- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility
HOW TO WRITE A THESIS: Steps by step guide

Introduction
In the academic world, one of the hallmark rites signifying mastery of a course or academic area is the writing of a thesis . Essentially a thesis is a typewritten work, usually 50 to 350 pages in length depending on institutions, discipline, and educational level which is often aimed at addressing a particular problem in a given field.
While a thesis is inadequate to address all the problems in a given field, it is succinct enough to address a specialized aspect of the problem by taking a stance or making a claim on what the resolution of the problem should be. Writing a thesis can be a very daunting task because most times it is the first complex research undertaking for the student. The lack of research and writing skills to write a thesis coupled with fear and a limited time frame are factors that makes the writing of a thesis daunting. However, commitment to excellence on the part of the student combined with some of the techniques and methods that will be discussed below gives a fair chance that the student will be able to deliver an excellent thesis regardless of the subject area, the depth of the research specialization and the daunting amount of materials that must be comprehended(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
Contact us now if you need help with writing your thesis. Check out our services
Visit our facebookpage
What is a thesis?
A thesis is a statement, theory, argument, proposal or proposition, which is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. It explains the stand someone takes on an issue and how the person intends to justify the stand. It is always better to pick a topic that will be able to render professional help, a topic that you will be happy to talk about with anybody, a topic you have personal interest and passion for, because when writing a thesis gets frustrating personal interest, happiness and passion coupled with the professional help it will be easier to write a great thesis (see you through the thesis). One has to source for a lot of information concerning the topic one is writing a thesis on in order to know the important question, because for you to take a good stand on an issue you have to study the evidence first.
Qualities of a good thesis
A good thesis has the following qualities
- A good thesis must solve an existing problem in the society, organisation, government among others.
- A good thesis should be contestable, it should propose a point that is arguable which people can agree with or disagree.
- It is specific, clear and focused.
- A good thesis does not use general terms and abstractions.
- The claims of a good thesis should be definable and arguable.
- It anticipates the counter-argument s
- It does not use unclear language
- It avoids the first person. (“In my opinion”)
- A strong thesis should be able to take a stand and not just taking a stand but should be able to justify the stand that is taken, so that the reader will be tempted to ask questions like how or why.
- The thesis should be arguable, contestable, focused, specific, and clear. Make your thesis clear, strong and easy to find.
- The conclusion of a thesis should be based on evidence.
Steps in writing a Thesis
- First, think about good topics and theories that you can write before writing the thesis, then pick a topic. The topic or thesis statement is derived from a review of existing literature in the area of study that the researcher wants to explore. This route is taken when the unknowns in an area of study are not yet defined. Some areas of study have existing problems yearning to be solved and the drafting of the thesis topic or statement revolves around a selection of one of these problems.
- Once you have a good thesis, put it down and draw an outline . The outline is like a map of the whole thesis and it covers more commonly the introduction, literature review, discussion of methodology, discussion of results and the thesis’ conclusions and recommendations. The outline might differ from one institution to another but the one described in the preceding sentence is what is more commonly obtainable. It is imperative at this point to note that the outline drew still requires other mini- outlines for each of the sections mentioned. The outlines and mini- outlines provide a graphical over- view of the whole project and can also be used in allocating the word- count for each section and sub- section based on the overall word- count requirement of the thesis(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
- Literature search. Remember to draw a good outline you need to do literature search to familiarize yourself with the concepts and the works of others. Similarly, to achieve this, you need to read as much material that contains necessary information as you can. There will always be a counter argument for everything so anticipate it because it will help shape your thesis. Read everything you can–academic research, trade literature, and information in the popular press and on the Internet(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
- After getting all the information you need, the knowledge you gathered should help in suggesting the aim of your thesis.
Remember; a thesis is not supposed to be a question or a list, thesis should specific and as clear as possible. The claims of a thesis should be definable and also arguable.
- Then collecting and analyzing data, after data analysis, the result of the analysis should be written and discussed, followed by summary, conclusion, recommendations, list of references and the appendices
- The last step is editing of the thesis and proper spell checking.
Structure of a Thesis
A conventional thesis has five chapters – chapter 1-5 which will be discussed in detail below. However, it is important to state that a thesis is not limited to any chapter or section as the case may be. In fact, a thesis can be five, six, seven or even eight chapters. What determines the number of chapters in a thesis includes institution rules/ guideline, researcher choice, supervisor choice, programme or educational level. In fact, most PhD thesis are usually more than 5 chapters(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
Preliminaries Pages: The preliminaries are the cover page, the title page, the table of contents page, and the abstract.
The introduction: The introduction is the first section and it provides as the name implies an introduction to the thesis. The introduction contains such aspects as the background to the study which provides information on the topic in the context of what is happening in the world as related to the topic. It also discusses the relevance of the topic to society, policies formulated success and failure. The introduction also contains the statement of the problem which is essentially a succinct description of the problem that the thesis want to solve and what the trend will be if the problem is not solved. The concluding part of the statement of problem ends with an outline of the research questions. These are the questions which when answered helps in achieving the aim of the thesis. The third section is the outline of research objectives. Conventionally research objectives re a conversion the research questions into an active statement form. Other parts of the introduction are a discussion of hypotheses (if any), the significance of the study, delimitations, proposed methodology and a discussion of the structure of the study(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
The main body includes the following; the literature review, methodology, research results and discussion of the result, the summary, conclusion and recommendations, the list of references and the appendices.
The literature review : The literature review is often the most voluminous aspects of a thesis because it reviews past empirical and theoretical literature about the problem being studied. This section starts by discussing the concepts relevant to the problem as indicated in the topic, the relationship between the concepts and what discoveries have being made on topic based on the choice of methodologies. The validity of the studies reviewed are questioned and findings are compared in order to get a comprehensive picture of the problem. The literature review also discusses the theories and theoretical frameworks that are relevant to the problem, the gaps that are evident in literature and how the thesis being written helps in resolving some of the gaps.
The major importance of Literature review is that it specifies the gap in the existing knowledge (gap in literature). The source of the literature that is being reviewed should be specified. For instance; ‘It has been argued that if the rural youth are to be aware of their community development role they need to be educated’ Effiong, (1992). The author’s name can be at the beginning, end or in between the literature. The literature should be discussed and not just stated (RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
The methodology: The third section is a discussion of the research methodology adopted in the thesis and touches on aspects such as the research design, the area, population and sample that will be considered for the study as well as the sampling procedure. These aspects are discussed in terms of choice, method and rationale. This section also covers the sub- section of data collection, data analysis and measures of ensuring validity of study. It is the chapter 3. This chapter explains the method used in data collection and data analysis. It explains the methodology adopted and why it is the best method to be used, it also explains every step of data collection and analysis. The data used could be primary data or secondary data. While analysing the data, proper statistical tool should be used in order to fit the stated objectives of the thesis. The statistical tool could be; the spearman rank order correlation, chi square, analysis of variance (ANOVA) etc (RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
The findings and discussion of result : The next section is a discussion of findings based on the data collection instrumentation used and the objectives or hypotheses of study if any. It is the chapter 4. It is research results. This is the part that describes the research. It shows the result gotten from data that is collected and analysed. It discusses the result and how it relates to your profession.
Summary, Conclusion and Recommendation: This is normally the chapter 5. The last section discusses the summary of the study and the conclusions arrived at based on the findings discussed in the previous section. This section also presents any policy recommendations that the researcher wants to propose (RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
References: It cite all ideas, concepts, text, data that are not your own. It is acceptable to put the initials of the individual authors behind their last names. The way single author is referenced is different from the way more than one author is referenced (RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
The appendices; it includes all data in the appendix. Reference data or materials that is not easily available. It includes tables and calculations, List of equipment used for an experiment or details of complicated procedures. If a large number of references are consulted but all are not cited, it may also be included in the appendix. The appendices also contain supportive or complementary information like the questionnaire, the interview schedule, tables and charts while the references section contain an ordered list of all literature, academic and contemporary cited in the thesis. Different schools have their own preferred referencing styles(RE: write a thesis or writing a thesis).
Follow the following steps to achieve successful thesis writing
Start writing early. Do not delay writing until you have finished your project or research. Write complete and concise “Technical Reports” as and when you finish each nugget of work. This way, you will remember everything you did and document it accurately, when the work is still fresh in your mind. This is especially so if your work involves programming.
Spot errors early. A well-written “Technical Report” will force you to think about what you have done, before you move on to something else. If anything is amiss, you will detect it at once and can easily correct it, rather than have to re-visit the work later, when you may be pressured for time and have lost touch with it.
Write your thesis from the inside out. Begin with the chapters on your own experimental work. You will develop confidence in writing them because you know your own work better than anyone else. Once you have overcome the initial inertia, move on to the other chapters.
End with a bang, not a whimper. First things first, and save the best for last. First and last impressions persist. Arrange your chapters so that your first and last experimental chapters are sound and solid.
Write the Introduction after writing the Conclusions. The examiner will read the Introduction first, and then the Conclusions, to see if the promises made in the former are indeed fulfilled in the latter. Ensure that your introduction and Conclusions match.
“No man is an Island”. The critical review of the literature places your work in context. Usually, one third of the PhD thesis is about others’ work; two thirds, what you have done yourself. After a thorough and critical literature review, the PhD candidate must be able to identify the major researchers in the field and make a sound proposal for doctoral research. Estimate the time to write your thesis and then multiply it by three to get the correct estimate. Writing at one stretch is very demanding and it is all too easy to underestimate the time required for it; inflating your first estimate by a factor of three is more realistic.
Punctuating your thesis
Punctuation Good punctuation makes reading easy. The simplest way to find out where to punctuate is to read aloud what you have written. Each time you pause, you should add a punctuation symbol. There are four major pause symbols, arranged below in ascending order of “degree of pause”:
- Comma. Use the comma to indicate a short pause or to separate items in a list. A pair of commas may delimit the beginning and end of a subordinate clause or phrase. Sometimes, this is also done with a pair of “em dashes” which are printed like this:
- Semi-colon. The semi-colon signifies a longer pause than the comma. It separates segments of a sentence that are “further apart” in position, or meaning, but which are nevertheless related. If the ideas were “closer together”, a comma would have been used. It is also used to separate two clauses that may stand on their own but which are too closely related for a colon or full stop to intervene between them.
- Colon. The colon is used before one or more examples of a concept, and whenever items are to be listed in a visually separate fashion. The sentence that introduced the itemized list you are now reading ended in a colon. It may also be used to separate two fairly—but not totally—independent clauses in a sentence.
- Full stop or period. The full stop ends a sentence. If the sentence embodies a question or an exclamation, then, of course, it is ended with a question mark or exclamation mark, respectively. The full stop is also used to terminate abbreviations like etc., (for et cetera), e.g., (for exempli gratia), et al., (for et alia) etc., but not with abbreviations for SI units. The readability of your writing will improve greatly if you take the trouble to learn the basic rules of punctuation given above.
Don't forget to contact us for your thesis and other academic assistance
35 thoughts on “how to write a thesis: steps by step guide”.
wow.. thanks for sharing
Thanks for the article it’s very helpful
It’s very good
This is a great deal
Thank you much respect from here.
Thanks for the education.
thank you for the guide ,is very educating.
What can I say but THANK YOU. I will read your post many times in the future to clear my doubts.
Just came across this insightful article when about to start my PhD program. This is helpful thanks
Very informative website.
I’m really interested in your help. I’m doing my Master and this is my real challenge. I have given my thesis topic already.
chat with us on 09062671816
thanks so much and i will keep on reading till I get much more understanding.
thanks so much i will get in touch with you
Thanks for sharing…
Thanyou for sharing…
You can write my ms thesis
Pingback: My Site
There is perceptibly a bunch to realize about this. I assume you made some nice points in features also.
Loving the information on this web site, you have done great job on the blog posts.
Am happy to come across this web site, thanks a lot may God bless. In few months time I will be back.
anafranil prices
colchicine tablet brand name in india
can i buy colchicine without a prescription
synthroid over the counter online
Wow, marvelous blog format! How long have you been running a blog for? you make running a blog glance easy. The entire look of your site is wonderful, let alone the content!
thank you very much
Helpful info. Lucky me I discovered your website accidentally, and I’m surprised why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Helpful info. Lucky me I discovered your website accidentally, aand I’m surprised why this accident did nnot happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
For newest news you have to pay a visit internet and on internet I found this site as a most excellent web page for hottest updates.
Great info and right to the point. I am not sure if this is really the best place to ask but do you guys have any thoughts on where to get some professional writers? Thank you
Wow, this article is good, my sister is analyzing these kinds of things, so I am going to inform her.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3 Constructing the Thesis and Argument—From the Ground Up
Moving beyond the five-paragraph theme.
As an instructor, I’ve noted that a number of new (and sometimes not-so-new) students are skilled wordsmiths and generally clear thinkers but are nevertheless stuck in a high-school style of writing. They struggle to let go of certain assumptions about how an academic paper should be . Chapter 1 points to the essay portion of the SAT as a representative artifact of the writing skills that K-12 education imparts. Some students who have mastered that form, and enjoyed a lot of success from doing so, assume that college writing is simply more of the same. The skills that go into a very basic kind of essay—often called the five-paragraph theme —are indispensable. If you’re good at the five-paragraph theme, then you’re good at identifying a clear and consistent thesis, arranging cohesive paragraphs, organizing evidence for key points, and situating an argument within a broader context through the intro and conclusion.
In college you need to build on those essential skills. The five-paragraph theme, as such, is bland and formulaic; it doesn’t compel deep thinking. Your professors are looking for a more ambitious and arguable thesis, a nuanced and compelling argument, and real-life evidence for all key points, all in an organically [1] structured paper.
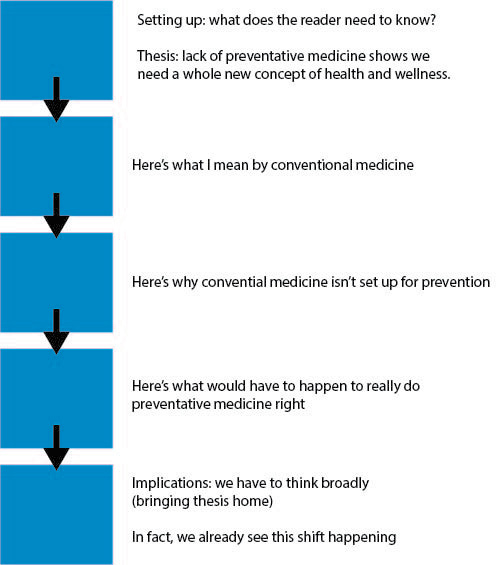
Figures 3.1 and 3.2 contrast the standard five-paragraph theme and the organic college paper. The five-paragraph theme, outlined in Figure 3.1 is probably what you’re used to: the introductory paragraph starts broad and gradually narrows to a thesis, which readers expect to find at the very end of that paragraph. In this idealized format, the thesis invokes the magic number of three: three reasons why a statement is true. Each of those reasons is explained and justified in the three body paragraphs, and then the final paragraph restates the thesis before gradually getting broader. This format is easy for readers to follow, and it helps writers organize their points and the evidence that goes with them. That’s why you learned this format.
Figure 3.2, in contrast, represents a paper on the same topic that has the more organic form expected in college. The first key difference is the thesis. Rather than simply positing a number of reasons to think that something is true, it puts forward an arguable statement: one with which a reasonable person might disagree. An arguable thesis gives the paper purpose. It surprises readers and draws them in. You hope your reader thinks, “Huh. Why would they come to that conclusion?” and then feels compelled to read on. The body paragraphs, then, build on one another to carry out this ambitious argument. In the classic five-paragraph theme (Figure 3.1) it hardly matters which of the three reasons you explain first or second. In the more organic structure (Figure 3.2) each paragraph specifically leads to the next.

The last key difference is seen in the conclusion. Because the organic essay is driven by an ambitious, non-obvious argument, the reader comes to the concluding section thinking “OK, I’m convinced by the argument. What do you, author, make of it? Why does it matter?” The conclusion of an organically structured paper has a real job to do. It doesn’t just reiterate the thesis; it explains why the thesis matters.
The substantial time you spent mastering the five-paragraph form in Figure 3.1 was time well spent; it’s hard to imagine anyone succeeding with the more organic form without the organizational skills and habits of mind inherent in the simpler form. But if you assume that you must adhere rigidly to the simpler form, you’re blunting your intellectual ambition. Your professors will not be impressed by obvious theses, loosely related body paragraphs, and repetitive conclusions. They want you to undertake an ambitious independent analysis, one that will yield a thesis that is somewhat surprising and challenging to explain.
The three-story thesis: from the ground up
You have no doubt been drilled on the need for a thesis statement and its proper location at the end of the introduction. And you also know that all of the key points of the paper should clearly support the central driving thesis. Indeed, the whole model of the five-paragraph theme hinges on a clearly stated and consistent thesis. However, some students are surprised—and dismayed—when some of their early college papers are criticized for not having a good thesis. Their professor might even claim that the paper doesn’t have a thesis when, in the author’s view it clearly does. So, what makes a good thesis in college?
- A good thesis is non-obvious . High school teachers needed to make sure that you and all your classmates mastered the basic form of the academic essay. Thus, they were mostly concerned that you had a clear and consistent thesis, even if it was something obvious like “sustainability is important.” A thesis statement like that has a wide-enough scope to incorporate several supporting points and concurring evidence, enabling the writer to demonstrate his or her mastery of the five-paragraph form. Good enough! When they can, high school teachers nudge students to develop arguments that are less obvious and more engaging. College instructors, though, fully expect you to produce something more developed.
- A good thesis is arguable . In everyday life, “arguable” is often used as a synonym for “doubtful.” For a thesis, though, “arguable” means that it’s worth arguing: it’s something with which a reasonable person might disagree. This arguability criterion dovetails with the non-obvious one: it shows that the author has deeply explored a problem and arrived at an argument that legitimately needs 3, 5, 10, or 20 pages to explain and justify. In that way, a good thesis sets an ambitious agenda for a paper. A thesis like “sustainability is important” isn’t at all difficult to argue for, and the reader would have little intrinsic motivation to read the rest of the paper. However, an arguable thesis like “sustainability policies will inevitably fail if they do not incorporate social justice,” brings up some healthy skepticism. Thus, the arguable thesis makes the reader want to keep reading.
- A good thesis is well specified . Some student writers fear that they’re giving away the game if they specify their thesis up front; they think that a purposefully vague thesis might be more intriguing to the reader. However, consider movie trailers: they always include the most exciting and poignant moments from the film to attract an audience. In academic papers, too, a well specified thesis indicates that the author has thought rigorously about an issue and done thorough research, which makes the reader want to keep reading. Don’t just say that a particular policy is effective or fair; say what makes it is so. If you want to argue that a particular claim is dubious or incomplete, say why in your thesis.
- A good thesis includes implications . Suppose your assignment is to write a paper about some aspect of the history of linen production and trade, a topic that may seem exceedingly arcane. And suppose you have constructed a well supported and creative argument that linen was so widely traded in the ancient Mediterranean that it actually served as a kind of currency. [2] That’s a strong, insightful, arguable, well specified thesis. But which of these thesis statements do you find more engaging?
Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade.
Linen served as a form of currency in the ancient Mediterranean world, connecting rival empires through circuits of trade. The economic role of linen raises important questions about how shifting environmental conditions can influence economic relationships and, by extension, political conflicts.
Putting your claims in their broader context makes them more interesting to your reader and more impressive to your professors who, after all, assign topics that they think have enduring significance. Finding that significance for yourself makes the most of both your paper and your learning.
How do you produce a good, strong thesis? And how do you know when you’ve gotten there? Many instructors and writers find useful a metaphor based on this passage by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr.: [3]
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight.
One-story theses state inarguable facts. Two-story theses bring in an arguable (interpretive or analytical) point. Three-story theses nest that point within its larger, compelling implications. [4]
The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately. Then, with that first story built, you can layer on the second story by formulating the insightful, arguable point that animates the analysis. That’s often the most effortful part: brainstorming, elaborating and comparing alternative ideas, finalizing your point. With that specified, you can frame up the third story by articulating why the point you make matters beyond its particular topic or case.
Thesis: that’s the word that pops at me whenever I write an essay. Seeing this word in the prompt scared me and made me think to myself, “Oh great, what are they really looking for?” or “How am I going to make a thesis for a college paper?” When rehearing that I would be focusing on theses again in a class, I said to myself, “Here we go again!” But after learning about the three story thesis, I never had a problem with writing another thesis. In fact, I look forward to being asked on a paper to create a thesis.
Timothée Pizarro
For example, imagine you have been assigned a paper about the impact of online learning in higher education. You would first construct an account of the origins and multiple forms of online learning and assess research findings about its use and effectiveness. If you’ve done that well, you’ll probably come up with a well considered opinion that wouldn’t be obvious to readers who haven’t looked at the issue in depth. Maybe you’ll want to argue that online learning is a threat to the academic community. Or perhaps you’ll want to make the case that online learning opens up pathways to college degrees that traditional campus-based learning does not. In the course of developing your central, argumentative point, you’ll come to recognize its larger context; in this example, you may claim that online learning can serve to better integrate higher education with the rest of society, as online learners bring their educational and career experiences together. To outline this example:
- First story : Online learning is becoming more prevalent and takes many different forms.
- Second story : While most observers see it as a transformation of higher education, online learning is better thought of an extension of higher education in that it reaches learners who aren’t disposed to participate in traditional campus-based education.
- Third story : Online learning appears to be a promising way to better integrate higher education with other institutions in society, as online learners integrate their educational experiences with the other realms of their life, promoting the freer flow of ideas between the academy and the rest of society.
Here’s another example of a three-story thesis: [5]
- First story : Edith Wharton did not consider herself a modernist writer, and she didn’t write like her modernist contemporaries.
- Second story : However, in her work we can see her grappling with both the questions and literary forms that fascinated modernist writers of her era. While not an avowed modernist, she did engage with modernist themes and questions.
- Third story : Thus, it is more revealing to think of modernism as a conversation rather than a category or practice.
Here’s one more example:
- First story : Scientists disagree about the likely impact in the U.S. of the light brown apple moth (LBAM) , an agricultural pest native to Australia.
- Second story : Research findings to date suggest that the decision to spray pheromones over the skies of several southern Californian counties to combat the LBAM was poorly thought out.
- Third story : Together, the scientific ambiguities and the controversial response strengthen the claim that industrial-style approaches to pest management are inherently unsustainable.
A thesis statement that stops at the first story isn’t usually considered a thesis. A two-story thesis is usually considered competent, though some two-story theses are more intriguing and ambitious than others. A thoughtfully crafted and well informed three-story thesis puts the author on a smooth path toward an excellent paper.
The concept of a three-story thesis framework was the most helpful piece of information I gained from the writing component of DCC 100. The first time I utilized it in a college paper, my professor included “good thesis” and “excellent introduction” in her notes and graded it significantly higher than my previous papers. You can expect similar results if you dig deeper to form three-story theses. More importantly, doing so will make the actual writing of your paper more straightforward as well. Arguing something specific makes the structure of your paper much easier to design.
Peter Farrell
Three-story theses and the organically structured argument
The three-story thesis is a beautiful thing. For one, it gives a paper authentic momentum. The first paragraph doesn’t just start with some broad, vague statement; every sentence is crucial for setting up the thesis. The body paragraphs build on one another, moving through each step of the logical chain. Each paragraph leads inevitably to the next, making the transitions from paragraph to paragraph feel wholly natural. The conclusion, instead of being a mirror-image paraphrase of the introduction, builds out the third story by explaining the broader implications of the argument. It offers new insight without departing from the flow of the analysis.
I should note here that a paper with this kind of momentum often reads like it was knocked out in one inspired sitting. But in reality, just like accomplished athletes and artists, masterful writers make the difficult thing look easy. As writer Anne Lamott notes, reading a well written piece feels like its author sat down and typed it out, “bounding along like huskies across the snow.” However, she continues,
This is just the fantasy of the uninitiated. I know some very great writers, writers you love who write beautifully and have made a great deal of money, and not one of them sits down routinely feeling wildly enthusiastic and confident. Not one of them writes elegant first drafts. All right, one of them does, but we do not like her very much. [6]
Experienced writers don’t figure out what they want to say and then write it. They write in order to figure out what they want to say.
Experienced writers develop theses in dialog with the body of the essay. An initial characterization of the problem leads to a tentative thesis, and then drafting the body of the paper reveals thorny contradictions or critical areas of ambiguity, prompting the writer to revisit or expand the body of evidence and then refine the thesis based on that fresh look. The revised thesis may require that body paragraphs be reordered and reshaped to fit the emerging three-story thesis. Throughout the process, the thesis serves as an anchor point while the author wades through the morass of facts and ideas. The dialogue between thesis and body continues until the author is satisfied or the due date arrives, whatever comes first. It’s an effortful and sometimes tedious process. Novice writers, in contrast, usually oversimplify the writing process. They formulate some first-impression thesis, produce a reasonably organized outline, and then flesh it out with text, never taking the time to reflect or truly revise their work. They assume that revision is a step backward when, in reality, it is a major step forward.
Everyone has a different way that they like to write. For instance, I like to pop my earbuds in, blast dubstep music and write on a white board. I like using the white board because it is a lot easier to revise and edit while you write. After I finish writing a paragraph that I am completely satisfied with on the white board, I sit in front of it with my laptop and just type it up.
Kaethe Leonard
Another benefit of the three-story thesis framework is that it demystifies what a “strong” argument is in academic culture. In an era of political polarization, many students may think that a strong argument is based on a simple, bold, combative statement that is promoted it in the most forceful way possible. “Gun control is a travesty!” “Shakespeare is the best writer who ever lived!” When students are encouraged to consider contrasting perspectives in their papers, they fear that doing so will make their own thesis seem mushy and weak. However, in academics a “strong” argument is comprehensive and nuanced, not simple and polemical. The purpose of the argument is to explain to readers why the author—through the course of his or her in-depth study—has arrived at a somewhat surprising point. On that basis, it has to consider plausible counter-arguments and contradictory information. Academic argumentation exemplifies the popular adage about all writing: show, don’t tell. In crafting and carrying out the three-story thesis, you are showing your reader the work you have done.
The model of the organically structured paper and the three-story thesis framework explained here is the very foundation of the paper itself and the process that produces it. The subsequent chapters, focusing on sources, paragraphs, and sentence-level wordsmithing, all follow from the notion that you are writing to think and writing to learn as much as you are writing to communicate. Your professors assume that you have the self-motivation and organizational skills to pursue your analysis with both rigor and flexibility; that is, they envision you developing, testing, refining and sometimes discarding your own ideas based on a clear-eyed and open-minded assessment of the evidence before you.
Other resources
- The Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill offers an excellent, readable run-down on the five-paragraph theme, why most college writing assignments want you to go beyond it, and those times when the simpler structure is actually a better choice.
- There are many useful websites that describe good thesis statements and provide examples. Those from the writing centers at Hamilton College , Purdue University , and Clarkson University are especially helpful.
- Find a scholarly article or book that is interesting to you. Focusing on the abstract and introduction, outline the first, second, and third stories of its thesis.
- Television programming includes content that some find objectionable.
- The percent of children and youth who are overweight or obese has risen in recent decades.
- First-year college students must learn how to independently manage their time.
- The things we surround ourselves with symbolize who we are.
- Find an example of a five-paragraph theme (online essay mills, your own high school work), produce an alternative three-story thesis, and outline an organically structured paper to carry that thesis out.
- “Organic” here doesn’t mean “pesticide-free” or containing carbon; it means the paper grows and develops, sort of like a living thing. ↵
- For more see Fabio Lopez-Lazaro “Linen.” In Encyclopedia of World Trade from Ancient Times to the Present . Armonk: M.E. Sharpe, 2005. ↵
- Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., The Poet at the Breakfast Table (New York: Houghton & Mifflin, 1892). ↵
- The metaphor is extraordinarily useful even though the passage is annoying. Beyond the sexist language of the time, I don’t appreciate the condescension toward “fact-collectors.” which reflects a general modernist tendency to elevate the abstract and denigrate the concrete. In reality, data-collection is a creative and demanding craft, arguably more important than theorizing. ↵
- Drawn from Jennifer Haytock, Edith Wharton and the Conversations of Literary Modernism (New York: Palgrave-MacMillan, 2008). ↵
- Anne Lamott, Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life (New York: Pantheon, 1994), 21. ↵
Writing in College Copyright © 2016 by Amy Guptill is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
II. Getting Started
2.5 Writing Thesis Statements
Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; and Kirk Swenson
To be effective, all support in an essay must work together to convey a central point; otherwise, an essay can fall into the trap of being out of order and confusing. Just as a topic sentence focuses and unifies a single paragraph, the thesis statement focuses and unifies an entire essay. This statement is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination; it tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point.
Because writing is not a linear process, you may find that the best thesis statement develops near the end of your first draft. However, creating a draft or working thesis early in the writing project helps give the drafting process clear direction. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
A thesis is not just a topic, but rather the writer’s comment or interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic you select (for example, school uniforms, social networking), you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful, and confident.
In the majority of essays, a thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of the introductory paragraph. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body paragraphs. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
Working Thesis Statements
A strong thesis statement must have the following qualities:
- It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable.
- It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence (reasons, facts, examples).
- It must be specific. A thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and remain focused on the topic.
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxson in the play Fences symbolize the challenges of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
Pitfalls to Avoid
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
Your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement, an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing. Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and develop new ideas and reasons for those ideas. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
- Pinpoint and replace all non specific words, such as people, everything, society, or life, with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Pinpoint and Replace Example
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use, and be appreciated for, their talents.
Explanation: The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus their research and gain more direction in their writing. The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard.
- Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Clarify Example
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
Explanation: A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke and more accurately defines their stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
- Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Replace with Action Verbs Example
Working thesis: Kansas City school teachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
Explanation: The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions.
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- How much is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results?
- Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Omit General Claims Example
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on the internet and social media are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
Explanation: It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition . 2nd ed. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8 . Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Relating to lines; a way of explaining information logically and/or sequentially; can refer to the chronological relaying of information.
A brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work. To summarize is to create a brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work.
To analyze closely or minutely; to scrutinize every aspect. Unlike the fields of biology, anatomy, or medicine, in rhetoric and writing, dissect does not refer to the cutting apart of a physical body but to the taking apart the body of an argument or idea piece by piece to understand it better.
A logical, rational, lucid, or understandable expression of an idea, concept, or notion; consistent and harmonious explanation.
Assertion or announcement of belief, understanding, or knowledge; a formal statement or proclamation.
Without a defined number or limit; unlimited, infinite, or undetermined.
An altered version of a written work. Revising means to rewrite in order to improve and make corrections. Unlike editing, which involves minor changes, revisions include major and noticeable changes to a written work.
Not relevant; unimportant; beside the point; not relating to the matter at hand.
Attractive, tempting, or seductive; to have an appealing and charismatic quality.
To influence or convince; to produce a certain or specific result through the use of force.
2.5 Writing Thesis Statements Copyright © 2022 by Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; and Kirk Swenson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Continuing Studies
- Toggle Navigation
- Liberal Arts Studies
- Current Students
- Completion of Final Work & Graduation
- Thesis Information
Thesis Process
What is a thesis.
A thesis is essentially a lengthy research paper that engages deeply with the wider body of scholarly work on the chosen topic. The name “thesis” is deliberate, because this paper needs to have a strong thesis — an original and creative point to make — and an argument to support it using research sources effectively.
The type of research can vary depending on the field; a sociology thesis might be based on a survey and/or interview instrument and its findings; a literature thesis might be focused on a particular author or literary movement, drawing on both primary and secondary sources. Clarity on the research you want to do is essential to getting started on thesis work.
Liberal Arts Studies (LAS) students who decide to write a master’s thesis to complete their program of study are required to take two 3-credit-hour courses designed to assist in the process. Thesis I is designated as a research course, and Thesis II is for actually writing the thesis. A 3.0 GPA is required in order to begin writing a proposal and enrolling in these courses.
If this option interests you, start thinking about it in the early stages of your program. The most effective topics are those that get your adrenaline going – something you are really excited about, want to study more deeply, and even follow up on the topic in your future life and work.
The steps involved in the thesis process include:
- selecting a topic in consultation with the program director
- finding a faculty advisor
- developing a thesis proposal
- forming a thesis committee
- registering for and completing Thesis classes
- adhering to established deadlines
- gaining format approval on your printed thesis
- defending your thesis
- completing your thesis
More details about each step can be found below.
Choosing a Topic and a Faculty Advisor
The first order of business in pursuing your thesis is discussing your preliminary ideas with the Liberal Arts Studies Program Director, who can assist you in formulating a topic and exploring possibilities for finding an advisor.
Your advisor should be someone:
- with whom you are comfortable
- who shares your passion for the topic
- to help you identify resources and shape the project
- to provide feedback and suggestions on your research and drafted paper
Often this advising relationship emerges from a course you have taken in your Liberal Arts Studies program. Your advisor will work with you to ensure that the thesis is at the appropriate level of graduate work. As the thesis is a permanent record of your scholarly work, it is important to be fastidious in its preparation.
Advisors are normally chosen from the University’s Graduate Faculty list . If you find an advisor who is not a member of the Graduate Faculty, make arrangements with the Program Assistant for the advisor’s temporary appointment to the Graduate Faculty.
You are responsible for approaching potential thesis advisors. A professor may decline the opportunity because the topic is not a good match with their area of expertise, or they do not have the time to commit. Serving as a Liberal Arts Studies advisor is overload work for faculty (for which they receive a modest stipend). If no professor is available to work with you on your topic of first choice, be flexible about choosing another topic. Note: Faculty members carrying a reduced teaching load (for research leave or administrative duties) cannot take on additional work during the semester the reduced load is given. Please check with your advisor about this.
Once you have secured a faculty member to be your advisor, submit the advisor’s name to the Liberal Arts Studies Director for approval. Your advisor will need to sign your Thesis Proposal Form . Their department chair’s signature is also required as approval of their work overload.
Thesis Proposal
Once you and your advisor have agreed on your topic, you should begin working with your advisor to develop your ideas for your research and writing. Your proposed plan should be described in 1,000 words or less and attached to the Thesis Proposal Form as a Word document.
Your proposal should:
- indicate the nature and scope of your topic
- discuss the approach to be used in developing the topic
- provide an overview of research to be conducted and materials available to support it
- describe anticipated outcomes you hope to achieve
- establish the validity of the topic as a thesis
Please check The Thesis Proposal page for guidelines. Once the proposal is finished, submit it along with the signed Thesis Proposal Form to the Liberal Arts Studies Director for approval.
You will be notified if the proposal is approved by the Liberal Arts Studies Director, and may then begin work on the thesis. If the proposal is not approved, it will be sent back for revision. You will want to begin the thesis proposal process well before the beginning of the semester in which you would like to begin the actual thesis work. Be mindful of deadlines!
Once the thesis proposal is signed by the appropriate parties and approved by the LAS Director, you may request to be registered for LBS 791 (Thesis Research). This is a 3-credit hour course with the scheduled meeting times determined by you and your advisor.
Your proposal is not set in stone. You may find that your thesis varies from the original plan as you go along. This is to be expected in a developing idea. Your proposal is a broad guideline, not a straitjacket. The approval of the proposal is on the basis of the topic, the general approach to the topic, and the depth at which the topic will be handled. Your final product may differ from the proposal as stated.
Note: if your developing thesis turns out to be fundamentally different from the original proposal, to the extent that you are changing your topic or adding or deleting a major portion of your proposed research and methods, you will be required to submit a new description to the Liberal Arts Studies Director for additional approval.
You and your thesis advisor should meet regularly to maintain progress on your work. You are responsible for maintaining contact with your advisor so that you can have a continuing exchange of ideas and guidance. Your advisor will help you develop your thesis to meet the appropriate graduate standards for content, level, and format. Your thesis should be at least 50-60 pages in length.
Thesis Committee Selection
As your thesis work progresses, you will also need to form a thesis committee that includes your advisor and two other faculty members who are either part of the Graduate Faculty or have received approval for Temporary Graduate Faculty status. No more than one faculty member of the three individuals serving on a thesis committee may have Temporary Graduate Faculty status.
Typically the two thesis committee members (also referred to as “readers”) do not work with you on your thesis. Rather, their role is evaluative, and their contribution to your thesis is through their participation in your oral defense when your paper is completed. There is no remuneration for serving on the thesis committee of a Liberal Arts Studies student. Please inform the Liberal Arts Studies Office of the names of your thesis committee members as soon as you have determined who they are. The Program Director does not normally sit on the committee, but does review the thesis before the defense takes place.
Register for Thesis I (research) and Thesis II (writing) in the semesters in which your actual work is being done. Your advisor is required to turn in a grade (Satisfactory or Unsatisfactory) indicating whether you are making progress on the thesis. If you cannot finish by the time you complete Thesis I and II, you must register for “Graduate Fee” for the semesters until you finish as continuous enrollment is required for the program. You must be registered in the semester in which you intend to graduate.
A Liberal Arts Studies student can graduate in August, December, or May. For each semester, there are deadlines that must be met. The dates for the deadlines for each semester can be found on the Graduate School Calendar .
Application for Candidacy & Intent to Graduate Form
This form requires the signature of your advisor and the Liberal Arts Studies Director. It must be turned in to Graduate School Office by the deadline noted in the Calendar.
Format Approval
Formatting requirements are very specific, so pay close attention to all the details.
- One copy of the title page and one chapter of your thesis must be submitted to the Graduate School Office for a check of the format.
- The Assistant to the Dean will look over these materials to confirm that the format of the thesis is correct.
- The full thesis must also be reviewed in the Liberal Arts Studies office.
- When you submit the copies of the thesis to your committee members for the initial review (usually at least 2 weeks prior to the defense meeting), an additional copy should be given to the Liberal Arts Studies office.
Thesis Defense
You should plan to have your thesis defense at least two weeks before the Last Day to Defend . This arrangement will give you enough time to make any changes requested at the thesis defense meeting.
Completed Thesis
The completed and approved thesis must be submitted to the Graduate School Office by the submission deadlines.
Thesis Defense Meeting
Scheduling the meeting.
In consultation with your thesis committee members, you should schedule a time and place for the defense of your thesis. You must inform the Graduate School and Liberal Arts Studies Office of the date and time. The defense must be held by the Last Day to Defend as indicated on the Graduate School Academic Calendar , although it may be held at any time during a semester.
Give your thesis committee members and the Liberal Arts Studies Program Director at least two weeks to read the thesis prior to the defense meeting. Don’t forget that a copy of the thesis must also be turned in to the Liberal Arts Studies office at this same time.
Scope of the Meeting
Discuss with your advisor the expectations he/she has for the thesis defense. The meeting is presided over by the more senior faculty member who is not the advisor. However, it is the advisor who begins the session with the first question. After the first question, the defense usually develops into a give and take discussion between you and the three thesis committee members. You should be prepared to answer questions on your research, your argument, and your conclusions.
The defense usually lasts about one hour, after which you leave the room while the examiners discuss the quality of the thesis and its defense. The examiners will formally vote for either:
- Unconditional Pass
- Pass upon Rectifying Minor Deficiencies
- Pass upon Rectifying Major Deficiencies
Failure is extremely rare because usually an advisor will not allow a student to schedule a defense if he or she has any doubts about the acceptability of the thesis. It is most typical for a student to pass and be required to make minor changes of content and typographical edits.
As soon as the committee has made the decision, the advisor will invite you back into the room to report the outcome. If there are changes to be made, the advisor will want to schedule a time to go over them with you. These changes must be made and submitted to 6 the advisor for approval. The final draft must be turned in before the Graduate School deadline .
Format of Final Copy
The format of the Liberal Arts Studies thesis is dictated by the guidelines provided by the Graduate School on its website.
Examples of Theses
Bound theses are available through the year 2008 and are available in the print collections of the Z. Smith Reynolds Library. Beginning with 2009, theses are available in digital format through the Z. Smith Reynolds Library.
If you have questions about the Liberal Arts Studies M.A. program, please contact us so we can help you! [email protected]
336.758.6032

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.

Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statement to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling idea —the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe . These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement , an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
1. Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people , everything , society , or life , with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
2. Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke . The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
3. Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
4. Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
In the first section of Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Research Process
- Getting Started with Research: Credo
- Brainstorming
- Identify Key Search Terms
- Finding Books
- Finding Articles
- Library Search Strategies
- Using Google
- CRAAP Method
- The ACT UP Method
- Evaluating News Sources
- More Resources
- Chicago (Turabian)
- Presentation and Printing Resources This link opens in a new window
Thesis Introduction
Thesis Statement
One of the most important components to any essay is having an effective thesis statement!
Explanation of a thesis statement
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement is the main point of your essay. Usually composed of one or two sentences, the thesis statement tells the reader what your paper is about. It should be debatable and not a statement of fact. Aside from guiding the reader, it also helps you while you are writing to keep your paper focused.
Thesis Graphic

From: Library and Learning Commons
Tips for writing a thesis
Tips for writing a working thesis statement!
After you have identified and developed your research topic, formulate a good research question that can help you create your thesis statement. Your thesis should answer your research question, challenge the reader, and be supported by evidence.
When creating your thesis statement, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is my thesis statement clear and specific?
Be sure your thesis is as specific and clear as possible so the reader knows what your essay is about. Remember, as with the research process, your thesis is a work in progress and you may end up revising it in order to accommodate your research.
- Is my thesis statement too broad or general?
Having a thesis statement that is too broad can lead you to having too much information that may not be relevant. You want to be very clear and specific with your argument and provide as much detail on your specific points so readers know exactly what is going on in your essay.
- Where do I put my thesis statement?
Generally, your thesis should appear early on in your essay in order to effectively state your claim and guide the reader.
Video on Thesis Statement
Check out this video on writing thesis statements!
From: tuslaccprof
Additional links for thesis statements
For more help with thesis statements visit:
Purdue University Writing Lab
https://owl.purdue.edu/search.html?q=thesis
Credit for Page
This page was created by Magen Nosworthy (Fall 2018 ENGL 489)
- << Previous: Background
- Next: Identify Key Search Terms >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 2:55 PM
- URL: https://nicholls.libguides.com/research_process

3 Point Thesis Statement
Ai generator.
A 3-point thesis statement is a concise yet potent tool that outlines the main arguments of your paper. By presenting three key points, it guides readers through your central ideas and supports your position. In this guide, we’ll explore how to create compelling 3-point thesis statements , along with valuable tips to ensure clarity, coherence, and persuasive strength in your academic writing.
Definition of a 3 Point Thesis Statement
A 3-point thesis statement is a succinct and focused sentence that outlines the main arguments or points you intend to address in your paper. It serves as a roadmap for your readers, indicating the core topics or themes you’ll explore while presenting your stance or perspective on a particular issue.
Example of a 3 Point Thesis Statement
Topic: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
Thesis Statement: “The accelerating effects of climate change threaten global biodiversity through temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns.”
In this example, the 3-point thesis statement clearly presents the three main points that will be discussed in the paper: temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns. These points provide a structured framework for the upcoming argumentative analysis.
100 Three Point Thesis Statement Examples

Size: 643 KB
A 3-point thesis statement succinctly outlines central arguments, providing a roadmap for focused discussions. Below are 100 examples spanning various subjects, each followed by a brief 60-word description:
- Cyberbullying Effects on Adolescents Cyberbullying adversely impacts adolescents’ mental health, self-esteem, and academic performance. This thesis addresses the detrimental effects of cyberbullying on adolescents’ psychological well-being, academic achievement, and self-perception.
- Renewable Energy Solutions Renewable energy systems contribute to sustainability through reduced emissions, resource conservation, and energy independence. This thesis explores the multifaceted benefits of renewable energy, including its role in combating climate change, conserving resources, and fostering energy autonomy.
- Gender Stereotypes in Media Media perpetuates gender stereotypes through representation, roles, and normalized behaviors. Focusing on media’s influence, this thesis analyzes how gender stereotypes are reinforced through portrayal, societal roles, and the reinforcement of normalized behaviors.
- The Impact of Social Media on Politics Social media shapes political discourse by influencing awareness, engagement, and public opinion. Examining the intersection of technology and politics, this thesis delves into how social media platforms shape political discussions by impacting awareness, engagement, and public sentiment.
- Cultural Diversity in Education Incorporating diverse perspectives in education enhances critical thinking, empathy, and global understanding. This thesis underscores the significance of integrating diverse viewpoints into educational curricula, fostering skills such as critical thinking, empathy, and cross-cultural awareness.
- Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Job Market Artificial intelligence transforms employment landscapes by reshaping job roles, skill demands, and the need for adaptability. Investigating AI’s influence on jobs, this thesis explores how automation shifts job responsibilities, necessitates new skills, and emphasizes the importance of adaptability.
- Effects of Social Media on Teenage Body Image Social media shapes teenage body image through comparisons, idealized representations, and societal beauty standards. This thesis delves into how social media influences teenagers’ perceptions of body image by promoting comparisons, unrealistic ideals, and cultural beauty norms.
- Ethical Implications of Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering raises ethical concerns over altering organisms, patenting life forms, and unforeseen ecological consequences. Analyzing the ethical dimensions, this thesis examines debates surrounding genetic modification, including ethical dilemmas, intellectual property, and environmental risks.
- Education’s Role in Addressing Poverty Education is a catalyst for poverty alleviation by fostering skills, knowledge, and socio-economic mobility. This thesis emphasizes education’s pivotal role in breaking the cycle of poverty through skill development, knowledge acquisition, and improved economic prospects.
- Media’s Influence on Political Polarization Media exacerbates political polarization by disseminating biased information, echo chambers, and fostering extremism. Investigating media’s role, this thesis explores how biased reporting, echo chambers, and extremist content contribute to the widening political divide.
- Environmental Conservation and Economic Growth Environmental conservation and economic growth can coexist through sustainable practices, green technologies, and eco-tourism. This thesis examines the compatibility of preserving the environment and promoting economic development by emphasizing sustainable practices, technology, and eco-friendly industries.
- Impacts of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships Social media alters interpersonal relationships by affecting communication dynamics, intimacy, and personal interactions. Exploring technology’s influence on relationships, this thesis analyzes how social media shapes communication patterns, intimacy levels, and face-to-face interactions.
- Globalization’s Effects on Cultural Diversity Globalization both enriches and endangers cultural diversity through cultural exchange, homogenization, and cultural appropriation. This thesis examines globalization’s dual effects, including the enrichment of cultural exchange and the challenges of cultural homogenization and appropriation.
- The Role of Education in Promoting Environmental Stewardship Education fosters environmental stewardship by instilling awareness, responsibility, and sustainable behaviors. Addressing the intersection of education and the environment, this thesis underscores how education cultivates environmental consciousness, accountability, and sustainable practices.
- Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare Diagnostics Artificial intelligence revolutionizes healthcare diagnostics through precise analysis, early detection, and improved patient outcomes. Exploring AI’s impact on healthcare, this thesis assesses how AI enhances medical diagnoses by providing accurate analyses, detecting conditions earlier, and optimizing patient care.
- Media’s Influence on Consumer Behavior Media shapes consumer behavior by creating desires, trends, and influencing purchasing decisions. Focusing on media’s sway, this thesis examines how advertising and media content drive consumer desires, shape trends, and impact buying choices.
- Education’s Role in Fostering Tolerance and Inclusion Education cultivates tolerance and inclusion by promoting empathy, understanding, and dismantling stereotypes. This thesis highlights how education plays a vital role in creating inclusive societies through empathy-building, stereotype deconstruction, and fostering understanding.
- Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence Development Ethical concerns surround AI development due to bias, privacy invasion, and the potential for autonomous decision-making. Addressing the ethical dimensions, this thesis evaluates the moral implications associated with AI development, including issues of bias, privacy, and decision-making autonomy.
- Media’s Influence on Political Engagement Media influences political engagement by shaping public opinion, mobilizing activism, and framing political narratives. Examining media’s role in politics, this thesis analyzes how media outlets shape public perceptions, drive activism, and contribute to the framing of political issues.
- Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security Sustainable agriculture ensures food security through ecological practices, crop diversity, and responsible resource management. Investigating the relationship between agriculture and food security, this thesis explores how sustainable practices, diverse crops, and resource conservation bolster global food supplies
- Technology’s Impact on Education Technology transforms education through online learning, personalized instruction, and innovative teaching methods. Examining the intersection of technology and education, this thesis assesses how digital tools reshape learning environments, enhance personalization, and revolutionize teaching techniques.
- Effects of Social Media on Mental Health Social media affects mental health through comparison, cyberbullying, and the pressure of maintaining online personas. Investigating mental health implications, this thesis explores how social media contributes to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges through comparison, bullying, and curated online identities.
- The Role of Literature in Shaping Societal Norms Literature shapes societal norms by reflecting culture, challenging conventions, and fostering critical discourse. Examining literature’s impact, this thesis analyzes how literary works influence societal values, prompt reflection, and challenge established norms.
- Online Privacy and Personal Data Protection Online privacy hinges on protecting personal data from breaches, surveillance, and unauthorized use. Addressing digital security, this thesis explores the complexities of safeguarding personal information from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and surveillance.
- Media’s Role in Shaping Historical Narratives Media influences historical narratives by framing events, shaping memory, and emphasizing certain perspectives. Focusing on media’s historical impact, this thesis examines how media narratives influence collective memory, historical understanding, and the framing of significant events.
- Economic Inequality and Access to Education Economic inequality affects education access through disparities in resources, quality, and opportunities. Addressing the connection between wealth disparity and education, this thesis explores how economic inequalities impact access to quality education and opportunities.
- Influence of Social Media on Democracy Social media affects democracy by shaping political discourse, enabling citizen participation, and disseminating information. Examining the intersection of technology and politics, this thesis assesses how social media platforms influence democratic processes, political engagement, and information dissemination.
- Effects of Climate Change on Coastal Communities Climate change poses risks to coastal communities through rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and erosion. Investigating climate impacts, this thesis explores how rising temperatures and changing weather patterns threaten coastal areas with sea-level rise, storms, and erosion.
- The Role of Art in Cultural Preservation Art contributes to cultural preservation by conveying heritage, identity, and historical narratives. Focusing on artistic expression, this thesis examines how art serves as a vessel for cultural memory, preservation of traditions, and the portrayal of historical stories.
- Media’s Influence on Beauty Standards Media shapes beauty standards through idealized images, promoting unrealistic ideals, and setting cultural norms. Analyzing media’s role in shaping perceptions of beauty, this thesis explores how media images influence cultural definitions of attractiveness and self-worth.
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Ethics Artificial intelligence raises ethical concerns related to bias, decision-making, and the potential for autonomous systems. Addressing the ethical dimensions of AI, this thesis evaluates how machine learning technologies introduce ethical dilemmas in areas such as bias, decision-making, and autonomy.
- Literature’s Exploration of Social Injustice Literature critiques social injustice by depicting marginalized experiences, advocating for change, and prompting reflection. This thesis analyzes how literary works shed light on societal inequalities, advocate for marginalized voices, and inspire social change.
- Effects of Video Games on Cognitive Development Video games impact cognitive development through problem-solving, spatial awareness, and enhanced multitasking skills. Examining the influence of gaming, this thesis explores how interactive digital entertainment contributes to cognitive skill development in areas such as problem-solving and multitasking.
- The Role of Education in Gender Equality Education empowers gender equality by challenging stereotypes, promoting opportunities, and fostering inclusive mindsets. Addressing the intersection of education and gender, this thesis emphasizes how educational systems contribute to dismantling gender stereotypes, increasing opportunities, and promoting gender inclusivity.
- Effects of Social Media on News Consumption Social media shapes news consumption patterns through personalized feeds, viral content, and the spread of misinformation. Investigating media’s impact on news consumption, this thesis examines how social media algorithms, viral content, and misinformation affect the way individuals access and interpret news.
- Urbanization’s Impact on Mental Health Urbanization affects mental health through overcrowding, noise pollution, and limited access to green spaces. Exploring the psychological consequences of urban living, this thesis analyzes how city environments influence mental well-being through factors such as noise, density, and lack of natural spaces.
- The Role of Literature in Empathy Cultivation Literature cultivates empathy by portraying diverse experiences, fostering emotional connections, and promoting understanding. This thesis explores how literary narratives foster empathy by encouraging readers to connect emotionally with characters from various backgrounds and circumstances.
- Effects of Online Learning on Educational Equity Online learning impacts educational equity by addressing accessibility, offering flexible options, and widening disparities. Focusing on digital education, this thesis examines how online learning platforms both address and exacerbate disparities in education access and quality.
- Media’s Influence on Public Health Attitudes Media shapes public health attitudes by disseminating health information, addressing stigmas, and promoting healthy behaviors. Examining media’s role in health communication, this thesis analyzes how media platforms influence public perceptions, spread health-related information, and contribute to behavior change.
- Impact of Technology on Family Dynamics Technology affects family dynamics by altering communication, screen time habits, and the balance between virtual and face-to-face interactions. This thesis explores how technology influences the ways families communicate, spend time together, and navigate the integration of digital devices into daily life
- Impacts of Social Media on Teen Mental Health Social media influences teen mental health through comparison, online bullying, and the pressure to curate a perfect image. Focusing on adolescent well-being, this thesis examines how social media usage affects mental health, contributing to issues such as low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.
- The Role of Literature in Empowerment Literature empowers individuals by providing representation, voicing marginalized perspectives, and fostering a sense of agency. Addressing the transformative power of literature, this thesis explores how literary works empower individuals by offering diverse role models, amplifying underrepresented voices, and encouraging self-expression.
- Effects of Screen Time on Child Development Excessive screen time influences child development through cognitive impacts, sedentary behaviors, and altered social interactions. Investigating digital media’s impact on children, this thesis analyzes how prolonged screen time affects cognitive development, physical activity, and social skills in early childhood.
- Media’s Role in Shaping Cultural Identities Media influences cultural identities by reflecting representation, perpetuating stereotypes, and shaping societal perceptions. This thesis examines how media shapes cultural identities by influencing how different groups are represented, constructing stereotypes, and influencing cultural perceptions.
- The Impact of Online Shopping on Retail Industry Online shopping transforms the retail industry through convenience, global access, and the rise of e-commerce platforms. Focusing on the evolving retail landscape, this thesis explores how digital commerce platforms have revolutionized shopping behaviors, affecting traditional retail structures.
- The Role of Literature in Social Change Literature drives social change by sparking awareness, prompting activism, and encouraging critical engagement with societal issues. This thesis delves into how literature serves as a catalyst for social transformation by raising awareness, mobilizing readers, and advocating for change.
- Effects of Technology on Sleep Patterns Technology disrupts sleep patterns through blue light exposure, screen time before bed, and the impact on circadian rhythms. This thesis examines how technology usage, particularly before sleep, affects sleep quality, circadian rhythms, and overall well-being.
- Media’s Influence on Consumerism Media drives consumerism through advertising, influencing purchasing behavior, and shaping materialistic values. Investigating media’s impact on consumption, this thesis analyzes how advertisements, marketing strategies, and media content influence consumer choices and materialistic attitudes.
- The Impact of Virtual Reality on Education Virtual reality transforms education through immersive learning experiences, simulations, and interactive engagement. Exploring the intersection of technology and education, this thesis assesses how virtual reality enhances learning by creating immersive environments, simulations, and interactive content.
- Effects of Social Media on Friendship Dynamics Social media affects friendship dynamics by redefining connection, altering communication, and influencing group dynamics. Analyzing the digitalization of friendships, this thesis explores how social media platforms impact the nature of friendships, communication patterns, and group interactions.
- The Role of Literature in Fostering Resilience Literature fosters resilience by portraying characters’ coping strategies, resilience narratives, and encouraging emotional growth. This thesis highlights how literary narratives provide readers with insights into resilience strategies, offering examples of characters overcoming adversity and promoting emotional growth.
- Effects of Technology on Workplace Productivity Technology influences workplace productivity through automation, remote work tools, and digital communication platforms. Examining technology’s influence on work environments, this thesis assesses how digital tools enhance efficiency, promote remote collaboration, and reshape traditional work structures.
- Media’s Role in Public Opinion Formation Media shapes public opinion by framing news, influencing perceptions, and molding societal attitudes toward current events. Investigating media’s impact on public discourse, this thesis analyzes how media outlets influence public perceptions, frame news narratives, and contribute to the formation of public opinions.
- The Impact of Music on Mood Regulation Music influences mood regulation through emotional resonance, stress reduction, and the ability to evoke specific feelings. Focusing on the therapeutic effects of music, this thesis examines how music selection and listening habits impact emotional well-being, stress management, and mood enhancement.
- The Role of Literature in Environmental Awareness Literature raises environmental awareness by highlighting ecological issues, inspiring stewardship, and promoting sustainable values. Addressing the environmental impact of literature, this thesis explores how literary works contribute to environmental consciousness, advocacy for sustainable practices, and the dissemination of ecological knowledge.
- Effects of Online Communication on Language Evolution Online communication affects language evolution through text abbreviations, emojis, and the emergence of digital linguistic norms. Exploring the linguistic impact of digital communication, this thesis assesses how online platforms influence language evolution, leading to the emergence of new linguistic norms, abbreviations, and visual symbols.
- Media’s Influence on Political Participation Media shapes political participation by influencing voter engagement, political awareness, and mobilization efforts. Focusing on media’s role in democracy, this thesis analyzes how media platforms impact political engagement, disseminate information, and influence citizens’ participation in political processes.
- The Impact of Technology on Creative Expression Technology transforms creative expression through digital tools, online platforms, and innovative art forms. This thesis examines how technology empowers artists to explore new mediums, collaborate globally, and redefine creative boundaries in the digital age.
- The Role of Literature in Historical Preservation Literature preserves history by documenting cultural narratives, recording lived experiences, and offering insights into past societies. Addressing literature’s historical significance, this thesis explores how literary works serve as windows into past eras, preserving cultural memories and societal contexts.
- Effects of Video Game Violence on Aggression Video game violence influences aggression through desensitization, aggressive thoughts, and altered social behaviors. Investigating the psychological impact of gaming, this thesis analyzes how exposure to violent video games affects aggression levels, cognitive responses, and social interactions
- The Impact of Technology on Family Communication Technology alters family communication through digital devices, social media, and virtual interactions. Focusing on family dynamics, this thesis explores how technology affects communication patterns, family bonding, and the challenges of maintaining meaningful connections in the digital era.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Polarization Social media exacerbates political polarization through filter bubbles, echo chambers, and the reinforcement of ideological beliefs. Analyzing the relationship between social media and politics, this thesis investigates how online platforms contribute to the polarization of public opinion by reinforcing preexisting beliefs and narrowing exposure to diverse perspectives.
- The Role of Literature in Identity Formation Literature contributes to identity formation by reflecting cultural heritage, exploring self-discovery, and examining personal narratives. Addressing the intersection of literature and identity, this thesis explores how literary works contribute to the formation of individual and cultural identities, fostering self-awareness and cultural understanding.
- Effects of Technology on Human Relationships Technology impacts human relationships by altering social interactions, intimacy dynamics, and the balance between virtual and real-world connections. Investigating the influence of digital devices on interpersonal connections, this thesis examines how technology shapes the nature of relationships, emotional intimacy, and face-to-face interactions.
- Media’s Influence on Fear and Perception Media shapes fear and perception through sensationalism, framing, and the selective presentation of information. Focusing on media’s psychological impact, this thesis analyzes how media content affects public perceptions, triggers fear responses, and influences the framing of news events.
- The Impact of Technology on Privacy Technology challenges privacy through data collection, surveillance, and the blurring of online and offline boundaries. Addressing privacy concerns in the digital age, this thesis explores how technology threatens personal privacy by enabling data collection, surveillance practices, and the erosion of traditional boundaries between public and private spaces.
- Effects of Social Media on Body Image Social media influences body image through comparison, unrealistic beauty ideals, and promoting appearance-focused self-worth. Examining the psychological effects of digital media, this thesis assesses how social media platforms impact body image perceptions, self-esteem, and psychological well-being.
- The Role of Literature in Challenging Authority Literature challenges authority by critiquing power structures, questioning norms, and advocating for social change. Focusing on literature’s subversive potential, this thesis explores how literary works engage with themes of power, resistance, and social critique, challenging established authority and advocating for reform.
- Effects of Technology on Mental Health Technology influences mental health through screen addiction, social isolation, and the pressure to maintain an ideal online image. Investigating the relationship between technology usage and psychological well-being, this thesis analyzes how digital devices impact mental health, contributing to issues such as addiction, isolation, and negative self-comparisons.
- Media’s Role in Promoting Health Behaviors Media influences health behaviors by disseminating health information, promoting positive habits, and shaping public health narratives. Addressing media’s impact on public health, this thesis explores how media platforms contribute to health awareness, behavioral change, and the dissemination of health-related information.
- The Impact of Technology on Education Equity Technology impacts education equity by addressing access barriers, facilitating personalized learning, and promoting digital literacy. Focusing on technology’s educational implications, this thesis examines how digital tools can both bridge and exacerbate educational disparities, fostering access, inclusivity, and skills development.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Activism Social media amplifies political activism through digital mobilization, online advocacy, and the spread of social causes. Analyzing the role of technology in political engagement, this thesis assesses how social media platforms empower individuals and groups to mobilize for political change, share advocacy messages, and influence social issues.
- The Role of Literature in Promoting Empathy Literature fosters empathy by immersing readers in diverse experiences, building emotional connections, and enhancing understanding. Investigating literature’s capacity to cultivate compassion, this thesis explores how narrative empathy promotes understanding, encourages readers to embrace diverse perspectives, and fosters emotional resonance.
- Effects of Technology on Attention Span Technology impacts attention span through constant stimuli, information overload, and the allure of multitasking. Addressing technology’s cognitive effects, this thesis examines how digital devices influence attentional capabilities, cognitive focus, and the challenges of sustained concentration in a digitalized world.
- Media’s Influence on Political Disinformation Media platforms contribute to political disinformation through the spread of false information, echo chambers, and the manipulation of public opinion. Examining media’s role in disseminating misinformation, this thesis investigates how fake news, echo chambers, and algorithmic biases impact the accuracy of public discourse and democratic decision-making.
- The Impact of Technology on Creativity Technology enhances creativity through digital tools, collaborative platforms, and the democratization of creative expression. Focusing on the relationship between technology and creative processes, this thesis explores how digital innovations empower individuals to explore new artistic mediums, collaborate across boundaries, and engage in creative experimentation.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Engagement Social media influences political engagement through information dissemination, fostering online communities, and encouraging civic participation. This thesis investigates how social media platforms amplify political involvement by facilitating information-sharing, building virtual communities, and motivating individuals to engage in civic activities.
- The Role of Literature in Teaching Moral Lessons Literature imparts moral lessons by portraying ethical dilemmas, consequences of actions, and encouraging ethical reflection. Exploring literature’s moral dimensions, this thesis examines how literary narratives serve as vehicles for discussing ethical challenges, prompting readers to contemplate consequences and engage in moral reasoning.
- Effects of Technology on Physical Health Technology impacts physical health through sedentary behaviors, screen-related health issues, and disruptions to sleep patterns. Investigating the relationship between technology and physical well-being, this thesis analyzes how digital devices influence physical activity levels, posture, and overall health outcomes.
- Media’s Influence on Social Perception Media shapes social perception through portrayal, stereotypes, and influencing attitudes toward various societal groups. Analyzing media’s role in shaping public perceptions, this thesis assesses how media content constructs societal narratives, influences attitudes, and contributes to the formation of stereotypes
- The Impact of Technology on Privacy in Relationships Technology affects privacy in relationships through digital communication, surveillance concerns, and the blurring of boundaries. Focusing on the interplay of technology and personal relationships, this thesis explores how digital devices influence privacy dynamics, communication norms, and the challenges of maintaining boundaries.
- Effects of Social Media on Youth Empowerment Social media empowers youth through digital activism, amplification of voices, and the mobilization of social change. Investigating the role of social media in youth engagement, this thesis assesses how online platforms enable young individuals to advocate for causes, share perspectives, and shape societal narratives.
- The Role of Literature in Exploring Identity Literature explores identity by examining cultural heritage, personal experiences, and the journey of self-discovery. This thesis delves into how literature serves as a vehicle for individuals to explore their identities, offering insight into cultural backgrounds, personal struggles, and the quest for self-understanding.
- Effects of Technology on Memory and Cognitive Skills Technology impacts memory and cognitive skills through information overload, reliance on digital aids, and altered memory retention. Addressing technology’s cognitive effects, this thesis examines how digital devices influence memory processes, cognitive skills, and the capacity for deep learning and critical thinking.
- Media’s Influence on Political Trust Media shapes political trust through framing, information credibility, and influencing public perceptions of political figures. Analyzing media’s impact on political relationships, this thesis assesses how media coverage contributes to public trust or distrust in political institutions, leaders, and the information presented.
- The Impact of Technology on Language Evolution Technology influences language evolution through digital communication, new linguistic norms, and the emergence of online language varieties. Focusing on the linguistic impact of technology, this thesis explores how digital communication platforms contribute to the evolution of language, including the development of new forms and conventions.
- Effects of Social Media on Youth Mental Health Social media affects youth mental health through cyberbullying, the pressure to conform, and the impact of online peer comparisons. Investigating mental health challenges among young individuals, this thesis analyzes how social media contributes to anxiety, depression, and self-esteem issues among adolescents.
- The Role of Literature in Promoting Social Justice Literature advocates for social justice by depicting injustice, amplifying marginalized voices, and inspiring collective action. Addressing literature’s role in advocating for equality, this thesis explores how literary narratives illuminate social injustices, empower marginalized communities, and prompt readers to engage in activism.
- Effects of Technology on Human Productivity Technology influences human productivity through automation, digital distractions, and the challenges of multitasking. Examining the interplay of technology and productivity, this thesis assesses how digital devices both enhance and hinder efficiency, time management, and task completion.
- Media’s Influence on Cultural Appropriation Media shapes cultural appropriation through portrayal, perpetuating stereotypes, and commodifying cultural elements. Focusing on media’s impact on cultural understanding, this thesis analyzes how media content contributes to cultural appropriation by presenting distorted portrayals and commodifying cultural practices.
- The Impact of Technology on Parenting Styles Technology influences parenting styles through digital device usage, screen time management, and the challenge of balancing virtual and real-world interactions. Investigating the intersection of technology and parenting, this thesis explores how digital devices shape parenting approaches, influence family dynamics, and affect children’s development.
- Effects of Social Media on Political Information Seeking Social media influences political information seeking through personalized news feeds, echo chambers, and filter bubbles. This thesis examines how social media platforms impact the way individuals access, interpret, and seek out political information, contributing to the customization and potential polarization of news consumption.
- The Role of Literature in Addressing Mental Health Stigma Literature challenges mental health stigma by portraying mental health experiences, fostering empathy, and promoting open conversations. Focusing on the intersection of literature and mental health, this thesis explores how literary narratives contribute to destigmatizing mental health challenges by portraying characters’ struggles, emotions, and journeys to recovery.
- Effects of Technology on Social Interaction Technology influences social interaction through digital communication, altered face-to-face interactions, and the challenges of maintaining personal connections. Analyzing technology’s impact on human relationships, this thesis assesses how digital devices shape the ways individuals connect, communicate, and experience social interactions.
- Media’s Influence on Political Spin and Manipulation Media platforms contribute to political spin through biased reporting, framing, and the manipulation of public perception. Investigating media’s role in political communication, this thesis analyzes how media outlets shape public opinion by framing news narratives, promoting specific agendas, and influencing political discourse.
- The Impact of Technology on Learning Styles Technology transforms learning styles through personalized education, online resources, and the shift toward digital learning environments. Focusing on educational advancements, this thesis explores how technology accommodates diverse learning styles, fosters individualized instruction, and alters the way students engage with educational content.
- Effects of Social Media on Civic Engagement Social media influences civic engagement through digital activism, online petitions, and the mobilization of collective action. This thesis examines how social media platforms empower individuals to engage in civic activities, advocate for social change, and participate in online campaigns.
- The Role of Literature in Navigating Grief and Loss Literature provides solace in grief and loss by depicting the complexities of mourning, offering catharsis, and promoting emotional healing. Addressing literature’s role in emotional support, this thesis explores how literary narratives provide readers with ways to navigate the emotional challenges of grief, loss, and mourning.
- Effects of Technology on Environmental Awareness Technology impacts environmental awareness through online campaigns, virtual experiences, and the dissemination of environmental information. Investigating technology’s ecological impact, this thesis analyzes how digital platforms raise awareness about environmental issues, connect individuals with nature, and inspire pro-environmental behaviors.
- Media’s Influence on Public Perception of Climate Change Media shapes public perception of climate change through framing, information presentation, and the portrayal of scientific consensus. Focusing on the media’s role in environmental discourse, this thesis assesses how media coverage impacts public understanding of climate change, influencing attitudes, policy discussions, and societal responses.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for Argumentative Essay
- Gun Control Stricter gun control laws can reduce firearm-related violence by limiting access, implementing background checks, and regulating firearm sales. In an argumentative essay, explore the effectiveness of stricter gun control measures in curbing gun violence through access restrictions, background checks, and sales regulations.
- Climate Change Human activities are the primary drivers of climate change evidenced by rising temperatures, shrinking ice caps, and increasing carbon emissions. In this essay, argue that human actions are responsible for climate change, citing evidence like temperature increases, melting ice, and escalating carbon emissions.
- Education Reform Education reform requires revising curricula, enhancing teacher training, and implementing student-centered learning approaches to improve learning outcomes. Addressing education reform, argue that curricular updates, teacher preparation, and student-centered teaching methods are pivotal for enhancing academic achievements.
- Capital Punishment Capital punishment should be abolished due to the risk of wrongful execution, moral concerns, and lack of proven deterrence effect. In an argumentative context, advocate for the abolition of the death penalty by discussing the potential for wrongful executions, moral dilemmas, and the lack of conclusive evidence of deterrence.
- Online Privacy Stricter regulations, user education, and enhanced data encryption are necessary to safeguard online privacy in the digital age. Argue for improved online privacy by discussing the need for stringent regulations, educating users about digital risks, and implementing robust data encryption.
- Animal Testing Animal testing should be replaced with alternative methods such as in vitro testing, computer simulations, and human cell studies to ensure ethical research. Take a stance against animal testing by arguing for the adoption of humane alternatives, including in vitro experiments, computer models, and human cell research.
- School Uniforms School uniforms foster a sense of belonging, minimize socio-economic disparities, and create a focused learning environment conducive to academic success. Present a case for school uniforms, highlighting their benefits in promoting inclusivity, reducing inequality, and cultivating a focused educational environment.
- Social Media Addiction Social media addiction requires intervention through awareness campaigns, setting digital boundaries, and promoting face-to-face interactions. Argue against the harmful effects of social media addiction, advocating for strategies like awareness initiatives, self-regulation, and prioritizing offline connections.
- Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering raises ethical concerns due to potential ecological disruption, unforeseen health risks, and the alteration of natural genetic diversity. Present an argument against genetic engineering by discussing ecological impacts, health uncertainties, and potential consequences for biodiversity.
- Universal Healthcare The adoption of universal healthcare improves public health outcomes by providing equitable access to medical services, reducing financial burdens, and promoting preventive care. Advocate for universal healthcare by discussing its potential to ensure healthcare equity, alleviate financial strain, and prioritize preventative measures.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for an Essay
- Happiness Happiness is attainable through positive relationships, meaningful pursuits, and a balanced approach to life’s challenges. In this essay, explore the avenues to achieve happiness through fostering connections, pursuing fulfilling goals, and embracing life’s complexities.
- Travel Travel enriches personal growth by broadening cultural perspectives, encouraging adaptability, and promoting experiential learning. Discuss the benefits of travel, emphasizing its role in expanding cultural horizons, developing adaptability, and facilitating hands-on education.
- Leadership Effective leadership encompasses clear communication, empathetic understanding, and the ability to inspire and motivate others. Delve into the qualities of a successful leader, focusing on communication skills, empathy, and the capacity to inspire and lead by example.
- Dreams Pursuing dreams requires determination, overcoming obstacles, and embracing failure as a stepping stone towards eventual success. Explore the journey toward realizing dreams, emphasizing the importance of resilience, facing challenges, and learning from setbacks.
- Time Management Efficient time management involves setting priorities, utilizing effective strategies, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Discuss the significance of managing time wisely, covering aspects like prioritization, productivity techniques, and maintaining personal well-being.
- Healthy Eating Maintaining a healthy diet necessitates balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep to promote overall well-being and academic success. In this essay, advocate for healthy eating habits by discussing the importance of nutritional balance, exercise, and sufficient sleep in supporting academic performance.
- Creativity Nurturing creativity involves embracing curiosity, seeking inspiration from various sources, and welcoming experimentation without fear of failure. Examine the facets of creativity, emphasizing curiosity-driven exploration, diverse sources of inspiration, and the courage to experiment.
- Friendship Meaningful friendships are built on trust, mutual support, and shared experiences, contributing to emotional fulfillment and personal growth. Explore the essence of friendship, discussing the core elements of trust, mutual assistance, and the impact of shared moments.
- Resilience Resilience emerges from facing adversity, developing coping strategies, and maintaining a positive outlook during challenging times. Highlight the concept of resilience, showcasing how it evolves through confronting hardships, developing coping mechanisms, and nurturing optimism.
- Nature Conservation Nature conservation demands sustainable practices, community involvement, and legislative support to preserve biodiversity and ecological balance. Discuss the importance of protecting the environment, emphasizing sustainable behaviors, community engagement, and legal measures to maintain biodiversity.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples in Middle School
- Bullying Bullying prevention requires awareness campaigns, fostering empathy, and promoting open communication to create a safe and inclusive school environment. In middle school, discuss strategies to combat bullying by raising awareness, cultivating empathy, and encouraging open dialogue among students.
- Internet Safety Internet safety education involves responsible online behavior, recognizing digital risks, and safeguarding personal information to ensure a secure online experience. Address the importance of internet safety for middle school students, focusing on responsible online conduct, cyber awareness, and protecting personal data.
- Healthy Lifestyle Adopting a healthy lifestyle entails balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep to promote overall well-being and academic success. Discuss the significance of healthy habits for middle schoolers, emphasizing the role of balanced nutrition, exercise, and sufficient sleep in supporting academic performance.
- Peer Pressure Navigating peer pressure requires assertiveness, making informed choices, and seeking positive influences to maintain personal values and self-confidence. Address the challenges of peer pressure among middle school students, advocating for strategies like assertiveness training, informed decision-making, and seeking supportive friendships.
- Environmental Awareness Fostering environmental awareness involves learning about ecosystems, practicing eco-friendly habits, and participating in conservation efforts to protect the planet. Explore the importance of environmental education for middle schoolers, encouraging them to learn about ecosystems, adopt eco-conscious behaviors, and engage in conservation projects.
- Friendship Dynamics Nurturing positive friendships involves empathy, effective communication, and resolving conflicts to foster healthy and supportive relationships. Address the complexities of middle school friendships, emphasizing empathy, communication skills, and conflict resolution techniques for building strong connections.
- Time Management Developing time management skills encompasses setting priorities, using organizational tools, and establishing routines to balance academics and leisure activities. Discuss the relevance of time management for middle school students, introducing strategies like prioritization, organization, and establishing effective routines.
- Goal Setting Goal setting involves defining aspirations, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and persevering in the face of challenges to achieve personal ambitions. Explore the concept of goal setting among middle schoolers, encouraging them to define aspirations, create actionable plans, and cultivate resilience.
- Cultural Diversity Embracing cultural diversity involves understanding different perspectives, promoting inclusion, and celebrating various traditions to create a harmonious school community. Address cultural diversity in middle school, advocating for cultural understanding, inclusivity, and the importance of respecting diverse backgrounds.
- Cyberbullying Combating cyberbullying requires reporting incidents, practicing digital citizenship, and creating a culture of kindness to ensure online safety and well-being. Discuss the implications of cyberbullying for middle schoolers, emphasizing the importance of reporting, practicing responsible online behavior, and fostering a positive digital environment.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples in Literature
- The Great Gatsby “The Great Gatsby” portrays the disillusionment of the American Dream through characters’ pursuit of wealth, the facade of social status, and the inability to attain lasting happiness. Discuss the themes of disillusionment and the American Dream in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel, exploring how characters’ materialistic pursuits and social aspirations lead to unfulfilled desires.
- To Kill a Mockingbird “To Kill a Mockingbird” highlights social injustice through the lens of racism, the loss of innocence, and the importance of empathy in understanding others’ perspectives. Analyze Harper Lee’s novel, focusing on its exploration of racial inequality, the loss of innocence, and the value of empathy in addressing societal prejudices.
- Romeo and Juliet “Romeo and Juliet” examines the consequences of impulsivity, the impact of familial feuds, and the significance of love transcending societal boundaries. Explore William Shakespeare’s tragedy, discussing the themes of impulsive actions, familial conflicts, and the enduring power of love that defies societal constraints.
- 1984 “1984” critiques totalitarianism by depicting government surveillance, manipulation of language, and the suppression of individuality as dystopian manifestations of power. Analyze George Orwell’s dystopian novel, focusing on its portrayal of authoritarian control, the manipulation of information, and the degradation of personal freedoms.
- Pride and Prejudice “Pride and Prejudice” explores societal norms, gender expectations, and the complexities of love and self-discovery as characters navigate social hierarchies. Examine Jane Austen’s classic work, delving into its examination of social class, gender roles, and the transformative power of genuine affection in overcoming biases.
- The Catcher in the Rye “The Catcher in the Rye” presents the alienation of youth, the search for authenticity, and the complexities of growing up as Holden Caulfield navigates the challenges of adolescence. Discuss J.D. Salinger’s novel, focusing on the protagonist’s feelings of alienation, his quest for authenticity, and the portrayal of teenage angst and identity formation.
- The Lord of the Rings “The Lord of the Rings” explores the battle between good and evil, the hero’s journey, and the significance of fellowship as characters embark on an epic quest to save Middle-earth. Analyze J.R.R. Tolkien’s epic fantasy, discussing its themes of morality, heroism, and the power of camaraderie as characters confront the forces of darkness.
- Frankenstein “Frankenstein” delves into the consequences of unchecked ambition, the ethical implications of scientific creation, and the alienation of the outsider as Victor Frankenstein grapples with his monstrous creation. Examine Mary Shelley’s novel, addressing themes of ambition, ethics, and societal rejection as Victor Frankenstein’s scientific endeavors lead to unintended consequences.
- The Scarlet Letter “The Scarlet Letter” explores the consequences of societal judgment, the complexities of sin and redemption, and the resilience of the human spirit as Hester Prynne navigates the aftermath of her actions. Analyze Nathaniel Hawthorne’s work, discussing its examination of guilt, societal norms, and the capacity for personal growth in the face of adversity.
- Brave New World “Brave New World” critiques a dystopian future by depicting a society driven by consumerism, the suppression of individuality, and the manipulation of happiness as the ultimate goal. Explore Aldous Huxley’s dystopian vision, discussing its commentary on technological control, the pursuit of pleasure, and the loss of authentic human experience.
3 Point Thesis Statement Examples for Graphic Organizers
- Solar System Understanding the solar system involves recognizing the sun as the center, identifying planets and their characteristics, and comprehending the roles of asteroids, comets, and moons. Discuss the solar system using a graphic organizer, highlighting its key components including the sun, planets, asteroids, comets, and moons, along with their distinctive features.
- Ecosystems Exploring ecosystems involves categorizing biomes, understanding food chains and webs, and recognizing the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance. Utilize a graphic organizer to depict various biomes within ecosystems, illustrate food chains and webs, and emphasize the significance of biodiversity for ecological stability.
- Literary Elements Analyzing literature entails identifying plot elements, character traits, and thematic concepts to gain a comprehensive understanding of narrative structure and meaning. Create a graphic organizer to analyze literary works, mapping out key elements such as plot, characters, and themes to enhance comprehension of narrative elements.
- Historical Events Studying historical events requires sequencing chronological occurrences, contextualizing historical contexts, and identifying influential figures and their contributions. Construct a graphic organizer to explore historical events, arranging them chronologically, providing contextual information, and highlighting notable individuals and their impacts.
- Plant Life Cycle Exploring the plant life cycle involves identifying stages from seed germination to reproduction, understanding the roles of roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, and grasping the significance of pollination. Employ a graphic organizer to depict the plant life cycle, depicting stages from seed germination to pollination and reproduction, while illustrating the roles of different plant parts.
- Literary Genres Understanding literary genres requires categorizing fiction, non-fiction, poetry, drama, and identifying distinguishing characteristics that define each genre’s narrative style. Use a graphic organizer to differentiate literary genres, classifying fiction, non-fiction, poetry, and drama while highlighting the unique features that define each genre.
- Elements of a Story Analyzing the elements of a story involves identifying the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution to gain insight into narrative structure and development. Create a graphic organizer to explore the elements of a story, mapping out the key stages from exposition to resolution, enhancing comprehension of narrative progression.
- Food Groups Understanding dietary balance entails categorizing food groups such as fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy, and recognizing their nutritional contributions to overall health. Utilize a graphic organizer to depict food groups, categorizing fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy while emphasizing their roles in providing essential nutrients.
- Biographical Information Exploring biographies involves organizing key details like birth, achievements, contributions, and impact to gain insights into notable individuals’ lives and legacies. Construct a graphic organizer to analyze biographical information, arranging details such as birth, accomplishments, significant contributions, and lasting impact on society.
- Cause and Effect Relationships Understanding cause and effect relationships entails identifying triggers and outcomes, recognizing the interconnectedness of events, and comprehending the implications of actions. Design a graphic organizer to explore cause and effect relationships, mapping out causal factors and corresponding effects to illustrate the interconnected nature of events.
Free 3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheets Download
Download our free 3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheets to enhance your writing skills. These comprehensive resources provide structured guidance on crafting impactful thesis statements for various topics. Through step-by-step exercises, you’ll learn to formulate clear arguments with three supporting points, fostering effective communication and analytical thinking. Elevate your essay writing by mastering the art of concise and persuasive thesis statements with our downloadable worksheets.
3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheet

Size: 360 KB
3 Point Thesis Statement Worksheet Sample

Size: 160 KB
Three Point Thesis Statement Worksheet Download

Size: 170 KB
How to Write a 3 Point Thesis Statement? – Step by Step Guide
Crafting a compelling 3 Point Thesis Statement involves careful planning and a structured approach. Follow this step-by-step guide to create a clear and impactful thesis that effectively outlines your main argument and supporting points:
- Choose Your Topic: Select a specific topic that you want to address in your essay. Ensure it’s focused enough to be thoroughly explored within the scope of your work.
- Identify Your Main Argument: Determine the central point or argument you want to make about the chosen topic. This main idea will serve as the foundation for your thesis statement.
- Brainstorm Supporting Points: Identify three key points that support and reinforce your main argument. These points will guide your essay’s structure and content.
- Craft Your Thesis Statement: Combine your main argument and the three supporting points into a single, concise sentence. Ensure it clearly conveys the overall message of your essay.
- Order and Coherence: Arrange your supporting points logically. Typically, present them in the order you’ll address them in your essay, from strongest to weakest or chronologically.
- Avoid Ambiguity: Make sure your thesis statement is specific and unambiguous. Avoid vague language that might confuse or mislead readers.
- Precision and Clarity: Use clear and precise language in your thesis statement. Each word should contribute to the overall clarity and accuracy of your message.
- Revise for Consistency: Check that your thesis statement aligns with the content of your essay. Any deviations should be addressed to maintain coherence.
- Seek Feedback: Share your thesis statement with peers or mentors for feedback. Their insights can help you refine and strengthen your argument.
- Refine and Edit: Revise your thesis statement based on the feedback you receive. Edit for grammar, style, and conciseness.
- Finalize Your Thesis Statement: Once satisfied, incorporate your refined thesis statement into your essay’s introduction, ensuring it provides a roadmap for readers.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can create a powerful 3 Point Thesis Statement that effectively communicates your main argument and supporting points, setting the tone for a well-structured and persuasive essay.
Tips for Writing a 3 Point Thesis Statment
- Clarity is Key: Keep your thesis statement clear and straightforward, avoiding vague or convoluted language.
- Singular Focus: Center your thesis around a single, focused argument to maintain a clear message.
- Strong Supporting Points: Select three robust supporting points that directly bolster your main argument.
- Parallel Structure: Use consistent grammatical structure for your supporting points to enhance organization.
- Logical Order: Arrange supporting points logically, from strongest to weakest or in a coherent sequence.
- Specific Examples: Back up your points with concrete evidence, avoiding general statements.
- Avoid First-Person: Keep your thesis objective by refraining from using first-person pronouns.
- Highlight Importance: Explain the significance or broader implications of your main argument and points.
- Feedback Matters: Seek input from others to refine and strengthen your thesis statement.
- Connect and Transition: Ensure your thesis smoothly leads into the content of your essay’s body.
Mastering the art of crafting impactful 3 Point Thesis Statements elevates your writing prowess. With a clear main argument and well-chosen supporting points, your essays gain depth and structure. Following expert tips ensures clarity, conciseness, and logical organization. This skill empowers you to communicate effectively, fostering a deeper connection with readers and enhancing the overall impact of your work.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved July 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

File(s) under embargo
until file(s) become available
Using Chemical Genetics to Dissect Exocytosis in Arabidopsis
Exocytosis is crucial for delivering proteins, lipids, and cell wall polysaccharides to the plasma membrane and extracellular spaces, playing a vital role in normal plant development as well as responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. One key molecular player, the exocyst, is an octameric protein complex that tethers secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane (PM). Chapter 1 is a literature survey that introduces the function of the exocyst, as well as the characterization of Endosidin2 (ES2), a synthetic molecule that targets the EXO70 subunit of exocyst. This chapter also defines existing knowledge gaps in the profiling of cargo proteins trafficked by the exocyst and the identification of novel modulators of exocytosis. Chapter 2 employs a comparative proteomics approach to examine the changes of PM proteome of root cells following ES2-treatment. Proteins with decreased abundance at the PM were considered candidate cargo proteins of ES2-targeted trafficking and several were validated with quantitative live-cell imaging. Chapter 3 describes the use of ES2 as a tunable and reversible chemical genetics tool as demonstrated by the development and deployment of a large-scale mutant screen in Arabidopsis that identified 70 ES2 -hyper s ensitive mutants ( es2s ). Among these, candidate mutations for 14 non-allelic lines were mapped and reported. T-DNA insertion lines were subsequently screened as alternative alleles to identify causal mutations. In Chapter 4, the causal mutation of es2s-15-12 was confirmed as ArgJ with a second T-DNA insertion mutant allele as well as genetic and chemical complementation. ArgJ encodes an enzyme in the arginine biosynthesis pathway. It was demonstrated that arginine biosynthesis deficiency synergizes with ES2 to inhibit root growth in Arabidopsis. Root growth in argj mutants was not hypersensitive to other inhibitors with different modes of action, such as LatB, ES9-17, and BFA. Additionally, roots of argj-1 displayed a reduced abundance of PIN2 at the apical PM in epidermal cells; however, PIN2 polar distribution was not further reduced by ES2 treatment. Our findings point to a functional connection between arginine metabolism and exocytosis. Chapter 5 discusses potential future directions and experiments, including technological advances and the testing of new hypotheses. Overall, this study presents a detailed application of chemical genetics to dissect the exocytosis process in Arabidopsis and uncovers novel modulators of exocytosis in plants.
Degree Type
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Botany and Plant Pathology
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, usage metrics.
- Plant cell and molecular biology

- Business & Technology
FortiGuard Labs Threat Research
- Industry Trends
- Customer Stories
- PSIRT Blogs
- CISO Collective
The Growing Threat of Malware Concealed Behind Cloud Services
Affected Platforms: Linux Distributions Impacted Users: Any organization Impact: Remote attackers gain control of the vulnerable systems Severity Level: High
Cybersecurity threats are increasingly leveraging cloud services to store, distribute, and establish command and control (C2) servers, such as VCRUMS stored on AWS or SYK Crypter distributed via DriveHQ. This shift in strategy presents significant challenges for detection and prevention, as cloud services provide scalability, anonymity, and resilience that traditional hosting methods lack.
Over the past month, FortiGuard Labs has been monitoring botnets that have adopted this strategy, abusing cloud services to enhance their malicious capabilities. These botnets, such as UNSTABLE and Condi, have been observed leveraging cloud storage and computing services operators to distribute malware payloads and updates to a broad range of devices. Using cloud servers for C2 operations ensures persistent communication with compromised devices, making it harder for defenders to disrupt an attack. We have also observed a threat actor exploiting multiple vulnerabilities to target JAWS webservers, Dasan GPON home routers, Huawei HG532 routers, TP-Link Archer AX21, and Ivanti Connect Secure to amplify their attacks.

In this article, we will detail this threat actor's initial attack method and further explore the botnets being used.
UNSTABLE Botnet
Initial access by the UNSTABLE Botnet targets the JAWS Webserver RCE vulnerability, CVE-2016-20016, and retrieves the downloader script “jaws” from 45[.]128[.]232[.]15.

It includes multiple binary files for 13 architectures executed using the parameter “jaws.exploit.” The UNSTABLE Botnet is a Mirai variant that uses XOR to encode its configuration. It has three main modules: exploitation, scanner, and DDoS attack. The exploitation module targets three vulnerabilities: CVE-2016-20016, CVE-2018-10561/10562, and CVE-2017-17215.

The scanner module includes a hard-coded list of usernames and passwords that it uses for brute-force scanning of other endpoints in the network.

root | Zte521 | swsbzkgn |
taZz@23495859 | grouter | juantech |
tsgoingon | telnet | pass |
solokey | oelinux123 | password |
admin | tl789 | svgodie |
default | GM8182 | t0talc0ntr0l4! |
user | hunt5759 | zhongxing |
guest | telecomadmin | zlxx. |
telnetadmin | twe8ehome | zsun1188 |
1111 | h3c | xmhdipc |
12345 | nmgx_wapia | klv123 |
123456 | private | hi3518 |
54321 | abc123 | 7ujMko0vizxv |
88888888 | ROOT500 | 7ujMko0admin |
20080826 | ahetzip8 | dreambox |
666666 | anko | system |
888888 | ascend | iwkb |
1001chin | blender | realtek |
xc3511 | cat1029 | 00000000 |
vizxv | changeme | 12341234 |
5up | iDirect | huigu309 |
jvbzd | nflection | win1dows |
hg2x0 | ipcam_rt5350 | antslq |
Figure 5: Scanner module and hard-coded username/password
The DDoS attack module is a typical list that covers several protocols. The UNSTABLE botnet contains nine methods: attack_tcp_ack, attack_tcp_syn, attack_tcp_legit, attack_tcp_sack2, attack_udp_plain, attack_udp_vse, attack_udp_thread, attack_gre_ip, and attack_method_nudp. The botnets can choose the appropriate method based on commands from its C2 server.
Condi DDoS Botnet
FortiGuard Labs previously disclosed the Condi DDoS botnet, which continues to exploit CVE-2023-1389 to gain control of devices and execute its malicious activities. The binary file is hosted on “45[.]128[.]232[.]90” for distribution.
![point process thesis the Condi DDoS botnet hosts the binary file on 45[.]128[.]232[.]90](https://www.fortinet.com/blog/threat-research/growing-threat-of-malware-concealed-behind-cloud-services/_jcr_content/root/responsivegrid/table_content/par/image_1297912618_cop_1557389227.img.png/1719268827096/cloud-6-1.png)
Once a device is infected, the malware kills off the competition and specific processes. It then sets up a connection to a central Command and Control (C2) server, “trembolone[.]zapto[.]org.”

UDP Flooder and Process Checker
FortiGuard Labs noticed the incident as the payload “ping -c 20 209.141.35.56,” which seemed unusual within such an attack. Since the IP address is neither the attack source nor the destination intranet, we suppose these two IP addresses, 45[.]128[.]232[.]229 and 209[.]141[.]35[.]56, might be controlled by the attacker simultaneously and one of them is a command and control (C2) server.

The attack source IP address, “45[.]128[.]232[.]229,” has four files named “msgbox.exe,” “udp,” “udparm,” and “udpmips,” respectively. These are DoS tools for different Linux architectures, except “msgbox.exe,” which pops up a message box with the string “RAT.”
The following analysis examines the “udp” file.
The tool has an unmistakable usage message, “Usage: %s <IP> <SECONDS> [PORT],” while executing without any arguments.

When executing with the necessary “IP” and “SECONDS” arguments, the tool triggers a UDP flooding DoS attack using system-generated random characters.

The IP address “209[.]141[.]35[.]56” pinged by the compromised device is exploited by the attack source IP address “45[.]128[.]232[.]229” using the CVE-2023-1389 vulnerability. It was first met with a page that the FBI has seized due to its use as a DDoS service (Figure 12). However, FortiGuard Labs found the IP address also has another route, “hxxp://209[.]141[.]35[.]56/getters/,” which contains 19 malware variants for different Linux architectures. (see Figure 13)

aarch64 | microblazebe |
aarch64be | microblazeel |
arcle-750d | mips |
arcle-hs38 | mipsel |
armv4l | nios2 |
armv5l | openrisc |
armv6l | powerpc |
armv7l | riscv64 |
i586 | sh4 |
m68k | sparc |
m68k-68xxx | x86_64-core-i7 |
m68k-coldfire | x86-core2 |
m68k-coldfire.gdb | x86-i686 |
xtensa-lx60 |
|
Figure 13: The malware for different Linux architectures
We focus on analyzing the file for architecture “x86-i686.” The malware creates a socket and checks whether the C2 server is valid. If not, it terminates the program. If the server is confirmed reachable, the malware sets up a connection with C2 server “45[.]128[.]232[.]229,” which is the exploit CVE-2023-1389 source IP address, executes the “ps” command, and gathers process-related output information.

The malware executes the command “ps -eo pid,comm --no-headers” through “/bin/bash” to get all process PIDs (Process IDs) and command names running without a header line.

It then leverages the obtained PIDs (Process IDs) to further check the commands of those executing processes using “/proc/<PID>/comm.”

Afterward, the malware sends related information to the C2 server.

According to our analysis, the attackers seem to have a cloud command and control (C2) server (45[.]128[.]232[.]229) and a network-attached malware storage (209[.]141[.]35[.]56). The attacker first checks to see if the leveraged device can reach the network-attached malware storage to download malware and execute the following attack stages.
This malware, which we named “Skibidi,” was spread by the attacker using two different vulnerabilities simultaneously. One is CVE-2023-1389 in TP-Link Archer AX21, which botnets have continuously exploited since it was launched, as detailed in the report produced by FortiGuard Lab. The other is CVE-2024-21887 in Ivanti Connect Secure, which caused a sensation in April 2024.

Attackers first download the “Skibidi” malware with a downloader script. It downloads and executes each malware to determine the proper Linux architecture attack.

arm4 | mips |
arm5 | mipsel |
arm6 | ppc |
arm7 | sh4 |
x86_64 |
|
Figure 21: The malware targets Linux architectures
The following analysis is based on the malware “skibidi.x86_64.” While executing the malware, it displays the string “youre not skibidi enough.”

It then calls the Linux function “ptrace” to handle the process on the victim host. The malware sends signals like a debugger to the sub-program, the malware itself, to fork another process to evade detection.

The malware then decodes strings encoded by XOR for the behaviors creating process and popping up execution result string.

It calls the system function “prctl,” which manipulates the calling process by naming it with the XOR-encoded strings “-bash” and “x86_64.”

Afterward, the malware tries to connect with its C2 server through a socket. Meanwhile, it uses the system call “select” to listen to the events of files the attacker is interested in, such as process events.

The malware repeats these steps of listening to events and sends the results back to the server.
Cloud services' inherent flexibility and efficiency have unwittingly provided cybercriminals with a new arena for their activities. This shift to cloud-based operations marks a significant evolution in the threat landscape, with malware operators exploiting these platforms' advantages. Organizations must bolster their cloud security defenses as botnets and DDoS tools continue to leverage cloud services. Robust security measures and vigilant monitoring within cloud environments are imperative to combat these sophisticated attacks. Implementing a multi-layered security approach, including regular patching, updates, and network segmentation, is essential to isolate critical assets and mitigate potential breaches.
Fortinet Protections
The malware described in this report is detected and blocked by FortiGuard Antivirus as:
BASH/Mirai.AEH!tr.dldr
ELF/Gafgyt.ST!tr
ELF/Mirai.CDB!tr
ELF/Mirai.CEA!tr
ELF/Mirai.CPD!tr
ELF/Mirai.OX!tr
ELF/Skibidi.CQC!tr
ELF/UDPFlooder.1C8B!tr
ELF/UDPFlooder.1EE7!tr
ELF/UDPFlooder.E063!tr
Linux/Mirai.CPD!tr
Linux/Mirai.REAL!tr
FortiGate, FortiMail, FortiClient, and FortiEDR support the FortiGuard AntiVirus service. The FortiGuard AntiVirus engine is part of each of these solutions. As a result, customers who have these products with up-to-date protections are protected.
The FortiGuard Web Filtering Service blocks the C2 servers and downloads URLs.
FortiGuard Labs provides IPS signatures against attacks exploiting the following vulnerability:
CVE-2016-20016: JAWS.DVR.CCTV.Shell.Unauthenticated.Command.Execution
CVE-2017-17215: Huawei.HG532.Remote.Code.Execution
CVE-2018-10561: Dasan.GPON.Remote.Code.Execution
CVE-2018-10562: Dasan.GPON.Remote.Code.Execution
CVE-2023-1389: TP-Link.Archer.AX21.Unauthenticated.Command.Injection
CVE-2024-21887: Ivanti.Connect.Secure.Policy.Secure.Authentication.Bypass
We also suggest that organizations go through Fortinet’s free NSE training module: NSE 1 – Information Security Awareness. This module is designed to help end users learn how to identify and protect themselves from phishing attacks.
FortiGuard IP Reputation and Anti-Botnet Security Service proactively block these attacks by aggregating malicious source IP data from the Fortinet distributed network of threat sensors, CERTs, MITRE, cooperative competitors, and other global sources that collaborate to provide up-to-date threat intelligence about hostile sources.
If you believe this or any other cybersecurity threat has impacted your organization, please contact our Global FortiGuard Incident Response Team.
45[.]128[.]232[.]15
45[.]128[.]232[.]90
45[.]128[.]232[.]229
45[.]128[.]232[.]234
hxxp://45[.]128[.]232[.]15
hxxp://45[.]128[.]232[.]90
hxxp://45[.]128[.]232[.]229
hxxp://209[.]141[.]35[.]56/getters
hxxp://45[.]128[.]232[.]234
d5e81e9575dcdbbaa038a5b9251531d8beccedc93bd7d250a4bb2389c1615cd6
6226e896850de8c5550b63481b138067582ebf361f7c5448d9d0596062150d89
4c2dcd13685f24800b73856d1f3ec9a2c53c2b5480a9c10b73035a43df26c2e8
31914b317ba6a44a9d3acb99979ec8c163bef8667b0ae41524e335847d70afb0
5fbfc4c8204309e911d22d3b544773f8d4f9ab2edc71f8967bbdcce6cbc834ca
53daa1e4c2f5c11a75989334c2a0227689509606aeda9d7ab11dd200ee6138c6
a9690df4542f28fc4e3b9161b9f8d685d4ce8753bfd9b1f5c8aacd6aa4bef873
fb86bb0863d15ac65a916979052220f755765eb0d5bc4c1c47e34762738d2311
cd05eaa2b01ec1a4880839628d1c6e3bed9045478cacbfb88f14d1937ccf667b
c88da56b348f8d89b5ab99a710de7131bdbc2f1dba4bb9809b1b3fd27322630e
83a2608a93b643f68ab3dcfccf8de7b13394cc214a78fa59b6867e47fc56928c
3660fbe90420f60664e68859de918a5c592dd33024f69bebff8bb77ab41b8fca
75b594a20110e487e35ec4590a5211a425119cdf0fea6fcf030ee20cb548b7e5
ef2e57a5992d85ea2bfb5c5645f8b361dcd5c49eede38185a7b99ec00c287550
2e69d9942a4c0d6d0294d038263f2d12f3a5f6aef8d72279b01e025d32addab2
1a8508f62447e5ee624866b571a29cedc369d6ee8182782f32a75dcd58494d8c
305e0eb9b815dddd40d73f4464946a0ec21866b7727e4fe073692bf82bb46936
0092b27bee2df9536e8aff8948a1007ed1eb03f0e12e0348b72a113e7d4cb585
65f2850892365a4d6bafc303ed04379bef3b41a85336e274f9348603105d2f37
c569eb7f33dcec3e6cdcfee7195202813fda6b7bf9ecb786a4a909d6745cbbff
5110f8af13cdd872b904784d2aec75031c663baad01d68b5f05daa950d18ced3
eec122d6480803bcdd2c6906b0ae35bcffaf6bf5117dac8c7b2621f0b98b68ea
9f14cdea1b41ac1c7251e3f2d4186e12d480d108942bc8f1f7bcac133ed88ccc
5a0a8de050cc8ad2f9af41e4018b0317afc39c571f23bc9cfa115c6558205722
eb9ba3171a98dc543cbc599eb6ab9aa3a5a47cc6931afe511fa839c6a5fb889c
1825c787c308d3cb1125d416025af8c8344a158f0a0b3467df6c0c875d2d8800
eb926f93bdd9b38d44d2239b4ec9c1d45762f850bee80cf9556b23372b6f0639
8fb6110b2114e7786b1d4e7f600a08de0a25432417f863d9663d576a3c895e86
dc87ff82199cb60a8bcf59d4f8c0a706bf10051d0c15a911d37d1cda8fcf5f9e
1816c473ba94f4740c0931e118d038ecb0733f8ffb7cbb74dedc7b78952f8318
d4dbd379f914ff5ba40c1aac1be37602e4cde687e47cfd7793cb10192617f4af
d034664f627af11bd2a34ba1b228b5a6841309caabfd72a731bbd4724d947e27
4cc2110f89afac1de0c1989d0af07f8879003cac0803660f37cf394a0027db69
bd42e67e6238dfec0b7786797733c54ae1d92fe0e883758dddea779e113b5271
e758c4428a590519a281344a31f236146c996c784433fbe82eee009dd922516c
3a3581da268d0fdb8c8027e261b682b07b6715c62fbf2c8aca301b7e8dd9d637
6e21e400928f24630339441f6da0f3f1b66860bf480a9f5af20482878b686189
8363ecc977d426f0e922abbeb4f1e8ed06397c0b6951dd75233016d3b5af58c9
e511f5c8fc0bd713dc9b9742e8c682ba66177bb617e9118f84b150cf6ff4a07f
ddcb420c4141760feed2fc8c76425b72ab111d271385040c1446f6ab3993c6d7
2b526e5ac01916d74e7aa88770102a8f34d4c57cea7a4e45c501331670635e26
666eed520d2b430e1016eec555c0cd125912f9a8f7590d77c286eff52416fbaf
ba4229f5e44c378ae293b58139233a9bfbecbfd22fb51e05f74de38b186a071c
c376db6e6f6905113e7beb1f14d8e5a44b8374a959eefd0f5d25ab0f3cbabee2
ae999de92c369e53a3287ab034f2839367b44f7fd82d6ed56a5700c22ed44635
e94b6b99fae4dc8e5b0796c877ed01bf25f77ccab95fb43d24abed00e0f8a15a
8fcb5c4c5306f3e7ffa2a47dedaddc108c77ef8ef48ec0980a0c441333e0a18b
34f653119e418621c1cbfe7cf0614ea62e9a98dc345e4d7408eea96a08d3ac0d
a51333460fb711e0b172b6e4893d5bca6b9996f240b450fdaa5cbf14511c9e27
90a43ca83efb2d460b86ff897b1bc657170b6c79c2c804610cdfca8f24adc71e
c5b6320925963ca6d5439dca7154c526c3a26500e204b48ff30a50c3a1b875ad
e7d87e68265a9a324d76759cca4f613c28c590b36490c8c65ee3d17918e5d3ec
2867b3fd3c840aa9c868a88a5f6d417a09e4158f8209f0450a07eeb7e99ba4c8
botnets , cloud service providers
Related Posts
I’ve got trickbot under my screen, a wicked family of bots, report: cybercriminals are building an army of things creating a tipping point for cybersecurity, news & articles.
- News Releases
- News Articles
Security Research
- Threat Research
- FortiGuard Labs
- Ransomware Prevention
Connect With Us
- Fortinet Community
- Partner Portal
- Investor Relations
- Product Certifications
- Industry Awards
- Social Responsibility
- CyberGlossary
- Blog Sitemap
- (866) 868-3678
Copyright © 2024 Fortinet, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Open access
- Published: 02 July 2024
Improving lung point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) training and accreditation - a multidisciplinary, multi-centre and multi-pronged approach to development and delivery using the action learning process
- Mark ZY Tan 1 , 2 ,
- Annemarie Brunswicker 3 ,
- Harry Bamber 4 ,
- Alistair Cranfield 5 ,
- Evangelos Boultoukas 6 &
- Sam Latif 7
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 713 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) consists of a range of increasingly important imaging modalities across a variety of specialties. Despite a variety of accreditation pathways available in the UK, lung POCUS training remains difficult to deliver and accreditation rates remain suboptimal. We describe a multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged approach to lung POCUS education within a region.
A survey was conducted in a region. From these results, bottlenecks were identified for improvement. We utilised key stages in an established accreditation pathway, and the Action Learning process. Analysing participant feedback, consensus amongst the team, regional educational needs, and leveraging the expertise within the faculty, we implemented several solutions which were multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged. We also set up a database across several accreditation pathways to facilitate supervision and assessment of rotational trainees.
Utilising the Action Learning process, we implemented several improvements at elements of the lung ultrasound accreditation pathways. An initial regional survey identified key barriers to accreditation: lack of courses (52%), lack of mentors (93%), and difficulty arranging directly supervised scans (73%). A multidisciplinary team of trainers was assembled. Regular courses were organised and altered based on feedback and anecdotal educational needs within the region. Courses were set up to also facilitate continuing professional development and exchange of knowledge and ideas amongst trainers. The barrier of supervision was removed through the organisation of regular supervision sessions, facilitating up to fifty scans per half day per trainer. We collected feedback from courses and optimised them. Remote mentoring platforms were utilised to encourage asynchronous supervision. A database of trainers was collated to facilitate triggered assessments. These approaches promoted a conducive environment and a commitment to learning. Repeat survey results support this.
Lung ultrasound accreditation remains a complex educational training pathway. Utilising an education framework, recruiting a multidisciplinary team, ensuring a multi-pronged approach, and fostering a commitment to learning can improve accreditation success.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) consists of a range of increasingly important imaging modalities across a variety of specialties. The COVID19 pandemic highlighted the importance of the lung ultrasound [ 1 , 2 ]. Yet, lung POCUS training remains difficult to deliver. This report describes a multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged approach to developing and delivering lung POCUS training in a region.
One of the most established POCUS training pathways in the UK is FUSIC heart (previously known as Focused Intensive Care Echocardiography (FICE)). Unfortunately, accreditation rates across this (and other modalities like lung POCUS) are suboptimal [ 3 ]. Currently, lung POCUS features in several accreditation pathways in the UK: Focused Ultrasound in Intensive Care (FUSIC) from the Intensive Care Society [ 4 ], Focused Acute Medicine Ultrasound (FAMUS) from the Society of Acute Medicine [ 5 ], and the Royal College of Emergency Medicine POCUS curriculum (RCEM POCUS) [ 6 ]. In addition, the British Thoracic Society have published a clinical statement on the use of ultrasound for pleural procedures, and their stance on training for lung ultrasound [ 7 ]. Lung POCUS is a standalone module for FUSIC and FAMUS, but it is part of the shock module in RCEM POCUS, which also includes focused echocardiography. Alongside lung POCUS, BTS and FUSIC pathways include demonstration of US-guided chest aspiration and/or drainage, while the FAMUS pathway includes marking for drainage, but doesn’t specifically require candidates to perform aspiration or drainage. RCEM POCUS curriculum does not specify chest drainage either, but this is included in wider training requirements. Despite their differences, most accreditation pathways contain key elements: (1) initial learning via a course (e-learning or face-to-face), (2) directly supervised scans, (3) indirectly supervised scans, and (4) a triggered assessment (Table 1 ). The practical assessment is initiated by the candidate after completion of logbook (thus triggered), consists of performing and reporting a scan on a patient (real or simulated), and is ideally assessed by someone who is not the main trainer for the candidate.
The Northwest of England is a large training deanery responsible for the postgraduate education and training of 8000 doctors [ 8 ]. It hosts 12 specialty schools, including intensive care medicine, anaesthetics, medicine, emergency medicine, and others. Before the launch of FUSIC lung, and before the start of this project, the Northwest had good accreditation rates for FICE. Unfortunately, the rates for the other POCUS modalities, including lung ultrasound, were low. Amongst physiotherapists, however, there has been rapid increase in successful accreditation for FUSIC lung [ 9 ], which is also reflected in medical doctors discussed in this paper.
A baseline qualitative survey, via Google forms, was conducted in the region between September to November 2018 (Table 2 ). This was self-administered online, and participation was voluntary. It was disseminated through regional training channels (focusing on intensive care medicine) including email and text messaging groups. The survey was designed to target specific elements of the lung POCUS accreditation pathway (specifically FUSIC). This sought to identify key points within the accreditation pathway candidates struggle to complete.
We utilised the Action Learning process for this project [ 10 ]. This is a problem-solving approach characterised by cycles of action and reflection. The key stages in the process are (1) An important and complex problem, (2) A diverse problem-solving team, (3) An environment that promotes curiosity, inquiry, and reflection, (4) Talk that becomes action and solutions, and finally, (5) A collective commitment to learning. Action Learning has been used in a variety of educational contexts, including medical education. It has been shown to be particularly effective for supporting collaborative and cooperative approaches between disciplines and sectors [ 11 , 12 ].
Since the different accreditation pathways share many key elements (see introduction), we focused on the FUSIC pathway. We mapped out the key stages of accreditation, and designed interventions to maximise opportunities for candidates to achieve progression at each stage. We collected and analysed feedback from the courses, integrating them with anecdotal observations from senior clinicians and trainers in the region, and together with the emergence and desire for POCUS training from other specialties and towards different accreditation pathways, we continued to build a multidisciplinary approach to lung POCUS accreditation.
Whilst this project was not classified as research, we adhered to the UK Research and Innovation principles of ethics framework [ 13 ]. The risks of performing ultrasound scans are negligible, but the potential benefits are significant [ 14 , 15 ]. Trainers are all highly experienced clinicians regulated by the General Medical Council’s duties to uphold patients’ rights and dignity. Verbal consent is obtained from patients whenever possible. Scanning stopped if discomfort or deterioration was recognised. None of the trainers have conflict of interests, and all training scans are reviewed by our team of trainers, who also maintain communication with clinical teams should an unexpected finding be noticed.
The results below are presented in the format of the Action Learning process and framed within the FUSIC accreditation pathway. A further summary of these actions is presented in Table 3 .
An important and complex problem
There were 28 respondents for the survey between September to November 2018. Table 2 and Fig. 1 summarise their characteristics and key findings. Although 19 (68%) respondents had access to FUSIC heart mentors in their hospitals, 26 (93%) did not have access to trainers in other modalities (lung, abdomen, deep vein thrombosis). 12 (52%) found it difficult/very difficult to book onto a FUSIC lung course, and 17 (74%) found it difficult/very difficult to obtain their first ten supervised scans. The top three barriers to FUSIC lung accreditation were (1) lack of availability of courses, (2) lack of mentors, and (3) difficulty in arranging directly supervised scans. The lack of mentors and education is a common theme amongst other professional groups too [ 9 ]. Through this survey, we not only identified an important and complex problem, but also highlighted several areas which may have practical solutions. The FUSIC pathway was used as a template, acknowledging that most other pathways share many similar elements but differ in the overarching governance processes and recommended numbers.

Survey results from 2018 and 2024.
A survey was repeated in 2024 (Table 2 , Fig. 1 ). There were 20 respondents. 11-12 (55-60%) thought there was better availability of lung US courses and 6 (30%) found it easier to arrange directly supervised scans (Figs. 1 and 2 ). There were fewer respondents who found elements of the pathways difficult or very difficult (Fig. 1 ). 45% thought there have been mild to significant improvements in the use of remote mentoring platforms (Fig. 2 ).
Survey data showing improvements in the elements of the pathways
A diverse problem solving team
The first FUSIC course in the Northwest of England was delivered in February 2019. This course covered the modalities of lung, abdomen, deep vein thrombosis, and vascular access. 14 candidates attended this course. Several issues were noted. First, we only captured Intensive Care Medicine trainees (apparent from registration data), despite the increased emphasis on POCUS within the specialities of Emergency Medicine (RCEM POCUS), Acute Medicine (FAMUS) [ 16 ], and Respiratory Medicine (BTS pathway). Second, there was anecdotal evidence of desires for procedural skills within the region, which corresponded with the curriculum requirements of chest drain insertion for Emergency Medicine, Respiratory Medicine, and Intensive Care Medicine. This information was obtained from discussions with programme directors, consultants, and trainees in the region. Third, in 2019 and 2023, FUSIC and FAMUS respectively split into their modular components rather than a full suite of POCUS modalities.
With this knowledge, we redesigned the course into a one-day multidisciplinary lung ultrasound and chest drain course with faculty from intensive care medicine, acute medicine, respiratory medicine, emergency medicine, and cardiothoracic surgery. We actively recruited faculty across FUSIC, FAMUS, RCEM POCUS and BTS training pathways. This course was then delivered in October 2022, following the almost two-year hiatus in training opportunities due to the COVID19 pandemic (they are delivered twice a year now). Thirty candidates attended this course from a variety of specialities from intensive care medicine, emergency medicine, medicine, anaesthetics, surgery, and paediatrics, and from a wide range of seniorities. This was achieved by dissemination through the various specialties, facilitated by the multidisciplinary faculty. The course consisted of several lectures covering essential ultrasound and chest drain knowledge, and three practical sessions (lung ultrasound, seldinger chest drain insertion, surgical chest drain insertion). A healthy volunteer was used for the ultrasound scanning, while a mix of plastic models and pig thoraces were used for the chest drains. Each practical session lasted an hour, with at least two trainers to a group of ten candidates. Feedback from this reformatted course was very positive (Table 4 , Fig. 3 ). This is now run regularly.

Course feedback
An environment that promotes curiosity, inquiry, and reflection
Along with the diverse faculty at the course, there was a need to create a supportive training environment. Literature has highlighted the benefit of exchanging knowledge and skills between trainers [ 17 ], and the importance of maintaining effective relationships between different disciplines [ 18 ]. We utilised a small number of lectures for the courses. They transmit important technical information and fulfil the requirements of the various accreditation pathways. The lectures are taught by clinicians from different specialties, ensuring a multidisciplinary environment for learning.
For the practical stations in the courses, we ensured each group was taught by two trainers. Usually, a junior faculty is paired with a more senior trainer, promoting the development and exchange of teaching techniques. A teaching pair from different specialities also facilitates the exchange of skills, knowledge, and perspectives. For example, techniques used by cardiothoracic surgeons for chest drain insertion may differ from the usual practice of emergency physicians. Likewise, ultrasound location prior to chest drain insertion is almost always done by respiratory physicians but seldom by cardiothoracic surgeons. Through the pairing, such skills can be exchanged to promote patient safety and trainers can develop a wide range of teaching techniques.
A requirement that talk be converted into action and, ultimately, a solution
From the survey, it was clear that mentors were in short supply. As a result, directly supervised scans were tight bottlenecks in the accreditation pathway. To address this, we initially developed an additional day of mentored scanning in the Acute Medical Unit of a local hospital immediately after the course. Each trainer supervised four to six candidates. This, whilst effective for candidates, was difficult to organise. Trainers also found that six candidates were too many, citing the long time it took with each patient. Clearly, this was also unpleasant for the patients. Thus, this evolved into half-day supervised scanning sessions provided within the ICU of several hospitals. For these sessions, each trainer was able to supervise up to five candidates. We utilised a pragmatic approach to scanning, splitting the required skills into probe handling (including image optimisation) and image interpretation. Most sessions were attended by candidates with a mix of experience levels. First, the trainer assessed each candidate’s probe handling skills (if not already known). Upon satisfactory probe handling skills, each subsequent patient was only scanned by at most two candidates, and image interpretation was done by all candidates. Thus, all candidates got all the scans logged, even if they might not have physically manipulated the probe. The FAMUS pathway stipulates “recommended” number of scans, and both BTS and RCEM POCUS pathways do not require a fixed number of scans. As an approach, this also acknowledges prior experiences, and strikes a three-way balance between candidate needs, patient inconvenience, and trainer time. Using this model, each trainer was able to supervise up to ten lung scans per candidate, making a maximum of fifty supervised scans per half-day session. This means for most pathways, three half-day sessions are sufficient for a candidate to complete the requisite number of scans and triggered assessment. This model has been successfully implemented in several hospitals in the region.
For the indirectly supervised scans, initially, this was done as an in-person meeting between trainer and candidate. However, this was difficult to arrange. Some trainers did this asynchronously, reviewing scans on the US machine and then providing feedback to the candidate via text or email. This also took several communication points, which became difficult to keep track of. We then explored remote mentoring, and currently use SonoClipShare.com to facilitate asynchronous remote mentoring. This remote mentoring platform allows candidates to upload anonymised scans and send them to a named trainer for feedback and comments. Using this approach, a trainer need not be present for the scan, but will be able to provide ongoing mentoring and teaching to the candidate. Each full scan usually takes between five to ten minutes to review and provide comments on.
Responding to feedback from courses (Table 4 ), several changes were made. First, pre-course learning material was made available to reduce the load of lectures and prioritise practical scanning. Second, lectures were optimised to focus on scan protocols and pathologies, and physics was minimised and shifted to pre-course learning material.
A collective commitment to learning
Unfortunately, there is no centralised database for POCUS trainers in the UK. The details of FUSIC trainers are stored in the Intensive Care Society database but it is not searchable. FAMUS supervisors are still searchable at the time of writing, from the Society of Acute Medicine website. RCEM, like BTS, have devolved their training to local hospitals, negating the need for a centralised database. Yet, as highlighted, there are many similarities across the accreditation pathways, and much overlap between the skills of POCUS practitioners across different specialties. Recognising a collective commitment to learning and training, we employed several strategies amongst candidates and trainers.
First, candidates are encouraged to contact our faculty to be put in touch with trainers at their local hospitals. In the UK, rotational training of doctors results in candidates having difficulties searching for trainers when they rotate to a new hospital every three to six months. We maintain a database of trainers across the region, which is used to connect candidates and trainers. Second, we opted to recognise the skills of trainers from the different accreditation pathways. Their competencies are further confirmed through the pairing of trainers on our courses described above. Thus, supervision can be facilitated by trainers from a different accreditation body, with oversight of a main trainer from the candidate’s chosen pathway. This method also allows candidates to be trained by a multidisciplinary selection of trainers within the region, exposing them to different styles of teaching, allowing them to pick up a variety of techniques, and increasing the likelihood of successful accreditation. Third, our database allows for triggered assessments in the chosen pathways, even if it requires travel to a different hospital. Maintaining such a network helps to mitigate the initial paucity of trainers in a particular pathway and encourages interdisciplinary relationships. We currently have over fifty active trainers across the accreditation pathways within the region, and there are ongoing plans to systematically collect a complete dataset for the Northwest of England and develop this into a searchable regional database. Such a network is vital for ensuring the resilience of the educational endeavour [ 18 ].
Lung POCUS is becoming an increasingly important aspect of intensive care medicine, acute and respiratory medicine, and emergency medicine. Yet, POCUS training continues to be of varying availability and quality. We report a multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged approach to lung POCUS accreditation. The courses have continued to receive very positive feedback, with participants appreciating the multidisciplinary aspects. In 2023, each trainer within our core faculty has supported the accreditation of at least five candidates each.
Several factors contributed to the success of this educational intervention. First, there is a small number of enthusiastic and dedicated trainers who have consistently given up their time, expertise, and experience to work together for POCUS training in the region. Second, the strong network of POCUS trainers and practitioners within the region and across specialties helped to mitigate the initial bottleneck of lack of mentors. Equally, the multidisciplinary approach to POCUS for the courses and supervision helped to build upon existing relationships between specialties. Third, the multi-pronged approach was responsive to feedback and observations within the region and enabled us to design courses and programmes that are fit for purpose. Fourth, there is increasing demand for POCUS training amongst trainees, and a large cohort of trainees across several specialties who are interested in pursuing accreditation. Fifth, the multidisciplinary approach to our POCUS training leverages different skill sets and allows efficient use of educational resources. It also captures a diverse range of candidates and forges multidisciplinary links which we believe are increasingly important for our increasingly complex patient population.
There are strengths to this report. It considers lung POCUS as an entire pathway and provides support using different methods depending on the stage of the pathway candidates are at. The multi-pronged approach to accreditation utilises an established educational process. It helped us to focus on examining and improving each step of the entire pathway (Table 1 ). Our educational approach builds links across multiple specialties, which aligns with wider multidisciplinary aims in healthcare [ 19 ]. There are plans to include physiotherapists into the trainer network since there have been high accreditation rates in the region.
Several limitations persist. There may be bias in the respondents of the initial survey since the respondents were mostly from an Intensive Care Medicine background. However, other teams have corroborated our findings in different countries and specialties [ 20 , 21 ]. We have not followed every single candidate up through their accreditation processes. Since candidates are rotational and are spread across the entire region and beyond, it is difficult to obtain this data. In addition, we do not have access to interrogate such data for FUSIC or FAMUS, and pathways such as BTS and RCEM POCUS only require local sign-off, so it is challenging to obtain individual information. We plan to collect more robust data as a region in the future. Unfortunately, our database of trainers is not complete, but plans are in place to systematically identify trainers in the region. There is no validated way to maintain POCUS skills, and no agreed method for continuing professional development. Therefore, measurement of knowledge and skill retention continues to be difficult and stands out as a research priority.
There are several wider concerns about lung POCUS training. The presence of several different accreditation pathways makes it difficult for candidates to choose which is most appropriate for themselves and their professional development. Most trainers in our region do not have dedicated Supporting Professional Activities time to deliver training. There are discrepancies between the support given at trust, society, faculty, royal college, and national levels. For example, RCEM has advocated for Supporting Professional Activities time to support POCUS training across the country. Trainers therefore should get allowances within their job plans to deliver POCUS training. This is not the case for the Society of Acute Medicine or Intensive Care Society for FAMUS and FUSIC respectively. As a result, the burden of POCUS training is high considering the multiple steps of each accreditation pathway. As POCUS modalities become more diverse, the pathways may struggle to keep pace with innovation, and in turn, the burden caused by multiple accreditation modules will increase for candidates. There is therefore a need to explore single accreditation pathways across specialties, and maintain a robust, up-to-date, and searchable database which conforms to the General Data Protection Regulation principles.
These notwithstanding, POCUS training will continue to gain importance in medical practice, and innovative educational methods as described here should be shared to enable a more streamlined process with higher rates of successful accreditation. There are several plans which will help to gather more robust data on POCUS training in the region.
We have described how adopting a multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged approach, utilising an established educational process (e.g. Action Learning), can help to improve lung ultrasound accreditation rates across a variety of pathways. Focusing on relational and collaborative processes are vital for the success of complex ultrasound educational endeavours. Further work needs to be done on systematically collecting data for more robust evidence.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
Acute Internal Medicine
British Thoracic Society
Sars CoV-2 or Coronavirus 2019
Emergency Medicine
Focused Acute Medicine Ultrasoud
Focused Intensive Care Echocardiography
Focused Ultrasound in Intensive Care
Intensive Care Medicine
Intensive Care Unit
Point-of-care ultrasound
Royal College of Emergency Medicine
Supporting Professional Activities
Parulekar P, Powys-Lybbe J, Knight T, Smallwood N, Lasserson D, Rudge G, et al. CORONA (COre ultRasOund of covid in iNtensive care and Acute medicine) study: National service evaluation of lung and heart ultrasound in intensive care patients with suspected or proven COVID-19. J Intensive Care Soc. 2022;0(0):17511437211065612.
Google Scholar
Smith MJ, Hayward SA, Innes SM, Miller ASC. Point-of-care lung ultrasound in patients with COVID-19 - a narrative review. Anaesthesia. 2020;75(8):1096–104.
Article Google Scholar
Jacques A, Walden A, Pettipher A. Focused intensive care echocardiography: Lots of participation, not much accreditation. J Intensive Care Soc. 2017;18(1):73.
ICS. FUSIC: Intensive Care Society; 2023. Available from: https://ics.ac.uk/learning/fusic.html .
SAM. Focused Acute Medicine Ultrasound (FAMUS): Society of Acute Medicine; 2023. Available from: https://www.acutemedicine.org.uk/famus/ .
RCEM. Ultrasound Education & Training – 2021 Curriculum: Royal College of Emergency Medicine; 2021. Available from: https://rcem.ac.uk/ultrasound/ .
Opstad K. BTS Clinical Statement on Pleural Procedures: British Thoracic Society; 2022. Available from: https://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/media/455880/bts-clinical-statement-on-pleural-procedures-consultation-jun-2022.pdf .
HEENW. About us: Health Education England Northwest; 2023.
Hayward S, Innes S, Smith M. Challenges and opportunities in point-of-care ultrasound: A qualitative exploration of respiratory physiotherapists’ experiences of lung ultrasound training and its adoption in critical care. Ultrasound. 2022;30(2):126–33.
Revans R. ABC of action learning London: Lemos and Crane; 1998.
Siva V, Coughlan P, McNabola A. Building collaboration within a smart specialisation cluster through action learning. SOSC; 2017.
Calver J, Gold J, Stewart J. Action learning and the creative industries: the efficacy of an action learning set in building collaboration between a university and creative industries. Act Learn. 2013;10(1):25–38.
UKRI. Framework for Research Ethics: UK Research and Innovation; 2021. Available from: https://www.ukri.org/councils/esrc/guidance-for-applicants/research-ethics-guidance/framework-for-research-ethics/our-core-principles/#contents-list .
Abrokwa SK, Ruby LC, Heuvelings CC, Belard S. Task shifting for point of care ultrasound in primary healthcare in low- and middle-income countries-a systematic review. EClinicalMedicine. 2022;45:101333.
Goldsmith AJ, Shokoohi H, Loesche M, Patel RC, Kimberly H, Liteplo A. Point-of-care ultrasound in morbidity and mortality cases in emergency medicine: who benefits the most? West J Emerg Med. 2020;21(6):172.
Smallwood N, Dachsel M, Gilmore A. Focused acute medicine ultrasound (FAMUS): curriculum outline of a new ultrasound standard for acute internal medicine. Clin Med (Lond). 2017;17(Suppl 3): s24.
Simpson D, Marcdante K, Souza KH. The power of peers: faculty development for medical educators of the future. J Grad Med Educ. 2019;11(5):509–12.
Tan MZY, Prager G, McClelland A, Dark P. Healthcare resilience: a meta-narrative systematic review and synthesis of reviews. BMJ Open. 2023;13(9):e072136.
NHSEngland. Adult Critical Care Service Specifications: NHS England; 2019. Available from: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/220502S-adult-critical-care-service-specification.pdf .
Jarwan W, Alshamrani AA, Alghamdi A, Mahmood N, Kharal YM, Rajendram R, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound training: an assessment of interns’ needs and barriers to training. Cureus. 2020;12(10):e11209.
Schott CK, Wetherbee E, Khosla R, Nathanson R, Williams JP, Mader MJ, et al. Current use, training, and barriers to point-of-care ultrasound use in icus in the department of veterans affairs. CHEST Crit Care. 2023;1(2):100012.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Drs Judith Lyons, Farhan Ahmed, Nishant Cherian, Ollie Hill, Chris Craig have been involved in delivering POCUS training in the region and have contributed to the wider project. Prof Brendan McGrath has been an advisor for the POCUS courses. We would like to acknowledge all other faculty members and trainers, as well as the secretaries who have supported our courses.
There is no funding associated with this study. Courses are run on a non-profit basis and faculty do not gain financial benefit from teaching.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
ST7 anaesthesia and intensive care medicine trainee, Health Education England Northwest, Manchester, UK
Mark ZY Tan
NIHR academic clinical fellow, Humanitarian and Conflict Response Institute, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
ST8 thoracic surgery trainee, Health Education England Northwest, Manchester, UK
Annemarie Brunswicker
ST3 anaesthesia trainee, Health Education England Northwest, Manchester, UK
Harry Bamber
Consultant in anaesthesia and intensive care medicine, Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust, Salford, UK
Alistair Cranfield
Consultant in intensive care medicine, North Manchester General Hospital, Manchester, UK
Evangelos Boultoukas
Consultant in anaesthesia and intensive care medicine, Stockport NHS Foundation Trust, Stockport, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MT designed, delivered, and analysed the survey. All authors have organised, taught on, and arranged courses and supervision sessions. HB and MT analysed course feedback and prepared tables. HB and MT wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed, edited and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mark ZY Tan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
This is a service evaluation project, and according to Health Research Authority UK, does not require ethics approval nor consent to participate. https://www.hra.nhs.uk/approvals-amendments/what-approvals-do-i-need/
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tan, M.Z., Brunswicker, A., Bamber, H. et al. Improving lung point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) training and accreditation - a multidisciplinary, multi-centre and multi-pronged approach to development and delivery using the action learning process. BMC Med Educ 24 , 713 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05653-2
Download citation
Received : 27 February 2024
Accepted : 11 June 2024
Published : 02 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05653-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Chest drain
- Action learning
- Accreditation
- Lung ultrasound
- Credentialing
- Intensive care
- Emergency medicine
- Acute medicine
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A strong thesis should be able to take a stand and not just taking a stand but should be able to justify the stand that is taken, so that the reader will be tempted to ask questions like how or why. The thesis should be arguable, contestable, focused, specific, and clear. Make your thesis clear, strong and easy to find.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader. 2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
Throughout the process, the thesis serves as an anchor point while the author wades through the morass of facts and ideas. The dialogue between thesis and body continues until the author is satisfied or the due date arrives, whatever comes first. It's an effortful and sometimes tedious process. Novice writers, in contrast, usually ...
Working Thesis Statements. A strong thesis statement must have the following qualities: It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable. It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence ...
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can discover or refine one for your draft. Introduction Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
The steps involved in the thesis process include: selecting a topic in consultation with the program director. finding a faculty advisor. developing a thesis proposal. forming a thesis committee. registering for and completing Thesis classes. adhering to established deadlines.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated. A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence. A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
A thesis statement is the main point of your essay. Usually composed of one or two sentences, the thesis statement tells the reader what your paper is about. It should be debatable and not a statement of fact. Aside from guiding the reader, it also helps you while you are writing to keep your paper focused.
Thesis Statement: "The accelerating effects of climate change threaten global biodiversity through temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and altered migration patterns.". In this example, the 3-point thesis statement clearly presents the three main points that will be discussed in the paper: temperature shifts, habitat degradation, and ...
UNDERSTANDING A THESIS. A thesis is a substantial generalization that can stand by itself as the basis of an essay's development. It is an assertion of what the writer believes is right or wrong and why, and it is a statement that can be either true or false. A thesis clearly and concisely conveys the writer's main argument in an essay, and ...
Thesis Process: The student's first step is to choose a topic of desired research. Thesis ... will be the student's main point of contact throughout the thesis experience. With the Thesis First Reader, a student will establish a timeline, including hard deadlines, and
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Our findings point to a functional connection between arginine metabolism and exocytosis. Chapter 5 discusses potential future directions and experiments, including technological advances and the testing of new hypotheses. Overall, this study presents a detailed application of chemical genetics to dissect the exocytosis process in Arabidopsis ...
Republican National Committee co-Chair Lara Trump said Sunday the possibility of Democrats bypassing Vice President Harris and picking another candidate to replace President Biden, should he withdr…
Affected Platforms: Linux Distributions Impacted Users: Any organization Impact: Remote attackers gain control of the vulnerable systems Severity Level: High Cybersecurity threats are increasingly leveraging cloud services to store, distribute, and establish command and control (C2) servers, such as VCRUMS stored on AWS or SYK Crypter distributed via DriveHQ.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) consists of a range of increasingly important imaging modalities across a variety of specialties. Despite a variety of accreditation pathways available in the UK, lung POCUS training remains difficult to deliver and accreditation rates remain suboptimal. We describe a multidisciplinary, multi-centre, and multi-pronged approach to lung POCUS education within a ...
Biden's wishes could also become hugely important. He could try to influence the process by endorsing Harris, his vice president. And she would have an argument in her favor since she is already ...
Avelo Airlines has extended its schedule through early 2025, opening its booking channels for the holiday season and beyond. The carrier — which launched operations more than three years ago — will serve 49 destinations spanning 23 states and Puerto Rico, including 16 new destinations launched in recent months.
First, we present a novel 3D detection network architecture, 3D-ODN, which can accurately process object instance information from point clouds. Second, we develop a framework to construct the visibility map by incorporating semantic information and terrain analysis.