Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- Stanford Children’s Expands Simulation Innovation Center to Enhance Skills, Confidence, and Teamwork
- A Night of Glitz and Glamour for Stanford Children’s Patients
- Practical Tips for Dealing With Bedwetting
- Understanding Culture to Address Mental Health in the AANHPI Community
- Local Gardener Lifts Spirits by Grooming on the Hospital’s Animal Topiaries

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford School of Medicine
- Stanford Health Care
- Stanford University
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Opinion | Social-Emotional Learning
If we’re serious about student well-being, we must change the systems students learn in, here are five steps high schools can take to support students' mental health., by tim klein and belle liang oct 14, 2022.

Shutterstock / SvetaZi
This article is part of the upcoming guide: Making Sense of K-12 Student Mental Health.
Educators and parents started this school year with bated breath. Last year’s stress led to record levels of teacher burnout and mental health challenges for students.
Even before the pandemic, a mental health crisis among high schoolers loomed. According to a survey administered by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2019, 37 percent of high school students said they experienced persistent sadness or hopelessness and 19 percent reported suicidality. In response, more than half of all U.S. states mandated that schools have a mental health curriculum or include mental health in their standards .
As mental health professionals and co-authors of a book about the pressure and stress facing high school students, we’ve spent our entire careers supporting students’ mental health. Traditionally, mental health interventions are individualized and they focus on helping students manage and change their behaviors to cope with challenges they’re facing. But while working with schools and colleges across the globe as we conducted research for our book , we realized that most interventions don’t address systemic issues causing mental health problems in the first place.
It’s time we acknowledge that our education systems are directly contributing to the youth mental health crisis. And if we are serious about student well-being, we must change the systems they learn in.
Here are five bold steps that high schools can take to boost mental health.
Limit Homework or Make it Optional
Imagine applying for a job, and the hiring manager informs you that in addition to a full workday in the office, you’ll be assigned three more hours of work every night. Does this sound like a healthy work-life balance? Most adults would consider this expectation ridiculous and unsustainable. Yet, this is the workload most schools place on high school students.
Research shows that excessive homework leads to increased stress, physical health problems and a lack of balance in students' lives. And studies have shown that more than two hours of daily homework can be counterproductive , yet many teachers assign more.
Homework proponents argue that homework improves academic performance. Indeed, a meta-analysis of research on this issue found a correlation between homework and achievement. But correlation isn’t causation. Does homework cause achievement or do high achievers do more homework? While it’s likely that homework completion signals student engagement, which in turn leads to academic achievement, there’s little evidence to suggest that homework itself improves engagement in learning.
Another common argument is that homework helps students develop skills related to problem-solving, time-management and self-direction. But these skills can be explicitly taught during the school day rather than after school.
Limiting homework or moving to an optional homework policy not only supports student well-being, but it can also create a more equitable learning environment. According to the American Psychological Association, students from more affluent families are more likely to have access to resources such as devices, internet, dedicated work space and the support necessary to complete their work successfully—and homework can highlight those inequities .
Whether a school limits homework or makes it optional, it’s critical to remember that more important than the amount of homework assigned, is designing the type of activities that engage students in learning. When students are intrinsically motivated to do their homework, they are more engaged in the work, which in turn is associated with academic achievement.
Cap the Number of APs Students Can Take
Advanced Placement courses give students a taste of college-level work and, in theory, allow them to earn college credits early. Getting good grades on AP exams is associated with higher GPAs in high school and success in college, but the research tends to be correlational rather than causational.
In 2008, a little over 180,000 students took three or more AP exams. By 2018, that number had ballooned to almost 350,000 students .
However, this expansion has come at the expense of student well-being.
Over the years, we’ve heard many students express that they feel pressure to take as many AP classes as possible, which overloads them with work. That’s troubling because studies show that students who take AP classes and exams are twice as likely to report adverse physical and emotional health .
AP courses and exams also raise complex issues of equity. In 2019, two out of three Harvard freshmen reported taking AP Calculus in high school, according to Jeff Selingo, author of “ Who Gets In and Why: A Year Inside College Admissions ,” yet only half of all high schools in the country offer the course. And opportunity gaps exist for advanced coursework such as AP courses and dual enrollment, with inequitable distribution of funding and support impacting which students are enrolling and experiencing success. According to the Center for American Progress, “National data from the Civil Rights Data Collection show that students who are Black, Indigenous, and other non-Black people of color (BIPOC) are not enrolled in AP courses at rates comparable to their white and Asian peers and experience less success when they are—and the analysis for this report finds this to be true even when they attend schools with similar levels of AP course availability.”
Limiting the number of AP courses students take can protect mental health and create a more equitable experience for students.
Eliminate Class Rankings
In a study we conducted about mental health problems among high school girls, we found that a primary driver of stress was their perception of school as a hypercompetitive, zero-sum game where pervasive peer pressure to perform reigns supreme.
Class rankings fuel these cutthroat environments. They send a toxic message to young people: success requires doing better than your peers.
Ranking systems help highly selective colleges decide which students to admit or reject for admission. The purpose of high school is to develop students to their own full potential, rather than causing them to fixate on measuring up to others. Research shows that ranking systems undercut students’ learning and damage social relationships by turning peers into opponents.
Eliminating class rankings sends a powerful message to students that they are more than a number.
Become an Admission Test Objector
COVID-19 ushered in the era of test-optional admissions. De-centering standardized tests in the college application process is unequivocally a good thing. Standardized tests don’t predict student success in college , they only widen the achievement gap between privileged and underprivileged students and damage students' mental health .
Going “test optional” is an excellent first step, but it's not enough.
Even as more colleges have made tests optional, affluent students submit test scores at a higher rate than their lower-income peers and are admitted at higher rates , suggesting that testing still gives them an edge.
High schools must adhere to standardized test mandates, but they don’t have to endorse them. They can become test objectors by publicly proclaiming that these tests hold no inherent value. They can stop teaching to the test and educate parents on why they are doing so. Counseling departments can inform colleges that their school is a test objector so admission teams won’t penalize students.
Of course, students and families will still find ways to wield these tests as a competitive advantage. Over time, the more schools and educators unite to denounce these tests, the less power they will hold over students and families.
Big change starts with small steps.
Stand For What You Value
Critics may argue that such policies might hurt student outcomes. How will colleges evaluate school rigor if we limit AP courses and homework? How will students demonstrate their merits without class rankings and standardized test scores?
The truth is, the best school systems in the world succeed without homework, standardized test scores or an obsession with rigorous courses. And many U.S. schools have found creative and empowering ways to showcase student merit beyond rankings and test scores.
If we aren’t willing to change policies and practices that have been shown to harm students’ well-being, we have to ask ourselves: Do we really value mental health?
Thankfully, it doesn’t have to be an either/or scenario: We can design school systems that help students thrive academically and psychologically.
Belle Liang and Tim Klein are mental health professionals and co-authors of “How To Navigate Life: The New Science of Finding Your Way in School, Career and Life.”
Making Sense of K-12 Student Mental Health

Tackling the Youth Mental Health Crisis Head-On
By aaliyah a. samuel.

Adolescents Need More Proactive, Preventative Mental Health Supports in School
By sara potler lahayne.

Coronavirus
Kids’ mental health is in crisis. schools can get them help through a $1 billion fund, by nadia tamez-robledo.

When Student Anxiety Gets in the Way of Attending School
By daniel mollenkamp, more from edsurge.

EdSurge Podcast
Should chatbots tutor dissecting that viral ai demo with sal khan and his son, by jeffrey r. young.

Mental Health
Can young mental health navigators ease the crisis facing today's students, by emily tate sullivan.

Early Educators Deserve Better, Starting With Health Care and Retirement Benefits
By hayley village.

Inclusive by Design: Sharing Insights for Crafting Accessible Conferences
By amy lomellini.
Journalism that ignites your curiosity about education.
EdSurge is an editorially independent project of and
- Product Index
- Write for us
- Advertising
FOLLOW EDSURGE
© 2024 All Rights Reserved

Homework Struggles May Not Be a Behavior Problem
Exploring some options to understand and help..
Posted August 2, 2022 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework.
- Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation of a behavior problem—is key.
- Sleep and mental health needs can take priority over homework completion.
Chelsea was in 10th grade the first time I told her directly to stop doing her homework and get some sleep. I had been working with her since she was in middle school, treating her anxiety disorder. She deeply feared disappointing anyone—especially her teachers—and spent hours trying to finish homework perfectly. The more tired and anxious she got, the harder it got for her to finish the assignments.

One night Chelsea called me in despair, feeling hopeless. She was exhausted and couldn’t think straight. She felt like a failure and that she was a burden to everyone because she couldn’t finish her homework.
She was shocked when I told her that my prescription for her was to go to sleep now—not to figure out how to finish her work. I told her to leave her homework incomplete and go to sleep. We briefly discussed how we would figure it out the next day, with her mom and her teachers. At that moment, it clicked for her that it was futile to keep working—because nothing was getting done.
This was an inflection point for her awareness of when she was emotionally over-cooked and when she needed to stop and take a break or get some sleep. We repeated versions of this phone call several times over the course of her high school and college years, but she got much better at being able to do this for herself most of the time.
When Mental Health Symptoms Interfere with Homework
Kids with mental health or neurodevelopmental challenges often struggle mightily with homework. Challenges can come up in every step of the homework process, including, but not limited to:
- Remembering and tracking assignments and materials
- Getting the mental energy/organization to start homework
- Filtering distractions enough to persist with assignments
- Understanding unspoken or implied parts of the homework
- Remembering to bring finished homework to class
- Being in class long enough to know the material
- Tolerating the fear of not knowing or failing
- Not giving up the assignment because of a panic attack
- Tolerating frustration—such as not understanding—without emotional dysregulation
- Being able to ask for help—from a peer or a teacher and not being afraid to reach out
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD , autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety , generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression , dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and mental health challenges cause numerous learning differences and symptoms that can specifically and frequently interfere with getting homework done.

The Usual Diagnosis for Homework Problems is "Not Trying Hard Enough"
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their homework. That is the default “diagnosis” in classrooms and living rooms. And once this framework is drawn, the student is often seen as not trying hard enough, disrespectful, manipulative, or just plain lazy.
The fundamental disconnect here is that the diagnosis of homework struggles as a behavioral choice is, in fact, only one explanation, while there are so many other diagnoses and differences that impair children's ability to consistently do their homework. If we are trying to create solutions based on only one understanding of the problem, the solutions will not work. More devastatingly, the wrong solutions can worsen the child’s mental health and their long-term engagement with school and learning.
To be clear, we aren’t talking about children who sometimes struggle with or skip homework—kids who can change and adapt their behaviors and patterns in response to the outcomes of that struggle. For this discussion, we are talking about children with mental health and/or neurodevelopmental symptoms and challenges that create chronic difficulties with meeting homework demands.
How Can You Help a Child Who Struggles with Homework?
How can you help your child who is struggling to meet homework demands because of their ADHD, depression, anxiety, OCD , school avoidance, or any other neurodevelopmental or mental health differences? Let’s break this down into two broad areas—things you can do at home, and things you can do in communication with the school.

Helping at Home
The following suggestions for managing school demands at home can feel counterintuitive to parents—because we usually focus on helping our kids to complete their tasks. But mental health needs jump the line ahead of task completion. And starting at home will be key to developing an idea of what needs to change at school.
- Set an end time in the evening after which no more homework will be attempted. Kids need time to decompress and they need sleep—and pushing homework too close to or past bedtime doesn’t serve their educational needs. Even if your child hasn’t been able to approach the homework at all, even if they have avoided and argued the whole evening, it is still important for everyone to have a predictable time to shut down the whole process.
- If there are arguments almost every night about homework, if your child isn’t starting homework or finishing it, reframe it from failure into information. It’s data to put into problem-solving. We need to consider other possible explanations besides “behavioral choice” when trying to understand the problem and create effective solutions. What problems are getting in the way of our child’s meeting homework demands that their peers are meeting most of the time?
- Try not to argue about homework. If you can check your own anxiety and frustration, it can be more productive to ally with your child and be curious with them. Kids usually can’t tell you a clear “why” but maybe they can tell you how they are feeling and what they are thinking. And if your child can’t talk about it or just keeps saying “I don't know,” try not to push. Come back another time. Rushing, forcing, yelling, and threatening will predictably not help kids do homework.

Helping at School
The second area to explore when your neurodiverse child struggles frequently with homework is building communication and connections with school and teachers. Some places to focus on include the following.
- Label your child’s diagnoses and break down specific symptoms for the teachers and school team. Nonjudgmental, but specific language is essential for teachers to understand your child’s struggles. Breaking their challenges down into the problems specific to homework can help with building solutions. As your child gets older, help them identify their difficulties and communicate them to teachers.
- Let teachers and the school team know that your child’s mental health needs—including sleep—take priority over finishing homework. If your child is always struggling to complete homework and get enough sleep, or if completing homework is leading to emotional meltdowns every night, adjusting their homework demands will be more successful than continuing to push them into sleep deprivation or meltdowns.
- Request a child study team evaluation to determine if your child qualifies for services under special education law such as an IEP, or accommodations through section 504—and be sure that homework adjustments are included in any plan. Or if such a plan is already in place, be clear that modification of homework expectations needs to be part of it.
The Long-Term Story
I still work with Chelsea and she recently mentioned how those conversations so many years ago are still part of how she approaches work tasks or other demands that are spiking her anxiety when she finds herself in a vortex of distress. She stops what she is doing and prioritizes reducing her anxiety—whether it’s a break during her day or an ending to the task for the evening. She sees that this is crucial to managing her anxiety in her life and still succeeding at what she is doing.
Task completion at all costs is not a solution for kids with emotional needs. Her story (and the story of many of my patients) make this crystal clear.

Candida Fink, M.D. , is board certified in child/adolescent and general psychiatry. She practices in New York and has co-authored two books— The Ups and Downs of Raising a Bipolar Child and Bipolar Disorder for Dummies.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

When Is Homework Stressful? Its Effects on Students’ Mental Health

Are you wondering when is homework stressful? Well, homework is a vital constituent in keeping students attentive to the course covered in a class. By applying the lessons, students learned in class, they can gain a mastery of the material by reflecting on it in greater detail and applying what they learned through homework.
However, students get advantages from homework, as it improves soft skills like organisation and time management which are important after high school. However, the additional work usually causes anxiety for both the parents and the child. As their load of homework accumulates, some students may find themselves growing more and more bored.
Students may take assistance online and ask someone to do my online homework . As there are many platforms available for the students such as Chegg, Scholarly Help, and Quizlet offering academic services that can assist students in completing their homework on time.
Negative impact of homework
There are the following reasons why is homework stressful and leads to depression for students and affect their mental health. As they work hard on their assignments for alarmingly long periods, students’ mental health is repeatedly put at risk. Here are some serious arguments against too much homework.
No uniqueness
Homework should be intended to encourage children to express themselves more creatively. Teachers must assign kids intriguing assignments that highlight their uniqueness. similar to writing an essay on a topic they enjoy.
Moreover, the key is encouraging the child instead of criticizing him for writing a poor essay so that he can express himself more creatively.
Lack of sleep
One of the most prevalent adverse effects of schoolwork is lack of sleep. The average student only gets about 5 hours of sleep per night since they stay up late to complete their homework, even though the body needs at least 7 hours of sleep every day. Lack of sleep has an impact on both mental and physical health.
No pleasure
Students learn more effectively while they are having fun. They typically learn things more quickly when their minds are not clouded by fear. However, the fear factor that most teachers introduce into homework causes kids to turn to unethical means of completing their assignments.
Excessive homework
The lack of coordination between teachers in the existing educational system is a concern. As a result, teachers frequently end up assigning children far more work than they can handle. In such circumstances, children turn to cheat on their schoolwork by either copying their friends’ work or using online resources that assist with homework.
Anxiety level
Homework stress can increase anxiety levels and that could hurt the blood pressure norms in young people . Do you know? Around 3.5% of young people in the USA have high blood pressure. So why is homework stressful for children when homework is meant to be enjoyable and something they look forward to doing? It is simple to reject this claim by asserting that schoolwork is never enjoyable, yet with some careful consideration and preparation, homework may become pleasurable.
No time for personal matters
Students that have an excessive amount of homework miss out on personal time. They can’t get enough enjoyment. There is little time left over for hobbies, interpersonal interaction with colleagues, and other activities.
However, many students dislike doing their assignments since they don’t have enough time. As they grow to detest it, they can stop learning. In any case, it has a significant negative impact on their mental health.
Children are no different than everyone else in need of a break. Weekends with no homework should be considered by schools so that kids have time to unwind and prepare for the coming week. Without a break, doing homework all week long might be stressful.

How do parents help kids with homework?
Encouraging children’s well-being and health begins with parents being involved in their children’s lives. By taking part in their homework routine, you can see any issues your child may be having and offer them the necessary support.
Set up a routine
Your student will develop and maintain good study habits if you have a clear and organized homework regimen. If there is still a lot of schoolwork to finish, try putting a time limit. Students must obtain regular, good sleep every single night.
Observe carefully
The student is ultimately responsible for their homework. Because of this, parents should only focus on ensuring that their children are on track with their assignments and leave it to the teacher to determine what skills the students have and have not learned in class.
Listen to your child
One of the nicest things a parent can do for their kids is to ask open-ended questions and listen to their responses. Many kids are reluctant to acknowledge they are struggling with their homework because they fear being labelled as failures or lazy if they do.
However, every parent wants their child to succeed to the best of their ability, but it’s crucial to be prepared to ease the pressure if your child starts to show signs of being overburdened with homework.
Talk to your teachers
Also, make sure to contact the teacher with any problems regarding your homework by phone or email. Additionally, it demonstrates to your student that you and their teacher are working together to further their education.
Homework with friends
If you are still thinking is homework stressful then It’s better to do homework with buddies because it gives them these advantages. Their stress is reduced by collaborating, interacting, and sharing with peers.
Additionally, students are more relaxed when they work on homework with pals. It makes even having too much homework manageable by ensuring they receive the support they require when working on the assignment. Additionally, it improves their communication abilities.
However, doing homework with friends guarantees that one learns how to communicate well and express themselves.
Review homework plan
Create a schedule for finishing schoolwork on time with your child. Every few weeks, review the strategy and make any necessary adjustments. Gratefully, more schools are making an effort to control the quantity of homework assigned to children to lessen the stress this produces.
Bottom line
Finally, be aware that homework-related stress is fairly prevalent and is likely to occasionally affect you or your student. Sometimes all you or your kid needs to calm down and get back on track is a brief moment of comfort. So if you are a student and wondering if is homework stressful then you must go through this blog.
While homework is a crucial component of a student’s education, when kids are overwhelmed by the amount of work they have to perform, the advantages of homework can be lost and grades can suffer. Finding a balance that ensures students understand the material covered in class without becoming overburdened is therefore essential.
Zuella Montemayor did her degree in psychology at the University of Toronto. She is interested in mental health, wellness, and lifestyle.

Psychreg is a digital media company and not a clinical company. Our content does not constitute a medical or psychological consultation. See a certified medical or mental health professional for diagnosis.
- Privacy Policy
© Copyright 2014–2034 Psychreg Ltd
- PSYCHREG JOURNAL
- MEET OUR WRITERS
- MEET THE TEAM
- How It Works
- Sleep Meditation
- VA Workers and Veterans

- How It Works 01
- Sleep Meditation 02
- Mental Fitness 03
- Neurofeedback 04
- Healium for Business 05
- VA Workers and Veterans 06
- Sports Meditation 07
- VR Experiences 08
- Social Purpose 11
Does Homework Cause Stress? Exploring the Impact on Students’ Mental Health
How much homework is too much?

Jump to: The Link Between Homework and Stress | Homework’s Impact on Mental Health | Benefits of Homework | How Much Homework Should Teacher’s Assign? | Advice for Students | How Healium Helps
Homework has become a matter of concern for educators, parents, and researchers due to its potential effects on students’ stress levels. It’s no secret students often find themselves grappling with high levels of stress and anxiety throughout their academic careers, so understanding the extent to which homework affects those stress levels is important.
By delving into the latest research and understanding the underlying factors at play, we hope to curate insights for educators, parents, and students who are wondering is homework causing stress in their lives?
The Link Between Homework and Stress: What the Research Says
Over the years, numerous studies investigated the relationship between homework and stress levels in students.
One study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that students who reported spending more than two hours per night on homework experienced higher stress levels and physical health issues . Those same students reported over three hours of homework a night on average.
This study, conducted by Stanford lecturer Denise Pope, has been heavily cited throughout the years, with WebMD eproducing the below video on the topic– part of their special report series on teens and stress :
Additional studies published by Sleep Health Journal found that long hours on homework on may be a risk factor for depression while also suggesting that reducing workload outside of class may benefit sleep and mental fitness .
Lastly, a study presented by Frontiers in Psychology highlighted significant health implications for high school students facing chronic stress, including emotional exhaustion and alcohol and drug use.
Homework’s Potential Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects.
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming.
• Sleep Disturbances : Homework-related stress can disrupt students’ sleep patterns, leading to sleep anxiety or sleep deprivation, both of which can negatively impact cognitive function and emotional regulation.
• Reduced Motivation: Excessive homework demands could drain students’ motivation, causing them to feel fatigued and disengaged from their studies. Reduced motivation may lead to a lack of interest in learning, hindering overall academic performance.
2. Potential Physical Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Impaired Immune Function: Prolonged stress could weaken the immune system, making students more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
• Disrupted Hormonal Balance : The body’s stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which, when chronically elevated due to stress, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.
• Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Stress has been known to affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, and other digestive problems.
• Cardiovascular Impact: The increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure associated with stress can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of heart-related issues in the long run.
• Brain impact: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones may impact the brain’s functioning , affecting memory, concentration, and cognitive abilities.
The Benefits of Homework
It’s important to note that homework also offers many benefits that contribute to students’ academic growth and development, such as:
• Development of Time Management Skills: Completing homework within specified deadlines encourages students to manage their time efficiently. This valuable skill extends beyond academics and becomes essential in various aspects of life.
• Preparation for Future Challenges : Homework helps prepare students for future academic challenges and responsibilities. It fosters a sense of discipline and responsibility, qualities that are crucial for success in higher education and professional life.
• Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Homework often presents students with challenging problems to solve. Tackling these problems independently nurtures critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
While homework can foster discipline, time management, and self-directed learning, the middle ground may be to strike a balance that promotes both academic growth and mental well-being .
How Much Homework Should Teachers Assign?
As a general guideline, educators suggest assigning a workload that allows students to grasp concepts effectively without overwhelming them . Quality over quantity is key, ensuring that homework assignments are purposeful, relevant, and targeted towards specific objectives.
Advice for Students: How to balance Homework and Well-being
Finding a balance between academic responsibilities and well-being is crucial for students. Here are some practical tips and techniques to help manage homework-related stress and foster a healthier approach to learning:
• Effective Time Management : Encourage students to create a structured study schedule that allocates sufficient time for homework, breaks, and other activities. Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can prevent last-minute rushes and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
• Break Tasks into Smaller Chunks : Large assignments can be daunting and may contribute to stress. Students should break such tasks into smaller, manageable parts. This approach not only makes the workload seem less intimidating but also provides a sense of accomplishment as each section is completed.
• Find a Distraction-Free Zone : Establish a designated study area that is free from distractions like smartphones, television, or social media. This setting will improve focus and productivity, reducing time needed to complete homework.
• Be Active : Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and enhance mood. Encourage students to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, whether it’s going for a walk, playing a sport, or doing yoga.
• Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques : Encourage students to engage in mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to alleviate stress and improve concentration. Taking short breaks to relax and clear the mind can enhance overall well-being and cognitive performance.
• Seek Support : Teachers, parents, and school counselors play an essential role in supporting students. Create an open and supportive environment where students feel comfortable expressing their concerns and seeking help when needed.
How Healium is Helping in Schools
Stress is caused by so many factors and not just the amount of work students are taking home. Our company created a virtual reality stress management solution… a mental fitness tool called “Healium” that’s teaching students how to learn to self-regulate their stress and downshift in a drugless way. Schools implementing Healium have seen improvements from supporting dysregulated students and ADHD challenges to empowering students with body awareness and learning to self-regulate stress . Here’s one of their stories.
By providing students with the tools they need to self-manage stress and anxiety, we represent a forward-looking approach to education that prioritizes the holistic development of every student.
To learn more about how Healium works, watch the video below.
About the Author

Sarah Hill , a former interactive TV news journalist at NBC, ABC, and CBS affiliates in Missouri, gained recognition for pioneering interactive news broadcasting using Google Hangouts. She is now the CEO of Healium, the world’s first biometrically powered immersive media channel, helping those with stress, anxiety, insomnia, and other struggles through biofeedback storytelling. With patents, clinical validation, and over seven million views, she has reshaped the landscape of immersive media.
Homework as a Mental Health Concern It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health practitioners, especially those who work in schools. Over the years, we have tried to emphasize the idea that schools need to ensure that homework is designed as "motivated practice," and parents need to avoid turning homework into a battleground. These views are embedded in many of the Center documents. At this time, we hope you will join in a discussion of what problems you see arising related to homework and what you recommend as ways to deal with such problems, what positive homework practices you know about, and so forth. Read the material that follows, and then, let us hear from you on this topic. Contact: [email protected] ######################### As one stimulus, here's a piece by Sharon Cromwell from Education World prepared for teachers " The Homework Dilemma: How Much Should Parents Get Involved? " http://www.education-world.com/a_curr/curr053.shtml . What can teachers do to help parents help their children with homework? Just what kind of parental involvement -- and how much involvement -- truly helps children with their homework? The most useful stance parents can take, many experts agree, is to be somewhat but not overly involved in homework. The emphasis needs to be on parents' helping children do their homework themselves -- not on doing it for them. In an Instructor magazine article, How to Make Parents Your Homework Partner s, study-skills consultant Judy Dodge maintains that involving students in homework is largely the teacher's job, yet parents can help by "creating a home environment that's conducive to kids getting their homework done." Children who spend more time on homework, on average, do better academically than children who don't, and the academic benefits of homework increase in the upper grades, according to Helping Your Child With Homework , a handbook by the Office of Education Research and Improvement in the U.S. Department of Education. The handbook offers ideas for helping children finish homework assignments successfully and answers questions that parents and people who care for elementary and junior high school students often ask about homework. One of the Goals 2000 goals involves the parent/school relationship. The goal reads, "Every school will promote partnerships that will increase parental involvement and participation in promoting the social, emotional, and academic growth of children." Teachers can pursue the goal, in part, by communicating to parents their reasons for assigning homework. For example, the handbook states, homework can help children to review and practice what they have learned; prepare for the next day's class; use resources, such as libraries and reference materials; investigate topics more fully than time allows in the classroom. Parents can help children excel at homework by setting a regular time; choosing a place; removing distractions; having supplies and resources on hand; monitoring assignments; and providing guidance. The handbook cautions against actually doing the homework for a child, but talking about the assignment so the child can figure out what needs to be done is OK. And reviewing a completed assignment with a child can also be helpful. The kind of help that works best depends, of course, partly on the child's age. Elementary school students who are doing homework for the first time may need more direct involvement than older students. HOMEWORK "TIPS" Specific methods have been developed for encouraging the optimal parental involvement in homework. TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) Interactive Homework process was designed by researchers at Johns Hopkins University and teachers in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia to meet parents' and teachers' needs, says the Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin . The September 1997 bulletin reported the effects of TIPS-Language Arts on middle-grade students' writing skills, language arts report card grades, and attitudes toward TIPS as well as parents' reactions to interactive homework. TIPS interactive homework assignments involve students in demonstrating or discussing homework with a family member. Parents are asked to monitor, interact, and support their children. They are not required to read or direct the students' assignments because that is the students' responsibility. All TIPS homework has a section for home-to-school communication where parents indicate their interaction with the student about the homework. The goals of the TIPS process are for parents to gain knowledge about their children's school work, students to gain mastery in academic subjects by enhancing school lessons at home, and teachers to have an understanding of the parental contribution to student learning. "TIPS" RESULTS Nearly all parents involved in the TIPS program said TIPS provided them with information about what their children were studying in school. About 90 percent of the parents wanted the school to continue TIPS the following year. More than 80 percent of the families liked the TIPS process (44 percent a lot; 36% a little). TIPS activities were better than regular homework, according to 60 percent of the students who participated. About 70 percent wanted the school to use TIPS the next year. According to Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin , more family involvement helped students' writing skills increase, even when prior writing skills were taken into account. And completing more TIPS assignments improved students' language arts grades on report cards, even after prior report card grades and attendance were taken into account. Of the eight teachers involved, six liked the TIPS process and intended to go on using it without help or supplies from the researchers. Furthermore, seven of the eight teachers said TIPS "helps families see what their children are learning in class." OTHER TIPS In "How to Make Parents Your Homework Partners," Judy Dodge suggests that teachers begin giving parent workshops to provide practical tips for "winning the homework battle." At the workshop, teachers should focus on three key study skills: Organizational skills -- Help put students in control of work and to feel sure that they can master what they need to learn and do. Parents can, for example, help students find a "steady study spot" with the materials they need at hand. Time-management skills -- Enable students to complete work without feeling too much pressure and to have free time. By working with students to set a definite study time, for example, parents can help with time management. Active study strategies -- Help students to achieve better outcomes from studying. Parents suggest, for instance, that students write questions they think will be on a test and then recite their answers out loud. Related Resources Homework Without Tears by Lee Canter and Lee Hauser (Perennial Library, 1987). A down-to-earth book by well-known experts suggests how to deal with specific homework problems. Megaskills: How Families Can Help Children Succeed in School and Beyond by Dorothy Rich (Houghton Mifflin Company, 1992). Families can help children develop skills that nurture success in and out of school. "Helping Your Student Get the Most Out of Homework" by the National PTA and the National Education Association (1995). This booklet for teachers to use with students is sold in packages of 25 through the National PTA. The Catalog item is #B307. Call 312-549-3253 or write National PTA Orders, 135 South LaSalle Street, Dept. 1860, Chicago, IL 60674-1860. Related Sites A cornucopia of homework help is available for children who use a computer or whose parents are willing to help them get started online. The following LINKS include Internet sites that can be used for reference, research, and overall resources for both homework and schoolwork. Dr. Internet. The Dr. Internet Web site, part of the Internet Public Library, helps students with science and math homework or projects. It includes a science project resource guide Help With Homework. His extensive listing of Internet links is divided into Language Art Links, Science Links, Social Studies Links, Homework Help, Kids Education, and Universities. If students know what they are looking for, the site could be invaluable. Kidz-Net... Links to places where you can get help with homework. An array of homework help links is offered here, from Ask Dr. Math (which provides answers to math questions) to Roget's Thesaurus and the White House. Surfing the Net With Kids: Got Questions? Links to people -- such as teachers, librarians, experts, authors, and other students -- who will help students with questions about homework. Barbara J. Feldman put together the links. Kidsurfer: For Kids and Teens The site, from the National Children's Coalition, includes a Homework/Reference section for many subjects, including science, geography, music, history, and language arts. Homework: Parents' Work, Kid's Work, or School Work? A quick search of this title in the Education Week Archives and you'll find an article presenting a parent's viewpoint on helping children with homework. @#@#@#@@# As another stimulus for the discussion, here is an excerpt from our online continuing education module Enhancing Classroom Approaches for Addressing Barriers to Learning ( https://smhp.psych.ucla.edu ) Turning Homework into Motivated Practice Most of us have had the experience of wanting to be good at something such as playing a musical instrument or participating in a sport. What we found out was that becoming good at it meant a great deal of practice, and the practicing often was not very much fun. In the face of this fact, many of us turned to other pursuits. In some cases, individuals were compelled by their parents to labor on, and many of these sufferers grew to dislike the activity. (A few, of course, commend their parents for pushing them, but be assured these are a small minority. Ask your friends who were compelled to practice the piano.) Becoming good at reading, mathematics, writing, and other academic pursuits requires practice outside the classroom. This, of course, is called homework. Properly designed, homework can benefit students. Inappropriately designed homework, however, can lead to avoidance, parent-child conflicts, teacher reproval, and student dislike of various arenas of learning. Well-designed homework involves assignments that emphasize motivated practice. As with all learning processes that engage students, motivated practice requires designing activities that the student perceives as worthwhile and doable with an appropriate amount of effort. In effect, the intent is to personalize in-class practice and homework. This does not mean every student has a different practice activity. Teachers quickly learn what their students find engaging and can provide three or four practice options that will be effective for most students in a class. The idea of motivated practice is not without its critics. I don't doubt that students would prefer an approach to homework that emphasized motivated practice. But �� that's not preparing them properly for the real world. People need to work even when it isn't fun, and most of the time work isn't fun. Also, if a person wants to be good at something, they need to practice it day in and day out, and that's not fun! In the end, won't all this emphasis on motivation spoil people so that they won't want to work unless it's personally relevant and interesting? We believe that a great deal of learning and practice activities can be enjoyable. But even if they are not, they can be motivating if they are viewed as worthwhile and experienced as satisfying. At the same time, we do recognize that there are many things people have to do in their lives that will not be viewed and experienced in a positive way. How we all learn to put up with such circumstances is an interesting question, but one for which psychologists have yet to find a satisfactory answer. It is doubtful, however, that people have to experience the learning and practice of basic knowledge and skills as drudgery in order to learn to tolerate boring situations. Also in response to critics of motivated practice, there is the reality that many students do not master what they have been learning because they do not pursue the necessary practice activities. Thus, at least for such individuals, it seems essential to facilitate motivated practice. Minimally, facilitating motivated practice requires establishing a variety of task options that are potentially challenging -- neither too easy nor too hard. However, as we have stressed, the processes by which tasks are chosen must lead to perceptions on the part of the learner that practice activities, task outcomes, or both are worthwhile -- especially as potential sources of personal satisfaction. The examples in the following exhibit illustrate ways in which activities can be varied to provide for motivated learning and practice. Because most people have experienced a variety of reading and writing activities, the focus here is on other types of activity. Students can be encouraged to pursue such activity with classsmates and/or family members. Friends with common interests can provide positive models and support that can enhance productivity and even creativity. Research on motivation indicates that one of the most powerful factors keeping a person on a task is the expectation of feeling some sense of satisfaction when the task is completed. For example, task persistence results from the expectation that one will feel smart or competent while performing the task or at least will feel that way after the skill is mastered. Within some limits, the stronger the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more likely practice will be pursued even when the practice activities are rather dull. The weaker the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more the practice activities themselves need to be positively motivating. Exhibit � Homework and Motivated Practice Learning and practicing by (1) doing using movement and manipulation of objects to explore a topic (e.g., using coins to learn to add and subtract) dramatization of events (e.g., historical, current) role playing and simulations (e.g., learning about democratic vs. autocratic government by trying different models in class; learning about contemporary life and finances by living on a budget) actual interactions (e.g., learning about human psychology through analysis of daily behavior) applied activities (e.g., school newspapers, film and video productions, band, sports) actual work experience (e.g., on-the-job learning) (2) listening reading to students (e.g., to enhance their valuing of literature) audio media (e.g., tapes, records, and radio presentations of music, stories, events) listening games and activities (e.g., Simon Says; imitating rhymes, rhythms, and animal sounds) analyzing actual oral material (e.g., learning to detect details and ideas in advertisements or propaganda presented on radio or television, learning to identify feelings and motives underlying statements of others) (3) looking directly observing experts, role models, and demonstrations visual media visual games and activities (e.g., puzzles, reproducing designs, map activities) analyzing actual visual material (e.g., learning to find and identify ideas observed in daily events) (4) asking information gathering (e.g., investigative reporting, interviewing, and opinion sampling at school and in the community) brainstorming answers to current problems and puzzling questions inquiry learning (e.g., learning social studies and science by identifying puzzling questions, formulating hypotheses, gathering and interpreting information, generalizing answers, and raising new questions) question-and-answer games and activities (e.g., twenty questions, provocative and confrontational questions) questioning everyday events (e.g., learning about a topic by asking people about how it effects their lives) O.K. That's should be enough to get you going. What's your take on all this? What do you think we all should be telling teachers and parents about homework? Let us hear from you ( [email protected] ). Back to Hot Topic Home Page Hot Topic Home Page --> Table of Contents Home Page Search Send Us Email School Mental Health Project-UCLA Center for Mental Health in Schools WebMaster: Perry Nelson ([email protected])

THE ALGONQUIN HARBINGER
- Excessive homework negatively impacts mental health, causes unnecessary stress

Caroline Lou
Opinion Editor Jula Utzschneider writes on the overwhelming chip on every student’s shoulder: homework.
Jula Utzschneider , Opinion Editor November 10, 2021
When the bell rings to end last period every day, I feel a sense of relief. However, this feeling soon wears off as I realize just how much work I have to do after the already-stressful school day ends.
While homework can be beneficial, more often than not, it is assigned excessively and unnecessarily. Teachers give a significant amount of homework, often due the next day. This causes students to spend far too much time doing such assignments and can be detrimental.
A 2013 study conducted at Stanford University found that students in top-performing school districts who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance in their lives and alienation from society. That study, published in The Journal of Experimental Education , suggested that any more than two hours of homework per night is counterproductive. However, students who participated in the study reported doing slightly more than three hours of homework every night.
And, yes, the amount of homework given to students depends on the course level they take. But, with increasingly competitive college acceptance rates (demanding more extracurriculars and college-level classes), many students feel forced to take these more challenging courses. This is a huge problem, especially as teachers give homework only thinking about their own class, not the five or six others students have.
Additionally, when it came to stress, more than 70% of students in the Stanford study said they were “often or always stressed over schoolwork,” with 56% listing homework as a primary stressor. More than 80% of students reported having at least one stress-related symptom (such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, stomach problems and more) in the past month, and 44% said they had experienced three or more symptoms.
Less than 1% of the students said homework was not a stressor, demonstrating that the vast majority feel overwhelmed and pressured by the amount of work they receive.
Not to mention, the time spent on these assignments could easily be spent doing something enjoyable. Many students feel forced or obligated to choose homework over practicing other talents or skills, which should never be the case. Teachers should be encouraging these extracurriculars, rather than making it impossible for students to partake in them.
In terms of what teachers can do, it’s quite simple, really. Homework is intended for students to either practice a subject further or to cover topics teachers couldn’t during the allotted class time. It should not be busywork that just wastes a student’s time.
Teachers should be giving students work that is absolutely necessary (not busy work), and eliminate it altogether where they can. It is extremely important that students not only get through high school but thrive and enjoy it too.
How much time do you spend doing homework on an average school night?
Sorry, there was an error loading this poll.
A donation of $40 or more includes a subscription to the 2023-24 print issues of The Harbinger. We will mail a copy of our fall, winter, spring and graduation issues to the recipient of your choice. Your donation supports the student journalists of Algonquin Regional High School and allows our extracurricular publication to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs.

Jula began writing for The Harbinger her freshman year after taking Journalism. While at first hesitant, she grew to love reporting and specifically opinion...

- Limitations are necessary for freedom of speech
- Mocking accents spreads unjust, offensive stereotypes
- The Great Debate: Should modern literature replace the classics in English class?
- The Director’s Eye: Heathers
- Students given too much homework, not enough time
How will you be studying for finals?
- Study sessions at Panera
- Flashcards on Quizlet
- Old tests and homework
- I'll wing it!
View Results
- Polls Archive

Senior Reflection: How poetry became my coping mechanism

Senior Reflection: Lessons learned on the road to graduation

Senior Reflection: Beyond the books and embracing the moment

Senior Reflection: The lessons of a bloomed wallflower

Senior Reflection: Learning is forever

EDITORIAL: We must champion diversity

Senior Reflection: The only thing I remember from pre-calculus

Senior Reflection: Advice for my fourteen-year-old self

Senior Reflection: ‘High School Musical’…in real life?

High school perspectives on Israel-Hamas War college campus protests
The official student news site of Algonquin Regional High School in Northborough, MA
- Corrections
Comments (3)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
m • May 4, 2023 at 12:41 pm
m • Jan 4, 2024 at 12:10 pm
sophia • Mar 8, 2023 at 1:57 pm
very true in fact i am writing a essay right now this is resurch

- The Great Debate
- Senior Issue
- Movies & TV
- Video Games
- Pro & College
- Cafe Takeaways
- Chicken Sandwich Chasers
- Club Detectors
- Hidden Gems
- The Racer Ru-view
- Print Issues
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
The Impact of Homework on Student Mental Health
By Happy Sharer

Introduction
Homework is a key part of the educational process. It is often seen as an essential part of learning and helping students to develop important skills. However, there is growing evidence that too much homework can have a negative effect on student mental health. This article will explore the impact of homework on student mental health, examining the correlation between workload and stress levels, analyzing the effects of too much homework on student anxiety, and understanding how homework can lead to depression in students.

Exploring the Impact of Homework on Student Mental Health
Homework has long been seen as an important part of the educational process, but it can also become a source of stress for students. A recent study by the American Psychological Association found that more than two-thirds of students reported feeling overwhelmed by their homework load. The study also found that students who felt overwhelmed were more likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety. It is clear that the amount of homework assigned to students can have a significant impact on their mental health.

Examining the Correlation Between Homework and Student Stress Levels
The amount of homework assigned to students can have a direct impact on their stress levels. Too much homework can lead to feelings of frustration and overwhelm, which can then lead to increased stress levels. A study published in the journal Developmental Psychology found that when students had more homework assignments, they experienced higher levels of stress. The study also found that students who had more homework assignments were more likely to report feeling overwhelmed and anxious.
It is also important to consider the relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have suggested that too much homework can lead to decreased academic performance, which can then lead to increased stress levels. A study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that when students had more homework, their performance on tests was lower than those with less homework. This suggests that too much homework can lead to increased stress levels, as students feel pressure to perform at a higher level.
In order to reduce homework-related stress, it is important for students to prioritize their work. Planning ahead and breaking down tasks into smaller, more manageable chunks can help students to feel more organized and in control. Taking regular breaks throughout the day can also help students to stay focused and motivated. Finally, it is important to ensure that students are getting enough sleep in order to maintain their energy levels and reduce stress.

Analyzing the Effects of Too Much Homework on Student Anxiety
Too much homework can also lead to increased anxiety levels in students. A study published in the journal Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review found that when students had more homework, they were more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety. The study also found that students with excessive amounts of homework were more likely to report feeling overwhelmed and unable to cope with the workload.
It is important to understand the psychological effects of too much homework on students. Excessive amounts of homework can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness, which can then lead to increased anxiety levels. Furthermore, students may start to see homework as a burden rather than an opportunity to learn, which can lead to decreased motivation and further feelings of anxiety.
In order to reduce homework-related anxiety, it is important to set realistic goals and expectations. Setting achievable goals and deadlines can help students to stay focused and motivated. It is also important to ensure that students are getting enough rest and taking regular breaks throughout the day. Finally, it is important to talk to teachers and parents about any concerns or worries that students may have about their workload.
Understanding How Homework Can Lead to Depression in Students
Too much homework can also lead to depression in students. A study published in the journal Pediatrics found that when students had more homework, they were more likely to experience symptoms of depression. The study also found that students with excessive amounts of homework were more likely to report feeling overwhelmed, frustrated, and helpless.
It is important to understand the psychological effects of too much homework on students. Excessive amounts of homework can lead to feelings of hopelessness and failure, which can then lead to increased depression levels. Furthermore, students may start to see homework as a chore rather than an opportunity to learn, which can lead to decreased motivation and further feelings of depression.
In order to reduce homework-related depression, it is important to focus on developing positive coping skills. Taking time to relax and practice mindfulness can help students to manage their emotions and stay focused. It is also important to ensure that students are getting enough sleep and taking regular breaks throughout the day. Finally, it is important to talk to teachers and parents about any concerns or worries that students may have about their workload.
Investigating the Relationship Between Homework and Student Self-Esteem
Finally, it is important to consider the relationship between homework and student self-esteem. A study published in the journal Developmental Psychology found that when students had more homework, they were more likely to report feeling inadequate and inferior. The study also found that students with excessive amounts of homework were more likely to report feeling overwhelmed and helpless.
It is important to understand the psychological effects of too much homework on students. Excessive amounts of homework can lead to feelings of worthlessness and failure, which can then lead to decreased self-esteem. Furthermore, students may start to see homework as a burden rather than an opportunity to learn, which can lead to decreased motivation and further feelings of inadequacy.
In order to increase homework-related self-esteem, it is important to focus on developing positive self-talk. Taking time to recognize achievements and celebrate successes can help students to stay motivated and build confidence. It is also important to ensure that students are getting enough rest and taking regular breaks throughout the day. Finally, it is important to talk to teachers and parents about any concerns or worries that students may have about their workload.
In conclusion, it is clear that the amount of homework assigned to students can have a significant impact on their mental health. Too much homework can lead to increased stress levels, anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem. It is therefore important to ensure that students are not overloaded with homework and are given the opportunity to learn in a healthy environment. By reducing the amount of homework assigned to students, we can help them to develop important skills without compromising their mental wellbeing.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Jack hanna keto gummies: real reviews, price, how much exercise does a border collie need a comprehensive guide, a comprehensive guide to the ornish diet: reshaping your health and well-being, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.
- Close Menu Search
- Current Events
- Entertainment

Does Homework Affect Our Mental Health?

Junior Emma studies for a test after a long night of practice and homework.
Megan McCall , Writer December 1, 2018
As a Loyola Academy junior, I am no stranger to cramming for tests, finishing homework two minutes before class starts, and staying up late stressing about everything I need to do. But, I’ve never stood back and thought, “Is all this homework affecting my mental health?”
At Loyola, joining clubs, sports and extracurricular activities is encouraged and promoted. After being at school eight hours, going to practice, commuting home, then doing homework, there is barely enough time to relax or even spend time with family. Without time to de-stress after having a long day, anxiety and emotions build up and up.
According to the Mayo Clinic, too much stress can cause social withdrawal, angry outbursts, drug and alcohol abuse and so much more. I asked one of my classmates, Adeline Dunbar, if she thought homework was the main source of her stress. She replied, “Without so much homework I would be a different person, I would have time to be with my friends, focus on things other than school and actually sit down and relax.”
Teachers have extremely high expectations of students, and although that may not always be a bad thing, sometimes teacher assume we have more time than we actually do. I asked 40 students, among all four grades, how much time they spend a night doing homework and studying.
Out of all those students, more than 60% said they spend more than two hours a night doing homework. Usually, study time is spent late at night, (after school, extracurriculars, dinner etc.) which are made for sleep.
The recommended amount of sleep for teenagers is 9-10 hours each night, but the average amount that teens get is seven hours. This lack of sleep causes problems with attention, memory, decision making and the overall cognitive abilities. Students with more sleep are proven to have less stress, anxiety and depression and also have higher tests scores. If students spend hours upon doing homework and studying late into the night, they are lessening their chances of doing well by losing sleep.
In conclusion, homework may have perks, but too much of it is not good for the well-being of students. Maintaining everything in our daily lives can be difficult, but when it comes to our mental health, it should always be put first.

My name is Megan McCall and I am a senior! I have been writing in the Prep for two years and hope to continue my writing journey in college! I am in Misericordia...
- Polls Archive

Winter Formal Flop

Loyola’s Soups for the Soul
Ranking Thanksgiving Food

Dress for Success
How To: Survive College Process

The Impact of Loyola’s Attendance Policies
Not Your Average School Lunch

Parking Pandemonium
New 3p.m. Dismissal Change at Loyola Academy

Joe Donut: A Must-Try Breakfast Place
The Student News Site of Loyola Academy
Comments (2)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Clint Jay Nocasa • Nov 26, 2020 at 9:22 pm
Was this article revised or updated? if yes, when?
adviser • Dec 2, 2020 at 8:52 am
It has not been updated since it was published.
- Close Menu Search
- Recommend a Story

The Lion's Roar
May 24 Party Like It’s 1989: Lions Capture the 2024 Diamond Classic
May 24 Why Does the Early 20th Century Tend to Spark Nostalgia?
May 24 O.J Simpson Dead at 76: Football Star Turned Murderer
May 24 NAIA Bans Transgender Women From Women’s Sports
May 24 From Papyrus to Ashes: The Story of the Great Library of Alexandria
How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health
Jessica Amabile '24 , Staff Writer March 25, 2022
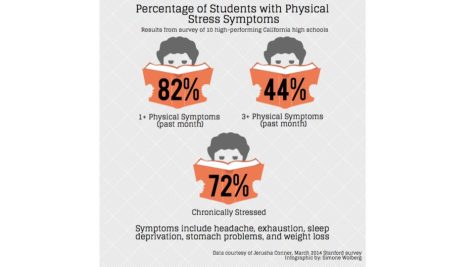
“[Students] average about 3.1 hours of homework each night,” according to an article published by Stanford . Teens across the country come home from school, exhausted from a long day, only to do more schoolwork. They sit at their computers, working on homework assignments for hours on end. To say the relentless amount of work they have to do is overwhelming would be an understatement. The sheer amount of homework given has many negative impacts on teenagers.
Students have had homework for decades, but in more recent years it has become increasingly more demanding. Multiple studies have shown that students average about three hours of homework per night. The Atlantic mentioned that students now have twice as much homework as students did in the 1990s. This is extremely detrimental to teens’ mental health and levels of stress. Students have a lot to do after school, such as spending time with family, extracurricular activities, taking care of siblings or other family members, hanging out with friends, or all of the above. Having to juggle all of this as well as hours on end of homework is unreasonable because teenagers already have enough to think or worry about.
According to a student- run survey conducted in Cherry Hill West, students reported that they received the most homework in math, history, and language arts classes. They receive anywhere from 1 to 4 or more hours of homework every day, but only about 22.7% somewhat or strongly agree that it helps them learn. Of the students who participated, 63.6% think schools should continue to give out homework sometimes, while 27.3% said they should not give out homework at all. In an open-ended response section, students had a lot to say. One student wrote, “I think we should get homework to practice work if we are seen struggling, or didn’t finish work in class. But if we get homework, I think it just shows that the teacher needs more time to teach and instead of speeding up, gives us more work.” Another added, “Homework is important to learn the material. However, too much may lead to the student not learning that much, or it may become stressful to do homework everyday.” Others wrote, “The work I get in chemistry doesn’t help me learn at all if anything it confuses me more,” and “I think math is the only class I could use homework as that helps me learn while world language is supposed to help me learn but feels more like a time waste.” A student admitted, “I think homework is beneficial for students but the amount of homework teachers give us each day is very overwhelming and puts a lot of stress on kids. I always have my work done but all of the homework I have really changes my emotions and it effects me.” Another pointed out, “you are at school for most of your day waking up before the sun and still after all of that they send you home each day with work you need to do before the next day. Does that really make sense[?]”
As an article from Healthline mentioned, “Researchers asked students whether they experienced physical symptoms of stress… More than 80 percent of students reported having at least one stress-related symptom in the past month, and 44 percent said they had experienced three or more symptoms.” If school is causing students physical symptoms of stress, it needs to re-evaluate whether or not homework is beneficial to students, especially teenagers. Students aren’t learning anything if they have hours of “busy work” every night, so much so that it gives them symptoms of stress, such as headaches, weight loss, sleep deprivation, and so on. The continuous hours of work are doing nothing but harming students mentally and physically.

The mental effects of homework can be harmful as well. Mental health issues are often ignored, even when schools can be the root of the problem. An article from USA Today contained a quote from a licensed therapist and social worker named Cynthia Catchings, which reads, “ heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.” Mental health problems are not beneficial in any way to education. In fact, it makes it more difficult for students to focus and learn.
Some studies have suggested that students should receive less homework. To an extent, homework can help students in certain areas, such as math. However, too much has detrimental impacts on their mental and physical health. Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, has a suggestion. She mentioned, “I don’t think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That’s something that needs to be scrapped entirely,” she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments,” according to USA Today . Students don’t have much control over the homework they receive, but if enough people could explain to teachers the negative impacts it has on them, they might be convinced. Teachers need to realize that their students have other classes and other assignments to do. While this may not work for everything, it would at least be a start, which would be beneficial to students.
The sole purpose of schools is to educate children and young adults to help them later on in life. However, school curriculums have gone too far if hours of homework for each class are seen as necessary and beneficial to learning. Many studies have shown that homework has harmful effects on students, so how does it make sense to keep assigning it? At this rate, the amount of time spent on homework will increase in years to come, along with the effects of poor mental and physical health. Currently, students do an average of 3 hours of homework, according to the Washington Post, and the estimated amount of teenagers suffering from at least one mental illness is 1 in 5, as Polaris Teen Center stated. This is already bad enough–it’s worrisome to think it could get much worse. Homework is not more important than physical or mental health, by any standards.
What time should high school should start?
- 7:00 AM or earlier
- 7:30 AM (Current Start Time)
- After 9:00 AM
View Results
- Polls Archive

Why Does the Early 20th Century Tend to Spark Nostalgia?

Superchunk’s Debut: They Can Only Go Up From Here

Dirty Bird: An Underrated Indie Gem

My Suggestions on Fun Horror Games You Should Play!

Breakdown of All Fighting Scenes in The Hunger Games: Ballad of the Songbirds and Snakes

15 Memes that Everyone Will Recognize

Causes of Fights in High Schools

Imaginary: My Predictions and Thoughts

Let’s Rank: Every Album by The Beatles

Homeroom Policy – Pros and Cons
Comments (0)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Study Finds Home Health Aides Struggle with Mental Health
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share on Email

A 2022 report from the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) found 800,000 people on waiting lists for home care and waits often lasting years. Credit: Shutterstock
Home health aides (HHAs) are vulnerable to stress, isolation and depressive symptoms, which impact their own health as well as their patients’ desire to age in place, according to Weill Cornell Medicine researchers. HHAs are a rapidly growing workforce trained and certified to provide personal and medical care, as well as emotional support, in the home.
“As a doctor, I’ve learned that home health aides are a critical part of patients’ well-being,” said senior author Dr. Madeline Sterling , associate professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine and a primary care physician at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “Our study identified aspects of their job that affect their mood and stress levels, and suggested ways to address these challenges, including interventions that bring them closer to their colleagues.”

Dr. Madeline Sterling
As part of the study , published June 6 in JAMA Network Open, researchers interviewed 28 HHAs in New York City at risk of poor mental health. The study was conducted in collaboration with 1199SEIU Training and Employment Fund, a part of the 1199SEIU United Healthcare Workers East, the largest health care union in the United States.
The Need for Home Health Aides Outstrips Availability
Several themes emerged from the study including how interactions with patients and their families can affect aides’ moods in both positive and negative ways. The researchers also explored the participants’ attitudes toward mental health and well-being which can carry stigma due to personal and cultural factors. While the aides reported having different coping mechanisms, many said they would welcome more support, including programs that bring them closer to their colleagues.
The need to address the emotional well-being of HHAs comes at a time of increased demand for their services. “We have tsunami coming of people who will require care at home,” said co-author, Faith Wiggins, director of long-term care at 1199SEIU Training and Employment Fund. In fact, a 2022 report from the American Association of Retired Persons (AARP) found 800,000 people on waiting lists for home care and waits often lasting years.
Dr. Sterling noted that HHAs are an “overlooked and undervalued but increasingly vital workforce.” The Centers for Disease Control estimates that 73 million people in the United States will be 65 years or older by 2030, and the majority would like to age at home. Home health care also has the added benefit of lower cost than institutionalized care.
Previous research from Dr. Sterling, who is also the director of the Initiative on Home Care Work at Cornell’s School of Industrial and Labor Relations, found that before Covid-19 more than a quarter of HHAs nationally had fair or poor general health, and a fifth had poor mental health. Post pandemic, their health has worsened according to studies by Dr. Sterling and Wiggins and others.

Faith Wiggins
These professionals are paid hourly rates slightly above minimum wage with few benefits—under what can be difficult and isolating circumstances. “We need a way to repair those problems and retain their talent,” said Wiggins.
The new study outlines ways to address the challenges faced by HHAs through improving salaries and benefits and interventions that support mental health. Organized peer coaching, for instance, could help train and support aides, and enhance workplace safety and healthy behavior. If issues related to mood and stress were incorporated into peer coaching, aides would benefit even further. Acquiring coaching skills could also help provide a home health career ladder or pathway for aides to earn higher wages as health coaches.
The authors suggest additional research is needed to test and implement culturally and occupationally tailored interventions. “For our patients to do well,” Dr. Sterling said, “we need to support this workforce.”
This study was supported by Clinical Scientist Development Award DDCF 2022053 from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation.
Related News
- Modern Medicine Can Do a Better Job Addressing Maternal Mental Health Disorders
- Esteemed International Leader Dr. Javaid I. Sheikh Honored with 2024 Weill Award
- Awards & Honors: May
Back to News
Weill Cornell Medicine Office of External Affairs New York, NY --> Phone: (646) 962-9476
Going to bed late could damage your mental health, new study says
How staying up late could be harming your mental health

Are you a night owl or a morning lark? We all operate on a sleep schedule that works for the routines and rhythms of our unique lives, but many of us would describe ourselves as being either a natural early riser, someone who prefers to stay up late into the night — or sitting somewhere in the middle.
However, new research suggests that night owl behavior could be harming our mental health. A large study conducted by scientists at Stanford Medicine indicates that those who admit to staying awake into the early hours of the morning had higher rates of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety.
Key takeaways from the new study:
- Those who go to bed later are more likely to suffer from poor mental health
- Those who go to bed and wake early have best mental health
- For healthy ageing, it's recommended that you go to sleep before 1am
Regardless of whether study participants were staying up late out of necessity or following a natural urge to burn the midnight oil, researchers discovered that going to sleep after 1am had a detrimental effect on their mental health.
Here, we’ll take a closer look at what this study means for our sleep behavior, plus explore ways we can shift our sleep patterns with the help of a chartered psychologist.
What are chronotypes and how do they impact sleep?
As well as our schedules and routines, there’s also a biological reason for our tendency to either stay up late, wake up early, or sit somewhere between both. This is due to our chronotype, which helps determine when you feel the natural urge to sleep.
As well as when you feel most inclined to sleep, our chronotype — determined by genetics, age and other factors — can also influence your core body temperature and your eating habits. There are four main chronotypes, each with a different preferred window of productivity, wake and sleep times.
Unlike our circadian rhythm (the body’s internal clock), you’re unable to change your chronotype. While that doesn’t mean you’re unable to sleep outside of what feels most natural, it can be difficult to maintain a sleep schedule that goes against your chronotype.
Sign up to get the BEST of Tom’s Guide direct to your inbox.
Upgrade your life with a daily dose of the biggest tech news, lifestyle hacks and our curated analysis. Be the first to know about cutting-edge gadgets and the hottest deals.
How staying up late could affect mental health

Researchers at Stanford Medicine followed the sleep habits of over 73,888 adults in the UK, each of whom identified as a morning type, evening type, or somewhere in the middle. At the end of the study, they found that evening types were more likely to suffer from poorer mental health.
Regardless of whether study participants were staying up late out of necessity or following a natural urge determined by their chronotype, the outcome — higher rates of mental and behavioral disorders — remained the same.
“We found that alignment with your chronotype is not crucial here, and that really it’s being up late that is not good for your mental health,” Jamie Zeitzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and the senior author of the study, told the Stanford Medicine news center . “The big unknown is why.”
The study found that morning types, those who go to bed early and wake early, had the best mental health of all groups.
How to fix your sleep schedule in 5 steps
If you’re a night owl looking to shift your sleep schedule to earlier in the morning, you can. We spoke to Dr Lindsay Browning , a chartered psychologist and neuroscientist, earlier last year to find out exactly how to fix a broken sleep schedule . Whether your nighttime habits have become skewed due to parenting, nighttime procrastination, here are Dr Browning's top tips to retraining your body to going to sleep earlier.
1. Shift your bedtime back by 20 minutes
If you're currently going to bed at 1am and you'd like to be in bed by 11pm, it can be temping to hop into bed at 10.55pm and hope for the best - resist the urge to do this.
“Yes you can fix this straight off and get up two hours earlier than you are right now, but that will be harder initially than if you were to fix your sleep schedule over several days,@ explains Dr Browning. "Shifting your sleep by 20 minutes a day is easily doable and has no negative effects whatsoever.”
Using this method means that you could shift your sleep schedule forwards by an entire hour over the course of one weekend.
2. Shift your wake time forward by 20 minutes

If you're adjusting your bed time, you need to adjust your wake time, too. “Don’t forget that if you’re moving your bedtime back by 20 minutes a night, you need to move your wake time forward by 20 minutes a day," says Dr Browning. "And it’s really important to get up straight away because if you let yourself sleep in, all of this work is pointless. Pressing the snooze button several times is one of the worst things you can do for your sleep.”
3. Set a bedtime reminder
“Owl types need to set bedtime reminders, because otherwise they’ll keep going and then before they know it, it’s 2am and they have to be up at 7am for work," explains Dr Browning. "All that happens there is the owl misses out on sleep. On weekends, resist the temptation to go to bed late and wake up late because that’s going to shift your body clock again."
4. Don't skip breakfast

As a night owl, you also need to think about when you're eating, because if you skip breakfast and don’t eat until around 11am, your body won’t think it’s morning until 11am. "Even if you can’t face eating a full breakfast upon waking up, have something small to wake up your digestive system. Otherwise you’ll be sleepwalking through the morning."
5. Get plenty of early sunlight exposure
We might not be able to change our chronotype, but we can adjust our circadian rhythm - and one of the most effective tools at our disposal is natural daylight. “Owls aren’t at their best first thing, so it’s more important for them to get really good sun exposure first thing to help boost them into feeling more awake," explains Dr Browning.
Early morning daylight exposure prompts your body to produce a hormone called serotonin, which helps you feel alert and refreshed. Serotonin later becomes metabolised into melatonin, the hormone which helps signal to your body that it's time for sleep, which will make it easier for you to nod off at night.
Nicola Appleton is Sleep Features Editor at Tom’s Guide, specialising in quality news content surrounding sleep and wellbeing. Nicola cut her teeth as a journalist in a busy newsroom in Bristol, UK, 15 years ago as part of a team at Britain's largest independent press agency. Since then, her job as a journalist has taken her to the States, to Sydney, and then back to Blighty, where she has written and edited features for a whole host of prominent British and international brands, including The Independent, The Sydney Morning Herald, HuffPost, Refinery29, Stylist and more. As well as tackling the vast topic of sleep, Nicola will be joining the raft of expert mattress reviewers at Tom's Guide, helping steer readers towards the very best mattresses on the market.
This brainwave-reading headband promises sleep on demand — futuristic dream or a sci-fi nightmare?
I’m a mattress writer — 7 mistakes people make after buying a new mattress topper
Sleep well for less – 5 great-value mattresses that cost under $600 for a queen
Most Popular
- 2 Zotac’s new gaming handheld has me even more excited than the ROG Ally X — here’s why
- 3 Brooks summer sale — 7 deals I recommend from $11
- 4 This brainwave-reading headband promises sleep on demand – futuristic dream or a sci-fi nightmare?
- 5 How to connect Google Drive to ChatGPT for AI-assisted file management
- 2 Zotac’s new PC gaming handheld has me even more excited than the ROG Ally X — here’s why

IMAGES
COMMENTS
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Health Hazards of Homework. Pediatrics. A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework "experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.".
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they ...
Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The ...
Beyond that point, kids don't absorb much useful information, Cooper says. In fact, too much homework can do more harm than good. Researchers have cited drawbacks, including boredom and burnout toward academic material, less time for family and extracurricular activities, lack of sleep and increased stress.
Keywords: homework, stress, mental health The outcomes of adolescent mental health is a threat to students' health and wellbeing, more so than it ever has been in the modern era. As of 2019, the CDC reported a nearly 40. percent increase in feelings of sadness or hopelessness over the last ten years, and similar.
Research shows that excessive homework leads to increased stress, physical health problems and a lack of balance in students' lives. And studies have shown that more than two hours of daily homework can be counterproductive, yet many teachers assign more.. Homework proponents argue that homework improves academic performance. Indeed, a meta-analysis of research on this issue found a ...
Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework. Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation ...
Negative impact of homework. There are the following reasons why is homework stressful and leads to depression for students and affect their mental health. As they work hard on their assignments for alarmingly long periods, students' mental health is repeatedly put at risk. Here are some serious arguments against too much homework. No uniqueness
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress: • Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming. • Sleep Disturbances: Homework-related stress ...
It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health practitioners, especially those who work ...
Homework anxiety often starts in early grade school. It can affect any child. But it's an especially big issue for kids who are struggling in school. They may think they can't do the work. Or they may not have the right support to get it done. Keep in mind that some kids may seem anxious about homework but are actually anxious about ...
However, this feeling soon wears off as I realize just how much work I have to do after the already-stressful school day ends. While homework can be beneficial, more often than not, it is assigned excessively and unnecessarily. Teachers give a significant amount of homework, often due the next day.
How Does Homework Affect Students Mental Health The Negative Side of Homework Diminished Leisure Time: A heavy load of homework can eat into the time meant for relaxation and hobbies, leaving students with limited opportunities to unwind. This lack of leisure can contribute to feelings of burnout and negatively impact their overall mental well ...
Conclusion. In conclusion, it is clear that the amount of homework assigned to students can have a significant impact on their mental health. Too much homework can lead to increased stress levels, anxiety, depression, and decreased self-esteem. It is therefore important to ensure that students are not overloaded with homework and are given the ...
Chinese schoolgirl uses robot to do her homework. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big ...
If students spend hours upon doing homework and studying late into the night, they are lessening their chances of doing well by losing sleep. In conclusion, homework may have perks, but too much of it is not good for the well-being of students. Maintaining everything in our daily lives can be difficult, but when it comes to our mental health ...
The mental effects of homework can be harmful as well. Mental health issues are often ignored, even when schools can be the root of the problem. An article from USA Today contained a quote from a licensed therapist and social worker named Cynthia Catchings, which reads, " heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the ...
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students ...
Sleep deprivation is one of the most common negative effects of homework. The body requires an average of at least 7 hours of sleep daily, most scholars end up getting barely 5 hours of sleep daily due to taking on their homework late into the night. Missing out on sleep affects both mental and physical health. Poor Social Activity.
The findings are from a review, published Tuesday in the journal PLOS Mental Health, of 12 neuroimaging studies of a few hundred adolescents ages 10 to 19 between 2013 and 2022. Ad Feedback ...
Digital mental health interventions can support college students' mental health, but few studies point to effectiveness of the nine most popular tools on the market. jacoblund/iStock/Getty Images Plus. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, colleges and universities have invested in additional online mental health resources to support students, but how ...
Anger is bad for your health in more ways than you think. Getting angry doesn't just hurt our mental health, it's also damaging to our hearts, brains and gastrointestinal systems, according to ...
Scientists want social media giants to share their internal data on how their products affect teenagers' mental health. If Jordy had a switch to instantly shut down social media, she would flip it.
Myth #1: Autism is a disease. Let's start with the most basic misconception, that ASD is a disease. "Autism isn't an illness at all," Dr. Cuffman clarifies. "It's just the way your brain ...
Several themes emerged from the study including how interactions with patients and their families can affect aides' moods in both positive and negative ways. The researchers also explored the participants' attitudes toward mental health and well-being which can carry stigma due to personal and cultural factors. While the aides reported ...
The study found that morning types, those who go to bed early and wake early, had the best mental health of all groups. How to fix your sleep schedule in 5 steps
The most common oral health conditions include cavities, gum disease, tooth loss and oral cancer, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). About 90% of U.S. adults 20 years and older have ...