- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board

Overcoming Speech Impediment: Symptoms to Treatment
There are many causes and solutions for impaired speech
- Types and Symptoms
- Speech Therapy
- Building Confidence
Speech impediments are conditions that can cause a variety of symptoms, such as an inability to understand language or speak with a stable sense of tone, speed, or fluidity. There are many different types of speech impediments, and they can begin during childhood or develop during adulthood.
Common causes include physical trauma, neurological disorders, or anxiety. If you or your child is experiencing signs of a speech impediment, you need to know that these conditions can be diagnosed and treated with professional speech therapy.
This article will discuss what you can do if you are concerned about a speech impediment and what you can expect during your diagnostic process and therapy.
FG Trade / Getty Images
Types and Symptoms of Speech Impediment
People can have speech problems due to developmental conditions that begin to show symptoms during early childhood or as a result of conditions that may occur during adulthood.
The main classifications of speech impairment are aphasia (difficulty understanding or producing the correct words or phrases) or dysarthria (difficulty enunciating words).
Often, speech problems can be part of neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders that also cause other symptoms, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or autism spectrum disorder .
There are several different symptoms of speech impediments, and you may experience one or more.
Can Symptoms Worsen?
Most speech disorders cause persistent symptoms and can temporarily get worse when you are tired, anxious, or sick.
Symptoms of dysarthria can include:
- Slurred speech
- Slow speech
- Choppy speech
- Hesitant speech
- Inability to control the volume of your speech
- Shaking or tremulous speech pattern
- Inability to pronounce certain sounds
Symptoms of aphasia may involve:
- Speech apraxia (difficulty coordinating speech)
- Difficulty understanding the meaning of what other people are saying
- Inability to use the correct words
- Inability to repeat words or phases
- Speech that has an irregular rhythm
You can have one or more of these speech patterns as part of your speech impediment, and their combination and frequency will help determine the type and cause of your speech problem.
Causes of Speech Impediment
The conditions that cause speech impediments can include developmental problems that are present from birth, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease , or sudden neurological events, such as a stroke .
Some people can also experience temporary speech impairment due to anxiety, intoxication, medication side effects, postictal state (the time immediately after a seizure), or a change of consciousness.
Speech Impairment in Children
Children can have speech disorders associated with neurodevelopmental problems, which can interfere with speech development. Some childhood neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders may cause a regression (backsliding) of speech skills.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include:
- Autism spectrum disorder : A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development
- Cerebral palsy : A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement
- Hearing loss : Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech
- Rett syndrome : A genetic neurodevelopmental condition that causes regression of physical and social skills beginning during the early school-age years.
- Adrenoleukodystrophy : A genetic disorder that causes a decline in motor and cognitive skills beginning during early childhood
- Childhood metabolic disorders : A group of conditions that affects the way children break down nutrients, often resulting in toxic damage to organs
- Brain tumor : A growth that may damage areas of the brain, including those that control speech or language
- Encephalitis : Brain inflammation or infection that may affect the way regions in the brain function
- Hydrocephalus : Excess fluid within the skull, which may develop after brain surgery and can cause brain damage
Do Childhood Speech Disorders Persist?
Speech disorders during childhood can have persistent effects throughout life. Therapy can often help improve speech skills.
Speech Impairment in Adulthood
Adult speech disorders develop due to conditions that damage the speech areas of the brain.
Common causes of adult speech impairment include:
- Head trauma
- Nerve injury
- Throat tumor
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Essential tremor
- Brain tumor
- Brain infection
Additionally, people may develop changes in speech with advancing age, even without a specific neurological cause. This can happen due to presbyphonia , which is a change in the volume and control of speech due to declining hormone levels and reduced elasticity and movement of the vocal cords.
Do Speech Disorders Resolve on Their Own?
Children and adults who have persistent speech disorders are unlikely to experience spontaneous improvement without therapy and should seek professional attention.
Steps to Treating Speech Impediment
If you or your child has a speech impediment, your healthcare providers will work to diagnose the type of speech impediment as well as the underlying condition that caused it. Defining the cause and type of speech impediment will help determine your prognosis and treatment plan.
Sometimes the cause is known before symptoms begin, as is the case with trauma or MS. Impaired speech may first be a symptom of a condition, such as a stroke that causes aphasia as the primary symptom.
The diagnosis will include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and a thorough evaluation of speech and language. Diagnostic testing is directed by the medical history and clinical evaluation.
Diagnostic testing may include:
- Brain imaging , such as brain computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic residence imaging (MRI), if there’s concern about a disease process in the brain
- Swallowing evaluation if there’s concern about dysfunction of the muscles in the throat
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (aka nerve conduction velocity, or NCV) if there’s concern about nerve and muscle damage
- Blood tests, which can help in diagnosing inflammatory disorders or infections
Your diagnostic tests will help pinpoint the cause of your speech problem. Your treatment will include specific therapy to help improve your speech, as well as medication or other interventions to treat the underlying disorder.
For example, if you are diagnosed with MS, you would likely receive disease-modifying therapy to help prevent MS progression. And if you are diagnosed with a brain tumor, you may need surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation to treat the tumor.
Therapy to Address Speech Impediment
Therapy for speech impairment is interactive and directed by a specialist who is experienced in treating speech problems . Sometimes, children receive speech therapy as part of a specialized learning program at school.
The duration and frequency of your speech therapy program depend on the underlying cause of your impediment, your improvement, and approval from your health insurance.
If you or your child has a serious speech problem, you may qualify for speech therapy. Working with your therapist can help you build confidence, particularly as you begin to see improvement.
Exercises during speech therapy may include:
- Pronouncing individual sounds, such as la la la or da da da
- Practicing pronunciation of words that you have trouble pronouncing
- Adjusting the rate or volume of your speech
- Mouth exercises
- Practicing language skills by naming objects or repeating what the therapist is saying
These therapies are meant to help achieve more fluent and understandable speech as well as an increased comfort level with speech and language.
Building Confidence With Speech Problems
Some types of speech impairment might not qualify for therapy. If you have speech difficulties due to anxiety or a social phobia or if you don’t have access to therapy, you might benefit from activities that can help you practice your speech.
You might consider one or more of the following for you or your child:
- Joining a local theater group
- Volunteering in a school or community activity that involves interaction with the public
- Signing up for a class that requires a significant amount of class participation
- Joining a support group for people who have problems with speech
Activities that you do on your own to improve your confidence with speaking can be most beneficial when you are in a non-judgmental and safe space.
Many different types of speech problems can affect children and adults. Some of these are congenital (present from birth), while others are acquired due to health conditions, medication side effects, substances, or mood and anxiety disorders. Because there are so many different types of speech problems, seeking a medical diagnosis so you can get the right therapy for your specific disorder is crucial.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders in children .
Han C, Tang J, Tang B, et al. The effectiveness and safety of noninvasive brain stimulation technology combined with speech training on aphasia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(2):e36880. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036880
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, language .
Mackey J, McCulloch H, Scheiner G, et al. Speech pathologists' perspectives on the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices with people with acquired brain injury and reflections from lived experience . Brain Impair. 2023;24(2):168-184. doi:10.1017/BrImp.2023.9
Allison KM, Doherty KM. Relation of speech-language profile and communication modality to participation of children with cerebral palsy . Am J Speech Lang Pathol . 2024:1-11. doi:10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00267
Saccente-Kennedy B, Gillies F, Desjardins M, et al. A systematic review of speech-language pathology interventions for presbyphonia using the rehabilitation treatment specification system . J Voice. 2024:S0892-1997(23)00396-X. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.12.010
By Heidi Moawad, MD Dr. Moawad is a neurologist and expert in brain health. She regularly writes and edits health content for medical books and publications.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Speaking Skills
How to Get Rid of a Speech Disorder
Last Updated: December 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Devin Fisher, CCC-SLP . Devin Fisher is a Speech-Language Pathologist based in Las Vegas, Nevada. Devin specializes in speech and language therapy for individuals with aphasia, swallowing, voice, articulation, phonological social-pragmatic, motor speech, and fluency disorders. Furthermore, Devin treats cognitive-communication impairment, language delay, and Parkinson's Disease. He holds a BS and MS in Speech-Language Pathology from Fontbonne University. Devin also runs a related website and blog that offers speech-language therapy resources and information for clinicians and clients. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 330,555 times.
Many people feel insecure about their speech impediments, whether they're dealing with a lisp or an inability to articulate words. Although it may not seem like it—particularly if you have been dealing with this problem for years—you may be able to get rid of or improve your speech impediment with a few speech-training practices and some major confidence-boosters. And don't forget to seek out the professional opinion of a speech and language therapist/pathologist for more information.
Helping Yourself with a Speech Disorder

- One modern approach is to use technology. There are apps that can run on smartphones and tablets that listen to what you say and then give you feedback. For example, on Android there is the free app "Talking English." You can also find similar apps in the Apple App Store.

Stephanie Jeret
Cues and picture boards can help those with aphasia find words and express thoughts. For aphasia or trouble finding words, cues like the first sound can help jog your memory. Picture boards are great too, especially if speaking is very difficult. These tools allow people to communicate their needs and thoughts through other means.
Using Your Body to Improve Speech

- Shoulders relaxed
- Back straight
- Feet steady

- Sit comfortably and with an erect posture. Breathe in deeply through your nose. You should use your hand to feel your stomach expanding like a balloon being inflated. Hold the breath and then release it slowly, feeling your stomach deflating beneath your hand. Repeat this exercise before you have to speak publicly to relieve stress.

Getting Professional Help

- Speech therapy is helpful for correcting your impediment. The therapist will point out the part of speech where you're having problems, and will work with you to correct it. Private speech therapy sessions do not come cheap, although most insurance policies will fund services needed to treat speech disorders.
- There's no substitute for learning and practice when it comes to the proper and effective use of language. Take every opportunity to speak, to practice and brush up on the correct pronunciation and enunciation provided to you by a professional.

- Every time the dentist adjusts your braces (or even dentures), you need to train yourself to talk and to eat properly. It may be quite painful at first, but remember not to go too far, lest you end up with a mouth injury.
- Most braces are used for orthodontic purposes, although some braces can be used as decorations. Braces are rather expensive, and you may need to take out a dental plan or cash in on dental insurance to pay for them.
- Kids and teenagers don't like to wear braces because they're often teased as “metal mouths” or “railroad faces.” The fact is that braces are still the best way to correct a lisp caused by misaligned teeth.
Assessing Your Speech Disorder

- Cleft lips and palates were a major cause of speech impediments until surgery became affordable. Now, children born with clefts can have reconstructive surgery and a multidisciplinary team of providers that help with feeding and speech and language development. [14] X Research source
- Malocclusion is when the teeth do not have the proper normal bite. Malocclusions are usually corrected through braces, although orthodontic surgery is necessary in some cases. Individuals with this condition may talk with a lisp, make a whistle sound when certain words are spoken, or mumble.
- Neurological disorders caused by accidents or brain and nerve tumors can cause a speech disorder called dysprosody. Dysprosody involves difficulty in expressing the tonal and emotional qualities of speech such as inflection and emphasis.

Expert Q&A

- Welcome good speech. Look forward to it, and accept and celebrate even little improvements. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to slow down and pronounce each word properly, as this can also help when trying to overcome a speech problem. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- See a Speech Pathologist who maintains their Certification of Clinical Competence from the American Speech and Hearing Association. These professionals are able to evaluate, diagnose and treat speech impairments. Nothing replaces sound medical advice from a specialist. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.uts.edu.au/sites/default/files/2018-10/Camperdown%20Program%20Treatment%20Guide%20June%202018.pdf
- ↑ Devin Fisher, CCC-SLP. Speech Language Pathologist. Expert Interview. 15 January 2021.
- ↑ https://www.stutteringhelp.org/sites/default/files/Migrate/Book_0012_tenth_ed.pdf
- ↑ http://www.coli.uni-saarland.de/~steiner/publications/ISSP2014.pdf
- ↑ https://sps.columbia.edu/news/five-ways-improve-your-body-language-during-speech
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/self-help/guides-tools-and-activities/breathing-exercises-for-stress/
- ↑ http://kidshealth.org/teen/diseases_conditions/sight/speech_disorders.html#
- ↑ https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/stuttering
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001058.htm
- ↑ http://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/CleftLip/
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/developmentaldisabilities/language-disorders.html
- ↑ https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=stuttering-90-P02290
- ↑ https://raisingchildren.net.au/preschoolers/development/language-development/stuttering
About This Article

Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bikash Pokharel
Apr 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Mar 28, 2016
Manisha Singh
Feb 22, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Speech Impediment Guide: Definition, Causes, and Resources
December 8, 2020

Tables of Contents
What Is a Speech Impediment?
Types of speech disorders, speech impediment causes, how to fix a speech impediment, making a difference in speech disorders.
Communication is a cornerstone of human relationships. When an individual struggles to verbalize information, thoughts, and feelings, it can cause major barriers in personal, learning, and business interactions.
Speech impediments, or speech disorders, can lead to feelings of insecurity and frustration. They can also cause worry for family members and friends who don’t know how to help their loved ones express themselves.
Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured. Health professionals in fields including speech-language pathology and audiology can work with patients to overcome communication disorders, and individuals and families can learn techniques to help.

Commonly referred to as a speech disorder, a speech impediment is a condition that impacts an individual’s ability to speak fluently, correctly, or with clear resonance or tone. Individuals with speech disorders have problems creating understandable sounds or forming words, leading to communication difficulties.
Some 7.7% of U.S. children — or 1 in 12 youths between the ages of 3 and 17 — have speech, voice, language, or swallowing disorders, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). About 70 million people worldwide, including some 3 million Americans, experience stuttering difficulties, according to the Stuttering Foundation.
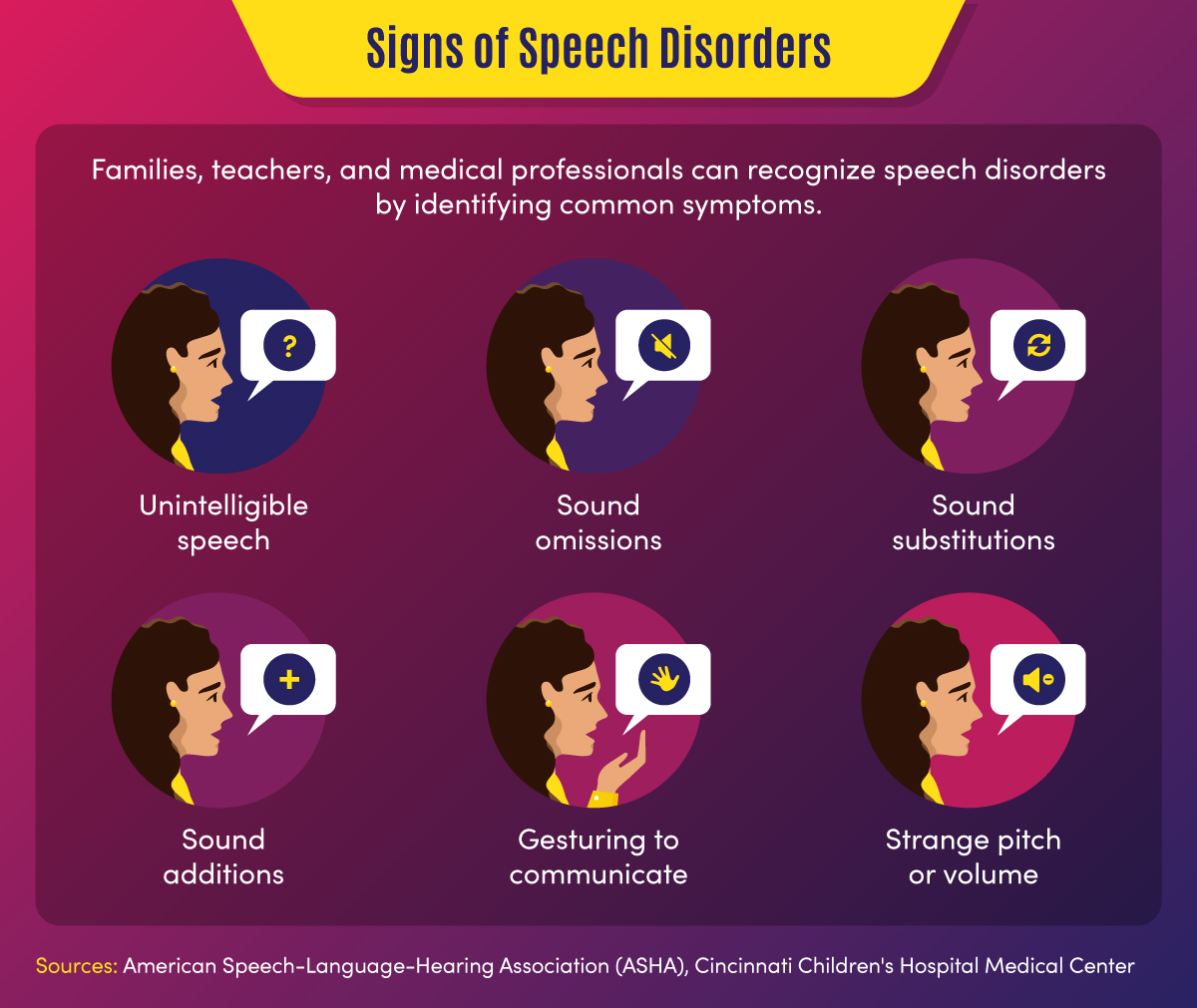
Common signs of a speech disorder
There are several symptoms and indicators that can point to a speech disorder.
- Unintelligible speech — A speech disorder may be present when others have difficulty understanding a person’s verbalizations.
- Omitted sounds — This symptom can include the omission of part of a word, such as saying “bo” instead of “boat,” and may include omission of consonants or syllables.
- Added sounds — This can involve adding extra sounds in a word, such as “buhlack” instead of “black,” or repeating sounds like “b-b-b-ball.”
- Substituted sounds — When sounds are substituted or distorted, such as saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit,” it may indicate a speech disorder.
- Use of gestures — When individuals use gestures to communicate instead of words, a speech impediment may be the cause.
- Inappropriate pitch — This symptom is characterized by speaking with a strange pitch or volume.
In children, signs might also include a lack of babbling or making limited sounds. Symptoms may also include the incorrect use of specific sounds in words, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). This may include the sounds p, m, b, w, and h among children aged 1-2, and k, f, g, d, n, and t for children aged 2-3.
Back To Top
Categories of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments can range from speech sound disorders (articulation and phonological disorders) to voice disorders. Speech sound disorders may be organic — resulting from a motor or sensory cause — or may be functional with no known cause. Voice disorders deal with physical problems that limit speech. The main categories of speech impediments include the following:
Fluency disorders occur when a patient has trouble with speech timing or rhythms. This can lead to hesitations, repetitions, or prolonged sounds. Fluency disorders include stuttering (repetition of sounds) or (rapid or irregular rate of speech).
Resonance disorders are related to voice quality that is impacted by the shape of the nose, throat, and/or mouth. Examples of resonance disorders include hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance.
Articulation disorders occur when a patient has difficulty producing speech sounds. These disorders may stem from physical or anatomical limitations such as muscular, neuromuscular, or skeletal support. Examples of articulation speech impairments include sound omissions, substitutions, and distortions.
Phonological disorders result in the misuse of certain speech sounds to form words. Conditions include fronting, stopping, and the omission of final consonants.
Voice disorders are the result of problems in the larynx that harm the quality or use of an individual’s voice. This can impact pitch, resonance, and loudness.
Impact of Speech Disorders
Some speech disorders have little impact on socialization and daily activities, but other conditions can make some tasks difficult for individuals. Following are a few of the impacts of speech impediments.
- Poor communication — Children may be unable to participate in certain learning activities, such as answering questions or reading out loud, due to communication difficulties. Adults may avoid work or social activities such as giving speeches or attending parties.
- Mental health and confidence — Speech disorders may cause children or adults to feel different from peers, leading to a lack of self-confidence and, potentially, self-isolation.
Resources on Speech Disorders
The following resources may help those who are seeking more information about speech impediments.
Health Information : Information and statistics on common voice and speech disorders from the NIDCD
Speech Disorders : Information on childhood speech disorders from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Speech, Language, and Swallowing : Resources about speech and language development from the ASHA
Children and adults can suffer from a variety of speech impairments that may have mild to severe impacts on their ability to communicate. The following 10 conditions are examples of specific types of speech disorders and voice disorders.
1. Stuttering
This condition is one of the most common speech disorders. Stuttering is the repetition of syllables or words, interruptions in speech, or prolonged use of a sound.
This organic speech disorder is a result of damage to the neural pathways that connect the brain to speech-producing muscles. This results in a person knowing what they want to say, but being unable to speak the words.
This consists of the lost ability to speak, understand, or write languages. It is common in stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury patients.
4. Dysarthria
This condition is an organic speech sound disorder that involves difficulty expressing certain noises. This may involve slurring, or poor pronunciation, and rhythm differences related to nerve or brain disorders.
The condition of lisping is the replacing of sounds in words, including “th” for “s.” Lisping is a functional speech impediment.
6. Hyponasality
This condition is a resonance disorder related to limited sound coming through the nose, causing a “stopped up” quality to speech.
7. Cul-de-sac resonance
This speech disorder is the result of blockage in the mouth, throat, or nose that results in quiet or muffled speech.
8. Orofacial myofunctional disorders
These conditions involve abnormal patterns of mouth and face movement. Conditions include tongue thrusting (fronting), where individuals push out their tongue while eating or talking.
9. Spasmodic Dysphonia
This condition is a voice disorder in which spasms in the vocal cords produce speech that is hoarse, strained, or jittery.
10. Other voice disorders
These conditions can include having a voice that sounds breathy, hoarse, or scratchy. Some disorders deal with vocal folds closing when they should open (paradoxical vocal fold movement) or the presence of polyps or nodules in the vocal folds.
Speech Disorders vs. Language Disorders
Speech disorders deal with difficulty in creating sounds due to articulation, fluency, phonology, and voice problems. These problems are typically related to physical, motor, sensory, neurological, or mental health issues.
Language disorders, on the other hand, occur when individuals have difficulty communicating the meaning of what they want to express. Common in children, these disorders may result in low vocabulary and difficulty saying complex sentences. Such a disorder may reflect difficulty in comprehending school lessons or adopting new words, or it may be related to a learning disability such as dyslexia. Language disorders can also involve receptive language difficulties, where individuals have trouble understanding the messages that others are trying to convey.

Resources on Types of Speech Disorders
The following resources may provide additional information on the types of speech impediments.
Common Speech Disorders: A guide to the most common speech impediments from GreatSpeech
Speech impairment in adults: Descriptions of common adult speech issues from MedlinePlus
Stuttering Facts: Information on stuttering indications and causes from the Stuttering Foundation
Speech disorders may be caused by a variety of factors related to physical features, neurological ailments, or mental health conditions. In children, they may be related to developmental issues or unknown causes and may go away naturally over time.
Physical and neurological issues. Speech impediment causes related to physical characteristics may include:
- Brain damage
- Nervous system damage
- Respiratory system damage
- Hearing difficulties
- Cancerous or noncancerous growths
- Muscle and bone problems such as dental issues or cleft palate
Mental health issues. Some speech disorders are related to clinical conditions such as:
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Down syndrome or other genetic syndromes
- Cerebral palsy or other neurological disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
Some speech impairments may also have to do with family history, such as when parents or siblings have experienced language or speech difficulties. Other causes may include premature birth, pregnancy complications, or delivery difficulties. Voice overuse and chronic coughs can also cause speech issues.
The most common way that speech disorders are treated involves seeking professional help. If patients and families feel that symptoms warrant therapy, health professionals can help determine how to fix a speech impediment. Early treatment is best to curb speech disorders, but impairments can also be treated later in life.
Professionals in the speech therapy field include speech-language pathologists (SLPs) . These practitioners assess, diagnose, and treat communication disorders including speech, language, social, cognitive, and swallowing disorders in both adults and children. They may have an SLP assistant to help with diagnostic and therapy activities.
Speech-language pathologists may also share a practice with audiologists and audiology assistants. Audiologists help identify and treat hearing, balance, and other auditory disorders.
How Are Speech Disorders Diagnosed?
Typically, a pediatrician, social worker, teacher, or other concerned party will recognize the symptoms of a speech disorder in children. These individuals, who frequently deal with speech and language conditions and are more familiar with symptoms, will recommend that parents have their child evaluated. Adults who struggle with speech problems may seek direct guidance from a physician or speech evaluation specialist.
When evaluating a patient for a potential speech impediment, a physician will:
- Conduct hearing and vision tests
- Evaluate patient records
- Observe patient symptoms
A speech-language pathologist will conduct an initial screening that might include:
- An evaluation of speech sounds in words and sentences
- An evaluation of oral motor function
- An orofacial examination
- An assessment of language comprehension
The initial screening might result in no action if speech symptoms are determined to be developmentally appropriate. If a disorder is suspected, the initial screening might result in a referral for a comprehensive speech sound assessment, comprehensive language assessment, audiology evaluation, or other medical services.
Initial assessments and more in-depth screenings might occur in a private speech therapy practice, rehabilitation center, school, childcare program, or early intervention center. For older adults, skilled nursing centers and nursing homes may assess patients for speech, hearing, and language disorders.
How Are Speech Impediments Treated?
Once an evaluation determines precisely what type of speech sound disorder is present, patients can begin treatment. Speech-language pathologists use a combination of therapy, exercise, and assistive devices to treat speech disorders.
Speech therapy might focus on motor production (articulation) or linguistic (phonological or language-based) elements of speech, according to ASHA. There are various types of speech therapy available to patients.
Contextual Utilization — This therapeutic approach teaches methods for producing sounds consistently in different syllable-based contexts, such as phonemic or phonetic contexts. These methods are helpful for patients who produce sounds inconsistently.
Phonological Contrast — This approach focuses on improving speech through emphasis of phonemic contrasts that serve to differentiate words. Examples might include minimal opposition words (pot vs. spot) or maximal oppositions (mall vs. call). These therapy methods can help patients who use phonological error patterns.
Distinctive Feature — In this category of therapy, SLPs focus on elements that are missing in speech, such as articulation or nasality. This helps patients who substitute sounds by teaching them to distinguish target sounds from substituted sounds.
Core Vocabulary — This therapeutic approach involves practicing whole words that are commonly used in a specific patient’s communications. It is effective for patients with inconsistent sound production.
Metaphon — In this type of therapy, patients are taught to identify phonological language structures. The technique focuses on contrasting sound elements, such as loud vs. quiet, and helps patients with unintelligible speech issues.
Oral-Motor — This approach uses non-speech exercises to supplement sound therapies. This helps patients gain oral-motor strength and control to improve articulation.
Other methods professionals may use to help fix speech impediments include relaxation, breathing, muscle strengthening, and voice exercises. They may also recommend assistive devices, which may include:
- Radio transmission systems
- Personal amplifiers
- Picture boards
- Touch screens
- Text displays
- Speech-generating devices
- Hearing aids
- Cochlear implants
Resources for Professionals on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide information for speech therapists and other health professionals.
Assistive Devices: Information on hearing and speech aids from the NIDCD
Information for Audiologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for audiologists from ASHA
Information for Speech-Language Pathologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for SLPs from ASHA
Speech Disorder Tips for Families
For parents who are concerned that their child might have a speech disorder — or who want to prevent the development of a disorder — there are a number of activities that can help. The following are tasks that parents can engage in on a regular basis to develop literacy and speech skills.
- Introducing new vocabulary words
- Reading picture and story books with various sounds and patterns
- Talking to children about objects and events
- Answering children’s questions during routine activities
- Encouraging drawing and scribbling
- Pointing to words while reading books
- Pointing out words and sentences in objects and signs
Parents can take the following steps to make sure that potential speech impediments are identified early on.
- Discussing concerns with physicians
- Asking for hearing, vision, and speech screenings from doctors
- Requesting special education assessments from school officials
- Requesting a referral to a speech-language pathologist, audiologist, or other specialist
When a child is engaged in speech therapy, speech-language pathologists will typically establish collaborative relationships with families, sharing information and encouraging parents to participate in therapy decisions and practices.
SLPs will work with patients and their families to set goals for therapy outcomes. In addition to therapy sessions, they may develop activities and exercises for families to work on at home. It is important that caregivers are encouraging and patient with children during therapy.
Resources for Parents on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide additional information on treatment options for speech disorders.
Speech, Language, and Swallowing Disorders Groups: Listing of self-help groups from ASHA
ProFind: Search tool for finding certified SLPs and audiologists from ASHA
Baby’s Hearing and Communication Development Checklist: Listing of milestones that children should meet by certain ages from the NIDCD
If identified during childhood, speech disorders can be corrected efficiently, giving children greater communication opportunities. If left untreated, speech impediments can cause a variety of problems in adulthood, and may be more difficult to diagnose and treat.
Parents, teachers, doctors, speech and language professionals, and other concerned parties all have unique responsibilities in recognizing and treating speech disorders. Through professional therapy, family engagement, positive encouragement and a strong support network, individuals with speech impediments can overcome their challenges and develop essential communication skills.
Additional Sources
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Speech Sound Disorders
Identify the Signs, Signs of Speech and Language Disorders
Intermountain Healthcare, Phonological Disorders
MedlinePlus, Speech disorders – children
National Institutes of Health, National Institutes on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, “Quick Statistics About Voice, Speech, Language”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Types of Speech Impediments
Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SanjanaGupta-d217a6bfa3094955b3361e021f77fcca.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
Phynart Studio / Getty Images
Articulation Errors
Ankyloglossia, treating speech disorders.
A speech impediment, also known as a speech disorder , is a condition that can affect a person’s ability to form sounds and words, making their speech difficult to understand.
Speech disorders generally become evident in early childhood, as children start speaking and learning language. While many children initially have trouble with certain sounds and words, most are able to speak easily by the time they are five years old. However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders.
There are many different types of speech impediments, including:
- Articulation errors
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different types of speech disorders.
Speech impediments that break the flow of speech are known as disfluencies. Stuttering is the most common form of disfluency, however there are other types as well.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Disfluencies
These are some of the characteristics of disfluencies:
- Repeating certain phrases, words, or sounds after the age of 4 (For example: “O…orange,” “I like…like orange juice,” “I want…I want orange juice”)
- Adding in extra sounds or words into sentences (For example: “We…uh…went to buy…um…orange juice”)
- Elongating words (For example: Saying “orange joooose” instead of "orange juice")
- Replacing words (For example: “What…Where is the orange juice?”)
- Hesitating while speaking (For example: A long pause while thinking)
- Pausing mid-speech (For example: Stopping abruptly mid-speech, due to lack of airflow, causing no sounds to come out, leading to a tense pause)
In addition, someone with disfluencies may also experience the following symptoms while speaking:
- Vocal tension and strain
- Head jerking
- Eye blinking
- Lip trembling
Causes of Disfluencies
People with disfluencies tend to have neurological differences in areas of the brain that control language processing and coordinate speech, which may be caused by:
- Genetic factors
- Trauma or infection to the brain
- Environmental stressors that cause anxiety or emotional distress
- Neurodevelopmental conditions like attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Articulation disorders occur when a person has trouble placing their tongue in the correct position to form certain speech sounds. Lisping is the most common type of articulation disorder.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Articulation Errors
These are some of the characteristics of articulation disorders:
- Substituting one sound for another . People typically have trouble with ‘r’ and ‘l’ sounds. (For example: Being unable to say “rabbit” and saying “wabbit” instead)
- Lisping , which refers specifically to difficulty with ‘s’ and ‘z’ sounds. (For example: Saying “thugar” instead of “sugar” or producing a whistling sound while trying to pronounce these letters)
- Omitting sounds (For example: Saying “coo” instead of “school”)
- Adding sounds (For example: Saying “pinanio” instead of “piano”)
- Making other speech errors that can make it difficult to decipher what the person is saying. For instance, only family members may be able to understand what they’re trying to say.
Causes of Articulation Errors
Articulation errors may be caused by:
- Genetic factors, as it can run in families
- Hearing loss , as mishearing sounds can affect the person’s ability to reproduce the sound
- Changes in the bones or muscles that are needed for speech, including a cleft palate (a hole in the roof of the mouth) and tooth problems
- Damage to the nerves or parts of the brain that coordinate speech, caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy , for instance
Ankyloglossia, also known as tongue-tie, is a condition where the person’s tongue is attached to the bottom of their mouth. This can restrict the tongue’s movement and make it hard for the person to move their tongue.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is characterized by difficulty pronouncing ‘d,’ ‘n,’ ‘s,’ ‘t,’ ‘th,’ and ‘z’ sounds that require the person’s tongue to touch the roof of their mouth or their upper teeth, as their tongue may not be able to reach there.
Apart from speech impediments, people with ankyloglossia may also experience other symptoms as a result of their tongue-tie. These symptoms include:
- Difficulty breastfeeding in newborns
- Trouble swallowing
- Limited ability to move the tongue from side to side or stick it out
- Difficulty with activities like playing wind instruments, licking ice cream, or kissing
- Mouth breathing
Causes of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is a congenital condition, which means it is present from birth. A tissue known as the lingual frenulum attaches the tongue to the base of the mouth. People with ankyloglossia have a shorter lingual frenulum, or it is attached further along their tongue than most people’s.
Dysarthria is a condition where people slur their words because they cannot control the muscles that are required for speech, due to brain, nerve, or organ damage.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is characterized by:
- Slurred, choppy, or robotic speech
- Rapid, slow, or soft speech
- Breathy, hoarse, or nasal voice
Additionally, someone with dysarthria may also have other symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and inability to move their tongue, lips, or jaw easily.
Causes of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is caused by paralysis or weakness of the speech muscles. The causes of the weakness can vary depending on the type of dysarthria the person has:
- Central dysarthria is caused by brain damage. It may be the result of neuromuscular diseases, such as cerebral palsy, Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or Lou Gehrig’s disease. Central dysarthria may also be caused by injuries or illnesses that damage the brain, such as dementia, stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury .
- Peripheral dysarthria is caused by damage to the organs involved in speech. It may be caused by congenital structural problems, trauma to the mouth or face, or surgery to the tongue, mouth, head, neck, or voice box.
Apraxia, also known as dyspraxia, verbal apraxia, or apraxia of speech, is a neurological condition that can cause a person to have trouble moving the muscles they need to create sounds or words. The person’s brain knows what they want to say, but is unable to plan and sequence the words accordingly.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Apraxia
These are some of the characteristics of apraxia:
- Distorting sounds: The person may have trouble pronouncing certain sounds, particularly vowels, because they may be unable to move their tongue or jaw in the manner required to produce the right sound. Longer or more complex words may be especially harder to manage.
- Being inconsistent in their speech: For instance, the person may be able to pronounce a word correctly once, but may not be able to repeat it. Or, they may pronounce it correctly today and differently on another day.
- Grasping for words: The person may appear to be searching for the right word or sound, or attempt the pronunciation several times before getting it right.
- Making errors with the rhythm or tone of speech: The person may struggle with using tone and inflection to communicate meaning. For instance, they may not stress any of the words in a sentence, have trouble going from one syllable in a word to another, or pause at an inappropriate part of a sentence.
Causes of Apraxia
Apraxia occurs when nerve pathways in the brain are interrupted, which can make it difficult for the brain to send messages to the organs involved in speaking. The causes of these neurological disturbances can vary depending on the type of apraxia the person has:
- Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS): This condition is present from birth and is often hereditary. A person may be more likely to have it if a biological relative has a learning disability or communication disorder.
- Acquired apraxia of speech (AOS): This condition can occur in adults, due to brain damage as a result of a tumor, head injury , stroke, or other illness that affects the parts of the brain involved in speech.
If you have a speech impediment, or suspect your child might have one, it can be helpful to visit your healthcare provider. Your primary care physician can refer you to a speech-language pathologist, who can evaluate speech, diagnose speech disorders, and recommend treatment options.
The diagnostic process may involve a physical examination as well as psychological, neurological, or hearing tests, in order to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes.
Treatment for speech disorders often involves speech therapy, which can help you learn how to move your muscles and position your tongue correctly in order to create specific sounds. It can be quite effective in improving your speech.
Children often grow out of milder speech disorders; however, special education and speech therapy can help with more serious ones.
For ankyloglossia, or tongue-tie, a minor surgery known as a frenectomy can help detach the tongue from the bottom of the mouth.
A Word From Verywell
A speech impediment can make it difficult to pronounce certain sounds, speak clearly, or communicate fluently.
Living with a speech disorder can be frustrating because people may cut you off while you’re speaking, try to finish your sentences, or treat you differently. It can be helpful to talk to your healthcare providers about how to cope with these situations.
You may also benefit from joining a support group, where you can connect with others living with speech disorders.
National Library of Medicine. Speech disorders . Medline Plus.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders .
Cincinnati Children's Hospital. Stuttering .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, and language .
Cleveland Clinic. Speech impediment .
Lee H, Sim H, Lee E, Choi D. Disfluency characteristics of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms . J Commun Disord . 2017;65:54-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2016.12.001
Nemours Foundation. Speech problems .
Penn Medicine. Speech and language disorders .
Cleveland Clinic. Tongue-tie .
University of Rochester Medical Center. Ankyloglossia .
Cleveland Clinic. Dysarthria .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Apraxia of speech .
Cleveland Clinic. Childhood apraxia of speech .
Stanford Children’s Hospital. Speech sound disorders in children .
Abbastabar H, Alizadeh A, Darparesh M, Mohseni S, Roozbeh N. Spatial distribution and the prevalence of speech disorders in the provinces of Iran . J Med Life . 2015;8(Spec Iss 2):99-104.
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

On this page:
What is stuttering?
Who stutters, how is speech normally produced, what are the causes and types of stuttering, how is stuttering diagnosed, how is stuttering treated, what research is being conducted on stuttering, where can i find additional information about stuttering.
Stuttering is a speech disorder characterized by repetition of sounds, syllables, or words; prolongation of sounds; and interruptions in speech known as blocks. An individual who stutters exactly knows what he or she would like to say but has trouble producing a normal flow of speech. These speech disruptions may be accompanied by struggle behaviors, such as rapid eye blinks or tremors of the lips. Stuttering can make it difficult to communicate with other people, which often affects a person’s quality of life and interpersonal relationships. Stuttering can also negatively influence job performance and opportunities, and treatment can come at a high financial cost.
Symptoms of stuttering can vary significantly throughout a person’s day. In general, speaking before a group or talking on the telephone may make a person’s stuttering more severe, while singing, reading, or speaking in unison may temporarily reduce stuttering.
Stuttering is sometimes referred to as stammering and by a broader term, disfluent speech .
Roughly 3 million Americans stutter. Stuttering affects people of all ages. It occurs most often in children between the ages of 2 and 6 as they are developing their language skills. Approximately 5 to 10 percent of all children will stutter for some period in their life, lasting from a few weeks to several years. Boys are 2 to 3 times as likely to stutter as girls and as they get older this gender difference increases; the number of boys who continue to stutter is three to four times larger than the number of girls. Most children outgrow stuttering. Approximately 75 percent of children recover from stuttering. For the remaining 25 percent who continue to stutter, stuttering can persist as a lifelong communication disorder.
We make speech sounds through a series of precisely coordinated muscle movements involving breathing, phonation (voice production), and articulation (movement of the throat, palate, tongue, and lips). Muscle movements are controlled by the brain and monitored through our senses of hearing and touch.
The precise mechanisms that cause stuttering are not understood. Stuttering is commonly grouped into two types termed developmental and neurogenic.
Developmental stuttering
Developmental stuttering occurs in young children while they are still learning speech and language skills. It is the most common form of stuttering. Some scientists and clinicians believe that developmental stuttering occurs when children’s speech and language abilities are unable to meet the child’s verbal demands. Most scientists and clinicians believe that developmental stuttering stems from complex interactions of multiple factors. Recent brain imaging studies have shown consistent differences in those who stutter compared to nonstuttering peers. Developmental stuttering may also run in families and research has shown that genetic factors contribute to this type of stuttering. Starting in 2010, researchers at the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) have identified four different genes in which mutations are associated with stuttering. More information on the genetics of stuttering can be found in the research section of this fact sheet.
Neurogenic stuttering
Neurogenic stuttering may occur after a stroke, head trauma, or other type of brain injury. With neurogenic stuttering, the brain has difficulty coordinating the different brain regions involved in speaking, resulting in problems in production of clear, fluent speech.
At one time, all stuttering was believed to be psychogenic, caused by emotional trauma, but today we know that psychogenic stuttering is rare.
Stuttering is usually diagnosed by a speech-language pathologist, a health professional who is trained to test and treat individuals with voice, speech, and language disorders. The speech-language pathologist will consider a variety of factors, including the child’s case history (such as when the stuttering was first noticed and under what circumstances), an analysis of the child’s stuttering behaviors, and an evaluation of the child’s speech and language abilities and the impact of stuttering on his or her life.
When evaluating a young child for stuttering, a speech-language pathologist will try to determine if the child is likely to continue his or her stuttering behavior or outgrow it. To determine this difference, the speech-language pathologist will consider such factors as the family’s history of stuttering, whether the child’s stuttering has lasted 6 months or longer, and whether the child exhibits other speech or language problems.
Although there is currently no cure for stuttering, there are a variety of treatments available. The nature of the treatment will differ, based upon a person’s age, communication goals, and other factors. If you or your child stutters, it is important to work with a speech-language pathologist to determine the best treatment options.
Therapy for children
For very young children, early treatment may prevent developmental stuttering from becoming a lifelong problem. Certain strategies can help children learn to improve their speech fluency while developing positive attitudes toward communication. Health professionals generally recommend that a child be evaluated if he or she has stuttered for 3 to 6 months, exhibits struggle behaviors associated with stuttering, or has a family history of stuttering or related communication disorders. Some researchers recommend that a child be evaluated every 3 months to determine if the stuttering is increasing or decreasing. Treatment often involves teaching parents about ways to support their child’s production of fluent speech. Parents may be encouraged to:
- Provide a relaxed home environment that allows many opportunities for the child to speak. This includes setting aside time to talk to one another, especially when the child is excited and has a lot to say.
- Listen attentively when the child speaks and focus on the content of the message, rather than responding to how it is said or interruptng the child.
- Speak in a slightly slowed and relaxed manner. This can help reduce time pressures the child may be experiencing.
- Listen attentively when the child speaks and wait for him or her to say the intended word. Don't try to complete the child’s sentences. Also, help the child learn that a person can communicate successfully even when stuttering occurs.
- Talk openly and honestly to the child about stuttering if he or she brings up the subject. Let the child know that it is okay for some disruptions to occur.
Stuttering therapy
Many of the current therapies for teens and adults who stutter focus on helping them learn ways to minimize stuttering when they speak, such as by speaking more slowly, regulating their breathing, or gradually progressing from single-syllable responses to longer words and more complex sentences. Most of these therapies also help address the anxiety a person who stutters may feel in certain speaking situations.
Drug therapy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not approved any drug for the treatment of stuttering. However, some drugs that are approved to treat other health problems—such as epilepsy, anxiety, or depression—have been used to treat stuttering. These drugs often have side effects that make them difficult to use over a long period of time.
Electronic devices
Some people who stutter use electronic devices to help control fluency. For example, one type of device fits into the ear canal, much like a hearing aid, and digitally replays a slightly altered version of the wearer’s voice into the ear so that it sounds as if he or she is speaking in unison with another person. In some people, electronic devices may help improve fluency in a relatively short period of time. Additional research is needed to determine how long such effects may last and whether people are able to easily use and benefit from these devices in real-world situations. For these reasons, researchers are continuing to study the long-term effectiveness of these devices.
Self-help groups
Many people find that they achieve their greatest success through a combination of self-study and therapy. Self-help groups provide a way for people who stutter to find resources and support as they face the challenges of stuttering.
Researchers around the world are exploring ways to improve the early identification and treatment of stuttering and to identify its causes. For example, scientists have been working to identify the possible genes responsible for stuttering that tend to run in families. NIDCD scientists have now identified variants in four such genes that account for some cases of stuttering in many populations around the world, including the United States and Europe. All of these genes encode proteins that direct traffic within cells, ensuring that various cell components get to their proper location within the cell. Such deficits in cellular trafficking are a newly recognized cause of many neurological disorders. Researchers are now studying how this defect in cellular trafficking leads to specific deficits in speech fluency.
Researchers are also working to help speech-language pathologists determine which children are most likely to outgrow their stuttering and which children are at risk for continuing to stutter into adulthood. In addition, researchers are examining ways to identify groups of individuals who exhibit similar stuttering patterns and behaviors that may be associated with a common cause.
Scientists are using brain imaging tools such as PET (positron emission tomography) and functional MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans to investigate brain activity in people who stutter. NIDCD-funded researchers are also using brain imaging to examine brain structure and functional changes that occur during childhood that differentiate children who continue to stutter from those who recover from stuttering. Brain imaging may be used in the future as a way to help treat people who stutter. Researchers are studying whether volunteer patients who stutter can learn to recognize, with the help of a computer program, specific speech patterns that are linked to stuttering and to avoid using those patterns when speaking.
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, taste, smell, voice, speech, and language.
Use the following keywords to help you find organizations that can answer questions and provide information on stuttering:
- Speech-language pathologists
- Physician/practitioner referrals
For more information, contact us at:
NIDCD Information Clearinghouse 1 Communication Avenue Bethesda, MD 20892-3456 Toll-free voice: (800) 241-1044 Toll-free TTY: (800) 241-1055 Email: [email protected]
NIH Pub. No. 97-4232 February 2016
* Note: PDF files require a viewer such as the free Adobe Reader .
- Patient Care & Health Information
- Diseases & Conditions
Stuttering is a speech condition that disrupts the normal flow of speech. Fluency means having an easy and smooth flow and rhythm when speaking. With stuttering, the interruptions in flow happen often and cause problems for the speaker. Other names for stuttering are stammering and childhood-onset fluency disorder.
People who stutter know what they want to say, but they have a hard time saying it. For example, they may repeat or stretch out a word, a syllable, or a consonant or vowel sound. Or they may pause during speech because they've reached a word or sound that's hard to get out.
Stuttering is common among young children as a usual part of learning to speak. Some young children may stutter when their speech and language abilities aren't developed enough to keep up with what they want to say. Most children outgrow this type of stuttering, called developmental stuttering.
But sometimes stuttering is a long-term condition that remains into adulthood. This type of stuttering can affect self-esteem and communicating with other people.
Children and adults who stutter may be helped by treatments such as speech therapy, electronic devices to improve speech fluency or a form of mental health therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy.
Products & Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Stuttering symptoms may include:
- Having a hard time starting a word, phrase or sentence.
- Stretching out a word or sounds within a word.
- Repeating a sound, syllable or word.
- Brief silence for certain syllables or words, or pausing before or within a word.
- Adding extra words such as "um" if expecting to have problems moving to the next word.
- A lot of tension, tightness or movement of the face or upper body when saying a word.
- Anxiety about talking.
- Not being able to communicate well with others.
These actions may happen when stuttering:
- Rapid eye blinks.
- Trembling of the lips or jaw.
- Unusual face movements, sometimes called facial tics.
- Head nodding.
- Tightening of fists.
Stuttering may be worse when the person is excited, tired or under stress, or when feeling self-conscious, hurried or pressured. Situations such as speaking in front of a group or talking on the phone can be especially hard for people who stutter.
But most people who stutter can speak without stuttering when they talk to themselves and when they sing or speak along with someone else.
When to see a doctor or speech-language pathologist
It's common for children between the ages of 2 and 5 years to go through periods when they may stutter. For most children, this is part of learning to speak, and it gets better on its own. But stuttering that continues may need treatment to improve speech fluency.
Call your healthcare professional for a referral to a specialist in speech and language called a speech-language pathologist. Or you can contact the speech-language pathologist directly for an appointment. Ask for help if stuttering:
- Lasts more than six months.
- Happens along with other speech or language problems.
- Happens more often or continues as the child grows older.
- Includes muscle tightening or physically struggling when trying to speak.
- Affects the ability to effectively communicate at school or work or in social situations.
- Causes anxiety or emotional problems, such as fear of or not taking part in situations that require speaking.
- Begins as an adult.
Researchers continue to study the underlying causes of developmental stuttering. A combination of factors may be involved.
Developmental stuttering
Stuttering that happens in children while they're learning to speak is called developmental stuttering. Possible causes of developmental stuttering include:
- Problems with speech motor control. Some evidence shows that problems in speech motor control, such as timing, sensory and motor coordination, may be involved.
- Genetics. Stuttering tends to run in families. It appears that stuttering can happen from changes in genes passed down from parents to children.
Stuttering that happens from other causes
Speech fluency can be disrupted from causes other than developmental stuttering.
- Neurogenic stuttering. A stroke, traumatic brain injury or other brain disorders can cause speech that is slow or has pauses or repeated sounds.
- Emotional distress. Speech fluency can be disrupted during times of emotional distress. Speakers who usually do not stutter may experience problems with fluency when they are nervous or feel pressured. These situations also may cause speakers who stutter to have greater problems with fluency.
- Psychogenic stuttering. Speech difficulties that appear after an emotional trauma are uncommon and not the same as developmental stuttering.
Risk factors
Males are much more likely to stutter than females are. Things that raise the risk of stuttering include:
- Having a childhood developmental condition. Children who have developmental conditions, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, autism or developmental delays, may be more likely to stutter. This is true for children with other speech problems too.
- Having relatives who stutter. Stuttering tends to run in families.
- Stress. Stress in the family and other types of stress or pressure can worsen existing stuttering.
Complications
Stuttering can lead to:
- Problems communicating with others.
- Not speaking or staying away from situations that require speaking.
- Not taking part in social, school or work activities and opportunities for success.
- Being bullied or teased.
- Low self-esteem.
- Stuttering. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. https://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/stuttering/. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- Fluency disorders. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. https://www.asha.org/practice-portal/clinical-topics/fluency-disorders/. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- Childhood-onset fluency disorder (stuttering). In: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5-TR. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2022. https://dsm.psychiatryonline.org. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- Stuttering. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/stuttering. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- Sander RW, et al. Stuttering: Understanding and treating a common disability. American Family Physician. 2019;100:556.
- Laiho A, et al. Stuttering interventions for children, adolescents and adults: A systematic review as part of the clinical guidelines. Journal of Communication Disorders. 2022; doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2022.106242.
- 6 tips for speaking with someone who stutters. The Stuttering Foundation. https://www.stutteringhelp.org/6-tips-speaking-someone-who-stutters-0. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- 7 tips for talking with your child. The Stuttering Foundation. https://www.stutteringhelp.org/7-tips-talking-your-child-0. Accessed Feb. 2, 2024.
- Clark HM (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. Feb. 11, 2024.
Associated Procedures
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Symptoms & causes
- Diagnosis & treatment
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.

- Speech Pathology Master’s Programs: Which is Right for You?
- What Can You Do with a Bachelor’s in Speech Pathology?
- Speech Pathology Doctoral Programs
- Online Masters in Speech Pathology at Emerson College (sponsored program)
- Online Masters in Speech Pathology at New York University (sponsored program)
- How to Become a Speech Pathologist: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Guide to Applying to Speech Pathology School
- How to Make a Career Change to Speech Pathology
- Is a Speech Pathology Degree Worth It?
- 10 Reasons to Love Being a Speech Pathologist
- What Is a CCC-SLP and Why It’s Important
- CCC-SLP Requirements: Become a CCC-SLP
- Guide to Applying for CCC-SLP Certification
- CCC-SLP Salary and Career Outlook
- The Guide to the ASHA Speech Pathology Certification Standards
- State-by-State Guide for Speech Pathology License Requirements
- 8 SLP Certifications that May Help Advance Your Career
- How to Become an Effective ASHA Clinical Fellowship Mentor
- How to Complete the ASHA Clinical Fellowship
- The Guide to Speech Pathology Job and Salary Negotiations
- What to Expect at Your First Speech Pathologist Job
- Bilingual Speech Pathologist Salary and Careers
- Child Speech Therapist Career and Salary Outlook
- Speech Pathology Assistant Careers and Salary Outlook
- How to Choose Your Speech Pathologist Career Setting
- Become a Speech Pathologist in a School Setting
- Become a Speech Pathologist in a Hospital Work Setting
- Opening a Speech Therapy Telepractice: What You Need to Know
- Speech Pathology Internships Guide
- Guide to Speech Therapy Volunteer Opportunities
- Choosing Between Speech Pathology or Occupational Therapy
- How to Become an Audiologist
- Scholarships
- Day in the Life of an SLP Student
- Speech Disorder Resources for College Students
- Common Speech Language Pathology Assessment Tools
- The SLP Guide to Evidence-Based Practice
- When to Take Your Bilingual Child to the Speech Pathologist
- When to Take Your Child to the SLP
Home / Resources
What are the Most Common Speech Disorders?
July 24, 2020
Speech disorders impact millions of people and their ability to communicate. The National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders estimates that 5% of children in the U.S. ages 3 to 17 have had a speech disorder in the past 12 months. Some speech disorders can be overcome, while others are lifelong conditions. In either case, therapy with a speech pathologist can help a person make the most of their speech capabilities and develop alternative methods of communication.
Speech pathologists or speech therapists complete a master’s program to be able to evaluate a person’s speech and communication, create a treatment plan and provide treatment to improve a person’s speech and other communication methods. Some speech pathologists’ careers deal with research and development treatment guidelines for various speech and language disorders.
What Is a Speech Disorder?
Speech is how people make sounds and words , according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). Speech problems can include the inability to make sounds clearly, having a raspy voice or stuttering (repeating sounds or pauses when speaking).
Language is not the same thing as speech; it is the words we use to share ideas. Problems with language can include difficulty understanding, talking, reading or writing.
According to ASHA, a speech disorder is an impairment of the articulation of sounds, fluency or voice. It is one of many types of communication disorders, which also include language and hearing disorders.
Types of Speech Disorders
There are three categories of speech disorders :
- Articulation disorders : An unusual production of speech sounds involving substitutions, omissions, additions or distortions that might interfere with whether the sounds are intelligible to others.
- Fluency disorders : Interruptions in the flow of a person’s speech, such as an uncommon rate, rhythm, or repetition of sounds, syllables, words or phrases.
- Voice disorders : An abnormal production or absence of vocal quality, pitch, volume, resonance or duration that’s inappropriate for the person’s age and sex.
Speech Disorder Causes
The medical community doesn’t know the cause of all speech disorders and, for many, the cause can vary. Potential causes for speech disorders include:
- Brain damage : Some speech and other communication disorders are due to a congenital condition. A child or adult who suffers a traumatic brain injury might sustain damage to a portion of the brain that impacts speech. Also, diseases and conditions such as stroke, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, Huntington’s disease, MS, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, cancer and benign brain tumors can impact speech.
- Nervous system condition : A disorder that affects a person’s nervous system can affect the muscles in their mouth, jaw, lips, or tongue or their vocal folds (voice box).
- Nerve damage : Nerve damage in the voice box can impact the vocal folds and cause voice disorders, which are a type of speech disorder.
- Stress : In some cases, it’s believed that stress can trigger certain speech disorders.
10 Common Speech Disorders
1. childhood apraxia of speech.
To talk, messages from the brain tell the muscles around the mouth and throat to move. In childhood apraxia, the messages don’t get through to the muscles correctly, according to ASHA. The child’s muscles aren’t weak, but they can’t move their mouth or tongue the right way to make the necessary sounds. The severity of this condition can vary. In more severe cases, a child might not be able to talk much.
Childhood apraxia is not a developmental issue that a child can grow out of. With the help of a speech therapist, a child’s speech can improve. But ultimately, the way the child learns to make speech sounds won’t be typical of other children.
2. Adult Apraxia
Apraxia of speech in adults is also called acquired apraxia of speech, verbal apraxia and dyspraxia. Adults suffer from verbal apraxia because of brain damage, such as a stroke, oxygen deprivation or a traumatic brain injury.
Acquired apraxia in adults can affect their speech in various ways. A person might make a new sound, leave out sounds or say something the wrong way. They might not be able to make a sound the right way consistently. A person might have a hard time controlling their mouth, lips and tongue to make the right sounds. They might have to talk slowly. In severe cases, an adult might not be able to talk at all.
3. Dysarthria
Dysarthria is the result of muscle weakness due to brain damage. The severity of the condition can vary, and it can be accompanied by other conditions, like speech apraxia. People with dysarthria might slur their words, speak slowly or too fast, talk softly, sound robotic and not be able to move their mouth or tongue well. Some people’s voices sound different than before their injury.
4. Orofacial Myofunctional Disorders
People of any age can have an orofacial myofunctional disorder (OMD). An OMD might interfere with the development of the bones and muscles in a person’s face and mouth. This can impact a person’s ability to breathe, swallow, eat and talk. Various issues can cause an OMD, including anything that causes a person to rest their tongue in the right place or keep their lips together when at rest.
One type of OMC is called tongue thrusting, which involves children pushing their tongue out when they try to talk, drink or eat.
5. Speech Sound Disorders
A child who can’t correctly make speech sounds by 4 years old might have a speech sound disorder, also known as a phonological disorder or articulation disorder. Speech sound disorders are not only in children, though. Adults might have suffered from a disorder since childhood or acquired this disorder after sustaining brain damage.
With a speech sound disorder, a person might make one sound in place of another, add sounds, change a sound or leave a sound out. The changes can be severe enough to make it hard for others to understand them. It’s important to note that people with accents will do some of these things, like replace one sound with another. An accent or dialect is not a speech sound disorder.

6. Stuttering
A person who stutters might repeat whole words or sounds, stretch out sounds or have a hard time saying certain words. These are known as repetitions, prolongations and blocks, respectively. While everyone might stutter once in a while, stuttering becomes a speech disorder when it gets in the way of a person’s ability to communicate with others and is accompanied by negative feelings about talking.
There’s no specific cause for stuttering. It might be the result of differences in children’s brains. In many cases, there’s a family history of stuttering. Most children start to stutter between the ages of 2 and 6 years. If the stuttering lasts for more than 6 months, then treatment with a speech pathologist might be necessary.
7. Voice Disorders
Several conditions impact a person’s voice, and therefore, their ability to talk. These include:
Chronic cough : A cough that lasts more than four weeks in children and eight weeks in adults is considered chronic. It can alter the sound of a person’s voice or their ability to talk.
Paradoxical vocal fold movement : PVFM is when a person’s vocal folds (inside the voice box) close partly or all the way when they should open. This can cause breathing difficulties, change a person’s voice, or cause someone to lose their voice. PVFM can be triggered by acid reflux, stress, smoke, pollen, other allergens, exercise or breathing cold air, though no one knows the underlying cause.
Spasmodic dysphonia : With this long-term condition, a person’s vocal folds don’t move properly. A person with this disorder might not be able to speak all the time, though, at other times, their voice might sound normal. Their vocal folds might spasm or tighten when they talk, which can make them sound jerky or hoarse. A brain or nervous system disorder can cause this condition.
Vocal fold nodules and polyps : Growths on a person’s vocal folds can change their voice and cause discomfort and pain. This condition is usually caused by vocal abuse — typically long-term overuse or abuse.
Vocal fold paralysis : Vocal fold paralysis happens when one or both of your vocal folds can’t move. If they can’t come together, separate and vibrate, then a person doesn’t have a voice. It also causes issues with breathing and swallowing. When one fold is paralyzed, a person’s voice might be quiet. They might be limited in their pitch and tone and sound breathy. When two folds are paralyzed, the person might need a tracheotomy.
Aphasia is technically a language disorder caused by brain damage to the left side of the brain. People with aphasia might have a hard time understanding other people, speaking, reading or writing. For example, a person with aphasia might hear another person and understand them, but then have a difficult time responding with the correct speech sounds. Aphasia can cause people to not remember the right word, say the wrong word, make up words, have a hard time speaking in full sentences or have a hard time speaking coherent sentences.
9. Selective Mutism
Selective mutism is a childhood language disorder, often associated with a child being extremely shy, afraid of embarrassment, traumatized, wanting to be alone or having an anxiety disorder. A child might refuse to talk in certain situations, say in public or at school.
10. Childhood Speech Delays
A child who is significantly delayed in developing their language and speech skills might have a language disorder. These are called preschool language disorders. Delayed speech is also called alalia. Some children have a hard time with receptive language, which helps them follow directions, understand gestures and answer questions. Others have difficulties with expressive language, like asking questions, naming objects or putting words together for a sentence. Some children have trouble with both.
Speech Disorder Treatments
Many speech disorders cannot be cured, but by receiving speech and language therapy with a licensed speech pathologist, many children and adults can improve their speech or adapt to alternative communication methods.
Speech therapists can help individuals learn the correct way to make a sound, including when and how to move their mouth and tongue, practice saying certain sounds, learn to tell when a sound is correct or wrong and practice using sounds in longer sentences. Speech pathologists can give children and adults exercises to improve their speech. Additionally, depending on the type of speech disorder, other medical or mental health care might be necessary.
Speech disorders impact children and adults from all walks of life. But these disorders don’t have to stand in the way of their communication, education and careers. Licensed speech pathologists can help individuals improve their speaking, and when helpful, learn to use augmentative and alternative communication methods.
Information last updated June 2020
Sponsored online speech pathology programs

Online MS: Pursue SLP Certification. Study FT/PT
Speech@Emerson enables you to earn an MS online and pursue SLP certification in as few as 20 mos. Learn the same curriculum as the on-campus program. Study FT or PT.
- Prepares you to pursue certification as an SLP generalist
- In-person clinical placements at faculty-approved partner sites
- As few as 20 months to complete
info SPONSORED

Want to Become an SLP? Earn an MS Online at NYU
NYU Steinhardt’s online master of science program in Communicative Sciences and Disorders prepares aspiring speech-language pathologists with a comprehensive professional education.
- Prepares students to pursue SLP licensure
- Accredited by ASHA’s Council on Academic Accreditation
- As few as six terms to complete
- Full-time and part-time plans of study
Skip to content
Childhood Apraxia of Speech
Center for childhood communication, what is childhood apraxia of speech.
Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) is a speech disorder where your child's mouth cannot make the quick movements needed to speak, even after their brain tells their mouth what to do. There is usually no muscle weakness. If your child has CAS, it may be difficult for them to plan and complete the quick mouth movements needed to make sounds into syllables, words and sentences (motor planning). CAS is also sometimes called verbal apraxia, developmental apraxia of speech or verbal dyspraxia.
Causes of childhood apraxia of speech
In most cases the cause of CAS is unknown. Here at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), we are always working to find out more about why this condition occurs in some children. We know it is a rare disorder. It only affects about 3 to 5% of all preschoolers with diagnosed speech disorders. It is more common for children to have other developmental speech disorders. CAS is sometimes seen with other conditions like genetic, neurological or developmental disorders. But sometimes there are no other conditions present.
Symptoms of childhood apraxia of speech
The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association lists three features as the most common you may notice if your child has CAS:
- Your child says the same word differently each time they say it.
- Your child has difficulty starting or transitioning between sounds or words, making their speech sound disconnected or “choppy”.
- Your child finds the timing, rhythm and flow of speech challenging.
A child with CAS is often hard to understand. In addition to the three symptoms above, your child may:
- Produce vowel sound errors
- Have a slow rate of speech
- Have stress or voicing errors
- Have a tough time starting oral movements to say something
- Have multiple sound errors that do not follow the patterns expected in young children
- Use a limited variety of consonant and vowel sounds
- Have difficulty with longer words
- Use extra mouth movements when trying to make speech sounds
- Say a word or words with an additional sound
- Say a word once perfectly but not be able to say it again
- Say automatic words (like “hi” and “thank you”) more easily than less routine words
- Switch sounds in words or add sounds or syllables to words
- Have differences in the quality of the voice that come from sound vibrations in the throat, mouth and nose (resonance or nasality differences)
- Have a history of late development of first words and sounds
Testing and diagnosis for childhood apraxia of speech
Here at CHOP, we have a dedicated team of licensed speech-language pathologists (SLP) who can diagnose whether your child has CAS. Your child may be referred to our SLPs for evaluation by their pediatrician, neurologist or developmental pediatrician. Our SLP will first do a speech and language evaluation.
During the speech and language evaluation, our SLP will review your child’s birth, medical and developmental histories. They will evaluate your child’s ability to:
- Understand and use language
- Communicate using speech, sign language and/or gestures
- Produce consonant and vowel sounds, syllables, words and phrases
- Speak with appropriate timing, rhythm and flow of speech
- Move parts of their mouth, including tongue, lips and jaw
- Play and interact with others
Our SLP will look for signs of CAS by asking your child to say certain sounds, words and phrases. It is harder to diagnose CAS in very young children and children with limited language skills. Our SLP may not be able to diagnose or rule out CAS on the first visit. They may recommend therapy, teach you language-building activities to do with your child at home, or ask you to come back in a few months to check your child’s progress.
Treatment for childhood apraxia of speech
Our SLP will create goals to support your child’s ability to be understood by others. The therapy approach will depend on your child’s specific needs. Goals may include learning how to say speech sounds, syllables, words and phrases.
If your child has a limited number of words in their vocabulary, therapy will start with improving their functional communication skills. This may include having your child practice with word approximations, picture communication systems, and speech-generating devices. To reduce frustration, some children with CAS may use one of these methods to express themselves while their speech develops. As your child’s speech improves, these systems may no longer be needed.
Speech-language therapy sessions will involve you, your child, their other caregiver(s) and our SLP. Sessions may be play-based or structured with tabletop activities. This will depend on your child’s needs and abilities. Sessions will also include your child's interests and your family's culture. This leads to better engagement, relevance, learning and fun.
At CHOP, our goal is to identify and treat CAS so your child can have the best communication outcomes.
Frequently asked questions
How long will speech therapy last.
Children improve at different rates. In general, if your child has CAS, they may be in speech therapy longer than children with other speech disorders. The length of therapy depends on the severity of your child’s CAS (mild, moderate or severe), but intensive therapy may last several years.
Speech therapy may occur in your home, at your child’s school and/or with a private SLP. As your child’s speech gets clearer and their sentences become longer, therapy intensity may be gradually reduced. Children with milder forms of CAS and young children (younger than age two) may require therapy less often. If your child has no other language, cognitive or behavioral concerns, they will usually make faster progress. If you have concerns about your child’s language, cognitive or behavioral development, it is important to address those concerns as well.
What will my child do in speech therapy?
It is important for therapy to be motivating and rewarding. Activities may include games, play and drill-work, along with engaging in strategies like repetition, feedback, cues (visual, touch and/or verbal) and imitation.
Our SLP may focus on developing a core vocabulary or “power words” with your child, like their name, age, names of family members and pets, “help”, “open”, “yes”, “no” and “all done.” These words and phrases will improve your child’s overall communication and decrease their frustration. Gestures, sign language, picture boards and electronic devices may also be introduced to support your child’s verbal communication.
Will my child need to do oral motor exercises?
In general, your child must practice talking. All practice with mouth movements should relate to a specific sound or word that your child is practicing. For example, our SLP may ask your child to, “Round your lips” for the “w” sound in “want”, when asking for a toy. Rounding lips to blow bubbles or a whistle will not directly improve your child’s speech production skills.
What can I do for my child at home?
Your child’s SLP will teach you how to help your child practice and communicate at home. If your child has CAS, they will need to practice speech outside of the therapy room. We recommend practicing for a few minutes, a few times each day. This tends to be more effective than practicing once per week for a longer amount of time. Your practice activities at home should include things that your child can do easily and well. This makes home practice fun and successful and builds your child’s confidence when speaking.
Does a child with CAS often have needs other than speech therapy?
Children with CAS often have difficulties with language skills, as well. Your child may need help with learning to speak in sentences, using correct grammar and communicating during social interactions and play. As children with CAS get older, they may have additional learning difficulties (like reading skills). Some children with CAS may have gross motor or fine motor issues requiring occupational or physical therapy.
Reviewed by Arielle Berne, MA, CCC-SLP
Common Speech Impediments: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Support
Speech impediments include a variety of both language and speech disorders, some of which can be addressed through online speech therapy with speech-language pathologists. They can arise because of heredity and genetics, developmental delays, or even damage to Broca’s area—the part of the brain that’s involved in language skills and speech skills. They may also be linked to other conditions like autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, dyslexia, or even hearing loss. It depends on the type and the cause, but most speech impediments and speech impairments can be treated through speech therapy.
That said, recognizing when a speech impediment may be present can help you get yourself or your child the treatment and support they may need for improved academic and/or social functioning and self-confidence.

Common symptoms of a speech impediment
There are many different types of speech impediments a person can have, so the symptoms can vary. That said, those listed below are common symptoms that could be initial indicators that you or your child may be experiencing speech problems or challenges:
- Elongating words
- Quiet or muffled speech
- Blinking frequently
- Distorted sounds while talking
- Frequent changes in pitch
- Poor voice quality
- Visible frustration when trying to communicate
- Overall difficulty communicating and expressing thoughts and ideas
- Inability to repeat words
- Inability to pronounce words the same way twice
- A phobia of speaking in public
- Speaking slowly and carefully
- Speech delay
- Frequent pauses when talking
- Limited vocabulary over several years, delayed language development
Some speech and language disorders are consistent with underlying mental health conditions such as autism. You can visit licensed health professionals or speech therapists to receive an accurate diagnosis and find out how to treat a speech impediment or language disorder, and its underlying cause, if applicable.
Key categories of speech impediments
Speech impediments or communication disorders can take many forms, from speech sound disorders to voice-related disorders. While speech sound disorders mostly result from sensory or motor causes, voice-related disorders deal with physical problems regarding speech. Read on for a list of some of the most common categories of speech impediments.
Voice disorders
Voice disorders primarily arise due to issues regarding the health and structure of the larynx or the voice box. They can impact pitch, resonance, volume, and voice quality. Symptoms of a voice disorder may include having a hoarse, quivering, strained, choppy, or weak and whispery voice, which can make it difficult to produce speech sounds.
The root cause of these disorders can be either organic, like alterations to respiratory, laryngeal, or vocal tract mechanisms, or functional, like improper use of the voice. Some risk factors that may contribute to vocal health challenges include allergies, psychological stress, age, excessive alcohol or drug use, screaming, scarring from neck surgery, or even gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Examples of voice disorders include laryngitis, vocal cord paralysis/weakness, polyps or nodes present on the vocal cords, leukoplakia, or muscle tension dysphonia.
Fluency disorders
A person may be diagnosed with a fluency disorder if they have trouble with speech timing and rhythm which makes it difficult to create a normal speech pattern. These disorders are characterized by interruptions in the typical flow of speaking, including abnormal repetitions, hesitation, and prolongations. Their cause is unknown, but it may be genetic. Symptoms can also be exacerbated by stress and anxiety. Stuttering is the most common example of fluency disorders.
Symptoms of a fluency disorder may include dragging out syllables, speaking breathlessly, repetition of words, speaking slowly, and being tense while speaking. Secondary symptoms may include fidgeting, mumbling, saying “um” or “uh” often, not using certain problematic words, rearranging words in sentences, and anxiety around speaking. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder. With stuttering, for example, slowing down, practicing, using speech monitors, attending speech therapy, and receiving cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are all potential treatment options.
Articulation disorders and phonological disorders
Articulation and phonological disorders are two types of speech disorders classified as speech sound disorders that may impact communication. An articulation disorder includes speech that commonly exhibits errors such as substitution, omission, distortion, and/or addition (SODA). Although the actual causes of articulation disorders aren’t well understood, contributing factors may include brain injuries, a cleft palate/cleft lip, or nerve damage. Phonological disorders typically involve producing sounds correctly but using them in the wrong place and are more predictable than articulation errors. There may also be a genetic factor that contributes to both disorders and other families may be impacted as well. A licensed speech-language pathologist (SLP) can determine if an individual may have an articulation disorder or a phonological disorder. Ongoing speech therapy is typically the recommended treatment method.
Speech impediments versus language impairments
A speech impediment is typically characterized by difficulty creating sound due to factors like fluency disorders or other voice problems. These disorders may arise from underlying mental health issues, neurological problems, or physical factors or conditions impacting speech muscles.
Language impairments, on the other hand, are more about difficulty processing, reading, and writing and can be connected to an issue processing receptive language. They’re common in children, especially when they first start school. Language impairments relate to meaning, whereas speech impediments relate to sound. It’s also very common for a language impairment disorder to present alongside a learning disability like dyslexia.

Examples of speech impediments
Below is a brief overview of a few of the most common speech disorders and speech impediments, along with symptoms and potential treatment options.
Apraxia of speech is a speech sound disorder that affects the pathways of the brain. It’s characterized by a person having difficulty expressing their thoughts accurately and consistently. It involves the brain being able to form the words and knowing exactly what to say, but the person then being unable to properly execute the required speech movements to deliver accurate sounds. In mild cases, a person will only have small limitations in their ability to form speech sounds. In severe cases, alternate communication methods may need to be used.
An SLP is the type of provider who can diagnose apraxia. To diagnose speech disorders, including both childhood apraxia (sometimes called verbal apraxia) and acquired apraxia, they may ask the individual to perform simple speech tasks like repeating a particular word several times or repeating a list of words that increase in length. Apraxia generally needs to be monitored by both parents and an SLP over time for an accurate diagnosis to be possible.
There are various treatment options for apraxia, the most common being one-on-one meetings with a speech pathologist. They’ll likely help you or your child build helpful strategies and skills to help strengthen problem areas and communicate more clearly. Some other treatment methods include improving speech intelligibility or using alternate forms of communication, like electronic speech or manual signs and gestures.
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders describes aphasia as a communication disorder that results in a person’s inability to speak, write, and/or understand language. Like other communication disorders, it may occur because of damage to the portions of the brain that are involved in language, which is common in those who have experienced a stroke. It may also come on gradually in those who have a tumor or a progressive neurological disease like Alzheimer’s. Symptoms may include saying or writing sentences that don’t make sense, a reduction in a person’s ability to understand a conversation, and substituting certain sounds and words for others.
Since this disorder is usually caused by damage to parts of the brain, it will typically first be recognized in an MRI or CT scan that can confirm the presence of a brain injury. The extent and type of aphasia can generally only be determined by observing the affected part of the brain and determining how extensively it has been damaged, which is often done with the help of an SLP.
Treatment options for aphasia can be restorative (aimed at restoring impaired function) or compensatory (aimed at compensating for deficits).
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is usually caused by brain damage or facial paralysis that affects the muscles of the jaw, tongue, or throat, which may result in deficits in a person’s speech. It may also be caused by other conditions like Lou Gehrig’s disease, Parkinson’s, or a stroke. It’s considered a nervous system disorder, subclassified as a motor speech disorder. It’s commonly seen in those who already have other speech disorders, such as aphasia or apraxia. Symptoms of dysarthria include slurred speech, speaking too slowly, speaking too quickly, speaking very softly, being unable to move one’s lips or jaw, and having monotonous speech.
Dysarthria can be diagnosed by an expert in speech-language pathology through an exam and tests like MRI, CT, electromyography, or the Denver articulation screening examination. Treatment depends upon the severity and rate of progression of the disorder. Some potential examples include tactics like slowing down while talking, doing exercises to help strengthen jaw muscles, moving the lips and tongue more, and learning strategies for speaking more loudly. Hand gestures and speech machines may also help.
The importance of treatment
It is important to treat speech disorders; the consequences of an untreated speech or language impediment can vary widely depending on the type, symptoms, and severity, as well as the age and life situation of the individual. In general, it’s usually helpful to seek professional advice on treating speech disorders as soon as you notice or suspect an impediment present in yours or your child’s speech. Especially for moderate to severe cases, some potential effects of leaving these common speech disorders untreated can include:
- Poor academic performance/dropping out of school
- Decrease in quality of life
- Social anxiety and an inability to connect with people
- Damaged relationships
- Social isolation
- Hospitalization

Seeking professional support
Meeting with an SLP is usually the recommended first step for someone who believes they or their child may have a speech impediment. If you have a teenager with dyslexia, there are resources for dyslexic teens that can give supportive information about the condition. Healthcare providers may also provide helpful insights and ask about your family members’ history when it comes to speech and language-related issues as they can be hereditary. While these professionals can help with the physical aspects of a variety of speech and language impediments, you or your child may also benefit from emotional support in relation to the mental health effects of having an impediment. A therapist may be able to provide this type of guidance. If your child is experiencing a speech impediment, a counselor may be able to work with them to process their feelings of frustration and learn healthy coping mechanisms for stress. They can help you manage the same feelings if you receive a speech or language impediment diagnosis, or may be able to support you in your journey of parenting a child with a speech or language impediment diagnosis.
In addition to support at home, teenagers with a diagnosed speech impairment or impediment can receive special education services at school. The Centers for Disease Control notes that under the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) and Section 504, schools must provide support and accommodations for students with speech disorders. For some children, support groups can provide outlets for social connections and advice for coping.
Meeting with a therapist in person is an option if there are providers in your area. That said, many people find it less intimidating or more comfortable to meet with a therapist virtually. For example, a teen who is experiencing a speech or language impediment may feel better interacting with a counselor through the online chat feature that virtual therapy platforms like TeenCounseling provide. It may allow them to express themselves more clearly than they could face-to-face or over the phone. Parents who need support in caring for a child with a speech or language impediment may find the availability and convenience of meeting with a therapist through an online therapy service like BetterHelp to be most beneficial. Research suggests that online and in-person therapy offer similar benefits for a variety of conditions, so you can choose the format that’s best for you.
Counselor reviews
See below for reviews of TeenCounseling therapists written by parents who sought help for their children through this service.
“Kathleen has been good for my daughter to talk to. I am thankful for her to give my daughter someone else's perspective other than her parents. Thank you.”
“I love Ms. Jones. She doesn’t over-talk or judge you. She gives really good advice and if you're confused she knows how to break it down or explain whatever it is so you can understand. If you need to talk about anything, she’s always an open ear and responds quickly. Not only does she give you points from others' perspectives but she steps into yours so she can understand why certain things are the way they are. In my first session, I was nervous and I think she could tell. She’ll crack a joke every now and then to make me feel more comfortable. She’s just such a bundle of joy and a good counselor to have.”
Speech and language impediments can vary widely in terms of types, causes, symptoms, and severity. These are diagnosed by professionals in the field of speech and language pathology or by a medical doctor. A therapist can provide emotional support for those who are having difficulty coping with their own or their child’s diagnosis or other related challenges.
What are the 3 speech impediments?
Speech impediments can manifest in a variety of ways. Three of the most common are listed below:
- Voice disorders affect the tone, pitch, quality, and volume of a person’s voice. A person with a voice disorder may have difficulty speaking or being heard clearly by others. Voice disorders can be either functional or organic. Functional disorders occur due to improper use of the parts of the throat that produce speech, such as overuse of the voice leading to vocal fatigue. Organic voice disorders result from physical anatomical changes, such as nodules on the vocal cords.
- Fluency disorders affect the rate, rhythm, and cadence of speech. Those with fluency disorders may speak in a disjointed, choppy, or prolonged fashion, making them difficult for others to understand clearly. While many types of fluency disorders exist, stuttering is likely the best-known. Speech often requires precise timing to convey a message accurately, which fluency disorders can disrupt.
- Speech sound disorders are a broad category of disorders that interferes with a person’s ability to produce sounds and words correctly. Speech sound disorders can present very differently from person to person. Sometimes word sounds are omitted or added where not appropriate, and sometimes word sounds are distorted or substituted completely. A typical example of a speech sound disorder is the substitution of “r” for “w” in words like “rabbit” (becoming “wabbit”). Many children experience that substitution, but it does not become a disorder until the child does not outgrow it.
Other types of disorders can cause problems with expressive communication or tongue-tie those experiencing them, such as developmental language disorder. Language disorders also cause concerns related to expressive communication, but the concerns are due to a lack of understanding of one or more components of language, not an inability to produce or use word sounds.
What do you call a speech impediment?
Speech impediments are typically referred to as speech disorders . Speech refers to the ability to form speech sounds using the vocal cords, mouth, lips, and tongue. Speech also requires that a rhythm and cadence be maintained. Speech disorders indicate a problem producing intelligible speech; word sounds may be omitted or misplaced, the rhythm of the speech may be difficult to follow, or a person’s voice might be strangely pitched or too soft to hear clearly.
It is important not to confuse speech disorders with language disorders . Language disorders arise due to difficulty understanding what words mean, how word sounds fit together, or how to use spoken language to communicate. Language problems may affect how a person speaks, but the root cause of the concern is linked to their understanding of language, not their ability to produce intelligible speech.
How do I know if I have a speech impediment?
If you’re experiencing a sudden onset of impaired speech with no apparent cause, seek medical attention immediately. Strokes, traumatic brain injuries, and other serious medical conditions can cause sudden changes in speaking ability. Gradual changes in speaking ability may also indicate an underlying medical problem. If you’re concerned that your speaking ability has been gradually deteriorating, consider making an appointment with a healthcare provider in the near future.
Most people with a speech disorder are diagnosed in childhood. Parents often identify speech-related concerns in early childhood based on their child’s speech patterns. The child’s pediatrician may also refer the child to a speech-language pathologist, a professional specializing in evaluating and treating speech disorders. If problems persist until the child is in school, teachers and other school officials might initiate a referral for an evaluation if they believe speech concerns are present. Children often receive speech and language therapy that resolves or improves their speech problems.
Speech disorders also appear in adulthood, often due to injury or illness. It is also possible, although rare, for speech problems to be misdiagnosed or missed outright during a person’s childhood. In that case, the speech disorder may have been present since childhood and symptoms persisted into adulthood.
If you’re finding it difficult to communicate verbally with others, have an easily identifiable speech problem (like stuttering), or receive feedback that others have trouble understanding you, consider making an appointment with your doctor for an evaluation and referral to the appropriate healthcare providers.
What are 5 causes of speech impairment?
Speech and language disorders can result from conditions that interfere with the development of perceptual, structural, motor, cognitive, or socioemotional functions. The cause of many speech disorders is unknown, but research has indicated several underlying factors that may be responsible:
- Pre-existing genetic conditions, like Down’s syndrome or Fragile X syndrome. Evidence suggests that genes may play a role even if genetic abnormalities do not result in a diagnosable genetic condition.
- Physical abnormalities, such as damage or improper development of the respiratory system, facial muscles, or cranial nerves.
- Hearing problems, which can delay a child’s acquisition of speech.
- Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, may interfere with speech development. There is also evidence to suggest that those with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder may have a more challenging time acquiring speech skills.
- Neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy.
Mental health concerns can also cause problems communicating with others. For example, an underlying anxiety disorder may lead to selective mutism , wherein a child speaks only under certain circumstances.
Is speech impediment a disability?
A speech-language disorder is considered a “ communication disability ” under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The ADA requires government and businesses to establish “effective communication” with people who have communication disabilities. Effective communication can be established in several ways. For those with a speech disorder, accommodation may be as simple as ensuring the person can get hold of writing materials if they need to express themselves quickly. In some cases, organizations may use a transliterator, or person trained to recognize unclear speech and repeat it clearly.
Because speech disorders are known to lead to academic struggles in K-12 and higher education settings, they are categorized as a disability under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEIA) . The IDEIA sets guidelines for all schools in the United States, public or not public, guaranteeing each child a right to accommodations and interventions for their speech disorder.
Can I fix my speech impediment?
Whether or not a speech disorder can be completely eliminated depends heavily on individual factors. The cause of the disorder, its severity, and the type of speech dysfunction all play a role in determining whether a particular disorder can be completely resolved. While it is not possible to guarantee that a speech disorder can be “cured,” nearly all disorders are treatable, and improvement is likely possible.
Can you treat a speech impediment?
Yes, many speech disorders are highly treatable. Most people receive treatment as children when most speech disorders become apparent. For children, speech-language pathologists will identify the specific speech disorder, search for an underlying cause, and design an intervention that targets that child’s speech problem. For example, a child who struggles with articulation errors and producing word sounds consistently may benefit from a contextual utilization approach . Contextual utilization leverages the fact that one sound is easier or more difficult to pronounce depending on which other sounds surround it.
Speech disorders that emerge in adulthood may be more challenging to treat due to underlying factors, such as brain injury. Suppose an adult experiences a traumatic brain injury that affects their speaking ability. In that case, a speech-language pathologist may help them find alternative communication methods, such as using a computer. They may also help them directly restore some of their speaking ability by leading them through exercises that improve nerve function and muscle control.
Is a speech impediment mental?
Speech disorders can be caused by various factors, many of which have nothing to do with the brain. However, there is a relationship between psychiatric mental health concerns and difficulty with spoken communication . Although researchers are still unsure of the exact cause, studies have identified a significant link between speech disorders and mental health disorders like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression.
Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, are also associated with an increased risk of developing a speech disorder. Although the link between neurodevelopmental disorders and speech disorders is not fully understood, evidence suggests that treating the speech disorder is still possible.
Finally, speech disorders can also be caused by illness or injury in the brain, such as cancer, an infection, or traumatic brain injury. Although these are not considered mental or developmental disorders, they may affect brain function and mental acuity. Speaking is a complex process, and there are many ways it can be affected.
Is autism a speech impediment?
Autism spectrum disorder is not a speech disorder, but it is heavily associated with communication problems. Those on the autism spectrum often use repetitive or rigid language and may not follow communication norms. They may repeat phrases continuously, use a modified tone of voice, or introduce information that has little to do with the conversation at hand.
Those on the autism spectrum are often able to form word sounds properly. The communication deficits of autism spectrum disorder are more closely related to language disorders than speech disorders. Speech disorders are associated with difficulty producing or using word sounds correctly, whereas language disorders are associated with a lack of understanding of one or more language components.
Autism spectrum disorder is also characterized by difficulties using pragmatic communication, or communication that is appropriate to a specific social situation. Although not a disorder of speech, a limited ability to recognize the socioemotional content of speech can significantly impact interpersonal communication and social interactions.
- Recognizing And Navigating Teen Depression Medically reviewed by Elizabeth Erban , LMFT, IMH-E
- ADHD Signs In Women, Men, And Children Medically reviewed by Julie Dodson , MA
- Relationships and Relations
CogniFit Blog: Brain Health News
Brain Training, Mental Health, and Wellness

Rhotacism: A complete guide to this speech impediment
Remember when you were a child and spoke by making your “R’s” sound like “W’s” and everything thought it was cute? That’s known as rhotacism and some people live with it even as adults. What is rhotacism, what is it like in other languages, and what are its symptoms? What does it look like as a speech impediment and what are some examples? What are its causes? How does it affect the brain ? Is it curable and how can it be fixed? This article will answer all your doubts about rhotacism.
What is rhotacism?
Rhotacism is a speech impediment that is defined by the lack of ability, or difficulty in, pronouncing the sound R . Some speech pathologists, those who work with speech impediments may call this impediment de-rhotacization because the sounds don’t become rhotic, rather they lose their rhotic quality. It could also be called a residual R error.
It’s not such an uncommon phenomenon and actually also happens with the letter L , a phenomenon known as lambdacism . Sometimes people mistake these speech impediments for a lisp, of which they are not. Within the 2000-2001 school year, more than 700,000 students within the American public school system were categorized as having either a language impediment or a speech impediment. Ironically, all three speech impediments contain the troubled letter within them.
The word rhotacism comes from the New Latin rhotacism meaning peculiar or excessive use of [r]. The Latin word came from Ancient Greek word rhōtakismós which means to incorrectly use “rho” which is the equivalent of the Greek R. For language nerds, here’s a really great explanation of how the word came into being.
How does rhotacism work in different languages?
Rhotacism is, in theory , more common among people whose native language has a trilled R. For example, in Spanish the “rr” is a trilled R. Other languages with a trilled R include Bulgarian, Hungarian, Arabic, Finnish, Romanian, Indonesian, Russian , Italian, and most Swedish speakers. Some people might mock Asians, specifically Chinese, for not being able to pronounce the English word “broccoli” correctly- rather pronouncing it “browccoli”. This isn’t due to a rhotacism, however. It’s actually due to the fact that Mandarin (Chinese) words can have an “r” sound in the beginning of a word, but not in the middle or end of a word. This leads them to have issues in their phonotactics and creates an inability to pronounce the English “R” in the middle of words.
The leader of Hezbollah, Hasan Nasrallah, is a Lebanese leader and is mocked for his rhotacism when he says, “ Amwīka ” and “ Iswā’īl ” for the Arabic Amrīka (America), and Isrā’īl (Israel). He is a native Arabic speaker- a language which has the trilled R. Notice how he puts a W sound in those two words where the R sound usually is.
Symptoms of rhotacism
- Some people try to hide their impediment by avoiding words with R ’s in them.
- An overall inability to say R sounds
- Using trilled R’s or guttural R’s (such as the French R) when trying to pronounce the regular English R.
Rhotacism as a speech impediment
Using a strict classification, only about 5%-10% of the human population speaks in a completely normal way. Everyone else suffers from some type of speech disorder or another. For children of any language, the R sounds are usually the hardest to master and often end up being the last ones a child learns. That’s why baby talk if you think about it, doesn’t really use explicit or strong R sounds. In English, rhotacism often comes off as a W sound which is why “Roger Rabbit” sounds like “Woger Wabbit”. R is often more difficult because a child has to learn the different combination of the /r/ sounds, not just the letter itself, unlike other letters. For example, when it comes before and after vowel sounds. The combination of a vowel with the /r/ sound is called a phenome and in English, there are eight combinations of these:
– The prevocalic R , such as “rain”
– The RL , such as “girl”
– The IRE, such as “tire”
– The AR, such as “car”
– The EAR , “such as “beer”
– The OR , such as “seashore”
– The ER , such as “butter”
– The AIR , such as “software”
A speech impediment is a speech disorder , not a language disorder . Speech disorders are problems in being able to produce the sounds of speech whereas language disorders are problems with understanding and/or being able to use words. Language disorders, unlike speech disorders, have nothing to do with speech production.
Often what happens is that the person speaking isn’t tensing their tongue enough, or not moving their tongue correctly (up and backward depending on the dialect) which makes the W or “uh” sound come out. It may also be that the person is moving their lips instead of their tongue.

Examples of rhotacism
- Barry Kripke from the TV show The Big Bang Theory has both rhotacism and lambdacism- meaning he has issues pronouncing both his R ’s and his L ’s.
- The most famous of rhotacism would be Elmer Fudd from Looney Tunes . He pronounces the word “rabbit” [ˈɹ̠ʷæbɪ̈t] as “wabbit” [ˈwæbɪ̈t]
- In Monty Python’s Life of Brian , the 1979 film’s character Pilate suffers from rhotacism. In the film, people mock him for his inability to be understood easily.
Here’s a video with a woman who suffers from rhotacism. She explains how difficult it can be to have the speech impediment.
Causes of rhotacism
For many people, the causes of rhotacism are relatively unknown-, especially in adults. However, scientists theorize that the biggest cause is that the person grew up in an environment where they heard R ’s in a weird way, the shape of their mouths are different than normal, or their tongues and lips never learned how to produce the letter. In children, this could happen because the parents or adults around think the way the child talks (using baby talk) is cute and the child never actually learns how to produce it.
For one internet forum user, it has to do with how they learned the language , “I speak various languages, I pronounce the “R” normal in Dutch, French, and Spanish, but I have a rhotacism when speaking English. It’s the way I learnt it.”
For other people, speech issues are a secondary condition to an already existing, serious condition. Physically, it would be a cleft lip or a cleft palate. Neurologically, it could be a condition such as cerebral palsy. It may also be a tongue tie . Almost everyone has a stretch of skin that runs along the bottom of their tongue. If that skin is too tight and reaches the tip of the tongue, it can make pronouncing (and learning how to pronounce) R ’s and L ’s difficult. If the tongue tie isn’t fixed early on, it can be incredibly difficult to fix and learn how to pronounce later.
How the brain affects rhotacism
The brain affects rhotacism only for those who suffer from it not due to a physical impediment (such as a cleft palate). For some, this could happen because the brain doesn’t have the phonemic awareness and never actually learned what the letter R is supposed to sound like. This is common with kids whose parents spoke to them in “baby talk” and encouraged the child’s baby talk, too. This kind of behavior only strengthens a child’s inner concept that / R / is pronounced like “w” or “uh”.
Another reason could be that the brain connections simply don’t allow the lips or mouth to move in the way they need to in order to pronounce the R . This inability has little to do with physical incapabilities and more to do with mental ones. Some people with rhotacism have an issue with their oral-motor skills which means that there isn’t sufficient communication in the parts of the brain responsible for speech production.
Treatment for rhotacism
Is rhotacism curable.
It can have negative social effects- especially among younger children, such as bullying, which lowers self-esteem and can have a lasting effect. However, if the impediment is caught early enough on and is treated rather quickly, there is a good overall prognosis meaning it’s curable.
However, some people never end up being able to properly pronounce that R and they end up substituting other sounds, such as the velar approximant (like w sounds) , the uvular approximant (also known as the “French R ”), and the uvular trill ( like the trilled R in Spanish).
How to fix rhotacism
Rhotacism is fixed by speech therapy . Before anything else, there needs to be an assessment from a Speech Language Pathologist (SLP) who will help decide if the problem can be fixed. If a child is involved, the SLP would predict if the child can outgrow the problem or not. After the diagnosis, a speech therapist will work with the person who suffers from the speech impediment by possibly having weekly visits with some homework and practice instructions. Therapy happens in spouts- a period of a few weeks and a break. There is a follow-up to see if there has been an improvement in pronunciation. In the U.S., children who are in school and have a speech disorder are placed in a special education program. Most school districts provide these children with speech therapy during school hours.
Another option, often used alongside speech therapy, is using a speech therapy hand-held tool that helps isolate the sound being pronounced badly and gives an image of the proper tongue placement to enable better pronunciation.
One study tested a handheld tactical tool (known as Speech Buddies) and the traditional speech therapy methods. The study found that students who used the hand-held tool (alongside speech therapy) improved 33% faster than those who used only the traditional speech therapy methods.
Have you or someone you know ever struggled with rhotacism? Let us know what you think in the comments below!
- Category: Wellness
- Tag: language , Language Disorder

- Overcoming Anxiety At Work: Steps to Promote Wellness Towards Successful Career

Pin It on Pinterest
Share this post with your friends!
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Signs and Symptoms
- Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Data and Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Autism Materials and Resources
- Diagnosis ASD
- Information on ASD for Healthcare Providers
- Acceptance Month Partner Toolkit
- 2023 Community Report on Autism
- Autism Data Visualization Tool
About Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain.
- Some people with ASD have a known difference, such as a genetic condition. Other causes are not yet known.
- Scientists believe there are multiple causes of ASD that act together to change the most common ways people develop. We still have much to learn about these causes and how they impact people with ASD.
- Early intervention services can greatly improve the development of a child with ASD.

People with ASD may behave, communicate, interact, and learn in ways that are different from most other people. There is often nothing about how they look that sets them apart from other people. The abilities of people with ASD can vary significantly. For example, some people with ASD may have advanced conversation skills whereas others may be nonverbal. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives; others can work and live with little to no support.
ASD begins before the age of 3 years and can last throughout a person's life, although symptoms may improve over time. Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life. In others, symptoms may not show up until 24 months of age or later. Some children with ASD gain new skills and meet developmental milestones until around 18 to 24 months of age, and then they stop gaining new skills or lose the skills they once had.
As children with ASD become adolescents and young adults, they may have difficulties developing and maintaining friendships, communicating with peers and adults, or understanding what behaviors are expected in school or on the job. They may come to the attention of healthcare providers because they also have conditions such as anxiety, depression, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which occur more often in people with ASD than in people without ASD.

Signs and symptoms
People with ASD often have problems with social communication and interaction, and restricted or repetitive behaviors or interests. People with ASD may also have different ways of learning, moving, or paying attention. These characteristics can make life very challenging . It is important to note that some people without ASD might also have some of these symptoms.
As a parent, you already have what it takes to help your young child learn and grow. CDC has developed materials to help you track your child's developmental milestones and share that progress, or any concerns, with your child's doctor at every check-up.
Track your child's development
Risk factors.
There is not just one cause of ASD. Many different factors have been identified that may make a child more likely to have ASD, including environmental, biologic, and genetic factors.
Although we know little about specific causes, the available evidence suggests that the following may put children at greater risk for developing ASD:
- Having a sibling with ASD
- Having certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis
- Experiencing complications at birth
- Being born to older parents
CDC is currently working on one of the largest US studies to date on ASD. This study, called the Study to Explore Early Development (SEED), was designed to look at the risk factors and behaviors related to ASD. CDC is now conducting a follow-up study of older children who were enrolled in SEED to determine the health, functioning, and needs of people with ASD and other developmental disabilities as they mature.
Screening and diagnosis
Diagnosing ASD can be difficult since there is no medical test, like a blood test, to diagnose the disorder. Doctors look at the child's behavior and development to make a diagnosis.
ASD can sometimes be detected at 18 months of age or younger. By age 2 years, a diagnosis by an experienced professional can be considered reliable. 1 However, many children do not receive a final diagnosis until they are much older. Some people are not diagnosed until they are adolescents or adults. This delay means that people with ASD might not get the early help they need.

Current treatments for ASD seek to reduce symptoms that interfere with daily functioning and quality of life. ASD affects each person differently, meaning that people with ASD have unique strengths and challenges and different treatment needs. 2 Treatment plans usually involve multiple professionals and are catered to the individual.
What CDC is doing
Promoting early identification of asd.
We naturally think of a child's growth as height and weight, but from birth to 5 years, a child should reach milestones in how they play, learn, speak, act, and move. A delay in any of these areas could be a sign of ASD or other developmental disability.
Through the Learn the Signs. Act Early. program, CDC and its partners aim to improve early identification of children with ASD and other developmental disabilities by promoting developmental monitoring , so children and families can get the services and support they need.
Did you know?
Understanding risk factors and causes of asd.
Understanding the risk factors that make a person more likely to develop ASD will help us learn more about the causes. CDC is currently funding and working on one of the largest US studies to date, called Study to Explore Early Development (SEED) .
SEED will help identify factors that may put children at risk for ASD and other developmental disabilities. SEED is a multi-year study being conducted at six sites and a data coordinating center, called the Centers for Autism and Developmental Disabilities Research and Epidemiology (CADDRE) network.
Determining how many people have ASD
There continue to be many children living with ASD who need services and support, both now and as they grow into adolescence and adulthood.
By studying the number of people identified with ASD over time, we can find out if the number is rising, dropping, or staying the same. We can also compare the number of children with ASD in different areas of the country and different groups of people. This information can help us look for causes of ASD.
CDC's Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network has been estimating the number of 8-year-old children with ASD in the United States since 2000. ASD occurs in all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups. It is more than 4 times more common among boys than among girls.
If you’re concerned
Research shows that early intervention services can greatly improve a child's development. 3 4 In order to make sure your child reaches their full potential, it is very important to receive services as soon as possible. Contact your child's doctor if you think your child might have ASD or if you have any other concerns about the way your child plays, learns, speaks, or acts.
Referral to a specialist
If you are still concerned, ask the doctor for a referral to a specialist who can do a more in-depth evaluation of your child. Specialists who can do a more in-depth evaluation and make a diagnosis include
- Developmental pediatricians (doctors who have special training in child development and children with special needs)
- Child neurologists (doctors who work on the brain, spine, and nerves)
- Child psychologists or psychiatrists (doctors who know about the human mind)
Free evaluations
At the same time, call your state's public early childhood system to request a free evaluation , sometimes called a Child Find evaluation, to find out if your child qualifies for intervention services. You do not need to wait for a doctor's referral or a medical diagnosis to make this call. Where to call for a free evaluation from the state depends on your child's age.
If your child is not yet 3 years old
- Contact your local early intervention system.
- You can find the right contact information for your state by calling the Early Childhood Technical Assistance Center (ECTA) at 919-962-2001.
- Or visit the ECTA website.
If your child is 3 years old or older
- If your child is 3 years old or older, contact your local public school system.
- Even if your child is not yet old enough for kindergarten or enrolled in a public school, call your local elementary school or board of education and ask to speak with someone who can help you have your child evaluated.
- If you're not sure who to contact, call the ECTA at 919-962-2001.
- Lord C, Risi S, DiLavore PS, Shulman C, Thurm A, Pickles A. Autism from 2 to 9 years of age . Arch Gen Psychiatry . 2006;63(6):694-701.
- Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM; COUNCIL ON CHILDREN WITH DISABILITIES, SECTION ON DEVELOPMENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS. Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics . 2020;145(1):e20193447.
- Handleman, Jan S., and Sandra L. Harris, eds. Preschool education programs for children with autism . Austin, TX: Pro-Ed, 2001.
- National Research Council. Educating Children with Autism . National Academies Press, 2001.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges. CDC is committed to continuing to provide essential data on ASD and develop resources that help identify children with ASD as early as possible.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.
Migraine can be a disabling disorder. New medications are giving some patients relief
‘a lot of people endure a lot, and they're not treated properly,' neurologist says.

Social Sharing

Read transcribed audio
The stereotypical image of a migraine sufferer is someone lying in a dark, quiet room for hours with an ice pack on their head.
And while that is still true in some cases, new effective medications specifically designed for migraine have changed the outlook for many patients of this often misunderstood neurological disorder, experts say.
"The problem with migraine is that a lot of people endure a lot, and they're not treated properly," Elizabeth Leroux, a neurologist in Montreal specializing in headaches and migraine, told Dr. Brian Goldman, host of CBC's The Dose .
"I see a lot of patients who know more than their doctors sometimes."
What is a migraine?
Unlike a regular headache that only involves head pain, a migraine is a neurological event that usually comes with other symptoms — nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and noise, neck pain and visual auras are all possible.
Frequency can vary, and chronic migraine is defined as having a headache at least 15 days per month, with at least half of them having migraine symptoms.

Compared to a tension headache, a migraine is often disabling, said Dr. Lara Cooke, a professor of neurology at the University of Calgary's Cumming School of Medicine.
"If you wish you could turn down the volume on the world or you could turn down the brightness of the sun … likely, it's a migraine," said Cooke, who has a specialty in headache medicine.
What causes migraine?
Though the exact science behind migraine isn't fully understood, researchers now understand more about the nature of the pain, according to Leroux.
Migraine pain comes from an interaction between the trigeminal nerves and certain systems in the brain, said Cooke.
The two trigeminal nerves run down each side of the face and send touch and pain sensations from the face to the brain.
When something triggers a migraine, those nerves get fired up and release calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a brain chemical that interacts with blood vessels in the head, causing throbbing pain.

Who gets migraines?
Migraines can start in childhood and affect all genders. Research shows that after puberty, more women than men experience migraine.
Some migraines are tied to the menstrual cycle and often improve post-menopause.
"It's very clear that ups and downs with estrogen play a very important role in migraines in women," said Cooke.
- Like 'cayenne pepper' on your brain: migraine sufferers describe the unique pain of an attack
Some hormones, including progesterone and oxytocin, make the female brain more prone to chronic pain diseases in general, including migraine, said Leroux.
Migraine triggers
Experts say there are a few common migraine triggers, such as alcohol, lack of sleep and weather changes . They differ for everyone, so it's worth figuring out your individual triggers.
A common theory around migraine is that everyone has a threshold for their triggers, and if several triggers coincide and the threshold is surpassed, a migraine will follow.
"You had a bad sleep, you're stressed, and then you had a glass of red wine … the sort of perfect storm," said Cooke.

Managing your triggers can help with migraine, but it can only go so far, said Leroux.
"Sometimes, your threshold is so low that just living and going to work and doing things with your family is unbearable," she said.
"And that's where I think medical care comes in."
New medications for migraine
There are two general categories of medication to treat migraine: those that treat a migraine attack and those that can prevent attacks.
Medications used to treat acute migraine attacks usually include a category of prescription drugs called triptans, which act on serotonin and block some pain signals. Over-the-counter medications, including anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help treat some of the milder symptoms.
Doctors have, for many years, also been prescribing various medications originally designed to treat other conditions, such as epilepsy, depression or high blood pressure, to try and prevent migraine attacks or at least reduce their frequency and/or intensity.
But for some with frequent migraine, a new category of preventive medication called CGRP blockers , or anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies — designed specifically to treat migraine — has made a huge difference, said Leroux.
"[Patients] come to me after decades of migraine — their life has changed … they don't fear the next attack," she said.
These medications — which came onto the market in 2018 — block CGRP, the protein in the brain that causes the pain of a migraine attack, and can reduce the intensity and frequency of migraine attacks over time.
There are four such medications approved in Canada: erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab and eptinezumab — sold under the brand names Aimovig, Ajovy, Emgality and Vyepti. The first three are self-injected once a month, and eptinezumab is infused intravenously every three months.
Another class of CGRP antagonists, known as gepants, come in pill form and can be used to treat acute migraine attacks or preventatively. Three are approved in Canada: ubrogepant, rimegepant and atogepant — sold under the brand names Ubrelvy, Nurtec and Qulipta.
- B.C. adds migraine medication to coverage, but 'life-changing' drug left off the list
CGRP medications are expensive, costing more than $600 per injection and around $20 per tablet, and not all provincial drug plans fully cover them. Coverage by private insurance plans varies.
Relief from new drug
Christina Sall has been taking the anti-CGRP antibody Aimovig (erenumab) since 2019 and said it has been "the best experience."
Sall, a registered nurse from Surrey, B.C., started getting migraines when she was five years old.
As a teen, the attacks intensified. They became so bad in her early 20s that she had more than 15 days a month with a migraine.
Sall tried preventive medications, but they didn't work and gave her terrible side effects, even landing her in the emergency room.
"Being dismissed at the ER that these aren't even real symptoms and that I'm just having anxiety is really frustrating," Sall said.
"It was a really, really dark time in my life."
- B.C. woman petitions province to cover cost of 'life-changing' migraine medication
- Q&A Scientists win prize for migraine research that offers 'light at the end of the tunnel'
Sall's migraines were so bad that she was forced to drop out of school during her nursing degree, but after taking anti-CGRP antibodies was able to return.
CGRP blockers aren't effective for everyone, cautioned Leroux, but she said that if they work for you, they can vastly improve your quality of life.
Botox injections were approved as a preventive for chronic migraine in Canada in 2011 and have been shown to be effective for some patients, say experts.
The toxin in Botox gets taken up in the nerve endings and prevents the nerve from releasing the neurochemicals believed to cause migraine pain, said Cooke.
In order to be approved for Botox, patients often need to confirm that they tried other preventive medications that didn't work.
Sall is grateful for the advances in migraine treatment in the past few years but cautioned it can be challenging for each individual to find medication that works.
"It does take time to make sure that you're on the right track," she said.
"Changes to your lifestyle can help to an extent, but it isn't going to miraculously get rid of migraine. It is a neurological disorder."
Corrections
- An earlier version of this story incorrectly stated that the drug eptinezumab is self-injected once a month. In fact, it's administered intravenously every three months. May 13, 2024 2:16 PM ET
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Reporter and producer
Isabelle Gallant is an Acadian radio producer and web writer based in Prince Edward Island. She has worked at the CBC since 2008.
With files from Sameer Chhabra
Related Stories
Add some “good” to your morning and evening.
A vital dose of the week's news in health and medicine, from CBC Health. Delivered to your inbox every Saturday morning.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Google Terms of Service apply.
Social media slams Harrison Butker for 'sexist' commencement speech: 'You kick a silly little ball'

Harrison Butker , a kicker for the Kansas City Chiefs, has become one of the internet's most hotly discussed people after a commencement speech he delivered earlier this week went viral for its message rife with rhetoric that has been widely recognized as misogynistic and homophobic.
Butker managed to make enemies of several groups with his 20-minute speech, including but not limited to women and female-presenting people, Swifties, the LGBTQIA+ community, Jewish people , people of certain political parties and people impacted by COVID.
"I think it is you, the women, who have had the most diabolic lies told to you," Butker said at one point during his speech at Benedictine College, a private Catholic liberal arts institution in Atchison, Kansas. "Some of you may go on to lead successful careers in the world but I would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world."
He went on to say that his wife would agree with the assertion that "homemaker" is the most important position for a woman, saying, "I can tell you that my beautiful wife Isabelle would be the first to say her life truly started when she started living her vocation as a wife and as a mother."
He also took time to crusade against Joe Biden and the LGBTQIA+ community, disparaging the existence of Pride month and speaking on "dangerous gender ideologies."
More: Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker's speech was ugly. He's only part of a bigger problem.
"Not the deadly sins sort of Pride that has an entire month dedicated to it," Butker said, "but the true God-centered pride that is cooperating with the Holy Ghost to glorify Him."
Butker also shared his thoughts on COVID-19, which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported has killed nearly 1.2 million people in the United States.
"While COVID might have played a large role throughout your formative years, it is not unique," Butker said. "The bad policies and poor leadership have negatively impacted major life issues. Things like abortion, IVF, surrogacy, euthanasia, as well as a growing support for the degenerate cultural values and media all stem from pervasiveness of disorder."
Multiple petitions have since been created to demand Butker's resignation or dismissal from the league.
Harrison Butker dubbed 'Smallest Man Who Ever Lived' after Taylor Swift quote
Despite these assertions and his criticism of working women, Butker also quoted Taylor Swift in his speech, one of the most successful music artists of all time who currently boasts a $1.1 billion net worth, according to Forbes.
"This undue familiarity will prove to be problematic every time," Butker said, referring to Swift's relationship with Chiefs tight end Travis Kelce. "Because as my teammate's girlfriend says, ‘Familiarity breeds contempt.'"
Naturally, this did not land well with Switfies, who quickly began using another song to describe him: "The Smallest Man Who Ever Lived," a track from Swift's recent album "The Tortured Poets Department. "
The backlash came in two-fold for Butker's insistence on calling Swift his "teammate's girlfriend," considering Swift is an international superstar and Kelce's fame and net worth trail significantly behind her own.
More: Chiefs' Harrison Butker strikes against Pride Month, lauds wife's role as 'homemaker'
Social media users slams Butker's 'hypocrisy' and 'ignorance'
The irony of Butker's mother being an accomplished physicist with multiple degrees was likewise not lost on the internet. Elizabeth Keller Butker MS, DABR, is a Clinical Medical Physicist in the Department of Radiation Oncology at Emory University School of Medicine.
Between her MS in medical physics from Georgia Institute of Technology and her nearly 40-year career in the field, social media users couldn't help but point out that Keller Butker not only didn't appear to stay home in her kitchen, as her son attested is the primary role of women, but also worked a lucrative career that benefited her son and the family's financial situation greatly.
The people of TikTok quickly took to the platform to start a trend of empowered women sharing their many accomplishments, with some pointing out that their jobs as scientists, doctors, teachers and beyond require more education and know-how than "kicking a ball."
Many set their videos to the song "Labour" by Paris Paloma , a feminist anthem that explores and pushes back at the historical subjugation of women.
One such video posted by user "World.of.grace" shared a slideshow of her accomplishments, including working through nursing school, graduating with the highest honors and becoming a nurse in the neonatal intensive care unit.
"But you kick a silly little ball," she says in the penultimate slide before sharing an image of herself in a football uniform with the caption "What, like it's hard?" Beneath the video, she clarifies "I wasn't the kicker, I was the cornerback."
Another TikTok, posted by MIT engineer and space expert Emily Calandrelli, challenged universities to "maybe let women choose your commencement speaker next year," accompanied by a video of herself preparing to deliver a different commencement speech with the caption "there are better options." The post has more than 4 million views and 1 million likes.
Other videos under the sound compared the speech to a scene from "The Handmaid's Tale," warning women, "When a man like this feels comfortable making that speech at a college graduation in 2024, we are in danger, ladies."
"You kick around a football for a living. You and me? We aren't the same" said user @brittany.hoyle after sharing her credentials as an educator. "I won’t stand for disrespect from a man whose job is to kick a ball for triple my salary a year," she said in the caption.
Another woman going by the username @triplediesel hopped on the trend to discuss being raised by a single mother and going on to graduate Cume Laude with a BS in biomedical science while working two jobs, conducting and presenting research at prestigious institutions, and the process of applying to med school.
"You kick a ball for a living," she said on the final slide which featured a picture of Butker. "We are NOT the same."
NFL responds, Chargers take a jab at Butker
The NFL has already made efforts to separate themselves from Butker's comments, though many fans online have expressed distaste for what they feel to be a lackluster response from the league.
"Harrison Butker gave a speech in his personal capacity," said Jonathan Beane, the senior vice president and chief diversity and inclusion officer at the NFL, in a statement. "His views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger."
Former Kansas City commissioner Justice Horn also took to social media to condemn Butker , saying "Harrison Butker doesn't represent Kansas City nor has he ever. Kansas City has always been a place that welcomes, affirms, and embraces our LGBTQ+ community members."
Other teams in the NFL jumped on the opportunity to diss Butker. The Los Angeles Chargers, known for sharing videos that poke fun at rival teams, posted its yearly NFL rollout schedule on Wednesday, a video made using The Sims and featuring digital characters look-alikes resembling teams and players.
The social media team couldn't help but take a jab at Butker, placing his character, complete with red number 7 jersey, in the same kitchen he told women to get back into during his speech.
Maren Morris, Hoda Kotb and Jenna Bush Hager react to Harrison Butker's speech
Butker's speech was so unpopular with so many that it prompted outcry not only from average netizens but also from celebrities and public figures.
Singer-songwriter Maren Morris shared a clip of the speech on her Instagram stories soon after the video began to circulate, saying "I choose the bear," a reference to a trend in which women choose between encountering a bear or man in the woods and explain why. (Hint: the trend went extra viral after women began answering "the bear" by and large, opening up a conversation of violence committed against women by men.)
Maria Shriver, author, member of the Kennedy family, former First Lady of California, and the founder of The Women's Alzheimer's Movement, also shot back with a post on X, formerly Twitter, and Instagram .
"What point was Harrison Butker really trying to make to women in his graduation speech about their present-day life choices? Did he really want them, aka us, to believe that our lives truly only begin when we lean into the vocation of wife and mother?" Shriver wrote.
"As a woman who has leaned into my vocation of living a meaningful life and working inside and outside the home to not only raise good humans but also raise up our country in various ways, I think it's demeaning to women to imply that their choices outside of wife and motherhood pale in comparison to that of homemaker," she added.
Hoda Kotb and Jenna Bush Hager of "The Today Show" also ripped the speech, discussing it during a segment and pointing out, "Well, I’m where I am today because I have a husband who leans into his vocation which is being an equal partner, and I tell him that all the time. But also, who is he to tell us?"
Journalist and former sportscaster Lisa Guerrero also posted on X , addressing the NFL directly, saying: “Hey @NFL – If you want to continue to grow your female fan base and any other marginalized group (straight white men are already watching your product), come get your boy."
Even Flava Flav got in on the action, sharing a post on X, formerly Twitter, reading: "Sounds like some players need to stay in their lanes and shouldn’t be giving commencement speeches."
Whoopi Goldberg defends Harrison Butker amid controversial speech
A few prominent names defended Butker, including Whoopi Goldberg who said on talk show "The View" that she "likes it when people say what they need to say."
"He’s at a Catholic college, he’s a staunch Catholic. These are his beliefs and he’s welcome to them. I don’t have to believe them. I don’t have to accept them," the co-host added. "The ladies that were sitting in that audience do not have to accept them."
Some commentators on social media also expressed support for Butker, arguing that he is practicing free speech or saying that he was simply right in his statements.
"Not a word Harrison Butker says here should be remotely controversial. He’s 100% correct," said T.J. Moe , a contributor to the conservative media site "The Blaze," in a post with 8.7k likes and 2.2k reshares. "Those trying to convince women that being assistant VP of lending & intentionally childless at age 40 is more fulfilling than making a family and home are evil."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A speech impediment, or speech disorder, is a condition that makes it hard for you to communicate. There are many types of speech impediments, and anyone can develop one. In some cases, children are born with conditions that affect speech. Other times, people have conditions or injuries that affect speech. Speech therapy can help.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include: Autism spectrum disorder: A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development. Cerebral palsy: A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement. Hearing loss: Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech.
Speech disorders affect a person's ability to produce sounds that create words, and they can make verbal communication more difficult. Types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and ...
3. Practice diaphragmatic breathing. Sometimes, impediments in speech, like stuttering, grow from nerves and anxiety. Before you have to speak in front of a group, go through a deep breathing activity to calm your nerves, relax your body, and get you in the right mental state for proper speech.
Diagnosis. Stuttering is diagnosed by a healthcare professional trained to evaluate and treat children and adults who have a problem with speech and language. This professional is called a speech-language pathologist. The speech-language pathologist listens and talks with the adult or child in different types of situations.
Speech impediments can cause communication problems and feelings of insecurity. Learn about causes and types of speech disorders and how they can be treated. Skip to main. ... Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured. Health professionals in fields including speech-language pathology ...
A hearing test may also be done to rule out hearing loss as a cause of the speech disorder. Treatment. Children may outgrow milder forms of speech disorders. The type of treatment will depend on the severity of the speech disorder and its cause. Speech therapy may help with more severe symptoms or any speech problems that do not improve.
Each treatment plan is specifically tailored to the patient. Treatment plans can address difficulties with: Speech sounds, fluency or voice. Understanding language. Sharing thoughts, ideas and feelings. Organizing thoughts, paying attention, remembering, planning or problem-solving. Feeding and swallowing.
However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders. There are many different types of speech impediments, including: Disfluency. Articulation errors. Ankyloglossia. Dysarthria. Apraxia. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different ...
Stuttering is a speech disorder that affects the rhythm and flow of how you talk. This disorder disrupts how you speak, causing unintended sounds, pauses or other problems with talking smoothly. ... Can a stutter be cured? There's no cure for stuttering, but you can recover from it. Speech therapy and other treatments can help make recovery ...
Diagnosis. To evaluate your child's condition, a speech-language pathologist reviews your child's symptoms and medical history. The speech-language pathologist also conducts an exam of the muscles used for speech, and looks at how your child produces speech sounds, words and phrases. Your child's speech-language pathologist also may assess your ...
Dysarthria symptoms include: Slurred speech or mumbling when you talk. Speaking too quickly or more slowly than intended. Speaking quieter or louder than intended. Sounding hoarse, harsh, strained, breathy, nasal, robotic or monotone. Speaking in short, choppy bursts with several pauses, instead of in complete sentences.
Stuttering is a speech disorder characterized by repetition of sounds, syllables, or words; prolongation of sounds; and interruptions in speech known as blocks. An individual who stutters exactly knows what he or she would like to say but has trouble producing a normal flow of speech. These speech disruptions may be accompanied by struggle ...
Speech fluency can be disrupted from causes other than developmental stuttering. Neurogenic stuttering. A stroke, traumatic brain injury or other brain disorders can cause speech that is slow or has pauses or repeated sounds. Emotional distress. Speech fluency can be disrupted during times of emotional distress.
Misaligned teeth or jaw structures can disrupt the production of specific sounds, often leading to a type of lisp known as a dental lisp. A dental lisp occurs when the tongue remains in contact with the front teeth during speech, creating a muffled or distorted articulation, particularly for sibilant sounds like "s" and "z."
Speech disorders impact millions of people and their ability to communicate. The National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders estimates that 5% of children in the U.S. ages 3 to 17 have had a speech disorder in the past 12 months. Some speech disorders can be overcome, while others are lifelong conditions.
Stuttering is a speech disorder. There are various ways to stop or reduce a stutter. ... While there is no cure for stuttering, speech therapy can be particularly effective in helping people gain ...
During the speech and language evaluation, our SLP will review your child's birth, medical and developmental histories. They will evaluate your child's ability to: Understand and use language. Communicate using speech, sign language and/or gestures. Produce consonant and vowel sounds, syllables, words and phrases.
Speech and language impediments can vary widely in terms of types, causes, symptoms, and severity. These are diagnosed by professionals in the field of speech and language pathology or by a medical doctor. ... While it is not possible to guarantee that a speech disorder can be "cured," nearly all disorders are treatable, and improvement is ...
Rhotacism as a speech impediment. Using a strict classification, only about 5%-10% of the human population speaks in a completely normal way. Everyone else suffers from some type of speech disorder or another. For children of any language, the R sounds are usually the hardest to master and often end up being the last ones a child learns.
There is no cure for CP, but treatment can improve the lives of those who have the condition. ... or speech; Changes in the spine (such as scoliosis A) Joint problems (such as contractures B) Types. Doctors classify CP according to the main type of movement disorder involved. Depending on which areas of the brain are affected, one or more of ...
Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives; others can work and live with little to no support. ASD begins before the age of 3 years and can last throughout a person's life, although symptoms may improve over time. Some children show ASD symptoms within the first 12 months of life.
Botox injections were approved as a preventive for chronic migraine in Canada in 2011 and have been shown to be effective for some patients, say experts. The toxin in Botox gets taken up in the ...
3 tips for speaking in a more authoritative way. 1. Come prepared. Speaking in public requires forethought. If you wish for people to listen, you need to hold their attention by telling them why ...
Here's The Full Speech. Ladies and gentlemen of the class of 2024, I would like to start off by congratulating all of you for successfully making it to this achievement today.
Whoopi Goldberg defends Harrison Butker amid controversial speech. A few prominent names defended Butker, including Whoopi Goldberg who said on talk show "The View" that she "likes it when people ...