Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
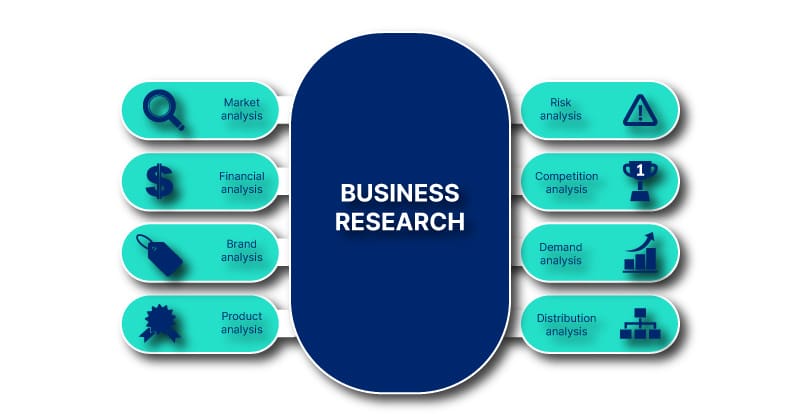
- Business Research

Try Qualtrics for free
Business research: definition, types & methods.
10 min read What is business research and why does it matter? Here are some of the ways business research can be helpful to your company, whichever method you choose to carry it out.
What is business research?
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad – it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels. Or it could involve sizing up the competition through competitor research.
Often when carrying out business research, companies are looking at their own data, sourced from their employees, their customers and their business records. However, business researchers can go beyond their own company in order to collect relevant information and understand patterns that may help leaders make informed decisions. For example, a business may carry out ethnographic research where the participants are studied in the context of their everyday lives, rather than just in their role as consumer, or look at secondary data sources such as open access public records and empirical research carried out in academic studies.
There is also a body of knowledge about business in general that can be mined for business research purposes. For example organizational theory and general studies on consumer behavior.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
Why is business research important?
We live in a time of high speed technological progress and hyper-connectedness. Customers have an entire market at their fingertips and can easily switch brands if a competitor is offering something better than you are. At the same time, the world of business has evolved to the point of near-saturation. It’s hard to think of a need that hasn’t been addressed by someone’s innovative product or service.
The combination of ease of switching, high consumer awareness and a super-evolved marketplace crowded with companies and their offerings means that businesses must do whatever they can to find and maintain an edge. Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market.
Thanks to the standard of modern business research tools and methods, it’s now possible for business analysts to track the intricate relationships between competitors, financial markets, social trends, geopolitical changes, world events, and more.
Find out how to conduct your own market research and make use of existing market research data with our Ultimate guide to market research
Types of business research
Business research methods vary widely, but they can be grouped into two broad categories – qualitative research and quantitative research .
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people’s thoughts, feelings and opinions. It relies heavily on the observations of researchers, who collect data from a relatively small number of participants – often through direct interactions.
Qualitative research interviews take place one-on-one between a researcher and participant. In a business context, the participant might be a customer, a supplier, an employee or other stakeholder. Using open-ended questions , the researcher conducts the interview in either a structured or unstructured format. Structured interviews stick closely to a question list and scripted phrases, while unstructured interviews are more conversational and exploratory. As well as listening to the participant’s responses, the interviewer will observe non-verbal information such as posture, tone of voice and facial expression.
Focus groups
Like the qualitative interview, a focus group is a form of business research that uses direct interaction between the researcher and participants to collect data. In focus groups , a small number of participants (usually around 10) take part in a group discussion led by a researcher who acts as moderator. The researcher asks questions and takes note of the responses, as in a qualitative research interview. Sampling for focus groups is usually purposive rather than random, so that the group members represent varied points of view.
Observational studies
In an observational study, the researcher may not directly interact with participants at all, but will pay attention to practical situations, such as a busy sales floor full of potential customers, or a conference for some relevant business activity. They will hear people speak and watch their interactions , then record relevant data such as behavior patterns that relate to the subject they are interested in. Observational studies can be classified as a type of ethnographic research. They can be used to gain insight about a company’s target audience in their everyday lives, or study employee behaviors in actual business situations.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive design of research where one observes peoples’ behavior in their natural environment. Ethnography was most commonly found in the anthropology field and is now practices across a wide range of social sciences.
Ehnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use.
The ethnographic research process is a popular methodology used in the software development lifecycle. It helps create better UI/UX flow based on the real needs of the end-users.
If you truly want to understand your customers’ needs, wants, desires, pain-points “walking a mile” in their shoes enables this. Ethnographic research is this deeply rooted part of research where you truly learn your targe audiences’ problem to craft the perfect solution.
Case study research
A case study is a detailed piece of research that provides in depth knowledge about a specific person, place or organization. In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new theories about how businesses operate. Proponents of case study research feel that it adds significant value in making theoretical and empirical advances. However its detractors point out that it can be time consuming and expensive, requiring highly skilled researchers to carry it out.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding the patterns and relationships that emerge from mass data – for example by analyzing the material posted on social media platforms, or via surveys of the target audience. Data collected through quantitative methods is empirical in nature and can be analyzed using statistical techniques. Unlike qualitative approaches, a quantitative research method is usually reliant on finding the right sample size, as this will determine whether the results are representative. These are just a few methods – there are many more.
Surveys are one of the most effective ways to conduct business research. They use a highly structured questionnaire which is distributed to participants, typically online (although in the past, face to face and telephone surveys were widely used). The questions are predominantly closed-ended, limiting the range of responses so that they can be grouped and analyzed at scale using statistical tools. However surveys can also be used to get a better understanding of the pain points customers face by providing open field responses where they can express themselves in their own words. Both types of data can be captured on the same questionnaire, which offers efficiency of time and cost to the researcher.
Correlational research
Correlational research looks at the relationship between two entities, neither of which are manipulated by the researcher. For example, this might be the in-store sales of a certain product line and the proportion of female customers subscribed to a mailing list. Using statistical analysis methods, researchers can determine the strength of the correlation and even discover intricate relationships between the two variables. Compared with simple observation and intuition, correlation may identify further information about business activity and its impact, pointing the way towards potential improvements and more revenue.
Experimental research
It may sound like something that is strictly for scientists, but experimental research is used by both businesses and scholars alike. When conducted as part of the business intelligence process, experimental research is used to test different tactics to see which ones are most successful – for example one marketing approach versus another. In the simplest form of experimental research, the researcher identifies a dependent variable and an independent variable. The hypothesis is that the independent variable has no effect on the dependent variable, and the researcher will change the independent one to test this assumption. In a business context, the hypothesis might be that price has no relationship to customer satisfaction. The researcher manipulates the price and observes the C-Sat scores to see if there’s an effect.
The best tools for business research
You can make the business research process much quicker and more efficient by selecting the right tools. Business research methods like surveys and interviews demand tools and technologies that can store vast quantities of data while making them easy to access and navigate. If your system can also carry out statistical analysis, and provide predictive recommendations to help you with your business decisions, so much the better.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
What Are the Functions of Business Research?
- Small Business
- Advertising & Marketing
- Business Research
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Relationship Between Research and Business Decisions
What is the meaning of quantitative approach, how to export email messages from incredimail 2.
- Description of a Marketing Department
- What Are the Benefits of a Competitive Intelligence Organization?
Successful business leaders have a well-thought out and well-researched business plan because they want to make decisions based on facts. Every business decision has an element of risk involved; thus, the function of business research exists to help business leaders evaluate scenarios and make better moves to build the company's size and to increase revenues. Business research gives a company the required data, innovative ideas and new products to stay competitive.
Functions of Business Research
Business research is the gathering of information to help a business leader make a decision about the progress and path for the company. Executives look at an array of public information, news stories and industry data as well as internal metrics to determine if product development, marketing strategies and other growth avenues can succeed. Business research takes historical data and existing reports, and then makes projections based on designed strategies.
As the old adage goes, knowledge is power. When business leaders have information, they are able to see trends and changes in the market or the company. Recognizing what is likely to happen based on historical and current data gives a keen business leader insight about planning the next company move. This could be to ramp up production because the trends show a bigger demand. It could also mean changing how a product is marketed or bundled. Without the data, business leaders are merely guessing at the next step for the business. Guessing is the biggest risk of all for any company.
Types of Business Research
There are various types of business research companies conduct. The most common is market research. Companies look at demographics and consumer issues or desires to determine the best path to sell customers needing a solution. Market research often starts with demographics and target consumers but can extend to industry comparisons and segmented markets. Companies may conduct surveys or test groups to get feedback on various components or changes in product design or delivery.
Research and development is another area where companies spend a lot of resources, both time and money. A new product or improving an existing one is critical for most companies to compete with global market competitors. Some companies, such a technology or pharmaceutical companies spend significant portions of their annual budget on research and development. Even smaller companies need to consider what new trends are coming out and address the new demands of the market. For example, a water bottle re-seller needs to know if there is a new insulated mug or safer plastic product to use. If stock and inventory aren't adjusted, the re-seller will have perfectly good products that customers no longer want.
Relevance of Research in Business
The relevance of research is to keep a company relevant and ahead of all competition. Clothing stores want to know what the new fall colors are going to be in the spring when orders are made for fall inventory. Technology companies must constantly upgrade or create new products to stay ahead of the influx of competitors. A financial services company must understand the market trends and look for reasonable expectations for clients in the future. An insurance company must adapt existing policies to new regulations, laws and technology. Think about how auto insurance will change, as self-driving cars capture bigger numbers on roadways.
Even at a micro level, a business leader needs to see how his company performs, using the data available. If the company is doing well and the market data shows that market penetration isn't saturated, leadership might choose to add more staff. They may increase production or adjust costs. Each of these decisions is based on business research.
- Forbes: Step 3 for a Successful Startup: The Importance of Market Research
- Forsyth Tech: The Importance of Business/Marketing Research
With more than 15 years of small business ownership including owning a State Farm agency in Southern California, Kimberlee understands the needs of business owners first hand. When not writing, Kimberlee enjoys chasing waterfalls with her son in Hawaii.
Related Articles
The role of data in business, differences between marketing research & marketing strategy, how to restore a peachtree general ledger report, examples of product development strategy, business development strategies in accessing new markets, exporting a cell to another cell in excel, how to write a marketing sampling plan, how to add two lines to a powerpoint chart, why is the business research process necessary to assist managers, most popular.
- 1 The Role of Data in Business
- 2 Differences Between Marketing Research & Marketing Strategy
- 3 How to Restore a Peachtree General Ledger Report
- 4 Examples of Product Development Strategy

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Business Research: Types, Methods, Examples
- Updated on
- Jan 29, 2024

Ever wondered what it takes to build a flourishing business ? Aiming to provide maximum sales and profit, business research helps you to gather comprehensive information about your business and accordingly make relevant changes if required. So, in this process of being successful, we gather all types of data to better define our strategies and understand what products or services customers want. And in case, you’re planning to expand your business, research can help you determine your odds of positive results. In this blog, we’ll help you understand the basics of research and analysis .
“Whoever gets closer to the customer, wins.” – Bernadette Jiwa
This Blog Includes:
What is business research, business research example, importance of business research, types & methods, focus groups , case study research , ethnographic research, survey , correlation research , experimental research , advantages and disadvantages of business research, scope of business research, role of business research, business research books, business research report, top 10 tools for business research, business research partners, top 10 business research topics, career prospects , [bonus] best mba colleges in the world.
Business Research can be simply defined as a process of gathering comprehensive data and information on all the areas of business and incorporating this information for sales and profit maximization. If you are wondering what is Business Research, it is a systematic management activity helping companies to determine which product will be most profitable for companies to produce. Also, there are multiple steps in conducting research, with each thoroughly reviewed to ensure that the best decision is made for the company as a whole.
Also Read: Scope of MBA in International Business
Let’s say there’s an automobile company that is planning to launch a car that runs on CNG. To promote cleaner fuel, the company will be involved in developing different plans and strategies to identify the demand for the car they intend to launch. Other than this, the company will also look for competitors, and the target audience, keeping in mind the distribution of CNG in India. Hence the research is conducted on various ideas to formulate a sustainable and more efficient design.
When it comes to the question of why Business Research is important, it has an essential role to play in varied areas of business. Here are some of the reasons describing the importance of Business Research:
- It helps businesses gain better insights into their target customer’s preferences, buying patterns, pain points, as well as demographics.
- Business Research also provides businesses with a detailed overview of their target markets, what’s in trend, as well as market demand.
- By studying consumers’ buying patterns and preferences as well as market trends and demands with the help of business research, businesses can effectively and efficiently curate the best possible plans and strategies accordingly.
- The importance of business research also lies in highlighting the areas where unnecessary costs can be minimized and those areas in a business which need more attention and can bring in more customers and hence boost profits.
- Businesses can constantly innovate as per their customers’ preferences and interests and keep their attention on the brand.
- Business Research also plays the role of a catalyst as it helps businesses thrive in their markets by capturing all the available opportunities and also meeting the needs and preferences of their customers.
Also Read: Business Analyst vs Data Analyst

Business research plays an important role in the business intelligence process. This is usually conducted to determine if a company can succeed in a new region through competitive analyses and a better marketing approach. Due to this, this broad field has been distinguished into two types namely, Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research Method.
Here are the most important types of Business Research :
Qualitative Research Methods
It involves putting open-ended questions to the audience through different channels of communication to understand why researchers think in a particular manner. Stress is laid on understanding the intent, attitude, and beliefs to figure out the behaviour and response of the customers. Moreover, the goal of Qualitative Business Research is to get in-depth knowledge about the subjects of the research. Moreover, qualitative research enables us to put the perspective of the consumer in front of the researcher so that we can understand and see the alignment of the ideas between the market and the business.
The data collected in this type of business research is by the following methods:
- Interviews
- Case Study
- Ethnographic Research
- Website Visitor Profiling
- Content Analysis
Also Read: Study MBA in Music Business at Berklee College of Music!
Let us take a detailed look at some of the ways-
Interviews and surveys are similar. The only difference lies in the fact that the responder can put a question in an interview whilst it is not possible during a survey. Through interviews, it is easier to understand the detailed perspective of the person concerning the subject of research. A mobile brand researched to understand why certain colours are preferred by male and female customers. The research revealed that since red is assumed to be a feminine colour, it is more preferred by females than males.
Focus groups are a type of business research that involves only a set of individuals. Each selected individual represents a particular category of the target market. The major difference between interviews and focus groups is the number of people that it involves. To launch a new product for a particular group of society, focus groups prove to be the best way to understand the needs of the local audience.
For example, Tesla decides to launch their latest car model in India. The company, therefore, will require feedback from the Indian audience only.
Did you know? Amazon, the internet giant changed its payment strategy to enter the Indian market. Since the Indian economy was not entirely ready for online modes of payment, amazon introduced a new payment method and came up with ‘ cash on delivery ’ to gain consumers’ trust.
One of the most effective ways for business research is conducting case studies. With the motive to understand customer satisfaction, challenges that usually the customers face while using the product and hence, providing them with the right solution can be achieved by analysing data secured through data secured by case studies. Case study researchers are conducted in many fields of business that ultimately aid organisations in improving their products or services.
Ethnographic Research refers to understanding people as a whole. One must be able to grok their consumers or target audience which will help identify patterns, flaws, etc. Ethnography is a branch of anthropology that is the study of what elements or features make us humans. How did people live? What aspect made us so dependent on smartphones and technology? Why would people buy one product over the other? It refers to asking questions about lifestyle, communities, etc., and trying to gain insight into consumer behaviour and buying patterns.
For example, consider a random product. Are people looking for that product? Do they need it? Is it a necessity or a luxury? Which class of people are most likely to buy it? People often cannot comprehend what they are looking for. Gaining different perceptions can help us tailor our products accordingly to the consumers. Who would have thought that the majority of humans will need face masks for survival?
Also Read: How to Become a Research Analyst?
Quantitative Research Methods
With the employment of mathematical, statistical and computational techniques, quantitative research is carried out to deal with numbers. This systematical empirical investigation starts with the acquisition of the data and then moves on to analyzing it with the help of different tools. The goal is to identify clientele and then meet the targets of the audience. As the method of business research employs a questionnaire to determine the audience’s response, the questions are built around the idea that the audience knows about the product or the services that the firm offers. Some of the key questions answered in quantitative research methods include, who is connected with your network, how they qualify for the ‘product’ or how regularly they visit your website.
The data is collected based on the following research:
- Correlational
- Online
- Casual Comparative
- Experimental
It is the most common method under quantitative research via which a huge amount of data can be collected concerning a product or service. A common set of questions are asked to the people and they are asked to provide their inputs. To understand the nature of the market in-depth, this method is massively used by leading organisations all across the globe. Analysing data recorded through service helps organisations make suitable decisions.
Under this research, usually two entities are put together to examine the impact they create on each other. As suggested by the name it is the best process to understand patterns, relationships and trends. the data grasped through correlation research is generally combined with other tools as one cannot achieve a firm conclusion using this type of business research.
Experimental research is purely based on proving a particular theory that is pre-assumed. True experimental research companies can understand varied behavioural traits of the customers that further assist them in generating more revenue. Exposing a set of audience to common parameters, their behaviour is recorded and hence analysed. This can be understood as the main basis of the experimental research.
Also Read: Scope of Operation Research
There are certain pros and cons of business research that you must know about. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of Business Research.
Advantages of Business Research
- Business Research plays the role of a catalyst in identifying potential threats, issues as well as opportunities .
- It provides a detailed analysis of customers and the target audience , thus helping in building better relationships with one’s audience and capturing the areas which we might be missing out on.
- It also anticipates future problems thus the enterprise is able to tackle those uncertainties and prepare for them beforehand.
- It keeps a continuous track of competition in the market and gives businesses the scope to come up with better strategies to tackle their competitors.
- Business Research also conducts a thorough cost analysis thus helping the company efficiently manage resources and allocate them in an optimal manner.
- It keeps you updated with the latest trends and competitor analysis .
Disadvantages of Business Research
- Business Research can be expensive and time-consuming .
- It also has the danger of being assumptive and imprecise at times , because the focus groups might be small or can be highly based on assumptions.
- The market is ever-changing and ever-evolving and capturing the right trends or anticipating them can constitute a complicated process for business research.
Also Read: Types of Research Design
The process of business research can be as comprehensive and as detailed as a business wants it to be. Generally, a company takes up research with a certain aim or hypothesis in order to figure out the issues, opportunities and trends and how they can be leveraged in the best way.
Here is the step-by-step process of Business Research:
- Identifying the Opportunity or Problem – To begin with the research, we first need to know what is the problem or the opportunity we would be leveraging on. It can be a popular trend or a common problem that a business is facing and can potentially become the headstart for the research process. Once you know the problem or the opportunity, go ahead with giving an understandable statement of what it’s about, what the hypothesis of the research will be as well as its objectives.
- Decide and Plan the Research Design – The next step in the business research process to find the right research design which suits the objectives and overall plan of the research. The most popular research designs are Quantitative and Qualitative Research.
- Determining the Research Method – The research design is closely connected to the research method since both qualitative and quantitative research designs have different methods for data collection, analysis, amongst others. So, once you have put a finger on what the right research design will be, go ahead with finding the right research method as per the plan, types of data collection, objective, costs involved, and other determining factors.
- Collect Data – Utilizing the research method and design, the next step in the business research process is to collect data and assimilate it.
- Data Analysis and Evaluation – After assimilating the data required, the data analysis will take place to gather all the observations and findings.
- Communicate Results – The presentation of the business research report is the concluding step of this procedure after which the higher management works upon the best techniques and strategies to leverage the opportunity or tackle the issue.
Also Read: MBA in Business Analytics
The scope of Business Research is multifarious and reaches out to many specialisations and areas. Let’s take a look the scope of business research across various specialisations:
- Marketing Management When it comes to business research, becomes an important part of marketing management that analyses consumer behaviour, target audiences, competition, price policy, promotional plans and much more.
- Financial Management It also plays an essential role in budgeting, financial planning, cost allocation, capital raising, tackling fluctuations with international currency as well as taking finance-related decisions.
- Production Management Production Management also includes business research as it helps in product development, planning out for a newer one, finalizing the right technologies for production, and so on.
- Materials Management Business Research is an important aspect of checking the best materials and carrying out its production, supply chain management , logistics , as well as shortlisting negotiation strategies.
There is an incremental role of business research as its importance is across every aspect of the business. Let’s take a look at the role of business research in an enterprise:
- The most primary role of business research is that it helps across every decision in the business, from product innovation to marketing and promotional planning.
- Business Research also helps in forecasting a business, whether in terms of competition or any other types of problems it will be facing.
- Another key area where this plays a bigger role is ensuring consumer satisfaction as through research, we can carry out research and highlight areas where we can efficiently serve our target audience.
- Business research also helps in implementing cost-effectiveness in a business as it can assist in cutting costs wherever needed and investing more in those areas, where profit is coming from.
Want to understand and learn more about business research? Here are some of the books that will make you a pro in this field. Check out the list of business research books:
Also Read: Is It Possible to Study MBA in Europe Without GMAT?
The purpose of a report is to inform the other members, junior and subordinates of the team to provide information on the specific topic. There is a specific format of a business report which makes it look more professional and presentable. There should be a title with the date and nature. The second section includes the introduction, body, and then conclusion. Reports help to identify the issues and helps in resolving them at earlier stages. It can include graphs, surveys, interviews, flow, and piecharts also.
Are you wondering why is there a need to do business research? Business is not stable and it is vital to stay up to date with all the data and developments. It is also important to make business-related decisions, and keep track of competitors, customer feedback, and market changes. The basic objective of business research is to identify the issues and evaluate a plan to resolve them for better managerial functioning.
Now that you are familiar with the objective, importance, and advantages the next important step is to know how to conduct research. There are numerous tools available for free while for some advanced tools there is a membership. Check out the list of top 10 tools:
- Google Keyword Tools
- Google Analytics
- Google Trends
The one thing constant in a business is market changes. A new trend or change comes every time you blink an eye. To keep track of everything externally and internally a research partner comes helpful. There are a few things to keep in mind that will help you in choosing the right business partner. The first thing to keep in mind is that the person should have relevant work experience and expertise in that particular field. An experienced partner can help businesses reach new heights. Look for a partner that can provide well-curated solutions and not the generic ideas that every enterprise follows. Last but not least is that your business research partner should have knowledge of the latest tools and techniques.
Also Read: MBA in Sustainable Development: Courses & Universities
Is your big presentation coming up or your report is due on Monday but you still haven’t finalized your business research topic? Here are some of the trendiest research topics for you:
- How advertisements influence consumer behaviour?
- Does incentive motivation increase employee productivity?
- How to handle crises in the business?
- How to create a work-life balance in the organization?
- What are the things a small business owner has to face?
- How to expand the company globally?
- How is digital marketing helping every business type?
- How to maintain the quality and quantity of products?
- What are the struggles entrepreneurs of a start-up face?
- How to create a budget and maintain company finances?
In order to build a career in Research , you can simply grab a degree in the field of Management , Business or Administration. So, students with an understanding of the core concepts of business and an inclination for research can consider it as a go-to option. Other suitable programs can be Master in Management , MBA Business Analytics , and MBA Data Analytics , to name a few.
To know more, check out Qualitative Research Methods !
It can simply mean researching every area of a business and using the provided information and data to ensure profit maximization.
There are different types of business research such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, correlational research, ethnographic research, case study research, and quantitative research methods, amongst others.
It is essentially important for various aspects of a business such as profit maximization, cost-cutting, financial management , personnel management, consumer behaviour, etc.
The process of research depends upon the type of research design you are opting for. To start with, we first need to determine the aim or objective of the research, then plan out the whole process which includes the types of methods we will be using, then the actual research that takes place followed by the data found that helps in understanding the key observations and how they can be implemented to actualize research hypothesis.
If you’re thinking to start a product line in your existing business or planning a startup, business research is a fundamental process that helps you to navigate the opportunities and obstacles in the marketplace. Knowing your strengths and weaknesses can help you come up with advanced and powerful research techniques that will make it easier to manage. Are you planning to take your higher education abroad? Then, you can quickly book a counselling session with the experts at Leverage Edu and we can help you build the right platform for you to grow in the corporate world.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Great article! Your content is beneficial. Thank you, and Keep Sharing.
Thank you, Sophia!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Business Research: It’s Meaning, Process and Objectives
Meaning of business research.
Business research is the process of studying a company’s competitors, stakeholders, and profit & loss to meet the company objectives and maximize revenue & profits.
The research involves identifying the target market, estimating their current needs & wants, and then conducting product planning to meet those demands.
The research should be unbiased and factual as they form the basis for further analysis.
Business research is neither a pre-product launch nor a post-product launch analysis. Companies continuously conduct market research relating to their political environment, social demands, technological needs, competitors’ entry, etc. so that they can keep improving their products and continue to survive even in the fiercest times.
Thus, business research is purely the collection and interpretation of external as well as internal data for a company’s better performance.
Objectives of Business Research
Understanding customer requirements.
One of the major objectives of business research is to ascertain the target customers’ requirements. This helps to conduct in-depth research relating to customers’ needs. Further, it also provides information regarding market trends, future demands of customers, and thus, pros and cons of the product being developed for them.
Defining Stakeholders
Business research helps to differentiate between potential and non-potential customers. This way the company can quantify its market reach and conduct surveys amongst some of its customers related to their tastes and type. This will help them gain feedback from their customers which they can add back as features in their products!
Pain & Gain Points
Pain points are the areas where the company lags in the market and gain points are the areas where the company can stand out in the market.
The company can list its pain points by evaluating what customers want and what they are delivering. This way, they can focus on their weaknesses and take measures to rub off or improve them.
Rival Study
The strength of a company is a threat to its competitor and the weakness of a company is the opportunity of its competitor. Therefore, the company should analyze its threats i.e., make an in-depth study of its competitors and, thus brainstorm different ways in which it can convert its threats into opportunities.
Scope of Business Research
Business Research has wide scope in deciding a particular product’s journey in the market.
Right from its launch, Business research helps sellers grab the opportunity of pulling demand, gaining investments, being tech-enabled, beating the competition, conducting SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat) and PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal environment) analysis, standing out and disrupting the entire market.
Moreover, the scope of business research is not only restricted to the product market. It also plays a crucial role in personnel management and workforce development. Research made for employee motivation, grooming, training, and promotion inculcates more coordination in the organization and also nurtures productivity amongst employees.
When they are trained and awarded, they feel empowered and they put the best of their efforts into maximizing sales and outputs.
Nature of Business Research
- The main function of business research is to define the objectives and core values of any business. It tells how the company should manage and generate leads, create sales and develop a marketing strategy.
- Business Research also deals with competitors’ pricing policies and helps in setting own costs and prices.
- It helps companies to discover new growth avenues by pinpointing the weak points of competitors.
- It assists in planning projections of the company and shows hurdles that would likely arrive and hit business cycles.
In a nutshell, it gives proposals to companies on expansion and growth in customer base.
Process of Business Research
Identification of challenge.
The first and foremost task of every research is to set an objective by defining what are the prevalent problems in the marketplace and how a company can tackle them.
Creating Research Proposal
The next step in this process is developing research plans and proposals. Plans are futuristic and require assumptions. These assumptions, in business terms, are called premises.
Therefore, the research proposal can be researched on existing demand for the product, new entrants in the market, or re-setting pricing policies.
Execution of Research
Once the plan is made and the research proposal is developed, the company can toss alternative ways they can execute the research. The company can forward with research by random sampling (mass media survey) or can rely on previously collected data too.
Interpretation of Data
The data so collected should be organized in a systematized form. It can be further used to make reports, conduct SWOT and PESTEL analyses and take necessary actions thereafter.
Action Plan
Once data is collected, interpreted, and evaluated, the last step is to execute the product planning by either launching a product, expanding existing service, or bringing changes in any other core activities around which the research revolves.
Related posts:
- Business Level Strategy: Meaning, Types, Advantages, Examples
- What is Business? Definition, Nature, Types, and Objective
- Company: Formation process, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Characteristics and Features of Business Ethics
- Business Forecasting: Types, Techniques, Need, Advantages, Limitations
- Business Ethics: Importance, Types, Function
Add CommerceMates to your Homescreen!

MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Research Methodology » The Role of Business Research
The Role of Business Research
Research is a systematic search for information in order to obtain a clear picture concerning the underlying problem. Technically speaking, research is a process of identifying problem thoroughly, establishing an objective, collecting and analyzing the relevant data in order to determine the possible factors causing the problem. Thus, research activities are consistent search for information with the objective to get a clearer picture concerning the problem and to propose specific recommendation for the solution.
Role of Research in Business
Making the right decision is an ideal practice in any business whenever the organization encounters a problem. A good organization primarily conducts research to resolve the critical problems surrounding their business such as competition , customer satisfaction , product innovation , customer complaints, and new government policies affecting the industry.
Decision making process requires systematic and organized efforts to investigate a specific problem in a business setting. The first step in understanding the problem is to identify specifically the main issue that requires further investigation. The next steps are to identify factors associated with the problem, gather the relevant information, analyze data, interpret output and provide the recommendation to the manager for his decision-making. It simply means that the decision making process comprises a series of steps designed and executed with the goal of getting the best solution to the underlying problem faced by the organization.
Actually, the entire process in which the managers attempt to solve their problem is the steps in conducting a research project. The research definition in the previous section suggests that research involved the process of inquiry, investigation, examination, and experimentation that need to be conducted systematically, diligently, critically, objectively and in a logical order. Thus, the results of research would be the findings, which would help the managers to deal with the real situation. Therefore, we can define business research as an organized, systematic inquiry concerning the problem, and undertaken with the purpose of finding the best solution to a problem. In addition, the research findings should be able to clarify all ambiguities surrounding the problem. In research the ambiguities surrounding the problem are addressed in term of research questions.
Related posts:
- Role of Business Research in Decision Making Process
- Scientific Method in Business Research
- Business Analysis – Role of Business Analyst in Modern Organizations
- Strategic Business Decisions on Research and Development (R&D)
- Role of Profit in Business
- The Role of Strategist in a Business Organization
- Role of Technology in Modern Business
- Role of Digitalization in Business Growth
- Role of Business Ethics in Modern Organizations
- Role of Cultural Sensitivity in International Business
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
A Roadmap to Business Research
- First Online: 15 March 2023
Cite this chapter

- Merwe Oberholzer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7180-8865 3 &
- Pieter W. Buys ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5345-3594 3
558 Accesses
This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts. A literature study was conducted to investigate the research concept, the boundary of research, and the research process’ conceptual framework. This chapter summarized research as a systematic investigation to reveal new knowledge. In guiding industry-orientated business research, it is acknowledged that management action may solve some business problems. In contrast, higher levels of organizational issues and critical reflection of business issues may require actual research .
The framework for business research is divided into four parts: the research problem, research design, empirical evidence, and conclusion. The central part of the map is the design section that organizes the philosophic approach (theoretical foundation, research philosophy, and assumptions) on the one side and the applied research methods and techniques on the other side, with the research methodology acting as a bridge between the sides. The framework constitutes a guide when embarking on the journey to solve industry-orientated business research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
AS illustrated later, it must be noted not every business problem needs to be solved by scientific research.
Note that although conceptually four distinct elements, in actuality these ProDEC elements are highly integrated.
Note that the theoretical foundation may not be of equal importance in all paradigms, e.g., the pragmatist and design sciences paradigms where a pragmatic problem solution or artifact is the primary objective.
Abutabenjeh, S., & Jaradat, R. (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36 (3), 237–258.
Article Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2004). The practice of social research . Thomson/ Wadsworth.
Google Scholar
Brierley, J. A. (2017). The role of a pragmatist paradigm when adopting mixed methods in behavioural accounting research. International Journal of Behavioural Accounting and Finance, 6 (2), 140–154.
Collins. (2021). Definition of research . https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/research Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed method research . Sage.
Davis, C., & Fisher, M. (2018). Understanding Research Paradigms. JARNA, 21 (3), 21–25.
Delen, D., & Zolbanin, H. M. (2018). The analytics paradigm in business research. Journal of Business Research, 90 , 186–195.
Department of Education and Training, Western Sydney University. 2020. Research services. https://www.westernsydney.edu.au/research/researchers/preparing_a_grant_application/dest_definition_of_research . Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Elsayed, N., & Elbardan, H. (2018). Investigating the associations between executive compensation and firm performance: Agency theory or tournament theory. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 19 (2), 245–270.
FindAPhD.com. (2021). What are the criteria for a PhD? https://www.findaphd.com/advice/finding/criteria-for-phd.aspx Date of access: 18 August 2021.
Goldkuhl, G. (2011). Design research in search for a paradigm: Pragmatism is the answer. European Design Science Symposium (pp. 84–95). Springer.
Goldkuhl, G. (2020). Design Science Epistemology: A pragmatist inquiry. Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 32 (1), 39–79.
Hesse-Biber, S. N., & Leavy, P. (2011). The practice of qualitative research . Sage.
Henderson, K. A. (2011). Post-positivism and the pragmatics of leisure research. Leisure Sciences, 33 (4), 341–346.
Hevner, A.R., March, S.T., Park, J. & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS quarterly : 75–105.
Kessler, E. H. (Ed.). (2013). Encyclopedia of management theory . Sage.
Kankam, P. K. (2019). The use of paradigms in information research. Library & Information Science Research, 41 (2), 85–92.
Kekeya, J. (2019, November). The commonalities and differences between research paradigms. Contemporary PNG Studies: DWU Research Journal, 31 , 26–36.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7 (6), 44–53.
Kivunja, C., & Kuyini, A. B. (2017). Understanding and applying research paradigms in educational contexts. International Journal for Higher Education, 6 (5), 26–41.
Jansen, J. D. (2020a). What is a research question and why is it important? In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 2–14.
Jansen, J. D. (2020b). Introduction to the language of research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 16–24.
Lexico.com. (2021). Oxford English and Spanish dictionary, synonyms, and Spanish to English translator . https://www.lexico.com/definition/research Date of access: 22 July 2021.
Lincoln, Y. S., Lynham, S. A., & Guba, E. G. (2011). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 97–128). Sage.
Myers, M. D. (2020). Qualitative research in business & management . Sage.
Mouton, J. (1996). Understanding social research . Van Schaik.
Mouton, J. (2011). How to succeed in your master’s & doctoral studies: A South African guide and resource book. Van Schaik.
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2020). Introducing qualitative research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 56–76.
Pandey, P. & Pandey, M. M. (2015). Research methodology: Tools and techniques . Bridge Center: Buzau.
Pietersen, J. & Maree, K. (2020). Statistical analysis II: Inferential statistics. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 242–258.
Rahi, S. (2017). Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instrument development. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 6 (2), 1000403.
Rehman, A. A., & Alharthi, K. (2016). An introduction to research paradigms. International Journal of Educational Investigations, 3 (8), 51–59.
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research methods for business students . Pearson.
Sein, M. K., Henfridsson, O., Purao, S., Rossi, M., & Lindgren, R. (2011). Action Design Research. MIS Quarterly, 35 (1), 37–56.
Tubey, R. J., Rotich, J. K., & Bengat, J. K. (2015). Research paradigms: Theory and practice. Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 5 (5), 224–228.
Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (2020). Introduction to Design Science Research. In: Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (eds.), Design Science Research. Cases. Progress in IS. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46781-4_1 Date of access: 21 October 2021.
Voxco. (2022). Business research: Definition, types, and methods. https://www.voxco.com/blog/business-research-definition-types-and-methods/ Date of access: 23 May 2022.
Wilson, J. (2013). Essentials of business research: A guide to doing your research project. Sage. https://www.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/59838_Wilson_ch1.pdf Date of access: 3 June 2021.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management Cybernetics Research Entity, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Merwe Oberholzer & Pieter W. Buys
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pieter W. Buys .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pieter W. Buys
Merwe Oberholzer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Oberholzer, M., Buys, P.W. (2023). A Roadmap to Business Research. In: Buys, P.W., Oberholzer, M. (eds) Business Research . Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Published : 15 March 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-9478-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-9479-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Survey Software The world’s leading omnichannel survey software
- Online Survey Tools Create sophisticated surveys with ease.
- Mobile Offline Conduct efficient field surveys.
- Text Analysis
- Close The Loop
- Automated Translations
- NPS Dashboard
- CATI Manage high volume phone surveys efficiently
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud & on-premise dialer
- IVR Survey Software Boost productivity with automated call workflows.
- Analytics Analyze survey data with visual dashboards
- Panel Manager Nurture a loyal community of respondents.
- Survey Portal Best-in-class user friendly survey portal.
- Voxco Audience Conduct targeted sample research in hours.

Find the best survey software for you! (Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 40+ question types
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Skip logic and branching
- Multi-lingual survey
- Text piping
- Question library
- CSS customization
- White-label surveys
- Customizable ‘Thank You’ page
- Customizable survey theme
- Reminder send-outs
- Survey rewards
- Social media
- Website surveys
- Correlation analysis
- Cross-tabulation analysis
- Trend analysis
- Real-time dashboard
- Customizable report
- Email address validation
- Recaptcha validation
- SSL security
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Download feature sheet.
- Hospitality
- Financial Services
- Academic Research
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Product Experience
- Market Research
- Social Research
- Data Analysis
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
Get a Quote
- NPS Calculator
- CES Calculator
- A/B Testing Calculator
- Margin of Error Calculator
- Sample Size Calculator
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Market Research Hub
- Patient Experience Hub
- Employee Experience Hub
- Market Research Guide
- Customer Experience Guide
- The Voxco Guide to Customer Experience
- NPS Knowledge Hub
- Survey Research Guides
- Survey Template Library
- Webinars and Events
- Feature Sheets
- Try a sample survey
- Professional services
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.
Get the Guide Now

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Client Stories
- Voxco Reviews
- Why Voxco Research?
- Careers at Voxco
- Vulnerabilities and Ethical Hacking
Explore Regional Offices
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud on-premise dialer
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer 360
- Customer Loyalty
- Fraud & Risk Management
- AI/ML Enablement Services
- Credit Underwriting
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 100+ question types
- SMS surveys
- Banking & Financial Services
- Retail Solution
- Risk Management
- Customer Lifecycle Solutions
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Behaviour Analytics
- Customer Segmentation
- Data Unification
Explore Voxco
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Blogs & White papers
- Case Studies

VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Why Voxco Intelligence?
- Our clients
- Client stories
- Featuresheets
Business Research: Definition, Types, and Methods
- February 7, 2022
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON

What is Business Research?
Business research refers to the process of gathering information on all areas of business with the purpose of leveraging this data to promote organizational growth, increase sales, and maximize profit. It involves the systematic management activities that help companies decide which products or services will perform well in the market and will therefore be most profitable to produce.
Exploratory Research Guide
Conducting exploratory research seems tricky but an effective guide can help.
Why is Business Research Important?
Business research provides companies with comprehensive data on the target customer’s preferences, purchasing behavior, demographics, and pain points. Such information allows the business to strategize and create more effective marketing plans that resonate with the target audience. A thorough overview of the overall market will also give the business an understanding of market trends and market demands so that plans and strategies can be devised accordingly.
Another key use of business research is that it can bring attention to areas where costs can be minimized to increase profits. It provides businesses with a competitive edge in the market by ensuring that all identified opportunities are capitilized on and that decisions are made with customers in focus.
Business Research Methodologies
We can categorize business research methods in two ways:
- Quantitative and Qualitative
- Primary and Secondary
Quantitative vs Qualitative Business Research
Before we can delve into the specific kinds of research, it is important to have an understanding of the distinctions between the two key types of research: quantitative and qualitative business research.
Quantitative research involves data that is statistical and numerical in nature. Such data can be analysed using statistical techniques. Qualitative research, on the other hand, involves non-numeric data that generally takes a textual form.
Primary vs Secondary Business Research
Another way in which research methods can be classified is by primary and secondary research. Primary research refers to the collection of first-hand data, generally directly from the source. Some common methods of primary research are surveys, interviews, and observations.
Conversely, secondary research uses existing data that is already avalaible.
See Voxco survey software in action with a Free demo.
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods.
Some commonly used quantitative methods of business research are:
- Experimental Research : Experimental research refers to research studies that adhere to the scientific research design. This type of research aims to prove or disprove a theory, or hypothesis. Businesses generally use experimental research to study consumers’ behavioral traits.
- Survey Research : Survey research is one of the most commonly used methods of data collection because it is relatively easy and inexpensive to leverage. Surveys can be conducted in many different ways such as through social media polls or email surveys.
- Existing Literature : Existing research papers and online research are other sources of gathering quantitative data. This method is economical, accessible, and allows for the collection of vast amounts of data.
Qualitative Research Methods
Some commonly used qualitative methods of business research are:
- Interviews : Interviews are structured conversations that take place between an interviewer and an interviewee face-to-face, over the internet, or even through the phone. Generally, interviews involve the use of open-ended questions that provide respondents the flexibility to express their thoughts, perceptions, and opinions on the topic.
- Ethnographic Research : Ethnographic research where researchers immerse themselves in the participant’s real-life environment to observe and study their behaviour. It is generally used by organizations that want to understand cultural dynamics or factors. Although this method of research can help extract intensive and compelling data, it is extremely time-consuming and expensive.
- Case Study Research : Case study research refers to the detailed study of a specific subject. This method is used to produce in-depth, multi-faceted information on complex issues in the real-world setting.
FAQs on Business Research
Business research involves gathering information on all areas of business with the goal of maximising sales and revenue.
Business research methodologies can be categorized in two ways;
- Quantitative and qualitative
- Secondary and Primary
Some quantitative methods of business research are;
- Survey Research
- Experimental Research
- Existing Literature
Some primary research methods are interviews, surveys, and focus groups. Some secondary research methods are public sources, educational sources, and commercial sources.
Some qualitative methods of business research are;
- Ethnographic Research
- Case Study Research
Explore Voxco Survey Software
+ Omnichannel Survey Software
+ Online Survey Software
+ CATI Survey Software
+ IVR Survey Software
+ Market Research Tool
+ Customer Experience Tool
+ Product Experience Software
+ Enterprise Survey Software

Top 15 Market Research Tools
Top 15 Market Research Tools SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Market research tools are the backbone of every organization. The tools aid in
Go Viral with Social Media Surveys
Go Viral with Social Media Surveys SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Social media is a powerful marketing platform, especially for brands looking to
Mekko Chart
Mekko Chart SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents A Marimekko Chart (or mekko graph) is like a 2D Stacked Chart. In any case, as
Gap Analysis Report
Discovering the Power of Gap Analysis Report SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is Gap Analysis? Gap analysis is a strategic planning tool
Top 25 survey questions for business to ask people
Business Survey Questions: Your Passport to Market Insights SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Consider a food company that wants to know what people

ANOVA vs t-test: with a comparison chart
ANOVA vs t-Test: Definition & Working SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents When it comes to achieving the mean of two or more population
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Primary Research: What It Is, Purpose & Methods + Examples
As we continue exploring the exciting research world, we’ll come across two primary and secondary data approaches. This article will focus on primary research – what it is, how it’s done, and why it’s essential.
We’ll discuss the methods used to gather first-hand data and examples of how it’s applied in various fields. Get ready to discover how this research can be used to solve research problems , answer questions, and drive innovation.
What is Primary Research: Definition
Primary research is a methodology researchers use to collect data directly rather than depending on data collected from previously done research. Technically, they “own” the data. Primary research is solely carried out to address a certain problem, which requires in-depth analysis .
There are two forms of research:
- Primary Research
- Secondary Research
Businesses or organizations can conduct primary research or employ a third party to conduct research. One major advantage of primary research is this type of research is “pinpointed.” Research only focuses on a specific issue or problem and on obtaining related solutions.
For example, a brand is about to launch a new mobile phone model and wants to research the looks and features they will soon introduce.
Organizations can select a qualified sample of respondents closely resembling the population and conduct primary research with them to know their opinions. Based on this research, the brand can now think of probable solutions to make necessary changes in the looks and features of the mobile phone.
Primary Research Methods with Examples
In this technology-driven world, meaningful data is more valuable than gold. Organizations or businesses need highly validated data to make informed decisions. This is the very reason why many companies are proactive in gathering their own data so that the authenticity of data is maintained and they get first-hand data without any alterations.
Here are some of the primary research methods organizations or businesses use to collect data:
1. Interviews (telephonic or face-to-face)
Conducting interviews is a qualitative research method to collect data and has been a popular method for ages. These interviews can be conducted in person (face-to-face) or over the telephone. Interviews are an open-ended method that involves dialogues or interaction between the interviewer (researcher) and the interviewee (respondent).
Conducting a face-to-face interview method is said to generate a better response from respondents as it is a more personal approach. However, the success of face-to-face interviews depends heavily on the researcher’s ability to ask questions and his/her experience related to conducting such interviews in the past. The types of questions that are used in this type of research are mostly open-ended questions . These questions help to gain in-depth insights into the opinions and perceptions of respondents.
Personal interviews usually last up to 30 minutes or even longer, depending on the subject of research. If a researcher is running short of time conducting telephonic interviews can also be helpful to collect data.
2. Online surveys
Once conducted with pen and paper, surveys have come a long way since then. Today, most researchers use online surveys to send to respondents to gather information from them. Online surveys are convenient and can be sent by email or can be filled out online. These can be accessed on handheld devices like smartphones, tablets, iPads, and similar devices.
Once a survey is deployed, a certain amount of stipulated time is given to respondents to answer survey questions and send them back to the researcher. In order to get maximum information from respondents, surveys should have a good mix of open-ended questions and close-ended questions . The survey should not be lengthy. Respondents lose interest and tend to leave it half-done.
It is a good practice to reward respondents for successfully filling out surveys for their time and efforts and valuable information. Most organizations or businesses usually give away gift cards from reputed brands that respondents can redeem later.
3. Focus groups
This popular research technique is used to collect data from a small group of people, usually restricted to 6-10. Focus group brings together people who are experts in the subject matter for which research is being conducted.
Focus group has a moderator who stimulates discussions among the members to get greater insights. Organizations and businesses can make use of this method, especially to identify niche markets to learn about a specific group of consumers.
4. Observations
In this primary research method, there is no direct interaction between the researcher and the person/consumer being observed. The researcher observes the reactions of a subject and makes notes.
Trained observers or cameras are used to record reactions. Observations are noted in a predetermined situation. For example, a bakery brand wants to know how people react to its new biscuits, observes notes on consumers’ first reactions, and evaluates collective data to draw inferences .
Primary Research vs Secondary Research – The Differences
Primary and secondary research are two distinct approaches to gathering information, each with its own characteristics and advantages.
While primary research involves conducting surveys to gather firsthand data from potential customers, secondary market research is utilized to analyze existing industry reports and competitor data, providing valuable context and benchmarks for the survey findings.
Find out more details about the differences:
1. Definition
- Primary Research: Involves the direct collection of original data specifically for the research project at hand. Examples include surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments.
- Secondary Research: Involves analyzing and interpreting existing data, literature, or information. This can include sources like books, articles, databases, and reports.
2. Data Source
- Primary Research: Data is collected directly from individuals, experiments, or observations.
- Secondary Research: Data is gathered from already existing sources.
3. Time and Cost
- Primary Research: Often time-consuming and can be costly due to the need for designing and implementing research instruments and collecting new data.
- Secondary Research: Generally more time and cost-effective, as it relies on readily available data.
4. Customization
- Primary Research: Provides tailored and specific information, allowing researchers to address unique research questions.
- Secondary Research: Offers information that is pre-existing and may not be as customized to the specific needs of the researcher.
- Primary Research: Researchers have control over the research process, including study design, data collection methods , and participant selection.
- Secondary Research: Limited control, as researchers rely on data collected by others.
6. Originality
- Primary Research: Generates original data that hasn’t been analyzed before.
- Secondary Research: Involves the analysis of data that has been previously collected and analyzed.
7. Relevance and Timeliness
- Primary Research: Often provides more up-to-date and relevant data or information.
- Secondary Research: This may involve data that is outdated, but it can still be valuable for historical context or broad trends.
Advantages of Primary Research
Primary research has several advantages over other research methods, making it an indispensable tool for anyone seeking to understand their target market, improve their products or services, and stay ahead of the competition. So let’s dive in and explore the many benefits of primary research.
- One of the most important advantages is data collected is first-hand and accurate. In other words, there is no dilution of data. Also, this research method can be customized to suit organizations’ or businesses’ personal requirements and needs .
- I t focuses mainly on the problem at hand, which means entire attention is directed to finding probable solutions to a pinpointed subject matter. Primary research allows researchers to go in-depth about a matter and study all foreseeable options.
- Data collected can be controlled. I T gives a means to control how data is collected and used. It’s up to the discretion of businesses or organizations who are collecting data how to best make use of data to get meaningful research insights.
- I t is a time-tested method, therefore, one can rely on the results that are obtained from conducting this type of research.
Disadvantages of Primary Research
While primary research is a powerful tool for gathering unique and firsthand data, it also has its limitations. As we explore the drawbacks, we’ll gain a deeper understanding of when primary research may not be the best option and how to work around its challenges.
- One of the major disadvantages of primary research is it can be quite expensive to conduct. One may be required to spend a huge sum of money depending on the setup or primary research method used. Not all businesses or organizations may be able to spend a considerable amount of money.
- This type of research can be time-consuming. Conducting interviews and sending and receiving online surveys can be quite an exhaustive process and require investing time and patience for the process to work. Moreover, evaluating results and applying the findings to improve a product or service will need additional time.
- Sometimes, just using one primary research method may not be enough. In such cases, the use of more than one method is required, and this might increase both the time required to conduct research and the cost associated with it.
Every research is conducted with a purpose. Primary research is conducted by organizations or businesses to stay informed of the ever-changing market conditions and consumer perception. Excellent customer satisfaction (CSAT) has become a key goal and objective of many organizations.
A customer-centric organization knows the importance of providing exceptional products and services to its customers to increase customer loyalty and decrease customer churn. Organizations collect data and analyze it by conducting primary research to draw highly evaluated results and conclusions. Using this information, organizations are able to make informed decisions based on real data-oriented insights.
QuestionPro is a comprehensive survey platform that can be used to conduct primary research. Users can create custom surveys and distribute them to their target audience , whether it be through email, social media, or a website.
QuestionPro also offers advanced features such as skip logic, branching, and data analysis tools, making collecting and analyzing data easier. With QuestionPro, you can gather valuable insights and make informed decisions based on the results of your primary research. Start today for free!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

How Can I Help You? — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jun 5, 2024

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024

Top 8 Data Trends to Understand the Future of Data
May 30, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.12: Primary Functions of Management
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 47591
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Outcomes
- Explain the primary functions of management.
- Differentiate between the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling functions of management.
We have defined management as a process to achieve organizational goals. A process is a set of activities that are ongoing and interrelated. Ongoing means that the activities are not done in a linear, step-by-step fashion where responsibility is passed from one activity to the next. Instead, the activities are continued as new activities are started. Interrelated means that the results of each activity influence the other activities and tasks. It is the responsibility of management to see that essential activities are done efficiently (in the best possible way) and effectively (to achieve the desired result).
Effective management involves four primary functions and related skill sets: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Although there’s a logical sequence to the functions, in practice the four functions are often performed in a dynamic manner.
For example, a manager would need to develop or reference a departmental or organizational plan prior to executing on it just as you would reference a map prior to embarking on a road trip. The proverb “if you fail to prepare you are preparing to fail” underscores the importance of this function. However, just as when road or airport closures or other factors might cause you to change your original route, unanticipated internal or external factors might cause a manager to revisit and revise the original plan, requiring a change in the other functions and associated tasks. Thus, achieving organizational goals—arriving at your intended destination—requires ongoing management of the process and an understanding of the interrelationship of the four functions.
As Figure 1 illustrates, a factor that impacts leading, for example, will have implications for controlling, planning and organizing. In summary, it is a management responsibility to ensure that unanticipated changes are factored in to the process and the integrity of the process is maintained.

Planning means defining performance goals for the organization and determining what actions and resources are needed to achieve the goals. Through planning, management defines what the future of the organization should be and how to get there. Strategic plans are long-term and affect the entire organization. A strategic plan bridges the gap between what an organization is and what it will become. Tactical plans translate strategic plans into specific actions that need to be implemented by departments throughout the organization. The tactical plan defines what has to be done, who will do it, and the resources needed to do it.
For instance, recall the example used at the beginning of this module. It described how ThyssenKrupp AG decided to become an elevator manufacturing and servicing company because of increased competition from Chinese steel. The management of the company set a goal of deriving the majority of its revenue from elevator-related activities. To do this, the management team made plans to create partnerships or take over existing elevator companies. The team devised plans to develop new human resources and to acquire other material resources. The company also had to divest existing steel-related resources to raise capital for the new initiative. This example is a long-term strategic plan that will take years to complete and require many changes along the way. But it starts by defining a goal and a preliminary path to achieve it.
Once plans are made, decisions must be made about how to best implement the plans. The organizing function involves deciding how the organization will be structured (by departments, matrix teams, job responsibilities, etc.). Organizing involves assigning authority and responsibility to various departments, allocating resources across the organization, and defining how the activities of groups and individuals will be coordinated.
In the case of ThyssenKrupp AG, the management had to determine how to support two very different sets of activities in order to achieve its long-term goal. Management needed to continue steel production activities to provide continuity of funds as the emphasis gradually shifted to elevator production. It also had to develop new skills and resources to build the company’s elevator capabilities. A new organizational structure was needed that could support both business activities as one was downsized and the other built up.
Nearly everything that is accomplished in an organization is done by people. The best planning and organizing will not be effective if the people in the organization are not willing to support the plan. Leaders use knowledge, character, and charisma to generate enthusiasm and inspire effort to achieve goals. Managers must also lead by communicating goals throughout the organization, by building commitment to a common vision, by creating shared values and culture, and by encouraging high performance. Managers can use the power of reward and punishment to make people support plans and goals. Leaders inspire people to support plans, creating belief and commitment. Leadership and management skills are not the same, but they can and do appear in the most effective people.
It is very difficult to motivate people when plans involve radical change, particularly if they include downsizing and layoffs. Many people are naturally resistant to change. When the change means loss of jobs or status, people will be very resistant. At ThyssenKrupp, the labor unions vehemently opposed the shift from steel production to elevator manufacturing. Although the people involved in the new business functions were excited by the plans, people involved with steel production felt abandoned and demotivated. Management would have been wise to get union support for its vision of the company’s new future.
Controlling
There is a well-known military saying that says no battle plan survives contact with the enemy. This implies that planning is necessary for making preparations, but when it’s time to implement the plan, everything will not go as planned. Unexpected things will happen. Observing and responding to what actually happens is called controlling. Controlling is the process of monitoring activities, measuring performance, comparing results to objectives, and making modifications and corrections when needed. This is often described as a feedback loop , as shown in the illustration of a product design feedback loop.

Controlling may be the most important of the four management functions. It provides the information that keeps the corporate goal on track. By controlling their organizations, managers keep informed of what is happening; what is working and what isn’t; and what needs to be continued, improved, or changed. ThyssenKrupp had little experience in elevator manufacturing when it was making plans. It was developing new products and processes and entering new markets. The management knew it could not anticipate all the difficulties it would encounter. Close monitoring as the plan progressed allowed the company to make changes and state-of-the-art innovations that have resulted in a very successful transition.
Watch the following video for an overview of the management process and a simple example of how the management functions work together.
You can view the transcript for “The Management Process.mp4” here (opens in new window) .
Practice Questions
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/12140
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/12141
Who Directs Each Function?
Although these functions have been introduced in a particular order, it should be apparent that the different activities happen at the same time in any one organization. The control function ensures that new plans must be created. Leaders often step up as needed when a crisis or unexpected bump demands immediate action. All managers perform all of these functions at different times, although a manager’s position or level in the organization will affect how much of his or her time is spent planning as opposed to leading or to controlling.
Contributors and Attributions
- Primary Functions of Management. Authored by : John and Lynn Bruton. Published by Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image: Key Functions of the Management Process. Authored by : John and Lynn Bruton. Published by Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image: The key functions of management . Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Business Feedback Loop. Authored by : Tomwsulcer. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Business_Feedback_Loop_PNG_version.png . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- The Management Process. Authored by : Jeff Short. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Ir70kcHf-w . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
Module 1: Role of Business
Functional areas of business, learning objectives.
- Identify the primary functional areas within a business
- Identify key people and explain the activities within each functional area

One of the reasons for separating business operations into functional areas is to allow each to operate within its area of expertise, thus building efficiency and effectiveness across the business as a whole. Functional areas in a business vary according to the nature of the market and the size of the business. For example, manufacturing companies like Nike and Apple have significant Research and Development (R&D) departments in order to stay in the lead in their respective business segments. On the other hand, retail companies may have no R&D functional area per se, but will be heavily invested in Operations areas surrounding Supply Chain Management.
In general, the key functional areas of a business are the following:
Marketing/Sales
- Research and Development
Each of these functional areas is represented in the following organization chart.

The primary role of managers in business is to supervise other people’s performance. Most management activities fall into the following categories:
- Planning : Managers plan by setting long-term goals for the business, as well as short-term strategies needed to execute those goals.
- Organizing: Managers are responsible for organizing the operations of a business in the most efficient way—enabling the business to use its resources effectively.
- Controlling: A large percentage of a manager’s time is spent controlling the activities within the business to ensure that it’s on track to achieve its goals. When people or processes stray from the path, managers are often the first ones to notice and take corrective action.
- Leading : Managers serve as leaders for the organization, in practical as well as symbolic ways. The manager may lead work teams or groups through a new process or the development of a new product. The manager may also be seen as the leader of the organization when it interacts with the community, customers, and suppliers.
Operations is where inputs, or factors of production, are converted to outputs, which are goods and services. Operations is the heart of a business—providing goods and services in a quantity and of a quality that meets the needs of the customers. Operations controls the supply chain, including procurement and logistics.
Marketing consists of all that a company does to identify customers’ needs and design products and services that meet those needs. The marketing function also includes promoting goods and services, determining how the goods and services will be delivered and developing a pricing strategy to capture market share while remaining competitive. In today’s technology-driven business environment, marketing is also responsible for building and overseeing a company’s Internet presence (e.g., the company website, blogs, social media campaigns, etc.). Today, social media marketing is one of the fastest growing sectors within the marketing function.
The goal of Sales is to close the revenue the company needs in order to operate profitably, especially in B2B businesses. Again, depending on the nature of the market and the company size, Sales functional areas can vary in structure and approach: inside/outside representation, vertical/horizontal focus, direct, etc. Sales works to exploit the leads created by Marketing and activities generated by the sales force itself.
The Finance function involves planning for, obtaining, and managing a company’s funds. Finance managers plan for both short-term and long-term financial capital needs and analyze the impact that borrowing will have on the financial well-being of the business. A company’s finance department answers questions about how funds should be raised (loans vs. stocks), the long-term cost of borrowing funds, and the implications of financing decisions for the long-term health of the business.
Accounting is a crucial part of the Finance functional area. Accountants provide managers with information needed to make decisions about the allocation of company resources. This area is ultimately responsible for accurately representing the financial transactions of a business to internal and external parties, government agencies, and owners/investors. Financial accountants are primarily responsible for the preparation of financial statements to help entities both inside and outside the organization assess the financial strength of the company. Managerial accountants provide information regarding costs, budgets, asset allocation, and performance appraisal for internal use by management for the purpose of decision-making.
Key People Within Functional Areas
Here is an example of the functional areas of a large technology manufacturing corporation and the key functions and people within.
The Management functional area in most large corporations is led by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Depending on company size, there may be a President in position as well.
The Operations functional area is managed by the Chief Operations Officer (COO). In this example, Operations consists of Production, led by a Vice President (VP), a Supply Chain department, and a Procurement area with Director-level people in charge.
The Finance functional area is led by the Chief Financial Officer (CFO), who is one of the most important “C-level” executives. In addition to running Finance and Accounting, the CFO is responsible for reporting company results to the financial community. Finance also contains Human Resources (HR) in many companies and the Legal department as well. It is common for the CFO to have VPs of HR, Accounting, and Legal as direct reports. HR contains functions like employee training, compensation and benefits, and recruiting. Accounting has multiple functions, such as Accounts Payable, Receivable, record-keeping, and cash flow. The Legal department is responsible for contracts, copyrights, and various negotiations on behalf of the company.
The Marketing/Sales functional area is managed by the Chief Revenue Officer (CRO), which is a relatively new addition to C-level executives. The CRO may have a Sales VP and Marketing VP as direct reports, but in some cases, the CRO may act as VP of Sales or Marketing. This functional area may also contain Customer Service (and Support) with a Director-level manager in charge. Marketing has specialized functions, such as communications (press releases), social media, data science analysis, and product marketing. Customer Service is usually responsible for Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and problem resolution and support.
Finally, the Research and Development functional area is the lifeblood of manufacturing businesses. R&D is staffed with scientists, thought leaders, subject matter experts, and industry analysts striving to provide the organization with knowledge and ideas to keep up with, and ahead of, the competition. R&D is led by the Chief Technology Officer (CTO), who manages a Development VP or similar title, depending on what technology products are being produced: semiconductors, software systems, or dental appliances. In many organizations, the Information Technology area (IT), responsible for providing internal technology tools to the company’s employees, is housed in the R&D organization.
Practice Questions
- Reading: Functional Areas of Business. Authored by : Linda Williams and Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and adaptation. Authored by : Robert Danielson. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Practice Questions. Authored by : Robert Danielson. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Worker Bees. Authored by : Scott Kidder. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/skidder/434622114/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives

The Role of Business Intelligence: What it Is and Why it Matters
For a company’s operations to become informed by data, it will want to employ a business intelligence, or BI, strategy. BI tools allow an organization to make decisions that are guided not just by anecdote or a small collection of data, but with a complete picture of data. In this article, we will cover in detail what business intelligence means, how it can support a business, and what aspects to look for in business intelligence tools for your own organization.
What is business intelligence?
Business intelligence is the process of surfacing and analyzing data in an organization to make informed business decisions. BI covers a broad spectrum of technologies and methods, from the way that data is organized and analyzed, all the way to how findings are reported. BI is used to answer how a business performed in the past and why those outcomes came about.
Execution of a successful business intelligence strategy requires a strong organization of how data is used from start to finish:
- Data collection : A business needs to understand where they can collect data from visitors and customers, and how they can be organized into a form that can be analyzed.
- Data storage : Data relevant to businesses are numerous and often large in scope. In order to be useful, that data must be stored in a place that data stakeholders can reliably access, such as in a SQL database. A storage solution should always be up-to-date so that a company can act on changes in data quickly.
- Data analysis : The core of business intelligence is focused on descriptive and diagnostic analytics, which answers questions of where your company has been, where it is now, and why things are the way they are now. BI tools need to be able to draw from data storage to conduct these different types of analyses.
- Data reporting : All of our data and analyses will do no good if they do not reach decision makers and other stakeholders. BI should convey data and insights in ways that people with less context can still quickly understand and use them to make decisions.
In order to execute these steps, multiple tools and products need to be employed. There are two subsets of tools to consider here.
Data pipeline: data collection and storage
One class of tools are those used to collect and store data. Tools like Salesforce and Hubspot collect data on various aspects of a company’s visitors. Products like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake allow businesses to store their data in scalable data warehouses. And other products like Fivetran and Stitch can make it easy to connect data generators into data storage.
While products that perform data collection and storage are important parts of the BI process, they generally aren’t what people think of when it comes to business intelligence. The efforts put into this part of an organization’s data strategy can serve not just their business intelligence needs, but other parts of their data analytics plans. Instead, the strategies used by a business to collect and store data are often known as the data pipeline. The tools used in the data pipeline will fall under the label of data engineering.
Business intelligence tools: data analysis and reporting
Other tools are used to analyze and report on data; these are the products that are referred to as business intelligence tools. Setting up these BI tools allow you to connect to and query data repositories in order to analyze the data. They let you create visualizations and dashboards that are easy to read and understand. Good BI tools let you generate and send out reports to stakeholders so they can monitor performance indicators at a high level.
Business intelligence vs. business analytics
The term “business analytics” (BA) is a term related to business intelligence, with plenty of confusion over where they overlap. A common distinction between business intelligence and business analytics comes from the type of data analysis being performed.
Business intelligence is often characterized as concerned with the descriptive and diagnostic levels of analysis. That is, BI tries to address questions of what has previously happened, what is the current state of things, and why the observed pattern in the metrics came to be.
Business analytics, on the other hand, is concerned with predictive and prescriptive analytics. This type of analysis is concerned with predicting what will happen next, or what a company should be doing next. Performing BA tends to be a more specialized pursuit, since it requires a good descriptive and diagnostic foundation that comes from BI.
While some definitions of BI and BA make distinctions between them based on analysis methods or strategies, the differences in domain between past and present vs. future are fairly standard. This separation between business intelligence and business analytics can help narrow down what kinds of functionality you want a BI tool to have, and what can be left out.
How business intelligence supports businesses
The overall objective of business intelligence is to allow a business to make informed decisions. A company with a working BI strategy will have data that is accurate, complete, and organized. Business intelligence can be used to show historic patterns to help stakeholders gauge the health of their organization, alerting them to problems as well as potential improvements.
Business intelligence can also help organize teams, keeping them aware of key performance indicators (KPIs). Awareness of KPIs through dashboards and reports keeps teams aligned and focused on their goals. Easy access to metrics and KPIs also frees up time and energy to execute on the tasks that will impact the company’s performance.
Examples of business intelligence usage
Business intelligence tools can be used by all teams at a company, including sales, marketing, and customer support. Team members and executives can both make use of BI tools’ output. Data engineers and data analysts can also make use of the convenience of a BI tool when performing their own investigations.
Examples of how business intelligence is used include:
- Visualize the volume of visitors and users on a website over time
- Track potential customers through a sales pipeline
- Measure performance of business metrics against benchmarks and goals
- Evaluate performance of marketing campaigns and experiments
- Segment users by demographic characteristics
- Generate reports for team and executive decision-making
Modern business intelligence and self-service BI
A major driving force behind modern business intelligence is increasing the accessibility of data analysis to a larger audience. Traditionally, calculation of metrics and compilation of reports required a dedicated data professional or team to create. This was a significant bottleneck between a user noticing an interesting or concerning trend and being able to diagnose their observations.
Now, business intelligence solutions are becoming aligned with self-service BI . With self-service BI, anyone is able to access data directly and perform analyses without needing to go directly through a data team member. Self-service BI tools typically have graphical interfaces so that common data tasks are easy to perform without query language knowledge. While data teams are still important for maintaining data and who gets access to it, self-service BI can free up data specialists to perform more intricate and advanced analyses.
Features of business intelligence software
In order to perform business intelligence tasks, we need data to be collected and stored with data engineering tools, then made available to business intelligence tools for analysis and reporting. When looking for solutions to let your business draw insights from your data, pay attention to the points below to make sure that they satisfy your needs.
- Connections to data sources
First and foremost, you need to be able to get access to data in order to perform business intelligence. It’s important to make sure that your analysis-side BI tool is able to connect to your other solutions that take care of data storage. These data sources can include databases like MySQL, data warehouses like Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery, or even ad hoc data files in CSV format. Make sure that your BI tool is also able to access the most up-to-date data in order to make timely decisions. Try to avoid workflows that require custom data pipelines to be set up, since this can create disruption if there is a change or unexpected event in the raw data.
Data querying
In addition to being able to connect to data sources, it is also worth checking how easily the BI tool is able to connect between data sources. A good BI tool will make it easy to take queries from different data sources and join them into a new one. Connecting and merging data from multiple data sources provides the opportunity for additional insights that are not possible on their own.
Data visualization and dashboards
Data visualization is a core component of most business intelligence applications. A good chart can convey insights faster than a plain table of numbers. When considering BI tools, see what kinds of charts they have available and the amount of customization possible with them. A surprisingly large amount can be done with a fairly small number of chart types , but think about your use case carefully to see if you need software that can support a particularly specialized chart type for your organization.
A BI tool should also be able to arrange groups of charts and tables into dashboards. Dashboards allow for continual tracking of important business metrics in a single location. Make sure that your chosen BI tool is able to automatically update its dashboards so that viewers are always getting the most up-to-date information possible.
Data analysis
It’s important to keep in mind the type of analysis that can be handled by the data that is available. When there is an unexpected change in metrics, a BI tool should allow users to dig deeper into the data. A modern BI tool will allow users to modify and add on to previous queries in order to get deeper insights into the data. Another feature that supports analysis and exploration are dashboard-level filters that can affect multiple charts at the same time.
Recall as well that BI tends to be focused on descriptive and diagnostic analysis. While it might seem attractive for a BI tool to include more advanced capabilities such as machine learning or artificial intelligence, they are far from necessary. Making sense of these advanced techniques still requires specialized knowledge of the business and statistics to properly interpret what the algorithms find. A mature data team may well be better off performing predictive and prescriptive analyses outside of the bounds of BI tools’ functionality.
Data availability
It’s important to consider the freedom that business intelligence tools can provide to an organization. Modern BI tools can make it easier for data stakeholders to perform the investigations they need to themselves, freeing up data teams to perform more in-depth analyses.
Consider how easy it is for new users to be added to a BI tool and how easily they can access the data they need. Take note if there are different account types, if there are separate creator, editor, or viewer user accounts. Check if it is possible for multiple users to work collaboratively on the same dashboard.
Implementing a self-service BI tool can be a great way to drive an organization towards being data-driven. This is especially true for smaller businesses, which may not have the level of personnel to handle a more traditional BI strategy centered around a dedicated data team. When it is easier for users to get up to speed with a BI tool, the faster an organization can make use of and act on their data.
Deployment method
Another big consideration in choosing a business intelligence tool is how it will be deployed. Traditional BI software required an on-premises deployment, including hardware setup to software installation.
Modern business intelligence follows a cloud-based deployment model. Cloud-based BI tools require no specific hardware setup, sometimes just requiring an online connection. Since resources accessed remotely, a cloud-based BI strategy is quicker to get running and easier to scale with a company’s data needs. It is now much easier to perform complex analyses due to this scalability. While on-premises deployment can have some small advantages with customizability, it will be in your best interests to stick with a cloud-based BI solution.
Application support
Each BI application has its own learning curve that can take some time to overcome. This can be an important consideration especially if you want many people actively using the software – including those who may not have much technical or analytical experience. Check to see what resources each BI tool has for using their product, like documentation, tutorials, and FAQs. Certain providers may also offer active support lines to provide direct help on specific customer questions.
Make an honest attempt at using a BI tool in a product trial in order to see if it suits your needs. Before and during a trial, plan out and try implementing some of your use cases in the product. Pay attention to not only whether the product’s features actually solve your problem, but also where you get stuck and how the BI tool’s support resources help you out. Other users will encounter those problems after purchasing the product, so knowing the kind of support you need should be a factor in choosing a BI tool.
Best practices for implementing business intelligence
Implementing business intelligence doesn’t stop with just choosing the right tools: it also requires the proper support from the organization and its people. Keep in mind the following tips to ensure that when you invest in a BI strategy, the information it returns will be valuable to your company.
Ensure that the tool meets the company’s needs
Before you purchase a BI tool, make sure that its capabilities actually act as solutions for the organization’s questions before finalizing a commitment. Plan out how you expect the BI tool to be used by the company. Use the list of business intelligence features above to understand the priorities that you need in your BI strategy. Each BI tool provides tradeoffs between its features, so determine which features are most important for your business and select the tool that aligns best with your needs.
Establish a working data pipeline
Getting meaningful outputs from a BI tool requires meaningful inputs. Having a functional data pipeline for data collection and storage is a prerequisite to performing data analyses. When data is not clean, then it may be difficult to work with the data. If data is not thorough, then gaps in the data may result in bias in the results.
Make sure that your data is structured and organized before you start to analyze it. The people who manage the data will need to be in sync with what users need in order for analysis to be useful and actionable. Collecting data from many different sources and storing them in data lakes, warehouses, and marts can be a considerable effort in both time and money. Exercising good data management is a necessary step towards becoming data-informed, and work that you put in at the start can save you more pain later on.
Encourage active usage of business intelligence tools
It can take some effort to educate employees to use the BI tools you purchase. Education on proper tool use is necessary to ensure that users are drawing accurate insights from the data. However, while BI application interfaces have become more intuitive, learning how to work with a tool still requires patience.
It can help to have someone in charge of spearheading BI adoption efforts. Let them be an evangelist and leader to get more people engaged in using BI tools. Team leaders and executives can also provide valuable buy-in energy to support the building effort. When more people are using analysis tools, the more effective its implementation will be. Not only will more insights be generated, users can rely on each other to obtain the insights they need to perform informed decision making.
Business intelligence greatly enhances how a company approaches its decision-making by using data to answer questions of the company’s past and present. It can be used by teams across an organization to track key metrics and organize on goals. Modern business intelligence tools use self-service solutions to make it easier for stakeholders to access their data and explore it for themselves.
When evaluating a BI tool, make sure it satisfies your company’s needs in terms of:
- How data can be queried and connected between data sources
- Data visualizations and dashboards
- Report generation
- Depth of data analysis and drilldown
- Accessibility of data
- Help, documentation, and active application support
Business intelligence is a key investment to making a business more informed by data. When a BI tool is used in alignment with a business’s use cases, it can free up time for employees to take meaningful actions to keep the business moving forward. For more perspectives, check out our whitepaper on how BI can benefit an organization and how to choose the right BI tool .
similar articles
Domo vs. tableau vs. chartio.
If you’re debating between Domo vs. Tableau, you’re limiting your options. When considering the right business intelligence (BI) platform for your business, you need to consider a full spectrum of features and characteristics, not to mention as many platforms as you can find.
Self-Service BI: What You Need to Know
Self-service BI is indispensable for any company that calls itself “data-driven,” thanks to its ability to make data accessible to all. If you’re in the market for a self-service BI platform, here’s what you need to know.
A Step-by-Step Guide to BI Reporting
Reporting with business intelligence (BI) used to require extensive data modeling and deep SQL knowledge in order to find insights. Modern BI reporting is thankfully much simpler. If you’re starting from scratch, there are eight steps to modern BI reporting you need to go through.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Consumer health
What are the benefits of CBD — and is it safe to use?
A prescription cannabidiol (CBD) oil is considered an effective anti-seizure medication. However, further research is needed to determine CBD 's other benefits and safety.
CBD is a chemical found in marijuana. CBD doesn't contain tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive ingredient found in marijuana that produces a high. The usual CBD formulation is oil, but CBD is also sold as an extract, a vaporized liquid and an oil-based capsule. Food, drinks and beauty products are among the many CBD -infused products available online.
Currently, the only CBD product approved by the Food and Drug Administration is a prescription oil called Epidiolex. It's approved to treat two types of epilepsy. Aside from Epidiolex, state laws on the use of CBD vary. While CBD is being studied as a treatment for a wide range of conditions, including Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, diabetes, multiple sclerosis and anxiety, research supporting the drug's benefits is still limited.
CBD use also carries some risks. Though it's often well-tolerated, CBD can cause side effects, such as dry mouth, diarrhea, reduced appetite, drowsiness and fatigue. CBD can also interact with other medications you're taking, such as blood thinners.
Another cause for concern is the unreliability of the purity and dosage of CBD in products. A recent study of 84 CBD products bought online showed that more than a quarter of the products contained less CBD than labeled. In addition, THC was found in 18 products.
If you plan to use products containing CBD , talk to your doctor.
Brent A. Bauer, M.D.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
- Candida cleanse diet
- Colloidal silver supplements
- Miller B. Labeling accuracy of cannabidiol extracts sold online. JAMA. 2017;318:1708.
- FDA approves first drug compromised of an active ingredient derived from marijuana to treat rare, severe forms of epilepsy. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm611046.htm. Accessed Nov. 20, 2018.
- State medical marijuana laws. National Conference of State Legislatures. http://www.ncsl.org/research/health/state-medical-marijuana-laws.aspx#2. Accessed Nov. 27, 2018.
- Devinsky O, et al. Effect of cannabidiol on drop seizures in the Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2018;378:1888.
- Cannabidiol. Natural Medicines. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com. Accessed Nov. 5, 2018.
- Cannabidiol. Facts & Comparisons eAnswers. http://www.wolterskluwercdi.com/facts-comparisons-online/. Accessed Nov. 5, 2018.
- Portenoy RK, et al. Cancer pain management: Adjuvant analgesics (coanalgesics). https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Nov. 14, 2018.
Products and Services
- The Mayo Clinic Diet Online
- A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to Pain Relief
- A very happy brain
- Alternative cancer treatments: 11 options to consider
- Colon cleansing
- Detox foot pads
- Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
- Do infrared saunas have any health benefits?
- Prickly pear cactus
- Herbal supplements and heart drugs
- Kombucha tea
- Kratom: Unsafe and ineffective
- Kratom for opioid withdrawal
- Learn to reduce stress through mindful living
- Medical marijuana
- Meditation 2.0: A new way to meditate
- Mindfulness exercises
- Natural remedies for depression: Are they effective?
- Tai Chi and Cardiac Rehab
- Valerian: A safe and effective herbal sleep aid?
- Alternative psoriasis treatments
- Do zinc supplements shorten colds?
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Expert Answers
- CBD Safe and effective
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
Skip to Content

- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Faculty & Research
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
Pay Ratio Disclosure Doesn’t Reduce Pay Inequality, Research Shows

CESR is proud to celebrate research excellence from Leeds faculty in our three focus areas of Business Solutions to Environmental Challenges, Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion, and Ethical Leadership. One way we do this is through our annual research awards and grants.
This year, CESR’s Best Paper Award was shared between two papers that both considered executive compensation:
- Wonjae Chang, Michael Damba, Bryce Schonberger , and Inho Suk: Does Sensationalism Affect Executive Compensation? Evidence from Pay Ratio Disclosure Reform , Journal of Accounting Research, 2022
- Dejun “Tony” Kong , Sanghee Park, and Jian Peng: Appraising and Reacting to Perceived Pay For Performance: Leader Competence and Warmth as Critical Contingencies , Academy of Management Journal, 2023
We sat down with Bryce Schonberger , assistant professor of accounting at Leeds, to discuss this paper’s findings on the impact of a recent SEC rule requiring firms to disclose the ratio between the CEO and median employee pay and effective ways to address pay inequality. This interview has been lightly edited for length and clarity.
CESR: How would you broadly describe your research? What big questions are you trying to answer?
BS: One stream of my research, which includes this paper, looks at how firms’ disclosure requirements change their real decisions or their behavior. Traditionally, accounting researchers would look at what events happened for the firm and how this impacted their reporting. However, research shows that changing what firms are required to report changes their behavior.
CESR: Could you please share a little bit about your research on the pay ratio disclosure mandate in CEO compensation? What inspired you to look into this topic, and what did you discover?
BS: Regulators forced this disclosure in the hopes of reducing pay inequality. The proposal for the CEO pay ratio disclosure is one of the most actively commented on rules the SEC has ever proposed with 287,000 comments. It was divisive. Proponents said it would give information to investors and a useful benchmark about the value that a CEO creates and prompt useful changes in CEO pay. Detractors said that it doesn’t make much sense to require this disclosure. It doesn’t have any benefit, it just names and shames CEOs and stimulates adverse media coverage. Our interest in it was just that this debate was one we thought we could shed some light on. There were some nice features of the setting that allowed us to design the test in a way that we could isolate the causal effects of the pay ratio disclosure.
The headline result is that the firms that were required to report the pay ratio did not have any significant change in the level of CEO pay. The whole focus around the adoption of the rule was curtailing excess CEO compensation, but we didn’t see that the level of CEO compensation changed. We did see a significant reduction in pay for performance at firms subject to the CEO ratio disclosure. We suspect this is an unintended consequence. If anything, the rule should have required CEO compensation to be more tied to firm performance, as this would be more informative for investors. To the extent that CEOs dislike the rule and want to avoid negative coverage, this reduction in pay for performance makes sense because it reduces the risk in the amount of CEO pay.
We also find that there is negative media coverage of the firms that disclose a high ratio, but it’s not enough to discourage firms from offering excessive pay.

"...requiring these relatively simple measures of within-firm pay inequality are not enough to effect meaningful change to the executive compensation structure."
- says Bryce Schonberger
CESR: What are the implications of your findings?
BS: The implications are that requiring these relatively simple measures of within-firm pay inequality are not enough to effect meaningful change to the executive compensation structure. This makes sense because there is already so much information in the proxy statement on CEO compensation. The only new information is the median employee pay under the new disclosure requirement. There isn’t much new information here that can move the needle on the way that firms pay their CEOs.
I do think there are other mechanisms that seem more effective in changing rank and file worker pay and therefore impacting pay inequality. This includes requiring the disclosure of salary ranges in job postings and the increasing tendency of workers to voluntarily provide information on their own pay, on websites like Glassdoor. There’s starting to be much more disaggregated information on worker pay, which historically has not been the case. We already know a lot about CEO pay, so in pursuit of reducing income inequality, these new sources of information are probably the better spot to look for those impacts.
There’s some recent research looking into how Glassdoor reviews impact employee turnover. It’s certainly an area I want to do more work in.
CESR: Do you have thoughts on effective ways of decreasing pay inequality in organizations and controlling excessive executive compensation?
BS: Investors do have a lot of information regarding executive compensation in the C-suite. Research on say on pay votes has shown that these are effective on the margin in reducing CEO pay and aligning executive pay more closely with firm performance. Providing marginally more information on the process at the C-suite level is probably not going to change things a whole lot. Increasing access to information by workers has the potential for making a bigger impact. There’s also always the potential for regulatory changes, such as requirements to post salary ranges or changes to tax laws, that would have a major impact. Simply requiring more disclosures regarding executive compensation isn’t something I see as having a huge impact going forward.
CESR: Tell us about the significance of the opportunity to be recognized for doing research related to CESR’s focus areas.
BS: I was really honored to receive the award. For a number of years, I’ve been active on nonprofit boards. On the research side, it’s hard to focus on sustainability-related topics because you must go where data is available, where you are able to conduct research and draw inferences. Recognizing papers that are done in these areas is great. I enjoy having this award on my CV; it’s a nice conversation starter with nonprofits for future work.
The most important things for driving more research on ESG and sustainability would be having more data on environmental performance, including related to the new SEC climate disclosure rules coming online, plus human capital disclosures and risks. The more information that companies are required to disclose and that’s available from crowd-sourced platforms is going to encourage more work in these areas, which is fantastic.
"I do think there are other mechanisms that seem more effective in changing rank and file worker pay and therefore impacting pay inequality. This includes requiring the disclosure of salary ranges in job postings and the increasing tendency of workers to voluntarily provide information on their own pay, on websites like Glassdoor."
- says Bryce Schonberger
CESR: What are some big trends you’re seeing in your research that relate to ESG and sustainability?
BS: Lots more ESG research is taking place in accounting. We have faculty doing work on executive compensation and governance issues, which is the more traditional ESG-type research. Faculty are also doing research on environmental and social performance, which is the newer piece of ESG research. It’s going to be an ongoing and growing area of research in accounting, particularly as firms start to think about social and environmental bottom lines for the company and how to measure the factors that contribute to these bottom lines.
CESR: How do sustainability and ESG come into your teaching?
BS: I have to prepare students for the CPA exam, so there’s a core curriculum that has to be covered. While I’m not able to cover as much sustainability as I might like, I bring in examples wherever I can. One of the nonprofits I’m involved with (called Groundswell ) installs solar arrays in low-income communities. I discuss this work with my students to help them understand it as an investment opportunity.
Learn more about our Best Paper Co-Winner Tony Kong’s research and teaching in this interview from last year.
- CESR Thought Leadership
- Share via Twitter
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Google Plus
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via E-mail
E [email protected] P (+1) 303 492 3324
Leeds School of Business 995 Regent Drive KOBL 302 Boulder, CO 80309
Support CESR with a donation
Join the CESR Newsletter
What employees are saying about the future of remote work
As organizations look to the postpandemic future, many are planning a hybrid virtual model that combines remote work with time in the office. This sensible decision follows solid productivity increases during the pandemic.
But while productivity may have gone up, many employees report feeling anxious and burned out. Unless leaders address the sources of employee anxiety, pandemic-style productivity gains may prove unsustainable in the future. 1 Besides anxiety and burnout, longer-term productivity in a hybrid virtual model will also require addressing the organizational norms that help create a common culture, generate social cohesion, and build shared trust. See Andrea Alexander, Aaron De Smet, and Mihir Mysore, “ Reimagining the postpandemic workforce ,” McKinsey Quarterly , July 7, 2020. That’s because anxiety is known to reduce job satisfaction, negatively affect interpersonal relationships with colleagues, and decrease work performance.

A McKinsey Live event on ‘Getting hybrid work right: What employees are saying’
As organizational leaders chart the path toward the postpandemic world, they need to communicate more frequently with their employees—even if their plans have yet to solidify fully. Organizations that have articulated more specific policies and approaches for the future workplace have seen employee well-being and productivity rise.
The following charts examine our survey findings and shed light on what employees want from the future of work.
Feeling included. Even high-level communication about post-COVID-19 working arrangements boosts employee well-being and productivity. But organizations that convey more detailed, remote-relevant policies and approaches see greater increases. Employees who feel included in more detailed communication are nearly five times more likely to report increased productivity. Because communicating about the future can drive performance outcomes today, leaders should consider increasing the frequency of their employee updates—both to share what’s already decided and to communicate what is still uncertain.
Communication breakdown. Valuable as a detailed vision for postpandemic work might be to employees, 40 percent of them say they’ve yet to hear about any vision from their organizations, and another 28 percent say that what they’ve heard remains vague.
Anxiety at work. At organizations that are communicating vaguely, or not at all, about the future of postpandemic work, nearly half of employees say it’s causing them concern or anxiety. Anxiety is known to decrease work performance, reduce job satisfaction, and negatively affect interpersonal relationships with colleagues, among other ills. For the global economy, the loss of productivity because of poor mental health—including anxiety—might be as high as $1 trillion per year .
Burning out. The lack of clear communication about the future of postpandemic work also contributes to employee burnout. Nearly half of employees surveyed say they’re feeling some symptoms of being burned out at work. That may be an underestimate, since employees experiencing burnout are less likely to respond to survey requests, and the most burned-out individuals may have already left the workforce—as have many women, who’ve been disproportionately affected by the COVID-19 crisis.
Share more. Burnout is especially pronounced for people feeling anxious due to a lack of organizational communication. These employees were almost three times more likely to report feeling burned out. The obvious recommendation for organizational leaders: share more with employees, even if you’re uncertain about the future, to help improve employee well-being now.
Employees want flexibility. So how do organizations help their anxious and burned-out employees? One way is to find out what employees want for the future. More than half of employees told us they would like their organizations to adopt more flexible hybrid virtual-working models , in which employees are sometimes on-premises and sometimes working remotely. A hybrid model can help organizations make the most of talent wherever it resides, lower costs, and strengthen organizational performance .
Talent at risk. In fact, more than a quarter of those surveyed reported that they would consider switching employers if their organization returned to fully on-site work. Of course, even employees who say they might depart could ultimately decide to remain, depending on the policies companies end up adopting, the availability of jobs at the same or better rates of pay, and the role of automation in shifting the tasks people do .
Staying home. In describing the hybrid model of the future, more than half of government and corporate workers report that they would like to work from home at least three days a week once the pandemic is over. Across geographies, US employees are the most interested in having access to remote work, with nearly a third saying they would like to work remotely full time.
What parents say. Employees with young children are the most likely to prefer flexible work locations, with only 8 percent suggesting they would like to see a fully on-site model in the future. Employees without children under 18 are nearly three times as likely to prefer on-site work, but the majority still prefer more flexible models.
Hopes and fears. Across the board, employees are eager to see organizations put a greater emphasis on flexibility, competitive compensation, and well-being once the pandemic is over—and conversely, they’re concerned that future work, regardless of whether it is on-site or remote, will negatively affect these needs. Employees also fear that on-site work will lead to a greater chance of getting sick and that remote work will reduce community and collaboration between colleagues.
Policy matters. Which working arrangements and related policies do employees say will lead to the highest levels of well-being, social cohesion, and productivity? More than a third of respondents ranked clear hours and expectations for collaboration in their top five policies; several other collaboration policies, including technologies that enable on-site employees to dial-in to remote meetings and guidelines for documentation, also received significant support. Collaboration tools, and training for those tools, also rate highly for employees, as does reimbursement for remote-work office setups. Microconnectivity policies, meanwhile—from small team events to a listening and response strategy—were top policies for more than a quarter of all respondents.
Andrea Alexander is an associate partner in McKinsey’s Houston office. Aaron De Smet is a senior partner in the New Jersey office. Meredith Langstaff is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office, where Dan Ravid is a fellow, research and knowledge.
This article was edited by Lang Davison, an executive editor in the Seattle office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Reimagining the postpandemic workforce

What’s next for remote work: An analysis of 2,000 tasks, 800 jobs, and nine countries

The future of work after COVID-19

Watch these Dates for Key Market Research Reports

Make Your Voice Count in the Capital
- News & Media
- Florida Realtors News
Which AI Chatbot Is Best for Your Business?

The right AI tool can help agents create blogs, answer complex questions, build a brand and drive engagement. But which chatbot is the best to use?
NEW YORK – You’ve heard the buzz about AI transforming the real estate industry, but with so many chatbot options available, how can you find the one that best fits your business needs? Make an informed decision about which subscription is worth your hard-earned dollars.
Here’s a look at the strengths and weaknesses of five of the most popular AI chatbot subscriptions: ChatGPT, Claude AI, Google Gemini, Perplexity AI, and Jasper:

Learn More About Using AI Tools
Join the Top AI Tools for Realtors education session featuring Kevin Hawkins on Thursday, Aug. 22
To register for the convention and trade expo, click here .
- Strengths : ChatGPT excels at creating high-quality content, assisting with analyzing research, and answering questions, saving real estate professionals significant time and effort. It can generate human-like responses, making it a valuable tool for drafting informative and engaging content. Personalization has been improved with the recent addition of memory storage.
- Weaknesses: Despite its impressive capabilities, ChatGPT lacks integration with real-time data sources, which may result in outdated or inaccurate information. As news reports have shown, ChatGPT’s outputs could include biased or insensitive content if not carefully monitored and filtered.
- Real use case : A real estate agent can use ChatGPT to draft informative and engaging blog posts about local market trends, homebuying tips, or the benefits of buyers working with a real estate professional.
- Pricing : A free account provides access to the ChatGPT 3.5 model via web, iOS, and Android unlimited messages, interactions, and history. Pro account: Access to GPT-4 and access to additional tools like DALL·E, Browsing, Advanced Data Analysis, and more: $20 per month per individual.
- Strengths : Claude AI offers round-the-clock availability and highly personalized interactions. It provides valuable assistance with complex questions, making it a reliable resource for agents and clients. Claude’s ability to learn from previous interactions enables it to improve its responses and adapt to individual user needs continuously. It is one of the best content creation bots available today.
- Weaknesses : While Claude can handle many tasks and inquiries, it may struggle with complex, sensitive, or emotionally charged situations where empathy and understanding are crucial. Claude’s AI data training has a cutoff date of 2021 and may lack the ability to provide the most current information to inquiries.
- Real use case : A real estate agent can use Claude AI to create comprehensive and engaging neighborhood guides that showcase the unique features, amenities, and lifestyles of different areas within their market. These guides could serve as valuable resources for potential buyers, helping establish the agent as a local expert.
- Pricing : A free account provides limited access to basic features, such as answering simple questions and providing general information. The free version also has restrictions on the number of interactions. Claude Pro: For $20 per month per individual, users get full access to all features, including advanced question-answering capabilities and higher usage limits detailed here.
Google Gemini
- Strengths : Google Gemini can help agents enhance client communication and marketing efforts. Its ability to generate highly personalized content makes it a versatile tool for creating engaging marketing materials. Gemini’s superpower as a chatbot is its integration with Google Search, which makes it able to provide real-time information. It’s also great at summarizing content.
- Weaknesses : As a more general-purpose AI, Gemini’s responses to prompts tend to be shorter, limiting its ability to assist in creating blog posts that require more content. Also, Gemini raised ethical concerns, and its use requires extra caution within an industry that must adhere to fair housing rules and data privacy.
- Real use case : An agent can use Gemini to create personalized email campaigns that provide valuable information about local housing markets, financing options, or the benefits of homeownership to their client base.
- Pricing : Google Gemini offers a standard free version that reliably answers questions, summarizes text, and creates basic content (poems, scripts, etc.). Gemini Advanced, which requires a Google One AI Subscription, can provide coding assistance and debugging help, offer complex reasoning and logical problem solving, handle nuanced instructions for creative tasks, and provide longer and more in-depth content for $19.99 per month per individual.
Perplexity AI
- Strengths : Perplexity AI stands out for its integration, providing in-depth, well-researched, and tight responses by drawing information from multiple online sources. It is also highly flexible, allowing users to switch between different AI models, such as ChatGPT-4 and Claude 2.1, to find the best fit for your prompt. Bonus: You can use Perplexity to search Reddit.
- Weaknesses : Perplexity can be inconsistent with responses and does not handle problem-solving well. Moreover, while it may use search, it does not have the breadth of search coverage as a traditional search engine, as it is limited to the curated sources it has been trained on.
- Real use case : Perplexity AI does well with math and can help agents better analyze their marketing tracking data. For example, agents can input the performance of different social media posts, providing the content and results for each post to Perplexity, which can analyze the data and provide a summary of interesting trends.
- Pricing : A free individual account offers basic search functions with limited features. The Pro Plan is $20 a month for an individual (or $200 a year) and includes access to AI models like GPT-4.
- Strengths : Jasper is an AI marketing copilot. Its strength is its ability to create highly personalized content that helps real estate agents build their brand and drive engagement. It offers real estate-specific templates and creative writing support, enabling agents to produce social media posts, blog articles, and email campaigns. It does well in creating attention-grabbing content to help agents stand out.
- Weaknesses : Although Jasper can create engaging content, it may need a deeper understanding of local market dynamics and nuances crucial for effective real estate marketing. As with all AI-generated content, agents must carefully review and edit to ensure accuracy and brand alignment.
- Real use case : Jasper can help a real estate agent create compelling social media posts, such as showcasing a client success story, to build brand awareness and engagement by – looks incomplete
- Pricing : Jasper offers a 7-day free trial, allowing users to test the platform’s capabilities for any paid program during that time. Paid plans per seat start at $39/month (Creator – billed yearly) for one brand voice.
Building an AI chatbot toolkit
Choosing the right AI chatbot for your real estate business can significantly increase your productivity. By reviewing the strengths and weaknesses of each option – and testing out the free versions for yourself – you can find the best Chatbot for your AI toolkit.
Don’t forget that if you struggle with a chatbot or any technology, Tech Helpline analysts can help. This service is available to over 750,000 Realtors in North America as a member benefit from their MLS or Association.
Whatever you choose – ChatGPT, Claude AI, Google Gemini, Perplexity AI, or Jasper – the key is to find the AI chatbot you will use daily. With the right AI tool in your tech stack, you’ll have more time to focus on what matters most: building relationships and closing deals.
© 2024 Florida Realtors®
You May Also Like
- Millennials, Gen-Z Buy Homes Differently
- Surprise Property Issues Fuel Buyers’ Remorse
- Florida Takes 11 of Top 25 Fastest-Growing Cities

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad - it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market.
Business research is a part of the business intelligence process. It is usually conducted to determine whether a company can succeed in a new region, to understand its competitors, or simply select a marketing approach for a product. This research can be carried out using steps in qualitative research methods or quantitative research methods.
Put another way, in the honeycomb, the six main elements - namely: (1) research philosophy; (2) research approach; (3) research strategy; (4) research design; (5) data collection and (6) data analysis techniques - come together to form research methodology. This structure is characteristic of the main headings you will find in a methodology ...
Business research functions as a conduit to new ideas and concepts. Learning through research is not limited to a particular department or project or a particular point in the year. It can be ...
Business research is the process through which a business improves its profits and organizational performance by gathering and analyzing relevant data regarding its operations. It's a continuous process that involves all aspects of an organization's business environment, like the markets the company is involved in, its competitors, local and ...
The most primary role of business research is that it helps across every decision in the business, from product innovation to marketing and promotional planning. Business Research also helps in forecasting a business, whether in terms of competition or any other types of problems it will be facing.
Business research is the process of studying a company's competitors, stakeholders, and profit & loss to meet the company objectives and maximize revenue & profits. ... The main function of business research is to define the objectives and core values of any business. It tells how the company should manage and generate leads, create sales and ...
Business research can be defined as a systematic and objective process of gathering, recording and analysing data that provide information to guide business decisions. It is used to understand the market trends, or find the optimal marketing mix, devise effective HR policies, or find the best investment options.
The Role of Business Research. Research is a systematic search for information in order to obtain a clear picture concerning the underlying problem. Technically speaking, research is a process of identifying problem thoroughly, establishing an objective, collecting and analyzing the relevant data in order to determine the possible factors ...
The definition of research is broken into two main parts, i.e., the research process and the contribution. This section also demonstrates what research is not. ... Organizations are complex and non-static systems, resulting in highly agile and dynamic business functions. It is, therefore, perfectly justifiable to approach business research from ...
Primary vs Secondary Business Research. Another way in which research methods can be classified is by primary and secondary research. Primary research refers to the collection of first-hand data, generally directly from the source. Some common methods of primary research are surveys, interviews, and observations. ...
Here are some of the primary research methods organizations or businesses use to collect data: 1. Interviews (telephonic or face-to-face) Conducting interviews is a qualitative research method to collect data and has been a popular method for ages. These interviews can be conducted in person (face-to-face) or over the telephone.
Primary research is any research that you conduct yourself. It can be as simple as a 2-question survey, or as in-depth as a years-long longitudinal study. The only key is that data must be collected firsthand by you. Primary research is often used to supplement or strengthen existing secondary research.
Primary market research involves collecting original data directly from individuals, groups, or sources to address specific research objectives or business questions. Here are some examples of primary market research methods and how they can be applied: 1. Surveys. Surveys are a common method of primary research.
The need for business research increases as firms realize more opportunities, for example, in the form of increased trade globally and more competition. Business research is a truth-seeking function responsible for gathering, analyzing, interpreting, and reporting information so that business decision makers become more effective. There are few ...
Functions of Marketing Research As shown in Figure 1.3, marketing research serves four primary functions within an organiza - tion. The exploratory function of marketing research occurs when researchers have a limited understanding or no knowledge at all about a marketing situation or a particular outcome. For
15 examples of business functions. Here is a list of 15 examples of business functions, whether they are the primary focus of a company or a department within it: 1. Strategy. A strategy firm or department develops the strategy, approach and way to implement change for a company. Strategy-based businesses help others reach their goals and ...
Effective management involves four primary functions and related skill sets: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Although there's a logical sequence to the functions, in practice the four functions are often performed in a dynamic manner. For example, a manager would need to develop or reference a departmental or organizational ...
Management. The primary role of managers in business is to supervise other people's performance. Most management activities fall into the following categories: Planning: Managers plan by setting long-term goals for the business, as well as short-term strategies needed to execute those goals. Organizing: Managers are responsible for organizing ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) Which of the following are the primary functions of all organizations? A) production/operations, marketing, and human resources B) marketing, human resources, and finance/accounting C) sales, quality control, and production/operations D) marketing, production/operations, and finance/accounting E) research and development ...
Business intelligence is the process of surfacing and analyzing data in an organization to make informed business decisions. BI covers a broad spectrum of technologies and methods, from the way that data is organized and analyzed, all the way to how findings are reported. BI is used to answer how a business performed in the past and why those ...
Business functions are the foundation of a company's structure and operations. They include all the divisions, departments, and other components involved in creating a product or service. Within an organization, the main functional groups include manufacturing, sales & marketing, accounts & finance, and human resources.
Question: The primary function of business research is to: Select one: O a. Identify employee needs O b. Provide the solution to a business problem. O c. Attempt to forecast the employee behavior. O d. Provide information to assist managers in making business decisions. Show transcribed image text.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. ... This showcases how traditional office functions, such as ...
A prescription cannabidiol (CBD) oil is considered an effective anti-seizure medication. However, further research is needed to determine CBD's other benefits and safety.. CBD is a chemical found in marijuana.CBD doesn't contain tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive ingredient found in marijuana that produces a high. The usual CBD formulation is oil, but CBD is also sold as an extract ...
Large-scale organizational change has always been difficult, and there's no shortage of research showing that a majority of transformations continue to fail. Today's dynamic environment adds an extra level of urgency and complexity. Companies must increasingly react to sudden shifts in the marketplace, to other external shocks, and to the imperatives of new business models.
CESR is proud to celebrate research excellence from Leeds faculty in our three focus areas of Business Solutions to Environmental Challenges, Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion, and Ethical Leadership. One way we do this is through our annual research awards and grants. This year, CESR's Best Paper Award was shared between two papers that both considered executive compensation:
As organizations look to the postpandemic future, many are planning a hybrid virtual model that combines remote work with time in the office. This sensible decision follows solid productivity increases during the pandemic.. But while productivity may have gone up, many employees report feeling anxious and burned out.
Pricing: A free individual account offers basic search functions with limited features. The Pro Plan is $20 a month for an individual (or $200 a year) and includes access to AI models like GPT-4. Jasper. Strengths: Jasper is an AI marketing copilot. Its strength is its ability to create highly personalized content that helps real estate agents ...