
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7


What is Creative Thinking? An Ultimate Guide
Read this blog to know What is Creative Thinking, its features, examples, and significance as well as the tips to unleash your Creative Thinking. The key to find innovative solutions is by practicing Creative Thinking skills. Learn how you can develop your Creative Thinking skills to come up with solutions to complex problems.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Leadership Skills Training
- Instructional Design Training
- Design Thinking Course
- Business Development Training
- Leadership and Management Course

Do you want to give solutions to problems that are completely out of the box? Wouldn’t it be better if you could solve your problems in your workplace in a more creative manner? If you are wondering how you can do this, the answer is with the help of Creative Thinking. But do you know What is Creative Thinking, and how can you develop this skill to help you find creative solutions?
Creative Thinking allows you to find hidden patterns and generate solutions even to the most complex problems. Want to know more about What is Creative Thinking, its features, examples, and its importance? Read this blog to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is Creative Thinking?
2) Types of Creative Thinking
3) Importance of Creative Thinking
4) Benefits of Creative Thinking
5) 5 ways to improve Creative Thinking
6) Conclusion
What is Creative Thinking?
Defining Creative Thinking is important before one chooses to explore its depth. It is a crucial aspect of Design Thinking, characterised as the capacity to perceive scenarios, ideas, or challenges in novel, innovative, and often unconventional manners. It necessitates surpassing established patterns or notions, leading to the creation of original and impactful ideas. At its core, it represents the act of venturing beyond conventional boundaries.

Types of Creative Thinking
Let’s understand the various types of Creative Thinking so that you can employ the skills depending on the context or the problem at hand. Here are its five common types:
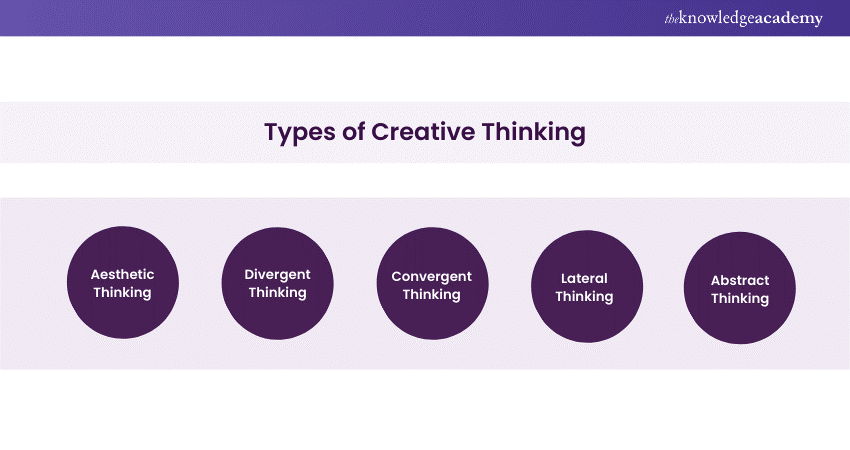
a) Divergent T hinking : This type of Thinking is about generating multiple solutions or ideas from a single starting point. It's similar to brainstorming, where the goal is to come up with as many answers or ideas as possible. Divergent Thinking is expansive, non-linear, and unrestrained, allowing for a wide array of potential solutions.
b) Convergent Thinking: Opposite to Divergent Thinking, Convergent Thinking seeks to narrow down options to find the single best solution to a problem. It involves analytical skills and logic to evaluate the ideas generated by divergent thinking, ultimately arriving at the most suitable answer.
c) Lateral Thinking: Coined by Edward de Bono, Lateral Thinking involves looking at a problem from a completely different perspective. It's about thinking "outside the box" and seeking solutions that might not be immediately obvious. Lateral thinkers often use indirect and creative approaches to problem-solving, making connections between seemingly unrelated concepts.
d) Abstract Thinking: This ability refers to the about concepts, ideas, or objects that are not physically present. It involves understanding complex ideas by breaking them down into their constituent parts and understanding how they relate to one another. Abstract thinkers are often good at seeing the "bigger picture" and understanding overarching themes and patterns.
e) Aesthetic Thinking: Rooted in the appreciation of beauty, art, and nature, Aesthetic Thinking is about recognising and creating harmony, balance, rhythm, and emotion. It's a form of Thinking often employed by artists, designers, musicians, and other creatives who seek to convey emotion, evoke reactions, or represent abstract ideas through their works.
Interested in building skills to guide those around you? Register for our Leadership Skills Courses !
Importance of Creative Thinking
In the contemporary job market, the enduring value of soft skills, such as Creative Thinking, extend across diverse industries. Employers increasingly prioritise adept at developing and experimenting with novel ideas. They actively seek analytical and outside-the-box thinkers, emphasising the iterative nature of Creative Thinking skills. These skills include creative problem-solving, innovative thinking, and analytical abilities. They hold particular significance in workplaces marked by constant evolution and the integration of emerging technologies.
Creative Thinking is a linchpin in the contemporary professional landscape. With the rising importance of soft skills, including resilience, flexibility, agility, motivation, self-awareness, curiosity, and a commitment to lifelong learning, these attributes complement and amplify the impact of Creative Thinking. They reflecting the multifaceted nature of skills demanded in an ever-evolving workplace.
Thus, Creative Thinking is not confined to specific roles or industries but emerges as a cross-cutting competency essential for addressing the complexity of modern challenges. As workplaces grapple with rapid technological advancements and paradigm shifts, professionals with impressive Creative Thinking skills stand out as valuable assets. Their ability to navigate challenges, devise innovative solutions, and adapt to changing market environments aligns with the demands of an era marked by continuous transformation.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Here are the key benefits of Creative Thinking skills across personal, academic, and leadership domains:
Improved problem-solving capabilities
Creative Thinking is a versatile problem-solving tool, not limited to workplace challenges. It accelerates problem resolution by introducing diverse thought techniques. The cultivated ability to discern patterns more swiftly broadens the scope of effective solutions, promoting agility in addressing many issues encountered in daily life.
Stronger interpersonal connections
Enhanced communication lies at the heart of Creative Thinking's impact on relationships. Clear articulation of ideas enriches conversations with friends, family, and colleagues. Moreover, collaborative Creative Thinking fosters a collective approach to problem-solving. This, in turn, strengthens bonds and generates innovative solutions through the synergy of diverse perspectives.
Heightened productivity
Contrary to misconceptions, Creative Thinking is not a diversion but a catalyst for productivity. When traditional thought patterns lead to frustration and stagnation, engaging in Creative Thinking strategies becomes a rejuvenating pause. It rekindles motivation, reignites passion, and unlocks new solutions. As a result, it prevents productivity decline by introducing fresh perspectives and approaches.
Higher self-awareness
Creative Thinking acts as a vehicle for self-discovery by encouraging the exploration of diverse perspectives. This process unveils assumptions, biases, and viewpoints that may have remained unnoticed.
Challenging conventional thinking nurtures self-awareness and bolsters emotional intelligence. The ability to reframe perspectives and embrace a growth mindset becomes a decisive outcome of this ongoing journey of self-exploration.
5 ways to improve Creative Thinking
Here are several ways that you can improve your Creative Thinking Skills:
1) Be curious
It is very crucial that you stay curious because it opens you up to new opportunities and helps you solve problems in a creative manner. Staying curious helps you develop your Creative Thinking skills. Staying curious will help you gain more knowledge, and you will be able to open yourself to many new experiences.
2) Open your mind
There are many professionals who lose out on amazing opportunities because they are unable to adapt to changes quickly. As a result, these opportunities are passed on to candidates who can readily adapt to market changes. Moreover, keeping yourself open to new experiences will help you improve your Creative Thinking skills. This will help you come up with more creative solutions.
3) Expand your knowledge horizon
If you have willingness to learn new skills and knowledge every day, you will be able to expand your Creative Thinking ability to solve complex problems. Try to read research papers, watch interactive videos, talk with professionals who are from different industries as well. This will open your capability to adapt to any new or sudden market changes, which will make you a capable candidate for your organisation.
4) Think how you can improve
To make sure that your Creative Thinking skills are being nurtured, try to always think about solutions or practice thinking about any random subject which you may find interesting. For example, you may find the subject of international public relations interesting, which necessarily doesn’t relate to your present career. Studying or thinking about a different subject matter allows you not only to increase your general knowledge but also to keep your mind active.
5) Practice brainstorming activities
The best way to improve your Creative Thinking skills is by practicing different games and activities which keeps your brain active. These games are mainly designed so that you’ll be challenged intellectually and induce sensory stimulation. It might not seem apparent to you but practicing brainstorming activities will help you improve the quality of your Creative Thinking.
6) Take inspiration from others
It is a very important factor while you are trying to improve your Creative Thinking skills. This is often overlooked because you might ask, “How can observing others help your Creative Thinking skills?” You need to understand that if you are inspired, your creativity will also improve. Creativity can be in many forms, whether it be cooking, drawing, reading, knitting, etc. Observing people who are good at these, will also inspire you to express your creative side and develop them.
7) Collaborate with your team
While you are solving problems, do not forget to collaborate with your team. Your team members are your strongest point in an organisation. When you collaborate with many people or members of your team, you get so many different ideas which when combined gives out Creative solutions to the problems. Also, collaboration helps you to look at a problem from different perspectives, which in turn nurtures your Creative Thinking.
Learn to be a dignified figure among your peers by joining our Introduction to Supervising a Team Course !
Conclusion
We hope that you understood What is Creative Thinking from this blog. This blog also discussed how Creative Thinking can transform and innovate problem-solving capabilities. As illustrated by examples, improving Creative Thinking skills can help you tackle immense challenges and enhance personal growth.
Curious about how the human mind works? Try our Creative and Analytical Thinking Training !
Frequently Asked Questions
Practising mindfulness directs us to the moment and helps us stop and see what we are feeling without judging it, whatever it is, thus coping with our moods and directing our attention. Practising Creative Thinking mainly involves learning how to think differently, provide fresh viewpoints, and seek solutions in an innovative manner by mixing divergent thinking and often drawing from transdisciplinary knowledge.
In structured business environments, Creative Thinking can be applied through design thinking, strategic innovation, and problem-solving methodologies.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Time Management Training, Attention Management Training, Exceptional Customer Service Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Personal Development methodologies .
Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Personal Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Personal Development skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
What is creative problem-solving?
Table of Contents
An introduction to creative problem-solving.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming . It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh perspectives becomes invaluable for individuals, businesses, and communities alike.
Importance of divergent and convergent thinking
At the heart of creative problem-solving lies the balance between divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking encourages free-flowing, unrestricted ideation, leading to a plethora of potential solutions. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is about narrowing down those options to find the most viable solution. This dual approach ensures both breadth and depth in the problem-solving process.
Emphasis on collaboration and diverse perspectives
No single perspective has a monopoly on insight. Collaborating with individuals from different backgrounds, experiences, and areas of expertise offers a richer tapestry of ideas. Embracing diverse perspectives not only broadens the pool of solutions but also ensures more holistic and well-rounded outcomes.
Nurturing a risk-taking and experimental mindset
The fear of failure can be the most significant barrier to any undertaking. It's essential to foster an environment where risk-taking and experimentation are celebrated. This involves viewing failures not as setbacks but as invaluable learning experiences that pave the way for eventual success.
The role of intuition and lateral thinking
Sometimes, the path to a solution is not linear. Lateral thinking and intuition allow for making connections between seemingly unrelated elements. These 'eureka' moments often lead to breakthrough solutions that conventional methods might overlook.
Stages of the creative problem-solving process
The creative problem-solving process is typically broken down into several stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in understanding, addressing, and resolving challenges in innovative ways.
Clarifying: Understanding the real problem or challenge
Before diving into solutions, one must first understand the problem at its core. This involves asking probing questions, gathering data, and viewing the challenge from various angles. A clear comprehension of the problem ensures that effort and resources are channeled correctly.
Ideating: Generating diverse and multiple solutions
Once the problem is clarified, the focus shifts to generating as many solutions as possible. This stage champions quantity over quality, as the aim is to explore the breadth of possibilities without immediately passing judgment.
Developing: Refining and honing promising solutions
With a list of potential solutions in hand, it's time to refine and develop the most promising ones. This involves evaluating each idea's feasibility, potential impact, and any associated risks, then enhancing or combining solutions to maximize effectiveness.
Implementing: Acting on the best solutions
Once a solution has been honed, it's time to put it into action. This involves planning, allocating resources, and monitoring the results to ensure the solution is effectively addressing the problem.
Techniques for creative problem-solving
Solving complex problems in a fresh way can be a daunting task to start on. Here are a few techniques that can help kickstart the process:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely-used technique that involves generating as many ideas as possible within a set timeframe. Variants like brainwriting (where ideas are written down rather than spoken) and reverse brainstorming (thinking of ways to cause the problem) can offer fresh perspectives and ensure broader participation.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps structure information, making connections between disparate pieces of data. It is particularly useful in organizing thoughts, visualizing relationships, and ensuring a comprehensive approach to a problem.
SCAMPER technique
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. This technique prompts individuals to look at existing products, services, or processes in new ways, leading to innovative solutions.
Benefits of creative problem-solving
Creative problem-solving offers numerous benefits, both at the individual and organizational levels. Some of the most prominent advantages include:
Finding novel solutions to old problems
Traditional problems that have resisted conventional solutions often succumb to creative approaches. By looking at challenges from fresh angles and blending different techniques, we can unlock novel solutions previously deemed impossible.
Enhanced adaptability in changing environments
In our rapidly evolving world, the ability to adapt is critical. Creative problem-solving equips individuals and organizations with the agility to pivot and adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring resilience and longevity.
Building collaborative and innovative teams
Teams that embrace creative problem-solving tend to be more collaborative and innovative. They value diversity of thought, are open to experimentation, and are more likely to challenge the status quo, leading to groundbreaking results.
Fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement
Creative problem-solving is not just about finding solutions; it's also about continuous learning and improvement. By encouraging an environment of curiosity and exploration, organizations can ensure that they are always at the cutting edge, ready to tackle future challenges head-on.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Creative Thinking Definition
Creative thinking examples, why is creative thinking important, how to include creative thinking skills in a job application, how to build creativity, what is creative thinking definition and examples.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Table of Contents
Creative thinking is the ability to come up with unique, original solutions. Also known as creative problem-solving, creative thinking is a valuable and marketable soft skill in a wide variety of careers. Here’s what you need to know about creative thinking at work and how to use it to land a job.
Creative thinking is all about developing innovative solutions to problems. Creative thinkers brainstorm not only a large number of ideas but also a variety and range of them. In the workplace, creative thinking is highly valuable because employers look to hire innovative employees who can help them solve the company’s problems.
So, what does creative thinking in the workplace look like? First, a creative person brainstorms their ideas, then they’ll experiment with them. They look at ideas from multiple perspectives and examine how their solutions fit into the scope of what they’re working on. Creative thinkers aren’t afraid to take risks and try new ideas. In fact, this ability to develop, test, and implement original solutions makes them a valuable asset to just about any workplace.
Creative thinking in the workplace might look like:
- Holding an interactive brainstorm to gather initial thoughts on a project
- Evaluating a current process and offering suggestions on how to improve it
- Researching other ways to market a product and leading experiments on new marketing channels
- Developing an innovative way to reach out to prospective clients
- Identifying a unique opportunity to promote the company brand and developing a strategy to do so
- Discovering a new way to measure a product initiative’s success and using learnings to iterate on the next version
Finding patterns in a company’s revenue growth and using data trends to strategize a new sales plan
Creative thinking includes the process of innovative problem-solving — from analyzing the facts to brainstorming to working with others. Creative thinking examples include analytical skills, innovation, and collaboration.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills are problem-solving skills that help you sort through facts, data, and information to develop rational solutions. These skills aid you in the first part of the creative thinking process as you brainstorm and start to generate ideas.
Analytical skills include:
- Data analysis
- Forecasting
- Interpreting
- Communication
Innovation is the ability to come up with something new; however, you don’t need to develop the first flying car to be an innovative thinker. “Something new” at work might mean a method you haven’t tried before or experimenting with an unfamiliar process. Innovators in the workplace aren’t afraid to step away from tradition and explore something original, even if it might fail.
Innovation skills include:
- Risk-taking
- Brainstorming
- Critical thinking
Collaboration
Creative thinking doesn’t have to happen alone; you might have your most creative ideas when bouncing your work off others. Collaboration skills ensure you consider multiple perspectives and ways of thinking when you develop and refine ideas.
Collaboration skills include:
- Written and verbal communication
- Active listening
- Inclusivity
A soft skill like creative thinking will always be valuable to employers, whether you’re looking for a marketing job or trying to land a career in finance . Employers need employees who can develop and experiment with new ideas to help them solve complex problems.
“Many employers seek candidates that are analytical and outside-the-box thinkers which are iterations of creative thinking skills,” says Alejandra Garcia, manager, alumni college and career success at Code2College and Forage content development partner. “Thus, creative thinking, creative problem solving, innovative thinking, and analytical skills are all valuable in the current workplace — these skills are especially important in our ever-changing workplaces with new emerging technologies.”
The data supports this idea, too. According to the World Economic Forum’s 2023 Future of Jobs report , creative thinking is the second most important skill for workers in 2023, preceded only by analytical skills. Other top skills include soft skills like resilience, flexibility and agility, motivation and self-awareness, and curiosity and lifelong learning .
“The ability to navigate new challenges quickly can benefit any workplace!” Laura Fontenot, resume writing expert, ACRW, and CPRW, says. “The current world of work is fast-paced, technically driven, and constantly changing. Being intuitive, creative, driven, and a problem solver are key.”
If creative thinking is one of the top soft skills employers look for, how do you show you have it in a job application? The key is to prove these skills through examples of how you’ve used them rather than just naming them.
On a Resume
While creative thinking is a skill employers might look for, you don’t necessarily need to write “creative thinking” on your resume to show you have this skill. Instead, it’s better to demonstrate how you’ve used creative thinking skills to drive results.
“Think of your best mental strengths,” says Fontenot. “Are you a great problem solver? Do you understand how to phrase things differently? Can you learn a new skill quickly? Those questions can help you find great words for the resume . Consider adding things like problem-solving, intuition, collaboration, fast learner, organized, or communication.”
Log in to view and download a customizable resume template with examples of how to include creative thinking skills:

On Your Professional Profiles
You can show these skills outside of your resume in creative ways — including on your LinkedIn profile and website (if you have one!).
“Early professionals can make creative thinking a part of their professional brand by explicitly adding creative thinking or creative problem solving to their list of skills on their resumes and LinkedIn profiles — this will help with ATS optimizations,” Garcia advises.
Yet beyond just listing this skill, Garcia adds that you can provide real proof of your creativity online, too.
“Consider adding projects or an online portfolio website link to your resume and LinkedIn where you can showcase projects you’ve worked on that demonstrate their problem-solving skills.”
In the Interview
In the interview , make sure you can describe your workflow and process for these projects or any other situation when you’ve used creative thinking. Elaborate how you brainstormed ideas, what range of ideas you had, how you tested and experimented, and how you decided on a final solution.
It’s best to use the STAR method to structure your answers. This will ensure you clearly explain the situation and the results you brought by using your creative thinking skills.
>>MORE: Prepare to speak about your soft skills by practicing answers to commonly asked behavioral interview questions .
1. Put Yourself in a Box
Creative thinking is about “thinking outside the box,” but putting limitations on your problem-solving can help you think more freely and innovatively. For example, if someone tells you to make dinner, you may struggle to come up with a meal you don’t always cook. Yet if they ask you to make a hot dinner with three specific ingredients and two spices, you’ll more likely come up with something original.
Putting yourself inside a box can help expand your thinking, whether that’s by telling yourself you need to include three charts in your presentation or giving yourself a strict word count for an article.
2. Switch up Your Routine
Routine can be a great productivity booster, but it also can get in the way of your creativity. So, switch up your routine for one project, day, or even an hour. This can be something as small as where you’re physically sitting when you do your work or something as big as your process for approaching projects. Challenging yourself to do something different will help you find creative ways to adapt to your new environment.
3. Challenge What’s Currently Working
Think about how you might expand or improve upon a current process. What would you do if you had more resources, whether that’s time, money, or another expert? What would you do if you had fewer resources? If this project was taking place at a different time of year? If the target audience was different? Imagining these different potential scenarios will force you to problem-solve and adjust for various (very possible!) circumstances.
4. Find Inspiration
Creative thinking doesn’t happen in a bubble. It’s vital to ask for others’ opinions and ideas. Creative thinkers consider multiple perspectives and are curious about how others think. Ask your colleague about their work processes, whether it’s how they research for a client deliverable or how they approach meeting an external buyer.
5. Ask for Feedback
The best way to improve a skill is to get feedback from others on how you’re using it — and you don’t need to set up a formal feedback session to do so. Instead, ask questions when you’re working with others about your work. Keep these questions open-ended and lead with curiosity instead of looking for a specific answer. What did they think of how you led the brainstorm? What would they have done differently? What strikes them about the final product? Keep an open mind and remember not to take the feedback personally. It’s an opportunity to grow, and growing those skills might just help you land your next job!
Two Sigma Professional Skills Development Program
Level up your non-technical skills and learn how to approach problems, set goals, and communicate clearly.
Avg. Time: 5-6 hours
Skills you’ll build: Project planning, project management, relationship management, explaining analysis
Image credit: Canva

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Build career skills recruiters are looking for.
19 Creative Thinking Skills (and How to Use Them!)

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, 54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
In a fast-moving world, being able to find new perspectives and create innovation is an increasingly valuable skill . Creative thinkers are often at the forefront of driving change, solving problems, and developing new ideas. Not only that, but those who bring creative thinking to how they work are often happier, more productive, and resilient too!
So you might be asking yourself, how can I develop my creative thinking skills and think more creatively at work? Whether you want to supercharge your interpersonal skills, advance your career or be happier and more satisfied in the work you do, it pays to learn to think more creatively.
For many people, creative thinking is the key that unlocks solutions, promotes diverse thinking, and leads to better relationships and job satisfaction. So how can you get started with creative thinking? As passionate believers in the value of creative thinking, we’re here to help and truly think unleashing your creativity can be key to your personal development!
In this post we’ll define what creative thinking is, highlight the benefits, explore 19 key creative thinking skills and give you some examples of how to apply them in the workplace . Let’s dig in!
What is creative thinking?
Why is creative thinking important, what are the benefits of creative thinking.
- What are creative thinking skills?
- Examples of creative thinking skills (and how to use them)
- How to use creative thinking skills at work?
How to improve your creative thinking skills?
Creative thinking is the ability to approach a problem or challenge from a new perspective, alternative angle, or with an atypical mindset. This might mean thinking outside of the box, taking techniques from one discipline and applying them to another, or simply creating space for new ideas and alternative solutions to present themselves through dialogue, experimentation, or reflection.
Bear in mind that the number of different creative approaches is as vast as the number of creative thinkers – if an approach helps you see things differently and approaching a challenge creatively, follow that impulse.
While there are some proven methods and guidelines that can help you be a better creative thinker, remember that everyone can be creative and finding what works for you is what is important, not the terminology or specific framework.
One misapprehension about creative thinking is that you have to be skilled at more traditional creative skills like drawing or writing. This isn’t true. What’s important is that you are open to exploring alternative solutions while employing fresh techniques and creative approaches to what you’re working on.
You don’t need to be a great artist or even work in a traditionally creative field – we believe everyone is capable of creative thinking and that it enriches your personal and professional lives when you learn to be more creative.
Another misconception about creative thinking is that it applies only to the ideation or technically creative parts of the process. All aspects of our lives and interactions with people and challenges can benefit from creative thinking – from the ability to see things differently.
At work, thinking creatively might mean finding better ways to communicate, improve your working practices, or developing and implementing fresh solutions too.
Creative thinking is important because it drives new ideas, encourages learning, and creates a safe space for experimentation and risk-taking.
As organizations and people grow, they often develop tried and tested ways of operating. While it’s important to have solid working practices and processes, unswerving dedication to the norm can lead to stagnation and a lack of innovation and growth.
Creative thinking is important because it drives new ideas, encourages learning and creates a safe space for experimentation and risk-taking. Simply put, creativity and creative thinking are part of what helps businesses and individuals succeed and grow .
Whether your team or business thinks of itself as a creative one, you can’t afford to miss out on the benefits of creative thinking if you want to grow , deliver change, and help your team bring their best selves to work.
Using creative thinking skills at work creates b enefits not only in the ways we solve problems but also in how we approach everything from communication to self-fulfillment, task management, and growth . Bringing a culture of creative thinking into a workshop or group is often the job of a talented facilitator but whatever your role, there are benefits to thinking more creatively. Let’s explore some of the benefits of thinking creatively at work and in your everyday life!
Build empathy
- Bust assumptions
- Become a better problem solver
Find ways to move quickly and effectively
- Increase happiness
Discover new talents and promote learning
- Boost resilience and deal with adversity
Boost your CV and employability
Empathy and creative thinking go hand-in-hand. By practicing creative thinking skills and regularly looking for new ideas and points of view, you can actively become better at understanding your colleagues, customers, and even your family and friends. One of the major barriers to having productive and meaningful relationships is an unwillingness to see things from a perspective other than your own or failing to understand how another person is feeling.
By developing this skill, you can engage more meaningfully and honestly with people, ideas, and perspectives in all aspects of life. What’s more, because of the benefits that creative thinking can bring, you’ll actively want to see things from new perspectives and be more empathic : something that’s fundamental to creating real change.
Bust assumptions
Assumptions can be harmful in both our personal and professional lives. Whether it’s making assumptions about why someone is behaving the way they are in a workshop or what features will make your customers happiest, holding onto incorrect or inadequately formed assumptions can be problematic . It can create difficulty and tension in relationships and what’s more, it can lead to the development or introduction of solutions that are simply unfit for purpose.
Using creative thinking skills to challenge assumptions, build clarity, and see things from new perspectives can be transformative. If an assumption someone else makes feels incorrect, think about why and try to find out more. If someone challenges an assumption you hold, be open and listen.
Become a better problem solver
An example of not being a creative thinker is sticking to a tried and tested approach and sticking to the norm in every situation without considering whether trying something new might not lead to better results.
When looking to solve a problem or create innovative solutions, going outside of what you know and being open to new ideas is not only exciting, but it can create more impactful solutions too. You might even try using problem-solving techniques alongside some of the creative thinking skills below to find the absolute best solutions!
Some processes and working practices can be slow, especially in large organizations with many moving parts – but do they all have to be? Thinking creatively can help you find lean, actionable solutions that you can put into practice quickly and test ahead of bigger changes .
Experimentation and a willingness to take risks are vital to growth and change, and creative thinking helps create a climate conducive to finding and trying quick, effective solutions.
Increase happiness and satisfaction
Finding fresh, appropriate solutions to problems can be incredibly satisfying and is a fast-track to finding happiness both in and out of work. Bringing your whole self to a situation and being enabled to think outside of the box is a great way to feel valued and engaged with what you are doing.
Feeling frustrated with how a situation or process at work is going? Try developing and employing your creative thinking skills alongside your colleagues to find a better, happier way to collaborate! Feel unfulfilled or that not all of your skills and interests are being utilized? Consider how you might creatively deploy the skills or talents that make you happy and scratch that itch.
As children, we are encouraged to see things differently and try new things as part of our learning and growing process. There’s no reason we shouldn’t do this as adults too! Trying new things and learning to think creatively can help you find new skills, talents, and things you didn’t even know you were good at.
Staying curious and following what interests you with an open mind is a prime example of what a small change in thinking can achieve. Remember that creative thinking is a gateway to learning and by actively developing your creative toolset, you can grow and discover more in all walks of life – a surefire path to personal development.
Get better at dealing with adversity
It’s easy to get frustrated when problems seem to come thick and fast and existing solutions or methods don’t work. Adversity is something all of us will face at some point in our personal and professional lives but there are ways you can become more able to handle problems when they arise .
A strong suite of creative thinking skills is an important aspect of how we can build resilience and be more flexible when adapting or creating change. By exploring alternative ways of thinking, you’ll be better prepared to face adversity more openly and find alternative ways to resolve challenges in whatever context they emerge.
Creative thinkers are valuable employees at organizations of any size. Whether it’s championing innovation, creating change in policy, or finding better ways to collaborate, people who can effectively solve problems and leverage their creative thinking skills are better positioned for success at work.
Consider how you might plug your skills gap and boost your CV by developing your creative skillset and you won’t just be more successful – you’ll be happier and more engaged at work too!
Whatever your background or role, you are capable of thinking creatively and bringing creativity into your life.
What are creative thinking skills?
Creative thinking skills are the methods or approaches you might use when trying to solve a problem differently and explore a fresh perspective. While some of these skills might come naturally to you, others might need a more considered, purposeful approach.
For example, you might be a natural visual thinker who is great at presenting and interpreting visual information but you might not be so good at freely experimenting or creating space for reflection. In this case, you might try some brainstorming exercises to loosen up your experimentation muscles or create scheduled time for reflection in your working routine.
While creative professions like artists, writers, or designers may see more obvious uses for creative thinking skills, all professions can benefit from developing and deploying creative thinking . If you find yourself having difficulty at work or in need of inspiration or motivation, finding space to build on your creative skillset is a way to not only move forward but have fun while doing so.
If you think you’re not creative or have no creative thinking skills, we’re here to tell you that whatever your background or role, you are capable of thinking creatively and bringing creativity into your life : you might just need a little push or to reframe how you think about creativity!
Save time planning your next creative workshop
Examples of creative thinking skills (and how to use them)
Creative thinking skills come in all shapes and sizes, ranging from things like abstract thinking and storytelling to finding ways to radically plan projects or recognize organizational patterns .
In this section, we’ll explore each of the example creative skills below and talk about how you might use them in your personal and professional practice. We’ll also point out some things to watch out for where appropriate so you can make the most out of your new creative skills and avoid potential setbacks.
We’ll also include a method from the SessionLab library that will help you practice and explore each skill, whether alone or with others .
Feel free to read and explore the creative thinking skill which feels most interesting or applicable to you and come back and experiment with others in the future!
Some example creative thinking skills include:
Experimentation
Open-mindedness, lateral thinking.
- Pattern recognition
Deep and active listening
Challenging norms, lean organization, simplification, radical planning.
- Collaborative thinking
Data collection
- Interpretation and analysis
Interdisciplinary thinking
Frameworks and rulesets, micro and macro thinking, visual thinking, abstract thinking, storytelling.
Note that this list is not exhaustive, and there are many more ways of thinking creatively – try to see these creative skills as a jumping-off point for seeing things differently and exploring creative thinking at work .
Let’s get started!
A core creative skill is the ability to experiment and try new things, whether that’s in your personal practice, in a closed environment, or even in the field. It can be easy to fall short of implementing new ideas or following through with creative projects because critical judgment or overthinking gets in the way . A good experimenter is a self-starter who makes informed decisions to kickstart projects and test hypotheses.
Think of a painter who throws paint at a canvas and introduces new materials without overthinking or being self-critical. While not everything they try will be perfect, that’s the point – not every experiment needs to be successful in order to teach you something useful. By experimenting, you can try things that might prove useful or will lead you towards new solutions and better ideas. Remember that the act of experimentation is generative and often fun so be sure to give it a try!
One thing to watch out for is being sure to effectively capture the results of your experiments and to continue developing and iterating on the results. Experimentation is a great place to start, but remember that it is part of a larger process. Without effective documentation, you might not trace what delivered the best results and be unable to reproduce the outcomes. Experimentation is a great example of why creative freedom should be paired with a strong process in order to be at its best.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
Four-Step Sketch is a great method for promoting experimentation. By following a process that enables quick brainstorming before development, you can help build an experimental mindset that also generates results.
Open-mindedness is a critical element of creativity and one of the best creative thinking skills you can try to build if you’re new to the practice. Being open-minded means being receptive to new ideas, different ways of thinking, and perspectives which are not your own. It means not closing down conversations or ideas prematurely and trying to actively explore what is presented to you.
Imagine that a colleague comes up with an idea that is so far out of the status quo it seems off-the-wall and bizarre. Being open-minded means actively engaging with what is presented and to refrain from forming judgments before first understanding where your colleague is coming from .
Your colleagues’ initial idea might not be perfect, but being open-minded and truly attempting to understand their perspective means you can create dialogue, foster creativity, and move forward as a team.
Being open-minded doesn’t mean accepting every new idea and agreeing wholesale with every different opinion. While you should always try to be open and receptive to new ideas and other perspectives, you should also critically appraise and engage with them as part of a larger creative process. Don’t be so open-minded you have no strong opinions of your own!
Heard, Seen, Respected (HSR) #issue analysis #empathy #communication #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can foster the empathetic capacity of participants to “walk in the shoes” of others. Many situations do not have immediate answers or clear resolutions. Recognizing these situations and responding with empathy can improve the “cultural climate” and build trust among group members. HSR helps individuals learn to respond in ways that do not overpromise or overcontrol. It helps members of a group notice unwanted patterns and work together on shifting to more productive interactions. Participants experience the practice of more compassion and the benefits it engenders.
Open-mindedness is particularly useful when it comes to meaningfully communicating with others. Whether its developing the ability to walk in the shoes of someone else or building empathy and listening skills, Heard, Seen, Respected is a great method to try when learning to be more open-minded.
Lateral thinking is a prime example of how we can creatively solve real-world problems in a measurable and easy-to-understand manner. Deploying lateral thinking means using reasoning or non-traditional logic to find an indirect or out-of-the-box approach to solving a problem.
A simple example might be a challenge like: we need to increase revenue. Traditional thinking might mean considering hiring new salespeople to try and get more direct sales. A lateral approach might mean engaging more with current customers to reduce churn, working with external partners to get new leads, working to get sponsorship, piloting an affiliate scheme or any number of new ways to solve the existing problem.
Broadly speaking, lateral thinking often means stepping back and considering solutions or approaches outside of the immediately obvious.
One potential danger with lateral thinking is spending time to create new solutions to problems that don’t need them. Not every problem needs to be solved laterally and the best solution might actually be the most straightforward. Be sure to tap into existing knowledge and appraise a problem before trying something radical to avoid wasted time or frustration!
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Developing your lateral thinking skills comes more naturally to some than others. The Creativity Dice is a great method for getting out of linear thinking habits and moving into different ways of thinking.
Pattern recognition
Pattern recognition is the ability to recognise existing or emerging patterns and make connections based on the patterns you have discerned . While pattern recognition goes back to our prehistoric roots, being able to spot patterns outside of the ordinary and consider what may not be immediately obvious is a vital creative thinking skill for today.
Consider how meetings between some members of a team might often end in conflict. While it might first seem that these two people just can’t get along, it might actually be that certain emotional triggers are being tripped or the format of the conversation isn’t working. Looking beyond your initial impressions and from a new perspective might let you find a repeating pattern that isn’t immediately obvious.
When trying to spot patterns, try to be mindful of existing biases so you avoid bending what is happening to fit a pattern you might be expecting. Be sure to interpret all data fairly and honestly, even if you believe a pattern is already forming.
Affinity Map #idea generation #gamestorming Most of us are familiar with brainstorming—a method by which a group generates as many ideas around a topic as possible in a limited amount of time. Brainstorming works to get a high quantity of information on the table. But it begs the follow-up question of how to gather meaning from all the data. Using a simple Affinity Diagram technique can help us discover embedded patterns (and sometimes break old patterns) of thinking by sorting and clustering language-based information into relationships. It can also give us a sense of where most people’s thinking is focused
Pattern recognition is a skill that benefits from thoughtful practice. Try starting with a deliberate pattern-finding process like Affinity Map to build the ability to see patterns where they might not first be obvious.
While it might not seem like it at first, being a good listener is a creative thinking skill. It asks that a person not only try to understand what is being said but also to engage with the why and how of the conversation in order to reframe prior thinking and see things from a new perspective.
Deep listening or active listening is not only hearing the words that someone is saying but actively seeking to interpret their intent, understand their position, and create a positive space for further conversation. Not only does this create a deeper conversation for both parties, but this act of engagement and understanding leads to more creative and dynamic results too.
Think of a workplace grievance that one person might have against another. Without actively listening and trying to understand the core issues from the perspective of everyone involved, you might not only fail to solve the issue but actually make staff feel less heard and valued too.
By employing this creative thinking skill in such a conversation you can see things more clearly and find a way to creatively satisfy the needs of everyone involved.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Trying to be more present in conversations is a great place to begin building your deep listening and active listening skills . Want to supercharge the process as a group? Try a role-play activity like Active Listening to more thoughtfully see and reflect on how important this skill can be.
Not all established working practices are the best way of doing things. People who practice this creative thinking skill are likely to question the status quo in search of something new which can deliver meaningful change. While any challenge to the established order needs to be conducted respectfully and thoughtfully, thinking of how to go beyond the norm is how innovation occurs and where creative thinkers excel.
When trying to practice this skill, be prepared to question existing methods and frameworks and ask if there might be a better way outside of the limits of the current system.
As with lateral thinking, it’s important to recognize that not everything is a problem that needs to be solved and so you may need to be selective in which norms should be challenged – otherwise, you may never make it out of the front door!
Additionally, challenging the established order often means questioning the work someone else has already done. While this is a necessary part of growth, it should always be done constructively and respectfully.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
Challenging norms without a considered approach can be ineffective and potentially frustrating. Taking the time to build shared understanding and push in the same direction with What, So What, Now What? is a great way to explore how your existing process is or isn’t working and challenge norms productively.
Creative thinking doesn’t mean being disorganized or chaotic just because you have an abundance of ideas. In order to facilitate creative thinking, it’s important to stay organized and approach the process with the right framework, mindset, and space. As a creative thinking skill, lean organization means considering what you absolutely need to do in order to make things happen, versus what you don’t.
Think of how a large, multi-discipline team might go about organizing themselves for a big project. While it’s vital everyone is aligned and kept up to date, a traditional system of scheduled meetings might not be the most productive. Lean organization means considering the needs of the team, the project and thinking creatively about what you need to stay organized, and keeping unnecessary admin to a minimum.
Thinking creatively about organization is something all leaders should practice but any project can benefit from thinking through the process by which it will be accomplished.
MoSCoW #define intentions #create #design #action #remote-friendly MoSCoW is a method that allows the team to prioritize the different features that they will work on. Features are then categorized into “Must have”, “Should have”, “Could have”, or “Would like but won‘t get”. To be used at the beginning of a timeslot (for example during Sprint planning) and when planning is needed.
Lean organization often means being honest and realistic about what is absolutely necessary versus nice to have. MoSCoW is an effective agile framework for planning work and also reframing your approach to organizing time, tasks and more!
Simplifying, presenting or decoding any information is a vital skill when working with others. In a creative thinking context, simplification is the act of seeing what is important about a task or piece of data and stripping away the extraneous parts to see things more clearly.
Some problems can feel unassailable because of their complexity or scale – simplification allows you to reconsider a problem in simple terms and reframe it in a way that means you can approach it productively.
An example of using this creative thinking skill at work might be when presenting the results of a project to the rest of your organization. People working on other teams and in different disciplines could become disengaged if exposed to too many complex moving parts or it might simply be a waste of time to discuss every detail.
By simplifying a project into more succinct terms, you not only can help your group connect with the material swiftly but also boil a project down to its most important elements . This is a great way to creatively re-energize a project and identify where you can make an impact immediately.
6 Words #ufmcs #red teaming This tool is designed to help critical thinkers focus on a core idea by writing a short phrase summarizing their thoughts into a set number of words that are clear, concise, and accurate. This idea is based on a complete short story written by Ernest Hemingway: “For sale, baby shoes – never worn.” Six Words forces people to synthesize their ideas in a succinct and meaningful way, cutting away fluff and distilling the idea to its bare essence.
One way of practicing simplification is by summarising or condensing thoughts, ideas of stories into a more concise, compressed form . 6 Words is a method for cutting away extraneous material from ideas that engages creative thinking and reframing approachably – great for groups!
Any major project requires some measure of planning in order to succeed, especially when working with others. But are there times where overplanning or traditional working processes feel too slow or frustrating for the project at hand? This is where these creative thinking skills come in handy! Radical planning is a way of approaching project planning from an alternative angle in order to generate fast, effective results.
When taking this planning approach, you will often shuffle the order of the normal planning process in order to create alternative outcomes and cut out elements you may not need. For example, with the backcasting workshop activity, the approach is to think of desired outcomes up to twenty years in the future and work backward to figure out how we can make small steps today.
You might also try planning with a mindset of what you and your team can each achieve immediately and in a more experimental fashion with an activity like 15% solutions .
By approaching planning with a creative thinking mindset, you can surface ideas and plans which may not have come up with a more traditional planning process. Another great benefit is to question the normal manner in which your team or organisation approaches planning and can help your team find a method that works best for you!
Backcasting #define intentions #create #design #action Backcasting is a method for planning the actions necessary to reach desired future goals. This method is often applied in a workshop format with stakeholders participating. To be used when a future goal (even if it is vague) has been identified.
Collaborative thinking
Effective collaboration requires us to bring many different skills together, but consciously considering how to be a more effective collaborator is worth mentioning separately. When a creative thinker approaches collaboration, they will try to think of how to use alternative approaches to make the collaborative process more effective while also helping everyone on the team contribute and be heard.
An example is when it comes to getting work done in meetings – if the current process isn’t enabling everyone to collaborate effectively, you might employ creative thinking to try finding an alternative format, consider working asynchronously, or timeboxing parts of your agenda.
The best collaborators also find ways to champion the work of others and create a safe space for everyone to contribute – it might not be enough to assume collaboration will be accomplished when you get people in a room.
Employing this creative thinking skill can make all the difference when it comes to job satisfaction, interpersonal relationships and group outcomes too! Try approaching your collaborative projects more mindfully and see how it changes things for you!
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Working together on a task as a team is an effective way of kickstarting collaborative thinking, especially if you approach the task mindfully . The Marshamllow Challenge with debriefing is a proven method for engaging teamwork and by adding reflection time afterward, your group can share and build on what they learned.
Collecting data might seem like a solely analytical skill, but it is another area where creative thinking can lead to productive, unexpected and transformative results. Approaching the data collection process creatively might mean trying new techniques or sources, or simply reconsidering the how and why of your data collection processes.
Imagine you are running a survey to measure customer happiness. You might try asking traditional survey questions, but find that your response rate is low and furthermore, your approach might be invasive and actively decrease happiness too!
If you were to approach this problem creatively, you might find that using a simplified form, asking for feedback at a different point in the customer journey, or utilizing an alternative measurement scheme delivers the data you are looking for. In many cases, thinking about the questions you are asking from a new point of view is what unlocks a better data collection process.
The key to this creative thinking skill is to try looking at the data collection process from a new, preferably customer-centric perspective while also considering why and how you are collecting data. You will likely find that by asking for input from your customers more creatively, you create space for more creative responses too!
3 Question Mingle #hyperisland #team #get-to-know An activity to support a group to get to know each other through a set of questions that they create themselves. The activity gets participants moving around and meeting each other one-on-one. It’s useful in the early stages of team development and/or for groups to reconnect with each other after a period of time apart.
3 Question Mingle is a get to know you activity that does double duty in demonstrating the power of approaching data collection creatively. By creating their own questions, a group can really think about what they want to know, how they ask questions, and how the results differ. Be sure to give it a try!
Interpretation and analysis
Interpretation skills can be varied though in a creative thinking context it means being able to successfully analyze an idea, solution, dataset, or conversation and draw effective conclusions. Great interpreters are people with a desire to listen, understand, and dig deeper in order to make their interpretation fully realised.
One of the ways creative thinking can improve interpretation is in helping us challenge assumptions or initial readings of data in order to consider other possible interpretations and perspectives.
Say your product is having a problem with losing lots of new customers shortly after signing up. You do a survey and people say that they leave because the product isn’t useful to them. Your initial interpretation of that data might be that you’re not the right fit for these customers or that the product needs new features.
If you were to apply creative thinking to the interpretation of this data, you might conduct further research and see that the product is fine, but people didn’t find the right features for them and that your onboarding process needs to be improved.
The key here is interpreting the data from various perspectives and then correlating that with other sources to form an accurate and representative interpretation, rather than going with your initial assumption . By following this process, you might also find that the way you are collecting data is flawed (perhaps not asking the right questions) or that more research and data collection is needed.
So long as you are sure to have data points and analysis to back up your findings, it pays to explore alternative interpretations so you can avoid bias and find the most accurate takeaways .
Fishbone diagram #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis Fishbone diagrams show the causes of a specific event.
Effective interpretation and analysis isn’t possible without a thorough exploration of the problem or topic at hand. Fishbone Diagram is a simple method for not only surfacing insights but framing them in a way that allows for proper and multi-perspective analysis.
Einstein is quoted as saying, “We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them.” In this mold, sometimes the best ideas and solutions come from fields and disciplines outside of our own. By considering how someone with a different skillset to your own would solve a problem or deploy solutions, you can often find ideas and techniques you may never have considered.
Consider being tasked with improving employee happiness. A social media manager with a background in illustration and events management would likely try a very different approach to a sales manager who is used to a culture of incentives and bonuses. If you were trying to develop a new product, think of how a developer would approach deciding on key features versus an academic or a customer success manager?
The important thing here is to try and use the perspective, skill set , and approach of another field or discipline to first consider and then solve a problem more fully . Where possible, try and include people from other disciplines in the process and try to avoid making assumptions.
As with all creative thinking skills, being open-minded and sourcing the expertise and opinions of others where necessary is vital when creating true innovation.
Mash-Up Innovation #hyperisland #innovation #idea generation Mash-ups is a collaborative idea generation method in which participants come up with innovative concepts by combining different elements together. In a first step, participants brainstorm around different areas, such as technologies, human needs, and existing services. In a second step, they rapidly combine elements from those areas to create new, fun and innovative concepts. Mash-ups demonstrates how fast and easy it can be to come up with innovative ideas.
Interdisciplinary thinking isn’t just for radical academics. By combining ideas from disparate fields in a fast, fun manner, Mash-Up Innovation is great for building creative thinking skills and generating results in one fell swoop!
All creative thinking skills are about reframing things in a new way of finding alternative approaches. This can often mean abandoning an existing framework and thinking outside of the box. That said , another way of applying creative thinking is by bringing rulesets, constraints, or frameworks to your approach in order to trigger deeper creative work and tap into a problem-solving mindset .
Consider a simple task like trying to generate more customers. With free reign, there are innumerable ways to accomplish this. But what happens if you create a rule like, we cannot spend any money, or, these must be driven by social media alone. In order to accomplish your goal under these conditions, you must think more creatively and deeply, deploying more concentrated problem-solving skills than if you could try any approach you wanted.
Alternatively, you might approach a problem with a framework that forces you to think under specific circumstances or with a rigid set of steps. Six thinking hats is a great workshop activity that asks participants to frame and reframe a problem from six different angles. While it might first seem counterintuitive, the use of rules or frameworks can create fertile ground for creative thinking and lead to more realized solutions!
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Not all problems are created equal. Depending on how much it directly affects you, you might see a given problem as being more or less important than your colleagues, leading to a different response and approach to solving the problem. This creative thinking skill is all about being able to switch between seeing the bigger picture while also considering how something might manifest on a smaller scale.
Think of how frustrating it can be when an executive team makes sweeping changes that affect frontline staff in a way they might not have anticipated. Micro and macro thinking means seeing both problems and potential solutions from multiple perspectives and adjusting accordingly.
Another key aspect of applying this approach is knowing the limits of your own knowledge and involving stakeholders from all levels of an organization to inform your ideation and problem-solving process.
If you’ve never worked in support and don’t regularly talk to your support team, you might not understand how a change to helpdesk software could impact your team and your clients – remember that a big part of any change in perspective is doing the research and talking to who will be affected !
Stakeholder Round Robin Brainstorm #idea generation #brainstorming #perspectives #remote-friendly #online A divergent process to generate ideas and understanding from different perspectives.
Learning to practice micro and macro thinking often starts with first listening to and understanding the needs and perspectives of others . Especially those who have varied positions in relation to the problem, solutions, or organization you are working with. Stakeholder Round Robin Brainstorm is an effective method of surfacing insights and perspectives quickly and productively.
Of all the creative thinking skills on this list, visual thinking might be one you are most familiar with. Visual thinking is a method of processing, learning, and presenting information and concepts with visual assets such as images.
Visual thinking is often associated with creative thinking because of the consumption and creation of images at its heart. Don’t let this make you think you have to be able to draw in order to be a visual thinker.
Applying this creative thinking skill means being able to interpret visual information, present concepts in an often simple visual manner, and communicate in a way that is more universally understood. Drawing stick people is actively encouraged!
Visual approaches to problem-solving can help foster shared understanding and help people be more succinct or creative in their ideas. Remember: if an idea is too complex to be put into pictures, perhaps it needs further refinement .
Imagie-ination #idea generation #gamestorming Images have the ability to spark insights and to create new associations and possible connections. That is why pictures help generate new ideas, which is exactly the point of this exercise.
While you might be able to jump straight into direct applications of visual thinking, it can help to try an exercise where you and a group explore using images simply and engagingly. Imagie-ination helps unlock the power of visual thinking as a team while also helping generate ideas too!
Abstraction or abstract thinking is the art of taking things out of their normal context and presenting them in a radical new light . While most creative thinking skills utilise abstraction in some form, it’s worth noting that actively trying to take an idea from one context and place it in another is a creative approach all on its own.
Think of Pablo Picasso’s cubist portraits – by taking something as common as a human face and bringing abstraction to his process, he created something radically different and innovative. You can create a similar effect by recontextualizing ideas, concepts, and problems and by looking at them from different, perhaps even conflicting points of view.
Abstract thinking is often built on engaging with absurdities, paradoxes, and unexpected connections . As such, it can often be fun, wild and surprising, and is a great way to generate creative ideas even in those who might be resistant to other forms of creative thinking. Lean into the weird!
Forced Analogy #divergent thinking #zoom #virtual #remote-friendly People compare something (e.g. themselves, their company, their team) to an object.
Forced Analogy is a quick, fun activity you can use to promote abstract thinking. Comparing one thing to another seemingly unrelated thing asks for a creative approach to context and metaphor and can really unlock a groups divergent thinking process.
Telling stories or narrativizing a problem can help us not only see things differently but understand where we share common ground with others. Everybody tells stories – whether that’s explaining our employment history, telling colleagues about what happened at the weekend, or when creating user personas and journeys.
Leverage this inclination to help people not only realize they are creative thinkers by nature but to help them share something of themselves too!
As a creative thinking skill, storytelling is about applying our natural proclivity for stories into new situations or thinking about how to reappraise or present material narratively . Think of the basic storytelling concept like the idea that all stories have a beginning, middle, and end – how might we bring this thinking to a tough challenge, a new product, or when solving a customer complaint?
You might even use storytelling tropes like the hero’s journey when exploring ideas or company conflicts. Whichever way you go, remember that stories are a universal element of culture and you have a rich lineage to dip into if you need a new perspective.
Telling Our Stories #hyperisland #team #teambuilding To work effectively together team members need to build relations, show trust, and be open with each other. This method supports those things through a process of structured storytelling. Team members answer questions related to their childhood, young adulthood, and now; then weave them into a story to share with the rest of their team.
Telling Stories in a collaborative space is one of the best ways you can approach creative thinking through narrative . By doing this activity as a team, you can help a group see the benefit of applying storytelling approaches outside of more traditional forms.
How many times have you had a tough problem that you can’t seem to solve so you get frustrated and leave your desk. Then, when you’re on a walk, standing in the supermarket, or falling asleep, a solution seems to arrive out of thin air? Often, you’ll find that creating space to reflect on a problem is an effective way to find a way forward.
The trick with making reflective space work as a larger part of your working practice is knowing when to take time to reflect, building space into your regular schedule, and finding techniques that allow things to surface effectively.
This might mean going for a walk with the intention to be present in noticing the world around you and gaining insights that can help your situation. It might also mean remembering to take time to rest or simply read and give your brain something good to chew on.
I notice, I wonder #design #observation #empathy #issue analysis Learn through careful observation. Observation and intuition are critical design tools. This exercise helps you leverage both. Find clues about the context you’re designing for that may be hidden in plain sight.
In a creative thinking context, reflection often means giving an idea time to unfurl and to resist the temptation to force it – by creating space to observe and reflect with I notice, I wonder you might see new ways of thinking emerge naturally.
How to use creative thinking skills at work?
At SessionLab, we’ve found many of the above creative thinking skills helpful when finding better ways to collaborate , handle workplace challenges or generate new ideas . Here are just a few small examples of things we’ve done that have benefited from thinking creatively as a team.
Using creative thinking to facilitate a site redesign
Using creative thinking to improve team communication, using creative thinking to improve collaboration.
Remember that creative thinking needn’t be explosive or radical to be useful – a simple shift in mindset or perspective can be all you need to create meaningful and impactful change.
When we began working on a site-wide redesign, we had to deploy a large number of creative thinking skills to make the process smooth and effective.
When first determining how to approach the project and scope the work, we reviewed how we had worked together on large projects in the past. While we saw there was room to improve, finding the best way to proceed and make the changes we needed was no easy task.
Challenging the entire process from start to finish with a creative thinking mindset and trying to stay open to alternative methods where possible was what unlocked the process for us. By reconsidering how we were running meetings, sharing feedback, and collaborating, we were able to identify where we were going wrong and then try alternative approaches more freely.
When it came to implementing solutions, we were also sure to stay open to experimentation while challenging our core assumptions of what would work and wouldn’t. This really helped us refine the working process and tailor it to our particular team and goals.
Another example came with finding a new approach when work stalled on a specific page. For our features page, we began by following the standard approach we had developed – writing the copy and structuring the page first before then following with illustrations and images.
In this case, our existing approach got us to an impasse : it felt difficult for our designer to be creative and find the best way to translate ideas into images if the copy had already been defined and the structure felt too rigid. What we decided to do was to reverse the workflow completely and allow the designer to create design elements before we wrote the copy and implemented too rigid a structure.
Throughout the project, creative thinking allowed us to challenge whether the existing way we did something was the right one and gave us scope to experiment and be open when finding solutions. Not only did this help us solve the immediate problems as they arose but they helped us come up with a great new design too!
Creative thinking can come in extremely handy when it comes to communicating. If one form of communication or working process isn’t working, approaching the discussion with a creative thinking mindset can help resolve the immediate issue and create lasting change in how we converse and work together too.
Like many virtual teams, we faced the challenge of some meetings feeling unproductive . The issues ranged from overrunning, crosstalk, not everyone feeling heard or able to contribute, or getting lost in ancillary discussions that were not productive or necessary. In an online setting, it can be hard to keep everyone on track and for things to run smoothly without accidentally talking over one another or causing frustration.
When it came to crosstalk, we wanted to avoid the frustration of interruption and disruption but also wanted to ensure people did not feel like they couldn’t contribute . Using the finger rules technique in a remote setting allowed people to easily show when they wanted to speak and what they wanted to discuss without disrupting the flow of the meeting.
We also found that the reason some daily meetings felt unproductive was because the meetings were for the purpose of daily updates and there didn’t always feel like there was a lot to say, thus leading to frustration or unproductive time being spent in these meetings.
In this example, we moved to a weekly format while also ensuring that we continue daily check-ins on Slack. This approach meant that we cut down on unnecessary meetings while still ensuring everyone’s needs were met .
This method is an example of creatively approaching a communication problem by thinking outside of the box and being prepared to challenge core assumptions . While we all wanted to stay informed, it really helped to reconsider the methods for staying informed and whether our current approach was the best way to achieve what we needed. It was also useful to reassess how we approached meeting agendas and goal-setting – follow the link for more on that if you’re having difficulty with unproductive meetings!
Remember that creative thinking needn’t be explosive or radical to be useful – a simple shift in mindset or perspective can be all you need to create meaningful and impactful change .
Remember that looking to others and being inspired by how they did things can be as transformative as trying to reinvent the wheel!
A final example is how we approached collaborating on creating the new design. While all projects at SessionLab feature collaboration between multiple parties, in this case we wanted to create space for everyone on the team to contribute.
We found that when trying to collectively brainstorm in a live, remote session, it became difficult for everyone to contribute and reflect on what was being shared by other members of the team effectively .
Some people had been able to prepare less than others, other people were less aware of all the circumstances of the project, or others were less able to switch gears during their working day. This led to some contributions being missed, a messier working process, and a feeling of being rushed – all of which lead to less effective outcomes than we might have hoped for.
In this case, we thought of how asynchronous work , reflection time, and some small process changes might help solve the problems we were running into. We wanted to be able to respond to what was being shared more effectively while also creating space for everyone to contribute in a way that was most productive for them.
Starting the brainstorming session in personal MURAL boards asynchronously and on our own time meant everyone was able to ideate at the time that was best for them and without any distractions . By then encouraging review and reflection on other people’s boards ahead of the main session, we were able to properly take in ideas and let them develop without feeling hurried.
This approach reduced the amount of time we actively spent working together in a meeting while improving the quality of the work . It helped people engage with the process, reduced potential frustration, and also meant we were more able to respond fully to the suggestions of others. This was a great example of how thinking creatively and learning from others can help create better outcomes and a more streamlined process.
It’s also worth noting that reflecting on our conversation with Anja Svetina Nabergoj regarding asynchronous learning and finding inspiration there was part of what helped this process along. Remember that looking to others and being inspired by how they did things can be as transformative as trying to reinvent the wheel!
Creative workshops and meetings made easy
Whether you find that creative thinking doesn’t come naturally, if your skills need some attention, or even if you just want to try new ways of working, it can be difficult to know where to begin .
Thinking about the creative thinking skills above and considering which you might be missing or could benefit from purposeful attention is a great place to start, though there are also some concrete ways you can approach the process and improve your creative thinking abilities in a pinch. Let’s see how!
Be present and aware of how you feel
Create space for new ideas, look to others for inspiration, throw yourself into new things, encourage creative thinking in others.
All skills get better with practice and creative thinking is no exception. Whether it’s active listening, experimentation or any other creative thinking style, it’s okay to not get it right the first time . The very act of being open to new approaches and perspectives is itself a way to improve your creative thinking skill set. However you try to implement creative thinking, know that exploration, iteration, and practice are fundamental parts of the process.
Try starting small and practice your creative thinking skills in your interpersonal relationships and collaborative projects. Take note of how it goes and try building up to larger and larger implementations of your creative thinking approaches.
A key part of cultivating or improving any new skill is to be fully present and aware when utilizing that skill. Consider how a sculptor needs to be aware of their materials, how they handle the material and place them on the board in order to be truly successful. Being present in the moment is important for any collaborative process, but is an especially vital aspect of creative thinking.
If you find yourself frustrated, excited, engaged, or stuck, make a mental note of how you are feeling and consider how you might do things differently. Staying present and actively engaging with how a situation makes you feel before responding is one of the most effective ways of cultivating and improving your creative thinking – be sure to give it a go!
As with many aspects of creativity, it’s not always effective to force it. Good ideas and finding new approaches can take time and an important part of the creative thinking process is creating space not only for reflection but to rest and allow things to surface. This might mean building more quiet, mindful time into your routine, reading and finding new inspiration, or simply learning to take a break.
While this can be difficult to get into the habit of, it does get easier with time. Try blocking out reflective time in your calendar or letting others know that you are taking the time in order to make it stick and avoid interruptions. Reflective space is important and useful, and by treating it as such, you can help ensure it happens and doesn’t get discarded or forgotten about.
One of the biggest barriers to thinking creatively is simply not being open to what is in front of you. Whether it’s rushing to use an existing solution without investigating alternatives, failing to listen or be present when something new is being presented, or sticking with your existing assumptions, a failure to stay open and reserve judgment can kill creative thinking.
Try to stay open and apply creative thinking without pressure or being overly critical in order to improve those skills and let more creative approaches surface in the future.
One of the best ways to find new perspectives and alternative ways of thinking is by looking to others. Whether it’s finding inspiration from other creative thinkers via conversation, reading and researching new sources, or simply listening and observing, looking outside of yourself is one of the most effective ways you can jolt your creative thinking.
Try finding sources outside of your normal circles, whatever the medium. It can be very easy to get into creative bubbles that might unwittingly exclude new forms of thinking. By broadening your social, creative and critical circles , you can be exposed to all kinds of potentially inspiring or creatively engaging ways of thinking and doing.
It’s hard to create space and an opportunity for new ways of thinking if you stick to the same routines and activities. You’ll often find that trying new things and exposing yourself to new hobbies, skills and approaches can be massively engaging and exciting too.
An important aspect of creative thinking is applying the learnings from one discipline or approach to another. If a developer were to throw themselves into learning how to dance, they might learn something they can apply to their role as a developer.
An open and honest desire to explore new experiences in and outside of your working life is a vital ingredient in the creative thinking process. Try saying yes to doing new things wherever you can find them – being alive to possibility and engaging in the world is a great way of supercharging your creativity!
Creativity is even better when shared. Whether it’s crowdsourcing new ideas, iterating together, or helping others build their creative thinking skills, sharing the experience is often a useful and generative process for all involved.
Try bringing a group together to explore thinking creatively together or run a workshop on developing creative thinking skills in the workplace. Not only will it help your participants with their own creative discovery, but it will also help you develop your own creative skills.
Over to you
As facilitators and advocates of the power of workshops, we’re passionate about how creative thinking can improve many aspects of a group’s personal and working lives. At its heart, creative thinking is an empathic, generative act, and by bringing those concepts to the fore, we believe everyone can see better outcomes when solving problems, generating ideas or communicating with others.
We hope we’ve given you some great examples of creative thinking at work and how you might discover and nurture your own creative thinking skills . That said, this list is by no means exhaustive and there are many more ways you might try thinking creatively. Think of this post as a jumping-off point for further exploration and creative development!
Do you have any concepts or approaches you’ve used to become a better creative thinker? Did you find any of the creative thinking methods above particularly helpful? We’d love to hear about your experience in the comments below!
James Smart is Head of Content at SessionLab. He’s also a creative facilitator who has run workshops and designed courses for establishments like the National Centre for Writing, UK. He especially enjoys working with young people and empowering others in their creative practice.
Very nice information. Thanks for posting such an informative blog. Creative thinking is an unconventional thinking that looks at an issue from different perspectives. Innovative thinking is a thinking that converts / commercializes a creative idea into practical application.
The Fosbury Flop is a very good example of a creative idea and trend when we apply “the learnings from one discipline or approach [Engineering] to another [High Jump].”
thanks alot…very informative and thoroug
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Back to All Programs /
Creative Thinking: Innovative Solutions to Complex Challenges
Learn how to grow a culture of creativity to innovate competitive solutions.
All Start Dates
8:30 AM – 4:30 PM ET
2 consecutive days
$2,990 Programs fill quickly — free cancellation up to 14 days prior
Registration Deadline
October 8, 2024
$3,100 Programs fill quickly — free cancellation up to 14 days prior
April 22, 2025
Overview: Creative Thinking Skills Course
The tech breakthrough that makes smartphones irrelevant, a new viral ad campaign, your company’s next big revenue generator — ideas like these could be sitting in your brain; all you need are the creative thinking skills and strategies to pull them out.
This interactive program focuses explicitly on the creative thinking skills you need to solve complex problems and design innovative solutions. Learn how to transform your thinking from the standard “why can’t we” to the powerful “how might we.” Crack the code on how to consistently leverage your team’s creative potential in order to drive innovation within your organization. Explore how to build a climate for innovation, remove barriers to creativity, cultivate courage, and create more agile, proactive, and inspired teams.
You will leave this program with new ideas about how to think more productively and how to introduce creative thinking skills into your organization. You can apply key takeaways immediately to implement a new leadership vision, inspire renewed enthusiasm, and enjoy the skills and tools to tackle challenges and seize opportunities.
Innovation experts Anne Manning and Susan Robertson bring to this highly-interactive and powerful program their decades of experience promoting corporate innovation, teaching the art of creative problem solving, and applying the principles of brain science to solve complex challenges.
Who Should Take Creative Thinking Skills Training?
This program is ideal for leaders with at least 3 years of management experience. It is designed for leaders who want to develop new strategies, frameworks, and tools for creative problem solving. Whether you are a team lead, project manager, sales director, or executive, you’ll learn powerful tools to lead your team and your organization to create innovative solutions to complex challenges.
All participants will earn a Certificate of Completion from the Harvard Division of Continuing Education.
Benefits of Creative Thinking Skills Training
The goal of this creative thinking program is to help you develop the strategic concepts and tactical skills to lead creative problem solving for your team and your organization. You will learn to:
- Retrain your brain to avoid negative cognitive biases and long-held beliefs and myths that sabotage creative problem solving and innovation
- Become a more nimble, proactive, and inspired thinker and leader
- Create the type of organizational culture that supports collaboration and nurtures rather than kills ideas
- Gain a practical toolkit for solving the “unsolvable” by incorporating creative thinking into day-to-day processes
- Understand cognitive preferences (yours and others’) to adapt the creative thinking process and drive your team’s success
- Develop techniques that promote effective brainstorming and enable you to reframe problems in a way that inspires innovative solutions
The curriculum in this highly interactive program utilizes research-based methodologies and techniques to build creative thinking skills and stimulate creative problem solving.
Through intensive group discussions and small-group exercises, you will focus on topics such as:
- The Creative Problem Solving process: a researched, learnable, repeatable process for uncovering new and useful ideas. This process includes a “how to” on clarifying, ideating, developing, and implementing new solutions to intractable problems
- The cognitive preferences that drive how we approach problems, and how to leverage those cognitive preferences for individual and team success
- How to develop—and implement— a methodology that overcomes barriers to innovative thinking and fosters the generation of new ideas, strategies, and techniques
- The role of language, including asking the right questions, in reframing problems, challenging assumptions, and driving successful creative problem solving
- Fostering a culture that values, nurtures, and rewards creative solutions
Considering this program?
Send yourself the details.
Related Programs
- Design Thinking: Creating Better Customer Experiences
- Agile Leadership: Transforming Mindsets and Capabilities in Your Organization
October Schedule
- Creative Challenges: A Team Sport
- The Place to Begin: Reframe the Challenge
- Ideas on Demand
- Building a Creative Organization
April Schedule
Instructors, anne manning, susan robertson.
I really enjoyed the way the instructors facilitated the program. The combination of theory and practical exercises was powerful and effectively reinforced the concepts.
Innovation and Educational Research, Director, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Certificates of Leadership Excellence
The Certificates of Leadership Excellence (CLE) are designed for leaders with the desire to enhance their business acumen, challenge current thinking, and expand their leadership skills.
This program is one of several CLE qualifying programs. Register today and get started earning your certificate.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Creative Problem Solving
What is creative problem solving.
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a process that design teams use to generate ideas and solutions in their work. Designers and design teams apply an approach where they clarify a problem to understand it, ideate to generate good solutions, develop the most promising one, and implement it to create a successful solution for their brand’s users.
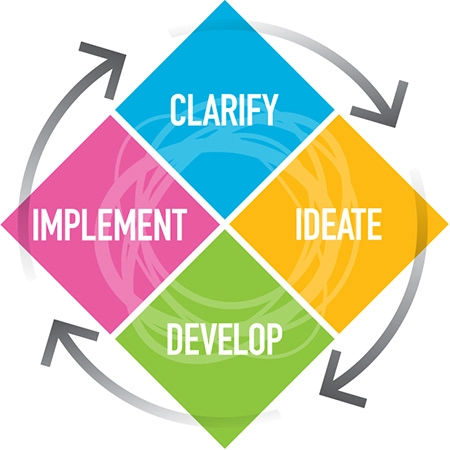
© Creative Education Foundation, Fair Use
Why is Creative Problem Solving in UX Design Important?
Creative thinking and problem solving are core parts of user experience (UX) design. Note: the abbreviation “CPS” can also refer to cyber-physical systems. Creative problem solving might sound somewhat generic or broad. However, it’s an ideation approach that’s extremely useful across many industries.
Not strictly a UX design-related approach, creative problem solving has its roots in psychology and education. Alex Osborn—who founded the Creative Education Foundation and devised brainstorming techniques—produced this approach to creative thinking in the 1940s. Along with Sid Parnes, he developed the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process. It was a new, systematic approach to problem solving and creativity fostering.
Osborn’s CPS Process.
© IdeaSandbox.com, Fair Use
The main focus of the creative problem solving model is to improve creative thinking and generate novel solutions to problems. An important distinction exists between it and a UX design process such as design thinking. It’s that designers consider user needs in creative problem solving techniques, but they don’t necessarily have to make their users’ needs the primary focus. For example, a design team might trigger totally novel ideas from random stimuli—as opposed to working systematically from the initial stages of empathizing with their users. Even so, creative problem solving methods still tend to follow a process with structured stages.
What are 4 Stages of Creative Problem Solving?
The model, adapted from Osborn’s original, typically features these steps:
Clarify: Design teams first explore the area they want to find a solution within. They work to spot the challenge, problem or even goal they want to identify. They also start to collect data or information about it. It’s vital to understand the exact nature of the problem at this stage. So, design teams must build a clear picture of the issue they seek to tackle creatively. When they define the problem like this, they can start to question it with potential solutions.
Ideate: Now that the team has a grasp of the problem that faces them, they can start to work to come up with potential solutions. They think divergently in brainstorming sessions and other ways to solve problems creatively, and approach the problem from as many angles as they can.
Develop: Once the team has explored the potential solutions, they evaluate these and find the strongest and weakest qualities in each. Then, they commit to the one they decide is the best option for the problem at hand.
Implement: Once the team has decided on the best fit for what they want to use, they discuss how to put this solution into action. They gauge its acceptability for stakeholders. Plus, they develop an accurate understanding of the activities and resources necessary to see it become a real, bankable solution.
What Else does CPS Involve?
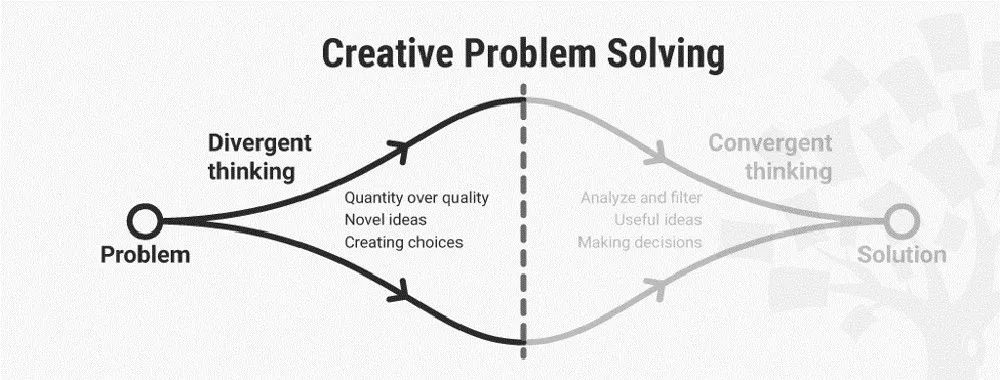
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Two keys to the enterprise of creative problem solving are:
Divergent Thinking
This is an ideation mode which designers leverage to widen their design space when they start to search for potential solutions. They generate as many new ideas as possible using various methods. For example, team members might use brainstorming or bad ideas to explore the vast area of possibilities. To think divergently means to go for:
Quantity over quality: Teams generate ideas without fear of judgment (critically evaluating these ideas comes later).
Novel ideas: Teams use disruptive and lateral thinking to break away from linear thinking and strive for truly original and extraordinary ideas.
Choice creation: The freedom to explore the design space helps teams maximize their options, not only regarding potential solutions but also about how they understand the problem itself.
Author and Human-Computer Interactivity Expert, Professor Alan Dix explains some techniques that are helpful for divergent thinking:
- Transcript loading…
Convergent Thinking
This is the complementary half of the equation. In this ideation mode, designers analyze, filter, evaluate, clarify and modify the ideas they generated during divergent thinking. They use analytical, vertical and linear thinking to isolate novel and useful ideas, understand the design space possibilities and get nearer to potential solutions that will work best. The purpose with convergent thinking is to carefully and creatively:
Look past logical norms (which people use in everyday critical thinking).
Examine how an idea stands in relation to the problem.
Understand the real dimensions of that problem.
Professor Alan Dix explains convergent thinking in this video:
What are the Benefits of Creative Problem Solving?
Design teams especially can benefit from this creative approach to problem solving because it:
Empowers teams to arrive at a fine-grained definition of the problem they need to ideate over in a given situation.
Gives a structured, learnable way to conduct problem-solving activities and direct them towards the most fruitful outcomes.
Involves numerous techniques such as brainstorming and SCAMPER, so teams have more chances to explore the problem space more thoroughly.
Can lead to large numbers of possible solutions thanks to a dedicated balance of divergent and convergent thinking.
Values and nurtures designers and teams to create innovative design solutions in an accepting, respectful atmosphere.
Is a collaborative approach that enables multiple participants to contribute—which makes for a positive environment with buy-in from those who participate.
Enables teams to work out the most optimal solution available and examine all angles carefully before they put it into action.
Is applicable in various contexts—such as business, arts and education—as well as in many areas of life in general.
It’s especially crucial to see the value of creative problem solving in how it promotes out-of-the-box thinking as one of the valuable ingredients for teams to leverage.
Watch as Professor Alan Dix explains how to think outside the box:
How to Conduct Creative Problem Solving Best?
It’s important to point out that designers should consider—and stick to—some best practices when it comes to applying creative problem solving techniques. They should also adhere to some “house rules,” which the facilitator should define in no uncertain terms at the start of each session. So, designers and design teams should:
Define the chief goal of the problem-solving activity: Everyone involved should be on the same page regarding their objective and what they want to achieve, why it’s essential to do it and how it aligns with the values of the brand. For example, SWOT analysis can help with this. Clarity is vital in this early stage. Before team members can hope to work on ideating for potential solutions, they must recognize and clearly identify what the problem to tackle is.
Have access to accurate information: A design team must be up to date with the realities that their brand faces, realities that their users and customers face, as well as what’s going on in the industry and facts about their competitors. A team must work to determine what the desired outcome is, as well as what the stakeholders’ needs and wants are. Another factor to consider in detail is what the benefits and risks of addressing a scenario or problem are—including the pros and cons that stakeholders and users would face if team members direct their attention on a particular area or problem.
Suspend judgment: This is particularly important for two main reasons. For one, participants can challenge assumptions that might be blocking healthy ideation when they suggest ideas or elements of ideas that would otherwise seem of little value through a “traditional” lens. Second, if everyone’s free to suggest ideas without constraints, it promotes a calmer environment of acceptance—and so team members will be more likely to ideate better. Judgment will come later, in convergent thinking when the team works to tighten the net around the most effective solution. So, everyone should keep to positive language and encourage improvisational tactics—such as “yes…and”—so ideas can develop well.
Balance divergent and convergent thinking: It’s important to know the difference between the two styles of thinking and when to practice them. This is why in a session like brainstorming, a facilitator must take control of proceedings and ensure the team engages in distinct divergent and convergent thinking sessions.
Approach problems as questions: For example, “How Might We” questions can prompt team members to generate a great deal of ideas. That’s because they’re open-ended—as opposed to questions with “yes” or “no” answers. When a team frames a problem so freely, it permits them to explore far into the problem space so they can find the edges of the real matter at hand.

UX Strategist and Consultant, William Hudson explains “How Might We” questions in this video:
Use a variety of ideation methods: For example, in the divergent stage, teams can apply methods such as random metaphors or bad ideas to venture into a vast expanse of uncharted territory. With random metaphors, a team prompts innovation by drawing creative associations. With bad ideas, the point is to come up with ideas that are weird, wild and outrageous, as team members can then determine if valuable points exist in the idea—or a “bad” idea might even expose flaws in conventional ways of seeing problems and situations.
Professor Alan Dix explains important points about bad ideas:
- Copyright holder: William Heath Robinson. Appearance time: 1:30 - 1:33 Copyright license and terms: Public domain. Link: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c9/William_Heath_Robinson_Inventions_-_Page_142.png
- Copyright holder: Rev Stan. Appearance time: 1:40 - 1:44 Copyright license and terms: CC BY 2.0 Link: As yummy as chocolate teapot courtesy of Choccywoccydoodah… _ Flickr.html
- Copyright holder: Fabel. Appearance time: 7:18 - 7:24 Copyright license and terms: CC BY-SA 3.0 Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hammer_nails_smithonian.jpg
- Copyright holder: Marcus Hansson. Appearance time: 05:54 - 05:58 Copyright license and terms: CC BY 2.0 Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/marcus_hansson/7758775386
What Special Considerations Should Designers Have for CPS?
Creative problem solving isn’t the only process design teams consider when thinking of potential risks. Teams that involve themselves in ideation sessions can run into problems, especially if they aren’t aware of them. Here are the main areas to watch:
Bias is natural and human. Unfortunately, it can get in the way of user research and prevent a team from being truly creative and innovative. What’s more, it can utterly hinder the iterative process that should drive creative ideas to the best destinations. Bias takes many forms. It can rear its head without a design team member even realizing it. So, it’s vital to remember this and check it. One team member may examine an angle of the problem at hand and unconsciously view it through a lens. Then, they might voice a suggestion without realizing how they might have framed it for team members to hear. Another risk is that other team members might, for example, apply confirmation bias and overlook important points about potential solutions because they’re not in line with what they’re looking for.
Professor Alan Dix explains bias and fixation as obstacles in creative problem solving examples, and how to overcome them:
Conventionalism
Even in the most hopeful ideation sessions, there’s the risk that some team members may slide back to conventional ways to address a problem. They might climb back inside “the box” and not even realize it. That’s why it’s important to mindfully explore new idea territories around the situation under scrutiny and not merely toy with the notion while clinging to a default “traditional” approach, just because it’s the way the brand or others have “always done things.”
Dominant Personalities and Rank Pulling
As with any group discussion, it’s vital for the facilitator to ensure that everyone has the chance to contribute. Team members with “louder” personalities can dominate the discussions and keep quieter members from offering their thoughts. Plus, without a level playing field, it can be hard for more junior members to join in without feeling a sense of talking out of place or even a fear of reprisal for disagreeing with senior members.
Another point is that ideation sessions naturally involve asking many questions, which can bring on two issues. First, some individuals may over-defend their ideas as they’re protective of them. Second, team members may feel self-conscious as they might think if they ask many questions that it makes them appear frivolous or unintelligent. So, it’s vital for facilitators to ensure that all team members can speak up and ask away, both in divergent thinking sessions when they can offer ideas and convergent thinking sessions when they analyze others’ ideas.
Premature Commitment
Another potential risk to any creativity exercise is that once a team senses a solution is the “best” one, everyone can start to shut off and overlook the chance that an alternative may still arise. This could be a symptom of ideation fatigue or a false consensus that a proposed solution is infallible. So, it’s vital that team members keep open minds and try to catch potential issues with the best-looking solution as early as possible. The key is an understanding of the need for iteration—something that’s integral to the design thinking process, for example.
Overall, creative problem solving can help give a design team the altitude—and attitude—they need to explore the problem and solution spaces thoroughly. Team members can leverage a range of techniques to trawl through the hordes of possibilities that exist for virtually any design scenario. As with any method or tool, though, it takes mindful application and awareness of potential hazards to wield it properly. The most effective creative problem-solving sessions will be ones that keep “creative,” “problem” and “solving” in sharp focus until what emerges for the target audience proves to be more than the sum of these parts.
Learn More About Creative Problem Solving
Take our course, Creativity: Methods to Design Better Products and Services .
Watch our Master Class Harness Your Creativity To Design Better Products with Alan Dix, Professor, Author and Creativity Expert.
Read our piece, 10 Simple Ideas to Get Your Creative Juices Flowing .
Go to Exploring the Art of Innovation: Design Thinking vs. Creative Problem Solving by Marcino Waas for further details.
Consult Creative Problem Solving by Harrison Stamell for more insights.
Read The Osborn Parnes Creative Problem-Solving Process by Leigh Espy for additional information.
See History of the creative problem-solving process by Jo North for more on the history of Creative Problem Solving.
Questions about Creative Problem Solving
To start with, work to understand the user’s needs and pain points. Do your user research—interviews, surveys and observations are helpful, for instance. Analyze this data so you can spot patterns and insights. Define the problem clearly—and it needs to be extremely clear for the solution to be able to address it—and make sure it lines up with the users’ goals and your project’s objectives.
You and your design team might hold a brainstorming session. It could be a variation such as brainwalking—where you move about the room ideating—or brainwriting, where you write down ideas. Alternatively, you could try generating weird and wonderful notions in a bad ideas ideation session.
There’s a wealth of techniques you can use. In any case, engage stakeholders in brainstorming sessions to bring different perspectives on board the team’s trains of thought. What’s more, you can use tools like a Problem Statement Template to articulate the problem concisely.
Take our course, Creativity: Methods to Design Better Products and Services .
Watch as Author and Human-Computer Interaction Expert, Professor Alan Dix explains important points about bad ideas:
Some things you might try are: 1. Change your environment: A new setting can stimulate fresh ideas. So, take a walk, visit a different room, or work outside.
2. Try to break the problem down into smaller parts: Focus on just one piece at a time—that should make the task far less overwhelming. Use techniques like mind mapping so you can start to visualize connections and come up with ideas.
3. Step away from work and indulge in activities that relax your mind: Is it listening to music for you? Or how about drawing? Or exercising? Whatever it is, if you break out of your routine and get into a relaxation groove, it can spark new thoughts and perspectives.
4. Collaborate with others: Discuss the problem with colleagues, stakeholders, or—as long as you don’t divulge sensitive information or company secrets—friends. It can help you to get different viewpoints, and sometimes those new angles and fresh perspectives can help unlock a solution.
5. Set aside dedicated time for creative thinking: Take time to get intense with creativity; prevent distractions and just immerse yourself in the problem as fully as you can with your team. Use techniques like brainstorming or the "Six Thinking Hats" to travel around the problem space and explore a wealth of angles.
Remember, a persistent spirit and an open mind are key; so, keep experimenting with different approaches until you get that breakthrough.
Watch as Professor Alan Dix explains important aspects of creativity and how to handle creative blocks:
Read our piece, 10 Simple Ideas to Get Your Creative Juices Flowing .
Watch as Professor Alan Dix explains the Six Thinking Hats ideation technique.
Creative thinking is about coming up with new and innovative ideas by looking at problems from different angles—and imagining solutions that are truly fresh and unique. It takes an emphasis on divergent thinking to get “out there” and be original in the problem space. You can use techniques like brainstorming, mind mapping and free association to explore hordes of possibilities, many of which might be “hiding” in obscure corners of your—or someone on your team’s—imagination.
Critical thinking is at the other end of the scale. It’s the convergent half of the divergent-convergent thinking approach. In that approach, once the ideation team have hauled in a good catch of ideas, it’s time for team members to analyze and evaluate these ideas to see how valid and effective each is. Everyone strives to consider the evidence, draw logical connections and eliminate any biases that could be creeping in to cloud judgments. Accuracy, sifting and refining are watchwords here.
Watch as Professor Alan Dix explains divergent and convergent thinking:
The tools you can use are in no short supply, and they’re readily available and inexpensive, too. Here are a few examples:
Tools like mind maps are great ways to help you visualize ideas and make connections between them and elements within them. Try sketching out your thoughts and see how they relate to each other—you might discover unexpected gems, or germs of an idea that can splinter into something better, with more thought and development.
The SCAMPER technique is another one you can try. It can help you catapult your mind into a new idea space as you Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse aspects of the problem you’re considering.
The “5 Whys” technique is a good one to drill down to root causes with. Once you’ve spotted a problem, you can start working your way back to see what’s behind it. Then you do the same to work back to the cause of the cause. Keep going; usually five times will be enough to see what started the other problems as the root cause.
Watch as the Father of UX Design, Don Norman explains the 5 Whys technique:
Read all about SCAMPER in our topic definition of it.
It’s natural for some things to get in the way of being creative in the face of a problem. It can be challenging enough to ideate creatively on your own, but it’s especially the case in group settings. Here are some common obstacles:
1. Fear of failure or appearing “silly”: when people worry about making mistakes or sounding silly, they avoid taking risks and exploring new ideas. This fear stifles creativity. That’s why ideation sessions like bad ideas are so valuable—it turns this fear on its head.
2. Rigid thinking: This can also raise itself as a high and thick barrier. If someone in an ideation session clings to established ways to approach problems (and potential solutions), it can hamper their ability to see different perspectives, let alone agree with them. They might even comment critically to dampen what might just be the brightest way forward. It takes an open mind and an awareness of one’s own bias to overcome this.
3. Time pressure and resource scarcity: When a team has tight deadlines to work to, they may rush to the first workable solution and ignore a wide range of possibilities where the true best solution might be hiding. That’s why stakeholders and managers should give everyone enough time—as well as any needed tools, materials and support—to ideate and experiment. The best solution is in everybody’s interest, after all.
It takes a few ingredients to get the environment just right for creative problem solving:
Get in the mood for creativity: This could be a relaxing activity before you start your session, or a warm-up activity in the room. Then, later, encourage short breaks—they can rejuvenate the mind and help bring on fresh insights.
Get the physical environment just right for creating problem solving: You and your team will want a comfortable and flexible workspace—preferably away from your workstations. Make sure the room is one where people can collaborate easily and also where they can work quietly. A meeting room is good as it will typically have room for whiteboards and comfortable space for group discussion. Note: you’ll also need sticky notes and other art supplies like markers.
Make the atmosphere conducive for creative problem solving: Someone will need to play facilitator so everyone has some ground rules to work with. Encourage everyone to share ideas, that all ideas are valuable, and that egos and seniority have no place in the room. Of course, this may take some enforcement and repetition—especially as "louder" team members may try to dominate proceedings, anyway, and others may be self-conscious about sounding "ridiculous."
Make sure you’ve got a diverse team: Diversity means different perspectives, which means richer and more innovative solutions can turn up. So, try to include individuals with different backgrounds, skills and viewpoints—sometimes, non-technical mindsets can spot ideas and points in a technical realm, which experienced programmers might miss, for instance.
Watch our Master Class Harness Your Creativity To Design Better Products with Alan Dix, Professor, Author and Creativity Expert.
Ideating alone? Watch as Professor Alan Dix gives valuable tips about how to nurture creativity:
- Copyright holder: GerritR. Appearance time: 6:54 - 6:59 Copyright license and terms: CC-BY-SA-4.0 Link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blick_auf_das_Dylan_Thomas_Boathouse_und_die_Trichterm%C3%BCndung_des_Taf,_Wales.jpg
Research plays a crucial role in any kind of creative problem solving, and in creative problem solving itself it’s about collecting information about the problem—and, by association, the users themselves. You and your team members need to have a well-defined grasp of what you’re facing before you can start reaching out into the wide expanses of the idea space.
Research helps you lay down a foundation of knowledge and avoid reinventing the wheel. Also, if you study existing solutions and industry trends, you’ll be able to understand what has worked before and what hasn't.
What’s more, research is what will validate the ideas that come out of your ideation efforts. From testing concepts and prototypes with real users, you’ll get precious input about your creative solutions so you can fine-tune them to be innovative and practical—and give users what they want in a way that’s fresh and successful.
Watch as UX Strategist and Consultant, William Hudson explains important points about user research:
First, it’s crucial for a facilitator to make sure the divergent stage of the creative problem solving is over and your team is on to the convergent stage. Only then should any analysis happen.
If others are being critical of your creative solutions, listen carefully and stay open-minded. Look on it as a chance to improve, and don’t take it personally. Indeed, the session facilitator should moderate to make sure everyone understands the nature of constructive criticism.
If something’s unclear, be sure to ask the team member to be more specific, so you can understand their points clearly.
Then, reflect on what you’ve heard. Is it valid? Something you can improve or explain? For example, in a bad ideas session, there may be an aspect of your idea that you can develop among the “bad” parts surrounding it.
So, if you can, clarify any misunderstandings and explain your thought process. Just stay positive and calm and explain things to your critic and other team member. The insights you’ve picked up may strengthen your solution and help to refine it.
Last—but not least—make sure you hear multiple perspectives. When you hear from different team members, chances are you’ll get a balanced view. It can also help you spot common themes and actionable improvements you might make.
Watch as Todd Zaki Warfel, Author, Speaker and Leadership Coach, explains how to present design ideas to clients, a valuable skill in light of discussing feedback from stakeholders.
Lateral thinking is a technique where you approach problems from new and unexpected angles. It encourages you to put aside conventional step-by-step logic and get “out there” to explore creative and unorthodox solutions. Author, physician and commentator Edward de Bono developed lateral thinking as a way to help break free from traditional patterns of thought.
In creative problem solving, you can use lateral thinking to come up with truly innovative ideas—ones that standard logical processes might overlook. It’s about bypassing these so you can challenge assumptions and explore alternatives that point you and your team to breakthrough solutions.
You can use techniques like brainstorming to apply lateral thinking and access ideas that are truly “outside the box” and what your team, your brand and your target audience really need to work on.
Professor Alan Dix explains lateral thinking in this video:
1. Baer, J. (2012). Domain Specificity and The Limits of Creativity Theory . The Journal of Creative Behavior, 46(1), 16–29. John Baer's influential paper challenged the notion of a domain-general theory of creativity and argued for the importance of considering domain-specific factors in creative problem solving. This work has been highly influential in shaping the understanding of creativity as a domain-specific phenomenon and has implications for the assessment and development of creativity in various domains.
2. Runco, M. A., & Jaeger, G. J. (2012). The Standard Definition of Creativity . Creativity Research Journal, 24(1), 92–96. Mark A. Runco and Gerard J. Jaeger's paper proposed a standard definition of creativity, which has been widely adopted in the field. They defined creativity as the production of original and effective ideas, products, or solutions that are appropriate to the task at hand. This definition has been influential in providing a common framework for creativity research and assessment.
1. Fogler, H. S., LeBlanc, S. E., & Rizzo, B. (2014). Strategies for Creative Problem Solving (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall.
This book focuses on developing creative problem-solving strategies, particularly in engineering and technical contexts. It introduces various heuristic problem-solving techniques, optimization methods, and design thinking principles. The authors provide a systematic framework for approaching ill-defined problems, generating and implementing solutions, and evaluating the outcomes. With its practical exercises and real-world examples, this book has been influential in equipping professionals and students with the skills to tackle complex challenges creatively.
2. De Bono, E. (1985). Six Thinking Hats . Little, Brown and Company.
Edward de Bono's Six Thinking Hats introduces a powerful technique for parallel thinking and decision-making. The book outlines six different "hats" or perspectives that individuals can adopt to approach a problem or situation from various angles. This structured approach encourages creative problem-solving by separating different modes of thinking, such as emotional, logical, and creative perspectives. De Bono's work has been highly influential in promoting lateral thinking and providing a practical framework for group problem solving.
3. Osborn, A. F. (1963). Applied Imagination: Principles and Procedures of Creative Problem-Solving (3rd ed.). Charles Scribner's Sons.
Alex F. Osborn's Applied Imagination is a pioneering work that introduced the concept of brainstorming and other creative problem-solving techniques. Osborn emphasized how important it is to defer judgment and generate a large quantity of ideas before evaluating them. This book laid the groundwork for many subsequent developments in the field of creative problem-solving, and it’s been influential in promoting the use of structured ideation processes in various domains.
Answer a Short Quiz to Earn a Gift
What is the first stage in the creative problem-solving process?
- Implementation
- Idea Generation
- Problem Identification
Which technique is commonly used during the idea generation stage of creative problem-solving?
- Brainstorming
- Prototyping
What is the main purpose of the evaluation stage in creative problem-solving?
- To generate as many ideas as possible
- To implement the solution
- To assess the feasibility and effectiveness of ideas
In the creative problem-solving process, what often follows after implementing a solution?
- Testing and Refinement
Which stage in the creative problem-solving process focuses on generating multiple possible solutions?
Better luck next time!
Do you want to improve your UX / UI Design skills? Join us now
Congratulations! You did amazing
You earned your gift with a perfect score! Let us send it to you.
Check Your Inbox
We’ve emailed your gift to [email protected] .
Literature on Creative Problem Solving
Here’s the entire UX literature on Creative Problem Solving by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Creative Problem Solving
Take a deep dive into Creative Problem Solving with our course Creativity: Methods to Design Better Products and Services .
The overall goal of this course is to help you design better products, services and experiences by helping you and your team develop innovative and useful solutions. You’ll learn a human-focused, creative design process.
We’re going to show you what creativity is as well as a wealth of ideation methods ―both for generating new ideas and for developing your ideas further. You’ll learn skills and step-by-step methods you can use throughout the entire creative process. We’ll supply you with lots of templates and guides so by the end of the course you’ll have lots of hands-on methods you can use for your and your team’s ideation sessions. You’re also going to learn how to plan and time-manage a creative process effectively.
Most of us need to be creative in our work regardless of if we design user interfaces, write content for a website, work out appropriate workflows for an organization or program new algorithms for system backend. However, we all get those times when the creative step, which we so desperately need, simply does not come. That can seem scary—but trust us when we say that anyone can learn how to be creative on demand . This course will teach you ways to break the impasse of the empty page. We'll teach you methods which will help you find novel and useful solutions to a particular problem, be it in interaction design, graphics, code or something completely different. It’s not a magic creativity machine, but when you learn to put yourself in this creative mental state, new and exciting things will happen.
In the “Build Your Portfolio: Ideation Project” , you’ll find a series of practical exercises which together form a complete ideation project so you can get your hands dirty right away. If you want to complete these optional exercises, you will get hands-on experience with the methods you learn and in the process you’ll create a case study for your portfolio which you can show your future employer or freelance customers.
Your instructor is Alan Dix . He’s a creativity expert, professor and co-author of the most popular and impactful textbook in the field of Human-Computer Interaction. Alan has worked with creativity for the last 30+ years, and he’ll teach you his favorite techniques as well as show you how to make room for creativity in your everyday work and life.
You earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you’ve completed the course. You can highlight it on your resume , your LinkedIn profile or your website .
All open-source articles on Creative Problem Solving
10 simple ideas to get your creative juices flowing.

- 4 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Module 5: Thinking and Analysis
Solving problems creatively, learning outcomes.
- Describe the role of creative thinking skills in problem-solving
Problem-Solving with Creative Thinking
Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving. It involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas—practices and solutions that are unique and effective. It’s about facing sometimes muddy and unclear problems and seeing how things can be done differently—how new solutions can be imagined. [1]
You have to remain open-minded, focus on your organizational skills, and learn to communicate your ideas well when you are using creative thinking to solve problems. If an employee at a café you own suggests serving breakfast in addition to the already-served lunch and dinner, keeping an open mind means thinking through the benefits of this new plan (e.g., potential new customers and increased profits) instead of merely focusing on the possible drawbacks (e.g., possible scheduling problems, added start-up costs, loss of lunch business). Implementing this plan would mean a new structure for buying, workers’ schedules and pay, and advertising, so you would have to organize all these component areas. And finally, you would need to communicate your ideas on how to make this new plan work not only to the staff who will work the new shift, but also to the public who frequent your café and the others you want to encourage to try your new hours.
We need creative solutions throughout the workplace—whether board room, emergency room, or classroom. It was no fluke that the 2001 revised Bloom’s cognitive taxonomy, originally developed in 1948, placed a new word at the apex— creating . That creating is the highest level of thinking skills.

Bloom’s Taxonomy is an important learning theory used by psychologists, cognitive scientists, and educators to demonstrate levels of thinking. Many assessments and lessons you’ve seen during your schooling have likely been arranged with Bloom’s in mind. Researchers recently revised it to place creativity—invention—as the highest level
“Because we’ve always done it that way” is not a valid reason to not try a new approach. It may very well be that the old process is a very good way to do things, but it also may just be that the old, comfortable routine is not as effective and efficient as a new process could be.
The good news is that we can always improve upon our problem-solving and creative-thinking skills—even if we don’t consider ourselves to be artists or creative. The following information may surprise and encourage you!
- Creative thinking (a companion to critical thinking) is an invaluable skill for college students. It’s important because it helps you look at problems and situations from a fresh perspective. Creative thinking is a way to develop novel or unorthodox solutions that do not depend wholly on past or current solutions. It’s a way of employing strategies to clear your mind so that your thoughts and ideas can transcend what appear to be the limitations of a problem. Creative thinking is a way of moving beyond barriers. [2]
- As a creative thinker, you are curious, optimistic, and imaginative. You see problems as interesting opportunities, and you challenge assumptions and suspend judgment. You don’t give up easily. You work hard. [3]
Is this you? Even if you don’t yet see yourself as a competent creative thinker or problem-solver, you can learn solid skills and techniques to help you become one.
Creative Problem-Solving: Fiction and Facts
As you continue to develop your creative thinking skills, be alert to perceptions about creative thinking that could slow down progress. Remember that creative thinking and problem-solving are ways to transcend the limitations of a problem and see past barriers. It’s a way to think outside the box.
| FICTION | FACTS | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Every problem has only one solution (or one right answer). | The goal of problem-solving is to solve the problem, and most problems can be solved in any number of ways. If you discover a solution that works, it’s a good solution. Other people may think up solutions that differ from yours, but that doesn’t make your solution wrong or unimportant. What is the solution to “putting words on paper”? Fountain pen, ballpoint, pencil, marker, typewriter, printer, printing press, word-processing . . .? |
| 2 | The best answer or solution or method has already been discovered. | Look at the history of any solution and you’ll see that improvements, new solutions, and new right answers are always being found. What is the solution to human transportation? The ox or horse, the cart, the wagon, the train, the car, the airplane, the jet, or the space shuttle? What is the best and last? |
| 3 | Creative answers are technologically complex. | Only a few problems require complex technological solutions. Most problems you’ll encounter need only a thoughtful solution involving personal action and perhaps a few simple tools. Even many problems that seem to require technology can be addressed in other ways. |
| 4 | Ideas either come or they don’t. Nothing will help— certainly not structure. | There are many successful techniques for generating ideas. One important technique is to include structure. Create guidelines, limiting parameters, and concrete goals for yourself that stimulate and shape your creativity. This strategy can help you get past the intimidation of the blank page. For example, if you want to write a story about a person who gained insight through experience, you can stoke your creativity by limiting or narrowing your theme to “a young girl in Cambodia who escaped the Khmer Rouge to find a new life as a nurse in France.” Apply this type of specificity and structure to any creative endeavor. |
creative problem-solving: a practice that seeks new and novel solutions to problems, often by using imagination rather than linear reason
- "Critical and Creative Thinking, MA." University of Massachusetts Boston . 2016. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- Mumaw, Stefan. "Born This Way: Is Creativity Innate or Learned?" Peachpit. Pearson, 27 Dec 2012. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- Harris, Robert. "Introduction to Creative Thinking." Virtual Salt. 2 Apr 2012. Web. 16 Feb 2016. ↵
- Ibid. ↵
- College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- College Success. Authored by : Amy Baldwin. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/7-2-creative-thinking . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Text adaptation. Authored by : Claire. Provided by : Ivy Tech. Located at : http://ivytech.edu/ . License : CC BY: Attribution


How you can use creative problem solving at work
Reading time: about 4 min
How many times have you tried to solve a problem only to get stuck in the process? In a business setting, this is a common occurrence. You’re faced with issues that traditional problem solving methods can’t solve. But you still need to find a way to fix the issue to move a project forward or resolve a conflict. This is when you may need to get creative to solve the problem at hand.
What is creative problem solving?
The definition of creative problem solving (CPS) will vary between organizations. At its core, CPS involves approaching a problem in an imaginative, innovative, and unconventional way. The process encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly.
7 steps of the creative problem solving process
The CPS process can be broken down into seven steps.
1. Identify the goal
Before solving the problem, you need to fully understand the problem you’re trying to solve. You may have overlooked or misunderstood some details. Take some time to analyze the conflict and clear up any confusion.
2. Gather data
Once you know what the problem is, you need to learn all you can about it. Who does the problem affect? Who is involved in solving the issue? Gather all the knowledge you can to gain a better understanding of the issue and to solve it.
3. Formulate challenge questions
After you’ve gathered the details, turn the problem into a question. Word the question in a way that encourages suggestions or ideas. It should be short, concise, and only focus on a single issue. Once you’ve created one or two questions, start trying to answer them.
4. Explore ideas
This step is where the brainstorming begins. You’ll be creating possible ideas or solutions to the problem you’re facing. This is usually when the creativity really starts to flow. With so many ideas flowing, it’s crucial that you write each of them down—even the stupid ones. Even if the idea you come up with has little to no chance of working, write it down. Trying to sort out bad ideas from the good ones during this step can squash creativity.
5. Come up with solutions.
Weed out the average ideas from the winners by testing each one. See if the possible solution actually solves the problem and if you can implement it successfully. If the potential solution doesn’t resolve the issue, move on to the next idea. Evaluating each idea will help you zero in on the perfect solution.
6. Create an action plan
Now that you have the perfect solution, you’ll need to create an action plan outlining implementation steps. Consider what resources you’ll need and how long it will take. Then write it all down. Once you create the plan, communicate the approach to the rest of the team so they’re aware of what’s happening.
To help you create an organized and detailed plan, you can use swimlanes in Lucidchart.
7. Take action
With your plan created and your team on board, it’s time to implement your solution and resolve the problem.
CPS techniques
Just knowing the process behind CPS isn’t enough. You’ll want to know about the common creative problem solving ideas or techniques that you can use to be more successful during each phase. Below are a few of the techniques you can use to help you through the CPS process:
Synectics: This technique helps to inspire thoughts that you might not be aware of. It is a way to approach creativity in a logical, rational manner.
TRIZ methodology (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving): This problem solving methodology is based on logic, data, and research—not intuition. It involves adapting existing solutions to your particular problem.
Brainstorming: Using this technique allows you to collect a number of ideas that can be a potential solution to a problem and can be used in either a group or individual setting.
Mind mapping: Mind mapping helps keeps your ideas organized by representing them in a graphical manner.
Reversal of problem: Trying to solve a problem using traditional problem solving methods can sometimes end in roadblocks.This technique forces you to think about a problem from a new perspective.
Looking beyond something’s function: Thinking about how you can use something beyond its typical function is a common CPS technique.
SCAMPER: This acronym can help you come up with new ideas. Each letter stands for a way you can manipulate an original idea to come up with something new:
- S ubstitute
- P ut to other uses
Why use CPS
No matter what profession you’re in, you will face challenges. There will be times when traditional problem solving techniques just don’t do the trick. That’s when you can take advantage of CPS to help uncover the best solution to your problem.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to brainstorm: 4 ways to get the creative juices flowing.
Brainstorming can promote problem-solving and innovative thinking to bring the best ideas forward. Follow these four steps and learn how to brainstorm ideas like a pro.
Affinity Diagrams: Your Key to More Creative Problem Solving
No matter the situation, affinity diagramming will help you to organize your thoughts and overcome your workplace challenges. Use these tips and templates to get started.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .

TheBalanceWork
Why Is Creative Problem Solving Important – 15 Possible Reasons
Why is creative problem-solving important? The main reason is: to keep up with the competition in today’s ever-changing business landscape.
Developing innovative solutions to complex problems is a critical skill for any organization.
15 Reasons Why Is Creative Problem Solving Important
There are many advantages to using creative problem-solving techniques in the workplace.
They can change the way employees think about problems. And it can help organizations to be more agile and adaptable.
Some of the benefits of creative problem-solving include the following:
1. Encourages Out-Of-The-Box Thinking:
Creative problem-solving techniques encourage employees to think outside the box. They come up with innovative solutions to problems.
This type of thinking is essential in today’s rapidly changing business environment .

When it comes to problem-solving, organizations need to adapt and change quickly . That’s why it’s important to have creative employees who can think outside the box.
When faced with a problem, they can devise an innovative solution others may not have thought of.
And to be able to do this, they need to be encouraged to think creatively.
2. Helps You Solve Complex Problems:
Creative problem-solving can also help you solve complex problems. Often, complex problems require more than one solution.
The alternatives through creative thinking can help you find the best possible solution.
With creative problem-solving, you’re not just looking for the first solution that comes to mind. Instead, you’re looking for the best possible solution.
So effective problem-solving requires both creative and critical thinking .
Thinking creatively can also help you find new ways to look at old problems. This can give you a different perspective and help you find new solutions.
3. Encourages Innovation:
Innovation is important for businesses to stay ahead of the competition. And it let them be able to offer new products and services .
Creative problem-solving can help encourage innovation . It allows businesses to develop new ideas and find new ways to do things.
Some of the world’s most successful businesses have grown because they innovated.
With time, many businesses lose their ability to be creative and innovative. This can lead to them becoming stagnant and eventually fail.
You can take Nokia as an example. The company was once the world’s leading mobile phone manufacturer.
However, it needed to innovate and keep up with the competition. As a result, its market share declined sharply, and it is now struggling to survive.
4. Builds Confidence:
Confidence is important in all areas of life. When you’re confident, you’re more likely to take risks and seize opportunities .
Learning how to solve problems creatively can help you build your confidence .
This is because you’ll know you have the skills to deal with whatever challenges come your way.
Some people are born confident. But for most of us, confidence needs to be developed.
If you lack confidence, solving problems creatively can help you build them up.
Your comfort zone is what limits you. So you must push yourself to try new things and solve problems uniquely. And you’ll slowly expand your comfort zone.
This can ripple effect on other areas of your life, making you more confident in everything you do.
5. Makes You More Resilient:
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from setbacks and keep going despite difficulties.
It’s a key quality for anyone who wants to achieve their goals.
And creative problem-solving can help you develop resilience.
When you face a problem, it’s natural to feel discouraged . But you need to view problems as opportunities to learn and grow. You’ll be more likely to find a creative solution .
This mindset will help you persevere when things get tough and overcome obstacles.
Some people are naturally more resilient than others. But everyone can benefit from developing this quality.
And creative problem-solving is one of the best ways to do
6. Develops Your Analytical Skills:
Creative problem solving doesn’t mean you never use logic or analysis. But, best solutions often come from a combination of creative and logical thinking.
To find a truly original solution, you need to be able to see problems from different angles. This requires both left-brain (logical) and right-brain (creative) thinking.

With creative problem-solving, you develop ability to analyze problems from many perspectives.
This will make you better at finding innovative solutions to complex challenges.
With better analytical skills, you’ll also be better equipped to handle difficult decisions. And you can solve problems quickly and efficiently.
7. Teaches You How to Be Proactive:
Proactive people don’t wait for things to happen. They make things happen.
The best way to achieve success is to take the initiative and be proactive.
When you’re proactive , you don’t wait for opportunities to come knocking on your door. Instead, you go out and create your opportunities .
When you’re proactive, you always look for ways to improve your situation. You’re constantly looking for ways to take your life to the next level.
8. It Helps You Develop A Positive Attitude:
A positive attitude is essential for achieving success in any area of life.
If you want to be successful, you need to start thinking positive thoughts .
Creative problem-solving helps you develop a positive attitude. It forces you to look at problems in a different light.
It helps you see that every problem has a solution. And, it helps you understand that every challenge is an opportunity to learn and grow.
Some people see problems as roadblocks . They think that every problem is a negative thing.
This way of thinking will only hold you back.
Creative problem-solving helps you see problems as opportunities. In addition, it helps you develop a positive attitude that will lead to success.
9. Helps Employees Handle Change:
Change is a constant in today’s business world. And it can be difficult for employees to deal with.
They’ll be better equipped to handle change if they’re trained in creative problem-solving.
They’ll be able to adapt and find new solutions to problems. Change is no longer a negative thing but an opportunity to grow.
When you embrace change, you open up a world of possibilities .
10. Maintains Employee Engagement:
Employee engagement is important for any business. And creative problem-solving can help maintain employee engagement.
Engaged employees are more likely to be productive and motivated . They’re also less likely to leave the company.

Engaged employees are an asset to any business. And creative problem-solving can help keep them engaged and resourceful .
Some ways you can encourage employee engagement through creative problem-solving are:
– Encourage employees to come up with new ideas and solutions to problems.
– Solicit feedback from employees regularly .
– Encourage employees to share their ideas with others.
– Create an environment that is conducive to creativity and innovation.
– Make sure employees feel like their work
11. Encourage Teamwork:
When employees work together to solve problems, it can help build morale. And it can foster a sense of camaraderie.
Creative thinking activities can help employees learn to work together and build trust .
Most creative thinking activities are in the form of groups. People in groups can share their ideas with each other and build on each other’s ideas.
Some examples of creative thinking activities that encourage teamwork are:
– Brainstorming
– Group discussion
– Team building exercises
12. Be Willing to Take Risks:
To encourage creative problem-solving, you need to be willing to take risks.
Encourage employees to experiment and try new things.
Make sure they feel comfortable making mistakes. And you can suggest ways to turn those mistakes into learning opportunities.

Some examples of ways to take risks are:
– Encourage employees to experiment
– Try new things
– Make mistakes and learn from them
13. Encourage A Growth Mindset:
A growth mindset is a belief that intelligence can be developed.
People with a growth mindset believe that they can improve their abilities by:
– Good teaching, and
– Persistence.
Creative problem solving requires a growth mindset. Without it, people give up too easily when they encounter a problem.
They may also be afraid to take risks, because they don’t want to look foolish.
Encouraging a growth mindset will help employees feel more confident about their abilities. And it can make them more likely to take risks and try new things.
14. Striving For Originality:
In order to be creative, you have to be willing to take risks. This means that you need to be okay with the possibility of failing.
You also need to be open to new ideas . And you need to be willing to experiment .
One way to encourage creativity is to set aside time for employees to explore new ideas . This can be through brainstorming sessions or another type of creativity exercise.
Originality comes from taking existing ideas and making them your own. This means that you need to be able to see the potential in other people’s ideas.
It also means that you need to be able to take those ideas and build on them. This takes a lot of imagination and creative thinking.
15. Be Persistent:
Creative problem-solving is not a one-time event. Instead, it’s a process you must go through again and again.
You need to be persistent in your search for new ideas. You also need to be persistent in trying out new solutions .
Keep going even if your first attempt doesn’t work. Instead, keep trying until you find a solution that does work.
And with creative problem solving, the more you practice , the better you’ll become at it.
So keep at it, and soon you’ll solve problems like a pro!
Final Word:
Why is creative problem-solving important? Above are some of the reasons why creative problem-solving is important. As you can see, it’s a very useful skill to have.
And it’s one that you can use in all areas of your life, both personal and professional.
So start practicing creative problem-solving today. And you will see how it can help you succeed in all areas of your life.
Last Updated on 5 months by Shahzaib Arshad
- Recent Posts
- 7 Great Signs Your Boss Wants to Help You - October 8, 2023
- How To Explain Dropping Out Of Law School? Detailed Guide - September 6, 2023
- 10 Reasons Employees Get Fired in Workplace - August 27, 2023
Respond To Interview Thank You Email In These 5 Steps + Sample Emails
How Long For HR To Approve Job Offer – Is It 2 Weeks?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
At TheBalanceWork, we always put our readers first. Simply reach out to us and we’ll do everything we can to assist you.
Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Condition
- Communication
- Office Address
- Postal Address
- Operation Manager

The science behind creativity
Psychologists and neuroscientists are exploring where creativity comes from and how to increase your own
Vol. 53 No. 3 Print version: page 40
- Neuropsychology
- Creativity and Innovation

Paul Seli, PhD, is falling asleep. As he nods off, a sleep-tracking glove called Dormio, developed by scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, detects his nascent sleep state and jars him awake. Pulled back from the brink, he jots down the artistic ideas that came to him during those semilucid moments.
Seli is an assistant professor of psychology and neuroscience at the Duke Institute for Brain Sciences and also an artist. He uses Dormio to tap into the world of hypnagogia, the transitional state that exists at the boundary between wakefulness and sleep. In a mini-experiment, he created a series of paintings inspired by ideas plucked from his hypnagogic state and another series from ideas that came to him during waking hours. Then he asked friends to rate how creative the paintings were, without telling them which were which. They judged the hypnagogic paintings as significantly more creative. “In dream states, we seem to be able to link things together that we normally wouldn’t connect,” Seli said. “It’s like there’s an artist in my brain that I get to know through hypnagogia.”
The experiment is one of many novel—and, yes, creative—ways that psychologists are studying the science of creativity. At an individual level, creativity can lead to personal fulfillment and positive academic and professional outcomes, and even be therapeutic. People take pleasure in creative thoughts, research suggests—even if they don’t think of themselves as especially creative. Beyond those individual benefits, creativity is an endeavor with implications for society, said Jonathan Schooler, PhD, a professor of psychological and brain sciences at the University of California, Santa Barbara. “Creativity is at the core of innovation. We rely on innovation for advancing humanity, as well as for pleasure and entertainment,” he said. “Creativity underlies so much of what humans value.”
In 1950, J. P. Guilford, PhD, then president of APA, laid out his vision for the psychological study of creativity ( American Psychologist , Vol. 5, No. 9, 1950). For half a century, researchers added to the scientific understanding of creativity incrementally, said John Kounios, PhD, an experimental psychologist who studies creativity and insight at Drexel University in Philadelphia. Much of that research focused on the personality traits linked to creativity and the cognitive aspects of the creative process.
But in the 21st century, the field has blossomed thanks to new advances in neuroimaging. “It’s become a tsunami of people studying creativity,” Kounios said. Psychologists and neuroscientists are uncovering new details about what it means to be creative and how to nurture that skill. “Creativity is of incredible real-world value,” Kounios said. “The ultimate goal is to figure out how to enhance it in a systematic way.”
Creativity in the brain
What, exactly, is creativity? The standard definition used by researchers characterizes creative ideas as those that are original and effective, as described by psychologist Mark A. Runco, PhD, director of creativity research and programming at Southern Oregon University ( Creativity Research Journal , Vol. 24, No. 1, 2012). But effectiveness, also called utility, is a slippery concept. Is a poem useful? What makes a sculpture effective? “Most researchers use some form of this definition, but most of us are also dissatisfied with it,” Kounios said.
Runco is working on an updated definition and has considered at least a dozen suggestions from colleagues for new components to consider. One frequently suggested feature is authenticity. “Creativity involves an honest expression,” he said.
Meanwhile, scientists are also struggling with the best way to measure the concept. As a marker of creativity, researchers often measure divergent thinking—the ability to generate a lot of possible solutions to a problem or question. The standard test of divergent thinking came from Guilford himself. Known as the alternate-uses test, the task asks participants to come up with novel uses for a common object such as a brick. But measures of divergent thinking haven’t been found to correlate well with real-world creativity. Does coming up with new uses for a brick imply a person will be good at abstract art or composing music or devising new methods for studying the brain? “It strikes me as using way too broad a brush,” Seli said. “I don’t think we measure creativity in the standard way that people think about creativity. As researchers, we need to be very clear about what we mean.”
One way to do that may be to move away from defining creativity based on a person’s creative output and focus instead on what’s going on in the brain, said Adam Green, PhD, a cognitive neuroscientist at Georgetown University and founder of the Society for the Neuroscience of Creativity . “The standard definition, that creativity is novel and useful, is a description of a product,” he noted. “By looking inward, we can see the process in action and start to identify the characteristics of creative thought. Neuroimaging is helping to shift the focus from creative product to creative process.”
That process seems to involve the coupling of disparate brain regions. Specifically, creativity often involves coordination between the cognitive control network, which is involved in executive functions such as planning and problem-solving, and the default mode network, which is most active during mind-wandering or daydreaming (Beaty, R. E., et al., Cerebral Cortex , Vol. 31, No. 10, 2021). The cooperation of those networks may be a unique feature of creativity, Green said. “These two systems are usually antagonistic. They rarely work together, but creativity seems to be one instance where they do.”
Green has also found evidence that an area called the frontopolar cortex, in the brain’s frontal lobes, is associated with creative thinking. And stimulating the area seems to boost creative abilities. He and his colleagues used transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) to stimulate the frontopolar cortex of participants as they tried to come up with novel analogies. Stimulating the area led participants to make analogies that were more semantically distant from one another—in other words, more creative ( Cerebral Cortex , Vol. 27, No. 4, 2017).
Green’s work suggests that targeting specific areas in the brain, either with neuromodulation or cognitive interventions, could enhance creativity. Yet no one is suggesting that a single brain region, or even a single neural network, is responsible for creative thought. “Creativity is not one system but many different mechanisms that, under ideal circumstances, work together in a seamless way,” Kounios said.
In search of the eureka moment
Creativity looks different from person to person. And even within one brain, there are different routes to a creative spark, Kounios explained. One involves what cognitive scientists call “System 1” (also called “Type 1”) processes: quick, unconscious thoughts—aha moments—that burst into consciousness. A second route involves “System 2” processes: thinking that is slow, deliberate, and conscious. “Creativity can use one or the other or a combination of the two,” he said. “You might use Type 1 thinking to generate ideas and Type 2 to critique and refine them.”
Which pathway a person uses might depend, in part, on their expertise. Kounios and his colleagues used electroencephalography (EEG) to examine what was happening in jazz musicians’ brains as they improvised on the piano. Then skilled jazz instructors rated those improvisations for creativity, and the researchers compared each musician’s most creative compositions. They found that for highly experienced musicians, the mechanisms used to generate creative ideas were largely automatic and unconscious, and they came from the left posterior part of the brain. Less-experienced pianists drew on more analytical, deliberative brain processes in the right frontal region to devise creative melodies, as Kounios and colleagues described in a special issue of NeuroImage on the neuroscience of creativity (Vol. 213, 2020). “It seems there are at least two pathways to get from where you are to a creative idea,” he said.
Coming up with an idea is only one part of the creative process. A painter needs to translate their vision to canvas. An inventor has to tinker with their concept to make a prototype that actually works. Still, the aha moment is an undeniably important component of the creative process. And science is beginning to illuminate those “lightbulb moments.”
Kounios examined the relationship between creative insight and the brain’s reward system by asking participants to solve anagrams in the lab. In people who were highly sensitive to rewards, a creative insight led to a burst of brain activity in the orbitofrontal cortex, the area of the brain that responds to basic pleasures like delicious food or addictive drugs ( NeuroImage , Vol. 214, 2020). That neural reward may explain, from an evolutionary standpoint, why humans seem driven to create, he said. “We seem wired to take pleasure in creative thoughts. There are neural rewards for thinking in a creative fashion, and that may be adaptive for our species.”
The rush you get from an aha moment might also signal that you’re onto something good, Schooler said. He and his colleagues studied these flashes of insight among creative writers and physicists. They surveyed the participants daily for two weeks, asking them to note their creative ideas and when they occurred. Participants reported that about a fifth of the most important ideas of the day happened when they were mind-wandering and not working on a task at hand ( Psychological Science , Vol. 30, No. 3, 2019). “These solutions were more likely to be associated with an aha moment and often overcoming an impasse of some sort,” Schooler said.
Six months later, the participants revisited those ideas and rated them for creative importance. This time, they rated their previous ideas as creative, but less important than they’d initially thought. That suggests that the spark of a eureka moment may not be a reliable clue that an idea has legs. “It seems like the aha experience may be a visceral marker of an important idea. But the aha experience can also inflate the meaningfulness of an idea that doesn’t have merit,” Schooler said. “We have to be careful of false ahas.”

Boosting your creativity
Much of the research in this realm has focused on creativity as a trait. Indeed, some people are naturally more creative than others. Creative individuals are more likely than others to possess the personality trait of openness. “Across different age groups, the best predictor of creativity is openness to new experiences,” said Anna Abraham, PhD, the E. Paul Torrance Professor and director of the Torrance Center for Creativity and Talent Development at the University of Georgia. “Creative people have the kind of curiosity that draws them toward learning new things and experiencing the world in new ways,” she said.
We can’t all be Thomas Edison or Maya Angelou. But creativity is also a state, and anyone can push themselves to be more creative. “Creativity is human capacity, and there’s always room for growth,” Runco said. A tolerant environment is often a necessary ingredient, he added. “Tolerant societies allow individuals to express themselves and explore new things. And as a parent or a teacher, you can model that creativity is valued and be open-minded when your child gives an answer you didn’t expect.”
One way to let your own creativity flow may be by tapping into your untethered mind. Seli is attempting to do so through his studies on hypnagogia. After pilot testing the idea on himself, he’s now working on a study that uses the sleep-tracking glove to explore creativity in a group of Duke undergrads. “In dream states, there seems to be connectivity between disparate ideas. You tend to link things together you normally wouldn’t, and this should lead to novel outcomes,” he said. “Neurally speaking, the idea is to increase connectivity between different areas of the brain.”
You don’t have to be asleep to forge those creative connections. Mind-wandering can also let the ideas flow. “Letting yourself daydream with a purpose, on a regular basis, might allow brain networks that don’t usually cooperate to literally form stronger connections,” Green said.
However, not all types of daydreams will get you there. Schooler found that people who engage in more personally meaningful daydreams (such as fantasizing about a future vacation or career change) report greater artistic achievement and more daily inspiration. People who are prone to fantastical daydreaming (such as inventing alternate realities or imaginary worlds) produced higher-quality creative writing in the lab and reported more daily creative behavior. But daydreams devoted to planning or problem-solving were not associated with creative behaviors ( Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts , Vol. 15, No. 4, 2021).
It’s not just what you think about when you daydream, but where you are when you do it. Some research suggests spending time in nature can enhance creativity. That may be because of the natural world’s ability to restore attention, or perhaps it’s due to the tendency to let your mind wander when you’re in the great outdoors (Williams, K. J. H., et al., Journal of Environmental Psychology , Vol. 59, 2018). “A lot of creative figures go on walks in big, expansive environments. In a large space, your perceptual attention expands and your scope of thought also expands,” Kounios said. “That’s why working in a cubicle is bad for creativity. But working near a window can help.”
Wherever you choose to do it, fostering creativity requires time and effort. “People want the booster shot for creativity. But creativity isn’t something that comes magically. It’s a skill, and as with any new skill, the more you practice, the better you get,” Abraham said. In a not-yet-published study, she found three factors predicted peak originality in teenagers: openness to experience, intelligence, and, importantly, time spent engaged in creative hobbies. That is, taking the time to work on creative pursuits makes a difference. And the same is true for adults, she said. “Carve out time for yourself, figure out the conditions that are conducive to your creativity, and recognize that you need to keep pushing yourself. You won’t get to where you want to go if you don’t try.”
Those efforts can benefit your own sense of creative fulfillment and perhaps lead to rewards on an even grander scale. “I think everyday creativity is the most important kind,” Runco said. “If we can support the creativity of each and every individual, we’ll change the world.”
How to become more creative
1. Put in the work: People often think of creativity as a bolt of inspiration, like a lightbulb clicking on. But being creative in a particular domain—whether in the arts, in your work, or in your day-to-day life—is a skill. Carve out time to learn and practice.
2. Let your mind wander: Experts recommend “daydreaming with purpose.” Make opportunities to let your daydreams flow, while gently nudging them toward the creative challenge at hand. Some research suggests meditation may help people develop the habit of purposeful daydreaming.
3. Practice remote associations: Brainstorm ideas, jotting down whatever thoughts or notions come to you, no matter how wild. You can always edit later.
4. Go outside: Spending time in nature and wide-open spaces can expand your attention, enhance beneficial mind-wandering, and boost creativity.
5. Revisit your creative ideas: Aha moments can give you a high—but that rush might make you overestimate the merit of a creative idea. Don’t be afraid to revisit ideas to critique and tweak them later.
Further reading
Creativity: An introduction Kaufman, J. C., and Sternberg, R. J. (Eds.), Cambridge University Press, 2021
The eureka factor: Aha moments, creative insight, and the brain Kounios, J., & Beeman, M., Random House, 2015
Creativity anxiety: Evidence for anxiety that is specific to creative thinking, from STEM to the arts Daker, R. J., et al., Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 2020
Predictors of creativity in young people: Using frequentist and Bayesian approaches in estimating the importance of individual and contextual factors Asquith, S. L., et al., Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts , 2020
Recommended Reading
Contact apa, you may also like.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.
Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author

Brain Power
What is creative thinking and why is it important.
Have you ever wondered why some can come up with amazing ideas while others can’t? The ability to connect the dots and see the larger picture all rest in a certain skill – creative thinking.
Creative thinking is our ability to look at ideas presented or a scenario, and find new alternatives that solve the problem. Best of all this skill isn’t bound to the creative people like designers, musicians, or other artists. A lot of people can benefit from thinking this way from time to time. They can also receive a number of benefits on top of a wide variety of ideas that can spark change.
Table of Contents
What is creative thinking, the importance of creative thinking, what are the creative thinking skills, some examples of creative thinking, bottom line, more tips to boost your creativity.
Defined by the Business Dictionary, creative thinking is: [1]
A way of looking at problems or situations from a fresh perspective that suggests unorthodox solutions (which may look unsettling at first). Creative thinking can be stimulated both by an unstructured process such as brainstorming, and by a structured process such as lateral thinking.
Creativity is, therefore, our ability to form something new out of what’s presented. It’s our ability to think differently and provide new angles and perspectives to a solution.
This can translate to a new solution that wasn’t there or even the realization that a problem doesn’t need a solution at the moment or at all.
True that many people may not care so much about new solutions or angles but that’s the point. Our brains have a natural tendency to fall into certain ‘shortcuts’.
Have you ever been in a situation where you hear or learn one piece of information and you use it all the time?
I bet you have, since we don’t need to relearn how to use a knife or a fork.
That way of thinking does have its perks in those situations but has some drawbacks in other situations. This is especially true with problem-solving.
Creative thinking and creative thinkers are needed in those situations because it pushes out of that linear way of thinking. It encourages us to look at other perspectives and even open up to the idea of new solutions.
Creative thinking is also important for other reasons:
Thinking creatively provides immense freedom.
When we create, we have the opportunity to engage with the world without judging ourselves. It’s similar to what we felt when we were a child. Back then we didn’t care what people thought of us.
Creative thinking provides self-awareness.
We start to think with authenticity as we use our own thoughts, feelings and beliefs. This creates biases in our ideas, but we can learn to set those aside and deeply learn about ourselves.
We become more confident in our ideas.
Maybe right now, you don’t present ideas or your ideas get shut down. By tapping into creative thinking, we can build our confidence in our ideas and start to contribute to the group and our work at large.
Creative thinking isn’t barred to those who learn in creative fashions. Anyone can pick up creative thinking skills and use them to enrich their lives and those around them.
Because anyone can learn this, there is no one “right” method or a set of skills you absolutely need. Some of us may need to strengthen one area while others may need to do more. Regardless, here are some skills that can complement creative thinking.
1. Perception & Empathy
Feeling surprised that this is one of the creative thinking skills? Being perceptive and empathetic works hand in hand with creative thinking. Being able to read the mood of a meeting or a discussion you’re having with people can help immensely.
This is key because there are times and places to share ideas. Specifically, you may find the best opportunities to share ideas when:
- You’re facing a major problem or issue and can’t seem to find a way to proceed and solve it.
- During times of change, when the future is more obscure than usual and you’re thinking of possibilities.
- When there is a clear divide between what people think needs to happen. It’s especially needed when no compromises can happen without considerable effort.
- When something new is needed and hasn’t been tried before.
Empathy also helps with how an idea is presented. Maybe in your workgroup, people aren’t always receptive to your ideas. However, there is that one person who always has a plan and people support.
Empathy is letting that person take “ownership” of that idea and be the voice behind the idea. In these sorts of scenarios, you build up more than empathy. It also builds the belief that your idea will prevail in the hands of someone else.
2. Analytical
Analytical skills help us in understanding many other situations outside of the social environment. Being able to read text or data and have a deeper understanding of what they mean will serve you in a variety of ways.
I find that with creative thinking, the first step is being able to intake information and digest it in various ways. Being able to analyze information is often the first step in the creative thinking process.
3. Open-Mindedness
Once you’ve taken in the information, it’s important that you have an open mind. This means you need to set aside your biases or assumptions and encourage yourself to look at a problem in a new way.
Biases and assumptions are some of the mental barriers you’ll face. But looking at the other barriers, they often stem from that sort of thinking. A strict and “this is how it should be” way of thinking. Other examples of limitations are that you’re thinking of a problem too logically or that creative thinking is somehow breaking the rules.
These are limiting because we know that to have an open mind is to succeed. Every successful entrepreneur in the world today had to break rules at some point in their lives. Consider Richard Branson or Elon Musk whose work revolutionized or created an entirely new industry. All because they didn’t back down to how things were. You can do the same thing within your own group in some fashion.
4. Organized
The last thing people associate creative thinkers is that they’re organized. While we think of great minds have messy rooms or desks, that’s not the case at all.
Being organized plays a crucial role in creative thinking in that it allows you to better organize our ideas. Not only that, but it also helps to present it as well. When we present ideas, it’s similar to a speech. There ought to be a structure, a vision, and have it easy to follow and understand.
Furthermore, if your idea is given the green light, you’ll need to form an action plan, set goals, and have specific deadlines. Being organized will keep you on your toes and prepared for almost anything.
5. Communication
Communication plays a vital role in all this as well. You can’t sell a group or an individual on an idea if you can’t communicate effectively. This applies to both written and verbal communication skills.
This goes back to empathy a bit in that you need to understand the situation you’re in. This also means you need to be a good listener and being able to ask the right questions .
6. Dissect Ideas
The last skill I’ll offer is a challenging one but can pay off in so many ways. Sometimes creative thinking means taking two ideas and merging them.
This helps because in most situations ideas in their base form might not be able to satisfy the original goal or problem. That or maybe the idea is outright terrible but, there are some good pieces of information in it.
The ability to look at ideas and be able to break them down and dissect them and merge with other ideas is a great skill to have. This could easily help solve disputes and help to find a middle ground.
The list of creative thinking examples is endless. In most situations, these examples will boost your creative thinking as well so I encourage you to try them out yourself:
- Designing anything from a logo, to a simple webpage layout, to a poster and more
- Creating a lesson plan for a group training course
- Writing in a journal, a blog, or any social platforms
- Creating a test or quiz from scratch just for fun
- Brainstorming project ideas at work, or decor/renovation ideas at home
- Finding procedures to improve the quality of a product or service
- Suggesting solutions to improve a product or service
The number of examples of creative thinking is endless but they are all challenging. This is a good thing as the world continues to change and grow. This pushes us to learn new skills, to think differently, and to start asking the more important questions. “Why?” and “Why not?”
These are skills and abilities that can change the world and that anyone can adopt. So long as you have the patience to learn and develop yourself, you too can be a creative thinker!
- What Is Creativity? We All Have It, and Need It
- 30 Tips to Rejuvenate Your Creativity
- 10 Fears Holding You Back from Creativity and How to Beat Them
Featured photo credit: Pexels via pexels.com
| [1] | ^ | Business Dictionary: |

How to Use a Planner Effectively

How to Be a Better Planner: Avoid the Planning Fallacy

5 Best Apps to Help You Delegate Tasks Easily

Delegating Leadership Style: What Is It & When To Use It?

The Fear of Delegating Work To Others

Why Is Delegation Important in Leadership?
7 Best Tools for Prioritizing Work

How to Deal with Competing Priorities Effectively
What Is the RICE Prioritization Model And How Does It Work?
4 Exercises to Improve Your Focus

What Is Chronic Procrastination and How To Deal with It

How to Snap Out of Procrastination With ADHD

Are Depression And Procrastination Connected?

Procrastination And Laziness: Their Differences & Connections

Bedtime Procrastination: Why You Do It And How To Break It

15 Books on Procrastination To Help You Start Taking Action

Productive Procrastination: Is It Good or Bad?

The Impact of Procrastination on Productivity

How to Cope With Anxiety-Induced Procrastination

How to Break the Perfectionism-Procrastination Loop

15 Work-Life Balance Books to Help You Take Control of Life
Work Life Balance for Women: What It Means & How to Find It

6 Essential Mindsets For Continuous Career Growth

How to Discover Your Next Career Move Amid the Great Resignation

The Key to Creating a Vibrant (And Magical Life) by Lee Cockerell

9 Tips on How To Disconnect From Work And Stay Present

Work-Life Integration vs Work-Life Balance: Is One Better Than the Other?

How To Practice Self-Advocacy in the Workplace (Go-to Guide)

How to Boost Your Focus And Attention Span
What Are Distractions in a Nutshell?

What Is Procrastination And How To End It

Prioritization — Using Your Time & Energy Effectively

Delegation — Leveraging Your Time & Resources

Your Guide to Effective Planning & Scheduling

The Ultimate Guide to Achieving Goals

How to Find Lasting Motivation
Complete Guide to Getting Back Your Energy

How to Have a Good Life Balance
Explore the time flow system.

About the Time Flow System

Key Philosophy I: Fluid Progress, Like Water
Key Philosophy II: Pragmatic Priorities

Key Philosophy III: Sustainable Momentum

Key Philosophy IV: Three Goal Focus
How the Time Flow System Works
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to improve your creative skills and supercharge your resume

Creative skills are the key to unlocking innovation and problem-solving excellence.
In the whirlwind of everyday professional challenges, we’ve all encountered moments when fresh ideas feel elusive. If you’ve found yourself struggling to inspire your team or spinning out during a brainstorming session , it may be a sign you need to develop your creative skills. Plus, creative problem-solving looks excellent on a resume .
As a leader or team member, your ability to think outside the box can ignite a spark of ingenuity that propels your team to new heights. Fan the flames of growth and learn how to improve your creative thinking (and highlight your new skills in your next job application).
What are creative skills?
Creative skills are crucial in today's rapidly changing world, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptability across various fields.
They drive innovation, provide competitive advantages in business, and foster personal growth. In an increasingly complex global landscape, creative thinking is essential for addressing challenges and seizing new opportunities.
Are creative skills important?
Creative skills are crucial in today's rapidly changing world, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptability across various fields. They drive innovation, provide competitive advantages in business, and foster personal growth. In an increasingly complex global landscape, creative thinking is essential for addressing challenges and seizing new opportunities.
15 creative skills examples
When you look at creativity as a set of particular abilities, it becomes easier to develop and perfect. These creative skill examples can help you thrive inside and outside of the workplace:
1. Open-mindedness
When you’re open-minded, you can readily adapt to new information and look for fresh problem-solving approaches. You’re receptive to the opinions and ideas of others because you view them as constructive rather than criticizing . This openness also encourages you to freely share your creative ideas without fearing judgement.
2. Curiosity
You might find that you tap into creative potential the most when you’re challenging convention and posing new ways of thinking. Analyzing processes and asking yourself how you can improve them is an exciting way to make more efficient systems.
Whether you’re new to a job or have worked at the company for years, you may wonder why procedures are what they are — lean into this curiosity to develop new and better ways to work.

3. Ability to brainstorm
There are numerous ways to solve a problem, and brainstorming helps to get them onto paper so you can weigh their pros and cons. This way of lateral thinking encourages you to view solutions as multifaceted rather than a single, straightforward answer.
4. Experimentation
Creative people experiment with various ways of solving a problem before deciding on the best way to take action. Emulate this mindset in your projects and tasks. For instance, if you work in web design, you might try several page layouts before deciding on a final visual identity for your client.
5. Networking
Speaking with people from different professional backgrounds is an excellent way to stimulate creative thinking and develop new perspectives. When you network with professionals with diverse skill sets and experiences, they might influence you to look at the world differently or suggest an innovative way to tackle a problem.
6. Observation
It’s important to know when to take the backseat and listen in. Observing how others tackle complex issues might inspire you to make changes within your team. Always keep an eye out for opportunities to learn from more experienced peers and innovative colleagues.
7. Organization
Although some individuals claim to thrive in clutter, k eeping your work organized creates an environment where you can work freely without distraction. This involves keeping your workspace tidy, creating clear to-do lists, and using visual maps to express your plans and processes.
8. Communication
Proper communication empowers you to share valuable insight and ideas with your teammates. You need strong verbal and written skills to pitch and describe your thoughts and actively listen to others’ feedback and advice.
9. Analysis
Before you can dream up a creative approach to an obstacle, you must fully understand the problem at hand. Without proper analysis , your solution may contain flaws, or you could miss important details of your problem. Practice sifting through every detail of the issue and pinpointing the causes.
10. Problem-solving
No matter your industry, problem-solving is always a valuable skill. Consider how to tackle a problem without asking the advice of others to see what creative solutions arise. This way, you can see what inventive ideas you can come up with before external opinions influence you.
11. Imagination
The ability to visualize concepts not present in reality. Thinking beyond the conventional, imagination fuels original thoughts and ideas.
12. Innovation
Introducing new ideas, methods, or products is at the heart of innovation. This capacity involves both improving existing processes and creating entirely novel solutions.
13. Adaptability
Being flexible and open to change is crucial for creative thinking. Adaptability allows individuals to adjust seamlessly to new conditions and challenges.
14. Collaboration
Sharing ideas and integrating different viewpoints are key to effective teamwork. Collaboration involves working with others to achieve common goals.
15. Storytelling
Engaging narratives captivate audiences across various mediums. Storytelling is essential in almost any industry to connect with others.
How to improve creative skills at work
Although some of your coworkers may seem to have a natural talent for creativity and creative thinking, it’s a skill anyone can develop and improve. Here are seven ways to advance your innovative problem-solving:
Reading is an effective way to exercise your mind, increase your vocabulary, and expose yourself to new ways of thinking. Whether your book is on a problem you’re facing at work or a new and exciting subject, reading is an excellent opportunity to learn. That’s right: simply cracking open a book can help you grow .
Keep a notepad nearby and write down thoughts and ideas as they arise. Writing helps you to process information, and you can revisit your musing whenever you need to get your creative juices flowing. If you’ve never tried journaling before, it’s an excellent way to process your thoughts and feelings in a safe and private space.
3. Exercise
Exercising improves your sleep and ability to cope with stress, making it easier to stay alert and contribute fresh ideas at work.
4. Listen to music
Music can affect your mood and place you in the mindset to solve problems. If you’re struggling with creative writing or creating a visual piece of work, listening to music could push you toward expressing yourself more meaningfully.
5. Ask for feedback
Collaboration and teamwork are key when developing creative solutions in the workplace. You can ask teammates or superiors for feedback on your ideas to gain insight into potential flaws in your reasoning and streamline your solutions.
6. Find a mentor or coach
Having an experienced person to bounce ideas off is a catalyst for creativity. A mentor or coach who’s dealt with similar obstacles can provide insight into what worked and what didn’t, saving you valuable brainstorming time.
7. Change your approach
If you’ve been approaching your tasks the same way, adjusting your processes may bring a fresh perspective and stimulate change. Ask yourself why you tackle work from a similar angle each time and consider more creative ways to conduct your day-to-day operations.
4 creative skills examples for your resume
Employers want to add creative people to their teams because solving problems takes a lot of ingenuity. Use these four examples and bullet points for inspiration when listing creative thinking skills on your resume.
On a graphic designer’s resume:
- Collaborated on rebranding [company’s] visual identity and social media content strategy
- Developed unique and innovative branding material for [company A] , [company B] , and [company C]
On a copywriter’s resume:
- Revised [company’s] website and blog content to be more engaging, exciting, and SEO-focused
- Contributed original and innovative articles on [topic] to [publication A] and [publication B]
On a public relations specialist’s resume:
- Increased [company’s] brand awareness by planning [event] to launch [product]
- Collaborated with [brand] on [product’s] creative marketing strategy to reach a wider audience
On a teacher’s resume:
- Developed a novel approach to teaching [subject or class] to students with various learning styles and needs
- Introduced [extracurricular] , the first of its kind in [the school board] , to engage students in [activity]
Sharpen your creativity
Critical and creative thinking broaden your perspective and allow you to devise unique solutions to everyday problems. You can develop your creative skills by changing your environment, learning from others, and adjusting your approach to work.
Regardless of how you choose to spark creativity at work, don’t be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and confidently contribute your ideas. You never know — you might just come up with the next big company innovation.
If you're looking for support or an accountability partner , a dedicated BetterUp Coach can help. They'll work with you to build out a personalized path to develop creativity in your day-to-day.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
The significance of written communication in the workplace
How to make yourself indispensable at work: pro tips, how to improve your listening skills for better communication, 17 essential transferable skills to boost your job search, eq versus iq: which should you leverage when, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, how to write a job application email that gets a reply, exploring leadership vs. management and how to excel at both, 15 teacher interview questions and how to answer them, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, how to develop critical thinking skills, what is creative thinking and how can i improve, what are professional skills, and which should you add to your resume, why creativity isn't just for creatives and how to find it anywhere, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, how to improve adaptability skills, professional leadership skills to incorporate on your resume, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
What Is Creative Thinking? Definition, Examples, and How to Showcase It During Your Job Search

Have you ever whipped up a delicious meal using random leftover ingredients? That silly example, friends, is creative thinking in action. In today's job market, where innovation is key, creative thinking is no longer just a bonus skill—it's a must-have.
But what exactly is the creative thinking definition? Why is creative thinking a good skill ? How can you showcase it to potential employers? We’ve got all the answers.
What is creative thinking?
Creative thinking is the ability to look at problems or situations from a fresh perspective. It involves thinking outside the box and coming up with unique, effective solutions. This skill is not limited to artistic fields but is essential in every profession, from business and science to technology and education. (Here are five ways to inject creativity into every single job —even ones that involve numbers.)
A creative thinker is someone who can adapt to changing circumstances and come up with original solutions. It's someone who’s curious, who asks questions and isn't afraid to try new things. They can see possibilities where others might see limitations, and they find joy in the process of exploration and discovery.
Apply your creative thinking skills to a job you love — check these amazing open jobs on The Muse and find the perfect fit for you »
Four different types of creative thinking
Creative thinking comes in various forms, each valuable in different contexts. Here are some key types of creative thinking:
1. Artistic creativity
This is likely the one that springs to mind first—it’s the ability to create something new and beautiful, whether it's a painting, a song, a book, or a well-designed website. Artistic creativity is crucial in fields like graphic design , advertising, and entertainment, where visual and auditory appeal play significant roles.
2. Analytical creativity
Analytical creativity is all about breaking down complex problems and finding innovative solutions through data, information, and logical thinking. It’s essential in fields like data science, engineering, and finance , where identifying patterns and making data-driven decisions can lead to significant advancements.
3. Lateral thinking
Lateral thinking involves looking at a problem from different angles and finding solutions that aren’t immediately obvious. This type of thinking is super important in roles that require problem-solving and innovation, such as product development, marketing, and management. It encourages thinking outside the box and finding creative ways to overcome challenges.
4. Divergent and convergent thinking
Divergent thinking is brainstorming a wide range of ideas, no matter how crazy and unusual they might seem at first. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, involves narrowing down these ideas to find the best possible solution. Both types are important in the creative process: divergent thinking sparks innovation, while convergent thinking refines and implements the ideas.
Examples of creative thinking
Now that we've explored the different types of creative thinking, let's see how these skills manifest:
Open-mindedness
This is the foundation of creative thinking. It's about being receptive to new ideas and new perspectives, even if they seem unconventional at first. For instance, in a team meeting, being open-minded might mean considering unconventional suggestions and exploring their potential before dismissing them.
Innovation and invention
Innovation involves creating new ideas, products, or methods, while invention is about bringing those ideas to life. Thinking creatively can be an asset in environments that encourage experimentation and risk-taking. An engineer who designs a groundbreaking app is a good example of this type of creative thinking.
Problem-solving
Problem-solving is a key aspect of creative thinking. It’s the ability to define a problem, create original solutions, and implement the best one. A project manager who overcomes a significant challenge by following a unique approach is showcasing creative problem-solving skills.
Collaborative thinking
Collaborative thinking involves working with others to generate and refine ideas. It requires communication, empathy, and the ability to build on others' input. For example, a creative thinker might lead a brainstorming session where team members feel encouraged to share their ideas, resulting in a collective, innovative solution.
Bonus tips to embrace your creative side
The more you learn, including outside your work environment, the more fodder you'll have for creative thinking. Take a look at these tips:
- Challenge yourself: Step outside your comfort zone! Try new hobbies , learn a new language, or a new instrument, or take a different route to work. Exposing yourself to new experiences sparks fresh ideas and helps you see the world from different perspectives.
- Embrace curiosity: Curiosity is the fuel that ignites creativity. Ask questions, explore different ideas, and be open to new information. Read books outside your usual genre, watch documentaries on unfamiliar topics, or start conversations with people from different backgrounds.
- Brainstorm like a boss: Sometimes the best ideas come from collaboration. Use brainstorming techniques like mind maps or group brainstorming sessions to generate a wide range of ideas. Don't be afraid to get a little silly—even weird ideas can spark something truly innovative.
- Turn obstacles into catalysts: Believe it or not, limitations can actually boost creativity . Think of a time you had to come up with a presentation using only 5 or 10 minutes. This challenge can force you to create unexpected solutions. So, the next time you face a constraint, see it as an opportunity to unleash your creative potential!
How to highlight your creative thinking during a job search
Employers look for creative thinkers because they can communicate ideas clearly and solve problems effectively. Now that you know the definition for creative thinking and its several types, it’s time to show you how to make this creative side stand out in your job search.
On your resume
When updating your resume , emphasize any creative projects or achievements. Detail the innovative solutions you've implemented and the impact they had. If you developed a new process that increased efficiency or created a marketing campaign that boosted engagement, these are perfect examples of creative thinking skills on a resume.
Using strong action verbs can make these contributions stand out. Try to use words like:
In your cover letter
Your cover letter is a great place to dive into specific examples of creative problem-solving. Describe situations where you faced a challenge and how a creative thought helped overcome them. If you found a unique way to market a product or solve a logistical issue, for example, these stories highlight your ability to think creatively.
It’s also important to personalize your cover letter to the job you're applying for by linking your creative thinking skills to the company's needs and goals. Explain how your ability to think creatively aligns with the job requirements and can help the company achieve its goals.
During interviews
In interviews , be ready to give concrete examples of your creative thinking in action. Discuss past experiences where your innovative ideas led to successful outcomes. Whether it was developing a new strategy, solving a complex problem, or improving a process, these examples will show your creative side.
Prepare to answer behavioral questions—those designed to evaluate how you handle some situations—with stories that highlight your creative problem-solving abilities. For example, if asked about a time you faced a significant challenge, describe how you used creativity and creative thinking to navigate the situation and achieve a positive result.
Put these tips into action! Read this to find your next career adventure: 16 High-Paying Jobs for Creative People in 2024
Creative Thinking, Problem Solving and Ideation Tools
- First Online: 05 August 2022
Cite this chapter

- Rouxelle de Villiers 2
3653 Accesses
It is a myth that creative genii sit quietly hoping for inspiration and insight come to them in a flash of illumination. Some discoveries are either by accident or the result of some form of creative “spark of genius”, but for most novel, valuable business solutions, problem-solving often starts with a design challenge/problem or opportunity. Thanks to decades of research and tried-and-tested tools applied in a range of domains and business disciplines, a treasure trove of creative problem-solving tools and techniques is available to creatives and innovators. These tools turn problems into possibilities, and provide opportunities to develop ideas, processes, products, or procedures that are new to that job, team or organization. Business Schools and industries have no shortage of models, frameworks and tools to improve business effectiveness or generate new and interesting problem solutions for clients. Thinking tools have merit and include divergent or convergent (or both) thinking techniques. We cover thirteen of the most well-known and useful tools and techniques in this chapter. There are many more, but the scope of this book limits what can be covered here.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Creative Problem-Solving

The Design Thinking Methodology at Work: Capturing and Understanding the Interplay of Methods and Techniques
Read the book by Stokes, P.D. (2006). Creativity from Constraints about the various disciplines, from literature to fashion, advertising and architecture, to music. ISBN 0–8261–7845-6
Osborn AF. Applied imagination. New York: Charles Schribner’s Sons; 1953.
Google Scholar
Janis IL. Groupthink. IEEE Eng Manag Rev. 2008;36(1):36.
Article Google Scholar
Paulus PG, Dzindolet MT, Poletes G, Camacho LM. The illusion of group productivity. Personal Soc Psychol Bull. 1993;19:78–89.
Paulus PG, Dzindolet MT. Social influence processes in group brainstorming. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1993;64:575–86.
McLeod S. Solomon Asch – conformity experiment. SimplyPsychology.org : simply psychology; 2018.
Greenfield R. Brainstorming doesn’t work; try this technique instead. FastCompnay; 2014. Available from: https://www.fastcompany.com/3033567/brainstorming-doesnt-work-try-this-technique-instead
Rietzschel EF, Nijstad BA, Stroebe W. Productivity is not enough: a comparison of interactive and nominal brainstorming groups on idea generation and selection. J Exp Soc Psychol. 2006;42(2):244–51.
Thompson L. Creative conspiracy: the new rules of breakthrough collaboration. Harvard Business Review Press; 2013.
Right Source. 2017. Available from: https://www.rightsourcemarketing.com/content-creation/everything-know-brainstorming-wrong/
Griffiths C, Costi M. The creative thinking handbook: your step-by-step guide to problem solving in business. New York: Kogan Page Ltd; 2019.
Ayshford E. Why your next brainstorm should begin with an embarrassing story. Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University; 2019. Available from: https://insight.kellogg.northwestern.edu/article/boost-creativity-brainstorm-embarrassment?utm_source=piano&utm_medium=onsite&utm_campaign=364L
Buzan T, Griffiths C. Mind maps for business: revolutionize your business thinking and practice. Harlow: BBC Active; 2010.
Eberle B. Scamper on: Games for imagination development. New York: D.O.K Publisher Inc; 1971.
De Bono E. Six thinking hats. London: Penguin; 2017.
De Bono E. Six thinking hats. New York: Little, Brown & Company; 1985.
Ohno T. Ask ‘why’ five times about every matter. 2006. Available from: https://www.toyota-myanmar.com/about-toyota/toyota-traditions/quality/ask-why-five-times-about-every-matter
Duncan K. The ideas book: 50 ways to general ideas visually. London: LID; 2014.
Gentner D, Bowdle B, Wolff P, Boronat C. Metaphor is like analogy. The analogical mind: perspectives from cognitive science. 2001. p. 99–253.
Gentner D. The mechanisms of analogical learning. In: Vosniadou S, Ortony A, editors. Similarity and analogical reasoning. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1989. p. 199–241.
Chapter Google Scholar
Gordon WJJ. Synetics: the development of creative capacity. New York: Harper & Row; 1961.
Det N. Synectics classroom demo by Dr. Chitra Sohani YouTube; 2019. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YwVelaJQCcs
Clapham MM. The development of innovative ideas through creativity training. In: Shavinina LV, editor. The international handbook on innovation. Oxford: Pergamon; 2003. p. 366–76.
Kostoff RN. Stimulating innovation. The international handbook on innovation. 2003. p. 388–400.
Dhanoa HK, Nanda S. Effect of synectics model on language creativity: a review. Int J Multidiscip Educ Res. 2019;8(1).
Prince G. The operational mechanism of synectics. J Creat Behav. 1968;2:1–13.
Nolan V. Whatever happened to Synectics? Creat Innov Manag. 2003;12(1):25.
Starko AJ. Creativity in the classroom: schools of curious delight. London: Routledge; 2010.
Sawyer RK. The science of human innovation: Explaining creativity. New York: Oxford University Press; 2012.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand
Rouxelle de Villiers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rouxelle de Villiers .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations, creativity laboratory, 1.1 activity i: self-directed brainwriting.
Write down a problem (or design challenge) as concisely and as accurate as possible in the first one of the framed boxes in Fig. 10.2 . ( If you cannot think of one, here is one for you to mentally chew on: Too few parents volunteer for parent-teacher events to help teachers raise funds for additional school resources .)
At the top of each Post-it note, next to the pin, write down a category or discipline you think can think of that may have something/nothing to do with the problem. Suggested: Furniture, Toys, Utensils, Tools, Scientific Instruments, Transportation, Appliances, Weapons, Health/Medicine, Fashion & Personal Accessories). (2) Brainstorm ideas – in your own mind! Do not stop until you have 5 or 6 ideas under each Post-It topic. (Try to list about 20 to 30 under each topic.) Challenge yourself even further: do not leave until you have 50 ideas or have spent 10 min by yourself contemplating the issue and generating ideas.
Set this list aside for at least an hour while you do other things (anything but actively thinking about this matter.)
Return to the Post-it notes and colour the stars next to the best ideas (you determine the criteria to be considered ‘best’.)
Write the starred idea in the next one of the framed boxes and repeat the process. Do this at least three times. Any luck?
Self-directed Brainwriting here
1.2 Activity II: The Problem with Private Property in Public Transport
Passengers keep leaving their umbrellas on public buses, causing huge problems for the bus company in storing and returning lost property. How can the transport services deal with this costly problem without simply shrugging it off as ‘not our problem’ and creating customer dissatisfaction? Use the three tools (SCAMPER, WWJD and Random Picture Technique) to ideate. Next, apply the 5WHYs framework to consider a range of causes. Then, use those causes to consider alternative solutions the bus company might use to either prevent or overcome this costly customer service. (If you are initially unsure how the job functions listed in the figure relate to the problem, try to make remote associations between the problem and the issues that job/role might deal with. How would someone in that role, solve the lost umbrella problem?) (Figs. 10.3 and 10.4 ).
Practice with three thinking tools
Five Wise Genii
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
de Villiers, R. (2022). Creative Thinking, Problem Solving and Ideation Tools. In: de Villiers, R. (eds) The Handbook of Creativity & Innovation in Business. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2180-3_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2180-3_10
Published : 05 August 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-2179-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-2180-3
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Shortform Books
The World's Best Book Summaries
The 5 Benefits of Creative Thinking & Why It’s Important
This article gives you a glimpse of what you can learn with Shortform. Shortform has the world’s best guides to 1000+ nonfiction books, plus other resources to help you accelerate your learning.
Want to learn faster and get smarter? Sign up for a free trial here .
Do you want to be more innovative? What are the benefits of creative thinking?
Creative thinking isn’t limited to just musicians, writers, and other artists. Creativity is a valuable tool for anyone to have in everyday life. When you stimulate your creative genius , you discover innovative ideas and find alternative solutions to problems.
Here are some of the benefits you’ll receive when you begin thinking creatively.
What Is Creativity?
In Big Magic , Elizabeth Gilbert defines creativity as the search for and excavation of universe-endowed gifts that are within us, hidden from our view. Our gifts are the talents, interests, and desires that make us us. You can have a gift for anything—stargazing, website design, or mushroom hunting , for instance—not just a traditionally artistic pursuit, like painting, writing, or performing.
In practice, Gilbert’s idea of searching for a gift and becoming creative might look something like this: All your life, you’ve felt that you get along well with animals. You’re not sure why, but it seems as though you can understand them better than other people can. Finally, after years of feeling this way, you decide to test out your hunch by volunteering at your local animal shelter. To your delight, you find that the shelter animals do indeed respond well to you. You are great at training them, playing with them, and bonding with them. Injured or abused animals grow healthier under your care. You have just excavated a creative gift that has always lived inside you, but which you never before searched for.
Notice that Gilbert does not define creativity as a professional pursuit or even as the main goal or mission of one’s life. It’s simply a commitment to exploring your depths and bringing to light the unique powers that exist within you.
Other Definitions of Creativity
Gilbert’s conception of creativity for this book is unique, perhaps because seasoned creators develop idiosyncratic definitions of this concept. If Gilbert’s definition doesn’t fully resonate with you, fellow writer Amy Tan has her own definition, which she presented in a popular TED Talk. Tan feels her creativity is the product of her upbringing, the big questions that preoccupy and interest her, and her quest to derive meaning from the world .
Steve Jobs’s definition of creativity was different still: He said that creativity was just a matter of forming novel connections . For Jobs, magic and mysticism figured far less into creativity than for Tan and Gilbert.
As a creator, you may wish to come up with a definition of creativity that most resonates in your life.
Benefits of Creativity
Now you know what creativity is, and you may have even come up with your own definition of it. But what will you gain out of creativity? There are actually many benefits of creative thinking, from spiritual enlightenment to priceless connections with other people .
Learn what perks you’ll get out of an innovative mindset to encourage you to start thinking differently.
1. Creativity Spawns Spiritual Enlightenment
The first benefit of creative thinking that Gilbert touches on Big Magic is that creativity spawns spiritual enlightenment. According to Gilbert, the central reason to develop your creativity is to come in touch with what she calls “Big Magic,” also known as Creative Sorcery. This is a mystical or spiritual force of creativity. This force is bigger than us and cannot be explained scientifically or proven empirically. It is an eternal cosmic entity that creatives must have faith in.
For Gilbert, coming into contact with Creative Sorcery is a transcendent experience. Touching Creative Sorcery lets you be moved by and interact with something greater than yourself . This communion with a higher creative energy constitutes the chief goal of Gilbert’s life.
Gilbert also explains that when you foster your creativity, Creative Sorcery will help you make your creative process more fluid. Creative Sorcery is an external creative spirit that will only guide you the more creative you want to be. You might be struggling to make progress on an idea and then suddenly realize you’ve just spent hours fully and blissfully immersed in your work—that was Creative Sorcery lending a hand.
2. Creativity Develops Problem-Solving Skills
The second benefit of creative thinking is that it develops your problem-solving skills . According to Barbara Oakley’s book A Mind for Numbers , creativity and problem-solving are closely related. Why? The answer is explained by a concept called diffuse-mode thinking. To get a better understanding of how creativity enhances your problem-solving skills, you need to know the ins and outs of diffuse-mode thinking, including when, how, and why it happens.
When: Diffuse-mode thinking happens when you relax or just let your mind wander . This is usually when you’re not focusing on anything.
How: Diffuse-mode thinking is associated more with the right hemisphere of the brain than the left (although both are involved), and with a resting state, where activity is not significantly elevated in any particular area of the brain . During diffuse-mode thinking, your thoughts traverse longer neural pathways between more diverse concepts.
Why: Diffuse-mode thinking continues to subconsciously process information from previous focused-mode thinking but in a different way. It can generate creative ideas and creative solutions to difficult problems, circumventing the Einstellung effect by allowing you to mentally step away from detailed problems and see the big picture .
This is particularly useful in math and science because, as said before, creativity and problem-solving are closely related: You can often approach a problem in a variety of ways, but a certain approach may offer advantages for a certain problem. Thinking up alternative, creative solutions can help you find the best method of solving the problem.
When you think outside the box and refuse to use traditional problem-solving techniques, you generate creative ideas and solutions to difficult problems. For this reason, creative thinking trumps conventional thinking any day.
3. You’ll Keep Getting Better
Creative minds are always searching for ways to improve. If you think you can’t improve, you won’t allow yourself to grow. David J. Schwartz’s book The Magic of Thinking Big emphasizes this with the example of the Ford Motor Company.
What if Ford Motor Company announced that it had just made the best car ever? “No better car will ever be possible. There is no more need for research, engineering, planning or designing.” With that attitude, the company would shrivel and die.
True success means continuous innovation. It’s true of companies, and it’s true of you as a person.
Creative people always ask themselves, “How can I do better?” Note that it’s not, “ Can I do better?” They know they can always do better, it’s just a matter of how . People with creative minds are the most successful people because of this mentality. Let’s look at an example of one of the most creative minds who found immense success through his innovation: Steve Jobs.
Steve Jobs and His Radical Innovation
In Steve Jobs , Walter Isaacson claims that what set Jobs apart as a technological pioneer wasn’t any skill as an engineer or programmer but his ability to imagine the future before it arrived. His mindset was fostered by the anarchistic counterculture of the 1960s and ’70s, in which rules and norms were routinely circumvented. Jobs embraced the counterculture’s emphasis on spiritual growth , which led to his belief that intuition is more powerful than intellect. His confidence in the strength of his own creativity and intuition let him see possibilities that others would miss.
To illustrate Jobs’s forward-looking imagination, when he was first shown Xerox’s graphical user interface, he didn’t just see it as a clever new system. Rather, says Isaacson, Jobs immediately intuited what all computers of the future would look like, and at Apple he developed the GUI concept far beyond what Xerox had created into the point-and-click interface we all use today.
Isaacson makes it clear that Jobs wasn’t a perfect oracle, but when he misstepped trends in computing, his response was to take the creative route and think unconventionally. For instance, Jobs failed to anticipate the popularity of burning music to CDs in the early 2000s—the iMac included a CD-ROM drive, but not with the ability to make music CDs. Instead of redesigning the iMac, Jobs moved forward to the next stage of music, the MP3 player. The launch of the iPod quickly made user-created CDs obsolete.
Instead of resting on the iPod’s success, Isaacson shows that Jobs was still looking to the future, particularly toward the cell phone market. Cell phones already had built-in cameras, and he knew that as soon as they incorporated music players they would kill the market for the iPod. Therefore, Jobs chose to get there first with the iPhone. Coupled with the iPad tablet, which came out shortly after, Jobs helped steer the digital age away from PCs as the primary computing devices of choice.
But Jobs didn’t see these as separate devices. According to Isaacson, Jobs envisioned an information landscape in which a desktop computer would serve as a “hub” for all of a user’s devices. This allowed for seamless integration from one device to another—an album or ebook bought on your iMac would instantly transfer to your tablet or phone. Toward the end of his life, Jobs believed that the hub for a person’s devices would no longer be their PC at all, but would move into the cloud.
While it can’t be said that Jobs created these trends, Isaacson illustrates Jobs’s uncanny ability to intuit future shifts in computing and position his company ahead of its competitors—all because of his creative mind.
4. Creativity Takes Advantage of All Your Strengths
The great thing about creativity is that there are no limitations. If you’re a writer, you don’t just have to write about one genre—you can write about many. If you’re an artist, you can create whatever you want, using whatever tools you want.
If you have multiple skill sets, having a creative mind will allow you to find a way to combine these skills to make something extraordinary. For example, Leonardo da Vinci is known as one of the greatest artists of all time, but it’s because his genius was his creativity. According to Walter Isaacson in his book Leonardo da Vinci , his creativity was the result of his unbridled imagination plus his scientific insights.
To illustrate how you can utilize all your strengths for one project, we’ve compiled a breakdown of how Leonardo expressed his creativity in three of his masterpieces:
- “Vitruvian Man” : Leonardo’s “Vitruvian Man” was the result of his explorations of mathematics and philosophy. 1) He drew the details of the man’s body, face, and hair with delicate traces, making his subject a metaphor for the human and the divine. 2) He followed architect Vitruvius’s instructions for the placement of the man inside the circle and the square precisely, but he made adjustments to the measurements of the man. Isaacson explains that those adjustments came from his studies of anatomy and his willingness to challenge received knowledge.
- “The Last Supper” : Between 1495 and 1498, Leonardo painted “The Last Supper” for Duke Ludovico—a commission that tested the duke’s patience but showcased Leonardo’s masterful application of narrative, symbology, and optics.
- “Mona Lisa” : Leonardo began working on this masterpiece in 1503 and continued perfecting it until his death, putting into practice his knowledge of optics, the human body and psyche, textures, and nature. One way he applied his knowledge of optics to the piece is that he created an artificial source of light to highlight the model’s features.
Not only did Leonardo value art in his work, he greatly took advantage of his knowledge from all fields of work. And because of that, he became known as one of the best creative minds in history.
5. Creativity Builds Valuable Connections
Many creative people feel discouraged during the creative process and doubt themselves. But by fostering your creativity and sharing your work , you can tap into a network of interested people with whom you can make valuable connections, writes Austin Kleon in his book Show Your Work! . These connections can serve a few purposes: They can become sources of creative collaboration and sources of support—financial and otherwise.
Collaborative Connections
According to Kleon, inspirations, techniques, and ideas have always spread from person to person in a network of influence. The internet in particular now enables this by allowing people to connect around shared interests and ideas and form collaborative relationships.
Whether you recognize it or not, you’ve probably been influenced by people who do things you admire—writers, musicians, businesspeople, and the like, whose work shapes your tastes and aspirations, writes Kleon. By discussing these influences and by sharing your own creative ideas, techniques, and inspirations with others, you can form friendships with like-minded individuals. Inevitably, many of these people will have creative interests and aspirations like yours—connecting with them will build a network of relationships that can lead to collaboration and new creative projects. Moreover, such relationships can serve as an incubator for all kinds of new creative ideas, says Kleon.
Supportive Connections
According to Kleon, sharing your work online is a solution to a lack of self-confidence because the online community is vast and surely includes people who can offer you support. Many of those people want to know how art is made—all the messy details and mistakes included—because they, too, want to make art. As you nurture your creativity, you’ll become a source of inspiration and encouragement for them. Kleon claims this dynamic is reciprocal: People you encourage will often happily encourage and support you. They’ll offer helpful feedback, or they’ll even support you financially because they want you to carry on.
The moral of Kleon’s lesson: Don’t be afraid to think outside the box and show off the results of your creativity to the world. You’ll end up making treasured connections that can boost your confidence in your work.
Final Words
Whether you’re a writer or a scientist, creativity is a valued skill in the workplace and everyday life. This is because everyone wants to stand out in a world dominated by traditional thinking, and creativity is the only way to do that. Break new ground and reap the rewards of your creative mind today.
Are there any more benefits of creative thinking? If so, leave your suggestions in the comments below!
Want to fast-track your learning? With Shortform, you’ll gain insights you won't find anywhere else .
Here's what you’ll get when you sign up for Shortform :
- Complicated ideas explained in simple and concise ways
- Smart analysis that connects what you’re reading to other key concepts
- Writing with zero fluff because we know how important your time is
- ← 3 Ways to Reduce Cognitive Dissonance (+ Why It Happens)
- Gen Z Goes Minimal: How Gen Z Reframes Financial Prosperity →
Somehow, Katie was able to pull off her childhood dream of creating a career around books after graduating with a degree in English and a concentration in Creative Writing. Her preferred genre of books has changed drastically over the years, from fantasy/dystopian young-adult to moving novels and non-fiction books on the human experience. Katie especially enjoys reading and writing about all things television, good and bad.
You May Also Like

Australian Retirement Planning: Top 3 Tips

Attributes of a Great Leader: Would You Make the Cut?

How to Develop Ideas: Turning Insights Into Innovations

Why Change Is Hard: Intriguing Answers From Physics

How to Be an Artist: 4 Steps to Creative Success

How to Get Focused: Control These 3 Emotions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Creative Thinking vs. Critical Thinking: Unleashing the Power of Both
Annie Walls
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two essential cognitive skills that play a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. While creative thinking involves generating new ideas, thinking outside the box, and exploring unconventional solutions, critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and making logical judgments. Both thinking styles have their unique characteristics and benefits. However, the true power lies in the synergy of creative and critical thinking. By combining these two approaches, individuals can enhance their problem-solving skills, promote innovation, and foster growth. In this article, we will explore the definitions, characteristics, and benefits of both creative and critical thinking, and discuss practical strategies for developing these skills and integrating them in education.
Key Takeaways
- Creative thinking involves generating new ideas and exploring unconventional solutions.
- Critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and making logical judgments.
- The synergy of creative and critical thinking enhances problem-solving skills.
- Combining creative and critical thinking promotes innovation and growth.
- Practical strategies can be used to develop and integrate creative and critical thinking skills in education.
Understanding Creative Thinkin
Defining creative thinking.
Creative thinking is the ability to generate new and innovative ideas, solutions, and perspectives. It involves thinking outside the box and challenging traditional ways of thinking. Creativity is a key driver of innovation and can lead to breakthrough ideas that can transform industries and solve complex problems. It is a dynamic and fluid process that requires an open mind and a willingness to explore different possibilities.
In the context of this article, creative thinking refers to the cognitive skills and mindset that enable individuals to come up with original and unconventional ideas. It is about pushing boundaries and embracing uncertainty to find unique solutions to challenges. Creative thinkers are often characterized by their curiosity , imagination , and willingness to take risks .
To better understand the concept of creative thinking, let's take a look at the following table that highlights some key characteristics of creative thinkers:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Curiosity | Creative thinkers have a strong desire to explore and learn new things. They ask questions and seek out new experiences. |
| Imagination | Creative thinkers have the ability to envision new possibilities and think beyond the constraints of the present. They can see connections and patterns that others may overlook. |
| Risk-taking | Creative thinkers are willing to take risks and embrace failure as a learning opportunity. They are not afraid to challenge the status quo and try new approaches. |
It is important to note that creative thinking is not limited to artistic or creative fields. It is a valuable skill that can be applied in any profession or industry. By cultivating creative thinking skills, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities, generate innovative ideas, and contribute to the growth and success of their organizations.
Characteristics of Creative Thinkers
Creative thinkers possess a unique set of characteristics that set them apart from others. They are known for their ability to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions to problems. Curiosity is a key trait of creative thinkers, as they are constantly seeking new knowledge and experiences. They are also open-minded and willing to consider different perspectives and ideas. Additionally, creative thinkers are often risk-takers , unafraid to take chances and explore unconventional paths. They are flexible and adaptable, able to adjust their thinking and approach as needed. Finally, creative thinkers are persistent and determined, willing to overcome obstacles and continue pursuing their ideas.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking offers numerous benefits that can enhance various aspects of our lives. It allows us to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions to problems. Creativity also promotes flexibility and adaptability , enabling us to navigate through challenges and embrace change. Additionally, creative thinking fosters self-expression and individuality , allowing us to express our unique perspectives and ideas. It encourages collaboration and teamwork , as it often involves bouncing ideas off others and building upon each other's creativity. Moreover, creative thinking can lead to personal growth and fulfillment , as it provides a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when we create something new and meaningful.
Exploring Critical Thinking
Defining critical thinking.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and evaluate information objectively and independently. It involves questioning assumptions, considering multiple perspectives, and making reasoned judgments based on evidence. Critical thinking is a key skill in problem-solving, decision-making, and effective communication. It helps individuals to identify biases, logical fallacies, and faulty reasoning, enabling them to make informed and rational choices. In order to develop critical thinking skills, it is important to practice active listening, ask probing questions, and seek out diverse sources of information. By cultivating critical thinking, individuals can become more discerning and analytical thinkers, capable of navigating complex issues and arriving at well-reasoned conclusions.
Here are some practical strategies for enhancing critical thinking:
- Question assumptions : Challenge preconceived notions and examine underlying assumptions.
- Consider multiple perspectives : Seek out diverse viewpoints and evaluate different arguments.
- Evaluate evidence : Assess the quality and reliability of information and sources.
- Identify biases : Recognize personal biases and strive for objectivity.
- Apply logical reasoning : Use logical and rational thinking to analyze and solve problems.
Remember, critical thinking is not about being critical for the sake of it, but rather about being thoughtful, analytical, and open-minded in our approach to information and ideas.
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers
Critical thinkers possess several key characteristics that set them apart. They are analytical and have a strong ability to evaluate information and arguments. They are also curious and have a desire to seek out new knowledge and perspectives. Critical thinkers are open-minded and willing to consider different viewpoints, even if they conflict with their own. They are skeptical and question assumptions and beliefs, looking for evidence and logical reasoning. Additionally, critical thinkers are reflective and take the time to analyze their own thinking and decision-making processes.
Benefits of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking has numerous benefits that can positively impact various aspects of life. It allows individuals to analyze information objectively and make informed decisions. Problem-solving is one of the key skills developed through critical thinking. By critically evaluating different options and considering various perspectives, individuals can find effective solutions to complex problems. Critical thinking also enhances communication skills , as it encourages individuals to articulate their thoughts and ideas clearly and logically. Additionally, critical thinking promotes creativity by challenging individuals to think outside the box and explore innovative solutions.
The Synergy of Creative and Critical Thinking
Complementary nature of creative and critical thinking.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are not opposing forces, but rather complementary skills that work together to enhance problem-solving and promote innovation and growth. While creative thinking involves generating new ideas, thinking outside the box, and exploring possibilities, critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information, reasoning logically, and making informed decisions.
When combined, these two thinking styles create a powerful synergy that allows individuals to approach problems from multiple perspectives and find innovative solutions. By leveraging creative thinking to generate a wide range of ideas and critical thinking to evaluate and refine those ideas, individuals can develop more effective problem-solving skills.
In addition, the complementary nature of creative and critical thinking is essential for promoting innovation and growth. Creative thinking allows individuals to envision new possibilities and challenge the status quo, while critical thinking ensures that these ideas are carefully evaluated and implemented in a practical and effective manner.
To fully unleash the power of both creative and critical thinking, individuals and organizations can implement practical strategies such as brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and design thinking to enhance creative thinking. Similarly, strategies such as analyzing data, conducting research, and engaging in logical reasoning can enhance critical thinking.
By integrating creative and critical thinking in education, students can develop a well-rounded set of thinking skills that will prepare them for future challenges and opportunities.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
Enhancing problem-solving skills is crucial for individuals and organizations alike. It allows us to tackle complex challenges and find effective solutions. One important strategy for improving problem-solving skills is to analyze the problem thoroughly. By breaking down the problem into smaller components and examining each one, we can gain a deeper understanding of the issue at hand.
Another useful technique is to brainstorm multiple solutions. This involves generating a wide range of ideas without judgment or evaluation. By encouraging creativity and divergent thinking, we can uncover innovative approaches that may not have been initially apparent.
To ensure a structured approach, it can be helpful to use a table to organize and compare different solutions. This allows us to evaluate the pros and cons of each option and make informed decisions.
In addition, it is important to collaborate with others when solving problems. By leveraging the diverse perspectives and expertise of a team, we can generate more comprehensive solutions and avoid potential blind spots.
Remember, problem-solving is an iterative process. It is essential to iterate and refine our solutions based on feedback and new information. This continuous improvement mindset enables us to adapt and find better solutions over time.
As Albert Einstein once said, "We cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them." By embracing creative and critical thinking, we can enhance our problem-solving skills and unlock new possibilities for growth and innovation.
Promoting Innovation and Growth
Promoting innovation and growth is a key outcome of combining creative and critical thinking. When these two thinking styles are integrated, individuals and organizations are able to approach challenges and opportunities with a holistic perspective. By leveraging creative thinking, new ideas and possibilities are generated, while critical thinking helps evaluate and refine these ideas to ensure their feasibility and effectiveness.
To promote innovation and growth, it is important to create an environment that encourages both creative and critical thinking. This can be achieved by fostering a culture of open-mindedness, curiosity, and experimentation. Encouraging collaboration and diverse perspectives also plays a crucial role in promoting innovation, as it allows for the exchange of ideas and the identification of new possibilities.
In addition, organizations can implement structured processes and frameworks that facilitate the integration of creative and critical thinking. This includes establishing clear problem-solving methodologies, providing training and resources for developing these thinking skills, and creating opportunities for reflection and continuous improvement.
By promoting the synergy of creative and critical thinking, organizations can unlock their full potential for innovation and growth, leading to competitive advantage and success in today's dynamic and rapidly changing world.
Developing Creative and Critical Thinking Skills
Practical strategies for enhancing creative thinking.
There are several strategies that can help enhance creative thinking. One effective strategy is to embrace curiosity. Curiosity allows individuals to explore new ideas, ask questions, and seek out different perspectives. By being curious, individuals can uncover unique insights and connections that can lead to innovative solutions.
Another strategy is to encourage brainstorming . Brainstorming is a technique that involves generating a large number of ideas without judgment. This allows for the exploration of various possibilities and encourages out-of-the-box thinking.
Additionally, divergent thinking can be a valuable strategy. Divergent thinking involves generating multiple solutions or ideas to a problem. This approach encourages creativity by exploring different options and perspectives.
Lastly, taking breaks can also enhance creative thinking. Stepping away from a problem or task allows the mind to relax and recharge. This can lead to fresh insights and new perspectives when returning to the task at hand.
Practical Strategies for Enhancing Critical Thinking
When it comes to enhancing critical thinking skills, there are several effective strategies that can be implemented. These strategies are designed to help individuals develop their analytical and logical reasoning abilities, enabling them to make well-informed decisions and solve complex problems.
One practical strategy is to engage in active reading and reflection. This involves critically analyzing and evaluating the information presented in texts, articles, or research papers. By asking questions, identifying assumptions, and evaluating evidence, individuals can deepen their understanding and develop a more critical perspective.
Another strategy is to practice active listening and effective communication. By actively listening to others and engaging in meaningful discussions, individuals can challenge their own assumptions and broaden their perspectives. This not only enhances critical thinking but also promotes collaboration and the exchange of diverse ideas.
Additionally, seeking out diverse perspectives and alternative viewpoints is crucial for enhancing critical thinking. By exposing oneself to different opinions and considering multiple perspectives, individuals can develop a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues and avoid biases.
In summary, enhancing critical thinking requires active engagement, reflection, and seeking out diverse perspectives. By implementing these strategies, individuals can strengthen their analytical skills and become more effective problem solvers.
Integrating Creative and Critical Thinking in Education
Integrating creative and critical thinking in education is essential for fostering well-rounded and innovative individuals. By combining these two types of thinking, students are able to develop a holistic approach to problem-solving and decision-making. This integration allows students to think outside the box while also critically evaluating their ideas and solutions.
One practical strategy for integrating creative and critical thinking in education is through project-based learning. This approach encourages students to work on real-world problems and challenges, allowing them to apply both creative and critical thinking skills. By engaging in hands-on projects, students can explore different perspectives, generate innovative ideas, and analyze the effectiveness of their solutions.
Another effective strategy is to incorporate open-ended questions and discussions into the curriculum. This encourages students to think critically about complex issues and encourages them to explore multiple viewpoints. By engaging in thoughtful discussions, students can develop their analytical skills and learn to consider different perspectives and evidence.
Additionally, educators can promote the integration of creative and critical thinking by providing opportunities for reflection and self-assessment. By encouraging students to reflect on their thinking processes and evaluate the effectiveness of their solutions, educators can help students develop metacognitive skills and become more self-aware learners.
In summary, integrating creative and critical thinking in education is crucial for developing well-rounded individuals who can think innovatively and critically. By incorporating strategies such as project-based learning, open-ended discussions, and reflection, educators can empower students to become effective problem solvers and decision makers.
Developing creative and critical thinking skills is essential in today's fast-paced and ever-changing world. Whether you're a student, professional, or entrepreneur, the ability to think creatively and critically can give you a competitive edge and open doors to new opportunities. At Keynote Speaker James Taylor , we specialize in inspiring creative minds and helping individuals and organizations unlock their full potential . With our engaging and thought-provoking presentations, workshops, and coaching sessions, we empower individuals to tap into their creative genius and develop the critical thinking skills needed to thrive in the 21st century. Visit our website today to learn more about how we can help you unleash your creativity and enhance your problem-solving abilities.
In conclusion, both creative thinking and critical thinking are essential skills that complement each other in problem-solving and decision-making. While creative thinking allows us to generate innovative ideas and explore new possibilities, critical thinking helps us evaluate and analyze these ideas to make informed decisions. By harnessing the power of both types of thinking, individuals and organizations can unlock their full potential and achieve greater success. So, whether you are brainstorming new ideas or analyzing data, remember to embrace both creative and critical thinking to unleash your true potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between creative thinking and critical thinking.
Creative thinking involves generating new ideas, while critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating existing ideas.
Can someone be both a creative thinker and a critical thinker?
Yes, individuals can develop and utilize both creative and critical thinking skills.
How can creative thinking benefit problem-solving?
Creative thinking allows for innovative and out-of-the-box solutions to problems.
What are the characteristics of a creative thinker?
Characteristics of a creative thinker include open-mindedness, curiosity, and willingness to take risks.
How does critical thinking contribute to decision-making?
Critical thinking helps in analyzing and evaluating options to make informed and logical decisions.
Is it possible to enhance creative and critical thinking skills?
Yes, through practice, exposure to diverse perspectives, and adopting creative thinking techniques.

Popular Posts
Robert hannigan – the power of neurodiversity in innovation, cybersecurity, gchq and counter-intelligence #342.
Explore key insights on intelligence and decision-making from Professor Sir David Omand’s book, focusing on critical thinking and creativity.
Sam Dixon of Womble Bond Dickinson, The Evolving Role of Lawyers in the AI Era #341
John craske of cms, collaboration between humans and machines in the legal industry #340, jd meier of microsoft, productivity strategies for success #339, sir david omand, author of how spies think – 10 lessons in critical thinking #338, meilleur conférencier principal en teambuilding.
Les conférences virtuelles et les sommets peuvent être des moyens très efficaces pour inspirer, informer
James is a top motivational keynote speaker who is booked as a creativity and innovation keynote speaker, AI speaker , sustainability speaker and leadership speaker . Recent destinations include: Dubai , Abu Dhabi , Orlando , Las Vegas , keynote speaker London , Barcelona , Bangkok , Miami , Berlin , Riyadh , New York , Zurich , motivational speaker Paris , Singapore and San Francisco
Latest News
- 415.800.3059
- [email protected]
- Media Interviews
- Meeting Planners
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
FIND ME ON SOCIAL
© 2024 James Taylor DBA P3 Music Ltd.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
Benefits of Creative Thinking. Here are the key benefits of Creative Thinking skills across personal, academic, and leadership domains: Improved problem-solving capabilities. Creative Thinking is a versatile problem-solving tool, not limited to workplace challenges. It accelerates problem resolution by introducing diverse thought techniques.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming. It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh ...
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals. In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll ...
Creative thinking doesn't just make you a better employee; it also makes you a better parent, student, and leader, too. By developing your creative thinking skills, the benefits of thinking creatively can show up throughout your daily life. Here are a few major benefits of creative thinking. Improved problem-solving capabilities
Also known as creative problem-solving, creative thinking is a valuable and marketable soft skill in a wide variety of careers. Here's what you need to know about creative thinking at work and how to use it to land a job. Creative Thinking Definition. Creative thinking is all about developing innovative solutions to problems.
What's more, because of the benefits that creative thinking can bring, you'll actively want to see things from new perspectives and be more empathic: something that's fundamental to creating real change. Bust assumptions . ... Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the ...
8. Practice Design Thinking. Practicing design thinking can make you a more creative problem-solver. While commonly associated with the workplace, adopting a design thinking mentality can also improve your everyday life. Here are several ways you can practice design thinking: Learn from others: There are many examples of design thinking in ...
The goal of this creative thinking program is to help you develop the strategic concepts and tactical skills to lead creative problem solving for your team and your organization. You will learn to: Retrain your brain to avoid negative cognitive biases and long-held beliefs and myths that sabotage creative problem solving and innovation
Creative thinking and problem solving are core parts of user experience (UX) design. Note: the abbreviation "CPS" can also refer to cyber-physical systems. Creative problem solving might sound somewhat generic or broad. However, it's an ideation approach that's extremely useful across many industries.
Problem-Solving with Creative Thinking. Creative problem-solving is a type of problem-solving. It involves searching for new and novel solutions to problems. Unlike critical thinking, which scrutinizes assumptions and uses reasoning, creative thinking is about generating alternative ideas—practices and solutions that are unique and effective.
What is creative problem solving? The definition of creative problem solving (CPS) will vary between organizations. At its core, CPS involves approaching a problem in an imaginative, innovative, and unconventional way. The process encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly. 7 ...
Brainstorming combines a relaxd, informal approach to problem solving with lateral thinking. It encourages people to come up with thoughts and ideas that can, at first, seem a bit crazy. Some of these ideas can be crafted into original, creative solutions to a problem, while others can spark even more ideas.
And it can help organizations to be more agile and adaptable. Some of the benefits of creative problem-solving include the following: 1. Encourages Out-Of-The-Box Thinking: Creative problem-solving techniques encourage employees to think outside the box. They come up with innovative solutions to problems.
4. Go outside: Spending time in nature and wide-open spaces can expand your attention, enhance beneficial mind-wandering, and boost creativity. 5. Revisit your creative ideas: Aha moments can give you a high—but that rush might make you overestimate the merit of a creative idea.
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
The ability to connect the dots and see the larger picture all rest in a certain skill - creative thinking. Creative thinking is our ability to look at ideas presented or a scenario, and find new alternatives that solve the problem. Best of all this skill isn't bound to the creative people like designers, musicians, or other artists.
Plus, creative problem-solving looks excellent on a resume. As a leader or team member, your ability to think outside the box can ignite a spark of ingenuity that propels your team to new heights. Fan the flames of growth and learn how to improve your creative thinking (and highlight your new skills in your next job application).
Creative Problem Solving: 5 Tips for Creative Problem-Solving. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Apr 20, 2022 • 3 min read. The creative problem-solving process is a brainstorming technique that promotes creative thinking and idea generation to find previously unknown solutions to complex problems.
Problem-solving is a key aspect of creative thinking. It's the ability to define a problem, create original solutions, and implement the best one. A project manager who overcomes a significant challenge by following a unique approach is showcasing creative problem-solving skills.
The Yellow Thinking Hat - Seeks Values and Benefits. ... It is a comprehensive creative problem-solving process, which addresses all stages of the creative process and emphasizes differentiation between idea generation and idea evaluation. Analogies. Synectics uses three metaphoric forms: the personal analogy emphasizes empathic involvement ...
Thinking up alternative, creative solutions can help you find the best method of solving the problem. When you think outside the box and refuse to use traditional problem-solving techniques, you generate creative ideas and solutions to difficult problems. For this reason, creative thinking trumps conventional thinking any day. 3.
Creative thinking and critical thinking are two essential cognitive skills that play a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation. While creative thinking involves generating new ideas, thinking outside the box, and exploring unconventional solutions, critical thinking focuses on analyzing, evaluating, and making logical ...
The benefits of problem-solving creatively. This strategy can help you find solutions when other approaches have been unsuccessful, which makes it a great approach for difficult challenges. It encourages innovation and finding new perspectives, which can lead to unique and unexpected solutions.