- NONFICTION BOOKS
- BEST NONFICTION 2023
- BEST NONFICTION 2024
- Historical Biographies
- The Best Memoirs and Autobiographies
- Philosophical Biographies
- World War 2
- World History
- American History
- British History
- Chinese History
- Russian History
- Ancient History (up to 500)
- Medieval History (500-1400)
- Military History
- Art History
- Travel Books
- Ancient Philosophy
- Contemporary Philosophy
- Ethics & Moral Philosophy
- Great Philosophers
- Social & Political Philosophy
- Classical Studies
- New Science Books
- Maths & Statistics
- Popular Science
- Physics Books
- Climate Change Books
- How to Write
- English Grammar & Usage
- Books for Learning Languages
- Linguistics
- Political Ideologies
- Foreign Policy & International Relations
- American Politics
- British Politics
- Religious History Books
- Mental Health
- Neuroscience
- Child Psychology
- Film & Cinema
- Opera & Classical Music
- Behavioural Economics
- Development Economics
- Economic History
- Financial Crisis
- World Economies
- Investing Books
- Artificial Intelligence/AI Books
- Data Science Books
- Sex & Sexuality
- Death & Dying
- Food & Cooking
- Sports, Games & Hobbies
- FICTION BOOKS
- BEST NOVELS 2024
- BEST FICTION 2023
- New Literary Fiction
- World Literature
- Literary Criticism
- Literary Figures
- Classic English Literature
- American Literature
- Comics & Graphic Novels
- Fairy Tales & Mythology
- Historical Fiction
- Crime Novels
- Science Fiction
- Short Stories
- South Africa
- United States
- Arctic & Antarctica
- Afghanistan
- Myanmar (Formerly Burma)
- Netherlands
- Kids Recommend Books for Kids
- High School Teachers Recommendations
- Prizewinning Kids' Books
- Popular Series Books for Kids
- BEST BOOKS FOR KIDS (ALL AGES)
- Ages Baby-2
- Books for Teens and Young Adults
- THE BEST SCIENCE BOOKS FOR KIDS
- BEST KIDS' BOOKS OF 2023
- BEST BOOKS FOR TEENS OF 2023
- Best Audiobooks for Kids
- Environment
- Best Books for Teens of 2023
- Best Kids' Books of 2023
- Political Novels
- New History Books
- New Historical Fiction
- New Biography
- New Memoirs
- New World Literature
- New Economics Books
- New Climate Books
- New Math Books
- New Philosophy Books
- New Psychology Books
- New Physics Books
- THE BEST AUDIOBOOKS
- Actors Read Great Books
- Books Narrated by Their Authors
- Best Audiobook Thrillers
- Best History Audiobooks
- Nobel Literature Prize
- Booker Prize (fiction)
- Baillie Gifford Prize (nonfiction)
- Financial Times (nonfiction)
- Wolfson Prize (history)
- Royal Society (science)
- Pushkin House Prize (Russia)
- Walter Scott Prize (historical fiction)
- Arthur C Clarke Prize (sci fi)
- The Hugos (sci fi & fantasy)
- Audie Awards (audiobooks)
Make Your Own List

Science » Lives of Scientists » Albert Einstein
The best books on albert einstein, recommended by andrew robinson.

Einstein: A Hundred Years of Relativity by Andrew Robinson
Andrew Robinson , author of a biography of Albert Einstein, picks and talks through the five best Albert Einstein books and discusses the life and times of the 'unique genius.'
Interview by Jo Marchant

Albert Einstein: A Biography by Albrecht Folsing

Einstein 1905: The Standard of Greatness by John S. Rigden

The Born-Einstein Letters,1916-1955 by Albert Einstein and Max Born

The Einstein File by Fred Jerome

Einstein on Politics by David Rowe and Robert Schulmann

1 Albert Einstein: A Biography by Albrecht Folsing
2 einstein 1905: the standard of greatness by john s. rigden, 3 the born-einstein letters,1916-1955 by albert einstein and max born, 4 the einstein file by fred jerome, 5 einstein on politics by david rowe and robert schulmann.
B efore we start talking generally about Albert Einstein books , can you give us a brief outline of the significance of Einstein and his work? You’re the author of a biography of Albert Einstein called Einstein: A Hundred Years of Relativity that was republished this year to coincide with the centenary of the theory of general relativity.
There must be literally hundreds of Albert Einstein books. Was it daunting for you to tackle someone of so much significance and interest?
And out of those 1700 Albert Einstein books, we’ve asked you to pick just five! Your first choice is Albert Einstein: A Biography by Albrecht Fölsing published in 1997. What makes this biography so good?
It’s comprehensive, for a start. It is a very big book — one of the biggest on Einstein’s life. Fölsing is a physicist by training so he is able to bring clear explanations of the physics into the life. He’s extremely good at quoting Einstein’s writings and comments in an illuminating way. What makes the book unique is that the author is German, when most biographers come from the English-speaking world. He is able to present Einstein’s ambivalence towards Germany both in physics and in politics and bring that to life in quite a subtle way. To have a German writing on Einstein is particularly interesting.
Just to illuminate that, could you briefly sketch the arc of Einstein’s life for us?
He was born in Germany in 1879 and grew up there until he was 16 when he went to join his parents in Italy. He was unhappy with the German educational system: He was not a very willing student in an authoritarian education system. In fact, his whole life was a battle against authority in different forms. Later in life he said—and it’s one of my favourite quotes from him —“To punish me for my contempt for authority, fate has made me an authority myself.” Finally, he was educated in Switzerland and that’s where he really belongs. He kept Swiss nationality throughout his life, until he went to the United States and became an American citizen when he was quite old, in 1940. So, he is not German by nationality, though he was born there.
“He was not very successful in his relationships with his university lecturers.”
The Swiss atmosphere was very productive for his physics, which started in about 1905 with special relativity and some other key work. He stayed in Germany until 1933, when the Nazis came to power, and he had to get out. He spent a little time in Europe, including in Britain in the early 1930s. Finally, he left Europe forever—never to return—in 1933. He lived in Princeton, New Jersey, at the Institute for Advanced Study, a sort of ivory tower. That suited him very well. He could just think and didn’t have to do any teaching. He lived in Princeton right up to his death in 1955. In that period he wasn’t so successful as a physicist — but became much more involved in political causes like the atomic bomb, the hydrogen bomb, pacifism, and Zionism. As a Jew, he was very interested in the founding of Israel and took an active role in that.
One of the most intriguing things about his life story is the fact that when he did his first really significant revolutionary work in physics, he wasn’t working as a physicist was he? He was working in a patent office and didn’t really have contact with other top physicists at the time.
That’s right. That’s always going to be one of the most intriguing aspects of Einstein and his life. He was a patent clerk in Bern and worked in the patent office for a number of years from 1902. After 1909/1910, he finally takes a position as a professional, academic physicist and moves to various institutions around Europe. Probably his most productive years are those years when he was a patent clerk. Having said that, he came up with general relativity when he was a professor of physics in Berlin. Also, at the patent office, although he was not known in the academic world, he had some contact with academic physicists like Max Planck who was a key supporter of relativity. But we should remember that he was always involved with those two worlds.
Are there any clues as to where his revelations came from? Did his unconventional background play a part in that?
Yes. It’s difficult to pin that down but from an early age—from his teens onwards—he was a great believer in self-education. Like many geniuses, he was not particularly successful in his university training. He attended a famous institution—in Zurich—but was always rebelling against his academic education, constantly reading the latest research on his own. He was not working with other people at all. He was not very successful in his relationships with his university lecturers. He was a rebel and, because he was so passionate about physics, his best ideas really came from his own reading and thinking. From his earliest days as a teenager he was a believer in what he called ‘thought experiments.’ He wasn’t involved with laboratories at all, these experiments were all in his head. One of the most famous ones concerns chasing a light ray. When he was 16 or 17, he imagined whether you could catch up with a light ray and what that would mean.
Did that help him to see things that other physicists didn’t, because he was free to think in his own way?
Let’s dig a little bit more into the science with your next choice which is Einstein 1905: The Standard of Greatness by John Rigden from 2005. This Albert Einstein book is about the so-called ‘miraculous’ year. Can you tell us a bit about that?
Einstein published five papers that year. All of them are considered of great value. The paper that Einstein regarded as the most revolutionary of his work in 1905 was actually about quantum theory. There was another paper about Brownian motion. He showed that the phenomenon of Brownian motion—which had been known for almost 100 years—was actually due to atoms bombarding particles. This was considered proof of the atomic theory of matter by his fellow physicists — the first time that atoms had really been proved to exist. Then, the last of the five papers concerned probably the most famous equation in science: E=mc2. This came out of his first paper on relativity and was published at the end of 1905. As everyone knows, E=mc2 is the basis for what happens with nuclear energy and the atomic bomb later in the century.
This is the principle that energy and mass are two aspects of the same thing. So, if you split apart mass, you’re going to release huge amounts of energy which is what drives nuclear energy and the atomic bomb.
Yes, and c is the speed of light. So, with E=mc2, you can immediately see that the amount of energy is enormous from a small amount of matter because c is such a large number. So, E=mc2 implies a very large amount of energy from a small amount of matter through the process of atomic fission and fusion which Einstein didn’t know about in 1905. Fission was not discovered until later — just before the Second World War , in fact.
Let’s talk about the theory of special relativity, then, which was one of the papers in this miraculous year. Can you talk us through that theory?
It’s a response to Newton’s idea of absolute time and absolute space which Einstein rejected after thinking about it deeply. John Rigden puts it quite well in his book. He says, “A world with absolute space existing apart from absolute time would turn into a world where space and time are joined”. This theory of relativity led to the concept of space-time which is a key thought in general relativity. It’s not easy to explain relativity in a few words, but it rejects absolute time and space, leading to the idea that all motion had to be defined relative to a coordinate system — and that different coordinate systems had to be compared. General relativity was much more comprehensive, it included gravitation and acceleration. In fact, Einstein’s great idea about general relativity was that gravitation and acceleration were equivalent and that we must build our idea of the universe on that thought, rather than regarding them as independent, as Newton did.
General relativity is what we often see illustrated with a rubber sheet with marbles on it distorting the sheet. Is that right?
Yes, the curvature of the rubber sheet is a way of expressing—not literally, it’s a symbol—the curvature of space-time. The experimental proof of general relativity came only later. Probably the most famous aspect of the experimental proof is the bending of a light-ray by the gravitational field of the sun. The light emitted by distant stars was observed to be bent by the gravitational field of the sun in 1919 during an astronomical expedition led by Sir Arthur Eddington, a British astronomer. After that expedition, physicists started to take general relativity much more seriously. There were other experimental proofs as well, but that was the beginning of the idea that general relativity was correct. Before that, it was unproven and Einstein asked astronomers to go looking for it. That’s what happened in 1919. Astronomers were able to back up his theory with observations.
So, after we had the proof of general relativity, how was science different? How did the universe look different? What are the implications of that for the way we see the world now?
The whole idea of the Big Bang has been explained, to a great extent, in terms of general relativity. This came much later than Einstein of course — he was dead by then. General relativity also explains the existence of black holes. Einstein didn’t think they existed, but, since the 1960s, experimental proofs have been found that they do. The whole structure of space and time which Newton imagined, an absolute coordinate system, has been abandoned in favour of a curved space-time formulation. That’s really the result of Einstein’s work.
Going back to the miraculous year of 1905, which is the focus of Rigden’s book. His achievements in so many papers in such a short period of time seems almost superhuman. But he was just human, right? Do we risk exaggerating his genius sometimes?
He was certainly very human and had many failings as well as an extraordinary scientific imagination. Scholars have looked closely at what Einstein was doing in the years up to 1905, there’s not enough evidence to be sure. There were a few letters to his wife, and he published a little bit. There is this feeling that it came out of the blue. It obviously didn’t. No genius works from a sudden eureka moment and it’s not like that, even with Einstein. The problem is that we don’t really know exactly what he was reading and how his thought process worked. What we do know is what he published in 1905 and that he was fascinated by contradictions in physics. He imagined chasing a light-ray in his mind and asked what a light-ray would look like if you caught up with it and came to the conclusion that it’s an impossible physical situation. That, according to Maxwell’s laws of electromagnetism, there was no such thing as catching a light-ray. From that, he concluded that light always moves at a constant speed — independent of the coordinate system you were using to measure it with. It didn’t matter how fast an observer moved, light would always move at a constant speed faster than the observer.
“Einstein’s great idea about general relativity was that gravitation and acceleration were equivalent and that we must build our idea of the universe on that thought.”
Another contradiction that fascinated him was to do with magnetism and electric charge. He imagined that if you had a stationary charge observed by a stationary observer, there would be no magnetic field which could be observed with a compass. But, if you kept the stationary charge and then the observer started to move, by Maxwell’s definition of electromagnetism, he/she would observe a magnetic field with a compass. So which was true? Was there a magnetic field or wasn’t there? He said that’s a contradiction, we have to resolve it. And he did resolve it, with his theory of relativity.
There’s often a temptation to move away from contradiction but it sounds like he just confronted it head-on.
Let’s talk about your next choice of Albert Einstein books which is the Born-Einstein Letters, 1916-1955 , which was republished in 2005. This is a collection of correspondence between Einstein and his friend, the German physicist, Max Born. What do they talk about in the letters?
It was a long friendship. It began with physics but developed into a relationship with many other overtones to do with politics, ethics, and the state of Germany during those years. Both of them won Nobel Prizes, so when we read them we’re exposed to a couple of very intelligent people writing about science. Throughout the letters, you get these human asides: It’s a very unique mixture of science and humanities. They disagreed frequently and they disagreed most famously about quantum theory. In one letter from Einstein to Born he says, ‘The old one does not play dice. I can’t accept the possibility of chance ruling the universe.’ And Born never agreed with that. Right to the end of the correspondence, they’re arguing about the role of probability in physics.
They’re also talking about the First World War and how they react to that and about Jewishness. They’re both Jewish but they have different attitudes to Jewishness. And they’re talking about the Nazi period, of course. During that time, Born escaped from Germany and went to Edinburgh and became a professor. Einstein had gone to the United States — so they didn’t meet. After 1933, they corresponded but they didn’t have any personal contact — which is good, as it means that their ideas are on paper rather than just spoken to each other. We learn a lot. Born edits the letters and has a lot of commentary where he responds after Einstein’s death. Einstein’s step-daughter wrote to him about his last few days in hospital and she said, ‘He left this world without sentimentality or regret.’ Born says, ‘we lost our dearest friend when he died.’ But ‘without sentimentality or regret’ is the keynote of the letters. Einstein can be quite inhuman. He doesn’t have normal human reactions to some things including, for instance, the death of his second wife. His family life was not particularly happy. He divorced his first wife and had a rather difficult relationship with his children. This comes into the book quite a lot because Born is a warmer personality than Einstein. The contrast is interesting.
You say he didn’t have normal human reactions to things. What kind of personality does come across then?
Let’s move on to your next choice of Albert Einstein book: The Einstein File by Fred Jerome, published in 2002. This is a book on an investigation of how the FBI, led by J. Edgar Hoover, spied on Einstein for 23 years. What happened exactly?
It started in the 1930s when Einstein moved to the United States. He had extremely mixed feelings about Russia and about communism . He had some sympathies for socialism but he wasn’t a communist. But the FBI and many right-wing Americans thought that he was. So, even after he became an American citizen in 1940, he was regarded with suspicion by them. He wrote a letter to President Roosevelt in 1939 advocating the building of an atomic bomb, along with some other physicists, which was taken seriously by the American government and Roosevelt. Eventually, the Manhattan Project got going, partly out of Einstein’s interest in the subject. Obviously other factors were involved as well, Einstein was not the only influence, but he was quite important. But even though he was involved in supporting this project, he was not allowed to have access to any secret documents. The army, who ran the Manhattan Project, did not give him security clearance. But it seems the FBI didn’t know that and when they started compiling their file in the 1940s, they assumed that Einstein could be a spy with access to secret information about the atomic bomb project and they acted accordingly.
“Long before many people had realised what a risk to world peace Nazi Germany posed, Einstein recognised it.”
J. Edgar Hoover was convinced he was a security risk and might be leaking information to the Russians. When the Klaus Fuchs spy case happened—around 1950—Hoover became even more convinced that Einstein was a risk. But what finally tipped the balance for Hoover was that Einstein gave a broadcast on television in 1950 where he openly told the whole of the United States that the hydrogen bomb, which President Truman had just announced as a project, could cause a poisoning of the atmosphere and would be a total disaster, that it shouldn’t be followed up. Hoover then became passionately convinced that Einstein’s every move should be tracked and that all political associations that he had should be put into this file. He was hoping to prove that Einstein was a communist and that he might be deported from the United States. That was a serious project of the FBI and the immigration service for five years between 1950 and his death in 1955.
And this didn’t come out until reasonably recently then, with freedom of information requests?
It didn’t come out until the 1990s. It’s quite disturbing, really, to think the FBI could have kept the secret for so long. In fact, some FBI agents—even though they were in the employment of the agency—were not aware about this secret file. Hoover knew that if it got out it would cause tremendous embarrassment to the United States government — this world famous scientist being pursued as a potential spy. He managed to keep the secret but how it was kept in the decades after the 1950s and 1960s is extraordinary and quite alarming, I think.
Was this campaign a complete failure? Or is there evidence that it was able to damage Einstein’s reputation or legacy in any way?
Ironically, I think it probably persuaded Einstein—because he was aware he was under surveillance, he didn’t know the details but he knew he was being watched—to come out and make a very public statement in the press in 1953 in support of intellectuals who were standing up against Joseph McCarthy’s campaign. McCarthy reacted very strongly to this and said Einstein was an ‘enemy of America.’ He later changed that to ‘a disloyal American,’ but he never went back on that statement. Einstein thought he might have to go to jail because he was recommending to people that they should not testify to congressional committees about their political views. He said that courage was needed by American intellectuals otherwise they would become slaves. That is what he felt the American government was trying to do during the Red Scare of the 1950s.
It was a very courageous thing to come out and say in that climate.
It was. It is quite moving to read his own private views and worries but he was quite old by then. He was prepared to stand up because he felt the situation had become so like Nazi Germany in the 1930s. He really felt that having lived through the rise of Nazi Germany, he had a duty to warn Americans that the same thing might happen with McCarthyism. I think you can say he was a real factor in the fall of McCarthy. Only one factor, but he was important. After the fall of McCarthy, Hoover realized there was no point in pursuing Einstein anymore. The whole file was wound down by the FBI just before Einstein’s death — but it does run to 1800 pages. One irony is that much of the file consists of associations to which Einstein had lent his name but very little of it consists of his views.
Let’s move on to Einstein’s political writings, that Hoover failed to read, in Einstein on Politics edited by David Rowe and Robert Schulmann from 2007. What picture do we get from this Albert Einstein book, then, of his political views?
This is the first book which really collects everything together which is why it’s valuable. There were a couple of books before that but this is the first collection in which everything is there that matters: letters, public statements, all of course in English (many of them were originally in German.) The general attitude has always been that Einstein was politically naïve. I don’t think that’s true. When you see what he did and what he stood for, you can’t call him naïve. He was a committed pacifist until 1933 and made a number of provocative speeches about pacifism. After he recognised what the Nazis stood for, he immediately changed his mind and said that there was no possibility of resisting Nazism without military force. He was prescient. Long before many people had realised what a risk to world peace Nazi Germany posed, Einstein recognised it and argued that the countries of the West would have to arm themselves and fight, eventually.
Get the weekly Five Books newsletter
He was not naïve about Israel . He supported the founding of Israel but persistently said to Israelis that they would have to find an ethical solution to their relationship with the Arabs. Otherwise, the whole state would fail and they had a duty to do so. He never changed his mind and when he was invited to be President of Israel in 1952—not long before his death—he refused saying ‘I have no talent for politics and I would have to say things to my fellow Jews in Israel that they would probably not want to hear about their relationship with the Arabs.’ Again, he was probably right. Whether he could have influenced events more than he did by becoming president, we’ll never know. But he was certainly regarded seriously by the Israelis as a thinker and as an activist. Then, on the matter on world-government, in 1945, it made sense. The United Nations had just started but they were already quarrelling in the Security Council. Einstein said the only way of controlling nationalism was by having a central, military authority. He tried to get both America and the Soviet Union and the British and some other nations involved in that, on the model of the Austro-Hungarian Empire which he had grown up under. He gave a speech at a Nobel Prize winning anniversary dinner in New York, saying, ‘The war is won but the peace is not.’ There was about two or three years of campaigning for world government with other physicists and thinkers. Of course it failed — but that was, I suppose, inevitable in the Cold War.
Is this book just of historical interest, to know what he thought, or do Einstein’s thoughts resonate for us today?
When you read his collected writings, you can’t help but see that there was a connection between his personal integrity and his political views which we all struggle with: how we behave as individuals and how we behave as a collective. His honesty and his courage do make me think. And he wrote well. He had a pungent style, his writing is not woolly, and he had a sense of history too. He also had a wonderful sense of humour. That comes through in virtually everything he writes about politics and human behaviour. Sometimes he was pretty caustic but he was often just gently ironic. I’m sure you’ve seen a photograph at the end of his life of him sticking his tongue out at the photographers. I think impudence and defiance of authority are the defining features of his political statements. I find that, on the whole, admirable.
That is something that seems to run through his scientific thinking and his political views.
He was a rebel, against orthodoxy of all kinds. We haven’t touched on his last 30 years as a physicist which are a bit notorious. He was trying to unify electromagnetism and gravitation — in other words, to extend general relativity to an even more universal understanding of the universe. He didn’t succeed, but in my book I’ve got a piece contributed by Steven Weinberg, the particle physicist, who says that even though Einstein failed we have to admire his determination to carry on and not accept quantum theory as the final theory. He said, ‘I can’t accept that as the final theory of physics, there must be something beyond it.’ He again showed his defiance of orthodoxy because almost every physicist thought he had lost his way. And some of them said so — Bohr, in particular. Niels Bohr came to Princeton in 1939 and Einstein had plenty of opportunity to meet him and talk to his old friend. But he didn’t want to because they disagreed so radically about physics. They spent quite a lot of time ignoring each other. Bohr was very upset about it but Einstein was determined not to reopen this old debate so kept his distance.
How should we remember Einstein?
As a unique genius. I’ve written two books on genius and I can’t think of anybody else who managed to combine science and decent human behaviour in the way that he did. And also as a humorous man. I really admire his jokes…
November 20, 2015
Five Books aims to keep its book recommendations and interviews up to date. If you are the interviewee and would like to update your choice of books (or even just what you say about them) please email us at [email protected]
Support Five Books
Five Books interviews are expensive to produce. If you've enjoyed this interview, please support us by donating a small amount .
Andrew Robinson
Andrew Robinson is a London-based writer and author of some twenty-five books on science; history of science; archaeology and scripts; and Indian history and culture. His recent books include a biography of Jean-François Champollion, Cracking the Egyptian Code and India: A Short History . He is author of Einstein: A Hundred Years of Relativity , republished in 2015 to celebrate the centenary of Einstein’s general theory of relativity and described by astronomer Patrick Moore as “by far the best book about Einstein that I have ever come across”.
We ask experts to recommend the five best books in their subject and explain their selection in an interview.
This site has an archive of more than one thousand seven hundred interviews, or eight thousand book recommendations. We publish at least two new interviews per week.
Five Books participates in the Amazon Associate program and earns money from qualifying purchases.
© Five Books 2024
Albert Einstein
One of the most influential scientists of the 20 th century, Albert Einstein was a physicist who developed the theory of relativity.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
Quick Facts
Early life, family, and education, einstein’s iq, patent clerk, inventions and discoveries, nobel prize in physics, wives and children, travel diaries, becoming a u.s. citizen, einstein and the atomic bomb, time travel and quantum theory, personal life, death and final words, einstein’s brain, einstein in books and movies: "oppenheimer" and more, who was albert einstein.
Albert Einstein was a German mathematician and physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. In the following decade, he immigrated to the United States after being targeted by the German Nazi Party. His work also had a major impact on the development of atomic energy. In his later years, Einstein focused on unified field theory. He died in April 1955 at age 76. With his passion for inquiry, Einstein is generally considered the most influential physicist of the 20 th century.
FULL NAME: Albert Einstein BORN: March 14, 1879 DIED: April 18, 1955 BIRTHPLACE: Ulm, Württemberg, Germany SPOUSES: Mileva Einstein-Maric (1903-1919) and Elsa Einstein (1919-1936) CHILDREN: Lieserl, Hans, and Eduard ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Pisces
Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879, in Ulm, Württemberg, Germany. He grew up in a secular Jewish family. His father, Hermann Einstein, was a salesman and engineer who, with his brother, founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a Munich-based company that mass-produced electrical equipment. Einstein’s mother, the former Pauline Koch, ran the family household. Einstein had one sister, Maja, born two years after him.
Einstein attended elementary school at the Luitpold Gymnasium in Munich. However, he felt alienated there and struggled with the institution’s rigid pedagogical style. He also had what were considered speech challenges. However, he developed a passion for classical music and playing the violin, which would stay with him into his later years. Most significantly, Einstein’s youth was marked by deep inquisitiveness and inquiry.
Toward the end of the 1880s, Max Talmud, a Polish medical student who sometimes dined with the Einstein family, became an informal tutor to young Einstein. Talmud had introduced his pupil to a children’s science text that inspired Einstein to dream about the nature of light. Thus, during his teens, Einstein penned what would be seen as his first major paper, “The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields.”
Hermann relocated the family to Milan, Italy, in the mid-1890s after his business lost out on a major contract. Einstein was left at a relative’s boarding house in Munich to complete his schooling at the Luitpold.
Faced with military duty when he turned of age, Einstein allegedly withdrew from classes, using a doctor’s note to excuse himself and claim nervous exhaustion. With their son rejoining them in Italy, his parents understood Einstein’s perspective but were concerned about his future prospects as a school dropout and draft dodger.
Einstein was eventually able to gain admission into the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, specifically due to his superb mathematics and physics scores on the entrance exam. He was still required to complete his pre-university education first and thus attended a high school in Aarau, Switzerland, helmed by Jost Winteler. Einstein lived with the schoolmaster’s family and fell in love with Winteler’s daughter Marie. Einstein later renounced his German citizenship and became a Swiss citizen at the dawn of the new century.
Einstein’s intelligence quotient was estimated to be around 160, but there are no indications he was ever actually tested.
Psychologist David Wechsler didn’t release the first edition of the WAIS cognitive test, which evolved into the WAIS-IV test commonly used today, until 1955—shortly before Einstein’s death. The maximum score of the current version is 160, with an IQ of 135 or higher ranking in the 99 th percentile.
Magazine columnist Marilyn vos Savant has the highest-ever recorded IQ at 228 and was featured in the Guinness Book of World Records in the late 1980s. However, Guinness discontinued the category because of debates about testing accuracy. According to Parade , individuals believed to have higher IQs than Einstein include Leonardo Da Vinci , Marie Curie , Nikola Tesla , and Nicolaus Copernicus .
After graduating from university, Einstein faced major challenges in terms of finding academic positions, having alienated some professors over not attending class more regularly in lieu of studying independently.
Einstein eventually found steady work in 1902 after receiving a referral for a clerk position in a Swiss patent office. While working at the patent office, Einstein had the time to further explore ideas that had taken hold during his university studies and thus cemented his theorems on what would be known as the principle of relativity.
In 1905—seen by many as a “miracle year” for the theorist—Einstein had four papers published in the Annalen der Physik , one of the best-known physics journals of the era. Two focused on the photoelectric effect and Brownian motion. The two others, which outlined E=MC 2 and the special theory of relativity, were defining for Einstein’s career and the course of the study of physics.
As a physicist, Einstein had many discoveries, but he is perhaps best known for his theory of relativity and the equation E=MC 2 , which foreshadowed the development of atomic power and the atomic bomb.
Theory of Relativity
Einstein first proposed a special theory of relativity in 1905 in his paper “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” which took physics in an electrifying new direction. The theory explains that space and time are actually connected, and Einstein called this joint structure space-time.
By November 1915, Einstein completed the general theory of relativity, which accounted for gravity’s relationship to space-time. Einstein considered this theory the culmination of his life research. He was convinced of the merits of general relativity because it allowed for a more accurate prediction of planetary orbits around the sun, which fell short in Isaac Newton ’s theory. It also offered a more expansive, nuanced explanation of how gravitational forces worked.
Einstein’s assertions were affirmed via observations and measurements by British astronomers Sir Frank Dyson and Sir Arthur Eddington during the 1919 solar eclipse, and thus a global science icon was born. Today, the theories of relativity underpin the accuracy of GPS technology, among other phenomena.
Even so, Einstein did make one mistake when developing his general theory, which naturally predicted the universe is either expanding or contracting. Einstein didn’t believe this prediction initially, instead holding onto the belief that the universe was a fixed, static entity. To account for, this he factored in a “cosmological constant” to his equation. His later theories directly contracted this idea and asserted that the universe could be in a state of flux. Then, astronomer Edwin Hubble deduced that we indeed inhabit an expanding universe. Hubble and Einstein met at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles in 1931.
Decades after Einstein’s death, in 2018, a team of scientists confirmed one aspect of Einstein’s general theory of relativity: that the light from a star passing close to a black hole would be stretched to longer wavelengths by the overwhelming gravitational field. Tracking star S2, their measurements indicated that the star’s orbital velocity increased to over 25 million kph as it neared the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy, its appearance shifting from blue to red as its wavelengths stretched to escape the pull of gravity.
Einstein’s E=MC²
Einstein’s 1905 paper on the matter-energy relationship proposed the equation E=MC²: the energy of a body (E) is equal to the mass (M) of that body times the speed of light squared (C²). This equation suggested that tiny particles of matter could be converted into huge amounts of energy, a discovery that heralded atomic power.
Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein, who thus became a star of the lecture circuit and academia, taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (today is known as the Max Planck Institute for Physics) from 1917 to 1933.
In 1921, Einstein won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect, since his ideas on relativity were still considered questionable. He wasn’t actually given the award until the following year due to a bureaucratic ruling, and during his acceptance speech, he still opted to speak about relativity.
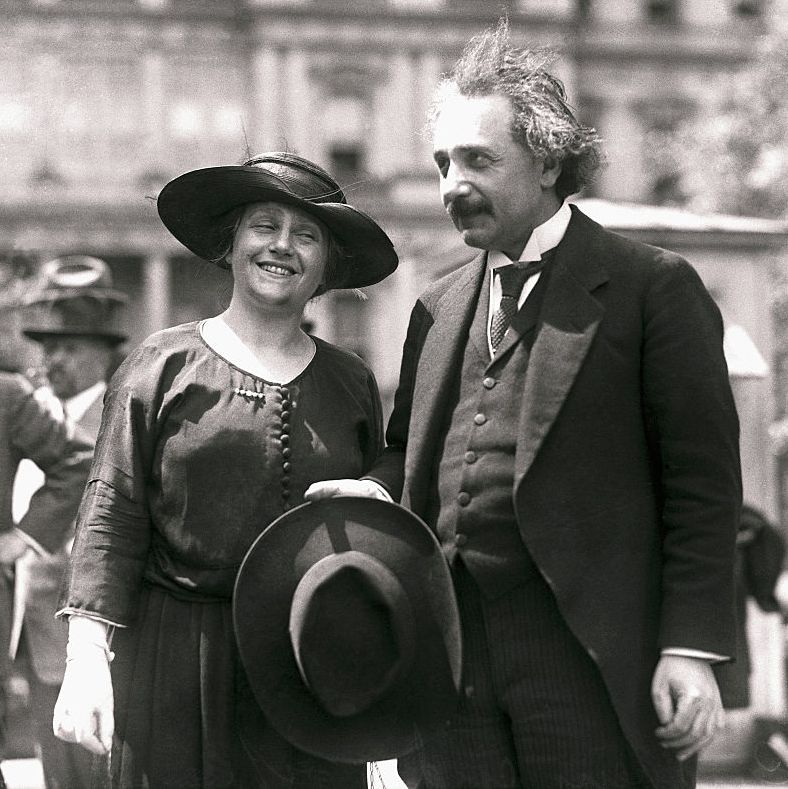

Einstein married Mileva Maric on January 6, 1903. While attending school in Zurich, Einstein met Maric, a Serbian physics student. Einstein continued to grow closer to Maric, but his parents were strongly against the relationship due to her ethnic background.
Nonetheless, Einstein continued to see her, with the two developing a correspondence via letters in which he expressed many of his scientific ideas. Einstein’s father passed away in 1902, and the couple married shortly thereafter.
Einstein and Mavic had three children. Their daughter, Lieserl, was born in 1902 before their wedding and might have been later raised by Maric’s relatives or given up for adoption. Her ultimate fate and whereabouts remain a mystery. The couple also had two sons: Hans Albert Einstein, who became a well-known hydraulic engineer, and Eduard “Tete” Einstein, who was diagnosed with schizophrenia as a young man.
The Einsteins’ marriage would not be a happy one, with the two divorcing in 1919 and Maric having an emotional breakdown in connection to the split. Einstein, as part of a settlement, agreed to give Maric any funds he might receive from possibly winning the Nobel Prize in the future.
During his marriage to Maric, Einstein had also begun an affair some time earlier with a cousin, Elsa Löwenthal . The couple wed in 1919, the same year of Einstein’s divorce. He would continue to see other women throughout his second marriage, which ended with Löwenthal’s death in 1936.
In his 40s, Einstein traveled extensively and journaled about his experiences. Some of his unfiltered private thoughts are shared two volumes of The Travel Diaries of Albert Einstein .
The first volume , published in 2018, focuses on his five-and-a-half month trip to the Far East, Palestine, and Spain. The scientist started a sea journey to Japan in Marseille, France, in autumn of 1922, accompanied by his second wife, Elsa. They journeyed through the Suez Canal, then to Sri Lanka, Singapore, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Japan. The couple returned to Germany via Palestine and Spain in March 1923.
The second volume , released in 2023, covers three months that he spent lecturing and traveling in Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil in 1925.
The Travel Diaries contain unflattering analyses of the people he came across, including the Chinese, Sri Lankans, and Argentinians, a surprise coming from a man known for vehemently denouncing racism in his later years. In an entry for November 1922, Einstein refers to residents of Hong Kong as “industrious, filthy, lethargic people.”
In 1933, Einstein took on a position at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, where he would spend the rest of his life.
At the time the Nazis, led by Adolf Hitler , were gaining prominence with violent propaganda and vitriol in an impoverished post-World War I Germany. The Nazi Party influenced other scientists to label Einstein’s work “Jewish physics.” Jewish citizens were barred from university work and other official jobs, and Einstein himself was targeted to be killed. Meanwhile, other European scientists also left regions threatened by Germany and immigrated to the United States, with concern over Nazi strategies to create an atomic weapon.
Not long after moving and beginning his career at IAS, Einstein expressed an appreciation for American meritocracy and the opportunities people had for free thought, a stark contrast to his own experiences coming of age. In 1935, Einstein was granted permanent residency in his adopted country and became an American citizen five years later.
In America, Einstein mostly devoted himself to working on a unified field theory, an all-embracing paradigm meant to unify the varied laws of physics. However, during World War II, he worked on Navy-based weapons systems and made big monetary donations to the military by auctioning off manuscripts worth millions.
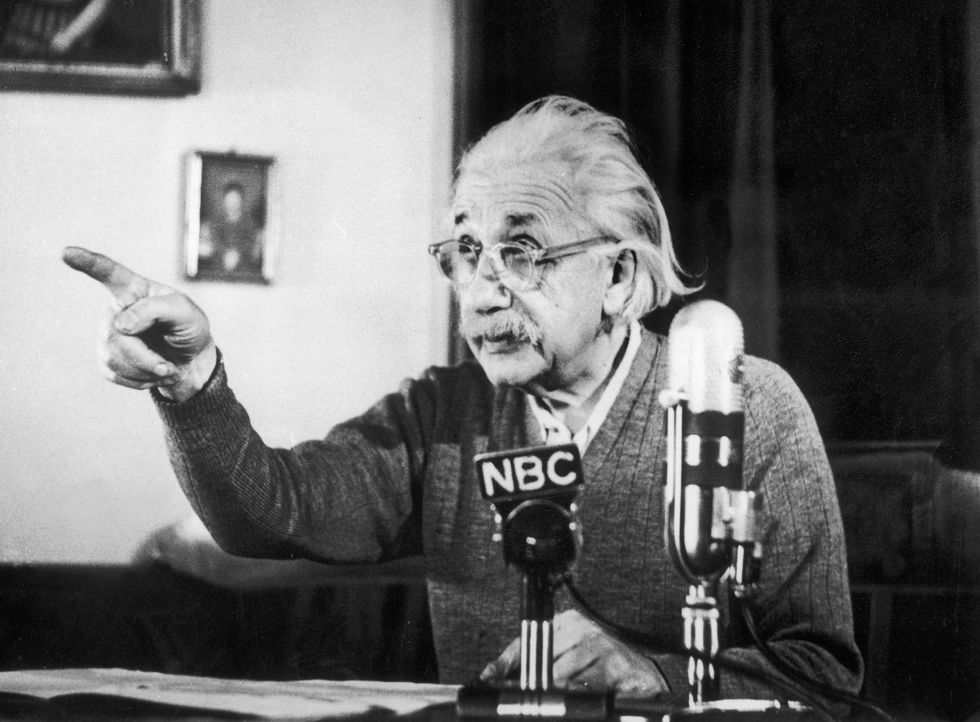

In 1939, Einstein and fellow physicist Leo Szilard wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt to alert him of the possibility of a Nazi bomb and to galvanize the United States to create its own nuclear weapons.
The United States would eventually initiate the Manhattan Project , though Einstein wouldn’t take a direct part in its implementation due to his pacifist and socialist affiliations. Einstein was also the recipient of much scrutiny and major distrust from FBI director J. Edgar Hoover . In July 1940, the U.S. Army Intelligence office denied Einstein a security clearance to participate in the project, meaning J. Robert Oppenheimer and the scientists working in Los Alamos were forbidden from consulting with him.
Einstein had no knowledge of the U.S. plan to use atomic bombs in Japan in 1945. When he heard of the first bombing at Hiroshima, he reportedly said, “Ach! The world is not ready for it.”
Einstein became a major player in efforts to curtail usage of the A-bomb. The following year, he and Szilard founded the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists, and in 1947, via an essay for The Atlantic Monthly , Einstein espoused working with the United Nations to maintain nuclear weapons as a deterrent to conflict.
After World War II, Einstein continued to work on his unified field theory and key aspects of his general theory of relativity, including time travel, wormholes, black holes, and the origins of the universe.
However, he felt isolated in his endeavors since the majority of his colleagues had begun focusing their attention on quantum theory. In the last decade of his life, Einstein, who had always seen himself as a loner, withdrew even further from any sort of spotlight, preferring to stay close to Princeton and immerse himself in processing ideas with colleagues.
In the late 1940s, Einstein became a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP), seeing the parallels between the treatment of Jews in Germany and Black people in the United States. He corresponded with scholar and activist W.E.B. Du Bois as well as performer Paul Robeson and campaigned for civil rights, calling racism a “disease” in a 1946 Lincoln University speech.
Einstein was very particular about his sleep schedule, claiming he needed 10 hours of sleep per day to function well. His theory of relativity allegedly came to him in a dream about cows being electrocuted. He was also known to take regular naps. He is said to have held objects like a spoon or pencil in his hand while falling asleep. That way, he could wake up before hitting the second stage of sleep—a hypnagogic process believed to boost creativity and capture sleep-inspired ideas.
Although sleep was important to Einstein, socks were not. He was famous for refusing to wear them. According to a letter he wrote to future wife Elsa, he stopped wearing them because he was annoyed by his big toe pushing through the material and creating a hole.
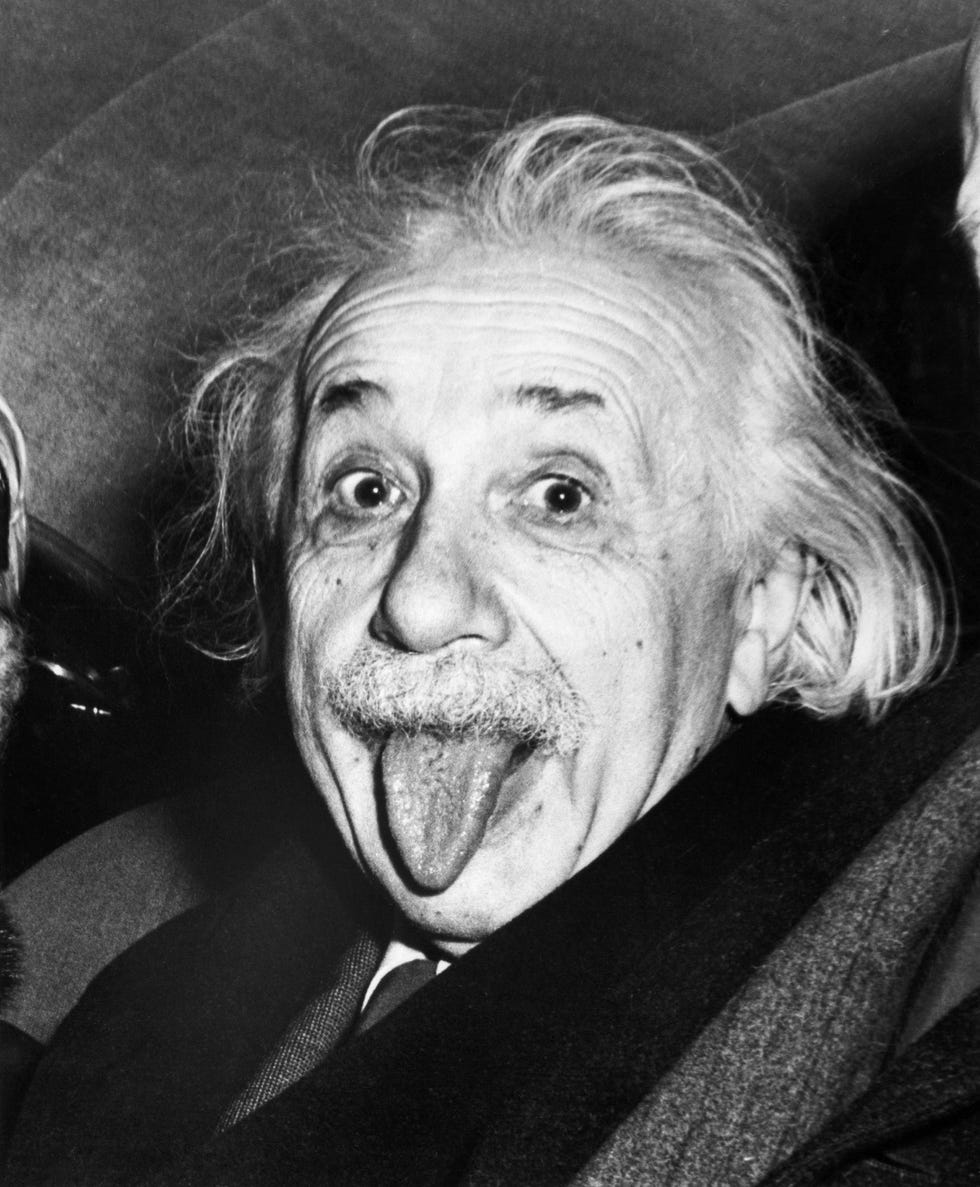

One of the most recognizable photos of the 20 th century shows Einstein sticking out his tongue while leaving his 72 nd birthday party on March 14, 1951.
According to Discovery.com , Einstein was leaving his party at Princeton when a swarm of reporters and photographers approached and asked him to smile. Tired from doing so all night, he refused and rebelliously stuck his tongue out at the crowd for a moment before turning away. UPI photographer Arthur Sasse captured the shot.
Einstein was amused by the picture and ordered several prints to give to his friends. He also signed a copy of the photo that sold for $125,000 at a 2017 auction.
Einstein died on April 18, 1955, at age 76 at the University Medical Center at Princeton. The previous day, while working on a speech to honor Israel’s seventh anniversary, Einstein suffered an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
He was taken to the hospital for treatment but refused surgery, believing that he had lived his life and was content to accept his fate. “I want to go when I want,” he stated at the time. “It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.”
According to the BBC, Einstein muttered a few words in German at the moment of his death. However, the nurse on duty didn’t speak German so their translation was lost forever.
In a 2014 interview , Life magazine photographer Ralph Morse said the hospital was swarmed by journalists, photographers, and onlookers once word of Einstein’s death spread. Morse decided to travel to Einstein’s office at the Institute for Advanced Studies, offering the superintendent alcohol to gain access. He was able to photograph the office just as Einstein left it.
After an autopsy, Einstein’s corpse was moved to a Princeton funeral home later that afternoon and then taken to Trenton, New Jersey, for a cremation ceremony. Morse said he was the only photographer present for the cremation, but Life managing editor Ed Thompson decided not to publish an exclusive story at the request of Einstein’s son Hans.
During Einstein’s autopsy, pathologist Thomas Stoltz Harvey had removed his brain, reportedly without his family’s consent, for preservation and future study by doctors of neuroscience.
However, during his life, Einstein participated in brain studies, and at least one biography claimed he hoped researchers would study his brain after he died. Einstein’s brain is now located at the Princeton University Medical Center. In keeping with his wishes, the rest of his body was cremated and the ashes scattered in a secret location.
In 1999, Canadian scientists who were studying Einstein’s brain found that his inferior parietal lobe, the area that processes spatial relationships, 3D-visualization, and mathematical thought, was 15 percent wider than in people who possess normal intelligence. According to The New York Times , the researchers believe it might help explain why Einstein was so intelligent.
In 2011, the Mütter Museum in Philadelphia received thin slices of Einstein’s brain from Dr. Lucy Rorke-Adams, a neuropathologist at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and put them on display. Rorke-Adams said she received the brain slides from Harvey.
Since Einstein’s death, a veritable mountain of books have been written on the iconic thinker’s life, including Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson and Einstein: A Biography by Jürgen Neffe, both from 2007. Einstein’s own words are presented in the collection The World As I See It .
Einstein has also been portrayed on screen. Michael Emil played a character called “The Professor,” clearly based on Einstein, in the 1985 film Insignificance —in which alternate versions of Einstein, Marilyn Monroe , Joe DiMaggio , and Joseph McCarthy cross paths in a New York City hotel.
Walter Matthau portrayed Einstein in the fictional 1994 comedy I.Q. , in which he plays matchmaker for his niece played by Meg Ryan . Einstein was also a character in the obscure comedy films I Killed Einstein, Gentlemen (1970) and Young Einstein (1988).
A much more historically accurate depiction of Einstein came in 2017, when he was the subject of the first season of Genius , a 10-part scripted miniseries by National Geographic. Johnny Flynn played a younger version of the scientist, while Geoffrey Rush portrayed Einstein in his later years after he had fled Germany. Ron Howard was the director.
Tom Conti plays Einstein in the 2023 biopic Oppenheimer , directed by Christopher Nolan and starring Cillian Murphy as scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer during his involvement with the Manhattan Project.
- The world is a dangerous place to live; not because of the people who are evil, but because of the people who don’t do anything about it.
- A question that sometimes drives me hazy: Am I or are the others crazy?
- A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new.
- Logic will get you from A to B. Imagination will take you everywhere.
- I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly.
- If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough.
- Nature shows us only the tail of the lion. But there is no doubt in my mind that the lion belongs with it even if he cannot reveal himself to the eye all at once because of his huge dimension. We see him only the way a louse sitting upon him would.
- [T]he distinction between past, present, and future is only an illusion, however persistent.
- Living in this “great age,” it is hard to understand that we belong to this mad, degenerate species, which imputes free will to itself. If only there were somewhere an island for the benevolent and the prudent! Then also I would want to be an ardent patriot.
- I, at any rate, am convinced that He [God] is not playing at dice.
- How strange is the lot of us mortals! Each of us is here for a brief sojourn; for what purpose he knows not, though he sometimes thinks he senses it.
- I regard class differences as contrary to justice and, in the last resort, based on force.
- I have never looked upon ease and happiness as ends in themselves—this critical basis I call the ideal of a pigsty. The ideals that have lighted my way, and time after time have given me new courage to face life cheerfully, have been Kindness, Beauty, and Truth.
- My political ideal is democracy. Let every man be respected as an individual and no man idolized. It is an irony of fate that I myself have been the recipient of excessive admiration and reverence from my fellow-beings, through no fault and no merit of my own.
- The most beautiful experience we can have is the mysterious. It is the fundamental emotion that stands at the cradle of true art and true science. Whoever does not know it and can no longer wonder, no longer marvel, is as good as dead, and his eyes are dimmed.
- An autocratic system of coercion, in my opinion, soon degenerates. For force always attracts men of low morality, and I believe it to be an invariable rule that tyrants of genius are succeeded by scoundrels.
- My passionate interest in social justice and social responsibility has always stood in curious contrast to a marked lack of desire for direct association with men and women. I am a horse for single harness, not cut out for tandem or team work. I have never belonged wholeheartedly to country or state, to my circle of friends, or even to my own family.
- Everybody is a genius.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams.
Nobel Prize Winners

Chien-Shiung Wu

The Solar Eclipse That Made Albert Einstein a Star

14 Hispanic Women Who Have Made History

Marie Curie

Martin Luther King Jr.

Henry Kissinger

Malala Yousafzai

Jimmy Carter

10 Famous Poets Whose Enduring Works We Still Read

22 Famous Scientists You Should Know

Wole Soyinka
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Albert Einstein
By: History.com Editors
Updated: May 16, 2019 | Original: October 27, 2009

The German-born physicist Albert Einstein developed the first of his groundbreaking theories while working as a clerk in the Swiss patent office in Bern. After making his name with four scientific articles published in 1905, he went on to win worldwide fame for his general theory of relativity and a Nobel Prize in 1921 for his explanation of the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. An outspoken pacifist who was publicly identified with the Zionist movement, Einstein emigrated from Germany to the United States when the Nazis took power before World War II. He lived and worked in Princeton, New Jersey, for the remainder of his life.
Einstein’s Early Life (1879-1904)
Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich. As a child, Einstein became fascinated by music (he played the violin), mathematics and science. He dropped out of school in 1894 and moved to Switzerland, where he resumed his schooling and later gained admission to the Swiss Federal Polytechnic Institute in Zurich. In 1896, he renounced his German citizenship, and remained officially stateless before becoming a Swiss citizen in 1901.
Did you know? Almost immediately after Albert Einstein learned of the atomic bomb's use in Japan, he became an advocate for nuclear disarmament. He formed the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists and backed Manhattan Project scientist J. Robert Oppenheimer in his opposition to the hydrogen bomb.
While at Zurich Polytechnic, Einstein fell in love with his fellow student Mileva Maric, but his parents opposed the match and he lacked the money to marry. The couple had an illegitimate daughter, Lieserl, born in early 1902, of whom little is known. After finding a position as a clerk at the Swiss patent office in Bern, Einstein married Maric in 1903; they would have two more children, Hans Albert (born 1904) and Eduard (born 1910).
Einstein’s Miracle Year (1905)
While working at the patent office, Einstein did some of the most creative work of his life, producing no fewer than four groundbreaking articles in 1905 alone. In the first paper, he applied the quantum theory (developed by German physicist Max Planck) to light in order to explain the phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect, by which a material will emit electrically charged particles when hit by light. The second article contained Einstein’s experimental proof of the existence of atoms, which he got by analyzing the phenomenon of Brownian motion, in which tiny particles were suspended in water.
In the third and most famous article, titled “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies,” Einstein confronted the apparent contradiction between two principal theories of physics: Isaac Newton’s concepts of absolute space and time and James Clerk Maxwell’s idea that the speed of light was a constant. To do this, Einstein introduced his special theory of relativity, which held that the laws of physics are the same even for objects moving in different inertial frames (i.e. at constant speeds relative to each other), and that the speed of light is a constant in all inertial frames. A fourth paper concerned the fundamental relationship between mass and energy, concepts viewed previously as completely separate. Einstein’s famous equation E = mc2 (where “c” was the constant speed of light) expressed this relationship.
From Zurich to Berlin (1906-1932)
Einstein continued working at the patent office until 1909, when he finally found a full-time academic post at the University of Zurich. In 1913, he arrived at the University of Berlin, where he was made director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. The move coincided with the beginning of Einstein’s romantic relationship with a cousin of his, Elsa Lowenthal, whom he would eventually marry after divorcing Mileva. In 1915, Einstein published the general theory of relativity, which he considered his masterwork. This theory found that gravity, as well as motion, can affect time and space. According to Einstein’s equivalence principle–which held that gravity’s pull in one direction is equivalent to an acceleration of speed in the opposite direction–if light is bent by acceleration, it must also be bent by gravity. In 1919, two expeditions sent to perform experiments during a solar eclipse found that light rays from distant stars were deflected or bent by the gravity of the sun in just the way Einstein had predicted.
The general theory of relativity was the first major theory of gravity since Newton’s, more than 250 years before, and the results made a tremendous splash worldwide, with the London Times proclaiming a “Revolution in Science” and a “New Theory of the Universe.” Einstein began touring the world, speaking in front of crowds of thousands in the United States, Britain, France and Japan. In 1921, he won the Nobel Prize for his work on the photoelectric effect, as his work on relativity remained controversial at the time. Einstein soon began building on his theories to form a new science of cosmology, which held that the universe was dynamic instead of static, and was capable of expanding and contracting.
Einstein Moves to the United States (1933-39)
A longtime pacifist and a Jew, Einstein became the target of hostility in Weimar Germany, where many citizens were suffering plummeting economic fortunes in the aftermath of defeat in the Great War. In December 1932, a month before Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany, Einstein made the decision to emigrate to the United States, where he took a position at the newly founded Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey . He would never again enter the country of his birth.
By the time Einstein’s wife Elsa died in 1936, he had been involved for more than a decade with his efforts to find a unified field theory, which would incorporate all the laws of the universe, and those of physics, into a single framework. In the process, Einstein became increasingly isolated from many of his colleagues, who were focused mainly on the quantum theory and its implications, rather than on relativity.
Einstein’s Later Life (1939-1955)
In the late 1930s, Einstein’s theories, including his equation E=mc2, helped form the basis of the development of the atomic bomb. In 1939, at the urging of the Hungarian physicist Leo Szilard, Einstein wrote to President Franklin D. Roosevelt advising him to approve funding for the development of uranium before Germany could gain the upper hand. Einstein, who became a U.S. citizen in 1940 but retained his Swiss citizenship, was never asked to participate in the resulting Manhattan Project , as the U.S. government suspected his socialist and pacifist views. In 1952, Einstein declined an offer extended by David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s premier, to become president of Israel .
Throughout the last years of his life, Einstein continued his quest for a unified field theory. Though he published an article on the theory in Scientific American in 1950, it remained unfinished when he died, of an aortic aneurysm, five years later. In the decades following his death, Einstein’s reputation and stature in the world of physics only grew, as physicists began to unravel the mystery of the so-called “strong force” (the missing piece of his unified field theory) and space satellites further verified the principles of his cosmology.

HISTORY Vault: Secrets of Einstein's Brain
Originally stolen by the doctor trusted to perform his autopsy, scientists over the decades have examined the brain of Albert Einstein to try and determine what made this seemingly normal man tick.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Biography Online

Albert Einstein Biography

Einstein is also well known as an original free-thinker, speaking on a range of humanitarian and global issues. After contributing to the theoretical development of nuclear physics and encouraging F.D. Roosevelt to start the Manhattan Project, he later spoke out against the use of nuclear weapons.
Born in Germany to Jewish parents, Einstein settled in Switzerland and then, after Hitler’s rise to power, the United States. Einstein was a truly global man and one of the undisputed genius’ of the Twentieth Century.
Early life Albert Einstein
Einstein was born 14 March 1879, in Ulm the German Empire. His parents were working-class (salesman/engineer) and non-observant Jews. Aged 15, the family moved to Milan, Italy, where his father hoped Albert would become a mechanical engineer. However, despite Einstein’s intellect and thirst for knowledge, his early academic reports suggested anything but a glittering career in academia. His teachers found him dim and slow to learn. Part of the problem was that Albert expressed no interest in learning languages and the learning by rote that was popular at the time.
“School failed me, and I failed the school. It bored me. The teachers behaved like Feldwebel (sergeants). I wanted to learn what I wanted to know, but they wanted me to learn for the exam.” Einstein and the Poet (1983)
At the age of 12, Einstein picked up a book on geometry and read it cover to cover. – He would later refer to it as his ‘holy booklet’. He became fascinated by maths and taught himself – becoming acquainted with the great scientific discoveries of the age.

Albert Einstein with wife Elsa
Despite Albert’s independent learning, he languished at school. Eventually, he was asked to leave by the authorities because his indifference was setting a bad example to other students.
He applied for admission to the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. His first attempt was a failure because he failed exams in botany, zoology and languages. However, he passed the next year and in 1900 became a Swiss citizen.
At college, he met a fellow student Mileva Maric, and after a long friendship, they married in 1903; they had two sons before divorcing several years later.
In 1896 Einstein renounced his German citizenship to avoid military conscription. For five years he was stateless, before successfully applying for Swiss citizenship in 1901. After graduating from Zurich college, he attempted to gain a teaching post but none was forthcoming; instead, he gained a job in the Swiss Patent Office.
While working at the Patent Office, Einstein continued his own scientific discoveries and began radical experiments to consider the nature of light and space.

Einstein in 1921
He published his first scientific paper in 1900, and by 1905 had completed his PhD entitled “ A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions . In addition to working on his PhD, Einstein also worked feverishly on other papers. In 1905, he published four pivotal scientific works, which would revolutionise modern physics. 1905 would later be referred to as his ‘ annus mirabilis .’
Einstein’s work started to gain recognition, and he was given a post at the University of Zurich (1909) and, in 1911, was offered the post of full-professor at the Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague (which was then part of Austria-Hungary Empire). He took Austrian-Hungary citizenship to accept the job. In 1914, he returned to Germany and was appointed a director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics. (1914–1932)
Albert Einstein’s Scientific Contributions
Quantum Theory
Einstein suggested that light doesn’t just travel as waves but as electric currents. This photoelectric effect could force metals to release a tiny stream of particles known as ‘quanta’. From this Quantum Theory, other inventors were able to develop devices such as television and movies. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921.
Special Theory of Relativity
This theory was written in a simple style with no footnotes or academic references. The core of his theory of relativity is that:
“Movement can only be detected and measured as relative movement; the change of position of one body in respect to another.”
Thus there is no fixed absolute standard of comparison for judging the motion of the earth or plants. It was revolutionary because previously people had thought time and distance are absolutes. But, Einstein proved this not to be true.
He also said that if electrons travelled at close to the speed of light, their weight would increase.
This lead to Einstein’s famous equation:
Where E = energy m = mass and c = speed of light.
General Theory of Relativity 1916
Working from a basis of special relativity. Einstein sought to express all physical laws using equations based on mathematical equations.
He devoted the last period of his life trying to formulate a final unified field theory which included a rational explanation for electromagnetism. However, he was to be frustrated in searching for this final breakthrough theory.
Solar eclipse of 1919
In 1911, Einstein predicted the sun’s gravity would bend the light of another star. He based this on his new general theory of relativity. On 29 May 1919, during a solar eclipse, British astronomer and physicist Sir Arthur Eddington was able to confirm Einstein’s prediction. The news was published in newspapers around the world, and it made Einstein internationally known as a leading physicist. It was also symbolic of international co-operation between British and German scientists after the horrors of the First World War.
In the 1920s, Einstein travelled around the world – including the UK, US, Japan, Palestine and other countries. Einstein gave lectures to packed audiences and became an internationally recognised figure for his work on physics, but also his wider observations on world affairs.
Bohr-Einstein debates
During the 1920s, other scientists started developing the work of Einstein and coming to different conclusions on Quantum Physics. In 1925 and 1926, Einstein took part in debates with Max Born about the nature of relativity and quantum physics. Although the two disagreed on physics, they shared a mutual admiration.
As a German Jew, Einstein was threatened by the rise of the Nazi party. In 1933, when the Nazi’s seized power, they confiscated Einstein’s property, and later started burning his books. Einstein, then in England, took an offer to go to Princeton University in the US. He later wrote that he never had strong opinions about race and nationality but saw himself as a citizen of the world.
“I do not believe in race as such. Race is a fraud. All modern people are the conglomeration of so many ethnic mixtures that no pure race remains.”
Once in the US, Einstein dedicated himself to a strict discipline of academic study. He would spend no time on maintaining his dress and image. He considered these things ‘inessential’ and meant less time for his research. Einstein was notoriously absent-minded. In his youth, he once left his suitcase at a friends house. His friend’s parents told Einstein’s parents: “ That young man will never amount to anything, because he can’t remember anything.”
Although a bit of a loner, and happy in his own company, he had a good sense of humour. On January 3, 1943, Einstein received a letter from a girl who was having difficulties with mathematics in her studies. Einstein consoled her when he wrote in reply to her letter
“Do not worry about your difficulties in mathematics. I can assure you that mine are still greater.”
Einstein professed belief in a God “Who reveals himself in the harmony of all being”. But, he followed no established religion. His view of God sought to establish a harmony between science and religion.
“Science without religion is lame, religion without science is blind.”
– Einstein, Science and Religion (1941)
Politics of Einstein
Einstein described himself as a Zionist Socialist. He did support the state of Israel but became concerned about the narrow nationalism of the new state. In 1952, he was offered the position as President of Israel, but he declined saying he had:
“neither the natural ability nor the experience to deal with human beings.” … “I am deeply moved by the offer from our State of Israel, and at once saddened and ashamed that I cannot accept it.”

Einstein receiving US citizenship.
Albert Einstein was involved in many civil rights movements such as the American campaign to end lynching. He joined the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) and considered racism, America’s worst disease. But he also spoke highly of the meritocracy in American society and the value of being able to speak freely.
On the outbreak of war in 1939, Einstein wrote to President Roosevelt about the prospect of Germany developing an atomic bomb. He warned Roosevelt that the Germans were working on a bomb with a devastating potential. Roosevelt headed his advice and started the Manhattan project to develop the US atom bomb. But, after the war ended, Einstein reverted to his pacifist views. Einstein said after the war.
“Had I known that the Germans would not succeed in producing an atomic bomb, I would not have lifted a finger.” (Newsweek, 10 March 1947)
In the post-war McCarthyite era, Einstein was scrutinised closely for potential Communist links. He wrote an article in favour of socialism, “Why Socialism” (1949) He criticised Capitalism and suggested a democratic socialist alternative. He was also a strong critic of the arms race. Einstein remarked:
“I do not know how the third World War will be fought, but I can tell you what they will use in the Fourth—rocks!”

Rabindranath Tagore and Einstein
Einstein was feted as a scientist, but he was a polymath with interests in many fields. In particular, he loved music. He wrote that if he had not been a scientist, he would have been a musician. Einstein played the violin to a high standard.
“I often think in music. I live my daydreams in music. I see my life in terms of music… I get most joy in life out of music.”
Einstein died in 1955, at his request his brain and vital organs were removed for scientific study.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “ Biography of Albert Einstein ”, Oxford, www.biographyonline.net 23 Feb. 2008. Updated 2nd March 2017.
Albert Einstein – His Life and Universe

Albert Einstein – His Life at Amazon
Related pages

53 Interesting and unusual facts about Albert Einstein.

19 Comments
Albert E is awesome! Thanks for this website!!
- January 11, 2019 3:00 PM
Albert Einstein is the best scientist ever! He shall live forever!
- January 10, 2019 4:11 PM
very inspiring
- December 23, 2018 8:06 PM
Wow it is good
- December 08, 2018 10:14 AM
Thank u Albert for discovering all this and all the wonderful things u did!!!!
- November 15, 2018 7:03 PM
- By Madalyn Silva
Thank you so much, This biography really motivates me a lot. and I Have started to copy of Sir Albert Einstein’s habit.
- November 02, 2018 3:37 PM
- By Ankit Gupta
Sooo inspiring thanks Albert E. You helped me in my report in school I love you Albert E. 🙂 <3
- October 17, 2018 4:39 PM
- By brooklynn
By this inspired has been I !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- October 12, 2018 4:25 PM
- By Richard Clarlk
Biography: Albert Einstein
- Famous Inventions
- Famous Inventors
- Patents & Trademarks
- Invention Timelines
- Computers & The Internet
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
Legendary scientist Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) first gained worldwide prominence in 1919 after British astronomers verified predictions of Einstein's general theory of relativity through measurements taken during a total eclipse. Einstein's theories expanded upon universal laws formulated by physicist Isaac Newton in the late seventeenth century.
Before E=MC2
Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child. The compass convinced him that there had to be "something behind things, something deeply hidden."
Even as a small boy Einstein was self-sufficient and thoughtful. According to one account, he was a slow talker, often pausing to consider what he would say next. His sister would recount the concentration and perseverance with which he would build houses of cards.
Einstein's first job was that of patent clerk. In 1933, he joined the staff of the newly created Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey. He accepted this position for life, and lived there until his death. Einstein is probably familiar to most people for his mathematical equation about the nature of energy, E = MC2.
E = MC2, Light and Heat
The formula E=MC2 is probably the most famous calculation from Einstein's special theory of relativity . The formula basically states that energy (E) equals mass (m) times the speed of light (c) squared (2). In essence, it means mass is just one form of energy. Since the speed of light squared is an enormous number, a small amount of mass can be converted to a phenomenal amount of energy. Or if there's a lot of energy available, some energy can be converted to mass and a new particle can be created. Nuclear reactors, for instance, work because nuclear reactions convert small amounts of mass into large amounts of energy.
Einstein wrote a paper based on the new understanding of the structure of light. He argued that light can act as though it consists of discrete, independent particles of energy similar to particles of a gas. A few years before, Max Planck's work had contained the first suggestion of discrete particles in energy. Einstein went far beyond this though and his revolutionary proposal seemed to contradict the universally accepted theory that light consists of smoothly oscillating electromagnetic waves. Einstein showed that light quanta, as he called the particles of energy, could help to explain phenomena being studied by experimental physicists. For example, he explained how light ejects electrons from metals.
While there was a well-known kinetic energy theory that explained heat as an effect of the ceaseless motion of atoms, it was Einstein who proposed a way to put the theory to a new and crucial experimental test. If tiny but visible particles were suspended in a liquid, he argued, the irregular bombardment by the liquid's invisible atoms should cause the suspended particles to move in a random jittering pattern. This should be observable through a microscope. If the predicted motion is not seen, the whole kinetic theory would be in grave danger. But such a random dance of microscopic particles had long since been observed. With the motion demonstrated in detail, Einstein had reinforced the kinetic theory and created a powerful new tool for studying the movement of atoms.
- Biography of Albert Einstein, Theoretical Physicist
- The Life and Work of Albert Einstein
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity
- Fundamental Physical Constants
- What Is a Photon in Physics?
- Introduction to the Major Laws of Physics
- Quantum Physics Overview
- 10 Things You Don't Know About Albert Einstein
- Top 10 Weird but Cool Physics Ideas
- Photon Definition
- Wave Particle Duality and How It Works
- A Brief History of Atomic Theory
- What Is a Boson?
- Photoelectric Effect: Electrons from Matter and Light
- Albert Einstein Printables
Best Books Hub
Reviews of The Best Books on Every Subject
20 Best Books on Albert Einstein (2022 Review)
September 16, 2020 by James Wilson

DISCLOSURE: This post may contain affiliate links, meaning when you click the links and make a purchase, I receive a commission. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Albert Einstein was an intelligent man who discovered groundbreaking theories. He was a german who changed the world of physics. He created the theory of relativity. He’s done so much for physicists and the world. His death was nearly a centennial, yet he’s still one of the most notable, if not the most notable, physicist to this day. He has done amazing work, but people just see him as the crazy smart physicist with wacky hair. Where did he grow up? What was his life like? What did he do to achieve his success?
What are the Best Albert Einstein Books to read?

These are some questions that the following 20 books can answer. This book discusses Einstein’s incredible achievements, but they also discuss the rest of his history. He was more than just a physicist. He did a lot of great work. These books will delve into just what he did, and the impact he has made.
Best Books on Albert Einstein: Our Top 20 Picks
Here are some of the best Albert Einstein books that you can consider to expand your knowledge on the subject:
1. Moonwalking with Einstein: The Art and Science of Remembering Everything

Moonwalking with Einstein: The Art and Science of Remembering Everything by Joshua Foer is not really about Einstein at all. This book is actually about memory techniques, and applying them to everyday life. The book draws inspiration from Foer who used this research to help his own memory. He does plenty of research in this book that helps back his claims.
The book is mostly about memory athletics. This is a very engaging book. It keeps readers drawn in and entertained. The book mixes the tips on memory techniques with stories about them. This book has a lot of incredible information, but it only includes a few techniques. It is more about the experience than it is about the advice.
- Authors : Joshua Foer (Author)
- Publisher : Penguin Books; Reprint Edition (February 28, 2012)
- Pages : 307 pages
2. Einstein: His Life and Universe

Albert Einstein was a noble man who did a lot of work. He was underappreciated during this time. After his death, the importance of his work was realized. He is one of the world’s greatest physicists. Einstein: His Life and Universe by Walter Isaacson discusses the life of Einstein and all of his achievements.
This book was based on personal letters that Albert Einstein wrote himself. Albert Einstein was not a “go with the flow” kind of guy. He questioned everything. He also sought the truth. This book is all about the way Einstein thought. It also discusses his personal life. He was a struggling father, the creator of the cosmos, and a true genius. This book is a great history of Albert Einstein that includes his own point of view.
- Authors : Walter Isaacson (Author)
- Publisher : Simon & Schuster; 1st Edition (April 10, 2007)
- Pages : 675 pages
3. Relativity: The Special and General Theory

The theory of relativity is arguably Albert Einstein’s greatest achievement. He did a lot of research, and spent countless hours discovering new information on physics. Relativity: The Special and General Theory by Albert Einstein is about Einstein’s process in discovering the theory of relativity. The good gives the basis for the many theories of relativity that Einstein worked with.
This book wasn’t really about Einstein’s life. It’s more about the science he pursued and the work he did. He explains it very well, but non-physicists may have a hard time grasping what Einstein is saying. This is a complicated read, but it’s very informative and has a lot of great knowledge. This is a wonderful read for those who appreciate Einstein and want to know more about his research.
- Authors : Albert Einstein (Author)
- Publisher : Dover Publications; Illustrated Edition (October 18, 2010)
- Pages : 192 pages
4. Einstein’s Dreams

Albert Einstein was an incredible man with deep, thoughtful ideas. Einstein’s Dream by Alan Lightman is a fictional collage of stories that Einstein dreamed up. This work puts a different light on Einstein and the work he did. It takes his importance to a new level. LIghtman was clever to think up this book. It’s interesting, intriguing, and fun. It’s a fairly quick read. It feels like no time goes by when reading this book.
This book is fiction, but it is based on Einstein and research that has been done on him. Historical fiction is great because it’s interesting, yet still educational and informed. This book will help readers have exciting, stimulating, and beautiful dreams. This book is thought-provoking, yet informative. Anyone who loves Albert Einstein will love this book.
- Authors : Alan Lightman (Author)
- Publisher : Vintage; Illustrated Edition (November 9, 2004)
- Pages : 144 pages
5. Who Was Albert Einstein?

Albert Einstein was a great man who did great work. Who Was Albert Einstein? By Jess Bralier is the perfect book for kids wanting to learn about Einstein and his work. The book is an easy read for kids, and does a great job of explaining who Einstein was. The book is funny and engaging. Kids will laugh and smile as they read about Einstein’s life.
This book is particularly perfect for essay assignments on Einstein. Kids will get to know every aspect of his life in an easy to read way. This is good read for young kids, too. Kids as young as seven can read this book and understand what it is saying. This is a wonderful chapter book that is fun, enlightening, and wonderful for kids of all ages. Einstein would be happy to know kids take an interest in him with this book.
- Authors : Jess Brallier (Author), Who HQ (Author), Robert Andrew Parker (Illustrator)
- Publisher : Penguin Workshop; Illustrated Edition (February 18, 2002)
- Pages : 112 pages
6. The World As I See It

Albert Einstein was known best as a physicist, but he was also a writer. The World As I See It by Albert Einstein is a book full of Einstein’s writings. He was a thoughtful man who was both charming and witty. He was perceptive and cared about the world.
This book is great, but it is edited down from Einstein’s original work. It picks and chooses what is shared, so it doesn’t include the full story. Where there are problems, there are also benefits. Because this book is editing down, it is a quick and simple read. It is interesting and contains easy language. The content of the book is great, but there are many grammatical errors that clutter the story and make it incomprehensible at times.
- Publisher : CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (January 2, 2014)
- Pages : 108 pages
7. I Am Albert Einstein

I Am Albert Einstein by Brad Meltzer is a great kids book about Einstein. The book has lots of great illustrations that accompany the biography. The book discusses Einstein’s childhood, a part of his life that kids can relate to. This book is a quick and easy read. Kids of all ages can enjoy this book, but it’s particularly great for kids aged five- eight. This book is non-fiction, but it reads like fiction. This is a great bedtime story for children that is also highly educational.
This book is part of a series on many other historical figures who did great things. The series does a great job of introducing kids to the people who shaped history, and explaining just what they did. This is a very fun read. It has great pictures and great information.
- Authors : Brad Meltzer (Author), Christopher Eliopoulos (Illustrator)
- Publisher : Dial Books (September 16, 2014)
- Pages : 40 pages
8. Ideas and Opinions

Ideas and Opinions by Albert Einstein is a book full of Einstein’s essays. This book includes essays for all parts of his life. The essays are full of all kinds of topics with all kinds of opinions. Einstein discusses relativity, war and peace, human rights, government, religion, science, and economics. These are some of Einstein’s most popular essays gathered in one place. Einstein has a lot of great perspectives.
This book goes to show how brilliant of a mind Einstein was. Einstein even goes on to explain the meaning of life, or what he considers the meaning of life. Einsteins was a brilliant physicist, but he was also a humanist with a large heart, and many thoughtful opinions. Anyone interested in learning about Einstein should read his essays first. They truly grasp his personality and who he was as a person.
- Publisher : Broadway Books; 3rd ed. Edition (June 6, 1995)
- Pages : 384 pages
9. Learn Like Einstein

Albert Einstein had one of the greatest minds in the world. Many others wish for that same mind. Learn Like Einstein by Peter Hollins is a book that does, in fact, helps readers learn like Einstein. This book focuses on tips for learning, studying, and memorizing information. Of course, it doesn’t actually give readers Einstein’s brain, but it bases studying habits on how he learned. This book can help readers increase their reading speed, improve focus and concentration, practice memory techniques created by experts, and cram information in the right way.
This book explores different learning methods and how people learn the way they do. The book looks into learning with music, learning through listening and movement, and how note taking can actually be a disadvantage when studying. This is the perfect book for those who have faulty memory and have a hard time studying for tests. The book is full of plenty of great tips that will help students who failed their past test, ace the next one.
- Authors : Peter Hollins (Author)
- Publisher : PH Learning Inc. (March 18, 2017)
- Pages : 162 pages
10. When Einstein Walked with Godel: Excursions to the Edge of Thought

When Einstein Walked with Godel: Excursion to the Edge of Thought by Jim Holt is more about the scientific aspect of Einstein’s life, and questions it poses today. The book addresses questions like “does time exist?” and “what is infinity?” This book helps readers explore the human mind, the cosmos, and more. Holt explains physics through humor and logic.
This book is informative and interesting. He uses sketches, experiments, and examples to help explain physics and Einstein’s work. The book has many essays on math, physics, and science. It is a lot of great information, but non-scientists should hold off on reading it, because the language is a bit complicated.
- Authors : Jim Holt (Author)
- Publisher : Farrar, Straus and Giroux; First Edition, First Printing (May 15, 2018)
11. Einstein’s Unfinished Revolution: The Search for What Lies Beyond the Quantum

Albert Einstein’s research on the theories of relativity and in quantum physics in general has changed the world of science. Einstein’s Unfinished Revolution: The Search for What Lies Beyond the Quantum is a book about another man’s research, Lee Smolin. Smolin has researched quantum physics and believes that some of the problems they face are unsolvable. This book has all kinds of information on physics.
The book is full of puzzles, stories, experiments, and so much more. This book delves into the fun part of physics: the labs. This book aims to complete the work Einstein created, and argues that completing his work should be a top priority. There are many quantum problems that the world faces. By working with Einstein’s previous work and creating new work, those problems could be solved.
- Authors : Lee Smolin (Author)
- Publisher : Penguin Press; Illustrated Edition (April 9, 2019)
- Pages : 352 pages
12. Einstein and the Quantum: The Quest of the Valiant Swabian

Einstein and the Quantum: The Quest of the Valiant Swabian by A. Douglas Stone is about the significance of Albert Einstein and his research. The book discusses Einstein’s relationships with quantum mechanics, religion, and more. The book is a combination of physics, biography, and science.
The book gives a glimpse into his life and how his personal relationships affected his science. Stone has so done so much research on Einstein and truly shares the person he was to the best of his ability. This book doesn’t diminish him to his work, but also discusses the person behind it. Albert Einstein was essential to the evolution of science, and Stone proves it with this book. This book is not too complicated of a read, and is actually very interesting. It’s a little long, but definitely worth the read.
- Authors : A. Douglas Stone (Author, Preface)
- Publisher : Princeton University Press; Revised Edition (October 6, 2015)
- Pages : 344 pages
13. Simply Einstein: Relativity Demystified

Simply Einstein: Relativity Demystified by Richard Wolfson is a book about relativity that is easy to read. This book was not created for physicists. In fact, it was made for everyone but. Wolfson is a physicist himself. With this book, he aims to explain different elements of physics and the ideas that are associated with them. Wolfson explains time travel, black holes, curved space, and more in this book. He was everyone to have an idea of how physics works. He answers many commonly asked questions.
This book isn’t easy to read, but it is much simpler than many other physics books. The language isn’t too complicated. It is a great book for beginners, and anyone else who wants to know about Einstein, physics, and the theory of relativity.
- Authors : Richard Wolfson (Author)
- Publisher : W. W. Norton & Company; Illustrated Edition (November 17, 2003)
- Pages : 288 pages
14. Relativity: The Special and the General Theory

Relativity: The Special and the General Theory by Albert Einstein is on its 100th anniversary edition. The book was written by Einstein, but this edition has commentary from Hanoch Gutfreund and Jürgen Renn. Einstein wrote this book for popular audiences. His intent was to explain relativity to modern audiences who wouldn’t ordinarily understand it. He wanted everyone to understand his work, not just physicists.
This book has an introduction, and an analysis of Einstein’s work that is contributed by Gutfreund and Renn. This book is the perfect read for curious minds who love Einstein. This book is very helpful for understanding Einstein and the work he did. He was a brilliant man who wanted everyone to understand him.
- Authors : Albert Einstein (Author), Hanoch Gutfreund (Commentary), Jürgen Renn (Commentary)
- Publisher : Princeton University Press; 100th Anniversary ed. Edition (June 16, 2015)
- Pages : 320 pages
15. Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein’s General Relativity

Gravity: An Introduction to Einstein’s General Relativity by James B. Hartie is an introduction to general relativity and the work of Einstein. This book is informative and thought-provoking. It is the perfect book for physics professors to use as their class textbook. The book has information on Einstein, but also on physics in general. The book is the perfect combination of math and science.
This book includes discussions on many topics: The Global Positioning System, black holes, X-ray sources, pulsars, quasars, the Big Bang, gravitational waves, and more. This book is super informative. It has lots of knowledge on physics that goes into depth on all of the topics. This book can be boring at times, but it is certainly not under-researched.
- Authors : James Hartle (Author)
- Publisher : Pearson (December 26, 2002)
- Pages : 608 pages
16. The Ultimate Quotable Einstein

Albert Einstein was a notable man who said a lot of great things. The Ultimate Quotable Einstein by Alice Calaprice includes some of the best quotes Einstein said. The book is full of 1,600 quotes that came from the brilliant mind of Einstein. The books fall understand different topics, like “On Race and Prejudice,” and “On and to Children.”
In addition to the many Einstein quotes this book has, it also has a chronology of Einstein’s life and achievements. This book is perfect for people who want to use an Einstein quote, but have no source to back it up. This book works perfectly for a “works cited” page in an essay. Instead of scouring through countless quotes, this book helps readers find and choose the best one for them.
- Authors : Albert Einstein (Author), Alice Calaprice (Editor), Freeman Dyson (Foreword)
- Publisher : Princeton University Press; Illustrated Edition (September 23, 2013)
17. Einstein’s War: How Relativity Triumphed Amid the Victorious Nationalism of World War I

Albert Einstein’s work spans wars, two of the most notable being World War I and World War II. Einstein’s War: How Relativity Triumphed Amid the Victorious Nationalism of World War I by Matthew Stanley discusses how Einstein’s work impacted World War I.
Even though Einstein is more associated with World War II, the first world war had a great deal in contributing to his success. It shaped him to be the person he was. During this war, Einstein was working on general relativity that helped blockading in Berlin. Even though he never fought, he did a lot of behind the scenes science work for the war. This book delves into the work Einstein did for the war. He did many notable things that would not have been possible without his position in the first world war.
- Authors : Matthew Stanley (Author)
- Publisher : Dutton; Illustrated Edition (May 21, 2019)
- Pages : 400 pages
18. Einstein’s Relativity and the Quantum Revolution: Modern Physics for Non-Scientists

Einstein’s Relativity and the Quantum Revolution: Modern Physics for Non- Scientists by Richard Wolfson and The Great Courses is an introduction to modern physics. The book is on its second edition, so it is up to date on all kinds of new information. The book is meant for non-scientists. It aims to help everyday people who don’t know about physics. This book makes complex concepts simple and easy to understand.
The book can be read, but it is also audible, so readers can enjoy listening to the actual lecture. This book is great for beginner scientists, and anyone who wants to understand physics and the work that Einstein spent his life committing to.
- Authors : Professor Richard Wolfson (Author)
19. Einstein: The Man, The Genius, and the Theory of Relativity

Albert Einstein was a great man of history. He spent his early years making science experiments in Germany before and the work he did when he moved to the United States. Einstein: The Man, The Genius, and the Theory of Relativity by Walter Issacson is all about Einstein’s life. This book discusses every aspect of Einstein’s life, from E= MC2 to his marriages and children.
The book isn’t too long, so it focuses on the highlights of Einstein’s life. Because of this, the book does not get too into depth into Einstein’s life. The book has lots of great information, but only scratches the surface on Einstein. The book has wonderful accompanying photos that help readers understand the content of the book in an interesting way.
- Publisher : Andre Deutsch; Illustrated Edition (August 7, 2018)
- Pages : 160 pages

20. Einstein on the Run: How Britain Saved The World’s Greatest Scientist

It is a known fact that Einstein is a German who lived in the United States. What is lesser known is the fact that he lived in Britain, too. Einstein on the Run: How Britain Saved the World’s Greatest Scientist by Andrew Robinson is about Einstein’s short residence in England. The place was a perfect refuge for Einstein against Nazi assasins.
The book recounts the work Einstein did in England, how the country saved his life, and why he eventually left. Einstein spent plenty of time in England, and almost became a citizen. But what changed? And what effect did it have on his science? These are the questions addressed in this book. Living in England wasn’t a huge part of Einstein’s life, but it was important.
- Authors : Andrew Robinson (Author)
- Publisher : Yale University Press; Illustrated Edition (October 8, 2019)
- Pages : 376 pages
Choosing the Best Albert Einstein Books
Albert Einstein was an incredible physicist, and an even more incredible man. He did amazing work with physics and science. When people hear E=MC2, they think of Einstein. He discovered the theory of relativity and changed the way people viewed and used physics. Einstein passed away in 1955, but he is still relevant in the world of science. He was a kind, empathetic soul who did amazing work. These books explain just the kind of man and he was, and helps readers understand him on a whole new level. They explain his history, his science, and best of all, they explain his character.

Subscribe To Email List
FREE Great Book Recommendations
Don't Miss Out On Books You Must Read
We won't send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time
Albert Einstein
- Occupation: Physicist
- Born: March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Germany
- Died: April 18, 1955 in Princeton, New Jersey
- Best known for: Founder of modern physics and the formula E=MC2
Overview and Interesting Facts

- His birthday, March 14, is also known as "Pi" day because 3/14 makes up the first three digits of the number pi (3.14).
- When a young Einstein was introduced to his new baby sister, he thought that she was a toy his parents had bought for him. After looking her over for a few minutes he responded "where are the wheels?"
- Einstein's parents initially wanted to name him "Abraham" but, according to Albert, they eventually thought the name sounded "too Jewish" and opted for another "A" name, "Albert."
- While working at the patent office, Einstein found he could get his daily job done in just a few hours. This left the rest of the day open for him to work on his own scientific theories.
- Einstein and two of his best friends formed a discussion group they jokingly called the Olympia Academy where they debated physics theories and philosophy.
- When his son Hans Albert announced that he wanted to be an engineer Einstein replied "I think it's a disgusting idea."
- In 1921, the United States Senate debated the Theory of Relativity while Einstein was visiting the United States.
- Einstein chose to exchange letters with Sigmund Freud in 1932 to discuss politics and war. Freud was also a known pacifist. Einstein suggested in his letters that the only way to end war was to have an international organization with more power than the current League of Nations.
- When Einstein discovered that the Germans had put a $5,000 bounty on his head he replied "I didn't know it was worth that much!"
- He once had a pet parrot named Bibo.
- The FBI gathered 1,427 pages of information while investigating Einstein to determine if he was a communist. Einstein wasn't a communist and no incriminating evidence was found. Oddly enough, Einstein did unknowingly have an affair with a Soviet spy. Fortunately for him, the FBI didn't discover the affair despite their ongoing investigation.
- When asked if he believed in immortality Einstein responded "No. And one life is enough for me."
- Einstein was once playing violin in a quartet that included a famous violin virtuoso. When Einstein's timing got off the frustrated virtuoso stopped playing and said "What's the matter professor, can't you count?"
- He nicknamed his violin Lina.
- Einstein loved to walk, but didn't drive. His wife Elsa once said "The professor does not drive. It's too complicated for him."

- Growing up Einstein
- Education, the Patent Office, and Marriage
- The Miracle Year
- Theory of General Relativity
- Academic Career and Nobel Prize
- Leaving Germany and World War II
- More Discoveries
- Later Life and Death
- Albert Einstein Quotes and Bibliography

The embodiment of genius and the pre-eminent scientist of the modern age, his theories and discoveries have profoundly affected the way people view and understand the world and their place in it. Einstein was also known as a philosopher and humanist who was keenly interested in and concerned about the affairs of the world.
His sagacious, wise, and humorous quotations, letters, and articles are widely used throughout popular culture as well as in historical and academic works. Einstein’s name and image are instantly recognizable everywhere in the world.
Albert Einstein was a theoretical physicist and the most famous scientist in human history. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics, alongside quantum mechanics. He is perhaps best known in popular culture for his mass/energy equivalence formula E=mc2. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his “services to theoretical physics”, and in particular his discovery of the photoelectric effect, a pivotal step in the evolution of quantum theory.
Einstein was born in Ulm, Germany on March 14, 1879. As a child, he exhibited an extraordinary curiosity for and understanding of the mysteries of science. The young Einstein also took music lessons, playing both violin and piano; stoking a passion for music that he maintained throughout his life. Moving first to Italy and then Switzerland, the young prodigy graduated from high school in 1896.
In 1905, while working as a patent clerk in Bern, Switzerland, Einstein had what came to be known as his “Annus Mirabilis” (miracle year). It was during this time that the young physicist obtained his Doctorate degree and published four of his most influential research papers, including the Special Theory of Relativity, the Photoelectric Effect, Brownian Motion, and Mass/Energy Equivalence, and his worldwide fame was assured. In 1915, Einstein completed his General Theory of Relativity, and brought to the world a fuller understanding of the interaction of space, time and gravity.
The practical applications of Einstein’s theories include the development of everyday and indispensable items such as Televisions, Remote Controls, Digital Cameras, and GPS tracking systems.
In 1999 Albert Einstein was recognized by TIME Magazine as the “Person of the Century”. Einstein’s intellect, along with his wise and passionate dedication to the causes of social justice and pacifism, left humanity with a fuller understanding of its place in the universe and with pioneering moral guidance for future generations.
32 fun and random facts about Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was much more than a scientific genius. From his political beliefs to his hatred of socks, here are 32 facts about Einstein you might not have heard before.

Albert Einstein was arguably the most famous scientist of the 20th century. Most people are familiar with his iconic E=mc^2 equation , but his life and work encompassed so much more than that. For instance, the brilliant physicist actually won the Nobel Prize for very different work. From his humble beginnings as a patent clerk to the offer to run a small country (that he turned down), here are 32 facts you may not have known about Einstein.
Einstein discovered that the universe has a "speed limit."

His special theory of relativity, which explains the relationship between mass, time and space, suggests that as an object approaches the speed of light, its mass and energy become infinite, as Space.com explains . That means that it's impossible for an object to travel faster than light.
He argued that space and time are interwoven.

While Einstein didn't invent the concept of space-time, which was first proposed by German mathematician Hermann Minkowski , his special theory of relativity showed that space and time grow and shrink relative to one another in order to keep the speed of light constant for the observer. Based on his theory , when we travel through space, time moves a tiny bit slower. At incredible speeds, like the speed of light, time stands still.
He won the Nobel Prize for his explanation of the photoelectric effect.

The photoelectric effect is the observation that metal plates eject electrons when hit by beams of high-energy light. The photoelectric effect can't be explained by classical physics, which saw light as a wave. Einstein proposed that we view light as both a particle and a wave — with the frequency of the wave determining the energy of the particle and vice versa.
Einstein transformed the way physicists view light.

Before Einstein's special theory of relativity, physicists thought that light traveled through a substance called "the luminiferous ether." Throughout the late 19th century, scientists ran experiments to try to prove its existence.
Einstein's fascination with physics was lifelong.

Beginning at age 5, Einstein became captivated by the invisible forces that moved the needle of his compass, according to the American Physical Society . That led to a lifelong quest to explain those invisible forces.
At the age of 12, he taught himself geometry.
To study, he read out of a textbook, which he dubbed his " holy geometry book " and "second miracle" (the first being his compass needle).
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
He wasn't well-liked by his teachers.

One of the instructors at the Luitpold-Gymnasium in Munich, where Einstein received much of his early education, told the young Einstein that nothing good would ever come of his life.
Einstein played the violin.

At 5 years old, his mother signed him up for lessons. At first, he didn't enjoy playing at all, according to the American Nuclear Society . But after discovering Mozart, he developed a love for the hobby and played into his old age.
He wrote his first scientific paper at the age of 16.

Titled " On the Investigation of the State of the Ether in a Magnetic Field ," the essay asked how magnetic fields impact " ether ," the theoretical substance that at the time was believed to transmit electromagnetic waves.
After university, Einstein was rejected from every academic position he applied for.

Eventually, he settled for a job evaluating patent claims for the Swiss government, according to the American Institute of Physics . He described the job, which gave him the time and energy to focus on solving the physics problems that underlie our world, as "a kind of salvation."
He helped convince the physics world that atoms exist.

Einstein was interested in the problem of Brownian motion , the observation that if you put tiny objects (like pollen) in water, they appear to jump around erratically. Einstein proposed that invisible particles were colliding with the pollen, causing it to move, and came up with a formula describing this phenomenon. In 1908, French physicist Jean Baptiste Perrin tested and confirmed Einstein's theory, swaying the physics world to accept the existence of atoms, according to the American Physical Society .
Einstein was a pacifist.

At 16, he left Germany to escape mandatory military service. Later, he was one of only four German intellectuals to openly declare their opposition to German participation in World War I, calling nationalism " the measles of the human race ."
Einstein's theories of relativity challenged the view that the universe was static.
His equations predicted a dynamic universe, one that was expanding or contracting. Flummoxed by this finding, Einstein assumed there was a flaw in his equations and introduced a " cosmological constant " which allowed for a universe that didn't change size. When Edwin Hubble confirmed that the universe is, indeed, expanding, Einstein called the cosmological constant "his greatest mistake."
Four of Einstein's most notable papers were all published in one year.

In 1905, dubbed his " year of miracles ," Einstein published his explanation of the photoelectric effect, his theory on Brownian motion, and two papers on his general theory of relativity.
He was friends with Charlie Chaplin.

Chaplin even invited Einstein and his wife , Elsa Einstein, as his guests of honor at the premier of his 1931 film "City Lights." There, Chaplin famously told Einstein : "The people applaud me because everybody understands me, and they applaud you because no one understands you."
Einstein believed in God.

However, he didn't believe in a personal god that answered prayers. Instead, he thought that God revealed himself through the "harmony" of the universe. "He [God] does not play dice," he famously wrote .
Einstein was a target for the Nazis.

They sponsored conferences and book burnings against Einstein and labeled his theories " Jewish physics ." In 1933, Einstein fled Germany to escape Nazi death threats, settling first in Britain and then eventually in Princeton, New Jersey.
His work enabled the development of the atomic bomb.

The equation E = mc2 provided the theoretical basis for the weapon's potential — but didn't explain how to build one.
At the start of World War II, he wrote to then-President Franklin D. Roosevelt, warning of possible German nuclear weapons research.

He urged the president to initiate development of an atomic bomb — but later regretted doing so, according to the American History of Natural History . In an interview with Newsweek, he said: "Had I known that the Germans would not succeed in developing an atomic bomb, I would have done nothing."
Later, he opposed the use of atomic weapons.

After the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, he formed the Emergency Committee of Atomic Scientists , an organization that educated Americans about the dangers of atomic weapons.
Einstein was a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).

He saw parallels between the experience of Black Americans and his experience as a Jew living in Nazi Germany. In a 1946 commencement speech delivered at the historically black college Lincoln University, Einstein decried segregation and called it "a disease of white people," Smithsonian magazine reported.
The FBI kept a 1,400-page dossier on Einstein.

His pacifist stance and left-leaning politics made him suspicious in the eyes of the agency as a potentially "extreme radical," National Geographic reported. This was especially true during the McCarthy era, when many people were accused of communism or blacklisted from work.
Einstein was asked to be the president of Israel.

However, when he was offered the position in 1952, he was already near the end of his life, according to the American Museum of Natural History . Due to his poor health and lack of experience "dealing properly with people," he declined.
He did not believe that black holes could exist.

In a 1939 article, he laid out a series of arguments trying to prove that black holes — objects with such high gravity that even light can't escape them — are impossible, Scientific American reported . Ironically, It's Einstein's general theory of relativity that shows us black holes do, in fact, exist.
He did believe in the possibility of wormholes.

In a 1935 paper published in the journal Physics Reviews , Einstein and physicist Nathan Rosen proposed that near objects of enormous mass, space-time might curve inward like a rubber tube, creating a tunnel between two different regions. If they exist, these objects would enable travel across vast distances of time and space, Space.com reported.
Einstein didn't wear socks.

Black holes weren't the only holes this physicist vehemently disagreed with. Because socks invariably develop holes, he disliked them to such an extent that he refused to wear them, according to the American Nuclear Society .
Einstein's brain was stolen.

After his death in 1955, pathologist Thomas Harvey dissected and stole Einstein's brain during an autopsy. Harvey, who wanted to discover the anatomical secrets of genius, eventually received permission from Einstein's son to use the brain for scientific research.
Research on Einstein's brain found extra folding.

The human brain's wrinkled surface gives it a much larger surface area than a smooth brain and is an important part of advanced cognition. Einstein's brain had extra folding in its gray matter, the site of conscious thinking, especially in the frontal lobe, where abstract thought and planning occurs.
He loved sailing.

However, the physicist was terrible at it — so terrible, in fact, that his neighbors frequently had to rescue him when is boat invariably capsized, according to the American Nuclear Society .
His birthday is Pi Day.

March 14 is a special date because written numerically, it matches the first three digits of mathematical constant pi: 3.14. However, that's not the only reason it's significant. It's also the birthday of Einstein , who was born in 1879.
Einstein invented a refrigerator.

The contraption, which he developed alongside colleague Leo Szilard, didn't require motors or coolant. Instead, it used boiling butane to suck energy from a compartment, lowering the temperature inside, Live Science previously reported.
Einstein's ultimate goal was to describe the workings of the entire universe — from subatomic particles to the farthest reaches of space — in one theory.

He called the concept " The Grand Unified Theory ." He never realized this dream, but physicists are still working to find it.
Isobel Whitcomb is a contributing writer for Live Science who covers the environment, animals and health. Her work has appeared in the New York Times, Fatherly, Atlas Obscura, Hakai Magazine and Scholastic's Science World Magazine. Isobel's roots are in science. She studied biology at Scripps College in Claremont, California, while working in two different labs and completing a fellowship at Crater Lake National Park. She completed her master's degree in journalism at NYU's Science, Health, and Environmental Reporting Program. She currently lives in Portland, Oregon.
'A force more powerful than gravity within the Earth': How magnetism locked itself inside our planet
Euclid space telescope reveals more than 300,000 new objects in 1st 24 hours of observations (photos)
2,000-year-old rock art, including nearly 140-foot-long snake, may mark ancient territories in Colombia, Venezuela
Most Popular
- 2 32 of the loudest animals on Earth
- 3 Space photo of the week: James Webb telescope spots galaxy churning out stars in overtime
- 4 'She is so old': One-eyed wolf in Yellowstone defies odds by having 10th litter of pups in 11 years
- 5 Things are finally looking up for the Voyager 1 interstellar spacecraft
- 2 GPT-4 didn't ace the bar exam after all, MIT research suggests — it didn't even break the 70th percentile
- 3 China's secret space plane has released another unknown object over Earth
- 4 Early Celtic elites inherited power through maternal lines, ancient DNA reveals
- 5 'She is so old': One-eyed wolf in Yellowstone defies odds by having 10th litter of pups in 11 years

- Teen & Young Adult
- Education & Reference

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Follow the author

The Manhattan Project and the Birth of the Atomic Bomb: From Albert Einstein's Theories to J. Robert Oppenheimer's Test. A 2023 Biography and ... The J. Robert Oppenheimer Legacy Series) Paperback – August 25, 2023
Purchase options and add-ons.
Did the recent cinematic masterpiece, the Oppenheimer movie directed by the brilliant Christopher Nolan with Cillian Murphy in the lead role, captivate your imagination? Drawing inspiration from the Pulitzer Prize-winning 2005 biography "American Prometheus Oppenheimer" by Kai Bird and Martin J. Sherwin, the film offers a mesmerizing glimpse into the enigmatic life of J. Robert Oppenheimer. But if it ignited a spark of curiosity within you, urging you to delve deeper into the intricate tapestry of events and personalities that birthed the atomic age, then you're on the precipice of an enlightening journey.
Venture into a world before the atomic era, where the interplay of global geopolitics, groundbreaking scientific discoveries, and societal shifts set the stage for monumental transformations. Discover the genius of Einstein, whose revolutionary theories in physics paved the way for the atomic age, and immerse yourself in the contributions of J. Robert Oppenheimer and the team of scientists who were instrumental in the Manhattan Project.
In this meticulously researched narrative, available in various formats including hardback, hardcover, paperback, Kindle, and soon as an audiobook, you'll traverse:
Einstein's Vision: Delving into the theories that reshaped our cosmic understanding and the atomic research challenges they presented.
The Manhattan Project's Pioneers: An exploration of Oppenheimer's role and the collaborative efforts of the brilliant minds that brought the project to fruition.
The Atomic Age Revealed: From the inaugural test in New Mexico's deserts, known as the Trinity test, to the cataclysmic events in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The Moral Crossroads: A reflection on the global response, Cold War espionage, and philosophical discourse surrounding the atomic bomb's deployment.
The Bomb's Legacy : An exploration of the atomic age's enduring influence on our contemporary world, including the controversies and ethical debates it sparked among 20th-century scientists, leaders, and influencers.
As you navigate this narrative, you'll be transported to an era marked by scientific brilliance, ethical quandaries, and decisions that altered the course of history. This book not only chronicles the events leading to the atomic bomb but also delves into the psyche of the visionaries who made it a reality.
Are you prepared to embark on a journey spanning from the early 20th-century scientific labs to the pivotal test sites of "The Manhattan Project and the Birth of the Atomic Bomb: From Einstein's Theories to Oppenheimer's Test"? Eager to grasp the intricate dance of science, ethics, and geopolitics that heralded the atomic age? This book promises a comprehensive, enlightening, and challenging voyage.
Embark on this enlightening odyssey, grasp the genesis of the atomic age, and unravel the stories of Einstein, Oppenheimer, and the atomic bomb's history.
From the making of the Hiroshima documentary to the "Day After" reflections, from the nuclear movies of 1986 to the weapons of power trailers, and from the historical nonfiction best sellers of 2023 to the DVD projects that encapsulate the era, this book encompasses it all. Dive into the heart of the Manhattan Project and the influence it had on the world.
Don't let this opportunity slip by. Dive in now and uncover the enigmas of the Manhattan Project and the atomic bomb's inception.
- Book 2 of 3 Pioneering Minds: The J. Robert Oppenheimer Legacy Series
- Print length 247 pages
- Language English
- Publication date August 25, 2023
- Dimensions 5 x 0.56 x 8 inches
- ISBN-13 979-8858783442
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Similar items that may deliver to you quickly

From the Publisher

Product details
- ASIN : B0CGL335Z4
- Publisher : Independently published (August 25, 2023)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 247 pages
- ISBN-13 : 979-8858783442
- Item Weight : 11.8 ounces
- Dimensions : 5 x 0.56 x 8 inches
- #23 in Teen & Young Adult 21st Century United States History
- #28 in Teen & Young Adult United States Biographical Fiction
- #59 in Teen & Young Adult Literary Biographies
About the author
Julian r. stonebridge.
Julian R. Stonebridge stands as a beacon in the literary world, celebrated for his unparalleled ability to intertwine the realms of science, history, and ethics into riveting narratives. His profound passion for the history of science, coupled with an insatiable curiosity about the intricacies of physics, has led to works that resonate deeply with scholars, students, and casual readers alike.
Born and raised amidst the historic charm and urban vibrancy of London, Stonebridge's formative years were a tapestry of exploration and discovery. The city's myriad museums, libraries, and cultural hubs served as his playground, fueling a voracious appetite for knowledge. This early immersion in a world of learning laid the foundation for an interdisciplinary approach that would later become the hallmark of his writing.
Beyond his literary pursuits, Stonebridge is a recognized figure in the global academic community. He has graced the stages of numerous science history symposiums, conferences, and workshops, captivating audiences with his thought-provoking lectures. His discussions often delve into the ethical quandaries posed by scientific advancements, the transformative role of science in human history, and the ever-evolving relationship between past discoveries and future innovations.
Stonebridge's commitment to knowledge extends beyond the written word and lecture halls. He has been instrumental in curating exhibitions that bring the wonders of science and history to the public. Collaborating with renowned institutions, he has helped design interactive experiences that bridge the gap between academia and the general populace.
In moments of respite, Stonebridge is often found wandering the English countryside, drawing inspiration from its serene landscapes. He's also an avid collector of antique books and scientific instruments, treasures that he believes hold stories waiting to be told. Engaging in spirited debates, attending book readings, and mentoring young writers are among his other cherished pastimes.
He often quips, "The universe is a vast tapestry of stories, and every day offers a new thread to weave." This philosophy is evident in his dedication to continuous learning and his drive to share the wonders of the world with his readers.
For a deeper dive into his research, upcoming projects, or to engage in enlightening discussions, follow Julian R. Stonebridge on Amazon and become part of his ever-expanding circle of inquisitive minds.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

COMMENTS
Interview by Jo Marchant. Einstein: A Hundred Years of Relativity. by Andrew Robinson. Read. 1 Albert Einstein: A Biography by Albrecht Folsing. 2 Einstein 1905: The Standard of Greatness by John S. Rigden. 3 The Born-Einstein Letters,1916-1955 by Albert Einstein and Max Born. 4 The Einstein File by Fred Jerome.
Physicist Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity and won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics. Read about his inventions, IQ, wives, death, and more.
Albert Einstein ( / ˈaɪnstaɪn / EYEN-styne; [4] German: [ˈalbɛɐt ˈʔaɪnʃtaɪn] ⓘ; 14 March 1879 - 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity, Einstein also made important ...
Albert Einstein (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Germany—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.) was a German-born physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity and won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921 for his explanation of the photoelectric effect.
Einstein's Early Life (1879-1904) Born on March 14, 1879, in the southern German city of Ulm, Albert Einstein grew up in a middle-class Jewish family in Munich.
Albert Einstein was born at Ulm, in Württemberg, Germany, on March 14, 1879. Six weeks later the family moved to Munich, where he later on began his schooling at the Luitpold Gymnasium. Later, they moved to Italy and Albert continued his education at Aarau, Switzerland and in 1896 he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich to be ...
A brief biography of Albert Einstein (March 14, 1879 - April 18, 1955), the scientist whose theories changed the way we think about the universe. ... Albert Einstein facts; Best binoculars 2024;
Albert Einstein Biography - Short bio of greatest scientist of the Twentieth Century. Einstein developed theory of relativity and was also noted humanitarian ... Early life Albert Einstein. ... Albert Einstein is the best scientist ever! He shall live forever! January 10, 2019 4:11 PM; By Blah; very inspiring. December 23, 2018 8:06 PM;
Albert Einstein. The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921. Born: 14 March 1879, Ulm, Germany. Died: 18 April 1955, Princeton, NJ, USA. Affiliation at the time of the award: Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut (now Max-Planck-Institut) für Physik, Berlin, Germany. Prize motivation: "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the ...
Albert Einstein was a theoretical physicist and the most famous scientist in human history. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics, alongside quantum mechanics. He is perhaps best known in popular culture for his mass/energy equivalence formula E=mc2. In 1921 he received the Nobel Prize in ...
Albert Einstein - Physics, Relativity, Nobel Prize: After graduation in 1900, Einstein faced one of the greatest crises in his life. Because he studied advanced subjects on his own, he often cut classes; this earned him the animosity of some professors, especially Heinrich Weber. Unfortunately, Einstein asked Weber for a letter of recommendation.
Albert Einstein, (born March 14, 1879, Ulm, Württemberg, Ger.—died April 18, 1955, Princeton, N.J., U.S.), German-born Swiss-U.S. scientist.Born to a Jewish family in Germany, he grew up in Munich, and in 1894 he moved to Aarau, Switz. He attended a technical school in Zürich (graduating in 1900) and during this period renounced his German citizenship; stateless for some years, he became a ...
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity, Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics, and was thus a central figure in the revolutionary reshaping of the scientific understanding of nature that modern physics ...
Albert Einstein: A Biography. Paperback - June 1, 1998. by Albrecht Folsing (Author), Ewald Osers (Translator) 4.5 44 ratings. See all formats and editions. A biography of Albert Einstein also delves into his development both personally and as a scientist, exploring everything from his childhood idiosyncrasies to overheard conversations with ...
Einstein: The Man and His Mind is an unprecedented visual biography that reveals Albert Einstein as a real person and the essence of his contributions. The visual—and artistically beautiful—format differentiates it from all previous books about him. "Gary Berger and Michael DiRuggiero's photographic exploration of Einstein is indubitably a ...
Before E=MC2. Einstein was born in Germany in 1879. Growing up, he enjoyed classical music and played the violin. One story Einstein liked to tell about his childhood was when he came across a magnetic compass. The needle's invariable northward swing, guided by an invisible force, profoundly impressed him as a child.
Albert Einstein's early life. Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879, Einstein was brought up in Munich. His parents were of Jewish German ancestry, and his father ran an electrical equipment plant. He ...
Albert Einstein: A Biography, by Albrecht Folsing, is a comprehensive and very readable biography of the 20th century's greatest scientist. A reader's lack of a college-level scientific background will not diminish the appeal and understanding of this book. ... This is the BEST biography of Einstein that I have read. The writing style is ...
12. Einstein and the Quantum: The Quest of the Valiant Swabian. Check Price on Amazon. Einstein and the Quantum: The Quest of the Valiant Swabian by A. Douglas Stone is about the significance of Albert Einstein and his research. The book discusses Einstein's relationships with quantum mechanics, religion, and more.
Albert Einstein was one of the greatest geniuses in the history of science. His theories, or ideas, led to new ways of thinking about the universe .
Albert Einstein. Author: Orren Jack Turner. Einstein was born in Germany in 1879 where he grew up and attended grade school. He later moved to Switzerland where he attended university. After gaining fame for his "Miracle Year" papers, he eventually returned to Germany as a professor until Hitler gained power in 1933.
Albert Einstein was a theoretical physicist and the most famous scientist in human history. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern physics, alongside quantum mechanics. He is perhaps best known in popular culture for his mass/energy equivalence formula E=mc2.
Albert Einstein was arguably the most famous scientist of the 20th century. Most people are familiar with his iconic E=mc^2 equation, but his life and work encompassed so much more than that.For ...
This item: Albert Einstein: The Genius Who Failed School - Biography Book Best Sellers Children's Biography Books $12.99 $ 12 . 99 Get it as soon as Saturday, May 25
Free Canva presentation template. Discover the genius of Albert Einstein with our charming beige slideshow template, crafted for everyone from students to educators. This cute, illustrative design breathes life into Einstein's incredible journey, making it perfect for history lessons, science classes, or intriguing storytelling sessions.
Amazon.com: The Manhattan Project and the Birth of the Atomic Bomb: From Albert Einstein's Theories to J. Robert Oppenheimer's Test. A 2023 Biography and ... The J. Robert Oppenheimer Legacy Series): 9798858783442: R. Stonebridge, Julian, Everyday Publications, A Better You: Books