
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students

Presentation Tips For Students – Show And Tell Like A Pro!
Updated: July 15, 2022
Published: May 4, 2020

Giving a presentation to fellow classmates can be a bit daunting, especially if you are new to oral and visual presenting. But with the right PowerPoint tips, public speaking skills, and plenty of practice, you can present like a pro at your upcoming presentation. Here, we’ve laid out the best college presentation tips for students. And once you have one successful presentation, you’ll get better each time!
The Best Presentation Tips for Students
1. arrive early and be technically prepared.
Get to the room early and make sure you leave plenty of time for technical set up and technical difficulties. Have several backup drives (including an online version if possible) so that you are prepared for anything!
2. Know More
Be educated on more than just what you are sharing. That way, you can add points, speak candidly and confidently, and be prepared to answer any audience or teacher questions.
3. Share Your Passion With Your Audience
Connect with your audience by showing that you are passionate about your topic. Do this with the right tone, eye contact, and enthusiasm in your speech.
Photo by Austin Distel on Unsplash
4. pace yourself.
When student presenters are nervous, they tend to speed up their speech. This can be a problem, however, because your speed may be distracting, hard to understand, and you may run under your time.
5. Rehearse Thoroughly
Don’t just practice, rehearse your college presentation. Rehearse the entire delivery, including standing up, using gestures, and going through the slides.
6. Show Your Personality
You don’t need to be professional to the point of stiffness during your college presentation . Don’t be afraid to show your personality while presenting. It will make your presentation more interesting, and you will seem more approachable and confident.
7. Improvise
You can’t be 100% certain what will happen during your presentation. If things aren’t exactly as you expected, don’t be afraid to improvise and run off script.
8. Pump Yourself Up
Get yourself excited and full of energy before your college presentation! Your mood sets the tone for your presentation, and if you get excited right before, you will likely carry that throughout and you’ll make your audience excited about your topic as well.
9. Remember To Pause
Pausing not only only prevents filler words and helps you recollect your thoughts, it can also be a powerful indicator of importance within your presentation.
10. Create “Um” Alternatives
Try hard not to use filler words as they make you look unprofessional and uncertain. The best alternatives to “um” “like” and “so” are taking a breath or a silent pause to collect your thoughts.
11. Using Your Hands
Using your hands makes your college presentation more interesting and helps to get your points across. Point at the slide, use common hand gestures, or mimic a motion.
12. Eye Contact
Eye contact is one of the most important presentation tips for students . Many students are nervous, so they look at their notes or their feet. It is important that you show your confidence and engage your audience by making eye contact. The more presentations you give, the more eye contact will feel natural.
13. The Right Tone
The best public speakers vary their tone and pitch throughout their presentation. Try to change it up, and choose the right tone for your message.
Preparing an Effective College Presentation
1. open strong.
Grab your fellow students’ attention by starting strong with a powerful quote, intriguing scenario, or prompt for internal dialogue.
2. Start With A Mind Map
Mind mapping is literally creating a map of the contents of your college presentation. It is a visual representation and flow of your topics and can help you see the big picture, along with smaller details.
Photo by Teemu Paananen on Unsplash
3. edit yourself.
Some students make the mistake of including too much information in their college presentations. Instead of putting all of the information in there, choose the most important or relevant points, and elaborate on the spot if you feel it’s necessary.
4. Tell A Story
People love stories — they capture interest in ways that figures and facts cannot. Make your presentation relatable by including a story, or presenting in a story format.
5. The Power Of Humor
Using humor in your college presentation is one of the best presentation tips for students. Laughter will relax both you and the audience, and make your presentation more interesting
PowerPoint Tips for Students
1. use key phrases.
Choose a few key phrases that remain throughout your PowerPoint presentation. These should be phrases that really illustrate your point, and items that your audience will remember afterwards.
2. Limit Number Of Slides
Having too many slides will cause you to feel you need to rush through them to finish on time. Instead, include key points on a slide and take the time to talk about them. Try to think about including one slide per one minute of speech.
3. Plan Slide Layouts
Take some time to plan out how information will be displayed on your PowerPoint. Titles should be at the top, and bullets underneath. You may want to add title slides if you are changing to a new topic.
Photo by NeONBRAND on Unsplash
4. the right fonts.
Choose an easy-to-read font that isn’t stylized. Sans serif fonts tend to be easier to read when they are large. Try to stick to only two different fonts as well to keep the presentation clean.
5. Choosing Colors And Images
When it comes to colors, use contrasting ones: light on dark or dark on light. Try to choose a few main colors to use throughout the presentation. Choose quality images, and make sure to provide the source for the images.
6. Use Beautiful Visual Aids
Keep your presentation interesting and your audience awake by adding visual aids to your PowerPoint. Add captivating photos, data representations, or infographics to illustrate your information.
7. Don’t Read Straight From Your Notes
When you read straight from your notes, your tone tends to remain monotonous, you don’t leave much room for eye contact. Try looking up often, or memorizing portions of your presentation.
8. Avoid Too Much Text
PowerPoint was made for images and bullets, not for your entire speech to be written in paragraph form. Too much text can lose your adiences’ interest and understanding.
9. Try A Theme
Choosing the right theme is one of those presentation tips for students that is often overlooked. When you find the right theme, you keep your college presentation looking interesting, professional, and relevant.
10. Be Careful With Transitions And Animations
Animations and transitions can add a lot to your presentation, but don’t add to many or it will end up being distracting.
Public Speaking Tips for Students
1. choose your topic wisely.
If you are able to pick your topic, try to pick something that interests you and something that you want to learn about. Your interest will come through your speech.
2. Visit The Room Beforehand
If your presentation is being held somewhere outside of class, try to visit the location beforehand to prep your mind and calm your nerves.
3. Practice Makes Perfect
Practice, practice, practice! The only way you will feel fully confident is by practicing many times, both on your own and in front of others.
Photo by Product School on Unsplash
4. talk to someone about anxiety.
If you feel anxious about your college presentation, tell someone. It could be a friend, family member, your teacher, or a counselor. They will be able to help you with some strategies that will work best for you.
5. Remind Yourself Of Your Audience
Remember, you are presenting to your peers! They all likely have to make a presentation too at some point, and so have been or will be in the same boat. Remembering that your audience is on your side will help you stay cool and collected.
6. Observe Other Speakers
Look at famous leaders, or just other students who typically do well presenting. Notice what they are doing and how you can adapt your performance in those ways.
7. Remind Yourself Of Your Message
If you can come up with a central message, or goal, of your college presentation, you can remind yourself of it throughout your speech and let it guide you.
8. Don’t Apologize
If you make a mistake, don’t apologize. It is likely that no one even noticed! If you do feel you need to point out your own mistake, simply say it and keep moving on with your presentation. No need to be embarrassed, it happens even to the best presenters!
When you smile, you appear warm and inviting as a speaker. You will also relax yourself with your own smile.
The Bottom Line
It can be nerve racking presenting as a college student, but if you use our presentation tips for students, preparing and presenting your college presentation will be a breeze!
Related Articles
Search form
- Speaking exams
- Typical speaking tasks
Oral presentation
Giving an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam can be quite scary, but we're here to help you. Watch two students giving presentations and then read the tips carefully. Which tips do they follow? Which ones don’t they follow?
Instructions
Watch the video of two students doing an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam. Then read the tips below.
Melissa: Hi, everyone! Today I would like to talk about how to become the most popular teen in school.
Firstly, I think getting good academic results is the first factor to make you become popular since, having a good academic result, your teacher will award you in front of your schoolmates. Then, your schoolmates will know who you are and maybe they would like to get to know you because they want to learn something good from you.
Secondly, I think participating in school clubs and student unions can help to make you become popular, since after participating in these school clubs or student union, people will know who you are and it can help you to make friends all around the school, no matter senior forms or junior forms.
In conclusion, I think to become the most popular teen in school we need to have good academic results and also participate in school clubs and student union. Thank you!
Kelvin: Good evening, everyone! So, today I want to talk about whether the sale of cigarettes should be made illegal.
As we all know, cigarettes are not good for our health, not only oneself but also other people around. Moreover, many people die of lung cancer every year because of smoking cigarettes.
But, should the government make it illegal? I don’t think so, because Hong Kong is a place where people can enjoy lots of freedom and if the government banned the sale of cigarettes, many people would disagree with this and stand up to fight for their freedom.
Moreover, Hong Kong is a free market. If there's such a huge government intervention, I think it’s not good for Hong Kong’s economy.
So, if the government wants people to stop smoking cigarettes, what should it do? I think the government can use other administrative ways to do so, for example education and increasing the tax on cigarettes. Also, the government can ban the smokers smoking in public areas. So, this is the end of my presentation. Thank you.
It’s not easy to give a good oral presentation but these tips will help you. Here are our top tips for oral presentations.
- Use the planning time to prepare what you’re going to say.
- If you are allowed to have a note card, write short notes in point form.
- Use more formal language.
- Use short, simple sentences to express your ideas clearly.
- Pause from time to time and don’t speak too quickly. This allows the listener to understand your ideas. Include a short pause after each idea.
- Speak clearly and at the right volume.
- Have your notes ready in case you forget anything.
- Practise your presentation. If possible record yourself and listen to your presentation. If you can’t record yourself, ask a friend to listen to you. Does your friend understand you?
- Make your opinions very clear. Use expressions to give your opinion .
- Look at the people who are listening to you.
- Write out the whole presentation and learn every word by heart.
- Write out the whole presentation and read it aloud.
- Use very informal language.
- Only look at your note card. It’s important to look up at your listeners when you are speaking.
Useful language for presentations
Explain what your presentation is about at the beginning:
I’m going to talk about ... I’d like to talk about ... The main focus of this presentation is ...
Use these expressions to order your ideas:
First of all, ... Firstly, ... Then, ... Secondly, ... Next, ... Finally, ... Lastly, ... To sum up, ... In conclusion, ...
Use these expressions to add more ideas from the same point of view:
In addition, ... What’s more, ... Also, ... Added to this, ...
To introduce the opposite point of view you can use these words and expressions:
However, ... On the other hand, ... Then again, ...
Example presentation topics
- Violent computer games should be banned.
- The sale of cigarettes should be made illegal.
- Homework should be limited to just two nights a week.
- Should school students be required to wear a school uniform?
- How to become the most popular teen in school.
- Dogs should be banned from cities.
Check your language: ordering - parts of a presentation
Check your understanding: grouping - useful phrases, worksheets and downloads.
Do you think these tips will help you in your next speaking exam? Remember to tell us how well you do in future speaking exams!

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action
- Professional development
- Planning lessons and courses
Student presentations
In this article I would like to give you a few tips and some advice on what I've learned from helping students prepare and deliver presentations.

- Why I get students to do presentations
- Syllabus fit
- Planning a presentation lesson
- Classroom Management
Why I get students to do presentations Presentations are a great way to have students practise all language systems areas (vocabulary, grammar, discourse and phonology) and skills (speaking, reading, writing and listening). They also build confidence, and presenting is a skill that most people will need in the world of work. I find that students who are good presenters are better communicators all round, since they are able to structure and express their ideas clearly.
- Presentation skills are extremely useful both in and outside the classroom. After completing a project, a presentation is a channel for students to share with others what they have learned. It is also a chance to challenge and expand on their understanding of the topic by having others ask questions. And in the world of work, a confident presenter is able to inform and persuade colleagues effectively.
- Presentations can also form a natural part of task based learning. By focussing on a particular language point or skill, the presentation is a very practical way to revise and extend book, pair and group work. The audience can also be set a task, for example, a set of questions to answer on the presentation, which is a way of getting students to listen to each other.
Syllabus fit Normally the presentation will come towards the end of a lesson or series of lessons that focus on a particular language or skill area. It is a type of freer practice. This is because the students need to feel relatively confident about what they are doing before they stand up and do it in front of other people. If I have been teaching the past simple plus time phrases to tell a story, for example, I give my students plenty of controlled and semi controlled practice activities, such as gapfills, drills and information swaps before I ask them to present on, say, an important event in their country's history, which involves much freer use of the target grammar point.
Planning a presentation lesson Normally a presentation lesson will have an outline like this:
- Revision of key language areas
- Example presentation, which could be from a textbook or given by the teacher
- Students are given a transcript or outline of the presentation
- Students identify key stages of the example presentation – greeting, introduction, main points in order of importance, conclusion
- Focus on linking and signalling words ('Next…', 'Now I'd like you to look at…', etc.). Students underline these in the transcript/place them in the correct order
- Students are put into small groups and write down aims
- Students then write down key points which they order, as in the example
- Students decide who is going to say what and how
- Students prepare visuals (keep the time for this limited as too many visuals become distracting)
- Students practise at their tables
- Students deliver the presentations in front of the class, with the audience having an observation task to complete (see 'Assessment' below)
- The teacher takes notes for feedback later
It is important that the students plan and deliver the presentations in groups at first, unless they are extremely confident and/or fluent. This is because:
- Shy students cannot present alone
- Students can support each other before, during and after the presentation
- Getting ready for the presentation is a practice task in itself
- When you have a large class, it takes a very long time for everyone to present individually!
I find it's a good idea to spend time training students in setting clear aims. It is also important that as teachers we think clearly about why we are asking students to present.
Aims Presentations normally have one or more of the following aims:
- To inform/ raise awareness of an important issue
- To persuade people to do something
- Form part of an exam, demonstrating public speaking/presentation skills in a first or second language
I set students a task where they answer these questions:
- Why are you making the presentation?
- What do you want people to learn?
- How are you going to make it interesting?
Let's say I want to tell people about volcanoes. I want people to know about why volcanoes form and why they erupt. This would be an informative/awareness-raising presentation. So by the end, everyone should know something new about volcanoes, and they should be able to tell others about them. My plan might look like this:
- Introduction - what is a volcano? (2 minutes)
- Types of volcano (5 minutes)
- Volcanoes around the world (2 minutes)
- My favourite volcano (2 minutes)
- Conclusion (2-3 minutes)
- Questions (2 minutes)
Classroom Management I find that presentation lessons pass very quickly, due the large amount of preparation involved. With a class of 20 students, it will probably take at least 3 hours. With feedback and follow-up tasks, it can last even longer. I try to put students into groups of 3 or 4 with classes of up to 20 students, and larger groups of 5 or 6 with classes up to 40. If you have a class larger than 40, it would be a good idea to do the presentation in a hall or even outside.
Classroom management can become difficult during a presentations lesson, especially during the final presenting stage, as the presenters are partly responsible for managing the class! There are a few points I find effective here:
- Training students to stand near people who are chatting and talk 'through' the chatter, by demonstration
- Training students to stop talking if chatter continues, again by demonstration
- Asking for the audience's attention ('Can I have your attention please?')
- Setting the audience an observation task, which is also assessed by the teacher
- Limiting the amount of time spent preparing visuals
- Arranging furniture so everyone is facing the front
Most of these points are self-explanatory, but I will cover the observation task in more detail in the next section, which deals with assessment.
Assessment The teacher needs to carefully consider the assessment criteria, so that s/he can give meaningful feedback. I usually run through a checklist that covers:
- Level - I can't expect Elementary students to use a wide range of tenses or vocabulary, for example, but I'd expect Advanced students to have clear pronunciation and to use a wide range of vocabulary and grammar
- Age - Younger learners do not (normally) have the maturity or general knowledge of adults, and the teacher's expectations need to reflect this
- Needs - What kind of students are they? Business English students need to have much more sophisticated communication skills than others. Students who are preparing for an exam need to practise the skills that will be assessed in the exam.
I write a list of language related points I'm looking for. This covers:
- Range / accuracy of vocabulary
- Range / accuracy of grammar
- Presentation / discourse management- is it well structured? What linking words are used and how?
- Use of visuals- Do they help or hinder the presentation?
- Paralinguistic features
'Paralinguistics' refers to non-verbal communication. This is important in a presentation because eye contact, directing your voice to all parts of the room, using pitch and tone to keep attention and so on are all part of engaging an audience.
I find it's a good idea to let students in on the assessment process by setting them a peer observation task. The simplest way to do this is to write a checklist that relates to the aims of the lesson. A task for presentations on major historical events might have a checklist like this:
- Does the presenter greet the audience? YES/NO
- Does the presenter use the past tense? YES/NO
And so on. This normally helps me to keep all members of the audience awake. To be really sure, though, I include a question that involves personal response to the presentation such as 'What did you like about this presentation and why?'. If working with young learners, it's a good idea to tell them you will look at their answers to the observation task. Otherwise they might simply tick random answers!
Conclusion Presentations are a great way to practise a wide range of skills and to build the general confidence of your students. Due to problems with timing, I would recommend one lesson per term, building confidence bit by bit throughout the year. In a school curriculum this leaves time to get through the core syllabus and prepare for exams.
Presentations - Adult students
- Log in or register to post comments
Presentation Article
Research and insight
Browse fascinating case studies, research papers, publications and books by researchers and ELT experts from around the world.
See our publications, research and insight
- Faculty and Staff
Assessment and Curriculum Support Center
Youtube videos for student to develop oral presentation skills.
HOW TO Give a Great Presentation – 7 Presentation Skills and Tips to Leave an Impression
Author : Practical Psychology Features : know your audience, structure your presentation, use visuals, use repetition, have a story to tell, be relatable, build your confidence with practice
10 Tips for Better Presentations: Simple Strategies for More Effective Talks (15:41)
Author : Barbara Chamberlin Organization : New Mexico State University
How to Give an Awesome (PowerPoint) Presentation (2:53)
Author : Wienot Films Features : Using story-telling and engaging visuals to introduce the key strategies for effective presentations: tell a story; less is more on PPT slide; practice and rehearse
Presentation Strategies by Mr. R.R. Panda (18:03)
Features : Knowledge-based presentation on strategies to deliver a presentation
6 Public Speaking Tips to Hook Any Audience
Author : Charisma on Command Features : techniques to engage the audience’s interest and emotion
How to open and close presentations? – Presentation lesson from Mark Powell
Author : Cambridge University Press ELT Features : excellent real life examples of good open and close presentations
Presentation Good/Bad Examples
Tips on Giving Oral Presentations
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

How to Use Oral Presentations to Help English Language Learners Succeed
Please try again

Excerpted from “ The ELL Teacher’s Toolbox: Hundreds of Practical Ideas to Support Your Students ,” by Larry Ferlazzo and Katie Hull Sypnieski, with permission from the authors.
Having the confidence to speak in front of others is challenging for most people. For English Language Learners, this anxiety can be heightened because they are also speaking in a new language. We’ve found several benefits to incorporating opportunities for students to present to their peers in a positive and safe classroom environment. It helps them focus on pronunciation and clarity and also boosts their confidence. This type of practice is useful since students will surely have to make presentations in other classes, in college, and/or in their future jobs. However, what may be even more valuable is giving students the chance to take these risks in a collaborative, supportive environment.
Presentations also offer students the opportunity to become the teacher—something we welcome and they enjoy! They can further provide valuable listening practice for the rest of the class, especially when students are given a task to focus their listening.
Research confirms that in order for ELLs to acquire English they must engage in oral language practice and be given the opportunity to use language in meaningful ways for social and academic purposes (Williams & Roberts, 2011). Teaching students to design effective oral presentations has also been found to support thinking development as “the quality of presentation actually improves the quality of thought, and vice versa” (Živković, 2014, p. 474). Additionally, t he Common Core Speaking and Listening Standards specifically focus on oral presentations. These standards call for students to make effective and well-organized presentations and to use technology to enhance understanding of them.
GUIDELINES AND APPLICATION
Oral presentations can take many different forms in the ELL classroom—ranging from students briefly presenting their learning in small groups to creating a multi-slide presentation for the whole class. In this section, we give some general guidelines for oral presentations with ELLs. We then share ideas for helping students develop their presentation skills and describe specific ways we scaffold both short and long oral presentations.
We keep the following guidelines in mind when incorporating oral presentations into ELL instruction:

Length —We have students develop and deliver short presentations (usually 2-4 minutes) on a regular basis so they can practice their presentation skills with smaller, less overwhelming tasks. These presentations are often to another student or a small group. Once or twice a semester, students do a longer presentation (usually 5-8 minutes), many times with a partner or in a small group.
Novelty —Mixing up how students present (in small groups, in pairs, individually) and what they use to present (a poster, a paper placed under the document camera, props, a slide presentation, etc.) can increase engagement for students and the teacher!
Whole Class Processing -- We want to avoid students “tuning out” during oral presentations. Not only can it be frustrating for the speakers, but students also miss out on valuable listening practice. During oral presentations, and in any activity, we want to maximize the probability that all students are thinking and learning all the time. Jim Peterson and Ted Appel, administrators with whom we’ve worked closely, call this “whole class processing” (Ferlazzo, 2011, August 16) and it is also known as active participation. All students can be encouraged to actively participate in oral presentations by being given a listening task-- taking notes on a graphic organizer, providing written feedback to the speaker, using a checklist to evaluate presenters, etc.
Language Support —It is critical to provide ELLs, especially at the lower levels of English proficiency, with language support for oral presentations. In other words, thinking about what vocabulary, language features and organizational structures they may need, and then providing students with scaffolding, like speaking frames and graphic organizers. Oral presentations can also provide an opportunity for students to practice their summarizing skills. When students are presenting information on a topic they have researched, we remind them to summarize using their own words and to give credit when using someone else’s words.
Technology Support —It can’t be assumed that students have experience using technology tools in presentations. We find it most helpful using simple tools that are easy for students to learn (like Powerpoint without all the “bells and whistles” or Google Slides). We also emphasize to students that digital media should be used to help the audience understand what they are saying and not just to make a presentation flashy or pretty. We also share with our students what is known as “The Picture Superiority Effect”-- a body of research showing that people are better able to learn and recall information presented as pictures as opposed to just being presented with words (Kagan, 2013).
Groups -- Giving ELLs the opportunity to work and present in small groups is helpful in several ways. Presenting as a group (as opposed to by yourself) can help students feel less anxious. It also offers language-building opportunities as students communicate to develop and practice their presentations. Creating new knowledge as a group promotes collaboration and language acquisition--an ideal equation for a successful ELL classroom!
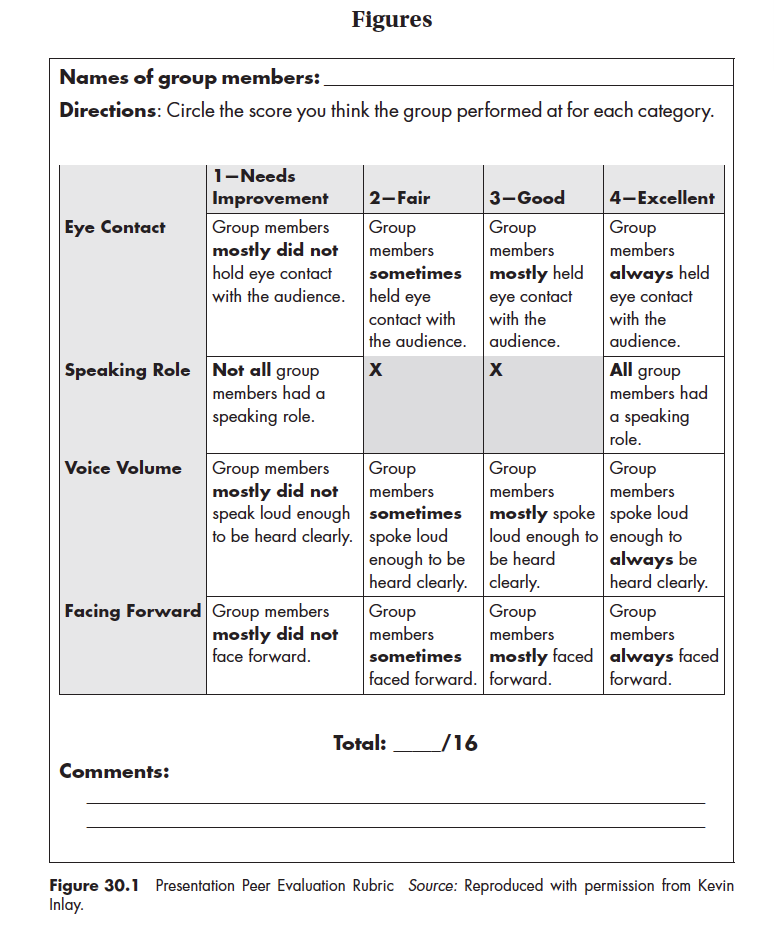
Teacher feedback/student evaluation --The focus of oral presentations with ELL students should be on the practice and skills they are gaining, not on the grade or “score” they are earning. Teachers can give out a simple rubric before students create their presentations. Then students can keep these expectations in mind as they develop and practice their presentations. The teacher, or classmates, can then use the rubric to offer feedback to the speaker. We also often ask students to reflect on their own presentation and complete the rubric as a form of self-assessment. Figure 30.1 – “Presentation Peer Evaluation Rubric” , developed by talented student teacher Kevin Inlay (who is now a teacher in his own classroom), is a simple rubric we used to improve group presentations in our ELL World History class.
Teaching Presentation Skills
We use the following two lesson ideas to explicitly teach how to develop effective presentation skills:
LESSON ONE: Speaking and Listening Do’s and Don’ts
We help our students understand and practice general presentation skills through an activity we call Speaking and Listening “Do’s and Don’ts.” We usually spread this lesson out among two class periods.
We first ask students to create a simple T-chart by folding a piece of paper in half and labeling one side “Do” and the other side “Don’t.” We then post Figure 30.2 “Speaking Do’s and Don’ts” on the document camera and display the first statement (the rest we cover with a blank sheet of paper).
We read the first statement, “Make eye contact with the audience,” and ask students if this is something they want to do when they are giving a presentation or if it is something they don’t want to do. Students write the statement where they think it belongs--under the “Do” column or “Don’t” Column. Students then share their answer with a partner and discuss why they put it in that column. After calling on a few pairs to share with the class, we move down the list repeating the same process of categorizing each statement as a “Do” or a “Don’t.” Students write it on their chart and discuss why it should be placed there.
After categorizing the statements for speaking, we give students Figure 30.3 “Listening Do’s and Don’ts .” We tell students to work in pairs to categorize the statements as something they do or something they don’t want to do when listening to a student presentation. This time, we ask students to make a quick poster with the headings “Do’s” and “Don’ts” for Listening. Under each heading students must list the corresponding statements--the teacher can circulate to check for accuracy. Students are asked to talk about why each statement belongs in each category and should be prepared to share their reasoning with the class. Students must also choose one “do” statement and one “don’t” statement to illustrate on their poster. Students can present their posters in small groups or with the whole class. This serves as a great opportunity to apply the speaking and listening “do’s” they just reviewed and heightens their awareness of the “don’ts!”

A fun twist, that also serves as a good review on a subsequent day, is to ask groups of students to pick two or three “do’s” and “don’ts” from both Speaking and Listening to act out in front of the class.
LESSON TWO Slide Presentations Concept Attainment
We periodically ask students to make slide presentations using PowerPoint or Google Slides to give them practice with developing visual aids (see the Home Culture activity later in this section). We show students how to make better slides, along with giving students the language support they may need in the form of an outline or sentence starters. An easy and effective way to do this is through Concept Attainment.
Concept Attainment involves the teacher identifying both "good" and "bad" examples of the intended learning objective. In this case, we use a PowerPoint containing three “good” slides and three “bad” ones (see them at The Best Resources For Teaching Students The Difference Between A Good and a Bad Slide ).
We start by showing students the first example of a “good” or “yes” slide (containing very little text and two images) and saying, “This is a yes.” However, we don’t explain why it is a “yes.” Then we show a “bad” or “no” example of a slide (containing multiple images randomly placed with a very “busy background”), saying, “This is a no” without explaining why. Students are then asked to think about them, and share with a partner why they think one is a "yes" and one is a "no."
At this point, we make a quick chart on a large sheet of paper (students can make individual charts on a piece of paper) and ask students to list the good and bad qualities they have observed so far. For example, under the “Good/Yes” column it might say “Has less words and the background is simple” and under the “Bad/No” column “Has too many pictures and the background is distracting.”
We then show the second “yes” example (containing one image with a short amount of text in a clear font) and the “no” example (containing way too much text and using a less clear font style). Students repeat the “think-pair-share” process and then the class again discusses what students are noticing about the “yes” and “no” examples. Then they add these observations to their chart.
Students repeat the whole process a final time with the third examples. The third “yes” example slide contains one image, minimal text and one bullet point. The third “no” example, on the other hand, contains multiple bullet points.
To reinforce this lesson at a later date, the teacher could show students more examples, or students could look for more “yes” and “no” examples online. They could continue to add more qualities of good and bad slides to their chart. See the Technology Connections section for links to good and bad PowerPoint examples, including the PowerPoint we use for this Concept Attainment lesson.
You can learn more about other presentations that support public speaking, such as home culture presentations, speed dating, talking points, top 5 and PechaKucha Book talks in our book, “ The ELL Teacher’s Toolbox: Hundreds of Practical Ideas to Support Your Students .”

Larry Ferlazzo has taught English Language Learners, mainstream and International Baccalaureate students at Luther Burbank High School in Sacramento for 15 years. He has authored eight books on education, hosts a popular blog for educators, and writes a weekly teacher advice column for Education Week Teacher . He was a community organizer for 19 years prior to becoming a high school teacher.

Katie Hull Sypnieski has worked with English Language Learners at the secondary level for over 20 years. She currently teaches middle school ELA and ELD at Rosa Parks K-8 School in Sacramento, California. She is a teaching consultant with the Area 3 Writing Project at the University of California, Davis and has leads professional development for teachers of ELLs. She is co-author (with Larry Ferlazzo) of The ESL/ELL Teacher’s Survival Guide and Navigating the Common Core with English Language Learners .

24 Oral Presentations
Many academic courses require students to present information to their peers and teachers in a classroom setting. This is usually in the form of a short talk, often, but not always, accompanied by visual aids such as a power point. Students often become nervous at the idea of speaking in front of a group.
This chapter is divided under five headings to establish a quick reference guide for oral presentations.

A beginner, who may have little or no experience, should read each section in full.

For the intermediate learner, who has some experience with oral presentations, review the sections you feel you need work on.

The Purpose of an Oral Presentation
Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated on their capacity to speak and deliver relevant information within a set timeframe. An oral presentation differs from a speech in that it usually has visual aids and may involve audience interaction; ideas are both shown and explained . A speech, on the other hand, is a formal verbal discourse addressing an audience, without visual aids and audience participation.
Types of Oral Presentations
Individual presentation.
- Breathe and remember that everyone gets nervous when speaking in public. You are in control. You’ve got this!
- Know your content. The number one way to have a smooth presentation is to know what you want to say and how you want to say it. Write it down and rehearse it until you feel relaxed and confident and do not have to rely heavily on notes while speaking.
- Eliminate ‘umms’ and ‘ahhs’ from your oral presentation vocabulary. Speak slowly and clearly and pause when you need to. It is not a contest to see who can race through their presentation the fastest or fit the most content within the time limit. The average person speaks at a rate of 125 words per minute. Therefore, if you are required to speak for 10 minutes, you will need to write and practice 1250 words for speaking. Ensure you time yourself and get it right.
- Ensure you meet the requirements of the marking criteria, including non-verbal communication skills. Make good eye contact with the audience; watch your posture; don’t fidget.
- Know the language requirements. Check if you are permitted to use a more casual, conversational tone and first-person pronouns, or do you need to keep a more formal, academic tone?
Group Presentation
- All of the above applies, however you are working as part of a group. So how should you approach group work?
- Firstly, if you are not assigned to a group by your lecturer/tutor, choose people based on their availability and accessibility. If you cannot meet face-to-face you may schedule online meetings.
- Get to know each other. It’s easier to work with friends than strangers.
- Also consider everyone’s strengths and weaknesses. This will involve a discussion that will often lead to task or role allocations within the group, however, everyone should be carrying an equal level of the workload.
- Some group members may be more focused on getting the script written, with a different section for each team member to say. Others may be more experienced with the presentation software and skilled in editing and refining power point slides so they are appropriate for the presentation. Use one visual aid (one set of power point slides) for the whole group. Take turns presenting information and ideas.
- Be patient and tolerant with each other’s learning style and personality. Do not judge people in your group based on their personal appearance, sexual orientation, gender, age, or cultural background.
- Rehearse as a group, more than once. Keep rehearsing until you have seamless transitions between speakers. Ensure you thank the previous speaker and introduce the one following you. If you are rehearsing online, but have to present in-person, try to schedule some face-to-face time that will allow you to physically practice using the technology and classroom space of the campus.
- For further information on working as a group see:
Working as a group – my.UQ – University of Queensland
Writing Your Presentation
Approach the oral presentation task just as you would any other assignment. Review the available topics, do some background reading and research to ensure you can talk about the topic for the appropriate length of time and in an informed manner. Break the question down as demonstrated in Chapter 17 Breaking Down an Assignment. Where it differs from writing an essay is that the information in the written speech must align with the visual aid. Therefore, with each idea, concept or new information you write, think about how this might be visually displayed through minimal text and the occasional use of images. Proceed to write your ideas in full, but consider that not all information will end up on a power point slide. After all, it is you who are doing the presenting , not the power point. Your presentation skills are being evaluated; this may include a small percentage for the actual visual aid. This is also why it is important that EVERYONE has a turn at speaking during the presentation, as each person receives their own individual grade.
Using Visual Aids
A whole chapter could be written about the visual aids alone, therefore I will simply refer to the key points as noted by my.UQ
To keep your audience engaged and help them to remember what you have to say, you may want to use visual aids, such as slides.
When designing slides for your presentation, make sure:
- any text is brief, grammatically correct and easy to read. Use dot points and space between lines, plus large font size (18-20 point).
- Resist the temptation to use dark slides with a light-coloured font; it is hard on the eyes
- if images and graphs are used to support your main points, they should be non-intrusive on the written work
Images and Graphs
- Your audience will respond better to slides that deliver information quickly – images and graphs are a good way to do this. However, they are not always appropriate or necessary.
When choosing images, it’s important to find images that:
- support your presentation and aren’t just decorative
- are high quality, however, using large HD picture files can make the power point file too large overall for submission via Turnitin
- you have permission to use (Creative Commons license, royalty-free, own images, or purchased)
- suggested sites for free-to-use images: Openclipart – Clipping Culture ; Beautiful Free Images & Pictures | Unsplash ; Pxfuel – Royalty free stock photos free download ; When we share, everyone wins – Creative Commons
This is a general guide. The specific requirements for your course may be different. Make sure you read through any assignment requirements carefully and ask your lecturer or tutor if you’re unsure how to meet them.
Using Visual Aids Effectively
Too often, students make an impressive power point though do not understand how to use it effectively to enhance their presentation.
- Rehearse with the power point.
- Keep the slides synchronized with your presentation; change them at the appropriate time.
- Refer to the information on the slides. Point out details; comment on images; note facts such as data.
- Don’t let the power point just be something happening in the background while you speak.
- Write notes in your script to indicate when to change slides or which slide number the information applies to.
- Pace yourself so you are not spending a disproportionate amount of time on slides at the beginning of the presentation and racing through them at the end.
- Practice, practice, practice.
Nonverbal Communication
It is clear by the name that nonverbal communication are the ways that we communicate without speaking. Many people are already aware of this, however here are a few tips that relate specifically to oral presentations.
Being confident and looking confident are two different things. Fake it until you make it.
- Avoid slouching or leaning – standing up straight instantly gives you an air of confidence.
- Move! When you’re glued to one spot as a presenter, you’re not perceived as either confident or dynamic. Use the available space effectively, though do not exaggerate your natural movements so you look ridiculous.
- If you’re someone who “speaks with their hands”, resist the urge to constantly wave them around. They detract from your message. Occasional gestures are fine.
- Be animated, but don’t fidget. Ask someone to watch you rehearse and identify if you have any nervous, repetitive habits you may be unaware of, for example, constantly touching or ‘finger-combing’ your hair, rubbing your face.
- Avoid ‘voice fidgets’ also. If you needs to cough or clear your throat, do so once then take a drink of water.
- Avoid distractions. No phone turned on. Water available but off to one side.
- Keep your distance. Don’t hover over front-row audience members; this can be intimidating.
- Have a cheerful demeaner. You do not need to grin like a Cheshire cat throughout the presentation, yet your facial expression should be relaxed and welcoming.
- Maintain an engaging TONE in your voice. Sometimes it’s not what you’re saying that is putting your audience to sleep, it’s your monotonous tone. Vary your tone and pace.
- Don’t read your presentation – PRESENT it! Internalize your script so you can speak with confidence and only occasionally refer to your notes if needed.
- Lastly, make good eye contact with your audience members so they know you are talking with them, not at them. You’re having a conversation. Watch the link below for some great speaking tips, including eye contact.
Below is a video of some great tips about public speaking from Amy Wolff at TEDx Portland [1]
- Wolff. A. [The Oregonion]. (2016, April 9). 5 public speaking tips from TEDxPortland speaker coach [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JNOXZumCXNM&ab_channel=TheOregonian ↵
communication of thought by word
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Our Mission
Honing Students’ Speaking Skills
Some guidelines for teaching all students to speak credibly and confidently—an essential skill for college and career success.

It’s been a long time since schools focused solely on the three Rs—reading, writing, and arithmetic. Along the way, we realized that there’s so much more that defines a successful student and citizen, and that schools play a central role in training students to improve on a multitude of skills and abilities.
As outlined in the Common Core State Standards , for example, we are now tasked to teach a set of speaking skills. More and more businesses are citing the ability to speak and communicate comprehensively as vital skills in terms of hiring and professional success. For K–12 teachers, this means more targeted lessons that are focused on oral presentation and verbal assessment.
The fear of public speaking, or glossophobia , strikes almost 80 percent of our general population. Throw in our country’s percentage of English-language learners (ELLs), which ranges from 10 to 25 percent of our K–12 population (depending on the state), and you have an issue that requires precise scaffolding to help prepare our students to hit grade-level speaking expectations. So how can we challenge students to improve their oral presentation skills?
Striving for Equity
I used to use TED talks as my oral presentation template, as many teachers do. As an English language arts teacher and recently retired coach of one of the largest middle school speech and debate teams in the country (Go Bulldogs!), I’ve relied on TED talks for both exemplars and research. But I found that despite my scaffolds, there was still a great divide in final presentation quality between those who could and those who couldn’t. Enter Ignite Talks .
TED and Ignite Talks have some similarities, but it’s their key differences that have worked out better for my high- and low-ability learners, native speakers, and ELLs, and for both extroverted and introverted students.
Here’s what these speech platforms have in common: They both use the format of advocacy: hook, background information, evidence, and a call to action. And they both blend writing genres—memoir/anecdote, argument/persuasive, and informational/expository—rather than segregate them.
And here’s how they differ: Ignite Talks include specific timing and pacing guidelines where TED talks do not. These guidelines, I find, work to bring out the best in all learners, leveling the playing field for students. In fact, with the Ignite Talks rules, I found that students who liked to talk were forced to be more concise. And those who were fearful really only had to muster their courage for a short, set period of time.
Ignite Talks break down as follows: 20 slides, with 15 seconds per slide = 5 minutes.
The slides are set to advance automatically, and because of this, they must be highly visual. So there’s an opening to teach symbolism as well as how to find and cite free images . Because of the speed, a speaker cannot rely on the slides as their script; there’s no room for bullet points or paragraphs. This encourages students to make eye contact and speak with their back to the screen and not to the audience.
The time limit reminds me of the math homework debate: If students struggle with five problems, why give them 50? And if they can conquer five, well, 50 won’t add to their learning. Having students present with a strict pacing structure helps to avoid repetition or babbling from those students who love to talk—or those who are underprepared. A strict pacing structure also helps those students who suffer from presentation paralysis.
Organizing the Speech
Sometimes students present independently. Other times, they work in small groups so they can divide up the Ignite Talks verbal workload. To help them break down the outline of a collaborative speech, I give them a choice in organization.
For the first option, I refer to the five steps for making a pitch like Elon Musk :
- Name the enemy.
- Paint a picture of the promised land.
- Explain away obstacles.
- Win them over with evidence.
I also offer an executive summary structure—background information, evidence, recommendations—to simplify a possible outline even further and bring more authentic writing to their presentation.
Both speech structures (Musk’s and mine) basically ask the students to provide research and take a strong stance on an issue, but they can select the structure that makes the most sense to them. The structure of both helps them to chunk their slides and images.
Before they get started with their planning, I always go over the oral presentation rubric, so there are no surprises. For my most recent project-based unit, I used a speech rubric when my students presented Ignite Talks as superhero leagues, focusing on global issues that they felt passionately needed to be solved. Incidentally, the groups were heterogeneous: ELLs presented alongside native English speakers, and it was an equitable success.
Depending on your group of learners, you will decide which works best—TED or Ignite Talks. What ultimately matters, though, is that you are taking on the charge of preparing your students to speak credibly and confidently out there in the world.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Academic Development Centre
Oral presentations

Using oral presentations to assess learning
Introduction.
Oral presentations are a form of assessment that calls on students to use the spoken word to express their knowledge and understanding of a topic. It allows capture of not only the research that the students have done but also a range of cognitive and transferable skills.
Different types of oral presentations
A common format is in-class presentations on a prepared topic, often supported by visual aids in the form of PowerPoint slides or a Prezi, with a standard length that varies between 10 and 20 minutes. In-class presentations can be performed individually or in a small group and are generally followed by a brief question and answer session.
Oral presentations are often combined with other modes of assessment; for example oral presentation of a project report, oral presentation of a poster, commentary on a practical exercise, etc.
Also common is the use of PechaKucha, a fast-paced presentation format consisting of a fixed number of slides that are set to move on every twenty seconds (Hirst, 2016). The original version was of 20 slides resulting in a 6 minute and 40 second presentation, however, you can reduce this to 10 or 15 to suit group size or topic complexity and coverage. One of the advantages of this format is that you can fit a large number of presentations in a short period of time and everyone has the same rules. It is also a format that enables students to express their creativity through the appropriate use of images on their slides to support their narrative.
When deciding which format of oral presentation best allows your students to demonstrate the learning outcomes, it is also useful to consider which format closely relates to real world practice in your subject area.
What can oral presentations assess?
The key questions to consider include:
- what will be assessed?
- who will be assessing?
This form of assessment places the emphasis on students’ capacity to arrange and present information in a clear, coherent and effective way’ rather than on their capacity to find relevant information and sources. However, as noted above, it could be used to assess both.
Oral presentations, depending on the task set, can be particularly useful in assessing:
- knowledge skills and critical analysis
- applied problem-solving abilities
- ability to research and prepare persuasive arguments
- ability to generate and synthesise ideas
- ability to communicate effectively
- ability to present information clearly and concisely
- ability to present information to an audience with appropriate use of visual and technical aids
- time management
- interpersonal and group skills.
When using this method you are likely to aim to assess a combination of the above to the extent specified by the learning outcomes. It is also important that all aspects being assessed are reflected in the marking criteria.
In the case of group presentation you might also assess:
- level of contribution to the group
- ability to contribute without dominating
- ability to maintain a clear role within the group.
See also the ‘ Assessing group work Link opens in a new window ’ section for further guidance.
As with all of the methods described in this resource it is important to ensure that the students are clear about what they expected to do and understand the criteria that will be used to asses them. (See Ginkel et al, 2017 for a useful case study.)
Although the use of oral presentations is increasingly common in higher education some students might not be familiar with this form of assessment. It is important therefore to provide opportunities to discuss expectations and practice in a safe environment, for example by building short presentation activities with discussion and feedback into class time.
Individual or group
It is not uncommon to assess group presentations. If you are opting for this format:
- will you assess outcome or process, or both?
- how will you distribute tasks and allocate marks?
- will group members contribute to the assessment by reporting group process?
Assessed oral presentations are often performed before a peer audience - either in-person or online. It is important to consider what role the peers will play and to ensure they are fully aware of expectations, ground rules and etiquette whether presentations take place online or on campus:
- will the presentation be peer assessed? If so how will you ensure everyone has a deep understanding of the criteria?
- will peers be required to interact during the presentation?
- will peers be required to ask questions after the presentation?
- what preparation will peers need to be able to perform their role?
- how will the presence and behaviour of peers impact on the assessment?
- how will you ensure equality of opportunities for students who are asked fewer/more/easier/harder questions by peers?
Hounsell and McCune (2001) note the importance of the physical setting and layout as one of the conditions which can impact on students’ performance; it is therefore advisable to offer students the opportunity to familiarise themselves with the space in which the presentations will take place and to agree layout of the space in advance.
Good practice
As a summary to the ideas above, Pickford and Brown (2006, p.65) list good practice, based on a number of case studies integrated in their text, which includes:
- make explicit the purpose and assessment criteria
- use the audience to contribute to the assessment process
- record [audio / video] presentations for self-assessment and reflection (you may have to do this for QA purposes anyway)
- keep presentations short
- consider bringing in externals from commerce / industry (to add authenticity)
- consider banning notes / audio visual aids (this may help if AI-generated/enhanced scripts run counter to intended learning outcomes)
- encourage students to engage in formative practice with peers (including formative practice of giving feedback)
- use a single presentation to assess synoptically; linking several parts / modules of the course
- give immediate oral feedback
- link back to the learning outcomes that the presentation is assessing; process or product.
Neumann in Havemann and Sherman (eds., 2017) provides a useful case study in chapter 19: Student Presentations at a Distance, and Grange & Enriquez in chapter 22: Moving from an Assessed Presentation during Class Time to a Video-based Assessment in a Spanish Culture Module.
Diversity & inclusion
Some students might feel more comfortable or be better able to express themselves orally than in writing, and vice versa . Others might have particular difficulties expressing themselves verbally, due for example to hearing or speech impediments, anxiety, personality, or language abilities. As with any other form of assessment it is important to be aware of elements that potentially put some students at a disadvantage and consider solutions that benefit all students.
Academic integrity
Oral presentations present relative low risk of academic misconduct if they are presented synchronously and in-class. Avoiding the use of a script can ensure that students are not simply reading out someone else’s text or an AI generated script, whilst the questions posed at the end can allow assessors to gauge the depth of understanding of the topic and structure presented. (Click here for further guidance on academic integrity .)
Recorded presentations (asynchronous) may be produced with help, and additional mechanisms to ensure that the work presented is their own work may be beneficial - such as a reflective account, or a live Q&A session. AI can create scripts, slides and presentations, copy real voices relatively convincingly, and create video avatars, these tools can enable students to create professional video content, and may make this sort of assessment more accessible. The desirability of such tools will depend upon what you are aiming to assess and how you will evaluate student performance.
Student and staff experience
Oral presentations provide a useful opportunity for students to practice skills which are required in the world of work. Through the process of preparing for an oral presentation, students can develop their ability to synthesise information and present to an audience. To improve authenticity the assessment might involve the use of an actual audience, realistic timeframes for preparation, collaboration between students and be situated in realistic contexts, which might include the use of AI tools.
As mentioned above it is important to remember that the stress of presenting information to a public audience might put some students at a disadvantage. Similarly non-native speakers might perceive language as an additional barrier. AI may reduce some of these challenges, but it will be important to ensure equal access to these tools to avoid disadvantaging students. Discussing criteria and expectations with your students, providing a clear structure, ensuring opportunities to practice and receive feedback will benefit all students.
Some disadvantages of oral presentations include:
- anxiety - students might feel anxious about this type of assessment and this might impact on their performance
- time - oral assessment can be time consuming both in terms of student preparation and performance
- time - to develop skill in designing slides if they are required; we cannot assume knowledge of PowerPoint etc.
- lack of anonymity and potential bias on the part of markers.
From a student perspective preparing for an oral presentation can be time consuming, especially if the presentation is supported by slides or a poster which also require careful design.
From a teacher’s point of view, presentations are generally assessed on the spot and feedback is immediate, which reduces marking time. It is therefore essential to have clearly defined marking criteria which help assessors to focus on the intended learning outcomes rather than simply on presentation style.
Useful resources
Joughin, G. (2010). A short guide to oral assessment . Leeds Metropolitan University/University of Wollongong http://eprints.leedsbeckett.ac.uk/2804/
Race, P. and Brown, S. (2007). The Lecturer’s Toolkit: a practical guide to teaching, learning and assessment. 2 nd edition. London, Routledge.
Annotated bibliography
Class participation
Concept maps
Essay variants: essays only with more focus
- briefing / policy papers
- research proposals
- articles and reviews
- essay plans
Film production
Laboratory notebooks and reports
Objective tests
- short-answer
- multiple choice questions
Patchwork assessment
Creative / artistic performance
- learning logs
- learning blogs
Simulations
Work-based assessment
Reference list
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

- Presentation
Oral presentation skill: what it is and how to develop it
- May 1, 2022

In each private and professional environment, effective communication is a fundamental skill. Among the various types of communication, oral shows stand out as an effective capability of conveying information, ideas, and opinions. Whether in academic, business, or social environments, the potential to deliver a compelling oral presentation can notably affect how your message is received. This article will discover what is oral presentation skills, the purpose of oral presentation, how to use them effectively, and when to use them in Presentation design services.

Table of Contents
What are Oral Presentation Skills?
Oral presentation skills refer to the ability to convey information and ideas through spoken words, body language, and visual aids in a structured and engaging manner. It involves organizing thoughts, tailoring content to the audience, and delivering the message confidently and clearly.
These skills encompass verbal and non-verbal communication techniques, ensuring your message is understood, remembered, and impactful.
The Purpose of Oral Presentation
These are the main purpose of Oral presentation skills:
1-Inform and Educate:
Oral presentations are an advantageous tool for disseminating know-how and information. Whether it is a business proposal, research finding, or an academic seminar, the main purpose is to inform and instruct the target market about the subject matter.
2-Persuade and Influence:
In a professional context, oral presentations are frequently used to persuade and affect stakeholders, customers, or colleagues. It could be a sales pitch, a project proposal, or a motivational talk to inspire action or change.
3-Showcase Skills:
Presentations can also showcase your expertise and proficiency in a particular field. A well-delivered presentation can leave a lasting impression and enhance credibility and reputation.

The different types of oral presentations
Luckily, there are different types of oral presentations. The type you give will depend on what’s needed in the situation! For example, an informative speech is typically used to educate your audience about something specific while a persuasive one tries convincing people around them that they should do/believe so-and it doesn’t matter if this works because both have their own purposes behind them anyway.
How to Use Oral Presentation Skills Effectively?
Here are some tips to improve your oral presentation skills effectively:
Know Your Audience:
Tailor your presentation to your audience’s needs, interests, and knowledge level. Understand their expectations and adjust your content accordingly to ensure maximum engagement.
Structure Your Presentation:
Organize your content into a clear and logical structure. Typically, a presentation consists of an introduction, main points with supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Ensure smooth transitions between sections to maintain flow.
Engaging Visuals:
Utilize visuals such as slides, videos, or props to complement your verbal message. Visual aids can enhance understanding and retention but avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information.
Practice and Rehearse:
Practice your presentation multiple times to become familiar with the content and delivery. Rehearsing also helps reduce nervousness and build confidence in communicating effectively.
Eye Contact and Body Language:
Maintain eye contact with the audience and use positive body language to create a connection. Gestures, facial expressions, and posture can convey confidence and enthusiasm, enhancing the impact of your message.
How to develop your oral presentation skills
To improve your oral presentation skills, be prepared and know the material inside out. Additionally, practice makes perfect! It’s helpful to pay attention not just to what you’re saying but also to how YOU are sounding–that is assuming people will actually listen anyway (which they won’t).
Eye contact can help engage an audience as well by making them feel like their opinion matters or that this person truly wants input from every single individual present at any given time during a speech/presentation session…all while smiling confidently with pride because these techniques work wonders even on oneself.
When do you need to Use Oral Presentation Skills?
1-academic settings:.
Students often use oral presentations to share research findings, present projects, or defend their theses. Mastering these skills boosts grades and prepares students for future professional endeavors.
2-Public Speaking Engagements:
Speaking at conferences, seminars, workshops, or occasions allows sharing knowledge, network, and construct recognition as a professional in your field.
3-Social and Personal Life :
Strong oral presentation capabilities are precious in daily life, whether or not speaking at family gatherings, handing over a toast at a wedding, or sharing thoughts in a neighborhood meeting.
4-Social and Personal Life:
Strong oral presentation skills are valuable in everyday life, whether speaking at family gatherings, delivering a toast at a wedding, or sharing ideas in a community meeting.

Tips for delivering an effective oral presentation
Here are a few tips to help you deliver an effective oral presentation. First, start off by grabbing your audience’s attention with an interesting opening sentence or phrase; keep them interested in what comes after that! And remember not everyone will understand all the jargon used during a technical conversation so try keeping things clear and simple – even if it means sacrificing some depth knowledge (which isn’t always bad!).
Practice makes perfect – the more you present, the better you’ll get!
Presentations are a common occurrence in today’s business world. Whether you’re giving an oral presentation to your team or pitching for investors, being able to communicate effectively and inspire lively will set clients’ minds at ease when they hear from YOU! Here is some advice on how best to approach this essential skill: Maintain eye contact with every person who speaks during yours as well as their own reactions; don’t get distracted by anything around them (including other people) because it can cause hesitation which makes someone else more comfortable speaking up instead – even if what was said wasn’t exactly relevant towards our current topic discussion., Use gestures often so everyone understands where certain points lie within the overall message.
Based on your current knowledge about what is Oral presentation skills, you are aware that they are valuable in today’s fast-paced and interconnected world. Mastering these skills allows you to communicate your ideas effectively, influence others positively, and showcase your expertise. You can become a confident and impactful communicator in any setting by understanding the purpose, honing the techniques, and recognizing when to employ oral presentation skills. So, embrace the challenge, practice, and watch as your ability to connect and inspire others soars to new heights.
What are the 5 Ps of oral presentation?
The 5Ps of Oral presentation are planning, preparation, practice, performance, and passion, which can guide you to a successful presentation.
What is the difference between public speaking and oral presentation?
The main factor of public speaking is the involvement with the live audience. However oral presentations can be carried out with or without a live audience.

- Graphic Design , UI-UX
How to Become a Motion Graphic Designer?

A Brief Overview of Lean UX

UX Strategy and Its Components
you'r more than welcome
7 days a week, 9:30 AM – 5:30 PM
contact info
[email protected] +971581974748
- LB07129, Jebel Ali Freezone, Dubai, UAE
Got a Project?
We’re a team of creatives who are excited about unique ideas and help companies to create amazing identity by offering wide range of digital services
© 2021 All rights reserved.
Be the first one who knows about updates!
enter your email address 📩
Welcome to the club 🎉.
From now on, Temis will inform you of its most valuable content and offers. You can also subscribe to this list at the moment. We will also protect your privacy
Oral Presentation Rubric

About this printout
This rubric is designed to be used for any oral presentation. Students are scored in three categories—delivery, content, and audience awareness.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try, related resources.
Oral presentation and speaking are important skills for students to master, especially in the intermediate grades. This oral presentation rubric is designed to fit any topic or subject area. The rubric allows teachers to assess students in several key areas of oral presentation. Students are scored on a scale of 1–4 in three major areas. The first area is Delivery, which includes eye contact, and voice inflection. The second area, Content/Organization, scores students based on their knowledge and understanding of the topic being presented and the overall organization of their presentation. The third area, Enthusiasm/Audience Awareness, assesses students based on their enthusiasm toward the topic and how well they came across to their intended audience. Give students the oral presentation rubric ahead of time so that they know and understand what they will be scored on. Discuss each of the major areas and how they relate to oral presentation.
- After students have completed their oral presentations, ask them to do a self-assessment with the same rubric and hold a conference with them to compare their self-assessment with your own assessment.
- Provide students with several examples of oral presentations before they plan and execute their own presentation. Ask students to evaluate and assess the exemplar presentations using the same rubric.
- Students can do a peer evaluation of oral presentations using this rubric. Students meet in partners or small groups to give each other feedback and explain their scoring.
- Lesson Plans
- Student Interactives
Students research engineering careers and create poetry to understand the vocabulary of STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics).
Useful for a wide variety of reading and writing activities, this outlining tool allows students to organize up to five levels of information.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

ORAL PRESENTATION SKILLS - A PRACTICAL GUIDE

Related Papers
International Journal of Learning and Teaching
Rizaldy Hanifa
The importance of being able to perform a good oral presentation is undeniably necessary for academician nowadays, including students of higher education. To show their capacity, the students need to be prepared in delivering their presentation. However, the current students' presentation skill is still far from the expectation. Therefore, this article aims at sharing several facts dealing with presentation skill in terms of preparations, problems faced during presentation, and the ways to cope with the problems. This study was conducted as a qualitative research with descriptive approach. Questionnaire and interview were distributed and performed to five respondents to gather the data needed. The findings show that preparation involving content mastery and practice are the keys to be successful in presentation. Meanwhile, the problems faced are highly related to the respondents' nervousness due to time limitation and audiences, which cause losing idea while performing. To overcome these, some strategies such as believing in their abilities, skipping less important points, and anticipating possible questions from the audiences were employed. Based on the research results, it is suggested that speaker should be trained to be more aware of the preparations and strategies needed for presentation since the main keys to the success of delivering good presentation are highly determined by knowing how to prepare well and being able to use the strategies more appropriately and frequently.
How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries?
An oral presentation is a form of communication, where you impart and then exchange information with your audience. This can be either one-way, a didactic, or two-way called a Socratic or a Dialectic presentation. There are many forms of oral presentation and you should find out where and when you are required to speak [1]. The National Training Laboratory in Maine, USA has suggested a ‘cone’ of learning or learning ‘pyramid’. In this, they have found that the most effective way of learning is through teaching others. Most students remembered only 10% of the material given in books but remembered 90% of the facts they learned when they had to teach others [2] (Fig. 38.1).
Journal of advances in linguistics
Conchi Hernández
ANNALS OF THE ORADEA UNIVERSITY. Fascicle of Management and Technological Engineering.
Ioana Horea
Peter Levrai , Averil Bolster
Oral Presentations are an important part of studying in an English-medium university environment and will be something many students face, whatever their field of study. Such presentations can be particularly challenging for non-native English speakers (NNES). Despite the importance of oral presentations as a form of academic discourse, they remain a relatively underresearched area and an area where there is limited targeted EAP presentation training materials. There is no clear conceptualization in the existing literature of which the authors are aware as to the key features that make a presentation academic. This paper aims to redress that issue with the aim of then evaluating the training materials currently available to help NNES develop their academic oral presentation skills.
Johannes Junge Ruhland
This worksheet is geared towards advanced undergraduate students majoring in literature, although much of it could be adapted for other disciplines and contexts. It provides guidance on crafting and delivering oral presentations, which are typically based on an article assigned by the instructor to the presenter and to be delivered to a class who has not read the article. The typical length of these presentations is 5 minutes, and presentations may include slideshows. Longer presentations have different parameters. This worksheet is paired with “Know Your Audience: Undergraduate Writing and Speaking.” For writing assignments, readers can refer to “How Do I Efficiently Write Essays in French?” This worksheet was first created in Fall 2021 and was last updated by its author in Summer 2023 with the valuable input and feedback of former students Marley Fortin, Merve Ozdemir, and Elizabeth Swanson.
Nafiseh Zarei
Success in oral pesentation skills contributes to students’ success in academic performance as well as their social life. It is important for teachers to know their students’ needs and social background in order to encourage them to share information relevant to their interests with their peers to improve their oral presentation skills. This study investigates the factors that affect oral presentation among undergraduates. This quantitative study used Likert scale questionnaire to collect data from 100 undergraduates at a private university in Malaysia (UNITAR International University). The data were analysed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) in the form of mean, standard deviation, and variance. The findings of the study showed four primary factors: confidence, nervousness, communication, and presentation skill that effect oral presentation among the undergraduate students. The results of the study demonstrated that the students were very nervous during presentat...
Averil Bolster , Peter Levrai
Australasian Journal of Paramedicine
Jamie Ranse
This article will not provide guidance on public speaking techniques or details on the use of presentation software programs commonly used at conferences.
Proceedings of CLaSIC 2014
Gavin Brooks , John Wilson
In many second language (L2) communication classes the majority of the class time is taken up by teacher-fronted, drill-oriented activities. Oral presentations are one example of a learner-centered, communicative activity that can be used to fix this problem. However, if not implemented correctly, the difficulty of the tasks involved in presenting in front of others can take away from the pedagogical benefits of using presentations in the classroom. Because of this, it is important that language teachers understand the skills involved in giving an effective presentation, and the potential difficulties oral presentations can cause for L2 learners. This paper focuses on one genre of oral presentations, the poster presentation, and examines the benefits of using poster presentations in the L2 classroom. It draws upon the practical experience the authors have gained from teaching and developing materials for presentation classes to provide a framework for how poster presentations can be used in the language classroom. By examining the tasks involved, and the pedagogical justification behind those tasks, it is hoped that this paper will encourage language teachers to use poster presentations in their classrooms in a way that benefits both the students and the teachers.
RELATED PAPERS
Pekka Korhonen
DAFFA RAJWA ANASTI
Palestinian Medical and Pharmaceutical Journal
Tareq Jubeh
The Journal of Nutrition
Giuseppe Bee
International journal of older people nursing
Ilene Wasserman
Inorganic Chemistry
Ceylan Balci
办ETH毕业证成绩单办理瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院假文凭定制 QQ微信1989 88881
Post Scriptum
Almedina Cengic
IOP conference series
Francois Avellan
Anshika Srivastava
Cancer Cell
Nikolaos S . Melis
Greenwich文凭证书 Greenwich毕业证成绩单
Imran Zualkernan
Jesus Perez da Silva
Jan Květina
International journal of health sciences
Dwi Partiningrum
办弗林德斯大学毕业证 flinders毕业证研究生文凭证书GRE证书原版一模一样
European Physical Journal B
FEBS Letters
Andrea Villarino
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Motivational Speaker Techniques To Encourage Students’ English Speaking Skills

As teachers, we’re always looking for ways to improve our students’ English speaking skills and build their confidence in speaking English. An effective way to do this is to integrate motivational speaking techniques into our teaching methods and teach our students some engaging speaking strategies to use.
It is important to point out to students that speakers in public talks such as TED talks or other significant speeches sound confident because of the key components that make up a successful talk. By adopting some of these, students can begin their journey to confidence and enjoyment in speaking English.
Great motivational speaker techniques
Knowledge and clarity.
Great motivational speakers possess a deep knowledge of their subject, which helps their audience trust in the speaker.
- For students, this emphasises the importance of understanding the content they are speaking about.
- Encourage students to research and fully understand the topics they discuss. This will ensure they can present information clearly and confidently.
- This can be practised through classroom presentations or group discussions where the focus is on explaining concepts in simplified terms.
Confidence and purpose
Confidence often comes from speakers feeling well-prepared and passionate about their subject.
- Teach students to define the purpose of their speeches and talks – whether to inform, persuade or entertain. This clarity helps them deliver their message with conviction and engage their audience more effectively.
- Role-playing different scenarios in class can help students build confidence and define their speaking goals.
Storytelling
Whether it’s a personal anecdote or something else, stories can captivate an audience and make the speech memorable.
- Remind students that by telling a story, the audience is instantly more engaged and likely to follow along throughout the talk.
- Help students develop their storytelling skills by integrating stories into language lessons. They could start with narrating simple personal experiences and gradually move to more complex narratives as their skills improve.
Audience awareness
Understanding the audience is crucial for effective communication.
- Have students think of a talk or presentation they’ve recently seen. Then, have them think about who the audience for the talk was.
- Tell students that speakers tailor their content and delivery to match the audience’s knowledge level and background. This involves using appropriate language, examples and explanations that the audience understands and can relate to.
- In class, students can practise audience awareness by presenting the same information in different ways to different groups and tailoring the language they are using and the way they are presenting the information.
A strong conclusion
A strong finish is essential in great motivational speaking. It reinforces the message and often includes a call to action that leaves the audience inspired.
- Teach students to summarise their key points effectively and end with a compelling conclusion that prompts further thought or action.
- This could be practised through debates or persuasive speeches in class, where students are encouraged to conclude with strong statements and a call to action.
Practical exercises to enhance English speaking skills
- Focus on activities that enhance clarity in communication. For example, paraphrasing or connecting complex ideas with simpler concepts.
- Have students do exercises that improve non-verbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact, using gestures and controlling hesitations.
- Help students reflect on the purpose of their talk or presentation, and choose language that aligns with their goals, for example, to convince, inform, teach or entertain.
- Have students discuss how best to explain complex ideas. Remind them that any information should be appropriate and understandable to the audience without requiring much prior knowledge.
- Explore the use of extreme adjectives and the connotations of words with your students, emphasising how language choice can inspire and motivate an audience.
Incorporating motivational speaking techniques into your lessons can have a significant impact on students’ engagement and confidence in communicating their ideas. By having these skills, students will not only improve their English proficiency but also gain valuable life skills in speaking and presenting to audiences.
You can read more about teaching your students presentation skills here. Or read our paper for in-depth advice on teaching English pronunciation.
You may also like
Helping advanced students overcome the language learning plateau, ‘play is for children’: myths about learning through play, differentiation strategies for challenging advanced learners, leave a reply cancel reply, recent posts, soft skills activities: ideas for your language classroom, keeping it human: four things every teacher should consider when using technology, how graded readers and engaging activities can ignite student interest in the magic of books, recent comments.
Copyright 2023 © Oxford University Press 2023
Read our Privacy Policy , Cookie Policy & Legal Notice .
This blog contains external links. OUP are not responsible for the content of external sites nor do we endorse any companies or organisations linked to. Any views or opinions expressed in the articles on these posts are those of the author(s).
Oxford University Press - ELT

- Publishing Policies
- For Organizers/Editors
- For Authors
- For Peer Reviewers
An Insight to Attitudes and Challenges in Oral Presentations Among University Students
Oral presentation skills are often seen as important skills that university students need to possess once graduated. However, face to face oral presentation is still seen as one of the biggest challenges a student face as they often experience nervousness and shyness, give no eye contact, do not address the audience, and many more. With this in view, more research evidence is needed to understand students’ attitude towards oral presentation, oral presentation courses and the difficulties that students’ face when presenting. Hence, this study has two aims. The first is to investigate students’ attitude towards oral presentations skills and oral presentation courses. Secondly, this study aims to find out the difficulty that students face when giving oral presentations. A quantitative analysis was carried out to analyze the data. The data was collected among 145 university students from an oral presentation course in a selected university. The data obtained was analyzed for mean and percentages using the SPSS version 26. This study found that though students are aware on the importance of oral presentation skills, many are still facing challenges when doing it. Results yielded from four aspects which are from the general presentations challenges, linguistic, background knowledge, and psychological challenges. It is hoped that this study will help to contribute to the understanding of oral presentations among university students.
Keywords: Anxiety , attitudes , challenges , oral presentation , university students
Introduction
Employers often regard communication skills (written, oral, and listening) as one of the most sought-after skills when hiring ( Alshare & Hindi, 2004 ). It is one of the reasons why job interviews are conducted, which is to assess candidate’s communication skills. Oral presentation is the most popular speaking genre in classes as well as the workplace ( Chang & Huang, 2015 ). Most higher education courses include presentations as a method of assessment as well as classroom teaching and learning activities. In addition, successful communicative goals include effective oral presentation skills ( Evans, 2013 ). According to Van Emden and Becker ( 2017 ), being able to speak effectively to an audience is one of the benefits that students can gain from their tertiary education. Also, being able to present effectively is a valuable skill for students in whatever subjects they study and will consequently give greater achievements in their academics, career prospects, and their working lives in the future ( Van Emden & Becker, 2017 ).
Christensen ( 2002 ) observes that tertiary level students are provided with plenty opportunities to practice their presentation skills. These opportunities range from participating in group discussions, voicing out opinions during lectures, presenting formal speeches during orientation programs and other formal functions to defending their final year project to be assessed by others. In fact, oral presentation assessments are common assessment types in higher education and the function is to measure a student’s ability to create and deliver an engaging, informed, and persuasive argument ( Nash et al., 2016 ). On top of that, many higher educational institutions offer oral presentation and public speaking courses to further develop students’ presentation skills.
In line with the importance of oral presentation skills, University Teknologi Mara, Malaysia offers the course English for Oral Presentations to its students. The course focuses on oral communication theory and practice with emphasis on the importance of verbal and non-verbal communication skills. Learning takes place through a variety of activities to enhance learners’ ability to use the correct language for a presentation, to exploit a variety of materials and sources, and to use visual aids appropriately in oral presentations. Upon completion of the course, students are expected to develop skills to participate in speech communication activities confidently and competently.
Definition of oral presentation
The Learning Centre of The University of New South Wales ( 2010 ) defines oral presentation as a short talk on an assigned topic delivered to a group of people. In an oral presentation, one or more students will present their views and positions on a topic based on their readings or research. According to the University of Wollongong (n.d.) oral presentations can be observed in social events, classrooms and workplaces. In addition, an oral presentation at university shows a student's ability to communicate relevant information effectively in an interesting and engaging manner.
Students attitude towards oral presentations
There have been many past studies written on students’ attitude towards oral presentations. One study by Dansieh et al. ( 2021 ) was done to investigate the possible causes of anxiety towards oral presentations among tertiary students from Technical University, Ghana. The exploratory case study on 46 students used surveys and interviews as the instruments. The study found that even though students are aware of the importance of oral presentations, 63% of the respondents experienced anxiety when asked to give oral presentations. Additionally, 23.9 % experienced nervousness while another 13% experienced stage fright when asked to give oral presentations. The study further revealed that the respondents associated their unfavourable experience to three causes: 1) fear of making mistakes (65.2%), 2) fear towards the audience (21.7%), and 3) lack of knowledge in oral presentations (13%).
Another recent study that measures students’ attitude towards oral presentations was conducted by Pham et al. ( 2022 ) on 600 second-year, third-year, and fourth-year students at the Faculty of Foreign Languages of Van Lang University in Vietnam. The quantitative study used a survey questionnaire with 38 questions. The study reported that 89.7% of the respondents agree that oral presentation skills are important for their career prospects, and 90.7% of the respondents believe that being able to give good oral presentations is an advantage to students. Additionally, the respondents of the study also acknowledged that oral presentations can help improve communication skills, build confidence, and increase creativity. Despite showing positive understanding towards the importance of oral presentations, 57.1% of the students dread the idea of standing and speaking in front of an audience.
The next study that shed light on students’ attitude towards oral presentation is by Marinho et al. ( 2017 ). The cross-sectional descriptive and analytic study was conducted on 1135 undergraduate students using two instruments: a questionnaire and the Self-statements During Public Speaking Scale (SSPS). The study reported that 89.3% of the respondents believe that oral presentation courses should be included in the curriculum. This implies that there was high awareness among students towards the importance of oral presentations. Additionally, the study also reported that 63.9% of the respondents expressed fear towards oral presentations and it is also highlighted that the female gender is prevalent in the percentage. Marinho et al. ( 2017 ) also claims that students with lesser experience in conducting oral presentations and students with negative self-perception tend to have more fear towards oral presentations.
There is also a qualitative study that was conducted on this subject. Grieve et al. ( 2021 ) studied 46 undergraduate students from University of the West of England (UWE), Bristol. Participants of the study expressed that they were aware of the importance of having oral presentation skills. The study also identified six themes: fear of being judged; physical symptoms; uncertainty about the topic; negative effect on university experience; practice and preparation; more practical support needed. These themes show that overall, students have fear towards oral presentations. Grieve et al. ( 2021 ) subsequently reported that the fear towards oral presentation that students have negatively impacted their learning and student experience, and also affected their mental wellbeing. The study concluded that there is a need to provide support to higher education students with public speaking fear.
Finally, a quantitative study conducted by Dellah et al. ( 2020 ) on 199 UiTM Melaka students investigated students’ anxiety level and the correlation between gender, program, language proficiency and oral presentation anxiety. The study used the adapted Foreign Language Classroom Anxiety Scale or FLCAS as questionnaire. The finding indicated that students experience moderate anxiety towards oral presentation. Dellah et al. ( 2020 ) elaborated that this could be because students were worried of other’s negative evaluation which hinders their readiness to present, and subsequently affect their learning performance in general. This study also concluded that while gender and program are not determining factors, language proficiency does impact students’ anxiety level.
Hence, it is clear that even though students depict their awareness on the importance of oral presentations, they have a negative attitude towards them. The next section of literature review will further elaborate on the challenges and difficulties that students have when dealing with oral presentations.
Challenges students faced during oral presentations
There has been much research done to understand the challenges and difficulties that students face when they are asked to give oral presentations. Imron and Hantari ( 2019 ) studied 23 students in Indonesia. The qualitative research aimed to examine the possible challenges that students face that result in their high anxiety when dealing with oral presentations and public speaking. The study concluded that there are four challenges that students face: 1) self-value (their confidence level), 2) discomposure (fear of failures, embarrassment, and making mistakes), 3) lack of preparation time, and 4) unfamiliarity with the topics. Imron and Hantari ( 2019 ) suggested that the academic institution should provide a supportive environment for students to learn about oral presentations.
Another study that investigated the challenges that students face when dealing with oral presentations was done by Soomro et al. ( 2019 ). The quantitative study was conducted on 100 engineering undergraduate students in Pakistan. The study used a questionnaire as the instrument and reported that there are seven factors that contribute as challenges to students The factors are stress and nervousness (71%), lack of motivation (63%), poor oral communication skills (55%), fear and anxiety (52%), shyness (51%) and low self-confidence (51%). The study suggested that in order to curb this problem, there is a need for institutions to provide training to students and also offer them ample opportunities to practice oral presentations ( Soomro et al., 2019 ).
Pham et al. ( 2022 ) reported a similar finding. The study depicted that three most prevalent challenges that students face regarding oral presentations are fear of making mistakes (53.8%), shyness (57.1%), and the lack of topical knowledge (64.1%). Pham et al. ( 2022 ) also elaborated that students are usually more confident and perform better when they present in their native language as compared to when they present in English. They argue that this happens because students mostly think using their native language and encounter difficulty translating it to English when presenting.
Hamad and Seyyedi ( 2020 ) conducted a more comprehensive study on the challenges that students face during oral presentations in Soran University, Iraq. Their quantitative study on 121 undergraduate students revealed that linguistic factors (language proficiency) were the primary cause for English speaking difficulties with 36.42%, followed by affective (fear of making mistakes and being evaluated, anxiety, low self-confidence and shyness) and sociocultural factors (environment and opportunities) with 35.63% and 27.95 % respectively. The study also concluded that the challenges are the result of a combination of interrelated and intersected psychological, linguistic and sociocultural factors.
One recent study by Bui et al. ( 2022 ) was conducted on 90 undergraduate students from Tay Do University, Vietnam. The study used questionnaires and interviews as instruments. The study revealed that 88.3% of the students acknowledged the importance of oral presentations and felt that they had been given ample opportunities to present. The study also depicted that the common difficulties faced by students stem from linguistic (vocabulary, pronunciation, grammar), background knowledge and psychological factors (anxiety, self-confidence, lack of motivation, fear of making mistakes). The interviews of teachers and students corroborated this finding.
Problem Statement
There are many obvious advantages of conducting oral presentations in language classrooms. According to Brooks and Wilson ( 2014 ), there are five benefits of conducting oral presentations: 1) it is a learner-centred activity; 2) it integrates the use of reading, writing, listening, and speaking; 3) it provides authentic context for language learning; 4) it adds value to using English outside of the class; and 5) it increases students’ motivation level. Additionally, Paxton and Truxal ( 2019 ) added that teaching oral presentations also promotes classroom diversity and allows more variety to assessment methods.
Due to its extensive benefits, many higher educational institutions offer oral presentation courses to their students. Dansieh et al. ( 2021 ) argues that despite these offered opportunities, students will try to avoid presenting to the extent that they choose to not attend an occasion when there is a possibility that they are asked to speak in front of an audience. Dansieh et al. ( 2021 ) claims that this is due to their heightened anxiety towards giving oral presentations. This is in spite of their awareness that oral presentation and public speaking skills are imperative communicative skills in both their academic and career advancement prospects. Grieve et al. ( 2021 ) also agreed to this notion. In their qualitative study, Grieve et al. ( 2021 ) found that students are afraid of oral presentations even though they are aware of the importance of oral presentations. In addition, the study also noted that students’ fear of oral presentations has negatively impacted their overall learning and student experience. Although there is much awareness of student’s anxiety in oral presentations, more research evidence is needed regarding students’ attitude towards oral presentation courses and the difficulties that students’ face when presenting. Hence, this study has two aims. The first is to investigate students' attitude towards oral presentations skills and oral presentation courses. Secondly, this study aims to find out the difficulty that students face when giving oral presentations.
Research Questions
What are students’ attitudes towards oral presentation skills and oral presentation course?
What are the difficulties that students encounter when performing oral presentations?
Research Methods
This quantitative research is done to investigate students’ attitude towards oral presentation skills, oral presentation course and the challenges they face when giving oral presentations. The instrument is a survey adapted from Bui et al. ( 2022 ) and Pham et al. ( 2022 ). 145 students who are taking the English for Oral Presentations subject were chosen using the purposive sampling method. The adapted questionnaire has four different sections. Section 1 has items on the demographic profile. In section 2, the 11 items are on students’ attitudes towards oral presentation skills. Section 3 has 8 items on students’ attitudes towards oral presentation course while the final section, has 20 items on the challenges that students face during oral presentations.
Table 1 above depicts the distribution of items in the survey. The reliability statistics for the instrument. SPSS analysis revealed a Cronbach alpha of .934 thus showing a high internal reliability of the instrument used. Data collection is performed via Google Form. Collected data is then analyzed using SPSS version 26 and is presented in the form of percentages and mean scores to answer the research questions;
Students’ demographic profile
In total, 145 respondents answered the survey and 75% of them were female students, while the remaining 25% were male students. Most of these students (63.4%) were students from social sciences and humanities programs. This is followed by students from the applied sciences (20%) and the students from the business programs (16.6%). The majority of the students were first year students (65.3%) followed by second- and third-year students with 27.1% and 7.6% respectively. Among these 145 students, 31.7% of them obtained grade A for their English paper in the SPM examination. 32.4% obtained grade B, 20% obtained grade C. 10.3% obtained grade D, while the remaining 5.5% obtained grade E for the examination. Hence, it can be said that the respondents constitute of mostly intermediate and higher intermediate students in the aspect of language proficiency.
R1: Students’ attitude towards oral presentation skills and oral presentation course
This section presents data to answer research question 1: What are students’ attitudes towards oral presentation skills and oral presentation course?
When evaluating the findings of students’ attitude towards oral presentation skills, it is found that their attitude can be categorised to the perceived importance of oral presentation skills on i) future use, ii) improvement of their language and communication skills, and iii) general learning purposes.
Table 2 illustrates how students perceive the importance of oral presentation skills for their future use. The most significant importance that students perceive is that presentation skills play a vital role for their future careers with the mean of 4.3. This is followed by the perceived importance of presentation skills on their confidence with studies and work with the mean score of 4.1. In terms of connecting them with success, the mean score achieved is 4.0 and the least mean score is 3.0 for the statement “Presentation skills are just one of the skills, so we do not need to be excellent or focus too much on the skill”.
Table 3 depicts the perceived importance of presentation skills on improvement of language and communication skills. It is revealed that most respondents feel that oral presentation skills help improve their communication skills with a mean of 4.3. This is followed by improving their language proficiency with 4.1. Respondents also feel that oral presentation skills help master their thought and improve their speaking ability with a mean score of 4.0.
Table 4 shows the results for students’ perceived importance of presentation skills for general learning purposes. Items AOPS2 and AOPS9 shows the highest score. Respondents feel that having the ability to give good presentations is necessary for students and that they give better presentations when it is for their favourite subject. For item AOPS7, 3.9 mean score is recorded, while a lower mean score of 3.4 is obtained for item AOPS10.
Table 5 illustrates students’ attitudes towards an oral presentation course. Oral presentation courses aim at providing students guidance to deal with external and internal factors that hinder effective presentation. For the external factors, it is found that respondents feel that the course helped them understand about body language when presenting the most with a mean score of 4.1. This is followed by a mean score of 4.0 for giving them knowledge on presentation skills. The same mean score of 3.9 is obtained for items AOPC1 and AOPC2. As for the internal factors that hinder effective presentations, the highest mean of 4.0 is obtained for item AOPC8. This is followed by a mean score of 3.9 for item AOPC3. Additionally, the respondents stated that the course helped them feel more confident about presenting (mean score= 3.7) and taught them how to deal with anxiety when presenting (mean score= 3.5).
R2: Challenges that students encounter when performing oral presentations
This section presents data to answer research question 2: What are the difficulties that students encounter when performing oral presentations? In the context of the current study, it is found that difficulties when performing oral presentations can be divided into four categories; general, linguistic, background knowledge and psychological challenges.
Table 6 presents the general challenges that students face during oral presentations. For general challenges, the highest mean is obtained for the statement “You have faced difficulties when making a presentation.” The next item with a mean of 3.7 is that students’ main difficulty is the lack of time for preparation and practice. Items DOP14 and DOP 16 both obtained the mean of 3.6. The lowest mean is for item DOP8 which states that students perceive their conversation skill as poor.
Table 7 shows the eight items on linguistics difficulties that students face during oral presentations. The highest mean (4.0) is obtained for item DOP3, followed by DOP 5 with a mean score of 3.8. Next, for item DOP9 and DOP2 that are items on vocabulary, the mean scores obtained are 3.7 and 3.6 respectively. The least mean is obtained for item DOP6 with 2.9 mean score, followed by item DOP4 with 3.0 mean score
Table 8 depicts students’ attitude towards challenges pertaining to background knowledge. Respondents of this study feel that background knowledge plays a significant role in oral presentation skills as mean score of 3.9 is achieved for this item. This is followed by a mean score of 3.8 for the statement “You meet difficulty voicing your opinion on unfamiliar topic”. Finally, a mean score of 3.6 is obtained for item DOP12.
Table 9 shows the mean score for psychological challenges that students face during oral presentations. The highest mean is obtained for DOP17 where respondents feel afraid of making mistakes. Items DOP16 and DOP18 have the same mean score of 3.9. For item DOP19, “You have high motivation for presentations in classrooms”, the lowest mean score of 3.1 is obtained, while the second lowest mean score is obtained by item DOP20 which is 3.2.
Students’ attitude towards oral presentation skills and oral presentation course
This study focuses on students’ attitude towards oral presentation skills and courses as well as the challenges that they face during oral presentations. The findings of this study can augment the existing literature, especially regarding students’ attitude on oral presentation course. From the findings of this study, it can be gauged that overall, students understand the vital roles that oral presentations play for their future career. They also view presentation skills as something that they have to master, in order to succeed in their study life, and to obtain better career opportunities. The findings of this study can corroborate previous studies by Dansieh et al. ( 2021 ) and Pham et al. ( 2022 ) that both depict students’ awareness on the importance of having good presentation skills.
Next, this study also found that students view oral presentations as a tool that can help them improve their communicative abilities, language proficiency, and help them in their studies in general. This finding is parallel to Pham et al. ( 2022 ) who also found that students believe that oral presentation skills can enhance their communicative ability, and Amelia ( 2022 ) who found that oral presentations can help students improve their language proficiency and aid in developing academic skills. Hence, it can be concluded that students are generally aware of the importance of presentation skills on their study, career prospects, and life in general.
The next finding of this study is that students view the oral presentation course they take, ELC590 as being able to help them externally and internally when it comes to oral presentation. Students feel that the subject gives them knowledge about oral presentations, and also teaches them about content and body language. Additionally, the subject also helps students deal with anxiety and build their confidence when presenting. The study of Pham et al. ( 2022 ) had similar results where students feel that oral presentation course helped them with knowledge and confidence level when presenting. Similar to this study, it was also established that taking an oral presentation course made students better presenters for other subjects.
The challenges that students face during oral presentations
Firstly, this study found that most students have faced challenges during oral presentations and having lack of time for preparation is also one of the biggest challenges they faced. This finding is similar to Bui et al. ( 2022 ) where most students responded “Agree” and “Strongly Agree” to the similar statement. Therefore, it is established that even though many are aware on the importance of oral presentation skills, students still do not know how to overcome challenges revolving around it.
Next, this study also found that even though not many students regard their conversational skill as poor, linguistic factor is still a major challenge that they face during oral presentations. This is similar to the findings by Hamad and Seyyedi ( 2020 ). To elaborate, this study found that most students feel that searching for the right word to use is a challenge they faced, and they also encountered difficulties with limited vocabulary. They also faced challenges when it comes to pronunciation and grammar, with pronunciation being the least worried element. This finding is contrary to Bui et al. ( 2022 ) who found that pronunciation is the biggest linguistic challenge, followed by vocabulary and grammar. This could be due to geographical factor as both studies were conducted in different countries. From this finding, it can be gauged that as second language learners, students’ language proficiency will always be a challenge, and to overcome this, students should be exposed to role plays or other speaking activities that require them to speak in English spontaneously.
For psychological factors, this study found that the biggest challenge that students have is fear of making mistakes. This is followed by anxiety when speaking in front of others, and fear of criticism and evaluation by others. The result is consistent with the study by Pham et al. ( 2022 ) who found that fear of making mistakes is the biggest psychological challenge that students faced. A study by Soomro et al. ( 2019 ) too stated anxiety as the major challenge but it was ranked first as compared to the findings of this study. Finally, the finding of this study can also corroborate to the finding by Imron and Hantari ( 2019 ) who found fear of making mistakes and anxiety as challenges that most students face during oral presentations. Based on this finding, it can be seen that even when students are taught anxiety and methods to overcome it in the oral presentation course, these psychological factors still exist and hinders students from creating effective presentations.
Pedagogical implications
Students attitude towards oral presentation skills and oral presentation courses, as well as the challenges they face when asked to conduct oral presentations are explored in this study. According to this study, students are generally aware on the importance of presentation skills on their study, career prospects, and life in general. However, many students still face difficulties when dealing with presentations. The challenges that they face can be divided into general, background knowledge, linguistic and psychological factors. Out of these four challenges, psychological factors recorded the highest mean collectively. Since the finding also found that students value oral presentation courses, it is suggested that educators incorporate strategies to overcome psychological factors in their courses. Students should be taught to increase the level of preparation they have, embrace anxiety, and use the nervous energy they have to create better presentations.
In addition, educators should also provide a friendly atmosphere that allows students to voice their opinion. Also, since fear of making mistakes is listed as one of the traits that students have, sharing sessions could be incorporated in lessons to allow students to practice speaking without the pressure of being evaluated or judged. Finally, a participatory approach in teaching and learning can be inculcated in lessons to reduce students’ communication apprehension.
Suggestions for future research
Since this study revolves only around 145 students of Universiti Teknologi Mara,Shah Alam, a greater sample size and a broader context could produce a more accurate result. Next, since it has been established that students are generally aware about the importance of oral presentations, studies on the factors that make students dread presentations could be done. In addition, it is also crucial to conduct experimental studies that investigate the effectiveness of oral presentation courses to delve on the ways these courses can further help students with oral presentation skills.
Alshare, K., & Hindi, N. M. (2004). The importance of presentation skills in the classroom: Students and instructors perspectives. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges, 19(4), 6-15
Amelia, R. (2022). Indonesian EFL students' attitude toward oral presentations. Indonesian Journal of Integrated English Language Teaching, 8(1), 15-30. DOI:
Brooks, G., & Wilson, J. (2014). Using oral presentations to improve students’ English language skills. Kwansei Gakuin University Humanities Review, 19(1), 199-212.
Bui, T. T. L., Huynh, T. M. D., Nguyen, T. M. N., Nguyen, T. N. C., & Nguyen, T. Y. N. (2022). The difficulties in oral presentation of English-majored juniors at tay do university, Vietnam. European Journal of English Language Teaching, 7(2). DOI:
Chang, Y., & Huang, H. (2015). Exploring TED Talks as a pedagogical resource for oral presentations: A corpus-based move analysis. English Teaching & Learning, 39(4), 29-62. DOI:
Christensen, J. P. (2002). Understanding and conducting a successful presentation assignment. Guidelines, 24(2), 23-28.
Dansieh, S. A., Owusu, E., & Seidu, G. A. (2021). Glossophobia: The Fear of Public Speaking in ESL Students in Ghana. Language Teaching, 1(1), 22. DOI:
Dellah, N. F., Zabidin, N., Nordin, N. A., Amanah, F. H., & Atan, M. A. (2020). Glossophobia: Evaluating University students' speaking anxiety in English Oral Presentations. Jurnal ILMI, 10(1), 116-126.
Evans, S. (2013). Just wanna give you guys a bit of an update: Insider perspectives on business presentations in Hong Kong. English for Speaking Purposes, 32(4), 195-207. DOI: 10.1016/j.esp.2013.05.003
Grieve, R., Woodley, J., Hunt, S. E., & McKay, A. (2021). Student fears of oral presentations and public speaking in higher education: a qualitative survey. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 45(9), 1–13. DOI:
Hamad, K. Q., & Seyyedi, K. (2020). Communication challenges facing Soran University students in speaking English as a Foreign Language. International Journal of Linguistics, Literature and Translation, 3(8), 40-53.
Imron, A., & Hantari, W. C. (2019). EFL students’ attitudes toward public speaking and anxiety in speaking impromptu speech. CaLLs (Journal of Culture, Arts, Literature, and Linguistics), 5(1), 49-58. DOI:
Marinho, A. C. F., de Medeiros, A. M., Gama, A. C. C., & Teixeira, L. C. (2017). Fear of public speaking: perception of college students and correlates. Journal of Voice, 31(1), 127-e7. DOI:
Nash, G., Crimmins, G., & Oprescu, F. (2016). If first-year students are afraid of public speaking assessments what can teachers do to alleviate such anxiety? Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 41(4), 586–600.
Paxton, S., & Truxal, D. (2019). From chinmoku to pera pera: Teaching presentation skills at university in japan. The Journal of Rikkyo University Language Center, 41, 63-73.
Pham, M. T., Nguyen, D. N. Q., Nguyen, T. K. C., Nguyen, H. N. M., Hoang, T. A. T., & Pham, V. P. H. (2022). The Reality of English Presentation Skills of English-majored Students in Vietnam: A Case Study at Van Lang University. International Journal of TESOL & Education, 2(2), 27-46. DOI:
Soomro, M. A., Siming, I. A., Shah, S. H. R., Rajper, M. A., Naz, S., & Channa, M. A. (2019). An investigation of anxiety factors during English oral presentation skills of engineering undergraduates in pakistan. International Journal of English Linguistics, 9(3), 203-210. DOI:
The University of New South Wales. (2010). Oral presentations for tutorial and seminars. https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/37858326/oral-presentations-the-learning-centre-university-of-new-south-
University of Wollongong. (n.d.). Oral presentations. https://www.uow.edu.au/student/learning-co-op/assessments/presentations/
Van Emden, J., & Becker, L. (2017). Presentation skills for students. Bloomsbury Publishing.
Copyright information

About this article
Publication date.
25 September 2023
Article Doi
https://doi.org/10.15405/epes.23097.49
978-1-80296-964-1
European Publisher
Print ISBN (optional)
Edition number.
1st Edition
Language, education, literature, linguistics
Cite this article as:
Zakaria, S. F., Rusli, R., Mat, N. H. C., & Tazijan, F. (2023). An Insight to Attitudes and Challenges in Oral Presentations Among University Students. In M. Rahim, A. A. Ab Aziz, I. Saja @ Mearaj, N. A. Kamarudin, O. L. Chong, N. Zaini, A. Bidin, N. Mohamad Ayob, Z. Mohd Sulaiman, Y. S. Chan, & N. H. M. Saad (Eds.), Embracing Change: Emancipating the Landscape of Research in Linguistic, Language and Literature, vol 7. European Proceedings of Educational Sciences (pp. 543-555). European Publisher. https://doi.org/10.15405/epes.23097.49
We care about your privacy
We use cookies or similar technologies to access personal data, including page visits and your IP address. We use this information about you, your devices and your online interactions with us to provide, analyse and improve our services. This may include personalising content or advertising for you. You can find out more in our privacy policy and cookie policy and manage the choices available to you at any time by going to ‘Privacy settings’ at the bottom of any page.
Manage My Preferences
You have control over your personal data. For more detailed information about your personal data, please see our Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy .
These cookies are essential in order to enable you to move around the site and use its features, such as accessing secure areas of the site. Without these cookies, services you have asked for cannot be provided.
Third-party advertising and social media cookies are used to (1) deliver advertisements more relevant to you and your interests; (2) limit the number of times you see an advertisement; (3) help measure the effectiveness of the advertising campaign; and (4) understand people’s behavior after they view an advertisement. They remember that you have visited a site and quite often they will be linked to site functionality provided by the other organization. This may impact the content and messages you see on other websites you visit.
Search form
Oral communication skills are important for students.
BY ANTON LUCANUS
Communication skills are vital for a student’s academic success and future career prospects. In today’s challenging environment, students must not only possess academic expertise, but also the requisite skills to enhance their learning and employability prospects in the future.
Communication is a dynamic process as it involves an interaction between two or more people i.e. the sender and the receiver. The main purpose of communication is to transmit thoughts and beliefs to another person. The major components of communication are verbal communication or oral communication and non-verbal communication. Oral communication is the process of expressing ideas through the medium of speech and this plays a crucial role in the life of students.
Importance of Oral Communication for Students
An individual learns the basics of oral communication right at home. The school environment takes this learning a notch higher by teaching the student how to interact with peers and teachers alike. The quality of communication in student life will define professional communication later in life.
Good communication enables students to assimilate more from the learning process by empowering them to ask relevant questions and discuss doubts.
Effective verbal communication nurtures the process of socialization by facilitating new friendships and these in turn aid the learning process.
Productive communication is a boost to career development. An ability to convey thoughts in a clear and precise manner would help a student to make a favorable impression at an interview and get the job that he deserves.
Communication skills inculcate professionalism in speaking styles, ways of self-expression and attitudes towards others, and these traits would hold students in good stead in their professional lives.
Dynamics of Oral Communication
The hallmark of a good student communicator is that he has mastered the art of preparing, organizing and delivering successful oral presentations. Oral communication includes real-time presentations, video presentations and interviews, with accompanying visual aids such as handouts and power-points.
Message is the key to a good oral communication. The substance of the presentation should be relevant to the audience and goals of the presentation.
Self-awareness is the starting point of good oral communication. A person who is aware of his strengths and weaknesses can put in the required efforts to improve communication skills.
Confidence is another vital aspect of good communication. A person may know the subject and yet not communicate adequately if he lacks confidence.
Simplicity in messaging is indispensable for good communication as assimilation of the message is directly proportional to clarity of its presentation.
Awareness of the audience is an important tool in the hands of an effective oral communicator. A good communicator can guage the impact of the by observing the body language and feedback of the audience and adjust his approach accordingly.
Interaction is the path to effectiveness. A student oral communicator can keep the audience engaged by asking questions and soliciting opinions on the subject matter at hand. This would also help in fine tuning the message and style of presentation, based on the feedback received from the audience.
The tone of voice of the presenter carries a lot of weight in delivery of the message. A confident tone keeps the audience engaged, whereas a low and monotonous tone can be off-putting. Voice modulation can also be employed to highlight the key points in the presentation and retain the attention of the audience.
Body language is an important component of effective oral communication. The student should adopt a stable and confident posture, make appropriate gestures, avoid being fidgety and establish eye contact during the presentation.
Oral communication is not merely the ability to speak, but also the capacity to listen. A good communicator is one who is attuned to the audience and is able to calibrate his message accordingly. An aspiring oral communicator should be willing to acquire and hone his listening skills over a period of time.
The Path to Effective Oral Communication
Oral communication is an art that can be learnt and polished through reading, presentation skills and practice.
An oral communicator should have intellectual curiosity. Reading is a means to the development of good communication skills. A well-educated mind would be able to communicate better as content is the soul of the communication process. He should also possess an attitude of discussion and deliberation as this would improve intellectual capabilities and thereby contribute to effective communication.
Effective writing skills and good verbal communication skills go hand-in-hand although they may appear antithetical to a newbie. A student with good writing skills would alone be in a position to organize and present his thoughts in a structured manner; an exposure to the nitty-gritty of essay writing would be immensely beneficial in that regard.
The age-old dictum ‘Practice makes a person perfect’ makes perfect sense in the world of oral communication. The first impression is the best impression and many students fail this test due to a various impediments such as stage fright, lack of self-confidence and performance anxiety. A student can conquer his fears and master the art of oral communication by participating in many real and mock presentations, and speech-based activities.
Active participation in the community would transform a student into a good communicator by honing his linguistic abilities. Moreover, a leadership position in an academic setting would be an important asset on the CV of a student.
To conclude, a student willing to put his nose to the grindstone can indeed make a smooth transition from a tentative speaker to an effective and seasoned oral communicator.
Byline – Anton Lucanus is the Director of Neliti. During his college years, he maintained a perfect GPA, was published in a top cancer journal, and received many of his country’s most prestigious undergraduate scholarships. Anton writes for The College Puzzle as a means to share the lessons learnt throughout his degree and to guide current students to achieve personal and educational fulfilment during college life.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

COMMENTS
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
Giving a presentation to fellow classmates can be a bit daunting, especially if you are new to oral and visual presenting. But with the right PowerPoint tips, public speaking skills, and plenty of practice, you can present like a pro at your upcoming presentation. Here, we've laid out the best college presentation tips for students.
Personal online tutoring. EnglishScore Tutors is the British Council's one-to-one tutoring platform for 13- to 17-year-olds. Giving an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam can be quite scary, but we're here to help you. Watch two students giving presentations and then read the tips carefully.
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
accomplished by delivering oral presentations in class, at conferences, in public lectures, or in company meetings. Therefore, learning to deliver effective presentations is a necessary skill to master both for college and further endeavors. Oral presentations typically involve three important steps: 1) planning, 2) practicing, and 3 ...
Presentations normally have one or more of the following aims: To inform/ raise awareness of an important issue. To persuade people to do something. Form part of an exam, demonstrating public speaking/presentation skills in a first or second language. I set students a task where they answer these questions:
Part 3 of the Oral presentations series.Many students approach writing their oral presentation the same way they approach writing an essay when, in fact, the...
HOW TO Give a Great Presentation - 7 Presentation Skills and Tips to Leave an Impression Author: Practical PsychologyFeatures: know your audience, structure your presentation, use visuals, use repetition, have a story to tell, be relatable, build your confidence with practice 10 Tips for Better Presentations: Simple Strategies for More Effective Talks (15:41) Author: Barbara ...
Research confirms that in order for ELLs to acquire English they must engage in oral language practice and be given the opportunity to use language in meaningful ways for social and academic purposes (Williams & Roberts, 2011). Teaching students to design effective oral presentations has also been found to support thinking development as "the ...
The Purpose of an Oral Presentation. Generally, oral presentation is public speaking, either individually or as a group, the aim of which is to provide information, entertain, persuade the audience, or educate. In an academic setting, oral presentations are often assessable tasks with a marking criteria. Therefore, students are being evaluated ...
This paper reports on an intervention which seeks to help students develop oral presentation skills and. at the same time help apprehensive presenters reduce their fear of delivering oral ...
- Peer assessment: Let students provide oral & written feedback (as part of the participation grade) using a checklist (see handout), so they become familiar with the required skills. • Activities - Help students develop mastery for presentation skill - To develop mastery, students must acquire component skills, practice integrating them,
Honing Students' Speaking Skills. Some guidelines for teaching all students to speak credibly and confidently—an essential skill for college and career success. It's been a long time since schools focused solely on the three Rs—reading, writing, and arithmetic. Along the way, we realized that there's so much more that defines a ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Delivering oral presentations is ubiquitous in tertiary settings across the globe. Presentations play a role in students' acquisition of knowledge and are often a mode of assessment in all disciplines. After graduation, presentation skills are still employed under many circumstances such as in job interviews and assignments in the workplace.
Oral presentations provide a useful opportunity for students to practice skills which are required in the world of work. Through the process of preparing for an oral presentation, students can develop their ability to synthesise information and present to an audience. To improve authenticity the assessment might involve the use of an actual ...
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Oral presentation skills refer to the ability to convey information and ideas through spoken words, body language, and visual aids in a structured and engaging manner. It involves organizing thoughts, tailoring content to the audience, and delivering the message confidently and clearly. ... Students often use oral presentations to share ...
Oral presentation and speaking are important skills for students to master, especially in the intermediate grades. This oral presentation rubric is designed to fit any topic or subject area. The rubric allows teachers to assess students in several key areas of oral presentation. Students are scored on a scale of 1-4 in three major areas.
Success in oral pesentation skills contributes to students' success in academic performance as well as their social life. It is important for teachers to know their students' needs and social background in order to encourage them to share information relevant to their interests with their peers to improve their oral presentation skills.
Practical exercises to enhance English speaking skills. Focus on activities that enhance clarity in communication. For example, paraphrasing or connecting complex ideas with simpler concepts. Have students do exercises that improve non-verbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact, using gestures and controlling hesitations.
Carl Storz et al. Oral Presentation Skills Août 2002 2 Preface This text, the result of years of experience and research, is intended to be an aid for anyone wishing to speak in public to fellow students, colleagues or other interested groups. This text provides the essential elements and some tips on preparing and organizing a
Abstract. Oral presentation skills are often seen as important skills that university students need to possess once graduated. However, face to face oral presentation is still seen as one of the biggest challenges a student face as they often experience nervousness and shyness, give no eye contact, do not address the audience, and many more.
Body language is an important component of effective oral communication. The student should adopt a stable and confident posture, make appropriate gestures, avoid being fidgety and establish eye contact during the presentation. Oral communication is not merely the ability to speak, but also the capacity to listen.