

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, should college athletes be paid an expert debate analysis.
Extracurriculars

The argumentative essay is one of the most frequently assigned types of essays in both high school and college writing-based courses. Instructors often ask students to write argumentative essays over topics that have “real-world relevance.” The question, “Should college athletes be paid?” is one of these real-world relevant topics that can make a great essay subject!
In this article, we’ll give you all the tools you need to write a solid essay arguing why college athletes should be paid and why college athletes should not be paid. We'll provide:
- An explanation of the NCAA and what role it plays in the lives of student athletes
- A summary of the pro side of the argument that's in favor of college athletes being paid
- A summary of the con side of the argument that believes college athletes shouldn't be paid
- Five tips that will help you write an argumentative essay that answers the question "Should college athletes be paid?"

The NCAA is the organization that oversees and regulates collegiate athletics.
What Is the NCAA?
In order to understand the context surrounding the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”, you have to understand what the NCAA is and how it relates to student-athletes.
NCAA stands for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (but people usually just call it the “N-C-double-A”). The NCAA is a nonprofit organization that serves as the national governing body for collegiate athletics.
The NCAA specifically regulates collegiate student athletes at the organization’s 1,098 “member schools.” Student-athletes at these member schools are required to follow the rules set by the NCAA for their academic performance and progress while in college and playing sports. Additionally, the NCAA sets the rules for each of their recognized sports to ensure everyone is playing by the same rules. ( They also change these rules occasionally, which can be pretty controversial! )
The NCAA website states that the organization is “dedicated to the well-being and lifelong success of college athletes” and prioritizes their well-being in academics, on the field, and in life beyond college sports. That means the NCAA sets some pretty strict guidelines about what their athletes can and can't do. And of course, right now, college athletes can't be paid for playing their sport.
As it stands, NCAA athletes are allowed to receive scholarships that cover their college tuition and related school expenses. But historically, they haven't been allowed to receive additional compensation. That meant athletes couldn't receive direct payment for their participation in sports in any form, including endorsement deals, product sponsorships, or gifts.
Athletes who violated the NCAA’s rules about compensation could be suspended from participating in college sports or kicked out of their athletic program altogether.

The Problem: Should College Athletes Be Paid?
You know now that one of the most well-known functions of the NCAA is regulating and limiting the compensation that student-athletes are able to receive. While many people might not question this policy, the question of why college athletes should be paid or shouldn't be paid has actually been a hot-button topic for several years.
The fact that people keep asking the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” indicates that there’s some heat out there surrounding this topic. The issue is frequently debated on sports talk shows , in the news media , and on social media . Most recently, the topic re-emerged in public discourse in the U.S. because of legislation that was passed by the state of California in 2019.
In September 2019, California governor Gavin Newsom signed a law that allowed college athletes in California to strike endorsement deals. An endorsement deal allows athletes to be paid for endorsing a product, like wearing a specific brand of shoes or appearing in an advertisement for a product.
In other words, endorsement deals allow athletes to receive compensation from companies and organizations because of their athletic talent. That means Governor Newsom’s bill explicitly contradicts the NCAA’s rules and regulations for financial compensation for student-athletes at member schools.
But why would Governor Newsom go against the NCAA? Here’s why: the California governor believes that it's unethical for the NCAA to make money based on the unpaid labor of its athletes . And the NCAA definitely makes money: each year, the NCAA upwards of a billion dollars in revenue as a result of its student-athlete talent, but the organization bans those same athletes from earning any money for their talent themselves. With the new California law, athletes would be able to book sponsorships and use agents to earn money, if they choose to do so.
The NCAA’s initial response to California’s new law was to push back hard. But after more states introduced similar legislation , the NCAA changed its tune. In October 2019, the NCAA pledged to pass new regulations when the board voted unanimously to allow student athletes to receive compensation for use of their name, image, and likeness.
Simply put: student athletes can now get paid through endorsement deals.
In the midst of new state legislation and the NCAA’s response, the ongoing debate about paying college athletes has returned to the spotlight. Everyone from politicians, to sports analysts, to college students are arguing about it. There are strong opinions on both sides of the issue, so we’ll look at how some of those opinions can serve as key points in an argumentative essay.

Let's take a look at the arguments in favor of paying student athletes!
The Pros: Why College Athletes Should B e Paid
Since the argument about whether college athletes should be paid has gotten a lot of public attention, there are some lines of reasoning that are frequently called upon to support the claim that college athletes should be paid.
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments in favor of why college athletes should be paid. We'll also give you some ideas on how you can support these arguments in an argumentative essay.
Argument 1: The Talent Should Receive Some of the Profits
This argument on why college athletes should be paid is probably the one people cite the most. It’s also the easiest one to support with facts and evidence.
Essentially, this argument states that the NCAA makes millions of dollars because people pay to watch college athletes compete, and it isn’t fair that the athletes don't get a share of the profits
Without the student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t earn over a billion dollars in annual revenue , and college and university athletic programs wouldn’t receive hundreds of thousands of dollars from the NCAA each year. In fact, without student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist at all.
Because student athletes are the ones who generate all this revenue, people in favor of paying college athletes argue they deserve to receive some of it back. Otherwise, t he NCAA and other organizations (like media companies, colleges, and universities) are exploiting a bunch of talented young people for their own financial gain.
To support this argument in favor of paying college athletes, you should include specific data and revenue numbers that show how much money the NCAA makes (and what portion of that actually goes to student athletes). For example, they might point out the fact that the schools that make the most money in college sports only spend around 10% of their tens of millions in athletics revenue on scholarships for student-athletes. Analyzing the spending practices of the NCAA and its member institutions could serve as strong evidence to support this argument in a “why college athletes should be paid” essay.

I've you've ever been a college athlete, then you know how hard you have to train in order to compete. It can feel like a part-time job...which is why some people believe athletes should be paid for their work!
Argument 2: College Athletes Don’t Have Time to Work Other Jobs
People sometimes casually refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job.” For many student athletes, this is literally true. The demands on a student-athlete’s time are intense. Their days are often scheduled down to the minute, from early in the morning until late at night.
One thing there typically isn’t time for in a student-athlete’s schedule? Working an actual job.
Sports programs can imply that student-athletes should treat their sport like a full-time job as well. This can be problematic for many student-athletes, who may not have any financial resources to cover their education. (Not all NCAA athletes receive full, or even partial, scholarships!) While it may not be expressly forbidden for student-athletes to get a part-time job, the pressure to go all-in for your team while still maintaining your eligibility can be tremendous.
In addition to being a financial burden, the inability to work a real job as a student-athlete can have consequences for their professional future. Other college students get internships or other career-specific experience during college—opportunities that student-athletes rarely have time for. When they graduate, proponents of this stance argue, student-athletes are under-experienced and may face challenges with starting a career outside of the sports world.
Because of these factors, some argue that if people are going to refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job,” then student-athletes should be paid for doing that job.
To support an argument of this nature, you can offer real-life examples of a student-athlete’s daily or weekly schedule to show that student-athletes have to treat their sport as a full-time job. For instance, this Twitter thread includes a range of responses from real student-athletes to an NCAA video portraying a rose-colored interpretation of a day in the life of a student-athlete.
Presenting the Twitter thread as one form of evidence in an essay would provide effective support for the claim that college athletes should be paid as if their sport is a “full-time job.” You might also take this stance in order to claim that if student-athletes aren’t getting paid, we must adjust our demands on their time and behavior.
Argument 3: Only Some Student Athletes Should Be Paid
This take on the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” sits in the middle ground between the more extreme stances on the issue. There are those who argue that only the student athletes who are big money-makers for their university and the NCAA should be paid.
The reasoning behind this argument? That’s just how capitalism works. There are always going to be student-athletes who are more talented and who have more media-magnetizing personalities. They’re the ones who are going to be the face of athletic programs, who lead their teams to playoffs and conference victories, and who are approached for endorsement opportunities.
Additionally, some sports don't make money for their schools. Many of these sports fall under Title IX, which states that no one can be excluded from participation in a federally-funded program (including sports) because of their gender or sex. Unfortunately, many of these programs aren't popular with the public , which means they don't make the same revenue as high-dollar sports like football or basketball .
In this line of thinking, since there isn’t realistically enough revenue to pay every single college athlete in every single sport, the ones who generate the most revenue are the only ones who should get a piece of the pie.
To prove this point, you can look at revenue numbers as well. For instance, the womens' basketball team at the University of Louisville lost $3.8 million dollars in revenue during the 2017-2018 season. In fact, the team generated less money than they pay for their coaching staff. In instances like these, you might argue that it makes less sense to pay athletes than it might in other situations (like for University of Alabama football, which rakes in over $110 million dollars a year .)

There are many people who think it's a bad idea to pay college athletes, too. Let's take a look at the opposing arguments.
The Cons: Why College Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid
People also have some pretty strong opinions about why college athletes shouldn't be paid. These arguments can make for a pretty compelling essay, too!
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments against paying college athletes. We'll also talk about how you can support each of these claims in an essay.
Argument 1: College Athletes Already Get Paid
On this side of the fence, the most common reason given for why college athletes should not be paid is that they already get paid: they receive free tuition and, in some cases, additional funding to cover their room, board, and miscellaneous educational expenses.
Proponents of this argument state that free tuition and covered educational expenses is compensation enough for student-athletes. While this money may not go straight into a college athlete's pocket, it's still a valuable resource . Considering most students graduate with nearly $30,000 in student loan debt , an athletic scholarship can have a huge impact when it comes to making college affordable .
Evidence for this argument might look at the financial support that student-athletes receive for their education, and compare those numbers to the financial support that non-athlete students receive for their schooling. You can also cite data that shows the real value of a college tuition at certain schools. For example, student athletes on scholarship at Duke may be "earning" over $200,000 over the course of their collegiate careers.
This argument works to highlight the ways in which student-athletes are compensated in financial and in non-financial ways during college , essentially arguing that the special treatment they often receive during college combined with their tuition-free ride is all the compensation they have earned.

Some people who are against paying athletes believe that compensating athletes will lead to amateur athletes being treated like professionals. Many believe this is unfair and will lead to more exploitation, not less.
Argument 2: Paying College Athletes Would Side-Step the Real Problem
Another argument against paying student athletes is that college sports are not professional sports , and treating student athletes like professionals exploits them and takes away the spirit of amateurism from college sports .
This stance may sound idealistic, but those who take this line of reasoning typically do so with the goal of protecting both student-athletes and the tradition of “amateurism” in college sports. This argument is built on the idea that the current system of college sports is problematic and needs to change, but that paying student-athletes is not the right solution.
Instead, this argument would claim that there is an even better way to fix the corrupt system of NCAA sports than just giving student-athletes a paycheck. To support such an argument, you might turn to the same evidence that’s cited in this NPR interview : the European model of supporting a true minor league system for most sports is effective, so the U.S. should implement a similar model.
In short: creating a minor league can ensure athletes who want a career in their sport get paid, while not putting the burden of paying all collegiate athletes on a university.
Creating and supporting a true professional minor league would allow the students who want to make money playing sports to do so. Universities could then confidently put earned revenue from sports back into the university, and student-athletes wouldn’t view their college sports as the best and only path to a career as a professional athlete. Those interested in playing professionally would be able to pursue this dream through the minor leagues instead, and student athletes could just be student athletes.
The goal of this argument is to sort of achieve a “best of both worlds” solution: with the development and support of a true minor league system, student-athletes would be able to focus on the foremost goal of getting an education, and those who want to get paid for their sport can do so through the minor league. Through this model, student-athletes’ pursuit of their education is protected, and college sports aren’t bogged down in ethical issues and logistical hang-ups.
Argument 3: It Would Be a Logistical Nightmare
This argument against paying student athletes takes a stance on the basis of logistics. Essentially, this argument states that while the current system is flawed, paying student athletes is just going to make the system worse. So until someone can prove that paying collegiate athletes will fix the system, it's better to maintain the status quo.
Formulating an argument around this perspective basically involves presenting the different proposals for how to go about paying college athletes, then poking holes in each proposed approach. Such an argument would probably culminate in stating that the challenges to implementing pay for college athletes are reason enough to abandon the idea altogether.
Here's what we mean. One popular proposed approach to paying college athletes is the notion of “pay-for-play.” In this scenario, all college athletes would receive the same weekly stipend to play their sport .
In this type of argument, you might explain the pay-for-play solution, then pose some questions toward the approach that expose its weaknesses, such as: Where would the money to pay athletes come from? How could you pay athletes who play certain sports, but not others? How would you avoid Title IX violations? Because there are no easy answers to these questions, you could argue that paying college athletes would just create more problems for the world of college sports to deal with.
Posing these difficult questions may persuade a reader that attempting to pay college athletes would cause too many issues and lead them to agree with the stance that college athletes should not be paid.

5 Tips for Writing About Paying College Athletes
If you’re assigned the prompt “Should college athletes be paid," don't panic. There are several steps you can take to write an amazing argumentative essay about the topic! We've broken our advice into five helpful tips that you can use to persuade your readers (and ace your assignment).
Tip 1: Plan Out a Logical Structure for Your Essay
In order to write a logical, well-organized argumentative essay, one of the first things you need to do is plan out a structure for your argument. Using a bare-bones argumentative outline for a “why college athletes should be paid” essay is a good place to start.
Check out our example of an argumentative essay outline for this topic below:
- The thesis statement must communicate the topic of the essay: Whether college athletes should be paid, and
- Convey a position on that topic: That college athletes should/ should not be paid, and
- State a couple of defendable, supportable reasons why college athletes should be paid (or vice versa).
- Support Point #1 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #2 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #3 with evidence
- New body paragraph addressing opposing viewpoints
- Concluding paragraph
This outline does a few things right. First, it makes sure you have a strong thesis statement. Second, it helps you break your argument down into main points (that support your thesis, of course). Lastly, it reminds you that you need to both include evidence and explain your evidence for each of your argumentative points.
While you can go off-book once you start drafting if you feel like you need to, having an outline to start with can help you visualize how many argumentative points you have, how much evidence you need, and where you should insert your own commentary throughout your essay.
Remember: the best argumentative essays are organized ones!
Tip 2: Create a Strong Thesis
T he most important part of the introduction to an argumentative essay claiming that college athletes should/should not be paid is the thesis statement. You can think of a thesis like a backbone: your thesis ties all of your essay parts together so your paper can stand on its own two feet!
So what does a good thesis look like? A solid thesis statement in this type of argumentative essay will convey your stance on the topic (“Should college athletes be paid?”) and present one or more supportable reasons why you’re making this argument.
With these goals in mind, here’s an example of a thesis statement that includes clear reasons that support the stance that college athletes should be paid:
Because the names, image, and talents of college athletes are used for massive financial gain, college athletes should be able to benefit from their athletic career in the same way that their universities do by getting endorsements.
Here's a thesis statement that takes the opposite stance--that college athletes shouldn’t be paid --and includes a reason supporting that stance:
In order to keep college athletics from becoming over-professionalized, compensation for college athletes should be restricted to covering college tuition and related educational expenses.
Both of these sample thesis statements make it clear that your essay is going to be dedicated to making an argument: either that college athletes should be paid, or that college athletes shouldn’t be paid. They both convey some reasons why you’re making this argument that can also be supported with evidence.
Your thesis statement gives your argumentative essay direction . Instead of ranting about why college athletes should/shouldn’t be paid in the remainder of your essay, you’ll find sources that help you explain the specific claim you made in your thesis statement. And a well-organized, adequately supported argument is the kind that readers will find persuasive!
Tip 3: Find Credible Sources That Support Your Thesis
In an argumentative essay, your commentary on the issue you’re arguing about is obviously going to be the most fun part to write. But great essays will cite outside sources and other facts to help substantiate their argumentative points. That's going to involve—you guessed it!—research.
For this particular topic, the issue of whether student athletes should be paid has been widely discussed in the news media (think The New York Times , NPR , or ESPN ).
For example, this data reported by the NCAA shows a breakdown of the gender and racial demographics of member-school administration, coaching staff, and student athletes. These are hard numbers that you could interpret and pair with the well-reasoned arguments of news media writers to support a particular point you’re making in your argument.
Though this may seem like a topic that wouldn’t generate much scholarly research, it’s worth a shot to check your library database for peer-reviewed studies of student athletes’ experiences in college to see if anything related to paying student athletes pops up. Scholarly research is the holy grail of evidence, so try to find relevant articles if you can.
Ultimately, if you can incorporate a mix of mainstream sources, quantitative or statistical evidence, and scholarly, peer-reviewed sources, you’ll be on-track to building an excellent argument in response to the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”

Having multiple argumentative points in your essay helps you support your thesis.
Tip 4: Develop and Support Multiple Points
We’ve reviewed how to write an intro and thesis statement addressing the issue of paying college athletes, so let’s talk next about the meat and potatoes of your argumentative essay: the body paragraphs.
The body paragraphs that are sandwiched between your intro paragraph and concluding paragraph are where you build and explain your argument. Generally speaking, each body paragraph should do the following:
- Start with a topic sentence that presents a point that supports your stance and that can be debated,
- Present summaries, paraphrases, or quotes from credible sources--evidence, in other words--that supports the point stated in the topic sentence, and
- Explain and interpret the evidence presented with your own, original commentary.
In an argumentative essay on why college athletes should be paid, for example, a body paragraph might look like this:
Thesis Statement : College athletes should not be paid because it would be a logistical nightmare for colleges and universities and ultimately cause negative consequences for college sports.
Body Paragraph #1: While the notion of paying college athletes is nice in theory, a major consequence of doing so would be the financial burden this decision would place on individual college sports programs. A recent study cited by the NCAA showed that only about 20 college athletic programs consistently operate in the black at the present time. If the NCAA allows student-athletes at all colleges and universities to be paid, the majority of athletic programs would not even have the funds to afford salaries for their players anyway. This would mean that the select few athletic programs that can afford to pay their athletes’ salaries would easily recruit the most talented players and, thus, have the tools to put together teams that destroy their competition. Though individual athletes would benefit from the NCAA allowing compensation for student-athletes, most athletic programs would suffer, and so would the spirit of healthy competition that college sports are known for.
If you read the example body paragraph above closely, you’ll notice that there’s a topic sentence that supports the claim made in the thesis statement. There’s also evidence given to support the claim made in the topic sentence--a recent study by the NCAA. Following the evidence, the writer interprets the evidence for the reader to show how it supports their opinion.
Following this topic sentence/evidence/explanation structure will help you construct a well-supported and developed argument that shows your readers that you’ve done your research and given your stance a lot of thought. And that's a key step in making sure you get an excellent grade on your essay!
Tip 5: Keep the Reader Thinking
The best argumentative essay conclusions reinterpret your thesis statement based on the evidence and explanations you provided throughout your essay. You would also make it clear why the argument about paying college athletes even matters in the first place.
There are several different approaches you can take to recap your argument and get your reader thinking in your conclusion paragraph. In addition to restating your topic and why it’s important, other effective ways to approach an argumentative essay conclusion could include one or more of the following:
While you don’t want to get too wordy in your conclusion or present new claims that you didn’t bring up in the body of your essay, you can write an effective conclusion and make all of the moves suggested in the bulleted list above.
Here’s an example conclusion for an argumentative essay on paying college athletes using approaches we just talked about:
Though it’s true that scholarships and financial aid are a form of compensation for college athletes, it’s also true that the current system of college sports places a lot of pressure on college athletes to behave like professional athletes in every way except getting paid. Future research should turn its attention to the various inequities within college sports and look at the long-term economic outcomes of these athletes. While college athletes aren't paid right now, that doesn’t necessarily mean that a paycheck is the best solution to the problem. To avoid the possibility of making the college athletics system even worse, people must consider the ramifications of paying college students and ensure that paying athletes doesn't create more harm than good.
This conclusion restates the argument of the essay (that college athletes shouldn't be paid and why), then uses the "Future Research" tactic to make the reader think more deeply about the topic.
If your conclusion sums up your thesis and keeps the reader thinking, you’ll make sure that your essay sticks in your readers' minds.

Should College Athletes Be Paid: Next Steps
Writing an argumentative essay can seem tough, but with a little expert guidance, you'll be well on your way to turning in a great paper . Our complete, expert guide to argumentative essays can give you the extra boost you need to ace your assignment!
Perhaps college athletics isn't your cup of tea. That's okay: there are tons of topics you can write about in an argumentative paper. We've compiled 113 amazing argumentative essay topics so that you're practically guaranteed to find an idea that resonates with you.
If you're not a super confident essay writer, it can be helpful to look at examples of what others have written. Our experts have broken down three real-life argumentative essays to show you what you should and shouldn't do in your own writing.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros and Cons
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
History of the debate: should college athletes be paid, why college athletes should be paid.
- Why College Athletes Shouldn’t Be Paid
- Where To Get Your Essay Edited For Free
College athletics provide big benefits for many schools: they increase their profile, generate millions of dollars in revenue, and have led to one of the most contentious questions in sports— should college athletes be paid? Like other difficult questions, there are good arguments on both sides of the issue of paying college athletes.
Historically, the debates over paying college athletes have only led to more questions, which is why it’s raged on for more than a century. Perhaps the earliest group to examine the quandary was Andrew Carnegie’s Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching, which produced a mammoth study in 1929 of amateur athletes and the profits they generate for their universities. You don’t have to get past the preface to find questions that feel at home in today’s world:
- “What relation has this astonishing athletic display to the work of an intelligence agency like a university?”
- “How do students, devoted to study, find either the time or the money to stage so costly a performance?”
Many of the questions asked way back in 1929 continue to resurface today, and many of them have eventually ended up seeking answers in court. The first case of note came in the 1950s, when the widow of Fort Lewis football player Ray Dennison took the college all the way to the Colorado Supreme Court in an effort to collect a death benefit after he was killed playing football. She lost the case, but future generations would have more success and have slowly whittled away at arguments against paying athletes.
The most noticeable victory for athletes occurred in 2019, when California Governor, Gavin Newsom, signed legislation effectively allowing college athletes in the state to earn compensation for the use of their likeness, sign endorsement deals, and hire agents to represent them.
The court fights between college athletes and the NCAA continue today—while not exactly about payment, a case regarding whether or not schools can offer athletes tens of thousands of dollars in education benefits such as computers, graduate scholarships, tutoring, study abroad, and internships was heard by the U.S. Supreme Court in March 2021. A decision is expected in June 2021.
There are a number of great reasons to pay college athletes, many of which will not only improve the lives of student-athletes, but also improve the product on the field and in the arena.
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid
In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those in marketing and media. The only people not receiving a paycheck are the stars of the show: the athletes.
A testament to the disparate allocation of funds generated by college sports, of the $18.9 billion in athletics revenue in 2019, $3.6 billion went toward financial aid for student-athletes, and $3.7 billion was used for coaches’ compensation. A February 2020 USA Today article found that the average total pay for Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football head coaches in 2020-21 was $2.7 million. The highest-paid college football coach—the University of Alabama’s Nick Saban—earns $9.3 million a year and is the highest-paid public employee in the country. He is not alone, college coaches dominate the list of public employees with the largest salaries.
If there’s money to provide college coaches with lavish seven-figure salaries (especially at public institutions), why shouldn’t there be funds to pay college athletes?
Vital Support for Athletes
A 2011 study published by the National College Players Association (NCPA) found that an overwhelming number of students on full athletics scholarships live below the federal poverty line—85% of athletes who live on campus and 86% athletes who live off-campus. “Full scholarship” itself is a misnomer; the same study found that the average annual scholarship for FBS athletes on “full” scholarships was actually $3,222. Find out more information about athletic scholarships .
Paying student-athletes would help eliminate the need for these student-athletes to take out loans, burden their families for monetary support, or add employment to their already busy schedules. The NCAA limits in-season practice time to 20 hours a week, but a 2008 NCAA report shows that in-season student-athletes commonly spent upward of 30 and 40 hours a week engaged in “athletic activities.”
Encouraged to Stay in College Longer
A report produced by the NCPA and Drexel University estimated the average annual fair market value of big-time college football and men’s basketball players between 2011 and 2015 was $137,357 and $289,031, respectively, and concluded that football players only receive about 17% of their fair market value, while men’s basketball players receive approximately 8% of theirs.
If colleges paid athletes even close to their worth, they would provide an incentive for the athletes to stay in college and earn degrees, rather than leaving college for a paycheck. This would also help keep top talents playing for college teams, improve the level of competition, and potentially lead to even higher revenue. On a side note, this would incentivize athletes to complete their degree, making them more employable after the end of their athletic career.
Limit Corruption
Just because there are rules prohibiting the compensation of college athletes doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen, and over the years there have been numerous scandals. For example, in 2009, six ex-University of Toledo players were indicted in a point-shaving scheme , and in 2010, Reggie Bush returned his Heisman Trophy after allegations that he was given hundreds of thousands of dollars from sports agents while he played for USC.
Paying college athletes will likely not totally eliminate corruption from college sports, but putting athletes in a less-precarious financial position would be a good step toward avoiding external influence, especially when you consider some of the players involved in the University of Toledo point-shaving scandal were paid as little as $500.
It’s a Job (and a Dangerous One)
As mentioned before, college athletes can put in upward of 40 hours a week practicing, training, and competing—being a “student-athlete” is a challenge when you’re devoting full-time hours to athletics. A New York Times study found a 0.20-point difference in average GPA between recruited male athletes and non-athletes. The difference is less pronounced among females, with non-athletes averaging a 3.24 GPA and recruited women athletes at 3.18.
It’s not just the time commitment that playing college athletics puts on student-athletes, it’s the risk to their health. A 2009-2010 CDC report found that more than 210,000 injuries are sustained by NCAA student-athletes each year. Full athletic scholarships are only guaranteed a year at a time, meaning student-athletes are one catastrophic injury away from potentially losing their scholarship. That is to say nothing of the lasting effects of an injury, like head traumas , which made up 7.4% of all injuries in college football players between 2004 and 2009.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Why College Athletes Should Not Be Paid
There are a lot of great reasons why college athletes should be paid, but there are also some compelling reasons why college athletes should not be paid—and why not paying athletes is actually good for both the institutions and athletes.
Compensation Conundrum
One of the most common reasons cited against paying college players is compensation. Will all college athletes get compensated equally? For example, will the star quarterback receive the same amount as the backup catcher on the softball team? A 2014 CNBC article estimated that Andrew Wiggins, a University of Kansas forward (and soon-to-be first-overall draft pick), had a fair market value of around $1.6 million.
Similarly, will compensation take into account talent? Will the All-American point guard get the same amount as the captain of the swim team? In all likelihood, paying college athletes will benefit big-time, revenue-generating sports and hurt less popular sports.
Eliminate Competitive Balance
According to the NCAA , in 2019, the 65 Power Five schools exceeded revenue by $7 million, while all other Division I colleges had a $23 million deficit between expenses and revenue. If college athletes were to get paid, then large, well-funded schools such as those of the Power Five would be best positioned to acquire top talent and gain a competitive advantage.
From a student’s point of view, paying college athletes will alter their college experience. No longer would fit, college, university reputation, and values factor into their college decisions—rather, choices would be made simply based on who was offering the most money.
Professionalism vs. the Classroom
There’s a feeling that paying college athletes sends the wrong message and incentivizes them to focus on athletics instead of academics, when the reality is that very few college athletes will go on to play sports professionally. Just 1.6% of college football players will take an NFL field. NCAA men’s basketball players have even slimmer odds of playing in a major professional league ( 1.2% ), while the chances of a professional career are particularly grim for women basketball players, at a mere 0.8% .
Although the odds of a college athlete turning pro are low, the probability of them earning a degree is high, thanks in part to the academic support athletes are given. According to data released by the NCAA, 90% of Division I athletes enrolled in 2013 earned a degree within six years.
It Will End Less-Popular, Unprofitable Sports
If colleges and universities pay their athletes, there is a fear that resources will only go to popular, revenue-generating sports. Programs like football and men’s basketball would likely benefit greatly, but smaller, unprofitable sports such as gymnastics, swimming and diving, tennis, track and field, volleyball, and wrestling could find themselves at best cash-strapped and, at the worst, cut altogether.
It’s just not less-popular sports that paying athletes could threaten—women’s programs could also find themselves in the crosshairs of budget-conscious administrators. Keep in mind, it was just in March 2021 that the NCAA made national news for its unequal treatment of the men’s and women’s NCAA basketball tournaments.
Financial Irresponsibility
Former ESPN, and current FOX Sports, personality Colin Cowherd made news in 2014 when he voiced a popular argument against paying college athletes: financial irresponsibility. In Cowherd’s words:
“I don’t think paying all college athletes is great… Not every college is loaded, and most 19-year-olds [are] gonna spend it—and let’s be honest, they’re gonna spend it on weed and kicks! And spare me the ‘they’re being extorted’ thing. Listen, 90 percent of these college guys are gonna spend it on tats, weed, kicks, Xboxes, beer and swag. They are, get over it!”
A look at the professional ranks bolsters Cowherd’s argument about athletes’ frivolous spending. According to CNBC , 60% of NBA players go broke within five years of departing the league and 78% of former NFL players experience financial distress two years after retirement.
Writing an Essay on This? Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Writing an essay on whether college athletes should or shouldn’t be paid? CollegeVine can help! Our peer review tool allows you to receive feedback and learn the strengths and weaknesses of your essay for free.
Looking for more debate, speech, or essay topics? Check out these other CollegeVine articles for ideas:
- 52 Argumentative Essays Ideas that are Actually Interesting
- 52 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
- 60 Debate Topics for High Schoolers

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Reasons Why or Why Not
January 3, 2022
Tables of Contents
Why are college athletes not getting paid by their schools?
How do student athlete scholarships work, what are the pros and cons of compensation for college athletes, keeping education at the center of college sports.
Since its inception in 1906, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) has governed intercollegiate sports and enforced a rule prohibiting college athletes to be paid. Football, basketball, and a handful of other college sports began to generate tremendous revenue for many schools in the mid-20th century, yet the NCAA continued to prohibit payments to athletes. The NCAA justified the restriction by claiming it was necessary to protect amateurism and distinguish “student athletes” from professionals.
The question of whether college athletes should be paid was answered in part by the Supreme Court’s June 21, 2021, ruling in National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston, et. al. The decision affirmed a lower court’s ruling that blocked the NCAA from enforcing its rules restricting the compensation that college athletes may receive.
- As a result of the NCAA v. Alston ruling, college athletes now have the right to profit from their name, image, and likeness (NIL) while retaining the right to participate in their sport at the college level. (The prohibition against schools paying athletes directly remains in effect.)
- Several states have passed laws that allow such compensation. Colleges and universities in those states must abide by these new laws when devising and implementing their own policies toward NIL compensation for college athletes.
Participating in sports benefits students in many ways: It helps them focus, provides motivation, builds resilience, and develops other skills that serve students in their careers and in their lives. The vast majority of college athletes will never become professional athletes and are happy to receive a full or partial scholarship that covers tuition and education expenses as their only compensation for playing sports.
Athletes playing Division I football, basketball, baseball, and other sports generate revenue for their schools and for third parties such as video game manufacturers and media companies. Many of these athletes believe it’s unfair for schools and businesses to profit from their hard work and talent without sharing the profits with them. They also point out that playing sports entails physical risk in addition to a considerable investment in time and effort.
This guide considers the reasons for and against paying college athletes, and the implications of recent court rulings and legislation on college athletes, their schools, their sports, and the role of the NCAA in the modern sports environment.
Back To Top
Discover a first-of-its-kind sport business management program
The online BS in Rawlings Sport Business Management from Maryville University will equip you with valuable skills in marketing, finance and public relations. No SAT or ACT scores required.
- Engage in a range of relevant course topics, from sports marketing to operations management.
- Gain real-world experience through professional internships.
The reasons why college athletes aren’t paid go back to the first organized sports competitions between colleges and universities in the late 19th century. Amateurism in college sports reflects the “ aristocratic amateurism ” of sports played in Europe at the time, even though most of the athletes at U.S. colleges had working-class backgrounds.
By the early 20th century, college football had gained a reputation for rowdiness and violence, much of which was attributed to the teams’ use of professional athletes. This led to the creation of the NCAA, which prohibited professionalism in college sports and enforced rules restricting compensation for college athletes. The rules are intended to preserve the amateurism of student participants. The NCAA justified the rules on two grounds:
- Fans would lose interest in the games if the players were professional athletes.
- Limiting compensation to capped scholarships ensures that college athletes remain part of the college community.
NCAA rules also prohibited college athletes from receiving payment to “ advertise, recommend, or promote ” any commercial product or service. Athletes were barred from participating in sports if they signed a contract to be represented by an agent as well. As a result of the NIL court decision, the NCAA will no longer enforce its rule relating to compensation for NIL activities and will allow athletes to sign contracts with agents.
Major college sports now generate billions in revenue for their schools each year
For decades, colleges and universities have operated under the assumption that scholarships are sufficient compensation for college athletes. Nearly all college sports cost more for the schools to operate than they generate in revenue for the institution, and scholarships are all that participants expect.
But while most sports don’t generate revenue, a handful, notably football and men’s and women’s basketball, stand out as significant exceptions to the rule:
- Many schools that field teams in the NCAA’s Division I football tier regularly earn tens of millions of dollars each year from the sport.
- The NCAA tournaments for men’s and women’s Division I basketball championships generated more than $1 billion in 2019 .
Many major colleges and universities generate a considerable amount of money from their athletic teams:
- The Power Five college sports conferences — the Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC), Big Ten, Big 12, Pac 12, and Southeastern Conference (SEC) — generated more than $2.9 billion in revenue from sports in fiscal 2020, according to federal tax records reported by USA Today .
- This figure represents an increase of $11 million from 2019, a total that was reduced because of restrictions related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- In the six years prior to 2020, the conferences recorded collective annual revenue increases averaging about $252 million.
What are name, image, likeness agreements for student athletes?
In recent years some college athletes at schools that field teams in the NCAA’s highest divisions have protested the restrictions placed on their ability to be compensated for third parties’ use of their name, image, and likeness. During the 2021 NCAA Division I basketball tournament known familiarly as March Madness, several players wore shirts bearing the hashtag “ #NotNCAAProperty ” to call attention to their objections.
Following the decision in NCAA v. Alston, the NCAA enacted a temporary policy allowing college athletes to enter into NIL agreements and other endorsements. The interim policy will be in place until federal legislation is enacted or new NCAA rules are created governing NIL contracts for college athletes.
- Student athletes are now able to sign endorsement deals, profit from their use of social media, and receive compensation for personal appearances and signing autographs.
- If they attend a school located in a state that has enacted NIL legislation, they are subject to any restrictions present in those state laws. As of mid-August 2021, 40 states had enacted laws governing NIL contracts for college athletes.
- If their school is in a state without such a law, the college or university will determine its own NIL policies, although the NCAA prohibits pay-for-play and improper recruiting inducements.
- Student athletes are allowed to sign with sports agents and enter into agreements with school boosters so long as the deals abide by state laws and school policies.
Within weeks of the NCAA policy change, premier college athletes began signing NIL agreements with the potential to earn them hundreds of thousands of dollars .
- Bryce Young, a sophomore quarterback for the University of Alabama, has nearly $1 million in endorsement deals.
- Quarterback Quinn Ewers decided to skip his last year of high school and enroll early at Ohio State University so he could make money from endorsements.
- A booster for the University of Miami pledged to pay each member of the school’s football team $500 for endorsing his business.
How will the change affect college athletes and their schools?
The repercussions of court decisions and state laws that allow college athletes to sign NIL agreements continue to be felt at campuses across the country, even though schools and athletes have received little guidance on how to manage the process.
- The top high school athletes in football, basketball, and other revenue-generating college sports will consider their potential for endorsement earnings while being recruited by various schools.
- The first NIL agreements highlight the disparity between what elite college athletes can expect to earn and what other athletes may realize. On one NIL platform, the average amount earned by Division I athletes was $471, yet one athlete made $210,000 in July alone.
- Most NIL deals at present are for small amounts, typically about $100 in free apparel, in exchange for endorsing a product on social media.
The presidents and other leaders of colleges and universities that field Division I sports have not yet responded to the changes in college athlete compensation other than to reiterate that they do not operate for-profit sports franchises. However, the NCAA requires that Division I sports programs be self-supporting, in contrast to sports programs at Division II and III institutions, which receive funding directly from their schools.
Many members of the Power 5 sports conferences have reported shortfalls in their operations, leading analysts to anticipate major structural reforms in the governing of college sports in the near future. The recent changes have also caused some people to believe the NCAA is no longer relevant or necessary.

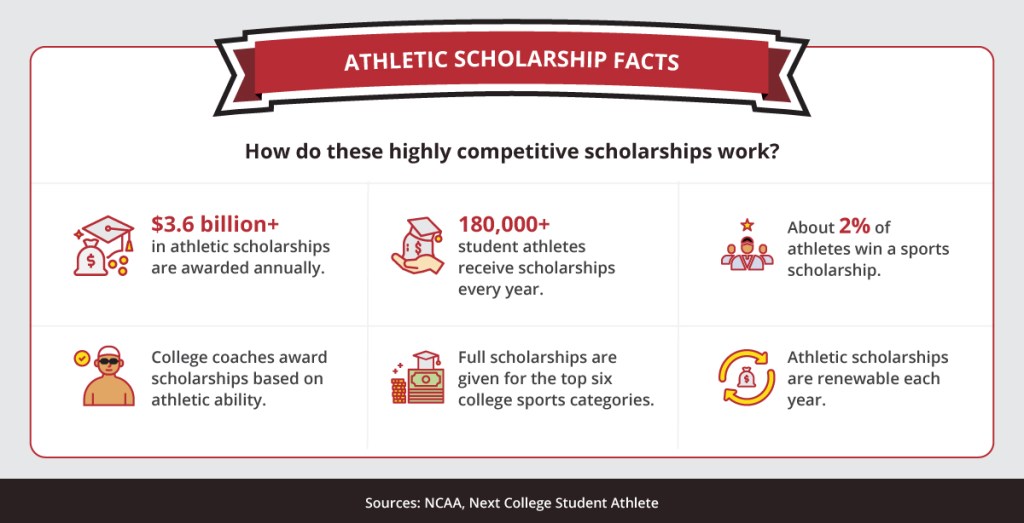
How do highly competitive athletic scholarships work? According to the NCAA and Next College Student Athlete: $3.6 billion+ in athletic scholarships are awarded annually, and 180,000+ student athletes receive scholarships every year. Additionally, about 2% of athletes win a sports scholarship; college coaches award scholarships based on athletic ability; full scholarships are given for the top six college sports categories; and athletic scholarships are renewable each year.
The primary financial compensation student athletes receive is a scholarship that pays all or part of their tuition and other college-related expenses. Other forms of financial assistance available to student athletes include grants, loans, and merit aid .
- Grants are also called “gift aid,” because students are not expected to pay them back (with some exceptions, such as failing to complete the course of study for which the grant was awarded). Grants are awarded based on a student’s financial need. The four types of grants awarded by the U.S. Department of Education are Federal Pell Grants , Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grants , Iraq and Afghanistan Service Grants , and Teacher Education Assistance for College or Higher Education (TEACH) Grants .
- Loans are available to cover education expenses from government agencies and private banks. Students must pay the loans back over a specified period after graduating from or leaving school, including interest charges. EducationData.org estimates that as of 2020, the average amount of school-related debt owed by college graduates was $37,693.
- Merit aid is awarded based on the student’s academic, athletic, artistic, and other achievements. Athletic scholarships are a form of merit aid that typically cover one academic year at a time and are renewable each year, although some are awarded for up to four years.
Full athletic scholarships vs. partial scholarships
When most people think of a student athlete scholarship, they have in mind a full-ride scholarship that covers nearly all college-related expenses. However, most student athletes receive partial scholarships that may pay tuition but not college fees and living expenses, for example.
A student athlete scholarship is a nonguaranteed financial agreement between the school and the student. The NCAA refers to full-ride scholarships awarded to student athletes entering certain Division I sports programs as head count scholarships because they are awarded per athlete. Conversely, equivalency sports divide scholarships among multiple athletes, some of whom may receive a full scholarship and some a partial scholarship. Equivalency awards are divided among a team’s athletes at the discretion of the coaches, as long as they do not exceed the allowed scholarships for their sport.
These Division I sports distribute scholarships per head count:
- Men’s football
- Men’s basketball
- Women’s basketball
- Women’s volleyball
- Women’s gymnastics
- Women’s tennis
These are among the Division I equivalency sports for men:
- Track and field
- Cross-country
These are the Division I equivalency sports for women:
- Field hockey
All Division II and National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics (NAIA) sports programs distribute scholarships on an equivalency basis. Division III sports programs do not award sports scholarships, although other forms of financial aid are available to student athletes at these schools.
How college athletic scholarships are awarded
In most cases, the coaching staff of a team determines which students will receive scholarships after spending time scouting and recruiting. The NCAA imposes strict rules for recruiting student athletes and provides a guide to help students determine their eligibility to play college sports.
Once a student has received a scholarship offer from a college or university, the person may sign a national letter of intent (NLI), which is a voluntary, legally binding contract between an athlete and the school committing the student to enroll and play the designated sport for that school only. The school agrees to provide financial aid for one academic year as long as the student is admitted and eligible to receive the aid.
After the student signs an NLI, other schools are prohibited from recruiting them. Students who have signed an NLI may ask the school to release them from the commitment; if a student attends a school other than the one with which they have an NLI agreement, they lose one full year of eligibility and must complete a full academic year at the new school before they can compete in their sport.
Very few student athletes are awarded a full scholarship, and even a “full” scholarship may not pay for all of a student’s college and living expenses. The average Division I sports scholarship in the 2019-20 fiscal year was about $18,000, according to figures compiled by ScholarshipStats.com, although some private universities had average scholarship awards that were more than twice that amount. However, EducationData.org estimates that the average cost of one year of college in the U.S. is $35,720. They estimate the following costs by type of school.
- The average annual cost for an in-state student attending a public four-year college or university is $25,615.
- Average in-state tuition for one year is $9,580, and out-of-state tuition costs an average of $27,437.
- The average cost at a private university is $53,949 per academic year, about $37,200 of which is tuition and fees.
Student athlete scholarship resources
- College Finance, “Full-Ride vs. Partial-Ride Athletic Scholarships” — The college expenses covered by full athletic scholarships, how to qualify for partial athletic scholarships, and alternatives to scholarships for paying college expenses
- Student First Educational Consulting, “Athletic Scholarship Issues for 2021-2022 and Beyond” — A discussion of the decline in the number of college athletic scholarships as schools drop athletic programs, and changes to the rules for college athletes transferring to new schools
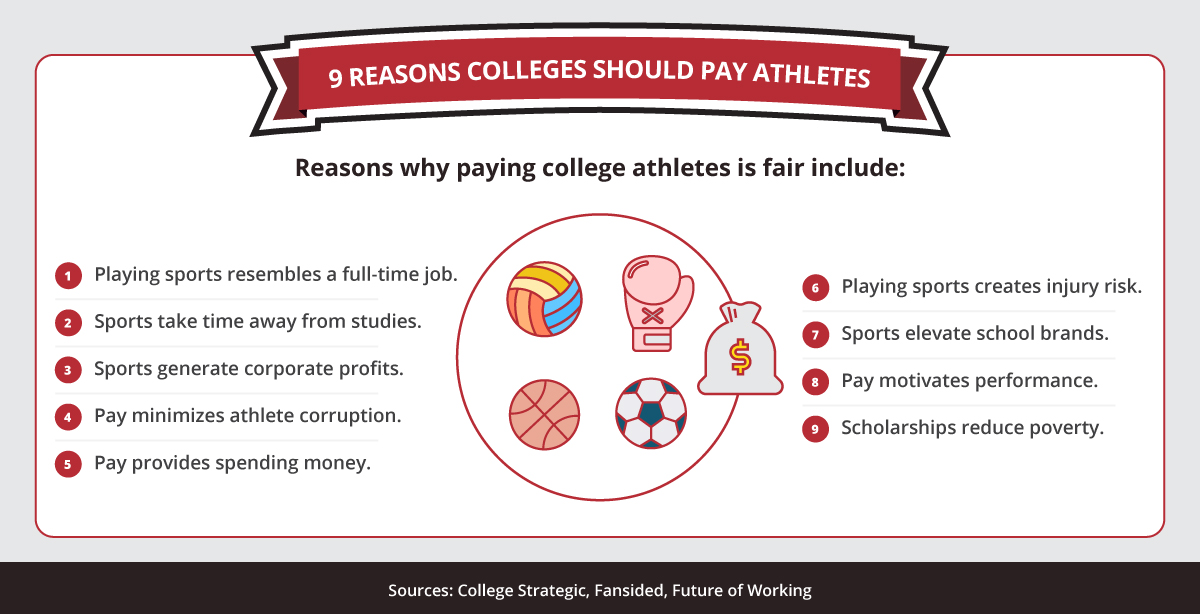
According to College Strategic, Fansided, and Future of Working, reasons why paying college athletes is fair include: 1. Playing sports resembles a full-time job. 2. Sports take time away from studies. 3. Sports generate corporate profits. 4. Pay minimizes athlete corruption. 5. Pay provides spending money. 6. Playing sports creates injury risk. 7. Sports elevate school brands. 8. Pay motivates performance. 9. Scholarships reduce poverty.
There are many reasons why student athletes should be paid, but there are also valid reasons why student athletes should not be paid in certain circumstances. The lifting of NCAA restrictions on NIL agreements for college athletes has altered the landscape of major college sports but will likely have little or no impact on the majority of student athletes, who will continue to compete as true amateurs.
Reasons why student athletes should be paid
The argument raised most often in favor of allowing college athletes to receive compensation is that colleges and universities profit from the sports they play but do not share the proceeds with the athletes who are the ultimate source of that profit.
- In 2017 (the most recent year for which figures are available), the NCAA recorded $1.07 billion in revenue. The organization’s president earned $2.7 million in 2018, and nine other NCAA executives had salaries greater than $500,000 that year.
- Elite college coaches earn millions of dollars a year in salary, topped by University of Alabama football coach Nick Saban’s $9.3 million annual salary.
- Many of the athletes at leading football and basketball programs are from low-income families, and the majority will not become professional athletes.
- College athletes take great physical risks to play their sports and put their future earning potential at risk. In school they may be directed toward nonchallenging courses, which denies them the education their fellow students receive.
Reasons why student athletes should not be paid
Opponents to paying college athletes rebut these arguments by pointing to the primary role of colleges and universities: to provide students with a rewarding educational experience that prepares them for their professional careers. These are among the reasons they give for not paying student athletes.
- Scholarships are the fairest form of compensation for student athletes considering the financial strain that college athletic departments are under. Most schools in Division I, II, and III spend more money on athletics than they receive in revenue from the sports.
- College athletes who receive scholarships are presented with an opportunity to earn a valuable education that will increase their earning power throughout their career outside of sports. A Gallup survey of NCAA athletes found that 70% graduate in four years or fewer , compared to 65% of all undergraduate students.
- Paying college athletes will “ diminish the spirit of amateurism ” that distinguishes college sports from their professional counterparts. Limiting compensation for playing a sport to the cost of attending school avoids creating a separate class of students who are profiting from their time in school.
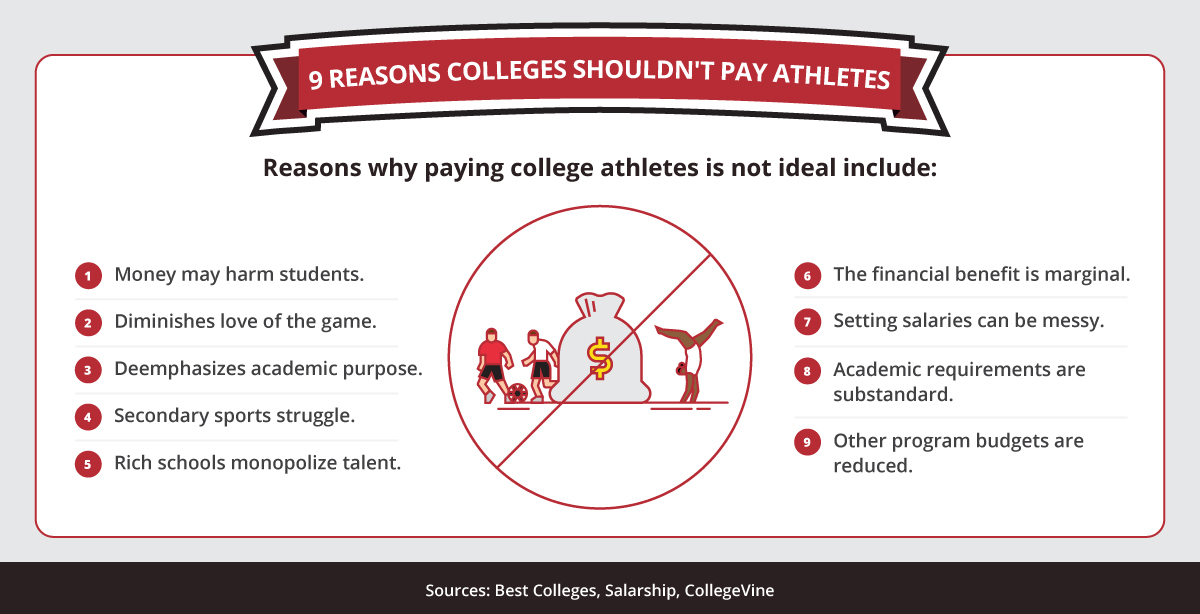
According to Best Colleges, Salarship, and CollegeVine, reasons why paying college athletes is less than ideal include: 1. Money may harm students. 2. Pay diminishes love of the game. 3. Pay deemphasizes academic purpose. 4. Secondary sports struggle. 5. Rich schools monopolize talent. 6. The financial benefit is marginal. 7. Setting salaries can be messy. 8. Academic requirements are substandard. 9. Other program budgets are reduced.
How do college athlete endorsements work?
Soon after the Supreme Court released its decision in NCAA v. Alston, the NCAA issued guidelines for schools that allow college athletes to make money from product endorsements, social media accounts, autographs, and other uses of their name, image, or likeness. This counters the NCAA’s longstanding opposition to student athletes profiting from endorsements. At present, implementation of the guidelines varies from school to school and state to state, which means athletes at some institutions may benefit more from NIL agreements than those attending other schools.
Several NIL consultancy firms are actively soliciting endorsements from college athletes in the aftermath of the rule change.
- Highly touted 19-year-old basketball recruit Hercy Miller, who joined the Tennessee State University basketball team in 2021, signed a $2 million endorsement deal with Web Apps America.
- University of Michigan quarterback Cade McNamara has entered into an endorsement deal with cryptocurrency company More Management that will pay him in cryptocurrency .
- Twin sisters Haley and Hanna Cavinder of the Fresno State University basketball team have marketing agreements to promote Boost Mobile and Six Star Pro Nutrition to the 3.3 million followers of their TikTok account.
- Gable Steveson, a wrestler for the University of Minnesota, entered into an endorsement deal with the delivery service Gopuff; Steveson has 245,000 followers on Instagram and 30,000 on Twitter.
Despite the rush of high-profile college athletes signing endorsement deals, some educators and analysts express concern about the impact of the endorsements on schools, athletes, and college sports.
- Schools with more favorable endorsement rules may entice student athletes away from the schools they are currently attending.
- Likewise, states that have enacted endorsement laws that provide more earning potential for college athletes may see more top recruits choosing to attend schools in those states.
- The time college athletes spend meeting the requirements of their endorsement contracts could detract from study and practice time. This can have an adverse effect on their education and athletic careers — if they are unable to maintain grade requirements, for example, they may be disqualified from playing.
- If a college athlete’s performance in the sport declines, they may be less likely to attract and retain endorsement deals. While the NCAA has banned NIL agreements based on the athlete meeting specific performance criteria, the group acknowledges that a student’s athletic performance may enhance their NIL value .
- Because of complicated contracts and tax laws, student athletes will have to rely on agents, advisers, and managers, which may leave them vulnerable to exploitation.
From the onset of intercollegiate sports, students have benefited from their participation by learning dedication to their sport, building relationships, and being part of a team. Sports allow students to acquire many important values, such as fair competition and physical and mental health. Education should remain at the forefront of all aspects of college, including sports, whether or not collegiate athletes are paid.
Infographic Source
Best Colleges, “Should College Athletes Be Paid?”
College Strategic, “Why College Athletes Should Be Paid”
CollegeVine, “Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros and Cons”
Fansided, “64 Reasons College Athletes Need to Be Paid”
Future of Working, “17 Advantages and Disadvantages of Paying College Athletes”
NCAA, “Scholarships”
Next College Student Athlete, “What Are the Different Types of Offers I Could Get?”
Salarship, “Should College Athletes Be Paid: Pros and Cons”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Should College Athletes Be Paid?
The Case For and Against
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
Should college athletes be able to make money from their sport? When the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) was founded in 1906, the organization’s answer was a firm “no,” as it sought to “ensure amateurism in college sports.”
Despite the NCAA’s official stance, the question has long been debated among college athletes, coaches, sports fans, and the American public. The case for financial compensation saw major developments in June 2021, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA cannot limit colleges from offering student-athletes “education-related benefits.”
In response, the NCAA issued an interim policy stating that its student-athletes were permitted to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , but not to earn a salary. This policy will remain in place until a more “permanent solution” can be found in conjunction with Congress.
Meanwhile, the landscape continues to shift, with new cases, decisions, and state legislation being brought forward. College athletes are currently permitted to receive “cost of attendance” stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% of U.S. adults favor paying college athletes with direct compensation.
Key Takeaways
- Despite the NCAA reporting nearly $1.3 billion in revenue in 2023, student-athletes are restricted to limited means of compensation.
- Although college sports regularly generate valuable publicity and billions of dollars in revenue for schools, even the highest-grossing college athletes tend to see only a small fraction of this.
- One argument for paying college athletes is the significant time commitment that their sport requires, which can impact their ability to earn income and divert time and energy away from academic work.
- Student-athletes may face limited prospects after college for a variety of reasons, including a high risk of injury, fierce competition to enter professional leagues, and lower-than-average graduation rates.
- The developing conversation around paying college athletes must take into account the practical challenges of determining and administering compensation, as well as the potential impacts on players and schools.
The Case for Paying College Athletes
There are numerous arguments in support of paying college athletes, many of which focus on ameliorating the athletes’ potential risks and negative impacts. Here are some of the typical arguments in favor of more compensation.
Financial Disparity
College sports generate billions of dollars in revenue for networks, sponsors, and institutions (namely schools and the NCAA). There is considerable money to be made from advertising and publicity, historically, most of which has not benefited those whose names, images, and likenesses are featured within it.
Of the 2019 NCAA Division I revenues ($15.8 billion in total), only 18.2% was returned to athletes through scholarships, medical treatment, and insurance. Additionally, any other money that goes back to college athletes is not distributed equally. An analysis of players by the National Bureau of Economic Research found major disparities between sports and players.
Nearly 50% of men’s football and basketball teams, the two highest revenue-generating college sports, are made up of Black players. However, these sports subsidize a range of other sports (such as men’s golf and baseball, and women’s basketball, soccer, and tennis) where only 11% of players are Black and which also tend to feature players from higher-income neighborhoods. In the end, financial redistribution between sports effectively funnels resources away from students who are more likely to be Black and come from lower-income neighborhoods toward those who are more likely to be White and come from higher-income neighborhoods.
Exposure and Marketing Value
Colleges’ finances can benefit both directly and indirectly from their athletic programs. The “Flutie Effect,” named after Boston College quarterback Doug Flutie, is an observed phenomenon whereby college applications and enrollments seem to increase after an unexpected upset victory or national football championship win by that college’s team. Researchers have also suggested that colleges that spend more on athletics may attract greater allocations of state funding and boost private donations to institutions.
Meanwhile, the marketing of college athletics is valued in the millions to billions of dollars. In 2023, the NCAA generated nearly $1.3 billion in revenue, $945.1 million of which came from media rights fees. In 2022, earnings from March Madness represented nearly 90% of the NCAA’s total revenue. Through this, athletes give schools major exposure and allow them to rack up huge revenues, which argues for making sure the players benefit, too.
Opportunity Cost, Financial Needs, and Risk of Injury
Because participation in college athletics represents a considerable commitment of time and energy, it necessarily takes away from academic and other pursuits, such as part-time employment. In addition to putting extra financial pressure on student-athletes, this can impact athletes’ studies and career outlook after graduation, particularly for those who can’t continue playing after college, whether due to injury or the immense competition to be accepted into a professional league.
Earning an income from sports and their significant time investment could be a way to diminish the opportunity cost of participating in them. This is particularly true in case of an injury that can have a long-term effect on an athlete’s future earning potential.
The Case Against Paying College Athletes
Arguments against paying college athletes tend to focus on the challenges and implications of a paid-athlete system. Here are some of the most common objections to paying college athletes.
Existing Scholarships
Opponents of a paid-athlete system tend to point to the fact that some college athletes already receive scholarships , some of which cover the cost of their tuition and other academic expenses in full. These are already intended to compensate athletes for their work and achievements.
Financial Implications for Schools
One of the main arguments against paying college athletes is the potential financial strain on colleges and universities. The majority of Division I college athletics departments’ expenditures actually surpass their revenues, with schools competing for players by hiring high-profile coaches, constructing state-of-the-art athletics facilities, and offering scholarships and awards.
With the degree of competition to attract talented athletes so high, some have pointed out that if college athletes were to be paid a salary on top of existing scholarships, it might unfairly burden those schools that recruit based on the offer of a scholarship.
‘Amateurism’ and the Challenges of a Paid-Athlete System
Historically, the NCAA has sought to promote and preserve a spirit of “amateurism” in college sports, on the basis that fans would be less interested in watching professional athletes compete in college sports, and that players would be less engaged in their academic studies and communities if they were compensated with anything other than scholarships.
The complexity of determining levels and administration of compensation across an already uneven playing field also poses a practical challenge. What would be the implications concerning Title IX legislation, for example, since there is already a disparity between male and female athletes and sports when it comes to funding, resources, opportunities, compensation, and viewership?
Another challenge is addressing the earnings potential of different sports (as many do not raise revenues comparable to high-profile sports like men’s football and basketball) or of individual athletes on a team. Salary disparities would almost certainly affect team morale and drive further competition between schools to bid for the best athletes.
The Era of Name, Image, and Likeness (NIL) Profiting
In 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA violated antitrust laws with its rules around compensation, holding that the NCAA’s current rules were “more restrictive than necessary” and that the NCAA could no longer “limit education-related compensation or benefits” for Division I football and basketball players.
In response, the NCAA released an interim policy allowing college athletes to benefit from their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , essentially providing the opportunity for players to profit off their personal brand through social media and endorsement deals. States then introduced their own rules around NIL, as did individual schools, whose coaches or compliance departments maintain oversight of NIL deals and the right to object to them in case of conflict with existing agreements.
Other court cases against the NCAA have resulted in legislative changes that now allow students to receive “cost of attendance” stipends up to a maximum of around $6,000 as well as unlimited education-related benefits and awards.
The future of NIL rules and student-athlete compensation remains to be seen. According to the NCAA, the intention is to “develop a national law that will help colleges and universities, student-athletes, and their families better navigate the name, image, and likeness landscape.” However, no timeline has been specified as of yet.
Why Should College Athletes Be Paid?
Common arguments in support of paying college athletes tend to focus on players’ financial needs, their high risk of injury, and the opportunity cost they face (especially in terms of academic achievement, part-time work, and long-term financial and career outlook). Proponents of paying college athletes also point to the extreme disparity between the billion-dollar revenues of schools and the NCAA and current player compensation.
Is It Illegal for College Athletes to Get Paid?
Although the NCAA once barred student-athletes from earning money from their sport, legislation around compensating college athletes is changing. In 2021, the NCAA released an interim policy permitting college athletes to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) through social media and endorsement and sponsorship deals. However, current regulations and laws vary by state.
What Percentage of Americans Support Paying College Athletes?
In 2023, a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults found that 67% of respondents were in favor of paying college athletes with direct compensation. Sixty-four percent said they supported athletes’ rights to obtain employee status, and 59% supported their right to collectively bargain as a labor union .
The Bottom Line
Although the NCAA is under growing pressure to share its billion-dollar revenues with the athletes it profits from, debate remains around whether, how, and how much college athletes should be paid. Future policy and legislation will need to take into account the financial impact on schools and athletes , the value of exposure and marketing, pay equity and employment rights, pay administration, and the nature of the relationship between college athletes and the institutions they represent.
NCAA. “ History .”
Marquette Sports Law Review. “ Weakening Its Own Defense? The NCAA’s Version of Amateurism ,” Page 260 (Page 5 of PDF).
U.S. Supreme Court. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston et al. ”
NCAA. “ NCAA Adopts Interim Name, Image and Likeness Policy .”
PBS NewsHour. “ Analysis: Who Is Winning in the High-Revenue World of College Sports? ”
Sportico. “ 67% of Americans Favor Paying College Athletes: Sportico/Harris Poll .”
Sportico. “ NCAA Took in Record Revenue in 2023 on Investment Jump .”
National Bureau of Economic Research. “ Revenue Redistribution in Big-Time College Sports .”
Appalachian State University, Walker College of Business. “ The Flutie Effect: The Influence of College Football Upsets and National Championships on the Quantity and Quality of Students at a University .”
Grand Canyon University. “ Should College Athletes Be Paid? ”
Flagler College Gargoyle. “ Facing Inequality On and Off the Court: The Disparities Between Male and Female Athletes .”
U.S. Department of Education. “ Title IX and Sex Discrimination .”
Congressional Research Service Reports. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston and the Debate Over Student Athlete Compensation .”
NCSA College Recruiting. “ NCAA Name, Image, Likeness Rule .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-151311702-a935ed8794c64194a53b5741d4be05f3.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Paying College Athletes — Leveling the Playing Field: An Argument for Paying College Athletes
Leveling The Playing Field: an Argument for Paying College Athletes
- Categories: Paying College Athletes Student Athletes
About this sample

Words: 730 |
Published: Mar 1, 2019
Words: 730 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Works Cited
- Edelman, M. (2016). Paying College Athletes: A Solution to the Problems Facing the NCAA. Seton Hall Journal of Sports and Entertainment Law, 26(2), 267-306.
- Eitzen, D. S., & Sage, G. H. (2015). Debating Issues in American Education: Should College Athletes Be Paid? SAGE Publications.
- Fleisher, A. A., Goff, B. L., & Tollison, R. D. (2013). The Case for Paying College Athletes. The Independent Review, 18(4), 537-553.
- Hawkins, B. (2018). The Case for Paying College Athletes. The Atlantic. Retrieved from https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2018/09/why-college-athletes-should-be-paid/570981/
- McMurphy, B. (2019). Athlete Compensation: What's Fair and What's Legal? National Collegiate Athletic Association. Retrieved from http://www.ncaa.org/about/resources/media-center/news/athlete-compensation-whats-fair-and-whats-legal
- Miller, K. (2018). Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros, Cons, and Perspectives. Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad, 30, 45-59.
- Sack, A. L. (2019). Pay for Play: A Historical Analysis of the Arguments Surrounding the Compensation of College Athletes. Virginia Sports & Entertainment Law Journal, 18(1), 1-37.
- Suggs, W. (2015). NCAA Athletic Departments and the Money They Make: Should College Athletes Be Compensated? Journal of Sport and Social Issues, 39(2), 106-128. doi:10.1177/0193723515576591
- Tulane University Law School. (n.d.). Pay for Play: The Ethics of Student-Athlete Compensation. Retrieved from https://scholarship.law.tulane.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1842&context=sportslaw
- Zimbalist, A. (2019). Unwinding Madness: What Went Wrong with College Sports and How to Fix It. Brookings Institution Press.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1316 words
1 pages / 436 words
3 pages / 1325 words
2 pages / 710 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Paying College Athletes
The question of whether coaches and players should receive equal compensation in the realm of professional sports is a topic that has sparked intense debate. The Should Coaches and Players Make the Same Amount of Money Essay [...]
In the past five to ten years, there has been a controversial question going around: should students who play a sport get paid as a reward of being a College Athlete? The answer is no. Student athletes should not get paid [...]
The discussion whether the college athletes should be paid has been re-hashed several times. There are those who advocates in favor and many against the idea of paying athlete who plays sports for their colleges. Many reasons [...]
Should college athletes be paid? The intensity of the argument to pay college athletes has escalated in the past few years. Picture a world where every college athlete was paid by their schools to play. The controversy it would [...]
Imagine dedicating 20 hours a week to playing a sport in college while having to balance your schedule with school work with no financial gain. In high school, I played three sports and often found myself struggling to excel in [...]
On common on average only 1/3 of college athletes are given a scholarship and a majority are half as much as a full scholarships as stated by the National Collegiate Athletic Association. From that 1/3 about two percent make it [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Survey shows most people want college athletes to be paid. You hear that, NCAA?
It's difficult for any fair-minded american to look at the vast amounts of money flowing into college sports and not see hypocrisy in its reliance on an unpaid labor force. .

When the legal threats to amateurism began to emerge about a dozen years ago, the NCAA’s main strategy was to claim that college sports would become less popular if athletes earned money.
Administrators said it repeatedly in the media. They said it in court. They even threatened to take their ball and go home if schools had to pay the athletes who help generate hundreds of millions of dollars playing college football and basketball.
And now they all need to admit that they were wrong. Historically, spectacularly, wrong.
A new national survey commissioned by Sportico in cooperation with The Harris Poll found that 67 percent of American adults believe college athletes should be paid — not just through name, image and likeness payments but in direct compensation from the school.
Further, 64 percent of those surveyed believed athletes should be able to claim status as employees, and 59 percent were in favor of college athletes being able to bargain as a union.
The numbers were relatively consistent across a variety of demographic groups. Whether man or woman, Democrat or Republican, white or Black, the notion of paying college athletes was supported by a majority of respondents. The only category registering less than 50 percent approval was respondents over the age of 58.
This is only one poll and one data point in a long-running narrative, but the trends are clear. College sports officials would be wise to pay attention.
TOP 25 RANKINGS: A closer look at every team in college football's preseason coaches poll
A similar survey conducted in 2014 by the Washington Post and ABC News found that only 33 percent supported paying college athletes, including just 24 percent of white people. So when former NCAA president Mark Emmert testified during the O’Bannon vs. NCAA trial in 2014 that paying athletes would be “tantamount to converting it into minor league sports, and we know that in the U.S., minor league sports aren’t very successful either for fan support or for the fan experience,” he had at least some data to support it.
But in the real world, there’s never been a link between the popularity of a sport and players being unable to make money.
Golf and tennis exploded across the world once they became fully professionalized. The International Olympic Committee was staunchly against including professional athletes until the 1980s. Once they opened the floodgates, the Olympics only got bigger and more popular. And even amidst all the consternation over the messy implementation of NIL in college, there’s absolutely nothing in the data from ticket sales to television ratings to suggest that fans are being turned off because the star quarterback has a nice car to drive.
It's been the same story time and time again throughout history: People like watching the games far more than they care about who’s getting paid to play them.
So perhaps former Big Ten commissioner Jim Delany was slightly out of touch when he said during the O’Bannon trial: “These games are owned by the institution, and the notion of paying athletes for participation in these games is foreign to the notion of amateurism.”
Maybe Delany and his colleagues really believed that at the time — or had convinced themselves of it — because they had spent their entire careers in the amateur model and had no other frame of reference for what college sports would look like if the athletes had the same access to large amounts of money that coaches and administrators did.
Or maybe they always knew they were full of it and used whatever rhetoric they could to preserve a dying system.
But you'd be laughed out of any room these days — and particularly a courtroom — if you tried to argue that college sports are widely consumed by the American public because players are unpaid students.
Not only is it flatly untrue, as Sportico’s poll illustrates, but it is difficult for any fair-minded American to look at the vast amounts of money flowing into college sports and not see hypocrisy in its reliance on an unpaid labor force.
We can have a good-faith argument about how sharing those revenues with college athletes would work and the variety of complications attached to things like Title IX, employment law and collective bargaining. The implementation might not be simple. But it wouldn’t offend the vast majority of fans, and it certainly wouldn’t lead to college sports turning into Triple-A baseball.
In fact, when you look at how quickly the attitudes have shifted from being pretty strongly against paying college athletes to a significant majority in favor, it likely wouldn’t be controversial at all within a few years.
The NCAA, which has built up a pretty bad track record in court trying to argue for amateurism over the last decade, simply can’t afford to ignore which way the wind is blowing on this. Even among some administrators, there is a growing resignation that revenue-sharing is the end game. Short of Congress giving the NCAA a lifeline, it’s probably the only way to end the stream of lawsuits that arise from a system that only restricts athletes’ earnings while everybody else’s go up, up and up.
If you believe that’s an important principle to preserve in the NCAA model, go right ahead. But arguing that fans will revolt if athletes get paid is now officially a talking point from the Stone Age.
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Essay Examples & Guide
- 👍 Advantages
- 👎 Disadvantages
- 💡 Essay Topics
- 📑 Outlining Your Paper
- 💸 Essay Example #1
- 🙅 Essay Example #2
🔗 References
There are a lot of benefits of doing sports in college, for everyone except the athletes themselves. Surely, your sports achievements can get you recognition and respect. But the issue here is not being paid at all.
You see, sport is arduous labor. And any labor, according to common sense, must be rewarded with a salary. On the other hand, doing sports for the sake of sports can also be justified. There is no clear answer for “Should college athletes be paid?”. Writing an essay, though, can help you find it.
⚖️ Should College Athletes Be Paid: Pros and Cons
This matter is very recent. Therefore, there is a lot of space for discussion here. Some may say that athletes are paid. They actually get scholarships for their work.
Others may argue that only 1% of all the sportspeople get the full amount of money. Both statements are true, and the correct answer doesn’t really exist. To help you form your own opinion on the topic, here are some pros and cons:
- It would be fair to pay sportspeople for their hard work.
- The sport takes a lot of time from studies, and it must be compensated.
- The health risk is very high, and the reward for it is a must.
- The sport would become an excellent alternative for a work-study job.
- Many athletes’ families require monetary support, which athlete payments can give.
- A lot more people would be attracted to doing sports.
- The athletes already enjoy enough compensations.
- The amount of actual future sports pros is depressing.
- It can undermine the overall studying experience.
- Most of the sports programs cannot afford salaries.
- It would create room for inequity.
- Mixing studying and sports would become even more difficult due to increased demand.
- The concept of playing for the love of sports would cease to exist.
We will look into them deeper in the next section.

👍 Paying College Athletes: Advantages
- It is simply fair to pay athletes for their endeavors. A single sportsperson can generate millions of dollars for their college. It would be only fair if the stars themselves got at least some of this money.
- It is a great way to compensate for taking away from studies. Sport is a time-consuming activity. And time is a valuable thing when you are a student. Let’s not forget that college athletes also need time to study. Or at least compensation for the time they put into the sport.
- The money would at least partially make up for possible injuries. While health is priceless, risking it must be rewarded properly. And that’s exactly what college athletes do. They put their well-being on the line for their universities. Unfortunately, universities don’t seem to give the favor back.
- It would be a great way to substitute work. An average athlete puts 40 hours a week into doing sports for his college. You can easily compare this amount of time to a generic work-study job. The only difference is the latter brings you money, and the former does not.
- It’s a great way to motivate athletes to continue their sports careers. After graduation, the majority of college athletes will stop playing for their team. They are far more likely to simply find a job and get a steady income. Paying them would make a choice between sports and career not that obvious.
- It would support a lot of students’ families. While college sportspeople bath in success, their families often suffer financially. Sustaining a starting athlete can be really costly at times. That’s where a salary would be a saving grace for struggling families.
- It is a great motivation for more students to pursue a sports career. The possibility of making money will attract more people into playing for a sports team. And that brings a better chance to find young talent.
👎 Paying College Athletes: Disadvantages
- The athletes already have their compensations. The coach’s advice, the medical treatment, the strength training. All of these cost money. But the athletes don’t have to pay a single cent for these and many other services. They are provided for free as compensation already.
- Not a lot of athletes will actually become professionals. Out of all college athletes, a mere 2% go pro as a result. Most of them see doing sports as a way to receive education and nothing more.
- It can harm other colleges’ programs. Since the salary would come from the college budget, there would be inevitable cutbacks. As a result, every student in the institution suffers.
- There are not many sports that make a profit. More often than not, sport doesn’t bring a lot of money. Exceptions are basketball and football. Should football players make more money than, for example, swimmers? Here’s where the next issue occurs.
- Possible inequity. You see, if some students participate in a sport that has no profit, then why pay them? As a result of such logic, whole college teams will cease to exist.
- Possible study problems. With the appearance of salaries, the expectations from the players will rise. Attending training sessions and games will become a definite must. No skips would be allowed. In this case, ping-ponging your priorities from sports to studies is much more difficult.
- The love for the game would go away. College students play sports mostly because they want to do what they love. Paying them might destroy the compassion for doing sport. The amateur leagues will be filled with players who are in it for the money and nothing else.
💡 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Topics
- Balancing college sports and academic mission.
- Payments to collegiate athletes.
- Top college athletes are worth six figures.
- Title IX in the female sports development .
- Kids and sports: Lack of professional sports guides.
- College athletes do not deserve the degrees they’re studying for.
- Steroid abuse in the world of sports .
- Shortage of officials at the high school sports level.
- College sports should be made professional.
- Steroid use effects on professional young athletes .
- Is it justified for college athletes to be paid?
- College sports should not require missing classes.
- Professional athletes allowed to use steroids.
- Paying college athletes: Reinforcing privilege or promoting growth?
- If colleges pay college athletes, it would increase the disparity between small and bigger college teams.
- School athletes and drug tests.
- Arguments for adequate remuneration for college athletes.
- The NCAA definition of college athletes as amateurs is outdated.
- Sports-related problems and conflicts.
- African American studies. Negro baseball league.
- The moral side: “A gentlemen never competes for money” (Walter Camp).
- Running injuries, workout and controversies.
- Should college athletes be paid?
- Ed O’Bannon’s lawsuit: Using athletes’ images in video games.
- Does youth sports play a part in character formation?
- Children participation in sports .
- Where does college sports money go?
- Sports analysis: steroids and HGH in sports.
- Steroid usage in professional sports.
- College athletes work as marketers for their college, as their success in sports improves admission rates.
- Physical activity and sports team participation.
- Using performance-enhancing drugs and in the world of sport .
- Research handbook of employment relations in sport.
- Successfully luring college athletes.
- College athletes should be paid.
Haven’t found anything inspiring in the list above? Try using our topic-generating tool !
📑 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Outline
Before writing your work, the first thing you want to do is outline. An argumentative-style essay would be perfect for writing on our topic.
We will go with a generic 5-paragraph format :
- Hook. A flashy sentence or two to evoke interest in your work. A joke or a shocking fact, for example.
- Background information. General info that the reader needs to know before going deeper into the essay.
- Thesis statement. It is a sentence that reflects the main idea of the further text. It leaves room for debate and briefly showcases the arguments you will discuss further.
- Body. The body is the biggest part of your work. In our case, it will be three paragraphs long. Each paragraph names and explains the argument you want to make.
- Conclusion. The end of your essay. Nothing new should be added. Just restate your thesis, summarize the points you made in the body, and be done with it.
💸 Why College Athletes Should Be Paid Essay Example
In 2017 National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) made over $1.04 billion in revenue. None of the college athletes have seen any part of this sum. A survey made the same year showed 60% of the sportspeople to be satisfied with the scholarship-only payments. The situation, however, has drastically changed over the years. The same 60% now agree that college athletes need monetary compensation. While college athletes' payments are a controversial topic, their hard work and health must be fairly compensated no matter what, and a salary seems to be the best way for it.
It is no surprise that doing sports consumes a solid number of things. Time is one of them. An average college student puts in their sports activities 35 hours a week. It can be compared to having a generic work-study job. The only difference is the job brings you money as any hard labor should. However, in the case of college sport, it seems to profit anyone but the athletes themselves. While the NCAA executives make six-figure salaries, the players, the actual stars of the competition, have the status of the unpaid workforce.
Another thing consumed by sports activities is health. In 2017 over 60% of all Division I players were reported to suffer a major injury. Although, this phenomenal danger to athletes' well-being seems to go unnoticed as well. The only "compensation" provided to people who risk their soundness for the sake of university is education itself. Usually, the health risk is considered a reason for a salary raise. Unfortunately, in our case, there is nothing to give a raise to.
Putting yourself to the fullest in any activity must be rewarded. And the sportspeople truly give it their best. Time, passion, health, everything is given. And for now, everything they give is given for nothing.
🙅 College Athletes Should Not Be Paid Essay Example
There are hundreds of sports college athletes do. Only two of them bring the college profit. The issue of paying the students involved with the college sports activities has been around for a while. Some are satisfied with their scholarship and the possibility to get an education. Others, however, demand more tangible rewards for their achievements. While payments may seem justified, the fact that the athletes already receive enough compensation for their work via scholarship and education is often overlooked.
National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) reports more than $3.6 billion in athletic scholarships to be provided annually to more than 180,000 student-athletes. A simple calculation shows $20.000 a year for each athlete. This sum is more than enough to cover the average cost of an academic year of $17,797.
Furthermore, most college athletic programs make barely enough money to sustain themselves, not to mention paying salaries. The only two kinds of sport that make enough profit to afford salaries are football and basketball. Others, sadly, do not. And this fact creates a significant equity problem. Do we pay all players equally? And if not, who do we pay more? All these questions remain unanswered.
While it seems just, creating salaries brings more problems than solves. The extent of the compensation necessary is, of course, negotiable. But all efforts made by college athletes are compensated in some way. That is a fact.
We hope that this info helped you with your assignment. Make sure to let us know what part you’ve found the most useful in the comments. And also, check out our title page maker . And good luck with your studies!
- 16 college athletes already getting paid under new NCAA rule
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? | BestColleges
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? Reasons Why or Why Not
- All college athletes in California can now get paid – KTVU
- Pay for Play: Should College Athletes Be Compensated?
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.
16 Reasons College Athletes should be Paid (And 5 Against)

College athletes should be paid because they bring a substantial amount of money into their colleges, boost admission rates, put in full-time hours, and do not have the time to get a full-time job on top of their sport.
And yet, ridiculously, in many sports, it’s illegal to pay college athletes because it’s considered amateur sports.
These are the overarching reasons for which student athletes should be paid. However, there are several more that are justified below.
Reasons Why College Athletes Should be Paid
1. student athletes bring in money.
College sports bring in tremendous amounts of money. Football, basketball, and baseball, in particular, generate billions of dollars a year for colleges in ticket sales, merchandise sales, and advertisements.
Considering the massive revenue generated for colleges because of the student athletes, it only makes sense to pay them for their time, commitment, and energy.
As the system currently operates, it may be argued that college athletes are being exploited. college athletics is the main avenue into professional sports. Thus, the athletes need to go through college athletics even if the pay is low or non-existent. As a result, they feel they have little choice but to put in free labor for the colleges.
Read Also: 42 Colleges with Bear Mascots
2. No time for a part-time job
Not all college athletes have the bank of mom and dad to back them up. Many college athletes are admitted into colleges on scholarships and have little extra money to support themselves.
Living costs such as rent, food, and textbooks add up so many students find part-time employment to cover these costs.
For college athletes, a part-time job really isn’t an option. College athletics take up a significant amount of time and are extremely physically and mentally demanding on top of college classes.
Many athletes therefore struggle to make ends meet even though they work day in and day out.
3. Transparency about revenues generated
College sports teams have budgets so there is some degree of knowledge as to where money is coming from and how much of it there is. However, the details are extremely murky, and athletes are often kept in the dark.
As a result, there is no guarantee that the sports teams will see the money they have brought in re-invested in their sport.
In other word, the athletes are bringing money into the colleges that is being redirect – often to inappropriate expenditures.
In fact, there have been several scandals now whereby certain college shareholders have used sports-generated funds inappropriately or even for personal gain.
4. Brings better athletes (higher incentive)
College sports are already incredibly competitive but add the element of payment into the mix, and the bar will raise even higher.
Many star athletes choose not to pursue their sport in college for the simple reason that it isn’t paid.
Payment would raise the incentive so the caliber would be even higher than it currently stands.
In fact, if the college athletics system changed, it may increase participation in sports overall meaning the pool of possible stars will grow.
5. Renowned sports teams increase college admissions
College sports do not just bring in revenue. They also attract students, which is another reason the athletes are valuable labor for the college.
There have been many instances of an average college (academically speaking) cultivating a champion sports team and therefore college applications skyrocket.
Further, once a college has a more competitive applicant pool and a renowned reputation, it can raise tuition fees. Thus, college sports can generate money for the school both directly and even indirectly.
6. Athletics are expensive
Playing a sport or doing an athletic activity at a college level usually means the athlete has dedicated a significant portion of their life and personal money to that skill.
In other words, you have to be very good to pursue a sport in college which means you have put in the work to get that good.
Athletics can be expensive and for a student to have practiced to the degree required to make it into college means that they have likely invested a fair amount of money over time.
Students should be paid if they are playing full-time in college as they have invested the resources to be there and should reap the rewards of that investment.
7. College athletes put in the same hours as a full-time job
Considering the hours of practice, games, travel, and physical and mental maintenance, the time commitment can be equal to that of a full-time job.
If someone is putting in the same hours as a full-time job which means they cannot get a job on top of their sport (as explained in point #2) then surely they should be paid for their time commitment.
8. Players bring in merch money
Another point about revenue generation is that merchandisers capitalize not only on teams but on specific players. For instance, if the top college football quarterback wears the number 14 then merchandisers will intentionally produce more merch with this number.
Thus, particular players are generating huge profits and often receive nothing monetary in return.
And it’s big money – NCAA merchandise deals are estimated to be worth hundreds of millions of dollars .
There are even stories about college athletes freelancing on the side by simply offering to go and do talks or meet-ups with fans who are willing to pay the athletes for their time. But, they’re still often unable to profit from the jerseys that have their own names on them!
9. College athletes should have a safety net in case they cannot go pro
Not every college athlete goes on to play in the NBA or the NFL and makes millions of dollars a year.
Those that graduate and do not make it into the professional realm of their sport are left with little to restart their lives on, particularly if their grades have slipped because of their commitment to their sport.
Most college athletes spend their entire childhood and adolescence working on their sport and then graduate college with few other skills. If college athletes were paid, then at least they would have a nest egg to live on while they figure out their next steps.
10. College coaches are paid handsomely
If you consider the situation closely, it seems strange that college sports teams are populated by students who are unpaid but are coached by professionals who are paid extremely well.
Without the athletes, there would be no team for the coach to coach so it seems unfair and frankly, confusing why one key stakeholder would be paid while the others wouldn’t.
For the sake of fairness, you would expect the revenues to be more evenly spread around all the people in the team.
11. The sport causes damage to their bodies
Sports like football cause serious damage to athletes’ bodies. Many can only play into their early 30s .
As a result, every year of their career is highly valuable and extremely important. While most white-collar jobs enable people to continue working in the profession into your mid-60s, these athletes are going to need to make a lot of their lifetime income in the span of about 10-20 years.
This makes the fact that they’re underpaid for several years of their careers even more unfair.
12. They are free media exposure for the schools
College athletics generates a lot of media exposure for schools. In fact, if it weren’t for college basketball and football, a lot of schools would never make it onto the television.
And yet, thanks to college athletics, schools have excellent media exposure that often presents them at their best: stadiums of fans wearing the college’s colors, cheering on their school.
This media exposure makes the colleges household names and inspires many young people to want to go to those colleges, even from a very young age.
13. It’s often an issue of racial justice
A significant number of college footballers and basketballers are young Black Americans. By contrast, the vast majority of the coaches are white.
The visuals of a team of young black athletes being underpaid and unpaid for their labor isn’t great for the colleges’ attempts at achieving racial justice. This is even more stark when we see how much the white coaches are paid. The coaches, after all, aren’t putting their bodies on the line.
14. They are expected to do extracurricular tasks
College athletes do more than training and playing. They often have to turn up for media appearances and college events throughout the year.
This makes the fact that they’re unpaid even more egregious. The hours they put into extracurricular and co-curricular activities should be paid – just like a job. For example, if an employee is expected to turn up to an event, they would rightly expect payment for their time.
15. They generate school spirit
Sports is perhaps the number one way schools generate spirit and a sense of community. The college and its supporters come together to cheer on their team.
This school spirit may be considered an intangible benefit to the school, but it has many flow-on benefits. It enhances the college’s image, motivates students, and increases the students’ satisfaction with their college experience.
A college with a buzz and a positive school spirit can lead to positive word-of-mouth reviews and attract future students.
16. They generate corporate sponsorships
Without college athletes, corporate sponsorships for colleges will never happen. Here is just another way in which they generate money for colleges without compensation.
Corporations sponsor teams that are successful and that have a great image. The sponsorship allows the corporation to generate positive attitudes toward their brand by association with the athletes.
If only a bit of the corporate sponsorship went toward paying the athletes, who often appear in the ads or next to the brand names on t-shirts and posters, then the athletes could have a much better standard of living.
Are there Arguments Against Paying College Athletes?
Some key arguments against paying college athletes are:
- They get scholarships: Most college athletes get a full ride scholarship, which is highly valuable and a form of payment for their labor. Nevertheless, they generally don’t get any monetary benefits that they can put in the bank for their futures.
- They don’t have to do it if they don’t want: If the athletes didn’t see a net benefit out of competing in college athletics, they wouldn’t do it. No one is forcing them into it! (Of course, the fact that it’s just about the only path to a career as an elite athlete makes it appear to be some degree of coercion).
- They get great training: The athletes get access to excellent coaches that they wouldn’t have access to otherwise. These coaches are world-class and expensive for the schools to hire. This is a form of non-monetary payment.
- It’s their chance to get seen: The athletes also get a benefit in the form of visibility to scouts. They get their name out there, get watched performing their sport, and get an opportunity to eventually get a contract that will be extremely lucrative. This is another great non-monetary benefit that the college is providing for the athletes.
- They will be paid handsomely afterward: If the athletes get a contract, it would likely be a million-dollar-plus contract that will make up for the lack of pay during their early years at college.
College athletes work extremely hard and arguably, are not far behind their professional counterparts. Furthermore, they bring in a great deal of money and goodwill to the colleges they serve. At the end of the day, they’re providing labor to the colleges. So, it makes little sense that they are unpaid.
Related debate topics
- Reasons school should start later
- Reasons should start earlier
- Reasons school is important

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.
Should College Athletes be Paid?
March 31, 2024
Okay, I won’t hide the ball: my answer to the question, “Should college athletes be paid?” is a resounding, “Yes.” But before I go through the reasons why (and some countervailing streams of thought as well), I think it’s important to place the question in the larger context of money in college sports. Why? Because there just so happens to be a ton of money in college sports. On Saturdays during football season, hundreds of thousands of fans across the nation flock to iconic stadiums —the Big House, Death Valley, the Swamp—and pay premium ticket prices to watch their favorite teams go at it.
Millions more tune in to the games from home, and the NCAA conferences take advantage of the sport’s popularity to the tune of billions of dollars. In 2022, the Big Ten, for example, inked a seven-year media rights agreement with Fox, CBS, and NBC worth upwards of $7 billion.
The coaches are very much in on the action, too. College football coaches, especially those who strategize from the sidelines of premiere football schools, boast yearly salaries that are truly jaw-dropping. In the last year before his retirement, Alabama’s Nick Saban made $11.41 million. The same year, Clemson’s Dabo Swinney pocketed $10.88 million, and Georgia’s Kirby Smart took home $10.71 million. Sure, those are some of the best football programs in the country. But still: more than a hundred Division I coaches earn over $1 million. The top 25 college football coaches earn an average of $5.2 million per year. The top 25 college basketba l l coaches earn an average of $3.2 million per year.
Should College Athletes be Paid (Continued)
Every year, the NCAA rakes in about a billion dollars from March Madness alone. In 2019, Connecticut senator Chris Murphy released a report titled “Madness, Inc.”, which took aim at what the report termed the “college sports industrial complex.” The report cites Department of Education data which showed that college sports programs brought in a whopping $14 billion in revenue in 2018 alone. In terms of revenue, college sports beat out every professional sports league in the world, except the NFL.
And here’s the kicker: college athletes—the product that millions of Americans pay to watch compete—aren’t compensated for their on-the-field performance. That’s because the NCAA’s long-enshrined policy of amateurism states that student-athletes are students first—thus “amateurs”—and are therefore not eligible for compensation. The good news? In 2021, the NCAA implemented an interim policy. This allows student-athletes to make money from their name, image, and likeness. The so-called NIL rule permits students to engage in money-making “NIL activities,” like selling autographs and memorabilia, making paid appearances, and going into business with brands. The new NIL policy is a step in the right direction, but it doesn’t address the root of the problem. In 2022, only 17% of student-athletes at Division I schools participated in NIL activities. The median compensation (note: not the average, which can be distorted by particularly high-earners) was $65 per NIL activity.
America seems to have come to a consensus on the question of should college athletes be paid. According to a recent poll , 67% of Americans believe that college athletes should be compensated for their performance. Not just for their name, image, and likeness.
Should college athletes be paid?
Now let’s confront the question head on: should college athletes be paid? I’ve already gone on record with an unequivocal, “yes.” But to preserve a sense of fairness, I’ll go through some of the arguments on the opposite side of the issue, and in so doing hopefully provide a sound justification for my answer.
Should college athletes be paid? No, they’re already paid in the form of scholarships
Should college athletes be paid? No, some say, because college athletes already receive full scholarships, which is tantamount to payment. Unfortunately, this argument doesn’t pass the sniff test. Every year, Division I and II colleges dole out about $2.9 billion in scholarships to some 150,000 student-athletes. That sounds great until you realize that the average yearly scholarship is just about $18,000; that’s far from sufficient to cover tuition at most private schools or out-of-state tuition at state schools. Overall, only 1% of student-athletes receive a “full ride” scholarship. Under a little scrutiny, then, the argument that college athletes receive compensation in the form of scholarships falls apart.
So college athletes aren’t paid via scholarships. Sure, that’s a fact, but not an argument as to why college athletes should be paid. Well, here’s the argument: given the money and exposure that athletes generate for their schools, any just system would require they be compensated for the value they add. A phenomenon known as the Flutie Effect describes how a college football team’s success leads to an increase in applications. When college football teams go from “mediocre to great,” applications increase by as much as 18%. And better performance on the gridiron results in more donations to the school. Donations go up significantly when football squads post better records.
To put it concisely: athletes bring significant value to their schools in the form of exposure and monetary donations, and scholarships do not amount to an adequate form of compensation. Therefore, college athletes deserve to be paid.
But it would be too complicated to figure out salaries!
The “it’s just too difficult!” argument is a common retort to the question of should college athletes be paid. It’s also a fixture in American political discourse. Should the U.S., say, move towards single-payer healthcare? Of course not—it’d be too difficult to implement!
Here, the “it’s-too-difficult” argument suggests that determining which college athletes would get compensated, and how much they’d get compensated, would be a complicated and messy undertaking. Therefore, it’d be better simply not to pay college athletes.
But appealing to the apparent intractability of a problem is no reason not to address it. The fact that it might be difficult to correct an iniquity is no justification for not trying to correct it at all.
Professional sports leagues are far from shining models of equity and fairness. UFC fighters—who aren’t unionized, by the way— are only paid about 20% of overall revenue , whereas unionized leagues like the NBA, MLB, and NFL share roughly 50% of their revenue with players. There are issues of gender equity across leagues, too. The average WNBA base salary is $120,600 ; the average NBA base salary is $5.4 million. However, there are plenty of professional sports leagues that have managed to figure out how to fairly compensate their athletes, from superstars to bench players. When one considers this fact, the “it’s too complicated” argument falls apart, too.
Where would the money come from?
Another oft-heard argument that answers, “no,” to the question of should college athletes be paid goes like this: because so few college athletics programs are cash-flow positive, schools would have to make cuts to minor sports programs to come up with the money to pay athletes who compete in premiere sports, like football and basketball. This line of reasoning assumes that paying marquee college athletes would preclude the possibility of paying athletes who compete in more minor or niche sports. But that assumption is not warranted.
As I noted previously, professional sports leagues—from the NFL to independent league baseball to professional jai alai —have figured out how to compensate players with different levels of skill and star power. There’s no reason to think the NCAA couldn’t do it as well.
The way resources are allocated reflects an institution’s values. At least one highly-paid college football coach has gone on record as saying he’d happily take less money if it meant his players would be paid .
Paying athletes would take away from the love of the game
In doing research for this article, I confronted this argument or one of its variations quite a lot. It goes like this: college athletics should compete not for financial gain but for a nebulous “love of the game.” Paying college athletes would tarnish the otherwise pure and idealistic realm of college sports.
But we’ve already established that college sports are a big business. The NCAA, conferences, schools, and coaches all benefit from that business. Why should the athletes be the only ones who have to work with no pay, just to fulfill some romanticized and unrealistic idea of college sports?
Plus, participating in college sports amounts to a full-time job. Although NCAA policy states that athletes may only dedicate 20 hours per week to sports-related activity, studies have shown that Division I athletes spend an average of 35 hours per week on sports activities. A lawsuit filed by two UNC football players alleged that the NCAA skirted around its own policies and deprived players of a meaningful education.
Those who answer “no” to the question of should college athletes be paid are therefore confronted with a dilemma. If student-athletes should only be competing for the “love of the game,” why does their participation in college sports look a lot like a full-time job? And if their participation in college sports looks like a full-time job, why are they not compensated accordingly?
Should college athletes be paid? – a few more thoughts
Participation in college sports takes up a large chunk of a student-athlete’s time, study time included. Right now, student-athletes are getting the worst of both worlds. They’re not compensated for their positions as athletes (nor are the vast majority of them getting those coveted “free ride” educations), and their participation in sports precludes them from fully dedicating themselves to their studies. Student-athletes make a major sacrifice to participate in sports. Further, this sacrifice that brings immense value to their schools and the NCAA. Student athletes ought to be compensated for that sacrifice.
Speaking of sacrifices, college athletes are at constant risk of injury. A serious on-the-field injury could result in an athlete losing his or her scholarship and the opportunity to play professionally. But let’s put aside the potential financial ramifications of an injury. A 2017 study examined the deceased bodies of former American football players. The findings were shocking: 91% of college football players had the degenerative brain disease CTE. If schools want their athletes to risk their mental and physical well-being, they should pay them according to that risk.
Let’s end with some straight up common sense—athletes need money just like everyone else. Participating in a college sport and keeping up with academic demands makes it virtually impossible for a student-athlete to earn extra money working a part-time job. Paying student-athletes would act as a corrective to this untenable situation.
Should College Athletes be Paid – Additional Resources
We hope you have found our article on whether college athletes should be paid to be insightful. We also want to recommend checking out the following resources:
- D1 vs. D2 vs D3 College Athletics – What is the Difference?
- Best and Loudest College Football Stadiums
- Who Has the Most College Football Championships
- All-Time Women’s College Basketball Scoring
- D1 Colleges in Texas
Dane Gebauer
Dane Gebauer is a writer and teacher living in Miami, FL. He received his MFA in fiction from Columbia University, and his writing has appeared in Complex Magazine and Sinking City Review .
- 2-Year Colleges
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Essay
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Private High School Spotlight
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Paying college athletes appears closer than ever. How could it work, what stands in the way?
A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a compensation model for college athletes.
An agreement has not been finalized and many questions remain unanswered. It is also unclear if new rules could withstand further legal scrutiny, but it appears college sports is heading down a revolutionary path with at least some schools directly paying athletes to participate. Here's what is known and what still needs to be figured out:
House vs. NCAA is a class-action federal lawsuit seeking damages for athletes who were denied the opportunity to earn money from use of their name, image or likeness going back to 2016. The plaintiffs, including former Arizona State swimmer Grant House, are also asking the court to rule that NIL compensation should include billions of dollars in media rights fees that go to the NCAA and the wealthiest conferences (Big Ten, Big 12, Atlantic Coast and Southeastern), mostly for football and basketball.
The settlement being discussed could have the NCAA paying nearly $3 billion in damages over 10 years, with help from insurance and withholding of distributions that would have gone to the four big conferences. Last year, NCAA revenue approached $1.3 billion and the association projects a steady rise in coming years, thanks mostly to increases baked into the television contract with CBS and Warner Bros. Discovery for the men's basketball tournament. A new, eight-year deal with ESPN worth $920 million for the Division I women's basketball tournament and other championship events takes effect in 2025.
The potential settlement also calls for a $300 million commitment from each school in those four conferences over 10 years, including about $20 million per year directed toward paying athletes. Administrators have warned that could lead to program cuts for the so-called non-revenue sports familiar to fans who watch the Olympics.
“It’s the Olympic sports that would be in jeopardy,” Alabama athletic director Greg Byrne said during a March panel in Washington led by Sen. Ted Cruz, R-Texas. “That’s men and women. If you look at the numbers for us at the University of Alabama, with our 19 sports outside of football and men’s basketball, we lost collectively almost $40 million."
Who gets paid?
It's not entirely clear. Presumably, it would start with the athletes in sports that produce most of the revenue: football and men's basketball players at the biggest and wealthiest programs. Women's basketball is likely next in line, but it is possible athletes in all sports could see some benefit – but probably not at all schools.
What's being considered is allowing schools to pay athletes, but not requiring those payments. Schools that don't rake in millions in TV revenue wouldn't necessarily be on the hook. There are also unanswered questions about whether the federal gender equity law Title IX would require equal funding for male and female athletes.
Who makes the call?
Getting the presidential boards of four conferences and the NCAA board of governors to approve a settlement is not a given, not to mention the plaintiffs in the House case. Still, the possibility of having to pay $4 billion in damages – and the NCAA has been on the losing end of many recent court cases – has spurred interest in a deal before trial begins in January.
The case is being heard in the Northern District of California by U.S. Judge Claudia Wilken, who has already ruled against the NCAA other landmark antitrust lawsuits and ordered the sides in House to seek a settlement.
Employment and collective bargaining
Settling existing cases is only one step. A new system for compensating college athletes would be needed to avoid similar challenges in the future; for example, anything that looks like a cap on compensation by, say, the four major conferences would be ripe for another lawsuit.
The NCAA has been asking Congress for some kind of antitrust exemption for years, but the emphasis has shifted lately from regulating NIL compensation to keeping the athletes from being deemed employees.
A ruling from an NLRB regional director paved the way for members of the Dartmouth men's basketball team to vote to join a union after being deemed employees, and many have advocated for collective bargaining as a solution to college sports' antitrust exposure.
Jason Stahl, executive director of the College Football Players Association advocacy group, says lawmakers should create a special status for college athletes that would give them the right to organize and collectively bargain without actual employee status.
Stahl said even though many college athletes are apprehensive about being employees and joining a union, they should have the right to decide that.
"My concern is there would be some type of one-two punch," Stahl said of a lawsuit settlement followed quickly by federal legislation to codify a revenue-sharing plan that precludes athletes from employee status and the right to organize. “A lot of things I'm hearing about this cap are not things I want to be hearing."
What's next?
There are so many moving parts that it is hard to say with certainty, though settling House seems to a priority for late spring or summer. The earliest for any true changes noticed on campus would be fall of 2025.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Paying Students to Play Would Ruin College Sports
A handful of programs would pay top dollar for a select few athletes, while other schools would get caught up in a bidding war they couldn’t afford.
By Cody J. McDavis
Mr. McDavis is a law student and former Division I college basketball player.
When the Duke University basketball star Zion Williamson injured his knee in a freak accident in a game on Wednesday, it reignited a debate over whether student-athletes competing as amateurs on college campuses should instead become paid professionals. If Williamson and other elite players like him are going to risk their professional futures by playing college sports, many wonder, shouldn’t they be financially compensated?
Paying student-athletes might sound like a fairer way to treat students who generate so much money and attention for their colleges (not to mention the television networks that broadcast their games). But paying athletes would distort the economics of college sports in a way that would hurt the broader community of student-athletes, universities, fans and alumni. A handful of big sports programs would pay top dollar for a select few athletes, while almost every other college would get caught up in a bidding war it couldn’t afford.
The 30 largest universities in the country each routinely generate annual revenues exceeding $100 million from sports , but according to the National Collegiate Athletic Association, most of those revenues are spent covering operating expenses for the school’s athletic programs and paying tuition for their student-athletes. The majority of Division I colleges in the N.C.A.A. operate at a loss. In fact, among the roughly 350 athletic departments in the N.C.A.A.’s Division I, only about 24 schools have generated more revenue than expenses in recent years. The nation’s top five conferences made over $6 billion in 2015, billions more than all other schools combined, according to an ESPN analysis of N.C.A.A. data.
Forcing the @NCAA to pay student-athletes would ruin college sports, says @CodyMcDavis . Watch his @Instagram Story: https://t.co/a2BY784nO4 and read his Op-Ed: https://t.co/cFdNkb6tSG pic.twitter.com/BkejmwutNK — New York Times Opinion (@nytopinion) February 26, 2019
For the have-not universities, however, to continue operating means relying on millions of dollars in debt, funding from their main campus and student fees. Even with that help, some of the major athletic departments are struggling. A recent N.C.A.A. study determined that only about 20 of the 1,000 or so college sports programs in the nation were profitable. What is going to happen when the competition to offer students money is supercharged?
A federal judge in Northern California, Claudia Wilken, will soon decide if student-athletes should instead be paid more like professionals. At the moment, thanks in part to the pressure exerted by a 2015 ruling by Judge Wilken, top N.C.A.A. athletes can receive scholarships totaling tens of thousands of dollars for tuition, room, board and stipends, as well as cost-of-attendance compensation. But the association still sets a ceiling on those benefits, and a group of Division I basketball and football players is awaiting Judge Wilken’s ruling on whether that ceiling should effectively be lifted.
If the plaintiffs in this case are successful, the arms race for top athletes may have no limit. The top 25 or so schools will pay because they can afford to. The remaining 325 or so will be forced to make a decision: not pay their athletes (and risk losing top talent to schools that do) or find a way to pay.
We have already had a preview of what happens when schools are put in this position. In August 2015, after the N.C.A.A. began allowing Division I universities to adopt “cost of attendance” stipends, North Dakota State University announced that it would offer such stipends in 16 sports, resulting in a new $600,000 annual expense to be paid by the athletic department. The school’s rival, the University of North Dakota, followed suit six days later. What happened? The University of North Dakota cut five teams over the next two years to help pay for the added expense.
The University of Wyoming, too, announced that it would offer stipends to its student-athletes in 2015, resulting in a new expected annual cost of $700,000 to the athletic department. A year later, calls were being made for a reduction in the athletic department because of budgetary concerns. (Those cuts almost certainly would have been made, had it not been for a $4 million subsidy from the state government.)
Gene Smith, the athletic director at Ohio State University, has said that if the N.C.A.A. pay ceiling were lifted and he were pushed to pay basketball and football student-athletes more than their full-ride scholarship packages, he would not expect to maintain the same number of sports. The chancellor at the University of Wisconsin, Rebecca Blank, has also said that her school would consider cutting sports programs altogether.
Forcing the N.C.A.A. to pay student-athletes would undermine opportunities for the vast majority of them. It would create a winner-take-all system in which only a handful of top recruits would get a paycheck on top of earning a diploma debt-free.
Similar problems would arise in the case of so-called third-party payments, in which student-athletes could be paid for things like endorsements. Major brands like Nike would pay top football and basketball talent at the biggest schools, while student-athletes in other sports or at smaller programs would be ignored. Currently, corporate funds go to athletic departments and are generally distributed among all sports; with third-party payments, those funds could instead mostly go directly to a few student-athletes, starving the rest.
I am not opposed to young athletes who decide they would prefer to be paid cash to play sports. For those who think that a free education is insufficient as compensation for playing sports, there are other options: The National Basketball Association’s developmental league, for instance, offers $125,000 contracts to top high-school talent. Such athletes can also pursue a career playing for other domestic or overseas professional leagues.
Millions of student-athletes devote their sweat, blood and tears to sports. Some play football and basketball; others swim, run cross-country, play soccer or compete as gymnasts. Only a fraction of them generate money for their schools. We must ensure that the N.C.A.A. is able to preserve its commitment to all of them.
Cody J. McDavis is a student at the U.C.L.A. School of Law who played basketball for the University of Northern Colorado from 2012 to 2015.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Twitter (@NYTopinion) and Instagram .
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Paying college athletes appears closer than ever. How could it work and what stands in the way?
FILE - Footballs stand ready before the Virginia Tech at Wake Forest NCAA college football game in Winston-Salem, N.C., Saturday Oct. 15, 2011. A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a new compensation model for college athletes. (AP Photo/Bob Leverone, File)
FILE - NCAA signage outside the headquarters in Indianapolis, Thursday, March 12, 2020. A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a new compensation model for college athletes. (AP Photo/Michael Conroy, File)
FILE - Referees try to break up an altercation between Alabama and Auburn during the second half of an NCAA college football game, Saturday, Nov. 25, 2023, in Auburn, Ala. A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a new compensation model for college athletes. (AP Photo/Vasha Hunt, File)
FILE - Boston College play SMU during the first half of the Fenway Bowl NCAA football game at Fenway Park Thursday, Dec. 28, 2023, in Boston. With the expanded College Football Playoff locked in through 2031, questions still remain about what the rest of the postseason will look like. One thing is certain, there will still be bowl games. (AP Photo/Winslow Townson, File)
FILE - Southern California coach Lincoln Riley has eggnog poured onto him after USC defeated Louisville in the Holiday Bowl NCAA college football game, Wednesday, Dec. 27, 2023, in San Diego. With the expanded College Football Playoff locked in through 2031, questions still remain about what the rest of the postseason will look like. One thing is certain, there will still be bowl games. (AP Photo/Denis Poroy, File)
FILE - In this Oct. 11, 2011, file photo, the new Big Ten Conference logo “B1G” is stained into the wood of the newly-renovated Crisler Arena court during NCAA college basketball media day in Ann Arbor, Mich. Southern California and UCLA will play two road games apiece against the Big Ten’s easternmost schools while fellow conference newcomers Oregon and Washington will make one cross-country trip each during the 2024-25 men’s basketball season. (AP Photo/Tony Ding, File)
- Copy Link copied
A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a compensation model for college athletes.
An agreement has not been finalized and many questions remain unanswered. It is also unclear if new rules could withstand further legal scrutiny, but it appears college sports is heading down a revolutionary path with at least some schools directly paying athletes to participate. Here’s what is known and what still needs to be figured out:
FILE - NCAA signage outside the headquarters in Indianapolis, Thursday, March 12, 2020. (AP Photo/Michael Conroy, File)
House vs. NCAA is a class-action federal lawsuit seeking damages for athletes who were denied the opportunity, going back to 2016, to earn money from use of their name, image or likeness — often referred to by the acronym NIL. The plaintiffs, including former Arizona State swimmer Grant House, are also asking the court to rule that NIL compensation should include billions of dollars in media rights fees that go to the NCAA and the wealthiest conferences (Big Ten, Big 12, Atlantic Coast and Southeastern), mostly for football and basketball.
FILE - Referees try to break up an altercation between Alabama and Auburn during the second half of an NCAA college football game, Saturday, Nov. 25, 2023, in Auburn, Ala. (AP Photo/Vasha Hunt, File)
The settlement being discussed could have the NCAA paying nearly $3 billion in damages over 10 years, with help from insurance and withholding of distributions that would have gone to the four big conferences. Last year, NCAA revenue approached $1.3 billion and the association projects a steady rise in coming years, thanks mostly to increases baked into the television contract with CBS and Warner Bros. Discovery for the men’s basketball tournament. A new, eight-year deal with ESPN worth $920 million for the Division I women’s basketball tournament and other championship events takes effect in 2025.
The potential settlement also calls for a $300 million commitment from each school in those four conferences over 10 years, including about $20 million per year directed toward paying athletes. Administrators have warned that could lead to program cuts for the so-called non-revenue sports familiar to fans who watch the Olympics.
“It’s the Olympic sports that would be in jeopardy,” Alabama athletic director Greg Byrne said during a March panel in Washington led by Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) . “That’s men and women. If you look at the numbers for us at the University of Alabama, with our 19 sports outside of football and men’s basketball, we lost collectively almost $40 million.”
WHO GETS PAID?
FILE - Boston College play SMU during the first half of the Fenway Bowl NCAA football game at Fenway Park Thursday, Dec. 28, 2023, in Boston. (AP Photo/Winslow Townson, File)
Not entirely clear. Presumably, it would start with the athletes in sports that produce most of the revenue: football and men’s basketball players at the biggest and wealthiest programs. Women’s basketball is likely next in line, but it is possible athletes in all sports could see some benefit — but probably not at all schools.
What’s being considered is allowing schools to pay athletes, but not requiring those payments. Schools that don’t rake in millions in TV revenue wouldn’t necessarily be on the hook. There are also unanswered questions about whether the federal gender equity law Title IX would require equal funding for male and female athletes.
WHO MAKES THE CALL?
FILE - Footballs stand ready before the Virginia Tech at Wake Forest NCAA college football game in Winston-Salem, N.C., Saturday Oct. 15, 2011. (AP Photo/Bob Leverone, File)
Getting the presidential boards of four conferences and the NCAA board of governors to approve a settlement is not a given, not to mention the plaintiffs in the House case. Still, the possibility of having to pay $4 billion in damages — and the NCAA has been on the losing end of many recent court cases — has spurred interest in a deal before trial begins in January.
The case is being heard in the Northern District of California by U.S. Judge Claudia Wilken, who has already ruled against the NCAA other landmark antitrust lawsuits and ordered the sides in House to seek a settlement.
EMPLOYMENT AND COLLECTIVE BARGAINING
Settling existing cases is only one step. A new system for compensating college athletes would be needed to avoid similar challenges in the future; for example, anything that looks like a cap on compensation by, say, the four major conferences would be ripe for another lawsuit.
The NCAA has been asking Congress for some kind of antitrust exemption for years, but the emphasis has shifted lately from regulating NIL compensation to keeping the athletes from being deemed employees.
A ruling from an NLRB regional director paved the way for members of the Dartmouth men’s basketball team to vote to join a union after being deemed employees, and many have advocated for collective bargaining as a solution to college sports’ antitrust exposure.
Jason Stahl, executive director of the College Football Players Association advocacy group, says lawmakers should create a special status for college athletes that would give them the right to organize and collectively bargain without actual employee status.
Stahl said even though many college athletes are apprehensive about being employees and joining a union, they should have the right to decide that.
“My concern is there would be some type of one-two punch,” Stahl said of a lawsuit settlement followed quickly by federal legislation to codify a revenue-sharing plan that precludes athletes from employee status and the right to organize. “A lot of things I’m hearing about this cap are not things I want to be hearing.”
WHAT’S NEXT
FILE - Southern California coach Lincoln Riley has eggnog poured onto him after USC defeated Louisville in the Holiday Bowl NCAA college football game, Wednesday, Dec. 27, 2023, in San Diego. (AP Photo/Denis Poroy, File)
There are so many moving parts that it is hard to say with certainty, though settling House seems to a priority for late spring or summer. The earliest for any true changes noticed on campus would be fall of 2025.
AP college football: https://apnews.com/hub/college-football
College athletes are closer than ever to getting paid. Here’s how it could work—and what stands in the way

A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a compensation model for college athletes .
An agreement has not been finalized and many questions remain unanswered. It is also unclear if new rules could withstand further legal scrutiny, but it appears college sports is heading down a revolutionary path with at least some schools directly paying athletes to participate. Here’s what is known and what still needs to be figured out:
House vs. NCAA is a class-action federal lawsuit seeking damages for athletes who were denied the opportunity, going back to 2016, to earn money from use of their name, image or likeness — often referred to by the acronym NIL. The plaintiffs, including former Arizona State swimmer Grant House, are also asking the court to rule that NIL compensation should include billions of dollars in media rights fees that go to the NCAA and the wealthiest conferences (Big Ten, Big 12, Atlantic Coast and Southeastern), mostly for football and basketball.
The settlement being discussed could have the NCAA paying nearly $3 billion in damages over 10 years, with help from insurance and withholding of distributions that would have gone to the four big conferences. Last year, NCAA revenue approached $1.3 billion and the association projects a steady rise in coming years, thanks mostly to increases baked into the television contract with CBS and Warner Bros. Discovery for the men’s basketball tournament. A new, eight-year deal with ESPN worth $920 million for the Division I women’s basketball tournament and other championship events takes effect in 2025.
The potential settlement also calls for a $300 million commitment from each school in those four conferences over 10 years, including about $20 million per year directed toward paying athletes. Administrators have warned that could lead to program cuts for the so-called non-revenue sports familiar to fans who watch the Olympics .
“It’s the Olympic sports that would be in jeopardy,” Alabama athletic director Greg Byrne said during a March panel in Washington led by Sen. Ted Cruz (R-Texas) . “That’s men and women. If you look at the numbers for us at the University of Alabama, with our 19 sports outside of football and men’s basketball, we lost collectively almost $40 million.”
Who gets paid?
Not entirely clear. Presumably, it would start with the athletes in sports that produce most of the revenue: football and men’s basketball players at the biggest and wealthiest programs. Women’s basketball is likely next in line, but it is possible athletes in all sports could see some benefit — but probably not at all schools.
What’s being considered is allowing schools to pay athletes, but not requiring those payments. Schools that don’t rake in millions in TV revenue wouldn’t necessarily be on the hook. There are also unanswered questions about whether the federal gender equity law Title IX would require equal funding for male and female athletes.
Who makes the call?
Getting the presidential boards of four conferences and the NCAA board of governors to approve a settlement is not a given, not to mention the plaintiffs in the House case. Still, the possibility of having to pay $4 billion in damages — and the NCAA has been on the losing end of many recent court cases — has spurred interest in a deal before trial begins in January.
The case is being heard in the Northern District of California by U.S. Judge Claudia Wilken, who has already ruled against the NCAA other landmark antitrust lawsuits and ordered the sides in House to seek a settlement.
Employment and collective bargaining
Settling existing cases is only one step. A new system for compensating college athletes would be needed to avoid similar challenges in the future; for example, anything that looks like a cap on compensation by, say, the four major conferences would be ripe for another lawsuit.
The NCAA has been asking Congress for some kind of antitrust exemption for years, but the emphasis has shifted lately from regulating NIL compensation to keeping the athletes from being deemed employees.
A ruling from an NLRB regional director paved the way for members of the Dartmouth men’s basketball team to vote to join a union after being deemed employees, and many have advocated for collective bargaining as a solution to college sports’ antitrust exposure.
Jason Stahl, executive director of the College Football Players Association advocacy group, says lawmakers should create a special status for college athletes that would give them the right to organize and collectively bargain without actual employee status.
Stahl said even though many college athletes are apprehensive about being employees and joining a union, they should have the right to decide that.
“My concern is there would be some type of one-two punch,” Stahl said of a lawsuit settlement followed quickly by federal legislation to codify a revenue-sharing plan that precludes athletes from employee status and the right to organize. “A lot of things I’m hearing about this cap are not things I want to be hearing.”
What’s next
There are so many moving parts that it is hard to say with certainty, though settling House seems to a priority for late spring or summer. The earliest for any true changes noticed on campus would be fall of 2025.
Latest in Success

AI music may be having a moment, but human songwriters would like a word

Sir Richard Branson—who hates being called a billionaire—sees net worth fall back to $3 billion, where it was in 2000

Gen Z and millennials are trying to save the planet (and ease their climate anxiety) by quitting jobs that aren’t eco-friendly

Who earns the most, CEOs or sports stars? It depends where you live

UAW faces test of its plan to unionize auto plants in anti-union South as vote wraps up at 2 Mercedes-Benz factories in Alabama

‘Weekend at Bernie’s vs. ‘One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest’—Scaramucci on the Trump/Biden rematch
Most popular.

Amazon raised warehouse wages to $15 an hour 5 years ago. Today, half of workers surveyed told researchers they struggle to afford food or rent

Florida HBCU launches investigation after record $238 million ‘gift’ from 30-year-old hemp mogul is deemed likely worthless: ‘I wanted it to be real’

Thousands of North Koreans stole Americans’ identities and took remote-work tech jobs at Fortune 500 companies, DOJ says

Billionaire investor Ray Dalio warns U.S. is ‘on the brink’ and estimates a more than 1 in 3 chance of civil war

Jeff Bezos revealed his secret to Amazon’s success 25 years ago: ‘I asked everyone around here to wake up terrified every morning, their sheets drenched in sweat’

Young adults are getting cold feet about their highly anticipated $84 trillion wealth transfer
Harrison Butker’s commencement speech: Wives should stay at home. His mom’s a medical physicist

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Harrison Butker is a three-time Super Bowl champion and one of the most accurate field-goal kickers in NFL history.
As such, the Kansas City Chiefs kicker was given a platform to express his views as the commencement speaker at Benedictine College .
The devout Christian used the opportunity to give some radical thoughts and controversial opinions during a 20-minute speech delivered at the ceremony honoring the 485 students graduating from the Catholic private liberal arts school in Atchison, Kan., on Saturday.
Butker took shots at gender roles, abortion, President Biden and Pride month during his Benedictine address. Now the NFL appears to be distancing itself from the 28-year-old.
“Harrison Butker gave a speech in his personal capacity,” Jonathan Beane, NFL senior vice president and chief diversity and inclusion officer, said in a statement emailed to The Times. “His views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger.”

Entertainment & Arts
What’s the deal with Jerry Seinfeld? His Duke University address sparks student walkout
Duke University enlisted Jerry Seinfeld to deliver its 2024 commencement speech, but a group of pro-Palestinian student protesters refused to stay for his punchline.
May 13, 2024
At Benedictine, Butker told the male graduates to “be unapologetic in your masculinity” and congratulated the female graduates on their “amazing accomplishment.” He went on to tell the women that he “would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world.”
Butker then told those women that “my beautiful wife, Isabelle, would be the first to say her life truly started when she began living her vocation as a wife and as a mother. I’m on this stage today and able to be the man I am because I have a wife who leans into her vocation.”
Butker — whose mother, Elizabeth Keller Butker, is a medical physicist at Emory University’s Winship Cancer Institute in Atlanta, where she’s worked since 1988 — then started getting choked up.
“I’m beyond blessed with the many talents God has given me,” Butker said, “but it cannot be overstated that all my success is made possible because a girl I met in band class back in middle school would convert to the faith, become my wife and embrace one of the most important titles of all: homemaker.”
That statement was met with 18 seconds of enthusiastic cheers and applause. Butker continued praising his wife and her role in their family.
“She’s the primary educator to our children. She’s the one who ensures I never let football or my business become a distraction from that of a husband and a father. She is the person that knows me best at my core and it is through our marriage that, Lord willing, we both will attain salvation.”

Silenced USC valedictorian walked the stage and the crowd reaction was anything but silent
Diplomas will be handed out Friday during individual school events for graduating seniors at USC.
May 10, 2024
During his opening remarks, Butker stated that “things like abortion , in vitro fertilization , surrogacy , euthanasia, as well as a growing support for the degenerate cultural values and media, all stem from the pervasiveness of disorder.”
He also said that Biden “has been so vocal in his support for the murder of innocent babies that I’m sure to many people it appears you can be both Catholic and pro-choice.”
At one point, Butker mentioned the word “pride” — then clarified that he wasn’t talking about “the deadly sins sort of Pride that has an entire month dedicated to it, but the true God-centered pride that is cooperating with the Holy Ghost to glorify Him.”
The comment, a jab at the LGBTQ+ community that celebrates Pride month every June, received a few chuckles from the audience.
When Butker finished his address, the crowd rose for an ovation. Susannah Leisegang , a former Benedictine track and field athlete who graduated Saturday with a degree in graphic design, said she was among the handful of people who did not stand.
“Some of us did boo — me and my roommate definitely did,” Leisegang said in a video she posted on TikTok . “There was a standing ovation from everyone in the room, except from me, my roommate and about 10 to 15 other women. You also have to keep in mind this was at a Catholic and conservative college, so a lot of the men were like, ‘F— yeah!’ They were excited. But it was horrible. Most of the women were looking back and forth at each other like, ‘What the f— is going on?’”
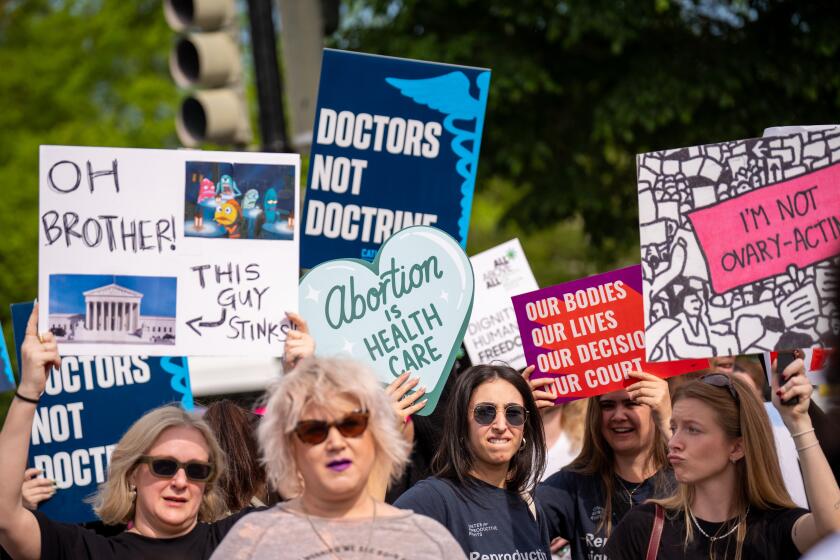

Supreme Court to pregnant women: Good luck with that
Forget the ‘split court’ garbage. This Supreme Court is not going to protect even emergency abortions. Here’s what you need to know.
April 25, 2024
Leisegang pointed out that she is 21 and has a job lined up in her field.
“Getting married and having kids is not my ideal situation right now,” she said. “So, yeah, it was definitely horrible and it definitely made graduation feel a little less special, knowing I had to sit through that and get told I’m nothing but a homemaker.”
Other members of the graduating class who participated in the ceremony have shared a variety of opinions on Butker’s speech. Elle Wilbers, 22, a future medical school student, told the Associated Press she thought Butker’s reference to the LGBTQ+ community was “horrible.”
“We should have compassion for the people who have been told all their life that the person they love is like, it’s not OK to love that person,” she said.
Kassidy Neuner, 22, who plans to teach for a year before going to law school, told the AP that being a stay-at-home parent is “a wonderful decision” but “it’s also not for everybody.”
“I think that he should have addressed more that it’s not always an option,” she said. “And, if it is your option in life, that’s amazing for you. But there’s also the option to be a mother and a career woman.”

Company Town
Hollywood’s stunt-driving industry is dominated by men. These women are fighting for change
Olivia Summers and Dee Bryant are building a team of all-women stunt drivers to make the stunt-driving industry more inclusive.
April 10, 2024
ValerieAnne Volpe, 20, who graduated with an art degree, told the AP she thought Butker said things that “people are scared to say.”
“You can just hear that he loves his wife,” Volpe said. “You can hear that he loves his family,” she said.
Butker has not commented publicly since the address. His previous social media posts are being used by people leaving comments both blasting and supporting his remarks. Heavy.com reports that all images of Isabelle Butker have been removed from her husband’s X and Instagram feeds in recent days.
Benedictine has not publicly addressed Butker’s controversial statements and did not immediately respond to multiple messages from The Times. The college’s social media feeds have been flooded with angry comments regarding Butker’s speech, and the comment section for the YouTube video of it has been disabled.
An article on Benedictine’s website about the commencement ceremony had initially referred to Butker’s speech as “inspiring.” The uncredited piece includes a reworked version of Butker’s “homemaker” quote that does not include that word, with no indication that the quote had been altered.

California high school football team refuses to play against girls, even after settling Title IX lawsuit
Despite settling a Title IX lawsuit, Santa Maria Valley Christian Academy again didn’t allow its high school football team to play against an opponent with female players.
Oct. 5, 2023
The Chiefs did not respond to a request for comment from The Times. Tavia Hunt, wife of Chiefs owner Clark Hunt , appeared to express her support for Butker in a lengthy Instagram post Thursday.
“Countless highly educated women devote their lives to nurturing and guiding their children,” she wrote. “Someone disagreeing with you doesn’t make them hateful; it simply means they have a different opinion. Let’s celebrate families, motherhood and fatherhood.”
Gracie Hunt, 25, one of Clark and Tavia Hunt’s three children was asked about Butker’s speech Friday on “ Fox & Friends .”
“I can only speak from my own experience, which is I had the most incredible mom who had the ability to stay home and be with us as kids growing up,” Gracie Hunt said. “And I understand that there are many women out there who can’t make that decision but for me in my life, I know it was really formative in shaping me and my siblings to be who we are.”
Asked if she understood what Butker was talking about, Hunt said, “For sure, and I really respect Harrison and his Christian faith and what he’s accomplished on and off the field.”
A change.org petition calling for the team to release the kicker because of his comments has received more than 185,000 signatures. Eight petitions supporting Butker appear on the site as well. One has more than 11,000 signatures while the rest have fewer than 800 each.
The Chargers poked fun at Butker on Wednesday in their schedule-release video, which is modeled after “The Sims” video game. In the video, Butker’s likeness is shown baking a pie, scrubbing a kitchen counter and arranging flowers.
should we REALLY make our schedule release video in the sims? yes yes yesyes yesyes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yes yesyes yes yes yes yesye yes yes yes yes yesyes pic.twitter.com/MXzfAPyhe8 — Los Angeles Chargers (@chargers) May 16, 2024
The official X account for Kansas City also appeared to attempt putting a humorous spin on the matter, posting a “reminder” that Butker lives in a different city Wednesday night before deleting it and posting an apology .
Earlier in the week on X, Kansas City Mayor Quinton Lucas appeared to defend Butker’s right to express his views .
Grown folks have opinions, even if they play sports. I disagree with many, but I recognize our right to different views. Nobody should have to stick to anything. Varied and shall I say—diverse—viewpoints help the world go round. — Mayor Q (@QuintonLucasKC) May 14, 2024
I think he holds a minority viewpoint, even in this state and the bordering one. I also believe more athletes, if freer to speak, would stand up for the voices of many marginalized communities. I hate “stick to sports” when used to muzzle Black athletes. I’m with consistency. — Mayor Q (@QuintonLucasKC) May 14, 2024
Last year, Butker gave the commencement address at his alma mater, Georgia Tech, advising the graduates to “ get married and start a family .”

The fight to move the Catholic Church in America to the right — and the little-known O.C. lawyer behind it
As Pope Francis nudges the Roman Catholic Church to the left globally, layman Tim Busch of Irvine is pushing American Catholicism to the right.
Dec. 18, 2023
More to Read

Granderson: A football player said something stupid about women. Let it go

Biden’s Morehouse College graduation invitation draws backlash
April 24, 2024

L.A. Affairs: I went to USC. He went to UCLA. Could I fight on in the name of love?
April 12, 2024
Get our high school sports newsletter
Prep Rally is devoted to the SoCal high school sports experience, bringing you scores, stories and a behind-the-scenes look at what makes prep sports so popular.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Chuck Schilken is a sports reporter on the Fast Break team. He spent more than 18 years with the Los Angeles Times’ Sports Department in a variety of roles. Before joining The Times, he worked for more than a decade as a sports reporter and editor at newspapers in Virginia and Maryland.
More From the Los Angeles Times
Science & Medicine
Newsom boosted California’s public health spending during COVID. Now he wants to cut it
May 17, 2024

Santa Ana mother charged with beating infant, breaking 16 bones

UC officials charge that academic workers strike over pro-Palestinian protests is illegal

‘I blew it big time.’ Former Facebook DEI head gets 5 years in prison for stealing millions

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Introduction paragraph with a thesis statement that establishes an arguable claim . The thesis statement must communicate the topic of the essay: Whether college athletes should be paid, and Convey a position on that topic: That college athletes should/should not be paid, and ; State a couple of defendable, supportable reasons why college athletes should be paid (or vice versa).
Now, the N.C.A.A. has approved a historic change to allow student-athletes to be compensated for use of their N.I.L., with schools and conferences allowed to adopt their own additional policies ...
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid. In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those ...
Reasons why student athletes should be paid. The argument raised most often in favor of allowing college athletes to receive compensation is that colleges and universities profit open_in_new from the sports they play but do not share the proceeds with the athletes who are the ultimate source of that profit.
College athletes are currently permitted to receive "cost of attendance" stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% ...
The NCAA is seemingly the final authority to decide whether college athletes should be paid to play college sports. However, in 2019, California Governor Gavin Newsom signed the Fair Play Act that allows college athletes to hire agents, sign endorsement deals, and be paid for the use of their likeness. [ 3] California was the first state to ...
Should college athletes be paid for playing? This question has sparked heated debates across the sports world, educational institutions, and society at... read full [Essay Sample] for free ... Why College Athletes Should Not Be Paid Essay. In the past five to ten years, there has been a controversial question going around: should students who ...
For more than a century, or as long as the N.C.A.A. has presided over college sports, athletes had no legal way to earn anything more tangible from their achievements than plaques and trophies.
College sports generate billions of dollars for schools, networks, and corporate sponsors. Everyone is making money off college athletics — except the players. The Supreme Court ruled that colleges can offer "education-related" payments to student-athletes. On a crisp Saturday afternoon in Ann Arbor, the University of Michigan is set to ...
athletes through a qualitative research analysis of whether college athletes should be compensated for playing their prospective sports. While there is great value in trying to analyze ... do they at the core of things think that athletes should get paid or not. These will create a good conversation as I get into the meat of things.
Congress is examining the issue. State legislatures are considering their own plans. And the N.C.A.A. has promised changes, but has long stopped athletes from making any money from their play.
This free essay sample from Edusson will explore the various reasons why college athletes should be paid and will provide a comprehensive analysis of the issue. Time Commitment and Workload. College athletes put in a tremendous amount of time and effort into their sport, often at the expense of their studies and personal life.
College athletes are often considered to be some of the luckiest young people in the world. Most of the time they're riding on full-fledged scholarships that cover all the costs of school; plus, they are in a prime position to make a reputation for themselves in the sporting world and prepare for the pros.
This study uses new data from the National Sports. and Society Survey ( N = 3,993) to assess recent public opinions about allowing college athletes. to be paid more than it costs them to go to ...
Historically, spectacularly, wrong. A new national survey commissioned by Sportico in cooperation with The Harris Poll found that 67 percent of American adults believe college athletes should be ...
💡 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Topics. Balancing college sports and academic mission. Payments to collegiate athletes. Top college athletes are worth six figures. Title IX in the female sports development. Kids and sports: Lack of professional sports guides. College athletes do not deserve the degrees they're studying for.
More than 80% of respondents ages 18-41 supported athlete payments, while people over age 58 were just 48% in favor. Ridpath said it sounds good in theory to allow athletes to be paid while in ...
For example, good thesis statements for an essay advocating that college athletes should be paid would be: "College athletes deserve to be compensated for their dedication, talent, and the immense revenue they generate for their institutions.". "College athletes should be compensated for their participation in collegiate sports due to the ...
Reasons Why College Athletes Should be Paid. 1. Student athletes bring in money. College sports bring in tremendous amounts of money. Football, basketball, and baseball, in particular, generate billions of dollars a year for colleges in ticket sales, merchandise sales, and advertisements. Considering the massive revenue generated for colleges ...
Atlantic Coast Conference: $3.6 billion, 15-year deal with ESPN/ABC. Southeastern Conference: $2.25 billion, 15-year deal with ESPN/ABC, and $825 million, 15-year deal with CBS College Sports. Big Ten Conference: $1 billion, 10-year deal with ESPN/ABC, and a $72 million, six-year deal with CBS for basketball only.
Overall, only 1% of student-athletes receive a "full ride" scholarship. Under a little scrutiny, then, the argument that college athletes receive compensation in the form of scholarships falls apart. So college athletes aren't paid via scholarships. Sure, that's a fact, but not an argument as to why college athletes should be paid.
There are plenty of arguments to be made for why college athletes should not be paid. Next, take a look at the arguments in favor of paying college athletes for their work — with the emphasis on the word "work." Collegiate sports do indeed represent a considerable commitment of time and effort, often resembling a full-time job. ...
A new, eight-year deal with ESPN worth $920 million for the Division I women's basketball tournament and other championship events takes effect in 2025. The potential settlement also calls for a ...
The nation's top five conferences made over $6 billion in 2015, billions more than all other schools combined, according to an ESPN analysis of N.C.A.A. data. Forcing the @NCAA to pay student ...
By RALPH D. RUSSO. Updated 5:31 PM PDT, May 6, 2024. A settlement being discussed in an antitrust lawsuit against the NCAA and major college conferences could cost billions and pave the way for a compensation model for college athletes. An agreement has not been finalized and many questions remain unanswered.
College athletes are closer than ever to getting paid. Here's how it could work—and what stands in the way. BY Ralph D. Russo and The Associated Press. May 7, 2024, 2:01 AM PDT. USC coach ...
Harrison Butker is a three-time Super Bowl champion and one of the most accurate field-goal kickers in NFL history. As such, the Kansas City Chiefs kicker was given a platform to express his views ...