- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Consider This from NPR

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
The Key To Happiness, According To A Decades-Long Study

Sending a text to a friend can bring a smile to your face. Now, research suggests it could also help bring long-term health benefits. guoya/Getty Images hide caption
Sending a text to a friend can bring a smile to your face. Now, research suggests it could also help bring long-term health benefits.
If you could change one thing in your life to become a happier person — like your income, a job, your relationships or your health — what would make the biggest difference? That's the question Harvard psychiatrist Dr. Robert Waldinger has been attempting to answer through decades of research. He's the director of "the world's longest-running scientific study of happiness," and he spoke with Ari Shapiro about the factor that appears to make the biggest difference in people's lives. Waldinger is a co-author of The Good Life: Lessons from the world's longest scientific study of happiness . In participating regions, you'll also hear a local news segment to help you make sense of what's going on in your community. Email us at [email protected] .
This episode was produced by Lee Hale and Megan Lim. It was edited by William Troop and Christopher Intagliata. Our executive producer is Sami Yenigun.

What the Longest Study on Human Happiness Found Is the Key to a Good Life
The Harvard Study of Adult Development has established a strong correlation between deep relationships and well-being. The question is, how does a person nurture those deep relationships?
This article was featured in One Story to Read Today, a newsletter in which our editors recommend a single must-read from The Atlantic , Monday through Friday. Sign up for it here.
T urn your mind for a moment to a friend or family member you cherish but don’t spend as much time with as you would like. This needn’t be your most significant relationship, just someone who makes you feel energized when you’re with them, and whom you’d like to see more regularly.
How often do you see that person? Every day? Once a month? Once a year? Do the math and project how many hours annually you spend with them. Write this number down and hang on to it.

For us, Bob and Marc, though we work closely together and meet every week by phone or video call, we see each other in person for only a total of about two days (48 hours) every year.
How does this add up for the coming years? Bob is 71 years old. Marc is 60. Let’s be (very) generous and say we will both be around to celebrate Bob’s 100th birthday. At two days a year for 29 years, that’s 58 days that we have left to spend together in our lifetimes.
Fifty-eight out of 10,585 days.
Of course, this is assuming a lot of good fortune, and the real number is almost certainly going to be lower.
Since 1938, the Harvard Study of Adult Development has been investigating what makes people flourish. After starting with 724 participants—boys from disadvantaged and troubled families in Boston, and Harvard undergraduates—the study incorporated the spouses of the original men and, more recently, more than 1,300 descendants of the initial group. Researchers periodically interview participants, ask them to fill out questionnaires, and collect information about their physical health. As the study’s director (Bob) and associate director (Marc), we’ve been able to watch participants fall in and out of relationships, find success and failure at their jobs, become mothers and fathers. It’s the longest in-depth longitudinal study on human life ever done, and it’s brought us to a simple and profound conclusion: Good relationships lead to health and happiness. The trick is that those relationships must be nurtured.
From the June 2009 issue: What makes us happy?
We don’t always put our relationships first. Consider the fact that the average American in 2018 spent 11 hours every day on solitary activities such as watching television and listening to the radio. Spending 58 days over 29 years with a friend is infinitesimal compared with the 4,851 days that Americans will spend interacting with media during that same time period. Distractions are hard to avoid.
Thinking about these numbers can help us put our own relationships in perspective. Try figuring out how much time you spend with a good friend or family member. We don’t have to spend every hour with our friends, and some relationships work because they’re exercised sparingly. But nearly all of us have people in our lives whom we’d like to see more. Are you spending time with the people you most care about? Is there a relationship in your life that would benefit both of you if you could spend more time together? Many of these are untapped resources, waiting for us to put them to use. And, enriching these relationships can in turn nourish our minds and bodies.
Y ou don’t have to examine scientific findings to recognize that relationships affect you physically. All you have to do is notice the invigoration you feel when you believe that someone has really understood you during a good conversation, or the tension and distress you feel after an argument, or how little sleep you get during a period of romantic strife.
In this sense, having healthy, fulfilling relationships is its own kind of fitness—social fitness—and like physical fitness, it takes work to maintain. Unlike stepping on the scale, taking a quick look in the mirror, or getting readouts for blood pressure and cholesterol, assessing our social fitness requires a bit more sustained self-reflection. It requires stepping back from the crush of modern life, taking stock of our relationships, and being honest with ourselves about where we’re devoting our time and whether we are tending to the connections that help us thrive. Finding the time for this type of reflection can be hard, and sometimes it’s uncomfortable. But it can yield enormous benefits.
Many of our Harvard Study participants have told us that filling out questionnaires every two years and being interviewed regularly have given them a welcome perspective on their life and relationships. We ask them to really think about themselves and the people they love, and that process of self-reflection helps some of them.
Read: 10 practical ways to improve happiness
This is a practice that could help anyone. Looking in the mirror and thinking honestly about where your life stands is a first step in trying to live a good life. Noticing where you are can help put into relief where you would like to be. Having some reservations about this kind of self-reflection is understandable. Our study participants were not always keen on filling out our questionnaires, or eager to consider the larger picture of their life. Some would skip difficult questions or leave entire pages blank, and some would just not return certain surveys. Some even wrote comments in the margins of their questionnaires about what they thought of our requests. “What kinds of questions are these!?” is a response we received occasionally, often from participants who preferred not to think about difficulties in their life. The experiences of the people who skipped questions or entire questionnaires were also important, though—they were just as crucial in understanding adult development as the experiences of people eager to share. A lot of useful data and gems of experience were buried in the shadowed corners of their lives. We just had to go through a little extra effort to excavate them.
One of these people was a man we’ll call Sterling Ainsley. (We are using a pseudonym to protect his confidentiality as a study participant.)
S terling Ainsley was a hopeful guy. He graduated from Harvard in the 1940s and then served in World War II. After he left the service, he got a job as a scientist and retired in his 60s. When asked to describe his philosophy for getting through hard times, he said, “You try not to let life get to you. You remember your victories and take a positive attitude.”
The year was 1986. George Vaillant, the then-director of the study, was on a long interview trek, driving through the Rocky Mountains to visit the study’s participants who lived in Colorado, Utah, Idaho, and Montana. Sterling had not returned the most recent survey, and there was some catching up to do. He met Vaillant at a hotel to give him a ride to the diner where Sterling wanted to do his scheduled interview. When Vaillant buckled himself into the passenger seat of Sterling’s car, the seat belt left a stripe of dust across his chest. “I was left to wonder,” he wrote, “the last time somebody had used it.”
Sterling was technically married, but his wife lived far away, and they hadn’t slept in the same room in years. They spoke only every few months.
Read: The six forces that fuel friendship
When asked why they had not gotten a divorce, he said, “I wouldn’t want to do that to the children,” even though his kids were grown and had children of their own. Sterling was proud of his kids and beamed when he spoke of them, saying they were the most important thing in his life. But he rarely saw them and seemed to prefer to keep his relationships with them thriving mostly in his imagination. Vaillant noted that Sterling seemed to be using optimism to push away some of his fears and avoid challenges in his life. Putting a positive spin on every matter and then pushing it out of his mind made it possible for him to believe that nothing was wrong, he was fine, he was happy, his kids didn’t need him.
He didn’t travel to see his son’s new home abroad, because he didn’t “want to be a burden”—even though he’d been learning a new language to prepare for the trip. He had another child who lived closer, but he hadn’t visited in more than a year. He didn’t have a relationship with his grandchildren, and he wasn’t in contact with any friends.
When asked about his older sister, Sterling seemed startled. “My sister?” he said.
Yes, the sister he had told the study so much about when he was younger.
Sterling thought about it for a long time, and then told Vaillant that it must have been decades since he last spoke with her. A frightened expression came over his face. “Would she still be living?” he said.
Sterling tried not to think about his relationships, and he was even less inclined to talk about them. This is a common experience. We don’t always know why we do things or why we don’t do things, and we may not understand what is holding us at a distance from the people in our life. Taking some time to look in the mirror can help. Sometimes there are needs inside of us that are looking for a voice, a way to get out. They might be things that we have never seen or articulated to ourselves.
This seemed to be the case with Sterling. Asked how he spent his evenings, he said he spent time with an elderly woman who lived in a nearby trailer. Each night he would walk over, and they’d watch TV and talk. Eventually she would fall asleep, and he would help her into bed and wash her dishes and close the shades before walking home. She was the closest thing he had to a confidant.
“I don’t know what I’ll do if she dies,” he said.
Listen to Robert Waldinger in conversation with Arthur Brooks and Rebecca Rashid on "How to Build a Happy Life":
L oneliness has a physical effect on the body. It can render people more sensitive to pain, suppress their immune system, diminish brain function, and disrupt sleep, which in turn can make an already lonely person even more tired and irritable. Research has found that, for older adults, loneliness is far more dangerous than obesity. Ongoing loneliness raises a person’s odds of death by 26 percent in any given year. A study in the U.K., the Environmental Risk (E-Risk) Longitudinal Twin Study, recently reported on the connections between loneliness and poorer health and self-care in young adults. This ongoing study includes more than 2,200 people born in England and Wales in 1994 and 1995. When they were 18, the researchers asked them how lonely they were. Those who reported being lonelier had a greater chance of facing mental-health issues, partaking in unsafe physical-health behaviors, and coping with stress in negative ways. Add to this the fact that a tide of loneliness is flooding through modern societies, and we have a serious problem. Recent stats should make us take notice.
In a study conducted online that sampled 55,000 respondents from across the world, one out of every three people of all ages reported that they often feel lonely. Among these, the loneliest group were 16-to-24-year-olds, 40 percent of whom reported feeling lonely “often or very often.” In the U.K., the economic cost of this loneliness—because lonely people are less productive and more prone to employment turnover—is estimated at more than £2.5 billion (about $3.1 billion) annually and helped lead to the establishment of a U.K. Ministry of Loneliness.
Read: Why do we look down on lonely people?
In Japan, 32 percent of adults expected to feel lonely most of the time during 2020. In the United States, a 2019 study suggested that three out of four adults felt moderate to high levels of loneliness. As of this writing, the long-term effects of the coronavirus pandemic, which separated us from one another on a massive scale and left many feeling more isolated than ever, are still being studied.
Alleviating this epidemic of loneliness is difficult because what makes one person feel lonely might have no effect on someone else. We can’t rely entirely on easily observed indicators such as whether or not one lives alone, because loneliness is a subjective experience. One person might have a significant other and too many friends to count and yet feel lonely, while another person might live alone and have a few close contacts and yet feel very connected. The objective facts of a person’s life are not enough to explain why someone is lonely. Regardless of your race or class or gender, the feeling resides in the difference between the kind of social contact you want and the social contact you actually have.

I t never hurts —especially if you’ve been feeling low—to take a minute to reflect on how your relationships are faring and what you wish could be different about them. If you’re the scheduling type, you could make it a regular thing; perhaps every year on New Year’s Day or the morning of your birthday, take a few moments to draw up your current social universe, and consider what you’re receiving, what you’re giving, and where you would like to be in another year. You could keep your chart or relationships assessment in a special place, so you know where to look the next time you want to peek at it to see how things have changed.
If nothing else, doing this reminds us of what’s most important. Repeatedly, when the participants in our study reached old age, they would make a point to say that what they treasured most were their relationships. Sterling Ainsley himself made that point. He loved his older sister deeply—but he lost touch with her. Some of his fondest memories were of his friends—whom he never contacted. There was nothing he cared more about than his children—whom he rarely saw. From the outside it might look like he didn’t care. That was not the case. Sterling was quite emotional in his recounting of his most cherished relationships, and his reluctance to answer certain study questions was clearly connected to the pain that keeping his distance had caused him over the years. Sterling never sat down to really think about how he might conduct his relationships or what he might do to properly care for the people he loved most.
Sterling’s life reminds us of the fragility of our connections, and it echoes the lessons of science: Relationships keep us happier and healthier throughout our life spans. We neglect our connections with others at our peril. Investing in our social fitness is possible each day, each week of our lives. Even small investments today in our relationships with others can create long-term ripples of well-being.
This article is adapted from Robert Waldinger and Marc Schulz’s new book, The Good Life: Lessons From the World’s Longest Scientific Study of Happiness .
When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.

When you buy a book using a link on this page, we receive a commission. Thank you for supporting The Atlantic.
- Commencement 2024
- Climate Solutions
What is the key to finding happiness? The Harvard community explores the physical, mental, social, and spiritual aspects of living a life filled with joy.
Explore moments of joy across campus

Learn how to be happy
Is there a formula for happiness, and can you apply it to your own life? Professor Arthur Brooks thinks so.
Read more from The Harvard Gazette
Studying happiness
Explore ancient Chinese philosophy, ethics, and political theory to challenge your assumptions of what it means to be happy, live a meaningful life, and change the world.
Understanding happiness
Learn how the origins of joy can improve the way we lead organizations—and our personal lives.
Practicing happiness
Research shows that short writing exercises reliving happy moments boosted the moods of adults recovering from addiction.
The Leadership and Happiness Laboratory
The Leadership and Happiness Laboratory conducts research and creates resources for leaders to learn the science of happiness, apply it in their own lives, and share it with others.
Learn about the lab
Managing Happiness
What if you can will yourself to be happy? This free online course gives participants data-backed strategies to make themselves happier.
Take the course
Health and happiness
Research has long indicated the link between our happiness and physical health. A study from the Harvard Chan School finds a host of health benefits that accompany an optimistic attitude.
Read more from the Harvard Chan School
Good genes are nice, but joy is better
When scientists began tracking the health of 268 Harvard sophomores in 1938, they hoped the study would reveal clues to leading healthy and happy lives. They got more than they ever expected.
Health and happiness go hand in hand
No matter your current state of happiness, there are ways to boost your outlook and give your mental and physical health a lift.
Linking happiness and wellbeing
A Harvard-led study found that younger adults have the lowest scores in a dozen wellbeing measures compared to other age groups.
Finding happiness in community
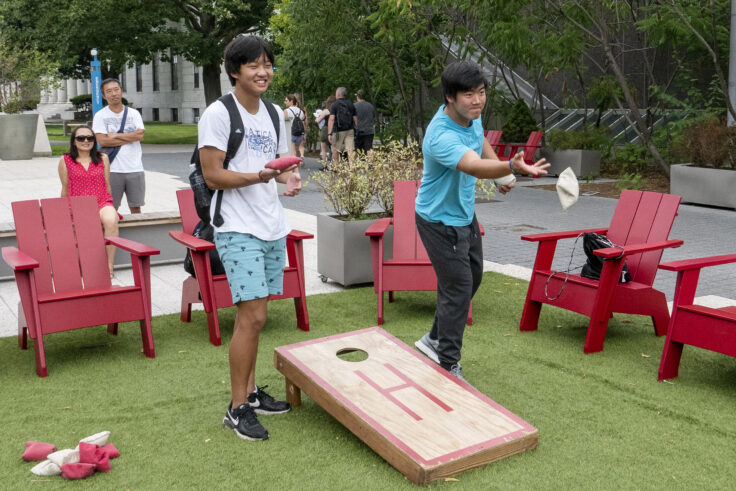

The value of relationships
Robert Waldinger, director of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, says one of the biggest surprises they encountered was that what makes people happy is also what helps keep them healthy—relationships.
A pet can change your life
Animals ease loneliness and boost oxytocin—the love hormone.

Mending fences
In a society roiled by division, how can we find common ground and build relationships with those who don’t share our views?

Reaching out
Research offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend.

Forgiveness can heal
Forgiveness transcends mere spiritual practice or good behavior—it fosters good mental health.

How do you measure and govern for happiness?
An international conference of academics, practitioners, corporate managers, and spiritual leaders at the Harvard Divinity School sought answers to the question of universal happiness.
Explore videos from the conference
Finding joy in our work

When working harder doesn’t work, reinvent your career

Playful summer learning

Fulfillment doesn't require big change

This summer, remember to refresh

Want to be happier? Make more free time.

Get out of your own way
You may also like
Related In Focus topics
- Healthy Living
- Mindfulness and Meditation

A block party during Carnival in Belo Horizonte, Brazil; 11 February 2024. Photo by Washington Alves/Reuters
Learning to be happier
In order to help improve my students’ mental health, i offered a course on the science of happiness. it worked – but why.
by Bruce Hood + BIO
In 2018, a tragic period enveloped the University of Bristol, when several students killed themselves related to work stress. Suicide is usually the ultimate culmination of a crisis in mental health, but these students weren’t alone in feeling extreme pressure: across the campus there was a pervasive sense that the general student body was not coping with the demands of higher education. My own tutee students, whom I met on a regular basis, were reporting poor mental health or asking for extensions because they were unable to meet deadlines that were stressing them out. They were overly obsessed with marks and other performance outcomes, and this impacted not only on them, but also on the teaching and support staff who were increasingly dealing with alleviating student anxiety. Students wanted more support that most felt was lacking and, in an effort to deal with the issue, the university had invested heavily, making more provision for mental health services. The problem with this strategy, however, is that by the time someone seeks out professional services, they are already at a crisis point. I felt compelled to do something.
At the time, Bristol University was described in the British press as a ‘toxic’ environment, but this was an unfair label as every higher education institution was, and still is, experiencing a similar mental health crisis. Even in the Ivy League universities in the United States, there was a problem, as I discovered when I became aware of a course on positive psychology that had become the most popular at Yale in the spring of 2018. On reading about the course, I was somewhat sceptical that simple interventions could make much difference until I learned that Yale’s ‘Psychology and the Good Life’ course was being delivered by a colleague of mine, Laurie Santos, who I knew would not associate herself with anything flaky.
That autumn term of 2018, I decided to try delivering a free lunchtime series of lectures, ‘The Science of Happiness’, based on the Yale course. Even though this pilot was not credit-bearing, more than 500 students gave up their Wednesday lunchtimes to attend. That was unusual as, in my experience, students rarely give up time or expend effort to undertake activities unless they are awarded credit or incentives. There would be 10 lectures, and everyone was requested to fill in self-report questionnaires assessing various mental health dimensions both before and after the course, to determine whether there had been any impact and, if so, how much.
The Science of Happiness had clearly piqued interest as indicated by the audience size, but I was still nervous. This was not my area of academic expertise and there was heightened sensitivity following the media attention over recent tragic events on campus. What were the students’ expectations? Talking about mental health seemed hazardous. Would I trigger adverse reactions simply by discussing these issues?
D espite my initial reservations, the final feedback after the course ended was overwhelmingly positive. That was gratifying but, as a scientist, I like hard evidence. What would the questionnaires tell us? The analysis of the before and after scores revealed that there had been a 10-15 per cent positive increase in mental wellbeing across the different measures of wellbeing, anxiety and loneliness. That may not sound much but it was the average, and a significant impact in the field of interventions. Who wouldn’t want to be 15 per cent happier, healthier or wealthier? I was no longer a sceptic; I was a convert. I would stop focusing on developmental psychology, my own area of research, and concentrate on making students happier. Even a 15 per cent improvement might lead to a degree of prevention that was better than dealing with a student who was already struggling.
The following year, we launched a credit-bearing course for first-year students who had room in their curriculum schedule to take an open unit, which has now been running for five years. These psychoeducational courses are not new and predate my efforts by at least a decade. But what makes the Bristol psychoeducational course unique (and I believe this is still the case) is that we persuaded the university to allow a credit-bearing course that had no graded examinations but was accredited based on engagement alone. Not only was I convinced by compelling arguments for why graded assessment is the wrong way to educate, but it would have been hypocritical of me to lecture about the failings of an education system based solely on assessment, and then give students an exam to determine if they had engaged. Rather, engagement required regular weekly attendance, meeting in peer-mentored small groups, but also undertaking positive psychology exercises and journaling about their experiences so that we could track progress. Again, to test the impact of the course, students were asked to fill in the various psychometric questionnaires to give us an insight to impact.
Meditation stops you thinking negative thoughts. Not exactly a scientific explanation
We now have five years’ worth of data and have published peer-reviewed scientific papers on evaluation of the course. As with the initial pilot, the consistent finding is that there is, on average, a 10-15 per cent significant increase in positive mental wellbeing over the duration of the course. The course improves mental wellbeing but there are limitations. Our most recent analysis over the longer term shows that the positive benefits we generate during the course, and the two months after, are lost within a year, returning to previous baseline scores, unless the students maintain some of the recommended activities. However, in those students who kept practising at least one of the positive psychology interventions (PPIs) such as journaling, meditation, exercise, expressing gratitude or any of the other evidence-based activities, they maintained their benefits up to two years later.
Why do interventions work and why do they stop working? As to the first question, there are countless self-help books promoting PPIs, but the level of explanation is either missing or tends to be circular. Acts of kindness work because they make you feel better. Meditation calms the mind and stops you thinking negative thoughts. Not exactly a scientific explanation or revelation. Even though I had largely put my experimental work with children on hold because of the demands of teaching such a large course, I was still intellectually intrigued by the same basic theoretical question that has always motivated my research. What is the mechanism underlying positive psychology?
T here are several plausible hypotheses out there from established academics in the field that explain some of the activities, but they lack a unifying thread that I thought must be operating across the board. I started considering the wide and diverse range of PPIs to see if there was any discernible pattern that might suggest underlying mechanisms. Two years ago, I had an insight and I think the answer can be found in the way we focus on our self.
In my role as a developmental psychologist, I see change and continuity everywhere in relation to human thought and behaviour. For some time, I have been fascinated by the concept of the self and how it emerges but must change over the course of a lifetime. I believe earlier childhood notions lay the foundation for later cognition which is why development is so critical to understanding adults. My most recent work concentrated on how ownership and possessions play major roles in our concept of self, and I was particularly interested in acts of sharing among children. Specifically, we had completed a set of studies demonstrating that, when children are instructed to talk about themselves, they thought about their own possessions differently and became less willing to share with others. Emphasising their self had made these children more selfish. This got me thinking about the role of self-focus in happiness.
The most pernicious aspect of self-focus is the tendency to keep comparing ourselves to others
Infants start off with an egocentric view of the world – a term and concept introduced by the psychologist Jean Piaget. Egocentric individuals tend to perceive the world from their own perspective, and many studies have shown that young children are egocentric in the way they see the world, act, talk, think and behave with others. Normal development requires adopting a more allocentric – or other-based perspective in order to be accepted. The sense of self changes from early ebullient egocentrism to an increasing awareness of one’s relative position in the social order. Children may become more other-focused but that also includes unfavourable comparisons. They increasingly become self-aware and concerned about what others think about them – a concern that transitions into a preoccupation when they enter adolescence that never really goes away. As for adults, like many features of the human mind, earlier ways of thinking are never entirely abandoned. This is why our self-focus can become a ‘curse’, as the psychologist Mark Leary describes , feeding the inner critic who is constantly negatively evaluating our position in life.
One reason that self-focus can become a curse is that we are ignorant of the biases our brains operate with that lead us to make wrong decisions and comparisons. When it comes to happy choices, we want something because we think it will make us happy, but our predictions are inaccurate. We think events will be more impactful than they turn out to be, and we fail to appreciate how fast we get used to things, both good and bad. This is called a failure of affective forecasting which is why the psychologist Dan Gilbert explains that our tendency to ‘stumble on happiness’ is because our emotional predictions are so way off. We don’t take into consideration how future circumstances will differ because we focus on just one element and we also forget how quickly we adapt to even the most pleasurable experiences. But the most pernicious aspect of self-focus is the tendency to keep comparing ourselves to others who seem to be leading happier lives. Social media is full of images of delicious plates of food, celebrity friends, exotic holidays, luxurious products, amazing parties and just about anything that qualifies as worthy of posting to bolster one’s status. Is it any wonder that the individuals who are the most prone to social comparison are the ones who feel the worst after viewing social media? As Gore Vidal once quipped: ‘Every time a friend succeeds, I die a little.’
If egocentric self-focus is problematic then maybe positive psychology works by altering our perspective to one that is more allocentric or ‘other-focused’? To do so is challenging because it is not easy to step out of ourselves under normal circumstances. Our stream of conscious awareness is from the first-person, or egocentric, perspective and, indeed, it is nigh-on-impossible to imagine an alternative version because our sensory systems, thought processes and representation of our selves are coded as such to enable us to interact within the world as coherent entities.
M any PPIs such as sharing, acts of kindness, gratitude letters or volunteering are clearly directed towards enriching the lives of others, but how can we explain the benefits of solitary practices where the self seems to be the focus of attention? The explanation lies with the self-representation circuitry in the brain known as the default mode network (DMN). One of the surprising discoveries from the early days of brain imaging is that, when we are not task-focused, rather than becoming inactive, the brain’s DMN goes into overdrive. Mind-wandering is commonly reported during bouts of DMN activity and, although that may be associated with positive daydreaming, we are also ruminating about unresolved problems that continue to concern us. According to one influential study that contacted people at random points of the day to ask them about what they were doing, what they were thinking and how they were feeling, people were more likely to be unhappy when their minds were wandering, which was about half of the waking day. Probably because they were focusing on their own predicaments.
If you focus on your problems, this can become difficult to control. There’s no point trying to stop yourself ruminating because the very act of trying not to think about a problem increases the likelihood that this becomes the very thought that occupies your mind. This was first described in an 1863 essay by Fyodor Dostoyevsky, when he observed the effect of trying not to think; he wrote: ‘Try to pose for yourself this task: not to think of a polar bear, and you will see that the cursed thing will come to mind every minute.’ My late colleague Dan Wegner would go on to study this phenomenon called ironic thought suppression , which he explained resulted from two mechanisms: the tendency to increase the strength of the representation of a thought by the act of trying to suppress it, and a corresponding increased vigilance to monitor when the thought comes to the fore in consciousness. Ironic thought suppression is one reason why it can be so difficult to fall asleep. This is why one of our recommended activities on our Science of Happiness course is to journal on a regular basis because this helps to process information in a much more controlled and objective way, rather than succumbing to the torment of automatic thinking.
Could the long-term benefits be something to do with altering the ego?
Other recommended activities that calibrate the level of self-focus also attenuate DMN activity. For example, mindfulness meditation advocates not trying to suppress spontaneous thoughts but rather deliberately turning attention to bodily sensations or external sounds. In this way, the spotlight of attention is directed away from the internal dialogue one is having with oneself. It is during such states that brain imaging studies reveal that various solitary interventions we recommend on the course – such as meditation or taking a walk in the country – are associated with lowered DMN activity and, correspondingly, less negative rumination. This is why achieving absorption or full immersion during optimal states of flow draws conscious awareness and attention out of egocentric preoccupation. To achieve states of flow, we recommend that students engage in activities that require a challenge that exceeds their skill level to an extent that they rise to the task, but do not feel overwhelmed by it. When individuals achieve flow states, their sense of self, and indeed time itself, appears to evaporate.
There are other more controversial ways to alter the egocentric self into one that is more allocentric. Currently, there is a growth in the use of psychedelics as a treatment for intractable depression and, so far, the initial findings from this emerging field are highly encouraging. One clinical study has shown that psychedelic-assisted therapy produced significant improvement in nearly three-quarters of patients who previously did not respond to conventional antidepressants. The primary mechanism of action of psychedelics is upon serotonin (5-HT 2A ) receptors within the DMN which, in turn, produce profound alterations of consciousness, including modulations in the sense of self, sensory perception and emotion. Could the long-term benefits be something to do with altering the ego? One of the most common reports from those who have undergone psychedelic-assisted therapy, aside from euphoria and vivid hallucinations, is a lasting, profound sense of connection to other people, the environment, nature and the cosmos. Across a variety of psychedelics, the sense of self becomes more interconnected, which is why a recent review concluded that there was consistent acute disruption in the resting state of the DMN.
I f chemically induced states of altered consciousness through psychedelics (which is currently still illegal in most places) is not your thing, then there are other ways to redress the balance between egocentrism and allocentrism. Engaging in group activities that generate synchronicity – such as rituals, dancing or singing in choirs – alter the sense of self and increase connection with others. But if group activities or psychedelic trips don’t work for you, then take a rocket trip. One of the most moving emotional and lasting experiences, known as ‘ the overview effect ’, occurs to those lucky individuals given the opportunity to view our planet from outer space. As the astronaut Edgar Mitchell described it, it creates an ‘explosion of awareness’ and an ‘overwhelming sense of oneness and connectedness … accompanied by an ecstasy … an epiphany.’
Back down on Earth, we can be happier when we simply acknowledge that we are all mortal, interconnected individuals who suffer personal losses and tragedies. No one’s life is perfect, and indeed you need to experience unhappiness in order recognise when things are going well. As the Stoic philosopher Epictetus put it: ‘Men are disturbed not by things, but by the views which they take of things.’ In other words, it’s not what happens to you, but how you respond, that matters, and that’s where positive psychology can make a difference – but only if you keep reminding yourself to get out of your own head.
Happiness hack
How to shift your egocentric self to one that is more allocentric using language
Consider a problem that is currently bothering you. A real problem – not a hypothetical one or a world problem beyond your control. Find something that makes you unhappy and then say to yourself: ‘I am worried about [whatever it is] because [whatever the reason may be] and this makes me upset.’ Now repeat the exercise but this time don’t use egocentric or first-person terms such as ‘I’ or ‘me’. Rather use your name and non-first-person language such as: ‘Bruce is worried about his [whatever it is] problem and this makes him upset.’
Speaking in non-first-person language should automatically transpose you out of the egocentric perspective to one that is other or allocentric, making the problem seem less.

Pleasure and pain
Eulogy for silence
Tinnitus is like a constant scream inside my head, depriving me of what I formerly treasured: the moments of serene quiet
Diego Ramírez Martín del Campo

History of ideas
Chaos and cause
Can a butterfly’s wings trigger a distant hurricane? The answer depends on the perspective you take: physics or human agency
Erik Van Aken

Philosophy of mind
Do plants have minds?
In the 1840s, the iconoclastic scientist Gustav Fechner made an inspired case for taking seriously the interior lives of plants
Rachael Petersen

Beauty and aesthetics
All aquiver
The Decadent movement taught that you should live your life with the greatest intensity – a dangerous and thrilling challenge

Sports and games
Performance-enhancing vices
Selfishness channels ambition, envy drives competition, pride aids the win. Does it take a bad person to be a good athlete?
Sabrina Little

Technology and the self
Tomorrow people
For the entire 20th century, it had felt like telepathy was just around the corner. Why is that especially true now?
Roger Luckhurst
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Does Happiness Really Mean?
It's not the same for everyone
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell/ Jiaqi Zhou
How to Cultivate Happiness
How to be a happier person.
Happiness is something that people seek to find, yet what defines happiness can vary from one person to the next. Typically, happiness is an emotional state characterized by feelings of joy, satisfaction, contentment, and fulfillment. While happiness has many different definitions, it is often described as involving positive emotions and life satisfaction.
When most people talk about the true meaning of happiness, they might be talking about how they feel in the present moment or referring to a more general sense of how they feel about life overall.
Because happiness tends to be such a broadly defined term, psychologists and other social scientists typically use the term ' subjective well-being ' when they talk about this emotional state. Just as it sounds, subjective well-being tends to focus on an individual's overall personal feelings about their life in the present.
Two key components of happiness (or subjective well-being) are:
- The balance of emotions: Everyone experiences both positive and negative emotions, feelings, and moods. Happiness is generally linked to experiencing more positive feelings than negative ones.
- Life satisfaction: This relates to how satisfied you feel with different areas of your life including your relationships, work, achievements, and other things that you consider important.
Another definition of happiness comes from the ancient philosopher Aristotle, who suggested that happiness is the one human desire, and all other human desires exist as a way to obtain happiness. He believed that there were four levels of happiness: happiness from immediate gratification, from comparison and achievement, from making positive contributions, and from achieving fulfillment.
Happiness, Aristotle suggested, could be achieved through the golden mean, which involves finding a balance between deficiency and excess.
Signs of Happiness
While perceptions of happiness may be different from one person to the next, there are some key signs that psychologists look for when measuring and assessing happiness.
Some key signs of happiness include:
- Feeling like you are living the life you wanted
- Going with the flow and a willingness to take life as it comes
- Feeling that the conditions of your life are good
- Enjoying positive, healthy relationships with other people
- Feeling that you have accomplished (or will accomplish) what you want in life
- Feeling satisfied with your life
- Feeling positive more than negative
- Being open to new ideas and experiences
- Practicing self-care and treating yourself with kindness and compassion
- Experiencing gratitude
- Feeling that you are living life with a sense of meaning and purpose
- Wanting to share your happiness and joy with others
One important thing to remember is that happiness isn't a state of constant euphoria . Instead, happiness is an overall sense of experiencing more positive emotions than negative ones.
Happy people still feel the whole range of human emotions—anger, frustrastion, boredom, loneliness, and even sadness—from time to time. But even when faced with discomfort, they have an underlying sense of optimism that things will get better, that they can deal with what is happening, and that they will be able to feel happy again.
"Even people who have experienced terrible trauma can still also experience happiness," says Hannah Owens, LMSW , "though it is important to recognize that it might be more difficult for them to obtain the balance generally associated with overall happiness, and that their happiness might look very different from others' who have not had to deal with such challenges."
Types of Happiness
There are many different ways of thinking about happiness. For example, the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle made a distinction between two different kinds of happiness: hedonia and eudaimonia.
- Hedonia: Hedonic happiness is derived from pleasure. It is most often associated with doing what feels good, self-care, fulfilling desires, experiencing enjoyment, and feeling a sense of satisfaction.
- Eudaimonia: This type of happiness is derived from seeking virtue and meaning. Important components of eudaimonic well-being including feeling that your life has meaning, value, and purpose. It is associated more with fulfilling responsibilities, investing in long-term goals, concern for the welfare of other people, and living up to personal ideals.
Hedonia and eudemonia are more commonly known today in psychology as pleasure and meaning, respectively. More recently, psychologists have suggested the addition of the third component that relates to engagement . These are feelings of commitment and participation in different areas of life.
Research suggests that happy people tend to rank pretty high on eudaimonic life satisfaction and better than average on their hedonic life satisfaction.
All of these can play an important role in the overall experience of happiness, although the relative value of each can be highly subjective. Some activities may be both pleasurable and meaningful, while others might skew more one way or the other.
For example, volunteering for a cause you believe in might be more meaningful than pleasurable. Watching your favorite tv show, on the other hand, might rank lower in meaning and higher on pleasure.
Some types of happiness that may fall under these three main categories include:
- Joy: A often relatively brief feeling that is felt in the present moment
- Excitement: A happy feeling that involves looking forward to something with positive anticipation
- Gratitude: A positive emotion that involves being thankful and appreciative
- Pride: A feeling of satisfaction in something that you have accomplished
- Optimism: This is a way of looking at life with a positive, upbeat outlook
- Contentment: This type of happiness involves a sense of satisfaction
While some people just tend to be naturally happier, there are things that you can do to cultivate your sense of happiness.
Pursue Intrinsic Goals
Achieving goals that you are intrinsically motivated to pursue, particularly ones that are focused on personal growth and community, can help boost happiness. Research suggests that pursuing these types of intrinsically-motivated goals can increase happiness more than pursuing extrinsic goals like gaining money or status.
Enjoy the Moment
Studies have found that people tend to over earn—they become so focused on accumulating things that they lose track of actually enjoying what they are doing.
So, rather than falling into the trap of mindlessly accumulating to the detriment of your own happiness, focus on practicing gratitude for the things you have and enjoying the process as you go.
Reframe Negative Thoughts
When you find yourself stuck in a pessimistic outlook or experiencing negativity, look for ways that you can reframe your thoughts in a more positive way.
People have a natural negativity bias , or a tendency to pay more attention to bad things than to good things. This can have an impact on everything from how you make decisions to how you form impressions of other people. Discounting the positive—a cognitive distortion where people focus on the negative and ignore the positive—can also contribute to negative thoughts.
Reframing these negative perceptions isn't about ignoring the bad. Instead, it means trying to take a more balanced, realistic look at events. It allows you to notice patterns in your thinking and then challenge negative thoughts.
Avoid Social Comparison
Another way to cultivate happiness and to make sure that you are able to maintain your happiness, Owens says, is to stop comparing yourself to others.
"No two lives are alike, and focusing on what others have is a sure-fire way to feel envy and regret. Focus on the good things in your own life, and you'll be more likely to find contentment in them," she says.
Impact of Happiness
Why is happiness so important? Happiness has been shown to predict positive outcomes in many different areas of life including mental well-being, physical health, and overall longevity.
- Positive emotions increase satisfaction with life.
- Happiness helps people build stronger coping skills and emotional resources.
- Positive emotions are linked to better health and longevity. One study found that people who experienced more positive emotions than negative ones were more likely to have survived over a 13 year period.
- Positive feelings increase resilience. Resilience helps people better manage stress and bounce back better when faced with setbacks. For example, one study found that happier people tend to have lower levels of the stress hormone cortisol and that these benefits tend to persist over time.
- People who report having a positive state of well-being are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors such as eating fruits and vegetables and engaging in regular physical exercise.
- Being happy may make help you get sick less often. Happier mental states are linked to increased immunity.
Some people seem to have a naturally higher baseline for happiness—one large-scale study of more than 2,000 twins suggested that around 50% of overall life satisfaction was due to genetics, 10% to external events, and 40% to individual activities.
So while you might not be able to control what your “base level” of happiness is, there are things that you can do to make your life happier and more fulfilling. Even the happiest of individuals can feel down from time to time and happiness is something that all people need to consciously pursue.
Cultivate Strong Relationships
Social support is an essential part of well-being. Research has found that good social relationships are the strongest predictor of happiness. Having positive and supportive connections with people you care about can provide a buffer against stress, improve your health, and help you become a happier person.
In the Harvard Study of Adult Development, a longitudinal study that looked at participants over 80 years, researchers found that relationships and how happy people are in those relationships strongly impacted overall health.
So if you are trying to improve your happiness, cultivating solid social connections is a great place to start. Consider deepening your existing relationships and explore ways to make new friends.
Get Regular Exercise
Exercise is good for both your body and mind. Physical activity is linked to a range of physical and psychological benefits including improved mood. Numerous studies have shown that regular exercise may play a role in warding off symptoms of depression, but evidence also suggests that it may also help make people happier, too.
In one analysis of past research on the connection between physical activity and happiness, researchers found a consistent positive link.
Even a little bit of exercise produces a happiness boost—people who were physically active for as little as 10 minutes a day or who worked out only once a week had higher levels of happiness than people who never exercised.
Show Gratitude
In one study, participants were asked to engage in a writing exercise for 10 to 20 minutes each night before bed. Some were instructed to write about daily hassles, some about neutral events, and some about things they were grateful for. The results found that people who had written about gratitude had increase positive emotions, increased subjective happiness, and improve life satisfaction.
As the authors of the study suggest, keeping a gratitude list is a relatively easy, affordable, simple, and pleasant way to boost your mood. Try setting aside a few minutes each night to write down or think about things in your life that you are grateful for.
Find a Sense of Purpose
Research has found that people who feel like they have a purpose have better well-being and feel more fulfilled. A sense of purpose involves seeing your life as having goals, direction, and meaning. It may help improve happiness by promoting healthier behaviors.
Some things you can do to help find a sense of purpose include:
- Explore your interests and passions
- Engage in prosocial and altruistic causes
- Work to address injustices
- Look for new things you might want to learn more about
This sense of purpose is influenced by a variety of factors, but it is also something that you can cultivate. It involves finding a goal that you care deeply about that will lead you to engage in productive, positive actions in order to work toward that goal.
Challenges of Finding Happiness
While seeking happiness is important, there are times when the pursuit of life satisfaction falls short. Some challenges to watch for include:
Valuing the Wrong Things
Money may not be able to buy happiness, but there is research that spending money on things like experiences can make you happier than spending it on material possessions.
One study, for example, found that spending money on things that buy time—such as spending money on time-saving services—can increase happiness and life satisfaction.
Rather than overvaluing things such as money, status, or material possessions, pursuing goals that result in more free time or enjoyable experiences may have a higher happiness reward.
Not Seeking Social Support
Social support means having friends and loved ones that you can turn to for support. Research has found that perceived social support plays an important role in subjective well-being. For example, one study found that perceptions of social support were responsible for 43% of a person's level of happiness.
It is important to remember that when it comes to social support, quality is more important than quantity. Having just a few very close and trusted friends will have a greater impact on your overall happiness than having many casual acquaintances.
Thinking of Happiness as an Endpoint
Happiness isn’t a goal that you can simply reach and be done with. It is a constant pursuit that requires continual nurturing and sustenance.
One study found that people who tend to value happiness most also tended to feel the least satisfied with their lives. Essentially, happiness becomes such a lofty goal that it becomes virtually unattainable.
“Valuing happiness could be self-defeating because the more people value happiness, the more likely they will feel disappointed,” suggest the authors of the study.
Perhaps the lesson is to not make something as broadly defined as “happiness” your goal. Instead, focus on building and cultivating the sort of life and relationships that bring fulfillment and satisfaction to your life.
It is also important to consider how you personally define happiness. Happiness is a broad term that means different things to different people. Rather than looking at happiness as an endpoint, it can be more helpful to think about what happiness really means to you and then work on small things that will help you become happier. This can make achieving these goals more manageable and less overwhelming.
History of Happiness
Happiness has long been recognized as a critical part of health and well-being. The "pursuit of happiness" is even given as an inalienable right in the U.S. Declaration of Independence. Our understanding of what will bring happiness, however, has shifted over time.
Psychologists have also proposed a number of different theories to explain how people experience and pursue happiness. These theories include:
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
The hierarchy of needs suggests that people are motivated to pursue increasingly complex needs. Once more basic needs are fulfilled, people are then motivated by more psychological and emotional needs.
At the peak of the hierarchy is the need for self-actualization, or the need to achieve one's full potential. The theory also stresses the importance of peak experiences or transcendent moments in which a person feels deep understanding, happiness, and joy.
Positive Psychology
The pursuit of happiness is central to the field of positive psychology . Psychologists who study positive psychology are interested in learning ways to increase positivity and helping people live happier, more satisfying lives.
Rather than focusing on mental pathologies, the field instead strives to find ways to help people, communities, and societies improve positive emotions and achieve greater happiness.
Finley K, Axner M, Vrooman K, Tse D. Ideal levels of prosocial involvement in relation to momentary affect and eudaimonia: Exploring the golden mean . Innov Aging . 2020;4(Suppl 1):614. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2083
Kringelbach ML, Berridge KC. The neuroscience of happiness and pleasure . Soc Res (New York) . 2010;77(2):659-678.
Panel on Measuring Subjective Well-Being in a Policy-Relevant Framework; Committee on National Statistics; Division on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; National Research Council; Stone AA, Mackie C, editors. Subjective Well-Being: Measuring Happiness, Suffering, and Other Dimensions of Experience [Internet]. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
Lee MA, Kawachi I. The keys to happiness: Associations between personal values regarding core life domains and happiness in South Korea . PLoS One . 2019;14(1):e0209821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0209821
Hsee CK, Zhang J, Cai CF, Zhang S. Overearning . Psychol Sci . 2013;24(6):852-9
Carstensen LL, Turan B, Scheibe S, et al. Emotional experience improves with age: evidence based on over 10 years of experience sampling . Psychol Aging . 2011;26(1):21‐33. doi:10.1037/a0021285
Steptoe A, Wardle J. Positive affect and biological function in everyday life . Neurobiol Aging . 2005;26 Suppl 1:108‐112. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.016
Sapranaviciute-Zabazlajeva L, Luksiene D, Virviciute D, Bobak M, Tamosiunas A. L ink between healthy lifestyle and psychological well-being in Lithuanian adults aged 45-72: a cross-sectional study . BMJ Open . 2017;7(4):e014240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014240
Costanzo ES, Lutgendorf SK, Kohut ML, et al. Mood and cytokine response to influenza virus in older adults . J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci . 2004;59(12):1328‐1333. doi:10.1093/gerona/59.12.1328
Lyubomirsky S, Sheldon KM, Schkade D. Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change . Review of General Psychology. 2005;9 (2):111–131. doi:0.1037/1089-2680.9.2.111
The Harvard Gazette. Good genes are nice, but joy is better .
Zhang Z, Chen W. A systematic review of the relationship between physical activity and happiness . J Happiness Stud 20, 1305–1322 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-018-9976-0
Cunha LF, Pellanda LC, Reppold CT. Positive psychology and gratitude interventions: a randomized clinical trial . Front Psychol . 2019;10:584. Published 2019 Mar 21. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00584
Ryff CD. Psychological well-being revisited: advances in the science and practice of eudaimonia . Psychother Psychosom . 2014;83(1):10‐28. doi:10.1159/000353263
Whillans AV, Dunn EW, Smeets P, Bekkers R, Norton MI. Buying time promotes happiness . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2017;114(32):8523‐8527. doi:10.1073/pnas.1706541114
Gulacti F. The effect of perceived social support on subjective well-being . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2010;2(2):3844-3849. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.03.602
Mauss IB, Tamir M, Anderson CL, Savino NS. Can seeking happiness make people unhappy? [corrected] Paradoxical effects of valuing happiness [published correction appears in Emotion. 2011 Aug;11(4):767]. Emotion . 2011;11(4):807‐815. doi:10.1037/a0022010
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to Find True Happiness (According to Psychology)

There are many philosophical schools of thought regarding the concept of happiness and its cultivation.
For instance, the pursuit of enduring happiness is at the core of many mindfulness practices, which often emphasize gratitude and seeking contentment in the present moment.
Other models of happiness suggest the importance of living in congruence with our values and in ways that satisfy our basic human needs. Some research even shows that whether we are happy or not can, in part, be boiled down to our genetics.
In what follows, we’ll walk you through several conceptualizations of happiness, show you how to measure each, and give you a wide range of strategies for cultivating whichever form of happiness you seek in your own life.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Happiness & Subjective Wellbeing Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients identify sources of authentic happiness and strategies to boost wellbeing.
This Article Contains:
What is happiness, how to measure happiness, what is true happiness, the wrong way to search for happiness, 7 ways to find happiness, 3 tips to form habits for happiness, a take-home message.
Defining happiness is no small task, but philosophers and researchers have drilled the notion down to two key conceptualizations.
These conceptualizations are known as hedonia and eudaimonia , and together, they represent two long-running traditions in the study of happiness that stem as far back as the times of ancient philosophers (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
Happiness as hedonia
The hedonic perspective of happiness argues that life’s goal is to experience the maximum amount of pleasure and the minimum amount of pain. According to this tradition, how happy we are can be boiled down to the sum of one’s total hedonic moments (Ryan & Deci, 2001).
When it comes to measuring hedonic happiness, modern psychologists tend to use assessments of Subjective Wellbeing (see How to Measure Happiness below; Diener & Lucas, 1999).
In the past, philosophers of hedonism adopted a fairly narrow view of pleasure and pain related to bodily sensations, appetites, and self-interests. Examples of such forms of hedonia include eating tasty food, enjoying sex, and being free of physical discomfort.
Today, psychologists adopting the hedonic view take an interest in both the pleasures of the body and mind in the broader study of wellbeing (Kahneman, 1999).
This broader, more psychological conceptualization of hedonic pleasure argues that happiness can flow from behaviors that promote mental stimulation, stress relief, feelings of social connectedness, positive mood, and more (Arnold & Reynolds, 2003).
This expanded conceptualization has resulted in the broadening of the study of hedonic pleasure to fields such as economics. For instance, hedonic conceptualizations of happiness are used to understand how shoppers make decisions between purchases, estimating how much pleasure or utility they stand to gain by choosing one product over another (Babin, Darden & Griffin, 1994).
Happiness as eudaimonia
The eudaimonic perspective of happiness presents an alternative to the hedonic view, arguing that true happiness is found when one behaves virtuously. Pursuing eudaimonia, therefore, is about doing what is worth doing .
In line with this, we can think about the eudaimonic perspective as being about reaching one’s true potential and living in congruence with one’s values and true self. It also involves developing one’s talents and strengthening relationships with those for whom we care. By living in this way, one should feel deeply engaged and fully alive (Waterman, 1993).
When it comes to measuring eudaimonic happiness, most researchers tend to use Ryff and Keyes’ (1995) multidimensional scales of psychological wellbeing (see How to Measure Happiness below).
According to the eudaimonic perspective, that which feels pleasurable is not always conducive to wellbeing. Likewise, that which is worth doing does not always feel pleasurable in the present moment.
For instance, volunteering for a cause one feels passionate about may not always feel pleasurable in the hedonic sense. It may involve spending long hours sweating in the sun, getting dirty, or dealing with challenging people or situations. Nonetheless, such pursuits may feed into our eudaimonic happiness as we live in unity with our values.
Interestingly, many traditional philosophers who championed the eudaimonic perspective denounced hedonic views of happiness, declaring them vulgar and overly self-centered. For instance, Aristotle considered hedonic happiness to make humans slavish followers of frivolous desires.
Spiritual conceptualizations of happiness
Today, we can consider a third perspective of happiness which lies in the practice of mindfulness.
Whereas the previous two perspectives consider happiness as something that must be sought, growing schools of thought argue that happiness in the form of contentment or inner peace are primarily available to us at any given moment, regardless of what we are doing.
Consider the following quote from neuroscientist and mindfulness practitioner Sam Harris (2014):
Most of us spend our time seeking happiness and security without acknowledging the underlying purpose of our search. Each of us is looking for a path back to the present: We are trying to find good enough reasons to be satisfied now. Acknowledging that this is the structure of the game we are playing allows us to play it differently. How we pay attention to the present moment largely determines the character of our experience and, therefore, the quality of our lives.
– Sam Harris, Waking Up, p. 3
Mindfulness-based perspectives on happiness and contentment have traditionally been a feature of eastern religions. These traditions hold the view that there exists a source of psychological wellbeing that is not dependent on gratifying one’s desires (hedonia) or pursuing an integrated, self-actualized sense of self (eudaimonia).
Rather, happiness can be achieved by cultivating present-moment awareness and self-transcendence . In other words, these arguments suggest that it is possible to give up the search for happiness and commit oneself to finding contentment in what is happening right now.
A rapidly growing body of psychological and neuroscientific evidence has emerged to support these claims (Hanson, 2009), pointing us toward another avenue for cultivating sustainable happiness.
Overall, happiness is likely to look different for different people. As an individual or practitioner, you may find the most value in considering how all three of these conceptualizations factor into you or your client’s life as a first step toward cultivating enduring happiness.

As noted, hedonic conceptualizations of happiness are often measured using assessments of subjective wellbeing (Diener & Lucas, 1999). Subjective wellbeing regards a person’s cognitive and affective evaluations of his or her life (Diener, 2000).
You can read more about measures of subjective well-being in our other dedicated articles. In these, we explore several commonly accepted measures of hedonic happiness. These include:
- The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (Watson, Clark & Tellegen, 1988);
- The Satisfaction with Life Scale (Diener, Emmons, Larsen & Griffin, 1985); and
- The Global Happiness Scale (Lyubomirsky & Lepper, 1999)
When it comes to assessing eudaimonic happiness, most scholars apply Ryff and Keyes’ (1995) multidimensional measure of psychological wellbeing (PWB).
The creators’ development of the measure was spurred by their observation that previous studies had treated happiness as synonymous with a balance between positive and negative affect or overall satisfaction with one’s life.
They argued that these approaches were too data-driven and not rooted in theory or lived experience. Therefore, these scholars designed and validated a measure based on responses from a representative sample of telephone interviews (Ryff & Keyes, 1995).
This measure assesses eudaimonic happiness according to six sub-dimensions:
- Autonomy The ability to resist social pressures, regulate behavior from within, and evaluate oneself based on personal standards.
- Environmental mastery Feelings of mastery and competence in a variety of situations, the ability to take advantage of opportunities, and the ability to craft one’s environment to suit one’s needs and values.
- Personal growth Feelings of ongoing development, the realization of one’s potential, and observing oneself changing in ways that signify acquired knowledge and increased effectiveness.
- Positive relations with others Possessing warm, trusting relationships with others characterized by give and take, and the capacity for intimacy and empathy.
- Purpose in life Having goals and a sense of meaning and belief that gives life purpose.
- Self-acceptance Possessing a positive attitude toward oneself, including both one’s good and bad qualities.
Two versions of this scale are available. The first is the original 42-item measure (Ryff, 1989a; 1989b), and there is also a shortened 18-item version (Ryff & Keyes, 1995).
You can find the items for both of these scales, as well as scale anchors and scoring information on Stanford University’s website .
For another useful tool that attempts to reconcile the hedonic and eudaimonic perspectives of happiness, take a look at Hervás and Vázquez’s (2013) Pemberton Happiness Index (PHI).
Upon recognizing that existing assessments of happiness measured either hedonic or eudaimonic conceptualizations of happiness, these scholars sought to design and validate a brief, comprehensive measure that assessed both.
The final 21-item scale also has the advantage of capturing both remembered and experienced wellbeing (Kahneman & Riis, 2005).
The former relies on participants’ memory and judgment about their overall lives, using items like, “I feel able to solve the majority of my daily problems.” In contrast, the latter assesses real-time affective states and feelings about the previous day, using items like, “I learned something interesting.”
As for assessing happiness flowing from conceptualizations in mindfulness, many researchers have administered short scales that capture momentary changes in emotions via diary study.
The purpose of a diary study is to assess fluctuations in states (e.g., moods, thoughts, etc.) throughout a given day. This type of study design, sometimes called a within-person design , runs contrary to many studies in psychology, which typically compare differences between people.
As an example, Diener and colleagues (2010) designed the 12-item Scale of Positive and Negative Experience (SPANE), which was designed to be quickly administered and assess the full range of emotions and feelings a person may experience. The scale, therefore, contains both general and specific emotional terms, such as “pleasant” and “sad.”
Thanks to its brevity, this scale can easily be administered multiple times a day. Therefore, it has been applied in diary studies assessing fluctuations in mindfulness throughout a day. For instance, Ding and colleagues (2019) used the scale in a study examining the link between state mindfulness and present-moment emotions.
The results indicated that state mindfulness was positively related to positive emotions, like happiness and contentment, and negatively related to negative emotions, like depression and boredom.
These authors also found that present-moment rumination, which involves fixation on negative thoughts, partially mediated this effect. In other words, maintaining a mindful state of awareness appears to block ruminative thought partially, helping us to enjoy more positive emotions throughout any given day.
In sum, it’s clear psychologists have done much of the heavy lifting when it comes to developing measures of happiness.
As a practitioner looking to assess your clients’ happiness, you should use the information above as a guide to ensure the content validity of your chosen measure. That is, take care to select a scale that has been shown to effectively assess the conceptualization of happiness (e.g., hedonic, eudaimonic) that you apply in your practice.
Neurological measures of happiness
You may have noticed that the measures of happiness discussed so far have all been self-report in nature. That is, each relies on participants providing information about their own subjective sense of their happiness.
But is there a more objective way to measure happiness?
To answer this question, philosophers and psychologists have been turning to neuroscience to better understand what happiness looks like in the brain.
This research has involved the use of sophisticated technologies, such as PET and fMRI scans, and EEG measures of electrical activity in the brain to identify how happiness manifests physiologically. (Murphy, Nimmo-Smith & Lawrence, 2003; Phan, Wager, Taylor & Liberzon, 2002; Lindquist, Wager, Kober, Bliss-Moreau & Barrett, 2012)

Download 3 Free Happiness Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to discover authentic happiness and cultivate subjective well-being.
Download 3 Free Happiness Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
To recap, we now have three conceptualizations of happiness: hedonia, eudaimonia, and contentment rooted in mindfulness.
We also have two ways to measure each form of happiness: self-reports and various physiological indicators in the brain.
But the question remains: Is there a secret to finding true happiness?
What has hopefully become apparent is that this question is somewhat of a trick question because there is no agreed-upon understanding of what constitutes ‘true’ happiness.
Think about it.
Imagine racing to your favorite Mexican restaurant and arriving at the ordering counter moments before the restaurant is about to close. The server takes your order, and a few minutes later, you’re handed your favorite taco.
What action would a scholar of each ‘happiness philosophy’ recommend at this moment when you receive your meal?
To a believer of hedonism, happiness would likely represent the moment you bite into the taco and delight in its flavors on your tongue.
To philosophers of the eudaimonic perspective, happiness would more likely involve the ritual of eating with someone you care about, thereby strengthening your connection with that person. It could also mean reaching your potential as a budding cook by learning to create a similarly tasty dish or giving the taco to someone hungry and in need.
Finally, followers of the mindfulness-based perspective would argue that contentment can be found in any or all of the above actions but that it is the quality of your attention, paid to your intentions, sensations, emotions, and interactions with others, that would dictate the happiness you derived from whatever you chose to do with the taco.
In sum, these examples indicate that searching for one ‘true’ source of happiness may be feeding into a fallacy. Rather, there appear to be several pathways to pursuing different sources of happiness.
The remainder of this article will outline scientifically evidenced pathways to cultivating each of these three forms of happiness.
But before setting off on your search, heed one warning…

There are at least three critical bodies of theory, thinking, and research that point to why sacrificing life’s present joy’s chasing happiness is likely to make us paradoxically more miserable.
We have already touched on the first perspective, which is based on the philosophy of mindfulness.
This perspective encourages us to give up the search for happiness entirely, harness our attention, and discover that contentment that can exist in stillness, no matter what we yearn for or have yet to achieve (Harris, 2014).
According to this perspective, by failing to acknowledge that contentment is available to us at any given moment, we will remain dissatisfied. This is because even if we achieve all our goals and get everything we want, some newer, shinier source of happiness will always arise for us to chase.
In other words, the grass will always appear greener somewhere else, meaning it is important to look for happiness wherever we are presently standing.
The second body of thinking lies in empirical findings from the psychology of expectancies and goal-pursuit.
One study in the journal, Emotion (Mauss, Tamir, Anderson & Savino, 2011), found that those who reported valuing happiness highly experienced greater disappointment and ultimately less happiness when circumstances that should have made them happy failed to meet their expectations. In other words, the findings paradoxically suggest that the more we desire happiness, the less likely we are to experience it.
Likewise, there is evidence that placing too much importance on achieving challenging goals in the distant future may also be a recipe for misery.
One study found that students who perceived they made poor progress toward their ambitious life goals tended to exhibit significant depressive symptoms two years later (Salmela-Aro & Nurmi, 1996). Moreover, the study evidenced a downward spiral of depressive symptoms; disappointed students proceeded to derive less enjoyment from their goal pursuits, thereby worsening their symptoms.
Together, these findings highlight the danger of hanging all our hopes for being happy on the realization of future events .
A third reason why chasing happiness may be a mistake relates to a process known as hedonic adaptation (or the hedonic treadmill ). Hedonic adaptation is the observed tendency of humans to quickly adapt to a baseline level of happiness, regardless of significant life events (Brickman & Campbell, 1971).
Indeed, it has been shown that even if one wins a major lottery, the happiness that person derives from day-to-day activities in life will eventually return to baseline (Brickman, Coates & Janoff-Bulman, 1978).
This finding highlights that we should not overestimate the effect that significant life events will have on our long-term happiness, serving as yet another reason to call off the search for happiness (Grant, 2013).
In sum, it is important to recognize that happiness is not somewhere off in the distance. There is always something to be gained by pausing to reflect on our reasons to be happy right now, such as by practicing gratitude.
We will explore this and several other strategies to find hedonic, eudaimonic, and present-moment happiness in the remaining sections.
You don’t find happiness, you create it – Katarina Blom
You now understand a key pitfall to avoid in your search for happiness. Next, let’s consider eight different sources of happiness you can leverage today to find joy in your own life.
Finding happiness through neurotransmitters
The first effective way to boost hedonic happiness is to engage in healthy behaviors that directly target neurotransmitters associated with pleasure.
While there are many neurotransmitters that affect our happiness, there are a few key ones worth focusing on: dopamine, serotonin, oxytocin, and endorphins.
Dopamine, otherwise known as the “feel-good” hormone, is a key feature of the brain’s reward system and associated with pleasure. Dopamine can be triggered in many ways, including through exercise , a healthy diet, sufficient sleep, listening to music, meditating, and ensuring you get a little sunlight each day (Breuning, 2015; Hansen, Stevens & Coast, 2001).
Next is serotonin. This hormone plays an essential role in stabilizing our mood and can be triggered in many of the same ways as dopamine, such as by getting consistent sleep, exercise, and ensuring you maintain a balanced diet (Breuning, 2015; Roman, Walstra, Luiten & Meerlo, 2005).
Third is oxytocin, which is the hormone associated with love, bonding, and close connection. This hormone is boosted primarily through physical touch and closeness with others, meaning that hugs, cuddling, and even simply spending time with others can significantly increase our happiness (Breuning, 2015; Uvnäs-Moberg, Handlin & Petersson, 2015).
The final neurotransmitters to consider are endorphins, which reduce physical pain and act as your body’s natural reward system. To increase this hormone, try engaging in behaviors that are ‘good’ for you, such as exercising or demonstrating sincere acts of kindness (Breuning, 2015). Studies have also shown that consuming cocoa, such as that in dark chocolate, can trigger endorphins in the brain (Ottley, 2000).
This was just a brief snapshot into the neurochemical bases of happiness.
To learn more and gain a range of practical tips to naturally boost your neurochemical happiness, take a look at Dr. Loretta Breuning’s book, Habits of a Happy Brain .
Finding happiness through real goods
A next important step in the search for happiness is to work toward securing the basic necessities for wellbeing and development, or what Aristotle called real goods .
Real goods satisfy the natural needs of our bodies, such as our needs for warmth and sustenance. Examples of such real goods include food, clothing, health, shelter, and safety (Moss, 2012).
We might liken this conceptualization to that of the lower levels of Maslow’s hierarchy , which argues that humans must satisfy basic physiological and safety-related needs before pursuing higher-order needs like esteem and self-actualization.
However, real goods also include “goods of the soul,” such as love, arts, music, and literature (Joseph, 2019). These goods clearly tap into the higher levels of Maslow’s hierarchy, and without them, it may be challenging to achieve eudaimonic happiness.
For instance, without a secure shelter in which to gain adequate rest, we would likely lack the energy to develop a new talent, such as painting. Nor would we gain this talent without exposure to sources of inspiration, such as other artists’ work or cultural influences.
In sum, Aristotle’s principles regarding real goods highlight two courses of action for improving happiness.
First, take steps toward securing the basics for your health and wellbeing. This means eating well, engaging in regular exercise, securing a stable income, and getting plenty of sleep.
Secondly, immerse yourself in environments that will bring out your best. For example, surround yourself with good company, knowledge, and cultures. In practice, this may mean stepping outside your comfort zone by meeting new people, learning new skills, or visiting new places.
Finding happiness through gratitude
Many studies stemming from the eudaimonic and mindfulness-based perspectives point to the practice of gratitude as a key source of happiness.
Gratitude can be defined as “the appreciation of what is valuable and meaningful to oneself… [representing] a general state of thankfulness and/or appreciation” (Sansone & Sansone, 2010, p. 18).
Two simple ways to practice gratitude include taking a moment at the end of the day to reflect on an occurrence for which you were grateful and sending a thoughtful message of appreciation to someone you care about.
For more ideas, take a look at some of our dedicated articles on this topic:
- 13 Most Popular Gratitude Exercises & Activities
- 41+ Gratitude Messages, Letters and Lists
- How To Express Gratitude to Others (19 Ideas + Gifts & Challenges)
- Gratitude Journal: A Collection of 66 Templates, Ideas, and Apps for Your Diary
Finding happiness through flow
Another way to achieve happiness is to take part in activities that bring about the experience of flow, otherwise known as the feeling of “being in the zone.”
In an interview, Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi , the researcher credited with having popularized the concept of flow, explained that those in a state of flow are:
…completely involved in an activity for its own sake. The ego falls away. Time flies. Every action, movement, and thought follows inevitably from the previous one, like playing jazz. Your whole being is involved, and you’re using your skills to the utmost.
(Geirland, 1996)
Examples of just a few activities that can generate flow include games, sports, dancing, cooking, gardening, work, driving, and artistic pursuits (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990).
Most followers of the eudaimonic perspective would view the flow experience as an indicator of eudaimonia. This is because flow experiences entail an optimal level of challenge, enabling us to develop our talents to their fullest (Csikszentmihalyi, 1990).
For more ideas on how to cultivate flow in your life, look at our dedicated articles on the topic:
- The Psychology and Theory Behind Flow
- 11 Activities and Exercises to Induce a Flow State (+ 6 Examples)
- What is Flow in Psychology? Definition and 10+ Activities to Induce Flow
- Flow at Work: The Science of Engagement and Optimal Performance
Finding happiness by living into our values
Several studies have found that making intentional efforts to live in congruence with our values can bolster our happiness or at least buffer against unhappiness (Brown, 2018; Veage et al., 2014).
For clarity, we can define values as “stable, general beliefs about what is desirable” (Feather, 1992, p. 111). Examples of values include fairness, creativity, and freedom.
Understanding our values is critical to achieving eudaimonic happiness because the eudaimonic perspective of happiness encourages us to engage in what is worth doing (Boniwell, 2008). In order to know what is worth doing, we must understand which actions generate valued outcomes, and we can only know this by looking closely at our core values.
Scientists and practitioners have developed a range of useful exercises to help individuals discover their core values. You can learn more about these in several of our other articles:
- 25 Values Worksheets to Enrich Your Clients’ Lives With More Meaning
- The 3 Best Questionnaires for Measuring Values
- Values Clarification: How Reflection On Core Values Is Used In CBT
Once you are clear on your core values, you can take steps to behave in a way that is congruent with these values, helping you live a happier life.
For instance, if you discover that one of your core values is growth, you might then consider the different ways to enact this value in day-to-day life. This could involve registering for a night class or pursuing new intellectual pursuits through reading.
Research also shows that the alignment between our values and professional pursuits plays an important role in determining our overall happiness (Chatman, 1989; Kristof-Brown, Zimmerman & Johnson, 2005).
Based on this, we see the emergence of research on job crafting , which involves altering one’s work to better align it with our preferences (Zhang & Parker, 2019), and that on hiring practices that facilitate good person-job fit (Sekiguchi, 2004).
Therefore, organizational leaders and HR professionals may wish to dig further into some of these concepts to strengthen the happiness of their staff.
Finding happiness through needs satisfaction
One prominent theory of happiness posits that to be happy, we must engage in behaviors that satisfy our three core human needs (Ryan & Deci, 2008):
- the need for competence (feeling effective);
- the need for autonomy (the feeling of being the origin of one’s behavior); and
- the need for psychological relatedness (feeling cared for and understood by other people).
Overall, the satisfaction of these needs represents an avenue for achieving happiness that falls under the eudaimonic conceptualization. This is because need satisfaction promotes long-term wellness rather than just temporary pleasure (Boniwell, 2008).
For a simple assessment to determine your overall satisfaction of core needs within your life, consider completing the 21-item Basic Needs Satisfaction in General Scale (BNSG-S; Gagné, 2003).
Upon completing the assessment, one can calculate their total score for each core need and identify an area for growth as a first step toward fostering greater eudaimonic happiness.
For instance, if you discover that your lowest-scoring need is competence, you might consider whether you can engage in work or hobbies that better utilize your skills, enabling you to derive a greater sense of competence from daily activities.
Again, this was just a brief snapshot into the science of needs satisfaction as a mechanism for achieving happiness. To learn more, look at our dedicated article on self-determination .
Finding happiness through mindfulness
Finally, and at the core of the mindfulness-based approach to finding happiness is the practice of mindfulness itself.
Mindfulness is typically defined as the practice of bringing one’s attention to the internal and external experiences occurring in the present moment, such as sensations, sights, thoughts, and emotions (Baer, 2003; Kabat-Zinn, 1994).
Mindfulness has existed for centuries and was first popularized among eastern traditions. The practice functions to better understand feelings and motivations, train the capacity for attention and relaxation, and free one’s mind from overidentification with negative thoughts and emotions (Fronsdal, 2004; 2006; Harris, 2014).
Often, regular meditation will lie at the core of mindfulness practice. However, other approaches to developing mindfulness can include journaling and yoga .
No matter how you practice mindfulness, the aim is typically for the practice’s benefits to spill over into your experience of day-to-day consciousness, enabling you to return to states of mindful awareness throughout your day and not be at the whim of negative thoughts and emotions.
If you’re interested in cultivating greater happiness through mindfulness, we have a range of articles throughout our blog to help you learn more:
- Mindfulness Meditation Videos, Exercises, Books and Courses (+PDF)
- How To Practice Mindfulness: 10 Practical Steps and Tips
- Practicing Mindfulness in Groups: 9 Activities and Exercises
- 18 Mindfulness Games, Worksheets and Activities for Kids

As with any behavior change, becoming happier requires that one form new, positive habits. For instance, if you wish to target happiness through neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, a first step may be to develop routines and habits associated with good sleep and regular exercise.
Likewise, if you wish to cultivate happiness through regular gratitude practice, commit to setting aside fifteen minutes each evening to fill in a gratitude journal.
Here are three tips related to the science of habit formation to help you develop your new habits for happiness.
First, set a goal to strengthen your happiness using a goal-setting framework . By using a framework to set a happiness goal, you can avoid accidentally setting a goal that is too vague, easily track your progress, and rest assured knowing your goal is realistic and within your reach.
Second, keep in mind that it takes approximately two months for a new behavior to become an automatic habit (Lally, van Jaarsveld, Potts & Wardle, 2010), so do whatever it takes to commit to your goal for at least this long.
That way, you can see if your new practice has enduring benefits and becomes easier with time. For instance, you may find you need to set daily reminders for yourself (e.g., to journal, settle in for bed) for a couple of months until your new habit becomes automatic.
Finally, consider linking up with a friend or small group and commit to becoming happier together. In the same way that groups like AA and Weight Watchers can help their members develop better habits associated with health, you can work with others to stay accountable and get support if you face any hurdles in your pursuit of greater happiness.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
The aim of cultivating human happiness is at the core of positive psychology.
It should, therefore, be no surprise that we have linked to many of our other posts exploring different approaches to fostering happiness throughout our discussion.
Now that you hopefully have a better sense of what you’re searching for when thinking about your own happiness, as well as pitfalls to avoid, we encourage you to select one area for growth. Once you’ve chosen an area, follow the links to read more and commit to developing one new habit for happiness.
By doing this, you’re letting go of the false conception of ‘true’ happiness as something elusive and far off in the future. Instead, you’ll be acknowledging happiness as something that can be achieved little-by-little, right now.
And if you ever find yourself getting lost in your search for happiness, consider reflecting on this famous quote:
Happiness is a journey, not a destination; happiness is to be found along the way not at the end of the road, for then the journey is over and it’s too late. The time for happiness is today not tomorrow.
Paul H. Dunn
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Happiness Exercises for free .
- Arnold, M. J., & Reynolds, K. E. (2003). Hedonic shopping motivations. Journal of Retailing , 79(2), 77-95.
- Babin, B. J., Darden, W. R., & Griffin, M. (1994). Work and/or fun: Measuring hedonic and utilitarian shopping value. Journal of Consumer Research , 20(4), 644-656.
- Baer, R. A. (2003). Mindfulness training as a clinical intervention: A conceptual and empirical review. Clinical psychology: Science and Practice , 10(2), 125-143.
- Boniwell, I. (2008). What is eudaimonia? The concept of eudaimonic well-being and happiness . Retrieved from http://positivepsychology.org.uk/the-concept-of-eudaimonic-well-being/
- Breuning, L. G. (2015). Habits of a happy brain: Retrain your brain to boost your serotonin, dopamine, oxytocin, & endorphin levels . Avon, MA: Simon and Schuster.
- Brickman, P., & Campbell, D. T. (1971). Hedonic relativism and planning the good society. In M. H. Appley (Ed.), Adaptation-level theor y (pp. 287–302). New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Brickman, P., Coates, D., & Janoff-Bulman, R. (1978). Lottery winners and accident victims: Is happiness relative? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 36(8), 917-927.
- Brown, B. (2018). Dare to lead: Brave work. Tough conversations. Whole hearts . London, UK: Vermilion.
- Chatman J. A. (1989). Improving interactional organizational research: A model of person–organization fit. Academy of Management Review , 14(3), 333-349.
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience . New York, NY: Harper & Row.
- Diener, E. (2000). Subjective well-being: The science of happiness and a proposal for a national index. American Psychologis t, 55(1), 34-43.
- Diener, E. D., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment , 49(1), 71-75.
- Diener, E., & Lucas, R. E. (1999). Personality and subjective well-being. In D. Kahneman, E. Diener, & N. Schwarz (Eds.), Well-being: The foundations of hedonic psycholog y (pp. 213–229). New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation.
- Diener, E., Wirtz, D., Tov, W., Kim-Prieto, C., Choi, D. W., Oishi, S., & Biswas-Diener, R. (2010). New well-being measures: Short scales to assess flourishing and positive and negative feelings. Social Indicators Research , 97(2), 143-156.
- Ding, X., Du, J., Zhou, Y., An, Y., Xu, W., & Zhang, N. (2019). State mindfulness, rumination, and emotions in daily life: An ambulatory assessment study. Asian Journal of Social Psychology , 22(4), 369-377.
- Feather, N. T. (1992). Values, valences, expectations, and actions. Journal of Social Issues , 48(2), 109–124.
- Fronsdal, G. (2004). Not-Knowing. Insight Meditation Center . Retrieved from https://www.insightmeditationcenter.org/books-articles/articles/not-knowing/.
- Fronsdal, G. (2006). Mindfulness meditation as a Buddhist practice. Insight Meditation Center . Retrieved from https://www.insightmeditationcenter.org/books-articles/articles/mindfulness-meditation-as-a-buddhist-practice/.
- Gagné, M. (2003). The role of autonomy support and autonomy orientation in prosocial behavior engagement. Motivation and Emotion , 27(3), 199-223.
- Geirland, J. (1996). Go with the flow. Wired . Retrieved from https://www.wired.com/1996/09/czik/
- Grant, A. (2013). Does trying to be happy make us unhappy? Psychology Today . Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/give-and-take/201305/does-trying-be-happy-make-us-unhappy
- Hansen, C. J., Stevens, L. C., & Coast, J. R. (2001). Exercise duration and mood state: How much is enough to feel better? Health Psychology , 20(4), 267-275.
- Hanson, R. (2009). Buddha’s brain: The practical neuroscience of happiness, love, and wisdom . Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications.
- Harris, S. (2014). Waking up: A guide to spirituality without religion . New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
- Hervás, G., & Vázquez, C. (2013). Construction and validation of a measure of integrative well-being in seven languages: The Pemberton Happiness Index. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes , 11(1), 1-13.
- Joseph, S. (2019). What is eudaimonic happiness? How and why positive psychologists are learning from Aristotle. Psychology Today . Retrieved from https://www.psychologytoday.com/au/blog/what-doesnt-kill-us/201901/what-is-eudaimonic-happiness
- Kabat-Zinn, J. (1994). Wherever you go, there you are: Mindfulness meditation in everyday life . New York, NY: Hyperion.
- Kahneman, D. (1999). Objective happiness. Well-being: The foundations of hedonic psychology , 3(25), 1-23.
- Kahneman, D., & Riis, J. (2005). Living and thinking about it: Two perspectives on life. In F. Huppert, N. Baylis & B. Kaverne (Eds.), The science of well-being (pp. 285-306). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
- Kristof‐Brown, A. L., Zimmerman, R. D., & Johnson, E. C. (2005). Consequences of individuals’ fit at work: A meta‐analysis of person-job, person-organization, person-group, and person-supervisor fit. Personnel Psychology , 58(2), 281-342.
- Lally, P., van Jaarsveld, C. H., Potts, H. W., & Wardle, J. (2010). How are habits formed: Modelling habit formation in the real world. European Journal of Social Psychology , 40(6), 998-1009.
- Lindquist, K. A., Wager, T. D., Kober, H., Bliss-Moreau, E., & Barrett, L. F. (2012). The brain basis of emotion: A meta-analytic review. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 35(3), 121-143.
- Lyubomirsky, S., & Lepper, H. S. (1999). A measure of subjective happiness: Preliminary reliability and construct validation. Social Indicators Research , 46(2), 137-155.
- Mauss, I. B., Tamir, M., Anderson, C. L., & Savino, N. S. (2011). Can seeking happiness make people unhappy? Paradoxical effects of valuing happiness. Emotion , 11(4), 807-815.
- Moss, J. (2012). Aristotle on the apparent good: Perception, phantasia, thought, and desire. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Murphy, F. C., Nimmo-Smith, I. A. N., & Lawrence, A. D. (2003). Functional neuroanatomy of emotions: A meta-analysis. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience , 3(3), 207-233.
- Ottley, C. (2000). Food and mood. Mental Health Practice , 4(4), 46-52.
- Phan, K. L., Wager, T., Taylor, S. F., & Liberzon, I. (2002). Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: A meta-analysis of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage , 16(2), 331-348.
- Roman, V., Walstra, I., Luiten, P. G., & Meerlo, P. (2005). Too little sleep gradually desensitizes the serotonin 1A receptor system. Sleep , 28(12), 1505-1510.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2001). On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annual Review of Psychology , 52(1), 141-166.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2008). Self-determination theory and the role of basic psychological needs in personality and the organization of behavior. In O. P. John, R. W. Robins, & L. A. Pervin (Eds.), Handbook of personality: Theory and research (p. 654–678). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
- Ryff, C. D. (1989a). Beyond Ponce de Leon and life satisfaction: New directions in quest of successful ageing. International Journal of Behavioral Development , 12(1), 35-55.
- Ryff, C. D. (1989b). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 57(6), 1069-1081.
- Ryff, C. D., & Keyes, C. L. M. (1995). The structure of psychological well-being revisited. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 69(4), 719-727.
- Salmela-Aro, K., & Nurmi, J. E. (1996). Depressive symptoms and personal project appraisals: A cross-lagged longitudinal study. Personality and Individual Differences , 21(3), 373-381.
- Sansone, R. A., & Sansone, L. A. (2010). Gratitude and well being. Psychiatry, 7(11), 18-22.
- Sekiguchi, T. (2004). Person-organization fit and person-job fit in employee selection: A review of the literature. Osaka Keidai Ronshu , 54(6), 179-196.
- Uvnäs-Moberg, K., Handlin, L., & Petersson, M. (2015). Self-soothing behaviors with particular reference to oxytocin release induced by non-noxious sensory stimulation. Frontiers in Psychology , 5.
- Veage, S., Ciarrochi, J., Deane, F. P., Andresen, R., Oades, L. G., & Crowe, T. P. (2014). Value congruence, importance and success and in the workplace: Links with well-being and burnout amongst mental health practitioners. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science , 3(4), 258-264.
- Waterman, A. S. (1993). Two conceptions of happiness: Contrasts of personal expressiveness (eudaimonia) and hedonic enjoyment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 64(4), 678-691.
- Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 54(6), 1063-1070.
- Zhang, F., & Parker, S. K. (2019). Reorienting job crafting research: A hierarchical structure of job crafting concepts and integrative review. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 40(2), 126-146.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Everyone has to realize that every person is going thru their own thing, every single person is different very different from one another. just because a person is learning something doing something at the same time as u does not mean they are disappointed at u also learning it the same time but rather are shocked because they thought of u as something bigger knowing it all. So just explain something that u went thru different from that person not to compare but to rather say u know dude/dudette I know I may seem big but I am I just was lost all my life and it makes me, however, feel privileged that I’m going thru the same thing as yourself though, it means a lot.
Hi i want to quickly share my story how i get rid of anxieties, not being happy and knowing who i am so it can help someone. I was looking for someting to fullfill my heart and be happy during my growing up i was searching all over internet and trying all the stuff. I was so despered that i even went to psychiatrist and psychologist so i tried that but nothing helped me. I went into spiritual teaching from buddhism to all the other and even shamanic ceremonies but still didnt found answers and fell more and more down. I felt like i really need change and new life. Then on youtube i found video from “last reformation” it shows followers of christ on streets healing the sick. I saw the proof of someting finaly. When i saw it i believed and through the map on their webside i found someone to baptise me. When i went to bathtub to be baptise i felt someting happened to my heart like some power cleansed me from all the bad stuff. Then i felt someting like heavenly honey being poured on me and i got filled with the Holy Spirit and spoke in tongues. After that i was crying with happiness becouse i knew that what happened was real and i finnaly found it. From that day i have never been the same and i found myself in Jesus. Becouse everyone who calls on him will be saved.
“Thanks for sharing this information about how to happy? Really a nice source of information about all people. I actually added your blog to my favorites list and look forward to getting the same quality content every time I visit your blog. Thank you”
wow, awesome article post. Fantastic
Great article. I was recently looking for ways to happiness. If you are on a similar quest I can also highly recommend Eisner Fjord’s “Simple ways to find happiness” where he interviewed hundreds of happy people to find their recipe for happiness. check him out on amazon
Nice post. According to me happiness is all around us. We just need to acknowledge.
Currently, I think I’m not happy with myself. I’m not sure what makes a person happy so I’ll buy inspirational books about happiness from a good store. Thanks for the ideas about what I can do to get better mentally, so hopefully the book has some ideas about it as well.
DFS thanks for the words of wisdom. All it takes is a little positive enhancement to becoming and having some faith on how we can maintain on just being happy. It’s so simple but I tend to make it complicated. I need to be more alive in staying healthy and more energetic to stay healthy. It feels good to be able to be somewhat flexible. Stretching has opened the door for me to feeling better.
Amazing article, very informative and non-fictional. I would love to read more of articles from this author/writer in the future.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Embracing JOMO: Finding Joy in Missing Out
We’ve probably all heard of FOMO, or ‘the fear of missing out’. FOMO is the currency of social media platforms, eager to encourage us to [...]

The True Meaning of Hedonism: A Philosophical Perspective
“If it feels good, do it, you only live once”. Hedonists are always up for a good time and believe the pursuit of pleasure and [...]

Happiness Economics: Can Money Buy Happiness?
Do you ever daydream about winning the lottery? After all, it only costs a small amount, a slight risk, with the possibility of a substantial [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (45)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Happiness Exercises Pack [PDF]
- Community Forum -
- Members Search -
- Magazine Forum -
The 10 keys to happiness, according to science
- RELATIONSHIPS
- PERSONAL GROWTH
- SCIENCE & PSYCHOLOGY
- HEALTH & BODY
- ART & CULTURE
- INSPIRATION & SPIRITUALITY
One seemingly simple question that most people wonder is: 'can we choose our happiness?'. Sonia Vadlamani explains how we can indeed cultivate happiness consciously by following the 10 keys to happiness.
Sometimes it’s difficult for us to feel happy, be it because of the unrealistic standards of beauty and perfection we impose on ourselves, or the negativity we surround ourselves with. It could also be due to the fear of failure embedded deep within our subconscious, or our inability to form friendships and meaningful communities as we grow older. There are several unhelpful habits or tendencies we ingrain that can make us miserable and unhappy. Thankfully, researchers maintain that it’s possible to intervene and cultivate happiness through will and a proper framework . By following the 10 keys to happiness, you could maximize your potential for a lifetime full of joy and contentment.
Happiness means different things to different people. The interesting news, however, is that our happiness is not set in stone. In her ground-breaking book The How of Happiness , researcher Sonja Lyubomirsky points out that while 50 per cent of our happiness is predetermined by our genetic makeup and personality traits, and 10 per cent of our personal happiness is determined by our circumstances and life experiences, about 40 per cent of our happiness can be chosen willfully by us, and depends largely on our daily actions.
RELATED: Is happiness genetic? Here's what science says
This goes to prove that while we cannot change our genes or predict the future, a significant portion of our happiness can be controlled by us. Unfortunately, our pursuit of happiness – as a society and on an individual level – can become very misguided.
Indeed, technological advancements and the pursuit of materialism propagated by media messages may advocate happiness based on our material choices. Psychologist Barry Schwartz addresses this erroneous pursuit of happiness in his book The Paradox of Choice , wherein he points out that the plethora of choices we have available today due to surge in consumerism can do more harm than good, even resulting in conditions like anxiety and depression .
The 10 keys to happiness: the ‘great dream’
“Happiness is not something ready-made. It comes from your own actions.”, articulates the Dalai Lama , who is also the patron of the charity Action for Happiness . While everyone’s idea of happiness may be different, Action for Happiness has identified 10 ‘keys’ to happiness, or practices that can consistently lead to a more fulfilling and happier life.
While the first five keys to happiness described here refer to our interactions with the outside world (Great), the latter five keys to happiness describe the traits that originate within us and are determined by our attitude towards life (Dream).
Outside: daily activities
1. take care of your body.
There is an overwhelming amount of research that deems exercise a vital key to happiness and well-being. A Yale study conducted on over 1.2 million Americans concludes that exercise is more important for our mental health than money . You need not run a marathon to be healthy and happy – opt for an activity of your preference that suits your health goals and lifestyle. Indulge in mindful running , unplug from technology with periodic forest bathing , or simply swap escalator commutes with stairs.
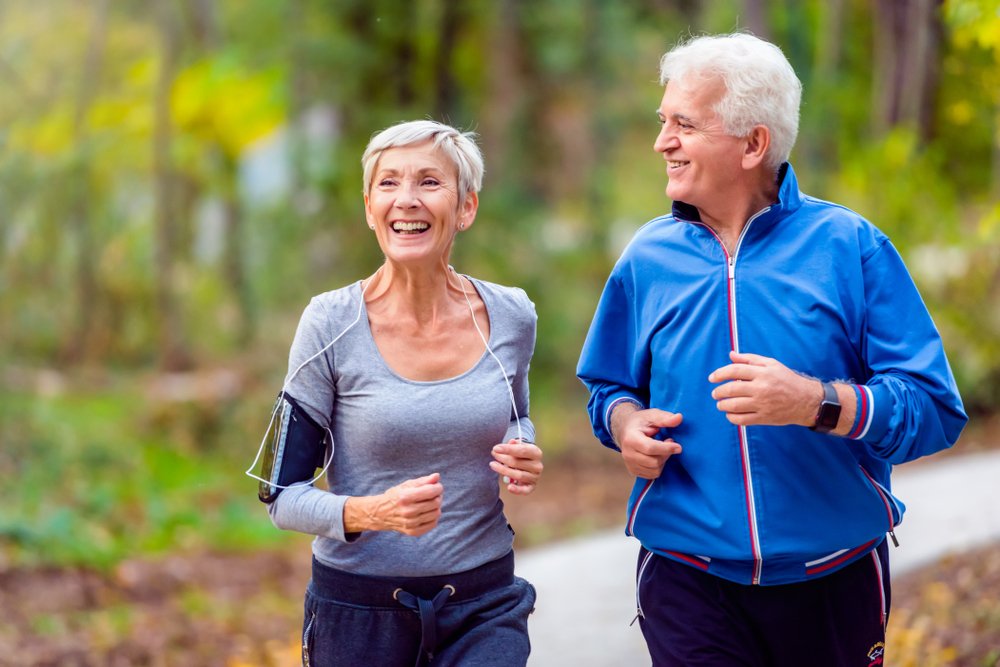

Eating right can contribute towards better health and happiness too. A balanced diet consisting of whole grains, fresh vegetables and fruit, lean poultry and healthy fats can help you achieve your health goals faster. Opt for foods which promote gut health instead of processed or junk food options for improved mood, better metabolism and to keep disease at bay.
2. Practise mindfulness
“ We’re happiest when we focus on the present moment , and the least happy when the mind is wandering”, reveals researcher Matt Killingsworth. Mindfulness refers to being in a state of awareness and taking notice of the present intentionally and with complete acceptance. Studies show that practising mindfulness can help manage stress levels , in addition to activating the areas of our brains related to feeling good.
Mindfulness can be developed using simple measures – start by paying attention to your feelings and thoughts as frequently throughout the day as possible. Meditation , mindful minute practices , and gratitude journaling can help in expanding awareness as well.
RELATED: 7 mindfulness tips for staying engaged
3. Make learning a habit
Research by Journal of Happiness Studies revealed that people who work on learning a new skill or honing an existing skill tend to experience greater happiness consistently. Interestingly, learning something new can be stressful and lower your happiness levels momentarily. However, the joy of acquiring or mastering a new skill can fulfill your need for autonomy or being self-directed, thus rewarding you with long-term happiness.
“There is an overwhelming amount of research that deems exercise a vital key to happiness and well-being. A Yale study concluded that exercise is more important for our mental health than money.”
Indeed, it’s important to find a suitable skill to master, or the right challenge to undertake that’ll allow you to push beyond your comfort zone yet enable you to find your flow state . Researchers also found that skills chosen by you offer better results in terms of improved self-esteem and a heightened sense of connection or ‘oneness’ with others.
4. Indulge in acts of kindness
Random acts of kindness are not just beneficial for others – in fact, caring for others’ happiness activates the areas linked to trust, enjoyment and social connection in our brains as well. An experiment involving seven-day kindness activities concluded that kindness is a vital key to happiness , whether extended to people who are close to you, complete strangers or even yourself. Doing things for others can help alleviate social anxiety , improve your mood and prevent illness , thus enabling you to lead a healthy, meaningful life.
5. Make meaningful connections
Human beings are social animals, and hence it’s hardly surprising when researchers found that forming meaningful connections and embracing community is one of the core values we associate with happiness . Indeed, the importance of a community as a key to happiness cannot be underestimated. In addition to the safety and support, we also derive the much-needed sense of togetherness and belonging when we find others who have the same values and interests as us.

Scientists agree that interacting with strangers , thus bolstering our ‘weak social ties’ also impacts our well-being positively. Take some time to connect with those who serve you coffee, your cab driver, or a friendly face you encounter during your daily strolls. Gestures like passing a casual compliment, wishing someone a good day, chatting with an elderly neighbor over a cuppa can make a world of difference to someone who’s been feeling down or struggling with loneliness .
Inside: Developing the right attitude
6. be at ease with who you are.
Self-acceptance forms an important cornerstone for our mental health and well-being, yet it’s a routine that we tend to practice the least, as revealed in a survey conducted by Action For Happiness. While acceptance was rated as the strongest predictor of life satisfaction and happiness amidst all the other traits and habits, only 5% of the respondents admitted to being kind to themselves and believed that they were perfect the way they were.
RELATED: 12 ways to practise self-acceptance
Practising acceptance as a habit can be difficult at first, but it’s possible to be good to yourself by shifting your perspective. Indeed, embracing imperfections as your unique traits and acknowledging your strengths –however insignificant they seem – can be a crucial key to happiness.
7. Set vital goals
Happiness doesn’t happen spontaneously – it requires planning and action towards pursuing things that matter to us. Goal setting is an important key to happiness, since it forms the outline for the life you envision for yourself. It’s important to set goals to look forward to – not only can proactive goal setting ensure fulfilment of your life ambitions and vision, following an actionable plan and achieving timebound targets using SMART goal setting can boost self-confidence and eliminate stress and anxiety .
8. Develop resilience
All of us may have faced hardships, loss and trauma along our way, and since our brains are wired for negativity bias , we tend to remember the adverse events in our lives as compared to the positive experiences. However, by changing our perspective and looking at hardships as stepping stones towards personal growth and success, we can learn to take back power every time we feel defeated by life . Indeed, building resilience can boost positive thinking, strengthen connections, and improve stress management skills.
“The importance of a community as a key to happiness cannot be underestimated. In addition to the safety and support, we also derive the much-needed sense of togetherness and belonging.”
In fact, researcher Dr Ann Masten describes resilience as ‘ ordinary magic ’ derived from everyday situations and resources, that helps us adapt better during hardships. There is surmounting scientific evidence that developing resilience as a life skill and finding ways to bounce back from adversities can contribute immensely to our well-being and happiness.
9. Cultivate a positive outlook
“Just as water lilies retract when sunlight fades, so do our minds when positivity fades”, states researcher Barbara Fredrickson in her book Positivity . Indeed, research suggests that experiencing ‘ upward spirals of positive emotions ’ like gratitude , joy, interest etc. more often allows us to counteract the downward spirals of negative emotions like stress, jealousy etc. Gratitude journaling , smiling more often, finding ways to incorporate awe into your life are some easy ways to boost positivity.

10. Find meaning in your life
Feeling connected to something larger than ourselves or possessing a sense of purpose in life is linked with greater life satisfaction , improved self-esteem, lasting relationships, and a more optimistic attitude. Leading a meaningful life could seem like a complicated process, but you can begin by prioritizing activities that bring you joy and a strong sense of purpose, like volunteering, networking for a cause, or trying to make a difference in others’ lives.
The key to happiness here is to understand where your calling lies and set out to follow your bliss . ‘Life Crafting’ , or the process of reflecting on your strengths and interests, and aligning them with your vision, passion and desires, can be used as the framework for setting goals conducive to the meaningful life you wish to lead.
Round-up: 10 keys to happiness
“It is work to be happy”, says psychologist Barry Schwartz. Indeed, there’s more to happiness than feeling good about pleasurable things, but the good news is that it can be cultivated by consistently encouraging the 10 keys to happiness or happy habits listed above into our lives.
Instead of trying to implement all the keys to happiness at once, try reflecting on what each individual key means for you, and devise ways to implement them using simple action plan, to be able to lead a rewarding and happier life.
happiness.com | The fine art of being: learn, practise, share
Are you a happiness.com member yet? Sign up for free now to enjoy:
■ our happiness magazine with practical life tips ■ share and support in our happiness forum ■ self-develop with free online classes in our Academy
Written by Sonia Vadlamani


YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
The january blues: 7 ways to beat it.
For many of us, once the festive holiday season is over the January blues start to set in. But there are ways you can fight back and feel better. Dee
The bright side of August: the good things that happened
There were many feel-good health and environmental stories in the press during August, but you may not have seen them. Ed Gould shares his Top 10
10 types of meditation: which style is best for you?
There are many different types of meditation. Discovering which style suits you best is useful – you'll be more likely to devote yourself to the
The Bright Side: feel-good news from July
There were many feel-good health and environmental stories in the press during July, but you may not have spotted them. Ed Gould shares his Top 10 to
Join the conversation
You are posting as a guest. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
× Pasted as rich text. Paste as plain text instead
Only 75 emoji are allowed.
× Your link has been automatically embedded. Display as a link instead
× Your previous content has been restored. Clear editor
× You cannot paste images directly. Upload or insert images from URL.
- Insert image from URL
- Submit Comment

Posted April 28, 2021
MY thought in friendship that if you like your friendship for a long time then please do not be more closely for each other's...
because if you are interested deeply in your friendship...
other person gets uncomfortable with you and then your friendship will become weeker. ? So live happy and make happy

Share this comment
Link to comment, share on other sites, similar articles, how bdsm submission brought me inner happiness.
Finding happiness isn't always as simple as opening a box labeled joy. Some people find it in the most unexpected places, like BDSM submission.
Self-compassion: a visual guide
Having a bad day? Don't beat yourself up: get some self-compassion instead. Thankfully, this infographic from Anna Vital is the perfect
A brief history of the School of Life
Have you heard of The School of Life? It's an organization set up by experts in their field dedicated to improving lives, especially when it comes
Forbidden fruit: the journey to accepting my sexuality
When Princess E started accepting her kinks and desires through exploring her sexual journey, she was well on her way to discovering her inner
Forum discussions
Thank you to happiness to introduce me.
By Ca**** , September 19, 2023 in Introduction Circle - A warm welcome to happiness!

- October 26, 2023
Reaching Out to say Hello! I'm an Inner Peace Coach! Maybe Happiness is a place I can share my voice.
By In**** , August 8, 2023 in Introduction Circle - A warm welcome to happiness!
- September 9, 2023
A warm welcome to happiness, what I want you to know about me...
By Ka**** , August 7, 2023 in Introduction Circle - A warm welcome to happiness!

- August 7, 2023
Share happiness and lifestyle tips with éverobody
By Ch**** , July 14, 2023 in Introduction Circle - A warm welcome to happiness!
- July 14, 2023
HAPPINESS AND ITS BENEFITS
By Kh**** , March 11, 2023 in Happiness & Life Advice Forum
- 1,042 views
- March 11, 2023
Happiness.com » Magazine » INSPIRATION & SPIRITUALITY » The 10 keys to happiness, according to science
10 Keys to Happier Living
Everyone's path to happiness is different. based on the latest research, we have identified 10 keys to happier living that consistently tend to make life happier and more fulfilling. together they spell great dream., you can explore them all below..
Do kind things for others
If you want to feel good, doing good is a great place to start..
Helping and being kind not only contributes to the happiness of others, it can also help us to feel happier ourselves! [1] Studies have shown that when we do kind things it can literally gives our brain a boost, activating its ‘reward centres’ [2] and that feels good. It can take our minds off our own worries too.
Giving and kindness also help us feel connected to others which is important for our wellbeing and contributes to building stronger communities and a happier society for everyone. [3]
There are lots of different ways we can give and help others .
Every act of kindness counts
From small acts like a friendly smile, a few kind words, helping with bags, or offering up our seat, through to regular volunteering - there are lots of different ways we can give or be kind. We can of course donate money to good causes if we are able to and we can give in lots of non-financial ways too, such as giving a moment of attention, some of our time, knowledge, ideas, energy or support, or even sometimes by giving people the benefit of the doubt, instead of instantly judging them. Acts of kindness add up for our own and others wellbeing and all contribute to creating happier communities. [4]
Reflection: What’s a small act of kindness you could do today?

Helping others can boost happiness in many ways
Scientific studies show that helping others can contribute to our happiness in different ways. These include: experiencing more positive emotions and satisfaction with life [5]; increasing our sense of meaning [6], and boosting our self-confidence. It can reduce stress and help us feel calmer too. [7] Some studies have found that people who volunteered regularly were found to be more hopeful and experience fewer symptoms of depression and anxiety and may even live longer. [8] Not all acts of helping boost how happy we feel – to maximise the benefits, it’s important that we’ve chosen if or how we help; we can see or sense that it will have a positive impact; and it helps us feel more connected to others. [9]
So if you want to feel good, find ways you can do good!
Reflection: When was a time that you chose to give or help others that boosted how happy you felt? What contributed to that?
Everyone needs kindness
Giving and being kind can help us feel more connected to others and contribute to nurturing our relationships - and that’s good for wellbeing all round! [10] Our acts of kindness might be for family, friends, colleagues, or neighbours or even strangers. They could be old or young, nearby or far away. It could be a one-off spontaneous gesture or something we do regularly. It could be a compassionate response in a time of crisis or need or simply because it’s a nice thing to do. There are always ways to be kind.
Reflection: Who have you been kind to recently? Who has been kind to you?
Create kindness ripples
Studies have shown that when we do something kind both the recipient and other people who witness that kind act are more likely to be kind themselves. [11] So our kindnesses are amplified, contributing to a happier world! Expressing gratitude for help others give us also ripples out too. [12]
Reflection: Who can you thank for what they give to you?
Ask for help when you need it
Think about it - if helping others boosts happiness, asking for help when we need it could give the person we ask the opportunity for a feel good boost. It can also mean they are then more likely to ask for help when they need it. Certainly communities where people feel they can rely on others to help are happier and more resilient. [13] Asking for help builds connection - so it isn’t only for when we are struggling. We can also ask for help to share experiences, when we’d value support, or when we want to learn something new.
Reflection: What’s something you’d like help with? Who can you ask?

Balancing your own needs and those of others
Helping is associated with increased happiness and health, but feeling obligated or overly burdened by it can be detrimental, [14] as can be the case for long-term carers. If you are a carer, taking care of your own wellbeing matters – for yourself and the people you are helping. Even small actions that give you a quick break or a boost can help you sustain your physical and psychological health and so your ability to continue caring for others.
Reflection: What is an action you can take to maintain your own wellbeing, to help you sustain caring for others?
Sustainable giving
As a general rule, we can be more effective, regular givers if we find ways to help that we enjoy, which are in line with our own strengths and feel worthwhile or meaningful. If we are happier givers, the recipients will likely benefit more, and we are more likely to continue to give. Choosing how we help and give to others, giving in ways that boost our sense of social connection and in which we feel effective and impactful all matter in order to sustain giving and helping others. [15] Happier people tend to help others more, so taking care of your own wellbeing helps you sustain giving too. [16]
Reflection: What ways of helping others do you enjoy or find energising?

1 Curry, O. S., Rowland, L. A., Van Lissa, C. J., Zlotowitz, S., McAlaney, J., & Whitehouse, H. (2018). Happy to help? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of performing acts of kindness on the well-being of the actor. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 76, 320-329. Aknin, L. B., Dunn, E. W., &; Norton, M. I. (2012). Happiness runs in a circular motion: Evidence for a positive feedback loop between prosocial spending and happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies, 13(2), 347-355.
2 Harbaugh, W. T., Mayr, U., &; Burghart, D. R. (2007). Neural responses to taxation and voluntary giving reveal motives for charitable donations. Science, 316(5831), 1622-1625.
3 Aknin, L. B., Whillans, A. V., Norton, M. I., & Dunn, E. W. (2019). Happiness and prosocial behavior: An evaluation of the evidence. World Happiness Report 2019, 67-86. Okabe-Miyamoto, K., &; Lyubomirsky, S. (2021). Social connection and well-being during COVID-19. World Happiness Report, 131-152.
4 Aknin, L. B., Whillans, A. V., Norton, M. I., & Dunn, E. W. (2019). Happiness and prosocial behavior: An evaluation of the evidence. World Happiness Report 2019, 67-86. Okabe-Miyamoto, K., &; Lyubomirsky, S. (2021). Social connection and well-being during COVID-19. World Happiness Report, 131-152.
5 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34.
6 What Works Centre for Wellbeing Briefing Paper (2020) Volunteer wellbeing: what works and who benefits? https://whatworkswellbeing.org/resources/volunteer-wellbeing-what-works-and-who-benefits/
7 Luks, A. A. (1988). Helper's high. Psychology Today, 22(10), 39.; Piliavin, J. (2003). Doing well by doing good: Benefits for the benefactor. In C. M. Keyes, J. Haidt, C. M. Keyes, J. Haidt (Eds.) , Flourishing: Positive psychology and the life well-lived (pp. 227-247). Washington, DC US: American Psychological Association.
8 Aknin, L. B., Whillans, A. V., Norton, M. I., & Dunn, E. W. (2019). Happiness and prosocial behavior: An evaluation of the evidence. World Happiness Report 2019, 67-86. Curry, O. S., Rowland, L. A., Van Lissa, C. J., Zlotowitz, S., McAlaney, J., &; Whitehouse, H. (2018). Happy to help? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of performing acts of kindness on the well-being of the actor. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 76, 320-329. King, V. (2016) 10 Keys to Happier Living – A Practical Guide for Happiness. Hachette. Lyubomirsky, S, Sheldon, K M, &; Schkade, D. (2005). Pursuing happiness: The architecture of sustainable change. Review of General Psychology, 9(2), 111 - 131
9 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34.; King, V. (2016) 10 Keys to Happier Living – A Practical Guide for Happiness. Hachette.
10 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34.; Helliwell, J. F., Aknin, L. B., Shiplett, H., Huang, H., & Wang, S. (2017). Social capital and prosocial behaviour as sources of well-being. National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper 23761
11 Jung, H., Seo, E., Han, E., Henderson, M. D., and Patall, E. A. (2020). Prosocial modeling: A meta-analytic review and synthesis. Psychological Bulletin, 146(8), 635
12 Algoe, S. B., Dwyer, P. C., Younge, A., &; Oveis, C. (2020). A new perspective on the social functions of emotions: Gratitude and the witnessing effect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 119(1), 40.
13 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34.; Helliwell, J. F., Aknin, L. B., Shiplett, H., Huang, H., &; Wang, S. (2017). Social capital and prosocial behaviour as sources of well-being. National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper 23761
14 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34
15 Aknin, L. B., & Whillans, A. V. (2021). Helping and happiness: A review and guide for public policy. Social Issues and Policy Review, 15(1), 3-34.; King, V. (2016) 10 Keys to Happier Living – A Practical Guide for Happiness. Hachette.
16 Aknin, L. B., Dunn, E. W., & Norton, M. I. (2012). Happiness runs in a circular motion: Evidence for a positive feedback loop between prosocial spending and happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies, 13(2), 347-355.

Take the 10 Keys to Happier Living online coaching programme.
No act of kindness no matter how small is ever wasted
No-one can take away from you that which you have given
Gratitude is like breathing in – letting ourselves be touched by the goodness in others and in our world. Generosity is like breathing out – sensing our mutual belonging and offering our care.
The 10 Keys
Interact with the buttons above to find out more., for each of the ten, you'll find information on the science, opportunities for reflection and practical actions to help apply them to your daily life..

Discover how to apply the 10 keys to your life and boost your wellbeing.

Discover how to be happier and create a happier world.
Our Daily Action - 1

Download the FREE Action for Happiness app for iOS or Android

Action for Happiness is a Registered Charity (1175160) and Company Limited by Guarantee (10722435) in England and Wales.
Built by 89up
Do you want to help create a happier and kinder world? If so, please join our movement, add your pledge and we'll send you practical action ideas to make a difference. By choosing to Join, you trust Action for Happiness to take care of your personal information and agree to our Privacy Policy .
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
The keys to happiness: Associations between personal values regarding core life domains and happiness in South Korea
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Department of Sociology, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, South Korea
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, United States of America
- Min-Ah Lee,
- Ichiro Kawachi

- Published: January 9, 2019
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821
- Reader Comments
Personal values refer to the beliefs, principles or ideas that are important to people’s lives. We investigated the associations between personal values and happiness. We inquired about the importance of four different categories of personal values: prioritizing social relationships, extrinsic achievements, physical health, and spirituality. Data were drawn from the Korean General Social Survey (KGSS), a nationally representative cross-sectional sample collected over three years (i.e., 2007, 2008, and 2009). The findings showed that respondents prioritizing religion (i.e., spirituality) were the most likely to be happy, followed by those prioritizing social relationships, including family, friends, and neighbors. Those who prioritized extrinsic achievements (money, power, educational attainment, work, and leisure) as well as health were least likely to be happy. The findings suggest that pursuing goals focused on self-enhancement or self-centered value are less likely to result in happiness compared to pursuing alter-centered collective goals or self-transcendence/selflessness.
Citation: Lee M-A, Kawachi I (2019) The keys to happiness: Associations between personal values regarding core life domains and happiness in South Korea. PLoS ONE 14(1): e0209821. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821
Editor: Shang E. Ha, Sogang University (South Korea), REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Received: August 21, 2018; Accepted: December 12, 2018; Published: January 9, 2019
Copyright: © 2019 Lee, Kawachi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The data are third party and are available from the Korean Social Science Data Archive (KOSSDA) database ( http://www.kossda.or.kr/ ).
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
A growing literature has addressed the science of happiness, or subjective well-being (SWB). Although material well-being is a critical ingredient of human well-being, it has also been recognized that an increase in material well-being beyond a certain threshold (i.e. once basic wants have been satisfied) does not guarantee further increases in happiness [ 1 – 2 ] (although this point has also been debated [ 3 ]). This has influenced many scholars to seek other factors that determine subjective well-being [ 4 – 5 ].
In this context, a considerable number of studies have examined personal values, goals, or aspirations as important factors associated with subjective well-being [ 5 – 7 ]. Personal values may affect individuals’ daily lives as well as major decisions regarding their lives and futures, shaping their life trajectories, social relationships, and subjective well-being in the long run. For example, it is well known that holding intrinsic values, such as personal growth and affiliation, is positively associated with happiness, in contrast to holding extrinsic values, such as economic success and popularity [ 5 , 8 ]. These studies clearly suggest that happiness is influenced by the personal values people hold in various life domains.
However, with the limitations of previous studies, questions remain regarding the association of personal values with subjective well-being. Although it is meaningful that previous studies have captured the relative propensity of individuals by using composite measures of personal values and goals [ 5 , 8 ], less is known about whether and how personal values attached to specific life domains are associated with happiness. For example, are people who prioritize family happier than those who prioritize money? Is valuing religion more strongly associated with happiness than family? These questions motivated the current study to directly investigate how prioritizing specific life domains relates to happiness.
Recent studies have shown that prioritizing time more highly than money is positively associated with happiness [ 9 – 10 ]. Individuals may choose to allocate more of their time to making money, but often do so at the expense of neglecting social relationships (spending time with family, friends, and the community). The millionaire rapper and songwriter Sean “Diddy” Combs recently said in an interview that “I can always make more money, but I can’t make time”, which expresses the ideas that (a) investing in relationships does not cost money, but (b) making more money is often traded off against other uses of time. It has been discussed that prioritizing time over money is beneficial for happiness because it can improve the quality of social relationships [ 9 – 10 ]. Although a recent study has shown that prioritizing family over work and leisure results in higher life satisfaction [ 11 ], most studies have compared a limited number of contrasting domains (i.e., time vs money, family vs. work), but not included diverse life domains together. Valuing specific life domains, such as family, power, money, or religion, not only indicates personal values and attitudes toward life, but also affects individual behaviors and decision making.
Furthermore, most studies regarding personal values and happiness have been conducted in Western societies, with a few exceptions [ 8 , 12 ], and have analyzed non-representative samples, such as convenience samples or samples of specific groups, such as college students [ 4 , 8 , 13 ]. It is therefore worth investigating these relationships using a representative sample in a non-Western societal setting such as South Korea. Korean society is traditionally founded on strong family-oriented values derived from Confucianism, although this has been weakening over the last several decades. In addition, religious influence on individual life might be stronger than other East Asian countries, although relatively weaker compared to other Western countries. As of 2015, it is reported that about 43.9% of Koreans have a religion. Among those who have a religion, 35.4% are Buddhists and 62.9% are Christians [ 14 ]. Among the total population, 15.5% are Buddhists while 27.7% are Christians [ 14 ]. This suggests that South Korea has a unique socio-cultural context in relation to Christianity and traditional values, which distinguishes it from other East Asian countries. For example, it is reported that only 1.5% of Japanese population are Christians as of 2012 [ 15 ]. South Korean society is therefore somewhat unique in the East Asian region for simultaneously maintaining Confucian family-oriented values together with Christianity.
In the current study we sought to investigate the effects of one’s personal values regarding core life domains on happiness. We used the Korean General Social Survey (KGSS) of a nationally representative sample, collected over three years (i.e., 2007, 2008, and 2009), which asked respondents to indicate their most valued life domain among the 10 presented, such as family and money, and to rate their happiness. We classified the personal values into four categories: prioritizing social relationships, extrinsic achievements, physical self, and spirituality. We begin with a literature review on the human value system and associations between personal values and subjective well-being.
Literature review
The structure and content of human values.
Exploring the human value system can increase understanding of the content of personal values embedded in the system, which can be used to classify diverse life domains into common categories based on the nature of those human values. Schwartz [ 16 – 17 ] provided a two-dimensional circumplex model explaining the structure and content of human values. According to Schwartz [ 16 – 17 ], 10 types of values differentiated by motivational goals can be classified into four value dimensions: self-transcendence; self-enhancement; openness to change; conservation. Each type of value may conflict with other values if it is located in the opposite direction of the value dimension [ 16 – 17 ]. For example, self-transcendence, including universalism and benevolence, is opposite to self-enhancement, including achievement and power, while openness to change is opposite to conservation [ 17 ].
The contrast between self-enhancement and self-transcendence can be likened to the contrast between extrinsic and intrinsic values, although they are not synonymous. Intrinsic and extrinsic values are well-known descriptions of the content of human values and have been used to examine their associations with subjective well-being [ 12 , 18 ]. Intrinsic values include personal growth, affiliation, community feeling, and physical health, whereas extrinsic values include financial success, image, and popularity, directed mainly toward external rewards [ 5 ]. In contrast to extrinsic values, intrinsic values are more related to psychological needs and fulfillment.
A few studies have explored and provided modified classifications of personal values based on early studies [ 4 – 5 , 16 – 17 ]. Burroughs and Rindfleisch [ 19 ] conceptualized materialism as a self-centered value that is opposed to collective-oriented values like family, community ties, and religious fulfillment. Based on the studies of Schwartz [ 16 – 17 ], materialism, achievement, hedonism, and power can be categorized into the dimension of self-enhancement, whereas religiosity can be categorized as self-transcendence [ 19 ]. Grouzet et al. [ 20 ] provided a modified two-dimensional value structure considering that some specific values can be neither intrinsic nor extrinsic. For example, spirituality is not classified as intrinsic or extrinsic value. Spirituality is included in self-transcendence, in the opposite direction of physical self (i.e., hedonism) [ 20 ].
Associations between personal values and happiness
Numerous studies have contrasted intrinsic and extrinsic values in terms of their associations with happiness. It has been widely observed that extrinsic values are negatively associated with happiness in Western as well as non-Western societies [ 8 , 18 ]. In contrast with intrinsic goals like self-acceptance, extrinsic values of economic success, popularity, and image are adversely associated with happiness in Peru [ 8 ], China [ 12 ], South Korea [ 13 ], and Japan [ 21 ], as well as in Western societies, such as Germany and the United States [ 18 ]. A specific indicator of extrinsic values, viz. materialism, is also adversely associated with overall subjective well-being [ 6 – 7 ], satisfaction with life in family [ 22 ], and work [ 23 ] and positively correlated with depression and anxiety [ 19 ].
A few studies have investigated more diverse or specific personal values. Compared with materialism, which is a self-centered value and similar to the dimension of self-enhancement, collective-oriented values, such as family, community and religious values, appear to be beneficial for well-being [ 19 ]. Spirituality measured by religious values or practice is positively associated with subjective well-being [ 7 , 19 ]. A longitudinal study has reported that prioritizing family over work and leisure results in higher life satisfaction [ 11 ]. Recent studies have also shown that prioritizing money more than time is adversely associated with happiness [ 9 – 10 ]. Although there are variations in terms of categorization of personal values, previous studies have provided quite consistent results showing that prioritizing extrinsic achievements, such as money, is adversely associated with subjective well-being in general.
Why are extrinsic or self-centered values adversely associated with happiness? On the one hand, it can be explained in that extrinsic values facilitate social comparison of oneself with others, which is harmful for subjective well-being. Extrinsic achievements are more easily compared with others than are intrinsic achievements, such as self-fulfillment or attachment. For example, people with high levels of materialism are more likely to compare themselves with others [ 24 ]. With greater social comparison, there is higher likelihood of frustration and dissatisfaction with individual achievements. People who prioritize extrinsic aspirations, such as power, money, or status, tend to have more difficulty of achieving and being satisfied with their goals.
On the other hand, extrinsic values can be harmful for interpersonal and social relationships. Pursuing material gains is negatively associated with quality of interpersonal relationships [ 25 – 26 ] and increases difficulty of achieving a family–work balance [ 27 ], which then decreases subjective well-being. People often need to decide whether they will spend time on social relationships or on extrinsic goals. People prioritizing extrinsic values are less likely to invest in social relationships, such as family and friends, which can decrease the quality of social relationships that is important for happiness. Recent studies have similarly argued that valuing money more than time may have deleterious impacts on social relationships [ 9 – 10 ]. These studies suggest that self-centered values or valuing self-enhancement is harmful for happiness, whereas collective-centered values or valuing social relationships is beneficial.
In this context, specific life domains might be differentially associated with happiness according to the attribute and nature of life domains. It is probable that prioritizing a specific life domain is negatively associated with happiness as the life domain is more based on self-centered value or self-interest. In contrast, we expect that life domains related to social relationships (alter-centered rather than self-centered) or self-transcendence are positively associated with happiness. In addition, life domains which have been classified as a same value category may have different effects on happiness depending on the degree to which they are self-centered value. For example, although health is conceptualized as intrinsic value [ 5 , 20 ], it may have different meaning and effect for individuals compared with other intrinsic values or goals such as prioritizing family and friend. Prioritizing health can be self-centered propensity more than other intrinsic values such as prioritizing family. We classified the personal values regarding diverse life domains into four categories: prioritizing social relationships, extrinsic achievements, physical self, and spirituality, which reflects the different levels of self-centered propensity.
Data were drawn from the Korean General Social Survey (KGSS) collected in 2007, 2008, and 2009. The KGSS is a nationally representative, cross-sectional survey conducted in South Korea [ 28 ]. The sampling method (i.e., multistage area proportional probability sampling), interview protocols, and data-processing procedures used for the KGSS conform to those used for the General Social Survey (GSS) conducted in the United States. Similar to the GSS, the KGSS includes special sets of questions every year in addition to core items, such as questions about socio-demographic factors. The KGSS in 2007–2009 included questions about personal values regarding life domains, happiness, and socio-demographic factors. Although the three years of data are not panel data, analyzing them as a pooled sample increases the statistical power for our analyses. The data were analyzed anonymously. The data for this study were made available by the Korean Social Science Data Archive (KOSSDA), Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea.
Our dependent variable was subjective well-being (SWB), or happiness. Respondents were asked to rate their happiness via the following question: “When considering your life, how happy or unhappy are you overall?” The response categories of the 2007 and 2008 KGSS ranged from 1 (very happy) to 4 (not happy at all), whereas the happiness of 2009 was measured by a 5-point scale with a neutral category in the middle of the response categories. Due to this difference in response categories, we coded happiness as a binary variable in which two positive responses (i.e., very happy and happy) were assigned value 1 and the other responses were assigned value 0.
Personal values.
To measure personal values regarding life domains, respondents were asked to choose two items as the first and second most important domain in life among the following 10 items: (1) leisure; (2) friends; (3) power; (4) neighbors; (5) health; (6) money; (7) educational attainment; (8) religion; (9) family; (10) work. We used a response for the first most important domain in life only for our analysis. We classified the responses into four categories: (1) social relationships; (2) extrinsic achievements; (3) physical self; and (4) spirituality. Social relationships included family, friends, and neighbors, and extrinsic achievements included leisure, power, money, educational attainment, and work. We included leisure in the category of extrinsic achievements because leisure can be considered an external reward related to self-interest. Physical self and spirituality were each represented by a single item (i.e., health and religion, respectively). Prioritizing physical self refers to placing importance on maintaining physical health and survival in the present study. In the analyses, the reference group of the variable was the respondents prioritizing social relationships. All categories of personal values were mutually exclusive.
Other covariates.
Socio-demographic factors including gender, age, educational attainment, and marital status were measured. Gender was a binary variable with reference category of male (female = 1). Age was measured in years, and education attainment was classified into three categories: less than high school; high school graduates; college or more. The reference group for educational attainment in the analytic models was high school graduates. Marital status was measured by asking the respondents whether they were currently married, widowed, separated/divorced, or never married. The reference group for marital status in the analytical models was married.
We controlled for monthly household income and perceived social status as potential confounders of the association between personal values and happiness. Monthly household income was measured as a continuous variable in Korean 10,000 Won increments. We adjusted household income for the inflation rate across the three years of data, using the 2010 consumer price index [ 29 ]. After adjusting for the inflation rate, household income was log-transformed for the analyses because it was skewed. Perceived social status was measured with the question: “In our society, there are groups that tend to be positioned toward the top and those positioned toward the bottom. From the bottom (1) to the top (10), where would you put yourself on the scale?” Self-rated health was measured on a 5-point scale, and it was included in additional models examining the 2007 and 2009 data only because the 2008 KGSS did not include a self-rated health question.
Analytical strategy
We used Poisson regression models with robust error variances for a binary outcome [ 30 ] given that our dependent variable (happiness) had high prevalence. Logistic regression results in misleading and overestimated odds ratios when it examines common outcomes whose incidence is higher than 10% [ 31 ]. Thus, relative risks of Poisson regression with a robust error variance would be appropriate for our dependent variable.
We conducted two sets of Poisson regression analyses to examine how personal values regarding the core life domains are associated with happiness. The first set comprised four models. Model 1 included personal values in life domains with year dummies only; Model 2 added the socio-demographic factors of gender, educational attainment, and marital status to Model 1. Model 3 added household income and perceived social status to examine whether personal values are associated with happiness even after controlling for these two variables. We analyzed Model 4, as a supplementary model, excluding the year 2009 (which had different response categories compared to other years) to check whether personal values remained associated with happiness.
We used the second set of Poisson regression models to examine the associations between personal values and happiness with age restriction and/or self-rated health as a covariate. We conducted supplementary analyses excluding respondents aged 60 years or older and controlling for self-rated health, measured in the 2007 and 2009 data.
Sample characteristics
Table 1 presents the descriptive characteristics of the sample for the pooled data and for each survey year. For the total sample of pooled data, about 66% of respondents reported that they were happy overall; by year, 76.6%, 73.5%, and 49.7% reported being happy overall in 2007, 2008, and 2009, respectively. It is notable that the percentage of those who were happy in 2009 was lower than in the other two years. This is most likely because the 2009 survey used a 5-point scale to measure happiness, rather than the 4-point scale of the other years, leading to a substantial number of respondents (37.9%, 606 of 1,599) choosing the neutral category (which we coded as 0 = not happy).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.t001
In terms of personal values regarding life domains, 50.7% of respondents considered health to be the most important domain in life; 31.8% chose family, friends, or neighbors; 13.7% chose extrinsic achievements including money, power, educational attainment, work, and leisure; and 3.8% chose religion. Across years, a higher percentage of respondents in 2009 prioritized social relationships than in 2007 and 2008 (i.e., 28.6% in 2007, 27.3% in 2008, and 38% in 2009). However, the percentages of those prioritizing extrinsic achievements were consistent across years (i.e., 14.3% in 2007, 13.3% in 2008, and 13.5% in 2009).
Table 2 summarizes the descriptive statistics across personal values and provides the results of the Chi-squared or analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests comparing proportions or means of variables across the categories of personal values. For happiness, 81.2% of those who prioritized religion the highest answered that they were happy overall, which was the highest percentage observed. In contrast, about 54.7% of respondents prioritizing extrinsic achievements answered that they were happy, which was the lowest observed value. Among respondents prioritizing social relationships and health, 70.7% and 65% answered that they were happy, respectively. Bivariate statistics comparing distributions or means of the variables depending on personal values showed that all variables had significant differences depending on personal values regarding life domains.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.t002
Fig 1 shows the percentages of those who were happy across personal values and survey years. Reported happiness varied across the survey years, but we also observed consistent patterns linking personal values with happiness ( Fig 1 ). Respondents prioritizing spirituality and social relationships showed higher percentages of happiness than the others. Respondents who valued extrinsic achievements showed the lowest percentages of happiness across all years. Note that percentages of reported happiness were lower across all personal values in 2009 than in 2007 and 2008 due to the different response categories used in 2009. It would be also possible that the percentage of reported happiness in 2009 was dropped because the data were collected after the global economic crisis in 2008.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.g001
Poisson regression models
Table 3 summaries the results of Poisson regression models with robust error variances examining associations between personal values and happiness. Models 1, 2, and 3 showed that all categories of personal values had significant relationships with happiness. Compared with those prioritizing social relationships, respondents valuing extrinsic achievements and health had lower likelihoods of being happy, whereas those prioritizing religion were happier than the reference group. The categories of personal values were significant, even after controlling for household income and perceived social status, as well as socio-demographic factors in Model 3. Relationships between personal values and happiness are also shown in Model 4, excluding the 2009 data. Prioritizing extrinsic achievements was again adversely associated with happiness. Respondents prioritizing health were also less likely to report happiness than those prioritizing social relationships. One notable difference between the results of Model 4 and the other models was that prioritizing religion was not significant in Model 4 from which the 2009 data were excluded.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.t003
Gender, age, and marital status were significantly associated with happiness in Models 3 and 4. Females tended to be happier than males. Married respondents tended to be happier than unmarried respondents. The likelihood of being happy decreased as age increased. In terms of socio-economic status, both household income and perceived social status were significantly associated with happiness. The likelihood of being happy increased as household income and perceived social status increased.
Table 4 presents the results of the additional models showing the associations between personal values regarding life domains and happiness with age restriction and/or controlling for self-rated health. Model 1 excluded respondents aged 60 or older from the total sample, and Model 2 included self-rated health as a control variable in the 2007 and 2009 data. In Model 3, the age restriction was also applied with self-rated health, so Models 2 and 3 included only 2007 and 2009 data because information on self-rated health was not collected in 2008. As listed in Table 4 , all categories of personal value were significantly associated with happiness, regardless of whether age and/or data restrictions were imposed. Compared with prioritizing social relationships, prioritizing extrinsic achievements was adversely associated with happiness even after controlling for self-rated health and excluding those aged 60 years or older in Model 3. Prioritizing physical self was, however, marginally significant in Model 3 with self-rated health and the age restriction. Respondents who prioritized religion were most likely to be happy.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.t004
In addition, we conducted two supplementary sets of Poisson and multiple linear regression analyses as sensitivity analyses. The supplementary sets of Poisson regression models included personal values in life domains with leisure as a single category. It would be worth examining leisure separately because it can be closer to hedonism compared with the other extrinsic achievements. The supplementary sets of multiple linear regression models included the dependent variable as a continuous variable by multiplying the 4-point scale by 5 and multiplying the 5-point scale by 4 so that we could examine the continuous dependent variable with a 20-point scale and test if it had consistent results with Poisson regression analyses examining the dichotomized dependent variable.
S1 Table presents the results of Poisson regression models corresponding to the analytical models of Table 3 . Prioritizing leisure was negatively associated with happiness ( S1 Table ). Other personal value variables had consistent results with the findings in Table 3 . S2 Table presents the results of selected four multiple regression models due to word limitation. However, we had consistent results with our findings across all corresponding models in terms of effects and significances of personal value variables. Only one difference from the results of the Poisson regression analyses was that spirituality was still significant when the 2009 data were excluded as presented in Models 3 and 4 ( S2 Table ).
Our findings showed that there were significant associations between personal values regarding life domains and happiness. Prioritizing social relationships, including family, friends, and neighbors, was associated with a greater likelihood of happiness, whereas prioritizing extrinsic achievements, such as money and power, or physical self (i.e., health) was adversely associated with happiness. Although prioritizing spirituality (i.e., religion) was not significant when excluding the 2009 data, it was significantly and positively associated with happiness in the models when the age restriction was employed, or with self-rated health, as well as for the total sample. Respondents prioritizing religion were most likely to report happiness, whereas respondents prioritizing extrinsic achievements were the least likely. A significant difference between prioritizing extrinsic achievements and prioritizing health persisted in our supplementary models ( S3 Table ), in which extrinsic achievements was set as the referent category. Thus, we found that the rank order of happiness across personal values regarding life domains, from the highest to lowest likelihood, was spirituality, social relationships, physical self, and extrinsic achievements. Although previous studies have consistently shown that religious affiliation is positively associated with happiness [ 32 – 33 ], our findings have newly shown that respondents prioritizing religion are most likely to be happy than others.
The current findings support previous studies showing adverse associations between extrinsic, self-enhancement, or self-centered values and happiness [ 6 – 7 , 18 ]. Adverse associations between prioritizing extrinsic achievements and happiness can be explained in that extrinsic values facilitate social comparisons [ 24 ] and decrease quality of interpersonal relationships [ 25 – 26 ]. Prioritizing family over work and leisure enhances life satisfaction by increasing family satisfaction [ 11 ]. Recent studies [ 9 – 10 ] have similarly suggested that prioritizing time over money is beneficial for happiness via increasing the quality of social relationships. It is likely that people who consider extrinsic achievements as the most important thing in life are less likely to be satisfied with their current achievements and less likely to invest in social relationships, such as family and friends.
We also found that prioritizing social relationships is important for happiness and more beneficial than valuing extrinsic achievements or even physical self. This finding is consistent with a previous study showing that collective-centered values are more beneficial for well-being than are self-centered values [ 19 ]. Respondents prioritizing social relationships may tend to have higher quality of social relationships than those who value extrinsic rewards or egos (i.e., physical self). Additionally, spirituality, which can be classified into the dimension of self-transcendence or selflessness, is even more beneficial for happiness than is prioritizing social relationships. Psychological fulfillment through religion can be beneficial for happiness. Spirituality also may increase happiness in that it promotes a non-materialistic attitude toward life and decreases social comparison [ 7 ].
In sum, our findings showed how level of happiness is ranked according to the priority assigned to different personal values, with the highest level of happiness associated with spirituality, followed by social relationships, physical self, and (lastly) extrinsic achievements. This suggests that a greater propensity toward being self-centered is inversely associated with happiness. Among the four personal values, prioritizing extrinsic achievements can be considered as the strongest self-centered propensity whereas spirituality is the least self-centered propensity in that it could be categorized as self-transcendence [ 19 ]. Physical self might be intermediate between prioritizing extrinsic achievements and prioritizing social relationships. Although health is often conceptualized as an intrinsic value [ 5 , 20 ], prioritizing health might be more self-centered than prioritizing social relationships.
Some limitations of this study merit consideration. First, the data are cross-sectional and therefore we are limited in our ability to draw causal inferences. For example, it is possible that people who are unhappy with their social relationships are more likely to direct their attention toward earning the respect of others by seeking status, wealth, and power (reverse causality). In this scenario, individuals who are currently focused on prioritizing extrinsic achievements might not achieve happiness by being counseled to redirect their attention to their social relationships. Second, we used only three-year data of the KGSS (2007, 2008, and 2009) although the KGSS has been collected annually from 2003 to 2014, and biannually from 2014. The KGSS included both the personal value and happiness questions analyzed in the study for the three-year period only.
Third, we should be cautious about generalizing the findings about spirituality. Prioritizing religion was not significant in Model 4, shown in Table 3 , from which the 2009 data were excluded, although it was significant in the other models overall even with age restriction or with controlling for self-rated health, as shown in Table 4 . The lack of significance of spirituality when excluding the 2009 data might be due to the resulting decrease in statistical power. Compared with the 2007 and 2008 surveys, a slightly higher percentage of respondents chose religion as the most important domain in 2009 (i.e., 3.8% in 2007, 2.9% in 2008, and 4.5% in 2009). Only 3.38% of respondents (i.e., 99 of 2,933) chose religion as the most important domain after excluding the 2009 data, which might decrease statistical power. Further studies on associations between spirituality and happiness are needed to clarify these relationships. Finally, although it is reasonable to classify the 10 investigated life domains into four categories, more diverse classifications are needed in further studies. For example, we could not categorize neighbors as a separate category from social relationships because of the limited number of respondents who chose neighbors (i.e., 0.95% of respondents).
In spite of the limitations, this study extends previous knowledge about personal values and happiness by examining individual priorities for specific life domains and their impacts on happiness. Happiness may increase as individuals prioritize alters over egos, and egos over extrinsic rewards, which provides an ironic, but important implications about happiness in the individualistic and materialistic world.
Supporting information
S1 table. poisson regression analyses with robust error variances including prioritizing leisure as a single category (relative risks)..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.s001
S2 Table. Multiple regression analyses examining associations between personal values on life domains and happiness.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.s002
S3 Table. Poisson regression analyses with robust error variances including extrinsic achievements as a referent category (relative risks).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209821.s003
- 1. Easterlin RA. Does economic growth improve the human lot? Some empirical evidence. In: David PA, Reder MW, editors. Nations and households in economic growth: Essays in honor of Moses Abramovitz. New York: Academic Press;1974. p.89–125.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 14. Statistics Korea. Population and household census, 2015. [cited 2018 Oct. 24] available from: http://kosis.kr/statisticsList/statisticsListIndex.do?menuId=M_01_01&vwcd=MT_ZTITLE&parmTabId=M_01_01 .
- 15. Central Intelligence Agency. The world factbook. [cites 2018 Oct. 24] available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ja.html
- 16. Schwartz SH. Universals in the content and structure of values: Theoretical advances and empirical tests in 20 countries, In: Zanna M, editor. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology. Orlando: Academic Press, Vol. 25;1992. p. 1–65.
- 24. Kasser T, Ryan RM, Couchman CE, Sheldon KM. Materialistic values: Their causes and consequences. In: Kasser T, Kannder AD, editors. Psychology and consumer culture: The struggle for a good life in a materialistic world. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association;2004. p.11–28.
- 26. Kasser T, Ryan RM. Be careful what you wish for: Optimal functioning and the relative attainment of intrinsic and extrinsic goals. In: Schmuck P, Sheldon KM, editors. Life Goals and Well-being: Towards a Positive Psychology of Human Striving. Göttingen, Germany: Hogrefe & Huber; 2001. p. 116–141.
- 28. Kim S, Kim J, Moon Y, Shin S. Korean General Social Survey, 2012. Seoul: Sungkyunkwan University Press;2013. Korean.
- 29. Statistics Korea. Consumer Price Index. 2016- [cited 2018 Jan. 12]. Available from: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1J0A001&conn_path=l2# .
- Career Advice
Life Is Short
By Brad Had
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.
When I was six years old, I asked my mother if it were true that we would all die someday. My question drew a laconic yes. After a few seconds of doleful reflection, I asked, “Then why do we work?” She didn’t answer.
Today, I work about 34 ( actual ) hours per week. I consider that a lot, but many in academe would consider 34 hours sheer slacking. When I started my Ph.D. program, a high-ranking professor was outraged at my leaving the office at 5 p.m.; he even wanted to know the name of my supervisor so he could have a word with him about my “dubious work ethic.”
What irks me is not the judgmental attitude; it’s how hard it is to work with people who expect you to be on 24-7. People with kids get a relative free pass; but I don’t have kids, so I’m expected to be available weekends and evenings. But I’m not. I understand that is frustrating for many people, but it’s also frustrating for me to spend a weekend working rather than enjoying quality time with family and friends.
Why am I so adamant about taking time off? As hackneyed as it may sound, life is woefully short. I’m not even two years into the Ph.D. process, and I’ve already heard of two people who died of cancer at a young age. The mere thought of death throws most of us into a fit of intense angst, so we act as if we had all the time in world. But thinking about mortality has its benefits; it reminds us how precious our time is. I’m 26 years old, and if I’m lucky enough to make it to 80, that leaves me less than 2,860 weekends left to enjoy. That’s not an awful lot! This life is all I have, and I don’t want to squander it all on work.
I’ve heard professors say their work is their life. They enjoy what they do so much that they don’t mind forgoing everything else, even friends and family. That might be true for some people but certainly not for everyone. If academics truly work long hours out of passion, their job satisfaction should increase or at least remain stable as they spend more time on research. But studies show that exactly the opposite happens: the more hours academics spend on research, they more dissatisfied they are with their jobs. The reason academics work so much isn’t out of sheer passion -- it’s out of pervasive publish-or-perish pressure.
The expectations of academe are exceedingly demanding. Students and faculty members feel guilty when they’re not working. And when they are, they have an all-too-familiar feeling that more can be done. We all know the consequences: social isolation, stress, burnout, anxiety, poor work-life balance and health issues, to name but a few.
But there’s more. In one of his famous essays , the philosopher Bertrand Russell lamented that “without a considerable amount of leisure a man is cut off from many of the best things.” Working too much means missing out on museums, festivals, pub crawls, casual reading, music, hiking, camping, canoeing, stargazing, socializing, exploring new cities, picnics, friends, family, romantic relationships, plays, road tripping, workouts, restaurants, lectures, long autumnal walks, video games, board games, sleep, sleeping in, meditation, origami, baseball games, reading poetry, being read poetry, learning a new language, woodworking and, most important, taking the time to see the big picture and take stock of one’s life. My mother still hasn’t answered my existential question, but I’ve figured it out for myself: we work so we can enjoy leisure and contemplation.
But overwork doesn’t have to be a foregone conclusion. I know a handful of researchers who publish in top journals and still manage to work fewer than 40 hours a week and take weekends off. Yes, all of them have children, and no, they’re not all tenured. Here’s what I learned from them:
They’re clear about their priorities. “He that judges not well of the importance of his affairs,” wrote William Penn in 1682, “though he may be always busy, he must make but a small progress.” Being clear about one’s priorities makes two things easier. First, priorities help you set boundaries. Some professors make it very explicit that weekends are off-limits and reserved for family and friends. They will answer the phone or check their professional email only during certain hours, as they know that nothing can be so urgent that it can’t wait until Monday.
Second, priorities help you set time limits that match the importance of the tasks at hand. You should allot high-priority tasks more time, although in reality people often spend little time on the important stuff. Setting time limits also makes you more efficient. Parkinson’s law that “work expands so as to fill the time available for its completion” has a lesser-known corollary: “Work contracts to fit into the time we give it.” This is one of the reasons why shorter workweeks have boosted productivity in Europe.
They plan ahead. A professor once told me that planning things out helped him make sure that his efforts were channeled toward his goals rather than whatever trifle came his way. Having a daily plan, he told me, meant he didn’t waste time every morning pondering what to do. Besides saving time, research clearly shows that planning helps people feel more in control of their time, lowers stress and anxiety, and boosts life satisfaction.
But, more important, planning helps you know what tasks must be completed in a given day and, therefore, when to stop working. Indeed, the hard thing about work isn’t getting started -- it’s knowing when to stop.
Planning ahead also means not having to worry about all the things you have to do. People tend to constantly think about unfinished projects (this is known as the Zeigarnik effect ), which saps precious brainpower that could be used to work on other projects. Research shows that if you have a written plan of how and when you’re going to carry out a task, you’ll stop worrying about it and be more efficient at dealing with other projects.
They’re very organized. People think organization saves time because it makes you more efficient. It’s true, but organization saves time mostly because it averts crises. Some professors use dead-simple note-taking tools; others have elaborate organization systems. In either case, being organized means nothing falls off the radar, becomes suddenly urgent or snowballs into a full-blown crisis -- and crises take an awful lot of time to mop up. (A stitch in time saves nine!)
They take time off. The most productive scholars I know also tend to be the most unapologetic about taking time off. And rightly so. In a little-known passage of The Wealth of Nations , Adam Smith suggested, “It will be found, I believe, in every sort of trade, that the man who works so moderately as to be able to work constantly not only preserves his health the longest, but, in the course of the year, executes the greatest quantity of work.”
Smith’s prescient remark is borne out by a slew of studies; working long hours is not only unhealthy, but also counterproductive. Taking time off, on the other hand, will make you healthier, more productive and more creative .
It’s very tempting to work more. After all, work provides money, and money buys leisure. But as economist G. S. Becker pointed out 50 years ago, leisure costs money and time. Vacationing in Cuba might cost $2,000 in money and about a week in time, but if one has no time left because of work, the $2,000 is basically worthless. At the end of the day, time management is all about putting your time where your mouth is, and matching your time investments with your priorities in life is a huge first step toward happiness.

Denied? That Top College Lied
Test scores matter more than elite colleges let on, David Blobaum writes.
Share This Article
More from career advice.

Bad-Faith Counteroffers
Black and other minoritized faculty don’t receive equitable ones if they receive them at all, which harms both them a

A 3-Step Process for Gaining a Tenure-Track Job
Susanna Semerdzhyan, a first-generation college graduate, shares strategies that helped her overcome the obstacles.

Let’s Finally Tackle the Problem of Pay Inequity
Higher ed must go beyond buzz words and stop hiding behind performative equity, which does not create change, w
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Create Free Account

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Does More Money Really Make Us More Happy?
- Elizabeth Dunn
- Chris Courtney

A big paycheck won’t necessarily bring you joy
Although some studies show that wealthier people tend to be happier, prioritizing money over time can actually have the opposite effect.
- But even having just a little bit of extra cash in your savings account ($500), can increase your life satisfaction. So how can you keep more cash on hand?
- Ask yourself: What do I buy that isn’t essential for my survival? Is the expense genuinely contributing to my happiness? If the answer to the second question is no, try taking a break from those expenses.
- Other research shows there are specific ways to spend your money to promote happiness, such as spending on experiences, buying time, and investing in others.
- Spending choices that promote happiness are also dependent on individual personalities, and future research may provide more individualized advice to help you get the most happiness from your money.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
How often have you willingly sacrificed your free time to make more money? You’re not alone. But new research suggests that prioritizing money over time may actually undermine our happiness.
- ED Elizabeth Dunn is a professor of psychology at the University of British Columbia and Chief Science Officer of Happy Money, a financial technology company with a mission to help borrowers become savers. She is also co-author of “ Happy Money: The Science of Happier Spending ” with Dr. Michael Norton. Her TED2019 talk on money and happiness was selected as one of the top 10 talks of the year by TED.
- CC Chris Courtney is the VP of Science at Happy Money. He utilizes his background in cognitive neuroscience, human-computer interaction, and machine learning to drive personalization and engagement in products designed to empower people to take control of their financial lives. His team is focused on creating innovative ways to provide more inclusionary financial services, while building tools to promote financial and psychological well-being and success.
Partner Center

The Secrets to True Happiness
Is our modern definition of happiness all wrong.
Posted June 12, 2024 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Many Western nations are becoming unhappier, data suggests.
- Research supports the notion that well-being goes beyond material wealth.
- Our modern definition of happiness may have it all wrong.
The World Happiness Report recently celebrated its 12th birthday. Not surprisingly, Finland has once again topped the list as the happiest country on the planet for its seventh consecutive year.
Perhaps even less surprising is the sharp drop in happiness rates for the youngest recorded cohorts (aged 15-24) in North America with a similar downward tendency for that age group in Western Europe. After all, the pressures of social media , climate change , world politics , and uncertainty have made growing up that much harder, even in wealthy societies.
It appears that wealth alone does not boost our happiness levels. In fact, some of the happiest places in the world according to one report —the Dominican Republic, Sri Lanka, and Tanzania—are all non-Western developing nations not known for their wealth and abundance. Perhaps there is something else going on here. These nations value family and social connections in ways other countries do not. In fact, human connection is the glue that keeps society—and ourselves—together.
According to one recent study by not-for-profit neuroscience research body Sapien Labs, London is considered the second unhappiest city in the world. While various research initiatives such as the Global Mind Project and the World Mental Health Survey Initiative rely on different methodologies, the details of capturing mental well-being are less important than the fact that happiness continues to be an important part of defining our quality of life.
And what if our definition of the very thing that makes our lives meaningful is completely different than what society has taught us to believe? What if happiness isn’t what we think it is?
Positive psychologist Stephanie Harrison claims we have gotten it all wrong. In her new book New Happy: Getting Happiness Right in a World That’s Got It Wrong , she states that much of what we have been told will bring us happiness is an outright lie—including perfection, financial success, and millions of Insta followers.
The true secret behind happiness is what she considers counterintuitive. In fact, it’s not about you at all. Helping others is a proven path to what Harrison terms the "new happy," the true definition of fulfillment and joy.
Harrison advises readers to disentangle themselves from the "old happy" that fixates on perfection and external accolades. While those are nice to have, they should not be the basis of your self-worth , which is intrinsic. In fact, you are not defined by your successes or failures, according to Harrison. Sharing our unique gifts and talents with the world will make us happy, no matter what comes of it. Plus, who are you to deny the world your happiness? Happiness is like love. The more you give it away, the more you will receive it.
Neuroscientist Nicole Vignola would agree. In her new release Rewire: Break the Cycle, Alter Your Thoughts and Create Lasting Change , she delves into the human mind and how we can find happiness and fulfillment. Pursuing hobbies, for instance, is a mood elevator and stress reducer, building what HBR contributor Gaetano DiNardi calls “creative confidence .” Vignola offers powerful ways to improve our well-being by breaking the drama cycle that often informs our lives. Reconnecting with self and others plays a big part in fostering mental health.
U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy is well-known for his research on loneliness , having published a book in 2020 aptly titled Together. It appears our post-pandemic world is still reeling from the profound disconnection and greater reliance on technology in our daily lives. It may be time for us all to take up that hobby we have since neglected while sharing those talents—and love—with the world.
The World Happiness Report. (2024). https://worldhappiness.report/
Price, R. (2024, March 10). UK second most miserable place in the world . The London Economic. https://www.thelondoneconomic.com/lifestyle/uk-second-most-miserable-pl… .
Newson, J. (2024, March 1). A comparison of measures and methodologies of the global mind project, world mental health survey initiative & world happiness report - sapien labs: Neuroscience: Human brain diversity project . Sapien Labs | Neuroscience | Human Brain Diversity Project. https://sapienlabs.org/a-comparison-of-measures-and-methodologies-of-th… .
Harrison, S. (2024). New happy: Getting happiness right in a world that’s got it wrong . TarcherPerigee, an imprint of Penguin Random House LLC.
Vignola, N. (2024). Rewire: Break the cycle, alter your thoughts and create lasting change . HarperOne, an imprint of HarperCollins Publishers.
Why you should work less and spend more time on hobbies . Harvard Business Review. (2023, January 3). https://hbr.org/2019/02/why-you-should-work-less-and-spend-more-time-on… .

Christine Louise Hohlbaum is the author of The Power of Slow: 101 Ways to Save Time in Our 24/7 World.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
😊 key points to use to write an outstanding happiness essay, 🏆 best happiness topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 most interesting happiness topics to write about, ⭐ simple & easy happiness essay titles, 👍 good research topics about happiness, 💡 interesting topics to write about happiness, ❓ research questions about happiness.
Writing a happiness essay may seem easy at first, but many students fail to achieve a high grade because their responses are too general. To avoid falling in this trap, read this post and take note of the key points to write about.
The Meaning of Happiness
The word “happiness” means various things to various people, and it would be a good idea to explore this topic in your paper. To get some perspectives, you could ask your friends or family members what happiness is to them. Alternatively, browse sample essays on happiness online. Once you’ve done your research, consider the following:
- What does happiness mean to you?
- Do you think that you are happy where you are now? Why or why not?
- Is achieving happiness essential to do you, or do you think that one can be satisfied with life without being truly happy?
The Importance of Happiness
This is probably among the most important happiness essay titles because there is a lot to talk about here. You would likely be surprised to find out that not all people view happiness as a crucial goal in life. In fact, most people live their days without considering whether or not they are happy. These are a few questions that you could think about:
- Why is happiness more important to some people than to others?
- Should a person strive to be happy? Why or why not?
- What is the influence of happiness on a person’s mind and body?
Sources of Happiness
The third point you could cover in your paper is the relationship between happiness and achievements. People often believe that they will be happy when they achieve certain things and their life.
Some examples are starting a profitable business, marrying their loved one, having kids, and traveling the world. If you want to examine the correlation between happiness and other factors, these questions should give you some ideas:
- Is happiness influenced by life circumstances and events? If so, how?
- Why do you think some people never become happy, even after achieving what they’ve always wanted?
- What external factor plays a key role in your happiness? Why do you think that is?
Happiness and Money
The link between happiness and money is possibly one of the most popular happiness essay ideas and titles.
Many people think that wealth has a direct influence on happiness, but others disagree. You could explore this theme in your paper using the following questions to guide your thoughts:
- In your opinion, can a person to buy happiness? If so, how?
- Why do you think people often associate happiness with wealth? If money is the key to happiness, why are there so many wealthy people who are unhappy?
- Do you believe that true happiness is possible without financial success? Why or why not?
Regardless of what you choose to write about, be sure to maintain a good essay structure throughout your paper. To assist you with this, create a detailed outline and stick to it while writing.
Start your paper with a happiness essay hook, a sentence to draw the reader’s attention to your work. Support your thoughts with relevant examples or research where applicable.
Finally, make sure to close off your paper with a happiness essay conclusion. If you want to learn more about essay structure, browse our website – we also have a good selection of essay topics and other useful materials!
- What Is Happiness Essay One would say that happiness is to be with a loved one, the second would say that happiness is the stability, and the third, on the contrary, would say that happiness is the unpredictability.
- Can Money Buy You Happiness? First of all, given that happiness is related to the satisfaction of personal needs, there is also a need to consider the essential need of human life such as housing, medicine, and food.
- Connection Between Money and Happiness Critical analysis of money-happiness relationship shows that socioeconomic factors determine the happiness of an individual; therefore, it is quite unsatisfactory to attribute money as the only factor and determinant of happiness.
- Money, Happiness and Relationship Between Them The research conducted in the different countries during which people were asked how satisfied they were with their lives clearly indicated the existence of a non-linear relationship between the amount of money and the size […]
- World Happiness Index and Its Six Factors This variable allows the researchers to evaluate the status of the economy since it is the estimation of the value of all products and services a company creates.
- I Don’t Believe Money Can Buy Happiness This shows that as much as money is essential in acquisition and satisfaction of our needs, it does not guarantee our happiness by its own and other aspects of life have to be incorporated to […]
- Life as a Human’s Struggle for Happiness He said he was eager to get his degree and live his life to the fullest. After a while, Ali understood that the answer to his question was life.
- Discussion: Can Money Buy Happiness? Reason Two: Second, people are psychologically predisposed to wanting more than they have, so the richer people are, the less feasible it is to satisfy their demands.
- Painfulness and Happiness of Childbirth The second stage is associated with the child’s passage through the birth canal; it begins after the complete opening of the cervix and ends with the birth of a child.
- Goals of the Life: Personal Experience of Responsibility for Life and Happiness I have a lot of goals in my life and do all my best to realize them in my life. The best way to achieve your goal is to make a plan of steps to […]
- The Key to Happiness and Satisfaction with Life For example, in the documentary ‘Happiness,’ the hunters and gatherers of Namibia in Africa were found to be having a high happiness index.
- Does Money Buy Happiness? Billions of people in all parts of the world sacrifice their ambitions and subconscious tensions on the altar of profitability and higher incomes. Yet, the opportunity costs of pursuing more money can be extremely high.
- Philosophy Issue: Truth vs. Happiness The only way the truth will be concealed and still lead to happiness is when the truth is substituted with a lie.
- The Psychology of Happiness The psychology of happiness is closely related to philosophy, as the science of happiness is based on three major theories, namely “the emotional state theory, the life satisfaction theory, and hedonism”. As far as happiness […]
- Happiness and Morality This paper will look at the meaning of happiness and morality, the relationship between morality and happiness and why many philosophers hold that in order to be happy, one has to be moral.
- Is Happiness the Beginning or the End? Jamie Anderson’s “Is Happiness the Beginning or the End?” discusses the view on happiness in the American cultural consciousness and the perceived ideological conflict regarding the specificities of its nature.
- Psychology of Happiness in the World Psychology of happiness touches on various fields of social and cultural life and seeks to interfere with the lives of individuals for improving their talents and endowing their normal existence with greater meaning.
- This I Believe: Happiness Is a Choice I know that I can choose to be happy. I was ashamed and worried that he would know I took it.
- Pursuit of Happiness Film Analysis Thus, while the film centers on the theme of “pursuit of happiness,” this paper shows that the film distorts the concept of happiness to represent the orientation of earthly goods through which our reality revolves […]
- Emotions of anger and happiness The emotion of anger is usually considered to be negative and it can lead to various negative consequences. On the other hand, the emotion of happiness is positive and it has numerous benefits to our […]
- Stay-Home Moms and Full-Time Working Mothers: Indicators of Happiness In some parts of the world, it’s considered well that a woman is working, but mostly in eastern countries, women are preferred to stay at home at look after their houses and children.
- Positive Psychology: The Science of Happiness Positive psychology is a science of positive features of the life of a human being, including happiness, welfare, and prosperity. According to him, happiness is freedom from pain in the body and a disturbance in […]
- How Is the “Greatest Happiness Principle” Supposed to Be Useful in Determining What I Ought to Do? Therefore, the main idea of the greatest happiness principle is to make sure that more people are satisfied, however, the volume of the satisfaction is not discussed as well as the level of harm caused […]
- Acts of Kindness and Happiness in Human Life The research at hand is aimed to prove that, to boost happiness through receiving positive emotions, a person should commit more actions that can be referred to as acts of kindness.
- Social Media in Enhancing Social Relationships and Happiness Social media and technology assist to foster and maintain relationships where the people live in different geographical regions. There is a major concern that social media and technology poses a threat to the traditional fabric […]
- Sigmund Freud’s Ideas of Happiness One of these means, and the only one that Freud seems to feel provides any sense of satisfaction as to why happiness cannot be obtained, is found in the realm of religion.
- Money, Happiness and Satisfaction With Life Nonetheless, the previously mentioned examples should be used to remind us that money alone is not a guarantee of happiness, satisfaction with life, and good health.
- Bhutanese Views on Happiness and Subjective Wellbeing The purpose of this task is to explore Bhutanese views on happiness as a form of positive psychology that depicts national progress.
- Relationships of Social Class and Happiness In the United States, for instance, the gap between the rich and the poor has been on the rise and the government seems to be doing very little to curb the sad realities of the […]
- My Relationship with Time and Its Effect on Happiness Eventually, I think that it is necessary to use time correctly, to sleep well and to work in the most productive hours.
- The idea of Happiness Although Weiner shows that trusting the leadership is a source of happiness by contrasting Bhutan with the people of Medova, one can still argue that so long as the leadership provides the required security, be […]
- Edwin Arlington Robinson: Money and Happiness in “Richard Cory” It is evident that money cannot guarantee happiness in one’s life due to the uncertainties that surround each one of us.
- Concept of Happiness in the Workplace The task of every employee is to find a way to work in harmony with their personal values and build successful relationships with colleagues and managers.
- Self-Happiness and Its Impact on Romantic Relationships This boosts self-happiness and contributes to the general success of a romantic relationship. Self-happiness is vital in maintaining relationships and the overall connection between partners for relationship success.
- The Role of Employee Happiness in the Productivity Among Government Employees The national UAE Program of Happiness features a set of three initiatives: Happiness in policies, programmes and services of all government entities and work environments; Promotion of values of positivity and happiness as a lifestyle […]
- Technology Fails to Deliver Happiness With the advancements in information technology and the massive use of the internet, communication has become quite effective as people can connect when they are in different countries around the world, at any time.
- Importance of Training Mind to Find Happiness and Meaning of Life According to Buddhist thinking, mind training “…is training in stability in order to “reveal the mystery” of the ultimate nature of reality, our own and that of other phenomena”.
- In the Pursuit of Liberty and Happiness: How the Life of Mohammad Yunus Continue to Impact the World By any standards, the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution of the United States can be termed as two of the most fundamental and enduring documents in the Nation’s history due to the very fact […]
- Happiness and Success as a Life Meaning I find meaning in my life when I help people that I encounter in my life. This means that life, when a person follows the Christian rules, is full of spirituality and thus meaning.
- Consumerism and Happiness To the surprise of Luedicke and Giesler, “The more goods produced and consumed in the society the higher the growth rate of the economy”.
- True Happiness by St. Augustine Augustine put emphasis on one’s soul and spiritual connection with God to be happy rather than material goods and body.St. I concur with this idea and believe that in seeking happiness, one should prioritize what […]
- Moral Virtue and Its Relation to Happiness Furthermore, Aristotle believed that moral virtue is the primary means to happiness and the most important of all things that are really good for people.
- Happiness in Mills’ Utilitarianism Theory Mill further supports his claim by explaining that the justice sentiment is based on utility and that the existence of rights is due to human happiness. The freedom from pain involving health issues and other […]
- Aristotle’s Understanding of Happiness If happiness is “wholeness”, then for a person to become happy, it is necessary to become “whole”. Thus, all a person has to do to become whole is lower goods.
- Happiness: Cuddy’s vs. Dowthwaite’s Articles Comparison Although Cuddy and Dowthwaite have different perspectives on the matter, they both concur that it is natural for individuals not always to be happy.
- Aristotle’s Concept of Happiness Aristotle’s concept of happiness is an expression of virtue that is similar to the flow state, happiness is a combination of the baseline level where basic needs are fulfilled and a broader area managed by […]
- The Happy Planet Index of Long-Term Happiness The Happy Planet Index contributes to answering the issue, “Is it possible to live happy lives without harming the environment?” The relationship between happiness and ecological footprints can be clearly understood by interpreting the data […]
- Environmental Injustice Impeding Health and Happiness The authors note that there is a constant flow of the white population to the areas most protected from flooding and the displacement of the black population from there.
- Leadership for Happiness in Workplaces The relationship between the leaders and the workforce determines how the employees react and perceive the decisions made by the management.
- Ways to Ensure Happiness at Work For employers to gain a high amount of trust from their workers, they have to believe that their workers have the organization’s best interest and that their actions are driven to better their services.
- Thoughts on Stress Management and Happiness Although she has all her financial needs met overwhelmingly, her failure to proceed with her studies and get employment makes her feel unsatisfied.
- Study of the Happiness Index Parameters Thus, the chronological data allow us to evaluate not only the countries among themselves according to this criterion but also to provide the dynamics of the change in the happiness index within the country.
- Happiness: Common and Personal Criteria Since the emergence of the term happiness in the times of Plato and Aristotle, the topic of happiness, its philosophical meaning, and its application to the real world became a case of many discussions.
- Happiness Areas and Goals in Personal Life The point that most of the global population leads a life of acting contributes significantly to the loss of happiness. That is why one of my goals to achieve the second area of happiness involved […]
- Aristotle’s View of Ethics and Happiness Aristotle guarantees that to find the human great, we should recognize the capacity of an individual. He set forth the thought that joy is a delight in magnificence and great.
- Changing a Client’s Life From a Mess to Happiness In the beginning, I disclosed these details to make the woman’s physical portrait.”She averages one meal per day”: The woman has a great risk of problems with gastritis due to the lack of vitamins and […]
- Happiness in Arts: Happiness Through Virtue This way, the premise of the Marble statue resembles that of the portrait of Antisthenes, namely, that happiness is the greatest good and it can be attained by nurturing goodness.
- Exegetical Paper on Aristotle: Meaning of Happiness It is in the balance, according to Aristotle, that the completeness of the human personality lies, and only through balance can a person find true self-satisfaction.
- Create Happiness Organization: Marketing Donor organizations, which are going to buy the Create Happiness Organization’s cards and card devices in order to use them for discounts and making bargains.
- Happiness: The Best Way to Achieve and Prolong It If a person can combine work and rest, lives a healthy life, and has time for hobbies and family, they will be able to attain lasting happiness.
- How Can Humans Find Happiness? Generally, evaluating the facts, it can be said that Aristotle’s concept of happiness is authentic, and happiness for a number of people is truly in acquiring knowledge, but this is not always true as there […]
- Mental Health: Happiness and Social Interaction It is quite curious to observe the way parents are teaching their children to be kind and good to others and right after the lesson they express quite negative feelings to a family member who […]
- Happiness and Deviant Behaviour in “Happiness” Movie In this manner, he was able to connect to Joy Jordan who happened to be the sister of Trish, the wife of his psychiatrist.
- Changed Views of Happiness: Context and Aim of the Definition The truest happiness arrives through the task of a person’s highest function: the utilization of the coherent rule of mind. The first one is “The universal run of individuals and the crudest,” which identifies happiness […]
- Influence of Television on People’s Happiness The idea of mass culture influencing the development of society is closely connected with a concept of a need to be happy.
- Effects of Gambling on Happiness: Research in the Nursing Homes The objective of the study was to determine whether the elderly in the nursing homes would prefer the introduction of gambling as a happiness stimulant.
- American Literature: Happiness Is Only Real When Shared This implies that he had started valuing the presence of other people in his life and the aversions that he had towards his parents started to wither after realizing that he had to share his […]
- Innocence and Experience: How Social Opinions Shape Our Perception of Happiness Although there does not seem to be any similarity between the two poems, they both show the contrast between experience and innocence.”Advice to My Son” is the advice of an experienced father to a son […]
- Women’s Quest to Attain Happiness in Literature Thus, our definition of the most important difference between the characters of Janie and Emma will sound as follows: whereas, Janie never ceased to be a woman in both: the physiological and psychological context of […]
- Roots and Fruits of Happiness The instinct of a researcher is to find demographic patterns in the trend of the variable. A possible hypothesis for clarifying our understanding of the relationship between happiness and close relationships could be: “People feel […]
- How Much Emphasis Should One Place on Personal Happiness or Fulfillment? The aim of the paper is to explore the main tenets of utilitarianism and happiness, apply them to personal vision of happiness and compare it to Aristotle’s notion of happiness and ideal life.
- Cultivating Happiness for Different People Though one of her daughters was born with Down’s syndrome, the lady is really happy to have her and she does not regret a moment in her life.
- Psychology: Happiness from a Personal Viewpoint Because of my ability to see the good in people, I think I am more inclined to want to do things that will help them, and these times I have done this have appeared in […]
- Aristotle and His Definition of Happiness The best taste a person can have in his life is happiness because of success. But in my point of view, happiness is the main feeling that comes from the success of any useful act […]
- Happiness at the Workplace in the UAE The primary approach that should be taken by the governmental entities of the UAE to improve the happiness of their employees should be focused on creating an appropriate environment.
- Psychology of Happiness and Effect on Human Health The main characteristics of the impact of feelings on human health are the rapid pulse and palpitations, the dilatation of pupils, and changes in the skin.
- Happiness in the United States If applied to the U.S.situation with citizen happiness, the methods of classification, cause and effect analysis, and comparison indicate the need for innovative and effective measures for the promotion of social support.
- Hurricane Katrina Survivors’ Happiness Factors The paper is dedicated to the study of factors influencing the happiness of women, whose lives were affected by the Katrina Hurricane, one and four years after the hurricane.
- Happiness: Health, Marriage, and Success In this paper, I will examine the issue of happiness by scrutinizing it through the lenses of health, marriage, and success the three components that previously appeared to me to be necessary for an individual […]
- The Architecture of Sustainable Happiness The feeling of happiness and the intention to change it were measured before and after the participants listened to the music.
- Happiness vs. Production in the Workplace I think that good leader has to clarify the possible levels of the job performance of their employees to understand what kind of work may be expected when goals can be achieved, and what rewards […]
- John Stuart Mill’s Happiness Philosophy Consequently, the outcome of a course of action that is on the course of being undertaken or is to be undertaken lies in the value of the outcome.
- Touchpoints for Improved Happiness Index in the UAE The study is aimed at establishing the critical success factors in quality management of service delivery charter in the UAE government institutions. Research question: What is the impact of the UAE government’s touchpoints in improving […]
- Emirati Happiness in National Agenda and Vision 2030 Using evidence from the existing literature, this report argues that the examination of touchpoints will help promote the objective of making the UAE the happiest nation across the world.
- Touchpoints in UAE Government’s Happiness Initiatives This paper aims at conducting a literature review on the concept of touchpoints with the objective of developing a sound argument regarding the extent to which they can effectively help the UAE to achieve remarkable […]
- Happiness Without Money in Sociology and Psychology The tendency’s mechanics are simple – being in the possession of any substantial sum of money increases a person’s chance to secure a dominant status within the society, which in turn will result in strengthening […]
- The Meaning of Happiness On the other hand, another study found that the birth of a child is associated with the loss of spousal love, and the decrease in the total level of happiness is stated to be the […]
- Volunteering Effects on Happiness Taking that into consideration, it is necessary to pay an increased attention to the effect that volunteering and all the people connected to it produce on representatives of one of the social groups whose opportunities […]
- David Leonhardt: May Be Money Does Buy Happiness After All The case study of Japanese citizens that support Easterlin paradox do not factor in the confounding psychological effects of the Second World War on the entire population and the country.
- Bhutan’s Concept of Gross National Happiness The concept of GNH in Bhutan emphasizes the need for gauging the progress of this country from the perspective of its population’s degree of happiness.
- Happiness and Its Influence on Decision-Making The strength of this paper is that it explores not only the meaning of the word but also the results of its offered revision, including the reconsideration of the importance of the phenomenon of competition, […]
- Happiness: Personal View and Suggestions For an individual to increase his or her level of happiness, it is necessary to be aware of the things that make him or her happy.
- Money and Happiness in Poor and Wealthy Societies Comprehending the motivations for pursuing money and happiness is the key to understanding this correlation. The Easterlin paradox summed this view by showing that income had a direct correlation with happiness.
- Thomas Jefferson’s Goals: Life, Liberty and Happiness Prior to the writing of this phrase, the right to life, liberty and pursuit of happiness were not acknowledged by the political systems of the day.
- Philosophy Terms: Justice, Happiness, Power and Virtue Socrates argues that autocratic leadership is an important structure of ensuring that the rule of law is followed and that the common good of all societal members is enhanced.
- Money and Happiness Connection – Philosophy Based on measures of happiness and household income, these economists have claimed that money, in this case, economic development, has a significant impact on happiness.
- Does Intelligence Predict Happiness? Overall, this concept can be described as the ability of a person to apply cognitive skills while using various types of information.
- The Definition of Happiness For example, Aristotle’s work raises questions such as, “What is the purpose of human life?”, “What is happiness?” and “Why do people do the things they do?” On the other hand, Plato’s text raises questions […]
- Psychological Research: Money Can Buy Happiness In the article, the author has given enough evidence to prove that money can be used to buy happiness. Based on the evidence presented in the article, it is obvious that proper utilization of money […]
- Mill’s Greatest Happiness Principles: A Practical Guide to the Theory of Life In the given question, Mill draws the line between the moral principles and the human mind. Hence, Mill questions the link between the moral and the ethical.
- Can Aristotle’s Theory of Happiness Be Achieved by Applying Friedman’s Ideas of Corporate Social Responsibilities? According to Aristotle, politics is the master of all arts since it is concerned with the end in itself. This is a central argument to the ideas of Aristotle and underscores his idea that politics […]
- Happiness Meaning and Theories This essay aims to analyze Happiness, what makes happiness special to people, the meaning of it and the essence of it. The second happiness is a general consensus about the goodness of your life at […]
- Secular Worldview: Attaining Earthly Happiness It is a form of religious worldview in which man is the overall measure that is; man is the ultimate judge of truth and also evaluates the values which are to be followed.
- Happiness: Philosophical Description Serenity of mind to Gertrude is found by accepting things that are beyond her control and seeking the strength and courage to change things that can be changed like cloth the naked, feed the hungry, […]
- Essence of Happiness of Indira’s Life According to Plato’s and Aristotle’s Views on Education She finds her inspiration in the languages and other subjects and, obviously, the girl knows that education is the best solution of solving a number of problems and difficulties that she may face during the […]
- Happiness is not always fun These words show what the movie is all about, the fluctuations that accompany the pursuit and maintenance of happiness. This close connection of the movie to the viewer facilitates the general acceptance of the intellectual […]
- Aristotle’s Ideas on Civic Relationships: Happiness, the Virtues, Deliberation, Justice, and Friendship On building trust at work, employers are required to give minimum supervision to the employees in an effort to make the latter feel a sense of belonging and responsibility.
- Influence on Happiness of Gender, Education Level and the Number of Children According to Easterlin, the number of children a family has is inversely proportional to the level of happiness the family will enjoy; this shows that the higher the number of children, the less happy the […]
- Gender, Education Level and the Number of Children Influencing Perception on Happiness It is also found out that the increase in the number of children leads to lack of love in the family and later leads to decline in the degree of happiness.
- Happiness and Its Social Psychological Aspects The well being of an individual is very critical to performance and several meaning of life to that particular individual. Several researchers have studied aspects like obedience, intervention of bystander, behavior and altruism as being […]
- Well-Being as a Happiness Definitions Michael Marmot in his book The Status Syndrome: How Social Standing Affects Our Health and Longevity tries to justify happiness from a social perspective.
- How Aristotle Views Happiness Aristotle notes that “the attainment of the good for one man alone is, to be sure, a source of satisfaction; yet to secure it for a nation and for states is nobler and more divine”.
- Which is Basic in Ethics: Happiness or Obligation Logically, the basic element in any pursuit is the end itself; consequently, the task here is to determine the element that stands out as the end as opposed to means to something else.
- The Beggar King and the Secret of Happiness – Folks and Fairy Tales “What seems like a blessing may be a curse. What seems like a curse may be a blessing”.
- The Beggar King and the Secret of Happiness The following essay is concerned with the book’ The Beggar King and the Secret of Happiness’ by Joel Ben Izzy. Joel Ben’s story,’ The Beggar King and the Secret of Happiness’ resonates in my life.
- Pursuit of Happiness by Women in Modern Day America Civil rights are what citizens in a democratic country are entitled to and they include rights such as the right to vote, right to equal treatment and opportunities, the right to life and the right […]
- Breaking the Stereotype: Why Urban Aboriginals Score Highly on Happiness Measures
- Electing Happiness: Does Happiness Effect Voting and Do Elections Affect Happiness
- Freedom, Justice, and the Pursuit of Happiness
- Individual and Contextual Factors of Happiness and Life Satisfaction in a Low Middle Income Country
- Technology and Its Effects on Satisfaction in Society
- Neural and Genetic Correlates of the Social Sharing of Happiness
- Emotional Intelligence as Mediator Between Need for Relatedness, Happiness, and Flourishing
- Serotonin the Happiness Hormone and Effect on Neurotransmitters
- Defining Happiness Through Metaphorical Expressions, a Person’s Behavior, and Its Relation to Success
- Cultural Capital and Happiness: Why the Rich Are Happier
- Relationship Between Spiritual Well-Being and Happiness
- Finding Happiness in Homosexuality, Overcoming Rejection, Identity, and Desire
- Measuring Happiness: From Fluctuating Satisfaction to Authentic, Durable Happiness
- Income and Happiness: Earning and Spending as Sources of Discontent
- Adaptation Amidst Prosperity and Adversity: Insights From Happiness Studies From Around the World
- Modern Ritualism for Finding Peace & Happiness & Living With Meaning
- Aristotle’s Eudaimonia: Are Pleasure and Happiness the Final Goals in Life
- Beauty and Equality: The Key Elements to the Pursuit of Happiness
- Collective Happiness: Labor Union Membership and Life Satisfaction
- Law, Sustainability, and the Pursuit of Happiness
- Against Positive Thinking: Uncertainty as to the Secret of Happiness
- Age and the Pursuit of Happiness Among Immigrants
- Happiness and Its Correlation With Marriage, Earnings, and Age
- Poor and Distressed, but Happy: Situational and Cultural Moderators of the Relationship Between Wealth and Happiness
- Job Satisfaction and Family Happiness: The Part-Time Work Problem
- Migrants, Health, and Happiness: Evidence That Health Assessments Travel With Migrants and Predict Well-Being
- Adult Happiness and Prior Traumatic Victimization in and Out of the Household
- Happiness and Growth the World Over: Time Series Evidence on the Happiness-Income Paradox
- Economic Growth Evens Out Happiness: Evidence From Six Surveys
- Children, Spousal Love, and Happiness: An Economic Analysis
- Our Relationship With God as the Pathway Toward Happiness
- Parenthood and Happiness: Direct and Indirect Impacts of Parenthood on Happiness
- Gender and Well-Being Around the World: Some Insights From the Economics of Happiness
- National Happiness and Genetic Distance: A Cautious Exploration
- Basic Needs and Wealth as Independent Determinants of Happiness
- Money and Happiness: Problems Understanding Its Dynamic Relationship
- Buddhism: Happiness and the Four Noble Truths
- Nicomachean Ethics and Reasons Role in Happiness and Virtue
- Commitment Beyond Self and Adolescence: The Issue of Happiness
- Absolute Income, Relative Income, and Happiness
- Does Economic Prosperity Bring About a Happier Society?
- What Does Sociology Bring to the Study of Happiness?
- What Affects Happiness: Absolute Income, Relative Income, or Expected Income?
- What’s Special About Happiness as a Social Indicator?
- What the Buddha Taught – Fundamental Principles Ensuring Human Happiness
- What Are the Relationship of Inequality, Happiness, and Relative Concerns?
- How Does Happiness Mediate the Organizational Virtuousness and Affective Commitment Relationship?
- What Are Happiness and Success?
- What Is Happiness? What Makes Life Happy?
- How Can People Find Happiness?
- What Are the Main Factors for Achieving Happiness?
- How Can Happiness Improve Productivity?
- Does Government Ideology Affect Personal Happiness?
- Happy for How Long? How Social Capital and Economic Growth Relate to Happiness Over Time
- How Do Gender and Age Effect Happiness?
- How the Economy and Institutions Affect Happiness?
- What Are the Differences Between Happiness and Self-Esteem?
- What Role Does Government Play in Human Happiness?
- What Can Economists Learn From Happiness?
- How Much Does Money Matter? Estimating the Causal Effects of Income on Happiness
- What Do Happiness Indices Tell Us About Life?
- How Can Enduring Happiness Arise From Friendship?
- Money Cannot Buy Happiness: What Are Your Views?
- What Can Happiness Research Tell Us About Altruism?
- Why We’re Happier When We’re Older?
- Happiness Explained: What Human Flourishing Is and How We Can Promote It?
- Why Happiness Eludes the Modern Woman?
- How Does the Economic Crisis Influence Adolescents’ Happiness?
- Do Fulfilling Desires Lead To Happiness?
- How Does Happiness Relate to Economic Behaviour?
- Psychology Questions
- Success Ideas
- Cultural Identity Research Topics
- Virtue Essay Ideas
- Conflict Resolution Essay Topics
- Freedom Topics
- Dreaming Essay Titles
- Human Development Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 27). 189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/happiness-essay-examples/
"189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 27 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/happiness-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 27 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/happiness-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/happiness-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "189 Happiness Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 27, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/happiness-essay-examples/.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Happiness
List of essays on happiness, essay on happiness – short essay (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on happiness – for kids and children (essay 2 – 200 words), essay on happiness – 10 lines on happiness written in english (essay 3 – 250 words), essay on happiness (essay 4 – 300 words), essay on happiness – ways to be happy (essay 5 – 400 words), essay on happiness – for school students (class 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 standard) (essay 6 – 500 words), essay on happiness – ways of developing happiness (essay 7 – 600 words), essay on happiness – sources of suffering, happiness and conclusion (essay 8 – 750 words), essay on happiness – long essay on happiness (essay 9 – 1000 words).
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. When we feel positive emotions we tend to feel happy. That is what happiness is all about. Happiness is also regarded as the mental state of a person in an optimistic manner.
Every person defines happiness in his/her own manner. In whatever manner you may define happiness; the truth is that it is vital for a healthy and prosperous life.
In order to make students understand what true happiness is all about, we have prepared short essays for students which shall enlighten them further on this topic.
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 3, 4 ,5, 6 and 7 Standard).
Introduction:
Happiness is a state of mind and the feeling expressed when things are going great. It is what we feel when we get our first car, buy a new house or graduate with the best grades. Happiness should be distinguished from joy. When joy is a constant state of mind, happiness depends on events in our lives.
Importance of Happiness:
The opposite of happiness is sadness which is a state of negativity in the mindset. When we remain sad for an extended period of time it can lead to depression. To avoid this state of mind we must always remind ourselves of happenings in our lives that made us happy.
Conclusion:
Though life throws countless challenges at us on a daily basis, if we drown in those challenges we would definitely become depressed. It is important that we find positive things in our daily lives to get excited about and feel the happiness.
Happiness is a state of mind which makes you feel accomplished in life and having everything in this world without a single reason to repent. Well, although there can be no perfect definition of happiness; happiness is when you feel you’re at the top of the world where a sense of complete satisfaction prevails.
The meaning of happiness is relative and varies from people to people. For some, happiness is when you experience professional success, reunions with family and friends, eating out, reading books or watching good movies. While for others, happiness can be accomplished by some weekend activities which might help you de-stress and get the satisfaction of mind.
If you involve yourself in social activities where you help the needy and provide support to the weaker section of the society, you can experience happiness if not anything else. When a young boy flies a kite, plays with mud, and watches the nature, for him, that is the greatest happiness in the world.
The happiness of mind is often considered quite contrary to jealousy and anger which you experience once you have failed or unaccomplished any desired goal. You should always try to rehearse the ways of keeping yourself satisfied and keeping away from negativity to experience peace and happiness in life. True happiness begins where desire ends!
What is happiness? It is a state of being happy. But it does not mean to be happy all the time. Happiness is a feeling of something good that is happening in our life. We feel happy when we achieve something. But happiness is spread when our dear one is happy as well. Some people find true happiness in playing with their pets, while some may find happiness in staying engaged in creative work.
Happiness is often derived from channelizing thoughts to positive thinking. However, it is not as simple as it may sound.
To achieve the state of complete happiness one has to practice on improving the state of life by:
1. Staying contended in life with what you have. Cribbing and grumbling never lead to happiness.
2. Staying focused on the current life instead of daydreaming of the good days or old days.
3. Stop blaming for something that went terribly wrong in life. The life is all about moving on. Stop worrying and set new goals in life.
4. Being thankful to God for all the good things that you have in your life.
5. Having good people around you who can boost up positivity in your life.
Everyone desires to be happy in life. Happiness cannot be achieved without establishing complete control of one’s thoughts as it is very easy to be carried away by the waves of thoughts and emotions surrounding us. Remind yourself of the good things of your life and be thankful about it.
What is happiness? Some would state that happiness implies being well off. Others would state that for them, happiness intends to be sound. You will discover individuals saying that for them happiness implies having love in their life, having numerous companions, a great job, or accomplishing a specific objective. There are individuals, who trust that the want of a specific wish would make happiness in their life; however, it may not be so. Having true happiness is something which is desired by all.
The Path to Happiness:
There are small things which when incorporated into our daily lives, can lead us to the path of happiness. For instance, instead of thinking about problems, we should actually be thinking about the solutions. Not only will we be happier but we shall also be able to solve our problems faster. Similarly, once in a while, you start the day with the longing to achieve a few targets. Toward the day’s end, you may feel disappointed and miserable, in light of the fact that you haven’t possessed the capacity to do those things. Take a look at what you have done, not at what you have not possessed the capacity to do. Regularly, regardless of whether you have achieved a ton amid the day, you let yourself feel disappointed, due to some minor assignments you didn’t achieve. This takes away happiness from you.
Again, now and then, you go throughout the day effectively completing numerous plans, yet as opposed to feeling cheerful and fulfilled, you see what was not cultivated and feel troubled. It is out of line towards you.
Each day accomplishes something good which you enjoy doing. It may tend to be something little, such as purchasing a book, eating something you cherish, viewing your most loved program on TV, heading out to a motion picture, or simply having a walk around the shoreline. Even small things can bring great levels of happiness in our lives and motivate us for new goals.
Happiness is not what you feel from outside, rather it is something which comes from your inner soul. We should find happiness in us rather than searching for it in worldly desires.
Happiness is defined by different people in different ways. Some find happiness in having a luxurious life while some find it in having loving people around them rather than money. True happiness lies within us and our expectation of happiness. It is something that should be felt and cannot be explained in words.
Even though this simple word has a lot of meaning hidden in it, many fail to understand the real one or feel the real happiness. Finding happiness in the outer world is the main reason for this failure. Nothing can buy you happiness, whether be the favorite thing you desire for or the person you love the most or the career you build, unless and until you feel it within yourself.
Ways to be Happy:
Bring happiness and soulful life to yourself rather than expecting it from the outside world like things, money, etc. Being happy is not as easy as advised to be one happier person. To be content and happy with whatever you have and yourself it takes time and patience. You should practice to be a happier person in all moments and eventually you will notice that no sorrow can sink you down.
Whatever good or bad happened in your past shouldn’t bother your present. Learn to live today with more happiness than yesterday and forget about your past sadness for a harmonious life. Thankfulness to the life you got is another important character you should acquire to be happy. If you compare yourself with someone with better luxurious life, then you will never be happy or content and do it the other way.
Don’t depress your mind with bad and negative thoughts about yourself and around. Try to find every goodness in a situation you face and accept the things that already happened, whether good or bad. Never forget to choose merrier and positive people to be closer to you so that their vibes will also help you in being one merrier person.
Whenever you feel low and depressed never hesitate to go to those around you to find happiness. But be aware of those negative ones that may pull you even deeper into the bad thoughts. Always surround yourself with positive thinking and motivating people so that you can rise higher even from the deepest fall.
Happiness is nothing but a feeling that will be seeded into your soul only if you wish to and nothing other than yourself can indulge this feeling in you. Don’t spoil your life finding happiness somewhere else.
Happiness is a very complicated thing. Happiness can be used both in emotional or mental state context and can vary largely from a feeling from contentment to very intense feeling of joy. It can also mean a life of satisfaction, good well-being and so many more. Happiness is a very difficult phenomenon to use words to describe as it is something that can be felt only. Happiness is very important if we want to lead a very good life. Sadly, happiness is absent from the lives of a lot of people nowadays. We all have our own very different concept of happiness. Some of us are of the opinion that we can get happiness through money, others believe they can only get true happiness in relationships, some even feel that happiness can only be gotten when they are excelling in their profession.
As we might probably know, happiness is nothing more than the state of one being content and happy. A lot of people in the past, present and some (even in the future will) have tried to define and explain what they think happiness really is. So far, the most reasonable one is the one that sees happiness as something that can only come from within a person and should not be sought for outside in the world.
Some very important points about happiness are discussed below:
1. Happiness can’t be bought with Money:
A lot of us try to find happiness where it is not. We associate and equate money with happiness. If at all there is happiness in money then all of the rich people we have around us would never feel sad. What we have come to see is that even the rich amongst us are the ones that suffer depression, relationship problems, stress, fear and even anxiousness. A lot of celebrities and successful people have committed suicide, this goes a long way to show that money or fame does not guarantee happiness. This does not mean that it is a bad thing to be rich and go after money. When you have money, you can afford many things that can make you and those around you very happy.
2. Happiness can only come from within:
There is a saying that explains that one can only get true happiness when one comes to the realisation that only one can make himself/herself happy. We can only find true happiness within ourselves and we can’t find it in other people. This saying and its meaning is always hammered on in different places but we still refuse to fully understand it and put it into good use. It is very important that we understand that happiness is nothing more than the state of a person’s mind. Happiness cannot come from all the physical things we see around us. Only we through our positive emotions that we can get through good thoughts have the ability to create true happiness.
Our emotions are created by our thoughts. Therefore, it is very important that we work on having only positive thoughts and this can be achieved when we see life in a positive light.
Happiness is desired by every person. However, there are very few persons that attain happiness easily in life.
It is quite tough to get happiness in life as people usually link it with the things and the people around them. The simple fact is that happiness usually starts as well as finishes with your own life. All those people who understand this fact easily get the true happiness in their life.
Happiness in Relationships:
There are lots of people who link happiness with the money and there are few others also who link it with the personal relations. It is very important to know that if you are not happy with yourself then, it is not possible to remain happy in your relationship as well.
The problems in the relationship have been increasing speedily and the main cause behind it is the huge amount of expectation that we have from the other individual. We always want them to make us feel happy. For example, some people feel happy if their partner plans a surprise for them or if he/she buy them a new dress. But all these things are not a true source of happiness in life.
Ways of Developing Happiness:
The lack of happiness in the relationship not only exists in couples but also in the relationship of friends, sister – brother or parent-child.
The following are the few ways that help in creating happiness in the relationships:
1. Pay Attention to Yourself:
You should always pay attention to yourself to get happiness. You should not give importance to any other person in your life in comparison to yourself and also expect the same from that person. Giving too much importance to the other and not receiving anything back from them makes a person disappointed and happiness gets lost.
2. Have some Initiative:
You can make the plan of traveling outside yourself. Don’t wait for your parent, partner or kid to take you outside. You can ask them to come along with you if they want. But, if they decline your offer then, don’t get discouraged and carry on your trip plan along with full happiness.
3. Provide some Space:
It is necessary to provide some amount of space to every individual and spend some time with oneself. It helps in creating happiness.
Happiness is Necessary for Good Life:
It does not matter that whether you are a working expert, a schoolchild, a retired person or a housewife, happiness is necessary for everybody to live a good and happy life. Happiness is essential for an individual’s emotional comfort. A person who is not fit emotionally will feel an impact on his complete health that will drain very soon.
Unluckily, despite the fact that happiness is tremendously necessary, people do not give so much importance to all those habits which can keep them happy. They are so excessively captivated inside their professional lives as well as other nuts and bolts of life that they overlook to relish the happy memories of their life. It is also the main reason that problems like anxiety, stress, and depression are increasing gradually in people’s lives today.
Happiness is an internal feeling. It is a healthy emotion. Happiness helps us to stay fit both mentally and physically. Happiness helps in lowering stress and keeping away from any health issues. The reason of happiness may be different for different person. You just need to find out what actually makes you happy. So, if you want real happiness in life then, you need to understand that only you can make yourself happy.
“There is no way to happiness, happiness is the way” this sentence has been attributed to Buddha. Well, at least that’s what it says on one sticker in my dorm room. The fact is that man has occupied himself with the path to happiness for millennia. Something happened during our evolution that made us deeply question the purpose of our existence. People like Buddha are part of the answer, or at least they try to give us the answer.
Since these questions have troubled us there have been many who sought to answer them and by doing so, they formed philosophies and religions. The search for earthly happiness will make many do incredible deeds but if this energy is used in the wrong way it can cause great suffering. How can we know which recipe for happiness is the best one and what we should devote our time and attention to? The trick is, there is no right answer and as the first sentence of this essay states, there is no way to be happy because being happy is the way. That’s how I got my head around this problem, let me explain some more.
Source of Suffering:
At the expense of sounding Buddhist, when you think about most of the things that make us unhappy are material in nature. They are the things that we really do not need but they make us feel happy. This notion is not just something the wise man from the 6 th century BC India expressed but many more have said this before and after him. Socrates and Jesus to name just a few.
What I find interesting in the struggle for happiness is the paradox present in the instructions to reach it. One has a thought all through life to be good and hard working so he can get the things he wants and needs later on in life but then as you start to struggle for the money you realize that your life is turning into a money grabbing game. So, the source of happiness and stability becomes the source of all your anxiety and aggression. Naturally, we can see how some people thought that all material things stand on the path to our happiness.
But what about the immaterial, what if you are in love with someone you are not supposed to love? The above instruction would tell you to surrender your heart’s desire and you will be free from constraints. Is this happiness? Or is it the struggle to do and achieve the impossible the real source of happiness?
Source of Happiness:
People often forget that they are animals and like all of them they have a logic to their nature and their own specific needs. Like all the other animal’s people are caught in the struggle for existence and sometimes surviving the day can be a real ordeal if you get caught in the wrong circumstances. Men has made himself safe from most of the things that could have harmed him in nature but in doing so he forgot what he has made.
Think about the present from a historical perspective. Even a hundred years ago most people lost up to 80% of all their children to diseases, clean water was a rarity for most of our existence, and people actually had to labor to make food and to have enough to feed their family all through the year. The fact is we have a lot to be grateful for in the present age and the fact that some of us are unhappy because we do not have all our heart’s desires is just a symptom of collective infancy. Having all of your loved ones around you, with a roof to shelter under and with lots of delicious food is the only source of happiness man needs everything else should just be a bonus.
Happiness cannot be found by rejecting everything that is material or by earning more money then you can spend. The trick is to find balance by looking at yourself and the lives of people around you and by understanding that there is a lot to be grateful for, the trick is to stop searching for a path and to understand that we are already walking on one. As long as we are making any type of list of the prerequisite for our life of happiness, we will end up unsatisfied because life does not grant wishes we are the ones that make them come true. Often the biggest change in our lives comes from a simple change of perspective rather than from anything we can own.
Happiness is the state of emotional wellbeing and being contented. Happiness is expressed through joyful moments and smiles. It is a desirable feeling that everybody want to have at all times. Being happy is influenced by situations, achievements and other circumstances. Happiness is an inner quality that reflects on the state of mind. A peaceful state of mind is considered to be happiness. The emotional state of happiness is mixture of feelings of joy, satisfaction, gratitude, euphoria and victory.
How happiness is achieved:
Happiness is achieved psychologically through having a peaceful state of mind. By a free state of mind, I mean that there should be no stressful factors to think about. Happiness is also achieved through accomplishment of goals that are set by individuals. There is always happiness that accompanies success and they present feelings of triumph and contentment.
To enable personal happiness in life, it is important that a person puts himself first and have good self-perception. Putting what makes you happy first, instead of putting other people or other things first is a true quest towards happiness. In life, people tend to disappoint and putting them as a priority always reduces happiness for individuals. There is also the concept of practicing self-love and self-acceptance. Loving oneself is the key to happiness because it will mean that it will not be hard to put yourself first when making decisions.
It is important for an individual to control the thoughts that goes on in their heads. A peaceful state of mind is achieved when thoughts are at peace. It is recommended that things that cause a stressful state of mind should be avoided.
Happiness is a personal decision that is influenced by choices made. There is a common phrase on happiness; “happiness is a choice” which is very true because people choose if they want to be happy or not. Happiness is caused by circumstances and people have the liberty to choose those circumstance and get away from those that make them unhappy.
Happiness is also achieved through the kind of support system that an individual has. Having a family or friends that are supportive will enable the achievement of happiness. Communicating and interacting with the outside world is important.
Factors Affecting Happiness:
Sleep patterns influence the state of mind thus influence happiness. Having enough sleep always leads to happy mornings and a good state of mind for rest of the day. Sleep that is adequate also affects the appearance of a person. There is satisfaction that comes with having enough sleep. Enough rest increases performance and productivity of an individual and thus more successes and achievements are realized and happiness is experienced.
Another factor affecting happiness is the support network of an individual. A strong support network of family and friends results in more happiness. Establishing good relationships with neighbors, friends and family through regular interactions brings more happiness to an individual. With support network, the incidences of stressful moments will be reduced because your family and friends will always be of help.
Sexual satisfaction has been established to affect happiness. It is not just about getting the right partner anymore. It is about having a partner that will satisfy you sexually. There is a relationship between sex and happiness because of the hormones secreted during sexual intercourse. The hormone is called oxytocin and responsible for the happiness due to sexual satisfaction. Satisfaction also strengthens the relationships between the partners and that creates happiness.
Wealth also plays a significant role in happiness. There is a common phrase that is against money and happiness: “money cannot buy happiness” is this true? Personally, I believe that being financially stable contributes to happiness because you will always have peace of mind and many achievements. Peace of mind is possible for wealthy people because they do not have stressors here and then compared to poor people. Also, when a person is wealthy, they can afford to engage in luxurious activities that relaxes the mind and create happiness. For a person to be wealthy, they will have had many achievements in life. These achievement make them happy.
A good state of health is an important factor that influences the happiness of individuals. A healthy person will be happy because there are no worries of diseases or pain that they are experiencing. When a person is healthy, their state of mind is at peace because they are not afraid of death or any other health concerns. Not only the health of individuals is important, but also the health of the support system of the person. Friends and family’s state of health will always have an impact on what we feel as individuals because we care about them and we get worried whenever they are having bad health.
Communication and interactions are important in relation to an individual’s happiness. Having a support system is not enough because people need to communicate and interact freely. Whenever there are interactions like a social gathering where people talk and eat together, more happiness is experienced. This concept is witnessed in parties because people are always laughing and smiling in parties whenever they are with friends.
Communication is key to happiness because it helps in problem solving and relieving stressors in life. Sharing experiences with a support system creates a state of wellbeing after the solution is sought. Sometime when I am sad, I take my phone and call a friend or a family member and by the time the phone call is over, I always feel better and relieved of my worries.
Happiness is an important emotion that influences how we live and feel on a daily basis. Happiness is achieved in simple ways. People have the liberty to choose happiness because we are not bound by any circumstances for life. Factors that influence happiness are those that contribute to emotional wellbeing. Physical wellbeing also affects happiness. Every individual finds happiness in their own because they know what makes them happy and what doesn’t.
Emotions , Happiness , Psychology
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Which is More Important in Life: Love or Money | Essay
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Solar Energy
- Essay on Biodiversity
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Happiness Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on happiness.
Happiness is something which we can’t describe in words it can only be felt from someone’s expression of a smile. Likewise, happiness is a signal or identification of good and prosperous life. Happiness is very simple to feel and difficult to describe. Moreover, happiness comes from within and no one can steal your happiness.

Can Money Buy You Happiness?
Every day we see and meet people who look happy from the outside but deep down they are broken and are sad from the inside. For many people, money is the main cause of happiness or grief. But this is not right. Money can buy you food, luxurious house, healthy lifestyle servants, and many more facilities but money can’t buy you happiness.
And if money can buy happiness then the rich would be the happiest person on the earth. But, we see a contrary image of the rich as they are sad, fearful, anxious, stressed, and suffering from various problems.
In addition, they have money still they lack in social life with their family especially their wives and this is the main cause of divorce among them.
Also, due to money, they feel insecurity that everyone is after their money so to safeguard their money and them they hire security. While the condition of the poor is just the opposite. They do not have money but they are happy with and stress-free from these problems.
In addition, they take care of their wife and children and their divorce rate is also very low.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Happiness Comes from Within
As we now know that we can’t buy happiness with money and there is no other shortcut to happiness. It is something that you feel from within.
In addition, true happiness comes from within yourself. Happiness is basically a state of mind.
Moreover, it can only be achieved by being positive and avoiding any negative thought in mind. And if we look at the bright side of ourselves only then we can be happy.
Happiness in a Relationship
People nowadays are not satisfied with their relationship because of their differences and much other reason. But for being happy in a relationship we have to understand that there are some rules or mutual understanding that keeps a relationship healthy and happy.
Firstly, take care of yourself then your partner because if you yourself are not happy then how can you make your partner happy.
Secondly, for a happy and healthy relationship give you partner some time and space. In addition, try to understand their feeling and comfort level because if you don’t understand these things then you won’t be able to properly understand your partner.
Most importantly, take initiative and plan to go out with your partner and family. Besides, if they have plans then go with them.
To conclude, we can say that happiness can only be achieved by having positive thinking and enjoying life. Also, for being happy and keeping the people around us happy we have to develop a healthy relationship with them. Additionally, we also have to give them the proper time.
FAQs about Happiness
Q.1 What is True Happiness? A.1 True happiness means the satisfaction that you find worthy. The long-lasting true happiness comes from life experience, a feeling of purpose, and a positive relationship.
Q.2 Who is happier the rich or the poor and who is more wealthy rich or poor? A.2 The poor are happier then the rich but if we talk about wealth the rich are more wealthy then the poor. Besides, wealth brings insecurity, anxiety and many other problems.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Will Retiring Early Make You Happier? It’s Complicated
Many people hate their jobs. But retiring early may not bring happiness.
- Newsletter sign up Newsletter

Editor’s note: "Will Retiring Early Make You Happier" is part five of an ongoing series throughout this year focused on how to retire early and the FIRE ("Financial Independence, Retire Early") movement. The introduction to the series is How to Retire Early in Six Steps . The second article is How to Retire Early by 40 . The third is How to Retire Early by 50 and the fourth is Retire Early for Adventure .
Research shows that anxiety and stress peak on Mondays , but it all starts to kick in the night before. There’s even a name for it: the “Sunday scaries.”
Meanwhile, in the greener pastures of retirement, people report higher levels of happiness. So, it seems logical: the earlier you retire, the happier you’ll be, right?
Subscribe to Kiplinger’s Personal Finance
Be a smarter, better informed investor.

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free E-Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
That's what Dr. Jordan Grumet believed when he discovered the financial independence, retire early (FIRE) movement. Burned out by the relentless demands of running his own medical practice, he dedicated himself to saving aggressively and achieved financial independence at 45. Goodbye, sleepless nights and Sunday evening dread.
But the reality was different. “Instead of feeling joy and excitement, I fell into a pit of anxiety and depression,” he recalls.
The FIRE movement advocates that you can achieve financial independence and retire early by saving 25 times your annual living expenses. That savings rate far surpasses what most Americans have stashed in their 401(k) . Still, the promise is alluring: do whatever you want with your time without worrying about making money.
Sleeping in. Hitting the gym when it’s empty. Traveling without the crowds. It sounds perfect, doesn't it?
So, does retiring early actually make you happier?
Yes, no, maybe.
The stories of Dr. Grumet and other FIRE achievers show that the relationship between financial independence, early retirement, and happiness is complex. Here's why.
The joys of retiring early
Freedom, enjoyment, stress-free.
These are the three positive words most commonly associated with retirement, according to a Transamerica Center for Retirement Studies report .
Jonathan Geserick, who achieved FIRE with his wife in 2023 at ages 46 and 45, echoes these sentiments. He says he feels happier these days, exclaiming, “The freedom to do something different rather than work at a job you hate is an awesome feeling.”
Like nearly 70% of U.S. workers who dislike their jobs, Geserick felt burned out working at a Fortune 500 company. Research has found burnout associated with a variety of physical and mental health issues. It’s no wonder many turn to the FIRE movement to escape their 9-5 grind.
A study in the Journal of Consumer Marketing identified “escapism & freedom from the current workplace” and “concern for physical & mental well-being” as primary motivators for adopting FIRE.
Furthermore, financial independence frees one of the stresses of money and job insecurity. With this freedom comes a greater sense of agency, which research suggests contributes to happiness.
Geserick has used his newfound flexibility to focus on his health, consistently going to the gym and losing significant weight, another cornerstone of happiness. Consider the 2024 MassMutual Retirement Happiness Study shows that retirees who prepare financially and focus on their health before retirement report higher happiness levels.
Geserick believes FIRE offers a unique advantage: “I have an extra 20 years in my prime to enjoy life rather than being tied to a desk.”
Dr. Grumet shares a similar sentiment on the joys of freedom: “I haven't had Sunday evening anxiety since I worked full-time,” he says.
However, with this newfound freedom came the struggle with some of the realities of early retirement.
The realities of early retirement
If you dislike your job or simply feel dissatisfied with life, it’s easy to think that financial independence will bring lasting happiness. But when you do make it, you may feel a temporary blip of euphoria that then fades, a psychological phenomenon called the “arrival fallacy.”
Ruminating about his own transition out of full-time work, Dr. Grumet says, “Finding out I was financially independent was a relief, but then I was left contemplating who I was and what was important to me.”
Studies suggest that those with a strong professional identity often struggle in retirement. This is a common experience among early retirees.
Researchers at the business school INSEAD found that while entrepreneurs who achieve FIRE report joy and freedom, they also face feelings of emptiness and anxiety due to limitless possibilities. They often grapple with the question, “What do I do now?” and search for new identities and purposes.
To put it in stark perspective: retiring at 40 and living to 80 means having around 350,400 hours to fill.
“Walking away from medicine was one of the hardest things I ever did. I spent the first four decades of my life, as well as countless hours in pursuit of this one thing. This one thing that became my whole sense of purpose and identity,” Dr. Grumet says.
Identity isn’t the only thing that may need to be replaced. The famous Harvard Study of Adult Development found that strong relationships are the most important contributor to happiness. Early retirees may struggle with loneliness if their peers are still working, and retired spouses can also face difficulties if their partners continue to work.
Ultimately, if your personal life isn’t fulfilling before retirement, it likely won't improve afterward. People who define themselves by their careers may face an identity crisis in retirement, potentially leading them back to work or into personal turmoil.
Conversely, if work or money concerns are the primary obstacles in an otherwise happy life, removing those stressors through FIRE can lead to greater happiness.
The key ingredients of happiness
The question of whether FIRE leads to happiness is complex because happiness itself is always a work in progress.
Arthur Brooks , a social scientist and Harvard professor, has studied happiness for decades. In his book Build the Life You Want , co-authored with Oprah Winfrey, he defines happiness not as a destination but as a direction, something that you should aim to increase without an end goal in mind.
Brooks identifies three key “macronutrients” for long-term happiness. First is enjoyment, which involves engaging in memorable activities that bring joy, especially with people you love.
The second is satisfaction, best described as the sense of accomplishment after achieving a goal, such as reaching financial independence. But it can include hobbies or other active pursuits that provide opportunities for growth.
Third and perhaps most important is purpose, or that which gives your life meaning.
Interestingly, many people who achieve FIRE spend their time on activities resembling work, such as blogging, podcasting, consulting and launching businesses. They find fulfillment not in the money but in the purpose these activities provide.
Dr. Grumet, for example, works 10 hours a week in hospice care because it “feels purposeful.” He also engages in podcasting , writing and public speaking, which bring him joy and meaning. “I don't consider anything I do work; I mostly consider it fun,” he says.
Geserick never intended to fully retire after achieving FIRE. He now spends 25-30 hours a week running an online estate attorney business. “My hobby is starting new businesses. Some fail, some succeed, but I enjoy the process,” he explains.
Just like maintaining a balanced diet, these happiness “macronutrients” must be continuously incorporated into your life.
Dr. Grumet elegantly put it this way: “When we reach financial independence is not as important as building a life of purpose, identity and connections, and then using a financial framework to spend your time engaging in these things.”
So, FIRE may not be the secret to happiness. But if happiness is truly a journey, then for those of us who hate Mondays, FIRE can help give us a head start.
- The Average 401(k) Balance by Age
- How to Retire Early in Six Steps
- How to Retire Early by 50
- When Will Social Security and Medicare Trust Fund Run Out of Money?
To continue reading this article please register for free
This is different from signing in to your print subscription
Why am I seeing this? Find out more here
Jacob Schroeder is a financial writer covering topics related to personal finance and retirement. Over the course of a decade in the financial services industry, he has written materials to educate people on saving, investing and life in retirement. With the love of telling a good story, his work has appeared in publications including Yahoo Finance, Wealth Management magazine, The Detroit News and, as a short-story writer, various literary journals. He is also the creator of the finance newsletter The Root of All ( https://rootofall.substack.com/ ), exploring how money shapes the world around us. Drawing from research and personal experiences, he relates lessons that readers can apply to make more informed financial decisions and live happier lives.

These questions go beyond the basics and may actually help you decide whether a particular financial planner is right for you.
By Evan T. Beach, CFP®, AWMA® Published 15 June 24
Stocks slump as a geopolitical stress, weaker consumer sentiment weighs on risk assets.
By Dan Burrows Published 14 June 24
- Contact Future's experts
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Advertise with us
Kiplinger is part of Future plc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site . © Future US, Inc. Full 7th Floor, 130 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036.
A researcher fired by OpenAI published a 165-page essay on what to expect from AI in the next decade. We asked GPT-4 to summarize it.
- Leopold Aschenbrenner, a fired OpenAI researcher, published a 165-page essay on the future of AI.
- Aschenbrenner's treatise discusses rapid AI progress, security implications, and societal impact.
- Here's what GPT-4 says about Aschenbrenner's predictions.

Over the past few months, several employees have left OpenAI , citing concerns about the company's commitment to safety.
Besides making pithy exit announcements on X, they haven't said much about why they're worried about OpenAI's approach to development — or the future of artificial intelligence.
That is until earlier this week, when Leopold Aschenbrenner, a researcher who was fired from OpenAI in April, published his thoughts on the AI revolution in an epic 165-page treatise.
Aschenbrenner worked on OpenAI's superalignment team, which was tasked with mitigating AI risks. Aschenbrenner said OpenAI fired him for leaking information about the company's readiness for artificial general intelligence .
For his part, Aschenbrenner said the information he shared was "totally normal" and that OpenAI might have just been looking for a reason to fire him. He was one of several employees who refused to sign a letter calling for CEO Sam Altman's return after the board briefly ousted Altman last year.
Aschenbrenner's essay doesn't appear to include sensitive details about OpenAI. Instead, as Aschenbrenner writes on the dedication page, it's based on "publicly available information, my own ideas, general field knowledge, or SF gossip."
Business Insider uploaded the tract to OpenAI's GPT-4 model . We asked it to summarize the work and relay the most significant takeaways. We also gently requested that the bot keep its summary clear and concise.
Here's ChatGPT's 57-word summary of Aschenbrenner's essay
ChatGPT distilled the essay into 57 words that outlined Aschenbrenner's views on the evolution of AI.
"Leopold Aschenbrenner's essay discusses the transformative potential of artificial general intelligence (AGI) and superintelligence, and forecasts significant advancements in AI technology in the near future. Aschenbrenner, formerly associated with OpenAI, outlines how the progression from current AI models like GPT-4 to AGI could occur much faster than anticipated, based on trends in computational power and algorithmic efficiency."
ChatGPT then offered four key takeaways from Aschenbrenner's essay
Rapid Progress in AI
Related stories
"Aschenbrenner argues that AI development is accelerating at an unprecedented rate. He predicts that by 2027, AI models could reach the capabilities of human AI researchers and engineers, potentially leading to an intelligence explosion where AI surpasses human intelligence."
Economic and Security Implications
"The essay highlights the immense economic and security implications of these advancements. Aschenbrenner points out that trillions of dollars are being invested into developing the infrastructure needed to support these AI systems, such as GPUs, data centers, and power generation. He also emphasizes the critical need for securing these technologies to prevent misuse, particularly by state actors like the CCP."
Technical and Ethical Challenges
"The essay discusses the significant challenges in controlling AI systems smarter than humans, referring to this as the 'superalignment' problem. Managing this will be crucial to prevent catastrophic outcomes."
Predictions and Societal Impact
"Aschenbrenner suggests that few people truly understand the scale of change that AI is about to bring. He discusses the potential for AI to reshape industries, enhance national security, and pose new ethical and governance challenges."
There's more
As Aschenbrenner wrote, there are probably only a few hundred people, most of them in AI labs in San Francisco, who have "situational awareness" about the industry. These people will most likely have the best insight into how AI will reshape the years ahead.
Aschenbrenner, as one of them, seems to believe AI will assume a critical role in national security.
We followed up our original prompt by asking ChatGPT to summarize the predictions Aschenbrenner made in his essay.
Here's how ChatGPT broke it down.
- AGI by 2027: "Aschenbrenner predicts that artificial general intelligence (AGI) is strikingly plausible by 2027, highlighting the rapid progress from GPT-2 to GPT-4, which saw AI models advancing from preschool-level to smart high-schooler abilities in just four years. He expects a similar leap in the next few years based on consistent improvements in compute and algorithmic efficiency."
- Superintelligence Following AGI: "Post-AGI, the author anticipates an 'intelligence explosion,' where AI rapidly advances from human-level to superhuman capabilities. This transition is expected to be fueled by AI's ability to automate and accelerate its own research and development."
- Trillion-Dollar AI Clusters: "Economically, Aschenbrenner suggests that the AI sector will see an increase in investment into trillion-dollar compute clusters as corporations and governments prepare for the implications of AGI and superintelligence."
- National and Global Security Dynamics: "There are predictions about intense national security measures being enacted to manage and control AI developments. The competition, particularly with the Chinese government, could intensify, possibly leading to an 'all-out war' if not managed properly."
- Superalignment Challenges: "One of the most critical predictions is the struggle with 'superalignment' — the challenge of keeping superintelligent AI aligned with human values and interests. This problem is anticipated to be one of the central hurdles as AI reaches and surpasses human intelligence levels."
- Societal and Economic Transformations: "Aschenbrenner expects AI to have a profound impact on society and the economy, potentially leading to a restructuring of industries and the job market due to AI's capability to perform tasks currently managed by humans."
- The Project Involvement by the US Government: "Predictions include the US government becoming significantly involved in AI development by around 2027-2028 through a dedicated AGI project, likely due to the strategic importance of AI technology."
- Technological Mobilization: "He anticipates a mobilization of technological and industrial resources similar to historical wartime efforts, focusing on AI and its supporting infrastructure as a priority for national policy."
Here's the full prompt we used:
Role: Act as an editor. Task: Read the attached essay about former OpenAI researcher Leopold Aschenbrenner. Instructions: Summarize the essay, highlighting the most significant takeaways. Focus on key contributions, research areas, and any notable impacts on the field. Ensure the summary is concise yet comprehensive, providing a clear understanding of Aschenbrenner's work and influence.
Watch: What is ChatGPT, and should we be afraid of AI chatbots?
- Main content
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
To Understand Elon Musk’s Descent, Look at His $46 Billion Pay Package

By J. Bradford DeLong
Dr. DeLong teaches economic history at the University of California, Berkeley, and is the author of “Slouching Towards Utopia: An Economic History of the Twentieth Century.”
This article has been updated to reflect news developments.
Elon Musk is not just another inconsequential Silicon Valley billionaire.
Most of his inconsequential peers have two primary accomplishments: showing up at the right place at the right time and being sufficiently arrogant to continue the course rather than diversify. Had their shoes been empty, someone else would have stepped into them, and things would have been much the same.
But Mr. Musk changed the world.
He wanted to jump-start the decarbonization of human civilization’s energy. He succeeded. He drove Tesla to create the electric vehicle industry as we know it. Yes, he overpromised. But he often overdelivered and overdelivered spectacularly. Truly wonderful things happened with Tesla’s performance as a technology inventor, deliverer and deployer.
But “happened” is in the past tense. Much has changed since 2018, the year Tesla dreamed up an unorthodox pay package that, in theory, tied Mr. Musk’s pay to the company’s performance. Problem is, the performance was not for making high-quality cars or making affordable cars or making cars at scale. The performance was for pushing Tesla’s stock price up.
This pay package was, I think, bad for Mr. Musk. And it was, I am sure, bad for Tesla and, by extension, our nation’s crucial fight against global warming, by far. On Thursday, Tesla shareholders reapproved this pay package , one that would hand Mr. Musk roughly $46 billion. I believe this pay package helped drive Mr. Musk’s descent from visionary business leader to bizarre carnival barker. I wish that this set of incentives and responses hadn’t just been validated.
Here I need to back up and tell you what meme stocks are. The standard example is GameStop, a company that runs about 4,000 video game and electronics stores. Trading at $5 a share at the start of December 2020, its price rose to a staggering roughly $150 a share at the end of January 2021. Mr. Musk joined the fun by tweeting one word — “Gamestonk!!” — and the shares soared to $483 two days later, before beginning a long, jagged decline. As of the start of 2024, it was almost $17 a share after a four-for-one stock split, far above the $5 of 2020, even though nothing much had changed about its (struggling) business. And a recent revival of GameStop mania has since pushed it up to $30 a share.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Waldinger is a co-author of The Good Life: Lessons from the world's longest scientific study of happiness. In participating regions, you'll also hear a local news segment to help you make sense of ...
A study in the U.K., the Environmental Risk (E-Risk) Longitudinal Twin Study, recently reported on the connections between loneliness and poorer health and self-care in young adults. This ongoing ...
Happiness. What is the key to finding happiness? The Harvard community explores the physical, mental, social, and spiritual aspects of living a life filled with joy. Explore moments of joy across campus Learn how to be happy. Is there a formula for happiness, and can you apply it to your own life? Professor Arthur Brooks thinks so.
Equanimity is an even-tempered state of mind that enables you to ride life's challenges with calmness and serenity, instead of being tossed about like a ship in a storm. Equanimity arises when ...
Modern psychology describes happiness as subjective wellbeing, or " people's evaluations of their lives and encompasses both cognitive judgments of satisfaction and affective appraisals of moods and emotions " (Kesebir & Diener, 2008, p. 118). The key components of subjective wellbeing are: Life satisfaction.
For example, a study by Lingnan University's Centre for Public Studies (2015) showed that there was an increase in the happiness index for people with a monthly household salary ranging from $10,000 to $20,000 by 7% while those with a monthly income less than $10,000 rose by 3%. Interestingly, those with high-income brackets of between ...
Happiness is often defined as "a state of well-being and con-tentment" (Merriam-Webster, n.d.). It is perhaps one of the most ... key dimensions of core values (i.e., self-transcendence, self-enhancement, openness to experience, and conservation; Tamir et al., 2016). We demonstrated that, across cultures, people desire
Happiness includes the ability to acknowledge and embrace every emotion, even the unpleasant ones. It involves seeing the big picture, rather than getting stuck in the details. Overall, being ...
The chapters in this section explore some of the central ideas about happiness from the history of philosophy, as well as some of the key methodological contributions of philosophy to current debates about happiness. The historical chapters show that there has been widespread disagreement about happiness, point out the importance of avoiding ...
His most recent book is The Science of Happiness: Seven Lessons for Living Well (2024). Edited by Nigel Warburton. 2,900 words. Syndicate this essay. In 2018, a tragic period enveloped the University of Bristol, when several students killed themselves related to work stress. Suicide is usually the ultimate culmination of a crisis in mental ...
Two key components of happiness (or subjective well-being) are: The balance of emotions: Everyone experiences both positive and negative emotions, feelings, and moods. Happiness is generally linked to experiencing more positive feelings than negative ones. Life satisfaction: This relates to how satisfied you feel with different areas of your ...
Finding happiness through needs satisfaction. One prominent theory of happiness posits that to be happy, we must engage in behaviors that satisfy our three core human needs (Ryan & Deci, 2008): the need for competence (feeling effective); the need for autonomy (the feeling of being the origin of one's behavior); and.
Opt for foods which promote gut health instead of processed or junk food options for improved mood, better metabolism and to keep disease at bay. 2. Practise mindfulness. "We're happiest when we focus on the present moment, and the least happy when the mind is wandering", reveals researcher Matt Killingsworth.
Scientific studies show that helping others can contribute to our happiness in different ways. These include: experiencing more positive emotions and satisfaction with life [5]; increasing our sense of meaning [6], and boosting our self-confidence. It can reduce stress and help us feel calmer too. [7]
One would say that happiness is to be with a loved one, the second would say that happiness is the stability, and the third, on the contrary, would say that happiness is the unpredictability. For someone, to be happy is to have a lot of money while for others - to be popular. All in all, there are plenty of different understandings of happiness.
Personal values refer to the beliefs, principles or ideas that are important to people's lives. We investigated the associations between personal values and happiness. We inquired about the importance of four different categories of personal values: prioritizing social relationships, extrinsic achievements, physical health, and spirituality. Data were drawn from the Korean General Social ...
Vacationing in Cuba might cost $2,000 in money and about a week in time, but if one has no time left because of work, the $2,000 is basically worthless. At the end of the day, time management is all about putting your time where your mouth is, and matching your time investments with your priorities in life is a huge first step toward happiness.
ProStock-Studio/Getty Images. Summary. Although some studies show that wealthier people tend to be happier, prioritizing money over time can actually have the opposite effect. But even having just ...
Key points. Many Western nations are becoming unhappier, data suggests. Research supports the notion that well-being goes beyond material wealth. Our modern definition of happiness may have it all ...
😊 Key Points to Use to Write an Outstanding Happiness Essay. Writing a happiness essay may seem easy at first, but many students fail to achieve a high grade because their responses are too general. To avoid falling in this trap, read this post and take note of the key points to write about.
16. Breathe in fresh air. Heading outdoors, even if you're not exercising, is powerful happiness medicine. In fact, last year Rubin challenged her podcast listeners to a "Go outside 23 in ...
Performing acts of kindness. Increasing social connections, including initiating conversations with people you don't know. Savouring experiences. Deliberately drawing attention to the positive events and aspects of the day. Practising feeling grateful, and endeavouring to thank people. Being physically active.
To achieve the state of complete happiness one has to practice on improving the state of life by: 1. Staying contended in life with what you have. Cribbing and grumbling never lead to happiness. 2. Staying focused on the current life instead of daydreaming of the good days or old days.
Now known as "Einstein's Theory of Happiness" the small handwritten note sold on October 24th, 2017 for a whole $1.56 million at an auction in Jerusalem. Some would say its price defeats its ...
500+ Words Essay on Happiness. Happiness is something which we can't describe in words it can only be felt from someone's expression of a smile. Likewise, happiness is a signal or identification of good and prosperous life. Happiness is very simple to feel and difficult to describe. Moreover, happiness comes from within and no one can steal ...
Optimism is the key to happiness. It helps us appreciate everything we have in life. It is within appreciation that we find happiness. Optimism is full of positive possibilities. It leads a person to happiness by reducing stress and pulling people towards a more positive future. Helen Keller wrote an essay on Optimism in 1903.
The key ingredients of happiness The question of whether FIRE leads to happiness is complex because happiness itself is always a work in progress. Arthur Brooks , a social scientist and Harvard ...
Leopold Aschenbrenner, a fired OpenAI researcher, published a 165-page essay on the future of AI. Aschenbrenner's treatise discusses rapid AI progress, security implications, and societal impact ...
The performance was for pushing Tesla's stock price up. This pay package was, I think, bad for Mr. Musk. And it was, I am sure, bad for Tesla and, by extension, our nation's crucial fight ...
Oman's potential nonhydrocarbon real GDP growth has trended downward since the global financial crisis, with a negative contribution from total factor productivity. This paper estimates productivity gains associated with structural reforms and identifies key binding constraints and reform priorities to boost productivity in Oman. Our results show that reforms to reduce the state's ...