Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Genetics research articles from across Nature Portfolio
Genetics research is the scientific discipline concerned with the study of the role of genes in traits such as the development of disease. It has a key role in identifying potential targets for therapeutic intervention and also in understanding genetically based variations in response to therapeutic interventions.
Latest Research and Reviews
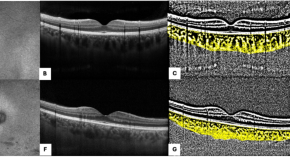
OCT analysis and MPOD assessment in patients affected by retinitis pigmentosa
- Maria Ludovica Ruggeri
- Luca Belloni Baroni
- Rodolfo Mastropasqua
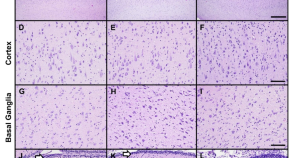
Extrauterine support of pre-term lambs achieves similar transcriptomic profiling to late pre-term lamb brains
- Jennifer L. Cohen
- Felix De Bie
- Alan W. Flake
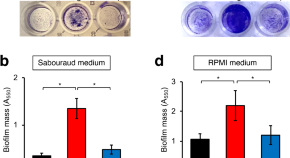
Role of Hog1-mediated stress tolerance in biofilm formation by the pathogenic fungus Trichosporon asahii
- Yasuhiko Matsumoto
- Mei Nakayama
- Takashi Sugita
Diagnostic efficacy and clinical utility of whole-exome sequencing in Czech pediatric patients with rare and undiagnosed diseases
- Katerina Slaba
- Petra Pokorna
- Ondrej Slaby
A cross-tissue transcriptome-wide association study reveals GRK4 as a novel susceptibility gene for COPD
- Guanglei Chen

Defective kinase activity of IKKα leads to combined immunodeficiency and disruption of immune tolerance in humans
IKKα is an essential regulator of the noncanonical NF-κB signalling, lack of which is incompatible with life. Here authors show that a homozygous missense variant in humans, G167R, disrupting its kinase activity upstream of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway, leads to disrupted innate and adaptive immune functions while largely sparing other major organ systems.
- Gökhan Cildir
- Baran Erman
News and Comment
Pushing the boundaries of rare disease diagnostics with the help of the first Undiagnosed Hackathon
In the first-ever Undiagnosed Hackathon, nearly 100 experts from 28 countries combined advanced phenotyping and genomic techniques for 48 hours, ultimately providing diagnoses to 40% of the previously undiagnosed families. This inspiring model demonstrates the power of multidisciplinary collaboration and patient partnership in precision diagnostics.
- Angelica Maria Delgado-Vega
- Helene Cederroth
- Ann Nordgren
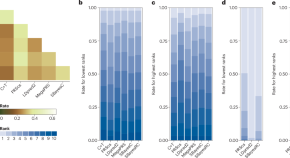
Inconsistent embryo selection across polygenic score methods
Private enterprises offer preimplantation genetic testing with polygenic scores to select embryos with ‘desirable’ potential. In silico simulations using biobank resources show that the selected embryo would rely substantially on the choice of polygenic score method and randomness in score construction, which raises ethical concerns.
- Shinichi Namba
- Masato Akiyama
- Yukinori Okada
SPARCL1 sparkles new insight into corneal dystrophies
- Joni A. Turunen
Systematic decision frameworks for the socially responsible use of precision medicine
Deep learning techniques and whole-genome sequencing promise to increase well-being but also risk perpetuating psychological essentialism, potentially justifying inequality. In this Comment, we offer two much-needed systematic frameworks for clinicians and researchers to avoid essentialist inferences and unfair treatment: (1) a data-driven method for detecting causal fairness in precision health and (2) an ethical framework for determining when it is morally permissible to use racial classifications in population health research.
- Ian S. Peebles
- David B. Kinney
- Emily Foster-Hanson
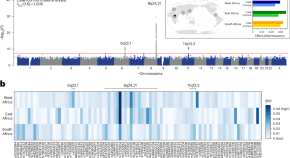
Pan-African analysis identifies genetic differences in prostate cancer risk
To understand the genetic basis of disease, it is essential to study diverse populations. We conducted the largest study to date of African men to evaluate the evolutionary genetics and causes of prostate cancer. Our findings reveal novel genetic associations, including those that were not observed in studies of non-African populations.
Multi-omics analyses of the environMENTAL project provide insights into mental health and disease
Integrative analyses that incorporate different levels of ‘-omics’ data represent a powerful tool for deciphering the biological mechanisms that underlie environmental influences on mental health and disease. This Comment highlights various aspects of such multi-omics approaches, using the example of the EU-funded environMENTAL project.
- Sylvane Desrivières
- Abigail Miller
- George Ogoh
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Black holes
- Classes and programs

Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Download RSS feed: News Articles / In the Media / Audio

A causal theory for studying the cause-and-effect relationships of genes
By sidestepping the need for costly interventions, a new method could potentially reveal gene regulatory programs, paving the way for targeted treatments.
November 7, 2024
Read full story →

Victor Ambros ’75, PhD ’79 and Gary Ruvkun share Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The scientists, who worked together as postdocs at MIT, are honored for their discovery of microRNA — a class of molecules that are critical for gene regulation.
October 7, 2024

Pursuing the secrets of a stealthy parasite
By unraveling the genetic pathways that help Toxoplasma gondii persist in human cells, Sebastian Lourido hopes to find new ways to treat toxoplasmosis.
August 25, 2024
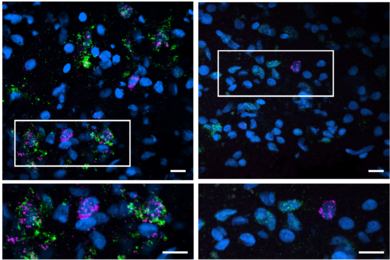
Study across multiple brain regions discerns Alzheimer’s vulnerability and resilience factors
Genomics and lab studies reveal numerous findings, including a key role for Reelin amid neuronal vulnerability, and for choline and antioxidants in sustaining cognition.
July 24, 2024

License plates of MIT
Custom plates display expressions of scholarship, creativity, and MIT pride among Institute affiliates.
July 22, 2024

Machine learning and the microscope
PhD student Xinyi Zhang is developing computational tools for analyzing cells in the age of multimodal data.
July 12, 2024

CHARMed collaboration creates a potent therapy candidate for fatal prion diseases
A new gene-silencing tool shows promise as a future therapy against prion diseases and paves the way for new approaches to treating disease.
June 27, 2024

Professor Emerita Mary-Lou Pardue, pioneering cellular and molecular biologist, dies at 90
Known for her rigorous approach to science and her influential research, Pardue paved the way for women in science at MIT and beyond.
June 21, 2024

Scientists preserve DNA in an amber-like polymer
With their “T-REX” method, DNA embedded in the polymer could be used for long-term storage of genomes or digital data such as photos and music.
June 13, 2024
New technique reveals how gene transcription is coordinated in cells
By capturing short-lived RNA molecules, scientists can map relationships between genes and the regulatory elements that control them.
June 5, 2024

The beauty of biology
Senior Hanjun Lee planned to pursue chemistry at MIT. A course in genetics changed that.
May 16, 2024
Taking RNAi from interesting science to impactful new treatments
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, founded by MIT professors and former postdocs, has turned the promise of RNAi research into a new class of powerful therapies.
May 13, 2024
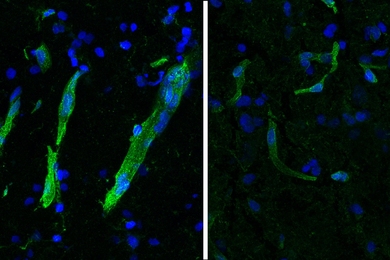
Study: Movement disorder ALS and cognitive disorder FTLD show strong molecular overlaps
Single-cell gene expression patterns in the brain, and evidence from follow-up experiments, reveal many shared cellular and molecular similarities that could be targeted for potential treatment.
March 22, 2024

A protein found in human sweat may protect against Lyme disease
Researchers also found that a variant of the protein is not as protective against the bacteria and increases susceptibility to the disease.
March 19, 2024

Scientists develop a rapid gene-editing screen to find effects of cancer mutations
With the new technique, MIT researchers hope to identify mutations that could be targeted with new cancer therapies.
March 12, 2024
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO