How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
There’s general research planning; then there’s an official, well-executed research plan. Whatever data-driven research project you’re gearing up for, the research plan will be your framework for execution. The plan should also be detailed and thorough, with a diligent set of criteria to formulate your research efforts. Not including these key elements in your plan can be just as harmful as having no plan at all.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project.
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement, devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes, demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:

Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews: this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies: this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting: participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups: use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies: ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys: get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing: tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing: ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project. Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty. But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

The scope of work should include the following sections: (1) introduction, (2) statement of objectives, (3) materials and methods, (4) expected results/format of report, and (5) literature citations. Your submitted scope of work should include the following:
1. The Cover Sheet . The cover sheet must include the tentative title, date, author(s), and MP advisor(s). The cover sheet must also include the author(s) and advisor(s) signature(s) to demonstrate faculty approval (Visit #1 on the Final Report page for more information on Cover Sheets or download the template ). 2. Introduction . Describe the problem you will be working on and why it is important. Include a concise literature review to relate your problem to previous work and set the stage for the approach you will take. If applicable, describe the client involved and their interest in the project. [2-4 pages] 3. Objectives . State the research questions your MP will answer or the hypotheses you will test. Be specific and succinct. You should be able to list your questions or hypotheses as a series of no more than 3 or 4 concrete bullet points. While you may fine-tune these questions after you begin your work, the initial description of your methods and expected results should follow directly from these objectives. [<1 page] 4. Methods and Sources of Support . Describe the methods/approach you plan to use including, as appropriate, your research approach, data or means of data collection, and plans for data analysis. Be specific and identify significant subtasks related to each part of your project. State any research support needed in terms of supplies, space, equipment and money. If needed, identify source(s) of financial support (e.g., case study funds, research project of professor, school support, grant, etc.). Note whether you will require Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval for data collection involving human subjects, or whether you will operate under a nondisclosure agreement . [2-3 pages] 5. Expected Results and Format of Report . Identify the expected results of the project and/or the deliverables to be produced (e.g., management plan, geospatial tool, scientific publication, policy recommendations, computer model, etc.). State the format of the final product and its intended audience. If appropriate, identify likely journals for publication of your research. [1-2 pages] 6. Literary Citations . Include full, standard citations for any references referred to in the text of your proposal. The Nicholas School does not require MPs to adhere to one specific citation style as long as citations are formatted consistently throughout the final document. Choose the appropriate manual of style for your project (for guidance, see Duke Libraries citation resources ). 7. Faculty . List all faculty who have agreed to serve as advisors or cooperators in your project, along with their affiliations (e.g., school or department). Indicate the primary adviser(s) responsible for evaluating the project.
Part II: Project Timeline
Part two should contain the timeline with anticipated deliverables, and may be attached as a separate document, if using Excel or other project management formats. Timeline of Tasks, Deliverables, and Events . Outline the various steps of project completion from start to finish. Include all significant milestones and recurring meetings with your teammates (if applicable) and MP advisor. For example, this could include completion of your literature review and other background research, as well as intermediate steps related to your data collection and planned analysis. It is highly recommended that you use a Gantt chart or an equivalent Excel spreadsheet (e.g. with individual tasks and milestones as rows and dates in columns), with ongoing tasks specified at a biweekly resolution. Your timeline should also include standing client meetings, if relevant.
Part III: Team Charter
The team charter should outline roles and responsibilities of the team and advisor. All students, including those completing an individual MPs, must include a team charter in the final Work Plan. If you are participating in an individual project, you and your MP advisor are considered a “team”.
Your team charter should include the following: 1. Team Roles and Responsibilities . Assign each team member a role and associated responsibilities to be fulfilled during completion of the MP. 2. Regular Meeting Schedule. Outline how often, in what way, and with whom your MP team will meet. This includes regular team meetings, as well as standing meetings with your advisor and, if relevant, client. Frequency and content of the meetings is up to the collective discretion of the team. 3. Team Expectations . Describe any additional agreements your MP team comes up with. (e.g., how to handle potential conflicts, preferred means of communication, data sharing and storage, etc.) 4. Team Purpose and Mission . Describe the top priorities and goals of each individual team member during the course of the project. 5. Team Cohesion and Conflict Resolution. Include a brief description that addresses these questions: How will your team resolve conflict? How can you most effectively handle scenarios in which team members are not pulling their weight or not living up to the expectations outlined in this charter? How will you have difficult conversations? What steps will you take to understand and know each other better? How do you want to promote ongoing integration and camaraderie within the team?
Site Login >
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, create a research plan: research plan.
- Research Plan
- Literature Review
- Ulrich's Global Serials Directory
- Related Guides
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan
1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question
2. Research methodology - describes your approach to the research question
3. Literature review, critical evaluation and synthesis - systematic approach to locating,
reviewing and evaluating the work (text, exhibitions, critiques, etc) relating to your topic
4. Communication - geared toward an intended audience, shows evidence of your inquiry
Research conceptualization refers to the ability to identify specific research questions, problems or opportunities that are worthy of inquiry. Research conceptualization also includes the skills and discipline that go beyond the initial moment of conception, and which enable the researcher to formulate and develop an idea into something researchable ( Newbury 373).
Research methodology refers to the knowledge and skills required to select and apply appropriate methods to carry through the research project ( Newbury 374) .
Method describes a single mode of proceeding; methodology describes the overall process.
Method - a way of doing anything especially according to a defined and regular plan; a mode of procedure in any activity
Methodology - the study of the direction and implications of empirical research, or the sustainability of techniques employed in it; a method or body of methods used in a particular field of study or activity *Browse a list of research methodology books or this guide on Art & Design Research
Literature Review, critical evaluation & synthesis
A literature review is a systematic approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating the published work and work in progress of scholars, researchers, and practitioners on a given topic.
Critical evaluation and synthesis is the ability to handle (or process) existing sources. It includes knowledge of the sources of literature and contextual research field within which the person is working ( Newbury 373).
Literature reviews are done for many reasons and situations. Here's a short list:
Sources to consult while conducting a literature review:
Online catalogs of local, regional, national, and special libraries
meta-catalogs such as worldcat , Art Discovery Group , europeana , world digital library or RIBA
subject-specific online article databases (such as the Avery Index, JSTOR, Project Muse)
digital institutional repositories such as Digital Commons @RISD ; see Registry of Open Access Repositories
Open Access Resources recommended by RISD Research LIbrarians
works cited in scholarly books and articles
print bibliographies
the internet-locate major nonprofit, research institutes, museum, university, and government websites
search google scholar to locate grey literature & referenced citations
trade and scholarly publishers
fellow scholars and peers
Communication
Communication refers to the ability to
- structure a coherent line of inquiry
- communicate your findings to your intended audience
- make skilled use of visual material to express ideas for presentations, writing, and the creation of exhibitions ( Newbury 374)
Research plan framework: Newbury, Darren. "Research Training in the Creative Arts and Design." The Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts . Ed. Michael Biggs and Henrik Karlsson. New York: Routledge, 2010. 368-87. Print.
About the author
Except where otherwise noted, this guide is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution license
source document
Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 20, 2023 5:05 PM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/researchplan
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Research Plan
- Research plan definition
- Purpose of a research plan
- Research plan structure
- Step-by-step writing guide
Tips for creating a research plan
- Research plan examples
Research plan: definition and significance
What is the purpose of a research plan.
- Bridging gaps in the existing knowledge related to their subject.
- Reinforcing established research about their subject.
- Introducing insights that contribute to subject understanding.
Research plan structure & template
Introduction.
- What is the existing knowledge about the subject?
- What gaps remain unanswered?
- How will your research enrich understanding, practice, and policy?
Literature review
Expected results.
- Express how your research can challenge established theories in your field.
- Highlight how your work lays the groundwork for future research endeavors.
- Emphasize how your work can potentially address real-world problems.
5 Steps to crafting an effective research plan
Step 1: define the project purpose, step 2: select the research method, step 3: manage the task and timeline, step 4: write a summary, step 5: plan the result presentation.
- Brainstorm Collaboratively: Initiate a collective brainstorming session with peers or experts. Outline the essential questions that warrant exploration and answers within your research.
- Prioritize and Feasibility: Evaluate the list of questions and prioritize those that are achievable and important. Focus on questions that can realistically be addressed.
- Define Key Terminology: Define technical terms pertinent to your research, fostering a shared understanding. Ensure that terms like “church” or “unreached people group” are well-defined to prevent ambiguity.
- Organize your approach: Once well-acquainted with your institution’s regulations, organize each aspect of your research by these guidelines. Allocate appropriate word counts for different sections and components of your research paper.
Research plan example

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Illustration by James Round
How to plan a research project
Whether for a paper or a thesis, define your question, review the work of others – and leave yourself open to discovery.
by Brooke Harrington + BIO
is professor of sociology at Dartmouth College in New Hampshire. Her research has won international awards both for scholarly quality and impact on public life. She has published dozens of articles and three books, most recently the bestseller Capital without Borders (2016), now translated into five languages.
Edited by Sam Haselby
Need to know
‘When curiosity turns to serious matters, it’s called research.’ – From Aphorisms (1880-1905) by Marie von Ebner-Eschenbach
Planning research projects is a time-honoured intellectual exercise: one that requires both creativity and sharp analytical skills. The purpose of this Guide is to make the process systematic and easy to understand. While there is a great deal of freedom and discovery involved – from the topics you choose, to the data and methods you apply – there are also some norms and constraints that obtain, no matter what your academic level or field of study. For those in high school through to doctoral students, and from art history to archaeology, research planning involves broadly similar steps, including: formulating a question, developing an argument or predictions based on previous research, then selecting the information needed to answer your question.
Some of this might sound self-evident but, as you’ll find, research requires a different way of approaching and using information than most of us are accustomed to in everyday life. That is why I include orienting yourself to knowledge-creation as an initial step in the process. This is a crucial and underappreciated phase in education, akin to making the transition from salaried employment to entrepreneurship: suddenly, you’re on your own, and that requires a new way of thinking about your work.
What follows is a distillation of what I’ve learned about this process over 27 years as a professional social scientist. It reflects the skills that my own professors imparted in the sociology doctoral programme at Harvard, as well as what I learned later on as a research supervisor for Ivy League PhD and MA students, and then as the author of award-winning scholarly books and articles. It can be adapted to the demands of both short projects (such as course term papers) and long ones, such as a thesis.
At its simplest, research planning involves the four distinct steps outlined below: orienting yourself to knowledge-creation; defining your research question; reviewing previous research on your question; and then choosing relevant data to formulate your own answers. Because the focus of this Guide is on planning a research project, as opposed to conducting a research project, this section won’t delve into the details of data-collection or analysis; those steps happen after you plan the project. In addition, the topic is vast: year-long doctoral courses are devoted to data and analysis. Instead, the fourth part of this section will outline some basic strategies you could use in planning a data-selection and analysis process appropriate to your research question.
Step 1: Orient yourself
Planning and conducting research requires you to make a transition, from thinking like a consumer of information to thinking like a producer of information. That sounds simple, but it’s actually a complex task. As a practical matter, this means putting aside the mindset of a student, which treats knowledge as something created by other people. As students, we are often passive receivers of knowledge: asked to do a specified set of readings, then graded on how well we reproduce what we’ve read.
Researchers, however, must take on an active role as knowledge producers . Doing research requires more of you than reading and absorbing what other people have written: you have to engage in a dialogue with it. That includes arguing with previous knowledge and perhaps trying to show that ideas we have accepted as given are actually wrong or incomplete. For example, rather than simply taking in the claims of an author you read, you’ll need to draw out the implications of those claims: if what the author is saying is true, what else does that suggest must be true? What predictions could you make based on the author’s claims?
In other words, rather than treating a reading as a source of truth – even if it comes from a revered source, such as Plato or Marie Curie – this orientation step asks you to treat the claims you read as provisional and subject to interrogation. That is one of the great pieces of wisdom that science and philosophy can teach us: that the biggest advances in human understanding have been made not by being correct about trivial things, but by being wrong in an interesting way . For example, Albert Einstein was wrong about quantum mechanics, but his arguments about it with his fellow physicist Niels Bohr have led to some of the biggest breakthroughs in science, even a century later.
Step 2: Define your research question
Students often give this step cursory attention, but experienced researchers know that formulating a good question is sometimes the most difficult part of the research planning process. That is because the precise language of the question frames the rest of the project. It’s therefore important to pose the question carefully, in a way that’s both possible to answer and likely to yield interesting results. Of course, you must choose a question that interests you, but that’s only the beginning of what’s likely to be an iterative process: most researchers come back to this step repeatedly, modifying their questions in light of previous research, resource limitations and other considerations.
Researchers face limits in terms of time and money. They, like everyone else, have to pose research questions that they can plausibly answer given the constraints they face. For example, it would be inadvisable to frame a project around the question ‘What are the roots of the Arab-Israeli conflict?’ if you have only a week to develop an answer and no background on that topic. That’s not to limit your imagination: you can come up with any question you’d like. But it typically does require some creativity to frame a question that you can answer well – that is, by investigating thoroughly and providing new insights – within the limits you face.
In addition to being interesting to you, and feasible within your resource constraints, the third and most important characteristic of a ‘good’ research topic is whether it allows you to create new knowledge. It might turn out that your question has already been asked and answered to your satisfaction: if so, you’ll find out in the next step of this process. On the other hand, you might come up with a research question that hasn’t been addressed previously. Before you get too excited about breaking uncharted ground, consider this: a lot of potentially researchable questions haven’t been studied for good reason ; they might have answers that are trivial or of very limited interest. This could include questions such as ‘Why does the area of a circle equal π r²?’ or ‘Did winter conditions affect Napoleon’s plans to invade Russia?’ Of course, you might be able to make the argument that a seemingly trivial question is actually vitally important, but you must be prepared to back that up with convincing evidence. The exercise in the ‘Learn More’ section below will help you think through some of these issues.
Finally, scholarly research questions must in some way lead to new and distinctive insights. For example, lots of people have studied gender roles in sports teams; what can you ask that hasn’t been asked before? Reinventing the wheel is the number-one no-no in this endeavour. That’s why the next step is so important: reviewing previous research on your topic. Depending on what you find in that step, you might need to revise your research question; iterating between your question and the existing literature is a normal process. But don’t worry: it doesn’t go on forever. In fact, the iterations taper off – and your research question stabilises – as you develop a firm grasp of the current state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 3: Review previous research
In academic research, from articles to books, it’s common to find a section called a ‘literature review’. The purpose of that section is to describe the state of the art in knowledge on the research question that a project has posed. It demonstrates that researchers have thoroughly and systematically reviewed the relevant findings of previous studies on their topic, and that they have something novel to contribute.
Your own research project should include something like this, even if it’s a high-school term paper. In the research planning process, you’ll want to list at least half a dozen bullet points stating the major findings on your topic by other people. In relation to those findings, you should be able to specify where your project could provide new and necessary insights. There are two basic rhetorical positions one can take in framing the novelty-plus-importance argument required of academic research:
- Position 1 requires you to build on or extend a set of existing ideas; that means saying something like: ‘Person A has argued that X is true about gender; this implies Y, which has not yet been tested. My project will test Y, and if I find evidence to support it, that will change the way we understand gender.’
- Position 2 is to argue that there is a gap in existing knowledge, either because previous research has reached conflicting conclusions or has failed to consider something important. For example, one could say that research on middle schoolers and gender has been limited by being conducted primarily in coeducational environments, and that findings might differ dramatically if research were conducted in more schools where the student body was all-male or all-female.
Your overall goal in this step of the process is to show that your research will be part of a larger conversation: that is, how your project flows from what’s already known, and how it advances, extends or challenges that existing body of knowledge. That will be the contribution of your project, and it constitutes the motivation for your research.
Two things are worth mentioning about your search for sources of relevant previous research. First, you needn’t look only at studies on your precise topic. For example, if you want to study gender-identity formation in schools, you shouldn’t restrict yourself to studies of schools; the empirical setting (schools) is secondary to the larger social process that interests you (how people form gender identity). That process occurs in many different settings, so cast a wide net. Second, be sure to use legitimate sources – meaning publications that have been through some sort of vetting process, whether that involves peer review (as with academic journal articles you might find via Google Scholar) or editorial review (as you’d find in well-known mass media publications, such as The Economist or The Washington Post ). What you’ll want to avoid is using unvetted sources such as personal blogs or Wikipedia. Why? Because anybody can write anything in those forums, and there is no way to know – unless you’re already an expert – if the claims you find there are accurate. Often, they’re not.
Step 4: Choose your data and methods
Whatever your research question is, eventually you’ll need to consider which data source and analytical strategy are most likely to provide the answers you’re seeking. One starting point is to consider whether your question would be best addressed by qualitative data (such as interviews, observations or historical records), quantitative data (such as surveys or census records) or some combination of both. Your ideas about data sources will, in turn, suggest options for analytical methods.
You might need to collect your own data, or you might find everything you need readily available in an existing dataset someone else has created. A great place to start is with a research librarian: university libraries always have them and, at public universities, those librarians can work with the public, including people who aren’t affiliated with the university. If you don’t happen to have a public university and its library close at hand, an ordinary public library can still be a good place to start: the librarians are often well versed in accessing data sources that might be relevant to your study, such as the census, or historical archives, or the Survey of Consumer Finances.
Because your task at this point is to plan research, rather than conduct it, the purpose of this step is not to commit you irrevocably to a course of action. Instead, your goal here is to think through a feasible approach to answering your research question. You’ll need to find out, for example, whether the data you want exist; if not, do you have a realistic chance of gathering the data yourself, or would it be better to modify your research question? In terms of analysis, would your strategy require you to apply statistical methods? If so, do you have those skills? If not, do you have time to learn them, or money to hire a research assistant to run the analysis for you?
Please be aware that qualitative methods in particular are not the casual undertaking they might appear to be. Many people make the mistake of thinking that only quantitative data and methods are scientific and systematic, while qualitative methods are just a fancy way of saying: ‘I talked to some people, read some old newspapers, and drew my own conclusions.’ Nothing could be further from the truth. In the final section of this guide, you’ll find some links to resources that will provide more insight on standards and procedures governing qualitative research, but suffice it to say: there are rules about what constitutes legitimate evidence and valid analytical procedure for qualitative data, just as there are for quantitative data.
Circle back and consider revising your initial plans
As you work through these four steps in planning your project, it’s perfectly normal to circle back and revise. Research planning is rarely a linear process. It’s also common for new and unexpected avenues to suggest themselves. As the sociologist Thorstein Veblen wrote in 1908 : ‘The outcome of any serious research can only be to make two questions grow where only one grew before.’ That’s as true of research planning as it is of a completed project. Try to enjoy the horizons that open up for you in this process, rather than becoming overwhelmed; the four steps, along with the two exercises that follow, will help you focus your plan and make it manageable.
Key points – How to plan a research project
- Planning a research project is essential no matter your academic level or field of study. There is no one ‘best’ way to design research, but there are certain guidelines that can be helpfully applied across disciplines.
- Orient yourself to knowledge-creation. Make the shift from being a consumer of information to being a producer of information.
- Define your research question. Your question frames the rest of your project, sets the scope, and determines the kinds of answers you can find.
- Review previous research on your question. Survey the existing body of relevant knowledge to ensure that your research will be part of a larger conversation.
- Choose your data and methods. For instance, will you be collecting qualitative data, via interviews, or numerical data, via surveys?
- Circle back and consider revising your initial plans. Expect your research question in particular to undergo multiple rounds of refinement as you learn more about your topic.
Good research questions tend to beget more questions. This can be frustrating for those who want to get down to business right away. Try to make room for the unexpected: this is usually how knowledge advances. Many of the most significant discoveries in human history have been made by people who were looking for something else entirely. There are ways to structure your research planning process without over-constraining yourself; the two exercises below are a start, and you can find further methods in the Links and Books section.
The following exercise provides a structured process for advancing your research project planning. After completing it, you’ll be able to do the following:
- describe clearly and concisely the question you’ve chosen to study
- summarise the state of the art in knowledge about the question, and where your project could contribute new insight
- identify the best strategy for gathering and analysing relevant data
In other words, the following provides a systematic means to establish the building blocks of your research project.
Exercise 1: Definition of research question and sources
This exercise prompts you to select and clarify your general interest area, develop a research question, and investigate sources of information. The annotated bibliography will also help you refine your research question so that you can begin the second assignment, a description of the phenomenon you wish to study.
Jot down a few bullet points in response to these two questions, with the understanding that you’ll probably go back and modify your answers as you begin reading other studies relevant to your topic:
- What will be the general topic of your paper?
- What will be the specific topic of your paper?
b) Research question(s)
Use the following guidelines to frame a research question – or questions – that will drive your analysis. As with Part 1 above, you’ll probably find it necessary to change or refine your research question(s) as you complete future assignments.
- Your question should be phrased so that it can’t be answered with a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’.
- Your question should have more than one plausible answer.
- Your question should draw relationships between two or more concepts; framing the question in terms of How? or What? often works better than asking Why ?
c) Annotated bibliography
Most or all of your background information should come from two sources: scholarly books and journals, or reputable mass media sources. You might be able to access journal articles electronically through your library, using search engines such as JSTOR and Google Scholar. This can save you a great deal of time compared with going to the library in person to search periodicals. General news sources, such as those accessible through LexisNexis, are acceptable, but should be cited sparingly, since they don’t carry the same level of credibility as scholarly sources. As discussed above, unvetted sources such as blogs and Wikipedia should be avoided, because the quality of the information they provide is unreliable and often misleading.
To create an annotated bibliography, provide the following information for at least 10 sources relevant to your specific topic, using the format suggested below.
Name of author(s):
Publication date:
Title of book, chapter, or article:
If a chapter or article, title of journal or book where they appear:
Brief description of this work, including main findings and methods ( c 75 words):
Summary of how this work contributes to your project ( c 75 words):
Brief description of the implications of this work ( c 25 words):
Identify any gap or controversy in knowledge this work points up, and how your project could address those problems ( c 50 words):
Exercise 2: Towards an analysis
Develop a short statement ( c 250 words) about the kind of data that would be useful to address your research question, and how you’d analyse it. Some questions to consider in writing this statement include:
- What are the central concepts or variables in your project? Offer a brief definition of each.
- Do any data sources exist on those concepts or variables, or would you need to collect data?
- Of the analytical strategies you could apply to that data, which would be the most appropriate to answer your question? Which would be the most feasible for you? Consider at least two methods, noting their advantages or disadvantages for your project.
Links & books
One of the best texts ever written about planning and executing research comes from a source that might be unexpected: a 60-year-old work on urban planning by a self-trained scholar. The classic book The Death and Life of Great American Cities (1961) by Jane Jacobs (available complete and free of charge via this link ) is worth reading in its entirety just for the pleasure of it. But the final 20 pages – a concluding chapter titled ‘The Kind of Problem a City Is’ – are really about the process of thinking through and investigating a problem. Highly recommended as a window into the craft of research.
Jacobs’s text references an essay on advancing human knowledge by the mathematician Warren Weaver. At the time, Weaver was director of the Rockefeller Foundation, in charge of funding basic research in the natural and medical sciences. Although the essay is titled ‘A Quarter Century in the Natural Sciences’ (1960) and appears at first blush to be merely a summation of one man’s career, it turns out to be something much bigger and more interesting: a meditation on the history of human beings seeking answers to big questions about the world. Weaver goes back to the 17th century to trace the origins of systematic research thinking, with enthusiasm and vivid anecdotes that make the process come alive. The essay is worth reading in its entirety, and is available free of charge via this link .
For those seeking a more in-depth, professional-level discussion of the logic of research design, the political scientist Harvey Starr provides insight in a compact format in the article ‘Cumulation from Proper Specification: Theory, Logic, Research Design, and “Nice” Laws’ (2005). Starr reviews the ‘research triad’, consisting of the interlinked considerations of formulating a question, selecting relevant theories and applying appropriate methods. The full text of the article, published in the scholarly journal Conflict Management and Peace Science , is available, free of charge, via this link .
Finally, the book Getting What You Came For (1992) by Robert Peters is not only an outstanding guide for anyone contemplating graduate school – from the application process onward – but it also includes several excellent chapters on planning and executing research, applicable across a wide variety of subject areas. It was an invaluable resource for me 25 years ago, and it remains in print with good reason; I recommend it to all my students, particularly Chapter 16 (‘The Thesis Topic: Finding It’), Chapter 17 (‘The Thesis Proposal’) and Chapter 18 (‘The Thesis: Writing It’).

How to cope with climate anxiety
It’s normal to feel troubled by the climate crisis. These practices can help keep your response manageable and constructive
by Lucia Tecuta

Emerging therapies
How to use cooking as a form of therapy
No matter your culinary skills, spend some reflective time in the kitchen to nourish and renew your sense of self
by Charlotte Hastings

Meaning and the good life
How to appreciate what you have
To better face an imperfect world, try a deeper reflection on the things, people and legacies that make your life possible
by Avram Alpert
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
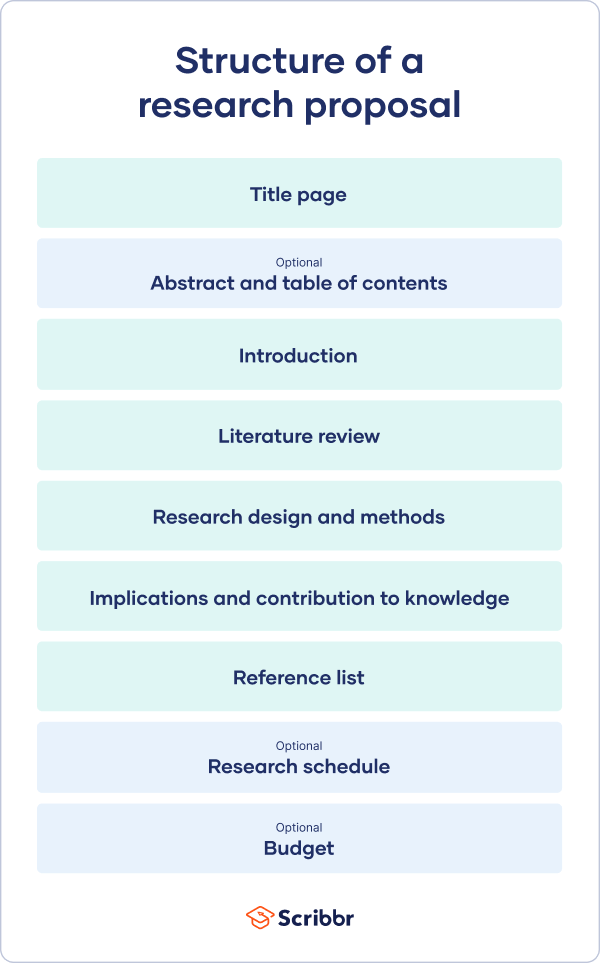
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Filter by Keywords
10 Free Research Plan Templates for Teams and Professionals
February 13, 2024
Starting a new research project from scratch can feel overwhelming. Without the right tools and templates, you’re left with a blank page and no direction. With them, starting a new project or organizing an existing one feels like a breeze.
That’s why you need to build a library of the best research plan templates. And we’re here to help you do it.
Stick with us as we run through the benefits of using a research plan template and share some of our favorites—all designed to help make your research projects run like magic.
What is a Research Plan Template?
What makes a good research plan template, 1. clickup user research plan template, 2. clickup market research template, 3. clickup research whiteboard template, 4. clickup equity research report template, 5. clickup seo research & management template, 6. clickup research report template, 7. clickup data analysis findings template, 8. clickup personal swot analysis template, 9. clickup case study template, 10. clickup investigation report template, how to write a research plan.
A research plan template is a document that’s designed to help you build the best research management plan possible. Instead of starting from scratch with a blank screen, a research plan document gives you the building blocks to fill in—so you won’t miss anything important.
There are a lot of solid research plan documents out there—covering everything from UX research (user experience) to case study templates . These templates can be helpful for any team, whether you’re working on product development prototypes or research objectives for a marketing project. They’re especially helpful for product design , UX research, and project management teams.
Some of the most popular research plan templates include:
- UX research plan templates
- Usability testing research templates
- Data analysis findings templates
- Project proposal templates
- Case study templates
- Research process templates
- Market research templates
- Competitive analysis templates
- Request for proposal templates
Each is there to guide you towards collecting, reviewing, and reporting on your research in a more strategic and organized way. Think of the research plan as your helpful research buddy—there to make things easier, provide guidance, and help you ace your project execution .
We’re all looking for something different when it comes to project templates. You might favor simplicity and order, while another team might prefer a more creative approach with lots of color and prompts.
Even though your needs are unique, there are some elements that almost always make a research plan template stand out above all the rest.
The best research plan templates:
- Keep you and your product team organized
- Help you standardize the research process and research method you use
- Keep you focused on the key project goals and deliverables
- Give you suggestions for metrics to record and analyze
- Help you keep your research questions in one place
- Help you stay on target with your project timeline
- Give you a defined place to store your thoughts and research findings
There’s no one perfect template for any individual or team. Consider what your purpose or goal is, what your project management workstreams look like, and which areas you need the most support or guidance in. This will help you choose which templates to feature and how you can use wiki software to build a collection of your go-to templates.
10 Research Plan Templates to Use in 2024
There are hundreds of research plan templates out there, but they’re not all alike. Some of them bring out the best of your project management skills , while others hinder them.
We’ve brought together the best of the best, to share with you the ultimate list of research plan templates to add to your workflow this year. Want to know what’s even better? You don’t need to get buy-in for an expensive pricing plan—these templates are all free!
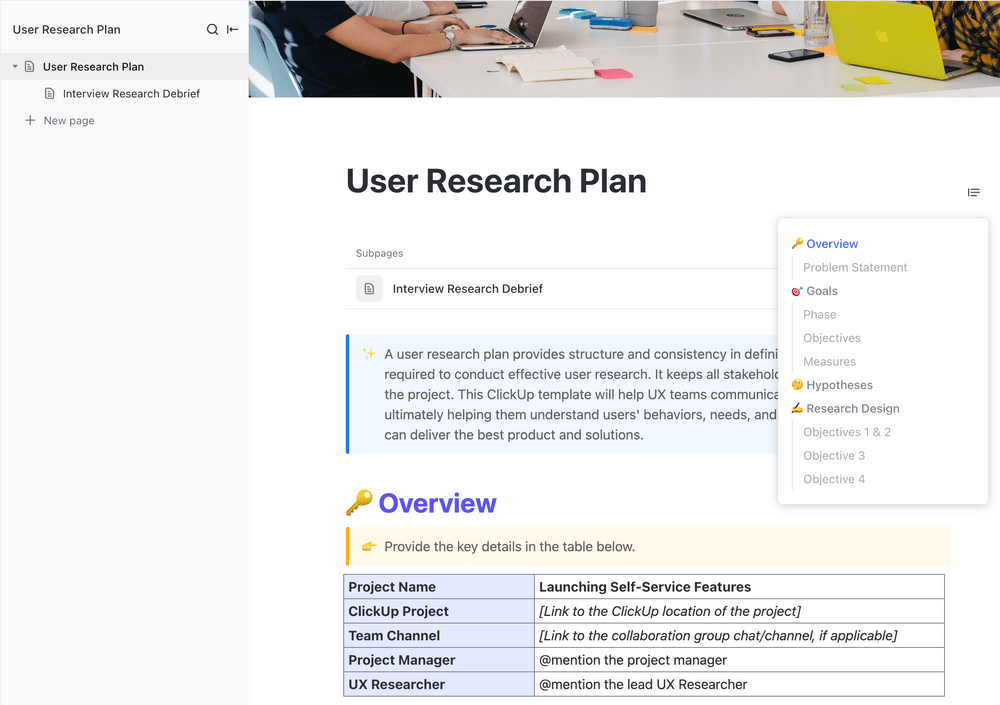
One of the first things that comes to mind when you say “research plan template” is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
The User Research Plan Template by ClickUp makes it easy for you to achieve that and more. There’s space to share your project overview and research goals, research objectives, hypotheses, and more—plus a bonus Interview Research Debrief doc.
This template acts as a central resource for all the stakeholders. Use it to bring your team together, reaffirm your goals and objectives, and stay on track as you execute your qualitative research project.
Bonus: UX design tools !
Planning your market research is a must-have if you want to get the best possible data. Give your team everything they need in one place and it helps your process run smoothly.
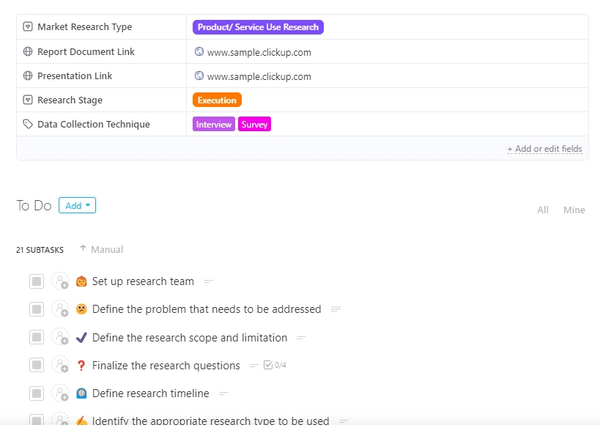
To help keep your team informed and ready to go, we developed the Market Research Template by ClickUp . It’s a Task template that brings you key information, all in one place.
Our Market Research Template features five custom fields—a research presentation link, market research type, report document link, data collection technique, and research stage. Add your clickable links, and use the dropdowns to assign the correct stage or type as you progress.

You can collect user research in so many ways. Questionnaires, user interviews, focus groups, user research sessions, or social media. Another super engaging way to do this is with a whiteboard.
Collaboration and user research feels interactive and fun with the Research Whiteboard Template by ClickUp . Encourage your team to share the insights they’ve collected in this highly visual template, with digital sticky notes instead of empty white boxes.
Use this ClickUp whiteboard template as a more engaging way to view your user research. You can also use this as a tool for internal research projects—invite your stakeholders by link and ask them to comment directly.
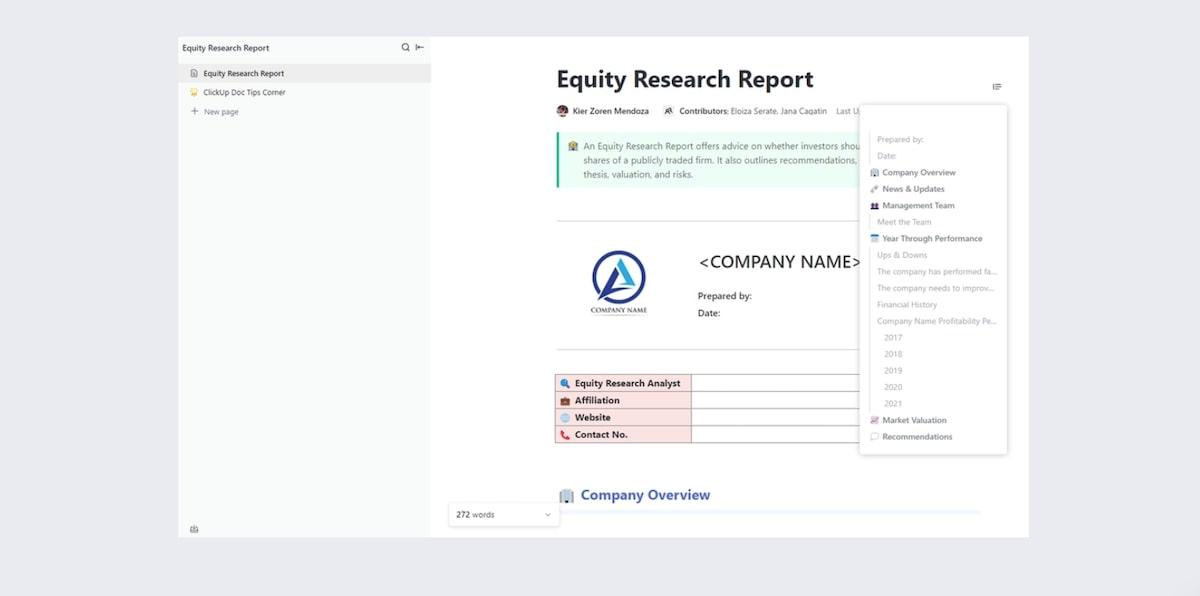
If you’re in the business of advising investors on what to do with their money, an equity report is a must-have. Instead of manually writing a new report every time, a research plan template can help you shortcut the process and get straight to the details.
Enter the Equity Research Report Template by ClickUp . It’s designed to help you share what you know in a more strategic way. Share an insight into the company overview, management team, performance, market valuation, and recommendations.
This research plan template has everything you need to present your findings to investors in an organized and effective way. Look like a pro to your investor clients and partners, and store all your data in a meaningful way to reflect on later.
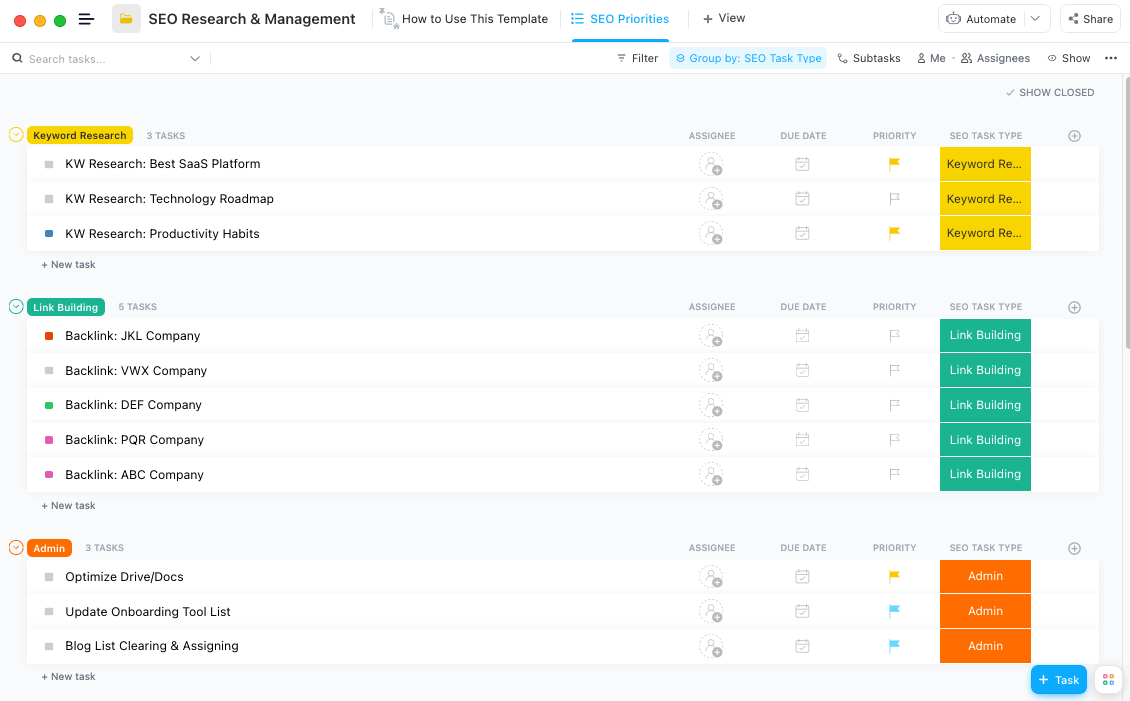
Staying on top of your company’s SEO performance is no easy task. There are so many moving parts, tools, projects, goals, and team members that you need a way to stay organized and productive.
Luckily for you, the SEO Research & Management Template by ClickUp is here to help simplify the process—and make you look good to your boss. This Folder template gives you a dedicated place to work on your SEO goals, with SEO-related custom fields and plenty of custom task types to help your team communicate progress and see roadblocks in your research plan.
Use this template to see at a glance where your SEO projects are, so you can be more proactive about how your team is working. You can also dive in to details and understand time estimates, publish dates, and where your rankings are at.
Check out these AI SEO Tools !
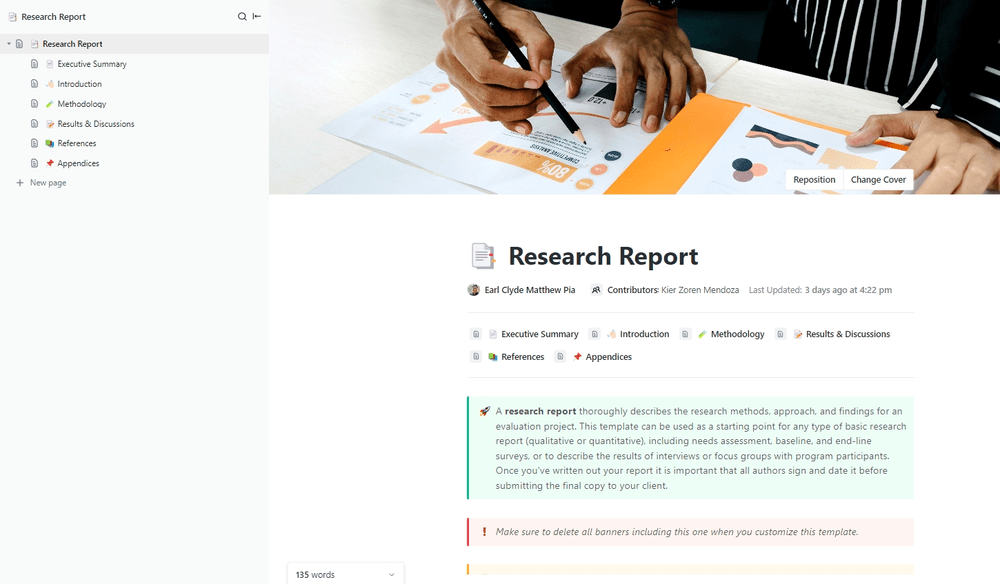
There’s no need to start from scratch every time you’re asked to put a research report together—instead use a template to make all your research questions and study reports as impressive as the last one.
Shortcut your way to success with the Research Report Template by ClickUp . There are sections for your executive summary, introduction, research method and techniques, results & discussion, references, and appendices. Add a report author and contributors, so you can recognize everyone that contributed to the report.
Share your research methods, approach, and findings with stakeholders and clients with this impressive template. It’s a useful foundation to help your team get organized and find a better way to update stakeholders on progress.

The Data Analysis Findings Template by ClickUp helps you present your data to everyone in a more meaningful way. Instead of presenting numbers and graphs, this template can help you go deeper into the problem statement, scope, analysis and research method, findings, and conclusion.
Use this template to help you organize your thoughts and communicate the results of your study in a transparent and easy-to-read way. Explain the context and background information alongside your approach, so your stakeholders can fully understand what the data shows.

A personal SWOT analysis can help you understand your (or your team’s) strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can not only help you work better, but it means you can be more intentional about your impact on the wider company.
The Personal SWOT Analysis Template by ClickUp can help you remember to work on your SWOT analysis. Find your strengths, weaknesses or pain points, opportunities, and threats. This Task template features several custom fields designed to help you monitor your progress—including your objective, timeline, and completion rate.
This template can be a helpful reminder to focus on your personal SWOT analysis, so you can be more intentional and aware of how you contribute to your team and company’s goals and objectives. Use your personal SWOT to help you set professional goals for work and make a bigger impact.

Case studies give you a powerful insight into what your brands, clients, or competitors are doing. They’re an in-depth look into a specific area of the business, based on your personal research and findings.
Simplify the process of building your case studies with the Case Study Template by ClickUp . This template gives you a strong foundation for presenting clear, insightful case studies with your team, stakeholders, or clients. Introduce the company, your case study objective, solutions and statistics, and your insights.
Use this template to help you create case studies at scale. Present your data in a clear and concise way, with all the context your team or stakeholders need to extract the most value from the case study as possible.
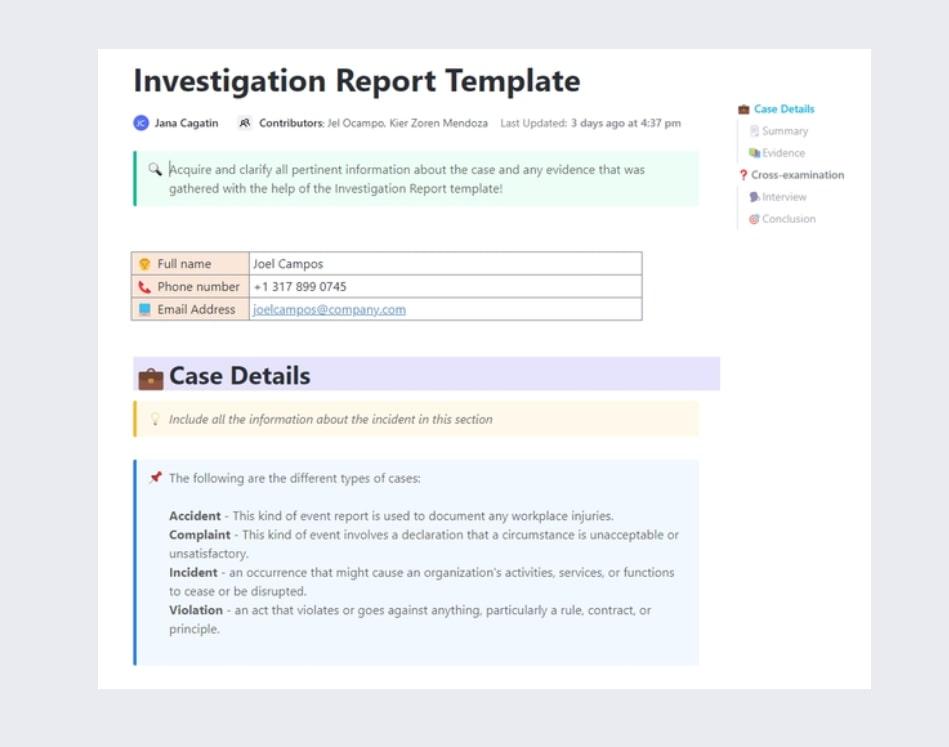
Often our research helps us understand the market, our competitors, or what our own company is doing. Sometimes, it’s to help us understand incidents and challenges instead.
That’s where the Investigation Report Template by ClickUp comes in. This template is designed to help you report on accidents, complaints, incidents, and violations. Explain the case details including a summary and evidence, then move into cross-examination with space for interview questions and answers, and your conclusion.
This template is a must-have for teams and companies that want to demonstrate how they overcome challenges or handle incidents. It’s great for transparency and trust-building, and serves as a useful way to document a trail of evidence for when you need it.
Now that you have a template for your research plan, let’s dive into the details of how to write one. Follow these steps to create an effective research plan that will guide your research and help you achieve your goals.
Step 1: Identify Your Research Question
The first step in writing a research plan is to clearly define your research question or topic. This will serve as the foundation for all of your research and help guide your methods and analysis. Make sure your question is specific, relevant, and achievable within the scope of your project.
Step 2: Outline Your Objectives
Next, you should outline the specific objectives or goals of your research. These objectives should be aligned with your research question and provide a clear roadmap for your project. Be sure to make them measurable and achievable.
Step 3: Choose Your Research Methods
Based on your research question and objectives, you can now determine the appropriate methods for gathering data and conducting analysis. This may include surveys, experiments, interviews, or literature reviews. It’s important to choose methods that are suitable for your research topic and will provide reliable and accurate results.
Step 4: Create a Timeline
A research plan should include a detailed timeline for each stage of the project. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you have enough time to complete each task. Be realistic with your timeline and build in some buffer time for unexpected delays or challenges.
Step 5: Consider Ethical Implications
When conducting research, it’s important to consider any potential ethical implications. This may include obtaining consent from participants, ensuring privacy and confidentiality, or following ethical guidelines set by your institution or governing body.
Step 6: Anticipate Potential Outcomes
As with any research project, there are always potential outcomes that can arise. These could be both positive and negative, and it’s important to anticipate and plan for them. This will help you be prepared for any potential challenges or changes that may occur during your research.
Step 7: Revise and Refine Your Plan
Once you have completed the previous steps, it’s essential to review and revise your research plan as needed. It’s common for plans to change as the project progresses, so be open to making adjustments and tweaking your methods or timeline as needed.
Stay Organized with the Best Research Plan Templates
Nobody likes a disorganized project—especially a research project. Let your team breathe a sigh of relief and make your stakeholders smile when they realize you’ve got it all under control.
Use these free research plan templates to help you get organized, streamline your workflows, and keep everyone informed. Build a collection of templates that work for your projects, and make them a central part of the way you work as a team. Standardize, simplify, and get productive.
All of these research plan templates are available right now, for free, inside our template library . Get access to these user-friendly templates, 100MB of storage, 1,000+ integrations, and more with ClickUp—free now, and forever!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

Research Project Plan Template

What is a Research Project Plan?
A research project plan outlines the processes and activities that need to be completed to achieve the desired results of a research project. The plan should provide a timeline for the research activities and identify any potential risks. It should also specify the resources and personnel needed, as well as the budget and timeline for the project. The plan should be both comprehensive and flexible, so that it can be modified as needed throughout the project.
What's included in this Research Project Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Research Project Plan template for?
The research project plan template is designed for research teams in academic, corporate, or non-profit sectors who need to plan and execute their research projects. The template provides a structure for outlining the processes and activities that must be completed in order to achieve the desired results of the research project. The template is designed to be comprehensive and flexible, allowing for modifications as needed throughout the project.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a specific area or topic that a research team is investigating. The focus area should be clearly defined and specific, so that the research team can develop objectives, projects, and KPIs that are relevant to the research project. Examples of focus areas could include developing new technologies, understanding customer behavior, or studying the effects of a particular policy.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the goals that a research team hopes to achieve by completing the research project. Objectives should be specific and measurable, and should be attainable within the timeline and budget of the research project. Examples of objectives could include developing a new technology, understanding customer behaviors, or studying the effects of a particular policy.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable targets that are used to evaluate the progress of a research project. KPIs should be specific and measurable, and should be established in order to track progress towards the objectives of the research project. Examples of KPIs could include product development timelines, customer satisfaction surveys, or policy implementation reviews.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects are the activities that need to be completed in order to achieve the objectives of the research project. Projects should be specific and achievable, and should be completed within the timeline and budget of the research project. Examples of projects could include running customer surveys, conducting interviews, or collecting data.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
The Cascade Strategy Execution Platform is a comprehensive software that helps research teams plan, manage, and track their research projects. The platform provides tools for project management, tracking KPIs, and monitoring progress. It also helps teams visualize their data and collaborate on initiatives. With Cascade, teams can save time and resources, and get faster results from their strategies.
42+ SAMPLE Research Work Plan in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages

Research Work Plan | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
42+ sample research work plan, what is a research work plan, different types of research work plans, basic components of a research work plan , how to write a research work plan, what are the major components of a research work plan, what are the advantages of a research work plan, what are some examples of research work plans, how to manage and monitor a research work plan.

Free Research Work Plan Template

Research Project Work Plan Template

Research Project Work Plan

Research Work Plan

Research Work Plan Development
Sample Research Work Plan
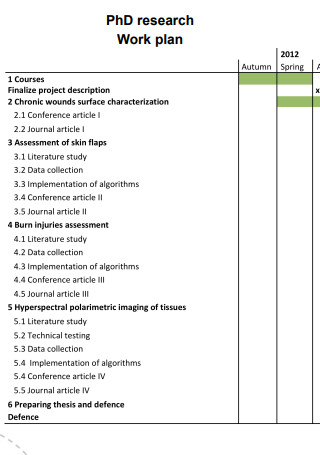
PhD Research Work Plan

Research Data Management Work Plan

Structure of Research Work Plan

Research Work Action Plan

Research Work Plan Outline

Work Plan for Research Project
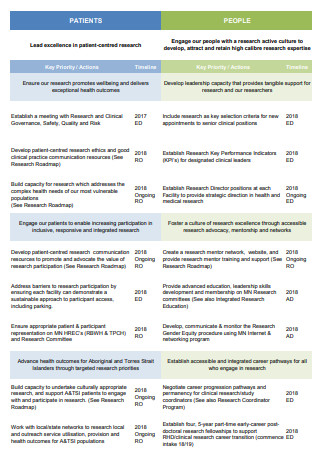
Transport Research Work Plan
Monthly Project Research Work Plan

Research Work Group Plan

Research Work Plan and Methodology

Half Yearly Research Work Plan
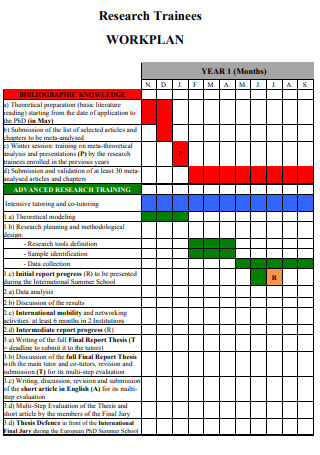
Research Trainee Work Plan

Research Team Work Plan

Research Work Continuity Plan

Simple Research Work Plan
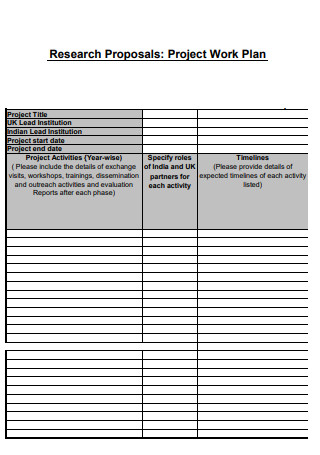
Research Work Plan Project Proposal

Gender Equality in Research Work Plan

Social Cohesion Research Work Plan

Strategic Research Work Plan

Formal Research Work Plan

Field Research Work Plan

Research Amplified Work Plan

Basic Research Work Plan

Central Research Team Work Plan
Research Interest and Work Plan

Research Community Work Plan

General Research Work Plan

Research Activity Work Plan
Research Safe Work Plan

Research Annual Work Plan

Research Work Plan Template

Research Mandate Work Plan

Research Commitee Work Plan

Research Administrative Work Plan

Research And Development Work Plan
Research Work And Performance Plan

Research Project Work Plan Example
1. field research plan , 2. phd research work plan, 3. covid-19 safety research work plan, 4. social cohesion research work plan, step 1: develop the introduction, focus of research, goals and methodology, step 2: summarize the research work , step 3: set a research timeline , step 4: add other details, step 5: proofread and prepare the overall plan, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 5+ sample investment company business plan in pdf.

What do you do when you have tons of spare cash lying around your home or burning a hole in your wallet or expensive jeans pocket? For some people, the…
41+ SAMPLE Unit Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
As a teacher, you might know about every school policy, the steps to keep classrooms safe for intellectual development, how to set up an organized classroom, and the proposed…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions

Thesis, major paper, and major project proposals
- Definitions
- Introductory section
- Literature review
- Methodology
Schedule/work plan
- Other potential elements
- Proposal references
- Ask for help

If you're unsure if your research proposal requires a schedule or work plan, please consult your project handbook and/or speak with your instructor, advisor, or supervisor.
The information about schedules or work plans in proposals was gathered from RRU thesis and major project handbooks, current in 2020, from programs in the Faculty of Social and Applied Sciences, the Faculty of Management, and the College of Interdisciplinary Studies. If the details here differ from the information provided in the handbook for your project, please follow the handbook's directions.
Image credit: Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay

- In RRU's Anxiety About Academic Writing guide, this resource is open to everyone.
How Do I Plan the Various Stages of My Research Project?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Planning and Practicalities, look for How Do I Plan the Various Stages of My Research Project? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Learning Skills: Time Management
- In RRU's Learning Skills guide, this resource is open to everyone.
What Do I Need to Know About Time and Timetabling?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Planning and Practicalities, look for the What Do I Need to Know About Time and Timetabling? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Image credit: Image by Mohamed Assan from Pixabay
- << Previous: Methodology
- Next: Other potential elements >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 12:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.royalroads.ca/proposals

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 5 Research Project Plan Templates with Samples and Examples
Samradni Pradhan
Research projects are essential to any business or organization's growth and success. Whether you're planning a market research study, conducting a scientific experiment, or developing a new product, a well-designed research project plan is vital to ensure that your project stays on track and achieves its objectives. With so many types of research projects, it can take some time to figure out where to start, when developing a project plan. That's where our PPT Templates come in. Using a pre-designed research project plan template can save time, reduce errors, and ensure that your project stays on track. In this blog post, we'll introduce you to the Top 5 Research Project Plan Templates with samples and examples, to help you choose the right template for your project.
Additionally, if you want to explore some research plan templates, you can check them out here !
Template 1: 30-60-90-Days Plan for Proposing and Designing Business Research Project Proposal
Here’s a comprehensive solution for anyone who wants to create a winning research proposal for their business project. This PPT Template contains all information, from the first initial planning stages to the final presentation of the proposal. The template is organized into three sections, each representing a different phase of the research project: the initial 30 days, the next 60 days, and the final 90 days. Each section includes an area that outlines the key tasks and deliverables for that phase of the project initiation . This PPT Layout acts as an essential tool for anyone who wants to create a compelling and effective research proposal. With its comprehensive structure, customizable slides, and engaging visuals, this template will help you win support for your project and take your business to the next level. Go ahead and download it right away!

Download Now!
Template 2: Plan Of Action for Designing and Proposing Business Research Project Services PPT Slideshow
Introducing a comprehensive and customizable solution for businesses and organizations looking to design and propose a research project. The template is divided into four stages: project initiation, research, analytics , and presentation. You can focus on your tasks and stay on track by comprehending information for each of these four stages. The PPT Slide also includes a range of graphics, charts, and diagrams that can be used to illustrate key points in the proposal visually. These graphics are designed to be easy to understand and visually appealing, making communicating complex ideas to stakeholders and decision-makers easier. This template will help you effectively plan, research , analyze, and present your research project, ensuring its success and a positive impact on your business or organization. Go ahead and grab this template today!
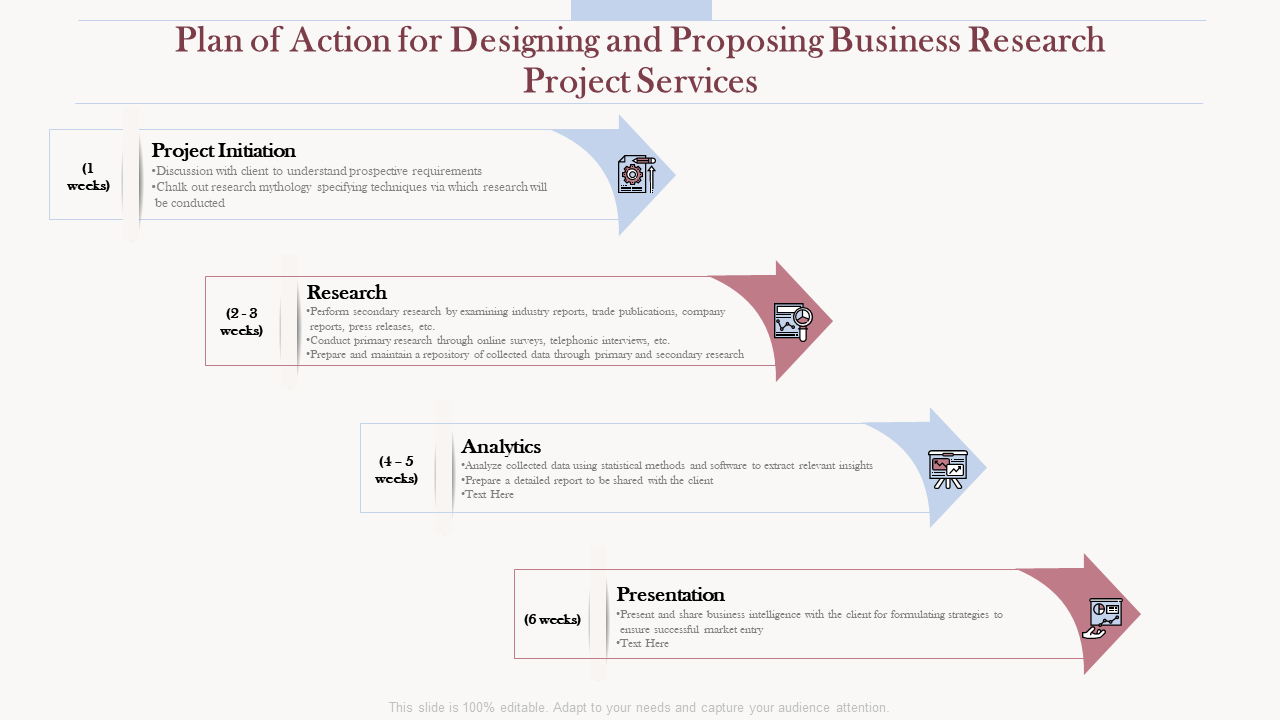
Template 3: Project Management Research Phases with Planning
Introducing an essential tool for businesses and organizations, looking to manage their research projects effectively. This comprehensive PPT Set is designed to guide users through each phase of the research project, from initiation to closing, ensuring that every aspect of the project is planned and executed efficiently. The template comprises five phases: initiation, planning, execution, controlling/monitoring, and closing. The initiation phase focuses on project plan creation and stakeholders' recognition. The planning phase comprises plan creation, resource identification, and cost projection. The execution phase includes information on task completion and resource acquisition. In the controlling/monitoring phase, reliability and expense estimates are tracked. Finally, stakeholder and resource management are included in the closing stage of project completion. This ensures that your work is correctly divided and also ensures that you focus on specific stages at the right time.
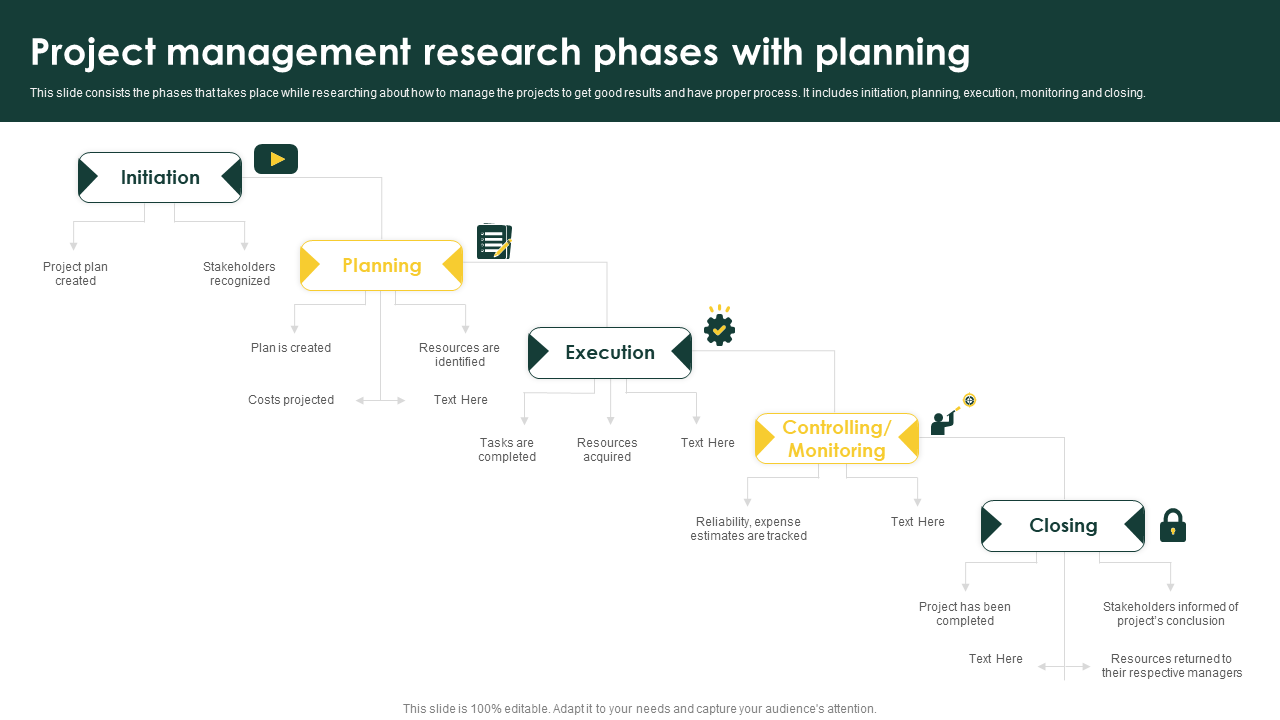
Template 4: Planning Process of Research Project Dissertation Timeline
Here is an all-in-one solution for anyone planning, organizing, and presenting a research project or dissertation. This PPT Template is designed to guide users through the four key stages of a research project: preparation, proposition, research, and drafting. The first stage, preparation, involves defining the research question or problem and developing a plan to tackle it. This stage includes creating a timeline, identifying key stakeholders and resources, and setting goals and objectives for the project. The proposition stage involves developing a proposal that outlines the research question, methods, and expected outcomes. The research stage involves conducting the research according to the methods and timeline established in the preparation and proposition stages. The drafting stage involves writing and presenting the final report, thesis, or dissertation. This stage includes organizing and structuring the report, developing key arguments and insights, and presenting the research findings clearly and engagingly. This template is a must-have for anyone!
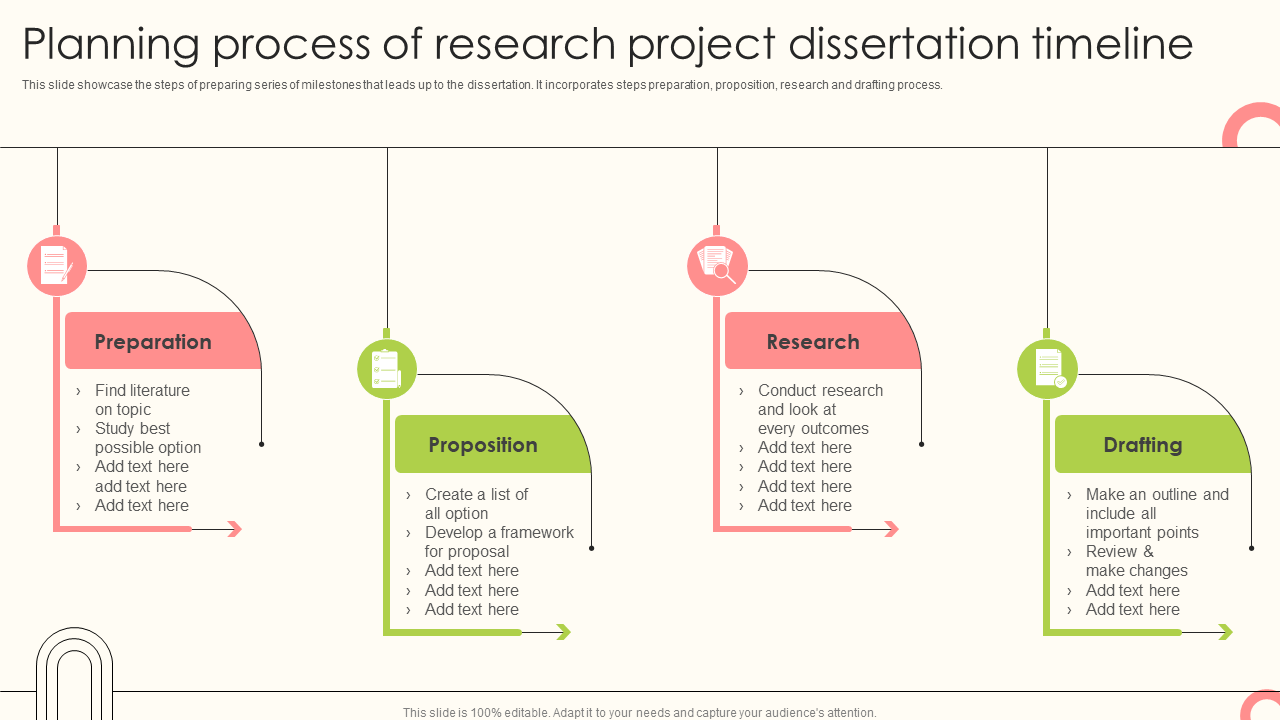
Template 5: Six Months Plan Timeline for a Marketing Research Project
Next up, we have a comprehensive template that is designed to guide users through the six key stages of a marketing research project: planning, research design, data collection, data analysis, report writing, and presentation . Each stage contains a set of customizable blocks that outline the key tasks and deliverables for that phase of the project. This allows users to plan and execute each stage of the project efficiently, ensuring that the project ensures to stay on track and meets its objectives. Overall, this template outlines a bird's eye view of the entire project. Go ahead and explore this template today!

EXPLORE THESE PROJECT RESEARCH PLAN TEMPLATES TODAY!
A research project is a time-consuming task, and it requires that you to stay on track every step of the way. While each department in a business organization may have its own ideas, ensuring to have a comprehensive template works wonders. This is where the professionally designed templates work the best. Download these premium PPT Slides through our monthly, semi-annual, annual, annual + custom design subscriptions here .
These project research plan templates can help you plan better, and with better planning comes better outcomes. These templates also help in creating a lasting impression in front of your audiences. There is nothing more you need to ask for; download these templates today!
FAQs on Research Plan
What is a research project plan.
A research project plan is a preemptive stage where you document the goals of your research project along with the objective of your project, what methods you are going to use, and the legitimate resources.
The whole idea of having a plan for a research project is to sketch down the mind map step-by-step, which you could refer to further progress with the project. A research plan also asks for a time period and budget to be set before proceeding, which is an efficient way of getting on a research project.
How do you write a research plan?
A research plan needs to be written systematically and sufficiently. Your research plan should be self-explanatory to whosoever is reading, the plan should be in the exact order you want to proceed in, and only enough should be written.
A well-written research plan should start with articulating the research question and, from there, proceed to mention the purpose, how your project is going to work, what resources you will require, grand of special permissions from organizations ( if needed), setting the deadline for each part to ending with the finance limitations for that project.
What are the four significant parts of the research plan?
Even though a research plan varies from one project type to another, there are four significant parts that you must structure your plan around for getting optimal ease and clarity:
- Attach a background of your research question where you highlight the purpose and the gaps in the existing field to be fulfilled via this research project.
- Evaluating the research structure, methods you will use, equipment needed, working procedure, and how you will present your research project.
- Time format: This part is where you assign a dedicated time period for finishing each goal in your research project. Here, you can set deadlines for minute tasks to end tasks.
- Counting in the resources, this is one of the most significant parts of the research plan where you point out the funding, equipment, references, permissions, or any data and artifacts needed for your research project.
What are the seven steps for creating a research plan?
Creating a research plan can get tricky, especially when you are at a very initial stage with your idea for the project. Hence, to make that process more approachable for generating a research plan:
- First, you must briefly introduce your research question.
- Thoroughly conduct research on the study area to identify the gaps and gain the needed knowledge.
- Apply for the grants and permissions you will require to conduct your research project securely.
- Finalize the resources important for your project, from funding, finding mentors, types of equipment, and so on.
- The next step is to plan out the experiments you will be conducting in the process.
- Filtering through all the collected data to come up with the most authentic ones.
- Citing the used resources in a standard format that is accepted. Examples- APA, Chicago, MLA, etc.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Website Project Plan Templates with Samples and Examples
- [Updated 2023] An All-Encompassing Guide to Project Planning (With 30+ PowerPoint Templates to Help You Get Started)
- Top 10 Research Paper Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Project Management Template with Samples and Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 7 UX Cover Letter Examples with Templates and Samples
Top 7 Project Implementation Plan Templates for Smooth Execution!
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

All Formats
Table of Contents
Plan template bundle, what is a research work plan, what is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal, what is the purpose of a research plan, what are the good research questions, what are the components of a work plan, free 12+ research work plan templates in pdf | ms word, 1. research work plan format template, 2. research project communication plan template, 3. free project research work plan template, 4. free research work plan example, 5. free research work group plan template, 6. half yearly research work plan template, 7. sample research work plan template, 8. free research work plan template in pdf, 9. free business research work plan template, 10. free project research work plan example, 11. monthly project research work plan template, 12. transport research work plan template, 13. free research work plan template in doc, how to develop a work plan, advantages of developing a work plan, plan templates, 12+ research work plan templates in pdf | ms word.
A work plan is an overview of a series of objectives and procedures by which a team and/or entity can achieve those goals and provide the reader with a clearer picture of the project’s context. No matter if it is used in professional or academic life, work plans serve the purpose of helping you stay focused when working on a certain project. You disintegrate a process into tiny, manageable tasks by work schedules , and define the tasks you want to achieve.

- Google Docs

- Apple Pages

Step 1: Think About the Objectives
Step 2: introduction and background, step 3: list the resources, step 4: anticipate and define limitations, step 5: assign roles, step 6: write the strategy, determine goals and objectives, organize teams and leadership, establish project timelines, set project budget, quality assurance and control, more in plan templates, research template for kids, animal research paper template, quantitative research template, educational research template, artist research template, action research template, artistic research template, longitudinal research template, prediction research template, education qualitative research template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
- Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
The value of a good research plan
A research plan is a guiding framework that can make or break the efficiency and success of your research project. Oftentimes teams avoid them because they’ve earned a reputation as a dry or actionless document — however, this doesn’t have to be the case.
In this article, we’ll go over the most important aspects of a good research plan and show you how they can be visual and actionable with monday.com Work OS.
Don’t miss more quality content!
Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project.
A research plan is pivotal to a research project because it identifies and helps define your focus, method, and goals while also outlining the research project from start to finish.
This type of plan is often necessary to:
- Apply for grants or internal company funding.
- Discover possible research partners or business partners.
- Take your research from an idea into reality.
It will also control the entire journey of the research project through every stage by defining crucial research questions and the hypothesis (theory) that you’ll strive to prove or disprove.
What goes into a research plan?
The contents of a thorough research plan should include a hypothesis, methodology, and more. There is some variation between academic and commercial research, but these are common elements:
- Hypothesis: the problem you are trying to solve and the basis for a theoretical solution. For example, if I reduce my intake of calories, I’ll lose weight.
- Research questions: research questions help guide your investigation into particular issues. If you were looking into the potential impact of outsourcing production, you might ask something like: how would outsourcing impact our production costs?
- Research method: the method you’ll use to get the data for your research. For example, a case study, survey, interviews, a clinical trial, or user tests.
- Definitions: a glossary for the research plan, explaining the terminology that you use throughout the document.
- Conceptual frameworks: a conceptual framework helps illustrate what you think you’ll discover with your research. In a sense, it’s a visual representation of a more complex hypothesis.
For commercial plans, there will also likely be a budget and timeline estimate, as well as concrete hypothetical benefits for the company (such as how much money the project should save you).
OK, so you’ve got a handle on the building blocks of a research plan, but how should you actually write it?
How do you write a research plan on monday.com?
The first, and perhaps most crucial part of having a good research plan is having the right medium for creating and sharing it. Using a pre-defined template can also make it much easier to get started.
On monday.com, you can choose from several templates like the Project Proposal Template or better yet the Research Power Tools Template to manage all aspects of your project including important communication with internal and external stakeholders and teammates.
Use your template to:
- Create workdocs
- Upload assets
- Provide feedback
- Assign task owners
- Automate communication
The next step in writing a research plan is choosing the topic. To pick the right topic, focus on these factors:
- What are the priorities of the potential funder/employer, such as the company or institution?
- Are there any relevant recent studies with results you can build on and explore with further research?
- Can you creatively adapt your experience — whether post-grad or professional — to make you the natural candidate? They don’t just need to believe in the research project, but also in your ability to manage it successfully.
Do your research, no pun intended. Once you’ve got the topic, you need to work on fleshing out the core ideas with the building blocks we mentioned above.
- Get specific with your research questions and goals. Don’t go with, “how can we revolutionize our HR practices?” Instead use, “what is the economic and environmental impact of only accepting digital CVs?”
- Use clear language aimed at gatekeepers. If it’s a CTO (Chief Technology Officer) or a lab committee, you can use well-known technical terms. If they aren’t technical experts, adjust accordingly.
- Include preliminary data or highlight similar studies. For companies, showing that a similar approach helped a competitor is a better argument than an empty assertion.
The recommended length of the plan depends on who you’re sending it to and their expectations. If possible, look at successful examples or directly ask your potential employers about their preferences. Not only do you need the right idea, but you also need to present it in the right way for your research project to have a fighting chance.
What is a good research plan?
A good research plan is one that gets accepted and funded to start doing the research.
If you want to plan a pivotal study, it’s not enough to consider the problem in a vacuum. You also need to evaluate how you can best communicate the value of your project to the gatekeepers.
Consider the entirety of your current situation and what that means for your project.
For example, inputs like funding, staff, IP, and how the scale of the project lines up with your company’s research budget. Or how it aligns with the goals of a University program. If the primary goal of the research is to impact a company or government agency directly, you should consider these stages of research engagement.

( Image Source )
- Inputs: anything from funding and staff to company IP that you need to both run the project and implement any results. Does this line up with the budget?
- Activities: case studies, trials, surveys, the actual research.
- Outputs: the final reports, any publications, and raw data.
- Outcome: how will it directly impact the company, organization, or larger society?
- Impacts: what are the indirect benefits or downsides?
In an internal research proposal, you can outline these aspects in separate sections. That allows different execs or managers to focus on the details that matter most to them. You must also work to engage stakeholders and make sure that they understand the importance of your project.
Frequently asked questions
What are the 5 purposes of research.
The 2 primary purposes of research are to gather information or test an existing theory. When broken down further, you can see 5 more specific purposes:
- Exploratory research is an early-stage inquiry that explores a topic for further study down the line, like exploring the deep ocean with a submersible vehicle.
- Descriptive research aims to explore and describe a specific substance, person, or phenomenon.
- Explanatory research is about figuring out the causal relationship, why something happens.
- Predictive research is all about trying to predict what might happen in specific situations based on the properties of the research object.
- Meta-research looks for overarching insights from multiple sources and tests the validity of common hypotheses.
What is a research work plan?
A research work plan is another name for a research plan, which is a critical component of any research proposal. Universities, labs, and companies use them to evaluate research projects before they decide to accept them.
As a researcher, it’s essential when targeting a funding opportunity of any kind.
What are the methods of research?
There are many research methods ranging from a simple online survey to a high-budget clinical study. Here are some examples of popular data collection methods:
- Clinical trials
- Experiments
- Case studies
- Observations
Which one is right for your plan depends on your hypothesis, goals, industry regulations, and more.
Create a dynamic research plan
If you want to turn your research project into a reality, you need to go beyond the academic and into management mode.
With a template from monday.com, you can plan out a research project from start to finish. Including goals and objectives, budget estimates, milestones, and more.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.

Research Project Plan

In business, you should never make decisions on the fly. This is true especially for important business decisions that deals with the financial status of the business. Making decisions without proper thought or extensive research is not only costly for the company but also affects the long-term sustainability of the organization. You may also see baseline project plan examples .
Research is important for business organizations, either for profit companies and also for nonprofit organizations. To help you create a research project plan, here are some research project plan examples you can use and download for free.
Research Project Plan Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 19 KB
Research Project Work Plan Template

Size: 30 KB
Research Project Action Plan Template

Size: 32 KB
Free Research Project Communication Plan Template

Size: 35 KB
Project Plan Action Items Template
Size: 100 KB
Project Plan Template

Size: 28 KB
Research Project Gantt Chart Template
Research Project Mind Map Template
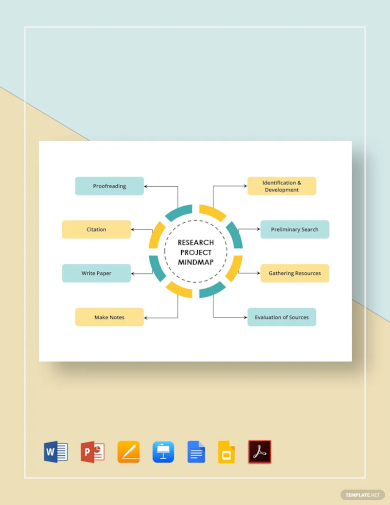
- Google Slides
- Apple Keynote
Size: 58 KB
Research Project Budget Template

- Google Sheets
- Apple Numbers
Size: 78 KB
Research Project Proposal Template

Size: 57 KB
Research Project Scope Template

Size: 157 KB
User Research Project Plan Example

Size: 71 KB
Template for Research Project Plan Example

Size: 65 KB
Simple Research Action Plan Example

Size: 62 KB
Tips in Creating a Research Project Plan
Here are some important tips in creating a research project plan. Take note that a research plan comprises one step in your company achieving profitability and sustainability. When you want to venture into a new business, specifically starting a new project, you first need to do research, and a research project plan helps you identify problems and create solutions for your new project.
1. Choose the right project
First and foremost, you need to choose a project that can help your business attain higher revenues. Never use company resources to fund a research plan for your own personal hobby. This does not benefit the company in any way and will only cause unnecessary losses for your company.
If you are a business owner, discuss possible projects with your management team. Together, you can brainstorm and finalize on the project you are going to pursue. Think of projects that are going to bring in income for your business. This may be an expansion project or a project that ventures into another industry (for example, your business provides laundry services but you want to invest in a fast-food chain).
Remember, choosing a project will not immediately mean that your going to fund it right away. That is why you need to create a research project plan first before you start purchasing materials or begin working on your actual project.
2. Utilize research materials
After a choosing the project to work on, it’s now time to work on the details of the actual research action plan . There are numerous research materials and research procedures you can choose from, but choosing the right ones will be crucial in the result of the research action plan.
The research materials will depend on the project you chose. Look for research materials that will help you identify problems as well as create solutions for the problems being identified.
Choose established theories and research strategies that can help you in your study. You can find these theories and strategies from hundreds of books, publications, journals, and online resources that are available at your disposal (or at your nearest public library).
3. Establish a timetable
Establishing a timeline will help you create a blueprint for your research action plan. The timetable helps you focus which tasks to prioritize and which tasks to work on later. Additionally, a timetable helps you set a concrete deadline for the research action plan. A timetable gives you additional focus and extra motivation. You may also see comprehensive project plan examples .
Remember that working on a project requires time, and you should not be in a rush to create your research action plan. Depending on the size of the project, the research action plan should amount to at least six months to one year including the data gathering phase, creating the first draft, presenting the plan to the management team, and making the final revisions of the research action plan.
Having a timeline also helps you eliminate last-minute stress in creating the action plan . When you establish a timetable beforehand, you will have more time to research and create a plan that will eventually result to a more well-researched and well-written research action plan.
4. Create a preliminary outline
Together with the timeline, a preliminary outline also gives you a guide on how to create an effective research action plan. Create an outline on what you are going to list down and discuss in the research action plan . To help you create a preliminary outline, list down the main topics that you intend to cover and organize them in a loose order.
To help you keep track of your progress, you can always write your outline in a journal. This way, you can easily revise and add ideas in which you can think can benefit the research action plan. Also in the journal, you can list down questions you think can further develop your research, as well as adding information from the sources you previously gathered. You may also like community project plan examples .
Research Proposal Questionnaire Example

Size: 300 KB
Intro Outline Research Plan Example

Size: 46 KB
Types of Data Gathering Procedures
Here are the types of data gathering procedures you can use for your research project plan . You may use one or a combination from the research gathering procedures listed below. Your research will be dependent on the data or information you gather. A research should never rely on mere assumptions, but data that is both gathered and analyzed.
1. Interview
Conducting an interview is one of the most common yet most effective forms of data gathering. Interviews can either be done in personal or by telephone (smartphone).
There is one rule of thumb when doing interviews: be prepared. You can never obtain quality information if you go into an interview without preparing the questions beforehand or making an outline on how to conduct the actual interview. You will only be embarrassing yourself to the respondent (or the recipient of the interview). You may also like migration project plan examples .
Take note that when making the questions for the interview, the questions should be focused, clear, and should encourage open-ended responses. Depending on the nature of your interview, you should get the most out of your respondents. Even if the questions are answerable by a phrase or a sentence, it should still encourage multiple answers from your respondents. You may also check out agile project plan examples .
2. Questionnaire
Handing out general questionnaires is also another popular and effective data gathering procedure. Compared to interviews, questionnaires are less formal since they are just given to the respondents and the researcher would just wait for the respondent to finish answering the questionnaires. Also, there is no pressure when the respondent answers the questionnaire compared to being interviewed face-to-face.
Sometimes in an interview, the interviewer asks a certain question and follows it up with another question, making the respondent uneasy in answering the question instead. The respondent may not be able to answer the question in the manner that he intended to be since he was pressured by the interviewer to answer a specific type of answer which will be preferred to his study. You might be interested in quality project plan examples .
Compared to open-ended answers from respondents in an interview, questionnaire or general survey results are easier to compile and analyze. Additionally, questionnaire responses can be analyzed with quantitative methods by assigning numerical values to Likert-type scales.
3. Observations
Observation meanwhile pertains to the researcher obtaining data by doing observations to a group of respondents. Observations allow researchers to study dynamics of a situation, frequency counts of target behaviors, or other behaviors as indicated by needs of the evaluation. You may also see marketing project plan examples .
Observations are specifically effective in obtaining information about a particular group and can also produce qualitative (e.g., narrative data) and quantitative data (e.g., frequency counts, mean length of interactions, and instructional time). You may also like what is a project management plan?
Observations, together with focus groups (as discussed below) are less used compared to interviews and questionnaires/surveys.
4. Focus Groups
Focus groups are similar to observations, but focused groups are conducted by groups instead of individuals. The aim of a focus group-type of data gathering procedure is to obtain information about combined perspectives and opinions. The responses meanwhile are often coded into categories and analyzed thematically. You may also check out nonprofit project plan examples .
5. Documents and Records
General Documents and records meanwhile pertain to the researcher basically gathering and examining data gathered from numerous sources (e.g., books, publications, novels, online sources). This type of data gathering procedure does not focus on the respondents but on the other information and analysis formulated in the research action plan.
Books and online references are not the only sources the researcher can obtain data, as he can also gather data from databases, meeting minutes, reports, attendance logs, financial records, and newsletters.
PhD Research Plan Example

Size: 99 KB
PhD Medical Research Plan Example

Investigative Research Project Plan Example

Size: 272 KB
Sample Research Project Plan Outline
To further help you in creating a research project plan, here is a sample research project plan outline. Take note that the research project plan below is only an outline and does not include comprehensive analysis, which is a requirement for a standard research project plan. You may also see construction project plan examples .
High Energy Sports Store, Inc. – Research Action Plan
1. introduction.
This research action plan aims to identify the possibility of High Energy Sports Store, Inc. opening one new store by the end of 2018 and two new stores by mid 2019. High Energy has been in operations for over three years, with three stores currently in operations. The store is the official authorized reseller of popular athletic shoe brand Nike, Adidas, and Under Armour and also sells various sportswear from the said brands. You may also like quality management plan examples .
2. Statement of the Problem
This research action plan aims to answer the following questions:
- Can High Energy break even from its investment in opening three new stores in a span of one year?
- On what year can High Energy break even and start earning revenues?
- What will be the total cost of High Energy’s investment in the three new stores (including cost of construction of a physical store, purchase of wholesale shoes and sports wear, initial working capital of ten total staff for all three stores?)
- Will the new stores apply a new interior theme or retain the same interior design as the current stores?
3. Methodology
The research will utilize the distribution of survey questionnaires as the main data gathering procedure. The research will involve 100 respondents and the demographic of the respondents are specifically regular customers of the current stores which are currently in operations.
The said survey questionnaires will be given to the customers once they arrive in the stores. If they are not available to fill out the questionnaires, the questionnaires will be sent to their respective email addresses or social media accounts. Before the questionnaires are given out, High Energy will have a master list of the respondents.
4. Recommendations
*The recommendations will base from the data gathered and analyzed from the respondents, and will also answer the questions as listed in the “ Statement of the Problem .”
5. Conclusion
*The conclusion will stem from the recommendations and will also support the findings from the data that was gathered and analyzed.
APA Format Research Plan Example

Size: 96 KB
Doctoral Research Project Plan Example

Size: 219 KB
We hope you found this article to be informative as well as helpful when you will be creating your own research action plan. A research action plan is necessary for the company to avoid jumping right into conclusions when deciding to invest in a new project or venture.
Take note that a research plan comprises one step in your company achieving profitability and sustainability. When you want to venture into a new business, specifically starting a new project, you first need to do research, and a research project plan helps you identify problems and create solutions for your new project.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Students & Educators —Menu
- Educational Resources
- Educators & Faculty
- College Planning
- ACS ChemClub
- Project SEED
- U.S. National Chemistry Olympiad
- Student Chapters
- ACS Meeting Information
- Undergraduate Research
- Internships, Summer Jobs & Coops
- Study Abroad Programs
- Finding a Mentor
- Two Year/Community College Students
- Social Distancing Socials
- Planning for Graduate School
- Grants & Fellowships
- Career Planning
- International Students
- Planning for Graduate Work in Chemistry
- ACS Bridge Project
- Graduate Student Organizations (GSOs)
- Schedule-at-a-Glance
- Standards & Guidelines
- Explore Chemistry
- Science Outreach
- Publications
- ACS Student Communities
- You are here:
- American Chemical Society
- Students & Educators
Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application
By Jason G. Gillmore, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, Hope College, Holland, MI
A research plan is more than a to-do list for this week in lab, or a manila folder full of ideas for maybe someday—at least if you are thinking of a tenure-track academic career in chemistry at virtually any bachelor’s or higher degree–granting institution in the country. A perusal of the academic job ads in C&EN every August–October will quickly reveal that most schools expect a cover letter (whether they say so or not), a CV, a teaching statement, and a research plan, along with reference letters and transcripts. So what is this document supposed to be, and why worry about it now when those job ads are still months away?
What Is a Research Plan?
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation. It must be a document that people at the department you hope to join will (a) read, and (b) be suitably excited about to invite you for an interview.
That much I knew when I was asked to write this article. More specifics I only really knew for my own institution, Hope College (a research intensive undergraduate liberal arts college with no graduate program), and even there you might get a dozen nuanced opinions among my dozen colleagues. So I polled a broad cross-section of my network, spanning chemical subdisciplines at institutions ranging from small, teaching-centered liberal arts colleges to our nation’s elite research programs, such as Scripps and MIT. The responses certainly varied, but they did center on a few main themes, or illustrate a trend across institution types. In this article I’ll share those commonalities, while also encouraging you to be unafraid to contact a search committee chair with a few specific questions, especially for the institutions you are particularly excited about and feel might be the best fit for you.
How Many Projects Should You Have?

While more senior advisors and members of search committees may have gotten their jobs with a single research project, conventional wisdom these days is that you need two to three distinct but related projects. How closely related to one another they should be is a matter of debate, but almost everyone I asked felt that there should be some unifying technique, problem or theme to them. However, the projects should be sufficiently disparate that a failure of one key idea, strategy, or technique will not hamstring your other projects.
For this reason, many applicants wisely choose to identify:
- One project that is a safe bet—doable, fundable, publishable, good but not earthshaking science.
- A second project that is pie-in-the-sky with high risks and rewards.
- A third project that fits somewhere in the middle.
Having more than three projects is probably unrealistic. But even the safest project must be worth doing, and even the riskiest must appear to have a reasonable chance of working.
How Closely Connected Should Your Research Be with Your Past?
Your proposed research must do more than extend what you have already done. In most subdisciplines, you must be sufficiently removed from your postdoctoral or graduate work that you will not be lambasted for clinging to an advisor’s apron strings. After all, if it is such a good idea in their immediate area of interest, why aren’t they pursuing it?!?
But you also must be able to make the case for why your training makes this a good problem for you to study—how you bring a unique skill set as well as unique ideas to this research. The five years you will have to do, fund, and publish the research before crafting your tenure package will go by too fast for you to break into something entirely outside your realm of expertise.
Biochemistry is a partial exception to this advice—in this subdiscipline it is quite common to bring a project with you from a postdoc (or more rarely your Ph.D.) to start your independent career. However, you should still articulate your original contribution to, and unique angle on the work. It is also wise to be sure your advisor tells that same story in his or her letter and articulates support of your pursuing this research in your career as a genuinely independent scientist (and not merely someone who could be perceived as his or her latest "flunky" of a collaborator.)
Should You Discuss Potential Collaborators?
Regarding collaboration, tread lightly as a young scientist seeking or starting an independent career. Being someone with whom others can collaborate in the future is great. Relying on collaborators for the success of your projects is unwise. Be cautious about proposing to continue collaborations you already have (especially with past advisors) and about starting new ones where you might not be perceived as the lead PI. Also beware of presuming you can help advance the research of someone already in a department. Are they still there? Are they still doing that research? Do they actually want that help—or will they feel like you are criticizing or condescending to them, trying to scoop them, or seeking to ride their coattails? Some places will view collaboration very favorably, but the safest route is to cautiously float such ideas during interviews while presenting research plans that are exciting and achievable on your own.
How Do You Show Your Fit?
Some faculty advise tailoring every application packet document to every institution to which you apply, while others suggest tweaking only the cover letter. Certainly the cover letter is the document most suited to introducing yourself and making the case for how you are the perfect fit for the advertised position at that institution. So save your greatest degree of tailoring for your cover letter. It is nice if you can tweak a few sentences of other documents to highlight your fit to a specific school, so long as it is not contrived.
Now, if you are applying to widely different types of institutions, a few different sets of documents will certainly be necessary. The research plan that you target in the middle to get you a job at both Harvard University and Hope College will not get you an interview at either! There are different realities of resources, scope, scale, and timeline. Not that my colleagues and I at Hope cannot tackle research that is just as exciting as Harvard’s. However, we need to have enough of a niche or a unique angle both to endure the longer timeframe necessitated by smaller groups of undergraduate researchers and to ensure that we still stand out. Furthermore, we generally need to be able to do it with more limited resources. If you do not demonstrate that understanding, you will be dismissed out of hand. But at many large Ph.D. programs, any consideration of "niche" can be inferred as a lack of confidence or ambition.
Also, be aware that department Web pages (especially those several pages deep in the site, or maintained by individual faculty) can be woefully out-of-date. If something you are planning to say is contingent on something you read on their Web site, find a way to confirm it!
While the research plan is not the place to articulate start-up needs, you should consider instrumentation and other resources that will be necessary to get started, and where you will go for funding or resources down the road. This will come up in interviews, and hopefully you will eventually need these details to negotiate a start-up package.
Who Is Your Audience?
Your research plan should show the big picture clearly and excite a broad audience of chemists across your sub-discipline. At many educational institutions, everyone in the department will read the proposal critically, at least if you make the short list to interview. Even at departments that leave it all to a committee of the subdiscipline, subdisciplines can be broad and might even still have an outside member on the committee. And the committee needs to justify their actions to the department at large, as well as to deans, provosts, and others. So having at least the introduction and executive summaries of your projects comprehensible and compelling to those outside your discipline is highly advantageous.
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind:
- Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should probably write it last. This page is something you could manageably consider tailoring to each institution.
- Provide sufficient details and references to convince the experts you know your stuff and actually have a plan for what your group will be doing in the lab. Give details of first and key experiments, and backup plans or fallback positions for their riskiest aspects.
- Hook your readers with your own ideas fairly early in the document, then strike a balance between your own new ideas and the necessary well referenced background, precedents, and justification throughout. Propose a reasonable tentative timeline, if you can do so in no more than a paragraph or two, which shows how you envision spacing out the experiments within and among your projects. This may fit well into your executive summary
- Show how you will involve students (whether undergraduates, graduate students, an eventual postdoc or two, possibly even high schoolers if the school has that sort of outreach, depending on the institutions to which you are applying) and divide the projects among students.
- Highlight how your work will contribute to the education of these students. While this is especially important at schools with greater teaching missions, it can help set you apart even at research intensive institutions. After all, we all have to demonstrate “broader impacts” to our funding agencies!
- Include where you will pursue funding, as well as publication, if you can smoothly work it in. This is especially true if there is doubt about how you plan to target or "market" your research. Otherwise, it is appropriate to hold off until the interview to discuss this strategy.
So, How Long Should Your Research Plan Be?

Learn more on the Blog
Here is where the answers diverged the most and without a unifying trend across institutions. Bottom line, you need space to make your case, but even more, you need people to read what you write.
A single page abstract or executive summary of all your projects together provides you an opportunity to make the case for unifying themes yet distinct projects. It may also provide space to articulate a timeline. Indeed, many readers will only read this single page in each application, at least until winnowing down to a more manageable list of potential candidates. At the most elite institutions, there may be literally hundreds of applicants, scores of them entirely well-suited to the job.
While three to five pages per proposal was a common response (single spaced, in 11-point Arial or 12-point Times with one inch margins), including references (which should be accurate, appropriate, and current!), some of my busiest colleagues have said they will not read more than about three pages total. Only a few actually indicated they would read up to 12-15 pages for three projects. In my opinion, ten pages total for your research plans should be a fairly firm upper limit unless you are specifically told otherwise by a search committee, and then only if you have two to three distinct proposals.
Why Start Now?
Hopefully, this question has answered itself already! Your research plan needs to be a well thought out document that is an integrated part of applications tailored to each institution to which you apply. It must represent mature ideas that you have had time to refine through multiple revisions and a great deal of critical review from everyone you can get to read them. Moreover, you may need a few different sets of these, especially if you will be applying to a broad range of institutions. So add “write research plans” to this week’s to do list (and every week’s for the next few months) and start writing up the ideas in that manila folder into some genuine research plans. See which ones survive the process and rise to the top and you should be well prepared when the job ads begin to appear in C&EN in August!

Jason G. Gillmore , Ph.D., is an Associate Professor of Chemistry at Hope College in Holland, MI. A native of New Jersey, he earned his B.S. (’96) and M.S. (’98) degrees in chemistry from Virginia Tech, and his Ph.D. (’03) in organic chemistry from the University of Rochester. After a short postdoctoral traineeship at Vanderbilt University, he joined the faculty at Hope in 2004. He has received the Dreyfus Start-up Award, Research Corporation Cottrell College Science Award, and NSF CAREER Award, and is currently on sabbatical as a Visiting Research Professor at Arizona State University. Professor Gillmore is the organizer of the Biennial Midwest Postdoc to PUI Professor (P3) Workshop co-sponsored by ACS, and a frequent panelist at the annual ACS Postdoc to Faculty (P2F) Workshops.
Other tips to help engage (or at least not turn off) your readers include:
- Avoid two-column formats.
- Avoid too-small fonts that hinder readability, especially as many will view the documents online rather than in print!
- Use good figures that are readable and broadly understandable!
- Use color as necessary but not gratuitously.
Accept & Close The ACS takes your privacy seriously as it relates to cookies. We use cookies to remember users, better understand ways to serve them, improve our value proposition, and optimize their experience. Learn more about managing your cookies at Cookies Policy .
1155 Sixteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA | service@acs.org | 1-800-333-9511 (US and Canada) | 614-447-3776 (outside North America)
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society
- Contact sales
Start free trial
What Is a Work Plan? How to Make a Work Plan In 7 Steps

Before you can accomplish your project goals, you need to plan how to reach them. A work plan creates a clear path project teams can follow to reach their desired goals and objectives. Along that path will be resources, constraints and other work management elements that need to be described in your work plan.
What Is a Work Plan?
As its name suggests, a work plan is an action plan that helps project teams achieve their goals. Work plans factor in key project planning elements such as tasks, milestones, deliverables, resources, budgetary requirements and a timeline to weave it all together.
The work plan won’t be written and initiated by a single person and it should be submitted to board members and stakeholders for approval. Once approved, you can continue building out the rest of your work plan.
Get your free
Work Plan Template
Use this free Work Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Why Do You Need a Work Plan?
As we mentioned, your work plan acts as your roadmap for the entire project execution. Not only will it keep you and your team organized, but it’ll ensure that you get buy-in from key stakeholders, related departments, relevant accountability/risk leaders and more.
Additionally, it helps manage expectations on both the stakeholder level as well as on the managerial and team member level—everyone that starts off on the right foot has a better chance of landing on the right foot, too.
Work plans guide project teams in a similar way project plans do. However, there’s a big difference between these two important project management documents .
Work Plan vs. Project Plan
Work plans are not as comprehensive as project plans , which have a wider scope and involve more components. The main difference between them is that project plans are created from a high-level view and address every aspect of project management. On the other hand, work plans focus on helping project teams achieve smaller objectives.
If you build your work plan in project management software like ProjectManager , then it’s easy to continue to iterate on your plan and make improvements over time. You can use robust project planning tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, project dashboards and much more. Get started today for free.
How to Make a Work Plan in 7 Steps
While work plans might take many forms, here are some simple work planning steps you can follow to make one.
1. Set Goals & Objectives
Before anything, it’s important to write down the goals and objectives that’ll be achieved through your work plan. These will describe the purpose of your plan. It’s important to use SMART goals : create goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-related. This should help you start your plan off on the right foot.
Your goals might sound like your purpose, but they’re more specific in that they’re more long-term oriented — i.e., your team learned more about the process of launching a bug fix or how to respond more directly to customer or market feedback.
Similarly, your project objectives should be measurable. For example, the objective of this project after launch is to create an increase of xx% of active monthly subscribers, or a certain dollar amount in revenue generated.
2. Define the Scope of Your Work Plan
Once you’ve identified your work plan goals, you should use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to identify all the tasks that must be executed to achieve them, which is your project scope. By breaking down your project scope, you can start assembling a team, estimating costs, creating a budget and drafting a project schedule.
3. Estimate What Resources Are Needed
When you break down your project scope using a WBS, you can better estimate what resources are needed for each task in your work plan. Make sure to include different types of project resources, such as human resources, raw materials, machinery, subcontractors or anything else that you might need for the execution of your work plan.
4. Assign Roles & Responsibilities
Now, assemble a project team and clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each member. Communicate with them and make sure they understand what their job is and how they can collaborate with each other.
5. Estimate Costs & Create a Budget
Once you have a clear idea of what resources are needed for your work plan, it’s time to estimate their costs and create a budget . To do so, simply establish a measurement unit for your labor, materials and other resources to then assign a price to them.
6. Create a Project Schedule
There are different tools and techniques you can use to create a project schedule for your work plan. In fact, most project managers use Gantt charts, project calendars, kanban boards
7. List Any Risks, Constraints and Assumptions
Remember that your work plan is the action plan that’ll guide your project, so the more details you have about constraints and potential risks, the better your team will perform their tasks to produce deliverables and achieve the goals and objectives.
Maybe some of your team members take a few sick days during this period of time; maybe unexpected tasks have to be executed; maybe some of your tools crash that requires more money pulled from the budget. Whatever your project constraints may be, factor in anything that might feel like a risk that can lead to a full-blown constraint, which may affect the completion of deliverables or even the goals and objectives of your project.
Free Work Plan Template
Our work plan template can help you document the steps explained above. Be sure to constantly monitor your template and update it as changes occur in your planning process. Or, if you’re looking for more dynamic project planning tools, you can use Gantt charts.
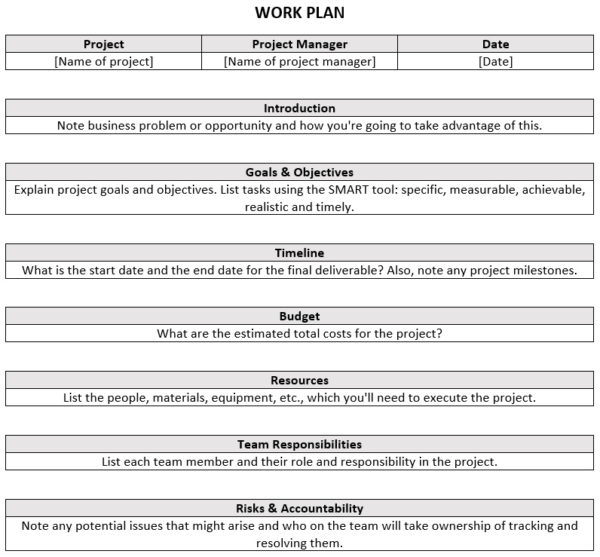
A work plan template can help you organize your thoughts, but in order to create your action plan and execute it, you’ll need dynamic project management software to help you throughout the planning, execution and monitoring phases.
Work Plan Example
Here’s a basic example to better illustrate how a work plan works. Let’s imagine you’re a business owner who wants to increase your production output by 25 percent by acquiring new machinery and hiring more production employees. While this project doesn’t involve producing tangible deliverables , you’ll still need a work plan.
Goals & Objectives It’s important to define one primary goal and then some smaller, more specific objectives needed for the completion of that goal.
Main Work Plan Goal Increase production output by 25 percent.
Work Plan Objectives
- Improve the company’s production capacity by acquiring new machinery
- Fill skill gaps in the production planning team
- Make sure machinery is well-maintained
Scope of the Work Plan Now, you should list individual activities that must be completed in order to achieve your goal and objectives. Here’s a simple breakdown of activities.
- Inspect the production line
- Perform preventive maintenance
- Optimize plant layout
- Acquire new machinery
- Assess the current team
- Hire new personnel
Resources/Roles & Responsibilities In this case, you’ll need a production manager, HR manager and maintenance team. They’re responsible for executing the tasks listed above.
Work Plan Budget Your budget should cover both the labor costs as well as the cost of the new equipment. Your labor costs will be the salaries of the production manager, HR manager and maintenance team. Make sure you estimate your project costs accurately before creating a budget.
Work Plan Schedule Define a timeframe for the analysis of your production line, the procurement of new machinery, preventive maintenance and hiring.
Risk, Assumptions & Constraints Think about any risks, assumptions or constraints that might affect your work plan. The best place to start is the triple constraint of time, budget and resources.
Creating a Work Plan With Project Management Software
To learn more about how project management tools such as Gantt charts , kanban boards and project dashboards can help you make the perfect work plan, watch the short video below. We’ll quickly show you all the ways that project planning software can improve your planning, execution and reporting—so you can make that work plan with confidence.
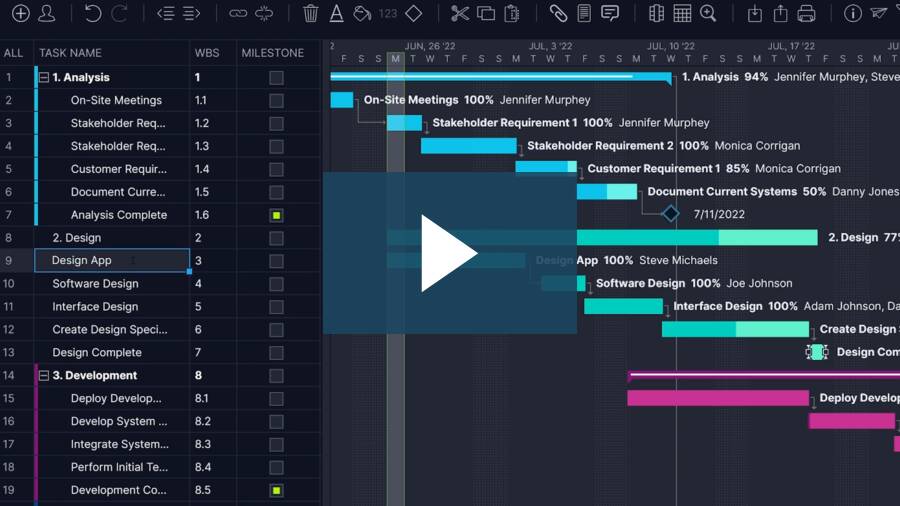
ProjectManager Can Help You With Your Work Plan
Getting every detail of a work plan sorted is no easy task—from managing your team to managing your stakeholders. It requires a delicate balance of understanding your project timeline, the tasks that make up the project scope, potential risks , balancing a budget and allocating resources. Not to mention, you’ll have to do this while keeping the customers’ ultimate needs and the project goals and objectives in mind.
With ProjectManager , our online Gantt charts let you schedule your entire project timeline, assign tasks, create dependencies and oversee tracking. Additionally, we have team collaboration features that allow your staff and managers to comment on tasks, attach necessary files, and interact with each other no matter where they’re located.
ProjectManager also features resource management tools that let you balance the hours worked across your team. This helps ensure that your time, tools and resources are balanced no matter what.
Related Work Management Content
- What Is Work Management? Creating a Work Management System
- Best Work Management Software of 2024 for Remote Teams
- What is a Statement of Work? Definition & Examples
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Creating a work plan and don’t know where to start? We’ve got you covered. With ProjectManager , you’ll get access to online software that helps you to better track your work plan from milestone to milestone. Start your free 30-day trial with ProjectManager today.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Personal Development
- Personal Goals
How to Write a Work Plan
Last Updated: September 10, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Sydney Axelrod . Sydney Axelrod is a certified life coach and the owner of Sydney Axelrod LLC, a life coaching business focused on professional and personal development. Through one-on-one coaching, digital courses, and group workshops, Sydney works with clients to discover their purpose, navigate life transitions, and set and accomplish goals. Sydney has over 1,000 hours of relevant coaching certifications and holds a BBA in Marketing and Finance from Emory University. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,697,017 times.
A work plan is an outline of a set of goals and processes by which a team and/or person can accomplish those goals, and offering the reader a better understanding of the scope of the project. Work plans, whether used in professional or academic life, help you stay organized while working on projects. [1] X Research source Through work plans, you break down a process into small, achievable tasks and identify the things you want to accomplish. Learn how to write a work plan so that you can be prepared for upcoming projects.
Mapping out Your Work Plan

- In the workplace, work plans help your supervisor know what projects you will be working on over the next several months. These often come right after an annual performance review or as teams undertake large projects. Work plans can also be the result of strategic planning sessions your organization holds at the beginning of a new calendar or fiscal year.
- In the academic world, work plans can help students create a schedule for a large project. They can also help teachers plan their course material for the semester.
- For a personal project, work plans will help you delineate what you intend to do, how you intend to do it, and by what date you intend to have it done. Personal work plans, while not strictly necessary, will help the individual keep track of his/her goals and progress.

- The introduction should be short and engaging. Remind your superiors why you are creating this work plan. Introduce the specific project(s) you will be working on during this time period.
- The background should highlight the reasons you are creating this work plan. For example, recite details or statistics from recent reports, identify problems that need to be addressed, or build off of recommendations or feedback you received during previous work projects.

- Goals should focus on the big picture of your project. List the desired ultimate outcome of your work plan. Keep it broad; for example, make your goal be to complete a research paper or to learn more about writing.
- Objectives should be specific and tangible. In other words, you should be able to check these off your list when you accomplish them. For example, finding people to interview for your research paper would make a good objective.
- Many work plans break down objectives into short- , middle- , and long-term objectives if they vary significantly. For example, a company's short-term goal to increase viewership 30% in three months may vary significantly from its long-term goal to strengthen brand visibility in social media outlets over the next year. [5] X Research source
- Objectives are generally written in the active voice and use action verbs with specific meanings (e.g. "plan," "write," "increase," and "measure") instead of verbs with vaguer meanings (e.g. "examine," "understand," "know," etc.). [6] X Research source

- Specific . What exactly are we going to do for whom? Lay out what population you are going to serve and any specific actions you will use to help that population.
- Remember that a baseline number needs to be established to quantify change. If you don't know the incidence rate of HIV/AIDS among South African newborns, it's going to be impossible to reliably say that you decreased incidence rates by 20%.
- In some cases, an expert or authority may need to be consulted to figure out if your work plan objectives are achievable.
- Relevant . Will this objective have an effect on the desired goal or strategy? Although it's probably important for overall health, does measuring the height and weight of high-schoolers directly lead to change in mental health procedures? Make sure your objectives and methods have a clear, intuitive relationship.
- Time bound . When will this objective be accomplished, and/or when will we know we are done? Specify a hard end date for the project. Stipulate which, if any, outcomes would cause your project to come to a premature end, with all outcomes having been achieved.

- At the workplace, resources can include things like financial budget, personnel, consultants, buildings or rooms, and books. A detailed budget may appear in an appendix if your work plan is more formal.
- In the academic arena, resources may include access to different libraries; research materials like books, newspapers, and journals; computer and Internet access; and professors or other individuals who can help you if you have questions.

- List specific action steps. Identify what needs to happen each day or week for you to complete your objectives. [10] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source Also, list steps other people on your team will need to take. Consider using project management software or a personal calendar to keep this information organized.
- Create a schedule. Though you can create a tentative work schedule, realize that unexpected things happen and you need to build space into your schedule to prevent falling behind.
Sample Plan and List of Things to Include

Expert Q&A
- Identify milestones if your project is especially large. Milestones are points throughout the project that highlight meeting certain objectives. They can also serve as a point of reflection, allowing you to look at here you are in the process and make sure you are still on track with the work plan. [11] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Make your work plan work for you. Work plans can be as detailed or as broad as you would like or need them to be. They can be written on a piece of paper or created on professional software, using graphics and colors. Use what is most natural and effective for you. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.insightful.io/blog/how-can-strategic-planning-improve-your-productivity
- ↑ http://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pm-pln.htm
- ↑ https://www.betterup.com/blog/how-to-create-a-work-plan
- ↑ Sydney Axelrod. Certified Life Coach. Expert Interview. 30 June 2020.
- ↑ https://smallbusiness.co.uk/short-mediumand-longterm-objectives-27759/
- ↑ http://rootedinrelationships.org/file_download/inline/1301eeee-df67-48b0-8445-f7daed9331b8
- ↑ SMART" objectives
- ↑ https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/make-work-plan
- ↑ https://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/structure/strategic-planning/identify-action-steps/main
- ↑ https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/milestones-project-management
About This Article

To write a work plan, start by defining a specific, measurable goal that you want to accomplish, like increasing sales by 50% by the end of the year. Then, list the resources that are available to help everyone involved accomplish the goal. You'll also want to mention any constraints or obstacles that might get in the way and how you plan on dealing with them. Also, make sure you clearly explain to everyone involved what they're accountable for. Finally, come up with a strategy for how you and your team are going to be successful. To learn more about how to break your plan into short-term and long-term goals, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Tadele Dekero
Jan 9, 2019
Did this article help you?

Caroline Fon
Oct 17, 2018
Stellah Lekalakala
Jul 11, 2016
Alice Lerotholi
Jun 1, 2017
Ahmad Muhammad
Apr 10, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- Research Data Lifecycle Guide
Developing a Data Management Plan
This section breaks down different topics required for the planning and preparation of data used in research at Case Western Reserve University. In this phase you should understand the research being conducted, the type and methods used for collecting data, the methods used to prepare and analyze the data, addressing budgets and resources required, and have a sound understanding of how you will manage data activities during your research project.
Many federal sponsors of Case Western Reserve funded research have required data sharing plans in research proposals since 2003. As of Jan. 25, 2023, the National Institutes of Health has revised its data management and sharing requirements.
This website is designed to provide basic information and best practices to seasoned and new investigators as well as detailed guidance for adhering to the revised NIH policy.
Basics of Research Data Management
What is research data management?
Research data management (RDM) comprises a set of best practices that include file organization, documentation, storage, backup, security, preservation, and sharing, which affords researchers the ability to more quickly, efficiently, and accurately find, access, and understand their own or others' research data.
Why should you care about research data management?
RDM practices, if applied consistently and as early in a project as possible, can save you considerable time and effort later, when specific data are needed, when others need to make sense of your data, or when you decide to share or otherwise upload your data to a digital repository. Adopting RDM practices will also help you more easily comply with the data management plan (DMP) required for obtaining grants from many funding agencies and institutions.
Does data need to be retained after a project is completed?
Research data must be retained in sufficient detail and for an adequate period of time to enable appropriate responses to questions about accuracy, authenticity, primacy and compliance with laws and regulations governing the conduct of the research. External funding agencies will each have different requirements regarding storage, retention, and availability of research data. Please carefully review your award or agreement for the disposition of data requirements and data retention policies.
A good data management plan begins by understanding the sponsor requirements funding your research. As a principal investigator (PI) it is your responsibility to be knowledgeable of sponsors requirements. The Data Management Plan Tool (DMPTool) has been designed to help PIs adhere to sponsor requirements efficiently and effectively. It is strongly recommended that you take advantage of the DMPTool.
CWRU has an institutional account with DMPTool that enables users to access all of its resources via your Single Sign On credentials. CWRU's DMPTool account is supported by members of the Digital Scholarship team with the Freedman Center for Digital Scholarship. Please use the RDM Intake Request form to schedule a consultation if you would like support or guidance regarding developing a Data Management Plan.
Some basic steps to get started:
- Sign into the DMPTool site to start creating a DMP for managing and sharing your data.
- On the DMPTool site, you can find the most up to date templates for creating a DMP for a long list of funders, including the NIH, NEH, NSF, and more.
- Explore sample DMPs to see examples of successful plans .
Be sure that your DMP is addressing any and all federal and/or funder requirements and associated DMP templates that may apply to your project. It is strongly recommended that investigators submitting proposals to the NIH utilize this tool.
The NIH is mandating Data Management and Sharing Plans for all proposals submitted after Jan. 25, 2023. Guidance for completing a NIH Data Management Plan has its own dedicated content to provide investigators detailed guidance on development of these plans for inclusion in proposals.
A Data Management Plan can help create and maintain reliable data and promote project success. DMPs, when carefully constructed and reliably adhered to, help guide elements of your research and data organization.
A DMP can help you:
Document your process and data.
- Maintain a file with information on researchers and collaborators and their roles, sponsors/funding sources, methods/techniques/protocols/standards used, instrumentation, software (w/versions), references used, any applicable restrictions on its distribution or use.
- Establish how you will document file changes, name changes, dates of changes, etc. Where will you record of these changes? Try to keep this sort of information in a plain text file located in the same folder as the files to which it pertains.
- How are derived data products created? A DMP encourages consistent description of data processing performed, software (including version number) used, and analyses applied to data.
- Establish regular forms or templates for data collection. This helps reduce gaps in your data, promotes consistency throughout the project.
Explain your data
- From the outset, consider why your data were collected, what the known and expected conditions may be for collection, and information such as time and place, resolution, and standards of data collected.
- What attributes, fields, or parameters will be studied and included in your data files? Identify and describe these in each file that employs them.
- For an overview of data dictionaries, see the USGS page here: https://www.usgs.gov/products/data-and-tools/data-management/data-dictionaries
DMP Requirements
Why are you being asked to include a data management plan (DMP) in your grant application? For grants awarded by US governmental agencies, two federal memos from the US Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), issued in 2013 and 2015 , respectively, have prompted this requirement. These memos mandate public access to federally- (and, thus, taxpayer-) funded research results, reflecting a commitment by the government to greater accountability and transparency. While "results" generally refers to the publications and reports produced from a research project, it is increasingly used to refer to the resulting data as well.
Federal research-funding agencies have responded to the OSTP memos by issuing their own guidelines and requirements for grant applicants (see below), specifying whether and how research data in particular are to be managed in order to be publicly and properly accessible.
- NSF—National Science Foundation "Proposals submitted or due on or after January 18, 2011, must include a supplementary document of no more than two pages labeled 'Data Management Plan'. This supplementary document should describe how the proposal will conform to NSF policy on the dissemination and sharing of research results." Note: Additional requirements may apply per Directorate, Office, Division, Program, or other NSF unit.
- NIH—National Institutes of Health "To facilitate data sharing, investigators submitting a research application requesting $500,000 or more of direct costs in any single year to NIH on or after October 1, 2003 are expected to include a plan for sharing final research data for research purposes, or state why data sharing is not possible."
- NASA—National Aeronautics and Space Administration "The purpose of a Data Management Plan (DMP) is to address the management of data from Earth science missions, from the time of their data collection/observation, to their entry into permanent archives."
- DOD—Department of Defense "A Data Management Plan (DMP) describing the scientific data expected to be created or gathered in the course of a research project must be submitted to DTIC at the start of each research effort. It is important that DoD researchers document plans for preserving data at the outset, keeping in mind the potential utility of the data for future research or to support transition to operational or other environments. Otherwise, the data is lost as researchers move on to other efforts. The essential descriptive elements of the DMP are listed in section 3 of DoDI 3200.12, although the format of the plan may be adjusted to conform to standards established by the relevant scientific discipline or one that meets the requirements of the responsible Component"
- Department of Education "The purpose of this document is to describe the implementation of this policy on public access to data and to provide guidance to applicants for preparing the Data Management Plan (DMP) that must outline data sharing and be submitted with the grant application. The DMP should describe a plan to provide discoverable and citable dataset(s) with sufficient documentation to support responsible use by other researchers, and should address four interrelated concerns—access, permissions, documentation, and resources—which must be considered in the earliest stages of planning for the grant."
- " Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI) Provides access to free, publicly-available research sponsored by the Department of Energy (DOE), including technical reports, bibliographic citations, journal articles, conference papers, books, multimedia, software, and data.
Data Management Best Practices
As you plan to collect data for research, keep in mind the following best practices.
Keep Your Data Accessible to You
- Store your temporary working files somewhere easily accessible, like on a local hard drive or shared server.
- While cloud storage is a convenient solution for storage and sharing, there are often concerns about data privacy and preservation. Be sure to only put data in the cloud that you are comfortable with and that your funding and/or departmental requirements allow.
- For long-term storage, data should be put into preservation systems that are well-managed. [U]Tech provides several long-term data storage options for cloud and campus.
- Don't keep your original data on a thumb drive or portable hard drive, as it can be easily lost or stolen.
- Think about file formats that have a long life and that are readable by many programs. Formats like ascii, .txt, .csv, .pdf are great for long term preservation.
- A DMP is not a replacement for good data management practices, but it can set you on the right path if it is consistently followed. Consistently revisit your plan to ensure you are following it and adhering to funder requirements.
Preservation
- Know the difference between storing and preserving your data. True preservation is the ongoing process of making sure your data are secure and accessible for future generations. Many sponsors have preferred or recommended data repositories. The DMP tool can help you identify these preferred repositories.
- Identify data with long-term value. Preserve the raw data and any intermediate/derived products that are expensive to reproduce or can be directly used for analysis. Preserve any scripted code that was used to clean and transform the data.
- Whenever converting your data from one format to another, keep a copy of the original file and format to avoid loss or corruption of your important files.
- Leverage online platforms like OSF can help your group organize, version, share, and preserve your data, if the sponsor hasn’t specified a specific platform.
- Adhere to federal sponsor requirements on utilizing accepted data repositories (NIH dbGaP, NIH SRA, NIH CRDC, etc.) for preservation.
Backup, Backup, Backup
- The general rule is to keep 3 copies of your data: 2 copies onsite, 1 offsite.
- Backup your data regularly and frequently - automate the process if possible. This may mean weekly duplication of your working files to a separate drive, syncing your folders to a cloud service like Box, or dedicating a block of time every week to ensure you've copied everything to another location.
Organization
- Establish a consistent, descriptive filing system that is intelligible to future researchers and does not rely on your own inside knowledge of your research.
- A descriptive directory and file-naming structure should guide users through the contents to help them find whatever they are looking for.
Naming Conventions
- Use consistent, descriptive filenames that reliably indicate the contents of the file.
- If your discipline requires or recommends particular naming conventions, use them!
- Do not use spaces between words. Use either camelcase or underscores to separate words
- Include LastnameFirstname descriptors where appropriate.
- Avoid using MM-DD-YYYY formats
- Do not append vague descriptors like "latest" or "final" to your file versions. Instead, append the version's date or a consistently iterated version number.
Clean Your Data
- Mistakes happen, and often researchers don't notice at first. If you are manually entering data, be sure to double-check the entries for consistency and duplication. Often having a fresh set of eyes will help to catch errors before they become problems.
- Tabular data can often be error checked by sorting the fields alphanumerically to catch simple typos, extra spaces, or otherwise extreme outliers. Be sure to save your data before sorting it to ensure you do not disrupt the records!
- Programs like OpenRefine are useful for checking for consistency in coding for records and variables, catching missing values, transforming data, and much more.
What should you do if you need assistance implementing RDM practices?
Whether it's because you need discipline-specific metadata standards for your data, help with securing sensitive data, or assistance writing a data management plan for a grant, help is available to you at CWRU. In addition to consulting the resources featured in this guide, you are encouraged to contact your department's liaison librarian.
If you are planning to submit a research proposal and need assistance with budgeting for data storage and or applications used to capture, manage, and or process data UTech provides information and assistance including resource boilerplates that list what centralized resources are available.
More specific guidance for including a budget for Data Management and Sharing is included on this document: Budgeting for Data Management and Sharing .
Custody of Research Data
The PI is the custodian of research data, unless agreed on in writing otherwise and the agreement is on file with the University, and is responsible for the collection, management, and retention of research data. The PI should adopt an orderly system of data organization and should communicate the chosen system to all members of a research group and to the appropriate administrative personnel, where applicable. Particularly for long-term research projects, the PI should establish and maintain procedures for the protection and management of essential records.
CWRU Custody of Research Data Policy
Data Sharing
Many funding agencies require data to be shared for the purposes of reproducibility and other important scientific goals. It is important to plan for the timely release and sharing of final research data for use by other researchers. The final release of data should be included as a key deliverable of the DMP. Knowledge of the discipline-specific database, data repository, data enclave, or archive store used to disseminate the data should also be documented as needed.
The NIH is mandating Data Management and Sharing Plans for all proposals submitted after Jan. 25, 2023. Guidance for completing a NIH Data Management and Sharing Plan has its own dedicated content to provide investigators detailed guidance on development of these plans for inclusion in proposals.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Violence Prevention
- Resources for Action
- Cardiff Model
Violence Prevention

About The Public Health Approach to Violence Prevention
Violence Topics

About Adverse Childhood Experiences
About Child Abuse and Neglect
About Community Violence
About Firearm Injury and Death
About Intimate Partner Violence
About Sexual Violence
About Youth Violence
About Abuse of Older Persons
About Violence Against Children and Youth Surveys
About The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey (NISVS)
About The National Violent Death Reporting System (NVDRS)
Featured Resources

Essentials for Parenting Teens

Essentials for Parenting Toddlers and Preschoolers

Cardiff Violence Prevention Model Toolkit
Violence is an urgent public health problem. CDC is committed to preventing violence so that everyone can be safe and healthy.
For Everyone
Public health.
How to Create a Project Tracker in Excel
By Kate Eby | May 17, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve compiled step-by-step directions on creating a project tracker to ensure the completion of all project tasks and keep projects progressing toward their deadlines.
Included in this article, you’ll find the following:
- Guide to creating a project tracker in Excel
- Excel project tracker template with sample data
- Useful chart to help you pick the best template
What Is a Project Tracker?
A project tracker is a project management tool used for monitoring multiple projects so that they stay on schedule and within budget. Managers can use project trackers as a single source of data for listing and auditing project tasks.
To accurately track all your projects’ tasks, owners, timelines, budgets, and hours, download the project tracker template from this page. Once you download the template, you can easily start tracking and managing your projects with the template’s user-friendly layout.
Use the following step-by-step instructions to create a project tracker in Excel.
1. Download and Open the Simple Multiple Project Tracking Template
Download the simple multiple project tracking template to your computer, and save it using your preferred file-naming conventions.
2. Enter the Company Name and Project Start Date
When you input the start date, the Gantt chart automatically updates to display the weekly timeline of your project.
3. Enter the Project Names, Task Titles, and Task Descriptions
Replace the sample text with your project and task names to customize the cells.
4. Enter the Task Owners and Start Dates
Enter the task owners and the start dates of each task.
5. Select a Status and Priority for Each Project and Task
Use the drop-down menus to select the status and priority of each project and task.
6. Enter the End Dates
The number of days for each project and task will auto-populate. The timelines will become visible in the Gantt chart.
7. Enter the Deliverables and Percentage Complete
As you enter the percentage completed for each deliverable, the template will automatically calculate the total percentage of the project’s completion.
8. Enter the Fixed Costs
As you enter the fixed cost for each deliverable, the template will automatically calculate the total fixed cost of the project.
9. Enter the Estimated and Actual Hours
As you enter the estimated and actual hours for each deliverable, the template will automatically calculate the total estimated and actual hours of the project.
Excel Simple Multiple Project Tracking Template
Download the Example Simple Multiple Project Tracking Template for Excel
Download the Blank Simple Multiple Project Tracking Template for Excel
This easy-to-use template is ideal for project managers who need to organize and track multiple projects simultaneously. The template features a week-by-week Gantt chart for a visual representation of each project’s and task’s progress. The Gantt chart auto-populates color-coded timelines as you enter start and end dates. This template also includes sections for tracking total costs and hours spent on each task.
For additional project tracking resources, check out these free project tracking templates .
Project Tracker Templates in Excel
Project tracker templates track many components of a project, including timelines, deadlines, budgets, and more. Check out the comprehensive list of project tracker templates below, and use the provided chart to choose the one that best fits your needs.
Excel Project Management Issue Tracking Template
To track project issues and their solutions, download this project management issue tracking template . It includes pie charts for a quick view of the status of outstanding issues. If you need a project management template, check out these top project management templates in Excel .
Project Time Tracking Template
To track the timeline of each project task, use this project time tracking template . Once you enter a task's start and end date, the template automatically updates the Gantt chart to reflect your project's timeline.
Multiple Project Budget Tracking Template
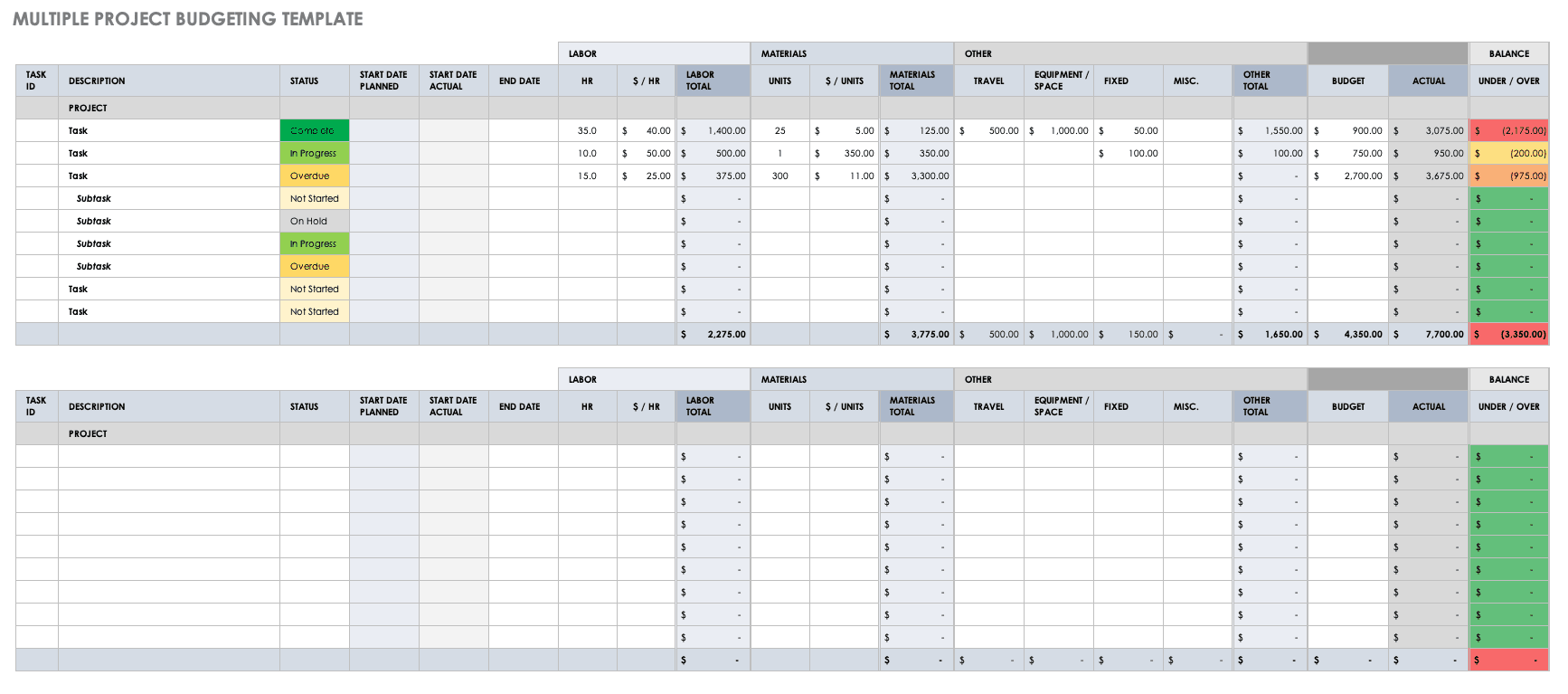
To track the budget of multiple projects, use this multiple project budget tracking template . It includes a section for tracking labor and materials used.
Agile Sprint Tracking Template
To track the sprints in an Agile project, use this Agile sprint tracking template . The color-coded Gantt chart makes it easy to follow the progress and duration of every sprint.
Multiple Project Schedule Template
To track the timelines of multiple projects’ tasks, use this multiple project schedule template . It allows you to schedule and track tasks monthly, quarterly, and annually.
If you’re having trouble deciding which template is right for you, refer to the following chart:
To guide and manage project execution, check out these top project plan templates .
Track Projects with Ease Using Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
News Roundup Spring 2024

CEGE Spring Graduation Celebration and Order of the Engineer
Forty-seven graduates of the undergraduate and grad student programs (pictured above) in the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering took part in the Order of the Engineer on graduation day. Distinguished Speakers at this departmental event included Katrina Kessler (MS EnvE 2021), Commissioner of the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, and student Brian Balquist. Following this event, students participated in the college-wide Commencement Ceremony at 3M Arena at Mariucci.
UNIVERSITY & DEPARTMENT
The University of Minnesota’s Crookston, Duluth, and Rochester campuses have been awarded the Carnegie Elective Classification for Community Engagement, joining the Twin Cities (2006, 2015) and Morris campuses (2015), and making the U of M the country’s first and only university system at which every individual campus has received this selective designation. Only 368 from nearly 4,000 qualifying U.S. universities and colleges have been granted this designation.
CEGE contributed strongly to the College of Science and Engineering’s efforts toward sustainability research. CEGE researchers are bringing in over $35 million in funded research to study carbon mineralization, nature and urban areas, circularity of water resources, and global snowfall patterns. This news was highlighted in the Fall 2023 issue of Inventing Tomorrow (pages 10-11). https://issuu.com/inventingtomorrow/docs/fall_2023_inventing_tomorrow-web
CEGE’s new program for a one-year master’s degree in structural engineering is now accepting applicants for Fall 2024. We owe a big thanks to DAN MURPHY and LAURA AMUNDSON for their volunteer work to help curate the program with Professor JIA-LIANG LE and EBRAHIM SHEMSHADIAN, the program director. Potential students and companies interested in hosting a summer intern can contact Ebrahim Shemshadian ( [email protected] ).
BERNIE BULLERT , CEGE benefactor and MN Water Research Fund founder, was profiled on the website of the University of Minnesota Foundation (UMF). There you can read more about his mission to share clean water technologies with smaller communities in Minnesota. Many have joined Bullert in this mission. MWRF Recognizes their Generous 2024 Partners. Gold Partners: Bernie Bullert, Hawkins, Inc., Minnesota Department of Health, Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, and SL-serco. Silver Partners: ISG, Karl and Pam Streed, Kasco, Kelly Lange-Haider and Mark Haider, ME Simpson, Naeem Qureshi, Dr. Paul H. Boening, TKDA, and Waterous. Bronze Partners: Bruce R. Bullert; Brenda Lenz, Ph.D., APRN FNP-C, CNE; CDM Smith; Central States Water Environment Association (CSWEA MN); Heidi and Steve Hamilton; Jim “Bulldog” Sadler; Lisa and Del Cerney; Magney Construction; Sambatek; Shannon and John Wolkerstorfer; Stantec; and Tenon Systems.
After retiring from Baker-Tilly, NICK DRAGISICH (BCE 1977) has taken on a new role: City Council member in Lake Elmo, Minnesota. After earning his BCE from the University of Minnesota, Dragisich earned a master’s degree in business administration from the University of St. Thomas. Dragisich retired in May from his position as managing director at Baker Tilly, where he had previously served as firm director. Prior to that, he served as assistant city manager in Spokane, Washington, was the city administrator and city engineer in Virginia, Minnesota, and was mayor of Chisholm, Minnesota—all adding up to more than 40 years of experience in local government. Dragisich was selected by a unanimous vote. His current term expires in December 2024.
PAUL F. GNIRK (Ph.D. 1966) passed away January 29, 2024, at the age of 86. A memorial service was held Saturday, February 24, at the South Dakota School of Mines and Technology (SDSM&T), where he started and ended his teaching career, though he had many other positions, professional and voluntary. In 2018 Paul was inducted into the SDSM&T Hardrocker Hall of Fame, and in 2022, he was inducted into the South Dakota Hall of Fame, joining his mother Adeline S. Gnirk, who had been inducted in 1987 for her work authoring nine books on the history of south central South Dakota.
ROGER M. HILL (BCE 1957) passed away on January 13, 2024, at the age of 90. His daughter, Kelly Robinson, wrote to CEGE that Roger was “a dedicated Gopher fan until the end, and we enjoyed many football games together in recent years. Thank you for everything.”
KAUSER JAHAN (Ph.D. 1993, advised by Walter Maier), PE, is now a civil and environmental engineering professor and department head at Henry M. Rowan College of Engineering. Jahan was awarded a 3-year (2022- 2025), $500,000 grant from the U.S. Department of Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). The grant supports her project, “WaterWorks: Developing the New Generation of Workforce for Water/Wastewater Utilities,” for the development of educational tools that will expose and prepare today’s students for careers in water and wastewater utilities.
SAURA JOST (BCE 2010, advised by Timothy LaPara) was elected to the St. Paul City Council for Ward 3. She is part of the historic group of women that make up the nation’s first all-female city council in a large city.
The 2024 ASCE Western Great Lakes Student Symposium combines several competitions for students involved in ASCE. CEGE sent a large contingent of competitors to Chicago. Each of the competition groups won awards: Ethics Paper 1st place Hans Lagerquist; Sustainable Solutions team 1st place overall in (qualifying them for the National competition in Utah in June); GeoWall 2nd place overall; Men’s Sprint for Concrete Canoe with rowers Sakthi Sundaram Saravanan and Owen McDonald 2nd place; Product Prototype for Concrete Canoe 2nd place; Steel Bridge (200 lb bridge weight) 2nd place in lightness; Scavenger Hunt 3rd place; and Aesthetics and Structural Efficiency for Steel Bridge 4th place.
Students competing on the Minnesota Environmental Engineers, Scientists, and Enthusiasts (MEESE) team earned second place in the Conference on the Environment undergraduate student design competition in November 2023. Erin Surdo is the MEESE Faculty Adviser. Pictured are NIKO DESHPANDE, ANNA RETTLER, and SYDNEY OLSON.
The CEGE CLASS OF 2023 raised money to help reduce the financial barrier for fellow students taking the Fundamentals of Engineering exam, a cost of $175 per test taker. As a result of this gift, they were able to make the exam more affordable for 15 current CEGE seniors. CEGE students who take the FE exam pass the first time at a rate well above national averages, demonstrating that CEGE does a great job of teaching engineering fundamentals. In 2023, 46 of 50 students passed the challenging exam on the first try.
This winter break, four CEGE students joined 10 other students from the College of Science and Engineering for the global seminar, Design for Life: Water in Tanzania. The students visited numerous sites in Tanzania, collected water source samples, designed rural water systems, and went on safari. Read the trip blog: http://globalblogs.cse.umn.edu/search/label/Tanzania%202024
Undergraduate Honor Student MALIK KHADAR (advised by Dr. Paul Capel) received honorable mention for the Computing Research Association (CRA) Outstanding Undergraduate Research Award for undergraduate students who show outstanding research potential in an area of computing research.
GRADUATE STUDENTS
AKASH BHAT (advised by William Arnold) presented his Ph.D. defense on Friday, October 27, 2023. Bhat’s thesis is “Photolysis of fluorochemicals: Tracking fluorine, use of UV-LEDs, and computational insights.” Bhat’s work investigating the degradation of fluorinated compounds will assist in the future design of fluorinated chemicals such that persistent and/or toxic byproducts are not formed in the environment.
ETHAN BOTMEN (advised by Bill Arnold) completed his Master of Science Final Exam February 28, 2024. His research topic was Degradation of Fluorinated Compounds by Nucleophilic Attack of Organo-fluorine Functional Groups.
XIATING CHEN , Ph.D. Candidate in Water Resources Engineering at the Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory is the recipient of the 2023 Nels Nelson Memorial Fellowship Award. Chen (advised by Xue Feng) is researching eco-hydrological functions of urban trees and other green infrastructure at both the local and watershed scale, through combined field observations and modeling approaches.
ALICE PRATES BISSO DAMBROZ has been a Visiting Student Researcher at the University of Minnesota since last August, on a Doctoral Dissertation Research Award from Fulbright. Her CEGE advisor is Dr. Paul Capel. Dambroz is a fourth year Ph.D. student in Soil Science at Universidade Federal de Santa Maria in Brazil, where she studies with her adviser Jean Minella. Her research focuses on the hydrological monitoring of a small agricultural watershed in Southern Brazil, which is located on a transition area between volcanic and sedimentary rocks. Its topography, shallow soils, and land use make it prone to runoff and erosion processes.
Yielding to people in crosswalks should be a very pedestrian topic. Yet graduate student researchers TIANYI LI, JOSHUA KLAVINS, TE XU, NIAZ MAHMUD ZAFRI (Dept.of Urban and Regional Planning at Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology), and Professor Raphael Stern found that drivers often do not yield to pedestrians, but they are influenced by the markings around a crosswalk. Their work was picked up by the Minnesota Reformer.
TIANYI LI (Ph.D. student advised by Raphael Stern) also won the Dwight David Eisenhower Transportation (DDET) Fellowship for the third time! Li (center) and Stern (right) are pictured at the Federal Highway Administration with Latoya Jones, the program manager for the DDET Fellowship.
The Three Minute Thesis Contest and the Minnesota Nice trophy has become an annual tradition in CEGE. 2023’s winner was EHSANUR RAHMAN , a Ph.D. student advised by Boya Xiong.
GUANJU (WILLIAM) WEI , a Ph.D. student advised by Judy Yang, is the recipient of the 2023 Heinz G. Stefan Fellowship. He presented his research entitled Microfluidic Investigation of the Biofilm Growth under Dynamic Fluid Environments and received his award at the St. Anthony Falls Research Laboratory April 9. The results of Wei's research can be used in industrial, medical, and scientific fields to control biofilm growth.
BILL ARNOLD stars in an award-winning video about prairie potholes. The Prairie Potholes Project film was made with the University of Delaware and highlights Arnold’s NSF research. The official winners of the 2024 Environmental Communications Awards Competition Grand Prize are Jon Cox and Ben Hemmings who produced and directed the film. Graduate student Marcia Pacheco (CFANS/LAAS) and Bill Arnold are the on-screen stars.
Four faculty from CEGE join the Center for Transportation Studies Faculty and Research Scholars for FY24–25: SEONGJIN CHOI, KETSON ROBERTO MAXIMIANO DOS SANTOS, PEDRAM MORTAZAVI, and BENJAMIN WORSFOLD . CTS Scholars are drawn from diverse fields including engineering, planning, computer science, environmental studies, and public policy.
XUE FENG is coauthor on an article in Nature Reviews Earth and Environment . The authors evaluate global plant responses to changing rainfall regimes that are now characterized by fewer and larger rainfall events. A news release written at Univ. of Maryland can be found here: https://webhost.essic. umd.edu/april-showers-bring-mayflowers- but-with-drizzles-or-downpours/ A long-running series of U of M research projects aimed at improving stormwater quality are beginning to see practical application by stormwater specialists from the Twin Cities metro area and beyond. JOHN GULLIVER has been studying best practices for stormwater management for about 16 years. Lately, he has focused specifically on mitigating phosphorous contamination. His research was highlighted by the Center for Transportation Studies.
JIAQI LI, BILL ARNOLD, and RAYMOND HOZALSKI published a paper on N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) precursors in Minnesota rivers. “Animal Feedlots and Domestic Wastewater Discharges are Likely Sources of N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) Precursors in Midwestern Watersheds,” Environmental Science and Technology (January 2024) doi: 10.1021/acs. est.3c09251
ALIREZA KHANI contributed to MnDOT research on Optimizing Charging Infrastructure for Electric Trucks. Electric options for medium- and heavy-duty electric trucks (e-trucks) are still largely in development. These trucks account for a substantial percentage of transportation greenhouse gas emissions. They have greater power needs and different charging needs than personal EVs. Proactively planning for e-truck charging stations will support MnDOT in helping to achieve the state’s greenhouse gas reduction goals. This research was featured in the webinar “Electrification of the Freight System in Minnesota,” hosted by the University of Minnesota’s Center for Transportation Studies. A recording of the event is now available online.
MICHAEL LEVIN has developed a unique course for CEGE students on Air Transportation Systems. It is the only class at UMN studying air transportation systems from an infrastructure design and management perspective. Spring 2024 saw the third offering of this course, which is offered for juniors, seniors, and graduate students.
Research Professor SOFIA (SONIA) MOGILEVSKAYA has been developing international connections. She visited the University of Seville, Spain, November 13–26, 2023, where she taught a short course titled “Fundamentals of Homogenization in Composites.” She also met with the graduate students to discuss collaborative research with Prof. Vladislav Mantic, from the Group of Continuum Mechanics and Structural Analysis at the University of Seville. Her visit was a part of planned activities within the DIAGONAL Consortium funded by the European Commission. CEGE UMN is a partner organization within DIAGONAL, represented by CEGE professors Mogilevskaya and Joseph Labuz. Mantic will visit CEGE summer 2024 to follow up on research developments and discuss plans for future collaboration and organization of short-term exchange visits for the graduate students from each institution.
DAVID NEWCOMB passed away in March. He was a professor in CEGE from 1989–99 in the area of pavement engineering. Newcomb led the research program on asphalt materials characterization. He was the technical director of Mn/ROAD pavement research facility, and he started an enduring collaboration with MnDOT that continues today. In 2000, he moved from Minnesota to become vice-president for Research and Technology at the National Asphalt Pavement Association. Later he moved to his native Texas, where he was appointed to the division head of Materials and Pavement at the Texas A&M Transportation Institute, a position from which he recently retired. He will be greatly missed.
PAIGE NOVAK won Minnesota ASCE’s 2023 Distinguished Engineer of the Year Award for her contributions to society through her engineering achievements and professional experiences.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) announced ten inaugural (NSF) Regional Innovation Engines awards, with a potential $1.6 billion investment nationally over the next decade. Great Lakes ReNEW is led by the Chicago-based water innovation hub, Current, and includes a team from the University of Minnesota, including PAIGE NOVAK. Current will receive $15 mil for the first two years, and up to $160 million over ten years to develop and grow a water-focused innovation engine in the Great Lakes region. The project’s ambitious plan is to create a decarbonized circular “blue economy” to leverage the region’s extraordinary water resources to transform the upper Midwest—Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, and Wisconsin. Brewing one pint of beer generates seven pints of wastewater, on average. So what can you do with that wastewater? PAIGE NOVAK and her team are exploring the possibilities of capturing pollutants in wastewater and using bacteria to transform them into energy.
BOYA XIONG has been selected as a recipient of the 2024 40 Under 40 Recognition Program by the American Academy of Environmental Engineers and Scientists. The award was presented at the 2024 AAEES Awards Ceremony, April 11, 2024, at the historic Howard University in Washington, D.C.
JUDY Q. YANG received a McKnight Land-Grant Professorship Award. This two-year award recognizes promising assistant professors and is intended to advance the careers of individuals who have the potential to make significant contributions to their departments and their scholarly fields.
Professor Emeritus CHARLES FAIRHURST , his son CHARLES EDWARD FAIRHURST , and his daughter MARGARET FAIRHURST DURENBERGER were on campus recently to present Department Head Paige Novak with a check for $25,000 for the Charles Fairhurst Fellowship in Earth Resources Engineering in support of graduate students studying geomechanics. The life of Charles Fairhurst through a discussion with his children is featured on the Engineering and Technology History Wiki at https://ethw.org/Oral-History:Charles_Fairhurst#00:00:14_INTRODUCTION
Related news releases
- Matthew J. Huber Student Award
- Catherine French, NAE
- Climate Change for Engineers
- Focused on the Road Ahead
- Randal Barnes receives Horace T Morace Award
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- CSE Dean's Club
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event

COMMENTS
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3. Proposed timeline
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
The completed work plan for your Master's Project should contain three parts: (1) scope of work, (2) project timeline, and (3) team charter. ... Be specific and identify significant subtasks related to each part of your project. State any research support needed in terms of supplies, space, equipment and money. If needed, identify source(s ...
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan. 1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Step 4: Write a summary. Prepare a project summary that serves as your research project guide. This invaluable tool aids recruitment interviews, meetings, and field studies. With a well-structured summary, you can stay on track during interactions, ensuring you address key project aspects.
In other words, the following provides a systematic means to establish the building blocks of your research project. Exercise 1: Definition of research question and sources. This exercise prompts you to select and clarify your general interest area, develop a research question, and investigate sources of information.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Within the character limit, include the important information to distinguish your project within the research area, your project's goals, and the research problem. Giving your project a title at the outset can help you stay focused and avoid a meandering Research Plan. So you may want to launch your writing by creating a well-defined title.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
1. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. ClickUp User Research Plan Template. One of the first things that comes to mind when you say "research plan template" is user research. For development and project teams, this is one step of the process where strategy and staying organized is essential.
The research project plan template is designed for research teams in academic, corporate, or non-profit sectors who need to plan and execute their research projects. The template provides a structure for outlining the processes and activities that must be completed in order to achieve the desired results of the research project. The template is ...
A research work plan is an integrated, comprehensive, and well-coordinated written document which is generally used for the successful development plan of a specific research project, thesis work, PhD research work, and/or other outputs of in-depth analysis and discovery. It also illustrates beneficial explanations of initial ideas and concepts ...
By identifying timelines, project goals, and due dates, both you and your advisor(s) will be able to evaluate if the proposed schedule is achievable within the required time frame of the project. If you're unsure if your research proposal requires a schedule or work plan, please consult your project handbook and/or speak with your instructor ...
A well-written research plan should start with articulating the research question and, from there, proceed to mention the purpose, how your project is going to work, what resources you will require, grand of special permissions from organizations ( if needed), setting the deadline for each part to ending with the finance limitations for that ...
12+ Research Work Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word. A work plan is an overview of a series of objectives and procedures by which a team and/or entity can achieve those goals and provide the reader with a clearer picture of the project's context. No matter if it is used in professional or academic life, work plans serve the purpose of helping you stay focused when working on a certain project.
research work, being asked to complete a research project for the first time might seem fairly intimidating. It doesn't need to be, though, and this study guide is designed to make sure that it isn't. This booklet is a guide to some of the most important aspects of research projects. Whether the project is as small as a research
To make a background research plan — a roadmap of the research questions you need to answer — follow these steps: Identify the keywords in the question for your science fair project. Brainstorm additional keywords and concepts. Use a table with the "question words" (why, how, who, what, when, where) to generate research questions from your ...
A research plan is pivotal to a research project because it identifies and helps define your focus, method, and goals while also outlining the research project from start to finish. This type of plan is often necessary to: Apply for grants or internal company funding. Discover possible research partners or business partners.
That is why you need to create a research project plan first before you start purchasing materials or begin working on your actual project. 2. Utilize research materials. After a choosing the project to work on, it's now time to work on the details of the actual research action plan. There are numerous research materials and research ...
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind: Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should ...
1. Set Goals & Objectives. Before anything, it's important to write down the goals and objectives that'll be achieved through your work plan. These will describe the purpose of your plan. It's important to use SMART goals: create goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-related.
A work plan is an outline of a set of goals and processes by which a team and/or person can accomplish those goals, and offering the reader a better understanding of the scope of the project. Work plans, whether used in professional or academic life, help you stay organized while working on projects. [1]
A phased plan also allows you to review and refine your work continuously, ensuring quality and coherence in your research. Add your perspective Help others by sharing more (125 characters min ...
A project proposal is a document that outlines the plan for a proposed project. It describes what the project is about, what needs to be done, and how it will be done. A project on the other hand, is the actual work that is carried out to achieve the objectives outlined in the project proposal.
"A Data Management Plan (DMP) describing the scientific data expected to be created or gathered in the course of a research project must be submitted to DTIC at the start of each research effort. It is important that DoD researchers document plans for preserving data at the outset, keeping in mind the potential utility of the data for future ...
Prepare the draft subcontract(s) to conduct project work with the selected consultant(s). The subcontract(s) shall contain a detailed work plan with adequate opportunity for review at appropriate stages of product completion, a payment schedule with payments tied to receipt of products, and project costs.
This page features all of CDC's violence prevention-related information.
To guide and manage project execution, check out these top project plan templates. Track Projects with Ease Using Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get ...
CEGE Spring Graduation Celebration and Order of the EngineerForty-seven graduates of the undergraduate and grad student programs (pictured above) in the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering took part in the Order of the Engineer on graduation day. Distinguished Speakers at this departmental event included Katrina Kessler (MS EnvE 2021), Commissioner of the Minnesota ...