Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.

What Does Reported Speech Mean?
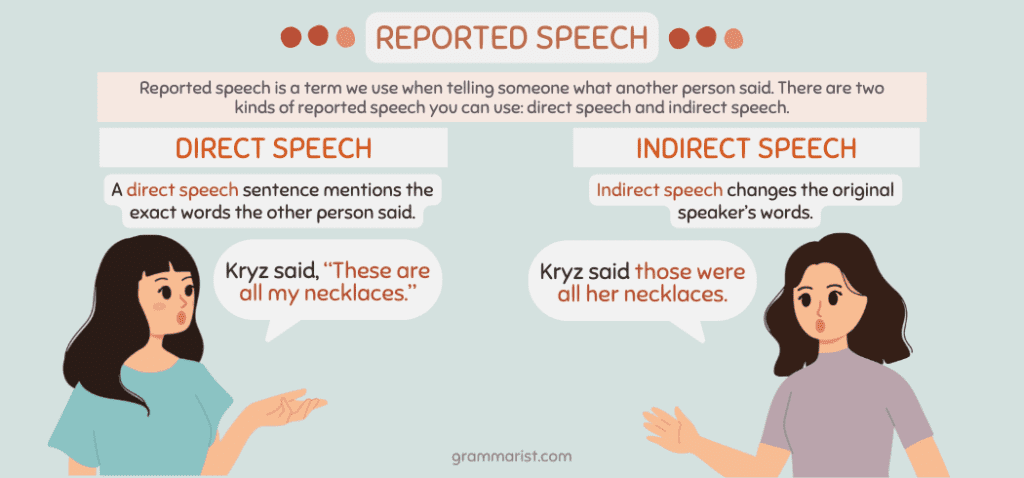
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
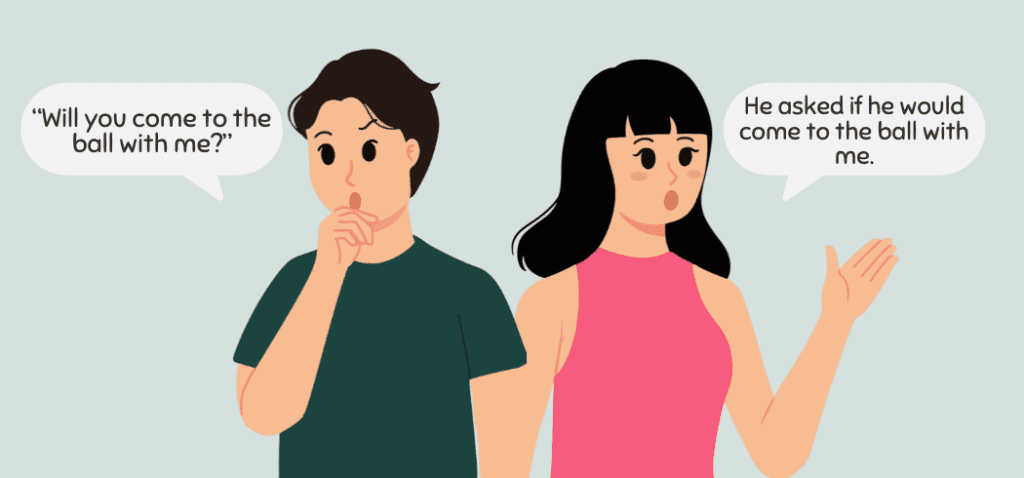
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes. You’ll also learn about modal verbs, changes in time and place, and different reporting verbs.
Reported Speech

What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when you tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, you use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Another example :
- Direct speech: She is doing her homework .
- Reported speech: He said (that) she was doing her homework.
Table of Changes :
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| I am | He said he was |
| I have | She said she had |
| I will | They said they would |
Reported Speech Rules
Verb tense changes in reported speech.
When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
The tenses generally move backward as follows:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Past Simple | |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Past Perfect | |
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Past Perfect | Past Perfect (remains unchanged) |
For sentences about the future, you also need to change the future verbs.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Here are the changes for future tenses:
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Will | Would |
| Will be | Would be |
| Will have | Would have |
| Will have been | Would have been |
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Modal verbs also change when used in reported speech.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Can | Could |
| Could | Could (unchanged) |
| Have to | Had to |
| Must | Must/Had to |
| May | Might |
| Might | Might (unchanged) |
| Should | Should (unchanged) |
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
Some modal verbs do not need to change tense because they fit naturally.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Here are both correct and incorrect examples of reported speech for clarity:
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
To correct these:
- Add ‘me’: He told me he should go to the park.
- Remove ‘me’ or add ‘to’: He said he should go to the park or He said to me he should go to the park.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
References to time and place often need to change when you use indirect speech. Here is a useful guide to these changes:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Here | There |
| This | That |
| Tomorrow | The following day/ The next day |
| Next week | The following week/ The week after |
| Yesterday | The previous day/ The day before |
| Last week | The previous week/ The week before |
| Ago | Previously/ Before |
| Tonight | That night |
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
In some cases, verb tenses do not change when you report speech indirectly. Here are the key instances:
- When the introductory verb is in the present , present perfect , or future .
- When the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- When the reported sentence contains a time clause .
- If the verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to , and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
Reporting verbs are crucial in indirect speech. Here is a list categorized by their usage:
- Basic Verbs : Tell, say, ask
- Verb + that + clause : Complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest
- Verb + to + infinitive : Agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : Advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn
- Verb + “ing” form : Admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest
- Verb + how : Explain to somebody
Reported Questions
When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, wonder, want to know, ask.
Reported Commands and Requests
Commands and requests in Indirect Speech are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive . Common reporting verbs include order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid.
Pronoun and tense changes are needed when shifting from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023

Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
| Simple present “I to go home.” | Simple past She said she to go home. |
| Present continuous “I a good book.” | Past continuous She said she a good book. |
| Simple past “I pasta for dinner last night.” | Past perfect She said she pasta for dinner the night before. |
| Present perfect “I just cleaning my room.” “My mother never to Japan.” | Past perfect She said she just cleaning her room. She said her mother never to Japan. |
| Can/can’t “I meet with you next Monday.” “Sorry, I talk now; I’m at work.” | Could/couldn’t She said she meet with me next Monday. She said she talk at the moment because she was at work. |
| Will/won’t “I pick him up from the airport.” “I tell anyone your secret.” | Would/wouldn’t She said she pick him up from the airport. She said she tell anyone my secret. |
| Should “You apologize.” | Should She said I apologize. |
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to Backshift in Reported Speech
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

British vs. American English Spelling

100 Superlatives: List & Examples

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.
StoryLearning
Learn A Language Through Stories
A Comprehensive Guide To Reported Speech In English
There are times when someone tells you something and you’ll have to report what they said to someone else.
How can you do this in English?
You’ll need to know how to use what's called reported speech in English and this is what you’ll learn in this blog post.
What Is Reported Speech In English?
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of retelling what someone else has said without repeating their exact words.
For example, let’s say you have a friend called Jon and one called Mary. Mary has organised a house party and has invited you and Jon.
Jon, however, is not feeling well. He says to you, “Sorry but I cannot come to the party. I spent all day working outside under the rain and I feel ill today.”
A few days after the party, you meet Sarah. She’s another one of your friends and she was at the party too, but she arrived late – a moment before you left. You only had time to say hello to each other.
She asks you, “I saw you at the party but I didn’t see Jon. Where was he?”
When Sarah asks you, “Where was Jon?” you can say,
“Jon said, ‘Sorry but I cannot come to the party. I spent all day working outside under the rain and I feel ill today’.”
However, it would be more natural to use indirect speech in this case. So you would say, “Jon said he couldn’t come to the party. He had spent all day working outside under the rain and he felt ill that day .”
Did you notice how the sentence changes in reported speech?
Here’s what happened:
- “I” became “he”
- “Cannot” became “couldn’t”
- “Spent” became “had spent”
- “I feel ill today” became “he felt ill on that day”
Let’s take a closer look at how we form reported speech.
How To Form Reported Speech In English
To form reported speech, you might have to make a few changes to the original sentence that was spoken (or written).
You may have to change pronouns, verb tenses, place and time expressions and, in the case of questions, the word order.
There are certain patterns to learn for reporting promises, agreements, orders, offers, requests, advice and suggestions.
Let’s have a look at all these cases one by one.
Reported Speech In English: Changing Verb Tenses
In general, when we use reported speech, the present tenses become past tenses.
We do this because we are often reporting someone else’s words at a different time (Jon’s words were spoken 3 days before you reported them to Sarah).
Here’s an example:
Jenny (on Saturday evening) says, “I don't like this place. I want to go home now.”(present tenses)
Matt (on Sunday morning) talks to James and says, “Jenny said that she didn't like the place, and she wanted to go home. (past tenses)
So this is how different verb tenses change:
Simple Present → Simple Past
DIRECT: I need money.
INDIRECT: She said she needed money.
Present Progressive → Past Progressive
DIRECT: My French is improving.
INDIRECT: He said his French was improving.
Present Perfect → Past Perfect
DIRECT: This has been an amazing holiday.
INDIRECT: She told me that it had been an amazing holiday.
What if there is a past simple form of the verb in direct speech? Well, in this case, it can stay the same in reported speech or you can change it to past perfect .
Past Simple → Past Simple Or Past Perfect
DIRECT: I didn’t go to work.
INDIRECT: Mary said that she didn’t go to work / Mary said that she hadn’t gone to work
Past Perfect Tenses Do Not Change

DIRECT: I arrived late because I had missed the bus.
INDIRECT: He said he arrived (or had arrived) late because he had missed the bus.
Modal verbs like “can,” “may,” and “will” also change in reported speech.
Will → Would
DIRECT: The exam will be difficult.
INDIRECT: They said that the exam would be difficult.
Can → Could
DIRECT: I can’t be there.
INDIRECT: He told me he couldn’t be there.
May → Might
DIRECT: We may go there another time.
INDIRECT: They said they might go there another time.
However, past modal verbs don’t change (would, must, could, should, etc.) don’t change in reported speech.
DIRECT: It would be nice if we could go to Paris.
INDIRECT: He said it would be nice if we could go to Paris.
Here are some other examples:
| “I am going to the store,” said John. | John said that he was going to the store. |
| “I love pizza,” said Jane. | Jane said that she loved pizza. |
| “I will finish the project today,” said Mary. | Mary said that she would finish the project that day. |
| “I can't come to the party,” said Tom. | Tom said that he couldn't come to the party. |
| “I have a headache,” said Sarah. | Sarah said that she had a headache. |
| “I saw a movie last night,” said Peter. | Peter said that he had seen a movie the previous night. |
| “I want to learn Spanish,” said Emily. | Emily said that she wanted to learn Spanish. |
| “I have been working on this project for a week,” said Sam. | Sam said that he had been working on the project for a week. |
| “I don't like this food,” said Mark. | Mark said that he didn't like that food. |
| “I am not feeling well,” said Alice. | Alice said that she was not feeling well. |
So, in summary,
- am/is → were
- do/does → did
- have/has → had
- had done → had done
- will → would
- can → could
- may → might
- could → could
- would → would
- like/love/buy/see → liked/loved/bought/saw or had liked/ had loved/had bought/had seen.
You make these verb tense shifts when you report the original words at a different time from when they were spoken. However, it is often also possible to keep the original speaker’s tenses when the situation is still the same.
For example,
1. DIRECT: I am feeling sick.
INDIRECT: She said she is feeling sick.
2. DIRECT: We have to leave now.
INDIRECT: They said they have to leave now.
3. DIRECT: I will call you later.
INDIRECT: He said he will call me later.
4. DIRECT: She is not coming to the party.
INDIRECT: He said she is not coming to the party.

5. DIRECT: They are working on a new project.
INDIRECT: She said they are working on a new project.
What about conditional sentences? How do they change in reported speech?
Sentences with “if” and “would” are usually unchanged.
DIRECT: It would be best if we went there early.
INDIRECT: He said it would be best if they went there early.
But conditional sentences used to describe unreal situations (e.g. second conditional or third conditional sentences) can change like this:
DIRECT: If I had more money I would buy a new car.
INDIRECT: She said if she had had more money, she would have bought a new car OR She said if she had more money, she would buy a new car.
Reported Speech In English: Changing Pronouns
In reported speech, because you’re reporting someone else’s words, there’s a change of speaker so this may mean a change of pronoun.
An example:
Jenny says, “I don't like this place. I want to go home now.”
Matt says, “Jenny said that she didn't like the place, and she wanted to go home.”
In this example, Jenny says “I” to refer to herself but Matt, talking about what Jenny said, uses “she”.
So the sentence in reported speech becomes:
- Jenny said that she didn’t like . . . ( not Jenny said that I didn’t like . . .)
Some other examples:

1 . DIRECT: I have been studying for hours.
INDIRECT: He said he had been studying for hours.
2. DIRECT: I don’t like that movie.
INDIRECT: She said she didn’t like that movie.
3. DIRECT: He doesn't like coffee.
INDIRECT: She said he doesn't like coffee.
4. DIRECT: We have a new car.
INDIRECT: They told me they had a new car.
5. DIRECT: We are going on vacation next week.
INDIRECT: They said they are going on vacation next week.
Reported Speech In English: Place And Time Expressions
When you’re reporting someone’s words, there is often a change of place and time. This may mean that you will need to change or remove words that are used to refer to places and time like “here,” “this,” “now,” “today,” “next,” “last,” “yesterday,” “tomorrow,” and so on.
Check the differences in the following sentences:
DIRECT: I'll be back next month.
INDIRECT: She said she would be back the next month , but I never saw her again.
DIRECT: Emma got her degree last Tuesday.
INDIRECT: He said Emma had got her degree the Tuesday before.
DIRECT: I had an argument with my mother-in-law yesterday .
INDIRECT: He said he’d had an argument with his mother-in-law the day before .

DIRECT: We're going to have an amazing party tomorrow.
INDIRECT: They said they were going to have an amazing party the next day.
DIRECT: Meet me here at 10 am.
INDIRECT: He told me to meet him there at 10 am.
DIRECT: This restaurant is really good.
INDIRECT: She said that the restaurant was really good.
DIRECT: I'm going to the gym now.
INDIRECT: He said he was going to the gym at that time.
DIRECT: Today is my birthday.
INDIRECT: She told me that it was her birthday that day .
DIRECT: I'm leaving for Europe next week.
INDIRECT: She said she was leaving for Europe the following week.
Reported Speech In English: Word Order In Questions
What if you have to report a question? For example, how would you report the following questions?
- Where’s Mark?
- When are you going to visit your grandmother?
- What do I need to buy for the celebration?
- Where are your best friend and his wife staying?
- Do you like coffee?
- Can you sing?
- Who’s your best friend?
- What time do you usually wake up?
- What would you do if you won the lottery?
- Do you ever read nonfiction books?
In reported questions, the subject normally comes before the verb and auxiliary “do” is not used.
So, here is what happens when you're reporting a question:
DIRECT: Where’s Mark?
INDIRECT: I asked where Mark was.
DIRECT: When are you going to visit your grandmother?
INDIRECT: He wanted to know when I was going to visit my grandmother.
DIRECT: What do I need to buy for the celebration?
INDIRECT: She asked what she needed to buy for the celebration.
DIRECT: Where are your best friend and his wife staying?
INDIRECT: I asked where his best friend and his wife were staying.

DIRECT: Do you like coffee?
INDIRECT: I asked if she liked coffee.
DIRECT: Can you sing?
INDIRECT: She asked me if I could sing.
DIRECT: Who’s your best friend?
INDIRECT: They asked me who my best friend was.
DIRECT: What time do you usually wake up?
INDIRECT: She asked me what time I usually wake up.
DIRECT: What would you do if you won the lottery?
INDIRECT: He asked me what I would do if I won the lottery.
DIRECT: Do you ever read nonfiction books?
INDIRECT: She asked me if I ever read nonfiction books.
You might have noticed that question marks are not used in reported questions and you don’t use “say” or “tell” either.
Promises, Agreements, Orders, Offers, Requests & Advice
When you’re reporting these, you can use the following verbs + an infinitive:
Here are some examples:
DIRECT SPEECH: I’ll always love you.
PROMISE IN INDIRECT SPEECH: She promised to love me.
DIRECT SPEECH: OK, let’s go to the pub.
INDIRECT SPEECH: He agreed to come to the pub with me.

DIRECT SPEECH: Sit down!
INDIRECT SPEECH: They told me to sit down OR they ordered me to sit down.
DIRECT SPEECH: I can go to the post office for you.
INDIRECT SPEECH: She offered to go to the post office.
DIRECT SPEECH: Could I please have the documentation by tomorrow evening?
INDIRECT SPEECH: She requested to have the documentation by the following evening.
DIRECT SPEECH: You should think twice before giving him your phone number.
INDIRECT SPEECH: She advised me to think twice before giving him my phone number.
Reported Speech In English
All right! I hope you have a much clearer idea about what reported speech is and how it’s used.
And the good news is that both direct and indirect speech structures are commonly used in stories, so why not try the StoryLearning method ?
You'll notice this grammatical pattern repeatedly in the context of short stories in English.
Not only will this help you acquire it naturally, but you will also have a fun learning experience by immersing yourself in an interesting and inspiring narrative.
Have a wonderful time learning through books in English !
Language Courses
- Language Blog
- Testimonials
- Meet Our Team
- StoryLearning Reviews
- Media & Press
Which language are you learning?
What is your current level in [language]?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
Where shall I send them?
We will protect your data in accordance with our data policy.
Download this article as a FREE PDF ?
What is your current level in Latin?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Latin tips…
Where shall I send the tips and your PDF?
What is your current level in Norwegian?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Norwegian tips…
Download Your Free StoryLearning® Kit!
Discover the world famous story-based method that 1,023,037 people have used to learn a language quickly…, not interested.
What can we do better ? If I could make something to help you right now, w hat would it be?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
What is your current level in Swedish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Swedish tips…
What is your current level in Danish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Danish tips…
What can we do better? If I could make something to help you right now, w hat would it be?
What is your current level in [language] ?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips, PLUS your free StoryLearning Kit…
Download this article as a FREE PDF?
Great! Where shall I send my best online teaching tips and your PDF?
Download this article as a FREE PDF ?
What is your current level in Arabic?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Arabic tips…
FREE StoryLearning Kit!
Join my email newsletter and get FREE access to your StoryLearning Kit — discover how to learn languages through the power of story!
Download a FREE Story in Japanese!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Japanese and start learning Japanese quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
What is your current level in Japanese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Japanese StoryLearning® Pack …
Where shall I send your download link?
Download Your FREE Natural Japanese Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Japanese Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Japanese grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Japanese Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in Portuguese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in German?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural German Grammar Pack …
Train as an Online Language Teacher and Earn from Home
The next cohort of my Certificate of Online Language Teaching will open soon. Join the waiting list, and we’ll notify you as soon as enrolment is open!
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Portuguese tips…
What is your current level in Turkish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Turkish tips…
What is your current level in French?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the French Vocab Power Pack …
What is your current level in Italian?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Italian Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the German Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Japanese Vocab Power Pack …
Download Your FREE Japanese Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Japanese Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Japanese words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE German Vocab Power Pack

Enter your email address below to get free access to my German Vocab Power Pack and learn essential German words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE Italian Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Italian Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Italian words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE French Vocab Power Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my French Vocab Power Pack and learn essential French words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Portuguese StoryLearning® Pack …
What is your current level in Russian?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Russian Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Russian StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Italian StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Italian Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the French StoryLearning® Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural French Grammar Pack …
What is your current level in Spanish?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Spanish Vocab Power Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Natural Spanish Grammar Pack …
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the Spanish StoryLearning® Pack …
Where shall I send them?
What is your current level in Korean?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Korean tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Russian tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Japanese tips…
What is your current level in Chinese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Chinese tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Spanish tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Italian tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] French tips…
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] German tips…
Download Your FREE Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Portuguese Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Portuguese grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural Russian Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Russian Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Russian grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural German Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural German Grammar Pack and learn to internalise German grammar quickly and naturally through stories.

Download Your FREE Natural French Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural French Grammar Pack and learn to internalise French grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Natural Italian Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Italian Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Italian grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Download a FREE Story in Portuguese!

Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Brazilian Portuguese and start learning Portuguese quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in Russian!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Russian and start learning Russian quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in German!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in German and start learning German quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Perfect! You’ve now got access to the German StoryLearning® Pack …
Download a FREE Story in Italian!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Italian and start learning Italian quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in French!

Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in French and start learning French quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
Download a FREE Story in Spanish!
Enter your email address below to get a FREE short story in Spanish and start learning Spanish quickly and naturally with my StoryLearning® method!
FREE Download:
The rules of language learning.

Enter your email address below to get free access to my Rules of Language Learning and discover 25 “rules” to learn a new language quickly and naturally through stories.
Download Your FREE Spanish Vocab Power Pack

Enter your email address below to get free access to my Spanish Vocab Power Pack and learn essential Spanish words and phrases quickly and naturally. (ALL levels!)
Download Your FREE Natural Spanish Grammar Pack
Enter your email address below to get free access to my Natural Spanish Grammar Pack and learn to internalise Spanish grammar quickly and naturally through stories.
Free Step-By-Step Guide:
How to generate a full-time income from home with your English… even with ZERO previous teaching experience.
What is your current level in Thai?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Thai tips…
What is your current level in Cantonese?
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] Cantonese tips…
Steal My Method?
I’ve written some simple emails explaining the techniques I’ve used to learn 8 languages…
I want to be skipped!
I’m the lead capture, man!
Join 84,574 other language learners getting StoryLearning tips by email…
“After I started to use your ideas, I learn better, for longer, with more passion. Thanks for the life-change!” – Dallas Nesbit
Perfect! You’ve now got access to my most effective [level] [language] tips…
Find The Perfect Language Course For You!
Looking for world-class training material to help you make a breakthrough in your language learning?
Click ‘start now’ and complete this short survey to find the perfect course for you!
Do you like the idea of learning through story?
Do you want…?
Reported Speech in English Grammar
What is reported speech.
Reported speech is when we repeat what another person has said but instead of using their exact words in quotation marks (direct speech), we use subordinate clause introduced by a reporting verb like the ones below:
Often, we have to change the tense, pronouns and time markers in reported speech.
Learn the rules for writing indirect speech in English with Lingolia’s simple explanation. In the exercises, you can test your grammar skills.
Changing direct speech to reported speech
Changing the tense (backshifting), no change of tenses, questions in reported speech, demands/requests, expressions with who/what/how + infinitive, typical changes to time and place markers.
- Exercises – Reported Speech
| “I’ve prepared a presentation about the product, if you’re interested?” “I would love to see it. … This product is exactly what my company has been looking for! Is there any room to negotiate on price?” “I’m happy to hear that. Unfortunately, pricing is fixed.” “That’s a shame, but I appreciate your transparency. Could you send me a written offer?” “Yes, I will contact you tomorrow to finalise the details.” |
| I had an appointment with a new client yesterday. I told him that and he said . |
When turning direct speech into reported speech, we may have to change all or some of the following:
- the pronouns
- information about time and place (see the table at the end of this page)
- the tense (backshift)
If the reporting verb is in the simple past (e.g. said, told, asked, replied … ), the tense has to be set back by one degree (see the table below). This is known as backshifting .
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech | |
|---|---|---|
| simple present | → | simple past |
| present progressive | → | past progressive |
| simple past | → | past perfect simple |
| present perfect simple | ||
| past perfect simple | ||
| past progressive | → | past perfect progressive |
| present perfect progressive | ||
| past perfect progressive | ||
| future with going to | → | was / were going to |
| future with will | → | conditional (would) |
| would |
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn’t, ought to, used to normally do not change.
If the reporting verb is in the simple present (e.g. says, tells, asks, replies … ), then the tense remains unchanged.
While the tense remains unchanged, we often still have to change the verb form to match the new pronouns.
that after a reporting verb
We often omit the word that after a reporting verb, especially in spoken language and informal contexts.
When turning questions into reported speech, we follow the same rules as for declarative sentences: we change the pronouns as well as the time and place markers and backshift the tense as needed.
In addition, we also have to bear in mind the following:
- instead of that , we use a question word after the reporting verb; if there is no question word, we use whether / if instead
- questions in reported speech follow declarative sentence word order (subject + verb)
- we don’t use the auxiliary verb do/did for questions in reported speech; instead, the main verb appears in the simple past without an auxiliary verb
- put the verb directly after who or what in subject questions.
Questions in reported speech do not end in a question mark.
When turning orders, demands and requests into reported speech, we only need to change the pronouns and the time and place information.
We don’t have to pay attention to the tense – we simply use an infinitive rather than a conjugated verb.
If the imperative is negated, then we use not + infinitive .
To express what someone should or can do in reported speech, we leave out the subject and the modal verb and instead we use the construction who/what/where/how + infinitive .
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| today | that day |
| now | then at that moment/time |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before |
| next year | the following year |
| tomorrow | the next day the following day |
| here | there |
| this | that |
| these | those |
say vs. tell
The words say and tell are not interchangeable.
- say = say something
- tell = say something to someone
Head over to the vocabulary section to learn more about the difference between say and tell .
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)
Exercises on reported speech.
If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker’s exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement, question or request.
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
- present tense verbs (3rd person singular)
- place and time expressions
- tenses (backshift)
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| “I speak English.” | |
| He says that he speaks English. | |
| He said that he spoke English. |
→ more on statements in reported speech
When transforming questions, check whether you have to change:
Also note that you have to:
- transform the question into an indirect question
- use the interrogative or if / whether
| Type | Example | |
|---|---|---|
| “Why don’t you speak English?” | ||
| He asked me why I didn’t speak English. | ||
| “Do you speak English?” | ||
| He asked me whether / if I spoke English. | ||
→ more on questions in reported speech
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Carol, speak English. | |
| He told Carol to speak English. |
→ more on requests in reported speech
Additional Information and Exeptions
Apart from the above mentioned basic rules, there are further aspects that you should keep in mind, for example:
- main clauses connected with and / but
- tense of the introductory clause
- reported speech for difficult tenses
- exeptions for backshift
- requests with must , should , ought to and let’s
→ more on additional information and exeptions in reported speech
Statements in Reported Speech
- no backshift – change of pronouns
- no backshift – change of pronouns and places
- with backshift
- with backshift and change of place and time expressions
Questions in Reported Speech
Requests in reported speech.
- Exercise 1 – requests (positive)
- Exercise 2 – requests (negative)
- Exercise 3 – requests (mixed)
Mixed Exercises on Reported Speech
- Exercise on reported speech with and without backshift
Grammar in Texts
- „ The Canterville Ghost “ (highlight direct speech and reported speech)
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) in English – Summary
How to use reported speech.
If you have a sentence in Direct Speech, try to follow our 5 steps to put the sentence into Reported Speech..
- Define the type of the sentence (statement, questions, command)
- What tense is used in the introductory sentence?
- Do you have to change the person (pronoun)?
- Do you have to backshift the tenses?
- Do you have to change expressions of time and place?
1. Statements, Questions, Commands
Mind the type of sentences when you use Reported Speech. There is more detailed information on the following pages.
- Commands, Requests
2. The introductory sentence
If you use Reported Speech there are mostly two main differences.
The introductory sentence in Reported Speech can be in the Present or in the Past .
If the introductory sentences is in the Simple Present, there is no backshift of tenses.
Direct Speech:
- Susan, “ Mary work s in an office.”
Reported Speech:
- Introductory sentence in the Simple Present → Susan says (that)* Mary work s in an office.
- Introductory sentence in the Simple Past → Susan said (that)* Mary work ed in an office.
3. Change of persons/pronouns
If there is a pronoun in Direct Speech, it has possibly to be changed in Reported Speech, depending on the siutation.
- Direct Speech → Susan, “I work in an office.”
- Reported Speech → Susan said (that)* she worked in an office.
Here I is changed to she .
4. Backshift of tenses
If there is backshift of tenses in Reported Speech, the tenses are shifted the following way.
- Direct Speech → Peter, “ I work in the garden.”
- Reported Speech → Peter said (that)* he work ed in the garden.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Simple forms | |
| Simple Present | Simple Past |
| Simple Past | Past Perfect |
| Present Perfect | |
| Past Perfect | |
| will | would |
| Progressive forms | |
| am/are/is | was/were |
| was/were | had been |
| has been | |
| had been | |
5. Conversion of expressions of time and place
If there is an expression of time/place in the sentence, it may be changed, depending on the situation.
- Direct Speech → Peter, “I worked in the garden yesterday .”
- Reported Speech → Peter said (that) he had worked in the garden the day before .
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| this evening | that evening |
| today/this day | that day |
| these days | those days |
| now | then |
| a week ago | a week before |
| last weekend | the weekend before / the previous weekend |
| next week | the following week |
| tomorrow | the next/following day |
| here | there |
6. Additional information
In some cases backshift of tenses is not necessary, e.g. when statements are still true. Backshift of tenses is never wrong.
- John, “My brother is at Leipzig university.”
- John said (that) his brother was at Leipzig university. or
- John said (that) his brother is at Leipzig university.
when you use general statements.
- Mandy, “The sun rises in the east.”
- Mandy said (that) the sun rose in the east. or
- Mandy said (that) the sun rises in the east.
* The word that is optional, that is the reason why we put it in brackets.
- You are here:
- Grammar Explanations
- Reported Speech

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Reported Speech: How to Use Reported Speech | Useful Rules
One of the most common mistakes when becoming familiar with this type of grammar is not knowing the difference between direct speech and reported speech and the changes related to these types of sentences.
Reported Speech
The reported speech reproduces the words of another person by adapting certain temporal and local references of the original speech to the situation of the speaker, for example, personal pronouns, demonstratives, verb tenses, and adverbs of place or time.
It is characterized by introducing the message that is reproduced with a speaking verb followed by conjunctions that or if. The speaking verb reveals the intention of the speaker to convey what another person has said.
The most frequent speaking verbs are: say, affirm , count, explain, ask, warn, suggest, order, etc.
Direct Speech vs. Reported Speech
Both are the two different ways to transmit what someone has said.
With direct speech, the message is reproduced as we have heard it, in quotes and after a color meanwhile with reported speech the message is reproduced with our words, without commas but using that or if after the verb.
Different Types of Sentences
- Reported statements : use that before the statement and the reporting verb said or told.
- Reported questions : use reported verbs like asked, requested, or wanted to know and omit the question mark. Remember that the order in reported questions changes. In the case of yes-no questions use whether or if.
- Reported requests or commands : use to or not to before the sentence and use verbs like asked, told, ordered, urged, advised, and begged.
Changes When Using Reported Speech
Tense Changes in Reported Speech
In short, the tense changes in the reported speech are made taking into account the verb in the direct speech. The tense changes are:
- Simple present -> simple past
- Present continuous -> past continuous
- Simple past -> past perfect simple
- Past continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Past perfect simple -> past perfect simple
- Past perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Present perfect -> past perfect simple
- Present perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Future simple -> would
- Future perfect -> would have
- Present passive -> past passive
- Present passive continuous -> past passive continuous
- Can -> could/would be able to
- May -> might
- May -> could/ would be allowed to
- Must -> must/ had to/ would have to
- Needn’t -> didn’t have to /didn’t need to /wouldn’t have to
- Shall -> would/should
- Will -> would
Place, Demonstratives, and Time Expressions
Just as there are certain changes in the verb tenses, you have to make changes in the demonstratives, pronouns , and expressions of time and place.
- Here -> there
- There -> there
- This -> that
Time Expressions
- Today -> that day
- Tomorrow -> the next day/ the following day
- Now -> at that moment/ then
- At the present -> At the time
- Present, current -> existing current
- In one hour -> one hour later
- Next year -> the following year
- Days ago -> days before
- Tonight -> that night
- In two week’s time -> two weeks later
- Ago -> before
Pronouns and Demonstratives
- I -> he, she
- Me -> him, her
- My -> his, her, the
- Mine -> his, hers
- We -> they
- Us -> them
- Our -> their, the
- Ours -> theirs
- You -> they, them, their, the
- Yours -> theirs
- This -> that, the
- These -> those, the
- This book -> that book
Reported Speech | Infographic

Other Changes in Reported Speech

Last Updated on October 25, 2023

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
EnglishPost.org
Reported Speech: Structures and Examples
Reported speech (Indirect Speech) is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say.
Reported Speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words
The structure of the independent clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question, or a command.
| Statement | She told me she was sick |
| Question | He asked me whether I was sick or not |
| Command | They ordered us to take a pill every day |
Table of Contents
Reported Speech Rules and Examples
Present tenses and reported speech, past tenses and reported speech, reported speech examples, reported speech and the simple present, reported speech and present continuous, reported speech and the simple past, reported speech and the past continuous, reported speech and the present perfect, reported speech and the past perfect, reported speech and ‘ can ’ and ‘can’t’, reported speech and ‘ will ’ and ‘ won’t ’, reported speech and could and couldn’t, reported speech and the future continuous, reported questions exercises online.
To turn sentences into Indirect Speech, you have to follow a set of rules and this is what makes reported speech difficult for some.
To make reported speech sentences, you need to manage English tenses well.
- Present Simple Tense changes into Past Simple Tense
- Present Progressive Tense changes into Past Progressive Tense
- Present Perfect Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Progressive Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense changes into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense changes into Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense doesn’t change
- Past Perfect Progressive Tense doesn’t change
- Future Simple Tense changes into would
- Future Progressive Tense changes into “would be”
- Future Perfect Tense changes into “would have·
- Future Perfect Progressive Tense changes into “would have been”
These are some examples of sentences using indirect speech
The present simple tense usually changes to the past simple
| He said that he travelled a lot in his job | |
| I play video games a lot | She said that he played video games a lot |
| We run every morning | They said that they ran every morning |
| I do yoga every weekend | She said that he did yoga every weekend |
The present continuous tense usually changes to the past continuous.
| She said that her mom was cooking | |
| My brother is watching TV | He said that his brother was watching TV |
| My family is eating dinner | She said that her family was eating dinner |
| I am doing Yoga | She said that she was doing yoga |
The past simple tense usually changes to the past perfect
| My mom cooked dinner | She said that her mom had cooked dinner |
| My brother watched a movie | He said that his brother had watched a movie |
| My family just ate dinner | She said that her family just had eaten dinner |
| I really enjoyed the party | |
| Bill on Saturday | He said that Bill on Saturday |
The past continuous tense usually changes to the past perfect continuous.
| She said that her mom had been cooking dinner | |
| My brother was watching a movie | He said that his brother had been watching a movie |
| My family was talking in the room | She said that her family had been talking in the room |
| Derek was doing Yoga | She said that Derek was doing Yoga |
The present perfect tense usually changes to the past perfect tense
| My mom has been kind | She said that her mom had always been kind |
| My brother has worked hard | He said that his brother had worked hard |
| My girlfriend has contributed a lot | He said that his girlfriend has contributed a lot |
| My family has always helped | She said that her family had always helped |
The past perfect tense does not change
| My mom had been kind | She said that her mom had always been kind |
| My brother had worked hard | He said that his brother had worked hard |
| He has played very well | He said that he had played very well |
| My family had always helped | She said that her family had always helped |
‘ Can ’ and ‘can’t’ in direct speech change to ‘ could ’ and ‘ couldn’t ’
| She said that her mom couldn’t remember his name | |
| My brother can play soccer well | He said that his brother could play soccer well |
| My family can help you a lot | She said that her family could help me a lot |
| My mom can lend me money | She said that she could lend me money |
‘ Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
| to my wedding | She said that her mom to her wedding |
| My brother in my team | He said that his brother in her team |
| My family me with some money | She said that her family her with some money |
| She to Europe | She said that she to Europe |
Could and couldn’t doesn’t change
| go to the wedding | She said that her mom go to the wedding |
| My brother be in your team | He said that his brother be in your team |
| My family help me out | She said that her family help me out |
Will ’ and ‘ won’t ’ in direct speech change to ‘ would ’ and ‘ wouldn’t ’
| peech | |
| the car next Friday | She said that she the car next Friday |
| home | He said that he home |
| I g in Norway | He said that he in Norway |
| I exercises | He said that he exercises |
These are some online exercises to learn more about reported questions
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise
Manuel Campos
I am Jose Manuel, English professor and creator of EnglishPost.org, a blog whose mission is to share lessons for those who want to learn and improve their English
Related Articles

The 60 Most Common Phrasal Verbs in English

Dependent Prepositions in English: Guide & Examples

How to Talk about Your Last Vacation in English

How to use Reported Speech

We use reported speech when we want to repeat what someone had previously said.
Let's look at the difference between direct speech and reported speech:
Direct Tomie said = ' I am tired.'
Reported Speech = 'Tomie said (that) she was tired.'
In reported speech we need to use the past tense form of the verb. In direct speech the present tense is used. As you can see, in the above sentence 'am' changes to 'was' when we use reported speech.
changing to the past tense to make reported speech
Here are some of the important verb changes we use when making reported speech:
am becomes was
Direct John: 'I am going.' Reported : 'John said that he was going.'
is becomes was
Direct John: 'She is tall.' Reported : 'John said that she was tall.'
do becomes did
Direct John: 'I always do my homework.' Reported : 'John said that he always did his homework.'
does becomes did
Direct John: 'My mother does the cleaning.' Reported : 'John said that his mother did the cleaning.'
have becomes had
Direct John: 'I have your number.' Reported : 'John said that he had my number.'
has becomes had
Direct John: 'He has caught a cold.' Reported : 'John said that he had caught a cold.'
go becomes went
Direct John: 'I go shopping on Sunday.' Reported : 'John said that he went shopping on Sunday.'
will becomes would
Direct John: 'I will call Frank.' Reported : 'John said that he would call Frank.'
can becomes could
Direct John: 'I can ride a horse.' Reported : 'John said that he could ride a horse.'
want becomes wanted
Direct John: 'I want a girlfriend.' Reported : 'John said that he wanted a girlfriend.'
When not to change the verb tense
When direct speech uses the past tense we do not need to make a change:
Direct John: 'I broke my arm.' Reported : 'John said that he broke his arm.'
It is also OK to change the past tense to the past perfect :
Direct John: 'I broke my arm.' Reported : 'John said that he had broken his arm.'
using reported speech for questions
So far we have looked at using 'said' in reported speech . When a question is asked we do not use 'said'. Instead we use 'asked'. We also need to use an interrogative (wh- word) or if / whether. Take a look at the examples:
questions using interrogatives
Direct John: 'What is your name?' Reported : 'John asked me what my name was.'
Direct John: ' Where does she live?' Reported : 'John asked me where she lived.'
questions using if / whether
Direct John: 'Does he play golf?' Reported : 'John asked if he played golf.' Reported : 'John asked whether he played golf.'
using reported speech for requests
As we have seen, 'said' is used for statements and 'asked' is used for requests. We use 'told' for requests and 'to' before the clause:
Direct John: 'Go home' Reported : 'John told me to go.'
Direct John: 'Stop crying' Reported : 'John told me to stop crying.'
using suggestions in reported speech
When someone gives us advice in direct speech we use 'suggested' or 'recommended' in reported speech:
Direct John: 'You should take a holiday' Reported : 'John suggested that I took a holiday.'
Direct John: 'You should take a holiday' Reported : 'John recommended that I took a holiday.'
For stronger language we can use 'insist' or 'demand':
Direct John: 'You must see a doctor.' Reported : 'John insisted that I saw a doctor.' Reported : 'John demanded that I saw a doctor.'
- 'My brothers are taller than me.' He said me his brothers were taller than him. He told me that his brothers are tall than him. He said that brothers are taller than him. He said that his brothers were taller than him.
- 'I will see you soon.' He said would see me soon. He said I will see me soon. He asked if he would see me soon. He said he would see me soon.
- 'I have a cold.' She said that she had a cold. She said had a cold. She said has a cold. She asked if I had a cold.
- 'I know the way.' He asked me the way. He said he know the way. He said that he knew the way. He told me he know the way.
- 'He lost his phone.' He said he has loses his phone. He said he losts his phone. He said that he had lost his phone. He said that lost his phone.
- 'Do you want a coffee?' He asked I wanted a coffee. He asked if I wants a coffee. He said if I wanted a coffee. He asked if I wanted a coffee.
- 'Are you Simon?' She asked whether if I was Simon. She asked whether I Simon. She asked whether I was Simon. She asked whether am simon.
- 'Why do you like Jazz?' She asked if I like Jazz. She asked why I liked Jazz. She ask why I like Jazz. She asked why I likes Jazz.
- 'Bring your ball.' He asked me if I brought my ball. He told me to bring my ball. He told me bring a ball. He tells me to bring my ball.
- 'You must come to my party.' She insisted that I came to her party. She asked me to come her party. She recommended that I come to her party. She said that I come to her party.
- Lesson Index

English language Schools
- Autocomplete
Ultimate B1 Grammar Course
- Please leave all questions, comments, and feedback here. :)
- B1 summary PDFs
- Download the section 1 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Present simple with 'do' for emphasis (1:15)
- Exercise - Present simple with 'do'
- Lesson 2: The present continuous for habits in the present (2:39)
- Exercise - The present continuous for habits in the present
- Lesson 3: The past simple and would with 'wish' (2:13)
- Exercise - The past simple and 'would' with 'wish'
- Lesson 4: The past simple for past habits and states (2:30)
- Exercise - Past simple for past habits and states
- Lesson 5: The past simple for ordering actions (2:22)
- Exercise - Past simple for ordering actions
- Section 1 review quiz
- Download the section 2 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Present perfect use to talk about 'how long' with 'for' and 'since' (1:10)
- Exercise - Present perfect use for how long with 'for' and 'since'
- Lesson 2: Present perfect use with 'just', 'yet' and 'already' (1:21)
- Exercise - Present perfect with 'yet' and 'already'
- Exercise - Present perfect with 'just'
- Lesson 3: Present perfect or past simple? (1:50)
- Exercise - Present perfect or past simple
- Section 2 review quiz
- Download the section 3 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Past continuous forms (1:53)
- Exercise - Past continuous positive and negative
- Exercise - Past continuous questions
- Lesson 2: Past continuous use: things in progress at a point in time (0:59)
- Exercise - Past continuous: events in progress at a certain time
- Lesson 3: Past continuous use: interrupted actions with the past simple (0:59)
- Exercise - Past continuous: actions with the past simple
- Lesson 4: Past continuous use: habits in the past (1:16)
- Exercise - Past continuous for habits in the past
- Lesson 5: Future in the past with 'was / were going to' (and 'would') (3:21)
- Exercise - Future in the past with 'was / were going to'
- Section 3 review quiz
- Download the section 4 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Future continuous forms (3:18)
- Exercise - Future continuous forms 1 (positive and negative)
- Exercise - Future continuous forms 2 (questions)
- Exercise - Future continuous forms 3 (mixed)
- Lesson 2: Future continuous for things in progress at a point (2:42)
- Exercise - Future continuous for things in progress at a point
- Lesson 3: Present perfect continuous forms (4:00)
- Exercise - Present perfect continuous forms 1 (positive and negative)
- Exercise - Present perfect continuous forms 2 (questions)
- Exercise - Present perfect continuous 3 (mixed)
- Lesson 4: Present perfect continuous for time up to now with for and since (2:10)
- Exercise - Present perfect continuous for time up to now
- Lesson 5: Past perfect forms (4:48)
- Exercise - Past perfect forms 1 (positive and negative)
- Exercise - Past perfect forms 2 (questions)
- Exercise - Past perfect 3 (mixed)
- Lesson 6: Past perfect for time up to then (2:47)
- Exercise - Past perfect for time up to then
- Section 4 review quiz
- Download the section 5 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Subject and object questions (3:13)
- Exercise - Subject and object questions
- Lesson 2: Question tags (5:20)
- Exercise - Question tags with the present simple 1
- Exercise - Question tags with the present simple 2
- Exercise - Question tags with the present continuous
- Exercise - Question tags with the past simple 1
- Exercise - Question tags with the past simple 2
- Exercise - Question tags with 'will'
- Exercise - Question tags with 'be going to'
- Exercise - Question tags with the present perfect
- Exercise - Question tags with the past perfect
- Exercise - Question tags with the future continuous
- Exercise - Question tags with the past continuous
- Lesson 3: Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' (5:23)
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the present simple
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the present continuous
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the past simple
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' and 'will'
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' and 'be going to'
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the present perfect
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the past perfect
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the future continuous
- Exercise - Short answers with 'so' and 'neither' in the past continuous
- Section 5 review quiz
- Download the section 6 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Verbs + infinitive without 'to' (make and let) (3:42)
- Exercise - Make and let + infinitive
- Lesson 2: Verbs with a direct object and 'to + infinitive' (3:32)
- Exercise - Verbs with a direct object and 'to + infinitive'
- Lesson 3: Verbs with two objects (1:25)
- Exercise - Verbs with two objects
- Section 6 review quiz
- Download the section 7 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Nouns that are always plural (2:37)
- Exercise - Nouns that are always plural
- Lesson 2: Collective nouns with singular or plural verbs (2:07)
- Exercise - Collective nouns with singular or plural verbs
- Lesson 3: Other / the other / another (3:13)
- Exercise - The other or other?
- Exercise - Another or the other?
- Lesson 4: The and no article with geographical names (1:24)
- Exercise - The and no article with geographical names
- Lesson 5: The with abstract nouns (3:28)
- Exercise - The with abstract nouns
- Section 7 review quiz
- Download the Section 8 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: 'Such' and 'such a' (0:54)
- Exercise - 'Such' and 'such a'
- Lesson 2: Either (0:43)
- Exercise - Either
- Lesson 3: Both ... and ... (0:34)
- Exercise - Both ... and...
- Section 8 quiz review
- Download the section 9 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: How to make the passive (7:06)
- Exercise - The present simple passive
- Exercise - The past simple passive
- Exercise - The present continuous passive
- Exercise - Mixed passive forms (present simple, present continuous, past simple)
- Exercise - The past continuous passive
- Exercise - The present perfect passive
- Exercise - The past perfect passive
- Exercise - The future with 'will' passive
- Exercise - Mixed passive forms (will, past continuous, present perfect, past perfect)
- Lesson 2: Passive infinitive introduction (with going to / have to / need to) (3:01)
- Exercise - Passive infinitive introduction (with going to / have to / need to)
- Section 9 quiz review
- Download the Section 10 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: How to make reported speech (9:13)
- Exercise - Reported speech with the present simple
- Exercise - Reported speech with the present continuous
- Exercise - Reported speech with the past simple
- Exercise - Reported speech with the present perfect
- Exercise - Reported speech with the past continuous
- Exercise - Reported speech with the future simple with 'will'
- Exercise - Reported speech with 'be going to'
- Exercise - Reported speech with the future continuous
- Exercise - Reported speech with the past perfect
- Lesson 2: Reported speech with modal verbs (1:35)
- Exercise - Reported speech with modal verbs
- Lesson 3: Reported questions with 'ask' (4:19)
- Exercise - reported 'wh' questions with 'ask'
- Exercise - reported 'yes / no' questions with 'ask'
- Lesson 4: Reported requests with 'ask' (2:11)
- Exercise - Reported requests with 'ask'
- Lesson 5: Reported orders with 'tell' (0:58)
- Exercise - Reported orders with 'tell'
- Lesson 6: Time expressions in reported speech (2:01)
- Exercise - Time expressions in reported speech
- Section 10 review quiz
- Download the Section 11 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: 'Must' and 'can't' for logical necessity (making guesses) about the present (3:39)
- Exercise - 'Must' and 'can't' for logical necessity
- Lesson 2: Could / might / etc for logical necessity (making guesses) about the present (1:22)
- Exercise - Could / might etc for logical necessity (making guesses) about the present
- Exercise - Mixed logical necessity for the present
- Lesson 3: 'Must' for recommendations and offers (1:12)
- Exercise - Must for recommendations and offers
- Lesson 4: 'Ought to' for advice (1:03)
- Exercise - 'Ought to' for advice
- Lesson 5: Be supposed to (2:52)
- Exercise - Be supposed to
- Lesson 6: Used to + infinitive (1:12)
- Exercise - Used to + infinitive
- Lesson 7: Be / get used to (2:58)
- Exercise - be / get used to
- Lesson 8: Modals for politeness (2:20)
- Exercise - Modals for politeness
- Section 11 review quiz
- Download the section 12 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Relative clauses introduction (1:52)
- Exercise - Where is the relative clause?
- Lesson 2: Defining and non-defining relative clauses (3:15)
- Exercise - Defining or non-defining?
- Lesson 3: Defining relative clauses with the pronoun as subject or object (2:53)
- Exercise - Is the relative pronoun the subject or the object?
- Exercise - Make defining relative clauses with 'who / that' as subject
- Exercise - Make defining relative clauses with 'that' as the object
- Lesson 4: Dropping the relative pronoun (1:21)
- Exercise - Dropping the relative pronoun
- Lesson 5: 'Who' or 'whom' in a relative clause? (1:45)
- Exercise - Who or whom?
- Lesson 6: 'Whose' in relative clauses (1:31)
- Exercise - Whose in relative clauses
- Lesson 7: 'When' in relative clauses (0:43)
- Exercise - 'When' in relative clauses
- Lesson 8: 'Where' in relative clauses (2:25)
- Exercise - 'Where' in relative clauses
- Section 12 review quiz
- Download the section 13 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Reflexive pronouns (4:05)
- Exercise - Reflexive pronouns 1 (reflexive pronoun or object pronoun?)
- Exercise - Reflexive pronouns 2 (reflexive pronouns with verbs like 'dress', 'wash' and 'concentrate')
- Lesson 2: Each other (2:08)
- Exercise - Each other
- Lesson 3: By myself = alone (0:44)
- Exercise - By myself
- Section 13 review quiz
- Download the section 14 PDFs
- Lesson 1: Zero conditionals (present real conditionals) (1:23)
- Exercise - Make zero conditionals
- Lesson 2: First conditionals (future real conditionals) (0:59)
- Exercise - Make first conditionals
- Lesson 3: Unless (0:59)
- Exercise - Unless
- Exercise - If and unless
- Lesson 4: Future real conditionals with modal verbs (might, can, must) (2:22)
- Exercise - Make future real conditionals with modals
- Lesson 5: Second conditionals (future unreal conditionals) (1:47)
- Exercise - Make second conditionals
- Lesson 6: 'Was' or 'were' with the second conditional? (1:55)
- Exercise - 'Was' or 'were' with the second conditional
- Lesson 7: If not and if so (1:21)
- Exercise - If so and if not
- Exercise - Make zero / first / second conditionals 1
- Exercise - Make zero / first / second conditionals 2
- Section 14 review quiz
- Download the section 15 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Order of adjectives (2:48)
- Exercise - Order of adjectives
- Lesson 2: Comparatives: get better and better (1:12)
- Exercise - Comparatives: get better and better
- Lesson 3: Comparatives: using a clause after 'than' (2:47)
- Exercise - Comparatives: using a clause after 'than'
- Lesson 4: Comparatives: verb+ing after 'than' (0:56)
- Exercise - Comparatives: verb+ing after 'than'
- Lesson 5: Superlatives with the present perfect tense (1:01)
- Exercise - Superlatives with the present perfect tense
- Lesson 6: Adjectives that are only used predicatively (asleep / alone / alive / alright / afraid) (2:14)
- Exercise - Adjectives that are only used predicatively
- Lesson 7: Compound adjectives (2:20)
- Exercise - Compound adjectives
- Section 15 review quiz
- Download the section 16 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: Adverbs of focus: even (2:27)
- Exercise - Even
- Lesson 2: Adverbs of focus: particularly / especially (1:16)
- Exercise - Particularly / especially
- Lesson 3: Adverbs of time: still (1:23)
- Exercise - Still
- Lesson 4: Adverbs of time: any more / any longer (1:26)
- Exercise - Any more / any longer
- Lesson 5: Adverbs for linking: although / though / however (1:32)
- Exercise - Although / though / however
- Lesson 6: Adverbs for linking: so / therefore (1:22)
- Exercise - So / therefore
- Lesson 7: Adverbs for linking: Because / as / since / because of / as a result of / on account of (2:21)
- Exercise - Because / as / since / because of / as a result of / on account of
- Lesson 8: Rather than / would rather (1:31)
- Exercise - Rather than / would rather
- Section 16 review quiz
- Download the section 17 PDFs here
- Lesson 1: 'As' and 'like' (1:48)
- Exercise - 'As' and 'like'
- Lesson 2: 'By' and 'with' to explain how we do something (1:20)
- Exercise - 'By' and 'with'
- Lesson 3: 'For' to show purpose (0:41)
- Exercise - 'For' to show purpose
- Lesson 4: 'At' or 'in' with buildings (1:29)
- Exercise - 'At' or 'in' with buildings
- Lesson 5: 'On time' or 'in time' (2:28)
- Exercise - 'On time' or 'in time'?
- Lesson 6: 'At the end' or 'in the end' (1:34)
- Exercise - 'At the end' or 'in the end'?
- Lesson 7: Prepositions after adjectives (2:55)
- Exercise - Prepositions after adjectives
- Lesson 8: Prepositions after verbs (2:35)
- Exercise - Prepositions after verbs
- Lesson 9: Prepositions after nouns (2:14)
- Exercise - Prepositions after nouns
- Section 17 review quiz
- Take the final quiz here. :)
- Please do the survey- click here!
Lesson 1: How to make reported speech
Here's how it works:
We use a reporting verb like 'say' or 'tell'. If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: "I love coffee."
- Reported speech: She says that she loves coffee.
We don't need to change the tense of the verb 'loves', though probably we do need to change the pronoun from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
But, if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech.
- Reported speech: She said that she loved coffee.
The verb 'love' changes from the present simple to the past simple ('loved'). This change is called 'backshifting'. It's just a grammatical change – we use it even if the thing is still true in real life.
Here are some more examples.
Present simple positive with 'be' ('am / is' change to 'was' and 'are' changes to 'were').
- Direct speech: "The children are hungry."
- Reported speech: She said that the children were hungry.
Present simple negative with 'be' ('am not / isn't' change to 'wasn't' and 'aren't' changes to 'weren't').
- Direct speech: "Lucy isn't from Brazil."
- Reported speech: She said that Lucy wasn't from Brazil.
Present simple positive with verbs that are not 'be' (present simple changes to past simple)
- Direct speech: "I work in a bank."
- Reported speech: He said that he worked in a bank.
Present simple negative with verbs that are not 'be' ('doesn't / don't' change to 'didn't').
- Direct speech: "The class doesn't start at ten."
- Reported speech: You said that the class didn't start at ten.
Now let's look at the present continuous. It changes to the past continuous.
- Direct speech: "I am going to work."
- Reported speech: She said that she was going to work.
- Direct speech: "I'm not sleeping."
- Reported speech: She said that she wasn't sleeping.
- Direct speech: "Lucy is working."
- Reported speech: She said that Lucy was working.
- Direct speech: "James isn't coming."
- Reported speech: She said that James wasn't coming.
The past simple is a little different. You have a choice! You can keep the past simple as the past simple, with no change. Or you can change it to the past perfect.
- Direct speech: "I went home."
- Reported speech: She said that she went home / had gone home.
- Direct speech: "They didn't meet Lucy."
- Reported speech: She said that they didn't meet / hadn't met Lucy.
- Direct speech: "The laptop broke."
- Reported speech: She said that the laptop broke / had broken.
- Direct speech: "We called Julie."
- Reported speech: She said that they had called Julie.
With the past continuous, we use 'had been + verb-ing'.
- Direct speech: "I was watching TV."
- Reported speech: She said that she had been watching TV.
- Direct speech: "The children weren't sleeping."
- Reported speech: She said that the children hadn't been sleeping.
- Direct speech: "We were chatting."
- Reported speech: She said that they had been chatting.
- Direct speech: "James was studying."
- Reported speech: She said that James had been studying.
With the present perfect, we use 'had + past participle' (the past perfect).
- Direct speech: "I have been to Mexico."
- Reported speech: She said that she had been to Mexico.
- Direct speech: "The students haven't finished the exam."
- Reported speech: She said that the students hadn't finished the exam.
- Direct speech: "Maria has gone out."
- Reported speech: She said that Maria had gone out.
- Direct speech: "He has lost his keys."
- Reported speech: She said that he had lost his keys.
With the past perfect, we don't need to change anything.
- Direct speech: "I had been late."
- Reported speech: She said that she had been late.
- Direct speech: "They hadn't had lunch."
- Reported speech: She said that they hadn't had lunch.
- Direct speech: "The boys had done their homework."
- Reported speech: She said that the boys had done their homework.
- Direct speech: "We had paid for everything."
- Reported speech: She said that they had paid for everything.
With 'will', we change it to 'would'.
- Direct speech: "I will come to the party."
- Reported speech: She said that she would come to the party.
- Direct speech: "They won't help."
- Reported speech: She said that they wouldn't help.
- Direct speech: "It will rain later."
- Reported speech: She said that it would rain later.
- Direct speech: "The children will be tired."
- Reported speech: She said that the children would be tired.
This is the same for the future continuous. We just change 'will' to 'would'.
- Direct speech: "I will be waiting."
- Reported speech: She said that she would be waiting.
- Direct speech: "They won't be coming."
- Reported speech: She said that they wouldn't be coming.
- Direct speech: "It will be snowing."
- Reported speech: She said that it would be snowing.
- Direct speech: "We will be sleeping."
- Reported speech: She said that they would be sleeping.
With 'be going to', we use 'was / were going to'.
- Direct speech: "I'm going to meet David."
- Reported speech: She said that she was going to meet David.
- Direct speech: "They aren't going to travel."
- Reported speech: She said that they weren't going to travel.
- Direct speech: "The students are going to pass the test."
- Reported speech: She said that the students were going to pass the test.
- Direct speech: "We are going to go to bed early."
- Reported speech: She said that they were going to go to bed early.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech
Reported speech is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say. There are two main types of reported speech: direct speech and indirect speech.
Click on a topic to learn more about reported speech.

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
24 hours a day, seven days a week: all the time

It’s as clear as mud! (Words and expressions that mean ‘difficult to understand’)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
How to Use 'Say' and 'Tell'
Perfect english grammar.

In reported statements, we can use either ' say ' or ' tell '. The meaning is the same, but the grammar is different. For example:
- John: "I'll be late".
- John said (that) he would be late.
- John told me (that) he was going to be late.
With 'tell' we NEED the object (e.g. 'me', 'you', 'her'). With 'say' we CAN'T use the object (e.g. 'me', 'them', 'us').
- “ John said me that he would be late. ”
- “ John told that he would be late. ”
- Julie said (that) she'd come to the party.
- I said (that) I was going to bed early.
- He told me (that) he loved living in London.
- They told John (that) they would arrive at six.
Learn more about reported speech here.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Advertisement
Supported by
How Israel Built a Modern-Day Trojan Horse: Exploding Pagers
The Israeli government did not tamper with the Hezbollah devices that exploded, defense and intelligence officials say. It manufactured them as part of an elaborate ruse.
- Share full article

By Sheera Frenkel Ronen Bergman and Hwaida Saad
Follow along with the latest Middle East updates as Israel-Hezbollah tensions escalate.
The pagers began beeping just after 3:30 in the afternoon in Lebanon on Tuesday, alerting Hezbollah operatives to a message from their leadership in a chorus of chimes, melodies, and buzzes.
But it wasn’t the militants’ leaders. The pagers had been sent by Hezbollah’s archenemy, and within seconds the alerts were followed by the sounds of explosions and cries of pain and panic in streets, shops and homes across Lebanon.
Powered by just a few ounces of an explosive compound concealed within the devices, the blasts sent grown men flying off motorcycles and slamming into walls, according to witnesses and video footage. People out shopping fell to the ground, writhing in agony, smoke snaking from their pockets.
Mohammed Awada, 52, and his son were driving by one man whose pager exploded, he said. “My son went crazy and started to scream when he saw the man’s hand flying away from him,” he said.
By the end of the day, at least a dozen people were dead and more than 2,700 were wounded, many of them maimed. And the following day, 20 more people were killed and hundreds wounded when walkie-talkies in Lebanon also began mysteriously exploding. Some of the dead and wounded were Hezbollah members, but others were not; four of the dead were children.

We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We can call this an 'order' in English, when someone tells you very directly to do something. For example: Direct speech: Sit down! In fact, we make this into reported speech in the same way as a request. We just use 'tell' instead of 'ask': Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
For example: Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken. Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken. Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form. Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting.
Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then.". 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example:
In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed. Reported Speech Examples. When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too. ...
For reported requests, we use "asked (someone) to do something": "Please make a copy of this report." (direct speech) She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech) For reported orders, we use "told (someone) to do something:". "Go to the bank." (direct speech)
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of retelling what someone else has said without repeating their exact words. For example, let's say you have a friend called Jon and one called Mary. Mary has organised a house party and has invited you and Jon. Jon, however, is not feeling well.
1. We use direct speech to quote a speaker's exact words. We put their words within quotation marks. We add a reporting verb such as "he said" or "she asked" before or after the quote. Example: He said, "I am happy.". 2. Reported speech is a way of reporting what someone said without using quotation marks.
Questions in reported speech. When turning questions into reported speech, we follow the same rules as for declarative sentences: we change the pronouns as well as the time and place markers and backshift the tense as needed.. In addition, we also have to bear in mind the following: instead of that, we use a question word after the reporting verb; if there is no question word, we use whether ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Exercises on Reported Speech. If we report what another person has said, we usually do not use the speaker's exact words (direct speech), but reported (indirect) speech. Therefore, you need to learn how to transform direct speech into reported speech. The structure is a little different depending on whether you want to transform a statement ...
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Reported Speech → Susan said (that)* she worked in an office. Here I is changed to she. 4. Backshift of tenses. If there is backshift of tenses in Reported Speech, the tenses are shifted the following way. Direct Speech → Peter, " I work in the garden." Reported Speech → Peter said (that)* he work ed in the garden.
Direct: "I do my exercises every morning.". Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning. Direct: "She is going to start a new job.". Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job. Direct: "I can solve this problem.". Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
Reported questions: use reported verbs like asked, requested, or wanted to know and omit the question mark. Remember that the order in reported questions changes. In the case of yes-no questions use whether or if. Reported requests or commands: use to or not to before the sentence and use verbs like asked, told, ordered, urged, advised, and begged.
Reported Speech Rules and Examples. To turn sentences into Indirect Speech, you have to follow a set of rules and this is what makes reported speech difficult for some. To make reported speech sentences, you need to manage English tenses well. Present Tenses and Reported Speech. Present Simple Tense changes into Past Simple Tense
In reported speech we need to use the past tense form of the verb. In direct speech the present tense is used. As you can see, in the above sentence 'am' changes to 'was' when we use reported speech. changing to the past tense to make reported speech. Here are some of the important verb changes we use when making reported speech: am becomes was
REPORTED SPEECH! https://7esl.com/reported-speech/Reported speech is often also called indirect speech in English.Direct Speech: https://7esl.com/direct-spee...
We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: "I love coffee." Reported speech: She says that she loves coffee. We don't need to change the tense of the verb 'loves', though probably we do need to change the pronoun from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
In this video, you will learn about what reported speech means, about the types pf specch [ direct and indirect speech], and about the changes made when cha...
Reported speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
In reported statements, we can use either ' say ' or ' tell '. The meaning is the same, but the grammar is different. For example: Direct speech: John: "I'll be late". John said (that) he would be late. John told me (that) he was going to be late. With 'tell' we NEED the object (e.g. 'me', 'you', 'her').
In Lebanon, as Israel picked off senior Hezbollah commandos with targeted assassinations, their leader came to a conclusion: If Israel was going high-tech, Hezbollah would go low.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky's visit to the White House on Thursday may be have been his final chance to convince a receptive American president of his country's war aims. And just ...
Vice President Kamala Harris will outline her economic vision to grow the middle class during a Pittsburgh speech Wednesday, as she seeks to draw clear contrasts between her policies and those of former President Trump.. Why it matters: The Harris campaign believes this speech could help define the Democratic presidential nominee as a champion of the middle class and Trump as being for ...