers they know into their count as they pass their finger along the objects. They also reuse numbers. If they have not finished and they have used up all their known numbers, they will begin using the same numbers again. For example, a child might decide to count eight shells she collects at the beach. She might line them up carefully, tag numbers to them by pointing as she slides her finger along the shells, quickly counting out loud, “one, two, three, four, five, one, two, three, four, five, one, two, three.”
In their drive to make meaning, children are eager to experiment as they acquire new small bits of mathematical knowledge. It is extremely important to respect their developing understanding and not expect “perfect” counting sequences.
By valuing children’s partial understanding, children will develop enthusiasm for numbers and become confident mathematicians.
Activities to boost number sense in Reception Year
Children need lots of opportunities to develop number sense and deepen their conceptual understanding. Here are some simple activities to get your Reception Year learners counting:
Crowd control
Display the number of children allowed in each area using pictorial representations of cubes on a 10 frame. Once the children begin to realise how many are allowed in the area, they start to discuss the meaning of more and less. For example, “no more children are allowed in,” or “you can come in because one more than three is four.”
Encourage children to show numbers using their fingers above their head. “Bunny ears six” means they place their fingers above their head to show six. They may decide to use three fingers on each hand. As they become more confident, you could introduce swapping, where they show the same number but with a different configuration of fingers, in this case two and four, or five and one.
Grouping straws
Each morning, drop different amounts of art straws all over the carpet. Say something like, �“oh no class, I can’t believe it. I’ve dropped all my straws again. They were all in 10s. Can you help me?” This activity helps children consolidate counting objects and gets them to think about stopping after they have made 10. Providing elastic bands helps them to keep track of their groups of 10.
Fastest 10 frames
This game can help distinguish between those who have developed a good understanding of number sense and those who need further support. Give each child their own frame and cubes. Tell them a number and observe how they place the cubes on the frame. If the children are working with the number eight, do they say each number name as they place the cube on the frame, or do they realise eight is two less than 10? If so, they should be able to place the cubes down faster than other children.
What do they do when you say the next number? For example, for the number five, do they automatically remove three cubes, or do they remove all of the cubes and start over counting from one to five?
Everyday questions to develop number sense
These questions for children aged five to six help develop their number sense and let them practice using mathematical terms.
When prepping lunch or a snack, count out the different types of food with your child, and as you lay the table, count out the different items. Ask your child questions like:
- How many grapes are there?
- How many tomatoes are there?
- How many plates are there?
Practice using the terms more than, fewer than and as many as by asking:
- Are there more grapes than tomatoes?
- Are there fewer tomatoes than grapes?
- Are there as many plates as people eating?
Remember to practice each sentence:
- There are more grapes than tomatoes
- There are fewer tomatoes than grapes
- There are as many plates as family members eating
When counting, make sure that you count one number for one item to strengthen your child’s sense of one-to-one correspondence.
Number Rhymes
Carefully select number rhymes to include those that children are familiar with from home. Make sure the rhymes include:
- Counting back and counting forward
- “No” or “none” (Five little ducks went swimming one day)
- Counting in pairs (two, four, six, eight, Mary at the cottage gate)
- Counting to five, 10 and beyond
Problem solving, reasoning and numeracy
The EYFS requires children to be supported in developing their understanding of problem solving, reasoning and numeracy in a broad range of contexts in which they can explore, enjoy, learn, practise and talk about their developing understanding. They must be provided with opportunities to practise these skills and gain confidence.
Young children learn best through play. For their learning to be effective, they need sensitive and informed support from adults.
All children can be successful with mathematics, provided they have opportunities to explore ideas in ways that make personal sense to them and opportunities to develop concepts and understanding. Children need to know that practitioners are interested in their thinking and respect their ideas.
Foundations
Maths — No Problem! Foundations is designed with all the theory and rigor that underpins a true mastery approach. It meets all the requirements of the national curriculum’s Early Years Foundation Stage. But Maths — No Problem! Foundations doesn’t shy away from embedding learning through play in Reception.
Genuine learning through play in the early years is something the team at Maths — No Problem! gets very excited about. What may appear to be simple games are actually carefully designed activities that have a deep maths mastery focus.
Maths — No Problem! Foundations is a complete Reception programme that includes Workbook Journals, Picture Books, and online Teacher Guides with printable resource sheets, all in one package.
The Maths — No Problem! suite of products — including textbooks, workbooks, a revolutionary online assessment tool, world-class teacher training, and much more — is based on the Singapore method, which combines 30 years of international research with painstaking craftsmanship and constant refinement.
Mark making
Research from Carruthers and Worthington into children’s mathematical graphics reveals young children use their own marks and representations to explore and communicate their mathematical thinking. These graphics include:
- Scribble-marks
- Tally-type marks
- Invented and standard symbols including numerals
Young children’s graphical exploration “builds on what they already know about marks and symbols and lays the foundations for understanding mathematical symbols and later use of standard forms of written mathematics,” the researchers said.
In a 2009 publication, the UK Department for Children, Schools and Families, says practitioners should: “Value children’s own graphic and practical explorations of problem solving” and observe “the context in which young children use their own graphics.”
Developing understanding with careful questioning
When children play and interact with other children, there are always opportunities for maths talk to help them develop a deep understanding, says Sabinra Pinnock.
For instance:
- I have made a pattern. What’s your pattern?
- How many blocks taller is my model compared to yours?
- How do we know this area is full?
- I have three cars, how many do you have?
- Do you have more?
- How do you know?
Give learners long enough to think about their answer and give their response, but not so long that it disrupts the flow of play.
Adding maths talk activities to your daily routine
Developing maths talk in your daily routine gives learners a chance to understand concepts while using real-life concepts. It also means that children can consolidate what they have learned.
The following activities can get you started:
How many children are at school?
Get your class to work out how many children are at school by placing a picture of themselves or a counter representation on large 10 frames. Ask them questions like:
- How do we know this 10 frame is full?
- How many children are absent?
- What can you tell me about number seven?
Sorting and grouping objects as a class
Sorting and grouping objects as a class helps children learn to reason and look for patterns. Give them a variety of buttons each day and ask open-ended questions like, “how can we sort the buttons?” They can use critical-thinking skills to come up with a range of ideas like sorting by size, colour, pattern, and shape.
Vote for a story
First, ask a child to pick two books. Everyone in the class gets to vote (using a piece of lego, for instance) on which of the books should be read. Tally the votes at the end of the day to determine the winner. This can lead to questions such as:
- How many more votes did one book have than the other?
The key to introducing mastery in the early years is to keep activities fun and part of your daily routine. The more learners explore maths through play, the more engaged they become.
Pattern Awareness
Dr. Sue Gifford, emeritus fellow at University of Roehampton, says recent research shows a child’s ability to spot mathematical patterns can predict later mathematical achievement, more so than other abilities such as counting. It also shows pattern awareness can vary a great deal between individuals.
Australian researchers, Papic, Mulligan and Mitchelmore have found pattern awareness can be taught effectively to preschoolers, with positive effects on their later number understanding.
Explicitly teaching pattern awareness links to encouraging “pattern sniffing” with older children in order to develop mathematical understanding and thinking.
What is mathematical pattern awareness?
Patterns are basically relationships with some kind of regularity between the elements. In the early years, Papic et al suggest there are three main kinds:
- Shapes with regular features, such as a square or triangles with equal sides and angles, and shapes made with some equally spaced dots
- A repeated sequence: the most common examples are AB sequences, like a red, blue, red blue pattern with cubes. More challenging are ABC or ABB patterns with repeating units like red, green, blue or red, blue, blue
- a growing pattern, such as a staircase with equal steps
Children who are highly pattern aware can spot this kind of regularity: they can reproduce patterns and predict how they will continue.
Why is pattern awareness important?
Spotting underlying patterns is important for identifying many different kinds of mathematical relationships. It underpins memorization of the counting sequence and understanding number operations, for instance recognizing that if you add numbers in a different order their total stays the same.
Pattern awareness has been described as early algebraic thinking, which involves:
- Noticing mathematical features
- Identifying the relationship between elements
- Observing regularities
The activity Pattern Making focuses on repeating patterns and suggests some engaging ways of developing pattern awareness, with prompts for considering children’s responses. Children can make trains with assorted toys, make patterns with twigs and leaves outside or create printing and sticking patterns in design activities.
Repeating Patterns
It is important to introduce children to a variety of repeating patterns, progressing from ABC and ABB to ABBC.
Focusing on alternating AB patterns can result in some young children thinking that ‘blue, red, red’ can’t make a pattern. They say things like, “That’s not a pattern, because you can’t have two of the same colour next to each other.”
Cognitive Load Theory
Cognitive Load Theory has gained a lot of traction in recent years as educators embrace evidence-based research to inform their evolving practice, says Ross Deans, a KS2 teacher and maths lead in Bournemouth, England.
What is Cognitive Load Theory and why is it important?
Why are new teachers so overwhelmed by tasks that more experienced teachers can juggle alongside multiple other responsibilities?
The answer is simple — new skills demand more attention.
This logic can be applied to any situation. When learning to drive, for example, you focus carefully on every small detail. That mental exertion can be very demanding. Compare that to the feeling of driving after you’ve been doing it for years; you may barely remember the drive, the process is so familiar.
Now put yourself in the shoes of your pupils. Each lesson provides fresh learning and new skills to master. Consider what happens inside your learners’ heads when they encounter new information, new skills and new vocabulary.

Working memory
Cognitive Load Theory , originated by John Sweller, acknowledges that working memory is very limited.
Working memory is the information we hold in our minds while we’re learning. The number of things that we can keep in working memory at one time is approximately four, plus or minus one, and perhaps even less for children.
It’s important to keep this in mind when planning and delivering lessons. If our learners cannot balance more than four things in their working memory, then we need to be very careful about the information we choose to present to them.
Intrinsic versus extraneous load
Intrinsic load includes anything that is necessary to learn a desired skill. In other words, the essential stuff.
Extraneous load is anything that will detract from desired learning. In other words, the stuff that should be reduced as much as possible.
It can be tempting while teaching to embellish lessons with child-friendly imagery and gimmicks. While It’s important to foster enjoyment, we should avoid distracting learners from the essential components of a lesson.
Supporting the transition to long-term memory
While acknowledging the impact of Cognitive Load Theory, we can consider the following to support our learners:
Focused learning objective
First and foremost, we must have a very clear idea of what we want our learners to achieve. Keep the limitations of the working memory in mind and let this guide the content you choose to include in a lesson.
Activate prior learning
At the start of the lesson, you may choose to design a task that encourages learners to retrieve essential skills. This means their working memory can hold on to new learning during the lesson.
Present information clearly
Take time when designing lessons to make sure information is presented clearly. Avoid unnecessary extras which may detract from the learning goal. Keep slides clean and similar in style.
Avoid cognitive overload
In maths, problems are often detailed and complex. Consider breaking questions up into chunks so that learners can digest each part separately. By taking away the final question, you can make a maths problem goal-free.
Maths mastery for Early Years
Given the importance of developing sound mathematical understanding in the early years, the maths mastery approach can be especially useful, considering its focus on problem solving and whole-class learning.
Early Years and CPA
If you’re teaching the Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract (CPA) approach in the early years, it’s best to focus on C and P. Here’s how to use concrete and pictorial representations effectively.
The CPA model works brilliantly in the primary years but for the youngest learners, moving onto abstract concepts too soon causes difficulties. Spending as much time as possible with concrete objects and pictorial representations helps children master number skills.
By the time they reach Key Stage 2, children need to develop their understanding of numbers by being able to visualise what the concrete looks like in their heads. Therefore, it’s positive that the revised EYFS framework focuses on numbers just to 10, from 20 previously.
If learners develop a deep understanding of numbers to 10, their chances of understanding larger numbers increases significantly.
C is for concrete
Concrete is the “doing” stage. During this stage, students use concrete objects to model problems. Unlike traditional maths teaching methods where teachers demonstrate how to solve a problem, the CPA approach brings concepts to life by allowing children to experience and handle physical (concrete) objects.
Spending time with real-life objects
The theorist Jerome Bruner stresses the importance of children spending time learning maths through tangible items. Spending lots of time using real-life objects, solving real-life problems, and manipulating abstract concrete objects (when ready) such as cubes and counters is essential in the early years.
Ideas include counting out fruit for snack time, comparing, sorting and counting a range of different buttons, pasta, and even ‘magic beans’ linked to specific topics.
Early years and number bonds
By mastering number bonds early on, pupils build the foundations needed for subsequent learning and are better equipped to develop mental strategies and mathematical fluency. By building a strong number sense, pupils can decide what action to take when trying to solve problems in their head.
How to teach number bonds
Children are usually introduced to number bonds through the Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract approach . Here’s just one way to introduce and teach number bonds.
Concrete step
Children start out by counting familiar real-world objects that they can interact with. They then use counters to represent the real-world objects. From here, they progress to grouping counters into two groups.
By putting five counters into two groups, children learn the different ways that five can be made. For example, 3 and 2 as illustrated below. With further exploration, children work out other ways to break numbers into two groups.
Pictorial step
Now that they understand the concept with hands-on objects and experience, children progress to writing number bonds in workbooks or on whiteboards. Early number bond explorations might simply reflect the two groups of counters that they created during the concrete step, along with other combinations.
Abstract step
With the concrete and pictorial steps done and dusted, children progress to representing abstract problems using mathematical notation (for example, 3 + 2 = 5).
Early Years and place value
Number and place value are foundational concepts for all mathematics learning. This means we need to address how to teach place value as early as possible so that pupils can secure their knowledge of the concept.
How do you develop an early understanding of place value in the primary school classroom? Let’s start by defining place value. It is a system for writing numerals where the position of each digit determines its value. Each value is a multiple of a common base of 10 in our decimal system.
Here are some teaching strategies I’ve found useful when helping learners develop an early understanding of place value.
Progress through concepts systematically
Developing an understanding of place value requires systematic progression. Each new concept should build on previous learning experiences so that pupils can gain deeper, relational understanding as they go.
This approach ensures knowledge is developed, refined and applied correctly as numbers become meaningful tools for solving problems rather than just a series of symbols on a page. Most importantly, this starts our learners on the path to becoming confident problem solvers and pattern spotters.
Use the CPA approach to establish meaning
The CPA ( Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract ) approach helps pupils connect a physical representation of a number (concrete manipulatives) to that same quantity as shown in drawings or graphics (pictorial), and finally to the actual written name and symbol for that number (abstract).
Concrete resources are meaning makers. They add meaning to abstract representations of numbers so that when learners progress to the abstract phase, they know what those numbers stand for, what they mean, and how they relate to each other.
If a pupil can identify the meaning of each component in a problem, they are far more confident in how they work to solve it.
Teach the ‘10-ness of 10’
At an early level, spend as much time as possible studying the numbers from 0 to 10, as understanding the 10-ness of 10 is crucial for maths attainment, and it cannot be rushed.
Once this understanding is locked-in, follow this with an introduction to number bonds. Start with the additive relationships between numbers less than 10, then progress to adding and subtracting up to 10. This ensures that learners see 10 as an important ‘base’ number in all of their future maths applications.

Progress to 20, then to 40
I make sure to take my time teaching 10 and teen numbers so that a solid understanding of place value with numbers up to 20 is properly established.
I then extend the place value concept by working with numbers up to 40 — followed by addition and subtraction to 40.
Because pupils have learned to make 10 and use number bonds, they are ready to begin working with multi-digit numbers and regrouping. Focusing on numbers to 40 while developing the concept of place value also allows learners to associate numbers with easily-managed, physical quantities (meaning makers).
Use base 10 blocks for 100 and 1000
The work we’ve done building a gradual understanding of place value will have prepared pupils to progress to three-digit numbers. So we can now move on to studying up to 100.
We start here by developing an understanding of numbers in multiple place value representations. For example, one thousand five hundred is 15 hundreds or 150 tens.
Once they get the hang of that, learners then sharpen their counting, reading, and writing skills for numbers up to 1,000. Moving into addition and subtraction with numbers up to 1,000 — with and without regrouping — is the next step.
Here is where our work establishing an early understanding of place value is key, because pupils will intrinsically know why these algorithms work for three and four-digit numbers. Base 10 blocks are a great tool to help solidify those earlier place value ideas when working with numbers up to the thousands.
Approach larger numbers the same way
The CPA approach is once again our answer to learning place value in larger numbers. Apply those skills and always be on the lookout for chances to extend number and place value concepts.
For example, you can identify and complete number patterns or find missing digits on a number line.
From there you can explore strategies for mental mathematics as well as addition and subtraction for numbers up to 10,000. Take learners even deeper by having them explore place value with an emphasis on multiplication, division, and decimals.
Mastering maths concepts like place value in the early years is not just key to success in the classroom. It prepares learners for a lifetime of deep mathematical understanding by giving them invaluable real-world tools like resilience and problem-solving ability.
And a confident problem solver in maths is a confident problem solver in life.
Well done on making it to the end of our Ultimate Guide to Early Years.
We’ve looked at the definition of Early Years and what the government recommends in its revised guidance, and we’ve taken a deep dive into some of the most-effective strategies for teaching mathematics mastery in the Early Years.
We’ve also discussed Cognitive Load Theory and what it means for teachers in the Early Years classroom.
If you’d like to learn more about Early Years, we recommend checking out the following links:
- NCETM: How Early Years children develop mathematical thinking (Podcast)
- NRICH: Early Years Foundation Stage Homepage
- The School of School: Episode 17 Play and early years (Podcast)
- Maths — No Problem! CPA approach
Also, don�’t miss our other Ultimate Guides:
- The Maths — No Problem! Ultimate Guide to Maths Mastery
- The Maths — No Problem! Ultimate Guide to Assessment
Share your success, be rewarded
Everyone needs a break. Especially the kids that are missing out.

By clicking “Accept All” , you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage and assist in our marketing efforts.

Building Problem-Solving Skills for Preschoolers
Definition and significance of problem-solving skills in preschoolers, overview of typical problem-solving scenarios for preschoolers, math problem-solving activities for preschoolers, creative problem-solving games and activities, utilizing problem-solving cards for interactive learning, how to teach problem-solving to preschoolers effectively, incorporating problem-solving steps into everyday activities, role of adults in facilitating problem-solving skills, recommended problem-solving books for preschoolers, reputable online resources, using problem-solving worksheets as a learning tool, real-life problem-solving scenarios for preschoolers to navigate.
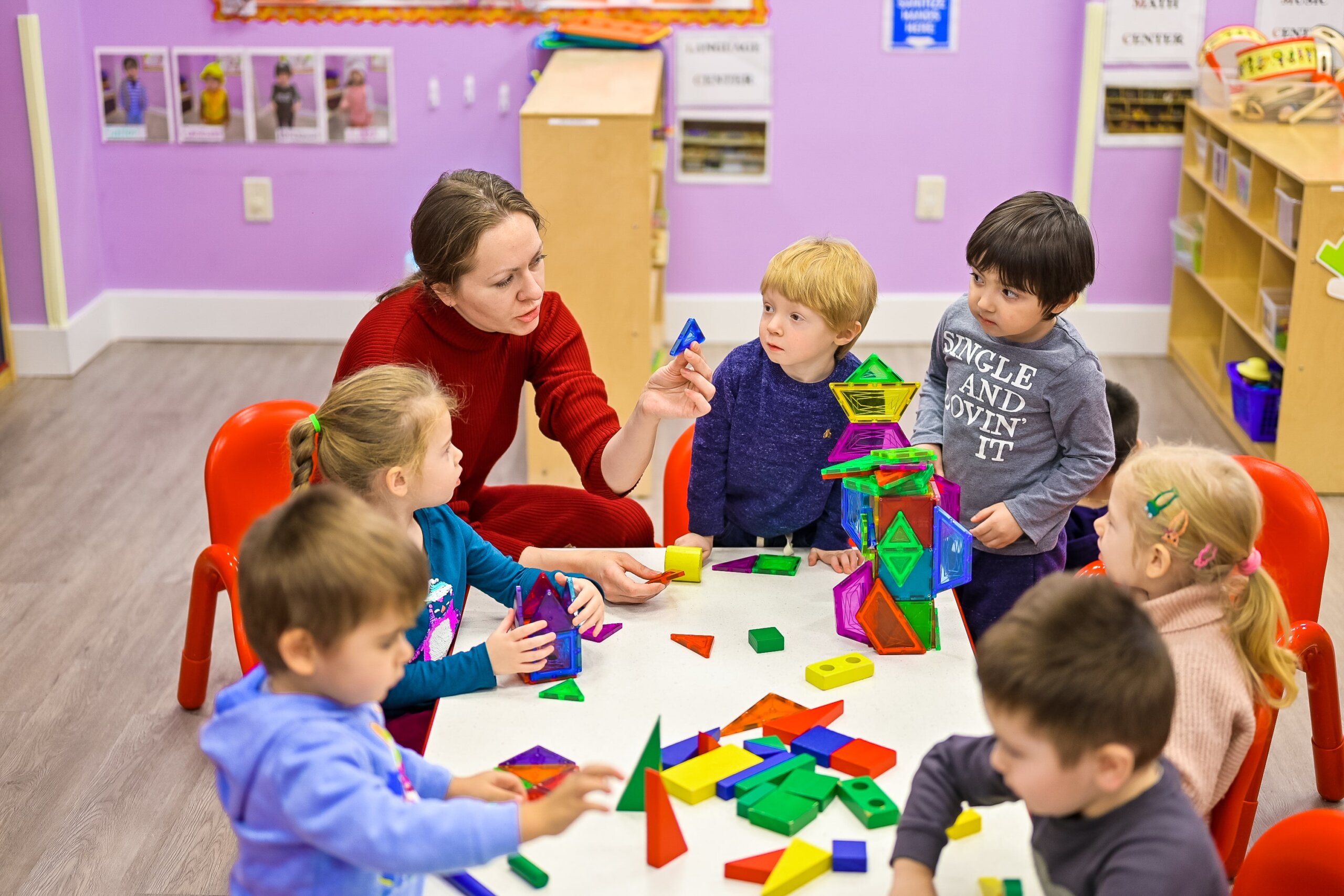

In the early years of childhood development, problem-solving skills are foundational to cognitive growth and practical learning. This article explores engaging activities, scenarios, and resources designed to foster these critical skills in young learners. Through a variety of methods, including interactive games, math activities, and educational books, preschoolers can develop the ability to navigate challenges, leading to enhanced learning experiences and a solid foundation for future academic success.
To cultivate these essential skills in your preschooler and lay a strong foundation for their future, explore the wealth of problem-solving activities, games, and resources available. Embrace the joy of learning together and watch as your child’s problem-solving abilities flourish. Begin this exciting journey now and open a world of possibilities for your little learner!
Understanding Problem-Solving for Preschoolers
Problem-solving skills in preschoolers refer to their ability to understand a problem, think through solutions, and execute a plan to overcome it. This capability is vital for their cognitive development and helps in navigating daily challenges. Preschoolers encounter problem-solving scenarios in various forms, such as puzzles, social interactions, and play activities, where they learn to make decisions, analyze outcomes, and adapt to new situations. Engaging them in targeted problem-solving activities and games can significantly enhance these skills, preparing them for future more complex tasks and decision-making processes.
Preschoolers encounter various problem-solving scenarios daily, which are crucial for their cognitive, social, and emotional development. These scenarios typically involve challenges or situations that require them to analyze, make decisions, and find solutions. Here’s an overview of common types of problem-solving situations preschoolers might face:
- Social Interactions: Learning to share toys, taking turns, and resolving conflicts with peers are common problems requiring negotiation and empathy.
- Self-care Tasks: Dressing themselves, tying shoelaces, or managing basic hygiene tasks demand practical problem-solving skills and fine motor coordination.
- Academic Challenges: Simple puzzles, building blocks, and age-appropriate educational games encourage critical thinking, pattern recognition, and logical reasoning.
- Emotional Regulation: Identifying and managing their feelings, like frustration or sadness, when things don’t go as planned, teaching them to find constructive solutions.
- Environmental Navigation: Overcoming physical obstacles, like reaching a high shelf or navigating a new play area, requires spatial awareness and physical judgment.
Problem-Solving Activities for Preschoolers

Math problem-solving activities for preschoolers should be engaging and hands-on, helping them understand basic mathematical concepts through play and exploration. Here’s a list of activities designed to enhance their math problem-solving skills:
- Sorting and Categorizing: Children sort objects by color, size, shape, or type, which develops their ability to recognize patterns and categories.
- Counting Games: Using toys, beads, or blocks to count aloud helps preschoolers understand numbers and quantity.
- Simple Puzzles: Completing puzzles with different shapes and sizes teaches spatial awareness and geometric concepts.
- Matching Activities: Pairing matching items or numbers with corresponding groups of objects enhances number recognition and counting skills.
- Shape Hunts: Finding objects of specific shapes in their environment helps children identify and classify geometric shapes.
- Measurement Activities: Using rulers, measuring tapes, or comparing objects directly teaches basic measurement and comparison skills.
- Number Stories: Creating simple stories that involve addition or subtraction helps in understanding basic arithmetic operations.
- Pattern Making: Using colored blocks or beads to create and extend patterns teaches sequencing and predictive logic.
Creative problem-solving activities encourage thinking outside the box and foster innovation. Here are some games and activities that can help develop these skills:
- Story Building: Participants add to a story one sentence at a time, promoting creative thinking and collaborative storytelling.
- Invention Scramble: Children use random objects to create a new invention, encouraging imaginative thinking and resourcefulness.
- Obstacle Course: Setting up an obstacle course with specific challenges requires planning and strategy to navigate.
- Riddle Solving: Engaging in riddles and brain teasers enhances critical thinking and comprehension skills.
- Building Challenges: Using blocks or LEGO, children are tasked with constructing a structure based on a theme or specific requirements.
- Role-Playing Games: Children take on different roles and scenarios, promoting empathy and creative problem-solving in social situations.
- Art Projects: Encouraging free-form art or specific thematic projects helps in exploring creativity and expressing ideas visually.
- Treasure Hunts: Organizing a treasure hunt with clues and challenges promotes logical reasoning and teamwork.
Problem-solving cards are a versatile tool that can be used to promote interactive learning. They typically feature scenarios, questions, or challenges that prompt learners to think critically and develop solutions. Here’s how they can be used effectively:
- Scenario-Based Learning: Cards can present real-life situations that require learners to apply knowledge and critical thinking to solve problems.
- Group Discussions: Using cards to initiate group discussions encourages collaboration and the sharing of diverse perspectives.
- Role-Playing Activities : Cards can set up role-playing exercises where learners must navigate and resolve conflicts or challenges.
- Game-Based Learning: Incorporating cards into games can make learning fun and competitive, motivating learners to engage more deeply with the content.
- Skill Development Workshops: Cards can be used in workshops to practice specific skills, such as negotiation, decision-making, or creative thinking.
List of Necessary Elements for Utilizing Problem-Solving Cards
To effectively use problem-solving cards in interactive learning, certain elements are necessary:
- Varied and Relevant Content: Cards should cover various topics and scenarios relevant to the learners’ experiences and learning objectives.
- Clear and Concise Instructions: Each card should have clear, concise instructions to ensure learners understand the problem or task.
- Adaptability: Cards should be versatile enough to be used in different teaching methods and learning environments, whether in-person or online.
- Interactive Design: Engaging visuals and interactive elements on the cards can enhance the learning experience.
- Feedback Mechanism: Incorporating a way to provide feedback on the solutions or discussions generated from the cards helps in assessing understanding and progress.
- Scalability: The difficulty level of the cards should be scalable to cater to different skill levels and learning stages.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Content on the cards should be culturally sensitive and inclusive, reflecting diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Supplementary Materials: Providing additional resources or information related to the scenarios on the cards can deepen understanding and extend learning.
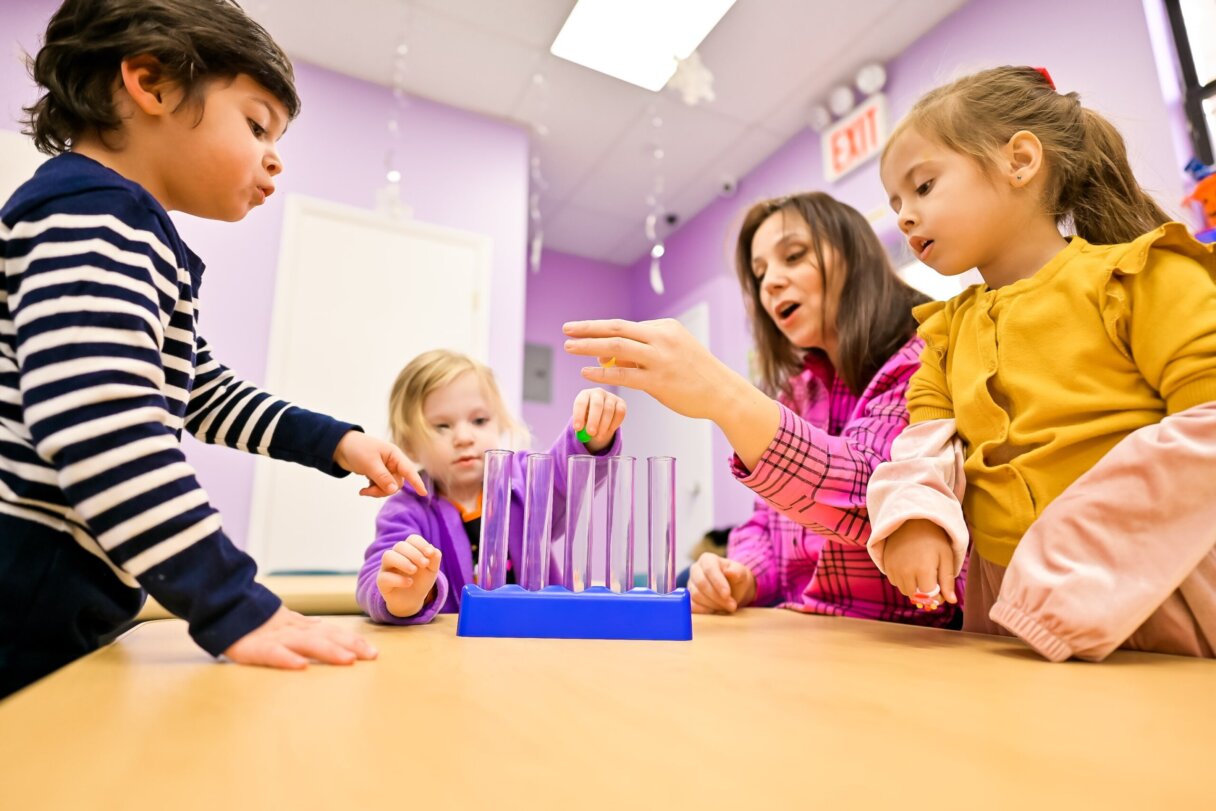

Teaching Strategies
Teaching problem-solving to preschoolers is about guiding them to think independently, make decisions, and learn from outcomes. Here’s how educators and parents can effectively teach problem-solving skills to preschoolers:
- Model Problem-Solving Behavior: Demonstrate how to approach problems calmly and thoughtfully, talking through the process out loud.
- Create a Safe Learning Environment: Ensure that the environment is supportive and non-judgmental, allowing children to explore solutions without fear of failure.
- Encourage Exploration and Play: Through play, children can experiment with different solutions and learn from trial and error.
- Ask Open-Ended Questions: Encourage thinking by asking questions that have no single right answer, prompting children to explore various possibilities.
- Facilitate, Don’t Solve: Guide children through the problem-solving process, helping them think of solutions, rather than providing answers.
- Use Storytelling: Stories can introduce problems in a relatable context, encouraging children to come up with creative solutions.
- Encourage Teamwork: Group activities can teach children how to collaborate, share ideas, and solve problems together.
- Teach Emotional Regulation: Help children recognize and manage their emotions, which is a critical part of solving problems effectively.
List of Necessary Elements for Teaching Problem-Solving to Preschoolers
To teach problem-solving effectively to preschoolers, certain elements are necessary:
- Patience and Time: Problem-solving skills develop over time, requiring patience and practice.
- Age-Appropriate Challenges: Problems should be relevant and challenging but achievable for their developmental stage.
- Variety of Materials: Provide diverse materials and resources to stimulate creative thinking and problem-solving.
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate successes and encourage perseverance, reinforcing the value of effort and learning from mistakes.
- Consistent Opportunities: Regularly integrate problem-solving activities into daily routines and learning experiences.
- Clear Guidance and Support: Offer clear instructions and support to help children understand the problem-solving process.
- Reflective Practice: Encourage children to reflect on the problem-solving process and outcomes to enhance learning.
- Cultural and Contextual Relevance: Ensure problems and scenarios are culturally relevant and relatable to the children’s experiences.
Incorporating problem-solving steps into everyday activities offers a practical and seamless way to enhance critical thinking skills. This approach involves identifying daily tasks or challenges and using them as opportunities to practice problem-solving.
For instance, during meal preparation, children can be involved in deciding what to cook, which ingredients are needed, and how to follow the recipe. This engages them in decision-making, sequencing, and logical thinking.
Similarly, when faced with conflicts or decisions, guiding children through identifying the issue, brainstorming possible solutions, evaluating these options, and then implementing and reflecting on the outcome can be very effective. This method makes problem-solving a natural part of daily life and helps children learn to apply these skills autonomously, preparing them for more complex challenges as they grow.
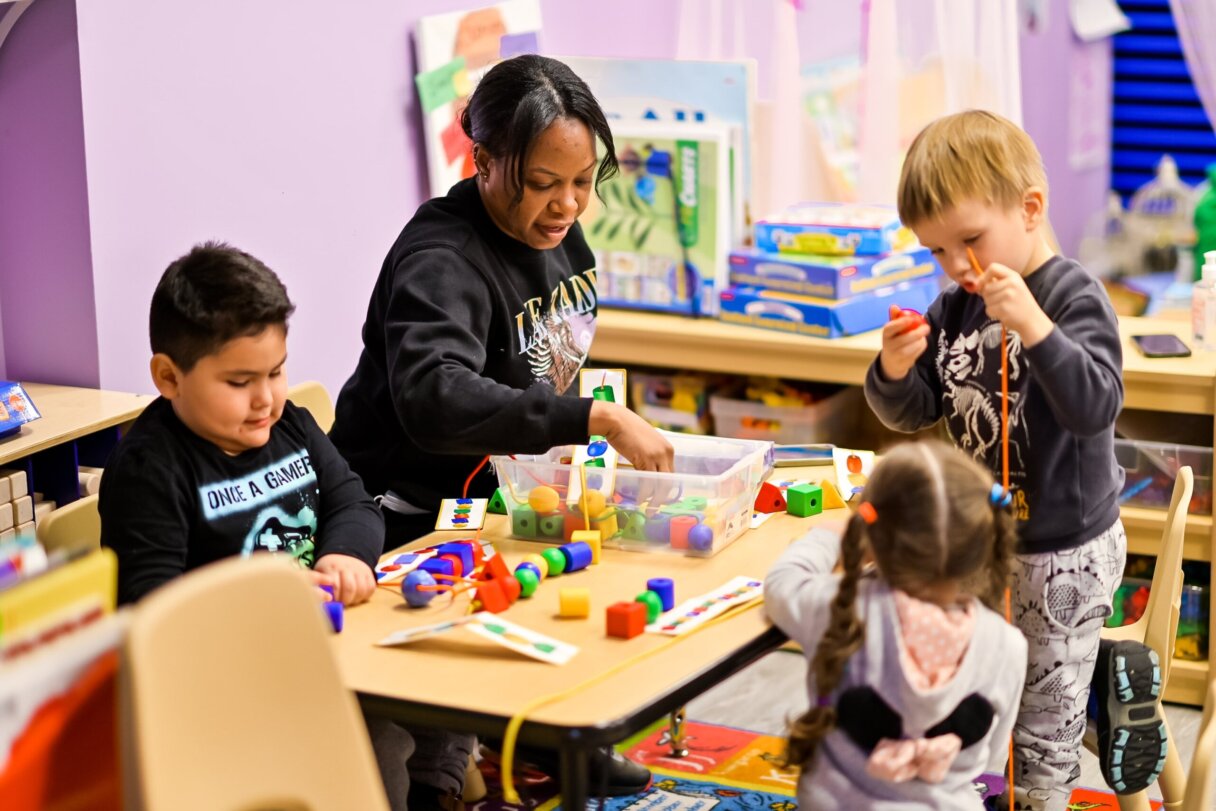

Adults play a crucial role in facilitating problem-solving skills among children by acting as guides, models, and supporters. They set the stage for learning by providing appropriate challenges and resources that encourage critical thinking and experimentation.
Through modeling problem-solving behavior—like verbalizing thought processes, showing how to evaluate options, and demonstrating persistence in the face of difficulties—adults provide a blueprint for children to follow. They also create a safe environment where children feel free to explore solutions without fear of judgment, offering guidance and encouragement rather than solutions, which promotes independence and confidence.
Additionally, by asking open-ended questions, adults can stimulate children’s thought processes and encourage them to see problems from different angles, further developing their critical thinking and decision-making skills. Adults are vital in nurturing an atmosphere where problem-solving can thrive, guiding children to become proficient problem-solvers.
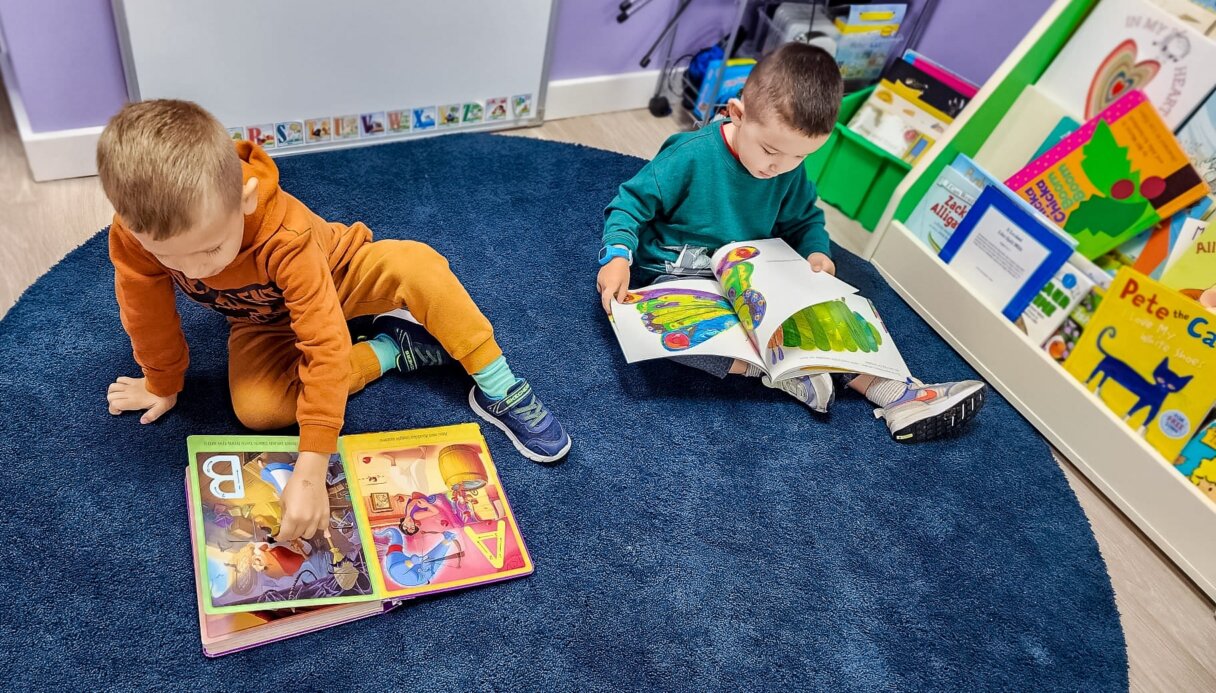

Educational Resources
Books can be a fantastic resource for developing problem-solving skills in preschoolers. Here are some highly recommended titles that engage young readers in the art of problem-solving:
- “Rosie Revere, Engineer” by Andrea Beaty: This book encourages innovation and perseverance, showing that failure is just a step towards success.
- “Curious George” series by H.A. Rey: The adventures of Curious George teach problem-solving and curiosity, as the little monkey often finds himself in tricky situations that require clever solutions.
- “The Most Magnificent Thing” by Ashley Spires: This story is about a girl who learns about frustration and perseverance while trying to create something magnificent.
- “Ish” by Peter H. Reynolds: Reynolds’ book teaches children that thinking “ish-ly” is more important than perfection, encouraging creative problem-solving.
- “Not a Box” by Antoinette Portis: This book stimulates imagination and creativity, showing how a simple box can be much more through innovative thinking.
- “The Dot” by Peter H. Reynolds: Another book by Reynolds, it inspires children to start small and see where their imagination and problem-solving can take them.
- “What Do You Do With a Problem?” by Kobi Yamada: This book personifies problems as opportunities to learn and grow, teaching children to face challenges head-on.
- “Beautiful Oops!” by Barney Saltzberg: Saltzberg’s book encourages finding beauty in mistakes and learning from them, promoting a positive attitude towards problem-solving.
Here’s a list of reputable online resources that provide valuable content on teaching problem-solving skills to preschoolers, including activities, strategies, and educational insights:
- NAEYC (National Association for the Education of Young Children) : Offers a wealth of resources on early childhood development, including articles and tips on promoting problem-solving skills.
- Teaching Strategies : Offers innovative, research-based teaching methods and resources for early childhood educators to enhance problem-solving skills in preschoolers.
- Education.com : Contains a wide range of problem-solving activities, worksheets, and games tailored for preschool-aged children.
These websites are well-regarded in the field of early childhood education and provide a range of tools and insights for effectively teaching problem-solving skills to preschoolers.
Problem-solving worksheets are an effective learning tool for developing critical thinking and analytical skills. They provide structured opportunities for students to practice and refine their approach to solving various types of problems.
List of Necessary Elements for Problem-Solving Worksheets
For problem-solving worksheets to be an effective learning tool, they should include:
- Clear Instructions: Directions should be concise and easy to understand, ensuring students know what is expected.
- Relevant Content: Problems should be age-appropriate and connected to real-world situations to enhance relevance and engagement.
- Structured Approach: Worksheets should guide students through the problem-solving process, possibly outlining steps like understanding the problem, devising a plan, carrying out the plan, and reviewing the solution.
- Variety in Problem Types: Including different types of problems, such as puzzles, logic problems, and word problems, can cater to various learning styles and interests.
- Space for Workings: Providing ample space for students to write down their thought processes and calculations is important for developing their ability to solve problems systematically.
- Engaging Design: Visually appealing worksheets with illustrations or graphics can motivate students and enhance their learning experience.

Practical Application
Preschoolers can learn valuable problem-solving skills through real-life scenarios they can relate to and navigate. Here’s a list of scenarios that can help preschoolers develop and practice these skills:
- Sharing Toys: Navigating how to share toys with siblings or friends, deciding who plays with what, and for how long.
- Dressing for the Weather: Choosing appropriate clothing for the day based on the weather conditions, like selecting a raincoat on a rainy day or a sunhat when it’s sunny.
- Meal Choices: Making decisions about what to eat for snacks or meals, balancing between healthy options and favorite treats.
- Cleaning Up: Figuring out how to organize and clean up toys and supplies efficiently after playtime.
- Lost Items: Developing strategies to find a lost toy or belonging, retracing steps, and thinking of places where it could be.
- Turn-taking Games: Learning to wait for a turn and cope with the delay in gratification during group games or activities.
- Building Structures: Deciding how to build a stable structure using blocks or other materials, which involves planning and adjusting techniques.
- Resolving Conflicts : Finding peaceful solutions to disputes with peers, like taking turns, sharing, or finding a compromise.
- Planning a Playdate: Participating in planning activities, considering what games to play and what snacks to have.
- Handling Emotions: Identifying and managing emotions when things don’t go as planned, such as calming down after a disappointment.
Nurturing problem-solving skills from a young age is beneficial and crucial for children’s cognitive and emotional development. As detailed in this article, integrating problem-solving activities into the daily routines of preschoolers can significantly enhance their ability to navigate and overcome challenges, fostering independence, creativity, and resilience.
Therefore, parents, educators, and caregivers must incorporate a variety of problem-solving activities into their interactions with young learners. From math games to social scenarios and creative play, every moment can be an opportunity to develop these vital skills. Let’s embrace the joy and responsibility of guiding our preschoolers through their problem-solving journey, equipping them with the tools they need to thrive in an ever-changing world. Encourage, facilitate, and revel in the process of discovery, and watch as the seeds of today’s problem-solving activities blossom into the critical thinking abilities of tomorrow.
Empower your little scholar with the gift of problem-solving! Join us at Little Scholars Daycare, where we turn everyday moments into exciting learning opportunities. Enroll your child today and watch them grow into confident, creative problem-solvers ready to take on the world!
Related articles

Celebrating St. Patrick’s Day with Kids

Balancing Screen Time and Playtime

A Journey Through the Senses: Unlocking the World for Our Little Scholars

Understanding and Supporting Social-Emotional Development in Young Children
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Early Years Careers
Problem solving in Early Years Settings
5th January 2016 by Kelly Leave a Comment
The role of the practitioner in supporting children’s problem solving skills
Some early years practitioners struggle with the definition of problem solving. It is all about the process of working through ideas to reach a solution. It is also about processing information and evaluating ideas and concepts.
As children are constantly learning new ideas, skills and concepts, these will all help them develop their problem solving skills. For those working in childcare it is important to remember that problem solving is not an activity it is the process in which children go through to find a solution.
Children need to be able to use their thinking skills and practitioner should encourage children think creatively. As well as all this learning the development of children’s language is fundamental as they need to be able to vocalise their thoughts. The development of language allows children interact with other s and share those ideas to help find the right solution
How can adults help support children’s problem solving skills
- Asking questions- adults need to use their skills to ask the right questions as these questions may hold the key to helping children solve that problem.
- Breaking down the task – Adults can help children break the task up to help them solve the problem in smaller steps.
- Scaffold the child’s learning – be careful not to answer the child’s questions yourself, questions should be open ended this will allow the children think, plan, predict, explain and recall as well as ask questions back.
- Listen attentively – practitioners should listen to children’s answers as this will show to the child that what they are thinking is important.
- Try not to overuse questioning.
Acting as an effective model is a key factor when supporting children’s problem solving skills, as children will look to adults for support and guidance.
Related Posts:

Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- NAEYC Login
- Member Profile
- Hello Community
- Accreditation Portal
- Online Learning
- Online Store
Popular Searches: DAP ; Coping with COVID-19 ; E-books ; Anti-Bias Education ; Online Store
The Power of Playful Learning in the Early Childhood Setting

You are here
Play versus learning represents a false dichotomy in education (e.g., Hirsh-Pasek & Golinkoff 2008). In part, the persistent belief that learning must be rigid and teacher directed—the opposite of play—is motivated by the lack of a clear definition of what constitutes playful learning (Zosh et al. 2018). And, in part, it is motivated by older perceptions of play and learning. Newer research, however, allows us to reframe the debate as learning via play—as playful learning.
This piece, which is an excerpt from Chapter 5 in Developmentally Appropriate Practice in Early Childhood Programs Serving Children from Birth Through Age 8, Fourth Edition (NAEYC 2022), suggests that defining play on a spectrum (Zosh et al. 2018, an idea first introduced by Bergen 1988) helps to resolve old divisions and provides a powerful framework that puts playful learning —rich curriculum coupled with a playful pedagogy—front and center as a model for all early childhood educators. ( See below for a discussion of play on a spectrum.)
This excerpt also illustrates the ways in which play and learning mutually support one another and how teachers connect learning goals to children’s play. Whether solitary, dramatic, parallel, social, cooperative, onlooker, object, fantasy, physical, constructive, or games with rules, play, in all of its forms, is a teaching practice that optimally facilitates young children’s development and learning. By maximizing children’s choice, promoting wonder and enthusiasm for learning, and leveraging joy, playful learning pedagogies support development across domains and content areas and increase learning relative to more didactic methods (Alfieri et al. 2011; Bonawitz et al. 2011; Sim & Xu 2015).
Playful Learning: A Powerful Teaching Tool

This narrowing of the curriculum and high-stakes assessment practices (such as paper-and-pencil tests for kindergartners) increased stress on educators, children, and families but failed to deliver on the promise of narrowing—let alone closing—the gap. All children need well-thought-out curricula, including reading and STEM experiences and an emphasis on executive function skills such as attention, impulse control, and memory (Duncan et al. 2007). But to promote happy, successful, lifelong learners, children must be immersed in developmentally appropriate practice and rich curricular learning that is culturally relevant (NAEYC 2020). Playful learning is a vehicle for achieving this. Schools must also address the inequitable access to play afforded to children (see “Both/And: Early Childhood Education Needs Both Play and Equity,” by Ijumaa Jordan.) All children should be afforded opportunities to play, regardless of their racial group, socioeconomic class, and disability if they have been diagnosed with one. We second the call of Maria Souto-Manning (2017): “Although play has traditionally been positioned as a privilege, it must be (re)positioned as a right, as outlined by the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child, Article 31” (785).
What Is Playful Learning?
Playful learning describes a learning context in which children learn content while playing freely (free play or self-directed play), with teacher guidance (guided play), or in a structured game. By harnessing children’s natural curiosity and their proclivities to experiment, explore, problem solve, and stay engaged in meaningful activities—especially when doing so with others—teachers maximize learning while individualizing learning goals. Central to this concept is the idea that teachers act more as the Socratic “guide at the side” than a “sage on the stage” (e.g., King 1993, 30; Smith 1993, 35). Rather than view children as empty vessels receiving information, teachers see children as active explorers and discoverers who bring their prior knowledge into the learning experience and construct an understanding of, for example, words such as forecast and low pressure as they explore weather patterns and the science behind them. In other words, teachers support children as active learners.
Importantly, playful learning pedagogies naturally align with the characteristics that research in the science of learning suggests help humans learn. Playful learning leverages the power of active (minds-on), engaging (not distracting), meaningful, socially interactive, and iterative thinking and learning (Zosh et al. 2018) in powerful ways that lead to increased learning.
Free play lets children explore and express themselves—to be the captains of their own ship. While free play is important, if a teacher has a learning goal, guided play and games are the road to successful outcomes for children (see Weisberg, Hirsh-Pasek, & Golinkoff 2013 for a review). Playful learning in the form of guided play, in which the teacher builds in the learning as part of a fun context such as a weather report, keeps the child’s agency but adds an intentional component to the play that helps children learn more from the experience. In fact, when researchers compared children’s skill development during free play in comparison to guided play, they found that children learned more vocabulary (Toub et al. 2018) and spatial skills (Fisher et al. 2013) in guided play than in free play.
Self-Directed Play, Free Play
NAEYC’s 2020 position statement on developmentally appropriate practice uses the term self-directed play to refer to play that is initiated and directed by children. Such play is termed free play in the larger works of the authors of this excerpt; therefore, free play is the primary term used in this article, with occasional references to self-directed play, the term used in the rest of the DAP book.
Imagine an everyday block corner. The children are immersed in play with each other—some trying to build high towers and others creating a tunnel for the small toy cars on the nearby shelves. But what if there were a few model pictures on the wall of what children could strive to make as they collaborated in that block corner? Might they rotate certain pieces purposely? Might they communicate with one another that the rectangle needs to go on top of the square? Again, a simple insertion of a design that children can try to copy turns a play situation into one ripe with spatial learning. Play is a particularly effective way to engage children with specific content learning when there is a learning goal.
Why Playful Learning Is Critical
Teachers play a crucial role in creating places and spaces where they can introduce playful learning to help all children master not only content but also the skills they will need for future success. The science of learning literature (e.g., Fisher et al. 2013; Weisberg, Hirsh-Pasek, & Golinkoff 2013; Zosh et al. 2018) suggests that playful learning can change the “old equation” for learning, which posited that direct, teacher-led instruction, such as lectures and worksheets, was the way to achieve rich content learning. This “new equation” moves beyond a sole focus on content and instead views playful learning as a way to support a breadth of skills while embracing developmentally appropriate practice guidelines (see Hirsh-Pasek et al. 2020).
Using a playful learning pedagogical approach leverages the skill sets of today’s educators and enhances their ability to help children attain curricular goals. It engages what has been termed active learning that is also developmentally appropriate and offers a more equitable way of engaging children by increasing access to participation. When topics are important and culturally relevant to children, they can better identify with the subject and the learning becomes more seamless.
While educators of younger children are already well versed in creating playful and joyful experiences to support social goals (e.g., taking turns and resolving conflicts), they can use this same skill set to support more content-focused curricular goals (e.g., mathematics and literacy). Similarly, while teachers of older children have plenty of experience determining concrete content-based learning goals (e.g., attaining Common Core Standards), they can build upon this set of skills and use playful learning as a pedagogy to meet those goals.
Learning Through Play: A Play Spectrum
As noted previously, play can be thought of as lying on a spectrum that includes free play (or self-directed play), guided play, games, playful instruction, and direct instruction (Bergen 1988; Zosh et al. 2018). For the purposes of this piece, we use a spectrum that includes the first three of these aspects of playful learning, as illustrated in “Play Spectrum Showing Three Types of Playful Learning Situations” below.
The following variables determine the degree to which an activity can be considered playful learning:
- level of adult involvement
- extent to which the child is directing the learning
- presence of a learning goal
Toward the left end of the spectrum are activities with more child agency, less adult involvement, and loosely defined or no particular learning goals. Further to the right, adults are more involved, but children still direct the activity or interaction.
Developmentally appropriate practice does not mean primarily that children play without a planned learning environment or learn mostly through direct instruction (NAEYC 2020). Educators in high-quality early childhood programs offer a range of learning experiences that fall all along this spectrum. By thinking of play as a spectrum, educators can more easily assess where their learning activities and lessons fall on this spectrum by considering the components and intentions of the lesson. Using their professional knowledge of how children develop and learn, their knowledge of individual children, and their understanding of social and cultural contexts, educators can then begin to think strategically about how to target playful learning (especially guided play and games) to leverage how children naturally learn. This more nuanced view of play and playful learning can be used to both meet age-appropriate learning objectives and support engaged, meaningful learning.

In the kindergarten classroom in the following vignette, children have ample time for play and exploration in centers, where they decide what to play with and what they want to create. These play centers are the focus of the room and the main tool for developing social and emotional as well as academic skills; they reflect and support what the children are learning through whole-group discussions, lessons, and skills-focused stations. In the vignette, the teacher embeds guided play opportunities within the children’s free play.
Studying Bears: Self-Directed Play that Extends What Kindergartners Are Learning
While studying the habits of animals in winter, the class is taking a deeper dive into the lives of American black bears, animals that make their homes in their region. In the block center, one small group of children uses short lengths and cross-sections of real tree branches as blocks along with construction paper to create a forest habitat for black bear figurines. They enlist their friends in the art center to assist in making trees and bushes. Two children are in the writing center. Hearing that their friends are looking for help to create a habitat, they look around and decide a hole punch and blue paper are the perfect tools for making blueberries—a snack black bears love to eat! Now multiple centers and groups of children are involved in making the block center become a black bear habitat.
In the dramatic play center, some of the children pretend to be bear biologists, using stethoscopes, scales, and magnifying glasses to study the health of a couple of plush black bears. When these checkups are complete, the teacher suggests the children could describe the bears’ health in a written “report,” thus embedding guided play within their free play. A few children at the easels in the art center are painting pictures of black bears.
Contributed by Amy Blessing
Free play, or self-directed play, is often heralded as the gold standard of play. It encourages children’s initiative, independence, and problem solving and has been linked to benefits in social and emotional development (e.g., Singer & Singer 1990; Pagani et al. 2010; Romano et al. 2010; Gray 2013) and language and literacy (e.g., Neuman & Roskos 1992). Through play, children explore and make sense of their world, develop imaginative and symbolic thinking, and develop physical competence. The kindergarten children in the example above were developing their fine motor and collaboration skills, displaying their understanding of science concepts (such as the needs of animals and living things), and exercising their literacy and writing skills. Such benefits are precisely why free play has an important role in developmentally appropriate practice. To maximize learning, teachers also provide guided play experiences.
Guided Play
While free play has great value for children, empirical evidence suggests that it is not always sufficient when there is a pedagogical goal at stake (Smith & Pellegrini 2008; Alfieri et al. 2011; Fisher et al. 2013; Lillard 2013; Weisberg, Hirsh-Pasek, & Golinkoff 2013; Toub et al. 2018). This is where guided play comes in.
Guided play allows teachers to focus children’s play around specific learning goals (e.g., standards-based goals), which can be applied to a variety of topics, from learning place value in math to identifying rhyming words in literacy activities. Note, however, that the teacher does not take over the play activity or even direct it. Instead, she asks probing questions that guide the next level of child-directed exploration. This is a perfect example of how a teacher can initiate a context for learning while still leaving the child in charge. In the previous kindergarten vignette, the teacher guided the children in developing their literacy skills as she embedded writing activities within the free play at the centers.
Facilitating Guided Play
Skilled teachers set up environments and facilitate development and learning throughout the early childhood years, such as in the following:
- Ms. Taglieri notices what 4-month-old Anthony looks at and shows interest in. Following his interest and attention, she plays Peekaboo, adjusting her actions (where she places the blanket and peeks out at him) to maintain engagement.
- Ms. Eberhard notices that 22-month-old Abe knows the color yellow. She prepares her environment based on this observation, placing a few yellow objects along with a few red ones on a small table. Abe immediately goes to the table, picking up each yellow item and verbally labeling them (“Lellow!”).
- Mr. Gorga creates intrigue and participation by inviting his preschool class to “be shape detectives” and to “discover the secret of shapes.” As the children explore the shapes, Mr. Gorga offers questions and prompts to guide children to answer the question “What makes them the same kind of shapes?”
An analogy for facilitating guided play is bumper bowling. If bumpers are in place, most children are more likely than not to knock down some pins when they throw the ball down the lane. That is different than teaching children exactly how to throw it (although some children, such as those who have disabilities or who become frustrated if they feel a challenge is too great, may require that level of support or instruction). Guided play is not a one-size-fits-all prescriptive pedagogical technique. Instead, teachers match the level of support they give in guided play to the children in front of them.
Critically, many teachers already implement these kinds of playful activities. When the children are excited by the birds they have seen outside of their window for the past couple of days, the teachers may capitalize on this interest and provide children with materials for a set of playful activities about bird names, diets, habitats, and songs. Asking children to use their hands to mimic an elephant’s trunk when learning vocabulary can promote learning through playful instruction that involves movement. Similarly, embedding vocabulary in stories that are culturally relevant promotes language and early literacy development (García-Alvarado, Arreguín, & Ruiz-Escalante 2020). For example, a teacher who has several children in his class with Mexican heritage decides to read aloud Too Many Tamales (by Gary Soto, illus. Ed Martinez) and have the children reenact scenes from it, learning about different literary themes and concepts through play. The children learn more vocabulary, have a better comprehension of the text, and see themselves and their experiences reflected. The teacher also adds some of the ingredients and props for making tamales into the sociodramatic play center (Salinas-González, Arreguín-Anderson, & Alanís 2018) and invites families to share stories about family tamaladas (tamale-making parties).
Evidence Supporting Guided Play as a Powerful Pedagogical Tool
Evidence from the science of learning suggests that discovery-based guided play actually results in increased learning for all children relative to both free play and direct instruction (see Alferi et al. 2011). These effects hold across content areas including spatial learning (Fisher et al. 2013), literacy (Han et al. 2010; Nicolopoulou et al. 2015; Hassinger-Das et al. 2016; Cavanaugh et al. 2017; Toub et al. 2018; Moedt & Holmes 2020), and mathematics (Zosh et al. 2016).
There are several possible reasons for guided play’s effectiveness. First, it harnesses the joy that is critical to creativity and learning (e.g., Isen, Daubman, & Nowicki 1987; Resnick 2007). Second, during guided play, the adults help “set the stage for thought and action” by essentially limiting the number of possible outcomes for the children so that the learning goal is discoverable, but children still direct the activity (Weisberg et al. 2014, 276). Teachers work to provide high-quality materials, eliminate distractions, and prepare the space, but then, critically, they let the child play the active role of construction. Third, in guided play, the teacher points the way toward a positive outcome and hence lessens the ambiguity (the degrees of freedom) without directing children to an answer or limiting children to a single discovery (e.g., Bonawitz et al. 2011). And finally, guided play provides the opportunity for new information to be integrated with existing knowledge and updated as children explore.
Reinforcing Numeracy with a Game
The children in Mr. Cohen’s preschool class are at varying levels of understanding in early numeracy skills (e.g., cardinality, one-to-one correspondence, order irrelevance). He knows that his children need some practice with these skills but wants to make the experience joyful while also building these foundational skills. One day, he brings out a new game for them to play—The Great Race. Carla and Michael look up expectantly, and their faces light up when they realize they will be playing a game instead of completing a worksheet. The two quickly pull out the box, setting up the board and choosing their game pieces. Michael begins by flicking the spinner with his finger, landing on 2. “Nice!” Carla exclaims, as Michael moves his game piece, counting “One, two.” Carla takes a turn next, spinning a 1 and promptly counting “one” as she moves her piece one space ahead. “My turn!” Michael says, eager to win the race. As he spins a 2, he pauses. “One . . . two,” he says, hesitating, as he moves his piece to space 4 on the board. Carla corrects him, “I think you mean ‘three, four,’ right? You have to count up from where you are on the board.” Michael nods, remembering the rules Mr. Cohen taught him earlier that day. “Right,” he says, “three, four.”
Similar to guided play, games can be designed in ways that help support learning goals (Hassinger-Das et al. 2017). In this case, instead of adults playing the role of curating the activity, the games themselves provide this type of external scaffolding. The example with Michael and Carla shows how children can learn through games, which is supported by research. In one well-known study, playing a board game (i.e., The Great Race) in which children navigated through a linear, numerical-based game board (i.e., the game board had equally spaced game spaces that go from left to right) resulted in increased numerical development as compared to playing the same game where the numbers were replaced by colors (Siegler & Ramani 2008) or with numbers organized in a circular fashion (Siegler & Ramani 2009). Structuring experiences so that the learning goal is intertwined naturally with children’s play supports their learning. A critical point with both guided play and games is that children are provided with support but still lead their own learning.
Digital educational games have become enormously popular, with tens of thousands of apps marketed as “educational,” although there is no independent review of these apps. Apps and digital games may have educational value when they inspire active, engaged, meaningful, and socially interactive experiences (Hirsh-Pasek et al. 2015), but recent research suggests that many of the most downloaded educational apps do not actually align with these characteristics that lead to learning (Meyer et al. 2021). Teachers should exercise caution and evaluate any activity—digital or not—to see how well it harnesses the power of playful learning.
Next Steps for Educators
Educators are uniquely positioned to prepare today’s children for achievement today and success tomorrow. Further, the evidence is mounting that playful pedagogies appear to be an accessible, powerful tool that harnesses the pillars of learning. This approach can be used across ages and is effective in learning across domains.
By leveraging children’s own interests and mindfully creating activities that let children play their way to new understanding and skills, educators can start using this powerful approach today. By harnessing the children’s interests at different ages and engaging them in playful learning activities, educators can help children learn while having fun. And, importantly, educators will have more fun too when they see children happy and engaged.
As the tide begins to change in individual classrooms, educators need to acknowledge that vast inequalities (e.g., socioeconomic achievement gaps) continue to exist (Kearney & Levine 2016). The larger challenge remains in propelling a cultural shift so that administrators, families, and policymakers understand the way in which educators can support the success of all children through high-quality, playful learning experiences.
Consider the following reflection questions as you reflect how to support equitable playful learning experiences for each and every child:
- One of the best places to start is by thinking about your teaching strengths. Perhaps you are great at sparking joy and engagement. Or maybe you are able to frequently leverage children’s home lives in your lessons. How can you expand practices you already use as an educator or are learning about in your courses to incorporate the playful learning described in this article?
- How can you share the information in this chapter with families, administrators, and other educators? How can you help them understand how play can engage children in deep, joyful learning?
This piece is excerpted from NAEYC’s recently published book Developmentally Appropriate Practice in Early Childhood Programs Serving Children from Birth Through Age 8, Fourth Edition. For more information about the book, visit NAEYC.org/resources/pubs/books/dap-fourth-edition .
Teaching Play Skills
Pamela Brillante
While many young children with autism spectrum disorder enjoy playing, they can have difficulty engaging in traditional play activities. They may engage in activities that do not look like ordinary play, including playing with only a few specific toys or playing in a specific, repetitive way.
Even though most children learn play skills naturally, sometimes families and teachers have to teach children how to play. Learning how to play will help develop many other skills young children need for the future, including
- social skills: taking turns, sharing, and working cooperatively
- cognitive skills: problem-solving skills, early academic skills
- communication skills: responding to others, asking questions
- physical skills: body awareness, fine and gross motor coordination
Several evidence-based therapeutic approaches to teaching young children with autism focus on teaching play skills, including
- The Play Project: https://playproject.org
- The Greenspan Floortime approach: https://stanleygreenspan.com
- Integrated Play Group (IPG) Model: www.wolfberg.com
While many children with autism have professionals and therapists working with them, teachers and families should work collaboratively and provide multiple opportunities for children to practice new skills and engage in play at their own level. For example, focus on simple activities that promote engagement between the adult and the child as well as the child and their peers without disabilities, including playing with things such as bubbles, cause-and-effect toys, and interactive books. You can also use the child’s preferred toy in the play, like having the Spider-Man figure be the one popping the bubbles.
Pamela Brillante , EdD, has spent 30 years working as a special education teacher, administrator, consultant, and professor. In addition to her full-time faculty position in the Department of Special Education, Professional Counseling and Disability Studies at William Paterson University of New Jersey, Dr. Brillante continues to consult with school districts and present to teachers and families on the topic of high-quality, inclusive early childhood practices.
Photographs: © Getty Images Copyright © 2022 by the National Association for the Education of Young Children. See Permissions and Reprints online at NAEYC.org/resources/permissions .
Alfieri, L., P.J. Brooks, N.J. Aldrich, & H.R. Tenenbaum. 2011. “Does Discovery-Based Instruction Enhance Learning?” Journal of Educational Psychology 103 (1): 1–18.
Bassok, D., S. Latham, & A. Rorem. 2016. “Is Kindergarten the New First Grade?” AERA Open 2 (1): 1–31. doi.10.1177/2332858415616358.
Bergen, D., ed. 1988. Play as a Medium for Learning and Development: A Handbook of Theory and Practice . Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann Educational Books.
Bonawitz, E.B., P. Shafto, H. Gweon, N.D. Goodman, E.S. Spelke, & L. Schulz. 2011. “The Double-Edged Sword of Pedagogy: Instruction Limits Spontaneous Exploration and Discovery.” Cognition 120 (3): 322–30.
Cavanaugh, D.M., K.J. Clemence, M.M. Teale, A.C. Rule, & S.E. Montgomery. 2017. “Kindergarten Scores, Storytelling, Executive Function, and Motivation Improved Through Literacy-Rich Guided Play.” Journal of Early Childhood Education 45 (6): 1–13.
Christakis, E. 2016. The Importance of Being Little: What Preschoolers Really Need from Grownups . New York: Penguin Books.
Duncan, G. J., A. Claessens, A.C. Huston, L.S. Pagani, M. Engel, H. Sexton, C.J. Dowsett, K. Magnuson, P. Klebanov, L. Feinstein, J. Brooks-Gunn, K. Duckworth, & C. Japel. 2007. “School Readiness and Later Achievement.” Developmental Psychology 43 (6): 1428–46. https://doi.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0012-1649.43.6.1428 .
Fisher, K.R., K. Hirsh-Pasek, N. Newcombe, & R.M. Golinkoff. 2013. “Taking Shape: Supporting Preschoolers’ Acquisition of Geometric Knowledge Through Guided Play.” Child Development 84 (6): 1872–78.
García-Alvarado, S., M.G. Arreguín, & J.A. Ruiz-Escalante. 2020. “Mexican-American Preschoolers as Co-Creators of Zones of Proximal Development During Retellings of Culturally Relevant Stories: A Participatory Study.” Journal of Early Childhood Literacy : 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1468798420930339 .
Gray, P. 2013. Free to Learn: Why Unleashing the Instinct to Play Will Make Our Children Happier, More Self-Reliant, and Better Students for Life . New York: Basic Books.
Han, M., N. Moore, C. Vukelich, & M. Buell. 2010. “Does Play Make a Difference? How Play Intervention Affects the Vocabulary Learning of At-Risk Preschoolers.” American Journal of Play 3 (1): 82–105.
Hannaway, J., & L. Hamilton. 2008. Accountability Policies: Implications for School and Classroom Practices . Washington, DC: Urban Institute. http://webarchive.urban.org/publications/411779.html .
Hassinger-Das, B., K. Ridge, A. Parker, R.M. Golinkoff, K. Hirsh-Pasek, & D.K. Dickinson. 2016. “Building Vocabulary Knowledge in Preschoolers Through Shared Book Reading and Gameplay.” Mind, Brain, and Education 10 (2): 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12103 .
Hassinger-Das, B., T.S. Toub, J.M. Zosh, J. Michnick, R. Golinkoff, & K. Hirsh-Pasek. 2017. “More Than Just Fun: A Place for Games in Playful Learning.” Infancia y aprendizaje: Journal for the Study of Education and Development 40 (2): 191–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/02103702.2017.1292684 .
Hirsh-Pasek, K., & R.M. Golinkoff. 2008. “Why Play = Learning.” In Encyclopedia on Early Childhood Development [online], eds. R.E. Tremblay, M. Boivin, & R.D. Peters, topic ed. P.K. Smith, 1–6. Centre of Excellence for Early Childhood Development and Strategic Knowledge Cluster on Early Child Development. www.child-encyclopedia.com/play/according-experts/why-play-learning .
Hirsh-Pasek, K., H. S. Hadani, E. Blinkoff, & R. M. Golinkoff. 2020. A new path to education reform: Playful learning promotes 21st-century skills in schools and beyond . The Brookings Institution: Big Ideas Policy Report. www.brookings.edu/policy2020/bigideas/a-new-path-to-education-reform-playful-learning-promotes-21st-century-skills-in-schools-and-beyond .
Hirsh-Pasek, K., J.M. Zosh, R.M. Golinkoff, J.H. Gray, M.B. Robb, & J. Kaufman. 2015. “Putting Education in ‘Educational’ Apps: Lessons from the Science of Learning.” Psychological Science in the Public Interest 16 (1): 3–34.
Isen, A.M., K.A. Daubman, & G.P. Nowicki. 1987. “Positive Affect Facilitates Creative Problem Solving.” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 52 (6): 1122–31.
Kearney, M.S., & P.B. Levine. (2016, Spring). Income, Inequality, Social Mobility, and the Decision to Drop Out of High School . Washington, DC: Brookings. www.brookings.edu/bpea-articles/income-inequality-social-mobility-and-the-decision-to-drop-out-of-high-school .
King, A. 1993. “From Sage on the Stage to Guide on the Side.” College Teaching 41 (1): 30–35.
Lillard, A.S. 2013. “Playful Learning and Montessori Education.” American Journal of Play 5 (2): 157–86.
Meyer, M., J.M. Zosh, C. McLaren, M. Robb, R.M. Golinkoff, K. Hirsh-Pasek, & J. Radesky. 2021. “How Educational Are ‘Educational’ Apps for Young Children? App Store Content Analysis Using the Four Pillars of Learning Framework.” Journal of Children and Media . Published online February 23.
Miller, E., & J. Almon. 2009. Crisis in the Kindergarten: Why Children Need to Play in School . College Park, MD: Alliance for Childhood. https:// files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED504839.pdf .
Moedt, K., & R.M. Holmes. 2020. “The Effects of Purposeful Play After Shared Storybook Readings on Kindergarten Children’s Reading Comprehension, Creativity, and Language Skills and Abilities.” Early Child Development and Care 190 (6): 839–54.
NAEYC. 2020. “Developmentally Appropriate Practice.” Position statement. Washington, DC: NAEYC. www.naeyc.org/resources/position-statements/dap .
Neuman, S.B., & K. Roskos. 1992. “Literacy Objects as Cultural Tools: Effects on Children’s Literacy Behaviors in Play.” Reading Research Quarterly 27 (3): 202–25.
Nicolopoulou, A., K.S. Cortina, H. Ilgaz, C.B. Cates, & A.B. de Sá. 2015. “Using a Narrative- and Play-Based Activity to Promote Low-Income Preschoolers’ Oral Language, Emergent Literacy, and Social Competence.” Early Childhood Research Quarterly 31 (2): 147–62.
Pagani, L.S., C. Fitzpatrick, I. Archambault, & M. Janosz. 2010. “School Readiness and Later Achievement: A French Canadian Replication and Extension.” Developmental Psychology 46 (5): 984–94.
Pedulla, J.J., L.M. Abrams, G.F. Madaus, M.K. Russell, M.A. Ramos, & J. Miao. 2003. “Perceived Effect of State-Mandated Testing Programs on Teaching and Learning: Findings from a National Survey of Teachers” (ED481836). ERIC. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED481836 .
Ravitch, D. 2010. “Why Public Schools Need Democratic Governance.” Phi Delta Kappan 91 (6): 24–27.
Resnick, M. 2007. “All I Really Need to Know (About Creative Thinking) I Learned (by Studying How Children Learn) in Kindergarten.” In Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCHI Conference on Creativity & Cognition , 1–6. New York: Association for Computing Machinery.
Romano, E., L. Babchishin, L.S. Pagani, & D. Kohen. 2010. “School Readiness and Later Achievement: Replication and Extension Using a Nationwide Canadian Survey.” Developmental Psychology 46 (5): 995–1007.
Salinas-González, I., M.G. Arreguín-Anderson, & I. Alanís. 2018. “Supporting Language: Culturally Rich Dramatic Play.” Teaching Young Children 11 (2): 4–6.
Siegler, R.S., & G.B. Ramani. 2008. “Playing Linear Numerical Board Games Promotes Low-Income Children’s Numerical Development.” Developmental Science 11 (5): 655–61.
Siegler, R.S., & G.B. Ramani. 2009. “Playing Linear Number Board Games—but Not Circular Ones—Improves Low-Income Preschoolers’ Numerical Understanding. Journal of Educational Psychology 101 (3): 545–60.
Sim, Z., & F. Xu. 2015. “Toddlers Learn from Facilitated Play, Not Free Play.” In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society , Berkeley, CA. https://cognitivesciencesociety.org/past-conferences .
Singer, D.G., & J.L. Singer. 1990. The House of Make-Believe: Children’s Play and the Developing Imagination . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Smith, K. 1993. “Becoming the ‘Guide on the Side.’” Educational Leadership 51 (2): 35–37.
Smith P.K., & A. Pellegrini. 2008. “Learning Through Play.” In Encyclopedia on Early Childhood Development [online], eds. R.E. Tremblay, M. Boivin, & R.D. Peters, 1–6. Centre of Excellence for Early Childhood Development and Strategic Knowledge Cluster on Early Child Development. https://www.child-encyclopedia.com/pdf/expert/play/according-experts/learning-through-play .
Souto-Manning, M. 2017. “Is Play a Privilege or a Right? And What’s Our Responsibility? On the Role of Play for Equity in Early Childhood Education.” Foreword. Early Child Development and Care 187 (5–6): 785–87. www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/03004430.2016.1266588 .
Toub, T.S., B. Hassinger-Das, K.T. Nesbitt, H. Ilgaz, D.S. Weisberg, K. Hirsh-Pasek, R.M. Golinkoff, A. Nicolopoulou, & D.K. Dickinson. 2018. “The Language of Play: Developing Preschool Vocabulary Through Play Following Shared Book-Reading.” Early Childhood Research Quarterly 45 (4): 1–17.
Weisberg, D.S., K. Hirsh-Pasek, & R.M. Golinkoff. 2013. “Guided Play: Where Curricular Goals Meet a Playful Pedagogy.” Mind, Brain, and Education 7 (2): 104–12.
Weisberg, D.S., K. Hirsh-Pasek, R.M. Golinkoff, & B.D. McCandliss. 2014. “Mise en place: Setting the Stage for Thought and Action.” Trends in Cognitive Science 18 (6): 276–78.
Zosh, J.M., B. Hassinger-Das, T.S. Toub, K. Hirsh-Pasek, & R. Golinkoff. 2016. “Playing with Mathematics: How Play Supports Learning and the Common Core State Standards.” Journal of Mathematics Education at Teachers College 7 (1): 45–49. https://doi.org/10.7916/jmetc.v7i1.787 .
Zosh, J.M., K. Hirsh-Pasek, E.J. Hopkins, H. Jensen, C. Liu, D. Neale, S.L. Solis, & D. Whitebread. 2018. “Accessing the Inaccessible: Redefining Play as a Spectrum.” Frontiers in Psychology 9: 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01124 .
Jennifer M. Zosh, PhD, is professor of human development and family studies at Penn State Brandywine. Most recently, her work has focused on technology and its impact on children as well as playful learning as a powerful pedagogy. She publishes journal articles, book chapters, blogs, and white papers and focuses on the dissemination of developmental research.
Caroline Gaudreau, PhD, is a research professional at the TMW Center for Early Learning + Public Health at the University of Chicago. She received her PhD from the University of Delaware, where she studied how children learn to ask questions and interact with screen media. She is passionate about disseminating research and interventions to families across the country.
Roberta Michnick Golinkoff, PhD, conducts research on language development, the benefits of play, spatial learning, and the effects of media on children. A member of the National Academy of Education, she is a cofounder of Playful Learning Landscapes, Learning Science Exchange, and the Ultimate Playbook for Reimagining Education. Her last book, Becoming Brilliant: What Science Tells Us About Raising Successful Children (American Psychological Association, 2016), reached the New York Times bestseller list.
Kathy Hirsh-Pasek, PhD, is the Lefkowitz Faculty Fellow in the Psychology and Neuroscience department at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She is also a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution. Her research examines the development of early language and literacy, the role of play in learning, and learning and technology. [email protected]
Vol. 77, No. 2
Print this article
- Teach Early Years
- Teach Primary
- Teach Secondary
- Technology & Innovation
- Advertise With Us

- Free Reports
- Have You Seen
- Learning & Development
- A Unique Child
- Enabling Environments
- Positive Relationships
Nursery Management
Home > Nursery Management
Maths in the EYFS – How to develop your provision
- Written By: Jo Baranek
- Subject: Maths
- View page as PDF: Download Now
Share this:
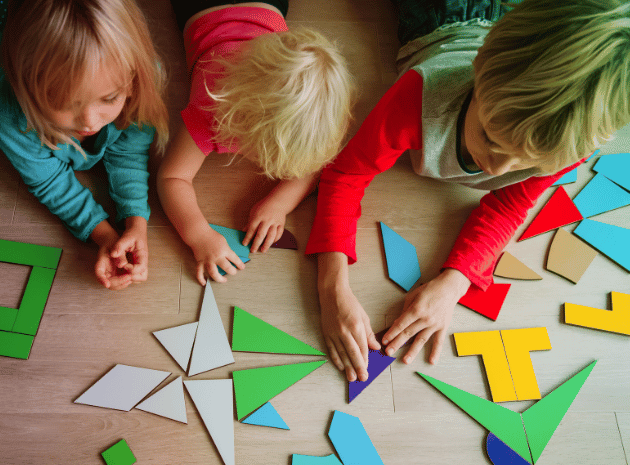

NDNA’s lead early years adviser, Jo Baranek, explains why, and how, we should be championing maths in the EYFS…
Q: Why is maths in the EYFS important?
A: Maths is an important part of the EYFS Framework , and an essential life skill for children. As well as developing numeracy, it supports skills such as problem solving , understanding and using shapes and measure. It also improves children’s spacial awareness.
It also helps them to recognise, create and describe patterns, which is essential for early problem-solving skills.
In short, introducing maths to children from an early age helps to develop their understanding of all elements of maths, problem-solving and reasoning in a broad range of contexts.
We need to be able to provide opportunities for children to practise their developing skills and knowledge. This is so they improve their competence and confidence in using them.
Q: What does a nursery need to provide to help children learn maths through play?
A: To give children the best opportunities to learn and develop mathematical skills, we should pay particular attention to four familiar themes:
- a unique child
- positive relationships
- enabling environments
- learning and development
All children can be successful with maths in the EYFS. This is provided we give them the opportunities to understand it in a way that makes sense to them.
Using the Characteristics of Effective Learning to ensure children are engaged, motivated and thinking critically for themselves is vital. For example, encourage children to problem-solve by asking, “How many spoons do we need for everyone in this group to have one each? How many have we got? How many more do we need?”.
From birth, children have a keen interest in the world around them. However, to have the confidence to explore it they need support from adults around them.
Positive relationships help give children the confidence to discover and develop their mathematical skills. Enabling environments help children to discover maths in the EYFS thorough indoor and outdoor play.
Outdoors, children can spot shapes and numbers naturally. They can explore, investigate and build dens. This helps them discover shape, space and measure using equipment like boxes, crates and building blocks.
Indoors, we can integrate numbers and shape, space and measure into all activities and areas of learning. For example, use measure to mix paint. Cooking activities help children learn about quantities and measures.
Learning and development is about providing a range of activities and resources that support children’s individual needs. Focus on maths by looking at shape, space and measure with imaginative play. Develop an understanding of maths in the EYFS through stories, songs and games.
Q: What can practitioners do to help children develop their skills?
A: To help children develop their maths skills, we also need to have confidence in our own abilities.
NDNA worked with the DfE to promote maths in the EYFS through the Maths Champions project . The DfE recognises the importance of maths in building essential life skills. It wants to help practitioners be confident enough to develop children’s abilities in this area.
To this end, the project aims to ensure practitioners have the skills and resources to provide the best possible mathematical opportunities for children in their care.
The project works with EYTs to support staff in improving their skills. In turn, they can then help children learn about maths in the EYFS through play.
Free resources
We share free resources and ideas with online audit tools and activity resources. We highlight opportunities to develop maths through play. NDNA also offers support tools and online training to improve practitioners’ maths skills. It also provides opportunities for you to talk to others and share ideas and good practice.
But it is not just through the Maths Champions project that NDNA supports mathematical development. We also run online maths courses that help practitioners develop their skills and suggest ways to incorporate behaviours such as integrating schemas, and children’s individual needs and interests, into mathematical learning.
We also provide an understanding of the brain and cognitive development of a young child and how it relates to mathematical development. This helps develop the skills we need to support maths skills in very young children.
Finally, as well as learning practical ways to help children in nursery, it’s helpful for mathematical learning to be carried through at home. These courses also support you to understand the importance of this.
NDNA is the national charity and membership association for children’s nurseries across the UK . It supports settings across all sectors to deliver the best possible care and early learning for children whilst ensuring they are sustainable businesses.
You may also be interested in...
- Great ways to support communication, language and literacy
- How to provide outstanding learning in the outdoors
- Award winners announced
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
I agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy & Cookies Policy.

Enhance your children’s learning environment with unique products from Profile Education

A shared vision for early years – reflecting on practice at the hey! conference

Find out how one nursery uses Tapestry to support their child-centred practice

Say farewell to ‘Lost Property’ with My Nametags
View all Top Products

Christmas Stable (Build Your Own)

Recommended for you...

Q&A: Ofsted Inspection Framework

Eco-friendly nursery – Training staff to create a sustainable setting
Editors picks

“The Revised EYFS is a Missed Opportunity”

Why Every Nursery Needs a Business Plan

- Nursery Management
8 Soft skills your nursery practitioners need and how to develop them

Nursery practitioner, Early Years Educator, or Childminder are all roles that require a huge number of skills. These roles are responsible for a child’s first educational interactions, social development and holistic progression, which is not an easy task! During your team’s apprenticeships and training courses, they will gain the necessary hard skills needed for a career in childcare. These hard skills will allow your staff to apply for qualified positions in your nursery; the soft skills learnt on the job are invaluable for a successful nursery team. This article explores the top 8 soft skills your team needs and how you can develop these skills.
What are hard and soft skills for nursery practitioners?
Hard skills within the Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) refer to the specific skills staff must have to be considered to work in the setting. These skills can be measured; (qualifications, training courses attended, meeting the EYFS qualification requirements .) Soft skills involve the social and emotional depth necessary to thrive in the nursery, including self-awareness, patience, communication, organisation, problem-solving, positivity, creativity, self-belief and personal drive . Your team need a balance of hard and soft skills to progress in their personal and professional development.
What soft skills are needed as a nursery practitioner?
Working in the nursery sector involves repetition, explanation, and perseverance (working with children and their families). Patience is a vital skill relied on to reach a target with a child. This target may be developing social skills or conflict resolution that will not be solved overnight. Through successful modelling and consistency, patience will pay off. Also necessary when interacting with adults, the ability to pause, reflect and think logically in times of stress or confrontation can allow for any disagreements between staff or parents to be settled intelligently.
How to build the soft skill of patience within your nursery practitioners
Patience can be an innate skill; due to many factors, people have varying frustration tolerances. Several strategies can be used to increase patience and frustration management with your team. Breathing strategies are proving useful for many. Pausing and taking a breath can reduce reactive responses in times of frustration. This may be when dealing with an irate parent or resolving disputes in the workplace. Sharing these strategies during team meetings regularly can help build frustration tolerance strategies, which can then be applied in times of stress.
Communication
Good communication skills span much further than being able to confidently interact with children and adults. Communication includes all verbal, non-verbal and written interactions with others. Linking with professional patience, this soft skill will allow your staff to listen to the needs of the children and parents, and work together to find a solution to the challenge. This may be communicating with children in a manner they are comfortable with, with appropriate language use and intonation to encourage verbal development. It is beneficial to use your communication systems well, as written interaction with parents is essential to maintaining highly effective working relationships.
How to improve communication skills within your nursery team
First, break down the type of communication you would like to focus on with your team: verbal, non-verbal and written communication. You can alter your policies and procedures regarding managing parents and even detail the type of language used with children for total consistency of practice. Focus on non-verbal communication, some examples include discussing:
- How body language can help the nervous child interact with their peers,
- How vital body language is at drop-off and pick-up times for positive interactions with parents.
Organisation
Excellent organisation skills can assist with the smooth running of your nursery, ultimately making staff observations and nursery management easier for you. There is a need to keep the setting tidy and accessible for the children to allow for independent play and accessibility to various playing equipment.
Timely organisation of learning resources needed for the day contributes to positive outcomes for children, to utilise every learning opportunity possible. Organisational skills also apply to those completing their Level 2 and 3 apprenticeships in childcare qualifications to ensure they are organised with evidence of the development of knowledge, skills, and behaviours.
How to develop organisational skills within your nursery team
A simple communication system can help significantly with organisational skills, by using easy-to-use functions to allow your staff to record all information quickly and efficiently. For those staff members who are training and will have 20% off-the-job time, ensure their mentor books in regular meetings to monitor their evidence gathering as well as help to encourage proactive use of the out-of-room time.
- Email Address *
Self-awareness
This is a soft skill often forgotten but is essential for your staff to develop and make the most out of the Continuous Professional Development (CPD) you offer them. Not all your team members will have found academic schooling easy; statistics show you will likely have a selection of team members who may have undiagnosed neurodiversity, potentially affecting their method of learning. Your staff should be encouraged to explore their preferred mode of learning, communication and conflict resolution. Your team are as diverse as the children you support.
How to encourage self-awareness in your staff
During staff meetings, focus on the pedagogy of learning, explore different learning methods, and use your staff meeting schedules to deliver them in different ways.
Problem-solving
Decision-making and problem-solving tie in with patience, communication, creativity, and positivity. It allows your staff to think on their feet when faced with a challenge from safeguarding, to differentiation of learning resources. Your staff should be encouraged to tackle challenges through a lens of curiosity. By asking reflective practice questions to gain more information and choosing an approach as a team, others can learn effective problem-solving methods in the Early Years.
How to encourage problem-solving skills in your nursery staff
Using scenario-based CPD sessions can help to develop this important soft skill. You can tailor these scenarios based on previous challenges your team have faced and which are personalised to your setting, or you can use the examples we discuss in our CPD blog .
Positive attitude and reflection
Working with children can be full-on; you are constantly interacting all day and creating new learning opportunities for their development. Enthusiasm and positivity after a full day of exploration walks, sensory play and completing observations help make your nursery the lively and vibrant place it is. After all, glitter and role-play areas are lifeless without the staff who inject the fun into them.

How to encourage positivity in your nursery team
Reflective practice is necessary to react positively to situations of challenge. This is another soft skill that some staff have in abundance where others may need more purposeful practice. Recognising positive responses in your staff can help to encourage repeat behaviours. For your staff to be feeling their best, they need a good diet, healthy sleeping patterns and regular exercise. When reviewing paperwork and policies, try to have mentally healthy habits in mind for your children and staff.
The ability to create wonder and awe from loose parts like a stick, some pebbles or fallen leaves is a talent not everyone possesses. It is a soft skill requirement for an outstanding Early Years Practitioner. Your team should have natural creativity and enthusiasm to create a game or learning opportunity from little resources.
How to develop creativity within your Early Years Practitioners
Some of your team may be more naturally creative than others; this can be an excellent learning opportunity for your less-creative team members. Utilising a mentor system, you can increase your staff’s understanding of what creativity may look like across different ages and rooms. You can make creativity development a focus of your team meetings by sharing a picture stimulus or piece of equipment to discuss game possibilities as a team.
Self-belief and drive
In any field of work, your team members will have self-doubt and even imposter syndrome about progressing to the next level of development in their career. As the manager, your role is to encourage your team to have self-belief and high aspirations for their development. Self-belief is a soft skill often ignored, yet, it is the difference between a team constantly striving for better rather than a stagnant team with little personal or team drive.
How to develop self-belief within your nursery staff
Completing additional apprenticeships and qualifications after the work day can be a daunting task for many of your staff. Family life takes over, and there is little room for additional study. When you complete staff performance reviews, encourage them towards upcoming additional training opportunities such as the Early Years SENDCO qualification.
Know someone who'd like to read this article?
Subscribe to receive expert advice and tips from seasoned professionals in the early years sector.
More like this:

Quality Nursery Management Software.
Nurseries across the UK use Blossom to increase efficiency across their finance, learning journeys, operations & occupancy.
- Testimonials
- Case Studies
- Nursery Cost Savings Calculator
- Nursery Management Software
- BE paid by Blossom
- Recommended devices
- Blossom On BBC
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Help Centre
- Blossom’s Blog
- Accessibility statement
- Early Years Guides
Breadcrumbs Section. Click here to navigate to respective pages.

Teaching Thinking Skills Across the Early Years
DOI link for Teaching Thinking Skills Across the Early Years
Get Citation
This book helps teachers incorporate problem-solving and thinking skills into the National Curriculum at the Foundation Phase and Key Stage 1, in line with QCA and DfES recommendations. It presents a range of activities for children aged 4-7 years, all of which have been tried and tested in classrooms. The ideas are cross-referenced with the Learning Objectives of the National Curriculum, and are enhanced with samples of children's work.
It provides sections on the core subjects of literacy, numeracy and science, and ideas for project work across the curriculum.
This book is aimed at teachers at the Foundation Phase and Key Stage 1. Teacher trainers, student teachers, teaching assistants, parents and all those working in early years settings will find it equally useful.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 | 42 pages, teaching problem-solving and thinking skills in the early years: working across the curriculum, chapter 2 | 43 pages, introducing the use of the tasc problem-solving wheel in reception and key stage 1 literacy: developing children's writing skills, chapter 3 | 32 pages, using the tasc wheel to develop problem-solving and thinking skills in mathematics in the early years, chapter 4 | 52 pages, using the tasc wheel to maximise children's thinking and problem-solving in early years science.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Taylor & Francis Online
- Taylor & Francis Group
- Students/Researchers
- Librarians/Institutions
Connect with us
Registered in England & Wales No. 3099067 5 Howick Place | London | SW1P 1WG © 2024 Informa UK Limited

EYFS best practice - All about ... problem-solving
Sheila Ebbutt, a freelance consultant and was formerly managing director of BEAM (Be A Mathematician) Tuesday, July 7, 2009
Responding to challenges and finding solutions is not confined to mathematics but arises in all areas of learning, says Sheila Ebbutt.

Mathematics in the EYFS is called Problem Solving, Reasoning and Numeracy. It's an odd title, probably chosen because it has a rhythmic assonance with Knowledge and Understanding of the World and Communication, Language and Literacy. It's odd, first because problem-solving and reasoning are applicable across all learning, not just maths, and second, because maths is about more than numeracy.
My dictionary defines being 'numerate' as 'able to perform arithmetical operations'. But 'mathematics' has a much wider definition: 'the science dealing with measurements, numbers, quantities, and shapes'. That's a gripe of mine, but let's focus on problem-solving and reasoning. Each of the areas of learning could have had 'problem solving, reasoning and ...' added to their titles.
UNPICKING THE EYFS
The Early Years Foundation Stage has a mixture of very clear, brief descriptions of learning development and more complex general ones.
Simple and brief:
'Continue a rhyming string'; 'respond to simple instructions'; 'handle books carefully'; 'recognise numerals 1 to 5'; 'say the number that is one more than a given number'; 'select a particular named shape'; 'use simple tools competently and effectively'; 'notice and comment on patterns'; 'sing a few familiar songs'; 'go backwards and forwards as well as sideways'.
Complex and general:
'Have an awareness and pride in self and as having own identity and abilities'; 'question why things happen, and give explanations'; 'use language for an increasing range of purposes'; 'use talk to connect ideas, explain what is happening and anticipate what might happen next'; 'use writing as a means of recording and communicating'; 'use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems'; 'describe solutions to practical problems, drawing on experience, talking about own ideas, methods and choices'; 'explain own knowledge and understanding, and ask appropriate questions of others'; 'collaborate in devising and sharing tasks, including those which involve accepting rules'; 'talk about personal intentions, describing what they were about to do'; 'work creatively on a large or small scale'.
It is easy to allocate the simple descriptions to particular curriculum areas, and these are recognisable discrete skills that we know we have to teach. 'Continue a rhyming string' is language and 'recognise numerals 1 to 5' is maths.
The general descriptions are harder to allocate, unless there are clues like 'mathematical' and 'writing'. These complex statements have embedded in them a problem-solving approach. How do you teach 'question ...', 'collaborate ...', 'pride ...', 'personal intentions ...'? Well, you don't. You have to set up the environment and the ethos that will encourage these things, and support the children with planned interventions.
It's difficult working with such a mix of complex concepts. You know how to approach 'begin to form recognisable letters' and 'select a particular named shape'. You show children how to form letters. You teach them the names of the shapes. But how do you ensure that this develops into 'use writing as a means of recording and communicating' and 'use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems'?
What are the children learning?
Clearly, children are learning about shapes and how they move and fit together; about how to manipulate large objects; about relative heights; about hollow and solid shapes; about filling spaces; about the properties of materials. But they are also learning about collaboration and working to a common goal, and about perseverance; and above all, they are setting themselves problems that they have to solve.
The work in the case study below involved a problem-solving chain, each one with its own goal to be set, obstacles to be overcome, and the solution to be found. One goal is to build a tower with tyres, but the problem is how to lift and place the tyres.
Another goal is to fetch the tyres to add to the tower, but the problem is how to get the tyres to the tower. Another goal is to make the tower as tall as possible, but the problem is how to reach the top of the growing tower - and so on.
Seeking solutions to the problems involves analytical reasoning, conscious or unconscious. How do I move the tyre? Turn it into a wheel by putting it on its edge and rolling it.
Later, during circle time, the children talked about their play with the tyres. Although there was not a lot of talk during the activity, just brief and necessary instructions and comments, the children were able to put into words what they had been doing.
THE NATURE OF PROBLEM-SOLVING
Problem-solving is an integral part of everyday provision, an expectation rather than an added extra, and it relies on a 'have a go' ethos. Successful problem solvers have these kinds of strategies:
- setting themselves a goal - recognising there are obstacles in the way of the goal - getting a feel for the nature of the obstacles - having a sense of possible ways of overcoming the obstacles - planning ahead, and predicting what will happen - checking progress as they go - trying out different possibilities in a systematic way - trying different approaches to see which will work best - looking for even better solutions.
Children who feel confident and secure in their surroundings, and free to make choices, are better able to solve problems, both on their own and collaboratively.
Problems can be minor and arise incidentally, or they can be major projects. But the most important thing is for children to set themselves a challenge, or to engage with the challenge that is there, and then to know that they can choose their own ways of solving it. If children are told the problem and then told the method to use to solve it, they are not problem-solving.
To become confident, proficient problem solvers, it stands to reason that children must have access to a wide range of appropriate resources they can use independently.
The ethos of the setting must support their investigations and allow them to move resources between areas of provision. For example, the children working with the tyres knew with confidence that they could move the tyres around, they could fetch a chair, and they could empty into the tower a range of objects at their disposal, without adult intervention. One of the important things about problem-solving is that it involves choice and that children have opportunities to reason and make decisions.
WHY IS PROBLEM-SOLVING IMPORTANT?
Two highly influential thinkers have stressed the importance of problem-solving as a vehicle for learning: Piaget and Vygotsky.
Piaget thought that children under seven saw the world differently from older children and adults, and they need time to explore the world in their own way. These are some of Piaget's key ideas:
- Children need to be in charge of their own learning by choosing their own activities and taking their own time in that exploration.
- We should provide children with materials to explore, such as block play, role-play materials, small-world toys, and so on. We should involve children in planning the uses of these resources, such as setting up a shoe shop or organising a picnic.
- We need to observe children to find out what they are focusing on and what their interests are, and respond to them if they ask for it. Our role as an adult is as a facilitator in their play.
- We should be aware of the stages of learning that children go through so that we can offer appropriate materials and activities for each stage, and note when children become 'ready' for the next stage.
- We should value each child as an individual.
Vygotsky emphasised collaborative and guided problem-solving. He focused on the social aspect of children's learning, and how they develop their thinking skills through shared experiences. This meant that language is a vital tool for thinking and for sharing ideas. He also looked at the roles of older children and adults in influencing learning. These are some of Vygotsky's key ideas:
- Children learn best through active self-directed play.
- Children learn more effectively in collaboration with other children and with adults.
- Our role is to offer help and support in helping children learn how to do things they cannot quite do on their own. Language is very important here.
- We need to observe children to find out where they are on their own learning trajectory.
- We must focus on language, as this is vital in helping children make sense of the world.
- We must be sensitive in how we take part in children's learning. Sometimes we can take the lead and instruct, at other times we will have minimal engagement.
The EPPE (Effective Provision of Pre-School Education) project corroborated Vygotsky's ideas, by finding that quality conversations between adults and children, and children and other children, enhanced children's problem-solving and reasoning skills. The work of the nursery settings in Reggio Emilia also puts into practice Vygotsky's ideas, with children and adults working collaboratively on long and complex projects.
Children's thinking will only develop well if they can spend their time solving problems. As they solve problems, their confidence and self-esteem increases. However, their self-esteem will decline if they fail too often to solve a problem. The role of the adult is so important in providing appropriate help, support, knowledge and skills.
Problem-solving involves reflection and thought. The adult can help by modelling strategies and encouraging children to talk about their methods. Children can develop a range of methods by collaborating with adults and with other children, and by discussing the range of methods.
HELPING CHILDREN BECOME PROBLEM-SOLVERS
- Create an atmosphere where exploration and having a go are more important than getting the right answer or doing the expected thing to please an adult.
- Provide a rich and stimulating environment, with plenty and varied activities, and don't make things too easy for the children.
- Be an opportunist and look for problem-solving possibilities in everyday activities, such as parties, picnics, tidying-up, arriving and leaving, charity events, a new baby, children's own interests.
- Approach everyday activities as problem-solving opportunities. In adult-led guided learning sessions, make sure children have choices within the framework of the objectives of the session. For example, if children are focusing on counting, play an interesting game that involves choices.
- If children ask you to be involved in their problem-solving, prompt them with comments or questions that will help them to continue to grapple with the problem themselves, or supply further resources that will keep the problem with them. A comment or a look can be as effective as questioning. Certainly, asking questions should not be an inquisition, but a collaborative conversation.
What do you think would help you to reach up there?
Mmm ... I don't know ... What have you tried so far?
Why didn't that work? I wonder if there is another way of doing it.
I wonder if we need anything else here to help us.
How does it look now?
I'm not sure I can do it either! Let's have another go.
- In group sessions, encourage children to describe their play, and the problems they tackled and overcame. Invite them to share ideas and thinking to show what they have done.
- If children are becoming frustrated, or if you feel they are on the cusp of new learning, introduce them to a technique or strategy for taking them on to the next step of learning. You can suggest breaking the problem down into smaller steps, or draw their attention to key features or clues.
- On the other hand, also allow children to get into a muddle so they can see that they need to think things through and develop systematic strategies. Don't take the problem away from the children. Healthy confusion is a good starting point for trying to sort things out.
- Make sure that children have long, uninterrupted periods of time at their own self-directed play.
- Observe children regularly to gain insights into their learning. Analyse and interpret these observations to help understand how to support them in their further learning.
For children to engage in and learn from problem-solving, they need to solve problems that they understand, in familiar contexts, where the outcomes matter to them, either on their own or in collaboration with others. They need to have control over the problem-solving process, and the problems should involve knowledge and skills they are confident with. They should have the opportunity to talk about the process, and have adult help to scaffold smaller steps in the process where they need it.
Two boys are playing with the tyres in the outdoor area of the setting. Their play leads them to start piling one tyre on top of the other. There are lots of tyres lying around the grassy area, and gradually they collect them and add them to their growing cylindrical tower.
Two more children join them, but in a different activity. They each find a container - one a bucket and spade and the other a dustpan and brush - and they gather up leaves and twigs and stones and empty them into the growing tyre cylinder.
The children building the tower have difficulty manipulating the tyres, as they are big and unwieldy. They have to turn each one on its edge and try to roll the tyre along. Sometimes another child sees this going on and volunteers to help.
Lifting the tyres increasingly higher is also difficult and reqiures two children, at least. As the tower grows, one child runs off and fetches a chair, puts it up against the tower, and lifts each tyre up on top. Meanwhile, the fillers continue to collect material to put into the central cavity.
Now that the hole is deeper, they add larger items such as lumps of wood and bark from the digging area. There are eight or nine tyres, one on top of the other. The children work at this activity for an hour and a half with no adult intervention. There is an adult observing from time to time and making notes.

Nursery World Print & Website
- Latest print issues
- Latest online articles
- Archive of more than 35,000 articles
- Free monthly activity poster
- Themed supplements
From £11 / month

Nursery World Full Membership
- Latest digital issues
- Exclusive offers
From £13 / month

Nursery World Digital Membership
© MA Education 2024. Published by MA Education Limited, St Jude's Church, Dulwich Road, Herne Hill, London SE24 0PB, a company registered in England and Wales no. 04002826. MA Education is part of the Mark Allen Group. – All Rights Reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Constructing camps and dens outdoors is a good way to give children the opportunity to be involved in lots of maths problem-solving experiences and construction skills learning. This experience offers opportunities for using the language of position, shape and space, and finding solutions to practical problems.
However, problem-solving is much more than number conundrums. Problem-solving is a key part of early years development and can support learning across many of the My First Five Years streams. The skill of problem-solving starts developing very early in a child's life and stems from the knowledge of the world that they are constantly building.[1].
The first article Mathematical Problem Solving in the Early Years pointed out that young children are natural problem setters and solvers: that is how they learn. This article suggests ways to develop children's problem solving strategies and confidence. Problem solving is an important way of learning, because it motivates children to connect previous knowledge with new situations and to ...
Early Years practitioners can help children apply problem solving skills to real life situations as well as various activities. For example, practitioners can encourage children to help set up at meal times, but pose them with a problem of not having enough cutlery for each child.
If we take a look at the steps involved in solving a problem, we can see that there are many layers involved and different types of skills. Here are the problem-solving steps according to the University of Ken. Step 1: Identify the problem. Step 2: Define the problem. Step 3: Examine the options.
Problem Solvers is a free, downloadable early math curriculum for children aged 30 to 48 months that includes: 22 play-based preschool and early math activities, spanning 7 domains of early math. 22 specially-composed songs that support early math learning in each activity. 22 book suggestions and extension activities that nurture early math ...
Through structuring the stages of the problem-solving process; Through explicitly and repeatedly providing children with opportunities to develop key problem-solving skills. In an Early Years (EY) setting, I would suggest that the first and third of these are particularly important. Choice of 'task': think resources and skilful questioning
All these resources link to the Early Years Foundation Stage Framework. Each of them has: • suggestions of rich contexts for exploring mathematical ideas and developing mathematical skills and concepts. • details of linked mathematics learning goals. • descriptions of the mathematical journey that the learners may take through the task.
Problem Solving, Reasoning and Numeracy in the Early Years Foundation Stage This booklet focuses on children's mathematical development, which is explored in the area of learning and development entitled Problem Solving, Reasoning and Numeracy (PSRN) in the Early Years Foundation Stage (EYFS) (DCSF, 2008).
And teaching and modeling problem-solving skills early on with preschool children builds a foundation of problem-solving and relationship skills that most children can access with adult support and start to use independently as they continue to develop. ... Research tells us that the early years are foundational for brain development. And ...
The teacher counts aloud as Ben lifts each finger, stopping at five. "I need five cakes then," Ben says. "Yes," the teacher agrees, "you need one more cake, and then there is one for each teddy". 3. Reminding. Educators can prompt children to remember and apply a previous strategy to solve a mathematical problem.
Mastery motivation is persistence—continuing to do or to try to do something that is difficult—at mastering challenging tasks or activities. Problem solving is natural for preschoolers. As teachers know, everyday routines can bring difficult challenges, like learning how to zip up a coat or ask for help before frustration sets in.
Once this understanding is locked-in, follow this with an introduction to number bonds. Start with the additive relationships between numbers less than 10, then progress to adding and subtracting up to 10. This ensures that learners see 10 as an important 'base' number in all of their future maths applications.
In the early years of childhood development, problem-solving skills are foundational to cognitive growth and practical learning. This article explores engaging activities, scenarios, and resources designed to foster these critical skills in young learners. ... Problem-solving skills in preschoolers refer to their ability to understand a problem ...
Cut two large circles, one from green paper and one from red. Write "stop" on the red and "go" on the green, and glue them (back to back) over a popsicle stick holder. This is your traffic light. Stand where your child has some room to move toward you, such as at the end of a hallway.
Problem-solving. The ability to think through a problem, to recognize there is more than one path to the answer. It means using past knowledge and logical thinking skills to find an answer. Carl (15 months old) looked at the shape-sorter—a plastic drum with 3 holes in the top. The holes were in the shape of a triangle, a circle and a square.
Some early years practitioners struggle with the definition of problem solving. It is all about the process of working through ideas to reach a solution. It is also about processing information and evaluating ideas and concepts. As children are constantly learning new ideas, skills and concepts, these will all help them develop their problem ...
cognitive skills: problem-solving skills, early academic skills communication skills: responding to others, asking questions physical skills: ... Pamela Brillante, EdD, has spent 30 years working as a special education teacher, administrator, consultant, and professor. In addition to her full-time faculty position in the Department of Special ...
As well as developing numeracy, it supports skills such as problem solving, understanding and using shapes and measure. It also improves children's spacial awareness. It also helps them to recognise, create and describe patterns, which is essential for early problem-solving skills. In short, introducing maths to children from an early age ...
These skills can be measured; (qualifications, training courses attended, meeting the EYFS qualification requirements .) Soft skills involve the social and emotional depth necessary to thrive in the nursery, including self-awareness, patience, communication, organisation, problem-solving, positivity, creativity, self-belief and personal drive.
This book helps teachers incorporate problem-solving and thinking skills into the National Curriculum at the Foundation Phase and Key Stage 1, in line with QCA and DfES recommendations. It presents a range of activities for children aged 4-7 years, all of which have been tried and tested in classrooms.
EYFS best practice - All about ... problem-solving. Sheila Ebbutt, a freelance consultant and was formerly managing director of BEAM (Be A Mathematician) Tuesday, July 7, 2009. Responding to challenges and finding solutions is not confined to mathematics but arises in all areas of learning, says Sheila Ebbutt.
Through our choice of task. gh structuring the stages of the problem-solving processThrough explicitly and repeatedly providing children. ith opportunities to develop key problem-solving skills.In an Early Years (EY) setting, I would suggest tha. Choice of 'task': think resources and skilful questioningI have deliberately used inverted commas ...