

Top 12 Potential PhD Viva Questions and How to Answer Them
Breathed a sigh of relief after submitting the PhD thesis you’ve burnt the midnight oil for? Not so soon! While submitting your thesis is a massive achievement, defending it decides whether you will receive the doctoral degree or not. Although every PhD viva examination is different, there are similarities in the types of questions asked at each. In this article, we shall discuss the most common and potential PhD viva questions and how to answer them.
Types of PhD Viva Questions
Generally, examiners prepare a series of questions for you to answer at the PhD viva voce examination. These questions are primarily based on your thesis. However, the questions asked in PhD viva examinations can be broadly grouped under four basic headings:
- General Questions
- Research Context and Methods
- Analysis and Findings
- Discussions and Conclusion/Implications
Therefore, while preparing for your PhD viva and defending your thesis , you must consider the types of questions you’re likely to be asked. This helps in practicing your answers in advance and not being baffled during the viva. Practicing how you would answer questions based on these four basic categories will take you a long way in your preparations.
Commonly Asked PhD Viva Questions and How to Answer Them
While sticking to answering the most commonly asked questions might sound simple, it is equally important to be prepared for counter questions. Furthermore, it’s easy to go off on a tangent due to nervousness. This leads to opening up other lines of enquiry from the examiners in areas you hadn’t probably expected to be questioned about.
Ideally, you aren’t expected to dictate your thesis as it is. Examiners are interested in knowing your understanding of the research, its methods, analysis and findings, conclusion and implications, etc.
Despite the differences in every PhD viva, you must be prepared to answer these common questions logically. Below are some popular PhD viva questions to prepare:
1. Tell me about yourself.
Introduce yourself and talk about your areas of interest related to research. More importantly, focus on the areas you are extremely positive about. Briefly speak about your past achievements without overwhelming the examiners and sounding boastful. Keep the introduction professional.
2. What is the reason for selecting this research question?
The response to this question is often generalized by saying that you are interested in the topic. However, examiners want to hear the specifications of your interest in the topic. You must plan your answer stating the most interesting aspect of your research and why did you choose the research question over another topic from the same or allied domain. Furthermore, cite certain instances that helped you in selecting the research topic and the particular field for your project.
3. What is the key focus of your research?
Remember that the answer to this question is not about summarizing your research. It involves talking about the area of primary focus of research. Most importantly, in order to demonstrate the viability of your research, it is essential to identify some of the key questions it addresses.
4. Did the research process go as per your plan or were there any unexpected circumstances that you had to deal with?
The purpose of this question is not only to see whether you can work as per your structured plan, but also to understand your readiness with backup plans in case of unforeseen situations. An ideal way to answer this is by clearly stating if the project went as per your predefined plan. Furthermore, be honest in mentioning if you were assisted by others in dealing with it, as it may lead to a new set of questioning from the examiners.
5. After completion of your research, which part of the process did you enjoy the most and why?
Remember that the examiners know about a PhD student’s stressful journey . Therefore, do not elaborate on the hardships that you went through during your research, unless asked otherwise. Emphasize on the aspects of the research project that you enjoyed and looked forward to every time you stepped in your laboratory. Describe how you developed interest in newer approaches to conduct research.
6. As a researcher, what change has this research brought in you?
This question demands a strong, progressive, and positive response. Remember your first day in the research laboratory and compare it to today. Identify the differences in your traits as a researcher. Mention how following, reading, and analyzing other researchers’ works have brought a positive change in you. Furthermore, address how you overcame your shortcomings as a researcher and upskilled yourself.
7. Summarize your thesis.
Be well versed with the entire project. Start by explaining why you selected the topic of your thesis and close your explanation by providing an optimum solution to the problem. You must prepare for 3 types of answers for this question. Prepare a 1-minute, 3-5 minutes, and 10-minute summary and use the correct one based on your audience at the viva.
8. What developments have you witnessed in this field since you began your doctorate? How did these developments change your research context?
Familiarize yourself with the advances in your field throughout your PhD. Mention works of researchers you have referred to while working on your project. Additionally, elaborate on how other researchers’ work influenced your research and directed you to finding results.
9. What original contribution has your thesis made to this field of study?
Answer this question by keeping in mind what was known before in published literature and what you have added as part of being awarded your PhD. Firstly, you must present a major piece of new information during your research project. Secondly, elaborate on how your research expands the existing literature. Thirdly, mention how your work is different from other researchers’ works that you referred. Finally, discuss how you developed a new product or improved an existing one.
10. How well did the study design work?
While answering this question, you must focus on how your planned methods and methodologies were executed. Furthermore, mention how you tackled difficulties in study design and concluded your research.
11. Elaborate on your main findings and how do they relate to literature in your field?
While answering this question, elaborate on how you evaluated the key findings in your research. Mention the key factors involved and the reason for choosing a particular process of evaluation. Furthermore, explain how your findings are related with the literature review of your project. Mention its significant contributions in your field of research. In addition, discuss how your research findings connect with your hypothesis as well as the conclusion of your research.
12. What is the strength and weakness of your research?
While you may want to impress the examiner by emphasizing on the strengths of your research, being aware of the weaknesses and planning a directional move to overcome them is also equally important. Hence, mention the strengths first and elaborate on how they connect with the key findings. Additionally, underline the limitations and the factors that could be transformed into strengths in future research.
How nervous were you while preparing for your PhD viva voce? Did you follow any specific tips to ace your PhD viva voce ? How important is it to prepare for these common PhD viva questions beforehand? Let us know how you prepared for your PhD viva voce in the comments section below! You can also visit our Q&A forum for frequently asked questions related to different aspects of research writing and publishing answered by our team that comprises subject-matter experts, eminent researchers, and publication experts.
Really useful in helping me put a plan / script together for my forthcoming viva. Some interesting questions that I hadn’t thought about before reading this article – the proof of the pudding will be how well the viva goes of course, but at least I now have a head start! Many thanks
Thank you, this is super helpful. I have my viva voce in a month and I’ll be using these questions as a guide
Well framed questions
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Addressing Barriers in Academia: Navigating unconscious biases in the Ph.D. journey
In the journey of academia, a Ph.D. marks a transitional phase, like that of a…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…
Intersectionality in Academia: Dealing with diverse perspectives
Meritocracy and Diversity in Science: Increasing inclusivity in STEM education
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

Top 18 PhD Viva Questions | Examples
The PhD viva is an oral assessment held by a committee during the PhD defense. This evaluation involves the committee posing inquiries to the PhD candidate regarding their research work and dissertation.
The candidate must showcase their expertise in the field and how it relates to their project’s focus. The primary aim of the PhD viva is to ascertain if the candidate has fulfilled the criteria for obtaining their degree.
This article explores the PhD viva questions, provides 18 sample questions, and offers advice on responding to them effectively.
- Table of Contents
A PhD viva, also known as a viva voce, is the concluding assessment where a candidate addresses inquiries posed by an academic committee regarding their completed work and understanding of their chosen field.
It serves to evaluate whether the candidate has effectively shown their comprehension of their specific research domain to produce original contributions.
The questions asked during a PhD viva typically come from the candidate’s original work proposal and other submitted written materials.
Types of PhD Viva Questions
Examiners typically prepare a set of questions for candidates to address during the PhD viva voce exam. These questions primarily center around the candidate’s thesis.
However, the questions asked in PhD viva exams can generally be categorized into four main areas:
- General Questions
- Research Context and Methods
- Analysis and Findings
- Discussions and Conclusion/Implications
Therefore, as you prepare for your PhD viva and defend your thesis, it’s crucial to consider the types of questions you might encounter.
This preparation allows you to practice your responses beforehand, ensuring you are not caught off guard during the viva.
Preparing and practicing your responses to questions from these four fundamental categories will significantly help in your preparation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions for PhD Vivas and How to Answer to Them
While focusing on addressing frequently asked questions may seem straightforward, it’s crucial to prepare for potential follow-up questions. Nervousness can sometimes cause digressions, leading to unexpected inquiries from examiners in areas that may not have been anticipated.
The expectation isn’t for you to simply repeat your thesis. Examiners want to assess your understanding of the research, including its methods, analysis, findings, conclusions, implications, and other relevant aspects.
You should be ready to answer these common questions logically, despite the differences in each PhD viva.
Here are some popular PhD viva questions to prepare for:
1. Tell me about yourself
Introduce yourself by discussing your research interests, emphasizing the areas that you feel strongly positive about. Mention your past accomplishments briefly and professionally, avoiding any tone of boasting or overwhelming the examiners.
I’m someone who’s deeply passionate about research, particularly in areas where I can make a meaningful impact. My main areas of interest revolve around [specific fields or topics], where I believe there’s immense potential for innovation and discovery. I approach research with a positive mindset, always looking for new insights and solutions to complex problems.
Throughout my academic journey, I’ve had the privilege of contributing to various research projects that have broadened my perspectives and honed my skills. These experiences have taught me the value of collaboration, critical thinking, and perseverance in the research process.
I’m particularly proud of [mention specific achievement or accomplishment], as it demonstrates my ability to navigate challenges and deliver results in a methodical and efficient manner. However, I also recognize that there’s always room for growth and learning in research, and I’m excited about the opportunities ahead to further contribute to the field.
Overall, I approach research with professionalism, enthusiasm, and a commitment to excellence, and I’m eager to continue exploring new avenues of inquiry and making meaningful contributions to the academic community.
2. Why did you choose this research question?
Examiners are interested in hearing specific details about why you are interested in a research topic, including the most captivating aspect, why you chose this research question over others in the same or related field, and any instances that influenced your selection of the research topic and field. It’s essential to plan your answer with these details in mind to provide a comprehensive response.
I chose this research question because it’s really important and can make a big difference in dealing with [specific issue or gap] in [field or discipline]. After looking at different research options, I found this question to be very interesting because it could add a lot to what we already know and help solve real problems. Also, it fits well with what I’ve studied before and what I’m interested in, so I can use my skills and knowledge to explore and solve problems in this area.
3. How did you come up with the idea for this research?
In explaining how you developed your research idea, demonstrate to the viva panel that you thoroughly evaluated all potential research options before choosing the one that optimized your time and resources. Provide specifics about your decision-making process, including why certain ideas were rejected in favor of others and the insights gained from exploring each possibility. This showcases your ability to narrow down options based on factors like feasibility.
I came up with the idea for this research through [specific process or inspiration, such as literature review, personal experience, academic discussions, etc.]. This process involved evaluating various research areas and identifying gaps or opportunities that led to the formulation of the research’s idea.
4. What is your research’s main area of focus?
Keep in mind that your response should not summarize your research but instead discuss the primary focus area of your research. Crucially, to showcase the viability of your research, it’s important to highlight some of the key questions it tackles.
The primary focus area of my research revolves around [specific topic or field], addressing key questions related to [core concepts or issues] within this domain.
5. What methods will you use to evaluate the effectiveness of your research?
To showcase to the viva panel that you have effectively evaluated your research’s effectiveness, contemplate utilizing both qualitative and quantitative measures. Qualitative measures encompass surveys and various data collection techniques that enable you to delve into the fundamental causes of issues, making them suitable for understanding people’s perceptions and sentiments regarding a subject. Quantitative measures involve numerical comparisons across different time frames or locations, such as sales data, providing a comprehensive perspective on performance trends over time. Utilizing these approaches demonstrates to the panel your thorough assessment of the research’s impact.
I will use [specific methods, such as surveys, experiments, interviews, data analysis, etc.] to evaluate the effectiveness of my research. These methods are chosen based on their ability to gather relevant data, analyze findings, and draw meaningful conclusions that address the research objectives and hypotheses.
6. Did the research process proceed as planned, or did you encounter any unexpected circumstances?
The purpose of the question about project execution in a PhD viva is to assess readiness with backup plans for unforeseen situations and to evaluate if the project adhered to the structured plan. It’s important to mention if assistance was received and be prepared for follow-up questions from examiners.
My research mostly went as planned, following the timeline and methods outlined in the proposal. Yet, there were times when unexpected things happened. I had to adjust and use backup plans to deal with these situations quickly, so they didn’t disrupt my research much.
7. What is the future of your research?
When addressing the future of your research area in your viva, it’s crucial to go beyond the current state and consider upcoming developments. Simply focusing on the present might suggest a limited understanding. Instead, provide a comprehensive response by discussing your vision for the research area’s future, its connection to the present, and its significance.
The future of my research involves exploring emerging trends and advancements in [specific area or field], leveraging new technologies and methodologies to address complex challenges. I plan to collaborate with experts in related disciplines, conduct further experiments or surveys, and analyze additional datasets to deepen our understanding of [research topic]. Ultimately, I aim to contribute novel insights and practical solutions that can benefit [target audience or community] and advance the overall knowledge in this field.
8. What are some limitations of your thesis?
If you’re asked about the limitations of your thesis during your PhD viva, ensure your response is clear and concise. To prepare, consider aspects that might be perceived as limitations and address these questions:
- Why is this considered a limitation?
- How could it be improved or made more effective?
- What changes could be made to the research design or data collection methods to address this?
- Are there potential solutions or enhancements that could mitigate this issue?
Some limitations of my thesis include [specific limitations, such as sample size constraints, data availability, potential biases, etc.]. These limitations are considered because [explain why each limitation is relevant]. To improve these limitations, potential strategies could include [suggestions for improvement, such as expanding the sample size, using additional data sources, addressing biases through robust methodologies, etc.]. These enhancements aim to strengthen the overall validity and reliability of the research findings.
9. Is this work original, or have others done something similar before?
When addressing whether your work is original or if others have conducted similar research before, it’s important to distinguish between your original contributions and existing research. You can then elaborate on how you’ve built upon previous work to develop your own ideas. If there are no entirely original aspects, consider discussing aspects of your research that are not yet published but have potential for further development. This approach can provide the panel with insights into the new ideas emerging from your research.
This work is original in [specific aspects or contributions], as it builds upon existing literature and presents novel findings or approaches. While others may have explored related topics or methodologies, the unique combination of [key elements or innovations] distinguishes this research from previous efforts.
10. What benefit does this research provide to society?
When discussing the benefit of your research to society, emphasize your clear and defined goal. Articulate how your research can impact society at large and how it can be utilized or adapted by other researchers working on similar issues.
When discussing the benefit of my research to society, I emphasize a clear and defined goal. My research aims to [specific goal or objective, such as improving healthcare outcomes, addressing environmental challenges, enhancing technological advancements, etc.]. This benefit is significant as it can [describe how the research can positively impact society at large, such as improving quality of life, advancing knowledge, solving practical problems, etc.]. Additionally, my research findings can be utilized or adapted by other researchers working on similar issues, further amplifying its societal impact and relevance.
11. What are the limitations of your research design?
When discussing limitations in your research design during your viva, acknowledge that every design has its constraints. Be transparent about these limitations and explain how you mitigated or addressed them in your study. If your design was particularly good, highlight how it contributed to your results. Conversely, if aspects of your study didn’t go as planned, use this as evidence to analyze potential flaws in your hypothesis.
Some limitations of my research design include [specific limitations, such as sample size constraints, data collection methods, potential biases, etc.]. While these limitations are inherent in any research design, I took several steps to mitigate their impact. For example, I [explain strategies used to address limitations, such as ensuring diverse sample representation, using validated measurement tools, implementing data analysis techniques, etc.]. These efforts aimed to enhance the validity and reliability of my study findings despite the identified limitations.
12. How might your research have been impacted if there were more data available on your topic?
To answer this question, start off by conveying to the panel any limitations found within your research. This is because it allows you to discuss whether additional research would have either prevented or minimised this outcome. For example, you might decide to tell the panel that additional data relevant to the research topic may have been beneficial because then you could test the hypothesis again by running the same tests in other communities. Then you could see if the result was the same with a different audience. Though, this may have resulted in a changed hypothesis.
If more data were available on my research topic, it would have significantly impacted the depth of my study. Firstly, a larger dataset would have allowed for more comprehensive analyses, such as subgroup analyses and advanced statistical modeling techniques. This could have led to more robust findings and a better understanding of the nuances within the data.
Additionally, with more data points, I could have explored additional variables or factors that may influence the outcomes studied in my research. This could have provided a more holistic view of the topic and allowed for a more nuanced interpretation of the results.
Furthermore, more data availability would have increased the statistical power of my study, potentially leading to more reliable and conclusive results. It would have also allowed for a more extensive validation of findings through cross-validation exercises and sensitivity analyses.
Overall, the availability of more data would have enhanced the quality, reliability, and generalizability of my research outcomes, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
13. Has your research challenged or changed how we think about the topic?
To address this question effectively, begin by outlining any constraints identified within your research. This approach enables a discussion on whether further research could have mitigated or avoided these limitations.
For instance, you could mention that having more relevant data on the research topic could have been advantageous. This additional data might have allowed you to retest the hypothesis across diverse communities, potentially leading to variations in results. However, it’s important to note that this could have also led to modifications in the hypothesis itself.
My research has challenged existing perceptions by uncovering previously unexplored facets of the topic. Specifically, I focused on [mention specific concept or theory] and conducted [briefly describe your study]. The results revealed [key findings or insights], which have prompted a reevaluation of [mention the paradigm or conventional understanding]. This shift in perspective has significant implications for [explain the broader impact on the field or applications of the research]. Overall, my research has contributed to a nuanced understanding of the topic and has initiated discussions on revising established frameworks in the academic discourse.
14. Do you think other researchers could replicate the results of your study?
The viva panel considers if other researchers can duplicate your findings to determine the credibility of your research within the field. To address this, consider the distinctiveness of your study compared to previous ones. If you identify unique aspects, explain how they facilitate easier replication by other researchers.
Yes, I believe other researchers would be able to replicate my results. The methodology used in my study is well-documented and follows established protocols, ensuring clarity and consistency in data collection and analysis. Additionally, the unique aspects of my research are clearly outlined, making it easier for others to understand and replicate key elements. Sharing relevant data and resources further enhances the feasibility of replication and promotes transparency in the research process.
15. Could there be other explanations for the results of your research?
This question is a method for the viva examiners to assess your ability to critically evaluate your own research. Begin by conducting a thorough review of the existing literature to identify any alternative explanations for your research findings. If such alternative explanations exist, explain them in detail. On the other hand, if there are no alternative explanations or they are not relevant to your findings, clarify why this is the case. It’s crucial to demonstrate consideration for these alternative perspectives as they contribute to the overall understanding of why your findings are significant.
In my research, I thoroughly examined the existing literature to explore potential alternative explanations for the findings. While there were some theories suggesting alternative interpretations, such as [mention specific theories], further analysis and empirical evidence indicated that these explanations were not as substantiated or relevant to my study’s context.
For instance, [provide an example or detail about why alternative explanations were not applicable]. This analysis supports the robustness and specificity of my findings, as they align with established theories and empirical evidence within the field.
Overall, my research process involved a critical evaluation of potential alternative explanations, ensuring that the conclusions drawn are well-supported and contribute meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge on the topic.
16. Given your research findings, what would be an appropriate course of action for another researcher to pursue in this field?
Consider the type of research you’re conducting as you address this question. Review your completed research and its conclusions to assess their alignment with the hypothesis. Identify any gaps in your research, explain their presence and significance, and discuss what they indicate. Utilize these gaps as a basis for further investigation, outlining your next steps as a student exploring these areas of study.
Based on the findings of my research, a suitable next step for other researchers in this area would be to conduct further investigations into [specific aspect or aspect]. This could involve [suggest a research direction or methodology], which would help to [describe the potential contribution or impact]. Additionally, exploring [related topic or factor] could provide valuable insights into [describe potential outcomes or implications]. Overall, building upon this research could lead to a deeper understanding of [topic or field], benefiting both academia and practical applications.
17. Summarize your thesis.
Familiarize yourself with the entire project, beginning with the rationale behind selecting your thesis topic and concluding with an optimal solution to the problem. Prepare for three types of responses: a 1-minute, 3-5 minutes, and 10-minute summary. Tailor your answer based on the audience’s expectations at the viva.
For the 1-minute summary:
“I chose the topic of my thesis because it addresses a critical gap in the literature and has significant relevance in [specific field]. The problem at hand is [briefly describe the problem]. Through extensive research, I identified key areas for investigation, including [mention key areas]. The optimum solution to this problem involves [briefly outline the solution or approach].”
For the 3-5 minutes summary:
“My thesis topic was carefully selected due to its relevance in [specific field]. The problem I aimed to address is [provide a brief overview of the problem]. This topic intrigued me because [explain why it interested you]. Through thorough research and analysis, I identified several key areas that required exploration, including [list key areas]. The optimal solution to this problem involves [describe the solution or approach in more detail, including any methodologies used].”
For the 10-minute summary:
“The topic of my thesis was chosen based on its critical importance in [specific field]. The problem I sought to tackle is [provide a comprehensive overview of the problem, including its significance]. I was drawn to this topic because [explain your personal interest or motivation]. To address this problem effectively, I conducted extensive literature reviews, data collection, and analysis, focusing on key areas such as [list key areas]. The optimal solution I propose involves [describe the solution or approach in detail, including any innovative methodologies or findings]. This solution not only addresses the immediate problem but also has broader implications for [mention broader implications or potential applications].”
18. What are the research’s strengths and weaknesses?
When discussing your research during a viva examination, it’s important to highlight both its strengths and weaknesses. Begin by emphasizing the strengths and how they connect with key findings, showcasing the robustness of your research. Then, address the limitations and discuss potential strategies to transform them into strengths in future research endeavors. This approach demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of your research and your ability to critically evaluate and improve upon its weaknesses.
The strength of my research lies in its comprehensive analysis of [specific aspect], which has led to significant insights into [key findings or contributions]. This strength is further bolstered by [mention additional strengths, such as methodology, data collection, etc.].
On the other hand, a potential weakness of my research is [identify a weakness, such as sample size limitations, data availability, etc.]. However, this limitation has provided opportunities for future research to explore [potential areas of improvement or expansion].
Overall, the strength of my research lies in its [highlight key strengths], while the weakness serves as a stepping stone for further advancements in the field.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more.
- PLS-SEM model
- Principal Components Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis
- Friedman Test
- Chi-Square Test (Χ²)
- Effect Size
- Critical Values in Statistics
- Statistical Analysis
- Calculate the Sample Size for Randomized Controlled Trials
- Covariate in Statistics
- Avoid Common Mistakes in Statistics
- Standard Deviation
- Derivatives & Formulas
- Build a PLS-SEM model using AMOS
- Principal Components Analysis using SPSS
- Statistical Tools
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- One-tailed and Two-tailed Test
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Citation Styles
- APA Reference Page
- MLA Citations
- Chicago Style Format
- “et al.” in APA, MLA, and Chicago Style
- Do All References in a Reference List Need to Be Cited in Text?
Comparision
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable – MIM Learnovate
- Research Article and Research Paper
- Proposition and Hypothesis
- Principal Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares
- Academic Research vs Industry Research
- Clinical Research vs Lab Research
- Research Lab and Hospital Lab
- Thesis Statement and Research Question
- Quantitative Researchers vs. Quantitative Traders
- Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
- Survey Vs Experiment
- Hypothesis and Theory
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- APA vs. MLA
- Ghost Authorship vs. Gift Authorship
- Basic and Applied Research
- Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
- Survey vs Questionnaire
- Open Ended vs Closed Ended Questions
- Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
- Inductive vs Deductive Approach
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Reliability vs Validity
- Population vs Sample
- Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Framework
- Bibliography and Reference
- Stratified vs Cluster Sampling
- Sampling Error vs Sampling Bias
- Internal Validity vs External Validity
- Full-Scale, Laboratory-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Research Methodology Vs. Research Method
- Mediator and Moderator
- Dissertation Topic
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto

Misbah Rashid, an expert in Technology Management, holds an MBA and an MS in Information Systems and Technology Management. She has experience teaching marketing and technology in business at the university level.
Related Posts
How to use meta ai for phd research, tips to prepare phd viva-voce presentation slides, who is a good peer reviewer, mastering the art of academic writing: strategies for ph.d. researchers, how to become a postdoctoral researcher, top 10 fellowships to support phd studies in usa, how long does it take for phd in usa | structure, 20 tips for completing your phd in 36 months, resources for phd literature review, top 10 highest paying phd degrees in 2023.
Comments are closed.

The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
Common PhD Viva Questions

It can be pretty difficult knowing how to prepare for your PhD viva. Having successfully defended my own STEM PhD remotely in the last year, I want to help you to prepare! What follows are some common PhD viva questions which your examiners may ask you. Plus some additional advice based off my own PhD viva experience.
For an intro to the PhD viva including the typical structure and potential outcomes please see my introductory post:
- How to Defend a Thesis: An Introduction to the PhD Viva
How Much Do You Need to Prepare For A PhD Viva?
There is no hard and fast rule for how much you need to prepare. And unlike a written exam, there are of course no past-papers to practice on!
It may help ease your mind to think about what the purpose of a PhD viva is. Namely the purpose of the PhD viva (or defence) is to check that:
- You did the work;
- You understand the work;
- The research is up to the standard for a PhD.
For more detail see my separate post here including Imperial’s PhD viva mark scheme.
In hindsight I probably didn’t spend as much time preparing for my viva as is normal. Though I did unexpectedly move house less than a week before !
Besides reading through my thesis once in the few days leading up to it, I didn’t spend much time thinking up answers to questions or “revising” certain topics which could come up. The viva went fine, but it wouldn’t have done me any harm to have been a little better prepared.
It certainly helped that I’d managed to schedule a viva which took place less than six weeks after I submitted the thesis so it was all very fresh in my mind. If you submitted your thesis months before your viva I’d suggest spending slightly more time refreshing your memory in preparation for questions you may get asked.
In summary, I think it’s useful for all PhD students to get an idea of some potential lines of questioning for their oral exam!
Update: Keen to get prepared for your viva? I’ve put together a set of viva preparation worksheets which are available in the resource library. Click the image below for free access!

Listed below are common PhD viva questions which I’ve roughly grouped together. We’ll start with some higher-level questions about your PhD which should be quite easy and friendly, then progress through to some more technical (and potentially unfriendly!) questions.
It is worth noting that many examiners will ask for a short presentation at the start of the viva and this could eliminate some potential questions. In this list I’ve left in the main questions I’d expect for this presentation to address, such as what future work you’d recommend.
Very few of the questions are ones you’re guaranteed to get asked, but I can assure you that you’ll get asked at least some of them!
General PhD Viva Questions – usually friendly!
These ones are simply inquisitive and you don’t really have to worry about getting caught out. The examiners are simply interested in the work and want an insight from someone who has spent the last few years working on it.
- What is the most important finding from your PhD work?
- What was the motivation behind this research?
- Who is your research relevant to?
- Which aspects of your work are you publishing? Follow on: and where?
- What future work would you recommend?
- What are the limitations of your research?
- Which aspect of your work surprised you the most?
- What are the potential applications of your PhD research?
Method-Specific Questions – mostly friendly!
These questions dive a little deeper but even so shouldn’t be too much of a cause for concern. They come down to your own judgement and as long as you justify your decicisions you’ll be fine in answering them.
- Why did you do [things] a certain way?
- What were the alternatives to [this certain method]?
- Why did you test [that specific number] of samples?
- What effect did you think changing [something in your method] would have?
- What do you think you could have gained by using [another approach]?
- Why did you not use [another technique]?
- How did you deal with the ethical implications of your work?
Results & Analysis-Specific Questions – mostly friendly!
In a similar manner to the previous section about your methodology, you’ll often get some questions targeting your analysis and presentation of results.
- What is this graphical figure illustrating?
- Why was [this analytical technique] appropriate? Follow on: why did you use [this other technique]?
- Which of your results do you find the most interesting?
- How do you know that your findings are correct?
Literature Questions – may be less friendly!
This is where things may get tough if your examiners want to try and test your limits. Even so, they’ll still likely cut you some slack. If you have 100+ references it’s very possible that under the nerves of your exam you can’t remember specifics for each and every reference. Just don’t make things up. They’d rather you were honest than trying to deceive them.
- Please explain the key findings of reference number [X]
- Which papers would you say had the biggest impact on your work?
- What do you think are the biggest differences between [these two previous studies]?
- What have been the biggest advancements in the field over the last 10 years?
- Why did you not reference [this other study]?
- How does your work compliment the existing literature?
- What do you think the next big advancements will be in the field?
Highly Technical Questions – potentially very unfriendly!
These are the ones I was a bit scared of getting, but it is a PhD viva after all. Of course it should be expected that you have a solid understanding of the principles that underpin your project. Even so it can be unnerving thinking of how large the range of potential questions like this can be!
Unlike at a conference or in other settings where you may be able to brush over things you’re not 100% comfortable with, there is no hiding when your examiners need to test your knowledge. Particularly when they have hours of time at their disposal to do so!
- Explain how [a technique] works. This could be anything from sample preparation, equipment and analysis through to statistics. I’ve known people to get asked to explain things like a statistical t-test from first principles, with follow-on questions being asked with every answer to drill deeper.
- Explain [some fundamental concept, phenomenon or principle]. Just like the last question but applied to basic-sciences. I’ve known students to get asked questions such as: explain energy (to a mechanical engineer) and explain toughness (to a materials scientist). I’m sure we can all explain these concepts to a certain level but my concern was whether or not I could explain them at a deep enough level to satisfy the examiner.
With both of these types of questions there ultimately comes a point where you (or the internal examiner ) can push back and say that answering that question was not the focus of your PhD!
What Questions I Got Asked at My Own PhD Viva
I was really surprised at my own viva how few questions I actually got in general.
The viva lasted a whopping five hours (excluding a quick break) and yet almost all of the time was spent discussing improvements to my viva to help with publishing papers.
Even so, I could have done with putting a bit more time into preparing for potential questions: which was my motivation to help you by putting together this post!
The few questions I had included:
- If you were to do the project again would you do anything differently?
- Clarification of what I meant by certain sentences in my thesis .
You may be wondering if I avoided getting asked deeper questions by the examiners because I already had a relationship with them so they were satisfied with my knowledge and capabilities. But I didn’t really know the examiners! I’d met my external examiner at a conference and he had seen me present but I’d never actually met my internal examiner before.
Instead, what I think did go a long way to helping was having already had something published in a respected journal.
Nevertheless, in a way I actually walked away a little unsatisfied by the lack of questioning at my PhD viva.
It was great to get so much feedback on my thesis which has already helped to get two more papers published since the viva, but I felt like it would have been nice to feel a bit more taxed and known that I could hold my own in the exam if it came down to it.
Now looking back on the viva 10 months later, I’m just happy to have the PhD done!
My Tips for Answering Common PhD Viva Questions
- Keep calm and take your time before answering . There is no rush to answer questions. Having a sip of a drink may help provide a pause for thinking up an answer.
- Tell the truth. If you don’t know something, just say so! It’s likely the examiners will quickly be able to tell that you don’t know what you’re talking about. Plus, there is the risk that they’ll ask deeper follow-on questions which could unravel any lies.
- Try to enjoy the experience. Think of it as a discussion, rather than a police investigation. Your examiners are interested in the work and want to hear more about it!
If you’d like personalised help with preparing for your PhD viva I am now starting to offer a small number of one-to-one sessions. Please contact me to find out more or click here to book a call.
I hope these common PhD viva questions can help you to prepare for your own viva.
If there are other aspects of the examination you want covered, just let me know.
I have many more upcoming PhD (and beyond!) posts . I f you want to get notified about them you can subscribe here:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

How to Master Data Management in Research
25th April 2024 27th April 2024

Thesis Title: Examples and Suggestions from a PhD Grad
23rd February 2024 23rd February 2024

How to Stay Healthy as a Student
25th January 2024 25th January 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

How to survive a PhD viva: 17 top tips
Just handed in your PhD thesis? Now it’s time to plan for the next hurdle: a viva. Academics offer their advice on how to best prepare
- Finishing your PhD thesis: tips from those in the know
- The key to a successful PhD thesis? Write in your own voice
- PhD: so what does it really stand for?
H anding in your PhD thesis is a massive achievement – but it’s not the end of the journey for doctoral students. Once you’ve submitted, you’ll need to prepare for the next intellectually-gruelling hurdle: a viva.
This oral examination is a chance for students to discuss their work with experts. Its formal purpose is to ensure that there’s no plagiarism involved, and that the student understands and can explain their thesis. It involves lots of penetrating questions, conceptually complex debates and is infamously terrifying.
How can PhD students best prepare? We asked a number of academics and recent survivors for their tips.
Preparing for the viva
1) Check your institution’s policies and practices
Institutional policies and practices vary. Find out who will attend your viva (eg will a supervisor attend, will there be an independent chair?) and what their roles are. Penny Tinkler and Carolyn Jackson, authors of The Doctoral Examination process: A Handbook for Students, Examiners and Supervisors
2) Re-read your thesis – and keep up-to-date with research
Don’t underestimate the amount of time the examiners will have spent reading and thinking about your thesis – however, you should remember that you are still likely to be the “expert in the room” on this particular topic. Check to see if any relevant recent papers have emerged since submitting the thesis and, if so, read these. Dianne Berry, dean of postgraduate research studies, University of Reading
3) As an examiner, you tend to stick to things you’re an expert in when driving the questioning
Your viva panel will consist of an external expertise in your subject area and an internal which may be in a subject field associated or directly related to yours. The external examiner is the one who mainly calls and fires all the shots and so it’s pretty important to have a knowledge of their published contributions, especially those that are related to your thesis in any way. Dr Bhavik Anil Patel, senior lecturer in physical and analytical chemistry
4) Think about what you will or won’t defend
Consider carefully what you will defend to the hilt in the viva, and what you are prepared to concede. It’s important to defend your claims about the originality of the thesis and its contribution to knowledge. However, no research is perfect, and showing that you have considered what could have been done differently, or even better, is not a bad thing. Penny Tinkler and Carolyn Jackson, authors of The Doctoral Examination process: A Handbook for Students, Examiners and Supervisors
5) Draw up lists of possible questions – especially ones you dread
I collected questions from a bunch of different places ( listed here ) which I then tailored to my PhD. Somebody I worked with also recommended that I put together my 10 nightmare questions. I found this really useful, by writing down and thinking about my dreaded questions, they were no longer so bad – it was almost as if I’d faced the beast.
Generally speaking, I was able to predict the questions that I was asked. There were a couple that were unexpected but they were either conceptual points or based on literature that I just didn’t know. Richard Budd, research assistant, University of Bristol who sat his viva in summer 2014 and has blogged about the experience
6) It’s not like sitting at a laptop where you can edit a sentence as you go along
By the time you finish your PhD you’ll know your thesis inside out. One of the things you won’t be as practised at is talking about it. When I was preparing for my viva, I practised vocalising answers. It’s not a case of needing to learn to answers verbatim – this would only work as a technique if you could guarantee the exact way your examiner will ask a question – but it is about thinking about how you will articulate certain things. A viva isn’t like sitting at a laptop where you can edit a sentence as you go along. Richard Budd, research assistant, University of Bristol who sat his viva in summer 2014 and has blogged about the experience
7) Bring a printed copy that is exactly the same as that of your examiners
Ensure you and your supervisor have a printed copy that is exactly the same as that of your examiners (specifically the same pagination). Mark with tabs the key sections and highlight for reference important quotes and points you might want to refer to. If you have some key diagrams it may help to have these printed larger on A4 sheets that can be used in a discussion.
There is a chance, albeit slim, that an examiner will wish to see some piece of experimental data, software, or other supporting evidence. Have this all neatly archived and accessible. You can do this after submission. Anthony Finkelstein, dean of the UCL faculty of engineering sciences who has blogged about surviving vivas

During the viva
8) Get off to a good start
Give a few detailed answers in the opening 15 minutes, demonstrating knowledge, describing your thinking and working - then the examiners are likely to relax into the viva. If the first few answers are short and non-specific, not demonstrating knowledge, this can begin to raise concerns, and that can set the tone for the whole viva. This is avoidable. Rowena Murray, author of How to Survive Your Viva: Defending a Thesis in an Oral Examination
9) Prepare for the icebreaker
Every viva opens with that dreaded icebreaker that is supposed to break you in gently but often seems to be the thing that gets students into a pickle. It’s so basic, students almost forget about it. Most often this would be to give a five to 10 minute introduction to your work and your key findings. This is such a common question that not preparing for it would be silly. Dr Bhavik Anil Patel, senior lecturer in physical and analytical chemistry
10) Silence doesn’t mean bad news
Don’t assume that you will be given any indication of the outcome at the start of the viva. The examiners may or may not offer comments on the thesis at this stage and candidates should not interpret a lack of comments at this point as a negative sign. In some cases institutional policy prohibits it. Penny Tinkler and Carolyn Jackson, authors of The Doctoral Examination process: A Handbook for Students, Examiners and Supervisors
11) Don’t point out your own weaknesses
Avoid shooting yourself in the foot by highlighting the weaknesses in the thesis by being overly humble (eg “I didn’t think this would be an acceptable piece of research given the way I handled x or y”) or by saying what you “failed to achieve” or “did not manage to carry out in a robust manner” etc. Leave that to the examiners to pick up in their reading, they don’t need help. Dr Mariana Bogdanova, lecturer in management, Queen’s University Belfast
12) Don’t talk like a politician There’s a danger of trying to over-prepare. Don’t learn answers off by heart – it removes the spontaneity and is obvious to examiners. If a student has pre-prepared answers they become a bit like politicians, answering questions they weren’t asked rather than the ones they were. I have come across mixed views on mock vivas. Some people really like them – and they can settle nerves – but other times it can remove spontaneity and steal your thunder. Jerry Wellington, head of research degrees at University of Sheffield and author of Succeeding with Your Doctorate
13) You may need to move from friendly questions to complex debates
Vivas can appear friendly and then suddenly go very conceptually complex. The language used is an alternation between accessible normal language and really specialised arguments. The student needs to be able to move orally between the two. Gina Wisker, professor of higher education and contemporary literature at Brighton University
14) If things get on top of you, use the excuse of having a look at the thesis
Make sure that before the viva you get plenty of sleep, eat properly and de-stress. If things get too much when you’re in there, use the excuse of having to look something up in your thesis. You could also pause and say “Can I write that down for a moment?” Stall for time until you get yourself back together again. Gina Wisker, professor of higher education and contemporary literature at Brighton University
15) Focus on your contribution
One of the most important things that the examiners will be looking for in your thesis, is the “contribution to knowledge”. It is the contribution which makes your work doctoral level. Be sure that you understand exactly what your contribution is, and that you are able to express and explain it clearly and concisely.
Write it down in a paragraph. Discuss it with you supervisor and fellow students. Make sure that you can relate your contribution to other work in your field and that you are able to explain how your work is different. Peter Smith, author of The PhD Viva
16) Expect your viva to last between one and three hours
Students frequently ask how long the viva is likely to be. Obviously they vary. Discipline differences are important. Our research suggests that most natural and applied sciences vivas were completed in one to three hours, whereas arts, humanities and social science vivas were typically less than two hours long. In the natural and applied sciences 43% of vivas lasted two hours or less, compared to 83% in arts, humanities and social sciences. Penny Tinkler and Carolyn Jackson, authors of The Doctoral Examination Process: A Handbook for S tudents, Examiners and Supervisors
17) Enjoy it
The best advice I ever got was “Try to enjoy it”. It seemed ludicrous at the time, but I actually found myself really getting into the discussion as the viva went on. It’s one of the earliest chances you get to talk to someone who not only informed your research (ideally) but is also conversant with your own. It’s a great chance to explore the contours of your research – treat it as such, and it doesn’t seem quite so daunting. Michael James Heron, school of computing science and digital media, Robert Gordon University
- Share any advice you have in the comments below.
Enter the Guardian university awards 2015 and join the higher education network for more comment, analysis and job opportunities, direct to your inbox. Follow us on Twitter @gdnhighered .
- Impact of research
- Universities
- Higher education
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
- Log in
- Site search
5 tips for passing your PhD viva
Every Doctoral researcher is expected to defend their thesis through an oral test - so discover how to prepare for your PhD viva and ensure you make a good impression on the examiners
What is a PhD viva?
A viva voce is an oral test, which literally translated means 'with the living voice'. It's a focused discussion giving you the opportunity to present your PhD thesis and then defend it in front of a panel of academic experts.
1. Understand what's expected of you
Traditionally, your thesis would always be discussed in person, with the interview style viva exam overseen by at least two (internal and external) examiners. Afterwards, they would provide you with a joint written report detailing any corrections that need to be made.
However, following the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, the online PhD viva has become more commonplace with this examination more likely to take place via Microsoft Teams, Skype or Zoom.
The virtual experience will still typically follow the same format, but you'll be briefed in advance about the arrangements and any technical aspects to bear in mind. You can prepare for an online PhD viva by reading our video interview tips .
The chair of the viva is usually the internal examiner, although it can be an independent person. If you and the examiners agree, your PhD supervisor can also be present.
The examiners' main objective is to ascertain that you've written your own thesis, so if you have and are ready to talk through how you completed it, there's no need to panic. You may even enjoy the viva voce test.
In addition to assessing your thesis, the examiners are also there to assist you in deciding how and where this research might be published.
There are various results between a 'pass' and 'fail' but it's very rare to slip up at this point of a PhD. Most Doctorate awards will be made upon the condition that a number of minor corrections are made, with re-submission requests far less common.
However, while the pass rate is high, the viva exam itself can still be intellectually demanding. This is because you'll be debating issues that are conceptually complex, so preparation is crucial to your success.
At the end of it, whatever the outcome, be prepared to take on board any advice, as the examiners are there to help you improve your argument or the presentation of your thesis.
2. Know your thesis inside out
While you can be sure this isn't a memory test - as you're fine bringing notes and a copy of your thesis with you to the PhD viva - it's still important to gain a good understanding of what you've written and be knowledge about your field of study.
You'll need to think carefully about where this original piece of work would be placed in the context of the wider body of research carried out in this field. Questions will surely be asked about this, as well as whether the project could possibly be developed further through any future research.
As you'll be explaining parts of the document to the examiners (who'll also have a digital or physical copy), make sure the pagination is the same in your version as the one they're looking at to avoid any issues regarding everybody being on the same page.
If you get stuck at any point during the viva exam, you can use looking at the thesis as an excuse to re-focus and gather your thoughts.
3. Anticipate the viva questions
The examiners will have prepared a series of questions for you to answer at the viva voce, but this is nothing to get too concerned about. The questions will all be based on your thesis - what it's about, what you did and what you found out - and why this matters, in relation to your field of study.
So when getting ready for the viva, consider the types of questions you're likely to be asked, including:
- What original contribution has your thesis made to this field of study?
- Explain the main research questions you were hoping to address.
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of your thesis?
- If you had to start the thesis again, what would you do differently?
- If funding was no object, describe how you'd follow on from this project.
- What are your plans for the future?
It can be helpful to practise your answers beforehand, ideally vocalising them by arranging a mock mini viva - although, as you aren't restricted in terms of referring to notes in the exam, you can leave room for spontaneity, and you don't need to learn it all off by heart. If your viva is being held online, you can ensure any technical issues are identified before the day by having a run through with your supervisor or a friend.
While it may sound simple, stick to answering the questions posed. It's really easy to go off on a tangent and this can open up other lines of enquiry from the examiners - possibly in areas you hadn't expected to be quizzed about.
On the other hand, it's completely fine to bring personality to your reasoning and use stories as a means of describing the learning process you've gone through and the techniques mastered over the last three or four years that have brought you to this point.
4. Learn about your examiners' own work
The senior and well-respected academics who'll be reading your thesis will have their own ideas on conducting PhD standard research. Therefore, it's worth taking a look online at their academic profiles to discover if there's any correlation with the research they've had published and your own work.
From this, you should be able to gain a better idea of their motivations, their possible views on your thesis and the kinds of questions they might wish to discuss after having read through it.
You should research up-to-date theories, read any recent papers on the subject and speak to others who've recently had their own viva exam. Think about how your work differentiates from the research carried out by others in your chosen field.
Prepare to provide any supporting evidence asked of you by the examiners - for example, they may request to see experimental data you mention once the exam is over.
It's also necessary to check the policies and practices in place at your university and be sure of what the roles of the examiners are and how the viva panel will be structured. In many cases, Doctoral students can choose the examiners conducting the PhD viva.
5. Plan towards the viva exam
From the moment you know the date of your viva voce, work backwards and plan the steps you'll need to take before the day itself. Allow enough time to assess and review your work so that as the day approaches, you can focus on the practicalities.
This encompasses everything from making sure you relax, eat and sleep well the day before to arranging transport so you get to the viva on time - if you're attending in person.
An online PhD viva will present its own challenges, so ensure your working space is presentable and you still make an effort in terms of what you'll be wearing.
It's always advisable to adhere to interview etiquette and go with something that's both smart and comfortable. By looking the part, this should get you in the right frame of mind to communicate in a professional manner.
In the build-up, avoid any situations that might make you feel stressed and instead try to adopt a positive attitude, one that results in a genuine eagerness to engage in a debate about the work you've been toiling over for a substantial period of time.
If you're travelling to the examination, be sure to check that you have everything you wish to take with you, including the thesis, plus any notes or other materials that will help support your claims.
The PhD viva can last between one and four hours - usually two - so it's necessary to pace yourself to get off to the best possible start.
Remember, the examiners aren't trying to trip you up - they want you to pass and are primarily there to hear you talk about your project. So, after the polite introductions they'll typically start with an icebreaker to put you at ease and help calm the nerves.
It's meant to be an open and honest conversation about your work, so feel free to politely disagree with the examiners, especially on areas you feel strongly about. Don't forget to use examples from your thesis to back up what you're saying, remembering to be clear and concise.
If you know your way around your thesis and can explain your thinking and way of working, this test shouldn't be a problem. And if you don't know the answer to a specific question - admit it, as it's better to concede your limitations in an area than ramble on and hope they don't notice you're struggling to come up with an explanation. No research is perfect, so it's important to appreciate this during the discussion - but don't be too overcritical about your work either, as that's not your job.
Finally, as the PhD viva can quickly move from a series of friendly questions to those that are more in-depth, take some time to think before answering. Don't worry about any periods of silence from the examiners, as this certainly isn't an indication that you're doing badly.
Find out more
- Explore possible careers at your PhD, what next?
- Consider getting an academic job .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page

Prepare for your viva. One question at a time.
Prepare answers to the most common phd viva questions with this interactive template. it’s free to download and it’s yours to keep forever. , the easiest way to prepare for your viva.
Our free PhD Viva Questions template lets you familiarise yourself with the most common questions. It’s been designed in collaboration with Professor Peter Smith, author of Palgrave’s The PhD Viva.
The template is interactive and editable, meaning you can fully prepare model answers in advance of the big day.
Enter your email address and we’ll deliver it straight to your inbox. For free. We’ll also send you tips and advice on how best to prepare for your viva and any corrections you may get.
I have read and agree to the terms & conditions

Maximise your chances of success
Enter your email address and we’ll deliver your free template direct to your inbox. we’ll also send you tips and advice on how best to prepare for your viva and any corrections you may get..
Amplifying The Voices Of PhD Students
Viva Question Repository

This is a repository of questions that were asked at Vivas of students, just like you.
Look up what questions you can expect in your Viva! Don’t get caught off-guard.
(Pro tip: Want to sort by more than one heading? Hold shift and click the headings you want to sort by.)
Did you have your Viva already?
Be a lamb, use the form below to add some of the questions you had and help other Ph.D. students out! 🙂
Add your questions even if they’re already in the list above because the more often a question pops up in the list above, the more PhD students will know which questions are more likely to be asked and which are not!
How To Us The Repository:
Use it to prepare for your Viva/Defense.
There are a bunch of various categories that you can search through.
You can use the search bar, or simply click on one of the category’s headers to order the rows A-Z or Z-A. You can sort by more than one column by holding shift while clicking the desired headers.
There are bound to be duplicate questions in the Repository, which tells you a little about how likely that type of question is to come up.
All the best!
Share this:

- Common PhD Interview Questions
- Applying to a PhD
In this guide, we’ll share 11 common PhD interview questions and our suggestions on how to answer them.
A PhD interview is an essential step in securing a doctorate position. This is because it enables the prospective supervisor to get to know you better and determine whether you’d be a good fit for the project. Equally, it provides you with the opportunity to learn more about the project and what the university offers. Although being asked to attend an interview by the admissions committee can be daunting, it’s actually a positive sign. It means that based on your application and academic qualification, the academic department believes you have the potential to make a good PhD student for the position.
Whilst most questions you’ll be asked during your PhD interview will focus on your proposed research project, a handful of generic questions will almost certainly be asked. To give yourself the best chance of succeeding in the interview, we highly recommend that you prepare answers to these generic questions beforehand.
Without further delay, here are 11 common PhD interview questions and tips on how you should answer them.
1. Tell Us About Yourself
It comes at no surprise that this common ice-breaker question is at the top of our list. This question will likely be asked to help you calm your initial nerves and settle into your interview. As this is a warm-up question, aim to give the interviewer a general overview about yourself as opposed to a detailed breakdown. To achieve this, structure your answer into three sections:

- Academic History : start with a summary of your academic background – where and what have you studied? What grades did you achieve?
- Research Topic : go onto explain your research interest in your chosen topic – what do you like about it? Do you intend to pursue a career related to it upon obtaining your degree?
- Why a PhD : Finish with why you want to undertake a PhD – do you want to make a contribution to science? Do you want to get a job in academia?
2. Why Do You Want to Do A PhD?
Although you may have touched on this in your answer to the above, your interviews will want to know more of the detail if they ask this question as a direct followup.
Though it may appear obvious, the interviewer is specifically interested in discovering your personal motivations for undertaking a PhD . Too often, students answer this question by listing the benefits of a PhD. Not only will the interviewer already know the benefits of a PhD, but a generic answer also won’t help you stand out among the other applicants.
To answer this question and leave a lasting impact, try to include an academic or personal experience that has strengthened your passion for research. As well as this, outline what your career aspirations are and explain how the proposed PhD will help you achieve them. The key to selling yourself here is to let the interviewer know how passionate you are about the project without having to say it.
3. Why Did You Choose This Project?
This is your chance to show that you have researched the University, supervisor and project.
First, talk about the project. Is there a particular aspect that you’re interested in? If so, mention it. This will show that you’re engaged in the topic and already have a basic understanding of the field. Besides this, a great way to show that you’ve really looked into the research topic would be to discuss a certain part of the methodology the project could adopt.
Next, talk about the University – there may be several universities offering similar projects, but what makes this one stand out? Is it their resources? Is it the prospective supervisor’s research group? Is it their previous involvement in previous influential studies? Again, show that you’ve adequately researched the University and clearly understand what makes it unique.
Finally, you can mention if your decision to apply to their university has been influenced by the expertise of the proposed supervisor. Given that the supervisor will be highly knowledgeable in the research topic you’re applying to, it’s possible they may have contributed to some significant findings in it. If so, it’s acceptable to acknowledge this by mentioning how you would like the opportunity to work under their guidance. However, be careful not to overdo. Although you may be sincere in your answer, it can go against you if your supervisor feels like you’re trying to flatter him. To avoid giving this impression, focus on how his or her expertise will help you develop into a competent researcher.
4. Why Should We Choose You?
A very blunt question, but your PhD supervisor will want to make sure you’re the best candidate for the position. This is especially true given they’ll be responsible for supporting you over the next few years. Therefore, the primary aim of your answer will be to reassure them you have the skills and experience required to undertake a doctoral study. To achieve this, identify the critical knowledge and skills required for the project and discuss how you meet each of these. Follow up each justification with a short, relevant example to help give your answers more impact.
When asked this question, some students tend to just summarise their academic CV and cover letter . This isn’t an effective way to answer the question as you’re telling the supervisor information they already know about you. It’s fine to reiterate a few key points, however, try to delve deeper into what you can offer going forward as opposed to what you’ve achieved in the past. As part of your answer, identify the soft skills which will be imperative to the doctorate and state how you have each of these. These can include skills such as effective communication, great time management, problem-solving, adaptability and high work ethic.
5. How Did You Come up With This Project?
If you’ve developed your own research proposal , then expect to have to defend it as part of your interview. You should have a thorough understanding of what the current gaps in knowledge are surrounding your research topic and how these could limit the findings of your study. Besides this, you’ll want to show that you’re clear on what the key aims and objectives of your project are and appreciate how they could contribute to your field of research. This last point is essential in convincing the interviewers this project is a worthy pursuit. What makes your project groundbreaking and worth dedicating several years to?
The interviewer wants to know if you have thought out all aspects of your project and so will likely scrutinise the finer details of your proposal. Therefore, be ready to outline the literature you’ve read and discuss how you evaluated different methodologies before suggesting your current one.
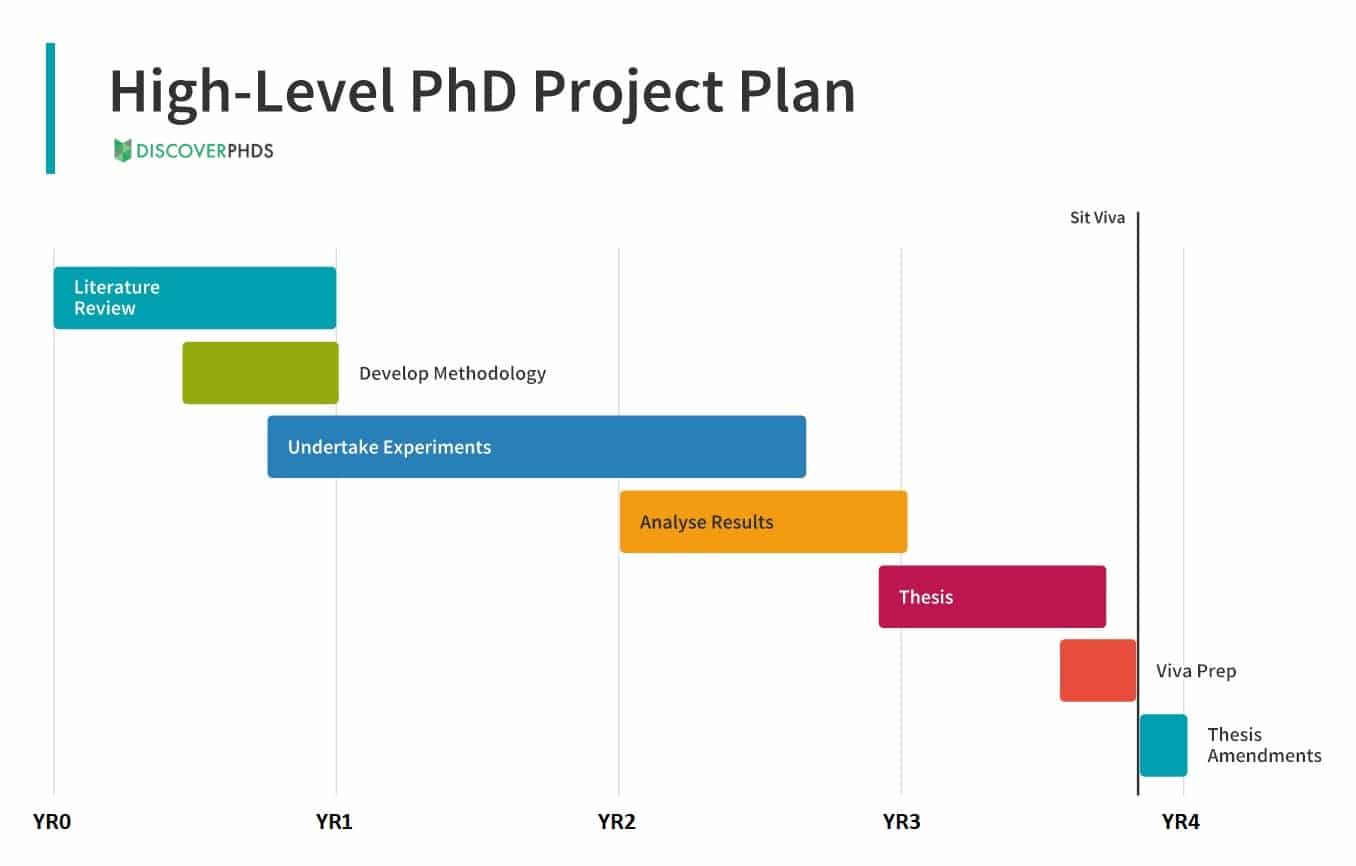
If you want an edge over other students, you can also produce a high-level plan, similar to the one below (but with more detail), which outlines the different phases of your research project. This can include stages such as the literature review, undertaking experiments, producing your thesis and preparing for your viva voce. Although they won’t expect your plan to be fully accurate, especially given how dynamic research projects can be, it will show your positive attitude towards being imitative and taking responsibility for your project.
6. What Challenges Are You Expecting to Encounter in This Project?
A common PhD interview question students struggle with is “What difficulties do you think you will face?” This purpose of this question is to check how much you’ve thought about the project. Students who provide a poor answer generally do so as they think admitting to any potential difficulties may make them seem incompetent. This couldn’t be any further from the truth.
Identifying potential difficulties shows the interviewers you’ve given serious thought to the project. This reassures the supervisor that should you run into difficulties during the research, you’re not only capable of identifying them but also mature enough to do so. Not highlighting potential difficulties, whether it’s due to a lack of confidence or understanding the project, suggests your project will be vulnerable to problems which could go amiss.
When answering this question, try to follow up on each potential difficulty with how you intend to address it. This can include measures such as making use of internal development opportunities, enrolling onto external training courses or signing up to specific research master classes.
7. What Are Your Strengths and Weaknesses?
This is a standard question for most interviews, and a PhD interview is no different.
Pick strengths that compliment your PhD programme. For example, if applying to a Physics or Engineering PhD, mentioning you have good attention to detail would be highly beneficial given the amount of data analysis involved. Try to support each of your claims with a relevant example. Using the above case as an example, you could discuss how as part of your Bachelor’s or Master’s dissertation project, your high attention to detail allowed you to streamline some of your experiments or identify potential problems with your data.
Likewise, try to discuss a weakness that won’t be detrimental to your research project. An example of something you would want to avoid would be “I have a tendency to put the hard tasks off until the end until I know I should really start working on them to not miss any deadlines“. Although this may seem like a harmless response, it will seriously concern the interview panel. This is because a model student will need to be consistent in their efforts to meet the challenging workload, even in times of difficulty. As before, follow up your weakness with a plan on how you intend to address it. For example, if you state your weakness as public speaking, a suitable follow up would be to discuss how you would like to work on it by presenting your research to undergraduate students and attending seminars.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
8. Can You Describe a Time You Encountered a Problem or Challenge and How You Approached It?
A key trait of all successful researchers is the ability to overcome problems independently. Given that even a minor problem can derail a research project, it’s important for your project supervisor to know whether you can adequately address them.
Despite what your example may me, try to cover the below three aspects as part of your answer:
- Identification – How did you identify the problem? Was a check you had in place triggered or did you stumble upon it naturally?
- Deconstruction – How did you break the problem down? Did you identify any assumptions or limitations which could have been associated with it? If so, how?
- Overcoming – How did you identify the solution? If you had several solutions, how did you determine the most sensible one? What did you learn from it?
Your example doesn’t need to relate directly to the research programme you’re applying to, however, it should be kept academic if possible. For example, you could discuss a challenge you encountered during your undergraduate dissertation project, such as limited literature on your research topic or inaccurate experiment results.
The key point to remember here is that a supervisor is there to supervise, not to fix all your problems. Not only will they not have the time do to this, but it will directly go against the ethical requirement of ensuring your work is yours and yours alone.
9. What Are Your Career Aspirations?

Your interviewers will want to see that you’ve considered what you will do after completing your PhD. This is to help them determine what your motivations are and to confirm that you want to enrol onto a PhD for the right reasons. It’s clear that anyone who has thought through their decision will have a long-term plan in mind, even if it’s a handful of well-considered options.
Don’t feel like your answer needs to relate to academia. One of the many benefits of a PhD degree is that it can lead to a variety of career paths. By being open with your true intentions, they can better determine what support and training you’ll require from them.
Despite your long-term goals, research into this and know the route you’d like to take post-PhD. A good understanding of your career plans and how to get there will go a long way in conveying your commitment to the project.
10. How Will You Fund This Project?
The interviewing panel will ask about this if your project is self-funded or conditionally funded (e.g. competitive funding schemes where funding is not guaranteed).
You don’t need to provide a complete breakdown of your savings, nor would they expect you to. The primary concern the interviewers want to address is that you’re fully aware of the costs associated with undertaking a PhD . If you intend to apply for external funding or take on a part-time job, mention this. In doing so, make sure you stress that you will base your part-time work around your PhD and not the other way around. The interviewers want to reassure themselves that you will make your research your top priority throughout the course of your degree.
11. Do You Have Any Questions for Us?
This interview is not only for the supervisors to evaluate you but also for you to evaluate them, the PhD project and University.
Although you will have already researched the position at length, ensure you ask questions when offered to do so. Asking questions will show that you’re engaged and are an individual who likes to make informed decisions. Not asking questions, or not asking well thought-out ones, will send the wrong message.
If you’re wondering what makes a great question, a quick internet search for “What questions should I ask at a PhD Interview?” show’s you’re not alone. Some examples of great questions to ask in a PhD interview are:
- Are there any major developments or partnerships planned for the department? – Although this won’t always be the case, the department may be planning to upgrade its research facilities or partner with another leading institution. Asking about this shows you’re genuinely enthusiastic about undertaking influential research.
- What are the supervision arrangements? – This is a great way to find out if your expectations match that of your potential supervisors. This can include aspects such as how often the two of you will meet and what level of support they intend to provide.
- Will there be any opportunities for teaching within the department? – If you intend to pursue an academic career after completing your research, this will be a brilliant way to show them you’re committed to your long-term plans. Even if you plan on following a different career path, asking will let you know whether there is any opportunity to earn whilst you study.
- What opportunities will I have for presenting my research? – This shows you intend to be an active member within your research field. This won’t be great only for your development but will help the university increase its research network and reputation in the wider community.
Other PhD Interview Tips and Advice to Help You Prepare
- Format – The format of the PhD interview varies depending on the University. If you’re unsure of what format your upcoming interview will follow, get in touch with the department you will interview with. They should be able to give you an idea about what to expect and how long it will typically last. This knowledge will prove invaluable when preparing for a PhD interview.
- Video interview – Some interviews will be conducted as either a phone interview or a skype interview. This is especially true if you’re an international student still within your home country. If so, conduct your interview in a place with a reliable internet connection and a clean backdrop.
- Attendance – Usually, your interview will comprise the primary and secondary supervisor. However, sometimes your interview panel can comprise non-technical staff or the Head of Department.
- Presentation – You may be asked to prepare a PhD interview presentation if you’re proposing your own research topic . If you’re requested to do this, keep it brief, use at least 80% of the time they permit and base it around your research proposal.
- Paperwork – Bring two to three copies of your application form, and if applicable, your research proposal. Although in most cases your interviewers would have bought their own copy, it’s better to be on the safe side.
- Etiquette – If you’re unsure of what to wear to a PhD interview, a good general rule of thumb is to wear what you would to a formal job interview. In other words, keep it formal. Additionally, learn how to pronounce the names of the interviewers and any other staff members you may mention beforehand.
- Practice – There’s a lot of truth in the old saying ‘practice makes perfect’. You will want to practise as many PhD interview questions as you can. Don’t just limit yourself to the ones discussed on here. Find as many PhD questions as you can and prepare draft answers for all of them. In fact, you don’t even need to limit yourself to questions specifically for PhD students. There are many out there that, although written for generic academic interviews or the job market, will be applicable to you. If you find yourself short on resources, try searching for ‘tell us a time when you…’ in google as these will provide great scenario-based questions you can practise with.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Teaching Matters blog
Promoting, discussing and celebrating teaching at the university of edinburgh, vive-ing la viva: how to answer viva questions.

Dr Jenny Scoles from the Institute of Academic Development provides some helpful tips in how to prepare for your PhD viva by being aware of how you answer the examiners’ questions. This post is part of the Learning and Teaching Enhancement theme: Showcasing the Doctoral College .
Just enjoy the viva, they say…. ha!
‘Enjoyment’ was not at the top of my list of adjectives when thinking about my viva. But I knew it was my only chance at speaking to people who had actually read my thesis and, unlike my long-suffering family and friends, were genuinely curious about why I didn’t use NVivo and why I hadn’t referenced the original citation on page 243. So, when it came to prepping for my PhD viva a few years ago (I submitted in a September and my viva wasn’t until the January so I had a decent amount of time to prepare/find multiple spelling mistakes), I made sure I was as ready as I could be.
I found a lot of online viva resources and blog posts that provided helpful lists of likely and possible questions you may be asked, so you can prepare your answers. However, what I found most helpful were the tips from my supervisors during my mock viva (tip 1: have a mock viva with your supervisors). Specifically, they talked about HOW I should answer the examiners’ questions, not necessarily WHAT to answer. Here are some examples:
Sign post your answers: You will undoubtedly be asked, in so many words, ‘What is your original contribution to knowledge?’. As with all replies, keep your answer clear; don’t make things too complicated. Structure the points you want so you can signpost the examiner to your main thesis contributions, just as you would have in your written conclusion. For example, I said ‘My thesis makes three original contributes to knowledge: firstly, a theoretical contribution… secondly a methodological contribution… and thirdly, a pedagogical/practical contribution….’, and kept it to a few sentences for each of the three points.
It’s a stamina game: It is easy at the beginning of the viva to want to just keep talking, through nerves, or a worry that you want to show off everything at once. My viva was only an hour and a half, but I’ve heard of some lasting over five hours – it just depends on the examiners, and what emerges on the day. Have faith that, when answering the first few questions, you don’t have to reel off your whole thesis there and then. Take your time; it is a tiring and exhaustive few hours. I hit the wall after an hour as I’d begun to relax into it, and my adrenaline dropped (I remember doing a few over-loud sighs without realising). So, pace yourself. If you are worried that you have not answered their question, you can politely ask if they would like you to expand any more.
Although it’s a defence of your thesis, don’t come across as defensive: This is a hugely useful distinction that I was made aware of. The examiners are there to critically pick apart your thesis, probing why you did certain things and not others. Yet this thesis is your baby, and no one but you can say your baby isn’t perfect. So your hackles rise, and perhaps, without realising it, the tone or manner in which you reply could come across as too defensive and it could make the examiners feel defensive too; they’re only human, after all. You can still defend your reasons politely but firmly… ‘That’s a really interesting way of looking at it, but I found, for my study, it was more helpful to look at it this way….’, or similar.
Don’t know the answer? Sometimes they may ask you something that you have not even thought about, let alone prepared for. At this point, have a few stock phrases up your sleeve to give yourself some time to mull it over:
Well, now that I think about it like that… I’m only starting to see this now… That’s a very good point, I’d like to look at this issue in more detail.
Practice speaking your answers aloud to get used to your voice: The best prep I did was with a colleague who had her viva at a similar time to me. We scheduled weekly Skype sessions in the weeks before and practised asking each other unseen questions. This helped me get used to hearing my own voice, and let me play with how I could verbalise concepts and ideas that I had only, up until then, put into writing and lived in my head.
Prepare your own questions: Like an interview scenario, it looks professional if you have a few prepared questions for the examiners for the ‘any questions?’ part, at the end. For example, you could ask their thoughts on where you could publish future journal articles from your PhD. Or, how a particular concept you developed fits with their own work (brownie points for having read the examiners’ latest papers).
And, finally, two tips from me after having survived:
Simplify the notes you take in with you: I was allowed to take in as many notes, thesis drafts, books, lucky mascots as I wanted. However, if you are relying too much on your answers coming from reading your notes, the flow of conversation will falter, and you may end up getting into a bit of a sweat. As part of the revision process, I made colourful mind maps that summarised the main points I wanted to make for each potential question. I took these in to the viva and lay them out in front of me, which meant I could flick my eyes to them if I had a mind-blank:

Enjoy it… or just get through it: It’s easy to say ‘just enjoy your viva!’ once you’re through the other side. So, if you enjoy it, bonus! If not, well-bloody-done for having got to the viva in the first place, and whatever happens, reward yourself big-style at the end:

This post was originally published on theofficedog blog .
Jenny Scoles
Dr Jenny Scoles is the editor of Teaching Matters. She is an Academic Developer (Learning and Teaching Enhancement), and a Senior Fellow HEA, in the Institute for Academic Development, and provides pedagogical support for University course and programme design. Her interests include student engagement, professional learning and sociomaterial methodologies.
Share this:
One comment.
Thanks for sharing this!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Viva Questions
- Updated on
- Jan 18, 2024

What are viva questions? A viva simply means a university examination during which students answer questions in speech and these questions are commonly based on a particular project or discipline. Viva questions are an important part of an academic program and often take place at the conclusion of a semester/year. Although viva questions can vary, they commonly focus on four aspects: “What the project is about?”, “What were the key findings or observations?”, “What was the process?” and “Why do the observations matter?”. However, in some cases, these questions can be more diverse. If you want to know how to tackle these PhD viva questions properly, then this blog is a must-read for you!
This Blog Includes:
1. summarize your project/thesis/research in 3 minutes, 2. what is the strength and weakness of your research, 3. what makes your thesis work original, 4. elaborate on how your findings relate to literature in your field, 5. tell me about yourself, 6. summarise your key findings, 7. highlight the strong and weak areas of your research, 8. what were the major motivations behind this research, 9. elucidate the process of evaluation, 10. what is the key focus of this research, 50 common viva questions, 25 phd viva questions , viva questions on research methodologies, analysis and research findings: viva questions, viva questions for physics, viva questions for chemistry, viva questions for biology, viva questions for higher education, tips and tricks to ace the viva, 10 most important viva questions with answers.
Whether you are a PhD or a school student, viva exams are equally tough for everyone. But don’t worry, we have a solution to calm you down! Here are 5 commonly asked questions with answers:
To answer this question correctly, you need to be well-versed in the entire project. Start with an answer by explaining why did you select the topic of your project/thesis/research and close your explanation by providing an optimum solution to the problem.
Carefully analyze the strength and weaknesses of your research and while answering, make sure you talk about your weaknesses also and not only your strengths.
While answering, keep in mind what was known before and what you have added as part of being awarded your PhD is to contribute novel knowledge.
Explain how your findings connect with the literature review of your project and what its contributions are in terms of the field of your research. Does it further expand the literature? Does it highlight some new observations? Does it add to the literature in this field? Answer these main questions.
Talk about yourself and your areas of interest. Focus on the areas you are extremely positive about. Talk about your past achievements and what brings you to this position. Keep it professional.
Must Read: How to Ace “Tell Me About Yourself” in College Interview?
For this common viva question, focus on what you observed and found through your research project, how it connects with your hypothesis as well as what concluded through this research.
Mention the strengths first and elaborate on how they connect with the key findings. Then, you can underline the weak areas and the factors that could have been transformed into strengths.
Focus on what inspired you to carry out this research, and cite certain instances which helped you select this topic as well as the field for your project.
Elaborate on how you evaluated the key findings in your research, the key factors involved, whether the evaluation process faced some obstacles, how it could have been better and what was the reason you choose a particular process of evaluation.
While answering this, keep a summarised version of your research in your mind and then talk about the area of the primary focus of research. In order to demonstrate that your research is viable, it is essential to identify some of the key questions that it addresses.
Mostly research-based viva questions are asked in the case of a doctoral thesis wherein the key aspect of the process is to identify the thought behind the development of the specific paper. It is done to determine the knowledge and originality of the researcher and to assess their further interest in the field.
Below are some of the most common viva questions.
- Tell me about yourself .
- Summarise your research/thesis in 3 minutes.
- Tell us how your research contributes to knowledge discourse.
- What are the practical applications of your research?
- What is the strength and weakness of your research?
- How does your research help solve the underlying problems?
- Can you explain your thesis in a sentence?
- How did you come up with the subject of your research/thesis?
- What was the source of inspiration behind this thesis/research?
- What is the key idea that is unexpendable to your thesis?
- What contributions are you looking forward to making in this area of study?
- What is the key focus of this research?
- Where can we locate the originality in your paper?
- What are the core areas of debate in this paper?
- What research methodology have you applied to address this issue?
- What were the alternative methods you could have used to address the subject matter of concern?
- Why did you feel it necessary to spend your resources in this area of study?
- What aids did you use to support your research?
- Which pertinent research papers did you use in your research?
- Can you name 3 remarkable research papers in this stream?
- Explain the recent developments in this field.
- How did you come up with these questions you have discussed in your paper?
- Describe the necessary decisions taken in your process.
- Elucidate the process of evaluation.
- Ponder over the strong and weak aspects of your research.
- What is the relevance of your research in the current scenario?
- Where do you think your research can be practically applied?
- Which aspects of your research are you looking forward to being published?
- Give us some insights into the references in your thesis.
- What have you achieved in the process of this PhD?
- Elaborate on how your findings relate to literature in your field.
- Highlight the strong and weak areas of your research.
- What were the major motivations behind this research?
- How would you propose future research as a follow-up to this project?
- Who will be more interested in this research project?
- How is your research project relevant to your fellow researchers?
- What was the process behind the research questions you selected?
- Name some alternatives to your chosen research methodology.
- Which of your research observations are you most interested in/curious about?
- Name some prominent achievements of your research.
A PhD viva is a final examination in which a candidate answers questions from an academic panel on their work and understanding of their chosen subject area. This is often used to determine whether the candidate has effectively proved that they have learned enough about their specialised study topic to produce original work.
During a PhD viva, the questions are frequently based on the original study proposal and any other written material that has already been provided. Read the top 25 PhD viva questions below:
- What is the area in which you wish to be examined?
- What have you done that merits a PhD?
- Summarise your key findings.
- What’s original about your work?
- Which topics overlap with your area?
- Where do current technologies fail such that you (could) make a contribution?
- Who are your closest competitors?
- Can you summarise your project in 2 lines?
- How can this research help other students working in the same field?
- Which of your findings is your personal favourite?
- Is your research inspired by some incident in your life?
- Why did you choose this method to conduct this research?
- What motivated you to conduct this research?
- What was the biggest challenge that came your way?
- What were the alternatives to this methodology?
- How would you evaluate your work?
- Were you short of any resources while conducting this research?
- Can you tell me about the strongest point of your research?
- What is the weakest point of your research?
- . How did you deal with the ethical implications of your work?
- What original contribution has your thesis made to this field of study?
- Whose work has most influenced yours?
- What ethical considerations did you apply?
- Did your study go as expected? If you had to start the thesis again, what would you do differently?
- Now that you’ve completed your study, what did you enjoy about the process?
Preparing for an interview for the Statistician or Survey Specialist role? Then worry not! Here are the most important viva questions on research methodologies:
- Under which circumstances are quantitative as well as qualitative research methods fruitful?
- Could you distinguish between case-based and observational-based research methods in a few words?
- What is a scientific study and what are its essential features?
- You must have faced some ethical issues while conducting research. How did you handle it?
- What method did you use to collect data?
- Was there any other way in which you could have assimilated the data? If yes, then how?
- What are the main achievements of your research?
- What advice would you give to a research student entering this area?
- What is the relevance of your work to other researchers?
- How did your research questions emerge?
Also Read: Research Institutes in India
When it comes to a career in Research, the outputs which you obtain are assessed on multiple factors. Enlisted are some viva questions which will help you prepare in advance:
- How would you summarise your findings in a few words?
- You have used 3 different techniques to analyse the final results. Could you elaborate on all of them?
- Was there any chance of implementing a different type of analysis technique?
- Apart from the topic, you selected, in what other applications can your research findings be used?
- Out of the given results, which of the findings, according to you, can be beneficial in the near future?
- Is the problem you have tackled worth tackling?
- What would you have gained by using another approach?
- Which are the three most important papers that relate to your thesis?
- What would have improved your work?
- What are the main issues and debates in this subject area?
- What motivated and inspired you to carry out this research?
Subjective Questions for School
Be it for Chemistry or Biology practicals , from 10th standard onwards, students have to appear for vivas. The concerned viva questions pertain to the subject that the students have studied in the course of the entire year. The viva that one appears for at the senior secondary level is based on the experiments that the students perform to test their understanding of the research. Apart from those experiments, the students are also asked several questions to estimate their practical understanding of the key areas of study.
Viva questions for Physics are mainly based on concepts and topics from Physics textbooks. Here are the most common viva questions for Physics Class 11 and Class 12:
Viva Questions for Class 12 Physics
- What is Ohm’s Law?
- What do you mean by ‘interference’?
- Define tangent law.
- Name the type of motion shown by the Torsional pendulum.
- What happens with resonance in the LCR circuit?
- What do you understand by the order of the spectrum?
- How is Wedge Film Experiment useful?
- Define parallax and how it is removed.
- How does the emission of light is carried out by LED?
Also Read: Physics Project for Class 12: Top 50 Ideas & Experiments
Viva Questions for Class 11 Physics
- Name the units of the vernier scale.
- What do you understand by Zero Error (Z.E)?
- What are the two parts of the Screw Gauge?
- Name one mechanical advantage of a Screw Gauge.
- What is Focal Length?
- What are the factors that impact surface tension?
- Define the time period of a bar.
- What is Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)?
Viva questions for Chemistry are mainly based on concepts and topics from Chemistry textbooks. Here are the most common viva questions for Chemistry Class 11 and Class 12:
Viva Questions for Class 12 Chemistry
- What is Valency?
- What is the value of Avogadro’s number?
- What is the monomer of Polyethylene?
- What are polymers?
- What is the IUPAC Name?
- Differentiate between addition and condensation polymer
- What is the oxidation and reduction reaction in the electrolytic process?
- What is Titration?
Also Read: Chemistry Project for Class 12: Topics & Sample Projects
Viva Questions for Class 11 Chemistry
- Define the term ‘crystallisation’
- What is solubility?
- Why is crystallization done?
- What is Kipp’s waste?
- What is a Saturated Solution?
PhD viva questions for Biology are mainly based on concepts and topics from Biology textbooks. Here are the most common viva questions for Biology Class 11 and Class 12:
Viva Questions for Class 12 Biology
- What is litter?
- What is the shape of a pollen grain
- What is tectum?
- What are pollutants
- What is hummus
- Define Mitosis
- Why is Mitosis called Somatic Cell Division
Also Read: How to Ace Class 12th Biology Practical?
Viva Questions for Class 11 Biology
- How many types of proteins are there
- What are enzymes
- What is nucleic acid?
- Examples of high-protein food
- Full form of DNA
- Full form of RNA
- What are Mendelian Laws
- What is placentation?
- What are monadelphous and diadelphous stamens?
- What is the flower’s importance to the plant?
- To which family china rose belongs?
Admission tutors at the postgraduate level conduct viva or interviews to establish whether graduates are committed to and prepared for studying the master’s or PhD level courses. These are less formal than a job interview , but you still need to take them seriously – your aspirations to pursue overseas education could depend on your performance.
Let’s say you come from a Mass Communication background and you’ve made a documentary on “ underprivileged sections of society” . Then you might be asked about the process of the development of the movie, how long did it take to gauge the key aspects of the film or the perspective behind the direction process.
Though the research you do in your PhD is a massive achievement, you need to be prepared for the exhaustive viva session with the experts. The PhD viva questions are a chance for students to discuss their work with professionals. Its formal purpose is to ensure that the student understands and can explain their thesis. It involves lots of stinging questions and conceptually complex debates. How can PhD scholars best prepare themselves? Let us take a look at the different tips for getting through your viva questions:
- Calm down and breathe
- Believe in yourself
- Do something fun
- Go in with a good attitude
- Look presentable
- Read your thesis
- Know the rules
- Make a list of your own corrections
- Make plans to celebrate
- Try to enjoy it
Must Read: How to Crack an Interview [20 Scientifically Proven Tips]
Related Reads:-
Ans. These are some of the basic viva questions: Tell me about yourself. Summarise your research/thesis in 3 minutes. Tell us how your research contributes to knowledge discourse. What are the practical applications of your research? What is the strength and weakness of your research?
Ans. Every institution is different; some have only two examiners, while others include a convenor as well. Some institutions may require you to prepare a talk to present before the viva (this was the situation for me, and it was excellent preparation for the exam).
Ans. The examiners will frequently begin a viva with an introductory question, such as “Spend five or ten minutes telling us about your work, what you have done, and what contribution you have made” or “Summarise your work for us in a single sentence.” These are some of the first PhD viva questions that you can encounter.
Preparing for the viva questions beforehand helps you confidently answer them in front of the panel of experts who not only test your subjective knowledge but also do grading on the basis of your level of confidence.
If you are looking for admission to a university abroad and want to impress the admission committee, Leverage Edu experts can provide you with tips and tricks to ace the interview. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
what should be an ideal answer for the question “tell me about yourself?”
There is no ideal answer to the question ‘Tell me about yourself’, as it is very subjective and depends on your career trajectory. But the best way you can answer it is by covering the following points:
1. Share your background 2. Tell them about your education 3. Share any volunteer, internship or work experience you have 4 You can also tell them about your hobbies
It is advisable that you share your experience chronologically so it does not get confusing for the interviewer.
For any study abroad-related query, please get in touch with our experts through this number: 1800572000 or drop us a mail at [email protected] .
Thanks Team Leverage Edu
Thank you for this helpful information… Its really good and givea confident to me …
Hi, Venkatesh! Thanks for your comment. We are referring you few blogs to explore: Profit and Loss Formula Questions Types of Reasoning Questions in Competitive Exams Interview Questions and Answers
Most useful information for a researcher. Thanks a lot for guiding several research students.
Hello! Glad that you found the blog informative.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
100 Machine Learning PhD viva Questions
100 machine learning phd viva questions: a comprehensive guide for defending your thesis.
Are you preparing for your Machine Learning PhD viva and feeling overwhelmed by the thought of the questions you might be asked? You’re not alone. The viva, or oral examination, is a crucial part of the PhD process, and it can be challenging to know how to prepare for it.
Fortunately, we’ve got you covered. In this article, we’ve compiled a list of 100 Machine Learning PhD viva questions that are likely to come up during your examination. By reviewing these questions and preparing thoughtful answers, you can boost your confidence and improve your chances of success.
- What is your research topic, and what motivated you to pursue it?
- What are the key research questions you aimed to answer in your PhD project?
- What is the main contribution of your research to the field of Machine Learning?
- Can you explain the technical approach you used to tackle your research problem?
- What are the limitations of your research, and how did you address them?
- What are the potential applications of your research in industry or academia?
- How does your work fit into the broader context of the Machine Learning field?
- What were the key challenges you faced during your research, and how did you overcome them?
- Can you explain the methodology you used to collect and analyze your data?
- What are the key insights you gained from your research , and how do they contribute to the field?
- What are the main strengths and weaknesses of the Machine Learning methods you used in your research?
- Can you explain the differences between supervised and unsupervised learning, and when to use each method?
- What are the key steps in building a successful Machine Learning model?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using deep learning models?
- How do you handle overfitting in your models, and what techniques do you use to prevent it?
- What is regularization, and how does it help prevent overfitting?
- How do you handle missing data in your Machine Learning models?
- What is cross-validation, and how does it help evaluate the performance of your models?
- Can you explain the difference between precision and recall, and why they are important metrics in Machine Learning?
- What is the curse of dimensionality, and how does it affect the performance of Machine Learning models?
- Can you explain the difference between a generative and a discriminative model?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using decision trees for Machine Learning?
- Can you explain the difference between gradient descent and stochastic gradient descent?
- What is backpropagation, and how does it work in training neural networks?
- What are convolutional neural networks, and how are they used in computer vision?
- Can you explain the difference between a convolutional layer and a pooling layer in a CNN?
- What are recurrent neural networks, and how are they used in natural language processing?
- Can you explain the difference between a LSTM and a GRU?
- What are autoencoders, and how are they used in unsupervised learning?
- What is transfer learning, and how can it be used to improve the performance of Machine Learning models?
- What are adversarial attacks, and how do they affect the robustness of Machine Learning models?
- What is reinforcement learning, and how does it differ from supervised and unsupervised learning?
- Can you explain the difference between on-policy and off-policy learning in reinforcement learning?
- What is Q-learning, and how does it work in reinforcement learning?
- What are the challenges in scaling Machine Learning models, and how can they be addressed?
- How do you evaluate the performance of a Machine Learning model, and what metrics do you use?
- Can you explain the difference between accuracy and F1 score, and when to use each metric?
- How do you interpret the results of a confusion matrix, and what insights can you gain from it?
- What are the different techniques for feature selection, and how do you decide which one to use?
- Can you explain the difference between feature extraction and feature selection, and when to use each technique?
- What are the different types of clustering algorithms, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering?
- What are the challenges in clustering high-dimensional data, and how can they be addressed?
- What are the different types of classification algorithms, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between logistic regression and support vector machines?
- What are the different types of ensemble learning methods, and how do they work?
- Can you explain the difference between bagging and boosting?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using random forests for classification tasks?
- What are the different types of time-series forecasting models, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between ARIMA and exponential smoothing models?
- What are the different types of anomaly detection algorithms, and how do they work?
- Can you explain the difference between unsupervised and semi-supervised anomaly detection?
- What are the different types of deep learning architectures, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between a feedforward neural network and a convolutional neural network?
- What are the different types of optimization algorithms, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between batch gradient descent and mini-batch gradient descent?
- What are the different regularization techniques, and how do they prevent overfitting?
- Can you explain the difference between L1 and L2 regularization?
- What are the different types of data augmentation techniques, and how do they improve the performance of Machine Learning models?
- Can you explain the difference between data augmentation and transfer learning?
- What are the different types of hyperparameter tuning techniques, and how do they help optimize Machine Learning models?
- Can you explain the difference between grid search and random search?
- What are the different types of model interpretability techniques, and how do they help understand the inner workings of Machine Learning models?
- Can you explain the difference between LIME and SHAP?
- What are the ethical considerations in Machine Learning, and how do you ensure that your research is ethically sound?
- Can you explain the difference between bias and variance in Machine Learning, and how do you balance them?
- What are the challenges in building Machine Learning models for real-world applications, and how do you address them?
- Can you explain the difference between batch learning and online learning, and when to use each method?
- What are the different types of data preprocessing techniques, and how do they prepare data for Machine Learning?
- Can you explain the difference between normalization and standardization?
- What are the different types of distance metrics, and how do they measure similarity between data points?
- What are the different types of optimization problems in Machine Learning, and how do you solve them?
- Can you explain the difference between convex and non-convex optimization problems?
- What are the different types of regularization techniques, and how do they prevent overfitting?
- Can you explain the difference between dropout and weight decay regularization?
- What are the different types of learning rate schedules, and how do they impact the training of Machine Learning models?
- Can you explain the difference between a fixed learning rate and an adaptive learning rate?
- What are the different types of data imbalance, and how do you handle them in Machine Learning?
- Can you explain the difference between oversampling and undersampling?
- What are the different types of neural network architectures for sequence modeling, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between a Recurrent Neural Network and a Transformer?
- What are the different types of attention mechanisms, and how do they improve the performance of Machine Learning models?
- What are the challenges in building Machine Learning models for natural language processing, and how do you address them?
- Can you explain the difference between word embeddings and character embeddings?
- What are the different types of text classification algorithms, and how do they differ from each other?
- What are the different types of named entity recognition algorithms, and how do they work?
- What are the different types of sentiment analysis algorithms, and how do they determine the sentiment of a piece of text?
- What are the different types of topic modeling algorithms, and how do they discover topics in a corpus of text?
- What are the different types of Machine Learning models for image classification, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between a Convolutional Neural Network and a Residual Neural Network?
- What are the different types of object detection algorithms, and how do they detect objects in an image?
- What are the different types of image segmentation algorithms, and how do they segment an image into regions?
- What are the different types of generative models, and how do they generate new data samples?
- Can you explain the difference between a Generative Adversarial Network and a Variational Autoencoder?
- What are the different types of Machine Learning models for speech recognition, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between a Hidden Markov Model and a Deep Neural Network for speech recognition?
- What are the different types of Machine Learning models for time-series forecasting, and how do they differ from each other?
- Can you explain the difference between a recurrent neural network and a convolutional neural network for time-series forecasting?
- What are the different types of Machine Learning models for recommender systems, and how do they recommend items to users?
- Can you explain the difference between collaborative filtering and content-based filtering for recommender systems?
These 100 Machine Learning PhD viva questions cover a wide range of topics and concepts in Machine Learning, from basic concepts such as linear regression and decision trees, to more advanced topics such as deep learning, natural language processing, and image recognition.
By preparing for these questions, you will be well-equipped to defend your thesis and demonstrate your knowledge and expertise in the field of Machine Learning. Remember to keep practicing and honing your skills, as the field of Machine Learning is constantly evolving and there is always something new to learn. Good luck with your viva!
Also Read: Top 50 Possible PhD Viva Questions
- artificial intelligence
- Data Science
- decision trees
- Deep Learning
- graduate school
- image recognition
- linear regression
- Machine Learning
- natural language processing
- neural networks
- PhD Viva Questions
- thesis defense
PhD in India 2024 – Cost, Duration, and Eligibility for Admission
Effective tips on how to read research paper, six effective tips to identify research gap, most popular, 100 connective words for research paper writing, phd supervisors – unsung heroes of doctoral students, india-canada collaborative industrial r&d grant, call for mobility plus project proposal – india and the czech republic, iitm & birmingham – joint master program, anna’s archive – download research papers for free, fulbright-kalam climate fellowship: fostering us-india collaboration, fulbright specialist program 2024-25, best for you, 24 best free plagiarism checkers in 2024, what is phd, popular posts, how to check scopus indexed journals 2024, how to write a research paper a complete guide, 480 ugc-care list of journals – science – 2024, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 258
- Journals 234
- Fellowship 128
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 92

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence


Boston College Libraries

The Answer Wall
Answering questions at Boston College O’Neill Library
I want to be a professor. Do I have a good chance in BC for a PhD program?


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examiners are interested in knowing your understanding of the research, its methods, analysis and findings, conclusion and implications, etc. Despite the differences in every PhD viva, you must be prepared to answer these common questions logically. Below are some popular PhD viva questions to prepare: 1. Tell me about yourself.
The PhD viva is an oral examination conducted by a panel that takes place as part of the PhD defence. The panel asks a PhD student questions about their research project and thesis, which requires the candidate to demonstrate knowledge in the subject area and understanding of how it applies to their project's topic.
Top 18 PhD Viva Questions | Examples. The PhD viva is an oral assessment held by a committee during the PhD defense. This evaluation involves the committee posing inquiries to the PhD candidate regarding their research work and dissertation. The candidate must showcase their expertise in the field and how it relates to their project's focus.
1. Tell us about your study. Usually the first question is an opener and is asked with the goal of breaking the ice and getting you talking about your thesis. The items the panel presents to you will start broad and get more specific and involved as your viva progresses.
Namely the purpose of the PhD viva (or defence) is to check that: You did the work; You understand the work; The research is up to the standard for a PhD. For more detail see my separate post here including Imperial's PhD viva mark scheme. In hindsight I probably didn't spend as much time preparing for my viva as is normal.
The viva voce, shortened to viva, is an oral examination where you are expected to 'defend' your thesis, and the quality of your research will be assessed. The viva will take place usually within 3 months of submitting your thesis; it is a required examination in order to achieve a postgraduate research degree.
Mosed Asked PhD Thesis Defense Viva-Voce Questions and Answers. These are all the 50 Common Dissertation PhD Viva Questions and Sample Answers you can prepare to answer during the defense. Thesis Title: "Understanding the Impact of Social Media Engagement on Consumer Behavior: A Mixed-Methods Approach". 1.
The viva voce, known commonly simply as the 'viva' or the. PhD 'defence', is a landmark occasion to evaluate a doctor-. al candidate's written thesis (or dissertation) and their com ...
A viva voce, more commonly referred to as 'viva', is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student's knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners. In order to assess the student and their work around their research ...
Give a few detailed answers in the opening 15 minutes, demonstrating knowledge, describing your thinking and working - then the examiners are likely to relax into the viva. If the first few ...
3. Anticipate the viva questions. The examiners will have prepared a series of questions for you to answer at the viva voce, but this is nothing to get too concerned about. The questions will all be based on your thesis - what it's about, what you did and what you found out - and why this matters, in relation to your field of study.
Our free PhD Viva Questions template lets you familiarise yourself with the most common questions. It's been designed in collaboration with Professor Peter Smith, author of Palgrave's The PhD Viva. The template is interactive and editable, meaning you can fully prepare model answers in advance of the big day. Enter your email address and we ...
PhD Viva Guide A Springboard for your PhD Viva Preparation. i This initiative was partially funded by the HEA under the Strategic Innovation Fund 2. ... After the question and answer discussion, it is customary to ask the candidate to step outside while the examiners deliberate. This
Viva Question Repository. The Viva Voce (aka Defense) Question Repository! This is a repository of questions that were asked at Vivas of students, just like you. Look up what questions you can expect in your Viva! Don't get caught off-guard. (Pro tip: Want to sort by more than one heading? Hold shift and click the headings you want to sort by.)
Common PhD Interview Questions. In this guide, we'll share 11 common PhD interview questions and our suggestions on how to answer them. A PhD interview is an essential step in securing a doctorate position. This is because it enables the prospective supervisor to get to know you better and determine whether you'd be a good fit for the project.
Credit: unsplash, CC0, @brandsandpeople. Dr Jenny Scoles from the Institute of Academic Development provides some helpful tips in how to prepare for your PhD viva by being aware of how you answer the examiners' questions. This post is part of the Learning and Teaching Enhancement theme: Showcasing the Doctoral College.
25 PhD Viva Questions A PhD viva is a final examination in which a candidate answers questions from an academic panel on their work and understanding of their chosen subject area. This is often used to determine whether the candidate has effectively proved that they have learned enough about their specialised study topic to produce original work.
Take a deep breath, gather your thoughts, and focus on understanding the question before formulating your response. Remember that your examiners are not trying to catch you off guard but rather assess your critical thinking and problem-solving skills. 2. Listen Attentively.
Hello friends. In this video I had discussed basic top 10 questions asked in PhD viva, research project viva.I had also given probable answer of each questio...
Be honest about the things you find challenging, but identify them as training needs and discuss how you expect to improve upon them as part of your PhD. Do answer: I feel that I'm a good written communicator. My existing academic and professional work demonstrates an ability to put forward ideas clearly and concisely.
These 100 Machine Learning PhD viva questions cover a wide range of topics and concepts in Machine Learning, from basic concepts such as linear regression and decision trees, to more advanced topics such as deep learning, natural language processing, and image recognition. By preparing for these questions, you will be well-equipped to defend ...
If you'd like a quicker answer to your question and don't mind talking to a human, ... Do I have a good chance in BC for a PhD program? May 7, 2024; May 7, 2024; Should I tell my roomies I'm in love with them? May 6, 2024 [Stars and a smiley face] May 6, 2024;