Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What is a Case Study in Research? Definition, Methods, and Examples
Case study methodology offers researchers an exciting opportunity to explore intricate phenomena within specific contexts using a wide range of data sources and collection methods. It is highly pertinent in health and social sciences, environmental studies, social work, education, and business studies. Its diverse applications, such as advancing theory, program evaluation, and intervention development, make it an invaluable tool for driving meaningful research and fostering positive change.[ 1]
Table of Contents
What is a Case Study?
A case study method involves a detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or community, to explore and understand complex issues in real-life contexts. By focusing on one specific case, researchers can gain a deep understanding of the factors and dynamics at play, understanding their complex relationships, which might be missed in broader, more quantitative studies.
When to do a Case Study?
A case study design is useful when you want to explore a phenomenon in-depth and in its natural context. Here are some examples of when to use a case study :[ 2]
- Exploratory Research: When you want to explore a new topic or phenomenon, a case study can help you understand the subject deeply. For example , a researcher studying a newly discovered plant species might use a case study to document its characteristics and behavior.
- Descriptive Research: If you want to describe a complex phenomenon or process, a case study can provide a detailed and comprehensive description. For instance, a case study design could describe the experiences of a group of individuals living with a rare disease.
- Explanatory Research: When you want to understand why a particular phenomenon occurs, a case study can help you identify causal relationships. A case study design could investigate the reasons behind the success or failure of a particular business strategy.
- Theory Building: Case studies can also be used to develop or refine theories. By systematically analyzing a series of cases, researchers can identify patterns and relationships that can contribute to developing new theories or refining existing ones.
- Critical Instance: Sometimes, a single case can be used to study a rare or unusual phenomenon, but it is important for theoretical or practical reasons. For example , the case of Phineas Gage, a man who survived a severe brain injury, has been widely studied to understand the relationship between the brain and behavior.
- Comparative Analysis: Case studies can also compare different cases or contexts. A case study example involves comparing the implementation of a particular policy in different countries to understand its effectiveness and identifying best practices.

How to Create a Case Study – Step by Step
Step 1: select a case .
Careful case selection ensures relevance, insight, and meaningful contribution to existing knowledge in your field. Here’s how you can choose a case study design :[ 3]
- Define Your Objectives: Clarify the purpose of your case study and what you hope to achieve. Do you want to provide new insights, challenge existing theories, propose solutions to a problem, or explore new research directions?
- Consider Unusual or Outlying Cases: Focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases that can provide unique insights.
- Choose a Representative Case: Alternatively, select a common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
- Avoid Bias: Ensure your selection process is unbiased using random or criteria-based selection.
- Be Clear and Specific: Clearly define the boundaries of your study design , including the scope, timeframe, and key stakeholders.
- Ethical Considerations: Consider ethical issues, such as confidentiality and informed consent.
Step 2: Build a Theoretical Framework
To ensure your case study has a solid academic foundation, it’s important to build a theoretical framework:
- Conduct a Literature Review: Identify key concepts and theories relevant to your case study .
- Establish Connections with Theory: Connect your case study with existing theories in the field.
- Guide Your Analysis and Interpretation: Use your theoretical framework to guide your analysis, ensuring your findings are grounded in established theories and concepts.
Step 3: Collect Your Data
To conduct a comprehensive case study , you can use various research methods. These include interviews, observations, primary and secondary sources analysis, surveys, and a mixed methods approach. The aim is to gather rich and diverse data to enable a detailed analysis of your case study .
Step 4: Describe and Analyze the Case
How you report your findings will depend on the type of research you’re conducting. Here are two approaches:
- Structured Approach: Follows a scientific paper format, making it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Narrative Approach: A more exploratory style aiming to analyze meanings and implications.
Regardless of the approach you choose, it’s important to include the following elements in your case study :
- Contextual Details: Provide background information about the case, including relevant historical, cultural, and social factors that may have influenced the outcome.
- Literature and Theory: Connect your case study to existing literature and theory in the field. Discuss how your findings contribute to or challenge existing knowledge.
- Wider Patterns or Debates: Consider how your case study fits into wider patterns or debates within the field. Discuss any implications your findings may have for future research or practice.

What Are the Benefits of a Case Study
Case studies offer a range of benefits , making them a powerful tool in research.
1. In-Depth Analysis
- Comprehensive Understanding: Case studies allow researchers to thoroughly explore a subject, understanding the complexities and nuances involved.
- Rich Data: They offer rich qualitative and sometimes quantitative data, capturing the intricacies of real-life contexts.
2. Contextual Insight
- Real-World Application: Case studies provide insights into real-world applications, making the findings highly relevant and practical.
- Context-Specific: They highlight how various factors interact within a specific context, offering a detailed picture of the situation.
3. Flexibility
- Methodological Diversity: Case studies can use various data collection methods, including interviews, observations, document analysis, and surveys.
- Adaptability: Researchers can adapt the case study approach to fit the specific needs and circumstances of the research.
4. Practical Solutions
- Actionable Insights: The detailed findings from case studies can inform practical solutions and recommendations for practitioners and policymakers.
- Problem-Solving: They help understand the root causes of problems and devise effective strategies to address them.
5. Unique Cases
- Rare Phenomena: Case studies are particularly valuable for studying rare or unique cases that other research methods may not capture.
- Detailed Documentation: They document and preserve detailed information about specific instances that might otherwise be overlooked.
What Are the Limitations of a Case Study
While case studies offer valuable insights and a detailed understanding of complex issues, they have several limitations .
1. Limited Generalizability
- Specific Context: Case studies often focus on a single case or a small number of cases, which may limit the generalization of findings to broader populations or different contexts.
- Unique Situations: The unique characteristics of the case may not be representative of other situations, reducing the applicability of the results.
2. Subjectivity
- Researcher Bias: The researcher’s perspectives and interpretations can influence the analysis and conclusions, potentially introducing bias.
- Participant Bias: Participants’ responses and behaviors may be influenced by their awareness of being studied, known as the Hawthorne effect.
3. Time-Consuming
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering detailed, in-depth data requires significant time and effort, making case studies more time-consuming than other research methods.
- Longitudinal Studies: If the case study observes changes over time, it can become even more prolonged.
4. Resource Intensive
- Financial and Human Resources: Conducting comprehensive case studies may require significant financial investment and human resources, including trained researchers and participant access.
- Access to Data: Accessing relevant and reliable data sources can be challenging, particularly in sensitive or proprietary contexts.
5. Replication Difficulties
- Unique Contexts: A case study’s specific and detailed context makes it difficult to replicate the study exactly, limiting the ability to validate findings through repetition.
- Variability: Differences in contexts, researchers, and methodologies can lead to variations in findings, complicating efforts to achieve consistent results.
By acknowledging and addressing these limitations , researchers can enhance the rigor and reliability of their case study findings.
Key Takeaways
Case studies are valuable in research because they provide an in-depth, contextual analysis of a single subject, event, or organization. They allow researchers to explore complex issues in real-world settings, capturing detailed qualitative and quantitative data. This method is useful for generating insights, developing theories, and offering practical solutions to problems. They are versatile, applicable in diverse fields such as business, education, and health, and can complement other research methods by providing rich, contextual evidence. However, their findings may have limited generalizability due to the focus on a specific case.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a case study in research?
A case study in research is an impactful tool for gaining a deep understanding of complex issues within their real-life context. It combines various data collection methods and provides rich, detailed insights that can inform theory development and practical applications.
Q: What are the advantages of using case studies in research?
Case studies are a powerful research method, offering advantages such as in-depth analysis, contextual insights, flexibility, rich data, and the ability to handle complex issues. They are particularly valuable for exploring new areas, generating hypotheses, and providing detailed, illustrative examples that can inform theory and practice.
Q: Can case studies be used in quantitative research?
While case studies are predominantly associated with qualitative research, they can effectively incorporate quantitative methods to provide a more comprehensive analysis. A mixed-methods approach leverages qualitative and quantitative research strengths, offering a powerful tool for exploring complex issues in a real-world context. For example , a new medical treatment case study can incorporate quantitative clinical outcomes (e.g., patient recovery rates and dosage levels) along with qualitative patient interviews.
Q: What are the key components of a case study?
A case study typically includes several key components:
- Introductio n, which provides an overview and sets the context by presenting the problem statement and research objectives;
- Literature review , which connects the study to existing theories and prior research;
- Methodology , which details the case study design , data collection methods, and analysis techniques;
- Findings , which present the data and results, including descriptions, patterns, and themes;
- Discussion and conclusion , which interpret the findings, discuss their implications, and offer conclusions, practical applications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Together, these components ensure a comprehensive, systematic, and insightful exploration of the case.
References
- de Vries, K. (2020). Case study methodology. In Critical qualitative health research (pp. 41-52). Routledge.
- Fidel, R. (1984). The case study method: A case study. Library and Information Science Research , 6 (3), 273-288.
- Thomas, G. (2021). How to do your case study. How to do your case study , 1-320.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Paperpal Review: Key Features, Pricing Plans, and How-to-Use

How to Structure a Dissertation?
- User Experience (UX) Testing User Interface (UI) Testing Ecommerce Testing Remote Usability Testing About the company ' data-html="true"> Why Trymata
- Usability testing
Run remote usability tests on any digital product to deep dive into your key user flows
- Product analytics
Learn how users are behaving on your website in real time and uncover points of frustration
- Research repository
A tool for collaborative analysis of qualitative data and for building your research repository and database.
See an example
- Trymata Blog
How-to articles, expert tips, and the latest news in user testing & user experience
- Knowledge Hub
Detailed explainers of Trymata’s features & plans, and UX research terms & topics
Visit Knowledge Hub
- Plans & Pricing
Get paid to test
- User Experience (UX) testing
- User Interface (UI) testing
- Ecommerce testing
- Remote usability testing
- Plans & Pricing
- Customer Stories
How do you want to use Trymata?
Conduct user testing, desktop usability video.
You’re on a business trip in Oakland, CA. You've been working late in downtown and now you're looking for a place nearby to grab a late dinner. You decided to check Zomato to try and find somewhere to eat. (Don't begin searching yet).
- Look around on the home page. Does anything seem interesting to you?
- How would you go about finding a place to eat near you in Downtown Oakland? You want something kind of quick, open late, not too expensive, and with a good rating.
- What do the reviews say about the restaurant you've chosen?
- What was the most important factor for you in choosing this spot?
- You're currently close to the 19th St Bart station, and it's 9PM. How would you get to this restaurant? Do you think you'll be able to make it before closing time?
- Your friend recommended you to check out a place called Belly while you're in Oakland. Try to find where it is, when it's open, and what kind of food options they have.
- Now go to any restaurant's page and try to leave a review (don't actually submit it).
What was the worst thing about your experience?
It was hard to find the bart station. The collections not being able to be sorted was a bit of a bummer
What other aspects of the experience could be improved?
Feedback from the owners would be nice
What did you like about the website?
The flow was good, lots of bright photos
What other comments do you have for the owner of the website?
I like that you can sort by what you are looking for and i like the idea of collections
You're going on a vacation to Italy next month, and you want to learn some basic Italian for getting around while there. You decided to try Duolingo.
- Please begin by downloading the app to your device.
- Choose Italian and get started with the first lesson (stop once you reach the first question).
- Now go all the way through the rest of the first lesson, describing your thoughts as you go.
- Get your profile set up, then view your account page. What information and options are there? Do you feel that these are useful? Why or why not?
- After a week in Italy, you're going to spend a few days in Austria. How would you take German lessons on Duolingo?
- What other languages does the app offer? Do any of them interest you?
I felt like there could have been a little more of an instructional component to the lesson.
It would be cool if there were some feature that could allow two learners studying the same language to take lessons together. I imagine that their screens would be synced and they could go through lessons together and chat along the way.
Overall, the app was very intuitive to use and visually appealing. I also liked the option to connect with others.
Overall, the app seemed very helpful and easy to use. I feel like it makes learning a new language fun and almost like a game. It would be nice, however, if it contained more of an instructional portion.
All accounts, tests, and data have been migrated to our new & improved system!
Use the same email and password to log in:
Legacy login: Our legacy system is still available in view-only mode, login here >
What’s the new system about? Read more about our transition & what it-->
What is a Case Study? Definition, Research Methods, Sampling and Examples
Conduct End-to-End User Testing & Research
What is a Case Study?
A case study is defined as an in-depth analysis of a particular subject, often a real-world situation, individual, group, or organization.
It is a research method that involves the comprehensive examination of a specific instance to gain a better understanding of its complexities, dynamics, and context.
Case studies are commonly used in various fields such as business, psychology, medicine, and education to explore and illustrate phenomena, theories, or practical applications.
In a typical case study, researchers collect and analyze a rich array of qualitative and/or quantitative data, including interviews, observations, documents, and other relevant sources. The goal is to provide a nuanced and holistic perspective on the subject under investigation.
The information gathered here is used to generate insights, draw conclusions, and often to inform broader theories or practices within the respective field.
Case studies offer a valuable method for researchers to explore real-world phenomena in their natural settings, providing an opportunity to delve deeply into the intricacies of a particular case. They are particularly useful when studying complex, multifaceted situations where various factors interact.
Additionally, case studies can be instrumental in generating hypotheses, testing theories, and offering practical insights that can be applied to similar situations. Overall, the comprehensive nature of case studies makes them a powerful tool for gaining a thorough understanding of specific instances within the broader context of academic and professional inquiry.
Key Characteristics of Case Study
Case studies are characterized by several key features that distinguish them from other research methods. Here are some essential characteristics of case studies:
- In-depth Exploration: Case studies involve a thorough and detailed examination of a specific case or instance. Researchers aim to explore the complexities and nuances of the subject under investigation, often using multiple data sources and methods to gather comprehensive information.
- Contextual Analysis: Case studies emphasize the importance of understanding the context in which the case unfolds. Researchers seek to examine the unique circumstances, background, and environmental factors that contribute to the dynamics of the case. Contextual analysis is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions and generalizing findings to similar situations.
- Holistic Perspective: Rather than focusing on isolated variables, case studies take a holistic approach to studying a phenomenon. Researchers consider a wide range of factors and their interrelationships, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of the case. This holistic perspective helps in providing a more complete understanding of the subject.
- Qualitative and/or Quantitative Data: Case studies can incorporate both qualitative and quantitative data, depending on the research question and objectives. Qualitative data often include interviews, observations, and document analysis, while quantitative data may involve statistical measures or numerical information. The combination of these data types enhances the depth and validity of the study.
- Longitudinal or Retrospective Design: Case studies can be designed as longitudinal studies, where the researcher follows the case over an extended period, or retrospective studies, where the focus is on examining past events. This temporal dimension allows researchers to capture changes and developments within the case.
- Unique and Unpredictable Nature: Each case study is unique, and the findings may not be easily generalized to other situations. The unpredictable nature of real-world cases adds a layer of authenticity to the study, making it an effective method for exploring complex and dynamic phenomena.
- Theory Building or Testing: Case studies can serve different purposes, including theory building or theory testing. In some cases, researchers use case studies to develop new theories or refine existing ones. In others, they may test existing theories by applying them to real-world situations and assessing their explanatory power.
Understanding these key characteristics is essential for researchers and practitioners using case studies as a methodological approach, as it helps guide the design, implementation, and analysis of the study.
Key Components of a Case Study
A well-constructed case study typically consists of several key components that collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject under investigation. Here are the key components of a case study:
- Provide an overview of the context and background information relevant to the case. This may include the history, industry, or setting in which the case is situated.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of the case study. Define what the study aims to achieve and the questions it seeks to answer.
- Clearly identify the subject of the case study. This could be an individual, a group, an organization, or a specific event.
- Define the boundaries and scope of the case study. Specify what aspects will be included and excluded from the investigation.
- Provide a brief review of relevant theories or concepts that will guide the analysis. This helps place the case study within the broader theoretical context.
- Summarize existing literature related to the subject, highlighting key findings and gaps in knowledge. This establishes the context for the current case study.
- Describe the research design chosen for the case study (e.g., exploratory, explanatory, descriptive). Justify why this design is appropriate for the research objectives.
- Specify the methods used to gather data, whether through interviews, observations, document analysis, surveys, or a combination of these. Detail the procedures followed to ensure data validity and reliability.
- Explain the criteria for selecting the case and any sampling considerations. Discuss why the chosen case is representative or relevant to the research questions.
- Describe how the collected data will be coded and categorized. Discuss the analytical framework or approach used to identify patterns, themes, or trends.
- If multiple data sources or methods are used, explain how they complement each other to enhance the credibility and validity of the findings.
- Present the key findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, charts, or quotes from participants to illustrate the results.
- Interpret the results in the context of the research objectives and theoretical framework. Discuss any unexpected findings and their implications.
- Provide a thorough interpretation of the results, connecting them to the research questions and relevant literature.
- Acknowledge the limitations of the study, such as constraints in data collection, sample size, or generalizability.
- Highlight the contributions of the case study to the existing body of knowledge and identify potential avenues for future research.
- Summarize the key findings and their significance in relation to the research objectives.
- Conclude with a concise summary of the case study, its implications, and potential practical applications.
- Provide a complete list of all the sources cited in the case study, following a consistent citation style.
- Include any additional materials or supplementary information, such as interview transcripts, survey instruments, or supporting documents.
By including these key components, a case study becomes a comprehensive and well-rounded exploration of a specific subject, offering valuable insights and contributing to the body of knowledge in the respective field.
Sampling in a Case Study Research
Sampling in case study research involves selecting a subset of cases or individuals from a larger population to study in depth. Unlike quantitative research where random sampling is often employed, case study sampling is typically purposeful and driven by the specific objectives of the study. Here are some key considerations for sampling in case study research:
- Criterion Sampling: Cases are selected based on specific criteria relevant to the research questions. For example, if studying successful business strategies, cases may be selected based on their demonstrated success.
- Maximum Variation Sampling: Cases are chosen to represent a broad range of variations related to key characteristics. This approach helps capture diversity within the sample.
- Selecting Cases with Rich Information: Researchers aim to choose cases that are information-rich and provide insights into the phenomenon under investigation. These cases should offer a depth of detail and variation relevant to the research objectives.
- Single Case vs. Multiple Cases: Decide whether the study will focus on a single case (single-case study) or multiple cases (multiple-case study). The choice depends on the research objectives, the complexity of the phenomenon, and the depth of understanding required.
- Emergent Nature of Sampling: In some case studies, the sampling strategy may evolve as the study progresses. This is known as theoretical sampling, where new cases are selected based on emerging findings and theoretical insights from earlier analysis.
- Data Saturation: Sampling may continue until data saturation is achieved, meaning that collecting additional cases or data does not yield new insights or information. Saturation indicates that the researcher has adequately explored the phenomenon.
- Defining Case Boundaries: Clearly define the boundaries of the case to ensure consistency and avoid ambiguity. Consider what is included and excluded from the case study, and justify these decisions.
- Practical Considerations: Assess the feasibility of accessing the selected cases. Consider factors such as availability, willingness to participate, and the practicality of data collection methods.
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring that they understand the purpose of the study and the ways in which their information will be used. Protect the confidentiality and anonymity of participants as needed.
- Pilot Testing the Sampling Strategy: Before conducting the full study, consider pilot testing the sampling strategy to identify potential challenges and refine the approach. This can help ensure the effectiveness of the sampling method.
- Transparent Reporting: Clearly document the sampling process in the research methodology section. Provide a rationale for the chosen sampling strategy and discuss any adjustments made during the study.
Sampling in case study research is a critical step that influences the depth and richness of the study’s findings. By carefully selecting cases based on specific criteria and considering the unique characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation, researchers can enhance the relevance and validity of their case study.
Case Study Research Methods With Examples
- Interviews:
- Interviews involve engaging with participants to gather detailed information, opinions, and insights. In a case study, interviews are often semi-structured, allowing flexibility in questioning.
- Example: A case study on workplace culture might involve conducting interviews with employees at different levels to understand their perceptions, experiences, and attitudes.
- Observations:
- Observations entail direct examination and recording of behavior, activities, or events in their natural setting. This method is valuable for understanding behaviors in context.
- Example: A case study investigating customer interactions at a retail store may involve observing and documenting customer behavior, staff interactions, and overall dynamics.
- Document Analysis:
- Document analysis involves reviewing and interpreting written or recorded materials, such as reports, memos, emails, and other relevant documents.
- Example: In a case study on organizational change, researchers may analyze internal documents, such as communication memos or strategic plans, to trace the evolution of the change process.
- Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Surveys and questionnaires collect structured data from a sample of participants. While less common in case studies, they can be used to supplement other methods.
- Example: A case study on the impact of a health intervention might include a survey to gather quantitative data on participants’ health outcomes.
- Focus Groups:
- Focus groups involve a facilitated discussion among a group of participants to explore their perceptions, attitudes, and experiences.
- Example: In a case study on community development, a focus group might be conducted with residents to discuss their views on recent initiatives and their impact.
- Archival Research:
- Archival research involves examining existing records, historical documents, or artifacts to gain insights into a particular phenomenon.
- Example: A case study on the history of a landmark building may involve archival research, exploring construction records, historical photos, and maintenance logs.
- Longitudinal Studies:
- Longitudinal studies involve the collection of data over an extended period to observe changes and developments.
- Example: A case study tracking the career progression of employees in a company may involve longitudinal interviews and document analysis over several years.
- Cross-Case Analysis:
- Cross-case analysis compares and contrasts multiple cases to identify patterns, similarities, and differences.
- Example: A comparative case study of different educational institutions may involve analyzing common challenges and successful strategies across various cases.
- Ethnography:
- Ethnography involves immersive, in-depth exploration within a cultural or social setting to understand the behaviors and perspectives of participants.
- Example: A case study using ethnographic methods might involve spending an extended period within a community to understand its social dynamics and cultural practices.
- Experimental Designs (Rare):
- While less common, experimental designs involve manipulating variables to observe their effects. In case studies, this might be applied in specific contexts.
- Example: A case study exploring the impact of a new teaching method might involve implementing the method in one classroom while comparing it to a traditional method in another.
These case study research methods offer a versatile toolkit for researchers to investigate and gain insights into complex phenomena across various disciplines. The choice of methods depends on the research questions, the nature of the case, and the desired depth of understanding.
Best Practices for a Case Study in 2024
Creating a high-quality case study involves adhering to best practices that ensure rigor, relevance, and credibility. Here are some key best practices for conducting and presenting a case study:
- Clearly articulate the purpose and objectives of the case study. Define the research questions or problems you aim to address, ensuring a focused and purposeful approach.
- Choose a case that aligns with the research objectives and provides the depth and richness needed for the study. Consider the uniqueness of the case and its relevance to the research questions.
- Develop a robust research design that aligns with the nature of the case study (single-case or multiple-case) and integrates appropriate research methods. Ensure the chosen design is suitable for exploring the complexities of the phenomenon.
- Use a variety of data sources to enhance the validity and reliability of the study. Combine methods such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and surveys to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Clearly document and describe the procedures for data collection to enhance transparency. Include details on participant selection, sampling strategy, and data collection methods to facilitate replication and evaluation.
- Implement measures to ensure the validity and reliability of the data. Triangulate information from different sources to cross-verify findings and strengthen the credibility of the study.
- Clearly define the boundaries of the case to avoid scope creep and maintain focus. Specify what is included and excluded from the study, providing a clear framework for analysis.
- Include perspectives from various stakeholders within the case to capture a holistic view. This might involve interviewing individuals at different organizational levels, customers, or community members, depending on the context.
- Adhere to ethical principles in research, including obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality, and addressing any potential conflicts of interest.
- Conduct a rigorous analysis of the data, using appropriate analytical techniques. Interpret the findings in the context of the research questions, theoretical framework, and relevant literature.
- Offer detailed and rich descriptions of the case, including the context, key events, and participant perspectives. This helps readers understand the intricacies of the case and supports the generalization of findings.
- Communicate findings in a clear and accessible manner. Avoid jargon and technical language that may hinder understanding. Use visuals, such as charts or graphs, to enhance clarity.
- Seek feedback from colleagues or experts in the field through peer review. This helps ensure the rigor and credibility of the case study and provides valuable insights for improvement.
- Connect the case study findings to existing theories or concepts, contributing to the theoretical understanding of the phenomenon. Discuss practical implications and potential applications in relevant contexts.
- Recognize that case study research is often an iterative process. Be open to revisiting and refining research questions, methods, or analysis as the study progresses. Practice reflexivity by acknowledging and addressing potential biases or preconceptions.
By incorporating these best practices, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their case studies, making valuable contributions to the academic and practical understanding of complex phenomena.
Interested in learning more about the fields of product, research, and design? Search our articles here for helpful information spanning a wide range of topics!
How to Conduct a Cognitive Walkthrough for Better UX
Using affinity mapping to improve usability testing insights, ecommerce testing for a secure and user-friendly website, top ux research methods for effective usability testing.
This website may not work correctly because your browser is out of date. Please update your browser .
A case study focuses on a particular unit - a person, a site, a project. It often uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative data.
Case studies can be particularly useful for understanding how different elements fit together and how different elements (implementation, context and other factors) have produced the observed impacts.
There are different types of case studies, which can be used for different purposes in evaluation. The GAO (Government Accountability Office) has described six different types of case study:
1. Illustrative : This is descriptive in character and intended to add realism and in-depth examples to other information about a program or policy. (These are often used to complement quantitative data by providing examples of the overall findings).
2. Exploratory : This is also descriptive but is aimed at generating hypotheses for later investigation rather than simply providing illustration.
3. Critical instance : This examines a single instance of unique interest, or serves as a critical test of an assertion about a program, problem or strategy.
4. Program implementation . This investigates operations, often at several sites, and often with reference to a set of norms or standards about implementation processes.
5. Program effects . This examines the causal links between the program and observed effects (outputs, outcomes or impacts, depending on the timing of the evaluation) and usually involves multisite, multimethod evaluations.
6. Cumulative . This brings together findings from many case studies to answer evaluative questions.
The following guides are particularly recommended because they distinguish between the research design (case study) and the type of data (qualitative or quantitative), and provide guidance on selecting cases, addressing causal inference, and generalizing from cases.
This guide from the US General Accounting Office outlines good practice in case study evaluation and establishes a set of principles for applying case studies to evaluations.
This paper, authored by Edith D. Balbach for the California Department of Health Services is designed to help evaluators decide whether to use a case study evaluation approach.
This guide, written by Linda G. Morra and Amy C. Friedlander for the World Bank, provides guidance and advice on the use of case studies.
Expand to view all resources related to 'Case study'
- Broadening the range of designs and methods for impact evaluations
- Case studies in action
- Case study evaluations - US General Accounting Office
- Case study evaluations - World Bank
- Comparative case studies
- Compasss: Comparative methods for systematic cross-case analysis
- Dealing with paradox – Stories and lessons from the first three years of consortium-building
- Designing and facilitating creative conversations & learning activities
- Estudo de caso: a avaliação externa de um programa
- Evaluation tools
- Evaluations that make a difference
- Introduction to qualitative research methodology
- Methods for monitoring and evaluation
- Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice
- Reflections on innovation, assessment and social change processes: A SPARC case study, India
- Toward a listening bank: A review of best practices and the efficacy of beneficiary assessment
- UNICEF webinar: Comparative case studies
- Using case studies to do program evaluation
'Case study' is referenced in:
- Week 32: Better use of case studies in evaluation
Back to top
© 2022 BetterEvaluation. All right reserved.
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
by Nitin Nohria

Summary .
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
Partner Center

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Stylistic devices
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources

Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Case Study – Definition, Types & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A case study is a research method that delves deeply into a specific instance to analyze its complexities and draw broader insights applicable to similar situations. Through a structured methodology , encompassing data collection, analysis, and interpretation, case studies offer a comprehensive understanding of real-life phenomena within their natural contexts. This approach allows researchers to explore intricate details, uncover patterns, and derive valuable implications.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Case study in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Case study
- 3 Types of case studies
- 4 When to perform a case study
- 5 Conducting a case study
- 6 Pros and cons
Case study in a nutshell
A case study is a detailed examination of a particular project, event, individual, or organization over a defined period. It focuses on the complexities and outcomes of real-life situations, providing an in-depth understanding of the factors leading to successes or failures.
Definition: Case study
A case study is a research methodology that involves an in-depth, detailed examination of a case or cases within a real-life context. It is used across various disciplines, including psychology, sociology, education, business, and law. The purpose of a case study is to explore and understand complex issues, processes, or behaviors by analyzing them from multiple angles and using multiple sources of evidence. Case studies are particularly useful for investigating phenomena that cannot be studied through experimental methods, offering insights into aspects of the subject that might be overlooked by other research methodologies.
Case studies are valuable for generating hypotheses that can be tested with other methods, developing theories, and providing practical solutions to real-world problems. They are particularly effective in capturing the nuances and complexities of situations that are too complex for more straightforward research designs . The following outlines the key characteristics of case studies.
Depth and detail
Contextual analysis, qualitative (and quantitative) data, multiple sources of evidence, specificity, flexibility.
Case studies provide a thorough understanding of the case in question, including its historical background, current situation, and the various factors influencing it.
They consider the subject’s context, recognizing that behaviors, decisions, and outcomes are often deeply influenced by environmental, social, and historical factors.
A mixed-methods case study approach relies on qualitative data like interviews , observations, and document analysis, and also includes quantitative data to support findings.
Case studies typically draw on various data sources, such as documents, archival records, interviews, direct observation, participant observation, and physical artifacts, to provide a comprehensive view of the overall case.
They focus on a specific case, event, individual, or organization, allowing for a detailed examination that might not be feasible with broader research methods.
Case study research is flexible, allowing researchers to adapt their approaches as new insights emerge during the investigation.
The goal is to gain insights and a deeper understanding of the case and its broader implications, rather than to generalize findings to all cases.
Types of case studies
Case studies vary widely in focus and purpose, adapting to the needs of different academic disciplines and professional fields. Each type of case study serves a different purpose and can be chosen based on the specific objectives of the research, the nature of the subject being studied, and the available resources. They are a powerful tool for researchers and practitioners alike, offering detailed insights and a deep understanding of complex phenomena, behaviors, and processes within their real-life contexts. Despite this diversity, they can generally be categorized into several main types based on their intent and approach.
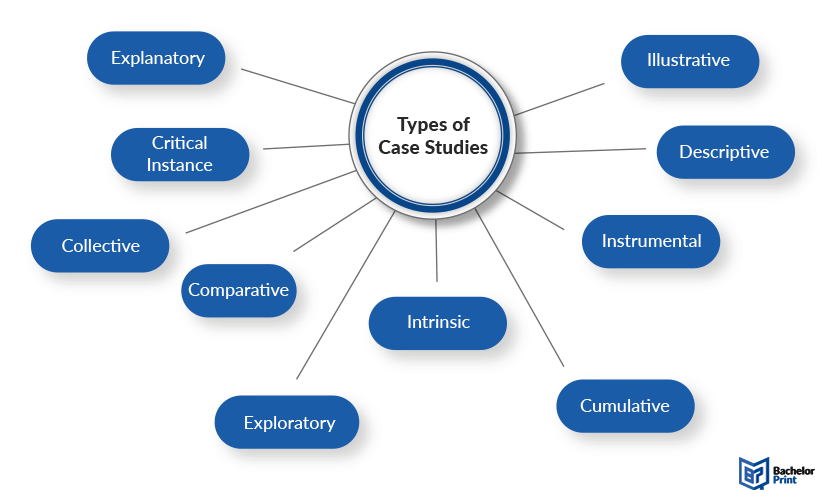
Collective case studies
A collective case study also referred to as a multiple case study, involves the detailed examination and analysis of several cases simultaneously or sequentially to investigate a phenomenon, condition, or situation. These cases are chosen because they are expected to exhibit particular features or outcomes significant to the research question or hypothesis. By studying multiple cases, researchers aim to gain a deeper, more comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand, identifying patterns, variations, and insights that might not be evident when conducting single case study research alone.
Characteristics
- Involves multiple cases, allowing for a comparison to identify similarities between different instances of the phenomenon.
- The cases are purposefully selected based on their ability and extent to provide insight into the research question of the case.
- Aims to understand the phenomenon within its real-life context, recognizing the influence of various complex factors.
- Data are individually and in aggregate analyzed, allowing researchers to identify overarching patterns across cases.
- Variability by acknowledging and exploring the differences between cases to understand the spectrum of possible outcomes.
- Enhances generalizability: Examining multiple cases, allows researchers to test the finding of one case against others, enhancing the generalizability of the observations.
- Rich insights: Collective case studies provide rich, multifaceted, contextual insights into the studied phenomenon, ensuring the possibility to investigate the complexity of real-life situations.
- Theory development: These studies are particularly useful for developing theories, allowing researchers to refine and build upon existing ones based on the findings.
Topic: Patient experiences with telehealth services
- Objective: Exploring patient satisfaction and challenges faced when using telehealth services across various demographics.
- Cases: Patients from different age groups, health conditions, and regions who have used telehealth services for at least six months.
- Result: A comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing patient satisfaction with telehealth, including technological literacy, communication quality, and access to care, informing improvements in telehealth practices.
Comparative case studies
A comparative case study is a research approach that involves the detailed analysis and comparison of two or more cases, which can be organizations, communities, individuals, events, etc. It aims to investigate and explore similarities, contrasts, and pattern variations across cases to gain a deeper understanding of the studied topic and why certain phenomena vary under different conditions.
- Systematically examines the differences and similarities between cases to draw insights that may not emerge from one case.
- Serves as a cornerstone for developing, testing, or refining existing theories or generating new theories and concepts.
- The cases are carefully selected based on the variations in dimensions to understand the influence of different conditions.
- Does not sacrifice the depth of understanding each case individually, allowing researchers to consider the contribution of contextual factors.
- This type of case study includes qualitative and quantitative methods and approaches for collecting and analyzing data.
- Rich insights: They provide contextual and detailed insights into the dynamics of each case, which is crucial for understanding complex phenomena.
- Theory development: Comparative case studies are conducive to testing existing theories in different contexts and building new theories based on observed patterns.
- Flexibility: Methods and approaches can be adapted as the study progresses, allowing for the exploration of unexpected findings or new research questions.
Topic: Impact of socioeconomic factors on academic achievement
- Objective: Exploring how socioeconomic status (SES) influences academic achievement in primary schools.
- Case A: Primary school located in an affluent neighborhood with high-income families.
- Case B: Primary school located in an area with primarily low-income families.
- Result: Emphasis on the importance of addressing disparities in resources, support systems, and community factors to ensure equitable educational opportunities for all the students.
Critical instance case studies
A critical instance case study entails focused research that investigates one or two instances to understand one occurrence rather than generalizing the situation. It explores a unique, unusual, or particularly informative phenomenon. These cases are typically chosen because they are expected to provide insight into an area of interest or to challenge or refine existing theoretical concepts and assumptions. The goal of this method is to understand the complexity and uniqueness of critical cases and how they inform broader understandings and generalizations about a topic.
- Dives into a specific case(s) to uncover the intricacies that contribute to its unique characteristics.
- Useful for examining phenomena that are too complex or rare to be captured through broader studies.
- Cases are selected for their potential to provide insight into an issue or to challenge universal opinions.
- A detailed qualitative analysis, but quantitative methods can also complement the examination.
- Creates a balance between the uniqueness of the case and the potential for making broader inferences.
- In-depth understanding: Critical instance case studies aim to provide an in-depth and nuanced understanding of a specific case or cases, underscoring the contextual factors that influence outcomes.
- Theory development: By focusing on cases that are expected to challenge or refine theoretical assumptions, this type of study contributes to developing and refining theories.
- Flexibility: The methods used can be adapted to the specific demands of the case, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of the unique aspects of the critical instance.
Topic: Impact of innovative teaching methods on student engagement in a rural school
- Objective: Investigating how the implementation of project-based learning in a rural primary school affects student engagement and learning outcomes.
- Case: A primary school in a rural area that has recently implemented project-based learning across all grades.
- Result: Detailed analysis of the challenges and successes of implementing innovative teaching methods in a resource-constrained environment, highlighting the role of community support and teacher adaptability in fostering positive educational outcomes and results.
Cumulative case studies
A cumulative case study involves aggregating information from several sites collected at different times. The goal is to collect past studies to increase generalization without costing more time or money on new, possibly repetitive studies. It synthesizes findings from multiple cases over adequate time to understand a broader phenomenon or to identify patterns and trends. These studies are chosen because their cumulative evidence can provide a more convincing and comprehensive insight into a subject of interest, supporting or contradicting theoretical assumptions through a wider lens of observation.
- Aggregates findings from different cases and existing sources to uncover common themes.
- Specifically, valuable for integrating and comparing data from already studied situations.
- Case selection based on whether they can compare and contrast multiple instances.
- Employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, facilitating a more comprehensive analysis.
- Strike a balance between diversity and the potential for generalization.
- Comprehensive synthesis: This approach aims to synthesize data across multiple instances, offering a broader perspective on the subject matter that highlights commonalities and differences.
- Pattern identification: By examining various cases collectively, this approach seeks to identify underlying patterns, trends, and themes that might not be apparent in single case study research.
- Cost-effectiveness: Accumulating evidence from existing studies, allows for a more resource-efficient way to gain a wide-ranging understanding. Thereby, the expenses and time of conducting new, individual studies can also be avoided.
Topic: Effectiveness of remote learning across different socio-economic backgrounds
- Objective: Analyzing how remote learning during school closures impacted students’ academic performance across various socio-economic backgrounds.
- Cases: Multiple schools from diverse socio-economic areas that implemented remote learning during the same period.
- Result: A comparative analysis revealing patterns of engagement, accessibility issues, and academic outcomes, highlighting the importance of addressing equity in access to technology and learning resources.
Descriptive case studies
A descriptive case study, a process-oriented case study, is a research approach focused on providing a detailed account and analysis of a specific case (or cases) within its real-life context. Unlike other types of case studies that might seek to test hypotheses or understand causal relationships, descriptive research aims to document the unique characteristics, conditions, processes, and outcomes of the case in question. The primary goal is to describe the phenomenon in depth and detail, offering a comprehensive understanding of the context and variables involved.
- Captures the nuances, providing a rich, detailed description that covers various aspects.
- Considers the environment of the case, recognizing the context’s significant influences.
- Employs a mixed-methods case study approach using qualitative and quantitative data.
- Identifies patterns that may inform future research, like hypotheses for causal research or theories.
- Illustrates a particular phenomenon within its real-world context, providing valuable insights.
- Comprehensive documentation: It provides an exhaustive description of a case, which involves documenting contexts, processes, and results, aiming to capture complexities.
- Insightful understanding: Descriptive case studies shed light on how and why things happen under specific circumstances through detailed examination. Their detailed outcomes help to inform practice, policy, or further research.
- Pattern identification: While not primarily focusing on hypothesis testing or theory development, descriptive research often suggests areas for further research by identifying patterns.
Topic: The role of community gardens in urban food security
- Objective: Exploring the impact of community gardens on food security in urban areas extensively, seeking to understand how the gardens contribute to the availability and accessibility of fresh produce for residents.
- Cases: Three community gardens that are located in different urban neighborhoods, each with varying levels of access to supermarkets or fresh food markets.
- Result: Detailed description and comparison of each garden’s operation, community involvement, challenges faced, and the benefits realized in terms of food security, emphasizing the importance of community leadership, support from local organizations, and adaptability of garden practices to local needs.
Explanatory case studies
Similar to the descriptive type, an explanatory case study is also a process-oriented case study, that seeks to explain the underlying mechanisms or reasons behind a particular phenomenon or set of outcomes within its real-life context. Unlike descriptive case studies, which focus primarily on providing a detailed account of a specific case, explanatory case studies aim to uncover how and why certain events occur, offering insights into causal pathways and processes leading to a particular outcome.
- Process-oriented case study that explores the causal mechanisms that lead to certain outcomes.
- Allows researchers to examine complex real-life contexts in their natural setting.
- Uses multiple sources of evidence, like qualitative data and sometimes quantitative data.
- Frequently employs existing theoretical framework to guide their analysis and explain findings.
- Contributes to the development and refinement of theoretical concepts, offering practical insights.
- Uncovering causal relationships: It explores the causal mechanisms that lead to certain outcomes within a case or across cases, seeking to elucidate the processes and factors that contribute to the studied topic.
- Theory development: This type of case study can be employed to test existing theories in new contexts or to refine and develop new theoretical frameworks based on its findings.
- Informing policy and practice: Provides valuable insights that can inform policy-making, strategy, and practical interventions, emphasizing its applicability to real-world challenges.
Topic: Impact of remote work on employee productivity and well-being
- Objective: Aiming to explain the causal relationships between remote work and its effects on employee productivity and well-being, seeking to uncover the mechanisms through which remote work influences these outcomes and to identify the conditions under which the effects are most pronounced.
- Cases: Examining three companies in different industries, technology, finance, and education, that implemented long-term remote work arrangements as a response to external factors like the global pandemic.
- Result: The comparative analysis reveals that the presence of supportive digital infrastructure, degree of flexibility in work arrangements, and opportunities for informal interactions are critical factors influencing the outcome of remote work policies, suggesting that it can enhance the productivity and well-being of employees.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are qualitative research methods used to conduct preliminary projects for little-understood phenomena to develop hypotheses and establish research priorities. Unlike explanatory or descriptive case studies that aim to explain the aspects of specific cases, exploratory case studies are often conducted when a problem is not clearly defined, and there is a need for further investigation to understand the context.
- Serves as an initial step in researching a new area, gathering as much information as possible.
- Flexible research design, allowing for adjustments as new insights are gained in the process.
- Generates hypotheses or theories that can be applied and tested in further research.
- Relies on qualitative data collection methods to gain an understanding of the case in real-life context.
- Foundation for explanatory studies, experimental designs , or large-scale quantitative research.
- Comprehensive understanding : Aims to gain a clear understanding of the studied phenomenon, especially when it is new, complex, or not well defined.
- Generating hypotheses: Through detailed observation, data collection, and analysis, it is geared towards generating hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
- Research priorities: Determines which aspects of the case merit further research by uncovering the most significant issues, challenges, or opportunities in association.
Topic: The adoption of virtual reality (VR) technologies in higher education
- Objective: Aiming to explore how and why higher education institutions are adopting VR technologies for teaching and learning purposes. The study seeks to understand the motivations, processes, challenges, and initial impacts of VR adoption on pedagogical practices and student engagement.
- Cases: Examining three universities that have recently integrated VR technologies into their curriculum, each representing a different approach such as for enhancing engineering and architecture courses, medical and healthcare training, and art and history courses.
- Result: The exploratory research uncovers various motivations, such as the desire to enhance student learning experiences, improve student engagement, and prepare students for future technological landscapes. Challenges identified across the cases include technical issues, high costs or implementation, and the need for faculty training and support.
Illustrative case studies
An illustrative case study primarily describes and demonstrates a particular phenomenon in a detailed and understandable way. It utilizes a descriptive approach, aiming to make the unfamiliar familiar by providing concrete examples that illuminate broader themes or issues. This type of case study is primarily used to provide insight into and highlight specific aspects of a research problem, helping to convey the complexities of real-life situations through the detailed examination of one or more instances.
- Provides a comprehensive description of the phenomenon that occurs within the case(s) being studied.
- Used as educational tools in various fields to help visualize complex theories and concepts.
- Simplifies particular points within a larger analysis, supporting the understanding of broader principles.
- Presents complex issues in a clear and accessible manner by focusing on specific instances.
- Primarily descriptive research, but also serves as a preliminary step towards further research.
- Clarification of complex phenomena: Aims to break down complex processes, making them more understandable by providing a detailed view.
- Introduction of issues: Introduces common and uncommon issues through detailed storytelling, shedding light on specific challenges or successes.
- Theory development: Enhances theoretical knowledge by providing concrete examples that support or exemplify theoretical concepts or frameworks.
Topic: Digital transformation in small businesses during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Objective: Aiming to illustrate the strategies and challenges small businesses faced while undergoing digital transformation due to the pandemic by highlighting how these businesses adapted to the sudden need for digital operations, the impact of these changes on their operations, and the lessons learned throughout.
- Case A: A family-owned restaurant that transitioned to online orders and delivery.
- Case B: A local bookstore that implemented an e-commerce platform for online sales and virtual book clubs.
- Case C: A small fitness studio that shifted to offering online workout classes.
- Result: The collective insights from these cases demonstrate the critical role of digital literacy, the need for flexible business models, and the importance of maintaining customer relationships during the transition. Conclusively, the study findings underscore the potential of digital transformation to not only sustain small businesses during crises but also to catalyze growth and innovation.
Instrumental case studies
An instrumental case study is an individual case study, focusing on a single subject to gain a broader understanding of a phenomenon. In contrast to other types of case studies that aim to describe or explain the case in great detail, instrumental case studies use the particular case as an instrument to understand something else. In other words, the case merely plays a supportive role in facilitating insight into larger issues or refining theoretical concepts.
- The case allows for thorough exploration and understanding of the broader phenomenon at hand.
- Instrumental case studies aim to extend findings beyond the case to address a broader issue.
- The research questions are framed to explore the broader phenomenon rather than just the specifics.
- Uses multiple sources of data and data collection methods within a real-life context.
- Develops theories by examining the representation of the broader issues in the specific case.
- Broader insights into particular issues: Uses the specific case as a vehicle to explain a broader phenomenon, contributing to refining theoretical frameworks.
- Informs policy or practice: Provides valuable insights that can guide decision-making processes that address the complexities of real-world situations.
- Identifies patterns: Explores the case in-depth to identify patterns that may apply to similar contexts by a detailed assessment of the case as a representative instance.
Topic: Integration of technology in high school education
- Objective: Aiming to explore the effect of integrating technology into high school education on student engagement and academic performance to understand how the use of technology and digital platforms can enhance the learning experience, foster engagement, and improve outcomes in high school settings.
- Cases: Examining three specific classrooms, such as science, literature, and mathematics, within the same high school that is known for integrating technology across all subject areas.
- Result: The study findings reveal that technology integration, when effectively implemented, significantly enhances student engagement and academic performance across the various subject areas. Thereby, it underscores the importance of strategic planning, professional development for teachers, and the selection of appropriate technological tools that align with educational objectives.
Intrinsic case studies
As opposed to instrumental case studies that aim to understand a broader phenomenon beyond the case, an intrinsic case study primarily focuses on the case itself. An intrinsic case study is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because it presents a unique phenomenon that is worth exploring thoroughly on its own merits. In other words, an intrinsic case study is used when a case is revealing, distinctive, or intriguing in a way that warrants detailed examination.
- An intrinsic case study focuses on the idiosyncrasies and specifics of a case due to its uniqueness.
- Captures the essence with a profound description of the case’s contexts, processes, and outcomes.
- The insights gained from intrinsic case studies can be primarily applied to the case itself.
- Understanding the case from various perspectives, involving a flexible research process.
- Intrinsic case studies primarily use qualitative research methods to gather rich and contextual data.
- Insight into the particular case: Aims to gain a deep understanding of the case for its own sake by focusing on the uniqueness and complexities of the case.
- Explorative and interpretative: Delves into outstanding features, challenges, conditions, and opportunities of the case to uncover its distinct intricacies.
- Contribution to theories: Through the detailed study of the case, patterns may be determined that offer insights, resonating with wider concepts or theories.
Topic: Transformation of a historic library into a community hub
- Objective: Aiming to explore the transformation of a historic library in a small town into a vibrant community hub by focusing on this particular library due to its unique position in the community’s history, architectural heritage, and the innovative approach it has taken to evolve beyond traditional library services.
- Case: It revolves around the Elmwood Library, built in the early 1900s and known for its architectural significance and deep-rooted place in the town’s history. Over time, its role and relevance faced challenges due to digitalization and the change in community needs. Thus, the study examines the redefinition of becoming a community hub of the library, focusing on digital access, community engagement, and preservation of historical essence.
- Result: The study findings uncover the multifaceted impact of Elmwood Library’s transformation by highlighting the successful navigation of its historical preservation alongside modernization to meet current community needs. Key outcomes include increased community engagement, enhanced digital literacy, and the library’s role in fostering a sense of communal identity.
When to perform a case study
A case study is the right research method for examining and gaining precise, contextual insights about a real-world problem or scenario. It gives researchers a method of studying the main characteristics, definitions, and inferences about a specific individual, group, event, or organization. The decision whether to perform a case study should be driven by the nature of the research question, objectives, and the value of gaining a contextualized understanding of the issues at hand. The following illustrates a few scenarios and research objectives that typically warrant the use of a case study.
Complex phenomenon
Rare & unique cases, testing & generating theories.
When the goal is to explore a complex phenomenon in detail, particularly within its real-life context, case studies serve as ideal methods for investigating and explaining multifaceted issues thoroughly.
Case study research is also relevant to conduct to examine rare or unique conditions that are not easily replicated or found in larger populations. Examples are studying a rare disease, unique institution, or significant event.
When you test theoretical models or hypotheses within real-life contexts, case studies allow you to observe how theoretical principles play out in practice, providing valuable insights into the applicability and limitations of these theories. Case studies also assist in generating new theories because existing theories do not adequately explain a phenomenon. They can identify patterns and relationships that lead to the formulation of new theoretical propositions through elaborate analysis.
Teaching and policy development
Prospective case studies, multifaceted approach.
Case studies are often relevant to use in educational settings to provide real-life examples for students to analyze. They are particularly valuable for policymakers and practitioners seeking an in-depth understanding of a scenario to inform decision-making processes.
Prospective case studies have the main objective of observing changes over an adequate time period within a specific context or group. Thus, prospective case studies are suitable for conducting research over extended periods to track developments, understand cause-and-effect relationships, and observe the impact of interventions.
Case studies are also relevant for research that benefits from a multi-perspective analysis, as they enable the use of multiple data sources and methods such as interviews, observations, and document analysis to provide a comprehensive view of the studied subject.
Conducting a case study
The process of conducting a case study can be divided into five crucial stages such as defining the case(s), selecting the case(s), collecting and analysis of data, interpreting data, and reporting the findings.
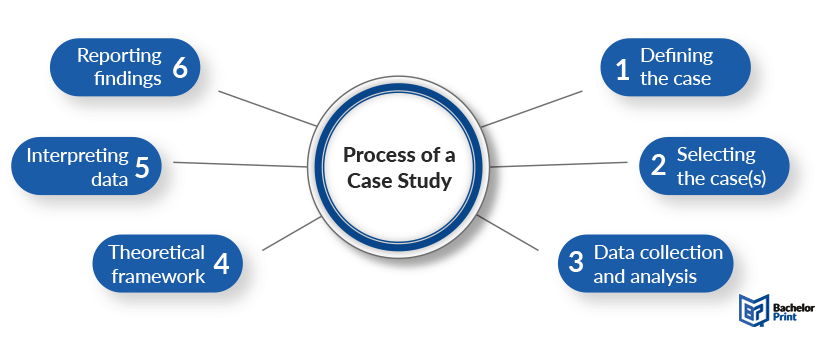
Defining the case(s)
Defining the case(s) for a case study involves specifying the unit of analysis or the main entity that you are investigating. This stage is crucial as it sets the boundaries of what is to be studied, guiding the focus of the research, and shaping the research questions, data collection, and analysis. A well-defined case is essential for ensuring the research is manageable, coherent, and capable of addressing the objectives effectively. It also requires a clear understanding of the purpose of the study research, context, and perspectives from which it will be explored.
In terms of the nature of the case, you must clarify whether the case is a group, organization, individual, event, or geographical unit. This in turn will affect the type of data and evidence that will be collected and further affect the interpretation of results. In addition to this, the scope of the case determines the time period and geographical boundaries.
Selecting the case
Selecting the case is a crucial stage, as it significantly influences the research questions, problem statement , depth of the research, and potential contribution to existing knowledge. Thus, it is imperative to choose a specific focus to ground your research. Key considerations in selecting the case are:
- Clearly define what you want to achieve with your case study; What are the research objectives?
- Determine the type of case study, as this will influence the type of case you select.
- Develop criteria that the case must meet to ensure it is suitable for your study.
- Identify cases that may have rich potential for contributing to your research objectives.
- Assess the potential cases against your selection criteria by considering the pros and cons.
- Offer the potential to answer your research questions, meet the aims, and ensure access to data.
- Justify how the case meets your selection criteria and how it will assist in reaching the research objectives.
- Ensure the case adheres to ethical considerations , like consent and confidentiality.
- Consider the feasibility of conducting the case such as resources, adequate time, and access to information.
Case studies usually focus on outliers rather than deliberate sampling techniques. Thus, they often do not require representative cases or random samples before research.
Collecting and analysis of data
For a case study approach, data is typically collected systematically, gathering detailed and comprehensive information that will support the analysis and conclusion of the study. This stage of the process is essential, as the relevance of the data impacts the depth and internal validity of the case study findings.
Case studies often employ multiple data sources or methods (data triangulation) that are primarily qualitative. Common methods include semi-structured interviews or structured interviews , direct observations , analyzing relevant documents, focus groups , or audiovisual materials. These types of qualitative methods can undergo thematic analysis , coding, or narrative analysis , depending on their relevance.
In some cases, quantitative methods are used to complement qualitative data to provide a broader understanding of the case study and enhance internal validity. These methods involve surveys and questionnaires or existing data sets that are relevant to the study for secondary data analysis. For these, you can employ, e.g., statistical analysis or trend analysis. Utilizing a mixed-methods case study approach offers the opportunity to provide a deeper and elaborate overview of the study.
Theoretical framework and interpreting data
Case studies overlook general theories in favor of specific details. A theoretical framework serves as the foundation that navigates every aspect of the study, ranging from data collection to data analysis and assists in interpreting findings within a broader context. Understanding its application in interpreting data is crucial for creating meaningful and impactful research.
The theoretical framework entails a variety of interrelated concepts and theories that guide your research, determining what will be measured and what statistical relationships may be looked for. It provides a general set of principles, explanations, and definitions that help organize the entire research process. A theoretical framework can be used to:
- Challenge an existing theory by investigating deviance that is not considered in the universal assumptions.
- Expand on established theories by proposing new ideas that should be included.
- Exemplify a given theory by showing the relationship between the case and the theory.
- Explain the theory for your research, grounding your study in a conceptual context.
- Guide the research question , influencing the research design, including what data to collect and interpret.
- Assist in identifying the limits to those generalizations your study can and cannot make.
- Provide a rationale for your research, indicating why it is a worthwhile contribution to knowledge.
Reporting findings
Reporting the findings of your case study poses one of the last crucial stages of finalizing your study. It involves presenting your data and analyses in a structured and compelling way and requires careful consideration of your audience, whether they are academics, industry professionals, or other stakeholders. This section is the heart of your report and should be given careful attention. Here is a short overview of the structure of reporting findings.
- Organize by theme or research question
- Support the findings with evidence from your data
- Incorporate tables, graphs, and charts to visualize data
- Present detailed narratives of events and processes clearly
For effective reporting, aim for clear and concise expression, explaining complex concepts clearly, and avoiding unnecessary jargon. Also, maintaining consistency in terms of formatting and presentation style throughout the report is vital to keeping academic integrity. Keep in mind that the goal fo your case study report is not just to present your findings, but to communicate their significance and implications effectively. Thus, tailoring your report to your audience in an engaging manner, will draw the reader into the study and thereby, enhance its impact and value.
Pros and cons
Case studies can take on the shapes of at least four research designs and can be associated with an array of types, each leading to different applications. Nonetheless, understanding their unique epistemological and ontological assumptions is important for the substantial methodological differences, they entail. The following table outlines the general benefits and limitations of using a case study for your research.
What are the four key sections of a case study?
A case study entails at least four sections:
- Introduction
- Body: background information, explaining the purpose, presenting the findings
What is the case study method in research?
The case study method is an in-depth investigation of a research subject, individual, or group. It is a focused research method that analyzes the causes and consequences of a specific phenomenon. A case study facilitates the exploration of a real-life issues within a defined context, using multiple date sources.
What are the types of case study?
Here is a list of the types of case studies:
- Comparative
- Critical instance
- Descriptive
- Explanatory
- Exploratory
- Illustrative
- Instrumental
What are examples of case studies?
Case studies are widely used in psychology and clinical contexts, analyzing rare or unique conditions. Popular ones are:
- Phineas Gage (the man who hat a railway spike through his head) – John Martin Marlow
- Little Hans and The Rat Man – Sigmund Freud
What is a case study in psychology?
In psychology, it is typically an individual case study, focusing on a single person, community, or event that relies on data in clinical contexts drawn from psychometric testing, observations, interviews, experiments, and existing case studies.
What are the limitations of a case study?
Case studies are often criticized for their subjectivity, bias, or lack of rigor, as they typically rely heavily on the researcher’s interpretations and selection of data, which is often influences by personal views, preferences, or assumptions.
Totally satisfied of the product overall quality, delivery (no possible...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
What is a Case Study? A case study method involves a detailed examination of a single subject, such as an individual, group, organization, event, or community, to explore and understand complex issues in real-life contexts. By focusing on one specific case, researchers can gain a deep understanding of the factors and dynamics at play ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
What is case study methodology? It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. In this post find definitions and a collection of multidisciplinary examples.
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a single person, group, event, or community. This research method involves intensively analyzing a subject to understand its complexity and context.
A case study is an in-depth analysis of specific, real-world situations or the scenarios inspired by them. Both teachers and professionals use them as training tools. They're used to present a problem, allowing individuals to interpret it and provide a solution.
A case study is defined as an in-depth analysis of a particular subject, often a real-world situation, individual, group, or organization. It is a research method that involves the comprehensive examination of a specific instance to gain a better understanding of its complexities, dynamics, and context.
A research design that focuses on understanding a unit (person, site or project) in its context, which can use a combination of qualitative and quantitative data.
Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment...
A case study is the right research method for examining and gaining precise, contextual insights about a real-world problem or scenario. It gives researchers a method of studying the main characteristics, definitions, and inferences about a specific individual, group, event, or organization.