- Health Science
- Business Education
- Computer Applications
- Career Readiness
- Teaching Strategies
« View All Posts
Computer Applications | High School

5 Best Computer Applications Lesson Plans for High School
- Share This Article
November 22nd, 2022 | 6 min. read

Print/Save as PDF
High school computer teachers face a unique challenge. You have hundreds of students to teach, so planning lessons takes hours of personal time every week.
Creating computer applications lessons that are current, engaging, and will prepare your students isn’t easy! Unfortunately, it can be overwhelming to find computer applications lesson plans that are engaging and relevant to high schoolers.
So where do you start?
In this article, we’ll share where you can find great computer applications lesson plans to teach 5 topics to high school students:
- Digital Literacy
- Microsoft Office
- Google Applications
- Internet Research
- Computer Science
We’ll start with the basics — digital literacy.
1. Digital Literacy Resources for High School Computer Classes

Digital literacy (sometimes called computer literacy) encompasses a number of skills related to using technology effectively and appropriately, making it critical for your students to understand.
When teaching digital literacy in high school be sure to include these six topics:
- Information literacy
- Ethical use of digital resources
- Understanding digital footprints
- Protecting yourself online
- Handling digital communication
- Cyberbullying
All of this knowledge provides an important base that students build upon throughout the rest of your course and later in their education!
For digital literacy lesson plans and activities, check out these five steps to teaching digital literacy in the classroom .
2. Microsoft Office Lesson Plans for High School

Teaching Microsoft Office in high school is a must. While some students may be familiar with these programs, it’s critical to familiarize your students so everyone is on the same page.
Also, high school students can go more in-depth with the advanced features of each application, compared to middle school students.
You can find a ton of resources out there to build lesson plans, but there are almost too many for one person to read.
Instead, decide which Microsoft applications you will cover and go from there. Also, consider if your students will take Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) certification exams. If so, include some exam prep lessons in your course.
To find lesson plan ideas that will work for your classroom, check out these Microsoft Office lesson plans that your students will love .
3. Google Apps Lesson Ideas for High School

Along with Microsoft Office, Google Apps are important for high school students to learn.
Your course standards may already include Google Apps, but if not, you should still consider including some lessons on Docs, Sheets, and Slides in your course.
It comes down to the fact that many employers are now using Google instead of Microsoft. That means your students should be prepared to use either application suite in their careers.
One way to teach Google Apps is to mirror your Microsoft Office lessons. Another option is to focus specifically on how the two suites differ, such as with the collaborative features in Google Docs.
Either way, you’ll need some lesson plans and activities!
To start, check out the Google Apps lesson plans every teacher should own .
4. Lessons to Teach Internet Research Skills in High School

Your students need internet research skills to use throughout the rest of their lives.
With the constant changes in how search engines work and the number of websites out there, these lessons are crucial.
Having good online research skills can help students prevent costly mistakes, such as citing false information in a final project or believing fake news.
There aren’t many resources about web research that are appropriate for high schoolers, but luckily Google has a series of lessons that could be just what you need.
There are three levels of expertise for each topic area, ensuring you can provide lessons based on your students’ levels of knowledge.
Additionally, some lessons have teacher presentations and Google includes a full lesson plan map for quick reference.
Check out the lessons from Google here: Search Literacy Lesson Plans .
5. Computer Science Lesson Plans for High School

Programming may be daunting to teach , but these skills are essential in today’s workforce. Knowing how to write code can set your students up for incredible careers in the future!
Luckily, there are a ton of resources out there to teach these skills. However, like Microsoft lessons, there are so many out there that it’s a challenge to comb through them all.
Fortunately, Common Sense Education has some great computer science activities and lessons for high school students.
Some of the tools come with lesson plans and teacher resources. Others are less structured, intended as an extra supplement to your lessons.
Check out Common Sense Education’s list of the best coding tools for high school students .
Start Teaching Computer Applications in High School Today!

Choosing the most appropriate computer applications lesson plans for your students can be the difference between your learners falling behind or being ready to begin exciting careers.
Any of the lessons in this article can help you get your students on the way to success with computer skills. But many teachers have found success when using a comprehensive CTE curriculum throughout their high school computer classes.
If you're looking for a cohesive learning experience for your high school students, consider iCEV. iCEV provides a high school computer curriculum with pre-built lessons, interactive activities, and automatically graded assessments designed to save you hours in the classroom.
Check out the iCEV computer curriculum to see if it's the right fit for your classroom:


- Lesson Plans
Technology Lesson Plans
Whether you are looking for technology lessons for your classroom or computer lab, The Teacher's Corner has organized some great lessons and resources around the following: management, integration, keyboarding, and more. Make sure your students are developing their 21st Century skills.
Your creativity can help other teachers. Submit your technology lesson plan or activity today. Don't forget to include any additional resources needed. We also love to get photos!
Technology Lesson Plans and Classroom Activities
| Printable Worksheets | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
Kidspiration Activities

Computer and Electronics Glossary This is an award winning Glossary site containing several thousand computer, electronics and telephony terms. Numerous educational groups and organizations have adopted the Glossary into the computer curriculum designed by them.
CyberSmart First-of-its-kind K-8 Curriculum co-published with Macmillan/McGraw-Hill and available free to educators. Original standards-based lesson plans.
Download.com A good place to hunt for freeware for your computer... educational games and more.
Fin Fur and Feather Bureau of Investigation The FFFBI is a fictional, animal-based government crime fighting agency that battles many foes, most notoriously CRUST (the Confederacy of Rascals and Unspeakably Suspicious Trouble Makers) and the Cyber Tooth Tigers. Kids ages 8-12 act as self-appointed field agents, filing their own reports to the Bureau and solving mysteries. The central idea is that through this series of fun and engaging interactive projects kids will learn to use the internet as a tool for research as well all kinds of investigation.
Funbrain.com Where kids get power! This is a neat site of educational games for kids.
How to Set-Up Computers in Your Classroom A great article that will help get you on the right track!
Teach With Movies Find various films to show in your classroom, along with Learning Guides to each recommended film describing the benefits of the movie, possible problems, and helpful background.
FreeMacFonts.com Fonts for your Mac Computer.
Microsoft in Education The Microsoft company had done some leg work for you! Looking for new and exciting ways to integrate technology into your classroom? Look no further.
1001 Free Fonts Fonts for your PC Computer.
| | |
We are currently working on making the site load faster, and work better on mobile & touch devices. This requires a full recode of the main structure of our website, then finding and fixing individual pages that could be effected, and this will all take a good amount of time. PLEASE let us know if you are having ANY issues. We try hard to fix issues before we make them live, so if you are having problems, then we don't know about it. Additionally, sending a screenshot of the issue can often help, but is definitely not necessary , just tell us which page and what isn't working properly. Just sending us the notification can get us working on it right away. Thank you for your patience while we work to improve our site! EMAIL: [email protected] .
Thank you for your patience, and pardon our dust! Chad Owner, TheTeachersCorner.net
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Eric Grimson
- Prof. John Guttag
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming
Assignments.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer
The development of computers has been a wonderful journey that has covered several centuries and is defined by a number of inventions and advancements made by our greatest scientists. Because of these scientists, we are using now the latest technology in the computer system.
Now we have Laptops , Desktop computers , notebooks , etc. which we are using today to make our lives easier, and most importantly we can communicate with the world from anywhere around the world with these things.
So, In today’s blog, I want you to explore the journey of computers with me that has been made by our scientists.
Note: If you haven’t read our History of Computer blog then must read first then come over here
let’s look at the evolution of computers/generations of computers
COMPUTER GENERATIONS
Computer generations are essential to understanding computing technology’s evolution. It divides computer history into periods marked by substantial advancements in hardware, software, and computing capabilities. So the first period of computers started from the year 1940 in the first generation of computers. let us see…
Table of Contents
Generations of computer
The generation of classified into five generations:
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computer(1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
| Computer Generations | Periods | Based on |
|---|---|---|
| First-generation of computer | 1940-1956 | Vacuum tubes |
| Second-generation of computer | 1956-1963 | Transistor |
| Third generation of computer | 1964-1971 | Integrated Circuit (ICs) |
| Fourth-generation of computer | 1971-present | Microprocessor |
| Fifth-generation of computer | Present and Beyond | AI (Artificial Intelligence) |
1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956)

The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Vacuum tubes” It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer “John Ambrose Fleming” . A vacuum tube is an electronic device used to control the flow of electric current in a vacuum. It is used in CRT(Cathode Ray Tube) TV , Radio , etc.

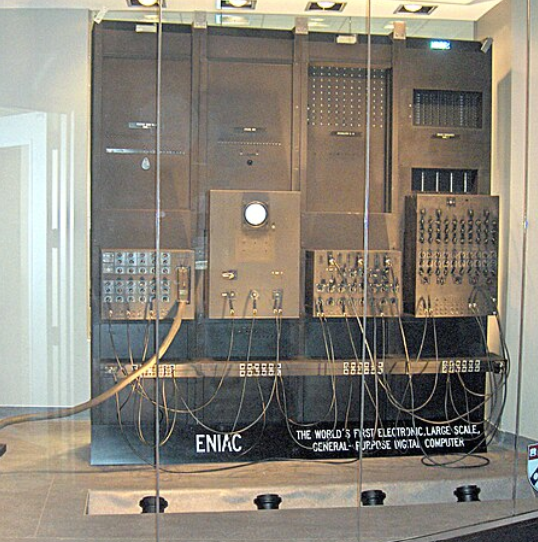
The first general-purpose programmable electronic computer was the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) which was completed in 1945 and introduced on Feb 14, 1946, to the public. It was built by two American engineers “J. Presper Eckert” and “John V Mauchly” at the University of Pennsylvania.

The ENIAC was 30-50 feet long, 30 tons weighted, contained 18000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 registers, and 10,000 capacitors, and it required 150000 watts of electricity, which makes it very expensive.
Later, Eckert and Mauchly developed the first commercially successful computer named UNIVAC(Univeral Automatic Computer) in 1952 .
Examples are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), UNIVAC-1 (Univeral Automatic Computer-1)

- These computers were designed by using vacuum tubes.
- These generations’ computers were simple architecture.
- These computers calculate data in a millisecond.
- This computer is used for scientific purposes.
DISADVANTAGES
- The computer was very costly.
- Very large.
- It takes up a lot of space and electricity
- The speed of these computers was very slow
- It is used for commercial purposes.
- It is very expensive.
- These computers heat a lot.
- Cooling is needed to operate these types of computers because they heat up very quickly.
2. SECOND GENERATION COMPUTER: Transistors (1956-1963)
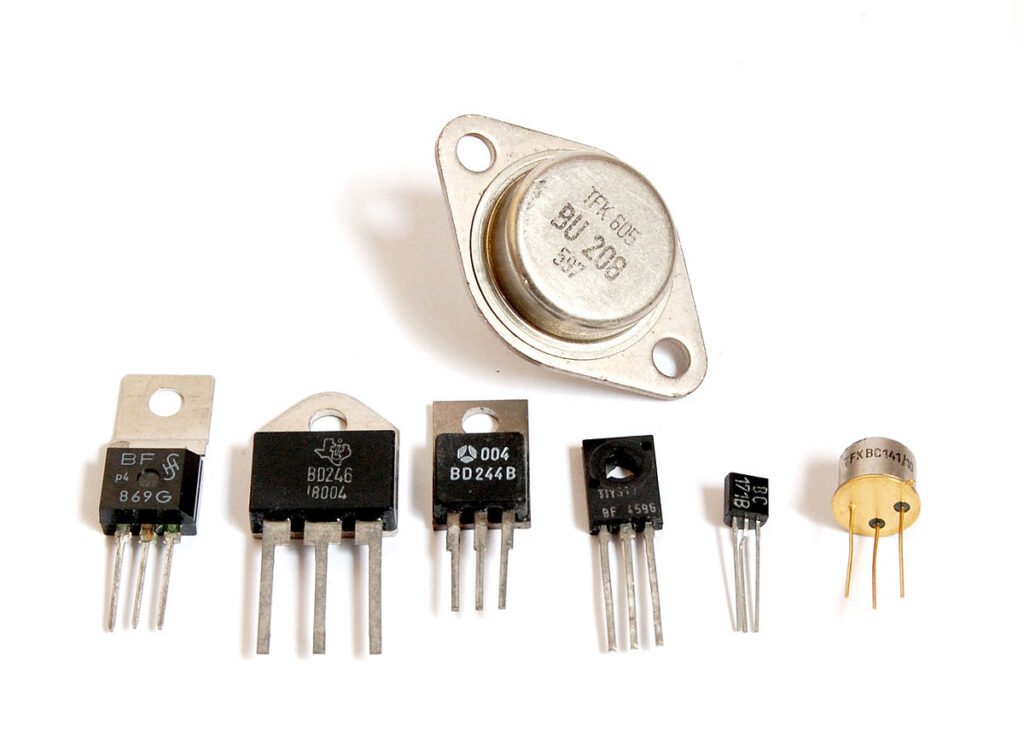
The second generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Transistors” and it was developed in 1947 by three American physicists “John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley” .

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals or open or close a circuit. It was invented in Bell labs, The transistors became the key ingredient of all digital circuits, including computers.
The invention of transistors replaced the bulky electric tubes from the first generation of computers.
Transistors perform the same functions as a Vacuum tube , except that electrons move through instead of through a vacuum. Transistors are made of semiconducting materials and they control the flow of electricity.
It is smaller than the first generation of computers, it is faster and less expensive compared to the first generation of computers. The second-generation computer has a high level of programming languages, including FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
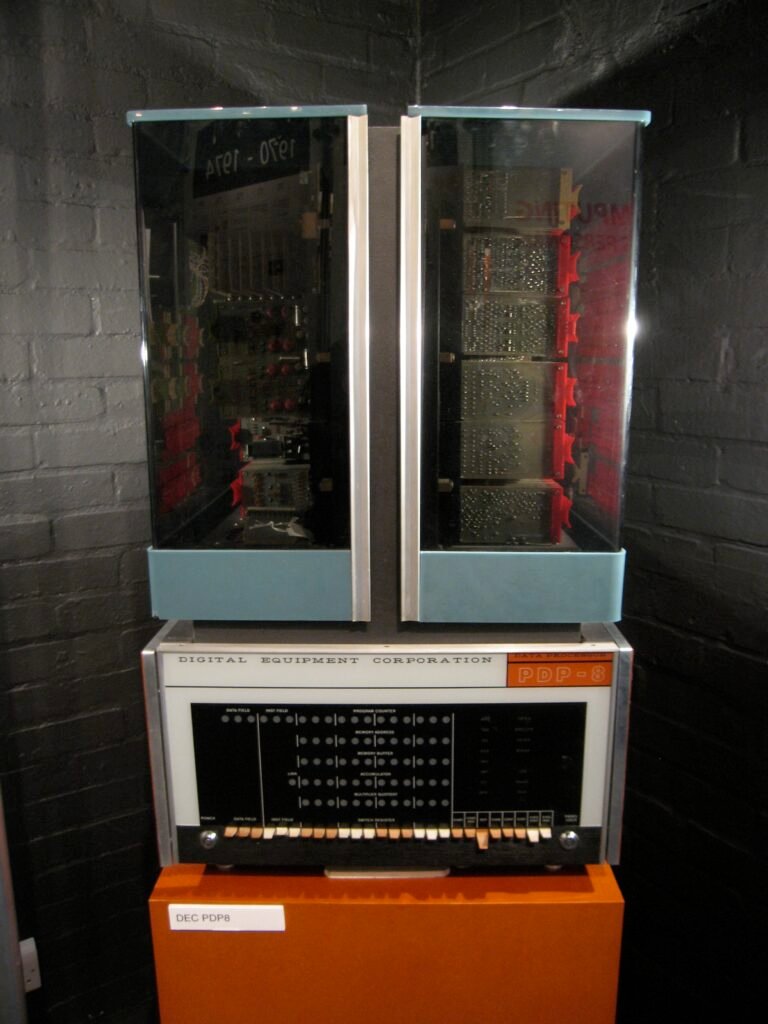
Examples are PDP-8 (Programmed Data Processor-8), IBM1400 (International business machine 1400 series), IBM 7090 (International business machine 7090 series), CDC 3600 ( Control Data Corporation 3600 series)

ADVANTAGES:
- It is smaller in size as compared to the first-generation computer
- It used less electricity
- Not heated as much as the first-generation computer.
- It has better speed
DISADVANTAGES:
- It is also costly and not versatile
- still, it is expensive for commercial purposes
- Cooling is still needed
- Punch cards were used for input
- The computer is used for a particular purpose
3. THIRD GENERATION COMPUTER: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971)
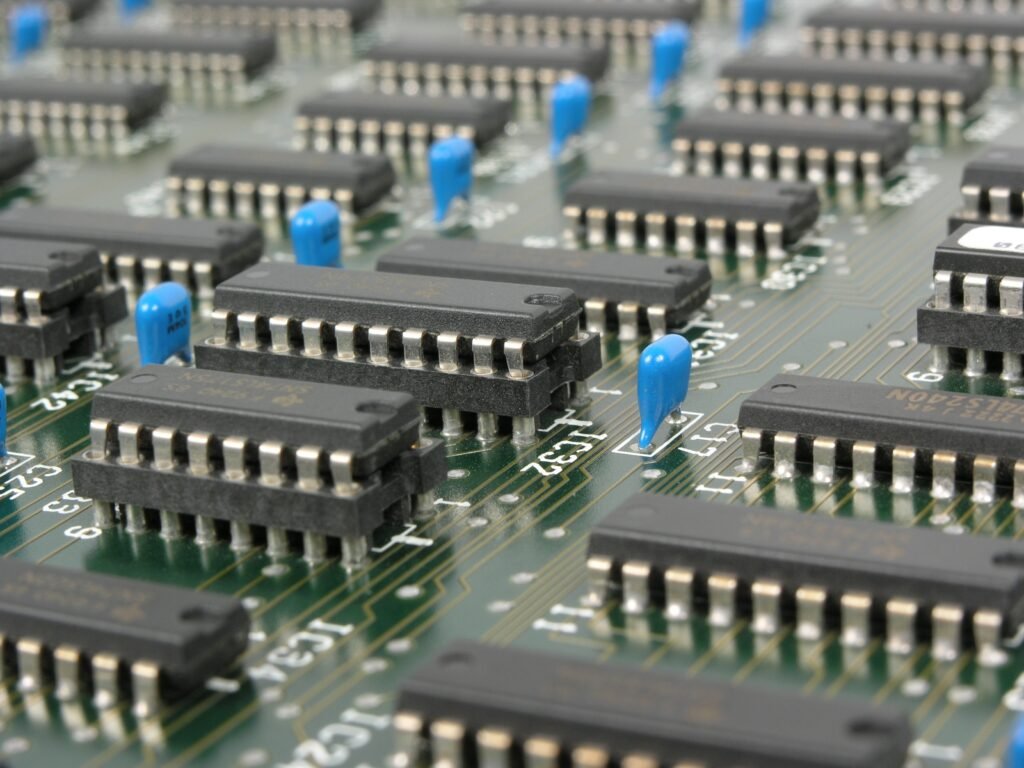
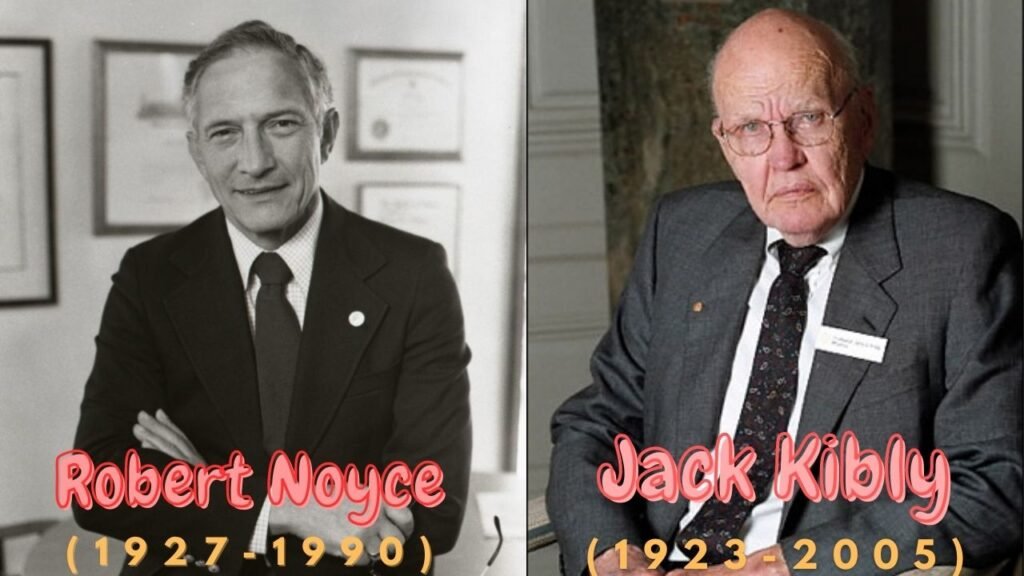
The Third generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Integrated Circuits” It was developed in 1958 by two American engineers “Robert Noyce” & “Jack Kilby” . The integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on small flat pieces of semiconductor that is normally known as silicon. The transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips which are called semiconductors, which drastically increased the efficiency and speed of the computers.
These ICs (integrated circuits) are popularly known as chips. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors built on a single slice of silicon.
This development made computers smaller in size, low cost, large memory, and processing. The speed of these computers is very high and it is efficient and reliable also.
These generations of computers have a higher level of languages such as Pascal PL/1, FORTON-II to V, COBOL, ALGOL-68, and BASIC(Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during these periods.
Examples are NCR 395 (National Cash Register), IBM 360,370 series, B6500

- These computers are smaller in size as compared to previous generations
- It consumed less energy and was more reliable
- More Versatile
- It produced less heat as compared to previous generations
- These computers are used for commercial and as well as general-purpose
- These computers used a fan for head discharge to prevent damage
- This generation of computers has increased the storage capacity of computers
- Still, a cooling system is needed.
- It is still very costly
- Sophisticated Technology is required to manufacture Integrated Circuits
- It is not easy to maintain the IC chips.
- The performance of these computers is degraded if we execute large applications.
4. FOURTH GENERATION OF COMPUTER: Microprocessor (1971-Present)
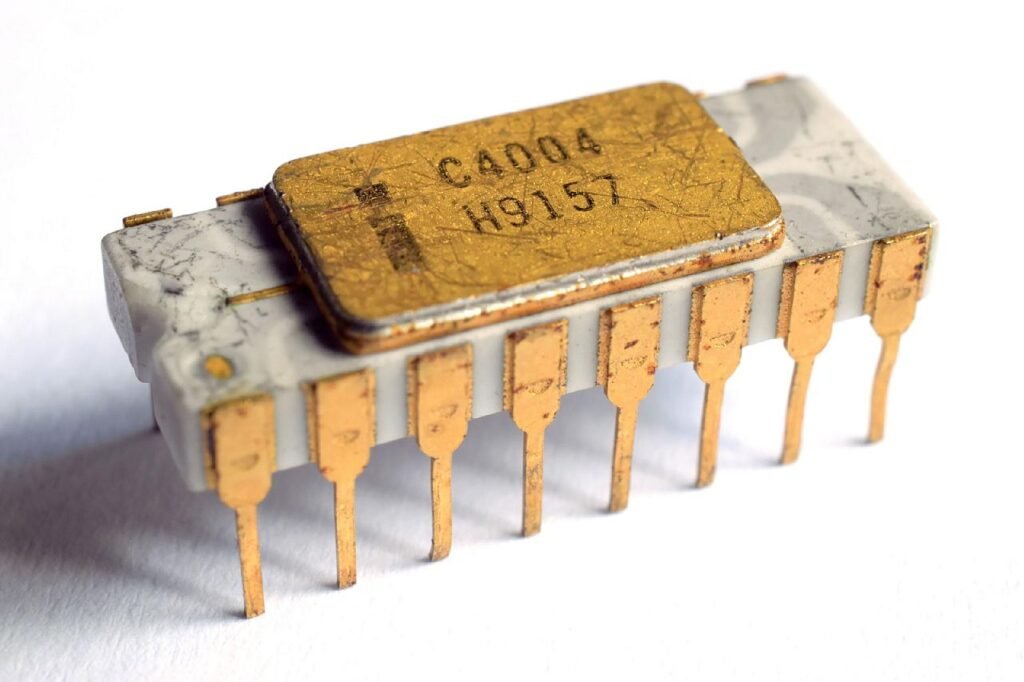
The fourth generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Microprocessor”. It was invented in the 1970s and It was developed by four inventors named are “Marcian Hoff, Masatoshi Shima, Federico Faggin, and Stanley Mazor “. The first microprocessor named was the “Intel 4004” CPU, it was the first microprocessor that was invented.

A microprocessor contains all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on a single chip. Because of microprocessors, fourth-generation includes more data processing capacity than equivalent-sized third-generation computers. Due to the development of microprocessors, it is possible to place the CPU(central processing unit) on a single chip. These computers are also known as microcomputers. The personal computer is a fourth-generation computer. It is the period when the evolution of computer networks takes place.
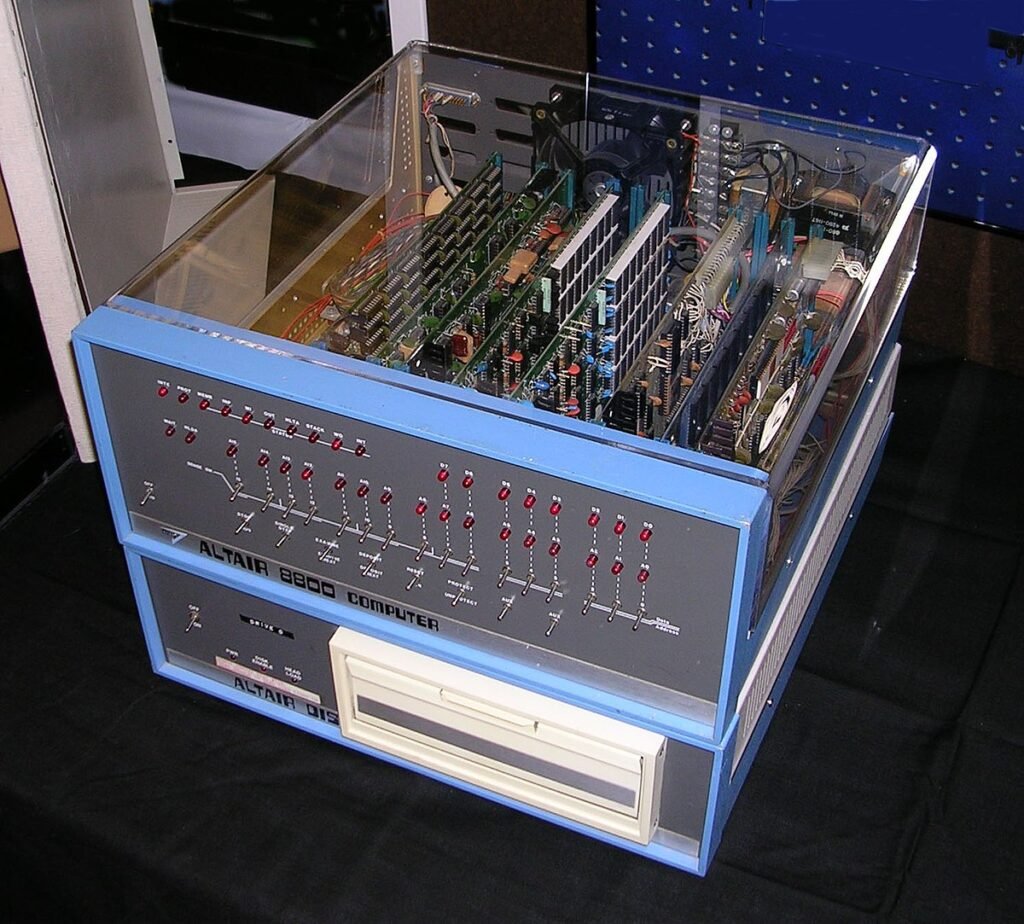
Examples are APPLE II, Alter 8800

- These computers are smaller in size and much more reliable as compared to other generations of computers.
- The heating issue on these computers is almost negligible
- No A/C or Air conditioner is required in a fourth-generation computer.
- In these computers, all types of higher languages can be used in this generation
- It is also used for the general purpose
- less expensive
- These computers are cheaper and portable
- Fans are required to operate these kinds of computers
- It required the latest technology for the need to make microprocessors and complex software
- These computers were highly sophisticated
- It also required advanced technology to make the ICs(Integrated circuits)
5. FIFTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (Present and beyond)
These generations of computers were based on AI (Artificial Intelligence) technology. Artificial technology is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans and allowing the computer to make its own decisions currently, no computers exhibit full artificial intelligence (that is, can simulate human behavior).

In the fifth generation of computers, VLSI technology and ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology are used and the speed of these computers is extremely high. This generation introduced machines with hundreds of processors that could all be working on different parts of a single program. The development of a more powerful computer is still in progress. It has been predicted that such a computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
In this generation, computers are also required to use a high level of languages like C language, c++, java, etc.
Examples are Desktop computers, laptops, notebooks, MacBooks, etc. These all are the computers which we are using.

- These computers are smaller in size and it is more compatible
- These computers are mighty cheaper
- It is obviously used for the general purpose
- Higher technology is used
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Advancement in Parallel Processing and Superconductor Technology.
- It tends to be sophisticated and complex tools
- It pushes the limit of transistor density.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many computer generations are there.
Mainly five generations are there:
First Generation Computer (1940-1956) Second Generation Computer (1956-1963) Third Generation Computer(1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
Which things were invented in the first generation of computers?
Vacuum Tubes
What is the fifth generation of computers?
The Fifth Generation of computers is entirely based on Artificial Intelligence. Where it predicts that the computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
What is the latest computer generation?
The latest generation of computers is Fifth which is totally based on Artificial Intelligence.
Who is the inventor of the Integrated Circuit?
“Robert Noyce” and “Jack Bily”
What is the full form of ENIAC ?
ENIAC Stands for “Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer” .
Related posts:
- What is a Computer System and Its Types?|Different types of Computer System
- How does the Computer System Work| With Diagram, Input, Output, processing
- The History of Computer Systems and its Generations
- Different Applications of Computer Systems in Various Fields | Top 12 Fields
- Explain Von Neumann Architecture?
- What are the input and Output Devices of Computer System with Examples
- What is Unicode and ASCII Code
- What is RAM and its Types?
- What is the difference between firmware and driver? | What are Firmware and Driver?
- What is Hardware and its Types
6 thoughts on “The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer”
It is really useful thanks
Glad to see
it is very useful information for the students of b.sc people who are seeing plz leave a comment to related post thank u
Love to see that this post is proving useful for the students.
It is useful information for students…thank u soo much for guide us
Most Welcome 🙂
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples
🏆 best computers topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics about computers, 💡 easy computer science essay topics, 🥇 computer science argumentative essay topics, 🎓 good research topics about computers, 🔍 interesting computer topics to write about, ❓ computer essay questions.
Looking for interesting topics about computer science? Look no further! Check out this list of trending computer science essay topics for your studies. Whether you’re a high school, college, or postgraduate student, you will find a suitable title for computer essay in this list.
- Life Without Computers Essay One of the major contributions of the computer technology in the world has been the enhancement of the quality of communication.
- How Computers Affect Our Lives In the entertainment industry, many of the movies and even songs will not be in use without computers because most of the graphics used and the animations we see are only possible with the help […]
- Computer Technology: Evolution and Developments The development of computer technology is characterized by the change in the technology used in building the devices. The semiconductors in the computers were improved to increase the scale of operation with the development of […]
- The Causes and Effect of the Computer Revolution Starting the discussion with the positive effect of the issue, it should be stated that the implementation of the computer technologies in the modern world has lead to the fact that most of the processes […]
- Impact of Computers on Business This paper seeks to explore the impact of the computer and technology, as well as the variety of its aspects, on the business world.
- The Use of Computers in the Aviation Industry The complicated nature of the software enables the Autopilot to capture all information related to an aircraft’s current position and uses the information to guide the aircraft’s control system.
- Dependency on Computers For example, even the author of this paper is not only using the computer to type the essay but they are also relying on the grammar checker to correct any grammatical errors in the paper. […]
- Impact of Computer Based Communication It started by explaining the impact of the internet in general then the paper will concentrate on the use of Instant Messaging and blogs.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Graphics Essay One is able to put all of his/her ideas in a model, carry out tests on the model using graphical applications, and then make possible changes.
- Apex Computers: Problems of Motivation Among Subordinates In the process of using intangible incentives, it is necessary to use, first of all, recognition of the merits of employees.
- Print and Broadcast Computer Advertisements The use of pictures and words to bring out the special features in any given computer and types of computers is therefore crucial in this type of advertisement because people have to see to be […]
- How to Build a Computer? Preparation and Materials In order to build a personal computer, it is necessary to choose the performance that you want by considering the aspects such as the desired processor speed, the memory, and storage capacity. […]
- Computers vs. Humans: What Can They Do? The differences between a human being and a computer can be partly explained by looking at their reaction to an external stimulus. To demonstrate this point, one can refer to chess computers that can assess […]
- Computer Use in Schools: Effects on the Education Field The learning efficiency of the student is significantly increased by the use of computers since the student is able to make use of the learning model most suited to him/her.
- Computer Hardware: Past, Present, and Future Overall, one can identify several important trends that profoundly affected the development of hardware, and one of them is the need to improve its design, functionality, and capacity.
- Mathematics as a Basis in Computer Science For example, my scores in physics and chemistry were also comparable to those I obtained in mathematics, a further testament to the importance of mathematics in other disciplines.
- Impact of Computer Technology on Economy and Social Life The rapid development of technologies and computer-human interactions influences not only the individual experience of a person but also the general conditions of social relations.
- History of Computers: From Abacus to Modern PC Calculators were among the early machines and an example of this is the Harvard Mark 1 Early man was in need of a way to count and do calculations.
- Computers Have Changed Education for the Better Considering the significant effects that computers have had in the educational field, this paper will set out to illustrate how computer systems have changed education for the better.
- Computer’s Memory Management Memory management is one of the primary responsibilities of the OS, a role that is achieved by the use of the memory management unit.
- Impact on Operations Resources of JIT at Dell Computer JIT inventory system stresses on the amount of time required to produce the correct order; at the right place and the right time.
- Computers Brief History: From Pre-Computer Hardware to Modern Computers This continued until the end of the first half of the twentieth century. This led to the introduction of first-generation computers.
- Introduction to Human-Computer Interaction It is a scope of study that explores how individuals view and ponder about computer related technologies, and also investigates both the human restrictions and the features that advance usability of computer structures.
- Solutions to Computer Viruses Efforts should also be made to ensure that once a computer system is infected with viruses, the information saved in it is salvaged.
- Computers in Education: More a Boon Than a Bane Thus, one of the greatest advantages of the computer as a tool in education is the fact that it builds the child’s capacity to learn things independently.
- The Concept of Computer Hardware and Software The physical devices can still be the components that are responsible for the execution of the programs in a computer such as a microprocessor.
- Tablet Computer Technology It weighs less than 500g and operates on the technology of AMOLED display with a resolution of WVGA 800 480 and a detachable input pen.
- The Popularity of Esports Among Computer Gamers E-sports or cybersports are the new terms that can sound odd to the men in the street but are well-known in the environment of video gamers.
- Viruses and Worms in Computers To prevent the spread of viruses and worms, there are certain precautionary measures that can be taken. With the correct measures and prevention, the spread of online viruses and worms can be controlled to a […]
- Bill Gates’ Contributions to Computer Technology Upon examination of articles written about Gates and quotations from Gates recounting his early childhood, several events stand out in significance as key to depicting the future potential of Gates to transform the world with […]
- Computers and Transformation From 1980 to 2020 The humanity dreams about innovative technologies and quantum machines, allowing to make the most complicated mathematical calculations in billionths of a second but forgets how quickly the progress of computers has occurred for the last […]
- Advantages of Using Computers at Work I have learned what I hoped to learn in that I have become more aware of the advantages of using computers and why I should not take them for granted.
- Computer Network Types and Classification For a computer to be functional it must meet three basic requirements, which are it must provide services, communications and most of all a connection whether wireless or physical.the connection is generally the hardware in […]
- The American Military and the Evolution of Computer Technology From the Early 1940s to Early 1960s During the 1940s-1960, the American military was the only wouldriver’ of computer development and innovations.”Though most of the research work took place at universities and in commercial firms, military research organizations such as the Office […]
- Computer-Based Technologies That Assist People With Disabilities The visually impaired To assist the visually impaired to use computers, there are Braille computer keyboards and Braille display to enable them to enter information and read it. Most of these devices are very expensive […]
- How Computer Works? In order for a computer to function, stuff such as data or programs have to be put through the necessary hardware, where they would be processed to produce the required output.
- Computer Hardware Components and Functions Hardware is the physical components of a computer, while the software is a collection of programs and related data to perform the computers desired function.
- Computer Laboratory Staff and Their Work This will depend on the discretion of the staff to look into it that the rules that have been set in the system are followed dully. This is the work of the staff in this […]
- How to Sell Computers: PC Type and End User Correlation The specification of each will depend on the major activities the user will conduct on the computer. The inbuilt software is also important to note.
- Computer System Electronic Components The Random Access Memory commonly referred to as RAM is another fundamental component in a computer system that is responsible for storing files and information temporarily when the computer is running. The other storage component […]
- Computer Technician and Labor Market When demand for a certain profession is high, then salaries and wages are expected to be high; on the other side when the demands of a certain profession is low, then wages and demand of […]
- Computer Components in the Future It must be noted though that liquid cooling systems utilize more electricity compared to traditional fan cooling systems due to the use of both a pump and a radiator in order to dissipate the heat […]
- Computers Will Not Replace Teachers On the other hand, real teachers can emotionally connect and relate to their students; in contrast, computers do not possess feeling and lack of empathy.
- The Usefulness of Computer Networks for Students The network has enabled us to make computer simulations in various projects we are undertaking and which are tested by other learners who act as users of the constructed simulations.
- Evolution of Computers in Commercial Industries and Healthcare Overall, healthcare information systems are ultimately vital and should be encouraged in all organizations to improve the quality of healthcare which is a very important need for all human beings.
- How Computers Have Changed the Way People Communicate Based upon its level of use in current society as it grows and expands in response to both consumer and corporate directives, it is safe to say that the internet will become even more integrated […]
- Use and Benefit of Computer Analysis The introduction of computers, therefore, has improved the level of service delivery and thus enhances convenience and comfort. Another benefit accruing from the introduction of computers is the ability of the world to manage networks […]
- How Computers Negatively Affect Student Growth Accessibility and suitability: most of the school and student do not have computers that imply that they cannot use computer programs for learning, lack of availability of internet facilities’ availability also makes the students lack […]
- Personal Computer Evolution Overview It is important to note that the first evolution of a personal computer occurred in the first century. This is because of the slowness of the mainframe computers to process information and deliver the output.
- Internship in the Computer Service Department In fact, I know that I am on track because I have been assessed by the leaders in the facility with the aim of establishing whether I have gained the required skills and knowledge.
- Computers and Information Gathering On the other hand, it would be correct to say that application of computers in gathering information has led to negative impacts in firms.
- Computer Viruses: Spreading, Multiplying and Damaging A computer virus is a software program designed to interfere with the normal computer functioning by infecting the computer operating system.
- Overview of Computer Languages – Python A computer language helps people to speak to the computer in a language that the computer understands. Also, Python Software Foundation, which is a not-for-profit consortium, directs the resources for the development of both Python […]
- Pointing Devices of Human-Computer Interaction The footpad also has a navigation ball that is rolled to the foot to move the cursor on a computer screen.
- Key Issues Concerning Computer Security, Ethics, and Privacy The issues facing computer use such as defense, ethics, and privacy continue to rise with the advent of extra ways of information exchange.
- Are We Too Dependent on Computers? To reinforce this assertion, this paper shall consider the various arguments put forward in support of the view that computers are not overused. This demonstrates that in the education field, computers only serve as a […]
- Computer-Aided Design in Knitted Apparel and Technical Textiles In doing so, the report provides an evaluation of the external context of CAD, a summary of the technology, and the various potential applications and recommendations of CAD.
- Computer Sciences Technology: Smart Clothes In this paper we find that the smart clothes are dated back to the early 20th century and they can be attributed to the works of artists and scientists.
- Doing Business in India: Outsourcing Manufacturing Activities of a New Tablet Computer to India Another aim of the report is to analyse the requirements for the establishment of the company in India, studying the competitors in the industry and their experience.
- Ethical and Illegal Computer Hacking For the ethical hackers, they pursue hacking in order to identify the unexploited areas or determine weaknesses in systems in order to fix them.
- Concept and Types of the Computer Networks As revealed by Tamara, authenticity is one of the most important elements of network security, which reinforces the security of the information relayed within the network system.
- Human-Computer Interface in Nursing Practice HCI in the healthcare impacts the quality of the care and patients’ safety since it influences communication among care providers and between the latter and their clients.
- Computer Evolution, Its Future and Societal Impact In spite of the computers being in existence since the abacus, it is the contemporary computers that have had a significant impact on the human life.
- Preparation of Correspondences by Typewriters and Computers On the other hand, the computer relies on software program to generate the words encoded by the computer user. The typewriter user has to press the keys of the typewriter with more force compared to […]
- Introduction to Computer Graphics: Lesson Plans Students should form their own idea of computer graphics, learn to identify their types and features, and consider areas of application of the new direction in the visual arts.
- The Computer Science Club Project’s Budget Planning The budget for the program is provided in Table 1 below. Budget The narrative for the budget is provided below: The coordinator will spend 100% of his time controlling the quality of the provided services […]
- Dependability of Computer Systems In the dependability on computer systems, reliability architects rely a great deal on statistics, probability and the theory of reliability. The purpose of reliability in computer dependability is to come up with a reliability requirement […]
- The Effectiveness of the Computer The modern computer is the product of close to a century of sequential inventions. We are in the information age, and the computer has become a central determinant of our performance.
- Computer Virus User Awareness It is actually similar to a biological virus wherein both the computer and biological virus share the same characteristic of “infecting” their hosts and have the ability to be passed on from one computer to […]
- Computer Financial Systems and the Labor Market This paper aims to describe the trend of technological progress, the causes and advantages of developments in computer financial systems, as well as the implications of the transition to digital tools for the labor market.
- The History of Computer Storage Thus, the scope of the project includes the history of crucial inventions for data storage, from the first punch cards to the latest flash memory storage technology.
- Computer Security and Computer Criminals The main thing that people need to know is how this breach of security and information occurs and also the possible ways through which they can be able to prevent it, and that’s why institutions […]
- Are We Too Dependent on Computers? The duration taken to restore the machine varies depending on the cause of the breakdown, expertise of the repairing engineer and the resources needed to restore the machine.
- Third Age Living and Computer Technologies in Old Age Learning This essay gives an analysis of factors which have contributed to the successful achievement of the Third Age by certain countries as a life phase for their populations.
- Challenges of Computer Technology Computer Technologies and Geology In fact, computer technologies are closely connected to any sphere of life, and it is not surprisingly that geology has a kind of dependence from the development of computers and innovative […]
- Computer Technology Use in Psychologic Assessment The use of software systems in the evaluation may lead a practitioner to misjudge and exceed their own competency if it gives the school psychologists a greater sense of safety.
- Computers: The History of Invention and Development It is treated as a reliable machine able to process and store a large amount of data and help out in any situation.”The storage, retrieval, and use of information are more important than ever” since […]
- Use of Robots in Computer Science Currently, the most significant development in the field of computer science is the inclusion of robots as teaching tools. The use of robots in teaching computer science has significantly helped to endow students with valuable […]
- Corporate Governance in Satyam Computer Services LTD The Chief Executive Officer of the company in the UK serves as the chairman of the board, but his/her powers are controlled by the other board members.
- Ethics in Computer Technology: Cybercrimes The first one is the category of crimes that are executed using a computer as a weapon. The second type of crime is the one that uses a computer as an accessory to the crime.
- Purchasing and Leasing Computer Equipment, Noting the Advantages and Disadvantages of Each In fact, this becomes hectic when the equipment ceases to be used in the organization before the end of the lease period. First, they should consider how fast the equipment needs to be updated and […]
- How to Teach Elderly Relatives to Use the Computer The necessary safety information: Do not operate the computer if there is external damage to the case or the insulation of the power cables.
- Approaches in Computer-Aided Design Process Challenges: The intricacy of the structure that resulted in the need to understand this process was the reason for this study.
- Computer Network: Data Flow and Protocol Layering The diagram below shows a simplex communication mode Half-duplex mode is one in which the flow of data is multidirectional; that is, information flow in both directions.
- Computer Forensics in Criminal Investigation In this section, this paper will address the components of a computer to photograph during forensic photography, the most emergent action an investigating officer should take upon arriving at a cyber-crime scene, the value of […]
- The Influence of Computer on the Living Standards of People All Over the World In the past, people considered computers to be a reserve for scientist, engineers, the army and the government. Media is a field that has demonstrated the quality and value of computers.
- Computer Forensics Tools and Evidence Processing The purpose of this paper is to analyze available forensic tools, identify and explain the challenges of investigations, and explain the legal implication of the First and Fourth Amendments as they relate to evidence processing […]
- Computer-Based Information Systems The present essay will seek to discuss computer-based information systems in the context of Porter’s competitive strategies and offer examples of how computer-based information systems can be used by different companies to gain a strategic […]
- How Computers Work: Components and Power The CPU of the computer determines the ultimate performance of a computer because it is the core-processing unit of a computer as shown in figure 2 in the appendix.
- Negative Impacts of Computer Technology For instance, they can erase human memory, enhance the ability of human memory, boost the effectiveness of the brain, utilize the human senses in computer systems, and also detect anomalies in the human body. The […]
- Computer Addiction in Modern Society Maressa’s definition that, computer addiction is an accurate description of what goes on when people spend large amount of time working on computers or online is true, timely, and ‘accurate’ and the writer of this […]
- Computer Aided Software Tools (CASE) The use of the repository is common to both the visual analyst and IBM rational software with varying differences evident on the utilization of services.
- Career Options for a Computer Programmer Once the system or software has been installed and is running, the computer programmer’s focus is on offering support in maintaining the system.
- Human Mind Simply: A Biological Computer When contemplating the man-like intelligence of machines, the computer immediately comes to mind but how does the amind’ of such a machine compare to the mind of man?
- Recommendations for Computer to Purchase This made me to look into and compare the different models of computers which can be good for the kind of work we do.
- Computer Security: Bell-Lapadula & Biba Models Cybersecurity policies require the formulation and implementation of security access control models like the Bell-LaPadula and the Biba, to successfully ensure availability, integrity, and confidentiality of information flows via network access.
- Computer Literacy: Parents and Guardians Role Filtering and monitoring content on the internet is one of the most important roles that parents in the contemporary world should play, and it reveals that parents care about their children.
- Graph Theory Application in Computer Science Speaking about the classification of graphs and the way to apply them, it needs to be noted that different graphs present structures helping to represent data related to various fields of knowledge.
- Computer Science: Threats to Internet Privacy Allegedly, the use of the Internet is considered to be a potential threat to the privacy of individuals and organizations. Internet privacy may be threatened by the ease of access to personal information as well […]
- Computer System Review and Upgrade The main purpose of this computer program is going to be the more effective identification of the hooligan groups and their organisation with the purpose to reduce the violation actions.
- Dell Computer Company and Michael Dell These numbers prove successful reputation of the company and make the organization improve their work in order to attract the attention of more people and help them make the right choice during the selection of […]
- HP Computer Marketing Concept The marketing concept is the criteria that firms and organizations use to meet the needs of their clients in the most conducive manner.
- Strategic Marketing: Dell and ASUSTeK Computer Inc. Another factor contributing to the success of iPad is the use of stylish, supreme marketing and excellent branding of the products.
- Computer-Based Testing: Beneficial or Detrimental? Clariana and Wallace found out that scores variations were caused by settings of the system in computer-based and level of strictness of examiners in paper-based. According to Meissner, use of computer based tests enhances security […]
- HP: Arguably the Best Computer Brand Today With this age of imitations, it is easy to get genuine HP computers as a result. While this is commendable, it is apparent that HP has stood out as the greatest computer brand recently.
- Computer Communication Network in Medical Schools Most medical schools have made it compulsory for any reporting student to have a computer and this point the place of computer communication network in medical schools now and in the future.
- Purchasing or Leasing Computer Equipment: Advantages and Disadvantages When the organization decides to lease this equipment for the installation, will be on the part of the owners and maintenance, as well.
- History of the Personal Computer: From 1804 to Nowadays The Analytical engine was a far more sophisticated general purpose computing device which included five of the key components that performed the basic of modern computers. A processor/Calculator/Mill-this is where all the calculations were performed.
- The Drawbacks of Computers in Human Lives Since the invention of computers, they have continued to be a blessing in many ways and more specifically changing the lives of many people.
- Melissa Virus and Its Effects on Computers The shutting down of the servers compromises the effectiveness of the agencies, and criminals could use such lapses to carry out acts that endanger the lives of the people.
- Microsoft Operating System for Personal Computers a Monopoly in the Markets Microsoft operating system has penetrated most of the markets and is considered to be the most popular of the operating systems in use today.
- The Future of Human Computer Interface and Interactions The computer is programmed to read the mind and respond to the demands of that mind. The future of human computer interface and interactivity is already here.
- Computer Safety: Types and Technologies The OS of a computer is a set of instructions communicating directly to the hardware of the computer and this enable it to process information given to it.
- Online Video and Computer Games Video and computer games emerged around the same time as role playing games during the 1970s, and there has always been a certain overlap between video and computer games and larger fantasy and sci-fi communities.
- Information Technology: Computer Software Computer software is a set of computer programs that instructs the computer on what to do and how to do it.
- Effects of Computer Programming and Technology on Human Behavior Phones transitioned from the basic feature phones people used to own for the sole purpose of calling and texting, to smart phones that have amazing capabilities and have adapted the concepts of computers.
- Writing Argumentative Essay With Computer Aided Formulation One has to see ideas in a systematic format in support of one position of the argument and disproval of the other.
- Computer-Based Communication Technology in Business Communication: Instant Messages and Wikis To solve the problems within the chosen filed, it is necessary to make people ready to challenges and provide them with the necessary amount of knowledge about IN and wikis’ peculiarities and properly explain the […]
- Computer Systems in Hospital The central database will be important to the physician as well as pharmacy department as it will be used to keep a record of those medicines that the hospital has stocked.
- Computer-Based Learning and Virtual Classrooms E-learning adds technology to instructions and also utilizes technologies to advance potential new approaches to the teaching and learning process. However, e-learners need to be prepared in the case of a technology failure which is […]
- The Impact of Computer-Based Technologies on Business Communication The Importance of Facebook to Business Communication Facebook is one of the most popular social networking tools among college students and businesspersons. Blogs and Facebook can be used for the benefit of an organization.
- How to Build a Gaming Computer The first step to creating a custom build for a PC is making a list of all the necessary components. This explanation of how to build a custom gaming computer demonstrates that the process is […]
- Pipeline Hazards in Computer Architecture Therefore, branch instructions are the primary reasons for these types of pipeline hazards to emerge. In conclusion, it is important to be able to distinguish between different pipeline types and their hazards in order to […]
- PayPal and Human-Computer Interaction One of the strong points of the PayPal brand is its capacity to use visual design in the process of creating new users. The ability of the Paypal website to transform answers to the need […]
- Personal Computer: The Tool for Technical Report In addition to this, computers, via the use of reification, make it feasible to reconfigure a process representation so that first-time users can examine and comprehend many facets of the procedures.
- Altera Quartus Computer Aided Design Tool So, the key to successful binary additions is a full adder. The complete adder circuit takes in three numbers, A, B, and C, adds them together, and outputs the sum and carry.
- Computer Graphics and Its Historical Background One of the examples of analog computer graphics can be seen in the game called Space Warriors, which was developed at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Hence, the entertainment industry was one of the main […]
- The Twelve-Cell Computer Battery Product: Weighted Average and Contracts Types There is a need to fully understand each of the choices, the cost, benefits, and risks involved for the individual or company to make the right decision.
- Computer Usage Evolution Through Years In the history of mankind, the computer has become one of the most important inventions. The diagnostics and treatment methods will be much easier with the help of computer intervention.
- How to Change a Computer Hard Drive Disk These instructions will allow the readers to change the HDD from a faulty computer step by step and switch on the computer to test the new HDD.
- Researching of Computer-Aided Design: Theory To draw a first-angle projection, one can imagine that the object is placed between the person drawing and the projection. To distinguish the first angle projection, technical drawings are marked with a specific symbol.
- Systems Development Life Cycle and Implementation of Computer Assisted Coding The potential risks the software must deal with are identified at this phase in addition to other system and hardware specifications.
- Why Is Speed More Important in Computer Storage Systems? While there are indications of how speed may be more significant than storage in the context of a computer system, both storage and speed are important to efficiency.
- Researching of Computer Simulation Theory Until then, people can only continue to study and try to come to unambiguous arguments regarding the possibility of human life in a computer simulation.
- Choosing a Computer for a Home Recording Studio The motherboard is responsible for the speed and stability of the system and should also have a large number of ports in case of many purposes of the computer in the studio.
- Computer Programming and Code The Maze game was the one I probably enjoyed the most since it was both engaging and not challenging, and I quickly understood what I needed to do.
- Computer-Aided-Design, Virtual and Augmented Realities in Business The usual applications of these technologies are in the field of data management, product visualization, and training; however, there is infinite potential in their development and integration with one another and this is why they […]
- Computer-Mediated Communication Competence in Learning The study showed that knowledge of the CMC medium was the strongest influence on participation with a =.41. In addition to that, teachers can use the results of this study to improve students’ experience with […]
- Anticipated Growth in Computer and Monitor Equipment Sales This presentations explores the computer equipment market to identify opportunities and device ways of using the opportunities to the advantage of EMI.
- Current Trends and Projects in Computer Networks and Security That means the management of a given organization can send a request to communicate to the network the intended outcome instead of coding and executing the single tasks manually.
- Acme Corp.: Designing a Better Computer Mouse The approach that the company is taking toward the early stages of the development process is to only include design engineers and brainstorm ideas.
- Apple Inc.’s Competitive Advantages in Computer Industry Competitive advantage is significant in any company A prerequisite of success It enhances sustainable profit growth It shows the company’s strengths Apple Inc.explores its core competencies to achieve it Apple Inc.is led by Tim […]
- Computer Forensic Incident All evidence should be collected in the presence of experts in order to avoid losing data as well as violating privacy rights.N.
- Computer Science Courses Project Management Second, the selected independent reviewers analyze the proposal according to the set criteria and submit the information to the NSF. The project is crucial for the school and the community, as students currently do not […]
- How Computer Based Training Can Help Teachers Learn New Teaching and Training Methods The content will be piloted in one of the high schools, in order to use the teachers as trainers for a reaching more schools with the same methodology.
- Acquiring Knowledge About Computers One of the key features of A.I.U.’s learning platform is the use of the Gradebook. The best feature of the instant messaging tool is the fact that it is easy to install with no additional […]
- Future of Forensic Accounting With Regards to Computer Use and CFRA There are different types of accounting; they include management accounting, product control, social accounting, non assurance services, resource consumption accounting, governmental accounting, project accounting, triple accounting, fund accounting and forensic accounting among others.
- Computer Museum: Personal Experience While in the Revolution, I got a chance to see a working replica of the Atanasoff-Berry Computer, which was the first real model of a working computer.
- Computer-Based Search Strategy Using Evidence-Based Research Methodology In this case, the question guiding my research is “Can additional choices of food and places to eat improve appetite and maintain weight in residents with dementia?” The population in this context will be the […]
- Recovering from Computer System Crashes In the event of a crash, the first step is to identify the type of crash and then determine the best way to recover from the crash.
- Effective Way to Handle a Computer Seizure Thus, it is important to device a method of investigation that may enhance the preservation and maintenance of the integrity of the evidence.
- VisualDX: Human-Computer Interaction VisualDX is structured such that the user is guided through the steps of using the software system without having to be a software specialist.
- Computer-Aided Software Engineering Tools Usage The inclusion of these tools will ensure that the time cycle is reduced and, at the same time, enhances the quality of the system.
- Training Nurses to Work With Computer Technologies and Information Systems The educational need at this stage will be to enhance the ability of the learners to work with computer technologies and information system.
- Computer Crime in the United Arab Emirates Computer crime is a new type of offense that is committed with the help of the computer and a network. This article aims at evaluating some of the laws established in the United Arab Emirates, […]
- Computer Science: “DICOM & HL7” In the transport of information, DICOM recognizes the receiver’s needs such as understanding the type of information required. This creates some form of interaction between the sender and the receiver of the information from one […]
- Majoring in Computer Science: Key Aspects Computer Science, abbreviated as CS, is the study of the fundamentals of information and computation procedures and of the hands-on methods for the execution and application in computer systems.
- How to Build a Desktop Personal Computer The processor will determine the speed of the system but the choice between the two major types-Intel and AMD- remains a matter of taste.
- Networking Concepts for Computer Science Students The firewall, on the other hand, is a hardware or software that secures a network against external threats. Based on these a single subnet mask is sufficient for the whole network.
- Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria The paper provides an overview of the concepts of security assurance and trusted systems, an evaluation of the ways of providing security assurance throughout the life cycle, an overview of the validation and verification, and […]
- Advanced Data & Computer Architecture
- Computer Hardware: Structure, Purpose, Pros and Cons
- Assessing and Mitigating the Risks to a Hypothetical Computer System
- Computer Technology: Databases
- The Reduction in Computer Performance
- Advancements in Computer Science and Their Effects on Wireless Networks
- Choosing an Appropriate Computer System for the Home Use
- Global Climate and Computer Science
- Threats to Computer Users
- Computer Network Security Legal Framework
- Computer Forensics and Audio Data Retrieval
- Computer Sciences Technology: E-Commerce
- Computer Forensics: Data Acquisition
- Computer Forensic Timeline Visualization Tool
- The Qatar Independence Schools’ Computer Network Security Control
- Human-Computer Interaction and Communication
- Computer Sciences Technology: Influencing Policy Letter
- Computer Control System in a Laboratory Setting
- Property and Computer Crimes
- Current Laws and Acts That Pertain to Computer Security
- Computer Network: Electronic Mail Server
- Honeypots and Honeynets in Network Security
- The Life, Achievement, and Legacy to Computer Systems of Bill Gates
- Life, Achievement, and Legacy to Computer Systems of Alan Turing
- Building a PC, Computer Structure
- Computer Sciences Technology and HTTPS Hacking Protection
- Computer Problems
- Protecting Computers From Security Threats
- Computer Sciences Technology: Admonition in IT Security
- Research Tools Used by Computer Forensic Teams
- Maintenance and Establishment of Computer Security
- Computer Tech Company’s Medical Leave Problem
- Sales Plan for Computer Equipment
- Smartwatches: Computer on the Wrist
- Purpose of the Computer Information Science Course
- Technological Facilities: Computers in Education
- Computers’ Critical Role in Modern Life
- Malware: Code Red Computer Worm
- Sidetrack Computer Tech Business Description
- Strayer University’s Computer Labs Policy
- Computer Assisted Language Learning in English
- TUI University: Computer Capacity Evaluation
- “Failure to Connect – How Computers Affect Our Children’s Minds and What We Can Do About It” by Jane M. Healy
- Computer Security System: Identity Theft
- Analogical Reasoning in Computer Ethics
- Dell Computer Corporation: Management Control System
- Computer Mediated Communication Enhance or Inhibit
- Technical Communication: Principles of Computer Security
- Why to Choose Mac Over Windows Personal Computer
- Biometrics and Computer Security
- Computer Addiction: Side Effects and Possible Solutions
- Marketing: Graphic and Voice Capabilities of a Computer Software Technology
- Boot Process of a CISCO Router and Computer
- Computer Systems: Technology Impact on Society
- State-Of-The-Art in Computer Numerical Control
- The Increasing Human Dependence on Computers
- Computer Adventure Games Analysis
- Legal and Ethical Issues in Computer Security
- Resolving Software Problem: Timberjack Company
- Computer and Information Tech Program in Education
- Computer Software and Wireless Information Systems
- Computer Vision: Tracking the Hand Using Bayesian Models
- Firewalls in Computer Security
- Computer Engineer Stephen Wozniak
- Gaming System for Dell Computer: Media Campaign Issues
- Computers: Science and Scientists Review
- Uniform Law for Computer Information Transactions
- Computer Science. Open Systems Interconnection Model
- Keystone Computers & Networks Inc.’s Audit Plan
- Computer Crimes: Viewing the Future
- Computer Forensics and Cyber Crime
- Computer Forensics: Identity Theft
- Computer Crime Investigation Processes and Analyses
- Dam Computers Company’s Strategic Business Planning
- Computer and Internet Security Notions
- Technical Requirements for Director Computer Work
- Allocating a Personal Computer
- Graphical Communication and Computer Modeling
- Computer-Based Systems Effective Implementation
- Computer Games and Instruction
- IBM.com Website and Human-Computer Interaction
- Computer Technology in the Student Registration Process
- Computer Hardware and Software Policies for Schools
- Education Goals in Computer Science Studies
- Enhancing Sepsis Collaborative: Computer Documentation
- Computers R Us Company’s Customer Satisfaction
- Apple Ipad: History of the Tablet Computers and Their Connection to Asia
- Dell Computer Corporation: Competitive Advantages
- Computer Emergency Readiness Team
- Computer Viruses, Their Types and Prevention
- Computers in Security, Education, Business Fields
- Epistemic Superiority Over Computer Simulations
- Fertil Company’s Computer and Information Security
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning: Barriers
- Computer-Assisted Second Language Learning Tools
- Computer-Assisted English Language Learning
- Computer Gaming Influence on the Academic Performance
- Computer Based Learning in Elementary Schools
- Computer and Digital Forensics and Cybercrimes
- Computer Reservations System in Hotel
- VSphere Computer Networking: Planning and Configuring
- Human Computer Interaction in Web Based Systems
- Cybercrime, Digital Evidence, Computer Forensics
- Human Overdependence on Computers
- Medical Uses of Computer-Mediated Communication
- Computer Architecture for a College Student
- HP Company’s Computer Networking Business
- Foreign Direct Investment in the South Korean Computer Industry
- Computer Mediated Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication
- Computer Apps for Productive Endeavors of Youth
- Computer-Mediated Communication Aspects and Influences
- Humanities and Computer Science Collaboration
- Globalization Influence on the Computer Technologies
- Euro Computer Systems and Order Fulfillment Center Conflict
- EFL and ESL Learners: Computer-Aided Cooperative Learning
- Computer Science Corporation Service Design
- Computer Security – Information Assurance
- Computer Technology in the Last 100 Years of Human History
- Computer Mediated Learning
- Environmental Friendly Strategy for Quality Computers Limited
- Computer R Us Company: Initiatives for Improving Customer Satisfaction
- Corporate Governance: Satyam Computer Service Limited
- Quasar Company’s Optical Computers
- Implementing Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL) in EFL Classrooms
- Computer Adaptive Testing and Using Computer Technology
- Computer Games: Morality in the Virtual World
- How Computer Based Training Can Help Teachers Learn New Teaching and Training Methods
- Hands-on Training Versus Computer Based Training
- Apple Computer, Inc.: Maintaining the Music Business
- Computer Forensics and Digital Evidence
- Human Computer Interface: Evolution and Changes
- Computer and Digital Music Players Industry: Apple Inc. Analysis
- Computer Manufacturer: Apple Computer Inc.
- Theft of Information and Unauthorized Computer Access
- Supply Chain Management at Dell Computers
- Turing Test From Computer Science
- The Computer-Mediated Learning Module
- Computer Security and Its Main Goals
- Apple Computer Inc. – History and Goals of This Multinational Corporation
- Computer Technology in Education
- Telecommunication and Computer Networking in Healthcare
- The Convergence of the Computer Graphics and the Moving Image
- Information Security Fundamentals: Computer Forensics
- Computer Forensics Related Ethics
- People Are Too Dependent on Computers
- Computer-Mediated Communication: Study Evaluation
- Computer Assisted Language Learning in the Middle East
- Apple Computer, Inc. Organizational Culture and Ethics
- Computer-Based Information Systems and E-Business Strategy
- Computer Sciences Corporation: Michael Horton
- The Role of Computer Forensics in Criminology
- Paralinguistic Cues in Computer-Mediated Communications in Personality Traits
- Computer-Mediated Communication
- Comparison of Three Tablet Computers: Ipad2, Motorola Xoom and Samsung Galaxy
- Decker Computers: E-Commerce Website App
- Apple Computer Inc. Marketing
- Ethics and Computer Security
- Human-Computer Interaction in Health Care
- Security of Your Computer and Ways of Protecting
- Reflections and Evaluations on Key Issues Concerning Computer
- ClubIT Computer Company: Information and Technology Solutions
- The Impact of Computers
- Tablet PCs Popularity and Application
- The Alliance for Childhood and Computers in Education
- The Evolution of the Personal Computer and the Internet
- Computers in the Classroom: Pros and Cons
- Computer Cookies: What Are They and How Do They Work
- Modeling, Prototyping and CASE Tools: The Inventions to Support the Computer Engineering
- Ergotron Inc Computer Workstation Environment
- Experts Respond to Questions Better Than Computers
- Through a Computer Display and What People See There: Communication Technologies and the Quality of Social Interactions
- Computer Based Training Verses Instructor Lead Training
- Social Implications of Computer Technology: Cybercrimes
- Leasing Computers at Persistent Learning
- Ethics in Computer Hacking
- Computer Forensics and Investigations
- Preparing a Computer Forensics Investigation Plan
- Basic Operations of Computer Forensic Laboratories
- Project Management and Computer Charting
- Computer Networks and Security
- The Computer Microchip Industry
- Network Security and Its Importance in Computer Networks
- Company Analysis: Apple Computer
- Responsibilities of Computer Professionals to Understanding and Protecting the Privacy Rights
- Computers & Preschool Children: Why They Are Required in Early Childhood Centers
- Computer and Telecommunication Technologies in the Worlds’ Economy
- Computer Survey Analysis: Preferences of the People
- Computer Security: Safeguard Private and Confidential Information
- Levels of Computer Science and Programming Languages
- Computer Fraud and Contracting
- Introduction to Computers Malicious Software (Trojan Horses)
- Computer Security Breaches and Hacking
- State Laws Regarding Computer Use and Abuse
- Apple Computer: The Twenty-First Century Innovator
- Computer Crimes Defense and Prevention
- How Have Computers Changed the Wage Structure?
- Do Computers and the Internet Help Students Learn?
- How Are Computers Used in Pavement Management?
- Are Americans Becoming Too Dependent on Computers?
- How Are Data Being Represented in Computers?
- Can Computers Replace Teachers?
- How Did Computers Affect the Privacy of Citizens?
- Are Computers Changing the Way Humans Think?
- How Are Computers and Technology Manifested in Every Aspect of an American’s Life?
- Can Computers Think?
- What Benefits Are Likely to Result From an Increasing Use of Computers?
- How Are Computers Essential in Criminal Justice Field?
- Are Computers Compromising Education?
- How Are Computers Used in the Military?
- Did Computers Really Change the World?
- How Have Computers Affected International Business?
- Should Computers Replace Textbooks?
- How Have Computers Made the World a Global Village?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages for Society of the Reliance on Communicating via Computers?
- Will Computers Control Humans in the Future?
- Cyber Security Topics
- Electronics Engineering Paper Topics
- Virtualization Essay Titles
- Dell Topics
- Intel Topics
- Microsoft Topics
- Apple Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/computers-essay-topics/
"412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/computers-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/computers-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/computers-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "412 Computers Topics & Essay Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/computers-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
- Analog computers
- Mainframe computer
- Supercomputer
- Minicomputer
- Microcomputer
- Laptop computer
- Embedded processors
- Central processing unit
- Main memory
- Secondary memory
- Input devices
- Output devices
- Communication devices
- Peripheral interfaces
- Fabrication
- Transistor size
- Power consumption
- Quantum computing
- Molecular computing
- Role of operating systems
- Multiuser systems
- Thin systems
- Reactive systems
- Operating system design approaches
- Local area networks
- Wide area networks
- Business and personal software
- Scientific and engineering software
- Internet and collaborative software
- Games and entertainment
Analog calculators: from Napier’s logarithms to the slide rule
Digital calculators: from the calculating clock to the arithmometer, the jacquard loom.
- The Difference Engine
- The Analytical Engine
- Ada Lovelace, the first programmer
- Herman Hollerith’s census tabulator
- Other early business machine companies
- Vannevar Bush’s Differential Analyzer
- Howard Aiken’s digital calculators
- The Turing machine
- The Atanasoff-Berry Computer
- The first computer network
- Konrad Zuse
- Bigger brains
- Von Neumann’s “Preliminary Discussion”
- The first stored-program machines
- Machine language
- Zuse’s Plankalkül
- Interpreters
- Grace Murray Hopper
- IBM develops FORTRAN
- Control programs
- The IBM 360
- Time-sharing from Project MAC to UNIX
- Minicomputers
- Integrated circuits
- The Intel 4004
- Early computer enthusiasts
- The hobby market expands
- From Star Trek to Microsoft
- Application software
- Commodore and Tandy enter the field
- The graphical user interface
- The IBM Personal Computer
- Microsoft’s Windows operating system
- Workstation computers
- Embedded systems
- Handheld digital devices
- The Internet
- Social networking
- Ubiquitous computing

- What is a computer?
- Who invented the computer?
- What can computers do?
- Are computers conscious?
- What is the impact of computer artificial intelligence (AI) on society?

History of computing
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- University of Rhode Island - College of Arts and Sciences - Department of Computer Science and Statistics - History of Computers
- LiveScience - History of Computers: A Brief Timeline
- Computer History Museum - Timeline of Computer history
- Engineering LibreTexts - What is a computer?
- Computer Hope - What is a Computer?
- computer - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- computer - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents
A computer might be described with deceptive simplicity as “an apparatus that performs routine calculations automatically.” Such a definition would owe its deceptiveness to a naive and narrow view of calculation as a strictly mathematical process. In fact, calculation underlies many activities that are not normally thought of as mathematical. Walking across a room, for instance, requires many complex, albeit subconscious, calculations. Computers, too, have proved capable of solving a vast array of problems, from balancing a checkbook to even—in the form of guidance systems for robots—walking across a room.
Recent News
Before the true power of computing could be realized, therefore, the naive view of calculation had to be overcome. The inventors who labored to bring the computer into the world had to learn that the thing they were inventing was not just a number cruncher, not merely a calculator. For example, they had to learn that it was not necessary to invent a new computer for every new calculation and that a computer could be designed to solve numerous problems, even problems not yet imagined when the computer was built. They also had to learn how to tell such a general problem-solving computer what problem to solve. In other words, they had to invent programming.
They had to solve all the heady problems of developing such a device, of implementing the design, of actually building the thing. The history of the solving of these problems is the history of the computer. That history is covered in this section, and links are provided to entries on many of the individuals and companies mentioned. In addition, see the articles computer science and supercomputer .
Early history
Computer precursors.
The earliest known calculating device is probably the abacus . It dates back at least to 1100 bce and is still in use today, particularly in Asia. Now, as then, it typically consists of a rectangular frame with thin parallel rods strung with beads. Long before any systematic positional notation was adopted for the writing of numbers, the abacus assigned different units, or weights, to each rod. This scheme allowed a wide range of numbers to be represented by just a few beads and, together with the invention of zero in India, may have inspired the invention of the Hindu-Arabic number system . In any case, abacus beads can be readily manipulated to perform the common arithmetical operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division—that are useful for commercial transactions and in bookkeeping.
The abacus is a digital device; that is, it represents values discretely. A bead is either in one predefined position or another, representing unambiguously, say, one or zero.
Calculating devices took a different turn when John Napier , a Scottish mathematician, published his discovery of logarithms in 1614. As any person can attest , adding two 10-digit numbers is much simpler than multiplying them together, and the transformation of a multiplication problem into an addition problem is exactly what logarithms enable. This simplification is possible because of the following logarithmic property: the logarithm of the product of two numbers is equal to the sum of the logarithms of the numbers. By 1624, tables with 14 significant digits were available for the logarithms of numbers from 1 to 20,000, and scientists quickly adopted the new labor-saving tool for tedious astronomical calculations.
Most significant for the development of computing, the transformation of multiplication into addition greatly simplified the possibility of mechanization. Analog calculating devices based on Napier’s logarithms—representing digital values with analogous physical lengths—soon appeared. In 1620 Edmund Gunter , the English mathematician who coined the terms cosine and cotangent , built a device for performing navigational calculations: the Gunter scale, or, as navigators simply called it, the gunter. About 1632 an English clergyman and mathematician named William Oughtred built the first slide rule , drawing on Napier’s ideas. That first slide rule was circular, but Oughtred also built the first rectangular one in 1633. The analog devices of Gunter and Oughtred had various advantages and disadvantages compared with digital devices such as the abacus. What is important is that the consequences of these design decisions were being tested in the real world.

In 1623 the German astronomer and mathematician Wilhelm Schickard built the first calculator . He described it in a letter to his friend the astronomer Johannes Kepler , and in 1624 he wrote again to explain that a machine he had commissioned to be built for Kepler was, apparently along with the prototype , destroyed in a fire. He called it a Calculating Clock , which modern engineers have been able to reproduce from details in his letters. Even general knowledge of the clock had been temporarily lost when Schickard and his entire family perished during the Thirty Years’ War .
But Schickard may not have been the true inventor of the calculator. A century earlier, Leonardo da Vinci sketched plans for a calculator that were sufficiently complete and correct for modern engineers to build a calculator on their basis.

The first calculator or adding machine to be produced in any quantity and actually used was the Pascaline, or Arithmetic Machine , designed and built by the French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal between 1642 and 1644. It could only do addition and subtraction, with numbers being entered by manipulating its dials. Pascal invented the machine for his father, a tax collector, so it was the first business machine too (if one does not count the abacus). He built 50 of them over the next 10 years.

In 1671 the German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz designed a calculating machine called the Step Reckoner . (It was first built in 1673.) The Step Reckoner expanded on Pascal’s ideas and did multiplication by repeated addition and shifting.
Leibniz was a strong advocate of the binary number system . Binary numbers are ideal for machines because they require only two digits, which can easily be represented by the on and off states of a switch. When computers became electronic, the binary system was particularly appropriate because an electrical circuit is either on or off. This meant that on could represent true, off could represent false, and the flow of current would directly represent the flow of logic.
Leibniz was prescient in seeing the appropriateness of the binary system in calculating machines, but his machine did not use it. Instead, the Step Reckoner represented numbers in decimal form, as positions on 10-position dials. Even decimal representation was not a given: in 1668 Samuel Morland invented an adding machine specialized for British money—a decidedly nondecimal system.
Pascal’s, Leibniz’s, and Morland’s devices were curiosities, but with the Industrial Revolution of the 18th century came a widespread need to perform repetitive operations efficiently. With other activities being mechanized, why not calculation? In 1820 Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar of France effectively met this challenge when he built his Arithmometer , the first commercial mass-produced calculating device. It could perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and, with some more elaborate user involvement, division. Based on Leibniz’s technology , it was extremely popular and sold for 90 years. In contrast to the modern calculator’s credit-card size, the Arithmometer was large enough to cover a desktop.
Calculators such as the Arithmometer remained a fascination after 1820, and their potential for commercial use was well understood. Many other mechanical devices built during the 19th century also performed repetitive functions more or less automatically, but few had any application to computing. There was one major exception: the Jacquard loom , invented in 1804–05 by a French weaver, Joseph-Marie Jacquard .

The Jacquard loom was a marvel of the Industrial Revolution. A textile-weaving loom , it could also be called the first practical information-processing device. The loom worked by tugging various-colored threads into patterns by means of an array of rods. By inserting a card punched with holes, an operator could control the motion of the rods and thereby alter the pattern of the weave. Moreover, the loom was equipped with a card-reading device that slipped a new card from a pre-punched deck into place every time the shuttle was thrown, so that complex weaving patterns could be automated.
What was extraordinary about the device was that it transferred the design process from a labor-intensive weaving stage to a card-punching stage. Once the cards had been punched and assembled, the design was complete, and the loom implemented the design automatically. The Jacquard loom, therefore, could be said to be programmed for different patterns by these decks of punched cards.
For those intent on mechanizing calculations, the Jacquard loom provided important lessons: the sequence of operations that a machine performs could be controlled to make the machine do something quite different; a punched card could be used as a medium for directing the machine; and, most important, a device could be directed to perform different tasks by feeding it instructions in a sort of language—i.e., making the machine programmable.
It is not too great a stretch to say that, in the Jacquard loom, programming was invented before the computer. The close relationship between the device and the program became apparent some 20 years later, with Charles Babbage’s invention of the first computer.

Generations of Computer 1st to 5th Explained with Pictures.
The history of computer technology is often used to refer to the origin of all the different generations of computers . From first to fifth each computer generation is characterized by significant technological development in their components, memory , and elements which essentially changed the way these devices work.
Several periods of generation from over the years advanced the technological evolution leads to the creation of today’s modern computer with more complex, more powerful, and increased capability and functionality.
Introduction to Computer Generations
This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.
During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size, type, and functionality.
By analyzing them, one can trace the evolution of computer technology, to see how the computer industry has changed over the years and how great capabilities and software progress has been made by humankind in under a hundred years , as a result, the creation of different generations.
At present, the computer is playing a significant part in human existence because today’s digital computer is being used for every work in each field. If someday an issue occurs in the computer or the server is down, at that point all the work stops. This is how significant it is for technology development!
In this article, I will introduce you to all the generations of computers with pictures by explaining the complete information about their characteristics , names, components , and examples too.
Generations of Computer From 1st to 5th
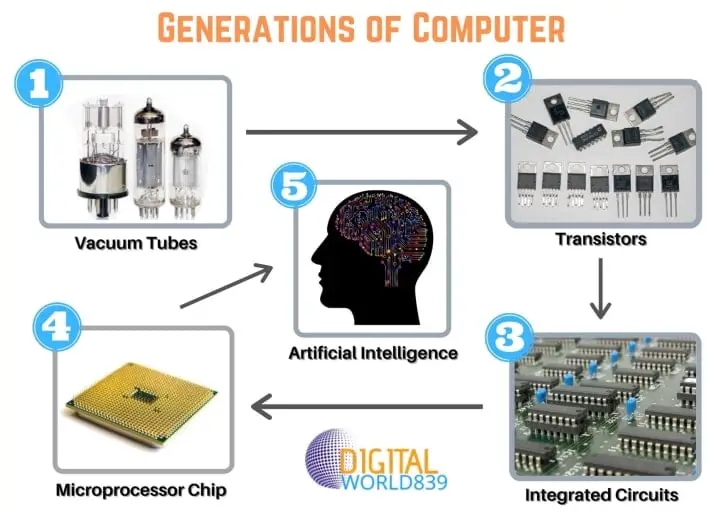
Let’s discover the series of computer generations in the following list:
1st Generation of Computer (1940-1956)
This first generation of computers was based on vacuum tube technology used for calculations, storage, and control, invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming. The vacuum tubes and diode valves were the chief components of the first generations of computers.

First-generation computers relied on the lowest-level machine language, in order to perform operations, and could only solve a single problem at a point of time.
Magnetic drums were used as the memory in these computers (were very slow in speed). The punched and magnetic tapes were used for the input and output function of the computer in order to display on prints even the results weren’t 100% accurate.

Also, the first generation of computers available was based on the 8-bit microprocessor.
The disadvantages of 1st gen computers are that they were very enormous in size and heavy in weight (made of thousands of vacuum tubes ) , occupying large rooms. Also, once they were kept in one place it was difficult to transfer. Another con like using a decimal number system and many switches and cables.
In addition, they were also very expensive to operate with using a large amount of electricity, the vacuum tubes produced large amounts of heat, so an air conditioner was required for the proper functioning unless a lot of heat can cause a malfunction.
The advantage of the first generation of computers is that they could calculate in milliseconds (about five thousand sums per second.)
The computers of first-generation were managed to use in different fields like weather forecasting, solving mathematical problems, energy tasks, also in space research, military, and other scientific tasks.
In the first generation of computers, the first computer of the world named “ENIAC” (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was discovered by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert in the year between 1943 to 1945.
ENIAC used panel-to-panel wiring and switches for programming, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, used about 18,000 vacuum tubes, and weighed 30 tons.
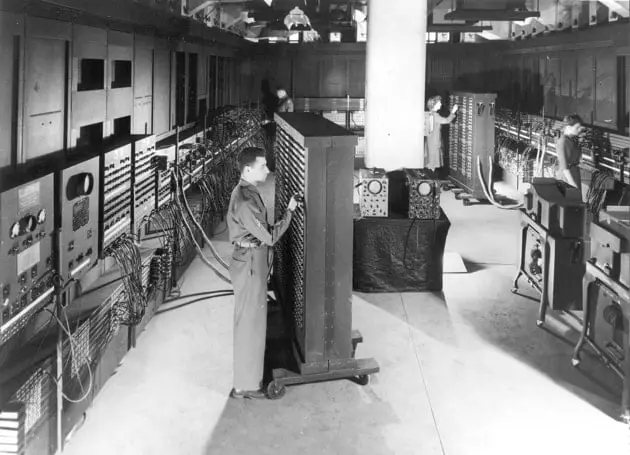
Characteristics of the 1st Generation of Computer:
- Vacuum tubes and diode valves were used as the main electronic component in the first generation computers.
- Punch cards, paper tape utilized for input and output operations.
- Magnetic drums used for storage.
- Huge in size and weight with a lot of power consumption.
- Very expensive in price also not reliable.
- Computers were programmed with low-level machine language also has low operating speed.
Examples of the first generation of computers are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) EDSEC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), (Electronic delay storage automatic calculator), IBM -701 and IBM 650.
ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer . This computer about 18,000 vacuum tubes used for the calculation result in huge in size, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, and weighed 30 tons. These were the harbingers of today’s digital computers. This first computing machine was designed by people J. P. Eckert, W. Mosley, J. W. Mauchly.
2nd Generation of Computer (1956-1964)
The second generation of computers replaced the vacuum tubes with a reliable component called transistors for manufacturing of computers was invented by William Shockley in 1947.

The transistors were the revolution in the computer field because this component advantaged the 2nd gen computer by increasing the performance, operating speed (hundreds of thousands of operations per second), as well as decreasing the electricity consumption of the computers.
Transistors were far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to get faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient made and possible to reduce the size of computing equipment and ultimately heat reduced and reliability improved.
Computers of second-generation are characterized by the use of the first high-level programming languages, allowing programmers to specify instructions in words. At this time, early versions of COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN languages were developed .
These were the first computers to store their instructions in their memory, which went from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology. During this period, the first computer game name “ Spacewar ” was seen on a PDP-1 computer.

Do you know~ that the oldest abacus was a computing machine designed to calculate thousands of years ago, which is still used in schools today to do calculations.
Also, the concept of Central Processing Unit (CPU), multi-programming operating systems, programming language, memory, and input and output units (I / O units) were developed in the timeline of second-generation computers.
The major disadvantages of Second-generation computers were they still relied on punch cards for input and hard copies for output as well as still it was difficult to move the computers for the reason they were enough large and even some computers needed ACs.
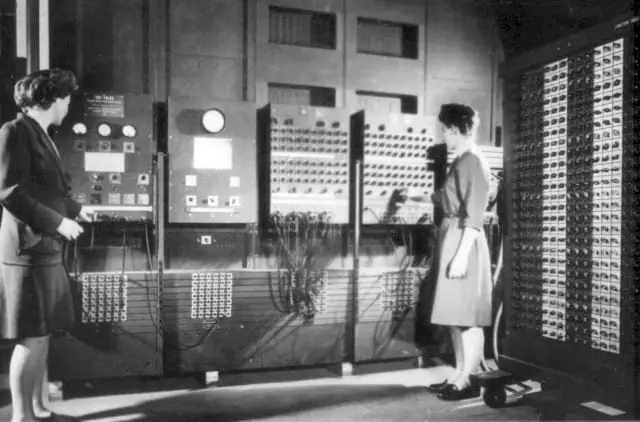

This second generation of computers was first used in the fields like the atomic energy industry and nuclear power plants and other commercial fields.
Characteristics of the 2nd Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- Magnetic Tape was used to store data.
- Relatively small in size and reduced weight with low energy consumption than 1st gen computers.
- Faster, reliable, and less expensive than the first generation.
- Use of storage devices, printers, and operating systems, etc.
- Higher-level languages like COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN were developed and used.
Examples of the second generation of computers include IBM 1620, CDC 1604, IBM 7094, UNIVAC 1108, IBM 620, CDC 3600, IBM 4044, Honeywell 400, IBM 1401 Mainframe, and PDP-1 minicomputer. IBM was actively working, producing transistor versions of its computers.
3rd Generation of Computer (1964-1971)
The third generation appeared in the form of integrated circuits (invented by Jack Kilby from 1958 to 1964). An IC (integrated circuit) is consists of many small transistors mounted on chips , which are called semiconductors.
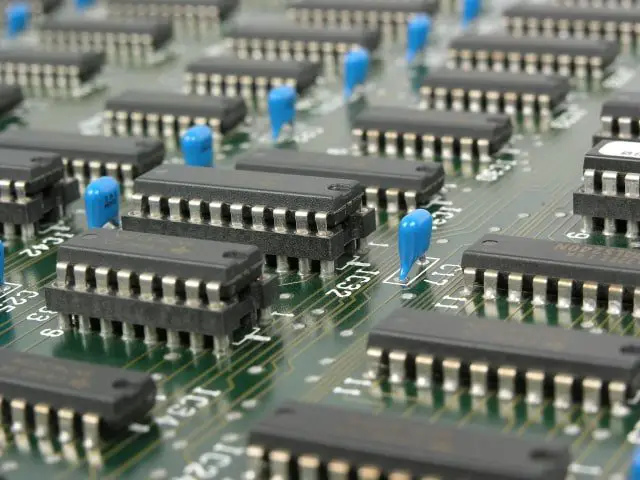
This synchronized chip became an important foundation for the third generation computers when scientists combined hundreds of transistors fit in this circuit result in a more powerful electronic segment called an integrated circuit.
Multiprogramming was implemented (this is when there are several executable programs in memory) at the same time that it diminished their manufacturing costs. In the mid-60s. IBM improved the term “computer architecture”. By the end of the 60s. mini-computers appeared.
This revolutionary innovation allowed to expansion of the processing capacity and memory of the machines.
Instead of punch cards and prints, users interacted via keyboards and monitors , and interacted with an operating system, allowing the device to run various applications at once with a central program that monitored the memory.

As you can see, the first appearance of computer monitors fell on the second generation of computers. The invention belongs to the company IBM, which in 1964 released the commercial display station IBM-2250.
it was used in the system/360 series. The model had a vector monochrome display measuring 12×12 inches, with a resolution of 1024×1024 pixels and a refresh rate of 40 Hz. This invention revolutionized today’s different types of monitors including LCD, LED, OLED monitors.
The invention of IC incredibly decreased the size of computers and made it easy for transportation from one place to another. The working speed and efficiency of this generation of computers were much faster than the previous generation and even cheaper.
High-end languages such as PASCAL, BASIC, FORTRAN – II TO IV, COBOL, ALGOL developed in this generation.
For the first time, they got access to a mass audience allowed computers to penetrate into different spheres of human activity since they were smaller and cheaper. Along these, they turned out to be more specialized (i.e., there were different computers for different tasks).
The 3rd generation of computers was the initial move towards the miniaturization of computers and quickly expanded their scope: control, automation of scientific experiments, data transmission, etc. In addition to being used in the manufacture of radios, TVs, and other similar devices .
Characteristics of the 3rd Generation of Computer:
- In this generation, computers based on Integrated Circuit was more powerful than the transistor.
- The size of the computers was likewise little because the size of the IC being more modest than the circuit size of the transistors.
- More reliable, inexpensive, faster, energy-efficient, as well as very light in weight than 2nd gen computers.
- The first Computer Mouse and Keyboard were appeared and used in the 3rd generation of computers
- Use of new versions of high-level languages like BASIC, COBOL, FORTRAN, PASCAL, and ALGOL
- Available for a mass audience and made it possible for general purpose usage.
Some of the most popular models of the 3rd generation of computers were the ICL 2903, ICL 1900, TDC-B16, IBM 360 and 370, Honeywell 6000, UNIVAC 1108, PDP-8, and PDP-11, which were ideal in their handling multiprocessing capabilities, reliability, and flexibility than previous generations.
4th Generation of Computer (1971-2010)
The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits equivalent to about millions of transistors were assembled and brought the whole central processing unit and other fundamental elements of the machine into a small chip called a microprocessor fitted on the CPU socket.
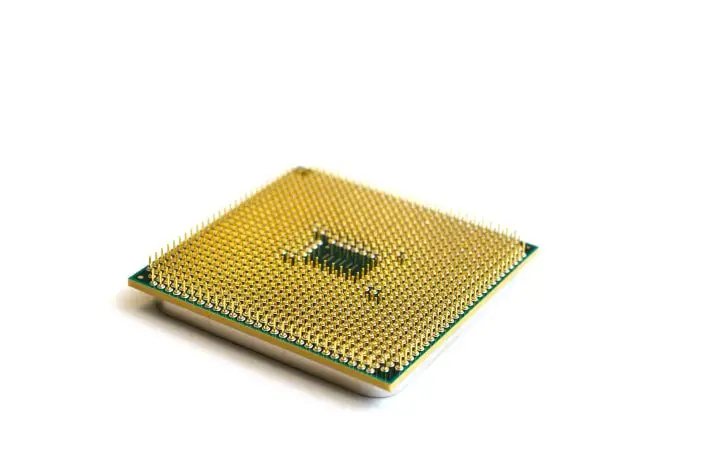
These computers used Very Large Scale Integrated circuits technology also called VLSI technology. After the invention, the microprocessor began to used in computing machines in the fourth and fifth generations of computers.
Within the framework of the considered generation in 1971, the first microprocessor appeared as an unexpected result of Intel’s work on calculator circuits and further development of minicomputers ( PDP-11 ).
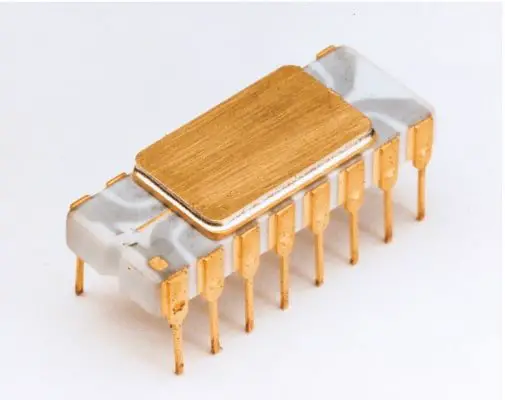
The first personal computer and a microcomputer was “ ALTAIR ” developed by the company MITS in 1974. Also, the first microprocessor was the Intel 4004, manufactured in 1971, initially for an electronic calculator. Whereas the computers of the first generation filled an entire room, while now the 4th generation ‘microprocessors’ fit in the palm of the hand.
This generation of computers used an operating system based on the graphical user interface (GUI), which means these numbers were very easy to perform mathematical and logical tasks.
The computers started to utilize high-speed memory systems on integrated circuits with a capacity of several megabytes. Computer performance has increased significantly (hundreds of millions of operations per second).
The high-level language like C, C ++, Java, PHP, Python, Visual Basic, was utilized to compose programs in the computers of the fourth generation.

The advent of the first personal computers in the mid-70s gave every common user the same computing resources that enormous computers had during the 60s. These computers were made more modest, faster, and less expensive can undoubtedly be put on a table or desk. Which marked the so-called era of personal computers .
Peripheral devices examples , such as mice, joysticks, handheld devices, etc., were developed during this 4th generation. Computers could be connected together in a network to share information with each other, this has played an important role in the birth and development of LAN, Ethernet, and the Internet .

The most popular companies in the world like Intel and AMD were rising. Then again, companies like Microsoft and Apple introduced their operating systems ‘Windows’ and ‘Macintosh’ in the generation of this computer. Because of which the act of multimedia started.
This is the era where personal computers were born, an idea that actually persists today. Also, these were the generation of DEC’s (Digital Equipment Corporation) minicomputers.
Characteristics of the 4th Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on microprocessors and VLSI technology .
- The computers of 4th gen were small in size, lightweight, and almost portable computers.
- The integrating of multi cores in processors like Dual core , Octa core, etc has began.
- The processing speed of this computer generation was much faster and reliable than the previous three generations.
- The size and cost of power supply units has reduced.
- Use of languages like C, C ++, .Net, Java, PHP, Python , Visual Basic.
- Use of GUI Based OS with more memory capacity.
- Accessible to the Internet .
- Due to the low cost of these computers, they were available to every common man.
Desktops, Laptops, Workstations, Tablets, Chromebooks , and Smartphones, are examples of the fourth generation of computers.
Good to Know~ Alan Turing is the father of modern computers born in England in 1912.
5th Generation of Computer (2010-At Present)
Artificial intelligence is the name of the fifth as well as the latest generation of computers based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology is the process of integrating or embedding millions of transistors on a single silicon microchip.

Computing in the 5th computer generation is versatile made portable, powerful, lightweight, innovative, comfortable with low electricity consumption . Because of the Internet’s advantages , it extended its limits of use to limits never before suspected.
The main objective of the latest fifth-generation computing and effort made by computer researchers is to make them smart by incorporating Artificial Intelligence so as to develop devices that respond to the input of natural language and are capable of learning and self-organizing even in 2022 it is under development.
This new information technology has greatly increased the size and working ability of the microprocessor, which has prompted the use of computers in the various fields of Entertainment, Accounting, Educational institutes , Film-making, Traffic-control, Business applications , and Hospitals, Engineering, Researches, Defense, etc.
That’s why a computer of the 5th generation is also known as the AI (Artificial Intelligence) generation of computers.
Some computers are being intended to do all the work themselves as a human act, behave, and communicate. The best example of this is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) based computing machine in the 5th generation of computers “ Sophia ” a robot.

Characteristics of the 5th Generation of Computer:
- The main focus on AI-based computers.
- Computers made of microprocessors based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology.
- The processing speed is quite high can perform billions of calculations in a second.
- Computers are portable, cheap, reliable, fast, and available in various forms and sizes like a Desktop, Laptop, Smartphone, Smartwatches, etc.
- Invention of the operating system such as Windows, Macintosh and ChromeOS of Chromebooks .
- Multimedia has evolved in this generation by combining Sound, Graphics, or Picture and Text.
- Development of Internet of Things.
Computers of the fifth generation are being made to think like us. For which continuous advancement of technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Robotics, etc. Although the examples of AI computing software such as Chatbots, Windows Cortana, Google Assistant, Apple Siri, Speech recognition, that are being used today.
Classification of the computer by generations
| ) | . | |||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) |
Factors/Reasons for the development of computer generations:
There below are the general factors associated with the development and change in the generations of electronic computers:
- Improvement of the element base,
- Downsizing,
- Technological progress (increased performance, speed, and memory)
- Reduced cost,
- Development of software ,
- Changes in architecture, expansion of the range of tasks solved by computers,
- Simplification and standardization of hardware.
- Changing the way of interaction between the user and the computer.
How many generations of computers have there been?
There are 5 computer generations till now i.e. vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, microprocessors, and the last one is artificial intelligence. 6th generation yet to come may be either in the form of quantum computers or developing the existing artificial intelligence technology to a greater extent.
What is the 6th generation of computers?
Electronic computers are usually divided into five generations now and the 6th generation is still in development but has the potential to give birth to the sixth generation of computers may be in the form of quantum computing.
Which is the current modern generation of computers today?
The technologies based on artificial intelligence are the current and the latest generation of computers(5th GEN) today.
What is the historical development of computers according to generation?
In accordance with the methodology for assessing the development of computer technology, the first generation was considered to be vacuum tube computers, the second – transistor computers, the third – computers on integrated circuits, the fourth – using microprocessors, and the fifth generation computers is based on the artificial intelligence.
What is the generation of a colossus computer?
Colossus computer was the first generation of the computer developed and designed by Tommy Flowers at Bletchley Park in the year 1944 with the purpose of cracking Hitler’s codes.
The sixth will also discover in the future since there are some flaws of technology in this generation that will be revived or resolved in the upcoming generation.
It takes much time and research to publish such an article ” Generation of Computer 1st to 5th “ If you liked the insights of the article you can support us by sharing this post on social networks.
Share this Post !
Similar Posts
How Much Electricity Does A Computer Use? » Electricity Consumption of Computer Explained.

Dell Wireless Mouse Not Working » Easy Troubleshooting Guide

Top 7 Dust Free Cases For » [Mini, Micro, Mid & Full Tower].
Meaning & 8 Difference Between System Software and Application Software Explained.
26 thoughts on “generations of computer 1st to 5th explained with pictures.”.
yes that awesome
You’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
This the best platform for student to learn from very gradual, this information is really helpful
It was so wonderful and interesting thank you so much
Hi Rachel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
You have explained the generation of computers very well, by reading this article anyone will understand about the generation of computers.
You’re welcome. Glad you learned some new & informative stuff.
Yes you right sir
Thanks for DIGITALWORLD839.COM for publication of the topics on computers
Wow it helped a lot
Hi Angel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you found this information helpful!
You’re welcome, Asif.
Thank you so much
You’re welcome, Zamzam.
thank you! you help me a lot
Very informative and really precise on the subjects. Thanks.
This’s really helped me with my school project. Thanks so much!
It’s outstanding To much details given by the writer
Well understood!
well understood! thank you
That sounds nice It’ll boost the academic performance of computer student?
Thanks i found this platform very interesting
Thanks for the information it’s really useful
That’s great
thank so much for the help much appreciated.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Newsletters
Where computing might go next
The future of computing depends in part on how we reckon with its past.

- Margaret O’Mara archive page
If the future of computing is anything like its past, then its trajectory will depend on things that have little to do with computing itself.
Technology does not appear from nowhere. It is rooted in time, place, and opportunity. No lab is an island; machines’ capabilities and constraints are determined not only by the laws of physics and chemistry but by who supports those technologies, who builds them, and where they grow.
Popular characterizations of computing have long emphasized the quirkiness and brilliance of those in the field, portraying a rule-breaking realm operating off on its own. Silicon Valley’s champions and boosters have perpetuated the mythos of an innovative land of garage startups and capitalist cowboys. The reality is different. Computing’s history is modern history—and especially American history—in miniature.
The United States’ extraordinary push to develop nuclear and other weapons during World War II unleashed a torrent of public spending on science and technology. The efforts thus funded trained a generation of technologists and fostered multiple computing projects, including ENIAC —the first all-digital computer, completed in 1946. Many of those funding streams eventually became permanent, financing basic and applied research at a scale unimaginable before the war.
The strategic priorities of the Cold War drove rapid development of transistorized technologies on both sides of the Iron Curtain. In a grim race for nuclear supremacy amid an optimistic age of scientific aspiration, government became computing’s biggest research sponsor and largest single customer. Colleges and universities churned out engineers and scientists. Electronic data processing defined the American age of the Organization Man, a nation built and sorted on punch cards.
The space race, especially after the Soviets beat the US into space with the launch of the Sputnik orbiter in late 1957, jump-started a silicon semiconductor industry in a sleepy agricultural region of Northern California, eventually shifting tech’s center of entrepreneurial gravity from East to West. Lanky engineers in white shirts and narrow ties turned giant machines into miniature electronic ones, sending Americans to the moon. (Of course, there were also women playing key, though often unrecognized, roles.)
In 1965, semiconductor pioneer Gordon Moore, who with colleagues had broken ranks with his boss William Shockley of Shockley Semiconductor to launch a new company, predicted that the number of transistors on an integrated circuit would double every year while costs would stay about the same. Moore’s Law was proved right. As computing power became greater and cheaper, digital innards replaced mechanical ones in nearly everything from cars to coffeemakers.
A new generation of computing innovators arrived in the Valley, beneficiaries of America’s great postwar prosperity but now protesting its wars and chafing against its culture. Their hair grew long; their shirts stayed untucked. Mainframes were seen as tools of the Establishment, and achievement on earth overshadowed shooting for the stars. Small was beautiful. Smiling young men crouched before home-brewed desktop terminals and built motherboards in garages. A beatific newly minted millionaire named Steve Jobs explained how a personal computer was like a bicycle for the mind. Despite their counterculture vibe, they were also ruthlessly competitive businesspeople. Government investment ebbed and private wealth grew.
The ARPANET became the commercial internet. What had been a walled garden accessible only to government-funded researchers became an extraordinary new platform for communication and business, as the screech of dial-up modems connected millions of home computers to the World Wide Web. Making this strange and exciting world accessible were very young companies with odd names: Netscape, eBay, Amazon.com, Yahoo.
By the turn of the millennium, a president had declared that the era of big government was over and the future lay in the internet’s vast expanse. Wall Street clamored for tech stocks, then didn’t; fortunes were made and lost in months. After the bust, new giants emerged. Computers became smaller: a smartphone in your pocket, a voice assistant in your kitchen. They grew larger, into the vast data banks and sprawling server farms of the cloud.
Fed with oceans of data, largely unfettered by regulation, computing got smarter. Autonomous vehicles trawled city streets, humanoid robots leaped across laboratories, algorithms tailored social media feeds and matched gig workers to customers. Fueled by the explosion of data and computation power, artificial intelligence became the new new thing. Silicon Valley was no longer a place in California but shorthand for a global industry, although tech wealth and power were consolidated ever more tightly in five US-based companies with a combined market capitalization greater than the GDP of Japan.
It was a trajectory of progress and wealth creation that some believed inevitable and enviable. Then, starting two years ago, resurgent nationalism and an economy-upending pandemic scrambled supply chains, curtailed the movement of people and capital, and reshuffled the global order. Smartphones recorded death on the streets and insurrection at the US Capitol. AI-enabled drones surveyed the enemy from above and waged war on those below. Tech moguls sat grimly before congressional committees, their talking points ringing hollow to freshly skeptical lawmakers.
Our relationship with computing had suddenly changed.
The past seven decades have produced stunning breakthroughs in science and engineering. The pace and scale of change would have amazed our mid-20th-century forebears. Yet techno-optimistic assurances about the positive social power of a networked computer on every desk have proved tragically naïve. The information age of late has been more effective at fomenting discord than advancing enlightenment, exacerbating social inequities and economic inequalities rather than transcending them.
The technology industry—produced and made wealthy by these immense advances in computing—has failed to imagine alternative futures both bold and practicable enough to address humanity’s gravest health and climatic challenges. Silicon Valley leaders promise space colonies while building grand corporate headquarters below sea level. They proclaim that the future lies in the metaverse , in the blockchain, in cryptocurrencies whose energy demands exceed those of entire nation-states.
The future of computing feels more tenuous, harder to map in a sea of information and disruption. That is not to say that predictions are futile, or that those who build and use technology have no control over where computing goes next. To the contrary: history abounds with examples of individual and collective action that altered social and political outcomes. But there are limits to the power of technology to overcome earthbound realities of politics, markets, and culture.
To understand computing’s future, look beyond the machine.
1. The hoodie problem
First, look to who will get to build the future of computing.
The tech industry long celebrated itself as a meritocracy, where anyone could get ahead on the strength of technical know-how and innovative spark. This assertion has been belied in recent years by the persistence of sharp racial and gender imbalances, particularly in the field’s topmost ranks. Men still vastly outnumber women in the C-suites and in key engineering roles at tech companies. Venture capital investors and venture-backed entrepreneurs remain mostly white and male. The number of Black and Latino technologists of any gender remains shamefully tiny.
Much of today’s computing innovation was born in Silicon Valley . And looking backward, it becomes easier to understand where tech’s meritocratic notions come from, as well as why its diversity problem has been difficult to solve.
Silicon Valley was once indeed a place where people without family money or connections could make a career and possibly a fortune. Those lanky engineers of the Valley’s space-age 1950s and 1960s were often heartland boys from middle-class backgrounds, riding the extraordinary escalator of upward mobility that America delivered to white men like them in the prosperous quarter-century after the end of World War II.
Many went to college on the GI Bill and won merit scholarships to places like Stanford and MIT, or paid minimal tuition at state universities like the University of California, Berkeley. They had their pick of engineering jobs as defense contracts fueled the growth of the electronics industry. Most had stay-at-home wives whose unpaid labor freed husbands to focus their energy on building new products, companies, markets. Public investments in suburban infrastructure made their cost of living reasonable, the commutes easy, the local schools excellent. Both law and market discrimination kept these suburbs nearly entirely white.
In the last half-century, political change and market restructuring slowed this escalator of upward mobility to a crawl , right at the time that women and minorities finally had opportunities to climb on. By the early 2000s, the homogeneity among those who built and financed tech products entrenched certain assumptions: that women were not suited for science, that tech talent always came dressed in a hoodie and had attended an elite school—whether or not someone graduated. It limited thinking about what problems to solve, what technologies to build, and what products to ship.
Having so much technology built by a narrow demographic—highly educated, West Coast based, and disproportionately white, male, and young—becomes especially problematic as the industry and its products grow and globalize. It has fueled considerable investment in driverless cars without enough attention to the roads and cities these cars will navigate. It has propelled an embrace of big data without enough attention to the human biases contained in that data . It has produced social media platforms that have fueled political disruption and violence at home and abroad. It has left rich areas of research and potentially vast market opportunities neglected.
Computing’s lack of diversity has always been a problem, but only in the past few years has it become a topic of public conversation and a target for corporate reform. That’s a positive sign. The immense wealth generated within Silicon Valley has also created a new generation of investors, including women and minorities who are deliberately putting their money in companies run by people who look like them.
But change is painfully slow. The market will not take care of imbalances on its own.
For the future of computing to include more diverse people and ideas, there needs to be a new escalator of upward mobility: inclusive investments in research, human capital, and communities that give a new generation the same assist the first generation of space-age engineers enjoyed. The builders cannot do it alone.
2. Brainpower monopolies
Then, look at who the industry's customers are and how it is regulated.
The military investment that undergirded computing’s first all-digital decades still casts a long shadow. Major tech hubs of today—the Bay Area, Boston, Seattle, Los Angeles—all began as centers of Cold War research and military spending. As the industry further commercialized in the 1970s and 1980s, defense activity faded from public view, but it hardly disappeared. For academic computer science, the Pentagon became an even more significant benefactor starting with Reagan-era programs like the Strategic Defense Initiative, the computer-enabled system of missile defense memorably nicknamed “Star Wars.”
In the past decade, after a brief lull in the early 2000s, the ties between the technology industry and the Pentagon have tightened once more. Some in Silicon Valley protest its engagement in the business of war, but their objections have done little to slow the growing stream of multibillion-dollar contracts for cloud computing and cyberweaponry. It is almost as if Silicon Valley is returning to its roots.
Defense work is one dimension of the increasingly visible and freshly contentious entanglement between the tech industry and the US government. Another is the growing call for new technology regulation and antitrust enforcement, with potentially significant consequences for how technological research will be funded and whose interests it will serve.
The extraordinary consolidation of wealth and power in the technology sector and the role the industry has played in spreading disinformation and sparking political ruptures have led to a dramatic change in the way lawmakers approach the industry. The US has had little appetite for reining in the tech business since the Department of Justice took on Microsoft 20 years ago. Yet after decades of bipartisan chumminess and laissez-faire tolerance, antitrust and privacy legislation is now moving through Congress. The Biden administration has appointed some of the industry’s most influential tech critics to key regulatory roles and has pushed for significant increases in regulatory enforcement.
The five giants—Amazon, Apple, Facebook, Google, and Microsoft—now spend as much or more lobbying in Washington, DC, as banks, pharmaceutical companies, and oil conglomerates, aiming to influence the shape of anticipated regulation. Tech leaders warn that breaking up large companies will open a path for Chinese firms to dominate global markets, and that regulatory intervention will squelch the innovation that made Silicon Valley great in the first place.
Viewed through a longer lens, the political pushback against Big Tech’s power is not surprising. Although sparked by the 2016 American presidential election, the Brexit referendum, and the role social media disinformation campaigns may have played in both, the political mood echoes one seen over a century ago.
We might be looking at a tech future where companies remain large but regulated, comparable to the technology and communications giants of the middle part of the 20th century. This model did not squelch technological innovation. Today, it could actually aid its growth and promote the sharing of new technologies.
Take the case of AT&T, a regulated monopoly for seven decades before its ultimate breakup in the early 1980s. In exchange for allowing it to provide universal telephone service, the US government required AT&T to stay out of other communication businesses, first by selling its telegraph subsidiary and later by steering clear of computing.
Like any for-profit enterprise, AT&T had a hard time sticking to the rules, especially after the computing field took off in the 1940s. One of these violations resulted in a 1956 consent decree under which the US required the telephone giant to license the inventions produced in its industrial research arm, Bell Laboratories, to other companies. One of those products was the transistor. Had AT&T not been forced to share this and related technological breakthroughs with other laboratories and firms, the trajectory of computing would have been dramatically different.
Right now, industrial research and development activities are extraordinarily concentrated once again. Regulators mostly looked the other way over the past two decades as tech firms pursued growth at all costs, and as large companies acquired smaller competitors. Top researchers left academia for high-paying jobs at the tech giants as well, consolidating a huge amount of the field’s brainpower in a few companies.
More so than at any other time in Silicon Valley’s ferociously entrepreneurial history, it is remarkably difficult for new entrants and their technologies to sustain meaningful market share without being subsumed or squelched by a larger, well-capitalized, market-dominant firm. More of computing’s big ideas are coming from a handful of industrial research labs and, not surprisingly, reflecting the business priorities of a select few large tech companies.
Tech firms may decry government intervention as antithetical to their ability to innovate. But follow the money, and the regulation, and it is clear that the public sector has played a critical role in fueling new computing discoveries—and building new markets around them—from the start.
3. Location, location, location
Last, think about where the business of computing happens.
The question of where “the next Silicon Valley” might grow has consumed politicians and business strategists around the world for far longer than you might imagine. French president Charles de Gaulle toured the Valley in 1960 to try to unlock its secrets. Many world leaders have followed in the decades since.
Silicon Somethings have sprung up across many continents, their gleaming research parks and California-style subdivisions designed to lure a globe-trotting workforce and cultivate a new set of tech entrepreneurs. Many have fallen short of their startup dreams, and all have fallen short of the standard set by the original, which has retained an extraordinary ability to generate one blockbuster company after another, through boom and bust.
While tech startups have begun to appear in a wider variety of places, about three in 10 venture capital firms and close to 60% of available investment dollars remain concentrated in the Bay Area. After more than half a century, it remains the center of computing innovation.
It does, however, have significant competition. China has been making the kinds of investments in higher education and advanced research that the US government made in the early Cold War, and its technology and internet sectors have produced enormous companies with global reach.
The specter of Chinese competition has driven bipartisan support for renewed American tech investment, including a potentially massive infusion of public subsidies into the US semiconductor industry. American companies have been losing ground to Asian competitors in the chip market for years. The economy-choking consequences of this became painfully clear when covid-related shutdowns slowed chip imports to a trickle, throttling production of the many consumer goods that rely on semiconductors to function.
As when Japan posed a competitive threat 40 years ago, the American agitation over China runs the risk of slipping into corrosive stereotypes and lightly veiled xenophobia. But it is also true that computing technology reflects the state and society that makes it, whether it be the American military-industrial complex of the late 20th century, the hippie-influenced West Coast culture of the 1970s, or the communist-capitalist China of today.
What’s next
Historians like me dislike making predictions. We know how difficult it is to map the future, especially when it comes to technology, and how often past forecasters have gotten things wrong.
Intensely forward-thinking and impatient with incrementalism, many modern technologists—especially those at the helm of large for-profit enterprises—are the opposite. They disdain politics, and resist getting dragged down by the realities of past and present as they imagine what lies over the horizon. They dream of a new age of quantum computers and artificial general intelligence, where machines do most of the work and much of the thinking.
They could use a healthy dose of historical thinking.
Whatever computing innovations will appear in the future, what matters most is how our culture, businesses, and society choose to use them. And those of us who analyze the past also should take some inspiration and direction from the technologists who have imagined what is not yet possible. Together, looking forward and backward, we may yet be able to get where we need to go.
Keep Reading
Most popular.

A controversial Chinese CRISPR scientist is still hopeful about embryo gene editing. Here’s why.
He Jiankui, who went to prison for three years for making the world’s first gene-edited babies, talked to MIT Technology Review about his new research plans.
- Zeyi Yang archive page

Why OpenAI’s new model is such a big deal
The bulk of LLM progress until now has been language-driven. This new model enters the realm of complex reasoning, with implications for physics, coding, and more.
- James O'Donnell archive page

Google DeepMind’s new AI systems can now solve complex math problems
AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2 are steps toward building systems that can reason, which could unlock exciting new capabilities.
- Rhiannon Williams archive page

Meet the radio-obsessed civilian shaping Ukraine’s drone defense
Since Russia’s invasion, Serhii “Flash” Beskrestnov has become an influential, if sometimes controversial, force—sharing expert advice and intel on the ever-evolving technology that’s taken over the skies. His work may determine the future of Ukraine, and wars far beyond it.
- Charlie Metcalfe archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Types of Computers
Pre-Requisite: Basics of Computer
A computer is an electronic device that has storage, computations, input (data), output (data) and networking capabilities. With the growing AI , computers also have learning capabilities from the data provided. The input and output data can be in different forms like text, images, audio and video. A computer processes the input according to the set of instructions provided to it by the user and gives the desired output. Computers are of various types and they can be categorized in two ways on the basis of size and on the basis of data handling capabilities.

Types of Computer
There are two bases on which we can define the types of computers. We will discuss the type of computers on the basis of size and data handling capabilities. We will discuss each type of computer in detail. Let’s see first what are the types of computers.
- Super Computer
Mainframe computer
- Mini Computer
Workstation Computer
Personal computer (pc), server computer, analog computer, digital computer, hybrid computer.
- Tablets and Smartphone
Now, we are going to discuss each of them in detail.
Supercomputer
When we talk about speed, then the first name that comes to mind when thinking of computers is supercomputers. They are the biggest and fastest computers (in terms of speed of processing data). Supercomputers are designed such that they can process a huge amount of data, like processing trillions of instructions or data just in a second. This is because of the thousands of interconnected processors in supercomputers. It is basically used in scientific and engineering applications such as weather forecasting, scientific simulations, and nuclear energy research. It was first developed by Roger Cray in 1976.

Super Computers
Characteristics of Supercomputers
- Supercomputers are the computers that are the fastest and they are also very expensive.
- It can calculate up to ten trillion individual calculations per second, this is also the reason which makes it even faster.
- It is used in the stock market or big organizations for managing the online currency world such as Bitcoin etc.
- It is used in scientific research areas for analyzing data obtained from exploring the solar system, satellites, etc.
Mainframe computers are designed in such a way that they can support hundreds or thousands of users at the same time. It also supports multiple programs simultaneously. So, they can execute different processes simultaneously. All these features make the mainframe computer ideal for big organizations like banking, telecom sectors, etc., which process a high volume of data in general.
Characteristics of Mainframe Computers
- It is also an expensive or costly computer.
- It has high storage capacity and great performance.
- It can process a huge amount of data (like data involved in the banking sector) very quickly.
- It runs smoothly for a long time and has a long life.
Minicomputer
Minicomputer is a medium size multiprocessing computer. In this type of computer, there are two or more processors, and it supports 4 to 200 users at one time. Minicomputer is similar to Microcontroller. Minicomputers are used in places like institutes or departments for different work like billing, accounting, inventory management, etc. It is smaller than a mainframe computer but larger in comparison to the microcomputer.
Characteristics of Minicomputer
- Its weight is low.
- Because of its low weight, it is easy to carry anywhere.
- less expensive than a mainframe computer.
- It is fast.
A workstation computer is designed for technical or scientific applications. It consists of a fast microprocessor, with a large amount of RAM and a high-speed graphic adapter. It is a single-user computer. It is generally used to perform a specific task with great accuracy.
Characteristics of Workstation Computer
- It is expensive or high in cost.
- They are exclusively made for complex work purposes.
- It provides large storage capacity, better graphics, and a more powerful CPU when compared to a PC.
- It is also used to handle animation, data analysis, CAD, audio and video creation, and editing.
Personal Computers is also known as a microcomputer. It is basically a general-purpose computer designed for individual use. It consists of a microprocessor as a central processing unit(CPU), memory, input unit, and output unit. This kind of computer is suitable for personal work such as making an assignment, watching a movie, or at the office for office work, etc. For example, Laptops and desktop computers.

Personal Computer
Characteristics of Personal Computer (PC)
- In this limited number of software can be used.
- It is the smallest in size.
- It is designed for personal use.
- It is easy to use.
Server Computers are computers that are combined data and programs. Electronic data and applications are stored and shared in the server computer. The working of a server computer is that it does not solve a bigger problem like a supercomputer but it solves many smaller similar ones. Examples of server computer are like Wikipedia, as when users put a request for any page, it finds what the user is looking for and sends it to the user.
Analog Computers are particularly designed to process analog data. Continuous data that changes continuously and cannot have discrete values are called analog data. So, an analog computer is used where we don’t need exact values or need approximate values such as speed, temperature, pressure, etc. It can directly accept the data from the measuring device without first converting it into numbers and codes. It measures the continuous changes in physical quantity. It gives output as a reading on a dial or scale. For example speedometer, mercury thermometer, etc.
Digital computers are designed in such a way that they can easily perform calculations and logical operations at high speed. It takes raw data as input and processes it with programs stored in its memory to produce the final output. It only understands the binary input 0 and 1, so the raw input data is converted to 0 and 1 by the computer and then it is processed by the computer to produce the result or final output. All modern computers, like laptops, desktops including smartphones are digital computers.
As the name suggests hybrid, which means made by combining two different things. Similarly, the hybrid computer is a combination of both analog and digital computers. Hybrid computers are fast like analog computers and have memory and accuracy like digital computers. So, it has the ability to process both continuous and discrete data. For working when it accepts analog signals as input then it converts them into digital form before processing the input data. So, it is widely used in specialized applications where both analog and digital data are required to be processed. A processor which is used in petrol pumps that converts the measurements of fuel flow into quantity and price is an example of a hybrid computer.
Tablet and Smartphones
Tablets and Smartphones are the types of computers that are pocket friendly and easy to carry is these are handy. This is one of the best use of modern technology. These devices have better hardware capabilities, extensive operating systems, and better multimedia functionality. smartphones and tablets contain a number of sensors and are also able to provide wireless communication protocols.

We generally classify computers on the basis of size, functionality, and data handling capabilities. For more, you can refer to Classification of Computers .
1. Which computer can deal with analog data?
(A) Analogue Computer
(B) Digital Computer
(C) both a and b
(D) None of the above
The correct option is A, i.e., Analogue computer Analogue computer is particularly designed to process analogue data. A continuous data that changes continuously and cannot have discrete values is called Analogue data.
2. __________ is also known as a Microcomputer.
(A) Supercomputer
(B) Minicomputer
(C) Workstation
(D) Personal computer
The correct option is D, i.e., Personal computer.
3. Which type of computer has two or more processors and supports 4 to 200 users at one time?
(A) Minicomputer
(B) Personal computer
(C) Analogue computer
(D) All of the above
The correct option is A, i.e., Minicomputer Minicomputer is a medium sized multiprocessing computer. In this type of computer, there are two or more processors and it supports 4 to 200 users at one time.
4. All modern computers, like laptops, desktops including smartphones, are ______________computers.
(A) Hybrid
(B) Analogue
(C) Digital
(D) Supercomputer
The correct option is C, i.e., digital.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- How to Report Someone on Discord
- How to add Bots to Discord Servers
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Apply by October 1 for spring term.

Current students
News + events, get involved, search metrostate.edu, procedure 701: computer assignment and replacement.
This PDF is the official text of this policy. If there are any incongruities between the text of the HTML version ( right below ) and the text within the PDF file, the PDF will be considered accurate and overriding.
Information Technology Procedure #701
Section 1. Purpose
This procedure is established to provide additional detail on the implementation of University Policy 7010.
Section 2. Definitions
- IET: Institutional Effectiveness and Technology division of Metropolitan State University.
- Standard employee: Includes resident faculty, administrators, and staff, but does not include community faculty, contractors, or temporary employees.
- Used computer: A computer that is still within the replacement cycle of three years, that has been returned to IET and, therefore, still has useful life and can be reissued.
- User: A person who is the primary person to whom a piece of equipment has been assigned. That person is expected to be the primary user of that piece of equipment.
Section 3. Procedure
As listed in Policy 7010 and detailed here, newly issued computers include robust specifications that meet the vast majority of campus use cases. Each standard employee shall be notified when equipment is due for replacement and shall receive a bundle of equipment including:
- 13 or 14-inch screen
- 16 GB of memory
- Current generation Intel i5 processor (or equivalent)
- 250+ GB solid state drive
- 24-inch screen
- Docking station and power supply
- Mobile power supply
- Keyboard and mouse
- Cabling and adapters for use with docking station, classrooms, and meeting rooms
Requests for custom specifications shall be evaluated for need and budget availability by a designee of the Vice President of Institutional Effectiveness/CIO. These requests must be submitted via the Service Portal at https://services.metrostate.edu and include the technical requirements of the hardware or software for the review. Examples include discrete graphics card, larger screen, larger or multiple monitors, larger storage drive, faster processor, extra accessories, etc.
In accordance with Policy 5200: Reasonable Accommodations in Employment and Minnesota State Board Procedure 1.B.0.1, requests for additional computer hardware and software as accommodations for faculty or staff with disabilities shall be based on appropriate prior documentation.
Allowable, non-routine equipment purchased with professional development funds (i.e., IFO contract, Article 19, Section B and Article 10, Section J; MSUAASF contract, Article 15, Sect A. Subd. 2) are also State of Minnesota property and are subject to the same policies and procedures.
IET shall work with Minnesota State vendors for the procurement of equipment defined in this procedure, including, but not limited to, budgeting, quoting, negotiating, contracting, ordering, receiving, and invoicing. Users and departments shall contact IET before engaging in these activities.
Lost, Stolen, or Equipment Not Returned
All equipment deployed by the University is State of Minnesota property. Equipment must be returned by the user to their supervisor before the end of their last day with the University. If equipment is not returned, is stolen, or lost, the user or user’s supervisor must obtain a police report and submit to IET. This information is required for a number of reasons:
- Police will track the asset for recovery purposes.
- The police report is included with the State of Minnesota asset record to prove we, as the original purchaser, are no longer responsible for it. For example, in the event of improper disposal of electronic waste, we are not subject to fines and penalties by the Environmental Protection Agency.
Equipment purchased with 19B and 10J funds are also State of Minnesota property and are subject to the same policies and procedures.
Accessibility
Metro State University and Institutional Effectiveness and Technology is dedicated to and responsible for ensuring that University email services are accessible to everyone provided with an email address. Individuals with email accessibility needs must contact Institutional Effectiveness and Technology for assistance.
Section 4. Authority
This procedure is issued pursuant to authority granted to the President by the Minnesota State Colleges and Universities System Board of Trustees.
Section 5. Effective Date
This procedure shall become effective upon signature by the President and shall remain in effect until modified or expressly revoked.
Section 6. Responsibility
Responsibility for implementation of this procedure is assigned to the Vice President of Institutional Effectiveness and Technology/CIO.
Section 7. Review
This procedure will be reviewed as needed, or at a minimum, every three years.
Section 8. Signature
Issued on this date: 09/20/2024
Virginia “Ginny” Arthur, JD President
Date of Implementation: 09/20/2024
Date of Last Review: 09/20/2024
Date and Subject of Amendments:
Additional History and/or Revision Dates:
New R’Mail Storage Quota in Place for UCR Alumni
The new 10.00 GB R'Mail alumni quota went into effect on September 3, 2024. Qualifying alumni R’Mail accounts that are over the 10.00 GB storage limit are being reset, which permanently deletes all data and email associated with the account. Please note that UCR cannot offer any exceptions and any lost data is unrecoverable.
For more information, please visit the ITS Blog.
Information Technology Solutions
Making IT Possible

Student Technology Fee Offers Tech Tools and Services to All Highlanders
The Student Technology Fee (STF) is a vital mechanism that enables UC Riverside to strategically invest in technologies that enhance our teaching and learning environment.
This student-centered initiative directly supports the acquisition and implementation of cutting-edge tools and resources across campus, providing students and faculty with the technological resources they need to succeed and ensuring that UCR remains at the forefront of educational innovation.
Read on to learn more about the wide array of services made possible by STF contributions.
24/7 Connection to Campus Wireless Network Services
Reliable and secure wireless network services keep Highlanders connected while on campus. Through STF, Information Technology Solutions (ITS) is able to expand, enhance, and maintain UCR’s wireless network to meet the needs of our growing campus population.
UCR offers three types of wireless internet access for all Highlanders and guests:
- UCR-SECURE - For faculty, staff, and students
- EDUROAM - For higher education partners
- UCR-GUEST - For campus guests
As a best practice, ITS encourages all Highlanders to utilize the campus virtual private network (VPN) service, GlobalProtect . If you use mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets to access secure UCR resources, it is important to learn how to keep your information secure in mobile devices .
Free Daily Access to a Laptop via Laptop Anytime Kiosks
To ensure that all students have access to the technology they need, STF offers Laptop Anytime Kiosks. Students can borrow a laptop free of charge through kiosks located across campus and use it for up to 24 hours. This is particularly useful for those who do not own a personal device or need a temporary replacement. A laptop kiosk functions much like a vending machine, allowing students to check out laptops using a touch screen at the kiosk that authenticates the student’s identity and then dispenses the laptop.
To learn how to check out and return a laptop using the Laptop Anytime Kiosk, visit the ITS Knowledge Base .
There are currently five Laptop Anytime Kiosks on campus, each housing 30 laptop computers (PCs and Macs). They are located in the following areas:
- First floor lobby of the Tomás Rivera Library (two kiosks)
- First floor lobby of the Orbach Science Library
- First floor lobby of the Highlander Union Building (HUB)
- First floor lobby of the Student Success Center (SSC)
Access to Essential Software and Programs
One of the offerings under STF is Software as a Service, which enables students to access essential academic software and specialized programs for different fields of study by providing software titles free of charge. All available software titles are found in the ITS Software Catalog within the IT service portal. Students can access this anytime and download the software they need without submitting a request to ITS.
The catalog includes commonly-used software such as Microsoft Office 365, Esri ArcGIS, and MathWorks Matlab. In addition, STF provides BCOE students free access to Ansys, SolidWorks, COMSOL, and LabVIEW software.
UCR’s virtual computer lab (VLab) service is also made possible by the Student Technology Fee. Through VLab, students can access specialty software from anywhere. It enables Highlanders to complete their coursework without needing to obtain a software license or use a specific computer operating system.
Open-Access Computer Labs
Student Technology Support (STS), a service that is partially funded via STF, maintains four open-access computer labs (including the virtual computer lab). The Arts Computer Lab houses Macintosh computers, while the Watkins Labs offer Windows desktops. The Watkins Labs provide a mixture of instructional and open-access student use and are managed by student employees supervised by ITS Staff.
For more information on UCR’s open-access computer labs, including their location, lab equipment, and available software, visit the ITS Knowledge Base .
Document Printing via WEPA Print Stations
WEPA is a secure, cloud-based printing solution available to the UCR community. Highlanders can upload their documents to the WEPA print cloud and print them from any of the WEPA print stations located on campus ( learn how ). Each student receives a $9.00 quarterly allowance equivalent to 100 black-and-white single-sided page prints. Students can also print beyond their quota for a small fee per page.
UCR has more than 20 WEPA printing stations across campus ( see their locations here ). As the campus community grows, additional stations may be added.
Training Resource for Graduate Students and Postdoctoral Scholars
Graduate Quantitative Methods Center (GradQuant) is a valuable resource for UCR graduate students and postdoctoral scholars. It empowers researchers across all disciplines by offering comprehensive training in quantitative data analysis, computer programming, and digital research methods. Through free, personalized consultations and specialized workshops, GradQuant equips scholars with the essential skills to analyze data effectively, conduct research, and advance their academic careers. For more information visit gradquant.ucr.edu .
Self-Service Accessibility Tool
SensusAccess is a self-service tool that allows users to easily convert non-accessible documents into alternate formats so that the information is accessible for individuals who have print-related disabilities or need to use assistive technology to read information. SensusAccess is available to UCR students, faculty, staff, and alumni. Its accessibility features include:
- Conversion of image files and image‐only PDF documents into Word, RTF, and text files
- Conversion of image‐only PDF documents into tagged PDF documents
- Conversion of PowerPoint presentations into web projects, tagged PDF, or RTF outline files
Users can also convert the most popular document types into formats such as MP3, DAISY, EPUB, EPUB3, and Mobi.
Highlanders do not need to install software to access the service. It’s an automated service available across platforms irrespective of operating system, browser, and hardware.
SensusAccess also seamlessly integrates with Canvas to provide accessibility support in online courses and activities, allowing users to convert and download files directly within the platform.
Skill Development Resource for Students, Staff, and Faculty
LinkedIn Learning is a valuable resource for UCR students and staff seeking to build academic and professional skills. It offers a wide range of expert-led videos that teach business, technology-related, and creative skills through a flexible platform that accommodates mobile access. Through LinkedIn Learning, students can access on-demand learning, develop professional skills, and build resumés. Faculty can also integrate LinkedIn Learning courses into their classes and take training courses on how to construct courses or improve teaching.
Cloud-Based Interactive Audience Response Tool
Poll Everywhere is a cloud‐based, interactive audience response tool that allows students to engage in real-time polls and quizzes during classes using their personal devices and existing campus login systems. This tool, which replaced the campus clicker system, enhances student participation and provides immediate feedback to instructors.
Poll Everywhere ties directly into Canvas so instructors no longer need to manage separate rosters to register students and upload data into the course. Integrating Poll Everywhere in class discussions can significantly boost students’ learning experience through active course participation and engagement.
How to Access Poll Everywhere:
- Website : Poll Everywhere
- Login : Students can log in with their UCR NetID and password
- Mobile App : Available for download on iOS and Android devices
Advanced Audio/Visual Technology for General Assignment Classrooms
One of the campus enhancement projects funded by STF is the renewal and replacement of the audio/visual (A/V) technology within General Assignment (GA) classrooms . These rooms are equipped with advanced A/V instruction technology and are refreshed every five years.
All GA classrooms are Zoom-capable, with front and rear-facing cameras and instructor and audience microphones. This enables instructors to engage with a remote audience or bring in a remote presenter.
This endeavor supports effective instruction by ensuring that UCR’s classroom technology meets the needs of instructors and students.
Enhance Your Academic Experience with STF Services
STF offers various essential services that empower students and faculty to excel academically. By spreading the word and encouraging utilization of these services, you're not only supporting individual success but also contributing to the overall advancement of our academic community.
Don't miss out on this opportunity to enhance your academic experience. Take advantage of the STF services today and discover the difference they can make in your studies and research!

COMMENTS
Functionalities of Computer. Any digital computer performs the following five operations: Step 1 − Accepts data as input. Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required. Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information. Step 4 − Provides the output.
Computer Science; We'll start with the basics — digital literacy. 1. Digital Literacy Resources for High School Computer Classes. Digital literacy (sometimes called computer literacy) encompasses a number of skills related to using technology effectively and appropriately, making it critical for your students to understand.
Covers the basics of computer hardware, software, and networking and helps students develop basic skills in using Windows and Microsoft Office, and creating web pages. Students also learn how to use computers safely, and to consider ethical issues related to computer usage.
1.5 Identify four basic categories of computer hardware, p. 22 1.6 Discuss the role of software as a part of the computer, p. 27 1.7 Explain the crucial link between data, users and technology, p. 28 Chapter Overview Th is chapter introduces you to the computer, inside and out. You'll learn about the types of computers that are in use today,
Identify, describe and use communications and networking terminology and technology to include Internet operations and its uses. Describe the major operating system functions and demonstrate usage of operating system services to include: disk management, file management, and memory management. Identify and discuss computer ethics and security ...
Computer Concepts INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 3 Fig. 1.1.1: Different Computer Operations Input: A computer accepts data that is provided by means of an input device, such as a keyboard. Processing: A computer performs operations on the data to transform it in some way. Output: A computer produces output on a device, such as a printer or a monitor, that shows
Technology Lesson Plans. Whether you are looking for technology lessons for your classroom or computer lab, The Teacher's Corner has organized some great lessons and resources around the following: management, integration, keyboarding, and more. Make sure your students are developing their 21st Century skills.
Please be advised that external sites may have terms and conditions, including license rights, that differ from ours. MIT OCW is not responsible for any content on third party sites, nor does a link suggest an endorsement of those sites and/or their content.
Basic Applications of Computers. Computers are used in every field of life, such as homes, businesses, educational institutions, research organizations, the medical field, government offices, entertainment, etc. Today we can not imagine growing our technology without computers. The various field where the computer is very essential are: Science ...
First Generation Computers. The technology behind the primary generation computers was a fragile glass device, which was called a vacuum tube. These computers were very heavy and really large. These weren't very reliable and programming on them was a tedious task as they used low-level programming language and used no OS. First-generation ...
computer, device for processing, storing, and displaying information. Computer once meant a person who did computations, but now the term almost universally refers to automated electronic machinery. The first section of this article focuses on modern digital electronic computers and their design, constituent parts, and applications.
1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes. The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of "Vacuum tubes" It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer "John Ambrose Fleming". A vacuum tube is an electronic device used to control the flow of electric current in a vacuum.
Impact of Computer Technology on Economy and Social Life. The rapid development of technologies and computer-human interactions influences not only the individual experience of a person but also the general conditions of social relations. History of Computers: From Abacus to Modern PC.
Mathematics is the source of two key concepts in the development of the computer—the idea that all information can be represented as sequences of zeros and ones and the abstract notion of a " stored program."In the binary number system, numbers are represented by a sequence of the binary digits 0 and 1 in the same way that numbers in the familiar decimal system are represented using the ...
Expect to work 6-9 hours per week on assignments for this course and submit one assignment at a time. To help you do this, please follow the time line posted as an Excel file at the top of the Assignments page. You can print it out for your own reference. You are encouraged to move forward but you should not miss the due date of each unit.
Computer - History, Technology, Innovation: A computer might be described with deceptive simplicity as "an apparatus that performs routine calculations automatically." Such a definition would owe its deceptiveness to a naive and narrow view of calculation as a strictly mathematical process. In fact, calculation underlies many activities that are not normally thought of as mathematical.
A computer is an electronic device that can receive, store, process, and output data. It is a machine that can perform a variety of tasks and operations, ranging from simple calculations to complex simulations and artificial intelligence. Computers consist of hardware components such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage devices ...
Introduction to Computer Generations. This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.. During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size ...
Margaret O'Mara. October 27, 2021. If the future of computing is anything like its past, then its trajectory will depend on things that have little to do with computing itself. Technology does ...
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Assignment-Article Review Sample of the assigment; Csis 110-final exam-and all quizzes reviewed; Preview text. Yashika McCoy March 9th , Article Review: Future of Computer Technology Bibliographic Reference. Shalf, J. (2020). The future of computing beyond Moore's law. ... As computer technology advances, it will be necessary to ensure that ...
Pre-Requisite: Basics of Computer A computer is an electronic device that has storage, computations, input (data), output (data) and networking capabilities. With the growing AI, computers also have learning capabilities from the data provided.The input and output data can be in different forms like text, images, audio and video.
Information Technology Procedure #701Section 1. PurposeThis procedure is established to provide additional detail on the implementation of University Policy 7010. Section 2. Definitions IET: Institutional Effectiveness and Technology division of Metropolitan State University. Standard employee: Includes resident faculty, administrators, and staff, but does not include community faculty ...
Open-Access Computer Labs. Student Technology Support (STS), a service that is partially funded via STF, maintains four open-access computer labs (including the virtual computer lab). ... Advanced Audio/Visual Technology for General Assignment Classrooms. One of the campus enhancement projects funded by STF is the renewal and replacement of the ...