

Coca-Cola Successful Marketing Research Process
Coca-Cola has perfected the art of understanding consumer preferences, uncovering trends, and crafting compelling campaigns that have left an indelible mark on the global beverage industry. Join us as we delve into the secrets behind Coca-Cola’s Successful Marketing Research Process, revealing the strategies and insights that have propelled this beloved brand to unparalleled heights in the world of fizzy refreshments. In this article, we will thrill you with a captivating exploration of how one of the world’s most iconic brands
Understanding the Importance of Marketing Research
Marketing research is a critical process that plays a pivotal role in guiding businesses toward success. By gathering valuable insights and data, it enables companies to make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, and stay ahead of the competition. In this section, we will delve into the core aspects that highlight the significance of marketing research, particularly in the context of a global giant like Coca-Cola.
Discover Fresh Marketing Insights!
Join other smart marketers to uncover amazing marketing strategies.
We will never give away, trade or sell your email address. You can unsubscribe at any time.
What is Marketing Research?
At its essence, marketing research is the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of relevant data about a target market, consumers, and the competitive landscape. It involves the use of various methodologies and techniques to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. By defining the scope and objectives of the research, companies like Coca-Cola can gain a deep understanding of their target audience, which in turn drives their marketing efforts.
Role of Marketing Research in Business Strategy
Marketing research serves as the foundation upon which a company’s business strategy is built. It empowers decision-makers at Coca-Cola to identify opportunities and challenges, anticipate market shifts, and tailor their products and messaging to meet consumer needs. By analyzing market trends and consumer feedback, Coca-Cola can make data-driven choices that resonate with its target audience, leading to more effective marketing campaigns and increased brand loyalty.
Significance of Market Research for Companies like Coca-Cola
For a globally recognized brand like Coca-Cola, market research is not just a useful tool; it is an indispensable part of their continued success. As consumer preferences evolve, staying attuned to their needs and desires becomes vital. Through comprehensive market research, Coca-Cola can identify emerging trends, assess the demand for new products, and gain a competitive edge in the ever-changing beverage industry.
In conclusion, marketing research is a fundamental process that helps companies like Coca-Cola gain valuable insights into their market, consumers, and competition. It allows them to develop effective strategies, stay relevant, and create long-lasting connections with their customers. By embracing the power of marketing research, Coca-Cola can continue to lead the beverage market and deliver products that resonate with consumers worldwide.
Overview of Coca Cola
Coca-Cola, a beverage giant with a rich history and global presence, has established itself as one of the most iconic and recognizable brands worldwide. In this section, we will delve into the company’s fascinating background, its extensive market presence, and the diverse range of products and brands it offers.
Brief History and Background
Coca-Cola’s journey began in 1886 when pharmacist John S. Pemberton concocted the original Coca-Cola formula in Atlanta, Georgia. The initial product was sold as a medicinal tonic, but it quickly gained popularity as a refreshing soda beverage. Asa Griggs Candler acquired the rights to the formula in 1888, laying the foundation for the modern-day Coca-Cola Company.
Over the years, Coca-Cola has witnessed remarkable growth and innovation. From its first bottling plant in 1894 to its global expansion in the 20th century, the company has constantly evolved to meet consumer demands and cultural preferences. Today, Coca-Cola is known for its iconic red and white logo, which has become synonymous with happiness and celebration.
Coca-Cola’s Market Presence and Global Reach
With a presence in over 200 countries, Coca-Cola stands as a true global leader in the beverage industry. Its products are sold in almost every corner of the world, making it a household name and an integral part of diverse cultures. The company’s extensive distribution network, strong marketing campaigns, and commitment to local adaptation have contributed to its unparalleled global reach.
Coca-Cola’s ability to penetrate both developed and emerging markets is a testament to its adaptability and market responsiveness. Through strategic partnerships, joint ventures, and localized production, Coca-Cola has successfully embedded itself in the hearts of consumers across continents.
Products and Brands Offered by Coca-Cola
Beyond its flagship Coca-Cola soda, the company boasts a vast portfolio of beverages catering to different tastes and preferences. From carbonated soft drinks to non-carbonated beverages, Coca-Cola’s product range is designed to appeal to a diverse consumer base. Some of the notable brands under Coca-Cola’s umbrella include:
- Coca-Cola Zero Sugar
- Minute Maid
These are just a few examples of the extensive lineup of beverages offered by Coca-Cola. The company continues to innovate and introduce new products to meet changing consumer demands and market trends.
In conclusion, Coca-Cola’s rich history, global presence, and diverse product range have solidified its position as a market leader in the beverage industry. Its ability to adapt to changing times while maintaining its core values and iconic branding has allowed it to thrive and remain a beloved brand worldwide.
Defining the Marketing Research Objectives
For an industry behemoth like Coca-Cola, the ability to stay ahead of consumer preferences and market trends is paramount to maintaining its position as a global beverage leader. This is where the first pillar of Coca-Cola’s successful marketing research process comes into play: defining the marketing research objectives.
Identifying Research Goals and Objectives
In the realm of marketing research , defining clear and specific objectives is crucial for the success of any study. In this section, we will explore the significance of understanding the purpose of marketing research and the importance of setting measurable objectives.
Understanding the Purpose of the Marketing Research
Before embarking on any marketing research endeavor, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of its purpose and how it aligns with the overall business objectives. Marketing research serves as a compass that guides decision-making processes and strategic planning. By identifying the purpose, such as gaining insights into consumer preferences, assessing market potential, or evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, Coca-Cola can ensure that the research efforts are focused and relevant.
By understanding the purpose of marketing research, Coca-Cola can better allocate resources, time, and efforts in a manner that maximizes the impact of the research findings. It allows them to gather the right data, ask relevant questions, and obtain valuable insights to address specific business challenges or capitalize on opportunities.
Setting Clear and Measurable Objectives for the Research
Clarity and measurability are the cornerstones of effective marketing research objectives. Ambiguous or vague objectives can lead to unfocused research efforts, making it challenging to derive meaningful conclusions. When crafting research objectives, Coca-Cola must ensure they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This approach facilitates a structured research process and provides a clear direction for the research team.
For example, if Coca-Cola aims to explore the consumer perception of a new beverage flavor, a SMART objective would be: “To assess the acceptance of the new flavor among the target demographic through a survey with a minimum of 500 respondents within the next two months.” This objective outlines the research scope, the target sample size, and the timeframe for completion, making it easier to gauge the research’s success.
Setting measurable objectives also enables Coca-Cola to track progress throughout the research process, ensuring that the data collected aligns with the defined goals. It allows for adjustments and refinements as needed, ultimately leading to more meaningful insights and actionable recommendations.
In conclusion, identifying the purpose of marketing research and setting clear, measurable objectives are pivotal steps in the marketing research process for Coca-Cola. By doing so, the company can ensure that its research efforts are focused, purpose-driven, and capable of providing valuable insights to inform marketing strategies and drive business success.
Types of Marketing Research Objectives
In the realm of marketing research, different types of research objectives serve distinct purposes and guide the research process. In this section, we will explore the three primary types of marketing research objectives: exploratory, descriptive, and causal.
Exploratory Research Objectives
Exploratory research aims to explore a problem or opportunity in-depth, often in situations where little is known or understood about the subject. The primary goal of exploratory research is to generate insights, ideas, and hypotheses that can further inform the research process. Coca-Cola might employ exploratory research when entering new markets, introducing innovative products, or understanding shifting consumer preferences.
Key Characteristics of Exploratory Research Objectives:
- Understanding New Phenomena: Exploratory research is particularly useful when dealing with emerging trends or unique market conditions where conventional data might be insufficient.
- Gathering Preliminary Information: This type of research helps Coca-Cola gain an initial understanding of a complex issue, which can then be investigated further with more focused research.
- Open-ended and Flexible Approach: Exploratory research often utilizes qualitative methods, such as focus groups or in-depth interviews, allowing for a more flexible exploration of ideas and opinions.
Descriptive Research Objectives
Descriptive research aims to provide a clear and detailed picture of a specific market, consumer behavior, or phenomenon. The primary focus is on describing the characteristics, patterns, and trends within the target population. Coca-Cola might employ descriptive research to understand the demographic profile of its consumers, track market shares, or assess customer satisfaction.
Key Characteristics of Descriptive Research Objectives:
- Quantitative Data Collection: Descriptive research relies heavily on quantitative methods, such as surveys and questionnaires, to gather data from a representative sample.
- Statistical Analysis: Data collected through descriptive research is often analyzed using statistical techniques to reveal patterns and correlations.
- Establishing Baselines: Descriptive research helps Coca-Cola establish benchmarks and reference points for measuring changes or improvements over time.
Causal Research Objectives
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research is concerned with understanding how changes in one variable influence another. Coca-Cola might employ causal research to determine the impact of specific marketing strategies on consumer behavior or assess the effectiveness of product packaging changes.
Key Characteristics of Causal Research Objectives:
- Manipulation of Variables: Causal research involves actively manipulating one or more variables to observe their effects on the outcome variable.
- Controlled Experiments: Causal research often employs controlled experiments, where researchers carefully control and monitor the conditions of the study to isolate the effects of the variables of interest.
- Inference and Causality: Causal research allows Coca-Cola to draw conclusions about the causal relationships between factors, providing valuable insights for decision-making and strategy development.
Understanding the different types of marketing research objectives—exploratory, descriptive, and causal—enables Coca-Cola to tailor its research approach to meet specific goals. Each type of research serves a distinct purpose in uncovering insights, describing market dynamics, or understanding cause-and-effect relationships, contributing to the company’s overall success and strategic decision-making.
The Relevance of Marketing Research for Coca-Cola
Marketing research plays a pivotal role in guiding the decision-making processes at Coca-Cola, enabling the company to stay ahead in the dynamic and competitive beverage industry. In this section, we will explore how marketing research drives decision-making and delve into specific objectives that Coca-Cola pursues in its marketing research efforts.
How Marketing Research Drives Decision-Making
- Understanding Consumer Behavior: Marketing research allows Coca-Cola to gain valuable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. By analyzing consumer perceptions, needs, and purchase patterns, the company can tailor its marketing strategies to resonate with its target audience effectively.
- Identifying Market Opportunities: Through market research, Coca-Cola can identify untapped opportunities and emerging trends within the beverage market. This knowledge empowers the company to introduce new products, flavors, or packaging innovations that align with evolving consumer demands.
- Evaluating Marketing Campaigns: Marketing research helps Coca-Cola assess the effectiveness of its advertising and promotional activities. By measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) and consumer responses, the company can optimize its marketing efforts to maximize impact and return on investment.
- Assessing Brand Perception: Understanding how consumers perceive the Coca-Cola brand is crucial for maintaining brand loyalty and reputation. Marketing research enables the company to gauge brand sentiment, identify potential issues, and implement strategies to enhance brand image.
- Monitoring Competitor Activity: Marketing research allows Coca-Cola to keep a close eye on competitor actions and product launches. This competitive intelligence helps the company stay agile, respond to market challenges, and maintain its position as a market leader.
Specific Objectives for Coca-Cola’s Marketing Research Efforts
- Product Innovation and Development: Coca-Cola engages in research to identify opportunities for new product innovations, explore new flavors, and create products that cater to diverse consumer tastes.
- Market Segmentation: To better understand its diverse customer base, Coca-Cola conducts research to segment markets based on demographics, preferences, and consumption habits.
- Pricing Strategy: Research into consumer price sensitivity and competitor pricing allows Coca-Cola to determine optimal pricing strategies for its products.
- Consumer Satisfaction and Feedback: Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms help Coca-Cola assess customer satisfaction levels and address any concerns or issues promptly.
- Market Expansion: Marketing research assists Coca-Cola in identifying potential new markets or regions for expansion, ensuring strategic growth.
- Advertising and Branding Effectiveness: By conducting research on advertising campaigns and brand perception, Coca-Cola can refine its messaging and branding strategies for better customer engagement.
Marketing research is indispensable for Coca-Cola’s decision-making process. By utilizing insights from research efforts, the company can understand consumer behavior, identify opportunities, and optimize its marketing strategies. Specific research objectives allow Coca-Cola to focus on key areas of interest, leading to informed and successful business decisions that contribute to its enduring global success.
Understanding the Research Methodology

In the dynamic and competitive world of the beverage industry, making informed decisions is a cornerstone of success. For Coca-Cola, a global giant with a legacy spanning over a century, understanding the intricate nuances of consumer behavior and market dynamics is crucial. Enter the second pivotal stage of Coca-Cola’s triumphant marketing research process: understanding the research methodology.
Primary vs. Secondary Research
In the field of marketing research, choosing the appropriate research methodology is crucial for obtaining reliable and relevant data. In this section, we will differentiate between primary and secondary research and explore the pros and cons of using each method.
Differentiating Primary and Secondary Data
Primary Research: Primary research involves the direct collection of new and original data specifically for the research study at hand. Coca-Cola gathers primary data through surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, and experiments. This method allows the company to tailor data collection to suit its research objectives, ensuring that the information collected is specific to its needs.
Pros of Primary Research:
- Relevance and Specificity: Coca-Cola can customize the data collection process to address its unique research questions and objectives.
- Control over Data Quality: The company has full control over the data collection process, ensuring data accuracy and reliability.
- Fresh Insights: Primary research provides up-to-date and relevant information, reflecting current market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Cons of Primary Research:
- Cost and Time-Intensive: Conducting primary research can be resource-intensive, requiring significant time, effort, and financial investment.
- Potential Bias: The presence of bias in the data collection process can impact the objectivity of the results.
- Limited Scope: Depending solely on primary research might limit access to broader industry trends and historical data.
Secondary Research: Secondary research, on the other hand, involves the use of existing data that has been previously collected and published by other sources. Coca-Cola can access secondary data from industry reports, government publications, academic journals, and online databases. This method is particularly useful for gathering background information and contextualizing research findings.
Pros of Secondary Research:
- Cost-Effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective and less time-consuming than primary research.
- Wider Scope: Coca-Cola can access a vast amount of data from various sources, providing a broader perspective on the industry and market trends.
- Historical Comparison: Secondary research allows for historical comparisons, enabling Coca-Cola to analyze trends over time.
Cons of Secondary Research:
- Potential Outdated Information: Some secondary data may be outdated, and its relevance to the current market might be limited.
- Lack of Control over Data Collection: Coca-Cola cannot control the methodology or quality of data collected by external sources, potentially affecting its accuracy.
- Limited Customization: Secondary data may not address the company’s specific research objectives, leading to less targeted insights.
Both primary and secondary research have their advantages and disadvantages. Coca-Cola may choose to use a combination of both methods to maximize the strengths of each approach and obtain a comprehensive understanding of the market, consumer behavior, and industry trends. The selection of the most appropriate research methodology depends on the research objectives, available resources, and the level of specificity required to inform the company’s marketing strategies effectively.
Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods are valuable tools for gaining in-depth insights into consumer behavior, attitudes, and perceptions. In this section, we will explore three popular qualitative research methods: focus groups, in-depth interviews, and ethnographic studies, and understand their applications in the context of Coca-Cola’s marketing research.
Focus Groups
Description: Focus groups involve gathering a small group of individuals (usually 6 to 10) who represent the target audience or consumer segment of interest. The participants engage in open discussions guided by a moderator, who explores specific topics related to Coca-Cola’s products, marketing strategies, or brand perception.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use focus groups to:
- Understand consumer preferences for a new beverage flavor.
- Evaluate reactions to potential marketing campaigns or advertisements.
- Gather feedback on packaging design or product innovations.
Advantages:
- Provides real-time group dynamics and interactions that generate rich qualitative data.
- Allows participants to build on each other’s ideas, leading to comprehensive insights.
- Offers flexibility in exploring unexpected topics that arise during the discussion.
Limitations:
- A small sample size may not fully represent the entire target market.
- Group dynamics may influence individual responses, leading to potential bias.
- Requires skilled moderation to ensure all participants have equal opportunity to express their opinions.
In-depth Interviews
Description: In-depth interviews involve one-on-one interactions between a trained researcher and individual participants. These interviews are semi-structured, allowing for probing questions to delve deeper into respondents’ thoughts and experiences related to Coca-Cola.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use in-depth interviews to:
- Gain in-depth insights into the decision-making process of consumers when choosing beverages.
- Explore the reasons behind consumer loyalty to Coca-Cola products.
- Investigate the impact of Coca-Cola’s marketing campaigns on brand perception.
- Enables a deep understanding of individual perspectives and motivations.
- Allows flexibility in tailoring questions based on each respondent’s responses.
- Ensures confidentiality, encouraging participants to share honest and candid feedback.
- Time-consuming and may require significant resources for recruiting and conducting interviews.
- Results may be influenced by the skills and biases of the interviewer.
- Limited opportunity to observe group dynamics and interactions.
Ethnographic Studies
Description: Ethnographic studies involve observing and immersing researchers in the natural environment and daily lives of consumers. Researchers observe behaviors, interactions, and rituals related to beverage consumption and Coca-Cola’s products.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use ethnographic studies to:
- Understand how consumers incorporate Coca-Cola products into their daily routines.
- Identify cultural factors that influence beverage choices in different regions.
- Explore the role of Coca-Cola products in social gatherings and celebrations.
- Provides a deep contextual understanding of consumer behaviors in real-life settings.
- Allows for observing behaviors that consumers may not consciously articulate.
- Uncovers cultural nuances and social influences on beverage consumption.
- Time-intensive and requires extended periods of observation and data collection.
- Researchers may influence behaviors by their presence, leading to the observer effect.
- Findings may not be easily generalized to larger populations.
In conclusion, qualitative research methods such as focus groups, in-depth interviews, and ethnographic studies offer unique opportunities for Coca-Cola to delve into the complexities of consumer perceptions and behaviors. By combining insights from qualitative research with other research methodologies, Coca-Cola can gain a comprehensive understanding of its target audience, leading to more effective marketing strategies and product innovations.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods involve the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to quantify trends, behaviors, and relationships. In this section, we will explore three common quantitative research methods: surveys and questionnaires, observational research, and experiments, and understand their relevance in Coca-Cola’s marketing research.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Description: Surveys and questionnaires involve the collection of data from a large sample of respondents using structured sets of questions. The questions can be close-ended (multiple choice, rating scales) or open-ended (allowing respondents to provide detailed responses). The data collected is analyzed statistically to draw conclusions.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use surveys and questionnaires to:
- Measure consumer satisfaction with their products and services.
- Understand the awareness and perception of Coca-Cola’s brand among different demographics.
- Gather data on consumer preferences for beverage flavors and packaging.
- Efficient data collection from a large number of respondents.
- Enables measurement of attitudes, opinions, and preferences in a standardized manner.
- Statistical analysis allows for the generalization of findings to larger populations.
- Limited ability to explore complex or nuanced responses.
- Response bias may impact the accuracy of results.
- Dependent on the quality of questionnaire design and respondent participation.
Observational Research
Description: Observational research involves the systematic observation and recording of behaviors, interactions, and events in natural settings without direct intervention. Researchers may use checklists, coding systems, or video recordings to collect data.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use observational research to:
- Monitor consumer behavior and purchasing patterns in retail settings.
- Assess how customers interact with Coca-Cola products during promotional events.
- Observe beverage consumption behaviors in social settings.
- Provides real-time and authentic data on actual behaviors.
- Minimizes potential biases that may arise from self-reported data.
- Allows for direct observation of consumer reactions and non-verbal cues.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive, particularly for extended periods of observation.
- May not capture reasons behind observed behaviors without supplementary data.
- Ethical considerations may arise when observing individuals without their consent.
Experiments
Description: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to observe their effect on an outcome of interest. Participants are randomly assigned to different groups to control for confounding factors, and the researcher measures the impact of the manipulated variables.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use experiments to:
- Test the effectiveness of different marketing messages on consumer behavior.
- Measure the impact of packaging design changes on product sales.
- Evaluate the response to new beverage formulations compared to existing products.
- Allows for causal inference and identification of cause-and-effect relationships.
- Rigorous control over variables enhances internal validity.
- Replicability strengthens the generalizability of findings.
- Artificial laboratory settings may not fully replicate real-world conditions.
- Practical and ethical constraints may limit the types of experiments that can be conducted.
- Results may not capture the complexity of consumer decision-making in natural settings.
Quantitative research methods, such as surveys and questionnaires, observational research, and experiments, provide valuable data for Coca-Cola’s marketing research efforts. Each method offers unique insights and complements qualitative research approaches. By leveraging a combination of quantitative and qualitative methodologies, Coca-Cola can gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer behaviors, preferences, and perceptions, leading to informed marketing strategies and product innovations.
Sampling Techniques for Marketing Research
Sampling techniques are essential in marketing research as they help in selecting a representative subset of the target population for data collection. In this section, we will explore three commonly used sampling techniques: random sampling, stratified sampling, and convenience sampling, and understand their applications in Coca-Cola’s marketing research.
Random Sampling
Description: Random sampling involves selecting a random and unbiased subset of the target population for data collection. Each member of the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample. This method ensures that the sample is representative and minimizes selection bias.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use random sampling to:
- Survey a random selection of customers to assess overall satisfaction with their products.
- Conduct taste tests on randomly selected individuals to evaluate the reception of new beverage flavors.
- Analyze data from a random sample of retail outlets to assess sales performance.
- Reduces bias and increases the generalizability of findings to the entire population.
- A simple and straightforward method of sampling that can be easily replicated.
- Eliminates researcher bias in participant selection.
- May not be feasible for large and geographically dispersed populations.
- Requires a complete list or sampling frame of the target population, which may not always be available.
- Potential for non-response bias if selected individuals decline to participate.
Stratified Sampling
Description: Stratified sampling involves dividing the target population into distinct subgroups or strata based on relevant characteristics. A random sample is then drawn from each stratum in proportion to its representation in the overall population. This method ensures that each subgroup is well-represented in the final sample.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use stratified sampling to:
- Ensure a balanced representation of different age groups when studying consumer preferences for specific beverage lines.
- Select samples from various regions to account for regional variations in consumer behavior.
- Stratify by beverage consumption patterns to analyze preferences based on customer segments.
- Increases the precision and accuracy of estimates by considering variability within strata.
- Ensures that specific subgroups of interest are adequately represented in the sample.
- Enables comparisons between different strata, providing deeper insights.
- Requires prior knowledge of population characteristics to create relevant strata.
- Complex sampling design may increase logistical challenges and costs.
- Non-response from specific strata may impact the representativeness of the sample.
Convenience Sampling
Description: Convenience sampling involves selecting participants who are readily available and accessible to the researcher. This method is easy to implement but may introduce bias as it does not ensure random or representative selection.
Applications: Coca-Cola may use convenience sampling to:
- Gather quick feedback from employees in a specific office location during an internal survey.
- Collect immediate customer feedback from individuals visiting a retail outlet or event.
- Conduct on-the-spot taste tests with individuals passing by a promotional booth.
- A simple and quick method for data collection.
- Requires minimal resources and time.
- Suitable for exploratory research and preliminary insights.
- Prone to selection bias as it may not represent the broader population accurately.
- Results may not be generalizable to the entire target market.
- Lack of control over participant characteristics may impact data quality.
The choice of sampling technique is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of marketing research findings. Random sampling, stratified sampling, and convenience sampling each have their strengths and weaknesses. Depending on the research objectives, available resources, and the level of precision required, Coca-Cola can select the most appropriate sampling method to obtain meaningful insights and inform its marketing strategies effectively.
Data Collection and Analysis

In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of marketing, data is king, and for Coca-Cola, mastering the art of data collection and analysis is a critical driver of their success. As a global beverage giant, Coca-Cola recognizes that the ability to gather, interpret, and leverage data effectively can make or break marketing campaigns, product innovations, and market strategies. Let’s delve into the role of data collection and analysis as a powerhouse within Coca-Cola’s marketing research process.
Data Collection Process
In this chapter, we will delve into the data collection process used by Coca-Cola during its market research efforts. Gathering accurate and reliable data is crucial to gaining valuable insights and making informed business decisions.
Data Gathering Tools and Techniques
Description: Coca-Cola employs a variety of data-gathering tools and techniques to collect information during their market research.
1. Surveys and Questionnaires: Coca-Cola designs structured surveys and questionnaires to gather quantitative data from a large sample of consumers. These surveys may be administered online, via phone, or in person during taste tests and promotional events.
2. Interviews: In-depth interviews with selected participants provide qualitative data, allowing Coca-Cola to explore consumers’ opinions, attitudes, and preferences in more detail. These interviews can be conducted face-to-face or through phone calls.
3. Focus Groups: Focus groups involve small, carefully selected groups of consumers who participate in facilitated discussions. Coca-Cola uses this technique to gain insights into consumers’ perceptions, feelings, and reactions to specific products or marketing strategies.
4. Observational Studies: Coca-Cola conducts observational studies to observe consumer behaviors directly. This could involve observing shoppers’ beverage choices at retail outlets or tracking consumer reactions during product testing sessions.
5. Experiments: Controlled experiments are conducted to study the impact of specific variables on consumer behavior. Coca-Cola may use experimental designs to test the effectiveness of marketing messages or packaging changes.
Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability
Description: Coca-Cola takes several measures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data collected during market research.
1. Sample Representativeness: Coca-Cola carefully selects samples that represent the target population to avoid bias and ensure the generalizability of findings.
2. Questionnaire Design: Questionnaires are designed using well-structured and unbiased questions to elicit accurate responses from participants.
3. Data Validation: Data is carefully validated to identify errors and inconsistencies. Validation checks are performed during data entry to maintain accuracy.
4. Quality Control: Coca-Cola implements quality control measures throughout the data collection process to minimize errors and ensure data integrity.
5. Researcher Training: The researchers conducting market research are trained to follow standardized procedures and avoid leading or suggestive questioning.
6. Triangulation: Coca-Cola employs triangulation, a technique where multiple methods or sources are used to cross-validate findings, ensuring reliability.
7. Ethical Considerations: Coca-Cola adheres to ethical guidelines in obtaining informed consent from participants and protecting their privacy.
8. Statistical Analysis: Rigorous statistical analysis is performed to interpret the data accurately and draw meaningful conclusions.
By adopting these data collection practices and maintaining strict quality control, Coca-Cola ensures that the information gathered during their market research efforts is accurate, and reliable, and provides valuable insights into consumer behaviors, preferences, and trends.
Data Analysis Techniques
In this chapter, we will explore the data analysis techniques used by Coca-Cola to derive meaningful insights from the collected data during their market research process.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Description: Qualitative data analysis involves the examination of non-numeric data, such as responses from interviews, focus groups, and open-ended survey questions. The goal is to identify patterns, themes, and trends to gain deeper insights into consumer perceptions and behaviors.
Process: Coca-Cola follows these steps in qualitative data analysis:
- Data Coding: Researchers assign codes to segments of data, categorizing information into themes or topics. This process helps in organizing and structuring qualitative data.
- Theme Identification: Common themes or patterns are identified across the dataset. Themes may relate to consumer preferences, perceptions, emotions, or attitudes.
- Pattern Recognition: Researchers look for recurring patterns and connections between different themes to uncover underlying insights.
- Data Interpretation: The data is interpreted to generate valuable insights and understand consumers’ motivations, preferences, and behaviors.
Applications: Coca-Cola uses qualitative data analysis to:
- Understand consumer perceptions of new beverage flavors or packaging designs.
- Explore consumer attitudes towards environmental sustainability and recycling initiatives.
- Uncover consumer motivations behind beverage preferences and loyalty.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Description: Quantitative data analysis involves the examination of numerical data collected through surveys, questionnaires, and structured experiments. The focus is on statistical analysis to draw conclusions and make data-driven decisions.
Process: Coca-Cola follows these steps in quantitative data analysis:
- Data Cleaning: Data is cleaned to remove errors, inconsistencies, and missing values.
- Descriptive Statistics: Descriptive statistics, such as mean, median, and standard deviation, are calculated to summarize the data.
- Inferential Statistics: Inferential statistics, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing, are used to draw conclusions and make predictions based on the data.
- Data Visualization: Graphs, charts, and plots are created to visualize the data and identify trends.
Applications: Coca-Cola uses quantitative data analysis to:
- Measure customer satisfaction levels and brand perception.
- Analyze sales performance across different regions and product lines.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and promotional activities.
Data Interpretation and Visualization
Description: After completing data analysis, Coca-Cola interprets the findings to draw meaningful insights and inform business decisions. Data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and infographics, are used to present the results in a clear and engaging manner.
Benefits: Data interpretation and visualization help in:
- Communicating complex findings to stakeholders in a simplified and visually appealing manner.
- Identifying trends, patterns, and actionable insights that support marketing strategies.
- Facilitating data-driven decision-making processes within the organization.
By employing both qualitative and quantitative data analysis techniques and leveraging data interpretation and visualization, Coca-Cola gains a comprehensive understanding of consumer behaviors, preferences, and market trends. These insights enable them to formulate effective marketing strategies, launch successful product campaigns, and stay competitive in the ever-evolving beverage industry.
Analyzing Research Findings
In this chapter, we will delve into how Coca-Cola analyzes the research findings obtained from its market research process. By drawing meaningful conclusions and identifying patterns and trends, Coca-Cola can make informed business decisions to drive its marketing strategies.
Drawing Conclusions from the Data
Data Review: Coca-Cola meticulously reviews the research data collected through various methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations. The data is carefully cleaned and validated to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Statistical Analysis: Coca-Cola employs statistical techniques to analyze both qualitative and quantitative data. This analysis allows them to derive valuable insights from the data, identify significant relationships, and determine the statistical significance of the findings.
Comparison and Benchmarking: The research findings are compared against historical data, industry benchmarks, and competitor insights to gain a comprehensive understanding of their market position and performance.
Hypothesis Testing: When applicable, Coca-Cola formulates hypotheses and performs hypothesis testing to validate or refute assumptions made during the research process.
Root Cause Analysis: In case of any challenges or negative trends identified, Coca-Cola conducts root cause analysis to identify the underlying factors contributing to the issues.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Pattern Recognition: Coca-Cola uses advanced data analytics tools to recognize patterns and trends within the data. They look for recurring themes, behaviors, and preferences across different customer segments.
Segmentation Analysis: The research findings are segmented based on demographics, geographics, psychographics, and behavioral factors to uncover specific patterns among different consumer groups.
Temporal Analysis: Coca-Cola examines trends over time to understand how consumer preferences and market dynamics evolve. This analysis helps in predicting future trends and preparing for changing consumer demands.
Data Visualization: Coca-Cola employs data visualization techniques such as charts, graphs, and infographics to present the research findings in a visually appealing and easily understandable format.
External Factors Analysis: Coca-Cola takes into account external factors such as economic conditions, social trends, and technological advancements that may impact its business and marketing strategies.
By analyzing research findings and identifying patterns and trends, Coca-Cola gains valuable insights into consumer behaviors, market preferences, and emerging opportunities. These insights guide their marketing efforts, product development, and overall business strategies, enabling them to stay ahead in the competitive beverage industry.
Extracting Actionable Insights
Coca-Cola is committed to utilizing the research findings derived from their comprehensive market research efforts to gain actionable insights. These insights serve as the foundation for making informed marketing decisions that drive their business forward.
Utilizing Research Findings
Consumer Behavior Analysis: Coca-Cola carefully examines consumer behaviors and preferences identified through the research process. This includes understanding what motivates consumers to choose their products, their perception of the brand, and the factors influencing their purchasing decisions.
Product Innovation: By analyzing research findings, Coca-Cola identifies opportunities for product innovation and improvement. They use consumer feedback and preferences to develop new beverage variants, packaging, and formulations that cater to changing tastes and trends.
Target Market Segmentation: The research findings aid in segmenting the target market effectively. Coca-Cola identifies specific consumer groups and tailors marketing strategies to address the unique needs and preferences of each segment.
Brand Positioning: Based on the insights from the research, Coca-Cola refines its brand positioning to resonate better with the target audience. They strive to create emotional connections with consumers and reinforce their brand identity.
Advertising and Communication: Coca-Cola utilizes the research findings to craft compelling advertising and communication campaigns. The messaging is designed to evoke desired emotions and create a lasting impact on consumers’ minds.
Pricing Strategies: Research insights guide Coca-Cola in setting competitive and appropriate pricing for its products. They consider factors such as perceived value, competitor pricing, and consumer willingness to pay.
Making Informed Marketing Decisions
Market Entry and Expansion: The research findings enable Coca-Cola to identify potential new markets and expansion opportunities. They make informed decisions about entering new territories and adapting their products and marketing to suit local preferences.
Competitive Analysis: Coca-Cola analyzes competitor data obtained through research to understand their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis informs their competitive strategies and helps them stay ahead in the market.
Promotional Activities: Based on research insights, Coca-Cola designs promotional activities that resonate with the target audience. These include sponsorships, partnerships, and experiential marketing to create brand loyalty.
Channel Optimization: Research findings assist Coca-Cola in optimizing its distribution channels. They ensure their products reach the right locations and outlets efficiently.
Long-Term Planning: The actionable insights extracted from research contribute to Coca-Cola’s long-term strategic planning. They align their marketing objectives with broader business goals to achieve sustainable growth.
By effectively utilizing research findings and making informed marketing decisions, Coca-Cola stays at the forefront of the beverage industry. Their commitment to data-driven decision-making enables them to adapt to market changes, connect with consumers, and maintain their position as one of the world’s leading beverage brands.
Measuring Research Effectiveness

In the world of marketing research, the quest for effectiveness is paramount. For Coca-Cola, an iconic brand synonymous with refreshment, measuring the effectiveness of its research efforts is an essential step in ensuring its strategies align with ever-evolving consumer tastes and market dynamics.
Evaluating the Success of Marketing Research
To measure the effectiveness of marketing research, Coca-Cola employs a range of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that provide valuable insights into the impact of their research efforts on their marketing strategies. These KPIs help Coca-Cola assess the success of its research initiatives and make data-driven decisions for future marketing endeavors.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Research
1. Consumer Satisfaction: Coca-Cola tracks customer satisfaction levels to gauge how well their products and marketing efforts are resonating with consumers. High customer satisfaction indicates that the company’s marketing strategies align with customer needs and preferences.
2. Sales and Revenue: Monitoring changes in sales and revenue is a fundamental KPI for evaluating research effectiveness. An increase in sales and revenue following the implementation of marketing strategies indicates that the research has led to successful outcomes.
3. Market Share: Coca-Cola measures changes in market share to determine their brand’s performance relative to competitors. Positive growth in market share suggests that the marketing strategies based on research insights are helping the brand gain a competitive edge.
4. Brand Awareness: Assessing brand awareness metrics, such as brand recall and recognition, helps Coca-Cola understand how well its marketing messages are reaching and resonating with the target audience.
5. Customer Loyalty and Retention: Measuring customer loyalty and retention rates is crucial for Coca-Cola to determine if its marketing strategies are fostering long-term customer relationships.
6. Return on Investment (ROI): Coca-Cola evaluates the ROI of its marketing research initiatives to ensure that the resources invested in research are yielding favorable results in terms of revenue growth and profitability.
7. Marketing Effectiveness: Various metrics, such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and engagement metrics, help assess the effectiveness of specific marketing campaigns and initiatives driven by research insights.
8. New Product Performance: When Coca-Cola launches new products based on research findings, it tracks the performance of these products in terms of sales, consumer feedback, and market acceptance.
Assessing the Impact on Coca-Cola’s Marketing Strategies
Coca-Cola assesses the impact of research on its marketing strategies through a systematic approach that involves:
Data Analysis: Thorough analysis of research data allows Coca-Cola to identify trends, patterns, and actionable insights that inform its marketing strategies.
Comparative Analysis: By comparing pre-research and post-research marketing metrics, Coca-Cola can identify any significant improvements or changes in performance that can be attributed to the research efforts.
Continuous Monitoring: Coca-Cola continuously monitors the performance of marketing campaigns to gauge how well they align with the research insights and whether they are achieving the desired objectives.
Feedback and Iteration: Feedback from consumers, stakeholders, and internal teams is gathered to evaluate the success of marketing strategies and identify areas that may require adjustments or improvements.
Periodic Reviews: Regular reviews of marketing performance and research impact are conducted to ensure that marketing strategies remain aligned with changing consumer preferences and market dynamics.
By evaluating the success of marketing research using these KPIs and assessment methods, Coca-Cola can fine-tune its marketing strategies, optimize its efforts, and maintain its position as a market leader in the beverage industry.
Ethical Considerations in Marketing Research
In the complex and ever-evolving world of marketing research, the importance of ethical considerations cannot be overstated. For a global powerhouse like Coca-Cola, ethical integrity is a fundamental pillar that underpins their research practices. Let’s explore how Coca-Cola places ethics at the forefront of its marketing research process.
Maintaining Ethical Standards in Marketing Research
As a responsible and ethical company, Coca-Cola prioritizes maintaining high ethical standards in its marketing research practices. Ethical considerations are crucial to ensure that research is conducted responsibly, with respect for the rights and well-being of participants and stakeholders involved. Two key aspects of maintaining ethical standards in marketing research are:
1. Protecting Participant Privacy and Confidentiality
Coca-Cola takes steps to protect the privacy and confidentiality of research participants to safeguard their personal information and maintain trust. This involves:
Informed Consent: Before involving participants in any research activity, Coca-Cola seeks informed consent, ensuring that individuals are fully aware of their participation’s purpose, potential risks, and the use of their data.
Anonymity and Confidentiality: Coca-Cola anonymizes and secures personal data to ensure that individual participants’ identities are not linked to their responses or information.
Data Security: Implementing robust data security measures helps protect participant information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Compliance with Regulations: Coca-Cola adheres to relevant data protection and privacy laws to safeguard participant rights.
2. Addressing Potential Conflicts of Interest
To maintain research integrity, Coca-Cola actively addresses and mitigates potential conflicts of interest in marketing research. This involves:
Independent Research: Coca-Cola ensures that research is conducted impartially, free from any undue influence that may compromise the objectivity and validity of findings.
Transparency: The company discloses any potential conflicts of interest that may arise from financial or other relationships with stakeholders to maintain transparency and research integrity.
Ethics Committees: When applicable, Coca-Cola seeks guidance from ethics committees or review boards to assess and address potential ethical concerns in research projects.
Unbiased Reporting: Coca-Cola is committed to unbiased reporting of research findings, regardless of whether the results align with the company’s interests or expectations.
By maintaining ethical standards in marketing research, Coca-Cola demonstrates its commitment to responsible business practices and upholds the trust of its stakeholders, including consumers, investors, and the general public. Ethical conduct in research reinforces the credibility of the company’s marketing strategies and enhances its reputation as a socially responsible and trustworthy brand.
Balancing Research Goals and Ethical Responsibilities
In marketing research, ethical dilemmas may arise when there is a conflict between the research goals and ethical responsibilities. As a responsible and ethical company, Coca-Cola acknowledges the importance of striking a balance between achieving research objectives and upholding ethical principles. Some common ethical dilemmas in marketing research include:
1. Informed Consent and Deception
Ethical Dilemma: Researchers may face the challenge of obtaining informed consent without revealing the true purpose of the study, which could bias participants’ responses if they are aware of the research objectives.
Coca-Cola’s Approach: Coca-Cola ensures that participants provide informed consent while maintaining transparency about the research’s purpose. If the study requires limited deception, the company minimizes its use and justifies its necessity for achieving unbiased results.
2. Data Privacy and Use
Ethical Dilemma: Balancing the need to collect comprehensive data for research with protecting participants’ privacy and ensuring data is used responsibly.
Coca-Cola’s Approach: The company implements stringent data privacy measures, including anonymization and encryption, to protect participant information. Data is used only for the specified research purposes and is securely stored and managed to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Avoiding Harm and Bias
Ethical Dilemma: Ensuring that research efforts do not cause harm to participants or perpetuate biases that could lead to discriminatory practices.
Coca-Cola’s Approach: The company adheres to research practices that prioritize participant well-being and avoids any actions that may perpetuate biases. Coca-Cola seeks to create an inclusive and diverse research environment to foster unbiased insights.

4. Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Dilemma: Addressing potential conflicts of interest that may arise when research findings could impact Coca-Cola’s business decisions.
Coca-Cola’s Approach: The company maintains a commitment to unbiased reporting and independent research to avoid any conflicts of interest. Research findings are presented transparently and objectively, regardless of their implications for the company.
5. Reporting Accuracy
Ethical Dilemma: Balancing the need to present positive findings that reflect well on Coca-Cola with the responsibility to report accurate research results, including negative or unfavorable findings.
Coca-Cola’s Approach: The company ensures that research findings are reported accurately, without selective reporting. Transparency and integrity are prioritized to present a complete and unbiased picture of the research outcomes.
By recognizing and addressing ethical dilemmas in marketing research, Coca-Cola ensures that its research efforts are conducted responsibly, uphold participant rights, and contribute to the development of ethical marketing strategies. The company’s commitment to ethical conduct reinforces its reputation as a socially responsible and trustworthy brand.
Throughout this article, we have delved into the world of marketing research and its significance in driving the success of Coca-Cola. Let’s recapitulate the key takeaways from our exploration:
- Understanding the Research Process: Marketing research involves a systematic and structured approach to gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to gain insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive dynamics.
- Identifying Research Objectives: Clear and well-defined research objectives are essential for guiding the entire research process. Coca-Cola establishes specific goals to address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
- Choosing Research Methods: A variety of research methods, including qualitative and quantitative techniques, focus groups, surveys, and observational studies, are employed to collect data relevant to Coca-Cola’s research goals.
- Selecting Sampling Techniques: Random, stratified, or convenience sampling methods are used to ensure that the data collected is representative of the target population.
- Ensuring Data Accuracy and Reliability: To maintain the integrity of research findings, Coca-Cola employs robust data collection tools and techniques while adhering to ethical standards.
- Analyzing Research Findings: Qualitative and quantitative data analysis techniques help extract actionable insights from the gathered data. Identifying patterns and trends aids in decision-making.
- Utilizing Research Findings: Coca-Cola leverages research insights to inform its marketing strategies, improve product offerings, explore new territories, and respond to competitive threats.
- Evaluating Research Effectiveness: Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to assess the success of marketing research efforts, enabling continuous improvement.
- Addressing Ethical Considerations: Coca-Cola places a strong emphasis on maintaining ethical standards in marketing research, including participant privacy, avoiding harm, and transparency in reporting.
- Balancing Research Goals and Ethical Responsibilities: Ethical dilemmas are addressed by prioritizing participant well-being, data privacy, and unbiased reporting.
In conclusion, marketing research plays a vital role in Coca-Cola’s success by providing the organization with valuable insights into consumer preferences, market dynamics, and strategic opportunities. Through a comprehensive and ethical research approach, Coca-Cola ensures that its marketing efforts remain customer-centric, innovative, and socially responsible. By embracing research-driven decision-making, Coca-Cola maintains its position as a global leader in the beverage industry, continuously adapting to meet the evolving needs of its consumers.
Similar Posts
How to make an ai image generator, marketing strategy of apple company.

7 Steps to a Successful Marketing Public Relations Plan
Welcome to our blog post, “7 Steps to a Successful Marketing Public Relations Plan.” In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, a well-crafted marketing public relations (PR) plan is essential for businesses to effectively communicate their message, build brand credibility, and connect with their target audience. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through seven…
11 Marketing Research Examples
Marketing research is a critical component of any successful business strategy. It’s the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including its consumers, competitors, and industry trends. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of marketing research through 11 real-world examples that showcase its diverse applications and significance in…

Marketing Strategy Vs Non-Market Strategy
In the realm of business and organizational management, strategies play a crucial role in achieving success and gaining a competitive edge. Among the various types of strategies, marketing strategy and non-market strategy are two key approaches that businesses employ to achieve their goals. While both strategies aim to influence outcomes, they operate in different domains…
10 Importance Of Business Ethics Pdf
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: 10 + eighteen =
Marketing guides, case studies, examples, and inspiration.

Coca-Cola’s Marketing Strategy Explained
Coca-Cola, one of the most recognizable brands in the world, has a marketing strategy that is a study in branding excellence and innovative approaches. Here’s an exploration of Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy.
The Power of Branding
The power of branding in Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy is nothing short of remarkable. The brand has achieved an almost unparalleled level of recognition worldwide, largely thanks to its consistent and iconic visual identity. The distinctive script font, known as Spencerian script, and the classic red-and-white color scheme, have become synonymous with the Coca-Cola brand. This strong and consistent branding transcends cultural and linguistic barriers, making Coca-Cola one of the most recognized words across the globe.

Central to Coca-Cola’s branding success is its ability to evoke feelings of nostalgia and happiness. The company has smartly leveraged its long history, dating back to 1886, to create a sense of tradition and timelessness. This approach to branding goes beyond mere aesthetics; it’s about forging an emotional connection with consumers. The mere sight of a Coca-Cola logo or bottle can evoke fond memories, making it more than just a beverage; it becomes a symbol of joyful moments and shared experiences.
This emotional resonance is further amplified through Coca-Cola’s consistent messaging. The brand has always positioned itself as a purveyor of happiness and togetherness, themes that are universally appealing and enduring. Whether through its classic ads or modern digital campaigns, Coca-Cola has maintained this message, ensuring that the brand remains relevant and relatable to each new generation.
Coca-Cola’s branding strategy also leverages the power of familiarity and presence. By ensuring that their branding is visible in a wide range of contexts – from billboards in bustling cities to small shops in remote villages – Coca-Cola has woven itself into the fabric of daily life around the world. This omnipresence makes the brand feel both global and accessible, a difficult balance that few brands achieve successfully.
Coca-Cola’s branding is a masterclass in how visual identity, emotional resonance, consistent messaging, and strategic visibility can combine to create a powerful and enduring brand. This branding isn’t just about selling a product; it’s about selling an experience and a feeling, one that has resonated with consumers for over a century.
Global Yet Local
Coca-Cola’s “Global yet Local” marketing strategy is a deft balancing act that has played a crucial role in its global success. The company has mastered the art of maintaining a consistent global brand while adapting to local tastes, cultures, and market dynamics. This approach, often termed “glocalization,” allows Coca-Cola to resonate with consumers worldwide, making it not just a global brand, but a locally relevant one as well.
At the heart of this strategy is Coca-Cola’s understanding and respect for cultural differences. In various countries, Coca-Cola tailors its marketing campaigns, product flavors, and even packaging to align with local preferences and traditions. For example, while the classic Coca-Cola flavor is universal, the brand has introduced variations like Thums Up in India and Inca Kola in Peru, catering to local palates. Similarly, Coca-Cola’s advertising campaigns are carefully crafted to reflect local languages, values, and norms, ensuring that the brand’s message is both globally consistent and locally relevant.
This localization goes beyond product and marketing adaptations. Coca-Cola also engages in local community initiatives and partnerships, which helps to build a strong local presence and foster goodwill. By investing in community projects and local economies, Coca-Cola positions itself as a brand that is not just selling a product, but also contributing to the welfare of the community.
The success of Coca-Cola’s “Global yet Local” strategy is evident in its worldwide popularity. In every corner of the world, Coca-Cola is perceived not as a foreign brand, but as one that understands and values local culture. This deep level of local engagement has enabled Coca-Cola to build strong, enduring connections with consumers across diverse geographies.

Coca-Cola’s ability to strike the perfect balance between global appeal and local relevance is a testament to its astute marketing acumen. By respecting and embracing cultural differences, Coca-Cola has become a global brand that is deeply rooted in local communities around the world. This unique approach to globalization has not only driven the brand’s international growth but has also cemented its place as a beloved and familiar presence in the lives of consumers everywhere.
Emotional Marketing

Digital Marketing Prowess
Coca-Cola’s digital marketing prowess reflects its adaptability and forward-thinking approach in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Recognizing the shifting patterns of media consumption, particularly among younger demographics, Coca-Cola has invested heavily in digital platforms to engage with consumers in innovative and interactive ways.
Social media has been a key component of Coca-Cola’s digital strategy. The brand skillfully uses platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook to create a dialogue with its audience, rather than just broadcasting advertisements. Through these platforms, Coca-Cola shares engaging content, from eye-catching visuals and heartwarming stories to interactive campaigns. This approach not only increases brand visibility but also fosters a sense of community among Coca-Cola consumers, encouraging them to share their own experiences and stories with the brand.
In addition to social media, Coca-Cola has embraced the power of influencer marketing. Collaborating with popular influencers, the brand reaches new audiences in a more authentic and relatable way. These influencers, with their dedicated followings, lend a sense of credibility and trust to the brand, particularly important when trying to connect with a more skeptical and advertising-savvy younger audience.
Coca-Cola has also been innovative in its use of digital technology to enhance the customer experience. For instance, interactive vending machines and augmented reality experiences in their advertising have brought an element of fun and novelty, turning the simple act of buying a Coke into an engaging experience. This use of technology not only surprises and delights consumers but also cements Coca-Cola’s image as a modern, forward-thinking brand.
The company’s digital strategy also extends to data analytics. By leveraging data, Coca-Cola gains valuable insights into consumer preferences and behaviors, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing campaigns. This data-driven approach ensures that Coca-Cola’s digital marketing is not only creative but also strategic and results-oriented.
Coca-Cola’s adeptness in the digital realm demonstrates a keen understanding of modern marketing dynamics. By effectively utilizing social media, influencer partnerships, interactive technology, and data analytics, Coca-Cola continues to strengthen its brand presence and connect with consumers in the digital age. This digital marketing prowess is essential in maintaining Coca-Cola’s position as a leading global brand, resonating with consumers in an increasingly digital world.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Coca-Cola’s approach to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is an integral aspect of its overall marketing strategy, demonstrating the brand’s commitment to not just profit, but also people and the planet. The company has undertaken various initiatives aimed at creating a positive impact on society and the environment, which in turn reinforces its brand image and strengthens consumer trust.

One of the key areas of focus for Coca-Cola’s CSR efforts is environmental sustainability. The company has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon footprint, water usage, and waste. This includes initiatives for improving water efficiency in its manufacturing processes, investing in sustainable packaging solutions, and supporting water replenishment projects around the world. Coca-Cola’s efforts in developing plant-based materials for their bottles and commitment to recycling are significant steps towards addressing the global challenge of plastic waste.
Another critical dimension of Coca-Cola’s CSR is community engagement and support. The brand actively participates in various local and global community projects, ranging from disaster relief efforts to programs that support education, health, and women’s empowerment. By investing in communities, Coca-Cola builds strong relationships with consumers and stakeholders, showing that the brand is about more than just selling beverages; it’s about making a positive difference in the world.
Coca-Cola also recognizes the importance of promoting health and wellness, particularly given the criticism faced by the soft drink industry over health concerns. The company has responded by diversifying its product portfolio to include healthier options, reducing sugar in some of its drinks, and supporting programs that promote physical activity and healthy living.
Through its CSR initiatives, Coca-Cola not only addresses key social and environmental challenges but also enhances its brand reputation. These efforts demonstrate a corporate conscience, helping to build trust and loyalty among consumers who increasingly favor brands that are responsible and ethical. Coca-Cola’s commitment to CSR reflects a modern approach to business, where corporate success is intertwined with social and environmental stewardship.
Constant Innovation
Coca-Cola’s commitment to constant innovation is a cornerstone of its marketing strategy, keeping the brand relevant and exciting in an ever-changing market. This innovation extends beyond mere product development; it encompasses packaging, marketing campaigns, and exploring new market segments, ensuring that the brand remains fresh and appealing to a wide range of consumers.
One of the most notable areas of innovation for Coca-Cola is in its product line. While the classic Coca-Cola formula remains a global favorite, the company has continuously experimented with new flavors and products. This includes the introduction of Diet Coke, Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, and a variety of flavored options like Vanilla Coke and Cherry Coke. These variations cater to diverse consumer tastes and dietary preferences, allowing Coca-Cola to appeal to a broader audience.
Packaging innovation is another area where Coca-Cola excels. The company has introduced various bottle designs and sizes, some of which have become collectibles. Limited edition packaging, often tied to events or holidays, adds an element of excitement and exclusivity, encouraging consumers to purchase. The brand also invests in sustainable packaging solutions, aligning with environmental concerns and consumer trends towards eco-friendliness.
Coca-Cola’s marketing campaigns are equally innovative. The brand is known for its creative and often groundbreaking advertising, which frequently sets trends in the marketing world. From interactive billboards to augmented reality experiences, Coca-Cola’s marketing strategies are designed to engage consumers in unique and memorable ways.
Coca-Cola’s innovation extends to exploring new market segments. The company has ventured into different beverage categories, such as water, juices, and energy drinks, responding to changing consumer preferences and expanding its market reach.
Through its commitment to constant innovation, Coca-Cola not only keeps its existing product lines vibrant and relevant but also stays ahead of market trends. This forward-thinking approach ensures that the brand remains a leader in the beverage industry, continually attracting new customers while retaining its loyal fan base.
Event Sponsorship
Event sponsorship plays a pivotal role in Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy, enhancing its brand visibility and association with positivity and excitement. The company has a long history of sponsoring major events, which not only boosts its brand recognition but also aligns Coca-Cola with moments of joy and celebration.
Coca-Cola’s involvement with the Olympic Games is a prime example of its strategic event sponsorship. As one of the longest continuous corporate sponsors of the Olympics, Coca-Cola has been able to associate its brand with the universal values of unity, excellence, and joy that the Games represent. This association goes beyond mere advertising; it immerses the brand in the fabric of a global event that brings people together from around the world, mirroring Coca-Cola’s own brand message of fostering connection and happiness.
Another significant event in Coca-Cola’s sponsorship portfolio is the FIFA World Cup. As a sponsor of the world’s most-watched sporting event, Coca-Cola reaches millions of viewers and fans, connecting its brand with the passion and excitement of football. These sponsorships are not just about logo visibility; they involve interactive fan experiences, unique advertising campaigns, and special edition products, all of which create a more engaging connection with the audience.
Beyond these global spectacles, Coca-Cola also sponsors numerous local events, ranging from music festivals to community sports leagues. These smaller-scale sponsorships allow Coca-Cola to engage with more targeted audiences, building brand affinity in diverse communities. They also demonstrate Coca-Cola’s commitment to supporting a wide range of interests and activities, reinforcing the brand’s image as an integral part of people’s lives.
Event sponsorship is a powerful tool for Coca-Cola, effectively leveraging the excitement and emotional engagement of events to enhance its brand appeal. By aligning with events that resonate with its target audience, Coca-Cola not only amplifies its brand presence but also strengthens its connection with consumers, creating lasting impressions that go beyond the events themselves.
Coca-Cola’s Storytelling
Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy is deeply rooted in the art of storytelling, a technique that has enabled the brand to forge a powerful emotional connection with its audience. Through its advertisements and marketing campaigns, Coca-Cola doesn’t just sell a beverage; it tells stories that resonate with people’s emotions, aspirations, and experiences. This approach to storytelling is evident in the way Coca-Cola ads often depict relatable, heartwarming narratives that capture moments of joy, friendship, and family.
One of the key strengths of Coca-Cola’s storytelling is its ability to evoke nostalgia. The brand often harks back to its rich history, reminding consumers of its enduring presence in their lives. Classic campaigns, like the annual holiday ads featuring Santa Claus or the iconic polar bears, tap into the collective memory and emotions of generations of consumers. These stories transcend the product itself, positioning Coca-Cola as a symbol of happiness and tradition.
Coca-Cola also excels in creating narratives that reflect contemporary themes and values. The brand’s campaigns frequently showcase diversity, inclusivity, and unity, aligning with modern societal movements and sentiments. By crafting stories that mirror the current social landscape, Coca-Cola remains relevant and engaging to a broad audience.
Another aspect of Coca-Cola’s storytelling is its adaptability to various media formats. From traditional TV commercials to digital content and social media storytelling, Coca-Cola ensures that its narratives are accessible and engaging across different platforms. This multi-channel approach allows the brand to reach its audience wherever they are, making its stories a part of people’s daily digital interactions.
Through storytelling, Coca-Cola doesn’t just communicate its brand message; it creates memorable experiences that elicit emotional responses. These narratives help build a deeper, more personal connection with the brand, making Coca-Cola a part of life’s special moments. By continuing to tell compelling stories, Coca-Cola maintains its position not just as a beverage company, but as a purveyor of joy and shared experiences.
Coca-Cola’s Marketing Strategy in Summary
- Iconic Branding: Strong visual identity with recognizable script font and red-and-white color scheme, evoking nostalgia and global recognition.
- Glocalization: Tailoring marketing and products to local cultures while maintaining a consistent global presence.
- Emotional Marketing: Creating emotional connections with consumers through campaigns like “Share a Coke” and festive advertising.
- Digital Marketing: Leveraging social media, influencer partnerships, and digital technology for modern, interactive consumer engagement.
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Focusing on environmental sustainability, community engagement, and health initiatives to enhance brand image.
- Constant Innovation: Regularly introducing new flavors, packaging designs, and entering different beverage segments to keep the brand fresh and relevant.
- Event Sponsorship: Sponsoring major global events like the Olympics and FIFA World Cup for brand visibility and association with positivity.
- Storytelling: Utilizing narrative-driven advertisements to create relatable, emotionally engaging content across various media.
- Consumer Engagement: Fostering a sense of community and connection with interactive campaigns and personalized experiences.
- Data-Driven Marketing: Utilizing consumer data and analytics for targeted, effective marketing strategies.
This multifaceted approach has kept Coca-Cola at the forefront of the beverage industry for decades.
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy: A 2024 Comprehensive Case Study
Introduced over a century ago, Coca-Cola remains the world’s most consumed soda, illustrating its unparalleled ability to engage and captivate consumers globally. This case study explores the marketing strategy of Coca-Cola that continues to make it the leading manufacturer and licensor of nonalcoholic beverages, offering a staggering 3,500 varieties across more than 200 countries.

From Pharmacist's Elixir to Global Refreshment Drink
On May 8, 1886, Dr. John Pemberton created what is now known as Coca-Cola. Originally sold at a pharmacy in Atlanta as a medicinal elixir, Coca-Cola has transformed into a global refreshment enjoyed daily by millions.
What is Coca-Cola's Marketing Strategy?
The strategic marketing decisions made by Coca-Cola are largely responsible for its success. The company's approach includes comprehensive branding , widespread distribution, creative advertising, and innovative customer engagement tactics. Coca-Cola’s overarching vision continues to drive its global agenda, remaining focused on refreshing the world in mind, body, and spirit and making a difference to the people and communities it serves. This vision has enabled the company to maintain direction and momentum through periods of uncertainty.
Coca-Cola Target Audience
- Age : Targets youths (10–35 years) with celebrity endorsements and vibrant campaigns, while also catering to health-conscious older adults with products like Diet Coke and Coke Zero.
- Income and Family Size: Offers various packaging options across different price points to ensure affordability for students, middle-class families, and low-income groups.
- Geographical Segmentation: Tailors its formulas to suit regional tastes, such as sweeter versions in Asia, to resonate with local preferences.
- Gender: Differentiates offerings like Coca-Cola Light for women and Coke Zero for men, focusing on taste preferences linked to gender.
Advertising

From early advertisements in newspapers to groundbreaking campaigns like "I’d Like to Buy the World a Coke," Coca-Cola has always known the power of effective advertising. Each campaign not only promoted their product but also cemented Coca-Cola’s place in the cultural landscape. Coca-Cola’s advertising campaigns are designed to resonate on a global scale while maintaining local relevance. These strategies include:
- Creative Campaigns: Engaging and visually appealing ads that capture the essence of joy and refreshment.
- Emotional Branding : Utilizing regional languages and culturally relevant content to connect emotionally with consumers.
- Celebrity Partnerships: Collaborating with local and international celebrities to widen reach.
- Wide Coverage: Utilizing multiple channels, from traditional media to digital platforms.
- Engagement : Interactive campaigns and social media strategies to engage with a younger audience.
- Sponsorships : Long-standing partnerships with major events like the Olympics, FIFA World Cup, American Idol and popular TV shows enhancing brand visibility and consumer connection globally.
Coca-Cola has also embraced personalization in its past campaigns, from names on bottles to personalized marketing emails, enhancing consumer loyalty and personal connection with the brand.
1. "Share a Coke" Campaign
Launched initially in Australia in 2011, the "Share a Coke" campaign is one of the most celebrated and successful marketing strategies in Coca-Cola's history. The campaign was groundbreaking in its approach—replacing the iconic Coca-Cola logo on bottles with common first names. The idea was simple yet powerful: personalize the Coke experience to encourage sharing and create a personal connection with the product. Consumers could find bottles with their names or the names of friends and family, making it not just a purchase but a personalized social experience. The campaign heavily leveraged social media, encouraging people to share their Coca-Cola moments online with the hashtag #ShareaCoke, which amplified the campaign's reach exponentially. After its initial success in Australia, the campaign rolled out in over 80 countries with country-specific names and designs, each resonating with local audiences and cultural nuances.
2. "I'd Like to Buy the World a Coke" (Hilltop)
Originally aired in 1971, the "Hilltop" commercial for Coca-Cola, also known as "I'd Like to Buy the World a Coke," remains one of the most iconic advertisements in the history of television. Conceived by Bill Backer of McCann Erickson, the commercial featured a diverse group of young people from all over the world singing on a hilltop in Italy. The ad's simple yet profound message of hope and unity, expressed through the lyrics "I'd like to buy the world a home and furnish it with love," struck a chord during a time of political unrest and social change. The commercial became more than just an ad; it became a cultural icon, evoking feelings of peace and camaraderie at a global scale. The ad's popularity led to several remakes and re-releases over the decades, including a famous 1990 version featuring the original singers and their children, and a Super Bowl version in 2011.
3. "The Happiness Machine"
As part of its "Open Happiness" campaign, Coca-Cola launched "The Happiness Machine" video in 2010. The campaign featured a specially designed Coke vending machine placed in a college campus that dispensed not just bottles of Coke but surprising acts of "happiness" – from pizza and flowers to balloon animals. The video quickly went viral, thanks to its genuine, unscripted reactions and feel-good vibe. It amassed millions of views on YouTube, bringing widespread attention and goodwill toward the brand. This campaign emphasized Coca-Cola's focus on selling experiences and emotions associated with the brand, not just the product. It highlighted the brand’s commitment to spreading joy and happiness. The success of the "Happiness Machine" led to the creation of similar campaigns globally, harnessing the power of viral marketing and showing the brand's innovative approach to engaging with younger audiences.
Social Media and Digital Marketing

Coca-Cola has evolved its marketing strateg y from traditional mediums to a more integrated, multi-channel approach. The focus is now on building personal connections with consumers and leveraging digital platforms for targeted and engaging marketing campaigns. This shift has allowed Coca-Cola to maintain its relevance. Coca-Cola has embraced the digital age with robust online presence across platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and Snapchat. The brand leverages SEO , email marketing , content marketing , and video marketing to engage a broader audience effectively.
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy
Coca-Cola employs a dual-channel marketing strategy :
- Personal Channels: Direct interaction with consumers to build personal connections.
- Non-Personal Channels: A mix of traditional and digital media, including newspapers, TV, social media, email, and outdoor advertising, to ensure widespread reach.
Coca-Cola’s Marketing Mix: The 4 Ps
- Product Strategy: Coca-Cola boasts an extensive portfolio of 500 products, positioned strategically within the market to maximize reach and profitability. Coca-Cola’s commitment to maintaining its original formula and ensuring product quality has fostered deep brand loyalty . Even when new recipes were introduced, such as New Coke, the public’s attachment to the original formula brought it swiftly back. To cater to diverse consumer tastes, Coca-Cola has expanded its product portfolio to include juices, teas, coffees, and other beverages. This diversification strategy helps the company penetrate different market segments.
- Pricing Strategy: Initially maintained a constant price for decades, it now employs a flexible pricing strategy to remain competitive without compromising perceived quality. Coca-Cola's pricing strategy is carefully crafted to remain competitive while ensuring profitability.
- Place Strategy: Operates a vast distribution network across six global regions, supported by an extensive supply chain involving bottling partners and distributors, ensuring global product availability.
- Promotion Strategy: Invests heavily in diverse advertising strategies to maintain brand visibility and consumer engagement across various platforms.

Coca-Cola's Growth Strategy
- Winning More Consumers : Expanding the consumer base through effective marketing and innovative product offerings.
- Gaining Market Share: Outperforming competitors by understanding consumer needs better and responding quickly.
- Maintaining Strong System Economics: Ensuring profitability and sustainability across the supply chain.
- Strengthening Impact Across Stakeholders: Building a positive influence on consumers, communities, and environments.
- Equipping for Future Success: Preparing the organization to meet future challenges through continuous learning and adaptation.
Additionally, sustainability is integral to Coca-Cola's growth strategy. The company has focused on reducing its environmental footprint, using resources more efficiently, and promoting recycling. These efforts are aligned with its mission to make a difference, ensuring that growth is sustainable over the long term.
These objectives serve as the north stars for Coca-Cola, guiding all strategic decisions and initiatives.
Brand Portfolio Optimization
The iconic Coca-Cola logo and the classic bottle design are instantly recognizable worldwide, making branding a cornerstone of their strategy. This section examines how consistent branding across various platforms plays a critical role in Coca-Cola's marketing . Keeping a uniform visual identity and engaging in significant sponsorships have allowed Coca-Cola to remain relevant and beloved by generations. In a significant move to optimize its brand portfolio , Coca-Cola reduced its brand count from 400 to 200 master brands. This strategic decision was aimed at focusing on those brands that align with and support the company's growth objectives. By doing so, Coca-Cola has ensured that it invests in brands with the highest potential for growth and profitability, balancing global, regional, and local brands to cover all drinking occasions.

Managing Missteps With Grace
Coca-Cola’s ability to handle marketing and business errors gracefully, such as the New Coke debacle, shows a brand well-versed in crisis management and responsive public relations.
Lessons for Marketers
- Brand Identity is Essential: A strong, consistent brand identity is vital for long-term success.
- Prioritize Product Quality : High product quality should always be a priority, supporting marketing efforts and building consumer trust.
- Strategic Pricing is Key: Effective pricing strategies can significantly impact brand perception and customer loyalty.
- Explore New Markets: Expanding into new markets can drive growth and help maintain relevance.
- Responsive PR Matters: Managing public relations actively and effectively can mitigate potential damages and boost brand image.
What Makes Coca-Cola’s Marketing Strategy So Successful?
Coca-Cola’s enduring success is attributed to its ability to adapt to consumer needs, maintain a strong emotional connection with customers, and continuously innovate its marketing strategies .
Coca-Cola's success story is a playbook for marketers aiming to build a lasting brand that not only survives but thrives through changing times. By understanding and implementing these strategies, other brands can aim to replicate Coca-Cola's enduring appeal.
.jpg)
Please fill out the form below if you have any advertising and partnership inquiries.

- Our company
- Sustainability
- Social impact
years of refreshing the world
The Coca‑Cola Company has been refreshing the world and making a difference for over 138 years. Explore our Purpose & Vision, History and more.
- Purpose & Company Vision
- The Coca‑Cola System
- Our Board of Directors
- COCA-COLA HISTORY
- Our Origins
- Our First Bottle
- Sustainability History
- Advertising History
brands worldwide
We've established a portfolio of drinks that are best positioned to grow in an ever-changing marketplace.
From trademark Coca‑Cola to Sports, Juice & Dairy Drinks, Alcohol Ready-to-Drink Beverages and more, discover some of our most popular brands in North America and from around the world.
- Coca‑Cola
- + View More
- COFFEE & TEA
- Costa Coffee
- Gold Peak Tea
- JUICES & DAIRY
- Minute Maid
- Fresca Mixed
- Jack Daniel's & Coca‑Cola
- Simply Spiked
- Topo Chico Hard Seltzer
OUR PLANET MATTERS
Our purpose is to refresh the world and make a difference. See how our company and system employees make this possible every day and learn more about our areas of focus in sustainability.
- 2030 Water Strategy Key Goals
- Agriculture
- Principles for Sustainable Agriculture (PSAs)
- Collection Strategy
- Packaging Design
- Partnership
- In Our Products
- Sugar Reduction
- 2023 Environmental Update
- 2022 Business & Sustainability Report
- Sustainability & Governance Resource Center
PEOPLE MATTER
We aim to improve people's lives, from our employees to those who touch our business to the many communities we call home.
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Leadership Council
- Employee Groups
- People & Communities
- Women Empowerment
- Project Last Mile
- HUMAN RIGHTS
- Human Rights Governance
- Stories of IMPACT
- Sports & Entertainment
- Paris 2024 Hub
- Coca‑Cola Foundation
- Partnerships
- Supplier Diversity
We believe working at The Coca‑Cola Company is an opportunity to build a meaningful career while helping us make a real difference on a global scale.
- LIFE AT COCA-COLA
- Career Development
- Work With Us
- CAREER AREAS
- Early Career
- Experienced Professionals
- Accessible Workplace
- HIRING PROCESS
- Application Process
- Coca‑Cola Company Jobs
- Coca‑Cola System Jobs
GET THE LATEST
Catch up on the latest Coca‑Cola news from around the globe - from exciting brand innovation to the latest sustainability projects.
- WHAT OTHERS ARE READING
- Taste the Transformation: Coca‑Cola and Grammy-Award Winning Artist Rosalía Break Boundaries With Limited-Edition Coke Creation
- Coca‑Cola Brings Together Iconic Andy Warhol Painting with Illustrious Roster of Master Classics and Contemporary Works in New Global 'Masterpiece' Campaign
- A Deeper Look at Coca‑Cola's Emerging Business in Alcohol
- LATEST ARTICLES
- Coca‑Cola Zero Sugar Invites Fans to #TakeATaste
- Simply Mixology Raises the Bar of the At-Home Mocktail and Cocktail Experience
- Sprite, Fresca and Seagram's Tap Mark Ronson and Madlib to Create a 'Clear' Connection
- View all news

How Coca‑Cola is Pivoting its Innovation and Commercial Strategies in the COVID-19 Era
The coronavirus pandemic has triggered seismic shifts in shopping behavior, challenging The Coca‑Cola Company and creating new opportunities in everything from brand launches and marketing campaigns to routes to market and revenue growth management strategies.
“We have made progress on becoming more nimble and faster to adapt, faster to pivot,” Chief Financial Officer John Murphy said at the Deutsche Bank Global Consumer Conference on June 12. “There's broad alignment and an objective to emerge from the crisis with an even stronger leadership position. I don't think we could have been better prepared with respect to overall quality of leadership and clarity on the strategic initiatives required to navigate through this.”
Here are key takeaways from Murphy’s remarks about how Coca‑Cola is responding to the pandemic:
Innovation Will Continue to be Source of Growth
Coronavirus has prompted the company to accelerate efforts to streamline its beverage portfolio, eliminating under-performing “zombie” brands and adapting its innovation pipeline. “We’ve seen tremendous expansion… a lot of experimentation, a lot of learning, but the pipeline has become rather busy and clogged,” Murphy said. The company is now balancing an entrepreneurial edge with a tighter focus on fewer, bigger and more relevant offerings with potential to scale to multiple markets.
“We are becoming more disciplined and making the tougher decisions to prune back and allow the (brands) that have the opportunity to grow to get the attention they deserve,” Murphy said.
Staying Focused on Consumers and Local Communities
“It’s important to remain consumer-centric, to remain close to the consumer and understand how the consumer is adapting and behaving through the crisis, and what behaviors are short-term versus those that may stick,” Murphy said.
The company is keeping a close eye on new trends emerging in the COVID-19 era and innovating accordingly. “The area of hygiene, for example, is one I think is going to be very much on consumers’ minds going forward,” Murphy said. “Building touchless solutions, therefore, in the away-from-home channel is a big opportunity we need to tap into. There also will be some new motivations in the functional arena that we need to bring into our portfolio faster.”
Maintaining a hyper-local focus is equally important. “Winning locally is something that should not change through this type of period,” Murphy said. “In these last 12 weeks, the intersection of what we do for our local communities, particularly through our bottling partners, and how that's perceived by consumers has never been more important. We're extremely proud of how we have stepped up in that regard.”
Helping Retail and Foodservice Customers Adapt
Coca‑Cola teams around the world are collaborating with grocery customers to adjust supply chains and prioritize delivery and promotion of core brands and SKUs like multipacks as people adjust to stay-at-home lifestyles and make fewer, quicker stock-up trips. “We’re doing what we need to do to keep the attention of the shopper,” Murphy said.
With consumers reaching for established, trusted brands during uncertain times, Coca‑Cola is taking steps to keep top-selling offerings in stock and scaling back or postponing planned brand launches.
“Customers are very focused in times like these on what moves,” Murphy said, while noting that the U.S. launch of AHA flavored sparkling water is off to a strong start despite a challenging environment. “So, the bigger brands, the bigger SKUs, get a lot of preference. We've tailored our approach accordingly.”
The company will continue to invest in packaging that meets consumer needs at different price points while maximizing per-outlet revenue, Murphy said, citing recent successes in Latin America, the Philippines and South Africa.
Marriage of the Digital and Physical Worlds Accelerating
To support the surge in e-commerce channels – which have doubled in some countries as more people order necessities for home delivery – the Coca‑Cola system is prioritizing package options that are fit-for-purpose for online sales, boosting investment in digital promotions, increasing in-app visibility with e-delivery grocers, and piloting digitally enabled fulfillment models. Bottlers are investing in digital B2B solutions to manage customer orders and deliveries, and the company is rolling out a B2C platform in Latin America that lets consumers order beverages and groceries from local mom-and-pop stores for home delivery.
“We are investing in improving our digital shelf capability, bringing to the digital shelf the same discipline and quality we have learned to do on the physical shelf,” Murphy said. “There's a lot underway in this regard, and I see that accelerating and forming an even bigger part of our plans going into the next couple of years.”
Recovery to Vary by Market
With countries around the world in varying stages of the outbreak along with varying levels of economic impact, Murphy said the company expects recovery to be segmented.
“We're not going to see one letter of the alphabet describing the rate or speed of recovery,” he said. “A few markets will be more on a V-shape recovery, whereas a number of markets will be either U or a form of L, and I think it's too early to be able to profess what those varying shapes will look like.”
He added, “With so many variables, our focus remains very much the same as it has been in previous crises. And that’s to make sure our North Star is to emerge stronger…”
Click here to listen to John Murphy’s Q&A, and here to download the full transcript.
Related Content
Coca‑Cola Collaborates with Tech Partners to Create Bottle Prototype Made from 100% Plant-Based Sources

Coca‑Cola Launches ‘Real Magic’ Brand Platform, Including Refreshed Visual Identity and Global Campaign

Iteration, for Good: How Project Last Mile is Supporting COVID-19 Vaccine Distribution in Africa and Beyond

- Marketplace
- Future Proof
How Coca-Cola stays refreshed

Director, Thought Leadership, Kantar BrandZ
How can brands survive for over a century and remain strong? To answer that question, we need to look no further than Coca-Cola. Founded in Atlanta, Georgia, in 1886, today Kantar BrandZ finds Coca-Cola to be the 10 th most valuable brand in the 2023 Most Valuable Global Brands report . Sold around the world, Coca-Cola is served 1.9 billion times a day, making it the most valuable Food & Beverages brand.
Of the Top 10 Most Valuable Global Brands, most are tech latecomers like Apple, Google, and Microsoft; only Louis Vuitton is older than Coca-Cola. So how does a humble soft drink hold its own against such powerhouse brands? Kantar’s new BrandSnapshot tool reveals Coca-Cola to be a Star in many countries, well-known and appreciated by many consumers despite its age.
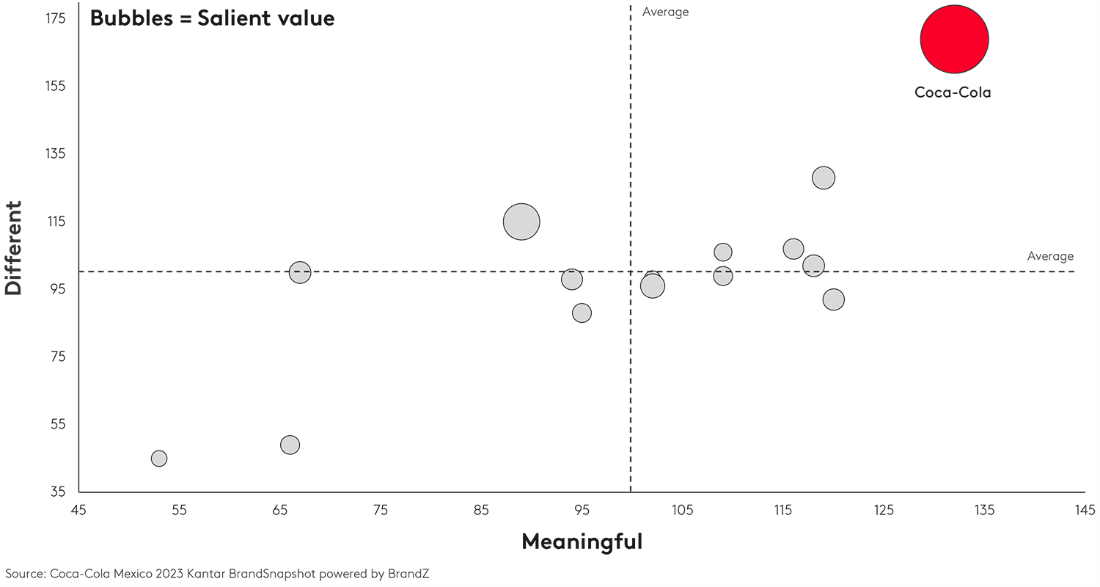
Strong brands like Coca-Cola have three important qualities:
- Meaningful: meeting peoples’ needs both functionally and emotionally
- Different: offering things others don’t and leading the way in their category
- Salient: coming to mind readily at key decision-making moments
Almost universal distribution, strong marketing, and a long heritage mean that Coca-Cola is one of the most salient brands in its category, but salience alone will not keep a brand strong. Consistent investment in innovation and marketing continually refreshes what Coca-Cola stands for in the minds of consumers, building on a positive and well-known experience to keep the brand not only salient but also meaningfully different.
Kantar’s BrandSnapshot finds that Coca-Cola has a justified premium in many countries, which can only happen when a brand is meaningful and different enough to create strong Pricing Power. This is no small achievement for a large, well-known brand, but Coca-Cola’s product and marketing initiatives have ensured that it is more likely to be perceived as having great advertising, tasting better, and being well-designed, even allowing for its size.
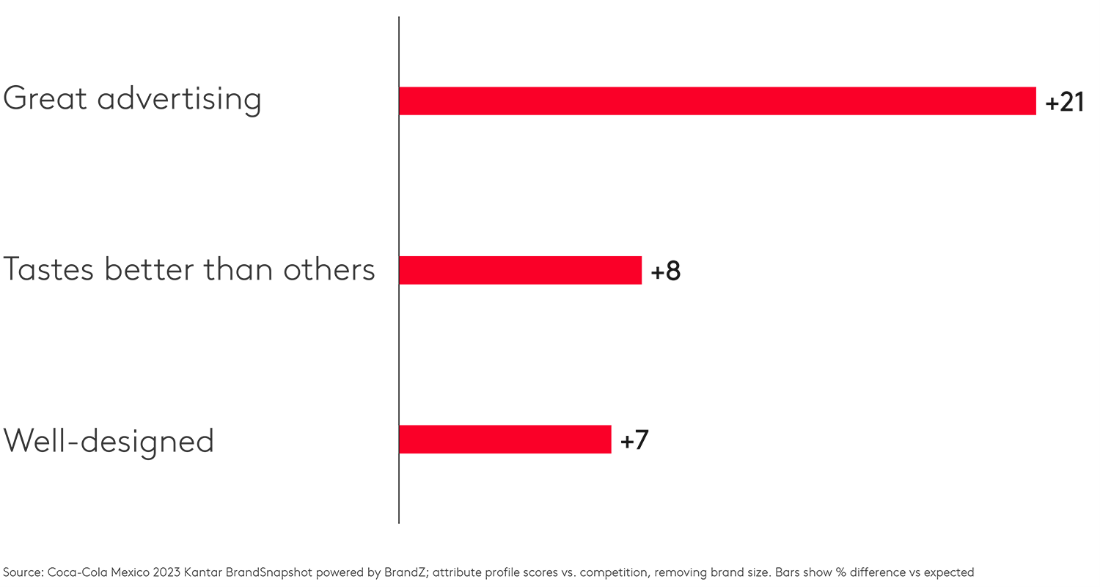
Coca-Cola makes a concerted effort to remain meaningful, different, and salient.
- The brand’s global innovation platform, Coca-Cola Creations, has led the brand’s foray into limited edition flavours, each launch coupled with a unique experience to engage younger consumers. While 2023’s futuristically flavoured Y3000 created with the help of AI may not have appealed to everyone, it still confirmed that the brand was at the forefront of recent trends.
- Strong brands do not wait to seize opportunities to enter new, profitable sub-categories, particularly if they can team up with another global icon. First launched in Mexico in 2022, Jack Daniel’s & Coca‑Cola RTD – a pre-mixed, canned cocktail – is now available in the US and UK. The Jack and Coke launch also exemplifies Coca-Cola’s willingness to leverage its global scale to identify likely winners.
- Coke’s history of inventive marketing strategies is legendary. From rebranding Father Christmas to animating polar bears, from The Happiness Factory to Share a Coke, which allowed people to buy a Coke with their name on, making human connections and breaking new ground are both key to Coke’s marketing. Mindful of its global reach, the brand is renowned for simple slogans that translate well around the world.
- Coca-Cola knows that being first to mind when someone wants a soft drink drives a huge part of its success. The brand leverages its distinctive brand assets effectively across all consumer touchpoints. To aid brand recognition, in 2015 the brand unified its packaging, including the logo, script, and ribbon on all variants, and integrating more of its iconic red into packaging.
The lesson is that refreshment is the key to long-term brand success. Brands that wish to emulate Coca-Cola’s longevity must innovate their offer so that they feel contemporary but without losing touch with their heritage.
Read more about the Kantar BrandZ Most Valuable Global Brands in the latest report, available at www.kantar.com/campaigns/brandz/global .
For an overarching view of brand performance, Kantar has launched a free interactive tool powered by BrandZ’s wealth of data and Meaningful Different Salient framework. Kantar BrandSnapshot delivers intelligence on 10,000 brands in 40+ markets, offering a quick read on a brand’s performance in a category. Explore for free on Kantar Marketplace today.
Want more like this?
Read: Revealed: the world’s most valuable brands of 2023
Read: Imbuing brands with a sense of difference
Read: Monzo and how it became the brand you can bank on

Coca-Cola Marketing Case Study

From the star ‘Coca-Cola’ drink to Inca Kola in North and South America, Vita in Africa, and Thumbs up in India, The Coca-Cola Company owns a product portfolio of more than 3500 products . With the presence in more than 200 countries and the daily average servings to 1.9 billion people, Coca-Cola Company has been listed as the world’s most valuable brand with 94% of the world’s population recognizing the red and white Coca-Cola brand Logo . Moreover, 3.1% of all beverages consumed around the world are Coca-Cola products. All this because of its great marketing strategy which we’ll discuss in this article on Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy .
Coca-Cola –
- has a Market capitalization of $192.8 Billion (as of May 2016).
- had 53 years of consecutive annual dividend increases.
- with the revenue of over $44.29 billion, is not just a company but an ECONOMY.
The world knows and has tasted the coca cola products. In fact, out of the 55 billion servings of all kinds of beverages drunk each day (other than water), 1.7 billion are Coca-Cola trademarked/licensed drinks.
Marketing history
Market research in the beginning.
It all started 130 years ago, in 1886, when a Confederate colonel in the Civil War, John Pemberton, wanted to create his own version of coca wine (cola with alcohol and cocaine) and sent his nephew Lewis Newman to conduct a market research with the samples to a local pharmacy (Jacobs pharmacy). This wasn’t a new idea back then. The original idea of Coca wines was discovered by a Parisian chemist named Angelo Mariani.
Pemberton’s sample was sold for 5 cents a glass and the feedback of the customers was relayed to him by his nephew. Hence, by the end of the year, Pemberton was ready with a unique recipe that was tailored to the customers taste.

Marketing Strategy In The Beginning
Pemberton soon had to make it non-alcoholic because of the laws prevailing in Atlanta. Once the product was launched, it was marketed by Pemberton as a “Brain Tonic” and “temperance drink” (anti-alcohol), claiming that it cured headaches, anxiety, depression, indigestion, and addiction. Cocaine was removed from Coke in 1903.
The name and the original (current) Trademark logo was the idea of Pemberton’s accountant Frank Robinson, who designed the logo in his own writing. Not changing the logo till date is the best strategy adopted by Coca-cola.
Soon after the formula was sold to Asa G Candler (in 1889), who converted it into a soda drink, the real marketing began.
Candler was a marketer. He distributed thousands of complimentary coca-cola glass coupons, along with souvenir calendars, clocks, etc. all depicting the trademark and made sure that the coca cola trademark was visible everywhere .
He also painted the syrup barrels red to differentiate Coca-Cola from others.
Various syrup manufacturing plants outside Atlanta were opened and in 1895, Candler announced about Coca-Cola being drunk in every state & territory in the US.

The Idea Of The Bottle
During Candler’s era, Coca-Cola was sold only through soda fountains. But two innovative minds, Benjamin F. Thomas and Joseph B. Whitehead, secured from Candler exclusive rights (at just $1) for bottled coca cola sales.
But Coca-Cola was so famous in the US that it was subjected to imitations. Early advertising campaigns like “Demand the genuine” and “Accept no substitutes” helped the brand somewhat but there was a dire need to differentiate. Hence, in 1916, the unique bottle of Coca-Cola was designed by the Root Glass Company of Terre Haute, Indiana. The trademark bottle design hasn’t been changed until now.

Coca-Cola Worldwide
In 1919, Candler sold the company to Robert Woodruff whose aim was to make Coca-Cola available to anyone, anytime and anyplace. Bottling plants were set up all over the world & coca cola became first truly global brand.
Robert Woodruff had some other strategies too. He was focused on maintaining a standard of excellence as the company scaled. He wanted to position Coca-Cola as a premium product that was worthy of more attention than any of its competitors. And he succeeded in it. Coca-Cola grew rapidly throughout the world.
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategies
The worldwide popularity of Coca-Cola was a result of simple yet groundbreaking marketing strategies like –
Consistency
Consistency can be seen from the logo to the bottle design & the price of the drink (the price was 5 cents from 1886 to 1959). Coca-Cola has kept it simple with every slogan revolving around the two terms ‘Enjoy’ and ‘happiness’.
From the star bottle to the calendars, watches and other unrelated products, Candler started the trend to make Coca-Cola visible everywhere. The company has followed the same branding strategy till now. Coca-Cola is everywhere and hence has the world’s most renowned logo.
Positioning
Coca-Cola didn’t position itself as a product. It was and it is an ‘Experience’ of happiness and joy.
Franchise model
The bottling rights were sold to different local entrepreneurs , which is continued till now. Hence, Coca-cola isn’t one giant company, it’s a system of many small companies reporting to one giant company.
Personalization & Socialization
Unlike other big companies, Coca-Cola has maintained its positioning as a social brand. It talks to the users. Coca-Cola isn’t a company anymore. It’s a part of us now. With its iconic advertising ideas which include “I’d Like to Buy the World a Coke” & “Share a Coke”, it has maintained a special spot in the heart of its users.
Diversification
Coca-Cola, after marking its presence all over the world, took its first step towards diversifying its portfolio in 1960 by buying Minute Maid. It now operates in all but 2 countries worldwide with a portfolio of more than 3500 brands.
Coca-Cola Marketing Facts
- Logo & bottle design hasn’t changed since the start.
- During its first year, Coca-Cola sold an average of 9 drinks a day.
- Norman Rockwell created art for Coke ads.
- Coke has had a huge role in shaping our image of Santa Clause.
- In the 1980s, the company attempted a “Coke in the Morning” campaign to try to win over coffee drinkers.
- In 1923, the company began selling bottles in packages of six, which became common practice in the beverage industry.
- Recently, it was in the news that Verizon acquired Yahoo for around $5 billion which is more or less the same amount the Coca-Cola Company spends on its advertisements.
- The number of employees working with the Coca-Cola Company (123,200 to be exact) is more than the population of many countries.

Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about Coca Cola Marketing Case Study in the comment section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.
Related Posts:


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy. Posted on September 16, 2024 by Daniel Pereira. The Coca-Cola Marketing Strategy is an exemplary model that has propelled the brand to unparalleled success in the global marketplace. Unlike traditional marketing methodologies, Coca-Cola’s approach has been nothing short of revolutionary, reshaping how businesses ...
Marketing research serves as the foundation upon which a company’s business strategy is built. It empowers decision-makers at Coca-Cola to identify opportunities and challenges, anticipate market shifts, and tailor their products and messaging to meet consumer needs.
The Coca-Cola Marketing Research Journey showcases the vital role of understanding consumer preferences in building a successful brand. Through a combination of focus groups, surveys,...
The pandemic accelerated Coke’s transformation into a digitized, data-driven organization that can execute marketing, commercial, sales and distribution strategies in both the online and physical worlds.
Coca-Cola, one of the most recognizable brands in the world, has a marketing strategy that is a study in branding excellence and innovative approaches. Here’s an exploration of Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy. Table of Contents. The Power of Branding. Global Yet Local. Emotional Marketing. Digital Marketing Prowess.
This case study explores the marketing strategy of Coca-Cola that continues to make it the leading manufacturer and licensor of nonalcoholic beverages, offering a staggering 3,500 varieties across more than 200 countries.
When your annual global marketing budget approaches $4 billion, your marketing strategy should be flawless. Here's how Coca-Cola keeps its marketing strategy focused.
The coronavirus pandemic has triggered seismic shifts in shopping behavior, challenging The Coca‑Cola Company and creating new opportunities in everything from brand launches and marketing campaigns to routes to market and revenue growth management strategies.
Agile Market Research BrandZ Brand. How can brands survive for over a century and remain strong? To answer that question, we need to look no further than Coca-Cola. Founded in Atlanta, Georgia, in 1886, today Kantar BrandZ finds Coca-Cola to be the 10 th most valuable brand in the 2023 Most Valuable Global Brands report.
Coca-Cola Marketing Facts. Logo & bottle design hasn’t changed since the start. During its first year, Coca-Cola sold an average of 9 drinks a day. Norman Rockwell created art for Coke ads. Coke has had a huge role in shaping our image of Santa Clause.