
- Innovative Prompts
- Strategies Packs
- Skills Packs
- SOPs Toolkits
- Business Ideas
- Super Guides
- Innovation Report
- Canvas Examples
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Discounted Bundles
- Search for:
No products in the cart.
Return to shop

IKEA SWOT Analysis
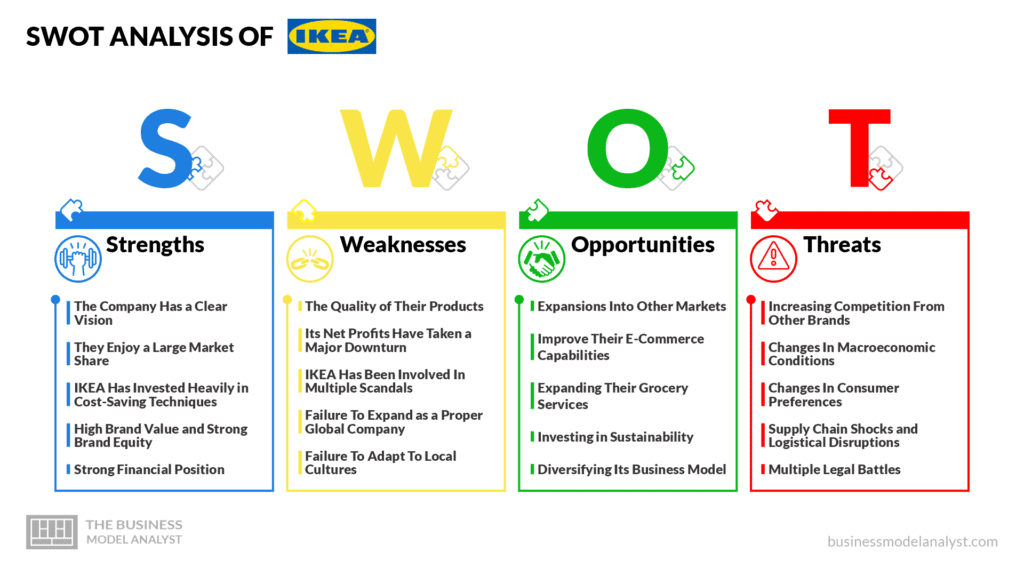
IKEA is an international brand that has built a reputation for itself as the largest furniture retailer in the world and an expert in the design of ready-to-assemble furniture. However, the company has since diversified into numerous sectors and has equally found success in a number of them. In order to understand the factors behind this success, let’s take a look at the IKEA SWOT analysis , examining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to its business model.
A Brief Look at IKEA
IKEA is a well-known brand in many countries, especially in North America, Europe, and Australia. The Swedish conglomerate is known for offering an impressive range of affordable ready-to-assemble furniture based on traditional Scandinavian designs. Not only are their products distinctive, but they also employ a wide range of innovative design techniques and a well-known self-assembly policy, which means that customers have to assemble the furniture themselves.
Initially starting from a humble beginning as a furniture company founded by Swedish business magnate Ingvar Kamprad in 1943, the company grew steadily over the years to become the world’s largest furniture retailer and a respected conglomerate with a wide investment portfolio. This includes stakes in a wide range of areas ranging from the food and dining industry to AI-based interior design, real estate, and even smart home technology.
The company operates in over 60 countries worldwide and has more than 230,000 workers. The company posted gross revenue of over €44 billion in 2022, making it one of the most profitable companies in the industry in terms of gross profit. However, that same year the company posted a net profit of about €700 million , indicating that it operates on a relatively slim profit margin. This is consistent with the company’s business plan, which involves providing quality furniture at a price that can be accessible to the broadest number of buyers within its target demographic.
IKEA Strengths
Let’s examine some of the key internal features which give IKEA a significant competitive advantage over its competitors.

The Company Has a Clear Vision
IKEA has always been a company with a clearly defined idea of what its brand stands for and how they plan to achieve this vision. This has enabled the brand to maintain a degree of stability over the years despite its expansion, successes, failures, and changes in the market environment. Such stability and clarity have also enabled them to build a well-organized and very successful business model whose benefits are passed on to the consumers as great products and top-notch, reliable services.
One of the aspects of this vision is its brand positioning. IKEA has carved out a niche for itself as a reliable source of affordable, yet surprisingly durable furniture and other home accessories. This allows it to target a very specific demographic who require such products and gain their trust with decades of reliable services.
They Enjoy a Large Market Share
IKEA has been the largest furniture retailer in the industry since 2008 and enjoys several benefits which come with this position. This includes a loyal customer base, a consistent revenue stream, favorable brand equity, and the advantages which come with the widespread popularity of the brand. A large market share also allows a business to spend less money on advertising and, by extension, reduces the Customer Acquisition Cost (a measure of how much a company pays in the process of acquiring new customers).
Another advantage is the high barrier of entry this situation creates for IKEA’s competitors. They have a more challenging time carving out a niche for themselves since IKEA is already fully entrenched within the market, meaning that they will spend more to acquire new customers (i.e., higher customer acquisition costs) while contending with lower revenue and more restricted access to capital.
IKEA Has Invested Heavily in Cost-Saving Techniques
IKEA as a company has built its image and entire business model as a budget-friendly alternative where people can purchase furniture, kitchen appliances, home decorations, and so on. They achieved this in several ways, but it can mainly be described as utilizing cost-saving techniques which allow the customer to enjoy lower prices. These techniques typically involve two key components; product and process innovation .
IKEA makes use of a flat packaging system that allows furniture to be transferred as disassembled pieces instead of a whole unit. This economizes space, cuts down shipping costs, and will enable customers to choose custom pieces. They also have beneficial arrangements with their raw materials suppliers, which allows them to make bulk purchases at significantly lower per-unit costs due to the advantages of economies of scale.
The company also makes use of a range of innovative design and production techniques, which allow them to cut down on costs by reducing the number of raw materials required. For example, their well-known technique of placing layers of wood over a honeycomb structure helps them cut down on wood usage without compromising on sturdiness and integrity.
IKEA also runs a string of self-help stores that allow customers to browse through and choose their furniture without too much interference from staff. This helps lower wage costs and, by extension, increases the profit margin of the company. Buyers are provided detailed installation guides to enable them to independently assemble the products they buy.
Alternatively, the business has acquired the freelancing company known as TaskRabbit, which also offers furniture installation services, allowing users to decide for themselves whether they require the services of these companies or not. IKEA also has a Take It Home policy, which will enable buyers to purchase and transport their items independently, allowing IKEA to avoid delivery costs.
High Brand Value and Strong Brand Equity
As we mentioned earlier, IKEA is the largest furniture retailer in the world and enjoyed a brand value of $17.43 billion in 2022. Your brand value is a monetary estimate of the value of your brand equity. Brand equity, on the other hand, refers to the commercial value enjoyed by a company based on the social perception of its products or services by consumers. There are three main components to brand equity; brand loyalty (how likely users are to stick with the brand), brand awareness (how well-known the brand and its products are), and brand association (how people feel about the brand).
These are essential areas where the company has a strong comparative advantage over competitors. IKEA is a well-known company with a loyal customer base that appreciates the affordable products the company offers and associates the brand with reliability, affordability, and pragmatism without sacrificing important aesthetics such as beauty and ergonomics.
Strong Financial Position
IKEA is a company that has long taken pride in financial responsibility, as well as its consistent profitability over the years. The company posted an annual profit of €44.6 billion in 2022, an increase from the €41.9 billion realized the previous year. This trend suggests one of steady growth within the company and lends credibility to the success of its business model. This improves investor confidence, allows the company to obtain low-interest financing, and gives them room to take more risks than their competitors as they have stronger backing.
Diverse Investment Portfolio
While IKEA is best known for its wide range of furniture and home appliances, the business has also invested in several other sectors. This includes areas such as design consultation services using AI technology, smart homes, real estate, renewable energy, and even furniture rentals. The company has also invested significantly in the food industry and now operates a chain of restaurants that contribute up to 5% of its total annual sales.
It has also invested in the hospitality industry with a chain of hotels all around the world, department stores, telecommunications, and ICT, as well as other key areas. This strengthens the position of the brand by allowing them to enjoy a diverse portfolio and increases the likelihood of profitability.
The Company Has Built a Highly Successful Franchise
Most IKEA stores are not owned directly by the company, but instead operate as franchises that pay an annual franchise fee to the parent company. There are several advantages of this to the franchisor (IKEA).
First of all, it gives the business access to capital, which can be obtained from the franchisees instead of accruing debt which is financed through bank loans. This reduces the debt burden of the company and also shifts a significant amount of the risk of starting up a new location to the franchisee. It also allows the company to expand more rapidly, as put the costs And logistical concerns involved in opening a new business are shared between IKEA and the franchisee.
It also helps improve the brand awareness of the business and, by extension, its customer base and market share. By operating a franchise, IKEA can reduce its involvement in certain operations such as employee training, hiring, logistical management, and so on.
Innovative Design Concepts
Despite their practical and ergonomic design, each piece of IKEA furniture employs a range of innovative techniques in terms of aesthetics, production, and even the design process itself. For example, the company practices what is called a reverse design process. This means that they start with a price range and then reverse engineer products that suit this cost in terms of materials used and design theme. The advantage of such a method is that it allows the company to keep its products within a tight price range.
Another important feature of the design themes is its diversity. The company offers a wide range of furniture and appliances suitable for workplaces, homes, studios, and so on. Each of these is well crafted to match and accentuate the atmosphere within which they are placed.
Strong Understanding of Its Target Demographic
It is common knowledge that IKEA is the dominant player within the retail furniture industry because it has carved out a strong niche for itself as an affordable source of quality products. Also, in its other business ventures, the company has invested a significant amount of resources in studying, analyzing, and noting certain characteristics and trends among its customers. This has allowed them to capitalize on chasing trends to invest in popular areas such as AI-aided design, smart home technology, and sustainable energy.
Their Products Are Easy To Assemble
IKEA sells ready-to-assemble furniture. This means the company does not assemble its furniture before selling it to a customer, but rather shifts this task to the buyer. Therefore, the business must make the process of assembly as quick, easy, and safe as possible. They have achieved this through the use of innovative design strategies as well as a well-detailed instruction manual that offers step-by-step directions on how to fully and safely assemble your furniture.
Successful Acquisitions and Partnerships
Over the years, the business has been able to strengthen its position as a global leader through a series of successful acquisitions and partnerships . Some notable acquisitions made by the company include the purchase of Veja Mate (an offshore wind farm located in the German Exclusive Economic Zone of the North Sea) in 2015, the AI imaging startup Geomagical Labs in 2016, and TaskRabbit Inc. This online marketplace allows buyers to hire the services of various freelancers in a wide range of everyday tasks such as delivery, cleaning, furniture assembly, and general repair work.
IKEA Weaknesses
Despite all their strengths, there are some areas within the IKEA business model which could be improved upon.

The Quality of Their Products
Although IKEA is well-known for the reliability of their products, the affordability of those same products comes at a cost which is quality. Accusations of shabby workmanship and a disregard for safety regulations are relatively commonplace, and have also become one of the somewhat defining features of the brand. For example, multiple complaints have been lodged over the flimsiness of several of their particleboard-based furniture, uncomfortable mattresses, weak glassware, as well as a host of other important complaints.
These complaints have also extended to their food courts, with the menu being described generally as straightforward, and affordable, with some standout dishes but generally mediocre. This, of course, detracts from their reputation and improves the position of competitors who offer higher-end products and services.
Its Net Profits Have Taken a Major Downturn
While the company is still in a strong place financially, its financial reports in 2022 showed a significant fall in net profits from €1.6 billion posted in 2021 to only €287 million posted in 2022 after taxes. The company has acknowledged the worrying nature of the reports. Still, it has also provided several reasons for this sudden fall in profitability, such as rising operating costs due to inflation and the sudden withdrawal of all its investments within the Russian space.
These developments reduced the company’s operating profit margins from 7% to 4%, a significant blow to a business model which already operates on an operating profit margin below the industry standard. This is especially difficult because the company’s business strategy is built strongly on offering cheaper prices than its competitors, so increasing the prices of its goods and services would be especially damaging to its reputation.
IKEA Has Been Involved In Multiple Scandals
It is nearly impossible for a business of this size in scope to survive for so long without a few scandals. IKEA has had its fair share of bad press with regard to a variety of delicate issues. For example, the environmental impacts of the company have been under significant scrutiny for years now, with the company being accused of being responsible for 1% of global wood consumption annually. While the company claims that most of this wood is sourced sustainably, and they have invested heavily in recycling, there is still evidence suggesting that a significant portion of this wood is sourced from illegal logging activities.
In the mid-2010s, the company also faced mounting pressure and criticism over several deaths among young children caused by poorly designed furniture. This led to the recall of over 29 million products and as well as a wrongful death lawsuit that cost the company over $50 million in compensation to the families of the deceased children.
In the early 2010s, IKEA in France was accused of intruding upon the privacy of its employees by illegally accessing private police reports. The company has also been mentioned in several other scandals, such as price discrimination, having negative impacts on the local businesses and communities with outlets to set up, cultural imperialism, as well as religious and ideological discrimination. There was also a significant stir within its food sector when it was discovered that its famous Swedish meatballs contained traces of horse meat, leading the brand to cut ties with several of its key suppliers. However, the damage had already been done.
Failure To Expand as a Proper Global Company
For a brand as well-known and successful as IKEA, the company has failed to adequately utilize its reputation and resources to expand into a wide range of markets. Currently, IKEA only has 460 outlets in 63 countries all around the globe, well below what would be expected from a global brand. While this is undoubtedly a significant accomplishment, it is not the level of globe-spanning dominance you would expect from the world’s largest furniture retailer.
The vast majority of these stores are concentrated In North America, Europe, and Australia, while China is the major location in Asia. They have a smattering of stores across South America, but the company is virtually nonexistent in Africa. This leaves an entire continent as an untapped market and means that there is a largely untapped market that their competitors could tap into.
Failure To Adapt To Local Cultures
Even within the relatively few regions where the company has expanded its presence, it has been accused of failing to adapt its products and advertising adequately to the local cultures and preferences of the people living there. Virtually all its products retain the original Scandinavian design for which the brand is known, irrespective of whom it is being sold.
However, the company has accepted this criticism. It has made some strides to improve its branding and marketing to unique cultures, as well as tweak product designs to better suit the preferences of users of these items.
Their Self-Assembly Model Is Somewhat Controversial
While allowing their customers to assemble their IKEA furniture themselves drives down costs as well as maximizes shipping space, it has also led to some controversies with customers encountering difficulty during the assembly process. This may be due to faulty design or a failure to follow the instructions during setup. Either way, this may lead to an unsatisfactory product with a shorter lifespan or even injury due to faulty furniture.
Accusations of Poor Working Conditions
IKEA has made strides to ensure that they ensure fair working conditions for all their employee. However, despite their efforts, there have been accusations of poor working conditions and unfair compensation, leading to multiple lawsuits, strikes, and union actions against the business. This, of course, leads to reduced productivity, loss of revenue due to the fall in productivity and compensation payments, as well as a negative brand image.
Some Customers Have a Negative Perception Of the Brand
IKEA has developed a reputation for providing affordable products. Still, some people have also perceived this as the company offering cheap or substandard products. This, of course, negatively affects the image of the company and drives down revenue, as many buyers may opt for other options.
IKEA Opportunities
Here are some external factors IKEA can capitalize on to improve its business model and position within the market.

Expansions Into Other Markets
IKEA should leverage its vast resources and superior brand value to expand into various untapped markets such as South America, Africa, and Asia. This will vastly increase their revenue and influence, as well as allow them to push out potential competitors before they can establish a strong foothold.
Improve Their E-Commerce Capabilities
The company has seen significant growth in its e-commerce capabilities, with the proportion of online sales climbing steadily over the years. E-commerce is fast becoming the most popular way people purchase items. By investing smartly in this area, IKEA can give itself a competitive advantage over other players in the industry. Most of its online sales come from its furniture and appliances section, but there is still room for the company to expand its e-commerce sales in other areas of the company.
Luckily, their development into online retail was spurred on by the pandemic. The sudden increase in online shoppers, coupled with the closing down of the majority of their physical outlets, led the company to invest significantly in creating a business model in which outlet stores were seen as fulfillment centers instead of warehouses where buyers had to physically inspect and purchase products. They could seamlessly make their purchases online and simply pick them up at an outlet if they decided against home delivery. Also, through their investment in AI-aided design, customers can digitally visualize how the furniture will appear without having to purchase it physically.
Expanding Their Grocery Services
The company is known for offering various groceries both as a part of its physical outlets and as a part of its online e-commerce site as well. Though the company has made significant investments in expanding this area within the past few years, there is more room for growth as groceries only make up a minor part of its revenue stream. Diversification will also help spread risk and increase the stability of the business if there is a downturn in any of its other investments.
Investing in Sustainability
IKEA has spent significant resources on ensuring that all the materials used for its products are derived from sustainable sources and follow standard ethical protocols. This is important because modern shoppers care not only about the quality of the materials they purchase, but also the sources.
Despite this, the company has been levied with allegations of sourcing some of the raw materials, especially wood, from illegal logging activities. Assuring both investors and customers of their dedication towards ending this practice, as well as improving the reusability of their raw materials, is sure to enhance their brand image and, by extension, sales.
Diversifying Its Business Model
One of the features for which IKEA is well-known is its utmost dedication to its business model of providing affordable yet durable furniture and home appliances. While this has served the business admirably over the years and is definitely one of the critical cornerstones of its success within the industry, it has also narrowed its vision in terms of diversifying into other well-known niches, such as providing high-end furniture.
The company has the resources, leadership skills, and brand equity to carry out such as pivot. It has also successfully launched several successful side brands in other sectors, such as food, design, AI, and the hospitality industry. Therefore, there is little reason to doubt that it could not break successfully into the high-end furniture market.
Further Acquisitions and Partnerships
IKEA still holds a dominant position within the market. Still, the presence of other strong competitors means that the brand must continuously innovate and strive to maintain this status. One of the ways it can achieve this is through investing in further successful acquisitions and partnerships, which can improve the ability of the brand to successfully carry out its core value proposition to its customers.
IKEA Threats
Here are some external factors that could be detrimental to the growth and survival of the company.

Increasing Competition From Other Brands
While IKEA is still the major player in the retail furniture industry, several other brands have appeared which offer the same value proposition of affordable furniture and home appliances. Brands such as Walmart now offer a wide range of furniture and home appliances which are also budget-friendly and also do not require any further assembly.
Changes In Macroeconomic Conditions
While this may sound counterintuitive, improved macroeconomic conditions may be harmful to the IKEA business model. The business idea is built around its ability to provide low-cost affordable housing appliances and furniture to customers. Improved macroeconomic conditions mean that these same customers are suddenly now more well off and may opt to purchase pricier furniture options, which also offer the promise of better quality as well.
Changes In Consumer Preferences
IKEA is also well known for being faithful to a particular aesthetic which has served them well over the years. However, rapid changes in customer preferences and a stubborn refusal to innovate and change with changing times may pose a significant risk to the continued survival of the business.
Supply Chain Shocks and Logistical Disruptions
IKEA runs a business that is strongly dependent on its ability to organize and capitalize on an increasingly complex supply chain that spans multiple continents and involves dozens of independent companies. The company has already seen significant disruptions to its supply chain in subsequent falls in revenue during the COVID pandemic, as well as during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Therefore, such unexpected supply chain disruptions significantly. Therefore, such unexpected supply chain disruptions cause significant harm to the business by rendering them unable to perform their core value proposition, leading to higher prices and reduced availability of merchandise.
Multiple Legal Battles
IKEA is a company that has seen its fair share of legal battles from issues ranging from injury claims to poor working conditions and even environmental sanctions. All of these lead to revenue loss as well as create a negative brand association which is detrimental to the business.
IKEA is a force to be reckoned with within the world of furniture retail. Its innovative design techniques, unique business model, and clear vision are some of its greatest strengths. However, recent global upheavals, a failure to improve its business model, or an inherent reluctance to change its primary design may be a significant threat to its position as a market leader. Despite this, IKEA does not seem poised to relinquish this position anytime soon.
Daniel Pereira
Related posts.
Dunkin’ Donuts SWOT Analysis
Dunkin’ Donuts is a popular American multinational coffee and doughnut company known for its delicious [...]
Nike SWOT Analysis
From their iconic “swoosh” logo to their equally iconic range of footwear, Nike, Inc. is [...]
Best Buy SWOT Analysis
Best Buy is an American multinational consumer electronics retailer headquartered in Richfield, Minnesota. It was [...]
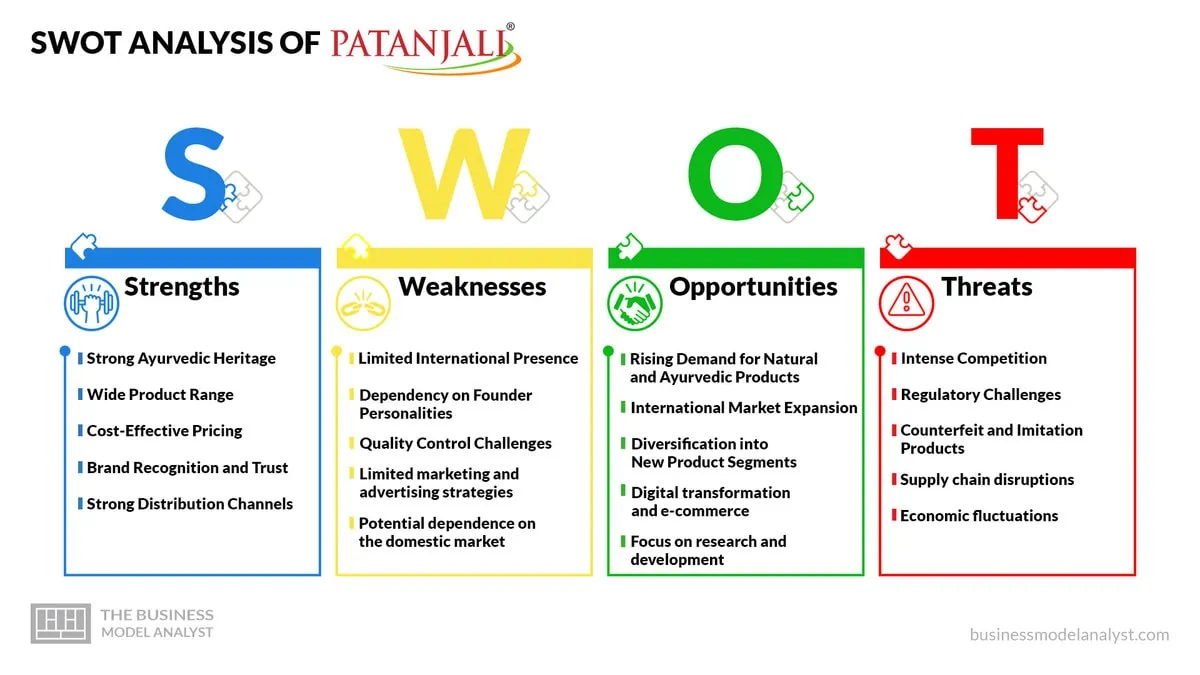
Patanjali SWOT Analysis
The Patanjali SWOT analysis delves into the internal dynamics and external factors influencing the trajectory [...]

Adidas SWOT Analysis
Adidas is a well-known company that creates and produces sporty and fashionable footwear, clothes, and [...]

McDonalds SWOT Analysis
Like every other company, McDonald’s SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the strengths, weaknesses, [...]
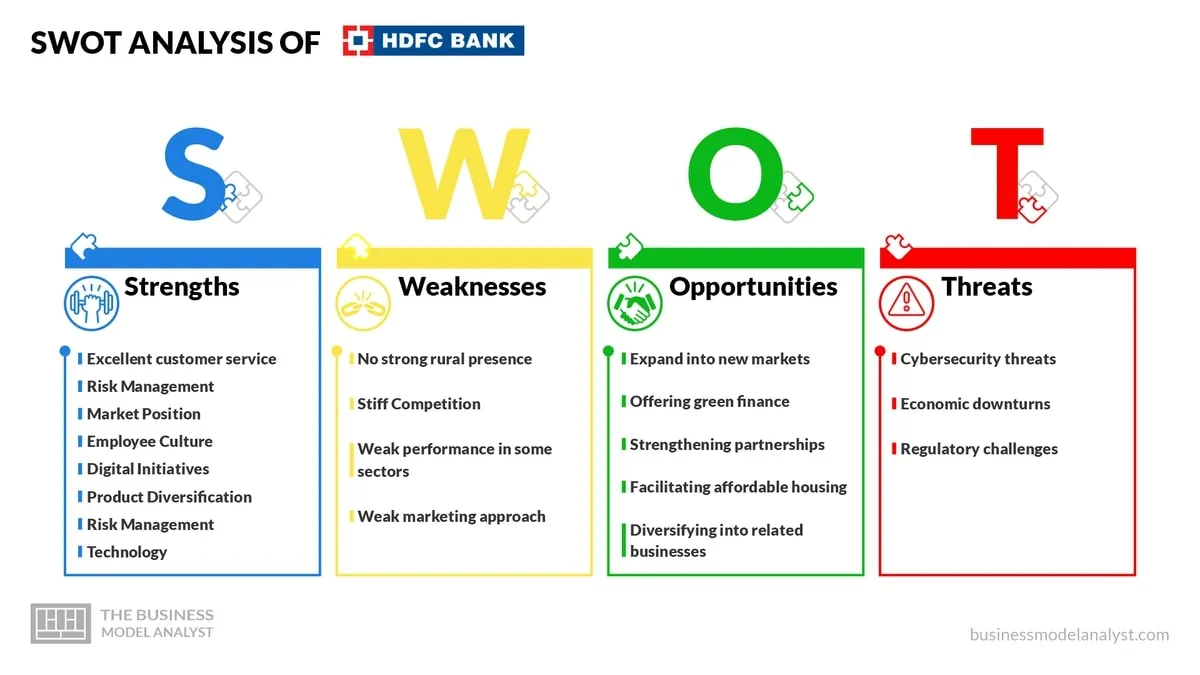
HDFC Bank SWOT Analysis
HDFC Bank, headquartered in Mumbai, India, is a leading private sector bank that provides a [...]
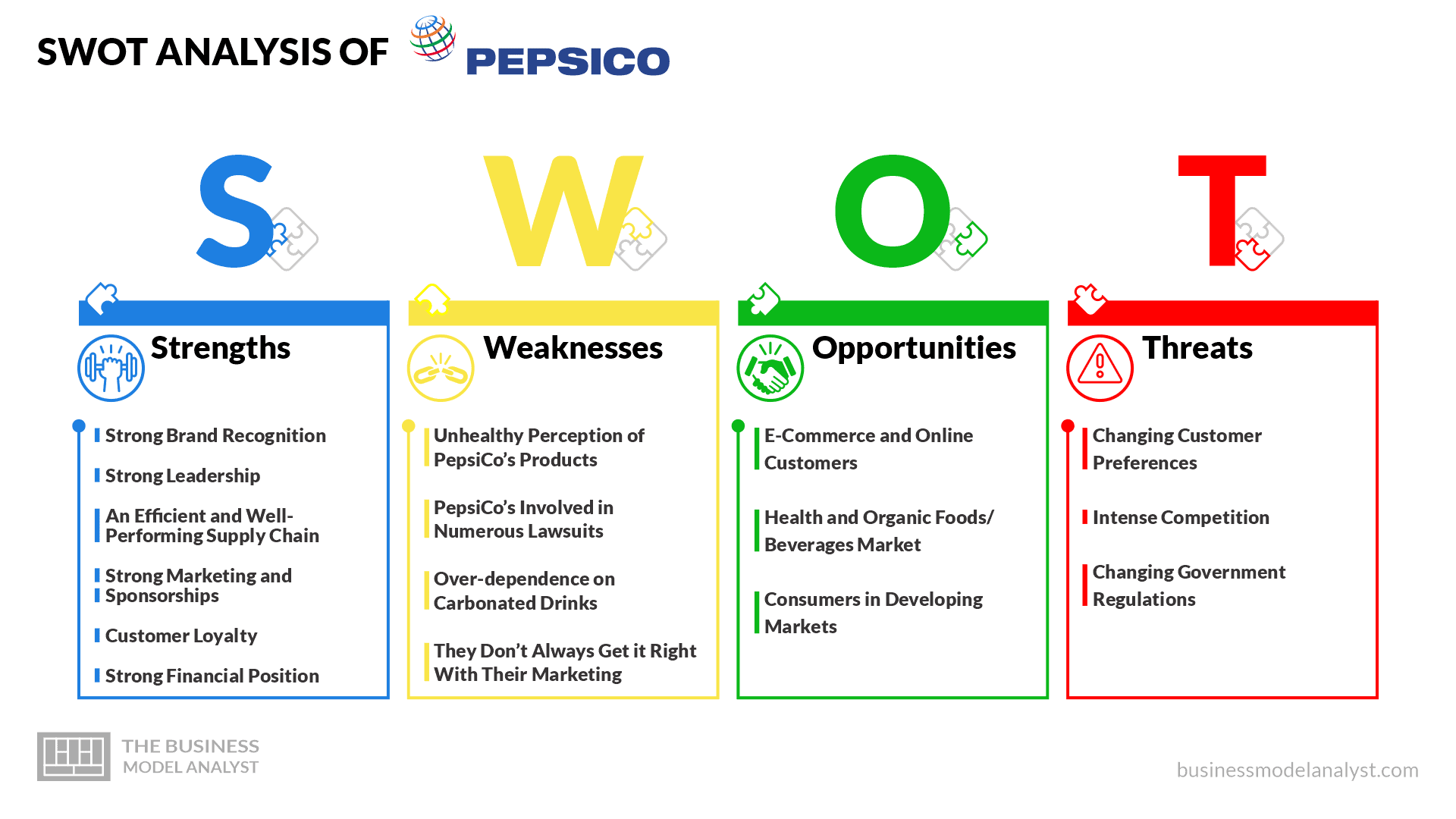
PepsiCo SWOT Analysis
PepsiCo is one of the leading food and beverage companies in the world. A typical [...]
RECEIVE OUR UPDATES
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?

SWOT Analysis of IKEA 2023

This is IKEA International Group SWOT analysis. For more information on how to do a SWOT analysis please refer to our article.
Company Overview
| Name | IKEA International Group |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1943 |
| Logo | |
| Industries served | Retail |
| Geographic areas served | Worldwide |
| Headquarters | Netherlands |
| Current CEO | Jon Abrahamsson Ring |
| Revenue (euros) | 44.6 billion € (2022) |
| Net Income (euros) | 0.287 billion € (2022) |
| Employees | 231,000 (2022) |
| Main Competitors | Argos, Ashley Furniture Home Stores, B&Q, Bob’s Discount, John Lewis, Pier 1 Import, Rooms To Go and many others. |
You can find more information about the business in its official website or Wikipedia’s article .
IKEA SWOT Analysis
| 1. Customer knowledge 2. Constantly using innovations to drive costs down 3. Supply chain integration 4. Brand reputation and market presence 5. Diversified product portfolio | 1. Negative publicity 2. Decreasing quality 3. Standard products |
| 1. Further expansion into developing economies 2. Growing online sales 3. Expansion to growing grocery market | 1. Intensifying competition 2. Growth of average consumer income |
- Customer knowledge. One of the key competitive advantages IKEA has is its extensive knowledge about the customers. The company understands the purchasing factors that influence customers to buy and implements the best practices to induce that decision. IKEA offers low prices and a huge range of products. Designers constantly introduce new design products that look stylish in the eyes of customers. All the products are designed so it would be easy to transport and assemble. Moreover, the company offers the widest product range and positive shopping experience. All of these factors are aligned with what customers want and need and which results in higher sales. Without such extensive customer knowledge and best practices to benefit from that knowledge, IKEA would be unable to outcompete its current competitors.
- Constantly using innovations to drive costs down. Low prices are the cornerstone of IKEA business idea and the the company always try to do things as efficient and cost-effective as possible. To drive costs down all the time, the company must find new and innovative ways to do that and to incorporate them in its businesses model. The business’ innovations include new materials that contribute more to sustainable environment and are less costly or using newest ways of packaging, handling and transporting materials.
- Supply chain integration. IKEA is committed to long lasting relationships with its suppliers. In this way, the company can order large volumes and benefit from lower prices and greater quality while suppliers are assured of guaranteed orders. IKEA sources its materials close to suppliers to reduce transporting costs. The company also uses IWAY approach to closely integrate suppliers with its supply chain. All the efforts of closely integrating supply chain results in lower costs and a competitive advantage.
- Brand reputation and market presence. According to Interbrand, IKEA is the most valuable furniture retailer brand in the world, valued at nearly $US 12.8 billion in 2012. The business operates 332 stores in 38 countries and is present in the major world markets. More than 600 million customers visit IKEA stores every year. Worldwide market presence and strong brand reputation ensures that customers will often choose IKEA over its competitors.
- Diversified product portfolio. Unlike IKEA’s largest competitors, the company has fairly diversified businesses. In addition to its furniture products, the company operates restaurants, houses and flats. Although, firm’s main business is designing, manufacturing and selling furniture it is not so affected by the changing forces in this market as other furniture retailers.
- Negative publicity. The company has been criticized many times for issues like poor treatment of employees, questionable advertising practices or lobbying government authorities. Negative publicity decreases brand reputation and customer loyalty.
- Low quality of products and services. IKEA is unable to find compromise between continuous cost reductions while maintaining the same quality of products. According to UK Customer Insights report on IKEA by Verdict, IKEA’s customers are less satisfied with its product and services quality than the average customer in UK buying at other stores. Firm’s cost reductions lead to decreasing product quality, which was followed by higher number of products returned and damaged brand.
- Standard products. IKEA’s main competitive advantage derives from low costs, which in part are achieved due to standardized products. Standardized products attract fewer customer segments. Therefore, the business inability to offer better quality more customized products allows its competitors to fill that niche and fortify their position in it.
Opportunities
- Further expansion into developing economies. Retail markets grew by at least 5% on average in emerging markets in the last year, opening huge opportunities for IKEA’s revenue growth. The company currently operates in most of the developed economies but hasn’t firmly stepped into developing economies, except China. There are great opportunities for IKEA to expand into Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia and Malaysia to increase its presence in these markets to sustain future growth.
- Growing online sales. Online retail sales account for 17% and 4% of total retail sales in UK and US respectively. Online sales grow constantly and with 870 million visitors to its website IKEA could exploit this opportunity and benefit from increased sales and lower costs.
- Expansion to growing grocery market. The current trend of eating healthier food has resulted in higher demand for grocery products in many developed economies. IKEA has an opportunity to expand its grocery business by introducing more grocery stores in its current retail places. The company is already successfully managing its food outlets, so this expansion opportunity would be well aligned with the current operations.
- Intensifying competition. Many low cost retailers such as Walmart, ASDA or Tesco are entering homeware specialists market where IKEA operates. These large retailers have similar specifics as IKEA, including low costs, well managed supply chain and huge market presence and can easily gain some market share from IKEA.
- Growth of average consumer income. Growth of average consumer income means that people buy less low price and low quality products, which is exactly what IKEA offers in its stores. With the rising income people will be less attracted to IKEA and will turn to retailers that offer higher quality homeware products.
- IKEA (2013). About IKEA. Available at: http://www.ikea.com/ms/en_GB/about_ikea/index.html
- The Times 100 (2012). Business Case Studies. Ikea case study. Available at: http://businesscasestudies.co.uk/ikea/swot-analysis-and-sustainable-business-planning/strengths.html#axzz2VB9TPpjz
- Interbrand (2012). Best Global Brands in 2012. Available at: http://www.interbrand.com/en/best-global-brands/2012/Best-Global-Brands-2012.aspx
- Wikipedia (2013). IKEA. Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IKEA
- SWOT Analysis of Walt Disney 2023
- SWOT Analysis of Blackberry 2023
- SWOT analysis of BMW 2023
- SWOT Analysis of eBay 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

IKEA SWOT Analysis

Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of IKEA. IKEA is a multinational company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and selling ready-to-assemble furniture, kitchen appliances, and home accessories. Founded in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad in Älmhult, Sweden, IKEA has become one of the world’s largest and most successful furniture retailers.
Business Model: IKEA’s business model is centered around providing affordable, functional, and stylish home furnishings to customers across the globe. The company achieves this through its unique combination of low-cost production, efficient supply chain management, and a self-service, warehouse-style shopping experience.
- Low-cost production: IKEA designs its products to be simple and easy to manufacture, which helps to reduce production costs. The company often uses flat packaging, which minimizes shipping and storage costs, and allows customers to assemble the products.
- Efficient supply chain management: IKEA maintains close relationships with its suppliers and works to optimize its supply chain, minimizing costs and ensuring timely delivery of products. This efficiency allows the company to maintain its competitive pricing.
- Self-service concept: IKEA stores are designed to facilitate a self-service shopping experience, with customers navigating through showrooms, picking up products from warehouse-like areas, and assembling the products at home. This approach reduces staffing costs and encourages customer involvement and satisfaction.
Product Range: IKEA offers a wide range of products, including furniture, storage solutions, lighting, textiles, kitchen appliances, and decorative items. The company’s products are designed to cater to a diverse range of customers, with various styles, materials, and price points available.
Global Presence: Since its inception, IKEA has expanded its operations to over 50 countries, operating more than 400 stores worldwide. In addition to its brick-and-mortar locations, IKEA also uses an e-commerce platform, allowing customers to purchase products online and deliver them directly to their homes.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility: IKEA is committed to sustainability and minimizing its impact on the environment. The company invests in renewable energy, focuses on using sustainable materials in its products, and aims to become a circular business by 2030. Additionally, IKEA is involved in various social initiatives and partnerships, such as working with UNICEF and Save the Children to improve the lives of needy children.
In summary, IKEA is a global leader in the home furnishings industry, known for its affordable, functional, and stylish products. The company’s unique business model, wide product range, global presence, and commitment to sustainability and social responsibility have contributed to its success and growth.
IKEA’s total retail sales for FY22 reached EUR 44.6 billion (EUR 41.9 billion in FY21). This includes sales of IKEA products, food, and services to customers.
Here is the SWOT analysis for IKEA
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of IKEA.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
- Economies of scale : As one of the largest furniture retailers globally, IKEA benefits from economies of scale, which allow the company to achieve cost advantages in production, procurement, and logistics. This enables IKEA to offer competitive pricing to its customers.
- Strong brand identity : IKEA has cultivated a unique and consistent brand identity. Its minimalistic Scandinavian design, affordable prices, and innovative furniture and home goods approach have made it a household name worldwide.
- Wide product range : IKEA offers a comprehensive range of products, catering to various customer segments, tastes, and budgets. This extensive product offering helps IKEA appeal to a broad audience and meet the diverse needs of its customers.
- Efficient supply chain : IKEA’s efficient supply chain management and close relationships with suppliers enable the company to streamline its operations, reduce costs, and maintain product availability, further enhancing its competitiveness in the market.
- Innovative store layout and customer experience : IKEA’s distinctive store layout, which combines showrooms and warehouse-style shopping, creates a unique and engaging customer experience. This self-service approach encourages customers to explore and interact with products, increasing the likelihood of sales.
- Global presence : With over 400 stores across more than 50 countries, IKEA has established a solid global footprint. This international presence enables the company to cater to local tastes and preferences while benefiting from global brand recognition.
- Commitment to sustainability : IKEA’s focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility has resonated with customers and helped to differentiate the brand from its competitors. The company’s initiatives, such as using sustainable materials and investing in renewable energy, contribute to a positive brand image.
- Digital transformation and e-commerce : IKEA has embraced digital transformation, investing in its online presence and e-commerce platform to cater to consumers’ changing shopping habits. This has allowed the company to expand its reach and maintain its relevance in the age of online shopping.
- Complex assembly process : Although IKEA’s flat-pack, ready-to-assemble products help reduce shipping and storage costs, some customers find the assembly process challenging or time-consuming. This could deter potential customers or lead to dissatisfaction among those who struggle with assembly.
- Perceived product quality : Due to its focus on affordability, some customers may perceive IKEA products as being lower quality than more expensive alternatives. This perception could limit IKEA’s appeal to customers seeking higher-end or longer-lasting furniture.
- Limited customization : IKEA’s standardized designs and production methods can restrict the level of customization available to customers. This might make it difficult for the company to cater to individual tastes and preferences, especially compared to smaller, bespoke furniture manufacturers.
- Dependency on large store formats : IKEA’s traditional reliance on large, out-of-town store locations can lead to higher operational costs and may not be as convenient for customers who prefer shopping in urban centers or online.
- Environmental impact : Despite its commitment to sustainability, IKEA’s business model is not without its environmental impact. The company’s reliance on wood and other raw materials and the transportation of goods can contribute to resource depletion and carbon emissions.
- Cultural adaptation challenges : As IKEA expands into new markets, it may face difficulties adapting its product offerings and store layouts to cater to the local culture, preferences, and regulations. This could affect IKEA’s ability to establish a strong presence in certain regions.
- Market saturation and competition : In some mature markets, IKEA faces increased competition from traditional furniture retailers and e-commerce platforms. This market saturation can lead to slower growth and increased pressure to differentiate its product offerings and customer experience.
- Supply chain disruptions : IKEA’s vast and complex global supply chain can be susceptible to disruptions, such as natural disasters, political instability, or global pandemics. These disruptions can impact product availability, increase costs, and negatively affect the company’s reputation.

Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets : IKEA can target untapped markets, particularly in Asia, Africa, and South America, to increase its global presence and tap into the growing demand for affordable and stylish home furnishings.
- Enhancing online presence and e-commerce : By investing in its e-commerce platform and digital marketing efforts, IKEA can cater to the increasing number of customers who prefer shopping online. This will help IKEA broaden its customer base and remain relevant in the digital age.
- Customization and personalization : Offering customers more options to customize and personalize their furniture can help IKEA differentiate itself from competitors and cater to the increasing demand for personalized products.
- Smaller and urban store formats : Opening smaller, urban store formats can help IKEA reach customers in densely populated cities where large store formats are not feasible. These smaller stores can offer a curated selection of products tailored to the needs of urban dwellers.
- Sustainability and circular economy : IKEA can further strengthen its commitment to sustainability by focusing on circular economy initiatives, such as promoting product reuse, repair, and recycling. This can improve IKEA’s brand image and appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers.
- Smart home technology integration : Integrating smart home technology into IKEA’s product offerings can help the company stay ahead of market trends and cater to the growing demand for connected, intelligent home solutions.
- Collaboration with designers and artists : By collaborating with renowned designers and artists, IKEA can introduce exclusive, limited-edition collections that can help differentiate its product offerings, create buzz, and attract new customers.
- Strengthening the supply chain : Investing in supply chain innovations, such as automation and artificial intelligence, can help IKEA further optimize its supply chain, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with disruptions.
- Intense competition : IKEA faces strong competition from both traditional brick-and-mortar furniture retailers and e-commerce platforms. Competitors may offer similar products at competitive prices, alternative designs, or superior customer experiences, putting pressure on IKEA to continually innovate and differentiate itself.
- Economic downturns : Economic recessions or downturns can lead to reduced consumer spending on discretionary items like furniture and home accessories. This can result in decreased sales and lower profits for IKEA.
- Fluctuations in raw material prices : IKEA relies heavily on raw materials, such as wood, textiles, and metals, to manufacture its products. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials can lead to increased production costs and potentially affect IKEA’s profitability and competitive pricing.
- Regulatory and political risks : As a global company, IKEA is exposed to various regulatory and political risks in its operating countries. Regulation changes, political instability, or trade restrictions can impact IKEA’s supply chain, operations, or market access, leading to increased costs or reduced sales.
- Changing consumer preferences : Consumer tastes, furniture, and home goods preferences can change rapidly. Failure to adapt to these changes and offer products that resonate with customers can decrease sales and market share.
- Environmental concerns : Growing concerns about the environmental impact of businesses, including resource depletion, carbon emissions, and waste generation, can affect IKEA’s reputation and demand for its products. Failing to address these concerns or meet evolving sustainability standards could harm IKEA’s brand image and customer loyalty.
- Technological disruptions : Rapid technological advancements, particularly in e-commerce, logistics, and manufacturing, can disrupt IKEA’s traditional business model. Failure to adapt and embrace new technologies can hinder IKEA’s competitiveness and market position.
- Supply chain disruptions : IKEA’s complex global supply chain is vulnerable to disruptions from natural disasters, political instability, labor strikes, or global health crises. These disruptions can lead to increased costs, delays, and damage to IKEA’s reputation for product availability.
Check out the SWOT Analysis of Global Businesses
Related posts.

SWOT Analysis of Customer Service

SWOT Analysis of a recruitment process

SWOT Analysis of a New Product Development

SWOT Analysis of Digital Marketing

SWOT Analysis of an insurance company

SWOT Analysis of a Supply Chain

SWOT Analysis of a Human Resources (HR) department

SWOT Analysis of the call center industry in the US
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Strategic Management
- SWOT Analysis of IKEA
Introduction
This article analyzes the strategy of the world’s leading furniture retailer, IKEA using the SWOT Methodology. The company was founded in 1943 and is known for its simple yet effective approach to retailing with the DIY or the Do It Yourself concept, which ensures that the company keeps costs to a minimum and passes on the value to the customers.
The products sold by IKEA are mostly ready to use and flat packed meaning that they can be assembled by the customers themselves. The company has a presence in the online world as well and the total sales from its online and offline businesses are more than a Billion Dollars per year. The key strategic driver of IKEA’s success is it’s no nonsense approach to retailing that has paid rich dividends for the company and its shareholders (literally and metaphorically).
The point to be noted here is that it is sometimes difficult to maintain quality in the context of increasing costs and the need to replicate standards across its locations worldwide.
Opportunities
IKEA is a well-known global trend and through its innovative business model and its focus on products, processes, and systems , it has managed to stay ahead of the competition in the furniture retailing business.
The company can diversify into other products and product lines as it can replicate its business model in other realms as well. To do this would require fresh thinking and a new approach to its strategy that would combine low cost leadership with additional drivers of success like scalability and focus on quality.
Finally, the company can enter the emerging markets where its products and its business model are likely to be met with success and the untapped customer base can be leveraged.
Related Articles
- SWOT Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of Google
- SWOT Analysis of Starbucks
- SWOT Analysis of Amazon
- SWOT Analysis of Nike
- SWOT Analysis of Microsoft
- Competitor Analysis
- What is Competitive Advantage ?
- Porter’s Five Forces Model
View All Articles
Authorship/Referencing - About the Author(s)
The article is Written and Reviewed by Management Study Guide Content Team . MSG Content Team comprises experienced Faculty Member, Professionals and Subject Matter Experts. We are a ISO 2001:2015 Certified Education Provider . To Know more, click on About Us . The use of this material is free for learning and education purpose. Please reference authorship of content used, including link(s) to ManagementStudyGuide.com and the content page url.
- Strategic Management - Introduction
- Strategy - Definition and Features
- Components of a Strategy Statement
- Vision & Mission Statements
- Strategic Management Process
- Environmental Scanning
- Strategy Formulation
- Strategy Implementation
- Strategy Formulation vs Implementation
- Strategy Evaluation
- Strategic Decisions
- Benefits of Strategic Management
- Business Policy
- SWOT Analysis of Blackberry
- Personal SWOT Analysis
- SWOT Analysis of China Mobile
- Human, Social, and Intellectual Capital as a Means of Competitive Advantage
- Blue Ocean Strategy and its Implications for Businesses
- Overfished Ocean Strategy: How to Drive Growth and Attain Profitability
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of the Airlines Industry in the United States
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of Samsung
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of Virgin Atlantic
- Porters Five Forces Analysis of China Mobile
- Strategic Leadership
- Some Pitfalls to be Avoided
- Corporate Governance
- Business Ethics
- Social Responsibilities of Managers
- Core Competencies
- Core Competency Theory of Strategy
- Ansoff Matrix
- Routes to Strategic Growth
- Diversification as a Viable Corporate Strategy
- 5 Configurations of Strategic Management
- Role of Planning, Plans and Planners
- Reasons for Avoiding Strategic Planning
- Strategic Management for the Millennials
- Strategizing for the Future
- PESTLE Analysis of the Global Aviation Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of Starbucks
- PESTLE Analysis of Samsung
- SWOT Analysis of Unilever
- Business Strategies to Beat the Downturn
- Analysis of Amazon’s Corporate Strategy
- How Amazon Can Improve its Corporate Strategy
- Cutting Costs Strategically
- Actualizing Business as Usual Strategies for Mission Critical Organizations and Functions
- Why Indian Firms Must Strive for Strategic Autonomy in Their Geoeconomic Strategies
Marketing91
SWOT Analysis of Ikea (Updated 2024)
May 20, 2024 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: SWOT of Brands
Let’s explore the SWOT analysis of IKEA in depth by understanding its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
IKEA is a global leader in inexpensive, fashionable furnishings. It changed the industry by introducing a flat-pack assembly and transport technique. Founded in 1943 by Ingvar Kamprad, it has evolved from a tiny corporation to a multinational retail giant known for its cost-effective operations and inventive product creation.
The company ’s success depends on its commitment to improving everyday living via its popular design that combines utility , quality, and value, all while emphasizing sustainability and social responsibility . IKEA’s distinct shopping experience and diverse product offering have solidified its standing as a beloved brand , which faces both difficulties and possibilities in a changing market context.
Overview of IKEA
- Company type: Private
- Industry: Retail
- Founded: 28 July 1943, 80 years ago in Sweden
- Founder: Ingvar Kamprad
- Headquarters: Delft, Netherlands
- Number of locations: 471 (2024)
- Area served: Worldwide
- Key people: Jesper Brodin ( Chairman and CEO of INGKA Holding), Jon Abrahamsson Ring (Chairman and CEO of Inter IKEA Holding)
- Products: Ready-to-assemble furniture, Homeware, Food products
Table of Contents
SWOT Analysis of IKEA

IKEA Strengths
1. High Brand Value and Strong Brand Equity
IKEA is the world’s largest furniture store, with a brand value of $22.9 billion in 2023. Brand equity includes the company’s reputation and customer views, supported by brand loyalty , awareness , and associations.
IKEA’s widespread recognition and devoted following among consumers, who associate the IKEA name with practical, stylish, and affordable home solutions, serve as evidence of its significant brand equity.
2. Strong Financial Position
Financial stability is one of IKEA’s essential qualities. The corporation reported revenue of €47.6 billion and profits of €1.6 billion in 2023, indicating a continuing growing trend. Online sales have stabilized at 23%, compared to 22% in FY22.
This solid financial position instills trust in investors, simplifies access to low-interest financing, and allows the company to take measured risks that fuel innovation and expansion, giving IKEA a competitive advantage in the market.
3. Diverse Investment Portfolio
Beyond furniture and home goods, IKEA has expanded its portfolio , including AI-driven design advisory services, smart home technologies, real estate, renewable energy, and even furniture rentals.
Its investments in the food sector have also shown potential, accounting for around 5% of its annual revenues. This strategic diversification strengthens IKEA’s market position and sustains its profitability.
4. The Company Has Built a Highly Successful Franchise
As of 2023, IKEA has 471 franchise stores around the world. This franchise-based business model neatly divides the cost and risk of launching additional stores, enabling rapid growth. With franchisees contributing funds and carrying some start-up risks, IKEA has a lower debt load and a more substantial brand presence.
This franchising strategy promotes growth and strengthens IKEA’s global market share while reducing operating costs.
5. Brand Recognition
IKEA’s trademark blue and yellow logo is internationally recognized as a symbol of low-cost furniture and home furnishings. With a remarkable 860 million customers visiting IKEA each year across 63 countries, the company’s brand recognition strengthens its position as an industry leader, with consumers consistently identifying IKEA as a go-to destination for home furnishings.
6. Countless Designs
IKEA has received recognition for its unique furniture designs that combine style and practicality, and the ease of travel and self-assembly are critical to its business model . This approach to furniture design allows customers to picture the finished product in-store while also transporting and assembling the items at home, boosting customer loyalty and the overall IKEA experience.
7. Affordability
The low cost of IKEA’s items is critical to its appeal. IKEA’s constant pursuit of affordability without sacrificing design quality demonstrates its dedication to providing value to customers and maintaining brand loyalty and market position.
8. A Supplier’s Dream
IKEA’s significant purchasing power allows it to negotiate lower rates from suppliers by purchasing in bulk, resulting in a win-win situation in which suppliers’ inventory costs are reduced. At the same time, IKEA benefits from cost reductions that contribute to its low-price strategy.
9. Customer Knowledge
IKEA is thoroughly aware of its customers, from their purchasing influences to their stylistic preferences. This consumer knowledge influences product design and store experiences that cater to clients’ desires, resulting in spectacular sales figures and a competitive advantage in the market.
10. Constantly Using Innovations to Drive Costs Down
To deliver reduced pricing , IKEA seeks creative cost-cutting measures such as using new, sustainable materials and optimizing packaging and transportation. This constant commitment to innovation is crucial to the brand’s value proposition and sustainability activities.
11. Supply Chain Integration
IKEA’s long-term collaborations with suppliers result in a symbiotic connection that enables a consistent flow of raw materials at a cheap cost while maintaining excellent quality. This supply chain integration increases efficiency, lowers prices, and gives IKEA a competitive edge.
12. Their Products Are Easy To Assemble
One of their distinctive features is the ease with which IKEA furniture products can be assembled. With clear assembly instructions, the company’s ready-to-assemble furniture model improves accessibility and demonstrates IKEA’s dedication to customer convenience.
IKEA Weaknesses
1. Low-Quality Products and Services
IKEA’s continued emphasis on cost-cutting has decreased the quality of its products and services. According to Verdict, the UK Customer Insights research on IKEA demonstrates that customers are less satisfied with IKEA’s services than the average UK consumer who shops elsewhere. The number of returned goods has increased as a result of cost-cutting efforts, which has also hurt the brand’s reputation.
2. Standardized Products
IKEA’s primary competitive advantage is its low costs, aided partly by its uniform product offers. However, because product customization is limited, IKEA caters to fewer client segments . The company’s failure to provide high-quality, unique items allows competitors to fill that gap and enhance their position.
3. Declining Net Profits
Despite its strong financial position, IKEA saw a significant decline in net profits, from €1.6 billion in 2021 to only €287 million in 2022 after taxes. This was primarily related to rising operational costs due to inflation and the withdrawal of investments in Russia, which reduced the company’s operating profit margins from 7% to 4%.
This impacted IKEA hard because its business strategy is based on offering cheaper pricing than competitors; raising prices might seriously harm its reputation.
4. Numerous Scandals
IKEA has not been immune to numerous crises involving delicate themes. The company’s reputation has been damaged by allegations of responsibility for 1% of global wood consumption each year, involvement in illegal logging activities, dangerous furniture designs that have killed children, privacy invasions, cultural imperialism, and suspected horse meat in Swedish meatballs.
5. Inadequate Global Expansion
Despite being a well-known company, IKEA must use its strong reputation and resources to expand globally. With only 471 stores in 63 countries, the world’s largest furniture retailer might have a more significant presence. Most IKEA locations focus on North America, Europe, Australia, and China, leaving a largely untapped African market for competitors to exploit.
6. Failure to Adapt to Local Cultures
IKEA is frequently criticized for not customizing its products and marketing techniques to local cultures and preferences. While the corporation works to enhance its approach, it still needs to make considerable progress in meeting specific cultural preferences.
7. Controversial Self-Assembly Model
While IKEA’s self-assembly model is cost-effective, it has generated controversy. Customers frequently encountered issues during assembly, resulting in discontent and possibly damage from lousy furniture.
8. Accusations of Unfair Working Conditions
Despite efforts to promote fair working conditions, IKEA has faced allegations of mistreatment and underpayment. This has resulted in several lawsuits, strikes, union activity, and a damaged brand image .
9. Delivery and Service Issues
In some regions, IKEA has received criticism for lengthy delivery times and poor customer service , resulting in customer dissatisfaction.
10. Limited High-End Market Offerings
With a focus on affordability, IKEA may miss out on addressing the high-end market segment , thus limiting its revenue streams.
11. Online Retail Challenges
Despite attempts to adapt to e- commerce , IKEA still needs to catch up to competitors who have excelled in delivery speed and digital customer experience .
12. Store Cannibalization
Opening new IKEA stores close to existing ones can potentially cannibalize the sales of those established outlets, leading to lower overall sales.
IKEA Opportunities
1. Rise of ‘Ethical Chic’
The growing trend of ethical consumption, known as “Ethical Chic,” presents a significant opportunity for IKEA. The brand’s commitment to a “green” business model puts it in a solid position to attract a growing audience of environmentally sensitive consumers. By utilizing its sustainability , IKEA can tap into an expanding client base that is willing to support brands that share their values.
2. Further Expansion into Developing Economies
Emerging markets are booming, with retail sectors growing by an average of 5% over the last year. IKEA, primarily in developed economies with limited expansion into emerging ones (China being an example), is on the verge of a massive opportunity.
The potential for development into countries such as Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, and Malaysia may significantly boost IKEA’s global presence and generate future revenue growth by capitalizing on these economies’ growing consumer bases.
3. Growing Online Sales
IKEA is well-positioned to benefit from this trend, with online retail sales accounting for 17% and 4% of total retail in the UK and US, respectively, and continuing to rise. Online sales have stabilized at 23%, compared to 22% in FY22. However, visitors to IKEA online channels were fewer in FY23, at 3.8 billion compared to 4.3 billion last year. This was mainly due to the complete lifting of COVID restrictions worldwide and a return to physical shopping.
4. Expansion to the Growing Grocery Market
The changing consumer preference for healthy eating habits has increased the demand for food in developed nations. IKEA’s expertise in managing food outlets positions it well for expanding its grocery section within its retail locations. This strategic expansion will complement IKEA’s present offers and meet the growing consumer demand for health-conscious food options.
5. Investing in Sustainability
IKEA has made significant efforts to ensure sustainability in its material sourcing and ethical standards . However, confronting charges of getting materials from unlawful logging activities allows IKEA to strengthen its commitment to sustainability.
By addressing these environmental concerns and improving the reusability of its materials, IKEA may boost its brand image and increase sales , aligning with the modern shopper’s emphasis on ethical sourcing.
6. Diversifying Its Business Model
IKEA’s success has been built on its ability to provide inexpensive, long-lasting furniture and household appliances. While this strategy has been the foundation of its success, the possibility of expanding into high-end furniture industries is tempting. IKEA’s extensive resources, strong leadership, and substantial brand equity position it well to expand its brand into premium segments, tapping into a new demographic and increasing its market reach.
7. Further Acquisitions and Partnerships
Strategic acquisitions and alliances can help IKEA maintain its supremacy in a competitive world. Such attempts can improve IKEA’s product offerings and service delivery, reinforcing its fundamental value proposition and assuring long-term market leadership.
By forming strategic alliances , IKEA can continually innovate, increase its consumer base, and maintain its competitive advantage in the global retail industry .
IKEA Threats
1. Intensifying Competition
The homeware sector has seen the introduction of numerous low-cost retail competitors such as Walmart , ASDA , and Tesco , creating a more competitive environment for IKEA. These emerging market players are similar to IKEA in that they provide low prices, well-managed supply chains, and a broad market reach, posing a substantial challenge to IKEA’s market dominance.
2. The Growth of Average Consumer Income
With rising average consumer incomes, people are shifting their shopping habits to high-quality, higher-priced products. This trend may devalue IKEA’s budget goods offerings and direct customers to businesses that provide more premium homeware products.
3. Physical Store Limitations
The rise of online shopping has highlighted a possible concern with IKEA’s business strategy of maintaining enormous physical stores, which might become a financial strain if in-store foot traffic reduces dramatically.
4. The Risk of Lawsuits
IKEA could face customer claims for damage caused by their products. Even the idea of wrongdoing on social media sites can stoke unfavorable public opinion, potentially harming IKEA’s reputation and consumer trust.
5. Increased Cash Flow
Contrary to popular belief, rising consumer incomes may put IKEA under pressure. As consumers’ discretionary income improves, their propensity to buy low-quality products may decline, posing challenges for IKEA, which has built its reputation on price.
6. Changes in Consumer Preferences
IKEA’s long-standing dedication to a specific style may only be practical if adjusted to changing consumer preferences. Their inability to adapt to shifting client patterns may harm their business continuity.
7. Supply Chain Shocks and Logistics Disruptions
IKEA’s business model closely relates to its vast and complex worldwide supply chain. Unexpected interruptions, such as the COVID-19 pandemic or geopolitical crises like Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, can significantly affect the delivery of IKEA’s value proposition, resulting in higher pricing and limited product availability.
8. Legal Battles
IKEA has faced several legal issues, ranging from injury claims to unacceptable working conditions and environmental infractions. These conflicts cost IKEA money and could potentially ruin the company’s reputation in the public eye.
9. Counterfeit Products
The immense popularity of IKEA designs has led to the emergence of counterfeit or knock-off versions, posing a risk of brand devaluation.
10. Exchange Rate Volatility
As a global player, IKEA is susceptible to fluctuations in currency exchange rates, which could impact its profitability.
11. Regulatory Challenges
Diverse and changing rules in several nations may impact IKEA’s key activities, ranging from product standards to labor laws. It can pose a constant threat to their business continuity.
A global leader in cheap furniture, IKEA exemplifies creativity , sustainability, and customer-centric design. The 1943-founded corporation has revolutionized furniture marketing and assembly, offering an international shopping experience. IKEA’s solid financial health, brand equity, and strategic diversification equip it for sustained competition, changing consumer tastes, and operational hazards.
IKEA may grow by developing underdeveloped nations, utilizing online sales, and promoting ethical consumerism . It must tackle threats with agility and foresight. IKEA must balance cost-efficiency and quality, add high-end products, and remain committed to sustainability to maintain market leadership and improve global living conditions.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on SWOT
Related posts:
- SWOT Analysis of Procter and Gamble – P & G SWOT analysis (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of Hewlett Packard – HP SWOT analysis (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of FedEx – FedEx SWOT Analysis (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of Verizon – Verizon SWOT (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of Bank of America – Bank of America SWOT (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of McDonalds (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of Adidas (Updated 2024)
- SWOT ANALYSIS OF PAYPAL (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of American Airlines (Updated 2024)
- SWOT Analysis of Exxon Mobil (Updated 2024)
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Web Scraping
- For Small Business
IKEA SWOT Analysis: Unraveling the Secrets of the Furniture Retail Giant‘s Success
- April 21, 2024
- by Tom Wells

IKEA, the world‘s largest furniture retailer, has revolutionized the industry with its affordable, stylish, and functional products. The company‘s success is attributed to its unique business model, strong brand recognition, and efficient operations. However, like any other business, IKEA faces challenges and opportunities that shape its strategies and future growth prospects. In this comprehensive SWOT analysis, we will delve into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that define IKEA‘s position in the highly competitive furniture retail market.
Strengths: The Pillars of IKEA‘s Success
1. unique business model: affordability meets quality.
IKEA‘s business model is the foundation of its success. The company‘s "democratic design" philosophy aims to create high-quality, functional, and appealing products at prices that are accessible to the masses. IKEA achieves this by:
- Designing products in-house to maintain control over style, functionality, and costs
- Sourcing materials and manufacturing products in bulk to leverage economies of scale
- Using flat packaging to reduce transportation costs and make products easier to handle
By controlling the entire value chain, from design to distribution, IKEA can offer products at significantly lower prices than its competitors without compromising on quality.
2. Strong Brand Recognition and Loyalty
IKEA has built a strong brand identity that resonates with customers worldwide. The company‘s brand is synonymous with affordability, sustainability, and Scandinavian design aesthetics. IKEA‘s brand loyalty is driven by:
- Consistency in product quality, design, and pricing across all markets
- Memorable and effective marketing campaigns that showcase IKEA‘s values and personality
- Positive customer experiences in-store and online, supported by helpful staff and user-friendly interfaces
According to a study by Interbrand, IKEA‘s brand value reached $18.4 billion in 2020, making it the 29th most valuable brand globally.
3. Vertically Integrated Supply Chain and Efficient Operations
IKEA‘s vertically integrated supply chain and efficient operations are crucial to its ability to offer affordable products while maintaining profitability. The company‘s supply chain strengths include:
- Long-term partnerships with suppliers to ensure consistent quality and supply of raw materials
- Ownership of manufacturing facilities in key markets to maintain control over production processes
- Efficient distribution networks that minimize transportation costs and delivery times
IKEA‘s operational efficiency is further enhanced by its:
- Flat organizational structure that promotes quick decision-making and adaptability
- Use of technology to optimize inventory management, logistics, and customer service
- Continuous improvement of processes to reduce waste and increase productivity
4. Focus on Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
IKEA has made sustainability a core part of its business strategy. The company‘s commitment to eco-friendly practices not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also helps to reduce costs and mitigate risks associated with resource scarcity. IKEA‘s sustainability initiatives include:
- Sourcing materials from renewable and recycled sources, such as using wood from responsibly managed forests
- Investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies in its stores and manufacturing facilities
- Designing products that are durable, repairable, and recyclable to promote a circular economy
- Collaborating with suppliers and NGOs to promote sustainable practices across the value chain
In 2019, IKEA announced its goal to become climate positive by 2030, meaning that it will reduce more greenhouse gas emissions than its value chain emits.
Weaknesses: Challenges and Limitations
1. self-assembly model: a double-edged sword.
While IKEA‘s self-assembly model helps to reduce costs and make products more affordable, it also poses challenges for some customers. The main issues with self-assembly include:
- Difficulty in understanding and following assembly instructions, leading to frustration and dissatisfaction
- Potential for missing or damaged parts, requiring customers to contact customer service or return to the store
- Time and effort required to assemble larger or more complex items, which may deter some customers
To address these challenges, IKEA has introduced assembly services in some markets, but these come at an additional cost and may not be available in all locations.
2. Standardized Product Offerings: Limited Customization
IKEA‘s standardized product offerings help to maintain affordability and efficiency, but they also limit customers‘ ability to customize their purchases. The main limitations of standardized products include:
- Limited color, size, and style options for certain products, which may not suit all customers‘ preferences or needs
- Difficulty in finding products that fit specific room dimensions or layouts, requiring customers to compromise or look elsewhere
- Potential for products to look "generic" or "cookie-cutter," especially when used in similar configurations by many customers
While IKEA does offer some customization options, such as with sofa covers or kitchen cabinet configurations, these are still limited compared to fully custom-made furniture.
3. Reliance on Third-Party Manufacturers: Quality and Supply Risks
Although IKEA owns some of its manufacturing facilities, the company still relies heavily on third-party manufacturers to produce its products. This reliance on external suppliers can pose risks, such as:
- Potential for inconsistencies in product quality, especially if suppliers do not adhere to IKEA‘s standards
- Vulnerability to supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical events, natural disasters, or supplier bankruptcies
- Reputational risks associated with unethical or unsustainable practices by suppliers, such as labor rights violations or environmental damage
To mitigate these risks, IKEA has strict supplier codes of conduct and conducts regular audits to ensure compliance. However, with a vast network of suppliers, it can be challenging to monitor and control all aspects of the supply chain.

4. Limited Physical Store Presence in Certain Markets
While IKEA has a strong presence in Europe and North America, the company has a limited number of physical stores in some regions, particularly in developing countries. The main limitations of a limited physical store presence include:
- Difficulty in reaching customers who prefer to see and touch products before making a purchase
- Higher shipping costs and longer delivery times for customers who live far from an IKEA store
- Reduced brand visibility and awareness in markets without a physical store presence
To address these limitations, IKEA has been expanding its e-commerce capabilities and exploring new store formats, such as smaller urban stores and pick-up points. However, these initiatives are still in the early stages and may not fully compensate for the lack of physical stores in some markets.
Opportunities: Avenues for Growth and Expansion
1. expansion into emerging markets.
As IKEA reaches saturation in its core markets of Europe and North America, emerging markets present significant growth opportunities. The main advantages of expanding into emerging markets include:
- Large and growing middle-class populations with increasing disposable incomes and aspirations for better living standards
- Relatively low competition from other furniture retailers, especially in the affordable segment
- Potential for high brand recognition and loyalty, as IKEA‘s reputation for quality and affordability is likely to resonate with cost-conscious consumers
However, expanding into emerging markets also comes with challenges, such as adapting to local cultural preferences, navigating complex regulations, and establishing reliable supply chains. IKEA has already made inroads into some emerging markets, such as China and India, but there is still significant room for growth in other regions, such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa.
2. Leveraging E-commerce and Digital Technologies
The rapid growth of e-commerce and digital technologies presents opportunities for IKEA to enhance its customer experience and reach new customers. The main opportunities in this area include:
- Improving the online shopping experience with features such as personalized recommendations, augmented reality product visualizations, and seamless checkout processes
- Offering more flexible delivery options, such as same-day or next-day delivery, to cater to customers‘ increasingly fast-paced lifestyles
- Using data analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize inventory management, pricing, and marketing strategies
- Developing mobile apps and digital services that complement the in-store experience, such as product information, assembly guides, and interior design tools
IKEA has already made significant investments in its e-commerce capabilities, with online sales growing by 45% in fiscal year 2020. However, there is still potential to further integrate digital technologies into the company‘s operations and customer touchpoints.
3. Product Line Expansions and Collaborations
While IKEA is primarily known for its furniture and home furnishings, there are opportunities to expand into adjacent product categories and collaborate with other brands to offer new and innovative products. Some potential product line expansions and collaborations include:
- Expanding into home electronics, such as smart home devices and audio-visual equipment, to offer complete home solutions
- Collaborating with fashion and lifestyle brands to create limited-edition collections that appeal to younger and trendier customers
- Developing more products and services for specific customer segments, such as students, seniors, or pet owners
- Partnering with local designers and artisans to create products that reflect regional cultural influences and support local communities
IKEA has already experimented with some of these strategies, such as its collaborations with brands like Adidas, Lego, and Sonos. However, there is still scope to explore new product categories and partnerships that align with IKEA‘s brand values and customer needs.
4. Capitalizing on the Growing Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Products
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is a growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. IKEA‘s focus on sustainability presents opportunities to differentiate itself from competitors and attract customers who prioritize environmental responsibility. The main opportunities in this area include:
- Developing more products made from recycled, renewable, or biodegradable materials, such as recycled plastic, bamboo, or hemp
- Offering more products and services that promote energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction, such as LED lighting, low-flow faucets, and composting solutions
- Educating customers about the environmental impact of their purchases and encouraging them to make more sustainable choices
- Collaborating with environmental organizations and influencers to raise awareness about sustainability and drive positive change in the industry
IKEA has already made significant progress in this area, with 60% of its product range being classified as "more sustainable" in 2020. However, there is still potential to further integrate sustainability into the company‘s products, operations, and marketing strategies.
Threats: Challenges and Risks
1. increasing competition from online and traditional retailers.
As the furniture retail market becomes more crowded, IKEA faces increasing competition from both online and traditional retailers. The main threats from competition include:
- Online retailers, such as Amazon and Wayfair, that offer a wide selection of furniture products with convenient delivery options and competitive prices
- Traditional furniture retailers, such as Ashley Furniture and Williams-Sonoma, that offer higher-end products and more personalized customer service
- Local and regional retailers that cater to specific market preferences and have lower overhead costs
- Discount retailers, such as Walmart and Target, that offer affordable furniture products as part of their broader product range
To maintain its competitive edge, IKEA needs to continuously innovate its products, services, and customer experience while maintaining its core value proposition of affordability and quality.
2. Fluctuating Raw Material Costs and Supply Chain Disruptions
As a global retailer, IKEA is exposed to fluctuations in raw material costs and supply chain disruptions that can impact its profitability and product availability. The main threats in this area include:
- Increases in the prices of key raw materials, such as wood, metal, and plastics, due to factors such as climate change, resource scarcity, and geopolitical events
- Supply chain disruptions caused by natural disasters, pandemics, trade disputes, or logistics bottlenecks
- Dependence on a limited number of suppliers for certain materials or components, which can create vulnerability to supply shortages or price hikes
To mitigate these threats, IKEA needs to diversify its supply chain, build strong relationships with suppliers, and invest in risk management and contingency planning.
3. Changing Consumer Preferences and Economic Downturns
As consumer preferences and economic conditions change over time, IKEA may face challenges in maintaining its relevance and profitability. The main threats in this area include:
- Shifts in consumer preferences towards more personalized, luxurious, or technology-enabled products that may not align with IKEA‘s standardized and affordable offerings
- Economic downturns or recessions that reduce consumer spending on discretionary items like furniture and home furnishings
- Changes in housing trends, such as smaller living spaces or more frequent moves, that may reduce demand for larger or more permanent furniture items
To address these threats, IKEA needs to stay attuned to changing consumer needs and adapt its products and services accordingly, while also maintaining a strong financial position to weather economic uncertainties.
4. Intellectual Property Disputes and Counterfeit Products
As a well-known brand with distinctive designs, IKEA is vulnerable to intellectual property disputes and counterfeit products that can damage its reputation and revenues. The main threats in this area include:
- Allegations of design infringement or copying by other furniture companies or designers
- Counterfeit products that imitate IKEA‘s designs and branding but are of inferior quality and safety standards
- Difficulty in enforcing intellectual property rights in certain markets with weaker legal protections or enforcement mechanisms
To protect its intellectual property and brand integrity, IKEA needs to invest in legal and technological solutions, such as patents, trademarks, and anti-counterfeiting measures, while also educating consumers about the risks of buying counterfeit products.
IKEA‘s SWOT analysis reveals a company with significant strengths, such as its unique business model, strong brand recognition, and efficient operations, that have enabled it to become a global leader in the furniture retail industry. However, the company also faces challenges and limitations, such as the self-assembly model, standardized product offerings, and reliance on third-party manufacturers.
Looking ahead, IKEA has several opportunities for growth and expansion, including entering emerging markets, leveraging e-commerce and digital technologies, expanding its product lines and collaborations, and capitalizing on the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. However, the company also needs to be aware of the threats posed by increasing competition, fluctuating raw material costs and supply chain disruptions, changing consumer preferences and economic downturns, and intellectual property disputes and counterfeit products.
To continue its success in the future, IKEA needs to build on its strengths while addressing its weaknesses, seizing opportunities for growth and innovation, and mitigating the risks and threats in its external environment. By doing so, IKEA can maintain its position as a leader in the global furniture retail market and continue to provide affordable, sustainable, and well-designed products that improve the everyday lives of people around the world.

IKEA SWOT ANALYSIS: Comprehensively Deconstructing a Furniture Giant
Introduction.
IKEA SWOT ANALYSIS : In the realm of home furnishing, IKEA has established itself as a global powerhouse, redefining the concept of affordable and stylish furniture. This Swedish retail giant has a unique business model that sets it apart from competitors, and it has continued to thrive over the years. To understand how IKEA has achieved such success, it is essential to conduct a thorough SWOT analysis , examining its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
IKEA SWOT ANALYSIS
Ikea strengths.
1. Global Market Presence:
IKEA’s global market presence is not only reflected in the number of stores but also in its market share. As of 2019, IKEA held approximately 33% of the US furniture market, solidifying its position as a dominant player. This market share allows for economies of scale, enabling-IKEA-to negotiate better deals with suppliers and maintain competitive prices.
2. Cost Leadership:
One of the key components of IKEA’s cost leadership strategy is its vertical integration. By owning various stages of the supply chain, including production facilities and forestry operations, IKEA reduces costs by cutting out middlemen. In addition, the company’s massive purchasing power gives it a significant advantage in negotiating lower prices from suppliers. These cost advantages are further amplified by efficient inventory management and logistics practices, allowing IKEA to pass on savings to customers.
3. Product Design and Innovation:
IKEA’s commitment to product design and innovation is evident in its vast range of products across different categories. The company invests heavily in research and development to create functional, stylish, and affordable furniture solutions. Moreover, IKEA’s flat-pack concept not only saves costs but also offers convenience for customers, enabling them to transport and assemble products easily. The company’s emphasis on innovative solutions has consistently garnered attention and resulted in numerous design awards and recognitions.
4. Sustainable Practices:
IKEA’s sustainability initiatives extend beyond its operations and supply chain. The company actively engages in partnerships with organizations such as WWF and UNICEF to promote sustainability and social responsibility. In terms of materials sourcing, IKEA aims to use renewable and recyclable materials, reducing its reliance on virgin resources. Additionally, the company implements energy-efficient measures in all stages of the product lifecycle, from production to transportation. By establishing itself as a leader in sustainability, IKEA not only aligns with consumer values but also gains a competitive advantage in a market increasingly driven by environmentally conscious buying behavior.
Additional Strength: Customer Loyalty Program
IKEA’s customer loyalty program, IKEA Family, contributes to its competitive advantage . This program offers various benefits, such as member discounts, extended warranties, free product insurance, and exclusive access to events and promotions. By nurturing a loyal customer base, IKEA can not only drive repeat purchases but also gather valuable customer data to enhance its marketing efforts and improve the overall shopping experience.
IKEA Weaknesses
1. Complex Store Layouts:
IKEA’s store layouts are intentionally designed to encourage customers to explore and engage with the products. However, the intricate maze-like layout can lead to inefficient navigation and difficulty finding specific items. This challenge is particularly pronounced during peak shopping periods, when crowds can further contribute to a confusing shopping experience. Streamlining the layout and providing clear signage can help alleviate this weakness and enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Criticisms Surrounding Quality:
While IKEA strives to offer products of good quality, some customers have expressed concerns about certain items’ durability and long-term performance. Improving quality control measures throughout the production process, enhancing product testing procedures, and adopting advanced manufacturing techniques can help address these concerns. Furthermore, investing in better packaging materials and providing clear instructions for assembly can minimize customer frustrations and enhance the overall perception of quality.
Additional Weakness: Limited Customization Options
One potential weakness for IKEA is the limited customization options available for its products. While the company offers a range of styles and configurations, customers who desire more personalized furniture choices may opt for competitors that provide greater flexibility. To address this weakness, IKEA can explore the introduction of customizable components or partnering with third-party vendors to offer additional customization options.
IKEA Opportunities
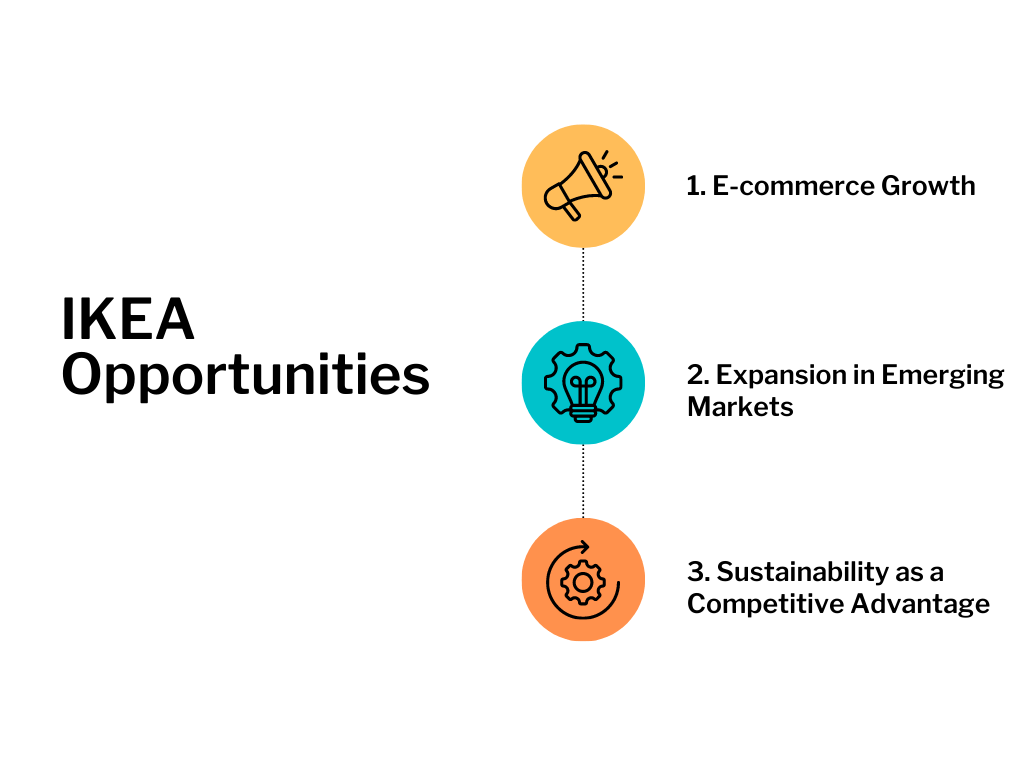
1. E-commerce Growth:
As the global e-commerce market continues to expand, IKEA has the opportunity to invest in its online channels and enhance the digital shopping experience. By leveraging technology, including augmented reality and 3D visualization tools, customers can virtually explore IKEA’s products and visualize them in their own spaces. Expanding e-commerce operations also allows IKEA to reach customers in geographically remote areas and adapt to changing consumer preferences for convenient and contactless shopping experiences.
2. Expansion in Emerging Markets:
Emerging markets, especially in Asia and Africa, present significant growth opportunities for IKEA. These regions are experiencing rising incomes, urbanization, and a growing middle class, leading to increased demand for affordable yet functional furniture solutions. By tailoring its product offerings, marketing campaigns, and store formats to meet the specific needs and preferences of consumers in these markets, IKEA can tap into new customer bases and establish a strong foothold.
3. Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage:
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability initiatives can serve as a powerful marketing and differentiation tool. IKEA can further amplify its sustainability practices by exploring innovative solutions, such as utilizing recycled materials in product manufacturing or adopting circular economy principles. Embedding sustainability into its brand strategy and effectively communicating these efforts to customers will position IKEA as a leader in environmental responsibility and attract consumers seeking authentic sustainable choices.
Additional Opportunity: Home Office Solutions
With the rise of remote work and the increasing number of people working from home, IKEA has the opportunity to develop and promote home office solutions. By offering a range of ergonomic furniture, innovative storage solutions, and efficient workspace designs, IKEA can cater to the evolving needs of customers in the post-pandemic era. Capitalizing on this trend can drive demand and stimulate growth in a rapidly expanding market segment.
IKEA Threats
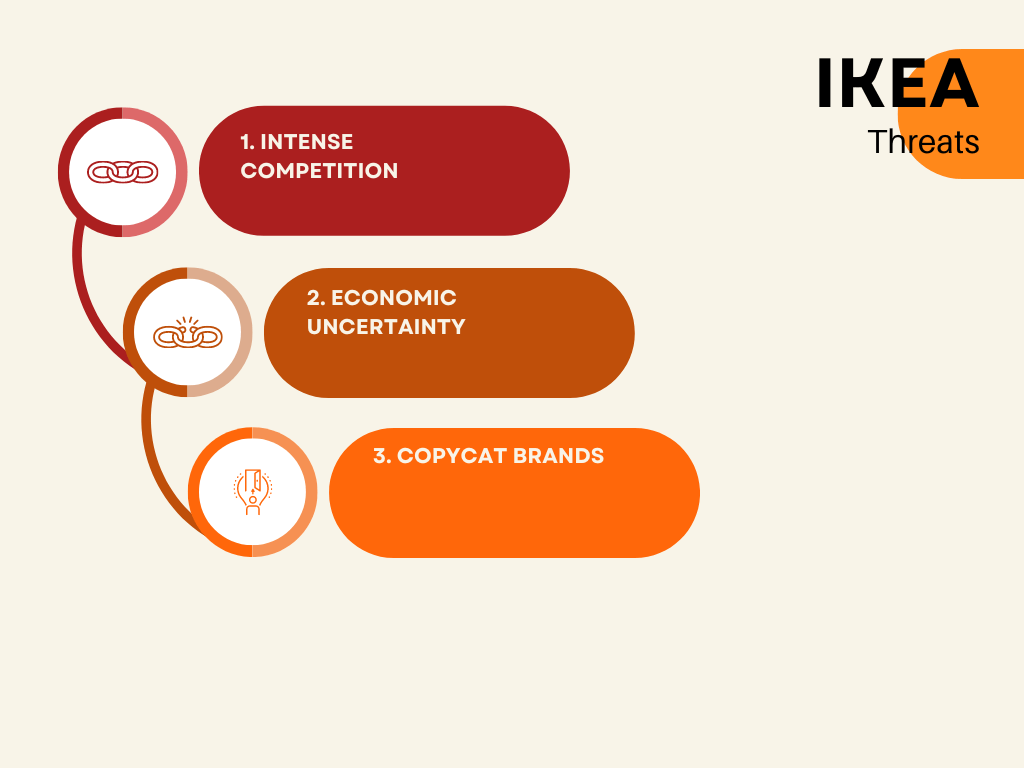
1. Intense Competition:
IKEA operates in a highly competitive market, facing both traditional and online competitors. Established furniture retailers, online marketplaces, and niche players pose constant challenges to IKEA’s market share. To stay ahead, IKEA must continue to invest in research and development, product innovation, and marketing efforts that promote the unique value propositions of its brand.
2. Economic Uncertainty:
Global economic downturns, fluctuations in consumer spending patterns, and currency exchange rate fluctuations can adversely affect IKEA’s revenue. During times of economic uncertainty, consumers tend to defer non-essential purchases, impacting the demand for furniture. Adapting pricing strategies, new market penetration efforts, and diversification into ancillary services or product segments can help mitigate the risks associated with economic fluctuations.
3. Copycat Brands:
Given IKEA’s successful business model, it faces the threat of copycat brands seeking to replicate its success and undercut prices. These brands often focus on imitating IKEA’s designs and offering similar products at lower costs, eroding IKEA’s market share. To combat this threat, IKEA must continue to differentiate itself through a combination of unique product offerings, strong brand loyalty, and ongoing investment in design innovation.
With its global market presence, cost leadership strategy, product design excellence, and commitment to sustainability, IKEA has carved a distinct niche in the home furnishings industry. By addressing weaknesses related to complex store layouts, product quality, and customization options, IKEA can enhance its customer experience and maintain its competitive advantage. Furthermore, seizing opportunities in e-commerce growth, expansion in emerging markets, sustainability, and home office solutions will allow IKEA to drive future growth. Mitigating threats from intense competition, economic uncertainties, and copycat brands requires proactive measures and continuous innovation. As IKEA continues to leverage its strengths, address weaknesses, and adapt to changing consumer preferences, it will remain a globally recognized leader in the flat-packed furniture market
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Entrepreneurs
- Permissions
- Privacy Policy

SWOT Analysis of IKEA: What's the Brand's True Strength?

In this article, I explain the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats — also known as a SWOT analysis — behind the furniture retailer, IKEA.
IKEA is well-known around the world for being that Swedish company offering inexpensive products for your home. It’s a staple for people with lower income who still desire design, but at a lower cost. And although this is exactly how IKEA became such a popular worldwide brand, it’s also a problem.
But first, let’s get into why IKEA is one of the leading furniture companies worldwide .
Read also: PESTLE analysis of IKEA .
SWOT analysis of IKEA: Strengths
Market research.
IKEA knows the ins-and-outs of their customers . If they didn’t, the company would have a hard time providing what their customers want. And what their customers want are a collection of affordable furniture and home appliances.
If IKEA didn’t know this is what their customers want, they wouldn’t be able to sell so many units. Nor would they bother to put in so much work into the development and design of their countless products.
Countless designs.
IKEA designers create stylish, newly designed products. But it goes further than physical decorations. The products are developed for easy transport and assembly. In the store, you’re able to see the finished, assembled piece. But when you walk out, you’re given each item in bits and pieces because it’s easier to put in your car and take home.
Affordability.
The inexpensiveness of IKEA products is the true strength of the brand . Maintaining that same level of cost-effectiveness is what keeps customers coming back for more.
The company searches for new ways to drive down costs, but without affecting the appearance of their products that consumers have come to expect.
A supplier’s dream.
IKEA is able to buy bulk quantities of products because of a long lasting relationship with their suppliers. For IKEA, buying large quantities is cheaper than buying a few pieces at a time. It’s also great for suppliers. The suppliers don’t worry about large quantities of inventory taking up space in their warehouses. They know IKEA can take the inventory and sell it hundreds of millions of customers.
Brand recognition.
IKEA is one of the most recognizable and well-known furniture brands worldwide. The brand has more than 600 million customers annually. And you can currently shop for IKEA products in more than 38 countries. Combine the brand recognition with the low-cost furniture options, and it’s no wonder IKEA is as popular or as well-known as it is.
SWOT analysis of IKEA: Weaknesses
IKEA has had a few run-ins with bad press. Employees have complained about poor treatment. The brand has faced ridicule for advertising techniques in non-western countries. And the worst offense: children being hurt or killed in relation to IKEA furniture. IKEA has also had to recall dangerous products because they’ve led to injuries.
Although the saying “any press is good press” may come into mind, in IKEA’s case, bad press leads to distrust from their customers.
Low quality.
IKEA products are known for being lesser quality. This seems to be a byproduct of offering inexpensive products. How can it be affordable and high quality? IKEA has yet to find a solution.
On social media , you’ll likely find someone criticizing IKEA’s less than stellar product quality.
And because they can’t live up to greater quality expectations, other companies now have the opportunity. Whether these companies can provide both quality and cost-effective furniture and kitchen appliances is yet to be determined.
SWOT analysis of IKEA: Opportunities
Few countries.
IKEA is only in 38 countries. This is a relatively low number considering how well-known the company is. They can branch out further, especially since IKEA is barely featured in developing countries. Places like Malaysia, Mexico, and Brazil are just a few locations IKEA should consider moving into.
Online shopping.
Additionally, you can purchase IKEA products through their website. Online shopping is becoming more popular as years go on. Especially around holidays like Black Friday, where people want to avoid long lines for fantastic sales.
IKEA is in a firm spot to accentuate their sales by offering more products online. Considering the company has more than 800 million online visitors, it’s definitely a sales channel IKEA should focus more efforts into .
Grocery stores.
Did you know about IKEA’s food outlets? With the growing demand for healthy food options, IKEA can push its grocery businesses into grocery stores.
SWOT analysis of IKEA: Threats
Some of the weaknesses of the IKEA brand are threats too.
Fast competition.
For instance, the competition for furniture products is growing. We’re seeing global brands like Walmart offering inexpensive home products . Although their catalogue isn’t as expansive as IKEA’s, that may only be a matter of time.
Possible lawsuits.
Then there’s the bad press. Depending on the specifics, IKEA may be subject to lawsuits from consumers who were injured by IKEA products. In truth, it doesn’t even require a lawsuit to crush a business. All it takes is a mob of angry consumers on social media to create more bad buzz, bad reviews, and intense backlash. IKEA needs to be aware of how they’re viewed online to counteract this perception.
Increase in cash.
Additionally, growing income can be a problem for the company too. As consumers have more excess cash, they’re less likely to buy cheap, low-quality products. Unfortunately, that’s the basis behind the IKEA brand. And since their quality is on the low-side, consumers will look for high quality, even if it costs a bit more.
Photo by Yaqi Zhai on Unsplash
Important SWOT Analysis Questions Everyone Should Ask
India's Bonds Spark Updated PESTLE and SWOT Analysis
Boeing swot analysis: from turbulence to triumph.
- In-Depth SWOT Analysis of IKEA

Introduction
IKEA has grown from humble beginnings to become the world's largest home furnishings retailer, with over 300 locations in a variety of nations. IKEA capitalizes on its strengths and mitigates certain shortcomings thanks to strong resource planning and allocation. The purpose of this IKEA SWOT analysis is to show the strengths, opportunities, and threats that exist in the home furnishing business, as well as how IKEA has succeeded to rise through the ranks. With its first store opening in Norway in 1963, the company entered the flat-pack furniture business. Following that, the business has been able to attract millions of new clients each year.
Indeed, IKEA has made great success over the world. In this IKEA SWOT analysis, we'll take a closer look at a variety of elements that have influenced the company's decision-making throughout the years. A significant emphasis is placed on the company's strengths as well as the numerous prospects. Meanwhile, some vulnerabilities and risks need to be addressed in the future.
2. IKEA's Strengths
IKEA's greatest strength is its clear vision, which is to provide value to its consumers regardless of market situations. This has resulted in a clear and well-defined company strategy and retailing method that is innovative in its simplicity, lethal in its competition targeting, and successful in its positioning.
Another significant asset of the firm is its straightforward idea, which converts into a variety of items that consumers can build themselves, resulting in massive cost savings that are then carried on to the consumers. IKEA has risen to become the world's biggest furniture retailer because of its single-minded concentration on cost leadership.
Increased use of recycled resources, wiser use of raw resources, creating and sustaining long-term partnerships with suppliers, and exploiting the efficiencies and synergies from economies of scale are some of the criteria used by IKEA to assess its strengths.
Moreover, this large selection of designs is reasonable for the typical person, and after acquiring the furniture, it assists in the delivery of your items to your house, thereby lowering consumer expenses.
3. IKEA's Weaknesses
Given that IKEA operates in several nations throughout the world, it is a large-scale and large-scale business, making it challenging to maintain consistent standards across sites. Though the organization makes every effort to ensure consistent quality across its product line and its locations, quality assurance that is reproducible and scalable is a major flaw.
Quality occasionally suffers as a result of the company's obsessive focus on cost leadership, especially in the current environment, when the costs of numerous inputs and raw materials have risen, affecting the company's financial performance. It's worth noting that maintaining quality in the face of rising expenses might be challenging at times.
The poor quality of their items has been the main source of worry. Many consumers have complained about their furniture falling within a few days after it was set up. When it comes to necessities in people's everyday lives, quality appears to be significantly more crucial when making purchasing selections.
IKEA's operations raise environmental issues, and the firm has difficulty explaining and expressing its environmental policy to consumers, shareholders, and other stakeholders.
4. IKEA's Opportunities
With its "green" marketing strategy, the business has a big possibility to attract clients who are interested in purchasing such items. The emergence of the ethical consumer, or the "Ethical Chic" purchase process, which indicates that buyers would want to buy ecologically aware items, is an opportunity waiting to be unleashed for the organization.
The company's cost leadership, which entails a single-minded concentration on cost at the detriment of all else, is maybe its largest opportunity. While this has generated quality issues, customers do not appear to mind because they are receiving their money's worth, and adding value to customers is another important possibility.
IKEA benefits from being a well-established market player, despite the severe rivalry in the furniture business. As a result, the corporation will have a better understanding of how to operate the business. As a result, expanding into additional nations may result in more new clients, resulting in more revenue. With the growth of the internet, more businesses are relocating their operations online.
The company's development into emerging countries and the developing globe, where it has an untapped client base that can be used for effective profitability, is the second potential. IKEA is already planning to enter areas such as China and India with a defined cost leadership strategy, which it expects would benefit the firm.
5. IKEA's Threats
IKEA's low-cost business strategy has been copied and duplicated by competitors, implying that the corporation must continually innovate to stay ahead of the pack. For example, some regional and local businesses have jumped on the DIY bandwagon and are concentrating on cost-cutting, forcing IKEA to develop new methods to remain flexible and adaptable.
DIY as a primary driver of strategic success is no longer the sole Unique Selling Proposition of IKEA, and the growth of online merchants that can provide even lower costs since they do not have a real presence means that they are closing in on IKEA.
Another issue is employee unhappiness, which has led to litigation and may cost the corporation millions in settlements and legal bills due to claims of maltreatment and unpaid overtime.
IKEA is also seeing a decrease in the number of new customers. Given the risks facing IKEA, it would be disastrous for the company's future if it did not come up with specific remedies to retain its market dominance.
6. Mind Map
The SWOT Analysis is used to examine the strategy of IKEA, the world's largest furniture store. The Do It Yourself (DIY) concept ensures that the company keeps costs low and passes on the value to customers. The company was founded in 1943 and is known for its simple yet effective approach to retailing with the DIY or Do It Yourself concept, which ensures that the company keeps costs low and passes on the value to customers. IKEA's items are typically ready to use and flat packaged, which means that buyers may put them together themselves. The corporation is also active in the internet realm, with annual revenues of more than a billion dollars from both online and offline operations.

7. Key Takeaways
A corporation may use a SWOT Analysis to get a thorough look at the aspects to consider while making decisions. As new possibilities arise, a corporation can learn how to take advantage of them. IKEA might also concentrate on potential risks and challenges to their business. IKEA can make their products models more adaptable and responsive to changing market conditions by making full use of the possibilities that occur. IKEA is a well-known worldwide trend, and it has managed to stay ahead of the competition in the furniture retailing market because of its creative business strategy and concentration on goods, processes, and systems.
The company may diversify into other items and product lines since its business model can be replicated in other areas. To do so, it would take new thinking and a new approach to its strategy, combining low-cost leadership with other success factors such as scalability and quality emphasis. Finally, the corporation may expand into new areas, where its products and business strategy are more likely to succeed, and an untapped client base can be exploited. It can all be summarized in a mind map diagram, just like below. You can make one or edit any template available in EdrawMind, and not only that, but you can also make the mind map diagram from scratch.
8. References
- SWOT Analysis of IKEA 2021: Strengths & Weaknesses

In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Tesla

In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Nike

McDonald's SWOT Analysis 2023

SWOT Analysis of Gucci

In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Netflix

Zara Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
SWOT Analysis of IKEA
Situational analysis of ikea: insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, strengths of ikea, 1. low costs through economies of scale, 2. cost leadership and penetration pricing, 3. strong vertical integration strategy, 4. unique value proposition of its products, 5. established global market presence, weaknesses of ikea, 1. standardization of production and output, 2. focus on cost leadership over quality, 3. multiple global operations and complications, 4. notable criticisms and negative publicity, opportunities for ikea, 1. emerging markets in developing countries.
The middle class is rising across the world, especially in developing countries. Hence, as the income of the greater population increases, so as the demand for residential real estate properties and related goods and services. This is one of the opportunities for IKEA.
2. Possibilities from Electronic Commerce
Improving its e-commerce capabilities and presence can help improve its sales while lowering its operational costs. There is no need for IKEA to build and maintain several brick-and-mortar stores in a particular country if it can maximize the advantage of online or digital sales channels such as its official website.
3. Product Diversification and Business Expansion
4. green business model for ethical consumers.
A sizeable number of consumers around the world have become more conscious about their consumption and behavior and choices. Countries are also promoting environment-related initiatives.
Threats to IKEA
1. disruptions in supply chain and logistics.
Furthermore, the company also suffered from more specific logistical problems that include delays in the shipment of production inputs, as well as the forwarding of processed inputs and final outputs. Note that Brexit and the Suez Canal blockage also disrupted the supply chain and logistics of the company.
2. Exposure to Foreign Currency Risks
3. regional and global economic downturns.
The disruptions in global trade due to notable events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and volatility in the foreign currency exchange market demonstrate how economic problems in a particular country, a global region, or the entire world can affect the sales performance of IKEA.
4. Increasing Intensity of Industry Competition
To illustrate further, note that other multinational retailers such as Walmart, Target, and Tesco have already ventured into the home furnishing market with similar value propositions. The market is also populated by other giants such as Amazon and the more reputable and established brands such as Sears and Wayfair.
5. Various Exposures to Regulatory Hurdles
Note that there are countries that limit the store size of retailers. Also, in other countries, there are special policies related to labeling and packaging requirements, especially for consumer-grade products. It is also possible for other countries to change their trade and business regulations depending on the economic and political climate.

IKEA SWOT Analysis – an overview
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps businesses to analyse internal and external factors affecting the bottom line. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that can be influenced by the company. Opportunities and threats, on the other hand, are external factors that have to be taken into account in strategic decision-making by the senior management. The following table illustrates IKEA SWOT analysis:
| 1. Market leadership in the global scale 2. Democratic design concept 3. Competency in cost-cutting through product and process innovation 4. Brand value and solid financial position 5. Vast, yet focused product range |
| 1. Weak presence in Asia 2. Damaged reputation due to a series of incidents 3. Competitive advantage difficult to sustain 4. Lack of differentiation of IKEA products and services 5. Lack of flexibility due to large size |
| 1. Increasing emphasis on CSR 2. Increasing presence in developing countries 3. Adding premium range of products into portfolio 4. Strengthening cost leadership competitive advantage through technological innovation 5. Benefiting from increasing digitalization of various business processes |
| 1. Decline in demand due to increase in consumer income 2. Unsustainability of ‘democratic design’ concept 3. Emergence of competition from Asia 4. Increasing costs of raw materials 5. Global economic and financial crisis |
SWOT Analysis summary for IKEA
Strengths in IKEA SWOT Analysis
1. IKEA is an undisputed market leader in the global market of home improvement and furnishing. The Swedish furniture chain has 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries. [1] Additionally, the furniture retailer has 22 Pick-up and Order Points in 11 countries, 41 Shopping Centres in 15 countries and 38 Distribution sites in 18 countries. [2] The current leadership position of the company provides substantial advantages in terms of the economies of scale and at the same time creating a substantial entry barrier for new competitors. This is the most considerable strength for SWOT Analysis for IKEA
2. IKEA has developed the notion of democratic design which implies achieving an attractive form, quality, function and sustainability at a low price. The company attempts to integrate this notion to all of its products. Consistently increasing revenues of the business is an indication of successful outcome of such attempts. IKEA works with more than 1,000 designers globally through their suppliers who operate under democratic design culture and implement the concept in practice on a daily basis. Furthermore, the Swedish furniture chain has 18 in-house designers working with product development across the entire range [3] . The home improvement and furnishing chain also organizes annual democratic design days to build upon its success with positive implications on the bottom line.
3. IKEA has been able to deliver attractively designed products at low costs thanks to its product innovation capabilities. Innovations by IKEA play an instrumental role in terms of achieving democratic design as discussed above. The company has an innovation lab dubbed Space 10 in Copenhagen which conducts a wide range of futuristic projects such as 3D-printed meatballs, urban farming, energy-harvesting furniture and air-improving windows.
The list of innovative products introduced by IKEA include, but not limited to Vava lamps made of leaves, adhesive-free furnishings, severed seat storage, building block kitchens, flat-pack funerals etc.
However, the most important innovation introduced by IKEA is a process innovation of selling furniture in the flat pack form. Specifically, the world’s largest furniture retailer pioneered the practice of selling furniture in flat pack forms, where assembly is done by customers following clear instructions and illustrations provided by the company. This process innovation can be specified as the biggest factor that enabled IKEA to offer its products at the lowest prices.
4. IKEA generated operating income of EUR 25,6 billion during financial year 2021 an increase of 8,5% compared to the previous year [4] . The company has a healthy profit margin and strong cash reserves. Thanks to its solid financial position, the company is able to commit to considerable R&D expenses to further strengthen its presence in the global marketplace. Moreover, IKEA’s financial strengths can play an important role of cushion in times of recessions and decline in demand. Furthermore, in 2021 Interbrand and Forbes estimated IKEA brand value as USD 20,03 billion and USD 15,80 billion respectively. Strong brand value is a convincing indicator of a high level of customer loyalty and an overall strength of the business.
5. IKEA offers about 12000 products, yet apart from food products its product portfolio is efficiently focused. Specifically, the company offers a wide range of furniture and home appliances products that share the common set of features such as innovative design, low price and a high level of practicality. Moreover, IKEA stays up-to-date with changes in customer needs and preferences. Highly focused pattern of IKEA product portfolio increases the effectiveness of brand identity with positive implications on consumer loyalty.
Weaknesses in IKEA SWOT Analysis
1. During FY2021 only 11,3% of global sales were generated in Asia region, at the same time when 71% of sales were generated in Europe’s saturating market [5] (see figure below). Taking into account rapidly expanding economies of Asian region and prolonging economic stagnation in Europe, it can be argued that IKEA’s current weak presence in Asian market might weaken the share of the business in the global marketplace in medium-term perspective. This is a major weakness within IKEA SWOT Analysis framework.
IKEA sales per region in FY21
2. IKEA brand image is yet to fully recover from a series of ethics-related incidents the company had to deal with during the past years. The most controversial incidents include using Photoshop to alter the images of women in its Saudi Arabia catalogue in September 2012. Revelations by Ernst & Young in the same year that IKEA did have businesses with suppliers based in communist East Germany 30 years ago that used forced labour to produce IKEA products also considerably weakened the brand image.
Furthermore, in February 2013 IKEA had to recall its meatballs after it was found that some of them contained traces of horse meat. [6] The global furniture retailer has also been accused of avoiding EUR 1 billion taxes according to a report the European parliament. [7] Most recently, The Swedish furniture chain had another blow to its brand image when the company was fined EUR 1 million over staff spying scandal, ex-France chief handed suspended sentence. [8] These and other similar incidents have weakened IKEA’s brand image to a considerable extent.
IKEA Group Report contains a full version of IKEA SWOT Analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on IKEA . Moreover, the report contains analyses of IKEA leadership, organizational structure, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of IKEA marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

[1] Inter IKEA Holding B.V. Annual report FY21
[2] Group Yearly Summary (2016) IKEA Group
[3] IKEA invests in doubling its in-house design department (2020) IKEA, Available at: https://about.ikea.com/en/newsroom/2020/03/11/ikea-invests-in-doubling-its-inhouse-design-department
[4] Inter IKEA Holding B.V. Annual report FY21
[5] Facts & Figures (2019) IKEA, Available at: https://www.ikea.com/ms/en_AU/about_ikea/facts_and_figures/
[6] Business Insider (2013) Available at: http://www.businessinsider.com/ikeas-reputation-has-taken-a-beating-2013
[7] Shen, L. (2016) “Ikea Has Been Accused of Avoiding 1 Billion Euros in Taxes” Fortune, Available at: http://fortune.com/2016/02/12/ikea-tax-avoidance/
[8] Ikea fined €1 million over staff spying scandal, ex-France chief handed suspended sentence (2021) France 24, Available at: https://www.france24.com/en/france/20210615-ikea-fined-%E2%82%AC1-million-ex-france-chief-handed-suspended-sentence-over-staff-spying-scandal
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

IKEA SWOT analysis, strategy and structure
Related Papers
Kevin Zentner , Rachel Killoh , Zhen Sun
Ikea is a worldwide success story; their stores were visited 915 million times and their website was accessed over 2 billion times in 2016 (Highlights, 2016). As the world’s largest furniture retailer, Ikea services a number of market segments. With significant volume discounts and a vertically integrated supply chain, the production of low-cost goods target young families and low income segments. Conversely, the flagship Stockholm line of furniture entices sophisticated consumers towards mid-priced, superior value products with quality materials such as walnut, bone china, and rustic grain leather.
Anthony Olabode Ayodele (Bode Ayodele)
kelvin mulenga
This Briefing Paper has been designed to critically evaluate the application of Total Quality Management (TQM) in the world’s leading furniture company, IKEA. The paper will further critique and outline how IKEA holistically approaches the concept of TQM, applying it numerous principles across the various aspects of the business, and in general as a whole. A 10 minute accompanying video linked via a picture at the end of the report is also included.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
IKEA case study SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning
- Download HTML
- Download PDF

- Home & Garden

- Style & Fashion

- Health & Fitness

- Current Events

- Food & Drink

- Arts & Entertainment

- IT & Technique

- Government & Politics

- Uncategorized

- Cars & Machinery

- Arts & Humanities
- Communications
IKEA case study SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning
Related documents.

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Dabur Balance Sheet
| 15,122.9 | 13,654.4 | 12,284.5 | |
| 4,830 | 4,212.9 | 3,862.7 | |
| 10,303.1 | 9,441.4 | 8,421.9 |

Dabur Cash Flow Statement
| 2,013.5 | 1,488.4 | 1,802.3 | |
| -971.7 | -586.5 | -1,275.5 | |
| -1,161.9 | -1,035.2 | -491 |

Dabur India SWOT Analysis

Strengths
- Market Share: Dabur India has an impressive market share within different segments like oral care (15.8%), beverages (19.8%) and hair care (18.9%).
- Economies of Scale: As it’s a big brand with economies of scale, it can compete at lower prices, and it would be difficult for its competitors to compete or fabricate its product at lower prices.
- Digital Marketing & E-Commerce presence: Dabur has an impressive e-commerce presence, helping it reach a wider consumer base.
- National Presence: Dabur is an Indian FMCG company that sells products based on Ayurveda. It has nearly 6.7 million retail outlets across India, and its portfolio includes eight brands in different sectors.
- Health Brand: Dabur successfully established itself as a healthcare brand. Its Ayurvedic preparations include health supplements, digestives and other OTC products.
Weaknesses
- Highly Competitive Industry: The FMCG industry is dynamic and highly competitive, with diverse consumer preferences and pricing strategies.
- Competition in International Markets: Dabur faced tough competition in international markets, especially in the toothpaste segment.
- Highly Regulated Market: Regulatory compliance is higher in Indian markets for FMCG companies.
- High Turnover Rate: Due to the frequent use and short shelf life of FMCG, the industry turnover rate is high. These goods are produced and manufactured in large quantities and sold in high volumes.
Opportunities
- Inelastic Demand: Usually, the demand for any product or industry is affected by various factors. However, the demand for FMCG is inelastic, i.e., changes in market conditions will have a minimal impact on demand.
- Strong Brand: Dabur has established itself as a strong brand, and people, even in rural areas, know it, making it a household name.
- Price Setters: Customers prefer choosing one product over another if they have brand loyalty. The sellers can also charge a marginally higher price and may become price setters to a certain extent.
- Ayurvedic Product Portfolio: Ayurvedic product demand is increasing in India & abroad.
- Focus on Health: Now, people focus more on healthcare products and brands, so Dabur is well placed in this segment.
Threats
- Monopolistic Competition: In monopolistic competition, there are many buyers and sellers. But they all do not sell homogeneous products. The products are similar, but all sellers sell slightly differentiated products. Hence, this sector is highly competitive.
- Big Portfolio: Dabur has a big portfolio and a wide product range. There is a threat of duplication from local brands that can make duplicate products and sell them under Dabur’s brand name.
Competitors of Dabur India
- Colgate-Palmolive
The company has a robust track record, making it a leading FMCG Company in India and the world’s largest Ayurvedic and natural healthcare company, with a portfolio of over 250 Herbal / Ayurvedic products. It maintains a clear vision for the future. However, competitors and regulations governing the FMCG industry present some challenges. As India grows and natural healthcare demand increases, Dabur is poised to play a significant role.
The company becomes a true winner against its competitors if it handles its challenges efficiently and takes advantage of future opportunities in a timely manner. Further, we recommend consulting with your financial advisor before making any investment decision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When did dabur india start trading at nse.
It started trading on November 3, 1994.
What type of market does Dabur India compete in?
It operates in a monopolistic market where many buyers and sellers compete with slightly differentiated products.
How many business segments does Dabur have?
It operates in three segments, namely 1) Home & Personal Care, 2) Health Care, and 3) Food & Beverages.
Who is the CEO of Dabur?
Mohit Malhotra is Dabur’s chief executive officer.
What makes Dabur Unique?
It blends traditional knowledge of Ayurveda with modern-day science and is famous for its natural ingredients.
Related Posts

Bikaji Foods Case Study – Product Portfolio, Financial Statements, & Swot Analysis

Bajaj Housing Finance IPO Case Study: Products, Financials, And SWOT Analysis

Ultratech Cement Case Study – Financials Statements, & Swot Analysis
Pocketful is an advanced trading platform that empowers traders with cutting-edge technology. we provide innovative tools and resources to make trading more accessible and practical., quick links.
- Open an Account
- Pocketful Web
- Pocketful App
- Investment Tool
- Trading Tool
- Support Portal
- Referral Program
- Calculators
- Stocks Pages
- Government Schemes
- Index Heat Map
- Stock Screener
- Mutual Funds
- Terms & Conditions
- Policies & Procedures
- Privacy Policy
- Press & Media
We are a concern of PACE Group. Pocketful is an investing platform that helps people be better investors. Pocketful unlocks the discoverability of new investment and trading ideas.
Join the waitlist.
Add your details and start your journey toward a better future with Pocketful in your investing career.
You have successfully subscribed to the newsletter
There was an error while trying to send your request. Please try again.
- Business Cycle
- Business Environment
- Consumer Protection
- Corporate Responsibility
- External Influences
- Globalisation
- Government Influence
- International Business
- Financial Risk
- Investment Appraisal
- Sources of Finance
- Competitive Advantage
- Customer Focus
- International Marketing
- Market Research
- Marketing Planning
- Marketing Strategies
- Product Launch
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Portfolio
- Segmentation
- The Marketing Mix
- Continuous Improvement
- Customer Service
- Health and Safety
- Lean Production
- Location of Business
- Management of Change
- Merger and Acquisition
- New Product Development
- New Technology
- Product Development
- Production Process
- Research and Development
- Supply Chain
- Communications
- Developing People
- Equal Opportunities
- Managing Change
- Organising People
- Protecting People
- Recruitment and Selection
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Skills and Competencies
- Aims and Objectives
- Business Expansion
- Business Organisation
- Business Planning
- Business Start-Up
- Business Strategy
- Decision Making
- Sectors of Industry
- Stakeholders
- Strategic Planning
- Types of Organisation
- External environment
- External Environment
- eBook Collections
- Audio Case Studies
- Printed Books By Edition
- Employee Retention
- HR Software
- Hybrid Working
- Managing People
- Motivating People
- Performance Management
- Recruitment
- Time Management
- Training and Development
- Business Acquisition
- Business Growth
- Business Plan
- Business Startup
- Entrepreneurship
- Small Business
- Strategic management
- Types of Business
- Accountants
- Bookkeeping
- Budgeting and Cash Flow
- Business Debt
- Business Financing
- Business Funding
- Business Insurance
- Business Investment
- Business Loans
- Business Payments
- Business Taxation
- Market Trading
- Advertising
- Affiliate Marketing
- Business Branding
- Business Events
- Content Marketing
- Conversion Rate Optimisation
- Customer Experience
- Digital Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Lead Generation
- Link Building
- Marketing Agencies
- Marketing Strategy
- Pay Per Click Advertising
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Business Efficiency
- Business Innovation
- Business Location
- Business Management
- Business Security
- Manufacturing
- Outsourcing
- Project Management
- Quality Management
- The Supply Chain
- Business Law
- Coronavirus
- Sustainable Business
- The Economy
- Stakeholder
- Ethical Business
- Business of Gambling
- Casino Bonuses
- Casino Games
- Casino Guides
- Mobile Gambling
- Online Casino
- Sports Betting
- Tips and Tricks
- Online Learning
- Schools and Colleges
- Students and Teachers
- Studying Internationally
- Universities
- Writing Services
- Cosmetic Procedures
- Cannabidiol (CBD)
- Cannabis/Marijuana
- Dental Care
- Mental Health
- Office Wellbeing
- Relationships
- Supplements
- Banking and Savings
- Credit Cards
- Credit Score and Report
- Debt Management
- International Money Transfers
- Investments
- Payday Loans
- Personal Insurance
- Personal Law
- Motor Accidents
- Motor Finance
- Motor Insurance
- Motoring Accessories
- Virtual Reality
- Gaming Accessories
- Mobile Gaming
- Online Gaming
- Video Games
- Buying Selling and Renting Property
- Construction
- Property Cleaning
- Property Investments
- Property Renovation
- Business Travel
- Camping Activities
- Travel Guides
- Travel Safety
- Visas and Citizenship
- Antiques and Art
- TV, Film & Music
- Mobile Apps
- Mobile Phone
- Photography
- Digital Transformation
- Crypto Exchange
- Crypto in Business
- Crypto Mining
- Crypto Regulation
- Crypto Trading
- Accessories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Programming
- Security & Privacy
- Software Development
- Web Analytics
- Website Design
- Website Development
- Website guides
- Website Hosting
- Guest Posting
- Membership Billing
- Membership Cancel
- Membership Invoice
- membership levels
- Your Profile
- Account Details
- Lost Password
No products in the basket.

IKEA is an internationally known home furnishing retailer. It has grown rapidly since it was founded in 1943. Today it is the world’s largest furniture retailer, recognised for its Scandinavian style. The majority of IKEA’s furniture is flat-pack, ready to be assembled by the consumer. This allows a reduction in costs and packaging. IKEA carries a range of 9,500 products, including home furniture and accessories. This wide range is available in all IKEA stores and customers can order much of the range online through IKEA’s website . There are 18 stores in the UK to date, the first of which opened in Warrington in 1987. In July 2009 IKEA opened a store in Dublin too – its first in Ireland.

IKEA stores include restaurants and cafes serving typical Swedish food. They also have small food shops selling Swedish groceries, everything from the famous meatballs to jam. Stores are located worldwide. In August 2008 the IKEA group had 253 stores in 24 countries, with a further 32 stores owned and run by franchisees . It welcomed a total of 565 million visitors to the stores during the year and a further 450 million visits were made to the IKEA website. IKEA sales reached 21.2 billion Euros in 2008 showing an increase of 7%. The biggest sales countries are Germany, the USA, France, the UK and Sweden. In 2008 IKEA opened 21 new stores in 11 countries and expects to open around 20 more in 2009 as part of its strategy for growth.
Low prices are one of the cornerstones of the IKEA concept and help to make customers want to buy from IKEA. This low price strategy is coupled with a wide range of well designed, functional products. IKEA’s products cater for every lifestyle and life stage of its customers, who come from all age groups and types of households. This is vital in times when the retail sector is depressed, as it increases IKEA’s potential market.
Since it was founded IKEA has always had concern for people and the environment. The IKEA vision ‘to create a better everyday life for many people puts this concern at the heart of the business. IKEA has responded to the public’s rising concern for sustainability in its choice of product range, suppliers, stores and communication. It has also spotted business potential in providing sustainable solutions. IKEA’s concern for people and the environment encourages it to make better use of both raw materials and energy. This keeps costs down and helps the company to reach its green targets and have an overall positive impact on the environment.
This case study will show why IKEA believes a strong environmental stance is good business practice.
SWOT analysis

IKEA’s goals of sustainability and environmental design are central to its business strategy. It has launched a new sustainability plan to take the company through to 2015. This will combine social, environmental and economic issues.
IKEA uses SWOT analysis to help it reach its objectives. This is a strategic planning tool. It helps the business to focus on key issues. SWOT is the first stage of planning and looks at the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats involved in a project or business venture.
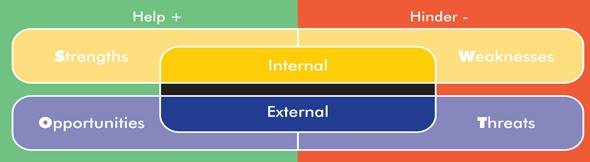
Strengths and weaknesses are internal aspects. This means that they are within the control of the business. They may refer to aspects of marketing, finance, manufacturing or organisation. Opportunities and threats are external factors. This means that they are outside the control of the business. These may include the environment, the economic situation, social changes or technological advances, such as the internet.
A business can create opportunities and counter threats by making the most of its strengths and addressing its weaknesses. For example, one of IKEA’s key strengths is its strategic aim to use no more material than necessary in the production of each item. In addition, it develops its product plans to increase its use of waste or recycled materials.
- One particular table, the NORDEN table, uses knotty birch wood. The knots in this wood usually mean it is rejected by other retailers and manufacturers as unsuitable for use. However, IKEA has made the knots part of its design feature.
- OGLA chairs are made using wood waste from sawmills and LACK tables use a ‘sandwich’ of stiff card between wood sheets to reduce the amount of solid wood needed.

Strengths could include a company’s specialist marketing expertise or its location. They are any aspect of the business that adds value to its product or service. IKEA’s strengths include:
- a strong global brand which attracts key consumer groups. It promises the same quality and range worldwide
- its vision ‘to create a better everyday life for many people’
- a strong concept based on offering a wide range of well designed, functional products at low prices
- a ‘democratic design’ reaching an ideal balance between function, quality, design and price. IKEA’s ‘Cost Consciousness’ means that low prices are taken into account when each product is designed from the outset.

These strengths contribute to IKEA being able to attract and retain its customers. One way IKEA measures its strengths is through the use of Key Performance Indicators (KPI). KPIs help IKEA to assess the progress of its vision and long-term goals by setting targets and monitoring progress towards these. An example of one of IKEA’s KPIs is the percentage of suppliers that are currently IWAY approved. The IWAY is the IKEA Way of Purchasing Home Furnishing Products. This guideline defines the social and environmental requirements IKEA expects of its suppliers.
IKEA has strengths right through its production processes:
- Increasing use of renewable materials IKEA improved its overall use from 71% in 2007 to 75% in 2009.
- ‘Smarter’ use of raw materials IKEA increased the use of recycled or reclaimed waste products in energy production across all stores from 84% in 2007 to 90% in 2009.
- Volume commitments IKEA believes in creating long-term partnerships with its suppliers in order to achieve this. By committing to buying large volumes over a number of years IKEA can negotiate lower prices. This also benefits the suppliers because they enjoy the greater security of having guaranteed orders.
- Economies of scale, for instance, bulk buying at cheaper unit costs.
- Sourcing materials close to the supply chain to reduce transport costs.
- Delivering products directly from the supplier to IKEA stores. This slashes handling costs reduces road miles and lowers the carbon footprint.
- Using new technologies, for example, IKEA’s OGLA chair has been in its range since 1980. The chair has changed through the years to reduce the amount of raw materials needed.
Opportunities

A business uses its strengths to take advantage of the opportunities that arise. IKEA believes that its environmentally focused business conduct will result in good returns even in a price sensitive market. As the company states:
‘There is a true business potential for IKEA in providing solutions that enable customers to live a more sustainable life at home. IKEA is developing effective solutions for customers in order to support them in recycling or reusing used products, aiming at no products ending up at landfill and the recycled materials used in producing new IKEA products.’
Some of the opportunities that IKEA takes advantage of through its sustainability agenda are:
- a growing demand for greener products
- a growing demand for low priced products. Trends in the current financial climate may result in consumers trading down from more expensive stores
- demand for reduced water usage and lower carbon footprints.

IKEA has a number of areas of focus in its work with sustainability, each of which it supports in various ways:
- Solutions for a sustainable life at home IKEA gives online tips and ideas for this.
- Sustainable use of resources. IKEA aims for zero waste to landfill, wastewater treatment and programmes to reduce its use of water.
- Reducing carbon footprint. IKEA aims to reduce energy use, use more renewable energy, cut its use of air transport and reduce packaging. Its green transport initiative includes an aim to reduce business flights by 20% in 2010 and 60% by 2015.
- Developing social responsibility. IKEA’s policy includes support for charities such as the World Wildlife Fund, UNICEF and Save the Children.
- Being open with all its stakeholders. This involves building trust through good communication with consumers, co-workers, key opinion formers and the press. Being sustainable is a central part of IKEA’s image.
Weaknesses and threats

IKEA has to acknowledge its weaknesses in order to improve and manage them. This can play a key role in helping it to set objectives and develop new strategies. IKEA’s weaknesses may include:
- The size and scale of its global business. This could make it hard to control standards and quality. Some countries where IKEA products are made do not implement legislation to control working conditions. This could represent a weak link in IKEA’s supply chain, affecting consumer views of IKEA’s products. The IWAY code is backed up by training and inspectors visiting factories to make sure that suppliers meet their requirements.
- The need for low cost products. This needs to be balanced against producing good quality. IKEA also needs to differentiate itself and its products from competitors. IKEA believes there is no compromise between offering good quality products and low prices.
- IKEA needs to keep good communication with its consumers and other stakeholders about its environmental activities. The scale of the business makes this a difficult task. IKEA produces publications in print and online (for example ‘People and the Environment’) and carries out major TV and radio campaigns to enable the business to communicate with different target audiences.

If a company is aware of possible external threats, it can plan to counteract them. By generating new ideas, IKEA can use a particular strength to defend against threats in the market. Threats to IKEA may stem from:
- Social trends such as the slowdown in first time buyers entering the housing market. This is a core market segment for IKEA products
- market forces more competitors entering the low price household and furnishings markets. IKEA needs to reinforce its unique qualities to compete with these
- economic factors the recession slows down consumer spending and disposable income reduces.
IKEA addresses these issues in many ways. It manages weaknesses and threats to create a positive outcome.

Social trends : IKEA is building online help to guide customers to a more sustainable life. Here it can focus on home improvement in the slowing housing market. It supports customers with tips and ideas on its website to reduce their impact on the environment. This will also save them money. Staff are trained on sustainability, both on what IKEA is doing and how they can take responsibility to become sustainable for themselves.
Market forces : IKEA is large enough to enjoy economies of scale. This lowers average costs in the long run through, for example, better use of technology or employing specialized managers. Economies of scale also give a business a competitive edge if cost savings are then passed on to customers in the form of lower prices. This puts up high barriers to entry for smaller companies entering the market.
Economic factors : IKEA’s low prices create appeal amongst its customers in tough financial times. It is vital to keep prices as low as possible when the retail sector is depressed. IKEA’s pricing strategy targets consumers with limited financial resources. Its products will also appeal to those with higher budgets through good quality and design. The company must ensure that it is always recognised as having the lowest prices on the market in the future. Communication plays an important role here.

IKEA is a well-known global brand with hundreds of stores across the world. In order to improve performance, it must assess its external and competitive environment. This will reveal the key opportunities it can take advantage of and the threats it must deal with. IKEA responds to both internal and external issues in a proactive and dynamic manner by using its strengths and reducing its weaknesses. Through this, IKEA is able to generate the strong growth it needs to retain a strong identity in the market.
IKEA’s passion combines design, low prices, economical use of resources, and responsibility for people and the environment. The company’s products, processes and systems all demonstrate its environmental stance. For example, clever use of packaging and design means more items can fit into a crate, which means fewer delivery journeys. This in turn reduces IKEA’s carbon footprint.
IKEA believes that there is no compromise between doing good business and being a good business. It aims to go beyond profitability and reputation. IKEA is intent on becoming a leading example in developing a sustainable business. This will create a better everyday life for its customers. IKEA has discovered a business truth being sustainable and responsible is not just good for customers and the planet, it is also good for business!
More from this company >
Vision values and mission in driving strategy, building a sustainable supply chain, swot analysis in action, to create a better everyday life for the many people, securing a market leading future through swot analysis, changing the views of business, more case studies >, ‘the luck of the irish’: the rise of the gambling industry in ireland , understanding the fees and interest rates of payday loans, 10 cost-efficient ways to strengthen your brand, 10 market analysis mistakes to avoid, 10 tips for writing your will, 3 tips for finding and choosing the right wood tone for your flooring, 5 key benefits of call handling services for small business, 5 keys to success for future ready companies, 5 negotiation tips to consider when buying a business.
Subscribe | Write for Us | Contact | Terms of Service | Privacy Policy | Copyright © Copyright 1995 - 2023 GC Digital Marketing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As we mentioned earlier, IKEA is the largest furniture retailer in the world and enjoyed a brand value of $17.43 billion in 2022. Your brand value is a monetary estimate of the value of your brand equity. Brand equity, on the other hand, refers to the commercial value enjoyed by a company based on the social perception of its products or ...
According to UK Customer Insights report on IKEA by Verdict, IKEA's customers are less satisfied with its product and services quality than the average customer in UK buying at other stores. Firm's cost reductions lead to decreasing product quality, which was followed by higher number of products returned and damaged brand.
Here is the SWOT analysis for IKEA. A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture's success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan.
This article performs a SWOT Analysis of IKEA by focusing on the key drivers of success for the company. The key themes in this article are that IKEA's business model of cost leadership has held it in good stead so far and to continue, the company needs to innovate and find newer strategic imperatives for itself. Further, the article also discusses the pioneering DIY or Do It Yourself ...
2. Strong Financial Position. Financial stability is one of IKEA's essential qualities. The corporation reported revenue of €47.6 billion and profits of €1.6 billion in 2023, indicating a continuing growing trend. Online sales have stabilized at 23%, compared to 22% in FY22.
According to a study by Interbrand, IKEA's brand value reached $18.4 billion in 2020, making it the 29th most valuable brand globally. 3. Vertically Integrated Supply Chain and Efficient Operations ... IKEA's SWOT analysis reveals a company with significant strengths, such as its unique business model, strong brand recognition, and ...
Introduction. IKEA SWOT ANALYSIS: In the realm of home furnishing, IKEA has established itself as a global powerhouse, redefining the concept of affordable and stylish furniture.This Swedish retail giant has a unique business model that sets it apart from competitors, and it has continued to thrive over the years. To understand how IKEA has achieved such success, it is essential to conduct a ...
Although the saying "any press is good press" may come into mind, in IKEA's case, bad press leads to distrust from their customers. Low quality. IKEA products are known for being lesser quality. This seems to be a byproduct of offering inexpensive products. ... SWOT analysis of IKEA: Opportunities. Few countries. IKEA is only in 38 ...
The SWOT Analysis is used to examine the strategy of IKEA, the world's largest furniture store. The Do It Yourself (DIY) concept ensures that the company keeps costs low and passes on the value to customers. The company was founded in 1943 and is known for its simple yet effective approach to retailing with the DIY or Do It Yourself concept ...
Weaknesses of IKEA. 1. Standardization of Production and Output. IKEA has achieved economies of scale in manufacturing and low-cost production due in part to the standardization of its production processes that in turn, result in the creation of standardized products. Remember that its products are intended for the mass market.
IKEA SWOT Analysis - an overview. SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. SWOT analysis is a strategic tool that helps businesses to analyse internal and external factors affecting the bottom line. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that can be influenced by the company.
2.3 THE IKEA STRATEGY Based on its shareholder analysis, IKEA has changed the entire retail market with its strategy of retailing by providing goods that are meant to be used immediately, products that are designed for the current date (IKEA case study, 2009). By the time the design or tastes change, people have to be able to afford something new.
IKEA's goals of sustainability and environmental design are central to its. business strategy. It has launched a new sustainability plan to take the company. through to 2015. This will combine social, environmental and economic issues. IKEA uses SWOT analysis to help it reach its objectives. This is a strategic.
Are you assigned an Ikea case study by your professor? Then this video is perfect for you. In this video, you will know the answer to the question- How is Ik...
IKEA Case Study[245] - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. [IKEA CASE STUDY] This document discusses a case study on IKEA. It begins by defining a SWOT analysis as a strategic planning tool used to analyze an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It explains that internal factors like strengths and ...
SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning: An IKEA case study Introduction Carrie Mo Minnie Chen Anne Meinecke The World's largest furniture retailer Include restaurants and cafe with Swedish food Stores in 24 countries, Germany, USA, France, UK and Sweden are the five
IKEA case study SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning Page 1: Introduction. IKEA is an internationally known home furnishing retailer. It has grown rapidly since it was founded in 1943. Today it is the world's largest furniture retailer, recognised for its Scandinavian style. The majority of IKEA's furniture is flat-pack, ready to be ...
SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning An IKEA case study • Introduction IKEA is an internationally known home furnishing retailer. It has grown rapidly since it was founded in 1943. Today it is the world's largest furniture retailer, recognised for its Scandinavian style. The majority of IKEA's furniture is flat-pack, ready to be assembled by the consumer.
Do you want to know how IKEA operates and its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats? Are you looking for a video to learn about them? Don't worry...
(IKEA,2013) The intention of writing this report swot analysis case study is to research the brand by its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. We as a group took an initiative to find out the way ikea uses swot analysis to achieve its vision for a sustainable life and how it helps focus on social, economic issues while ensuring the ...
IKEA's goals of sustainability and environmental. design are central to its business strategy. It has launched a new sustainability plan to take the company. through to 2015. This will combine social, environmental and economic issues. IKEA uses SWOT analysis to help it reach its objectives.
IKEA case study SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning Page 1: Introduction IKEA is an internationally known home furnishing retailer. It has grown rapidly since it was founded in 1943. Today it is the world's largest furniture retailer, recognised for its Scandinavian style. The majority of IKEA's furniture is flat-pack, ready to be ...
Dabur Case Study - Business Model, Financial Statements, & Swot Analysis June 29, 2024 June 29, 2024 Harjyot Singh 0 Dabur needs no introduction; it is one of India's most trusted and famous household brands.
This case study will show why IKEA believes a strong environmental stance is good business practice. SWOT analysis. IKEA's goals of sustainability and environmental design are central to its business strategy. It has launched a new sustainability plan to take the company through to 2015. This will combine social, environmental and economic ...