- How it works


Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Latest List of Best Diabetes Dissertation Topics
Published by Owen Ingram at January 2nd, 2023 , Revised On May 17, 2024
The prevalence of diabetes among the world’s population has been increasing steadily over the last few decades, thanks to the growing consumption of fast food and an increasingly comfortable lifestyle. With the field of diabetes evolving rapidly, it is essential to base your dissertation on a trending diabetes dissertation topic that fills a gap in research.
Finding a perfect research topic is one of the most challenging aspects of dissertation writing in any discipline . Several resources are available to students on the internet to help them conduct research and brainstorm to develop their topic selection, but this can take a significant amount of time. So, we decided to provide a list of well-researched, unique and intriguing diabetes research topics and ideas to help you get started.
Other Subject Links:
- Evidence-based Practice Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Child Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Palliative Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Mental Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Nursing Dissertation Topics
List of Diabetes Dissertation Topics
- Why do people recently diagnosed with diabetes have such difficulty accepting reality and controlling their health?
- What are the reactions of children who have recently been diagnosed with diabetes? What can be done to improve their grasp of how to treat the disease?
- In long-term research, people getting intensive therapy for the condition had a worse quality of life. What role should health professionals have in mitigating this effect?
- Why do so many individuals experience severe depression the months after their diagnosis despite displaying no other signs of deteriorating health?
- Discuss some of the advantages of a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet for people with diabetes
- Discuss the notion of diabetes in paediatrics and why it is necessary to do this research regularly.
- Explain the current threat and difficulty of childhood obesity and diabetes, stressing some areas where parents are failing in their position as guardians to avoid the situation
- Explain some of the difficulties that persons with diabetes have, particularly when obtaining the necessary information and medical treatment
- Explain some of the most frequent problems that people with diabetes face, as well as how they affect the prevalence of the disease. Put out steps that can be implemented to help the problem.
- Discuss the diabetes problem among Asian American teens
- Even though it is a worldwide disease, particular ethnic groups are more likely to be diagnosed as a function of nutrition and culture. What can be done to improve their health literacy?
- Explain how self-management may be beneficial in coping with diabetes, particularly for people unable to get prompt treatment for their illness
- Discuss the possibility of better management for those with diabetes who are hospitalised
- What current therapies have had the most influence on reducing the number of short-term problems in patients’ bodies?
- How have various types of steroids altered the way the body responds in people with hypoglycemia more frequently than usual?
- What effects do type 1, and type 2 diabetes have on the kidneys? How do the most widely used monitoring approaches influence this?
- Is it true that people from specific ethnic groups are more likely to acquire heart disease or eye illness due to their diabetes diagnosis?
- How has the new a1c test helped to reduce the detrimental consequences of diabetes on the body by detecting the condition early?
- Explain the difficulty of uncontrolled diabetes and how it can eventually harm the kidneys and the heart
- Discuss how the diabetic genetic strain may be handed down from generation to generation
- What difficulties do diabetic people have while attempting to check their glucose levels and keep a balanced food plan?
- How have some individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes managed to live better lives than others with the disease?
- Is it true that eating too much sugar causes diabetes, cavities, acne, hyperactivity, and weight gain?
- What effect does insulin treatment have on type 2 diabetes?
- How does diabetes contribute to depression?
- What impact does snap participation have on diabetes rates?
- Why has the number of persons who perform blood glucose self-tests decreased? Could other variables, such as social or environmental, have contributed to this decrease?
- Why do patients in the United States struggle to obtain the treatment they require to monitor and maintain appropriate glucose levels? Is this due to increased healthcare costs?
- Nutrition is critical to a healthy lifestyle, yet many diabetic patients are unaware of what they should consume. Discuss
- Why have injuries and diabetes been designated as national health priorities?
- What factors contribute to the growing prevalence of type II diabetes in adolescents?
- Does socioeconomic status influence the prevalence of diabetes?
- Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes: a critical assessment of the shared pathological traits
- What are the effects and consequences of diabetes on peripheral blood vessels?
- What is the link between genetic predisposition, obesity, and type 2 diabetes development?
- Diabetes modifies the activation and repression of pro- and anti-inflammatory signalling pathways in the vascular system.
- Understanding autoimmune diabetes through the tri-molecular complex prism
- Does economic status influence the regional variation of diabetes caused by malnutrition?
- What evidence is there for using traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to treat depression in people who also have diabetes?
- Why was the qualitative method used to evaluate diabetes programs?
- Investigate the most common symptoms of undiagnosed diabetes
- How can artificial intelligence help diabetes patients?
- What effect does the palaeolithic diet have on type 2 diabetes?
- What are the most common causes of diabetes and what are the treatments?
- What causes diabetes mellitus, and how does it affect the United Kingdom?
- The impact of sociodemographic factors on the development of type II diabetes
- An examination of the link between gut microbiome and diabetes risk
- The effectiveness of lifestyle interventions in preventing type II diabetes
- The role of maternal diabetes in offspring’s risk of developing diabetes
- Artificial intelligence in diabetes diagnosis and management
- Continuous glucose monitoring
- Telehealth interventions for improving diabetes self-management
- The role of wearable technology in diabetes management
- Personalised medicine approaches for diabetes treatment
- The impact of diabetes on mental health and well-being
- The link between diabetes and cognitive decline
- The potential of stem cell therapy for diabetes treatment
- Advances in closed-loop insulin delivery systems
- The use of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists in diabetes treatment
- Investigating the efficacy of new oral medications for type II diabetes
- The role of bariatric surgery in the management of type II diabetes
- Improving patient adherence to diabetes treatment regimens
- The role of social support in diabetes management
- Developing culturally sensitive diabetes education programs
- The role of dietary patterns in diabetes prevention and management
- Low-carbohydrate vs. Mediterranean diet for diabetes: A comparative study
- The use of artificial sweeteners in diabetes management: Benefits and risks
- The impact of the gut microbiome on dietary interventions for diabetes
- The role of exercise in improving glycemic control
- Developing effective exercise programs for individuals with diabetes
- The impact of physical activity on diabetic complications
- Promoting physical activity adherence in people with diabetes
- The use of exercise gamification to increase physical activity in diabetes
- The potential of CRISPR gene editing for diabetes treatment
- The role of the microbiome in the development and treatment of diabetes
- An analysis of the artificial Pancreas systems
- The use of big data analytics in diabetes research
- The impact of environmental factors on diabetes risk
- Cost-effectiveness of different diabetes treatment strategies
- Developing effective diabetes prevention programs for communities
- The role of government policies in addressing the diabetes epidemic
- Improving access to diabetes care in underserved populations
- The impact of social determinants of health on diabetes risk
- Management of diabetes in children and adolescents
- The unique challenges of diabetes management in older adults
- Diabetes in ethnic minorities: Disparities in prevalence and care
- The impact of diabetes on LGBTQ+ populations
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

You can contact our 24/7 customer service for a bespoke list of customised diabetes dissertation topics , proposals, or essays written by our experienced writers . Each of our professionals is accredited and well-trained to provide excellent content on a wide range of topics. Getting a good grade on your dissertation course is our priority, and we make sure that happens. Find out more here .
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find diabetes dissertation topics.
To find diabetes dissertation topics:
- Study recent research in diabetes.
- Focus on emerging trends.
- Explore prevention, treatment, tech, etc.
- Consider cultural or demographic aspects.
- Consult experts or professors.
- Select a niche that resonates with you.
You May Also Like
Counselling psychology is one of the various subfields of psychology. It addresses a variety of situational issues that affect people from different social groups. In order to receive a psychology degree, students must present a dissertation.
Need interesting and manageable religion, theology and philosophy dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending religion, theology and philosophy dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Students will undoubtedly experience anxiety when working on their dissertations on educational management. It is a fact that a topic like this necessitates in-depth study, and the paper.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples
When you write about the science behind nutrition, heart diseases, and alternative medicine, checking titles for diabetes research papers can be quite beneficial. Below, our experts have gathered original ideas and examples for the task.
🏆 Best Diabetes Essay Examples & Topics
⭐ most interesting diabetes research paper topics, ✅ simple & easy diabetes essay topics, 🎓 good research topics about diabetes, 💡 interesting topics to write about diabetes, 👍 good essay topics on diabetes, ❓ diabetes research question examples.
- Type 2 Diabetes The two major types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Doctor: The first step in the treatment of type 2 diabetes is consumption of healthy diet.
- Adult-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: Patient’s Profile Any immediate care as well as post-discharge treatment should be explained in the best manner possible that is accessible and understandable to the patient.
- Living With a Chronic Disease: Diabetes and Asthma This paper will look at the main effects of chronic diseases in the lifestyle of the individuals and analyze the causes and the preventive measures of diabetes as a chronic disease.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Symptoms, Types, Effects Insulin is the hormone that controls the levels of glucose in the blood, and when the pancreas releases it, immediately the high levels are controlled, like after a meal.
- Intervention Methods for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus An individual should maintain a regulated glycemic control using the tenets of self-management to reduce the possibility of complications related to diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes as a Public Health Issue In recent years, a steady increase in the incidence and prevalence of diabetes is observed in almost all countries of the world.
- Nursing Care Development Plan for Diabetes and Hypertension In addressing the first nursing diagnosis, the main aim of the nursing interventions will be to prevent the development of secondary hypoglycemia by increasing blood glucose levels.
- Diabetes in Adults in Oxfordshire On a national level, Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation aims to prevent the spread of the decease through research of the causes and effective treatment of diabetes 2 type.
- Case Study of Patient with DKA and Diabetes Mellitus It is manifested by a sharp increase in glucose levels and the concentration of ketone bodies in the blood, their appearance in the urine, regardless of the degree of violation of the patient’s consciousness.
- Qualitative Research in Diabetes Management in Elderly Patient To achieve the research aim, which is to find out the causes of diabetes among elderly people, the researcher will have to organize the research team.
- Diabetes Mellitus Management in the Elderly Diabetes mellitus is a health complication involving an increase in the concentration in the concentration of blood sugar either due to a failure by cells to effectively respond to the production of insulin in the […]
- Health Promotion: Diabetes Mellitus and Comorbidities This offers a unique challenge in the management of diabetes and other chronic diseases; the fragmented healthcare system that is geared towards management of short-term medical emergencies often is not well prepared for the patient […]
- Diabetes Management: Case Study Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes contrast based on their definitions, the causes, and the management of the conditions. Since the CDC promotes the avoidance of saturated fat and the increase of fiber intake for […]
- Leadership in Diabetes Management Nurses can collaborate and apply evidence-based strategies to empower their diabetic patients. The involvement of all key stakeholders is also necessary.
- A Study of Juvenile Type 1 Diabetes in the Northwest of England The total number of children under seventeen years living with type 1 diabetes in North West England by 2009 was 2,630.
- A Type 2 Diabetes Quantitative Article Critique Therefore, the main issue is the prevention of type 2 diabetes and its consequences, and this paper will examine one of the scientific studies that will be used for its exploration.
- Gestational Diabetes in a 38-Year-Old Woman The concept map, created to meet B.’s needs, considers her educational requirements and cultural and racial hurdles to recognize her risk factors and interventions to increase her adherence to the recommended course of treatment.B.said in […]
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications You call an ambulance and she is taken in to the ED. Background: Jean is still very active and works on the farm 3 days a week.
- Development of Comprehensive Inpatient and Outpatient Programs for Diabetes Overcoming the fiscal and resource utilization issues in the development of a comprehensive diabetes program is essential for the improvement of health and the reduction of treatment costs.
- Healthcare Cost Depending on Chronic Disease Management of Diabetes and Hypertension A sufficient level of process optimization and the presence of a professional treating staff in the necessary number will be able to help improve the indicators.
- Improving Glycemic Control in Black Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Information in them is critical for answering the question and supporting them with the data that might help to acquire an enhanced understanding of the issue under research. Finally, answering the PICOT question, it is […]
- Shared Decision-Making That Affects the Management of Diabetes The article by Peek et al.is a qualitative study investigating the phenomenon of shared decision-making that affects the management of diabetes. The researchers demonstrate the racial disparity that can arise in the choice of approaches […]
- Managing Obesity as a Strategy for Addressing Type 2 Diabetes When a patient, as in the case of Amanda, requires a quick solution to the existing problem, it is necessary to effectively evaluate all options in the shortest possible time.
- Tests and Screenings: Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease The test is offered to patients regardless of gender, while the age category is usually above 45 years. CDC1 recommends doing the test regardless of gender and is conducted once or twice to check the […]
- Obesity Management for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes American Diabetes Association states that for overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes who are ready to lose weight, a 5% weight reduction diet, physical exercise, and behavioral counseling should be provided.
- COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus Lim et al, in their article, “COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management”, explored how COVID-19 can worsen the symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
- The Importance of Physical Exercise in Diabetes II Patients The various activities help to improve blood sugar levels, reduce cardiovascular cases and promote the overall immunity of the patient. Subsequently, the aerobic part will help to promote muscle development and strengthen the bones.
- Diabetes Education Workflow Process Mapping DSN also introduces the patient to the roles of specialists involved in managing the condition, describes the patient’s actions, and offers the necessary educational materials.
- Diabetes: Treatment Complications and Adjustments One of the doctor’s main priorities is to check the compatibility of a patient’s medications. The prescriptions of other doctors need to be thoroughly checked and, if necessary, replaced with more appropriate medication.
- The Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus PICOT (Evidence-Based) Project Blood glucose levels, A1C, weight, and stress management are the parameters to indicate the adequacy of physical exercise in managing T2DM.
- Chronic Disease Cost Calculator (Diabetes) This paper aims at a thorough, detailed, and exhaustive explanation of such a chronic disease as diabetes in terms of the prevalence and cost of treatment in the United States and Maryland.
- Diabetes Mellitus Epidemiology Statistics This study entails a standard established observation order from the established starting time to an endpoint, in this case, the onset of disease, death, or the study’s end. It is crucial to state this value […]
- Epidemiology: Type II Diabetes in Hispanic Americans The prevalence of type II diabetes in Hispanic Americans is well-established, and the search for inexpensive prevention methods is in the limelight.
- Diabetes: Risk Factors and Effects Trends in improved medical care and the development of technology and medicine are certainly contributing to the reduction of the problem. All of the above indicates the seriousness of the problem of diabetes and insufficient […]
- Barriers to Engagement in Collaborative Care Treatment of Uncontrolled Diabetes The primary role of physicians, nurses, and other healthcare team members is to provide patients with medical treatment and coordinate that care while also working to keep costs down and expand access.
- Hereditary Diabetes Prevention With Lifestyle Modification Yeast infections between the fingers and toes, beneath the breast, and in or around the genital organs are the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
- Health Equity Regarding Type 2 Diabetes According to Tajkarimi, the number of research reports focusing on T2D’s prevalence and characteristics in underserved minorities in the U. Adapting the program’s toolkits to rural Americans’ eating and self-management habits could also be instrumental […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment Methods Moreover, according to the multiple findings conducted by Park et al, Billeter et al, and Tsilingiris et al, bariatric surgeries have a positive rate of sending diabetes into remission.
- Diagnosing Patient with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes The possible outcomes of the issues that can be achieved are discussing the violations with the patient’s family and convincing them to follow the medical regulations; convincing the girl’s family to leave her at the […]
- Human Service for Diabetes in Late Adulthood The mission of the Georgia Diabetic Foot Care Program is to make a positive difference in the health of persons living with diabetes.
- Diabetes: Symptoms and Risk Factors In terms of the problem, according to estimates, 415 million individuals worldwide had diabetes mellitus in 2015, and it is expected to rise to 642 million by the year 2040.
- Diabetes: Types and Management Diabetes is one of the most prevalent diseases in the United States caused when the body fails to optimally metabolize food into energy.
- Epidemiology of Diabetes and Forecasted Trends The authors note that urbanization and the rapid development of economies of different countries are the main causes of diabetes. The authors warn that current diabetes strategies are not effective since the rate of the […]
- The Aboriginal Diabetes Initiative in Canada The ADI’s goal in the CDS was to raise type 2 diabetes awareness and lower the incidence of associated consequences among Aboriginal people.
- Communicating the Issue of Diabetes The example with a CGM sensor is meant to show that doctors should focus on educating people with diabetes on how to manage their condition and what to do in extreme situations.
- Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 The goal is to define the features of patient information to provide data on the general course of the illness and its manifestations following the criteria of age, sex, BMI, and experimental data.
- The Prevention of Diabetes and Its Consequences on the Population At the same time, these findings can also be included in educational programs for people living with diabetes to warn them of the risks of fractures and prevent them.
- Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Treatment The data synthesis demonstrates that carefully chosen depression and anxiety treatment is likely to result in better A1C outcomes for the patient on the condition that the treatment is regular and convenient for the patients.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention and Education Schillinger et al.came to the same conclusion; thus, their findings on the study of the Bigger Picture campaign effectiveness among youth of color are necessary to explore diabetes prevention.
- A Diabetes Quantitative Article Analysis The article “Correlates of accelerometer-assessed physical activity and sedentary time among adults with type 2 diabetes” by Mathe et al.refers to the global issue of the prevention of diabetes and its complications.
- The Diabetes Prevention Articles by Ford and Mathe The main goal of the researchers was to measure the baseline MVPA of participants and increase their activity to the recommended 150 minutes per week through their participation in the Diabetes Community Lifestyle Improvement Program.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Hispanic Americans The HP2020 objectives and the “who, where, and when” of the problem highlight the significance of developing new, focused, culturally sensitive T2D prevention programs for Hispanic Americans.
- Diabetes Mellitus as Problem in US Healthcare Simultaneously, insurance companies are interested in decreasing the incidence of diabetes to reduce the costs of testing, treatment, and provision of medicines.
- Diabetes Prevention as a Change Project All of these queries are relevant and demonstrate the importance of including people at high risk of acquiring diabetes in the intervention.
- Evidence Synthesis Assignment: Prevention of Diabetes and Its Complications The purpose of this research is to analyze and synthesize evidence of good quality from three quantitative research and three non-research sources to present the problem of diabetes and justify the intervention to address it.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Causes and Health Challenges Second, the nature of this problem is a clear indication of other medical concerns in this country, such as poor health objectives and strategies and absence of resources.
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Disorder Case Study Analysis Thus, informing the patient about the importance of regular medication intake, physical activity, and adherence to diet in maintaining diabetes can solve the problem.
- Diabetes Mellitus in Young Adults Thus, programs for young adults should predominantly focus on the features of the transition from adolescence to adulthood. As a consequence, educational programs on diabetes improve the physical and psychological health of young adults.
- A Healthcare Issue of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus is seen as a primary healthcare issue that affects populations across the globe and necessitates the combination of a healthy lifestyle and medication to improve the quality of life of people who suffer […]
- Control of LDL Cholesterol Levels in Patients, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus In addition, some patients with hypercholesterolemia may have statin intolerance, which reduces adherence to therapy, limits treatment efficacy, and increases the risk of CVD.
- Exploring Glucose Tolerance and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus In the case of a glucose tolerance test for the purpose of diagnosing GDM type, the interpretation of the test results is carried out according to the norms for the overall population.
- Type 2 Diabetes Health Issue and Exercise This approach will motivate the patient to engage in exercise and achieve better results while reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Diabetes Interventions in Children The study aims to answer the PICOT Question: In children with obesity, how does the use of m-Health applications for controlling their dieting choices compare to the supervision of their parents affect children’s understanding of […]
- Diabetes Tracker Device and Its Advantages The proposed diabetes tracker is a device that combines the functionality of an electronic BGL tester and a personal assistant to help patients stick to their diet plan.
- Disease Management for Diabetes Mellitus The selection of the appropriate philosophical and theoretical basis for the lesson is essential as it allows for the use of an evidence-based method for learning about a particular disease.
- Latino People and Type 2 Diabetes The primary aim of the study is to determine the facilitators and barriers to investigating the decision-making process in the Latin population and their values associated with type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support Program The choice of this topic and question is based on the fact that despite the high prevalence of diabetes among adolescents in the United States, the use of DSMES among DM patients is relatively low, […]
- Diabetes Mellitus Care Coordination The aim is to establish what medical technologies, care coordination and community resources, and standards of nursing practice contribute to the quality of care and safety of patients with diabetes.
- Healthy Lifestyle Interventions in Comorbid Asthma and Diabetes In most research, the weight loss in cases of comorbid asthma and obesity is reached through a combination of dietary interventions and physical exercise programs.
- PDSA in Diabetes Prevention The second step in the “Do” phase would be to isolate a few members of the community who are affected by diabetes voluntarily.
- Diabetes: Statistics, Disparities, Therapies The inability to produce adequate insulin or the body’s resistance to the hormone is the primary cause of diabetes. Diabetes is a serious health condition in the U.S.and the world.
- Type 2 Diabetes Prescriptions and Interventions The disadvantage is the difficulty of obtaining a universal model due to the complexity of many factors that can affect the implementation of recommendations: from the variety of demographic data to the patient’s medical history.
- Health Education for Female African Americans With Diabetes In order to address and inform the public about the challenges, nurses are required to intervene by educating the population on the issues to enhance their understanding of the risks associated with the conditions they […]
- Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prevention It is one of the factors predisposing patients suffering from diabetes to various cardiovascular diseases. With diabetes, it is important to learn how to determine the presence of carbohydrates in foods.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Preventive Measures In addition to addressing the medical specialists who will be of service in disease prevention, it will emphasize the intervention programs required to help control the spread of the illness.
- “The Diabetes Online Community” by Litchman et al. The researchers applied the method of telephone interviews to determine the results and effectiveness of the program. The study described the value of DOC in providing support and knowledge to older diabetes patients.
- Mobile App for Improved Self-Management of Type 2 Diabetes The central focus of the study was to assess the effectiveness of the BlueStar app in controlling glucose levels among the participants.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Minorities from Cultural Perspective The purpose of this paper is to examine the ethical and cultural perspectives on the issue of T2DM in minorities. Level 2: What are the ethical obstacles to treating T2DM in ethnic and cultural minorities?
- Ethics of Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence in Minorities The purpose of this article analysis is to dwell on scholarly evidence that raises the question of ethical and cultural aspects of T2DM prevalence in minorities.
- Type 2 Diabetes in Minorities: Research Questions The Level 2 research questions are: What are the pathophysiological implications of T2DM in minorities? What are the statistical implications of T2DM in minorities?
- Improving Adherence to Diabetes Treatment in Primary Care Settings Additionally, the patients from the intervention group will receive a detailed explanation of the negative consequences of low adherence to diabetes treatment.
- An Advocacy Tool for Diabetes Care in the US To ensure the implementation and consideration of my plea, I sent a copy of the letter to the government officials so it could reach the president.
- Diabetes and Allergies: A Statistical Check The current dataset allowed us to test the OR for the relationship between family history of diabetes and the presence of diabetes in a particular patient: all variables were dichotomous and discrete and could take […]
- Type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents According to a National Diabetes Statistics Report released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the estimated prevalence of the disease was 25 cases per 10,000 adolescents in 2017. A proper understanding of T2D […]
- Analysis of Diabetes and Its Huge Effects In the US, diabetes is costly to treat and has caused much physical, emotional and mental harm to the people and the families of those who have been affected by the disease.
- Nursing: Self-Management of Type II Diabetes Sandra Fernandes and Shobha Naidu’s journal illustrates the authors’ understanding of a significant topic in the nursing profession.”Promoting Participation in self-care management among patients with diabetes mellitus” article exposes readers to Peplau’s theory to understand […]
- The Impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Diets on Diabetes Vegetarian diets are popular for a variety of reasons; according to the National Health Interview Survey in the United States, about 2% of the population reported following a vegetarian dietary pattern for health reasons in […]
- “Diabetes Prevention in U.S. Hispanic Adults” by McCurley et al. This information allows for supposing that face-to-face interventions can be suitable to my practicum project that considers measures to improve access to care among African Americans with heart failure diseases. Finally, it is possible to […]
- Diabetes Disease of the First and Second Types It is a decrease in the biological response of cells to one or more effects of insulin at its average concentration in the blood. During the first type of diabetes, insulin Degludec is required together […]
- Person-Centered Strategy of Diabetes and Dementia Care The population of focus for this study will be Afro-American women aged between sixty and ninety who have diabetes of the second type and dementia or are likely to develop dementia in the future.
- Video Consultations Between Patients and Clinicians in Diabetes, Cancer, and Heart Failure Services For example, during one of my interactions with the patient, I was asked whether the hospital had the policy to avoid face-to-face interaction during the pandemic with the help of video examinations.
- Diets to Prevent Heart Disease, Cancer, and Diabetes In order to prevent heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, people are required to adhere to strict routines, including in terms of diet. Additionally, people wanting to prevent heart disease, cancer, and diabetes also need to […]
- The Centers for Diabetes’ Risks Assessment In general, the business case for the Centers for Diabetes appears to be positive since the project is closely aligned with the needs of the community and the targets set by the Affordable Care Act.
- Diabetes Mellitus as Leading Cause of Disability The researchers used data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, where more than 12% of older people in the US live with the condition.
- Depression in Diabetes Patients The presence of depression concomitant to diabetes mellitus prevents the adaptation of the patient and negatively affects the course of the underlying disease.
- The Relationship Between Diabetes and COVID-19 After completing the research and analyzing the articles, it is possible to suggest a best practice that may be helpful and effective in defining the relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 and providing a way to […]
- Pre-diabetes and Urinary Incontinence Most recent reports indicate that a physiotherapy procedure gives a positive result in up to 80% of patients with stage I or SUI and mixed form and 50% of patients with stage II SUI.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Recommendations for Alternative Drug Treatments Then, they have to assess the existing levels of literacy and numeracy a patient has. Tailoring educational initiatives to a person’s unique ethnic and cultural background is the basis of cultural competence in patient education.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A Pharmacologic Update Diabetes presents one of the most common diagnoses in causes of ED visits among adults and one of the leading causes of death in the United States.
- Diabetes: Vulnerability, Resilience, and Care In nursing care, resilience is a critical concept that shows the possibility of a person to continue functioning and meeting objectives despite the existing challenges.
- Diabetes Prevention in the United States The analysis of these policies and the other strategies provides the opportunity to understand what role they might play in the improvement of human health. NDPP policy, on the other hand, emphasizes the role of […]
- Teaching Experience: Diabetes Prevention The primary objective of the seminar is to reduce the annual number of diabetes cases and familiarize the audience with the very first signs of this disease.
- Summary of Type 2 Diabetes: A Pharmacologic Update The authors first emphasize that T2D is one of the most widespread diseases in the United States and the seventh leading cause of death.
- Insulin Effects in a Diabetes Person I will use this source to support my research because the perception of diabetes patients on insulin therapy is essential for understanding the impact they cause on the person.
- Diabetes and Medical Intervention In the research conducted by Moin et al, the authors attempted to define the scope of efficiency of such a tool as an online diabetes prevention program in the prevention of diabetes among obese/overweight population […]
- Relation Between Diabetes And Nutrition Any efforts to lessen and eliminate the risk of developing diabetes must involve the dietary habit of limiting the consumption of carbohydrates, sugar, and fats. According to Belfort-DeAguiar and Dongju, the three factors of obesity, […]
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and a Healthy Lifestyle Relationship The advantage of this study over the first is that the method uses a medical approach to determining the level of fasting glucose, while the dependences in the study of Ugandans were found using a […]
- Diabetes and Its Economic Effect on Healthcare For many years, there has been an active increase in the number of cases of diabetes of all types among the global population, which further aggravates the situation.
- Diabetes: Epidemiological Analysis I would like to pose the following question: how can epidemiology principles be applied to these statistics for further improvements of policies that aim to reduce the impact of diabetes on the U.S.population? The limited […]
- Pathogenesis and Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension The hormone is produced by the cells of the islets of Langerhans found in the pancreas. It is attributed to the variation in the lifestyle of these individuals in these two geographical zones.
- Parental Intervention on Self-Management of an Adolescent With Diabetes Diabetes development and exposure are strongly tied to lifestyle, and the increasing incidents rate emphasizes the severity of the population’s health problem.
- Addressing the Needs of Hispanic Patients With Diabetes Similarly, in the program at hand, the needs of Hispanic patients with diabetes will be considered through the prism of the key specifics of the community, as well as the cultural background of the patients.
- Diabetes Issues: Insulin Price and Unaffordability According to the forecast of researchers from Stanford University, the number of people with type 2 diabetes who need insulin-containing drugs in the world will increase by about 79 million people by 2030, which will […]
- Diabetes: Epidemiologic Study Design For instance, the range of their parents’ involvement in the self-management practices can be a crucial factor in treatment and control.
- What to Know About Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is caused by autoimmune reaction that prevent realization of insulin in a body. Estimated 5-10% of people who have diabetes have type 1.
- Diabetes in Saudi Arabia It is expected that should this underlying factor be discovered, whether it is cultural, societal, or genetic in nature, this should help policymakers within Saudi Arabia create new governmental initiatives to address the problem of […]
- “Medical Nutrition Therapy: A Key to Diabetes Management and Prevention” Article Analysis In the process of MNT application, the dietitian keeps a record of the changes in the main components of food and other components of the blood such as blood sugars to determine the trend to […]
- Global and Societal Implications of the Diabetes Epidemic The main aim of the authors of this article seems to be alerting the reader on the consequences of diabetes to the society and to the whole world.
- Diabetes and Hypertension Avoiding Recommendations Thus, the promotion of a healthy lifestyle should entail the encouragement of the population to cease smoking and monitor for cholesterol levels.
- Pregnant Women With Type I Diabetes: COVID-19 Disease Management The grounded theory was selected for the given topic, and there are benefits and drawbacks of utilizing it to study the experiences of pregnant women with type I diabetes and COVID-19.
- Current Recommendations for the Glycemic Control in Diabetes Management of blood glucose is one of the critical issues in the care of people with diabetes. Therefore, the interval of the A1C testing should also depend on the condition of the patient, the physician’s […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Presentation, Treatment, and Examination Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrinologic disease, which is characterized by increased blood glucose concentration.
- Diabetes Problem at Country Walk Community: Intervention and Evaluation This presentation develops a community health nursing intervention and evaluation tool for the diabetes problem affecting Country Walk community.
- The Minority Diabetes Initiative Act’s Analysis The bill provides the right to the Department of Health and Human Services to generate grants to public and nonprofit private health care institutions with the aim of providing treatment for diabetes in minority communities.
- Communication Challenges Between Nurses and Patients With Type 2 Diabetes According to Pung and Goh, one of the limitations of communication in a multicultural environment is the language barrier that manifests itself in the direct interaction of nurses with patients and in the engagement work […]
- Diabetes Type 2 from Management Viewpoint Demonstrate the effects of type 2 diabetes and provide background information on the disease; Discuss the management plans of diabetes centers and critically analyze the frameworks implemented in the hospitals; Examine the existing methodology models […]
- Nursing Plan for the Patient with Diabetes Type 2, HTN, and CAD The health of the population is the most valuable achievement of society, so the preservation and strengthening of it is an essential task in which everyone should participate without exception.
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes is a serious public health concern that introduces a group of metabolic disorders caused by changes in the sugar blood level.
- Diabetes Mellitus Type II: A Case of a Female Adult Patient In this presentation, we are going to develop a care plan for a 47-year-old woman with a 3-year-old history of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (also known as Type II DM).
- Diabetes Insipidus: Disease Process With Implications for Healthcare Professionals This presentation will consider the topic of Diabetes Insipidus (DI) with a focus on its etiology and progress.
- The Nature of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 diabetes mellitus is a chronic autoimmune disease that has an active genetic component, which is identified by increased blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia.
- Imperial Diabetes Center Field Study The purpose is to examine the leadership’s practices used to maintain and improve the quality and safety standards of the facility and, using the observations and scholarly research, offer recommendations for improvement.
- Diabetes Risk Assessment After completing the questionnaire, I learned that my risk for the development of diabetes is above average. Modern risk assessment tools allow identifying the current state of health and possibilities of developing the disease.
- The Role of Telenursing in the Management of Diabetes Type 1 Telemedicine is the solution that could potentially increase the coverage and improve the situation for many t1DM patients in the world.
- Health Issues of Heart Failure and Pediatric Diabetes As for the population, which is intended to participate in the research, I am convinced that there is the need to specify the patients who should be examined and monitored.
- Juvenile Diabetes: Demographics, Statistics and Risk Factors Juvenile diabetes, also referred to as Type 2 diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, describes a health condition associated with the pancreas’s limited insulin production. The condition is characterized by the destruction of the cells that make […]
- Diabetes Mellitus: Pathophysiologic Processes The main function of insulin produced by cells within the pancreas in response to food intake is to lower blood sugar levels by the facilitation of glucose uptake in the cells of the liver, fat, […]
- Type 2 Diabetes Management in Gulf Countries One such study is the systematic review on the quality of type 2 diabetes management in the countries of the cooperation council for the Arab states of the Gulf, prepared by Alhyas, McKay, Balasanthiran, and […]
- Patient with Ataxia and Diabetes Mellitus Therefore, the therapist prioritizes using the cushion to the client and persuades the patient to accept the product by discussing the merits of the infinity cushion with a low profile in enabling the customer to […]
- Diabetes Evidence-Based Project: Disseminating Results In this presentation, the involvement of mentors and collaboration with administration and other stakeholders are the preferred steps, and the idea to use social networking and web pages has to be removed.
- The Problem of Diabetes Among African Americans Taking into consideration the results of the research and the information found in the articles, the problem of diabetes among African Americans has to be identified and discussed at different levels.
- Childhood Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Problems Based on the data given in the introduction it can be seen that childhood obesity is a real problem within the country and as such it is believed that through proper education children will be […]
- Hypertension and Antihypertensive Therapy and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus In particular, Acebutolol impairs the functions of epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are neurotransmitters that mediate the functioning of the heart and the sympathetic nervous system.
- Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment The disease is characterized by the pancreas almost not producing its own insulin, which leads to an increase in glucose levels in the blood.
- How to Manage Type 2 Diabetes The article is significant to the current research problem as the researchers concluded that the assessment of metabolic processes in diabetic patients was imperative for adjusting in the management of the condition.
- Type 2 Diabetes Analysis Thus, type 2 diabetes has medical costs, or the difficulties of coping up with the illness, economic ones, which are the financial costs of managing it, and the organizational ones for the healthcare systems.
- Clinical Trial of Diabetes Mellitus On the other hand, type II diabetes mellitus is caused by the failure of the liver and muscle cells to recognize the insulin produced by the pancreatic cells.
- Diabetes: Diagnosis and Related Prevention & Treatment Measures The information presented on the articles offers an insight in the diagnosis of diabetes among various groups of persons and the related preventive and treatment measures. The study identified 3666 cases of initial stages of […]
- Reinforcing Nutrition in Schools to Reduce Diabetes and Childhood Obesity For example, the 2010 report says that the rates of childhood obesity have peaked greatly compared to the previous decades: “Obesity has doubled in Maryland over the past 20 years, and nearly one-third of youth […]
- The Connection Between Diabetes and Consuming Red Meat In light of reporting the findings of this research, the Times Healthland gave a detailed report on the various aspects of this research.
- Synthesizing the Data From Relative Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes Speaking of such demographic factors as race, the white population suffers from it in the majority of cases, unlike the rest of the races, the remaining 0.
- Using Exenatide as Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults Kendal et al.analyzed the effects of exenatide as an adjunct to a combination of metformin and sulfonylurea against the combination of the same drugs without the adjunct.
- Enhancing Health Literacy for People With Type 2 Diabetes Two professionals, Andrew Long, a professor in the school of heath care in the University of Leeds, and Tina Gambling, senior lecturer in the school of health care studies from the University of Cardiff, conducted […]
- The Scientific Method of Understanding if Coffee Can Impact Diabetes The hypothesis of the experiment ought to be straightforward and understandable. The control group and the experiment group for the test are then identified.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Review This is because of the current patterns that show an increase in the prevalence of diabetes in offspring born to mothers with GDM.
- Health Service Management of Diabetes During the task, Fay makes a countless number of short calls and often takes water irrespective of the time of the day or the prevailing weather conditions.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: Pathophysiology, Role of Diabetes In the event of such an infection, the body becomes desperate to get rid of the intruders. For WBC, zero is given if the count is below 15cells/mm3, one is given if the count lies […]
- The Benefits of Sharing Knowledge About Diabetes With Physicians In this research, 3600 diabetic patients were surveyed from twelve hospitals, but due to exclusion criterion, only 1,200 were considered for this particular research. The system allocated numbers to the participants out of which 100 […]
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus – NSW, Australia We had a deeper evaluation of the implications of GDM and we cited the inadequacy of resources and technology as the contributors of GDM.
- Health and Wellness: Stress, Diabetes and Tobacco Related Problems Emotional health and well being refers to our ability to deal with our emotions as well as the emotions of those around us.
- 52-Year-Old Female Patient With Type II Diabetes
- Healthy People Project: Personal Review About Diabetes
- Nursing Diagnosis: Type 1 Diabetes & Hypertension
- Nursing Care For the Patient With Diabetes
- Coronary Heart Disease Aggravated by Type 2 Diabetes and Age
- Diabetes as the Scourge of the 21st Century: Locating the Solution
- Psychosocial Implications of Diabetes Management
- Gestational Diabetes in a Pregnant Woman
- Diabetes Mellitus: Prominent Metabolic Disorder
- Holistic Approach to Man’s Health: Diabetes Prevention
- Holistic Image in Prevention of Diabetes
- Educational Strategies for Diabetes to Patients
- Diabetes and Obesity in the United Arab Emirates
- Epidemiological Problem: Diabetes in Illinois
- Diabetes as a Chronic Condition
- Managing Diabetes Through Genetic Engineering
- Diabetes, Functions of Insulin, and Preventive Practices
- Treating of Diabetes in Adults
- Counseling and Education Session in Type II Diabetes
- Diabetes II: Reduction in the Incidence
- Community Health Advocacy Project: Diabetes Among Hispanics
- Community Health Advocacy Project: Hispanics With Diabetes
- Hispanics Are More Susceptible to Diabetes That Non-Hispanics
- Rates Diabetes Between Hispanics Males and Females
- Diabetes Mellitus and HFSON Conceptual Framework
- Prince Georges County Community Health Concern: Diabetes
- Fats and Proteins in Relation to Type 2 Diabetes
- Alcohol Interaction With Medication: Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Management and Evidence-Based Practice
- Critical Analysis of Policy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Australia
- The Treatment and Management of Diabetes
- Obesity and Diabetes: The Enemies Within
- Impact of Diabetes on the United Arab Emirates’ Economy
- Childhood Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Health Nursing and Managing Diabetes
- Diabetes Management: How Lifestyle, Daily Routine Affect Blood Sugar
- Diabetes Management: Diagnostics and Treatment
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: The Family Genetic History
- Diabetes Type II: Hormonal Mechanism and Intracellular Effects of Insulin
- Social, Behavioral, and Psychosocial Causes of Diseases: Type 2 Diabetes
- Supportive Intervention in the Control of Diabetes Mellitus
- Enhancing Foot Care Practices in Patients With Diabetes
- Community Health Promotion: The Fight Against Diabetes in a Community Setting
- Diabetes in Australia and Saudi Arabia
- Diabetes: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Point of Care Testing
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 or Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Prevention Measures in the Republic of the Marshall Islands
- Impact of Diabetes on Healthcare
- Gestational Diabetes: American Diabetes Association Publishers
- Gestational Diabetes: Child Bearing Experience
- Diabetes Mellitus Effects on Periodontal Disease
- Diabetes Type II Disease in the Community
- The Relationship of Type 2 Diabetes and Depression
- Glycemic Control in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
- The Diagnosis of Diabetes in Older Adults and Adolescents
- Physical Activity in Managing Type-2 Diabetes
- High Risk of Developing Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Children With Type 1 Diabetes in Clinical Practice
- Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Analysis
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Revealing the Diagnosis
- The Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: Lifestyle Choices
- Indigenous and Torres Strait Population and Diabetes
- Interpretation of the Diabetes Interview Transcript
- Type 1 Diabetes: Using Glucose Monitoring in Treatment
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes Patients’ Blood Sugar Prior to and After Surgical Procedures
- Diabetes Prevention: The Sanofi-Aventis Leaflet Review
- Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes: Medical Terminology Definition
- Modern Diabetes Treatment Tools
- Diabetes: Encapsulation to Treat a Disease
- Current Dietary for the Treatment of Diabetes
- Diabetes: Discussion of the Disease
- Stranahan on Diabetes Impairs Hippocampal Function
- A Clinical-Based Study of Young Adults Who Have Diabetes
- Panax Ginseng for Diabetes Treatment
- Depression and Diabetes Association in Adults
- Is There Anu Cure For Diabetes?
- Diabetes Self-Management: Evidence-Based Nursing
- Diabetes Type 2 in Children: Causes and Effects
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Case
- Health, Culture, and Identity as Diabetes Treatment Factors
- Diabetes Prevention in Chinese Elderly in Hunan
- “Experiences of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Starting Insulin Therapy” by Phillips
- Type 2 Diabetes: Nursing Change Project
- Diabetes and Health Promotion Concepts
- Type 2 Diabetes Project Results Dissemination
- Type 2 Diabetes in Geriatric Patients
- Type 2 Diabetes and Geriatric Evidence-Based Care
- Cultural Empowerment. Diabetes in Afro-Americans
- Diabetes Self-Management: Relationships & Expectations
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus
- Improving Comprehensive Care for Patients With Diabetes
- Diabetes Impact on Cardiovascular and Nervous Systems
- Side Effects of Metformin in Diabetes Treatment
- Type 2 Diabetes and Drug Treatments
- Diabetes Mellitus and Health Determinants
- Nursing Leadership in Diabetes Management
- Diabetes Education for African American Women
- Latent Autoimmune Adult Diabetes
- Obesity: Epidemiology and Health Consequences
- Diabetes in Urban Cities of United States
- Diabetes in Australia: Analysis
- Type 2 Diabetes in the Afro-American Bronx Community
- Type 2 Diabetes From Cultural and Genetic Aspects
- Type 2 Diabetes in Bronx: Evidence-Based Practice
- Type 2 Diabetes in Bronx Project for Social Change
- Ambition Diabetes and Diet on Macbeths’ Example
- Diabetes as Community Health Issue in the Bronx
- Diabetes Management Plan: Diagnosis and Development
- Diabetes Treatment and Care
- Transition from Pediatric to Adult Diabetes Care
- Diabetes Awareness Program and Strategic Planning
- Diabetes: Disease Control and Investigation
- Diabetes Pain Questionnaire and Patient Feedback
- Perception of Diabetes in the Hispanic Population
- Clinical Studies of Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Mellitus and Problems at Work
- Diabetes in the US: Cost Effectiveness Analysis
- Diabetes Investigation in Space Flight Research
- Diabetes Care Advice by Food and Drug Administration
- Artificial Intelligence for Diabetes: Project Experiences
- Diabetes Patients’ Long-Term Care and Life Quality
- Chronic Care Model for Diabetes Patients in the UAE
- Diabetes Among British Adults and Children
- Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes and Fibromyalgia
- Future Technologies: Diabetes Treatment and Care
- Epidemiology of Type 1 Diabetes
- Diabetes: Treatment Technology and Billing
- Pathophysiology of Mellitus and Insipidus Diabetes
- Cure for Diabetes: The Impossible Takes a Little Longer
- Stem Cell Therapy as a Potential Cure for Diabetes
- Stem Cell Therapy and Diabetes Medical Research
- Type II Diabetes Susceptibility and Socioeconomic Status
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: Pathophysiology and Treatment
- Obesity and Hypertension in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection and Type 2 Diabetes
- Socioeconomic Status and Susceptibility to Type II Diabetes
- Diabetes Mellitus: Differential Diagnosis
- Diabetes Disease in the USA Adults
- Education for African Americans With Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Treatment and Funding in Fulton County
- Diabetes Care: Leadership and Strategy Plan
- Diabetes Mellitus’ New Treatment: Principles and Process
- Diet and Nutrition: European Diabetes
- Preventing the Proliferation Diabetes
- Diabetes: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
- Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases in Medicine
- Ecological Models to Deal with Diabetes in Medicine
- Different Types of Diabetes Found in Different Countries
- Analysis of Program “Prevent Diabetes Live Life Well”
- The Effect of Physical, Social, and Health Variables on Diabetes
- Micro and Macro-Cosmos in Medicine and Care Models for Prevention of Diabetes
- Why Qualitative Method Was Chosen for Diabetes Program Evaluation
- Humanistic Image of Managing Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus Education and hemoglobin A1C level
- Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease
- Illuminate Diabetes Event Design
- Cause and Diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes
- Patient Voices: Type 2 Diabetes. Podcast Review
- Type I Diabetes: Pathogenesis and Treatment
- Human Body Organ Systems Disorders: Diabetes
- Age Influence on Physical Activity: Exercise and Diabetes
- Hemoglobin A1C Test for Diabetes
- Why Injury and Diabetes Have Been Identified as National Health Priority?
- What Factors Are Involved in the Increasing Prevalence of Type II Diabetes in Adolescents?
- Does the Socioeconomic Position Determine the Incidence of Diabetes?
- What Are the Four Types of Diabetes?
- How Fat and Obesity Cause Diabetes?
- How Exercise Affects Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Does the Treatment With Insulin Affect Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Diabetes Does Cause Depression?
- Does Diabetes Prevention Pay For Itself?
- How Does Snap Participation Affect Rates of Diabetes?
- Does Overeating Sugar Cause Diabetes, Cavities, Acne, Hyperactivity and Make You Fat?
- Why Diabetes Mellitus and How It Affects the United States?
- Does Alcohol Decrease the Risk of Diabetes?
- How Does a Person With Diabetes Feel?
- Does Periodontal Inflammation Affect Type 1 Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence?
- How Can the Paleolithic Diet Control Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Does Insulin Help Diabetes Be Controlled?
- Does Economic Status Matter for the Regional Variation of Malnutrition-Related Diabetes?
- How Can Artificial Intelligence Technology Be Used to Treat Diabetes?
- What Are the Main Causes and Treatments of Diabetes?
- What Evidence Exists for Treatments Depression With Comorbid Diabetes Using Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Products?
- Why Was Qualitative Method Chosen for Diabetes Program Evaluation?
- What Are the Three Types of Diabetes?
- How Does Poverty Affect Diabetes?
- What Is the Leading Cause of Diabetes?
- How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?
- What Are the Main Symptoms of Diabetes?
- How Diabetes Adversely Affects Your Body?
- What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Undiagnosed Diabetes?
- Epigenetics Essay Titles
- Alcohol Abuse Paper Topics
- Pathogenesis Research Ideas
- Therapeutics Research Ideas
- Hypertension Topics
- Osteoarthritis Ideas
- Cardiomyopathy Titles
- Malnutrition Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/
"357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/diabetes-essay-examples/.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Health Expect
- v.21(2); 2018 Apr
Diabetes‐related complications: Which research topics matter to diverse patients and caregivers?
Maman joyce dogba.
1 Department of Family and Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Laval University, Quebec City, QC, Canada
2 Office of Education and Professional Development, Faculty of Medicine, Laval University, Quebec City, QC, Canada
Mylène Tantchou Dipankui
Selma chipenda dansokho, france légaré, holly o. witteman.
3 Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Québec (CHU de Québec) Research Centre [Health of populations and best health practices axis], Quebec City, QC, Canada
Associated Data
Diabetes is a chronic disease with increasing prevalence worldwide. Although research has improved its treatment and management, little is known about which research topics matter to people living with diabetes, particularly among under‐represented groups.
To explore the importance of research topics among a diverse range of people living with any type of diabetes or caring for someone living with any type of diabetes.
We used a convergent mixed‐method design with quantitative and qualitative aspects. We surveyed a national sample of people living with diabetes and caregivers of people with diabetes, asking them to rate the importance of 10 predetermined important research topics. We also held three focus groups in two major cities to explore research concerns of people who are under‐represented in research.
469 adults (57% men, 42% women) in Canada completed the online survey, indicating that all 10 areas of research mattered to them, with the highest ratings accorded to preventing and treating kidney, eye and nerve complications. Fourteen individuals participated in three focus groups and similarly noted the importance of research on those three complications. Additionally, focus group participants also noted the importance of research around daily management. No new topics were identified.
Conclusions
This study confirmed the importance of research topics among a population of people living with or caring for someone with diabetes. Findings from this study were used to inform the vision for Diabetes Action Canada—a pan‐Canadian Strategy for Patient‐Oriented Research ( SPOR ) Network on diabetes and its complications.
1. INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic disease with increasing prevalence worldwide. 1 In 2014, an estimated 422 million adults, representing 8.5% of the global population, were living with diabetes. 2 The economic burden of this disease and its complications account for a growing proportion of local and national budgets. 3 , 4 For individuals, diabetes has negative psychosocial consequences that diminish quality of life. 5 While research has improved the treatment and management of diabetes and increased longevity, 6 mismatches between the focus of research and what matters to patients may lead to research waste. 7 , 8 Involving patients in the early stages of research is the first step in reducing such waste, as it helps increase the relevance of topics studied regarding such chronic diseases as diabetes. 9 People living with chronic diseases may develop a high degree of expertise which can provide new insight into how to improve their conditions and self‐care. 10 , 11 The patient perspective may complement that of the clinician and researcher by providing a more holistic interpretation of health and the experience of a health condition. 11
When seeking to involve patients as partners in research, it is critical to avoid reproducing or even exacerbating health inequities. Major disparities persist in the diagnosis, treatment, disease management and health outcomes of groups such as ethnic minorities, immigrants, people living in poverty, people whose mental health require regular follow‐up with a psychiatrist and seniors, all of whom are more vulnerable to diabetes‐related complications. 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 In spite of these continuing disparities, minority groups continue to be under‐represented in research, and engagement in defining research questions is no exception. Additionally, there is little guidance on how to facilitate the full participation of members of these groups in setting research priorities. 17 , 18 For example, although previous research in the United Kingdom has identified research priorities among people living with type 1 diabetes, those involved were predominantly white and female. 19
This study aimed to involve a national sample of people living with diabetes and caregivers of people living with diabetes in rating the importance of research topics around diabetes‐related complications. We further sought to capture the perspectives of people who are under‐represented in research. Our primary research question was as follows: What topics are most important to people living with or caring for someone living with diabetes regarding disease‐related complications as a means to help better orient future research priorities?
2.1. Study design
We used a multipronged mixed‐methods (QUAN + QUAL) approach with a convergent design 20 to capture what was important to people living with diabetes and caregivers regarding research on diabetes‐related complications. 21 , 22 According to the convergent mixed‐methods design, quantitative and qualitative methods are complementary during data collection, data analysis or both. In our case, we combined 21 the quantitative and qualitative data after we completed both sets of data collection. The study consisted of two components accordingly: (i) quantitative: an anonymous online survey to poll a national sample of people living with diabetes or caregivers of people living with diabetes on the importance of 10 predetermined research topics; and (ii) qualitative: holding focus groups with people living with diabetes who are members of under‐represented groups, in order to explore the views and experiences of those predicted to be under‐represented in the online survey. 23
2.2. Research ethics
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Board of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Québec (Quebec City, approval #: 2016‐2578). In agreeing to follow the link and take the online survey, participants provided implied consent. No survey questions were mandatory, meaning that respondents could skip questions if they wished. No attention filter was included. Prior to each focus group, we described the project and allowed participants to ask questions. Verbal consent of focus group participants was recorded.
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. online survey.
The online survey included questions on socio‐demographics, the person's experience with diabetes‐related complications and analog scales to rate the importance of 10 pertinent disease‐related complication research topics. These topics were identified in the literature describing previous priority‐setting exercises conducted with people living with type 1 diabetes, 19 and via email consultation with researchers, clinicians, representatives of patient organizations, caregivers and patient partners as part of a 6‐month funding application planning process.
Demographic data gathered from participants included: age, gender, ethnicity, income and education levels, geographical location and country of birth (inside or outside of Canada). Prior to finalizing the survey, all survey questions were iteratively reviewed by a person living with type 1 diabetes, a person living with type 2 diabetes, and a parent of a child with type 1 diabetes. The survey also contained three validated scales 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 to measure fear or distress associated with living with diabetes and its complications (see Appendix S1 ). These scales were included because we believed that fear or distress might influence how individuals rate the importance of research topics relative to the levels of fear they experience regarding these complications. If we were to observe large variations in ratings of importance, these data would allow us to explore potential reasons for the variation. The survey also included comment boxes where participants could provide additional information, including an open‐ended question asking for their ideas on additional topics concerning diabetes and diabetes‐related complications that require more research.
2.3.2. Survey participants
Over a 3‐day period in September 2015, we recruited participants through Qualtrics online sampling services. 29 To be included in the study, participants had to be living in Canada, aged ≥18 years, living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or caring for a child or an adult with diabetes and able to complete the survey in English or French. To ensure demographic diversity and offset variations in response rates, we established desired quotas based on gender (50/50 men and women), type of diabetes and relationship with diabetes (people with diabetes themselves, parents of children with diabetes, caregivers for adults with diabetes). We could not put quotas in place regarding ethnicity due to sampling constraints. In keeping with standard amounts for surveys administered by panel services, participants who completed the survey received $1.00‐$1.50 in compensation for their time answering our questions. We aimed for approximately 500 respondents. This target was selected as an achievable sample size that would allow for a broad sample of respondents and aligned with previous, similar research that sought feedback from 583 people living with diabetes about research questions they would like to see addressed. 19
2.3.3. Focus groups
Members of some groups may be less likely to complete online surveys, and thus, be under‐represented in survey‐based research. Therefore, we held 3 focus groups with patients and caregivers who were members of such groups. 30 To ensure variation in perspectives, we partnered with community organizations working with seniors, economically disadvantaged people, immigrants and people whose mental health requires follow‐up with a psychiatrist. 31 , 32 , 33 Two experienced qualitative researchers (MJD and MDT) conducted the focus groups using an established protocol. During the focus groups, patients were invited to discuss their experience with diabetes and its related complications, their perspectives and their concerns about the long‐term complications of diabetes. Participants also explained why, in their view, the concerns raised should be investigated by researchers.
2.3.4. Focus group participants
We used a convenience sample of members of under‐represented populations in the province of Quebec. We recruited focus group participants through three community‐based organizations that provide services to seniors, immigrants and people whose mental health requires regular follow‐up with a psychiatrist. To be eligible to participate in the focus groups, participants needed to be: living in Canada, aged ≥18 years, living with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes or caring for a person with diabetes, and able to understand and express themselves in French. Participants who were unable to comfortably express themselves in French were excluded from the study.
To recruit participants, the organizations circulated information about the study to its clients or members. Interested participants contacted the research associate either by email or by phone. The research associate contacted all potential participants to explain the study, assess their eligibility, answer questions and discuss logistics. A reminder call and/or email was sent to all participants 2 days prior to the scheduled focus group to confirm the time and location.
We held the three focus groups at times convenient for participants. Furthermore, to increase accessibility, the focus groups were held in the offices of the partnering community organizations; a common practice when working with members of vulnerable populations. 34 We conducted two focus groups in Quebec City: (i) seniors; and (ii) people whose mental health requires regular follow‐up with a psychiatrist. We conducted the third in Montreal with a group of immigrants. Each focus group was audio‐recorded and lasted between 70 and 90 minutes. Participants received $50 in appreciation for their time and 10$ for transportation. 19
2.4. Data analysis
Our interest in conducting both qualitative and quantitative portions was to ensure inclusion of diverse perspectives. In other words, while research often uses quantitative and qualitative methods to collect different types of data from the same population to inform a research question, we used different methods to collect data from groups both more and less likely to participate in different types of research, in an attempt to capture more representative results. Therefore, we carried out quantitative and qualitative analyses separately before bringing both parts together. Our first step was to conduct descriptive statistics using SPSS version 22 (Armonk, NY, USA: IBM Corp.) to measure central tendency and examine the range of variation in responses to our questions about the importance of 10 important diabetes research areas. We recorded focus group discussions and transcribed them verbatim. We performed a six‐stage thematic analysis 35 , 36 using NVivo qualitative analysis software (QSR International Pty Ltd. Version 10, 2012). We started by generating initial codes and themes, and inductively refining these themes based on the data. MTD analysed focus group data under the guidance of MJD. The codes were labelled with short phrases using the words of participants. Then, MTD sorted codes into potential themes and collated all relevant coded data extracts within the identified themes and subthemes. During this analysis, the codes, themes and subthemes were revised and refined. We used field notes 37 to validate and complete the information gathered during the focus groups. After separate analyses were completed, we combined the findings from each study to analyse how complementary or contradictory they were. We additionally examined how focus group findings could improve our interpretation of the statistical analysis.
3.1. Characteristics of participants
3.1.1. online survey.
Of the 500 participants surveyed, 31 were excluded from our analyses because they either completed the survey in a time deemed too fast to provide thoughtful answers (ie, 10 minutes or less) or because their responses were inconsistent with the questions. The remaining 469 participants were 57% men, had a mean age of 44 (SD = 15), came from across the 10 provinces and 3 territories of Canada, and represented a broad range of educational backgrounds and income levels. In line with our concerns and predictions about representation, participants predominantly identified as White or Caucasian (93%). Participants completed the survey in English (78%) or French (22%) and were either living with diabetes (96%) and/or caring for a child (<1%) or adult with diabetes (3%). Ten percent (10%) of participants were dealing with type 1 diabetes; 89% with type 2 diabetes; and 1% with another or unknown type. Median time living with diabetes was 19.5 years for type 1 diabetes (IQR 9.8‐30.0 years) and 8.0 years for type 2 diabetes (IQR 4.0‐15.0 years.) (See Table 1 A,B).
Online Survey Data
SD, sample standard deviation; IQR, interquartile range.
A vast majority of participants with type 1 or type 2 diabetes (45% and 60%, respectively) reported other health concerns, some of which may be diabetes‐related complications (see Table S1 ). These concerns were, for types 1 and 2 respectively, eye complications (34% and 15% of participants), heart complications (13% and 24% of participants), kidney complications (22% and 8% of participants), mental health complications (34% and 27% of participants) and nerve complications (40% and 30% of participants). Many participants reported not having been screened for these complications in the previous year. Of those with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, 63% and 78% reported not receiving screening for eye complications within the past year; 71% and 68% reported not receiving screening for heart complications; 53% and 70% reported not receiving screening for kidney complications; 68% and 86% reported not receiving screening for mental health complications; and 61% and 70% reported not receiving screening for nerve complications.
3.1.2. Focus groups
Of the 23 people who initially expressed an interest in participating in the study, 5 were ineligible because they neither had diabetes nor cared for a person with diabetes; 2 withdrew because they were unavailable on the day of the focus group and 2 withdrew without explanation. Of the 14 remaining individuals who participated in the 3 focus groups, 7 (50%) were female and 3 total (21%) were living with type 1 diabetes. The characteristics of participants are shown in Table 2 .
Focus Groups: Characteristics of the 14 participants
3.2. Data analysis
3.2.1. online survey.
We report here the medians rather than the means because the distribution of responses to the survey questions about the importance of research topics regarding preventing and treating the complications of diabetes was not symmetrical. The median scores for people with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes were between 84 and 100 (on a 0 to 100 rating scale, with 100 indicating extremely important) indicating that participants assigned high importance to all 10 predetermined research topics with relatively little variation between topics. Topics that had the highest median scores and the least variation in responses were preventing and treating kidney, eye, heart and nerve problems. Research topics for which participants had the widest interquartile range in scores were as follows: preventing and treating mental health problems, developing and testing smart insulin, patient and caregiver education, and artificial pancreas research (type 1) (see Table 3 ).
Online survey results regarding the importance of diabetes‐related research topics
Cronbach's alphas were .94, .93 and .94, respectively, for the Fear of Complications Scale, 28 Hypoglycemia Fear Scale 24 , 25 , 26 and Diabetes Distress Scale. 27 People with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes had mean scores of 23 (SD 10) and 18 (SD 10), respectively, on the Fear of Complications Scale (range 0‐45). Participants with type 1 diabetes had a mean score of 34 (SD 17) on the Hypoglycemia Fear Scale (range 0‐108) indicating sometimes fearing hypoglycaemia, while participants with type 2 diabetes had a mean score of 21 (SD 16) indicating being concerned less often. Finally, participants with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes had mean scores of 2.81 (SD 1.23) and 2.23 (SD 1.27) on the Diabetes Distress Scale. Using the cut‐off score recommended by Fisher et al 38 this indicates that on average, participants with type 1 diabetes had moderate but non‐clinical levels of distress (threshold = 3) (see Table S1 ).
Comments provided by participants in the open box sections of the survey aligned with the quantitative findings and illustrate the emotional distress linked to diabetes and diabetes management, the fear associated with episodes of hypoglycaemia and its consequences, and with the long‐term complications of the disease (see Table 3 ).
3.2.2. Focus groups
The thematic analysis allowed us to identify a set of general concerns about diabetes‐related complications as reported by members of under‐represented groups.
3.3. General concerns about diabetes‐related complications
Participants in the focus groups provided further insight into the nature of their concerns about the impact of diabetes on their quality of life, life‐expectancy (Table 4 , citation 1) and vulnerability to other diseases (Table 4 , citation 2). Most participants reported being most afraid of complications that potentially lead to functional impairment (blindness), additional morbidity (chronic renal failure) or death (hypoglycaemia) (Table 4 , citation 3). Furthermore, participants pointed to the challenge of continuously monitoring and managing the disease (Table 4 , citations 4, 5 and 6).
Citations from focus groups participants
In addition to these general and common concerns, four specific themes arose from the focus group discussions:
Theme 1: The bidirectional relation between individual history and socio‐economic context, and the management of diabetes
Two aspects of individual history and context were mentioned by participants: (i) the influence of previous life‐experiences on the management of diabetes; and (ii) the impact of socio‐economic conditions on the outcomes of the disease. Regarding the first point, participants said they suspected a strong relation between their previous life‐experiences and the management of diabetes‐related complications. They wished that this relation could be investigated. For example, one participant talked about adopting bad eating habits such as dieting during the day and binging at night because she saw a loved one in a diabetic coma. (Table 4 , citations 7 and 8).
With respect to the second point, discussions in both focus groups focused on the need for studies examining the cost of diabetes treatment (Table 4 , citation 9). For example, some participants argued that they sometimes had to choose between paying their rent and buying insulin and complained that this should be a concern to researchers.
Theme 2: The need to better understand the danger of polymedication toxicity in patients with multiple comorbidities
Focus group participants who were either elderly or had experienced mental health problems expressed their concerns about toxic drug interactions resulting from polymedication. They stressed the urgent need to understand, whether and/or to what extent, there may be interactions between their diabetes medication and other treatments (Table 4 , citation 10).
Theme 3: The need to better understand barriers to quality care for immigrants living with diabetes
Focus group participants who were immigrants had two core concerns regarding diabetes and its related complications for researchers to address, notably: (i) how to improve access to quality care for immigrants with diabetes; and (ii) how to make health‐care professionals more knowledgeable about the specific care needs of immigrants living with diabetes. Most immigrants in the study talked about cultural or linguistic barriers to navigating the health system. For example, one participant talked about how she had learned to be assertive in expressing her needs (Table 4 , citation 11). Another participant talked about his experience going back and forth between the doctor and the pharmacist without answers to his needs (Table 4 , citation 12). Finally, participants who were immigrants unanimously reported that health‐care professionals were inadequately trained to detect symptoms and diagnose diabetes among individuals who are newcomers to the country. One participant, for example, said that this led to a failure to recognise pre‐diabetes symptoms, forcing this person to consult multiple physicians before a glycaemia test was requested (Table 4 , citation 13).
Theme 4: The need for better dissemination of the research results on diabetes
Focus group participants also expressed concerns about not having access to updated information on diabetes. They reported being aware of on‐going research, but were never informed by community organizations about the research results (Table 4 , citations 14 and 15).
Participants also pointed to a need for better information for their loved ones and relatives, to help them understand and provide better support in the management of the disease (Table 4 , citations 16, 17, 18).
4. DISCUSSION
This study aimed to explore the importance of diabetes‐related complication research topics relevant to those living with or caring for someone living with diabetes. Additionally, we wished to explore the reasons why these topics are important from the perspective of under‐represented populations. Findings from both the quantitative and qualitative components of the study complement each other and can be summarized in three main points.
First, the alignment of what is important for patients in diabetes research. Both survey and focus group participants indicated the importance of preventing and treating well‐known complications of diabetes such as kidney, eye and nerve problems. This finding confirms that research on such complications matters to patients and caregivers. Second, the need for more research about the bidirectional influence of the “life context” on diabetes. Our participants also pointed out that there are a number of individual and contextual factors, such as individual circumstances (eg, life conditions, previous experiences), socio‐economic status and the experience of managing the condition that need further exploration, especially for the most under‐represented people included in this study. Finally, the third point was the need to deepen diabetes‐related research in under‐represented populations. Our results further suggest that research topics should be tailored to address specific challenges such as access to culturally relevant care for immigrants. 39
Consistent with other studies, 40 , 41 our quantitative data show that participants had moderate levels of emotional distress around diabetes‐related complications. Our qualitative analysis provided some insight into the nature of these concerns. For example, the fear that diabetes‐related complications (eg, kidney failure or blindness) may result in functional impairment or death (eg, as a result of a hypoglycaemia). Additionally, fears were often amplified not only by personal experience as shown in other studies, 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 but also by witnessing others dealing with such complications (such as having seen a loved one with kidney failure or experiencing a hypoglycaemic episode). These experiences impact how research topics are rated by those whose lives are touched by the disease. Unfortunately, further investigation of these questions was not possible with this study for two reasons: (i) the focus group participants were not asked to rate the complications as did online survey participants; and (ii) the focus groups were conducted separately from the quantitative portion of the study.
Overall, our findings point to a need for more research on diabetes, its complications and the bidirectional influence of a number of individual and contextual factors such as individual circumstances (eg, life conditions, previous experiences, emotional distress); socio‐economic status; and the experience of managing the condition, especially for the most under‐represented groups included in this study. It was suggested that research topics should be tailored to address specific challenges, such as access to culturally competent care for immigrants. 39
Our study did, however, have a few limitations. Due to time and budget constraints, focus group activities were restricted to Montreal and Quebec City, where our team is based. This limited our ability to recruit in other cities across Canada and also limited a true representation of the country's population. Although our respondents and their experiences reflect a broad sample of the population of Canada, several other groups who may have particular needs (eg, pregnant women, Indigenous peoples, parents or guardians of children with diabetes, as well as caregivers) were under‐represented in the online survey and were absent in the focus groups. Therefore, our sample lacks representation of some other under‐represented populations in Canada. Additionally, language barriers may have limited our selection of participants and excluded individuals, particularly those from under‐represented groups such as immigrants. Furthermore, because this online survey and focus group based study relied on participant self‐reports, the data could be limited by the subjects’ ability for introspection, their individual interpretations and social desirability bias. 47 Finally, because this was a preliminary study aimed at exploring the importance of different research topics to those living with diabetes and caregivers in Canada, we did not undertake prioritization activities that require trading‐off one priority against another to produce a ranked list. Such activities are planned for future research.
One strength of this study is its use of qualitative and quantitative methods to help capture the experiences of under‐represented groups and diverse participants from across Canada. This approach proved feasible as a method for efficiently exploring patients’ and caregivers’ preliminary views on research topics within a short period of time.

5. CONCLUSIONS
This study confirmed the importance of research topics regarding diabetes‐related complications within a population of people living with diabetes or caring for someone with diabetes, and further explored reasons why these topics might be important for certain groups of under‐represented people. The results of this study about what matters most to people living with, and caring for those living with diabetes, including people from under‐represented populations, informed the research program of a 5‐year pan‐Canadian Strategy for Patient‐Oriented Research Network on Diabetes and its related complications (2016‐2021). 39 A broad range of people living with diabetes are now involved as patient partners in this network, collaborating on research projects, research planning and supporting network governance. We anticipate that our results and on‐going work will contribute to the development of targeted interventions better aligned with improving the health and well‐being of people whose lives are touched by diabetes.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
M.J.D. provided the study concept and design, supervised the protocol development and research, enrolled patients for the qualitative stage, facilitated focus groups, analysed data and provided the first draft of the manuscript. S.C.D. conducted the descriptive statistics, wrote the quantitative part of the manuscript, reviewed and edited the manuscript. M.T.D. enrolled patients for the qualitative stage, facilitated focus groups, analysed data and wrote the manuscript. F.L. reviewed and edited the manuscript. H.O.W. supervised the survey data collection, reviewed and edited the manuscript. M.J.D. is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Acknowledgements.
The authors thank people living with diabetes, their caregivers and community organizations across Canada for their invaluable contributions to this study. The authors thank Judith Kashul for linguistic editing of this manuscript. Additionally, we thank Mary Zettl, for her contribution editing, coordinating and finalizing this article for publication.
Dogba MJ, Dipankui MT, Chipenda Dansokho S, Légaré F, Witteman HO. Diabetes‐related complications: Which research topics matter to diverse patients and caregivers? Health Expect . 2018; 21 :549–559. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.12649 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
This study was funded through a subgrant of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR SCD 139932)
271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles
If you’re looking for diabetes-related research topics, you’re at the right place! StudyCorgi has prepared a list of interesting diabetes thesis topics, presentation titles, and essay ideas to write about. Read on to discover the most engaging diabetes project titles and research questions!
👨⚕️ TOP 7 Diabetes Thesis Topics
🏆 best essay topics on diabetes, ❓ diabetes research questions, 👍 good diabetes research topics & essay examples, 🔎 current research questions about diabetes, 🌶️ hot diabetes topics for presentations, 📝 catchy titles for diabetes research paper, 🎓 most interesting diabetes project ideas, 💡 simple diabetes research paper topics, ✍️ diabetes essay topics for college.
- Diabetes: Causes and Effects of Disease
- Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes
- Reflection on Diabetes Program
- Comparison of Type 1 and 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes in a 50-Year-Old Male
- Diabetes and Diabetic Foot
- Diabetes Management in Primary Care
- Diabetes: Types, Causes, Symptoms and Cures Diabetes mellitus is a group of endocrine diseases that develop as a result of an absolute or relative deficiency of the hormone insulin.
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Discussion Diabetes mellitus type 1, normally known as Type 1 Diabetes, is a type of diabetes that is caused by the lack of insulin resulting from the destruction of insulin-producing cells.
- The Ageing and Diabetes Care Diabetes is chronic metabolic mayhem in which the body is unable to metabolize glucose-related carbohydrates, fats, and proteins because of a lack of insulin hormone.
- Caring for Patients With Diabetes This paper contains recommendations on caring for patients with diabetes mellitus, mainly providing a warm welcome to the patient in the clinic.
- Clinical Narrative: Conversation With a 30-Years-Old Woman With Diabetes This clinical narrative will outline a conversation with a patient that prompted a reflection about a nurse of the future.
- Diabetes in Children: The Prevalence and Prevention The Canadian Pediatric Association has laid down several recommendations in order to prevent the spread of the disease: encouraging physical activities, and a healthy diet, etc.
- Homeostatic Imbalance and Diabetes Symptoms The choice of treatment methods for diabetes mellitus depends on the type of disease, but any form of the disease requires a compulsory diet, exercise, and physical activity.
- Diabetes Type 1 and Type 2 and Its Causes This paper analyzes the causes of diabetes. They vary depending on genetic makeup, family history, ethnicity, health, and environmental factors.
- Type II Diabetes: Disease Analysis Diabetes is one of the diseases that can cause several complications on patients. Evidence has revealed that diabetic complication range from stroke, heart disease or death.
- Diabetes Mellitus Overview and Analysis Diabetes which is medically referred to as diabetes mellitus, is a metabolic disorder that occurs due to the lack of production or action of insulin in the body.
- Diabetes Type 2 Treatment and Health Promotion The purpose of this paper is to develop evidence-based management and a plan for a patient with diabetes type 2 and describe health promotion and possible follow-up.
- Improving Diabetes Lifestyle Diabetes is one of the health conditions affecting many people in different corners of the world. Individuals and family members affected by the condition should lead healthy lives.
- Role of Physical Activity in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes The paper analyzes facts on the interlinkages between metabolic outcomes, physical activity levels in patients with type 2 diabetes, and strategies.
- Diabetes: Anatomy and Physiology This paper analyses how diabetes affects the various body parts and the treatment and prevention methods. It is a condition that causes difficulties.
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Nursing Practice Gestational diabetes mellitus is widely debated as one of the controversial and less-researched medical conditions. Nurses play an important role in the treatment of GDM.
- Reducing Diabetic Foot Incidence and Its Related Complications Complications arising from the diabetic foot are caused by deep infections and gangrene, which increase the risk of the amputation of the lower limb.
- The Type II Diabetes in Obese Children Approximately 10% of school-going children aged between 5 years and 17 years can be described to be obese; a quarter of them are at a heightened risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Prevention of Type II Diabetes This article is devoted to the prevention of type 2 diabetes: the factors that can trigger the disease, as well as the categories of people who are at risk, are considered.
- Evidence-Based Practice in Diabetes Nursing Care While all nurses should be familiar with the importance of evidence-based practice in enhancing patient outcomes, few have received formal education on how to implement it.
- Type 1 Diabetes in Children: Genetic and Environmental Factors The prevalence rate of type 1 diabetes in children raises the question of the role of genetic and environmental factors in the increasing cases of this illness.
- Diabetes: Etiology and Expected Treatment Options This paper is a diabetes case study of a patient who has type I diabetes and has not been managing her blood sugars since she’s been ill and unable to keep any food down.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Cost-Effective Solution for India At present, a large number of people are experiencing health complications due to a sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activities, poor nutritional habits, and SUD.
- Digital Health Interventions for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes “Digital health interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes” is aimed to determine the patients’ perceptions about the diabetes self-management education (DSME) limitation.
- Diabetes Mellitus of Type I vs. Type II Unhealthy eating habits, obesity, and an inactive lifestyle are the most common associations with diabetes. These factors are among the main reasons for developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity, Diabetes and Self-Care The paper discusses being overweight or obese is a high-risk factor for diabetes mellitus and self-care among middle-aged diabetics is a function of education and income.
- Childhood Diabetes in Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia has one of the highest diabetes prevalence rates in the world. Five-year research determines that Saudi Arabia has an adult diabetes prevalence rate of 23.7%.
- Social Epidemiology: Diabetes Mellitus in Australian Indigenous People People are advised to engage in physical activity, take a balanced diet, avoid stress, and reduce food and drinks with high levels of sugar.
- Type 1 Diabetes in Children Type 1 diabetes is a major problem among young members of the population because they become infringed from their earliest years.
- Diabetes Conference as a Scholarly Activity I chose to attend a conference on diabetes held by Baptist Health South Florida, a non-profit medical organization. Diabetes is a too broad topic to be explained in a single day.
- Type 2 Diabetes Patients Care Plan The current paper dwells on the elaboration of a care plan for type 2 diabetes patients. The mortality rates connected to type 2 diabetes grow bigger with every other year.
- Which Type of Diabetes Begins in Childhood or Adolescence?
- Can Coffee Reduce the Risk of Diabetes?
- How Does a Child Get Childhood Diabetes?
- What Factor Is Most Predictive of Successful Compliance With Diabetes Treatment?
- Can Exercising and Dieting Prevent People From Type 2 Diabetes?
- What Is a Health Promotion Strategy for Diabetes?
- How Can We Prevent Diabetes in Children?
- What Are the Risk Factors and Complications of Diabetes?
- Can Food Stamps Help to Reduce Medicare Spending on Diabetes?
- How Is Childhood Diabetes Effectively Managed?
- What Affects the Quality of Life for People With Type 1 Diabetes?
- Does Diabetes Affect Cardiovascular Health?
- Can a Child Get Diabetes From Eating Too Much Sugar?
- What Are the 7 Steps to Control Diabetes?
- How Can Diabetes Management Be Improved?
- What Are the Components of a Successful Diabetes Care Team?
- Can Diabetes Go Away if You Lose Weight?
- When Does Type 1 Diabetes Need Insulin?
- What Is the Average Lifespan of a Person With Type 2 Diabetes?
- Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Controlled Without Medication?
- What Are Some of the Latest Advances in the Treatment of Diabetes?
- Does Stress Cause Gestational Diabetes?
- How Has Treatment for Diabetes Changed Over the Years?
- Can a Child Live a Normal Life With Diabetes?
- What Is the Best Way to Manage Diabetes?
- Diabetes Self-Management Education in Elderly This project proposal depicts the major details of the study aimed at improving the health outcomes of older adults suffering from diabetes through the provision of training.
- Type-2 Diabetes: Condition and Resources Analysis Type-2 diabetes is an increasingly prevalent health issue in the US, and its early onset has an aggressive disease phenotype and leads to unfavorable long-term prognosis.
- Insulin Pump Therapy in Diabetes This paper explores a study conducted by Johnson, Copper, Jones, and Davis to determine the long-term effect of using insulin pump therapy in the treatment of type 1 diabetes in children.
- Insulin Pharmacological Effects in Diabetes Management Insulin is a protein-peptide hormone produced by β-cells of the pancreas. This paper describes pharmacological properties and the effects of insulin in diabetes management.
- Metformin for Type 2 Diabetes Patients Metformin is not metabolized by the organism: research in patients shows that the drug is excreted unaltered in the urine with not metabolites identified.
- Diabetes Patient and Holistic Nursing Intervention The nurse-led diabetes intervention and care management is an effective method of treatment for the acute problems caused by the illness and prevention of the adverse outcomes.
- Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes The development of hypertension and diabetes stems from the use of Glucocorticoid medications. Glucocorticoids increases blood glucose production in the liver.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Diabetes in Canada Type 2 diabetes is a disease that presents a great danger to the life of a human being, and there is currently no cure for it.
- Pathophysiology of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Diabetes insipidus is a type of diabetes that is characterized by a reduced production of the ADH (antidiuretic hormone) also known as vasopressin in the body.
- Evidence-Based Practice Project on Diabetes A fundamental component of early Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treatment is patient education, which in turn sets the foundation for effective treatment.
- Annotated Bibliography to Health Literacy, Self-Care and Patients With Diabetes This annotated bibliography covers topics related to health literacy, self-care, and glycemic control among others in patients with diabetes.
- Diabetes Mellitus and Its Pathophysiology Diabetes mellitus is a disease that results in the increase of sugar level in the blood due to the inability of the body to produce sufficient insulin.
- Nutrition Impact in Developing Type II Diabetes Mellitus Type II diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease that affects the production and use of insulin in the body facilitating the uptake of glucose (blood sugar).
- Care Plan For the Patient With the Type 2 Diabetes The patients with the diagnosis of Diabetes type 2 require complex care of the professionals in different spheres, of the so-called diabetes care team.
- Diabetes Type 2 Self-Management Education The concept of diabetes self-management comprises several activities aimed to alleviate disease symptoms: medication intake, physical exercise, and diet.
- Diabetes in African American Patients This research project addresses the implications of diabetes for African American patients and reviews the possible ways of treating it.
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment and Management Type 1 diabetes mellitus is associated with different complications. The disease can occur naturally and make it impossible for many patients to lead quality lives.
- Type II Diabetes in Evidence-Based Pharmacology In this paper, diabetes mellitus (DM type 2) will be reviewed through a synthesis of relevant information about its pathophysiology, genomic issues, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Diabetes in Evidence-Based Nursing Practice The paper analyzes “Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Evidence-Based Treatment Update” and “Assessment of Diabetes-Related Knowledge among Nursing Staff in a Hospital Setting”.
- Diabetes Mellitus Type II: Diagnosis and Treatment Type II diabetes is caused by a combination of amplified tissue struggle to insulin, scarce insulin emission, or the surplus secretion of glucagon.
- A Diabetes-Related PICOT (Research) Question The study of the PICOT question involves the search and systematization of sources to find the most relevant evidence.
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes A nurse should not recommend medical treatment for excess weight to a patient who has not tried traditional methods of treatment.
- The Role Exercise Plays in Diabetes Prevention The paper states that exercise has a critical role in preventing diabetes. It helps control cholesterol, weight, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
- Ketones Diet and Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus The paper synthesizes evidence-based practices in nursing that can equip care providers with the necessary knowledge to educate diabetic patients.
- Healthy Lifestyle Program Impact on Type 2 Diabetes Patients The purpose of the paper is comparing the clinical results of exercise program implementation and conventional therapy in terms of type 2 diabetes interventions.
- Aspects of the Epidemiology of Diabetes The paper discusses the epidemiology of diabetes. It provides information about diabetes mellitus, explains the types of it, and shows how it varies.
- Diabetes Mellitus Self-Management The paper indicates a rising trend in diabetes mellitus diagnosis. Individuals who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes need information on self-management.
- Significance of the Diabetes Issue The paper states that diabetes is a severe health issue characterized by a high spread level and a range of symptoms that require constant monitoring.
- Diabetes Disease, Its Prevention and Treatment This paper states that the critical element of achieving success in the precluding of diabetes and its complications appears to be the prevention of diabetes.
- The Diabetes Epidemic in the United States Diabetes is one of the most common autoimmune diseases in the United States. This is a pressing issue for the nation, especially for nurses and doctors.
- Diabetes: Types, Causes, and Complications Diabetes is a serious and dangerous disease that, if untreated, can cause severe health problems or lead to death. There are several types of diabetes.
- Diabetes: Causes, Treatment, and Magnitude The importance of such problem as diabetes is obvious. This disease is the fastest growing in the world at the moment, taking a significant burden on healthcare professionals.
- Social Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes: Ecosocial Perspective The diaTribe Foundation aims to address the urgent issue of increased diabetes prevalence among racial minorities, who have poor awareness of diabetes.
- Habits to Prevent Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes The paper aims to raise awareness among various racial groups in Las Vegas about good preventive habits that prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes Prevention in Racial Minorities: Lifestyle Changes To help diabetic patients control weight loss, well-trained nurses need to promote education on healthy diets and physical activities.
- Incretin Mimetic Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes In patients with type 2 diabetes, there is a significant decrease in the incretin effect and a decrease in insulin secretion in response to an oral load.
- Discussion: Diabetes in the United States Diabetes diagnoses are more common in individuals who have completed high school or earned a GED, or have some college education than in those who hold a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- What is the role of gut microbiota in the development of insulin resistance?
- How to improve the accuracy of continuous glucose monitoring systems?
- What are the long-term effects of bariatric surgery for diabetes management?
- How does sleep quality influence glycemic control?
- How can telemedicine enhance diabetes care?
- What is the impact of diabetes on cognitive function and brain health?
- What are the best practices for diabetes prevention in children?
- What are the barriers to older adults’ diabetes self-management?
- How does gestational diabetes affect maternal and fetal health?
- How does continuous glucose monitoring impact patients’ quality of life?
- Care for Diabetes African-American Patients in Nevada There is an urgent need to promote the professional role of nurses for diabetes African-American patients in Nevada.
- Diabetes Patient Case Study: Endocrinology Mr. X’s situation can be analyzed through the lens of social determinants. The first determinant is health care access and quality.
- The Current Trends of Patients With Diabetes The study aims to observe the current trends of patients with diabetes aged sixty-five or older within the selected healthcare setting.
- Interventions Preventing Diabetes Development The patient was diagnosed with prediabetes three months ago. Possible interventions to prevent the development of diabetes type two were unable to succeed.
- Diabetes Health Care Information Collection This work aims at proposing a method of collecting information associated with diabetes, such as demographics, medications used, and other data.
- Reaching Optimal Health With Type 2 Diabetes To combat the symptoms of this disease and its consequences, it is necessary to adjust nutrition, which will normalize the level of insulin in the human body.
- Effects of Diabetes on Quality of Care in Massachusetts The patient involved was a male relative who is diabetic and receives treatment at the Massachusetts General Hospital.
- Epidemic of Type 2 Diabetes Among Hispanic Males Diabetes is a disease with a very high prevalence of 19% among Hispanic males. It is more common among Hispanics than all other races.
- Role of Genes in Diabetes Development Diabetes is a global pandemic whose effects cause immeasurable burden to the globe. About ten percent of the world’s population suffers from diabetes currently.
- Symptoms of Type I Diabetes The paper discusses the possible symptoms inherent to diabetes. They are unmotivated weak, have drowsiness, persistent thirst, and have dry mouths.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Information Collection This work aims at reviewing legislative considerations, collecting information and its life cycle, which are associated with diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes and Appropriate Therapeutic Diet The food intake and knowledge needed can be related to the education and subsequent application of the therapeutic diet.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Study Purpose, Design and Results Study results showed the developed glucose control and prompted variations in the muscle that are associated with improvement in metabolic wellbeing in type two diabetes patients.
- Evidence-Based Practices to Reduce the Risks of Diabetes A person’s lifestyle can directly affect their health in various ways. An unhealthy lifestyle can lead to a diverse range of diseases later in life.
- Supporting Patients With Diabetes in U.S. The central problem that this essay raises describes the characteristics of the U.S. health care system in supporting patients with diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Etiology Decreased insulin sensitivity in the muscle, tissue, and liver leads to increased insulin production by beta cells of the pancreas.
- Diabetes: Community Teaching The community setting is the Adult Day Care Center, yet this teaching plan also applies to hospitals and clinics with a high influx of diabetes patients.
- Type 2 Diabetes Management in Primary School Children The care plan for children with type 2 diabetes implies meeting specific objectives for managing the condition of this population group in the context of educational facilities.
- Awareness on Diabetes Causes and Treatment The need to increase awareness of diabetes causes and treatment is the reason why precisely this disease is chosen for this study.
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Children and Adolescents The increase of T2DM among children and adolescents in the last five years has surfaced in parallel with a surprising rise in the number of young people who are obese.
- Diabetes: Overview of the Problem and Treatment The percentage of people who have diabetes has increased lately due to the sedentary lifestyle that many individuals select.
- The Importance of Diabetes Prevention Education Diabetes has become a significant threat to society that’s why the annotated bibliography was selected to ensure that readers can acquire information regarding the disease.
- Scientific Method: The Risk of Contracting Diabetes The paper discusses that drinking coffee may reduce the risk of contracting diabetes. The control group produced a significant increase in blood sugar levels.
- Problem of Diabetes in the Elderly Despite the efforts made by health care organizations around the world, the number of people with diabetes is expected to grow.
- Educating the Client on Diabetes Medications In order to ascertain the reasons for polypharmacy, an interview was conducted with a client who takes several medications at once.
- Diabetes in African Americans and Effectiveness of Educational Sessions According to the Diabetes Research Institute Foundation, over a tenth of the population has diabetes and related conditions, and the number of new cases continues to rise rapidly.
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes Metformin is an antihyperglycemic drug prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes to increase their glucose tolerance.
- Australian Government Policy Response to Diabetes Mellitus Type II It is highly necessary to inform the health officer trainees about the main constraints and challenges that should be considered to handle the problem of diabetes pandemic.
- Diabetes Community Health Programs in Florida The discussion examines how the quality of life in Florida correlates with diabetes and proposed a powerful program for dealing with diabetes in children.
- Diabetes Prevention Lessons in the Community This paper discusses the problem of diabetes prevention in the community, elaborates the teaching plans to help all stakeholders affected by the diabetes problem.
- Understanding Biostatiscal Principles with Diabetes This paper is meant to review the effectiveness of Biostatistics applied by the information/news medium in communicating diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 related information.
- Patient Engagement in Type 2 Diabetes The presented research is not exactly in line with the existing literature since it does not demonstrate a statistically significant effect of the selected method by Smith et al.
- Community Obesity and Diabetes: Mississippi Focus Study The paper provides a detailed discussion of the correct method to be used in the state of Mississippi to control and avoid obesity and diabetes issues.
- Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes Mellitus This artticle describes Diabetes Mellitus, its etiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and nursing considerations.
- Weight Training and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Men Should research in media if the claim that little exercise is adequate to minimize the risk of type two diabetes.
- Childhood Diabetes in Saudi Arabia: The Prevalence of Type 1 Diabetes Among Children Diabetes is one of the major chronic ailments facing children in Saudi Arabia. This trend has been observed in recent years.
- Community Prevention: Type 2-Diabetes in California Community-based programs on prevention and control of type 2-diabetes will incorporate approximately four intensive and core sessions that will be offered every year.
- Microbiome matters: the link between gut microbiota and diabetes.
- Diabetes and the aging brain: cognitive impacts on older adults.
- Addressing cultural disparities in diabetes care.
- The complex relationship between diabetes and heart health.
- The influence of stress on diabetes development.
- Beyond blood sugar: the multi-organ effects of diabetes.
- The benefits of a plant-based diet for diabetes.
- Can type 2 diabetes be reversed?
- Unique challenges of adults with latent autoimmune diabetes.
- Diabetes and reproductive health: the impact on fertility.
- Diabetes Education Skills for Low Grade Literacy Patients This article is a guide for nurses to help them explain diabetes to patients with low medical literacy in simple terms.
- Reducing the Incidence of Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Foot in the Veteran Population The research proposes to use a comprehensive education program to reduce the incidence of diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot in the Veteran population.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Characteristics, Epidemiology Type 1 diabetes exhibits different characteristics depending on the person suffering from the disease, place, and time.
- Smartphone Role in Type 2 Diabetes Self-Management The current research paper endeavors to explore mat-analysis studies and past research studies on the role played by smartphones in type 2 diabetes self-management.
- Smartphone Application and Diabetes Reminder Management The proposed intervention implies the implementation of smartphone applications aimed at managing diabetes, the intervention has a lot of advantages.
- Diabetes Insipidus: Causes, Treatment, Pathophysiology The lack of sufficient antidiuretic hormone in the body results in diabetes insipidus. Diabetes insipidus can be managed by taking high amounts of fluids to keep the body hydrated.
- Type II Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Initial Signs, Symptoms, This paper discusses pathophysiology associated with type 2 diabetes, initial signs, symptoms, and type of vascular changes that occur early in type II diabetes.
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Guidelines The research paper recommends that ADA and other health bodies should customize DSME so that it can suit the needs of diverse patients in different unique communities.
- Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Inhaled Insulin Therapy The paper will focus on glycaemic control for patients with diabetes mellitus and will attempt to identify whether the use of inhaled insulin is beneficial for these patients.
- The Diabetes Study of Northern California The population-based study shows that Latinos in the United States are disproportionately affected by diabetes type-2 and have poor glycemic control.
- Lived Experience of Diabetes Among Older, Rural People The implied research question is, “what are the most significant issues associated with the self-management of diabetes among the elderly?”
- Diabetes Diagnosis: The Use of Magnetic Nanoparticles This paper will discuss the use of magnetic nanoparticles in the diagnosis of diabetes, its application in the children population, and its relevance to the nursing profession.
- “Bariatric Surgery v. Conventional Medical Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes” by Mingrone This paper critiqued a study “Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes” that aimed to compare traditional medical therapy and bariatric surgery.
- Depression Intervention Among Diabetes Patients The research examines the communication patterns used by depression care specialist nurses when communicating with patients suffering from diabetes.
- The New Jersey Diabetes Prevention and Control Program The aim of the New Jersey Diabetes Prevention and Control Program is to mitigate the high level of type II diabetes in the target population, through education on lifestyle.
- Type 2 Diabetes Patients and Self-Administer Insulin The importance of patient education to facilitate primary health care skills and knowledge in vulnerable populations has been broadly addressed in scholarly literature.
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology This paper explains Type 1 diabetes. The causes, symptoms, therapeutic procedures, and management procedures of the disease are also explained.
- Diabetes and Tuberculosis: Review of Articles in Nursing This paper discusses articles in nursing about different issues related to diabetes, trends in prevalence and control, and also about tuberculosis treatment.
- Reduction of Kidney Failure Due to Diabetes This proposal aims to outline the project’s matter for future advanced practice because of the prevalence of chronic kidney disease and its vast economic and health consequences.
- Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus This article discusses in detail how type 2 diabetes develops over time in patients with metabolic syndrome, focusing on the pathophysiological changes that occur.
- Diabetes Type 2 and Related Lifestyle Challenges Diabetes is continuously becoming a big challenge. There is more than one type of diabetes: type 2 seems to be the most challenging one.
- Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Foot Evaluation The research proposes to use a comprehensive education program to reduce incidences of diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot in the population.
- Screening and Management of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Guidelines Health care systems across the world are employing diverse screening strategies and criteria in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus among the population.
- Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus in Low-Income Communities The present paper offers a review of literature on the major reasons for diabetes prevalence in low-income communities.
- Diabetes: Danger Factors Analysis Diabetes is one of the most common diseases that older people are most affected by it. Danger factors include many points.
- Nursing Diabetes and Obesity Patients Nursing diabetes and obese patients are regarded as one of the most serious problems of contemporary nursing practices.
- Increasing Diabetes Infections Among the Hispanic Populations The article’s objective is centered around establishing whether chronic stress makes US Hispanics more susceptible to diabetes.
- Study of the Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects many systems in the body; it has both anatomical and biochemical consequences, which are manifested in various ways.
- Type II Diabetes: Treatments Metformin is the most common drug recommended for treating type II diabetes. This drug lowers blood glucose level by reducing the production of insulin.
- Diabetes in American Society To get prepared for diabetes, it is important to learn diabetes triggers, causes, complications, and other characteristics.
- A Peer Group Support in Intervention for Adolescent With Type One Diabetes Adolescents with diabetes usually experience difficulties in their physical, emotional, and social stress emerging from the complex medication regimen they have to comply with.
- Chronic Bronchitis, Heart Failure, Hypertension, and Diabetes Mellitus This paper discusses the symptoms and causes of such diseases as chronic bronchitis, heart failure, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus.
- Diabetes Type 1 and 2 Preventive Measures Diabetes is a common disease that can lead to adverse consequences for humans’ overall health if not treated properly.
- Effects of Intensive Blood-Pressure Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Blood pressure in diabetic patients remains controversial. The uncertainty surrounding its control complicates patients’ care as the risk of future cardiac events grows.
- The Prevalence of Diabetes in the Elderly From 2000 to 2009 The endeavor of this review is to determine the occurrence of diabetes in the American populace for the period spanning 2000 to 2009.
- The Connection Between Apoptosis and Diabetes The purpose of this study is to investigate the existing body of information regarding apoptosis processes and their connection with diabetes mellitus.
- Mobile Apps for Diabetes Mellitus Patients Research To address people with diabetes mellitus issues, researchers advocate that mobile health services might help them manage their life with the disease better.
- Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus in Low-Income Communities: An Ethical Aspect
- Diabetes: Preventive Measures and Diagnostics
- Diabetes Care Team Best Practices
- Impacts of Nutrition on the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Type II Diabetes Mellitus Overview
- The Role of Significant Others in Adolescent Diabetes, A Qualitative Study by Carroll and Marrero
- Incidence of Diabetes in the United States
- How Diabetes Works: Medical Analysis
- Mexican American Children and Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes Chronic Condition Management
- Mindful Eating Intervention and Diabetes Self-Management Intervention
- Patient Education Technology: MySugr Diabetes Logbook
- Diabetes Mellitus and Self-Care Education
- Insulin Pump Therapy in Children with Diabetes
- Evaluation of the Clinical Outcomes of Telehealth for Managing Diabetes
- Impact of Establishing a Communication Network of Family Physicians on Level of Hba1c and FBS in Patients With Diabetes
- Integrative Review on Adherence in Haitians With Diabetes
- Preventing Diabetes and Heart Failure Hospitalizations
- Diabetes Issues in the United States and Florida
- Diabetes Control and Education: Four-Week Project
- Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes Patients
- Bariatric Surgery in Type 2 Diabetes Management
- The Use of Diabetes Self-Management Apps by African-American Women
- Older Rural People with Diabetes: Life Expectancy
- EHR Database Management: Diabetes Prevention
- Diabetes Management for Older Adults in Long-Term Care
- Diabetes Mellitus II: Screening and Statistics
- Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Interventions and Prevention
- Type 2 Diabetes, Risk Factors, Medical Intervention
- Developmental Care for Type 1 Diabetes
- Evidence-Based Practice: Diabetes Prevalence
- Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy and Diabetes
- Educational Programs for Hispanic Patients with Diabetes
- Diabetes Negligence in the Pediatric Population
- Diabetes in Children: Symptoms and Diagnostics
- Foot Ulcers Management in Diabetes Patients
- Transition’s Impact for Patients With Diabetes
- Diabetes in Adolescents, Social and Medical Issues
- Education Strategies for Elderly Patients with Diabetes
- Diabetes Interventions for Aging African Americans
- Chronic Fatigue in Diabetes
- Diabetes Diagnosis and Classification
- Type II Diabetes Treatment
- Diabetes and High Blood Pressure Patient Teaching
- Diabetes 2 Complications: Neuropathy and Retinopathy
- Weight Gain, Atherosclerosis, Diabetes Relationship
- Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes
- Risk Assessment Models for Diabetes Complications
- Diabetes Among Hispanics in Miami: Risk Factors
- Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in China
- Diabetes and Status among Immigrants in California
- Chronic Disease: Diabetes Mellitus
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults
- Diabetes Genetic Risks in Diagnostics
- Patients With Diabetes and Concomitant Diseases’ Risk
- Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetes
- Using Dulaglutide in the Treatment of Patients with Diabetes
- Diabetic Nutritional Plan For a 15-Year-Old Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patient
- Diabetes Treatment: Computer-Based Intervention
- Diabetes: Country Walk Community’s Health Problem
- Wound Care Tests in Diabetes
- Treatment and Advances in Diabetes
- Type II Diabetes: Patient Case Study
- Types of Diabetes Mellitus: Role of Insulin
- Diabetes Mellitus Patients and Supporting Resources
- Diabetes and Its Economic Cost in the United States
- Food Diversion as a Type-2 Diabetes Treatment
- The Most Acute Problems With Patients With Diabetes
- Diabetes in American Adolescents and Its Effects
- Vitamin D Deficiency and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
- Diabetes and Possible Interventions
- Diabetes and Dementia Relationships and Nursing
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents
- Type 2 Diabetes: Disease Process and Screening
- Overweight Diabetes Patients With Cardiovascular Risk
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Integrated Management
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
- “Prandial Inhaled Insulin Plus Basal Insulin Glargine Versus Twice Daily Biaspart Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicentre Randomised Trial”: Article Review
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/diabetes-essay-topics/
"271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/diabetes-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/diabetes-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/diabetes-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "271 Diabetes Essay Topics, Research Questions, & Presentation Titles." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/diabetes-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Diabetes were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 22, 2024 .
- Open access
- Published: 21 June 2023
Association between neck circumference and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Dandan Li 1 na1 ,
- Yuxin Zhao 2 na1 ,
- Lifang Zhang 3 ,
- Qiqi You 4 ,
- Qingqing Jiang 4 ,
- Xiaoxv Yin 4 &
- Shiyi Cao 4
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome volume 15 , Article number: 133 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1473 Accesses
1 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Despite that several original researchers have investigated the association between neck circumference (NC) and the risk of diabetes mellitus (DM), their results remain controversial. This review aimed to quantitatively determine the risk of DM in relation to the NC.
We conducted a literature search of PubMed, Embase, and the Web of Science from these databases’ inception through September 2022 to identify observational studies that examined the association between NC and the risk of DM. A meta-analysis of the random-effects model was applied to combine the results of the enrolled studies.
Sixteen observational studies involving 4,764 patients with DM and 26,159 participants were assessed. The pooled results revealed that NC was significantly associated with the risk of type 2 DM (T2DM) (OR = 2.17; 95% CI: 1.30–3.62) and gestational DM (GDM) (OR = 1.31; 95% CI: 1.17–1.48). Subgroup analysis revealed that after controlling for BMI, the relationship between the NC and T2DM remained statistically significant (OR = 1.94; 95% CI: 1.35–2.79). Moreover, the pooled OR of T2DM was found to be 1.16 (95% CI: 1.07–1.27) for an increment per each centimeter in the NC.
Conclusions
Integrated epidemiological evidence supports the hypothesis that a greater NC is associated with an increased risk of T2DM and GDM.
The incidence of diabetes mellitus (DM) has increased substantially in recent decades [ 1 ], which has imposed a heavy burden on healthcare systems. Knowledge of early markers to predict the disease and the adoption of related preventive strategies are of vital public health significance for improving this situation.
Obesity is a well-established risk factor for DM [ 2 ]. Several studies have suggested that total body obesity and abdominal obesity, which can be assessed based on body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and waist/hip ratio, could predict the risk of developing DM [ 3 ]. Recently, upper body subcutaneous fat has drawn the attention of researchers, and a study has shown that it may confer higher risks than visceral abdominal fat [ 4 ]. Furthermore, neck circumference (NC) has been considered as a proxy measure for upper body subcutaneous fat distribution [ 5 ]. Compared with other anthropometric indexes, NC measurement is more convenient, shows minimal fluctuations, and is not affected by respiratory conditions and diet. A meta-analysis [ 6 ] indicated that NC was moderately accurate in identifying overweight and obesity in children and adolescents, and another study [ 7 ] arrived at a similar conclusion in men and women of different age groups. Moreover, some studies have demonstrated that NC may be independently correlated with metabolic risk factors above and beyond BMI and WC [ 5 , 8 ].
Over the past decades, numerous studies have assessed the relationship between NC and DM, but the results remain inconsistent. Some investigations have reported that NC has a direct relationship with DM [ 9 , 10 , 11 ], whereas others have shown that larger NC is not associated with the risk of DM [ 12 , 13 ]. Considering the inconsistencies in the findings of existing studies, a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational epidemiological studies were performed to evaluate the association between NC and the risk of DM.
Literature search strategy
The present systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement [ 14 ]. PubMed, Embase, and the Web of Science were searched from their inception until September 2022 using the following keywords with no restrictions to identify the relevant citations: ‘neck circumference’ in combination with ‘diabetes,’ ‘impaired glucose tolerance,’ ‘impaired fasting glucose,’ or ‘insulin resistance.’ The reference lists of the retrieved articles were also reviewed to identify any other pertinent studies.
Study selection
The studies were included in the meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (i) the study design was cross-sectional, cohort or case-control, (ii) the odds ratio (OR) or relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) of DM incidence related to the NC were reported or could be calculated from the provided data. Abstracts, non-original papers (reviews, editorials, or letters), gray literature, unpublished studies, and studies providing data on the relationship between the NC and diabetes-led mortality or complications were excluded. If there was more than one report from the same study, we only included the report with the most detailed information for both NC and the outcome.
Data extraction
Two authors (D.L. and Y.Z.) independently extracted the following information from the included studies: first author, publication year, country or region, study design, age, sample size, the number of men and women, the cutoff point for NC, adjusted OR/RR with 95% CI, and the adjusted factors. The differences in data extraction between the two investigators were resolved via discussion with the third investigator (S.C.).
Quality assessment
We assessed the methodological quality of cohort and case-control studies with reference to the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale, which awards a score of 0–9 based on the selection of participants, comparability of the groups, and exposure/outcome assessment [ 15 ]. Studies scoring 0–3, 4–6, and 7–9 were categorized as low-, moderate-, and high-quality studies, respectively.
The assessment tool involving 11 items, as recommended by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, was applied for cross-sectional studies [ 16 ]. The quality of the studies was first evaluated with reference to the established questions and then scored according to the following criteria: 1 point = if the item was considered in the study and 0 points = if the item was not considered or this aspect was ambiguous.
Each study was rated independently by two authors (D.L. and Y.Z.). Any disagreements were resolved via discussion with a third investigator (S.C.).
Statistical analysis
We considered OR as the common measure of association between the NC and the risk for DM. The reported RR was considered approximately as the OR. We calculated an overall pooled OR by using a random-effects model for the main analysis [ 17 ]. If studies reported results separately for different subgroups, we combined the subgroup estimates by using fixed-effect models before inclusion in the main meta-analysis. Q statistic with a significance level of < 0.10 and I 2 statistic were applied to test the heterogeneity. The I 2 statistic measures the percentage of total variation across studies because of heterogeneity rather than because of chance. It was calculated according to the formula by Higgins [ 18 ]. Substantial heterogeneity is an I 2 value of at least 50%. Sensitivity analyses and subgroup analyses were conducted to evaluate the influences of the study design and population characteristics on our results. All statistical analyses were conducted by using STATA statistical software version 13.0 (STATA Corp, College Station, Texas, USA). P values were two-sided with a significance level of 0.05.
Study selection and evaluation
The results of the literature research and selection are illustrated in Fig. 1 . Initially, we retrieved 163 citations from PubMed, 213 from Embase, and 304 from the Web of Science. After 353 duplicates were excluded, 327 citations were screened through titles and abstracts, of which 264 were excluded because they were reviews, editorials, letters, commentaries, news reports, case reports, or irrelevant studies. After assessing the full texts of the remaining 63 articles, we excluded 47 articles, as 28 of these did not study the relationship between NC and DM incidence while 19 did not provide useful data to calculate these parameters. Finally, 16 studies [ 4 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ] were included (including seven cohort studies, one case-control study, and eight cross-sectional studies).
Flow diagram of studies included in the systematic review and meta-analysis
Study characteristics
The main characteristics of the 16 studies are summarized in Table 1 . These studies were published between 2010 and 2022. The study samples ranged in size from 196 to 8,450, with a total of 26,159, while the number of cases of DM ranged from 29 to 2,068, with a total of 4,764. Of these studies on the relationship between NC and DM, nine were about type 2 DM (T2DM), and seven were about gestational DM (GDM). None of the studies focused on the risk of other types of diabetes in relation to the NC. The study locations were as follows: nine studies were from Asia, three from Europe, three from South America, and one from North America. In addition, the quality scores for the seven cohort studies ranged from 5 to 9, with an average score of 7.43 from a maximum of 9 (Table A.1 ). The quality score for one case-control study was 7 (Table A.2 ). The quality assessment scores for the eight cross-sectional studies ranged from 4 to 7, with a mean score of 5 from a maximum of 11 (Table A.3 ).
Results of the meta-analysis
Association between the nc and t2dm.
The results from the random-effects model combining the ORs for the relationship of T2DM with NC are shown in Fig. 2 . When compared with people with smaller NC, those with larger NC were at an increased risk for T2DM, and the pooled OR was 2.17 (95% CI: 1.30–3.62). Substantial heterogeneity was observed ( I 2 = 82.6%, P = 0.001).
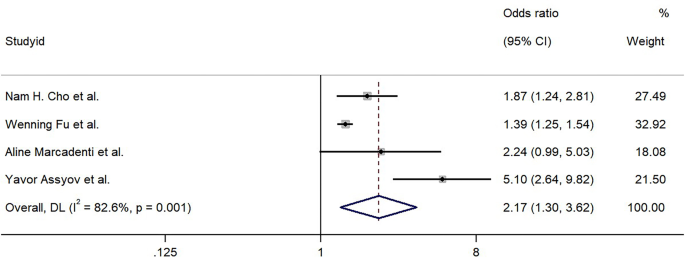
The association between neck circumference as a categorical variable and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk
Two studies [ 4 , 19 ] evaluated the risk of T2DM for per standard deviation increment in the NC, and the OR with 95% CI was 1.70 (95% CI: 1.35–2.13) and 2.06 (95% CI: 1.71–2.49), respectively. Three other studies [ 11 , 21 , 26 ] reported the risk of T2DM per 1-cm increase in the NC, and the OR with 95% CI was 1.43 (95% CI: 1.05–1.96), 1.05 (95% CI: 1.03–1.96), and 1.16 (95% CI: 1.10–1.23), respectively. We standardized the two results reporting OR per standard deviation increment in the NC to the form of OR per 1-cm increment and calculated the pooled OR by using a random-effects model. The pooled OR of T2DM for an increment per each centimeter in the NC was 1.16 (95% CI: 1.07–1.27), with substantial heterogeneity across studies ( I 2 = 83.9%, P < 0.001) (Fig. 3 ).
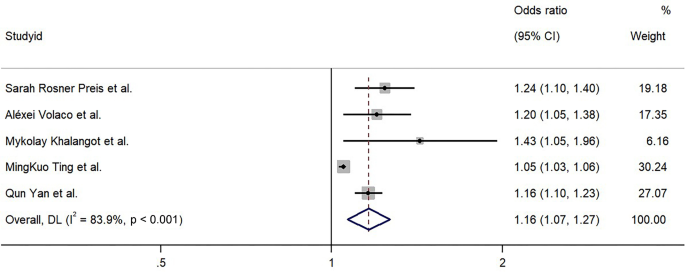
The association between neck circumference as a continuous variable and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk
Results of sensitivity analyses and subgroup analyses
To identify the potential influence of a single study on the pooled results, any single study was excluded in turn and the results of the remaining included studies were pooled. The pooled OR did not materially change and ranged from 1.55 (95% CI: 1.22–1.99) to 2.71 (95% CI: 1.43–5.14) (Fig. A1 ).
Table A.4 shows the results of subgroup analyses on the NC and T2DM risk. A larger NC was found to be associated with an increased risk for T2DM in most subgroups. Subgroup analysis by the state revealed that the participants from South America and Europe had a higher risk of T2DM, and the highest point estimate was recorded for Europe (OR = 5.10, 95% CI: 2.64–9.82). The difference in the pooled OR among these three groups showed statistical significance ( P = 0.003). Subgroup analysis by controlling for age also indicated a statistically significant difference in results ( P = 0.001). No significant difference was detected between the groups in terms of other variables. Notably, subgroup analyses by controlling for BMI indicated that the heterogeneity mainly arose from studies with unadjusted BMI ( I 2 = 93.2% for studies with unadjusted BMI and I 2 = 0% for studies with adjusted BMI).
Association between the NC and GDM
The results from the random-effects model combining the ORs for the relationship between GDM and NC are depicted in Fig. 4 . The pooled OR was 1.31 (95% CI: 1.17–1.48), and no significant heterogeneity was observed ( I 2 = 34.6%, P = 0.164).
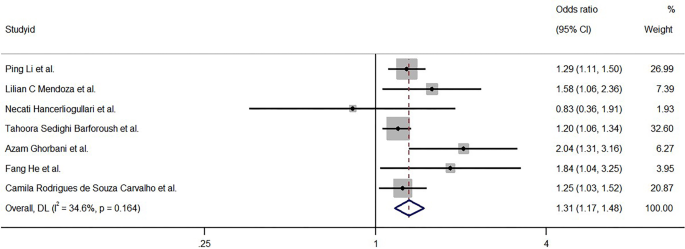
The association between neck circumference as a categorical variable and gestational diabetes mellitus risk
The sensitivity analysis indicated that the results were unaffected by any single study, with the pooled OR ranging from 1.25 (95% CI: 1.16–1.40) to 1.36 (95% CI: 1.15–1.61) (Fig. A2 ).
Table A.5 demonstrates the results of subgroup analyses about the NC and GDM risk. Subgroup analyses by the study design, state, and the cut-off point for NC, whether controlling for age and controlling for BMI showed no statistically significant difference in the outcomes. Most subgroups indicated a positive and statistically significant relationship between the NC and an increased risk of GDM.
NC, a novel anthropometric index, is considered a marker of subcutaneous fat distribution in the upper body and an independent predictor of metabolic disorders, such as glucose intolerance, hypertension, and fatty liver disease [ 29 , 30 , 31 ]. This systematic review and meta-analysis focused on the link between NC and the risk of DM. The investigation included 16 observational epidemiological studies involving 4,764 patients with DM and 26,159 participants. Pooled analysis revealed that NC was positively associated with the risk of DM. Specifically, compared with individuals who had smaller NC, those with larger NC had a 2.17 times increased risk of T2DM. Moreover, compared with pregnant women who had smaller NC, the risk of GDM was increased by 31% for those with larger NC.
Several potential mechanisms have so far been proposed to describe the relationship between NC and DM. First, NC is correlated positively with triglyceride levels and negatively with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, both of which are robust markers for decreased insulin sensitivity [ 9 , 32 ]. Additionally, larger NC with enhanced sympathetic activity may contribute to insulin resistance, thereby resulting in the development of DM [ 9 ]. Second, high NC values serve as a predictor of obstructive sleep apnea in short-sleeping obese men and women [ 33 ]. Certain studies have documented that obstructive sleep apnea is related to abnormal glucose metabolism [ 34 , 35 ].
Owing to the substantial heterogeneity in studies exploring the association between NC and the risk of T2DM, subgroup analyses were conducted based on various factors. The findings showed that the association between NC and T2DM risk remained significant in most subgroups. The percentage and distribution of body fat for the same BMI varies across different populations [ 36 ]. Therefore, a subgroup analysis based on the state was performed, which revealed significant differences. Considering the potential differences between men and women, sex-based subgroup analyses were conducted, the results of which demonstrated that larger NC was a risk factor for T2DM in both sexes. Moreover, subgroup analyses based on adjusted variables, such as BMI and age, were performed to explore their possible influence on the relationship between NC and T2DM risk. According to the obtained results, after adjusting for age, the combined OR was lower than the unadjusted one. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant, which indicated that age was a positive confounder and that the true correlation effect between NC and T2DM may be weaker.
NC exhibits several advantages against previously used indices, such as BMI and WC. Although BMI is the most widely used index for defining overweight and obesity, it cannot assess body fat distribution. Likewise, although WC is a commonly used index for evaluating abdominal obesity, it fluctuates greatly and can be easily affected by conditions and time [ 37 ]. NC is stable, time-saving, and convenient to measure. Previous studies have observed that NC performs better than WC in evaluating metabolic health [ 38 ] and that it can predict excess body fat [ 39 ] and cardiovascular risk factors [ 40 ]. This may suggest that NC can be considered in guidelines for assessing obesity, especially when conventional anthropometric measures are not available, convenient, or practicable [ 38 ].
Our study has several strengths. First, in this systematic review and meta-analysis, the relationship between NC and T2DM was evaluated for the first time. Although Rahnemaei FA et al.’s study involved NC and DM, the researchers concentrated on the relationship between various anthropometric indicators and GDM [ 41 ]. Second, consistent results from sensitivity analyses among the included studies indicate the robustness and reliability of our findings.
However, there are some limitations, which are of concern. First, adjusted confounders varied among the included studies. Some probably important residual confounders, such as BMI, sex, and age, were not adjusted in certain studies. Second, different cutoff points for NC size were defined across studies, which might have introduced heterogeneity in the obtained results. Third, publication bias was not evaluated owing to the small number of studies on T2DM risk and GDM risk that were included in the meta-analysis in relation to the NC.
The findings from this meta-analysis suggests that the risk of T2DM is elevated in individuals with a high NC. Moreover, pregnant women with high NC values have higher odds of GDM than those with low values. Nonetheless, the number of included studies was limited, and some possibly important residual confounders, such as BMI, were not adjusted in certain studies. Thus, more high-quality studies are required to confirm the predictive potential of NC for DM.
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Body mass index
Confidence interval
Diabetes mellitus
- Gestational diabetes mellitus
- Neck circumference
Relative risk
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Waist circumference
Koye DN, Magliano DJ, Nelson RG, Pavkov ME. The global epidemiology of diabetes and kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018;25:121–32.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Fletcher B, Gulanick M, Lamendola C. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2002;16:17–23.
Vazquez G, Duval S, Jacobs DR, Silventoinen K. Comparison of body mass index, waist circumference, and waist/hip ratio in predicting incident diabetes: a meta-analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29:115–28.
Preis SR, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, D’Agostino RB, Levy D, Robins SJ, et al. Neck circumference as a novel measure of cardiometabolic risk: the Framingham Heart study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:3701–10.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ben-Noun L, Laor A. Relationship of neck circumference to cardiovascular risk factors. Obes Res. 2003;11:226–31.
Ma C, Wang R, Liu Y, Lu Q, Liu X, Yin F. Diagnostic performance of neck circumference to identify overweight and obesity as defined by body mass index in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hum Biol. 2017;44:223–9.
Kroll C, Mastroeni S, Czarnobay SA, Ekwaru JP, Veugelers PJ, Mastroeni MF. The accuracy of neck circumference for assessing overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hum Biol. 2017;44:667–77.
Ben-Noun LL, Laor A. Relationship between changes in neck circumference and cardiovascular risk factors. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2006;11:14–20.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Cho NH, Oh TJ, Kim KM, Choi SH, Lee JH, Park KS, et al. Neck circumference and incidence of diabetes Mellitus over 10 years in the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES). Sci Rep. 2015;5:18565.
Assyov Y, Gateva A, Tsakova A, Kamenov Z. A comparison of the clinical usefulness of neck circumference and waist circumference in individuals with severe obesity. Endocr Res. 2017;42:6–14.
Khalangot M, Gurianov V, Okhrimenko N, Luzanchuk I, Kravchenko V. Neck circumference as a risk factor of screen-detected diabetes mellitus: community-based study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2016;8:12.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Marcadenti A, Fuchs FD, Moreira LB, Gus M, Fuchs SC. Adiposity phenotypes are associated with type-2 diabetes: LAP index, body adiposity index, and neck circumference. Atherosclerosis. 2017;266:145–50.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hancerliogullari N, Kansu-Celik H, Oskovi-Kaplan ZA, Kisa B, Engin-Ustun Y, Ozgu-Erdinc AS. Optimal maternal neck and waist circumference cutoff values for prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus at the first trimester in turkish population; a prospective cohort study. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2020;36:1002–5.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Wells GA SB, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Available from http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/nosgen.doc
Rostom A, Dubé C, Cranney A, Saloojee N, Sy R, Garritty C, et al. Celiac disease. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2004;104:1–6.
Google Scholar
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Volaco A, Martins CM, Soares JQ, Cavalcanti AM, Moyses ST, Filho RP, et al. Neck circumference and its correlation to other anthropometric parameters and finnish diabetes risk score (FINDRISC). Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14:464–71.
Fu W, Zou L, Yin X, Wu J, Zhang S, Mao J, et al. Association between neck circumference and cardiometabolic disease in chinese adults: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e026253.
Ting MK, Liao PJ, Wu IW, Chen SW, Yang NI, Lin TY, et al. Predicting Type 2 diabetes Mellitus occurrence using three-dimensional anthropometric body surface scanning measurements: a prospective cohort study. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:6742384.
Li P, Lin S, Cui J, Li L, Zhou S, Fan J. First Trimester Neck circumference as a predictor for the development of gestational diabetes Mellitus. Am J Med Sci. 2018;355:149–52.
Mendoza LC, Harreiter J, Simmons D, Desoye G, Adelantado JM, Juarez F, et al. Risk factors for hyperglycemia in pregnancy in the DALI study differ by period of pregnancy and OGTT time point. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018;179:39–49.
He F, He H, Liu W, Lin J, Chen B, Lin Y, et al. Neck circumference might predict gestational diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese women: a nested case-control study. J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8:168–73.
Barforoush TS, Ghadimi R, Pahlevan Z, Ahmadi N, Delavar MA. The relationship between neck circumference and gestational diabetes mellitus in iranian women. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;7:22.
Yan Q, Sun D, Li X, Zheng Q, Long H, Feng B. Neck circumference and incidence of type 2 diabetes in Chinese Elderly individuals: A Community-Based Cohort Study. Obes Facts. 2021;14:450–5.
de Souza Carvalho CR, Dualib PM, Mattar R, Dib SA, de Almeida-Pititto B. Neck circumference as a predictor of gestational diabetes and risk of adverse outcomes in pregnancy of brazilian woman with overweight and obesity. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022;66:439–45.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ghorbani A, Hashemipour S, Mohammadi Z, Zohal M, Lalooha F. Appropriate neck/waist circumference cut-off points for gestational diabetes prediction in iranian pregnant women: the baseline analysis of the Qazvin maternal and neonatal metabolic study (QMNMS), Iran. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022;16:102579.
Kaplan NM. The deadly quartet. Upper-body obesity, glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:1514–20.
Huang BX, Zhu MF, Wu T, Zhou JY, Liu Y, Chen XL, et al. Neck circumference, along with other anthropometric indices, has an independent and additional contribution in predicting fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0118071.
Gomez-Arbelaez D, Camacho PA, Cohen DD, Saavedra-Cortes S, Lopez-Lopez C, Lopez-Jaramillo P. Neck circumference as a predictor of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance and low-grade systemic inflammation in children: the ACFIES study. BMC Pediatr. 2016;16:31.
Byun AR, Lee SW, Lee HS, Shim KW. What is the most appropriate lipid profile ratio predictor for insulin resistance in each sex? A cross-sectional study in korean populations (the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey). Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2015;7:59.
Cizza G, de Jonge L, Piaggi P, Mattingly M, Zhao X, Lucassen E, et al. Neck circumference is a predictor of metabolic syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea in short-sleeping obese men and women. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2014;12:231–41.
Young T, Shahar E, Nieto FJ, Redline S, Newman AB, Gottlieb DJ, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in community-dwelling adults: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:893–900.
Cizza G, Piaggi P, Lucassen EA, de Jonge L, Walter M, Mattingly MS, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea is a predictor of abnormal glucose metabolism in chronically sleep deprived obese adults. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65400.
[Anonymous]. Appropriate body-mass index for asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–63.
Article Google Scholar
Zhou BF. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in chinese adults–study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in chinese adults. Biomed Environ Sci. 2002;15:83–96.
Joshipura K, Muñoz-Torres F, Vergara J, Palacios C, Pérez CM. Neck Circumference May be a better alternative to Standard Anthropometric Measures. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:6058916.
Gonçalves VSS, Faria ERD, Franceschini SDCC, Priore SE. Neck circumference as predictor of excess body fat and cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents. Revista de Nutrição. 2014;27:161–71.
Alfadhli EM, Sandokji AA, Zahid BN, Makkawi MA, Alshenaifi RF, Thani TS, et al. Neck circumference as a marker of obesity and a predictor of cardiometabolic risk among saudi subjects. Saudi Med J. 2017;38(12):1219–23.
Rahnemaei FA, Abdi F, Pakzad R, Sharami SH, Mokhtari F, Kazemian E. Association of body composition in early pregnancy with gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0271068.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Dandan Li and Yuxin Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Medical Records Management, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Shenzhen Fuyong People’s Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Medical Service, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Lifang Zhang
School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Qiqi You, Qingqing Jiang, Xiaoxv Yin & Shiyi Cao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.C. and X.Y. conceived the study. D.L. and Y.Z. wrote the main manuscript text. Q.Y. and Q.J. checked the related data information again and assessed their quality. L.Z. prepared figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dandan Li .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, D., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Association between neck circumference and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr 15 , 133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-023-01111-z
Download citation
Received : 06 March 2023
Accepted : 14 June 2023
Published : 21 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-023-01111-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Meta-analysis
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome
ISSN: 1758-5996
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Evidence-based Practice Nursing Dissertation Topics. Child Health Nursing Dissertation Topics. Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics. Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics. Palliative Care Nursing Dissertation Topics. Mental Health Nursing Dissertation Topics. Nursing Dissertation Topics. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Nursing Dissertation Topics.
357 Diabetes Essay Topics & Examples. Updated: Feb 25th, 2024. 25 min. When you write about the science behind nutrition, heart diseases, and alternative medicine, checking titles for diabetes research papers can be quite beneficial. Below, our experts have gathered original ideas and examples for the task. We will write.
The present study utilized a correlational. design to examine the relationships among diabetes distress, social support, self-efficacy, and. performance of diabetes self-care activities. A total of 33 adults with T2DM participated in the. study by completing a battery of surveys regarding performance of diabetes self-care activities.
diabetes were 15.1 million in 2000,3 the number of people with diabetes worldwide is projected to increase to 36.6 million by 2030.4 In 2007, 23.6 million ... This dissertation research is a theory based cross-sectional study using a patient self-administered questionnaire. The exploration of the relationships
Thesis title: Barriers to self-management in type II diabetes. Conducted at The University of Manchester by Emily Bland for the award of Master of Philosophy (MPhil) ... Background: Type II diabetes is both a worldwide and national healthcare. Certain self-management practices can help people with diabetes to control the condition, these ...
Diabetes mellitus (DM), o r simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has. high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do ...
The International Diabetes Federation has estimated that there were 3.72 million diagnosed. cases of T2DM in the Philippines with a 6.2% prevalence rate in adults in 2017 (104) and also it. is reported that around 1.76 million (2%) people with T2DM remain undiagnosed in 2014 (105). 3.
understanding of the experience of type 2 diabetes. I used quantitative and qualitative methodologies from the perspectives of both safety-net primary care clinic patients and health care providers (HCPs). Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a serious and chronic metabolic disorder in
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic condition wherein the beta cells. in the body do not produce enough insulin - a hormone that regulates blood. sugar - or the body does not use insulin well enough (also called insulin. resistance), or there is complete absence of insulin production.
Diabetes can be treated and its complications can be reduced by maintaining diet, physical activity, and proper medication and by regular monitoring of the complications [15,16,22-25]. Table 1. Genes behind monogenic diabetes and their clinical features. Features of Diabetes Gene Involved Clinical Outcome MODY GCK [26]
Diabetes Self-Management: Potential Risks and Resilience Factors. Roberta Lamptey. Michael Harris. 451 views. An innovative journal that advances our understanding of diabetes and its treatment in clinical settings and the community. It explores therapies, nutrition, complications and self-management, ulti...
Bachelor's thesis Published Autumn 2020 Number of pages 43 Title of publication Primary prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus Descriptive literature review Name of Degree Bachelor of Nursing Abstract The current prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus is critical and a vast number of peo-ple have a high risk for its onset.
Introduction. Type 2 diabetes contributes to a high burden of disease-associated complications and comorbidities. Disease pathogenesis is driven by both environmental and genetic factors, with elevated hepatic glucose production, impaired insulin secretion, and insulin resistance acting as key drivers in the development of disease [].Altered glucose-insulin homeostasis is typically associated ...
with Type 1 Diabetes. The first is a literature review of 29 papers that have explored family functioning in relation to adherence and metabolic control in adolescents with Type 1 diabetes Mellitus (T1DM). The paper has been written with intention to submit to the journal 'Diabetes Review'. The second paper
1. INTRODUCTION. Diabetes is a chronic disease with increasing prevalence worldwide. 1 In 2014, an estimated 422 million adults, representing 8.5% of the global population, were living with diabetes. 2 The economic burden of this disease and its complications account for a growing proportion of local and national budgets. 3, 4 For individuals, diabetes has negative psychosocial consequences ...
Background: People with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and impaired glucose regulation (IGR) are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes but lifestyle change can help to delay or prevent type 2 diabetes in these groups. Aims: This thesis comprises five publications which inform the development of lifestyle
StudyCorgi has prepared a list of interesting diabetes thesis topics, presentation titles, and essay ideas to write about. Read on to discover the most engaging diabetes project titles and research questions! ... Diabetes mellitus type 1, normally known as Type 1 Diabetes, is a type of diabetes that is caused by the lack of insulin resulting ...
researchable topics in the field of diabetes mellitus are also suggested as research areas for the future health students. KEYWORDS: Diabetes mellitus, Complications, Epidemiology, Causes and risk factors, ... TURKU UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES THESIS | Moses Langat Gestational diabetes, could be described as a form of glucose intolerance that
Diabetes mellitus is a common endocrine disorder, and affects more than 100 million people worldwide (World Health Organization, 1994). It is recognized as being a syndrome, a collection of disorders that have hyperglycaemia and glucose intolerance as a hallmark, due either to insulin deficiency or to impaired effectiveness of insulin's ...
Correlation Between the Gly482Ser Polymorphism and Increased Type 2 Diabetes Susceptibility. Dissertation Examples. Introduction 1 - Type 2 Diabetes 1.1 - Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Over the past 24 years, the number of people affected by Type 2 diabetes (T2D) has nearly quadrupled, growing from 108 million i... Last modified: 16th Dec 2019
The global figure of people suffering from diabetes mellitus is estimated to rise from current estimate of 415 million to 642 million by 2040. The number of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing in every country and 75% of people with diabetes mellitus are living in developing countries.2 With an
Background: A gut-microbial metabolite, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), has been associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Few previous prospective studies have addressed associations between the changes in TMAO and T2DM incidence. Methods: Data were derived from a longitudinal cohort conducted from 2019 to 2021 in rural areas of Fuxin County, Liaoning Province, China, and 1515 diabetes ...
Assessment Of The Effect Of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus And Metals Exposure In The Soweto First 1000 Days Cohort On Placental Epigenetic Programming And Placental & Birth Outcomes ... This dissertation has shown that epigenetics is one way in which we can capture the effects of these exposures and infer potential mechanisms of action. Date of ...
Background Despite that several original researchers have investigated the association between neck circumference (NC) and the risk of diabetes mellitus (DM), their results remain controversial. This review aimed to quantitatively determine the risk of DM in relation to the NC. Methods We conducted a literature search of PubMed, Embase, and the Web of Science from these databases' inception ...
Thesis Topic - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. diabetes