Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.

Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
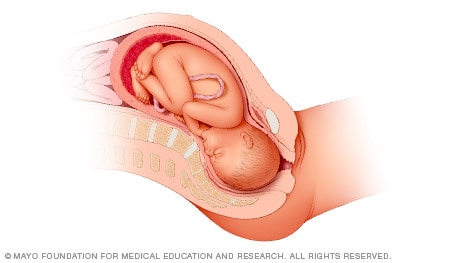
Head down, face up
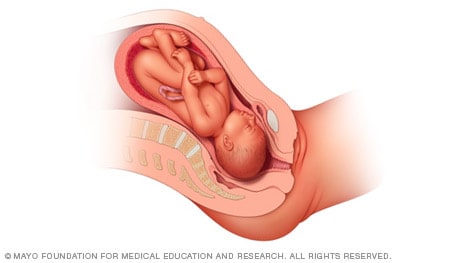
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
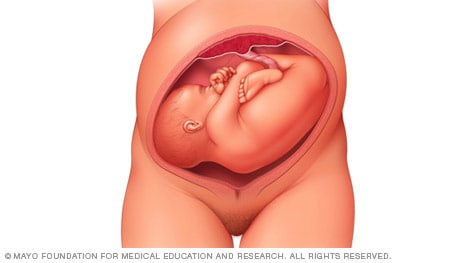
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

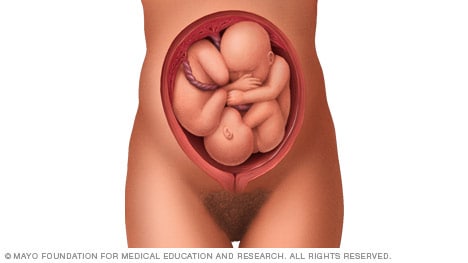
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic
RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
This topic will provide an overview of major issues related to breech presentation, including choosing the best route for delivery. Techniques for breech delivery, with a focus on the technique for vaginal breech delivery, are discussed separately. (See "Delivery of the singleton fetus in breech presentation" .)
TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION
● Frank breech – Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
● Complete breech – Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Breech?
When a fetus is delivered buttocks or feet first
- Types of Presentation
Risk Factors
Complications.
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor . Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
This article discusses the different types of breech presentations, risk factors that might make a breech presentation more likely, treatment options, and complications associated with a breech delivery.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Types of Breech Presentation
During the last few weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually rotates so that the head is positioned downward to come out of the vagina first. This is called the vertex position.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. Instead, the fetus’s buttocks or feet are positioned to come out of the vagina first.
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech.
The different types of breech presentations include:
- Complete : The fetus’s knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Frank : The fetus’s legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Footling : The fetus’s foot is showing first.
Signs of Breech
There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation.
Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.
A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination is the best way to determine how the fetus is lying in the uterus.
Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor. However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation.
These can include:
- Previous pregnancies
- Multiple fetuses in the uterus
- An abnormally shaped uterus
- Uterine fibroids , which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years
- Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta covers the opening to the uterus
- Preterm labor or prematurity of the fetus
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy)
- Fetal congenital abnormalities
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.
In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus. However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with cesarean delivery.
Before cesarean delivery, a healthcare provider might utilize the external cephalic version (ECV) procedure to turn the fetus so that the head is down and in the vertex position. This procedure involves pushing on the pregnant person’s belly to turn the fetus while viewing the maneuvers on an ultrasound. This can be an uncomfortable procedure, and it is usually done around 37 weeks gestation.
ECV reduces the risks associated with having a cesarean delivery. It is successful approximately 40%–60% of the time. The procedure cannot be done once a pregnant person is in active labor.
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor.
ECV is usually not recommended if the:
- Pregnant person is carrying more than one fetus
- Placenta is in the wrong place
- Healthcare provider has concerns about the health of the fetus
- Pregnant person has specific abnormalities of the reproductive system
Recommendations for Previous C-Sections
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that ECV can be considered if a person has had a previous cesarean delivery.
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
Complications associated with cesarean delivery include infection, bleeding, injury to other internal organs, and problems with future pregnancies.
A healthcare provider needs to weigh the risks and benefits of ECV, delivering a breech fetus vaginally, and cesarean delivery.
In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word From Verywell
Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, cesarean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
TeachMeObGyn. Breech presentation .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term . Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1;2015(4):CD000083. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3
By Christine Zink, MD Dr. Zink is a board-certified emergency medicine physician with expertise in the wilderness and global medicine.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Breech presentation.
Caron J. Gray ; Meaghan M. Shanahan .
Affiliations
Last Update: November 6, 2022 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
- Describe the pathophysiology of breech presentation.
- Review the physical exam of a patient with a breech presentation.
- Summarize the treatment options for breech presentation.
- Explain the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by breech presentation.
- Introduction
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the fetus sitting with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position. Finally, the incomplete breech can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended). [1] [2] [3]
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4] [5] These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
- Epidemiology
Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech.
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10%, and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
- Pathophysiology
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6] [7]
Conditions that change the vertical polarity or the uterine cavity, or affect the ease or ability of the fetus to turn into the vertex presentation in the third trimester include:
- Mullerian anomalies: Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and didelphys uterus
- Placentation: Placenta previa as the placenta is occupying the inferior portion of the uterine cavity. Therefore, the presenting part cannot engage
- Uterine leiomyoma: Mainly larger myomas located in the lower uterine segment, often intramural or submucosal, that prevent engagement of the presenting part.
- Prematurity
- Aneuploidies and fetal neuromuscular disorders commonly cause hypotonia of the fetus, inability to move effectively
- Congenital anomalies: Fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Polyhydramnios: Fetus is often in unstable lie, unable to engage
- Oligohydramnios: Fetus is unable to turn to vertex due to lack of fluid
- Laxity of the maternal abdominal wall: Uterus falls forward, the fetus is unable to engage in the pelvis.
The risk of cord prolapse varies depending on the type of breech. Incomplete or footling breech carries the highest risk of cord prolapse at 15% to 18%, while complete breech is lower at 4% to 6%, and frank breech is uncommon at 0.5%.
- History and Physical
During the physical exam, using the Leopold maneuvers, palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breech in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation.
During a cervical exam, findings may include the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted. If the patient has been laboring, caution is warranted as the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex.
Any of these findings should raise suspicion and ultrasound should be performed.
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
On ultrasound, the fetal lie and presenting part should be visualized and documented. If breech presentation is diagnosed, specific information including the specific type of breech, the degree of flexion of the fetal head, estimated fetal weight, amniotic fluid volume, placental location, and fetal anatomy review (if not already done previously) should be documented.
- Treatment / Management
Expertise in the delivery of the vaginal breech baby is becoming less common due to fewer vaginal breech deliveries being offered throughout the United States and in most industrialized countries. The Term Breech Trial (TBT), a well-designed, multicenter, international, randomized controlled trial published in 2000 compared planned vaginal delivery to planned cesarean delivery for the term breech infant. The investigators reported that delivery by planned cesarean resulted in significantly lower perinatal mortality, neonatal mortality, and serious neonatal morbidity. Also, there was no significant difference in maternal morbidity or mortality between the two groups. Since that time, the rate of term breech infants delivered by planned cesarean has increased dramatically. Follow-up studies to the TBT have been published looking at maternal morbidity and outcomes of the children at two years. Although these reports did not show any significant difference in the risk of death and neurodevelopmental, these studies were felt to be underpowered. [8] [9] [10] [11]
Since the TBT, many authors since have argued that there are still some specific situations that vaginal breech delivery is a potential, safe alternative to planned cesarean. Many smaller retrospective studies have reported no difference in neonatal morbidity or mortality using these specific criteria.
The initial criteria used in these reports were similar: gestational age greater than 37 weeks, frank or complete breech presentation, no fetal anomalies on ultrasound examination, adequate maternal pelvis, and estimated fetal weight between 2500 g and 4000 g. In addition, the protocol presented by one report required documentation of fetal head flexion and adequate amniotic fluid volume, defined as a 3-cm vertical pocket. Oxytocin induction or augmentation was not offered, and strict criteria were established for normal labor progress. CT pelvimetry did determine an adequate maternal pelvis.
Despite debate on both sides, the current recommendation for the breech presentation at term includes offering external cephalic version (ECV) to those patients that meet criteria, and for those whom are not candidates or decline external cephalic version, a planned cesarean section for delivery sometime after 39 weeks.
Regarding the premature breech, gestational age will determine the mode of delivery. Before 26 weeks, there is a lack of quality clinical evidence to guide mode of delivery. One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Face and brow presentation
- Fetal anomalies
- Fetal death
- Grand multiparity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Oligohydramnios
- Pelvis Anatomy
- Preterm labor
- Primigravida
- Uterine anomalies
- Pearls and Other Issues
In light of the decrease in planned vaginal breech deliveries, thus the decrease in expertise in managing this clinical scenario, it is prudent that policies requiring simulation and instruction in the delivery technique for vaginal breech birth are established to care for the emergency breech vaginal delivery.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12] [13] [14]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Caron Gray declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Meaghan Shanahan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation. [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. [Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997] [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. Krause M, Fischer T, Feige A. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997 Jul-Aug; 201(4):128-35.
- The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. [Early Hum Dev. 1993] The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. Sival DA, Prechtl HF, Sonder GH, Touwen BC. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Mar; 32(2-3):161-76.
- The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. [PLoS One. 2019] The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. Jennewein L, Allert R, Möllmann CJ, Paul B, Kielland-Kaisen U, Raimann FJ, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0225546. Epub 2019 Dec 2.
- Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. [Semin Perinatol. 2003] Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. Tunde-Byass MO, Hannah ME. Semin Perinatol. 2003 Feb; 27(1):34-45.
- Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. Mattuizzi A. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020 Jan; 48(1):70-80. Epub 2019 Nov 1.
Recent Activity
- Breech Presentation - StatPearls Breech Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Breech Position: What It Means if Your Baby Is Breech
Medical review policy, latest update:.
Medically reviewed for accuracy.
What does it mean if a baby is breech?
What are the different types of breech positions, what causes a baby to be breech, recommended reading, how can you tell if your baby is in a breech position, what does it mean to turn a breech baby, how can you turn a breech baby, how does labor usually start with a breech baby.
If your cervix dilates too slowly, if your baby doesn’t move down the birth canal steadily or if other problems arise, you’ll likely have a C-section. Talk your options over with your practitioner now to be prepared. Remember that though you may feel disappointed things didn’t turn out exactly as you envisioned, these feelings will melt away once your bundle of joy safely enters the world.
Updates history
Jump to your week of pregnancy, trending on what to expect, signs of labor, pregnancy calculator, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., top 1,000 baby girl names in the u.s., top 1,000 baby boy names in the u.s., braxton hicks contractions and false labor.

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
- Third Trimester
- Labor & Delivery
What Does It Mean to Have a Breech Baby?
You’re almost full term and the finish line is approaching, when suddenly your OB or midwife informs you that baby is breech—plot twist! If baby is in a breech position, it means their feet or bottom is pointed toward your cervix rather than their head. You’ve just encountered an early example of a universal truth in parenting: Few things ever go as perfectly as you planned.
A breech birth often means a c-section delivery is in store for you, and that can feel disappointing and worrisome, especially if you’ve been hoping to deliver vaginally. Deep breath— you may still have options; your doctor will talk you through everything well before the big day comes. In the meantime, it’s helpful to get a better grasp on all things breech baby. Want to know how to tell if baby is breech, what the position means for your pregnancy, how it affects delivery and ways your doctor (and you!) can try to turn baby? Read on for the full lowdown.
What Is a Breech Baby?
In the last few weeks of pregnancy, most babies move in the womb so that their heads are facing down, positioned to come out of the vagina first during delivery. But if baby is breech, their head is not approaching the birth canal; rather, it’s their feet or bottom that’s poised to come out first.
Types of breech positions
There are three different types of breech positions, according to the American Pregnancy Association :
- Complete. Baby’s buttocks are pointing down and legs are crossed beneath it
- Frank. Baby’s bottom is positioned down and legs are pointed up toward the head
- Footling. Baby has one leg pointed toward the cervix, poised to deliver before the rest of their body. “There’s also a double footling breech, where the baby’s feet and legs are facing down toward the cervix,” says Elizabeth Deckers , MD, director of the maternal quality and safety program at Hartford HealthCare.
Baby could also be in a transverse lie position (occasionally referred to as a transverse breech position). This means that they’re horizontal across the uterus instead of vertical.
What percentage of babies are breech?
According to the American Pregnancy Association, approximately 1 out of every 25 full-term births involves a baby in a breech position. That means roughly 4 percent of babies have their bottom and/or feet pointed down toward the birth canal.
Why a Breech Position Can Be a Concern
Your doctor won’t be too concerned if baby is in a breech position throughout most of your pregnancy. In fact, it’s likely that at some point in your second or early third trimester, baby will be breech. At this early stage, though, baby is smaller and has more room to move around and turn, notes Deckers.
As baby grows and your due date nears, a breech position becomes slightly more concerning. For starters, there’s some evidence linking a breech presentation—and its tendency to reduce the amount of space in the womb—with hip dysplasia , a condition where the ball and socket joint of baby’s hip doesn’t properly form.
Your doctor or midwife may raise a red flag if baby is in breech position at 36 weeks or later. At this point, they’ll probably start talking about the potential need for a c-section. “Vaginal breech delivery is no longer commonly done in the US because about 20 years ago there was a large, well-designed trial that showed there was more risk to the fetus of going through a vaginal breech delivery versus being born by a c-section,” says Deckers. The trial showed that breech babies born vaginally were more likely to have fetal fractures and a harder time getting out of the birth canal, says Amber Samuel , MD, medical director of Obstetrix Maternal-Fetal Medicine Specialists of Houston. Deckers reiterates this, noting that most babies in the US identified as breech will be born via c-section, as doctors “believe it’s safer in the short run for baby.”
What Causes a Breech Pregnancy?
Don’t beat yourself up or worry that you did something wrong in pregnancy to put baby into a breech position. The truth is there’s usually no rhyme or reason to explain baby’s breech presentation, says Samuel. That said, if you have a uterine anomaly, where your uterus is wider at the top or generally more narrow, it may play a role, she says. “If the shape is abnormal, some babies get stuck,” she says. Having too much amniotic fluid around baby might also be a potential factor.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) lists other factors that might contribute to baby being breech: you’ve been pregnant before, you’re expecting twins or multiples, you have placenta previa (where your placenta is covering part of your uterine opening) or baby is preterm . Suffice it to say, though, that these potential breech baby causes are out of your control.
How to Tell If Baby Is Breech
You might be able to detect that baby is breech if you feel them kick low near your cervix or feel their head under your ribs, says Deckers. Samuel notes that some moms who’ve had babies before are really good at determining how and where they’re positioned.
Doctors gauge baby’s position by placing their hands on different parts of your belly to feel where fetal parts are, a technique known as Leopold’s maneuvers, explains Samuel. They may also perform a cervical exam to see if they can feel any presenting parts. Sometime around 36 or 37 weeks, they’ll confirm baby’s position with an ultrasound.
What to Expect from a Breech Pregnancy
You may not know if or when baby is in a breech position. Earlier on in your pregnancy, when they’re smaller and have more room in the womb, they may flip all around; roughly 20 percent of babies are breech at 28 weeks, says Samuel. If you discover that your little acrobat is breech at this stage, don’t panic; there’s still more than enough time for them to flip into the preferred position (and then possibly do a few more rotations).
Are breech babies more painful to carry?
The good news: Breech presentation doesn’t typically cause discomfort or pain during pregnancy, Samuel says. Pain is more likely related to “prior scar tissue, the size of your baby and your pregnancy history,” she adds.
What to Expect from a Breech Delivery
There is a possibility for a vaginal breech birth under the right circumstances. Deckers notes that you may be a candidate if baby is in a frank or complete breech presentation and your pelvic structure is adequate for vaginal birth—and if your hospital has guidelines in place for a planned vaginal breech delivery. Unfortunately, the risk of the umbilical cord falling through the cervix is too high with a double footling breech; there’s also a higher risk that baby will get stuck during delivery, which can cause birth asphyxia. Of course, you’ll also want to ensure that your doctor has a lot of experience with vaginal breech delivery and that your hospital will allow it.
If baby is in a breech position beyond 36 weeks and your doctor feels that a vaginal birth is too risky, they’ll likely recommend that you allow them to try turning baby— more on that soon . If that’s not successful, you’ll be scheduled for a c-section, says Samuel.
Having twins where one is breech changes the game a little too. If the baby that’s poised to come out first is breech, you’ll have to deliver via c-section, says Deckers. But if the first baby is head down and second is not, you and your OB have three options: deliver both via c-section; deliver the first baby vaginally and then attempt to turn the second one to deliver vaginally (if it’s unsuccessful, you’ll proceed with a c-section) or deliver the first vaginally and then do a breech extraction of the second baby (your OB will reach inside to grasp baby’s feet and pull them down.)
“The ability to do a safe breech extraction depends on the gestational age of the babies, how well the mother and babies are tolerating labor, the size of the babies and a provider with experience in performing this procedure,” says Deckers.
How to Turn a Breech Baby
Many parents want to have a vaginal birth; what’s more, they know that a c-section is a major surgery with inherent risks. To that end, before scheduling a c-section, most doctors will suggest trying an external cephalic version (ECV), which is an attempt to turn baby from the outside.
First you’ll be given medication to relax your uterus; don’t worry, your doctor will continually monitor baby. “One hand elevates the fetal breech out of the pelvis and you push up and away from the pelvis,” says Samuel. “The other hand is on the back of baby’s head to induce them to turn over—it looks like an aggressive belly massage.”
Your doctor will push baby forward before attempting a backward roll. “You can tell pretty early into it whether it’s going to work or not—some babies are ready to flip, some aren’t,” says Samuel. “We try not to struggle too much with it.”
External cephalic versions are successful roughly 58 percent of the time, says Deckers, although there’s always the chance that baby will flip back to breech on their own. If the turning is successful and you’re at 39 weeks, you can choose to be induced. If it didn’t work, you’ll be scheduled for a c-section. ECVs should only be performed in hospitals equipped to perform emergency c-sections ; risks of the procedure, which are rare, include bleeding from the placenta, rupture of membranes and going into labor, says Samuel.
It’s also worth noting that not every mom is a candidate for an EVC. If you’re having multiples or there’s a problem with placental position, an EVC is too risky, according to the ACOG.
Safe ways to try to turn a breech baby at home
If you prefer to try to make things happen on your own, there are a few things you can do to help turn a breech baby from the comfort of your home. Deckers notes, though, that research on DIY techniques hasn’t provided strong enough evidence to prove that they really work.
A little bit of gentle prenatal yoga may help. One pose to practice? Deckers says some moms try “a head down/knee-to-chest position.” You can also assume a few different sleeping positions to turn a breech baby: “Mothers can try positional things like elevating your pelvis,” she says. Finally, Deckers mentions two Eastern medicine techniques that many moms actively seek out: acupuncture and moxibustion, a therapy that involves waving burning dried plant bundles over specific parts of the body to encourage baby to turn on their own. These methods have been long used, but she points out that the efficacy of these methods haven’t been proven in trials, so “the data isn’t compelling enough to say this is something you should do.”
What to Expect for a Breech Baby After Birth
If baby is presenting breech and you and your doctor decide to move forward with a vaginal delivery, there are some potential complications to be aware of that could ultimately affect baby’s health and well being.
It’s possible for baby’s head or shoulders to get wedged against your pelvic bones; a prolapsed umbilical cord could also decrease blood flow and cut off baby’s oxygen supply, explains the ACOG. That said, even a planned c-section comes with its own set of risks.
Welcoming a healthy baby into the world is the ultimate goal, regardless of how they’re delivered. Interestingly, babies who’ve been in breech presentation and are delivered via c-section tend to have nicely shaped heads because there’s none of the swelling and other head-shifting changes that occur in babies delivered through the birth canal, notes Deckers.
Do breech babies have problems later in life?
Sometimes babies who were breech have issues with their hips, as having one or both legs extended in a partially straight position rather than crossed can prevent a baby’s hip socket from developing properly. If your child was breech, Deckers recommends following up with your pediatrician.
Having a breech baby was probably not in your original birth plan. Your stubborn little one may turn before their grand debut, or they may—quite literally—put their foot down and refuse to budge. Either way, talk to your doctor about any concerns. And remember, the good news is that baby is coming soon, either way!
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
What to Expect During Your C-Section Recovery
The Best Prenatal Poses for Better Sleep
How to Care for Your C-Section Scar
Elizabeth Deckers , MD, is the director of the maternal quality and safety program at Hartford HealthCare. She received her medical degree from the University of Connecticut School of Medicine in Farmington.
Amber Samuel , MD, is the medical director of Obstetrix Maternal-Fetal Medicine Specialists of Houston. She earned her medical degree at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas.
American Pregnancy Association, Breech Presentation
Lancet, Planned caesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group , October 2000
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), If Your Baby Is Breech
Learn how we ensure the accuracy of our content through our editorial and medical review process .
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
Next on Your Reading List

Breech baby at the end of pregnancy
Published: July 2017
Please note that this information will be reviewed every 3 years after publication.
This patient information page provides advice if your baby is breech towards the end of pregnancy and the options available to you.
It may also be helpful if you are a partner, relative or friend of someone who is in this situation.
The information here aims to help you better understand your health and your options for treatment and care. Your healthcare team is there to support you in making decisions that are right for you. They can help by discussing your situation with you and answering your questions.
This information is for you if your baby remains in the breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy. Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies.
This information includes:
- What breech is and why your baby may be breech
- The different types of breech
- The options if your baby is breech towards the end of your pregnancy
- What turning a breech baby in the uterus involves (external cephalic version or ECV)
- How safe ECV is for you and your baby
- Options for birth if your baby remains breech
- Other information and support available
Within this information, we may use the terms ‘woman’ and ‘women’. However, it is not only people who identify as women who may want to access this information. Your care should be personalised, inclusive and sensitive to your needs, whatever your gender identity.
A glossary of medical terms is available at A-Z of medical terms .
- Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36–37 weeks of pregnancy most babies will turn into the head-first position. If your baby remains breech, it does not usually mean that you or your baby have any problems.
- Turning your baby into the head-first position so that you can have a vaginal delivery is a safe option.
- The alternative to turning your baby into the head-first position is to have a planned caesarean section or a planned vaginal breech birth.
Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies. Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, most babies turn naturally into the head-first position.
Towards the end of pregnancy, only 3-4 in every 100 (3-4%) babies are in the breech position.
A breech baby may be lying in one of the following positions:

It may just be a matter of chance that your baby has not turned into the head-first position. However, there are certain factors that make it more difficult for your baby to turn during pregnancy and therefore more likely to stay in the breech position. These include:
- if this is your first pregnancy
- if your placenta is in a low-lying position (also known as placenta praevia); see the RCOG patient information Placenta praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- if you have too much or too little fluid ( amniotic fluid ) around your baby
- if you are having more than one baby.
Very rarely, breech may be a sign of a problem with the baby. If this is the case, such problems may be picked up during the scan you are offered at around 20 weeks of pregnancy.
If your baby is breech at 36 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare professional will discuss the following options with you:
- trying to turn your baby in the uterus into the head-first position by external cephalic version (ECV)
- planned caesarean section
- planned vaginal breech birth.
What does ECV involve?
ECV involves applying gentle but firm pressure on your abdomen to help your baby turn in the uterus to lie head-first.
Relaxing the muscle of your uterus with medication has been shown to improve the chances of turning your baby. This medication is given by injection before the ECV and is safe for both you and your baby. It may make you feel flushed and you may become aware of your heart beating faster than usual but this will only be for a short time.
Before the ECV you will have an ultrasound scan to confirm your baby is breech, and your pulse and blood pressure will be checked. After the ECV, the ultrasound scan will be repeated to see whether your baby has turned. Your baby’s heart rate will also be monitored before and after the procedure. You will be advised to contact the hospital if you have any bleeding, abdominal pain, contractions or reduced fetal movements after ECV.
ECV is usually performed after 36 or 37 weeks of pregnancy. However, it can be performed right up until the early stages of labour. You do not need to make any preparations for your ECV.
ECV can be uncomfortable and occasionally painful but your healthcare professional will stop if you are experiencing pain and the procedure will only last for a few minutes. If your healthcare professional is unsuccessful at their first attempt in turning your baby then, with your consent, they may try again on another day.
If your blood type is rhesus D negative, you will be advised to have an anti-D injection after the ECV and to have a blood test. See the NICE patient information Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for women who are rhesus D negative , which is available at: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta156/informationforpublic .
Why turn my baby head-first?
If your ECV is successful and your baby is turned into the head-first position you are more likely to have a vaginal birth. Successful ECV lowers your chances of requiring a caesarean section and its associated risks.
Is ECV safe for me and my baby?
ECV is generally safe with a very low complication rate. Overall, there does not appear to be an increased risk to your baby from having ECV. After ECV has been performed, you will normally be able to go home on the same day.
When you do go into labour, your chances of needing an emergency caesarean section, forceps or vacuum (suction cup) birth is slightly higher than if your baby had always been in a head-down position.
Immediately after ECV, there is a 1 in 200 chance of you needing an emergency caesarean section because of bleeding from the placenta and/or changes in your baby’s heartbeat.
ECV should be carried out by a doctor or a midwife trained in ECV. It should be carried out in a hospital where you can have an emergency caesarean section if needed.
ECV can be carried out on most women, even if they have had one caesarean section before.

ECV should not be carried out if:
- you need a caesarean section for other reasons, such as placenta praevia; see the RCOG patient information Placenta praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- you have had recent vaginal bleeding
- your baby’s heart rate tracing (also known as CTG) is abnormal
- your waters have broken
- you are pregnant with more than one baby; see the RCOG patient information Multiple pregnancy: having more than one baby .
Is ECV always successful?
ECV is successful for about 50% of women. It is more likely to work if you have had a vaginal birth before. Your healthcare team should give you information about the chances of your baby turning based on their assessment of your pregnancy.
If your baby does not turn then your healthcare professional will discuss your options for birth (see below). It is possible to have another attempt at ECV on a different day.
If ECV is successful, there is still a small chance that your baby will turn back to the breech position. However, this happens to less than 5 in 100 (5%) women who have had a successful ECV.
There is no scientific evidence that lying down or sitting in a particular position can help your baby to turn. There is some evidence that the use of moxibustion (burning a Chinese herb called mugwort) at 33–35 weeks of pregnancy may help your baby to turn into the head-first position, possibly by encouraging your baby’s movements. This should be performed under the direction of a registered healthcare practitioner.
Depending on your situation, your choices are:
There are benefits and risks associated with both caesarean section and vaginal breech birth, and these should be discussed with you so that you can choose what is best for you and your baby.
Caesarean section
If your baby remains breech towards the end of pregnancy, you should be given the option of a caesarean section. Research has shown that planned caesarean section is safer for your baby than a vaginal breech birth. Caesarean section carries slightly more risk for you than a vaginal birth.
Caesarean section can increase your chances of problems in future pregnancies. These may include placental problems, difficulty with repeat caesarean section surgery and a small increase in stillbirth in subsequent pregnancies. See the RCOG patient information Choosing to have a caesarean section .
If you choose to have a caesarean section but then go into labour before your planned operation, your healthcare professional will examine you to assess whether it is safe to go ahead. If the baby is close to being born, it may be safer for you to have a vaginal breech birth.
Vaginal breech birth
After discussion with your healthcare professional about you and your baby’s suitability for a breech delivery, you may choose to have a vaginal breech birth. If you choose this option, you will need to be cared for by a team trained in helping women to have breech babies vaginally. You should plan a hospital birth where you can have an emergency caesarean section if needed, as 4 in 10 (40%) women planning a vaginal breech birth do need a caesarean section. Induction of labour is not usually recommended.
While a successful vaginal birth carries the least risks for you, it carries a small increased risk of your baby dying around the time of delivery. A vaginal breech birth may also cause serious short-term complications for your baby. However, these complications do not seem to have any long-term effects on your baby. Your individual risks should be discussed with you by your healthcare team.
Before choosing a vaginal breech birth, it is advised that you and your baby are assessed by your healthcare professional. They may advise against a vaginal birth if:
- your baby is a footling breech (one or both of the baby’s feet are below its bottom)
- your baby is larger or smaller than average (your healthcare team will discuss this with you)
- your baby is in a certain position, for example, if its neck is very tilted back (hyper extended)
- you have a low-lying placenta (placenta praevia); see the RCOG patient information Placenta Praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- you have pre-eclampsia or any other pregnancy problems; see the RCOG patient information Pre-eclampsia .
With a breech baby you have the same choices for pain relief as with a baby who is in the head-first position. If you choose to have an epidural, there is an increased chance of a caesarean section. However, whatever you choose, a calm atmosphere with continuous support should be provided.
If you have a vaginal breech birth, your baby’s heart rate will usually be monitored continuously as this has been shown to improve your baby’s chance of a good outcome.
In some circumstances, for example, if there are concerns about your baby’s heart rate or if your labour is not progressing, you may need an emergency caesarean section during labour. A paediatrician (a doctor who specialises in the care of babies, children and teenagers) will attend the birth to check your baby is doing well.
If you go into labour before 37 weeks of pregnancy, the balance of the benefits and risks of having a caesarean section or vaginal birth changes and will be discussed with you.
If you are having twins and the first baby is breech, your healthcare professional will usually recommend a planned caesarean section.
If, however, the first baby is head-first, the position of the second baby is less important. This is because, after the birth of the first baby, the second baby has lots more room to move. It may turn naturally into a head-first position or a doctor may be able to help the baby to turn. See the RCOG patient information Multiple pregnancy: having more than one baby .
If you would like further information on breech babies and breech birth, you should speak with your healthcare professional.
Further information
- NHS information on breech babies
- NCT information on breech babies
If you are asked to make a choice, you may have lots of questions that you want to ask. You may also want to talk over your options with your family or friends. It can help to write a list of the questions you want answered and take it to your appointment.
Ask 3 Questions
To begin with, try to make sure you get the answers to 3 key questions , if you are asked to make a choice about your healthcare:
- What are my options?
- What are the pros and cons of each option for me?
- How do I get support to help me make a decision that is right for me?
*Ask 3 Questions is based on Shepherd et al. Three questions that patients can ask to improve the quality of information physicians give about treatment options: A cross-over trial. Patient Education and Counselling, 2011;84:379-85
- https://aqua.nhs.uk/resources/shared-decision-making-case-studies/
Sources and acknowledgements
This information has been developed by the RCOG Patient Information Committee. It is based on the RCOG Green-top Clinical Guidelines No. 20a External Cephalic Version and Reducing Incidence of Term Breech Presentation and No. 20b Management of Breech Presentation . The guidelines contain a full list of the sources of evidence we have used.
This information was reviewed before publication by women attending clinics in Nottingham, Essex, Inverness, Manchester, London, Sussex, Bristol, Basildon and Oxford, by the RCOG Women’s Network and by the RCOG Women’s Voices Involvement Panel.
Please give us feedback by completing our feedback survey:
- Members of the public – patient information feedback
- Healthcare professionals – patient information feedback
External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation Green-top Guideline
Management of Breech Presentation Green-top Guideline
Breech at 20 weeks

You May Also Like
Planning Visitors During Hospital Stay
You’re pregnant how these moms reacted, jump to your week of pregnancy, trending on what to expect, moms share home remedies for pregnancy morning sickness, 8 expensive products moms say are worth the money, ⚠️ you can't see this cool content because you have ad block enabled., 14 moms on what labor really feels like, what are your go-to healthy snacks, things they don't tell you about: mom edition, pregnancy brain moments let's have a laugh, help keep our community safe, to create a safe place, please, on our end, we will.

- Flip a Breech
Our webpage information is free to pregnant parents. Those of you that serve birthing parents can refer parents to this page to help them understand more about helping breech babies find room in the womb to turn head down; cite the source but don’t copy and paste, please.
Not every suggestion is appropriate for everyone who wants to help their baby turn. Be mindful of your health and needs so you can be safe and comfortable.
We don’t force babies to turn. Many pregnant people can make room for their baby to turn by themselves.
- Read here for information to set your own plan
- Or, order the Helping ebook and get a simplified set of instructions: Helping Your Breech Baby Turn
- Find an Aware Practitioner for an in-person or online consultation
- When is Breech an Issue?
- Belly Mapping® Breech
When Baby Flips Head Down
- Breech & Bicornuate Uterus
- Breech for Providers
- What if My Breech Baby Doesn't Turn?
- Belly Mapping ®️ Method
- After Baby Turns
- Head Down is Not Enough
- Sideways/Transverse
- Asynclitism
- Oblique Lie
- Left Occiput Transverse
- Right Occiput Anterior
- Right Occiput Posterior
- Right Occiput Transverse
- Face Presentation
- Left Occiput Anterior
- OP Truths & Myths
- Anterior Placenta
- Body Balancing
Success is high with comprehensive body balancing
When any part of the pelvis is out of symmetry (crooked), then the ligaments supporting the womb are pulled and twisted too. The shape of the lower womb can be altered by this. The baby then has to find a way to fit that isn’t quite what nature intended. A twisted sacrum is common for breech (and posterior ).
Aligning the pelvis and relaxing tight uterine ligaments attached to the fascia near the pelvis are why chiropractic adjustments can often help breech babies flip to a head-down position.
Continue body balancing at home and with professionals after the baby turns head down. One thing I’ve observed is that when the breech baby does flip head down during the last month or two of pregnancy, the baby often moves to the head down, posterior (face forward) position.
Why is Baby Breech?
A breech position may be caused by an imbalance (asymmetry) in the mother’s pelvis or soft tissues. In other words, a tension or a twist in the lower uterine segment may be a “soft tissue” issue. This is not the woman’s fault, as we simply live in an era where a slight twist in the pelvis is common. Some causes of this may be:
- Long car rides
- Crossing our legs
- Sports injuries
- Abrupt stops (fender benders, etc.) torquing our torso
- Carrying a toddler on a hip or other hip rotation causing activities over time
- Serious falls
- A neck or ankle injury
All of these can twist the pelvis and, in turn, twist the uterus, resulting in asymmetry. Many chiropractors can loosen the ligaments by doing the Webster Technique. Adjusting the sacrum, for both a vertical twist or a buckled (horizontal wrinkle) sacrum will let the baby put their head down more readily because the bones won’t be in the way. It may often take balancing muscles and ligaments (soft tissues) and the pelvic joint alignment (not one without the other) for success.
4 Steps For Turning a Breech Baby
If the baby is still breech after 30 or 32 weeks gestation:
- Do self-care exercises, like the Three BalancesSM and Daily Activities and the releases in our Techniques pages.
- Watch the Breech Consultation video below
- Try our comprehensive, 6-day plan in Helping a Breech Baby Turn ebook
- Seek professional help
Combine bodywork techniques with stretches on the Daily Activities page and, perhaps more importantly, the Weekly Activities page for a more comprehensive approach. Do the weekly activities every day for a week or two. Add Rest Smart SM but don’t expect your posture or that sitting up or lying on your left will turn baby itself.
Seek professional body work if you don’t get results after a week. After 34 weeks, call and book a session (or series of sessions) with someone who understands anatomy and fetal position, such as a Spinning Babies ® Aware Practitioner or a chiropractor/osteopath with Webster certification.
Note: Body balance issues are common for breech presentation, but are not the only reason! We suggest our weekly activities on a daily basis when the baby is not head down. For video detail and more explanation, you may want to buy our Daily Essentials video for enhancing range of motion and suppleness. You can also attend a Parent Class in person, taught by one of our Spinning Babies ® Certified Parent Educators .
These techniques are working for many who do them repeatedly, but be sure to ask your doctor if there is a medical reason you couldn’t try some of these suggestions. Each individual begins with their own level of need for balance. Some need a little help while others are overcoming twists or tightnesses that need just the right techniques.
At Spinning Babies ® , we offer techniques that work for most pregnancies with a breech position. Your doctor or midwife can monitor your progress and give further suggestions for your particular situation.
Breech Consultation Video
Spinning Babies ® creator Gail Tully shows a couple two types of inversions to do together for making room for their breech baby to turn head down or to make an external cephalic version easier for the doctor to perform.
Things to keep in mind:
- Breech fetal position is common before 30 weeks and often okay at 32 weeks.
- Trust your baby and trust your body, but let your body trust your habits too.
- You can begin general balancing activities without knowing fetal position.
- Do not use the Breech Tilt and Open-Knee-Chest in pregnancy unless you know baby is breech.
- Put yourself in the position you want your baby to be in—head down!
- Share your plan with your caregiver before you begin.
- Talk to your baby, heart to heart, and tell your baby what you want – and ask your baby what he/she needs in this situation too.
- When your womb is in balance, the baby is likely to flip head down spontaneously.
- If the baby is still breech at 37 weeks or later, you may receive medical advice to have an external cephalic version (ECV) . Doing daily and weekly balancing activities before the ECV seems to help the procedure be more successful (and easier).
- Is one or both of your twins breech? Check out my article on twins .
When should I start?
- By 30-31 weeks, I highly recommend beginning the Forward-leaning Inversion position to encourage a head-down position.
- From 30 weeks on you can start the 6-day plan in our Helping Your Breech Baby Turn ebook.
- After 32-34 weeks, chiropractic adjustments are suggested.
- 34-35 weeks is the most successful time to use Moxibustion.
A detailed timeline is given for introducing techniques in pregnancies with breech babies. Look up your weeks gestation and do the suggestions for how to turn a breech baby listed there if you so choose. We have a handy exercise chart in our ebook as well.
Specific activities to try:

circles release minor adhesions in the leg socket and allow mobility in the connective tissue.
- The womb has a septum or unusual shape
- The baby is wrapped in a particular way by the cord (not as common as is claimed)
- If you’re having twins and one twin blocks the flipping movement of the breech twin
- Torsion causes reduced space in the lower uterine segment and it was not overcome or corrected by the woman’s selected activities (do more on the list above)
- There’s uncorrected torsion in the lower uterine segment (find another body worker)
- Intense core strength (6-pack belly)
Note: If you find that these exercises don’t work, it may increase emotional stress about having a breech birth. Whether or not the exercises work is not an indication of whether the vaginal breech birth will go smoothly or not.
Professional help for flipping a breech baby
For best success, begin professional help at 34 weeks. This opinion is shared by both Oxorn and Foote in Obstetrics Illustrated.
Professional help may include:
- Maya massage
- Chiropractic Webster Maneuver
- Chiropractic adjustment
- Therapeutic massage
- Acupuncture
- Fascial Therapy
- Craniosacral
- External cephalic version
You can see a list of professionals trained in our techniques in our Spinning Babies ® Aware Practitioner listings .
After the baby turns
If your baby was breech and is now head down, you can stop the inversions for a few days. Walk briskly for a mile or more every day for three days to get the baby’s head into the pelvis. After three days of walking, resume Forward-leaning Inversion once a day and the Abdominal and standing releases to continue the balance that will help the baby stay head down and rotate more readily once labor begins.
How can I tell when the baby flips?
You may or may not notice when the baby turns. You might be able to tell if the breech flips by feeling the feet kick where the head had been before. Usually, the strongest kicks are from the legs (not the arms) and will be high in the womb when the head is low.
An anterior placenta (one that gets on the front of the womb) can block the baby’s limb movement and confuse people who are trying to tell the baby’s position. More often, a mother will notice a difference in how she is carrying the baby.
Notice where your baby is kicking. If it is quite different and is now strong at the top of your womb, you may want to stop measures to flip the baby. If it stays the same, you might want to continue until you can get the midwife or doctor to verify the baby’s position.
I offer an article on Breech Belly Mapping or you can buy the Belly Mapping ® book.
What if I think my breech baby has flipped head down, but I’m not sure?
If you think the baby may have flipped head down, but you aren’t sure, you can either cease doing inversions until you do know for sure, or simply hold the Forward-leaning Inversion position for 30 seconds (or 3 long breaths).
If head down, will the baby flip breech if I do a Forward-leaning Inversion?
I think it’s unlikely that your baby will flip back to breech after balancing your body, unless the muscles and ligaments tighten up again. That said, keep your inversions short and do them only once a day. Don’t do the breech tilt if you think the baby may have gotten head down.
If you have a lot of amniotic fluid around your baby, so that a doctor needs to see you often, you should do other balancing activities like the Side-lying Release. Whether the baby flips on their own or with the help of an experienced midwife or doctor, the newly head-down baby is often in the right occiput posterior position .
A daily Forward-leaning Inversion can continue to help the baby get into an even better position for the start of labor. Remember, head down is only half the story!
If the breech baby doesn’t turn
Balancing techniques could help a vaginal breech birth go more smoothly. Always use physiologic breech birth practices (knee-elbow or hands-and-knees maternal position , hands-off the breech, natural childbirth, etc.).
Otherwise, a cesarean after labor begins gives the baby a bit of labor hormones to help transition into life outside the womb. Discuss these options with your midwife or doctor. There is currently better data in obstetrics to support physiological breech vaginal birth.
Consider that another week of healthy gestation, up to 40 weeks, has nothing but benefits for your baby. If you or your baby are not healthy, or if there is a prolapsed cord, you may need medical help.
Keep reading, keep balancing, and keep talking about what is beneficial for you and your baby with your provider. If you’d like to read more, here’s an article about the Window of Opportunity for Flipping Your Breech Baby .
Breech turning stories
Vbac-hopeful mama devotes a week to getting her baby head down.
I just wanted to let you know that I appreciated your help, and that at 34 weeks, me, my chiropractor, and my midwife are all pretty sure that the baby has flipped head down, to what your site basically calls a LOT position. It was a week-long process that wasn’t complete until I had done 3 Webster appointments, plus a bunch of inversions and doing your “daily activities” on your DVD every day, but it seems to have worked!
-Rebekah B.
A doula helps avoid a cesarean
Hi Gail. I was in your workshop in Farmington Hills. I’m a doula from Windsor, Ontario, and I really wanted to let you know that I have a client who is now due in 10 days and her OB was threatening a c-section as the baby was malpositioned [Erin later said the baby was breech]. But after we did the exercises, inversions, and fascial releases, we were able to make room for the baby to move. As of the last ultrasound, the baby is head down, and now mom will be able to have the delivery she wanted. Thank you so much for sharing your techniques.
-Erin M Seguin RMT, Doula
I just found out my baby is breech
I received this email from a woman who found out her baby is breech. You can read my response to her below.
I recently found out my baby is breech. This is a 2nd baby. My first was a very calm baby and was always head down. This one is QUITE active and apparently flipped in the 4 days between my midwife appointment and an ultrasound (they thought my placenta was low… it’s ok).
I exercise 3-5 times a week. I eat well and am in good shape. I am seeing a chiropractor … Initially, saw her for “shifty hips” that would pop out of joint… hasn’t happened since.
My only pregnancy problem (with both) is uterine irritability… I’ve tried cramp bark tea for this but usually the only solution is to sit down. If I don’t nip it in the bud, it progresses to quite strong contractions where I vomit. My uterus is often quite tight for hours on end when I am walking around or at work (I’m a nurse). I was much worse with my son (they kept thinking it was preterm labor but my cervix never opened). Of note, he was a very quick and easy labor/ birth (less than 4 hours)– maybe from all the uterine toning?
Here are my questions:
- The Chiropractor did a Webster Maneuver once; usually she is cracking my back and neck and hips and such. Should she be doing Webster every week? What should I be expecting from her? I’ve never seen a Chiro before. I haven’t seen her yet since the baby flipped.
- How does my uterine irritability play into all this? My midwife said I had very good abdominal tone also. Is this hurting things?
- I’m being more diligent about my posture now and I’ll start some tilts/ inversions (already doing pelvic rocks). I’ll see if my husband can try the Rebozo sifting on me– would a Maya wrap sling work okay for a scarf?
- I plan to have a home/water birth with a CNM. I know she won’t do breech births at home. I’d be willing to give it a go if there was a practitioner. My mom and grandma were both easy birthers and I’m shaped like my grandma who popped 10 kids out on the farm ?
- Any other thoughts/suggestions? Thank you so much for your time. I better go do my pelvic rocks– the baby is dancing around in there!
Gail’s reply:
Your contraction symptoms and the baby’s breech position seem to match the picture of asymmetrical ligaments.
- The Webster Maneuver would help the round ligaments.
- Inversions will help the cervical ligaments first and then help the broad and round ligaments somewhat as well.
- Pelvic adjustment releases any possible pulls on the ligaments supporting the womb from even a slight misalignment of the pelvic joints.
- Get the abdomen ligaments relaxed and then supported. A pregnancy belt may help the looseness that makes it hard for the baby to have a toned slope to settle head down on.
- When a baby is breech, the first action is to relax a twist in the womb using the above methods.
Now see my answers to your five questions below.
Question 1: The Chiropractor may have to adjust the pelvis in three ways
Suggest your chiropractor check:
- The sacrum vertically (SI joints) for a twist at the ala
- The sacrum horizontally for a buckle (wrinkle) that a sacral release will undo
- The pubis symphysis
The Webster Maneuver is a gentle press on the round ligaments in a specific direction to soften the ligament. It takes just a few moments and will soften a cramp, spasm, or even “good tone” to allow the baby to flip past the ligaments into a head-down position. Releasing a kink or tightness in the round ligaments also helps the uterus become more symmetrical, which helps the baby into an ideal starting position for labor.
The Webster can be done repeatedly, weekly, or bi-weekly if in the last month or two. It is one step in helping a breech baby flip. Sometimes it is the only step needed, especially if repeated about 3-4 times. However, occasionally you may need more body work or self-care to flip a breech baby.
Question 2: Pelvic alignment and ligament release will help uterine irritability, especially getting the sacrum “unbuckled”
After a sacral release , you may wear a belt as much as possible to support a loose abdominal wall. There are other ways to help uterine “irritability” as well. Good tone may be too tight for a broad ligament. A tight broad ligament often goes along with an asymmetry in the round ligaments. Releasing it helps the baby turn past it.
Carol Phillips, DC, who taught me about the myofascial world, says that premature contractions are often solved by a sacral release ( standing sacral release ). The moms that I suggested to have this type of bodywork done have found it to work. I also suggest a high protein, whole foods diet with plenty of leafy greens, yellow veggies, Omega 3s, liquids, and salt-to-taste (basically a Brewer Diet and then some).
Question 3: Posture, inversions, and Rebozo
Using the Rest Smart ℠ positions will be helpful, of course, but probably not enough to help the baby flip on his or her own after 32-34 weeks. However, you should have a clear idea of several things you can do yourself, and the body work that will help.
Continue with inversions. I suggest the method of getting upside down shown in the video demonstration on this page .
The Jiggle;, a Belly Hug; or Manteada with a Rebozo helps maintain the balance and releases tension in the abdomen. Traditional Midwives of Mexico, Central America and some South American countries use a Rebozo (a long woven cloth) helps relax the broad ligament if you can relax your belly into it like a hammock and your partner can lift the weight of the baby off your spine without scrunching into it. Start slowly and do short jiggles until your involuntary muscles can relax (about 3 minutes). Repeat daily as possible.
Traditional Russian midwives use a similar cloth in other ways to help balance the body.
Question 4: Finding an attendant for a vaginal breech birth
Your clarity on your ability to birth a breech baby is one of several aspects of safety for breech vaginal birth . An important physical assessment will help determine if a vaginal breech birth might be safe in your situation. Searching out an experienced midwife or physician in breech birth is a challenge, but a necessary one if you decide to have your baby naturally at home or in the hospital.
You will have to ask at midwifery circles, home birth support groups, cesarean prevention groups, and teaching hospitals for referrals. Having an experienced person reduces the risk of breech birth but doesn’t eliminate it altogether.
Question 5: Besides fascial therapy for uterine “irritability,” I suggest the following:
- Drink 3-4 cups of bulk red raspberry leaf tea daily (if you don’t have sensitivities to dried herbs, of course). Use 2 tablespoons in a wire mesh strainer and fill a quart jar with almost boiling water to steep for 5-6 minutes. Remove the herbs and drink hot or cold, and straight or with a splash of apple juice.
- Eat plenty of protein, but watch the peanut butter (it’s hard for a pregnant liver to process).
- Check for a calcium magnesium supplement that is easy to absorb.
- Wear a snug pregnancy belt.
Final thoughts on flipping a breech
The timing of body balance can allow baby to turn or be too late. Some will wait to try these techniques until they are already 34 weeks pregnant and for them, that may be too late. Others do one technique at 40 weeks and it works. How do you know which you will be?
Helping your baby flip head down is mostly a matter of finding what your womb needs for your baby, and listening to what your baby is telling you is needed in order to flip.
I believe you will do what your being feels comfortable doing. If not changing what you are doing is most comfortable to you, that’s ok. If exploring new activities, possibilities and people is comfortable, you will feel more ease in exploring your body and the balance this approach brings.
Think about a moment next year when you are looking back at this time. I hope you feel nurtured, bold, and proud of yourself for trying the things you felt were fine for you and in the amount of effort that was empowering to you.

Contact to Listing Owner
The influence of epidural anesthesia in pregnancies with scheduled vaginal breech delivery at term: a hospital-based retrospective analysis
- Maternal-Fetal Medicine
- Open access
- Published: 20 November 2023
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Roman Allert ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0051-4792 1 ,
- Dörthe Brüggmann 1 ,
- Florian J. Raimann 2 ,
- Nadja Zander 3 ,
- Frank Louwen 1 &
- Lukas Jennewein 1
781 Accesses
2 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Introduction
Epidural anesthesia is a well-established procedure in obstetrics for pain relief in labor and has been well researched as it comes to cephalic presentation. However, in vaginal intended breech delivery less research has addressed the influence of epidural anesthesia. The Greentop guideline on breech delivery states that there’s little evidence and recommends further evaluation.
The aim of this study was to compare maternal and neonatal outcomes in vaginally intended breech deliveries at term with and without an epidural anesthesia.
This study was a retrospective cohort study.
This study included 2122 women at term with a singleton breech pregnancy from 37 + 0 weeks of pregnancy on and a birth weight of at least 2500 g at the obstetric department of University hospital Frankfurt from January 2007 to December 2018.
Neonatal and maternal outcome was analyzed and compared between women receiving “walking” epidural anesthesia and women without an epidural anesthesia.
Fetal morbidity, measured with a modified PREMODA score, showed no significant difference between deliveries with (2.96%) or without (1.79%; p = 0.168) an epidural anesthesia. Cesarean delivery rates were significantly higher in deliveries with an epidural (35 vs. 26.2%, p = 0.0003), but after exclusion of multiparous women, cesarean delivery rates were not significantly different (40.2% cesarean deliveries with an epidural vs. 41.5%, p = 0.717). As compared to no epidurals, epidural anesthesia in vaginal delivery was associated with a significantly higher rate of manual assistance (33.8 versus 52.1%) and a longer duration of birth (223.7 ± 194 versus 516.2 ± 310 min) (both p < 0.0001)".
Epidural anesthesia can be offered as a safe option for pain relief without increasing neonatal or maternal morbidity and mortality. Nevertheless, it is associated with a longer birth duration and manually assisted delivery.
Similar content being viewed by others

Prophylactic tranexamic acid in Cesarean delivery: an updated meta-analysis with a trial sequential analysis
Antenatal perineal massage benefits in reducing perineal trauma and postpartum morbidities: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials

Abortion an Obstetric and Anesthesiologic Emergency: Skills and Simulation
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Regional anesthesia is a well-established procedure in obstetrics for pain relief in labor and is broadly recommended in guidelines [ 1 ]. A Cochrane review including data of 40 trials and over 11.000 women shows a higher chance of instrumental assisted delivery in trials before 2005, an effect that did not occur when trials before 2005 were excluded from the analysis. No difference was shown concerning neonatal outcome or the rate of cesarean delivery [ 2 ].
In deliveries with breech presentation evidence is scarce regarding the safety and effect of epidural anesthesia and recommendations are vague: the British Greentop guideline states that the effect of an epidural anesthesia on the success of vaginal breech birth is unclear and might increase the risk of intervention and recommends further research [ 3 ]. The French clinical practice guideline emphasizes the high level of evidence for epidural anesthesia in cephalic version, with no higher risk of cesarean or risk of vaginally assisted delivery and therefore encourages the use of epidural anesthesia in breech presentation [ 4 ]. The SOGC (Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of Canada) clinical practice guideline on breech delivery recommends avoiding dense epidural to maximize expulsive efforts, while neither ACOG (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists) nor RANZCOG (Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists) addresses the issue of epidural anesthesia [ 5 , 6 , 7 ].
In the term Breech trial epidural anesthesia was not associated with adverse perinatal outcome [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. The PREMODA (PREsentation et MODe d'Accouchement) trial does not report an impact of epidural anesthesia [ 11 ]. Even though safety of epidural anesthesia is established, there still are reports of associated increased adverse neonatal outcome, prolonged labor, or cesarean delivery rate [ 12 , 13 , 14 ].
In the FRABAT (FRAnkfurt Breech At Term Study Group) cohort, the demand for epidural analgesia was high, especially in primiparous women [ 15 ]. Thus, it can be assumed that the patients’ need for an epidural anesthesia during an intended vaginal breech birth is high and clinicians will be confronted with this topic frequently during clinical counseling.
Since every medical intervention with its possible complications should be discussed with patients before administration, it is mandatory to gain evidence in order to be able to give reliable information. The effect of epidural analgesia on vaginally intended birth out of breech presentation has not been elucidated properly because the respective recommendations are adopted from vertex presentations. We present a cohort study on the neonatal and maternal outcome in vaginally intended breech deliveries in light of the use of an epidural anesthesia. We hypothesize that an epidural anesthesia does not influence perinatal morbidity in vaginally intended breech deliveries provided the epidural keeps the motor function and patients are not immobilized.
Study design
We conducted a single center cohort study in all pregnant women at term (≥ 37 weeks of gestation) presenting with a breech presentation at the Goethe University Hospital Frankfurt, Germany, from January 2004 to December 2018. The analysis was performed in a retrospective manner through generating subgroups (deliveries with or without an epidural) within our study cohort.
The university hospital’s ethics committee gave consent (420/11). All data were assessed through the in-house patient data system as well as the Hessen Perinatalerhebung and were acquired after patient’s dismissal from the hospital. All patients received the standard clinical care. Because of the retrospective nature of data acquisition, the ethics committee waived an informed patient’s consent.
Exclusion criteria were fetal birth defect, uterine malformation, multiple pregnancies, contraindication for an epidural anesthesia, estimated birth weight less than 2500 g, and contraindications for vaginal approach.
Other studies with intersection cohorts have been published by different authors of the FRABAT group within previous publications. [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ].
Clinical procedure and counseling
All pregnant women with a breech presentation are counseled between 34 and 36 weeks of gestation. External cephalic version, vaginal attempted birth, as well as cesarean delivery are discussed with each patient, depending on the individual patient history and examination. During vaginal delivery, which is performed predominantly in an upright maternal position, manual assistance to deliver the arms or the fetal head is performed by a trained physician if necessary. A maternal upright position applies when the mother stands or is on all fours (hands and knees). An epidural is offered to every woman by their own choice if no contraindications (e.g., thrombocytopenia) are present. Counseling specifics and details on manual assistance in the upright maternal position have been published [ 17 , 20 ]
Outcome parameters
Primary outcome was perinatal fetal morbidity, which was assessed using the modified PREMODA Score, potentially associated with the delivery mode. The PREMODA Score is adapted from the PREMODA study [ 11 ] implies NICU stay > 4 days, trauma at birth, neurological deficits, intubation > 24 h, or an APGAR score of less than 4 at 5 min [ 9 ]. Secondary outcome measures were duration of labor, rate of cesarean delivery, and rate of assisted vaginal delivery.
Method of epidural anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia was administered by an in-house anesthesiologist. It was initiated with a dose of Ropivacaine and Sufentanil. After the loading dose, a patient controlled pump with Ropivacaine / Sufentanil was connected to maintain persistent pain reduction. Patients were not immobilized and the rate could be reduced if necessary. If analgesia was not sufficient patients could receive up to three additional boli per hour.
Statistical analysis
Groups of variables were tested for normal distribution with Kolmogorov–Smirnov test [ 21 ]. Group differences were analyzed using Pearson’s χ2 testing. Student’s T-test was utilized to compare continuous variables [ 22 , 23 ]. A nominal logistic regression analysis with Wald testing was performed.[ 24 ] We used JMP 14.0 software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) for our analyses. A p-value of below 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Of the 2122 women presenting for counseling with breech presentation at our center, 1413 attempted vaginal delivery.
744/1413 (52.7%) women received an epidural anesthesia (EPI group), 669/1413 (47.3%) did not (NEPI group, Table 1 ). Patients in the NEPI group were significantly older than patients in the EPI group (NEPI 32.7 (± 4.5), EPI 31.9 (± 4.3) p = 0.0009). BMI was equally distributed between both groups (Table 1 ). There were significantly more primiparous women in the EPI group (EPI 523, 70.3%; NEPI 316, 47.2%; p < 0.0001; Table 1 ). Mean birth weight was significantly higher in the EPI group (3388 g; NEPI: 3323 g; p = 0.002; Table 1 ). Duration of pregnancy was significantly longer in the EPI group (280 days) as compared to the NEPI group (278 days, p > 0.0001; Table 1 ).
There were significantly more manually assisted vaginal deliveries when women received an epidural anesthesia: In the NEPI group 327/669 (48.9%) women delivered vaginally, while 167/669 (25.0%) delivered with manual assistance. In the EPI group 232/744 (31.2%) women delivered spontaneous and 252/744 (33.9%) with assistance ( p < 0.0001). Cesarean delivery after onset of labor was performed in 175/669 (26.2%) in the NEPI group which is significantly less often than in the EPI group (260/744 (35.0%), p = 0.0003, Table 1 and Fig. 1 ).
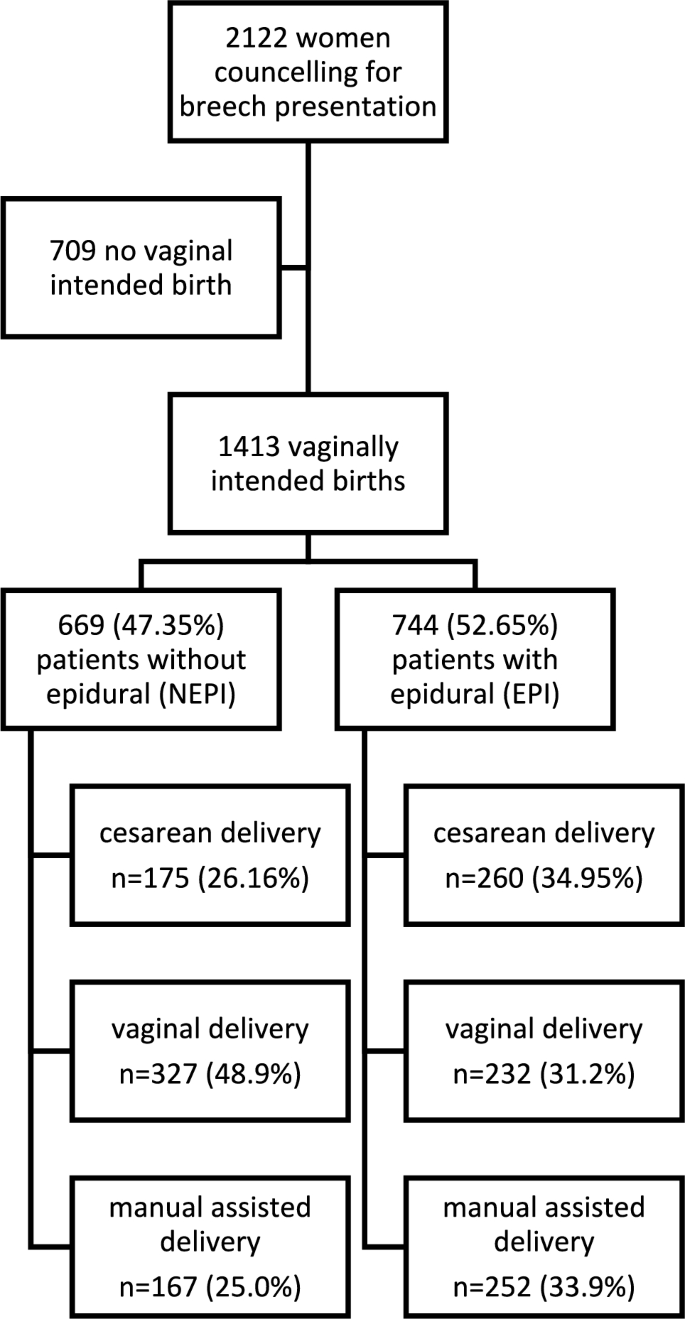
Flow chart of the study cohort
We investigated all vaginal deliveries in a sub-cohort analysis. There were significantly more primiparous women in the group of patients giving vaginal birth with an epidural anesthesia (vEPI group, n = 313, 64.7%) as compared to primiparous women without an epidural anesthesia (vNEPI group, n = 185, 37.5%; p < 0.0001, Table 2 ). Birth weight was not significantly different between vNEPI group (3307 ± 340 g) and vEPI group (3325 ± 391 g; p = 0.361; Table 2 ). Duration of labor was significantly longer in vaginal deliveries with an epidural anesthesia as compared to vaginal deliveries without epidural anesthesia (vEPI 516 ± 310 min; vNEPI 224 ± 194 min; p < 0.0001, Table 2 ). Manual assistance was significantly more often necessary in vaginal deliveries with an epidural anesthesia (vEPI: n = 252, 52.1%; vNEPI: n = 167 33.8%; p < 0.0001, Table 3 ). Fetal morbidity measured with the modified PREMODA score was not significantly different between both groups (vNEPI: 2.02%, vEPI: 3.31%; p = 0.2373; Table 2 ). There was no significant difference in high grade perineal tears between groups (vNEPI: n = 8; 1.6%, vEPI: n = 10; 3.3%, p = 0.642; Table 2 ), but perineal tears of all degrees were significantly more often in vaginal deliveries with an epidural anesthesia (vNEPI: n = 224; 45.3%, vEPI: n = 249; 51.4%, p = 0.0056; Table 2 ).
We investigated a subgroup of primiparous women ( n = 839). In the group of primiparous women with an epidural anesthesia (pEPI) birth weight was significantly higher as compared to deliveries of primiparous women without an epidural anesthesia (pNEPI: 3253 ± 411 g, pEPI: 3379 ± 416 g; p < 0.0001, Table 3 ). Cesarean delivery rate was not significantly different between groups in this sub-analysis (pNEPI: n = 131; 41.5%, pEPI: n = 210; 40.2%; p = 0.7174, Table 3 ). In primiparous women, there was no significant difference in the modified PREMODA score whether patients received an epidural or not (pNEPI: n = 5; 1.58%, pEPI: n = 20 3.82%; p = 0.0917, Table 3 ).
Within a multiple nominal logistic regression analysis, maternal age, birth weight, neonatal morbidity, and cesarean delivery were not significantly associated with an epidural anesthesia (Table 4 ). In contrast, primiparity (OR 2.295; 95% CI: 1.781–2.956; p < 0.0001) and pregnancy duration (OR 1.316; 95% CI: 1.182–1.465; p < 0.0001) were significantly associated with an epidural anesthesia (Table 4 ).
In the subgroup of vaginal deliveries, only duration of birth (OR 1.0055; 95% CI: 1.0044–1.0066; p < 0.0001) and manually assisted delivery (OR 2.23; 95% CI: 1.57–3.52; p < 0.0001) were significantly increased, whereas perineal injuries were not affected (Table 4 ).
Evidence is scarce on the impact of an epidural anesthesia in vaginally intended breech deliveries since all recommendations are based on studies investigating epidural analgesia in cephalic deliveries. We have performed a cohort study on vaginally intended breech deliveries analyzing the effect of epidural anesthesia on perinatal outcome.
Perinatal morbidity was not significantly different between deliveries with and without epidural anesthesia (see Tables 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ). Furthermore, Goffinet et al. [ 11 ] showed that increased short-term morbidity in breech deliveries did not translate into long-term morbidity. Primiparous women were analyzed separately because parity has an impact on delivery outcome measures. In our sub-cohort analyses of primiparous women (Table 3 ) and a nominal logistic regression model (Table 4 ), we were able to confirm the data seen in our whole cohort analyses concerning fetal morbidity. Here, PREMODA scores were consistently not different between deliveries with and without epidural anesthesia.
Patients receiving an epidural anesthesia had a higher probability for cesarean delivery after onset of labor in our main cohort (Table 1 ). But when only primiparous women were analyzed, cesarean delivery rates were not significantly different (Table 3 ). Also, a nominal logistic regression analysis found no association of cesarean delivery rate and epidural anesthesia (Table 4 ). The effect on cesarean delivery rates thus derives from the influence of parity. Primiparous women received an epidural anesthesia in 70.3% of cases, multiparous women only in 29.7% (Table 1 ). This finding contrasts the RCOG guideline; here authors stated that an epidural “might increase the risk of caesarean section” [ 3 ]. In vertex deliveries, a Cochrane analysis reports no effect on cesarean delivery rates linked to the use of epidurals [ 2 ].
New data suggest that not the epidural anesthesia but a prolonged labor and higher need for pain relief itself pose risk factors for an increased cesarean delivery likelihood; underlying problems are the actual cause rather than the analgesia itself [ 25 ].
In vaginal deliveries, the duration of the labor was significantly longer in deliveries with an epidural anesthesia. This effect has also been reported in vertex deliveries [ 26 , 27 ]. In these studies the immobilization though the application of an epidural is supposedly causative for a longer birth duration. In our center, patients are not immobilized after they receive pain relief by an epidural. This is important because women give birth predominantly in an upright position in order to reduce interventions and newborn morbidity [ 20 ]. This is both arguable in vertex and breech presentations. We believe that a “walking” epidural—keeping maternal motor function—is of important benefit for the course of labor: walking and an upright position reduce the duration of labor and the risk of cesarean [ 28 ].
Among the patients who delivered vaginally epidural anesthesia was associated with a higher chance of assisted vaginal delivery (see Tables 1 , 4 ). From vertex deliveries we have learned that operative vaginal deliveries are more often performed in deliveries with an epidural anesthesia [ 26 ].
When a vaginal operative delivery is indicated because of arrest of birth in active labor, women without an epidural anesthesia might prefer a cesarean section, while women with an epidural anesthesia might feel more equipped for a vaginal operative procedure.
In the cohort of women who experienced a successful vaginal breech delivery, maternal morbidity was not significantly increased in patients with an epidural anesthesia; in particular, we did not find a higher rate of third- and fourth-degree perineal tears or tear of all degrees (Tables 2 and 4 ). Our data imply that the use of an epidural for patients with a breech presentation undergoing labor is safe and not associated with a higher morbidity – neither for the fetus nor for the mother.
A strength of our study is a large cohort of patients, treated with a standardized protocol. This leads to homogeneity and comparability within our results.
A major limitation of our study is selection bias as all data derive from a single center. This is a retrospective analysis of an existing study cohort. Thus, only associations and not causative relationships can be concluded from our data. A prospective randomized controlled trial would be the gold standard to investigate a clinical intervention. Nevertheless, randomized controlled trials are hardly possible in women with breech delivery and an intention to deliver vaginally since only a few women would accept to stay without pain relief and to withhold an epidural due to a study design would be unethical.
In our data, only the application of an epidural analgesia was documented. The degree of actual pain relief and the time point of administration during labor were not recorded. Duration of pain relief of an epidural analgesia and patient satisfaction are important issues possibly influencing our outcome measures. In future studies, these items should be assessed in order to improve the quality of our results.
However, while the retrospective analysis has limitations, the absence of an influence on perinatal morbidity in our study adds value to the body of knowledge: our data show that mothers will not impact perinatal morbidity by requesting an epidural during labor, contrasting studies by Macharey or Toijonen. In these studies an epidural has been associated with adverse perinatal outcome in breech deliveries [ 12 , 14 ].
As in vertex presentations, an epidural anesthesia may be offered to ensure pain relief and is a safe gold standard for analgesia during labor. If manual assistance during birth is necessary, a sufficient pain relief might also be beneficial.
Further research in prospective settings would provide a more robust foundation for clinical decision-making and improve the understanding of the impact of epidural anesthesia on breech deliveries.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [RA], upon reasonable request.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics (2019) ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 209: Obstetric Analgesia and Anesthesia. Obstet Gynecol 133(3):e208–e225. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000003132 .
Anim-Somuah M, Smyth RM, Cyna AM, Cuthbert A (2018) Epidural versus non-epidural or no analgesia for pain management in labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5(5):CD000331. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000331.pub4
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Impey LWM et al (2017) Management of breech presentation. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol 124(7):E152–E177
Google Scholar
Parant O, Bayoumeu F (2020) Breech presentation: CNGOF guidelines for clinical practice—labour and induction. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol 48(1):136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gofs.2019.10.022
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
A. C. on O (2006) Practice, ACOG Committee Opinion No. 340. Mode of term singleton breech delivery. Obstet Gynecol 108(1):235–237.
The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Management of breech presentation at term. https://ranzcog.edu.au/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Management-of-breech-presentation.pdf .
Kotaska A, Menticoglou S (2019) No. 384-management of breech presentation at term. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 41(8):1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogc.2018.12.018
Hannah ME, Hannah WJ, Hewson SA, Hodnett ED, Saigal S, Willan AR (2000) Planned caesarean section versus planned vaginal birth for breech presentation at term: a randomised multicentre trial. Term Breech Trial Collaborative Group. Lancet Lond. Engl. 356(9239):1375–1383. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02840-3
Article CAS Google Scholar
Su M et al (2007) Factors associated with maternal morbidity in the term breech trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 29(4):324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1701-2163(16)32442-2
Su M et al (2003) Factors associated with adverse perinatal outcome in the Term Breech trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 189(3):740–745. https://doi.org/10.1067/S0002-9378(03)00822-6
Goffinet F et al (2006) Is planned vaginal delivery for breech presentation at term still an option? Results of an observational prospective survey in France and Belgium. Am J Obstet Gynecol 194(4):1002–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2005.10.817
Macharey G et al (2017) Risk factors associated with adverse perinatal outcome in planned vaginal breech labors at term: a retrospective population-based case-control study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 17(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-017-1278-8
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chadha YC, Mahmood TA, Dick MJ, Smith NC, Campbell DM, Templeton A (1992) Breech delivery and epidural analgesia. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol 99(2):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.1992.tb14462.x
Toijonen A, Heinonen S, Gissler M, Macharey G (2021) Risk factors for adverse outcomes in vaginal preterm breech labor. Arch Gynecol Obstet 303(1):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-020-05731-y
Kielland-Kaisen U et al (2020) Maternal and neonatal outcome after vaginal breech delivery of nulliparous versus multiparous women of singletons at term-A prospective evaluation of the Frankfurt breech at term cohort (FRABAT)“. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 252:583–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.04.029
Jennewein L et al (2018) Maternal and neonatal outcome after vaginal breech delivery at term of children weighing more or less than 3.8 kg: a FRABAT prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 13(8):e0202760. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202760
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jennewein L et al (2019) The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term: a FRABAT prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0225546. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225546
Möllmann CJ et al (2020) Vaginal breech delivery of pregnancy before and after the estimated due date-A prospective cohort study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 252:588–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.03.053
Paul B et al (2020) Maternal and neonatal outcome after vaginal breech delivery at term after cesarean section - a prospective cohort study of the Frankfurt breech at term cohort (FRABAT)“. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 252:594–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.04.030
Louwen F, Daviss B-A, Johnson KC, Reitter A (2017) Does breech delivery in an upright position instead of on the back improve outcomes and avoid cesareans? Int J Gynecol Obstet 136(2):151–161. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12033
Article Google Scholar
Massey FJ (1951) The kolmogorov-smirnov test for goodness of fit. J Am Stat Assoc 46(253):68–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1951.10500769
McHugh ML (2013) The Chi-square test of independence. Biochem Medica 23(2):143–149. https://doi.org/10.11613/BM.2013.018
Mishra P, Singh U, Pandey CM, Mishra P, Pandey G (2019) Application of student’s t-test, analysis of variance, and covariance. Ann Card Anaesth 22(4):407–411. https://doi.org/10.4103/aca.ACA_94_19
Boateng EY, Abaye DA (2019) A review of the logistic regression model with emphasis on medical research. J Data Anal Inf Process. 7:4. https://doi.org/10.4236/jdaip.2019.74012
Hawkins JL et al (2010) Epidural analgesia for labor and delivery. N Engl J Med 362(16):1503–1510
Lucovnik M, Blajic I, Verdenik I, Mirkovic T, Stopar Pintaric T (2018) Impact of epidural analgesia on cesarean and operative vaginal delivery rates classified by the Ten Groups Classification System. Int J Obstet Anesth 34:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijoa.2018.01.003
Shmueli A et al (2018) The impact of epidural analgesia on the duration of the second stage of labor. Birth Berkeley Calif 45(4):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1111/birt.12355
Lawrence A, Lewis L, Hofmeyr GJ, Styles C (2013) Maternal positions and mobility during first stage labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003934.pub4
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors are in great gratitude toward all participants and the whole team staff of the obstetrics department at Frankfurt Goethe University hospital.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital Frankfurt, Goethe University, 60590, Frankfurt, Germany
Roman Allert, Dörthe Brüggmann, Frank Louwen & Lukas Jennewein
Department of Anesthesiology, Intensive Care Medicine and Pain Therapy, University Hospital Frankfurt, Goethe University, 60590, Frankfurt, Germany
Florian J. Raimann
Department of Midwifery Frankfurt, Goethe University, 60590, Frankfurt, Germany
Nadja Zander
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
RA, DB, and FJR contributed to manuscript writing and editing, and data collection. NZ collected data. FL was responsible for protocol/project development. LJ performed protocol/project development, data analysis, and manuscript writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Roman Allert .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Allert, R., Brüggmann, D., Raimann, F.J. et al. The influence of epidural anesthesia in pregnancies with scheduled vaginal breech delivery at term: a hospital-based retrospective analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-023-07244-w
Download citation
Received : 03 April 2023
Accepted : 20 September 2023
Published : 20 November 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-023-07244-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Recommended
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to copy URL
Anna Delvey is using her next court appearance as a ‘fashion presentation’ for her brand
- View Author Archive
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.

Budding fashion publicist Anna Delvey is putting on the first-ever “court-appearance-as-fashion-presentation” later this week, Page Six has learned.
As we first reported, the beloved scam artiste launched a fashion PR consultancy, the OutLaw Agency, with biz legend Kelly Cutrone last year.
Its first event was a buzzed-about Fashion Week show for suiting atelier SHAO New York that the agency staged on the roof of “Fake Heiress” Delvey’s East Village apartment (where she was under house arrest at the time).

Now we’re told that OutLaw’s second event will be an upcoming immigration hearing at a New York courtroom, which will double (whether it likes it or not) as a press preview for new pieces from SHAO New York.
Outlaw announced to Page Six on Wednesday that Delvey — who will be appearing at a hearing about her $10,000 bail bond, whether or not a court-ordered ban on her social media will be lifted, and the terms of her house arrest — will be “wearing a custom SHAO New York black oversized twill suit with a high-waisted pencil skirt and a high slit paired with a white cotton button-down shirt with built-in shoulder pads and a silk velvet pussy bow tie” for the court date. Sketches for the look even include her now-trademark ankle monitor.

With designers facing ever-more difficulty getting attention for their wares, it seems that the OutLaw team figured they may as well harness the attention from her court appearance to get press for their client (which is, after all, the job of a fashion PR consultant).
During her 2019 trial for screwing hotels, banks, other businesses and individuals out of tens of thousands of dollars by posing as a German artistocrat, Delvey’s courtroom fashion made almost as many headlines as her crimes. Delvey — whose real name is Anna Sorokin — used a stylist for her court appearances and even refused to attend her own hearing on one occasion after designer duds failed to arrive at her cell in time for her to appear in appropriately chic attire.
We’re told Delvey and designer Shao Yang put together this week’s bold look as a comment on the expectation that defendants should wear demure outfits in front of judges.

“Why are we as women being asked to dress a certain way when we enter a courtroom, or a boardroom, or a dinner party? Why are others trying to control our level of innocence based on what we wear?,” OutLaw Agency co-founder Cutrone told us, “This is discrimination in its most subtle and intriguing form and we’re here to change it up. We have respect for the legal system and they should have respect for the fashion system.”
Delvey was convicted on attempted grand larceny, larceny in the second degree, and theft of services, and was sentenced to 4 to 12 years in prison .
She served two years and was remanded into the custody of ICE in 2022. She’s since been fighting to stay in the US rather than face deportation to Germany.
Share this article:

Advertisement
- CBSSports.com
- Fanatics Sportsbook
- CBS Sports Home
- Champions League
- Motor Sports
- High School
Football Pick'em
College Pick'em
Fantasy baseball, fantasy football, fantasy basketball, fantasy hockey, franchise games, 24/7 sports news network.
- CBS Sports Golazo Network
- PGA Championship
- UEFA Champions League
- UEFA Europa League
- Italian Serie A
- Watch CBS Sports Network
- TV Shows & Listings
The Early Edge
A Daily SportsLine Betting Podcast
With the First Pick
NFL Draft recap
- Podcasts Home
- The First Cut Golf
- Beyond the Arc
- We Need to Talk Now
- Eye On College Basketball
- NFL Pick Six
- Cover 3 College Football
- Fantasy Football Today
- My Teams Organize / See All Teams Help Account Settings Log Out
NFL schedule 2024: Full list of how many miles each team will travel and time zones they will cross
A look at the nfl travel data for the 2024 season.
All 32 NFL teams will have to travel at least eight times during the 2024 regular season, but some will travel more and much farther. Teams will have to travel cross country, while some will go off to Germany and England. Have you ever wondered how many miles each NFL team travels, and how many time zones they cross through? Well, that info has been put together for the upcoming season and released prior to the official NFL schedule release.
According to Bookies.com , the Los Angeles Chargers will travel the most miles of any team this season -- a whopping 26,803 miles. The Chargers will also travel through the most time zones: 36. As for the team that will travel the least amount of miles in 2024, that honor belongs to Dan Quinn's Washington Commanders .
The mileage for this list was calculated by using the linear air distance between each stadium on Google Earth. Check out the full list below:
Our Latest NFL Stories
Dak Prescott to connect with fan whose life he changed
Garrett podell • 3 min read.
Report: Steelers' Heyward to skip OTA's over contract
Bryan deardo • 1 min read.
Chiefs offensive linemen arrested
Jared dubin • 1 min read.
Jake Ferguson: 'I'm not even scratching surface'
Butker jersey sales top Chiefs after polarizing speech
Austin nivison • 2 min read.
WATCH: Former Pro Bowl QB plays in HS scrimmage
Bryan deardo • 2 min read, share video.

Full list of total miles each team will travel in 2024

Chiefs' bizarre scheduling quirk, other 2024 oddities

The good, bad of each team's 2024 schedule

2024 season: Week-by-week schedule

Top revenge games on 2024 schedule

NFL executive breaks down season schedule

Tua not present at Dolphins activities as QB eyes deal

Hockenson: No timeline yet on return from knee surgery

Taylor Swift tour dates forced NFL to adapt schedule

NFL exec: Brady can call any game on the schedule

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A breech baby (breech birth or breech presentation) ... If a baby is still breech at 37 weeks of pregnancy, your options for delivery may change. This is because there are risks to a vaginal delivery when a baby is breech. In many cases, a C-section is the best and safest option for birth.
Turning foetal breech presentation at 32-35 weeks of gestational age by acupuncture and moxibustion. ... New and old predictive factors for breech presentation: our experience in 14433 singleton pregnancies and a literature review. ... 20. weeks pregnant. 21. weeks pregnant. 22. weeks pregnant. 23. weeks pregnant. 24. weeks pregnant. 25.
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
The main types of breech presentation are: Frank breech - Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term. Complete breech - Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord. For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. ... At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include:
Epidemiology. Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech. Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10% ...
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation.A breech presentation occurs when the fetus's buttocks, feet, or both are in place to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
If you've had a previous breech baby, you run a somewhat higher chance of subsequent babies turning out breech as well. Premature birth. The earlier your baby is born, the higher the chance she'll be breech: About 25 percent of babies are breech at 28 weeks, but only 3 percent or so are breech at term. You or your partner were breech.
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
For starters, there's some evidence linking a breech presentation—and its tendency to reduce the amount of space in the womb—with hip dysplasia, ... Earlier on in your pregnancy, when they're smaller and have more room in the womb, they may flip all around; roughly 20 percent of babies are breech at 28 weeks, says Samuel. If you ...
Learn more about the types, causes, and risks of breech presentation, along with how breech babies are typically delivered. ... These are usually scheduled between 38 and 39 weeks of pregnancy ...
At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
During the month before 30 weeks, about 15% of babies are breech. Since breech baby's spine is vertical, the womb is "stretched" upwards. We expect babies to turn head down by 28-32 weeks. Breech may not be an issue until 32-34 weeks. If you know your womb has an unusual limitation in shape or size, such as a bicornate uterus then begin ...
Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. ... T +44 20 7772 6200; Support our work around the world by making a donation Donate now. Registered charity ...
Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies. Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, most babies turn naturally into the head-first position. Towards the end of pregnancy, only 3-4 in every 100 (3-4%) babies are in the breech ...
The incidence of breech presentation is approximately 20% at 28 weeks gestation, 16% at 32 weeks gestation and 3-4% at term. Therefore, breech presentation is more common in preterm labour . Most fetuses with breech presentation in the early third trimester will turn spontaneously and be cephalic at term.
Breech at 20 weeks. I had my 20 week anatomy scan a few days ago and baby boy is perfectly healthy, praise God. My only concern was that he is breech. I know there is plenty of time for him to turn, and the tech wasn't concerned, but both my other 2 kiddos were already head down at this point.
Throughout your pregnancy, your baby will be moving around and flip-flopping in your uterus. But by 36 weeks, most babies' heads are pointing down toward the birth canal and, without much room at this point, stay there until it's time for labour.However, about four percent of babies will end up in the breech position, where their heads are up and their bums are pointed toward the birth canal.
Turning a breech baby. If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you'll usually be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a healthcare professional, such as an obstetrician, tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by applying pressure on your abdomen. It's a safe procedure, although it can be a bit uncomfortable.
By 30-31 weeks, I highly recommend beginning the Forward-leaning Inversion position to encourage a head-down position. From 30 weeks on you can start the 6-day plan in our Helping Your Breech Baby Turn ebook. After 32-34 weeks, chiropractic adjustments are suggested. 34-35 weeks is the most successful time to use Moxibustion.
Introduction Epidural anesthesia is a well-established procedure in obstetrics for pain relief in labor and has been well researched as it comes to cephalic presentation. However, in vaginal intended breech delivery less research has addressed the influence of epidural anesthesia. The Greentop guideline on breech delivery states that there's little evidence and recommends further evaluation ...
2024 Wells Fargo Championship purse, prize money: Payout for winner Rory McIlroy, field from $20 million pool Plenty of green was on the line this week at The Green Mile, and McIlroy brought home ...
Published May 15, 2024, 6:34 p.m. ET. Anna Delvey's own PR consultancy, the OutLaw Agency, is using her upcoming court appearance as a fashion presentation for its client, SHAO New York. She ...
All 32 NFL teams will have to travel at least eight times during the 2024 regular season, but some will travel more and much farther. Teams will have to travel cross country, while some will go ...
Prior to GPT-4o, you could use Voice Mode to talk to ChatGPT with latencies of 2.8 seconds (GPT-3.5) and 5.4 seconds (GPT-4) on average. To achieve this, Voice Mode is a pipeline of three separate models: one simple model transcribes audio to text, GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 takes in text and outputs text, and a third simple model converts that text back to audio.