- Hands-on Python Tutorial »
- 1. Beginning With Python »

1.6. Variables and Assignment ¶
Each set-off line in this section should be tried in the Shell.
Nothing is displayed by the interpreter after this entry, so it is not clear anything happened. Something has happened. This is an assignment statement , with a variable , width , on the left. A variable is a name for a value. An assignment statement associates a variable name on the left of the equal sign with the value of an expression calculated from the right of the equal sign. Enter
Once a variable is assigned a value, the variable can be used in place of that value. The response to the expression width is the same as if its value had been entered.
The interpreter does not print a value after an assignment statement because the value of the expression on the right is not lost. It can be recovered if you like, by entering the variable name and we did above.
Try each of the following lines:
The equal sign is an unfortunate choice of symbol for assignment, since Python’s usage is not the mathematical usage of the equal sign. If the symbol ↤ had appeared on keyboards in the early 1990’s, it would probably have been used for assignment instead of =, emphasizing the asymmetry of assignment. In mathematics an equation is an assertion that both sides of the equal sign are already, in fact, equal . A Python assignment statement forces the variable on the left hand side to become associated with the value of the expression on the right side. The difference from the mathematical usage can be illustrated. Try:
so this is not equivalent in Python to width = 10 . The left hand side must be a variable, to which the assignment is made. Reversed, we get a syntax error . Try
This is, of course, nonsensical as mathematics, but it makes perfectly good sense as an assignment, with the right-hand side calculated first. Can you figure out the value that is now associated with width? Check by entering
In the assignment statement, the expression on the right is evaluated first . At that point width was associated with its original value 10, so width + 5 had the value of 10 + 5 which is 15. That value was then assigned to the variable on the left ( width again) to give it a new value. We will modify the value of variables in a similar way routinely.
Assignment and variables work equally well with strings. Try:
Try entering:
Note the different form of the error message. The earlier errors in these tutorials were syntax errors: errors in translation of the instruction. In this last case the syntax was legal, so the interpreter went on to execute the instruction. Only then did it find the error described. There are no quotes around fred , so the interpreter assumed fred was an identifier, but the name fred was not defined at the time the line was executed.
It is both easy to forget quotes where you need them for a literal string and to mistakenly put them around a variable name that should not have them!
Try in the Shell :
There fred , without the quotes, makes sense.
There are more subtleties to assignment and the idea of a variable being a “name for” a value, but we will worry about them later, in Issues with Mutable Objects . They do not come up if our variables are just numbers and strings.
Autocompletion: A handy short cut. Idle remembers all the variables you have defined at any moment. This is handy when editing. Without pressing Enter, type into the Shell just
Assuming you are following on the earlier variable entries to the Shell, you should see f autocompleted to be
This is particularly useful if you have long identifiers! You can press Alt-/ several times if more than one identifier starts with the initial sequence of characters you typed. If you press Alt-/ again you should see fred . Backspace and edit so you have fi , and then and press Alt-/ again. You should not see fred this time, since it does not start with fi .
1.6.1. Literals and Identifiers ¶
Expressions like 27 or 'hello' are called literals , coming from the fact that they literally mean exactly what they say. They are distinguished from variables, whose value is not directly determined by their name.
The sequence of characters used to form a variable name (and names for other Python entities later) is called an identifier . It identifies a Python variable or other entity.
There are some restrictions on the character sequence that make up an identifier:
The characters must all be letters, digits, or underscores _ , and must start with a letter. In particular, punctuation and blanks are not allowed.
There are some words that are reserved for special use in Python. You may not use these words as your own identifiers. They are easy to recognize in Idle, because they are automatically colored orange. For the curious, you may read the full list:
There are also identifiers that are automatically defined in Python, and that you could redefine, but you probably should not unless you really know what you are doing! When you start the editor, we will see how Idle uses color to help you know what identifies are predefined.
Python is case sensitive: The identifiers last , LAST , and LaSt are all different. Be sure to be consistent. Using the Alt-/ auto-completion shortcut in Idle helps ensure you are consistent.
What is legal is distinct from what is conventional or good practice or recommended. Meaningful names for variables are important for the humans who are looking at programs, understanding them, and revising them. That sometimes means you would like to use a name that is more than one word long, like price at opening , but blanks are illegal! One poor option is just leaving out the blanks, like priceatopening . Then it may be hard to figure out where words split. Two practical options are
- underscore separated: putting underscores (which are legal) in place of the blanks, like price_at_opening .
- using camel-case : omitting spaces and using all lowercase, except capitalizing all words after the first, like priceAtOpening
Use the choice that fits your taste (or the taste or convention of the people you are working with).
Table Of Contents
- 1.6.1. Literals and Identifiers
Previous topic
1.5. Strings, Part I
1.7. Print Function, Part I
- Show Source
Quick search
Enter search terms or a module, class or function name.

Python Numerical Methods

This notebook contains an excerpt from the Python Programming and Numerical Methods - A Guide for Engineers and Scientists , the content is also available at Berkeley Python Numerical Methods .
The copyright of the book belongs to Elsevier. We also have this interactive book online for a better learning experience. The code is released under the MIT license . If you find this content useful, please consider supporting the work on Elsevier or Amazon !
< 2.0 Variables and Basic Data Structures | Contents | 2.2 Data Structure - Strings >
Variables and Assignment ¶
When programming, it is useful to be able to store information in variables. A variable is a string of characters and numbers associated with a piece of information. The assignment operator , denoted by the “=” symbol, is the operator that is used to assign values to variables in Python. The line x=1 takes the known value, 1, and assigns that value to the variable with name “x”. After executing this line, this number will be stored into this variable. Until the value is changed or the variable deleted, the character x behaves like the value 1.
TRY IT! Assign the value 2 to the variable y. Multiply y by 3 to show that it behaves like the value 2.
A variable is more like a container to store the data in the computer’s memory, the name of the variable tells the computer where to find this value in the memory. For now, it is sufficient to know that the notebook has its own memory space to store all the variables in the notebook. As a result of the previous example, you will see the variable “x” and “y” in the memory. You can view a list of all the variables in the notebook using the magic command %whos .
TRY IT! List all the variables in this notebook
Note that the equal sign in programming is not the same as a truth statement in mathematics. In math, the statement x = 2 declares the universal truth within the given framework, x is 2 . In programming, the statement x=2 means a known value is being associated with a variable name, store 2 in x. Although it is perfectly valid to say 1 = x in mathematics, assignments in Python always go left : meaning the value to the right of the equal sign is assigned to the variable on the left of the equal sign. Therefore, 1=x will generate an error in Python. The assignment operator is always last in the order of operations relative to mathematical, logical, and comparison operators.
TRY IT! The mathematical statement x=x+1 has no solution for any value of x . In programming, if we initialize the value of x to be 1, then the statement makes perfect sense. It means, “Add x and 1, which is 2, then assign that value to the variable x”. Note that this operation overwrites the previous value stored in x .
There are some restrictions on the names variables can take. Variables can only contain alphanumeric characters (letters and numbers) as well as underscores. However, the first character of a variable name must be a letter or underscores. Spaces within a variable name are not permitted, and the variable names are case-sensitive (e.g., x and X will be considered different variables).
TIP! Unlike in pure mathematics, variables in programming almost always represent something tangible. It may be the distance between two points in space or the number of rabbits in a population. Therefore, as your code becomes increasingly complicated, it is very important that your variables carry a name that can easily be associated with what they represent. For example, the distance between two points in space is better represented by the variable dist than x , and the number of rabbits in a population is better represented by nRabbits than y .
Note that when a variable is assigned, it has no memory of how it was assigned. That is, if the value of a variable, y , is constructed from other variables, like x , reassigning the value of x will not change the value of y .
EXAMPLE: What value will y have after the following lines of code are executed?
WARNING! You can overwrite variables or functions that have been stored in Python. For example, the command help = 2 will store the value 2 in the variable with name help . After this assignment help will behave like the value 2 instead of the function help . Therefore, you should always be careful not to give your variables the same name as built-in functions or values.
TIP! Now that you know how to assign variables, it is important that you learn to never leave unassigned commands. An unassigned command is an operation that has a result, but that result is not assigned to a variable. For example, you should never use 2+2 . You should instead assign it to some variable x=2+2 . This allows you to “hold on” to the results of previous commands and will make your interaction with Python must less confusing.
You can clear a variable from the notebook using the del function. Typing del x will clear the variable x from the workspace. If you want to remove all the variables in the notebook, you can use the magic command %reset .
In mathematics, variables are usually associated with unknown numbers; in programming, variables are associated with a value of a certain type. There are many data types that can be assigned to variables. A data type is a classification of the type of information that is being stored in a variable. The basic data types that you will utilize throughout this book are boolean, int, float, string, list, tuple, dictionary, set. A formal description of these data types is given in the following sections.
Assignment Statements
Learn about assignment statements in Python.
- Assignment shortcuts
- Walrus operator
Assignment statements consist of a variable , an equal sign, and an expression .
Here’s an example:
Get hands-on with 1200+ tech skills courses.
- Contributors
Basic Statements in Python
Table of contents, what is a statement in python, statement set, multi-line statements, simple statements, expression statements, the assert statement, the try statement.

In Python, statements are instructions or commands that you write to perform specific actions or tasks. They are the building blocks of a Python program.
A statement is a line of code that performs a specific action. It is the smallest unit of code that can be executed by the Python interpreter.
Assignment Statement
In this example, the value 10 is assigned to the variable x using the assignment statement.
Conditional Statement
In this example, the if-else statement is used to check the value of x and print a corresponding message.
By using statements, programmers can instruct the computer to perform a variety of tasks, from simple arithmetic operations to complex decision-making processes. Proper use of statements is crucial to writing efficient and effective Python code.
Here's a table summarizing various types of statements in Python:
Please note that this table provides a brief overview of each statement type, and there may be additional details and variations for each statement.
Multi-line statements are a convenient way to write long code in Python without making it cluttered. They allow you to write several lines of code as a single statement, making it easier for developers to read and understand the code. Here are two examples of multi-line statements in Python:
- Using backslash:
- Using parentheses:
Simple statements are the smallest unit of execution in Python programming language and they do not contain any logical or conditional expressions. They are usually composed of a single line of code and can perform basic operations such as assigning values to variables , printing out values, or calling functions .
Examples of simple statements in Python:
Simple statements are essential to programming in Python and are often used in combination with more complex statements to create robust programs and applications.
Expression statements in Python are lines of code that evaluate and produce a value. They are used to assign values to variables, call functions, and perform other operations that produce a result.
In this example, we assign the value 5 to the variable x , then add 3 to x and assign the result ( 8 ) to the variable y . Finally, we print the value of y .
In this example, we define a function square that takes one argument ( x ) and returns its square. We then call the function with the argument 5 and assign the result ( 25 ) to the variable result . Finally, we print the value of result .
Overall, expression statements are an essential part of Python programming and allow for the execution of mathematical and computational operations.
The assert statement in Python is used to test conditions and trigger an error if the condition is not met. It is often used for debugging and testing purposes.
Where condition is the expression that is tested, and message is the optional error message that is displayed when the condition is not met.
In this example, the assert statement tests whether x is equal to 5 . If the condition is met, the statement has no effect. If the condition is not met, an error will be raised with the message x should be 5 .
In this example, the assert statement tests whether y is not equal to 0 before performing the division. If the condition is met, the division proceeds as normal. If the condition is not met, an error will be raised with the message Cannot divide by zero .
Overall, assert statements are a useful tool in Python for debugging and testing, as they can help catch errors early on. They are also easily disabled in production code to avoid any unnecessary overhead.
The try statement in Python is used to catch exceptions that may occur during the execution of a block of code. It ensures that even when an error occurs, the code does not stop running.
Examples of Error Processing
Dive deep into the topic.
- Match Statements
- Operators in Python Statements
- The IF Statement
Contribute with us!
Do not hesitate to contribute to Python tutorials on GitHub: create a fork, update content and issue a pull request.

Python Enhancement Proposals
- Python »
- PEP Index »
PEP 572 – Assignment Expressions
The importance of real code, exceptional cases, scope of the target, relative precedence of :=, change to evaluation order, differences between assignment expressions and assignment statements, specification changes during implementation, _pydecimal.py, datetime.py, sysconfig.py, simplifying list comprehensions, capturing condition values, changing the scope rules for comprehensions, alternative spellings, special-casing conditional statements, special-casing comprehensions, lowering operator precedence, allowing commas to the right, always requiring parentheses, why not just turn existing assignment into an expression, with assignment expressions, why bother with assignment statements, why not use a sublocal scope and prevent namespace pollution, style guide recommendations, acknowledgements, a numeric example, appendix b: rough code translations for comprehensions, appendix c: no changes to scope semantics.
This is a proposal for creating a way to assign to variables within an expression using the notation NAME := expr .
As part of this change, there is also an update to dictionary comprehension evaluation order to ensure key expressions are executed before value expressions (allowing the key to be bound to a name and then re-used as part of calculating the corresponding value).
During discussion of this PEP, the operator became informally known as “the walrus operator”. The construct’s formal name is “Assignment Expressions” (as per the PEP title), but they may also be referred to as “Named Expressions” (e.g. the CPython reference implementation uses that name internally).
Naming the result of an expression is an important part of programming, allowing a descriptive name to be used in place of a longer expression, and permitting reuse. Currently, this feature is available only in statement form, making it unavailable in list comprehensions and other expression contexts.
Additionally, naming sub-parts of a large expression can assist an interactive debugger, providing useful display hooks and partial results. Without a way to capture sub-expressions inline, this would require refactoring of the original code; with assignment expressions, this merely requires the insertion of a few name := markers. Removing the need to refactor reduces the likelihood that the code be inadvertently changed as part of debugging (a common cause of Heisenbugs), and is easier to dictate to another programmer.
During the development of this PEP many people (supporters and critics both) have had a tendency to focus on toy examples on the one hand, and on overly complex examples on the other.
The danger of toy examples is twofold: they are often too abstract to make anyone go “ooh, that’s compelling”, and they are easily refuted with “I would never write it that way anyway”.
The danger of overly complex examples is that they provide a convenient strawman for critics of the proposal to shoot down (“that’s obfuscated”).
Yet there is some use for both extremely simple and extremely complex examples: they are helpful to clarify the intended semantics. Therefore, there will be some of each below.
However, in order to be compelling , examples should be rooted in real code, i.e. code that was written without any thought of this PEP, as part of a useful application, however large or small. Tim Peters has been extremely helpful by going over his own personal code repository and picking examples of code he had written that (in his view) would have been clearer if rewritten with (sparing) use of assignment expressions. His conclusion: the current proposal would have allowed a modest but clear improvement in quite a few bits of code.
Another use of real code is to observe indirectly how much value programmers place on compactness. Guido van Rossum searched through a Dropbox code base and discovered some evidence that programmers value writing fewer lines over shorter lines.
Case in point: Guido found several examples where a programmer repeated a subexpression, slowing down the program, in order to save one line of code, e.g. instead of writing:
they would write:
Another example illustrates that programmers sometimes do more work to save an extra level of indentation:
This code tries to match pattern2 even if pattern1 has a match (in which case the match on pattern2 is never used). The more efficient rewrite would have been:
Syntax and semantics
In most contexts where arbitrary Python expressions can be used, a named expression can appear. This is of the form NAME := expr where expr is any valid Python expression other than an unparenthesized tuple, and NAME is an identifier.
The value of such a named expression is the same as the incorporated expression, with the additional side-effect that the target is assigned that value:
There are a few places where assignment expressions are not allowed, in order to avoid ambiguities or user confusion:
This rule is included to simplify the choice for the user between an assignment statement and an assignment expression – there is no syntactic position where both are valid.
Again, this rule is included to avoid two visually similar ways of saying the same thing.
This rule is included to disallow excessively confusing code, and because parsing keyword arguments is complex enough already.
This rule is included to discourage side effects in a position whose exact semantics are already confusing to many users (cf. the common style recommendation against mutable default values), and also to echo the similar prohibition in calls (the previous bullet).
The reasoning here is similar to the two previous cases; this ungrouped assortment of symbols and operators composed of : and = is hard to read correctly.
This allows lambda to always bind less tightly than := ; having a name binding at the top level inside a lambda function is unlikely to be of value, as there is no way to make use of it. In cases where the name will be used more than once, the expression is likely to need parenthesizing anyway, so this prohibition will rarely affect code.
This shows that what looks like an assignment operator in an f-string is not always an assignment operator. The f-string parser uses : to indicate formatting options. To preserve backwards compatibility, assignment operator usage inside of f-strings must be parenthesized. As noted above, this usage of the assignment operator is not recommended.
An assignment expression does not introduce a new scope. In most cases the scope in which the target will be bound is self-explanatory: it is the current scope. If this scope contains a nonlocal or global declaration for the target, the assignment expression honors that. A lambda (being an explicit, if anonymous, function definition) counts as a scope for this purpose.
There is one special case: an assignment expression occurring in a list, set or dict comprehension or in a generator expression (below collectively referred to as “comprehensions”) binds the target in the containing scope, honoring a nonlocal or global declaration for the target in that scope, if one exists. For the purpose of this rule the containing scope of a nested comprehension is the scope that contains the outermost comprehension. A lambda counts as a containing scope.
The motivation for this special case is twofold. First, it allows us to conveniently capture a “witness” for an any() expression, or a counterexample for all() , for example:
Second, it allows a compact way of updating mutable state from a comprehension, for example:
However, an assignment expression target name cannot be the same as a for -target name appearing in any comprehension containing the assignment expression. The latter names are local to the comprehension in which they appear, so it would be contradictory for a contained use of the same name to refer to the scope containing the outermost comprehension instead.
For example, [i := i+1 for i in range(5)] is invalid: the for i part establishes that i is local to the comprehension, but the i := part insists that i is not local to the comprehension. The same reason makes these examples invalid too:
While it’s technically possible to assign consistent semantics to these cases, it’s difficult to determine whether those semantics actually make sense in the absence of real use cases. Accordingly, the reference implementation [1] will ensure that such cases raise SyntaxError , rather than executing with implementation defined behaviour.
This restriction applies even if the assignment expression is never executed:
For the comprehension body (the part before the first “for” keyword) and the filter expression (the part after “if” and before any nested “for”), this restriction applies solely to target names that are also used as iteration variables in the comprehension. Lambda expressions appearing in these positions introduce a new explicit function scope, and hence may use assignment expressions with no additional restrictions.
Due to design constraints in the reference implementation (the symbol table analyser cannot easily detect when names are re-used between the leftmost comprehension iterable expression and the rest of the comprehension), named expressions are disallowed entirely as part of comprehension iterable expressions (the part after each “in”, and before any subsequent “if” or “for” keyword):
A further exception applies when an assignment expression occurs in a comprehension whose containing scope is a class scope. If the rules above were to result in the target being assigned in that class’s scope, the assignment expression is expressly invalid. This case also raises SyntaxError :
(The reason for the latter exception is the implicit function scope created for comprehensions – there is currently no runtime mechanism for a function to refer to a variable in the containing class scope, and we do not want to add such a mechanism. If this issue ever gets resolved this special case may be removed from the specification of assignment expressions. Note that the problem already exists for using a variable defined in the class scope from a comprehension.)
See Appendix B for some examples of how the rules for targets in comprehensions translate to equivalent code.
The := operator groups more tightly than a comma in all syntactic positions where it is legal, but less tightly than all other operators, including or , and , not , and conditional expressions ( A if C else B ). As follows from section “Exceptional cases” above, it is never allowed at the same level as = . In case a different grouping is desired, parentheses should be used.
The := operator may be used directly in a positional function call argument; however it is invalid directly in a keyword argument.
Some examples to clarify what’s technically valid or invalid:
Most of the “valid” examples above are not recommended, since human readers of Python source code who are quickly glancing at some code may miss the distinction. But simple cases are not objectionable:
This PEP recommends always putting spaces around := , similar to PEP 8 ’s recommendation for = when used for assignment, whereas the latter disallows spaces around = used for keyword arguments.)
In order to have precisely defined semantics, the proposal requires evaluation order to be well-defined. This is technically not a new requirement, as function calls may already have side effects. Python already has a rule that subexpressions are generally evaluated from left to right. However, assignment expressions make these side effects more visible, and we propose a single change to the current evaluation order:
- In a dict comprehension {X: Y for ...} , Y is currently evaluated before X . We propose to change this so that X is evaluated before Y . (In a dict display like {X: Y} this is already the case, and also in dict((X, Y) for ...) which should clearly be equivalent to the dict comprehension.)
Most importantly, since := is an expression, it can be used in contexts where statements are illegal, including lambda functions and comprehensions.
Conversely, assignment expressions don’t support the advanced features found in assignment statements:
- Multiple targets are not directly supported: x = y = z = 0 # Equivalent: (z := (y := (x := 0)))
- Single assignment targets other than a single NAME are not supported: # No equivalent a [ i ] = x self . rest = []
- Priority around commas is different: x = 1 , 2 # Sets x to (1, 2) ( x := 1 , 2 ) # Sets x to 1
- Iterable packing and unpacking (both regular or extended forms) are not supported: # Equivalent needs extra parentheses loc = x , y # Use (loc := (x, y)) info = name , phone , * rest # Use (info := (name, phone, *rest)) # No equivalent px , py , pz = position name , phone , email , * other_info = contact
- Inline type annotations are not supported: # Closest equivalent is "p: Optional[int]" as a separate declaration p : Optional [ int ] = None
- Augmented assignment is not supported: total += tax # Equivalent: (total := total + tax)
The following changes have been made based on implementation experience and additional review after the PEP was first accepted and before Python 3.8 was released:
- for consistency with other similar exceptions, and to avoid locking in an exception name that is not necessarily going to improve clarity for end users, the originally proposed TargetScopeError subclass of SyntaxError was dropped in favour of just raising SyntaxError directly. [3]
- due to a limitation in CPython’s symbol table analysis process, the reference implementation raises SyntaxError for all uses of named expressions inside comprehension iterable expressions, rather than only raising them when the named expression target conflicts with one of the iteration variables in the comprehension. This could be revisited given sufficiently compelling examples, but the extra complexity needed to implement the more selective restriction doesn’t seem worthwhile for purely hypothetical use cases.
Examples from the Python standard library
env_base is only used on these lines, putting its assignment on the if moves it as the “header” of the block.
- Current: env_base = os . environ . get ( "PYTHONUSERBASE" , None ) if env_base : return env_base
- Improved: if env_base := os . environ . get ( "PYTHONUSERBASE" , None ): return env_base
Avoid nested if and remove one indentation level.
- Current: if self . _is_special : ans = self . _check_nans ( context = context ) if ans : return ans
- Improved: if self . _is_special and ( ans := self . _check_nans ( context = context )): return ans
Code looks more regular and avoid multiple nested if. (See Appendix A for the origin of this example.)
- Current: reductor = dispatch_table . get ( cls ) if reductor : rv = reductor ( x ) else : reductor = getattr ( x , "__reduce_ex__" , None ) if reductor : rv = reductor ( 4 ) else : reductor = getattr ( x , "__reduce__" , None ) if reductor : rv = reductor () else : raise Error ( "un(deep)copyable object of type %s " % cls )
- Improved: if reductor := dispatch_table . get ( cls ): rv = reductor ( x ) elif reductor := getattr ( x , "__reduce_ex__" , None ): rv = reductor ( 4 ) elif reductor := getattr ( x , "__reduce__" , None ): rv = reductor () else : raise Error ( "un(deep)copyable object of type %s " % cls )
tz is only used for s += tz , moving its assignment inside the if helps to show its scope.
- Current: s = _format_time ( self . _hour , self . _minute , self . _second , self . _microsecond , timespec ) tz = self . _tzstr () if tz : s += tz return s
- Improved: s = _format_time ( self . _hour , self . _minute , self . _second , self . _microsecond , timespec ) if tz := self . _tzstr (): s += tz return s
Calling fp.readline() in the while condition and calling .match() on the if lines make the code more compact without making it harder to understand.
- Current: while True : line = fp . readline () if not line : break m = define_rx . match ( line ) if m : n , v = m . group ( 1 , 2 ) try : v = int ( v ) except ValueError : pass vars [ n ] = v else : m = undef_rx . match ( line ) if m : vars [ m . group ( 1 )] = 0
- Improved: while line := fp . readline (): if m := define_rx . match ( line ): n , v = m . group ( 1 , 2 ) try : v = int ( v ) except ValueError : pass vars [ n ] = v elif m := undef_rx . match ( line ): vars [ m . group ( 1 )] = 0
A list comprehension can map and filter efficiently by capturing the condition:
Similarly, a subexpression can be reused within the main expression, by giving it a name on first use:
Note that in both cases the variable y is bound in the containing scope (i.e. at the same level as results or stuff ).
Assignment expressions can be used to good effect in the header of an if or while statement:
Particularly with the while loop, this can remove the need to have an infinite loop, an assignment, and a condition. It also creates a smooth parallel between a loop which simply uses a function call as its condition, and one which uses that as its condition but also uses the actual value.
An example from the low-level UNIX world:
Rejected alternative proposals
Proposals broadly similar to this one have come up frequently on python-ideas. Below are a number of alternative syntaxes, some of them specific to comprehensions, which have been rejected in favour of the one given above.
A previous version of this PEP proposed subtle changes to the scope rules for comprehensions, to make them more usable in class scope and to unify the scope of the “outermost iterable” and the rest of the comprehension. However, this part of the proposal would have caused backwards incompatibilities, and has been withdrawn so the PEP can focus on assignment expressions.
Broadly the same semantics as the current proposal, but spelled differently.
Since EXPR as NAME already has meaning in import , except and with statements (with different semantics), this would create unnecessary confusion or require special-casing (e.g. to forbid assignment within the headers of these statements).
(Note that with EXPR as VAR does not simply assign the value of EXPR to VAR – it calls EXPR.__enter__() and assigns the result of that to VAR .)
Additional reasons to prefer := over this spelling include:
- In if f(x) as y the assignment target doesn’t jump out at you – it just reads like if f x blah blah and it is too similar visually to if f(x) and y .
- import foo as bar
- except Exc as var
- with ctxmgr() as var
To the contrary, the assignment expression does not belong to the if or while that starts the line, and we intentionally allow assignment expressions in other contexts as well.
- NAME = EXPR
- if NAME := EXPR
reinforces the visual recognition of assignment expressions.
This syntax is inspired by languages such as R and Haskell, and some programmable calculators. (Note that a left-facing arrow y <- f(x) is not possible in Python, as it would be interpreted as less-than and unary minus.) This syntax has a slight advantage over ‘as’ in that it does not conflict with with , except and import , but otherwise is equivalent. But it is entirely unrelated to Python’s other use of -> (function return type annotations), and compared to := (which dates back to Algol-58) it has a much weaker tradition.
This has the advantage that leaked usage can be readily detected, removing some forms of syntactic ambiguity. However, this would be the only place in Python where a variable’s scope is encoded into its name, making refactoring harder.
Execution order is inverted (the indented body is performed first, followed by the “header”). This requires a new keyword, unless an existing keyword is repurposed (most likely with: ). See PEP 3150 for prior discussion on this subject (with the proposed keyword being given: ).
This syntax has fewer conflicts than as does (conflicting only with the raise Exc from Exc notation), but is otherwise comparable to it. Instead of paralleling with expr as target: (which can be useful but can also be confusing), this has no parallels, but is evocative.
One of the most popular use-cases is if and while statements. Instead of a more general solution, this proposal enhances the syntax of these two statements to add a means of capturing the compared value:
This works beautifully if and ONLY if the desired condition is based on the truthiness of the captured value. It is thus effective for specific use-cases (regex matches, socket reads that return '' when done), and completely useless in more complicated cases (e.g. where the condition is f(x) < 0 and you want to capture the value of f(x) ). It also has no benefit to list comprehensions.
Advantages: No syntactic ambiguities. Disadvantages: Answers only a fraction of possible use-cases, even in if / while statements.
Another common use-case is comprehensions (list/set/dict, and genexps). As above, proposals have been made for comprehension-specific solutions.
This brings the subexpression to a location in between the ‘for’ loop and the expression. It introduces an additional language keyword, which creates conflicts. Of the three, where reads the most cleanly, but also has the greatest potential for conflict (e.g. SQLAlchemy and numpy have where methods, as does tkinter.dnd.Icon in the standard library).
As above, but reusing the with keyword. Doesn’t read too badly, and needs no additional language keyword. Is restricted to comprehensions, though, and cannot as easily be transformed into “longhand” for-loop syntax. Has the C problem that an equals sign in an expression can now create a name binding, rather than performing a comparison. Would raise the question of why “with NAME = EXPR:” cannot be used as a statement on its own.
As per option 2, but using as rather than an equals sign. Aligns syntactically with other uses of as for name binding, but a simple transformation to for-loop longhand would create drastically different semantics; the meaning of with inside a comprehension would be completely different from the meaning as a stand-alone statement, while retaining identical syntax.
Regardless of the spelling chosen, this introduces a stark difference between comprehensions and the equivalent unrolled long-hand form of the loop. It is no longer possible to unwrap the loop into statement form without reworking any name bindings. The only keyword that can be repurposed to this task is with , thus giving it sneakily different semantics in a comprehension than in a statement; alternatively, a new keyword is needed, with all the costs therein.
There are two logical precedences for the := operator. Either it should bind as loosely as possible, as does statement-assignment; or it should bind more tightly than comparison operators. Placing its precedence between the comparison and arithmetic operators (to be precise: just lower than bitwise OR) allows most uses inside while and if conditions to be spelled without parentheses, as it is most likely that you wish to capture the value of something, then perform a comparison on it:
Once find() returns -1, the loop terminates. If := binds as loosely as = does, this would capture the result of the comparison (generally either True or False ), which is less useful.
While this behaviour would be convenient in many situations, it is also harder to explain than “the := operator behaves just like the assignment statement”, and as such, the precedence for := has been made as close as possible to that of = (with the exception that it binds tighter than comma).
Some critics have claimed that the assignment expressions should allow unparenthesized tuples on the right, so that these two would be equivalent:
(With the current version of the proposal, the latter would be equivalent to ((point := x), y) .)
However, adopting this stance would logically lead to the conclusion that when used in a function call, assignment expressions also bind less tight than comma, so we’d have the following confusing equivalence:
The less confusing option is to make := bind more tightly than comma.
It’s been proposed to just always require parentheses around an assignment expression. This would resolve many ambiguities, and indeed parentheses will frequently be needed to extract the desired subexpression. But in the following cases the extra parentheses feel redundant:
Frequently Raised Objections
C and its derivatives define the = operator as an expression, rather than a statement as is Python’s way. This allows assignments in more contexts, including contexts where comparisons are more common. The syntactic similarity between if (x == y) and if (x = y) belies their drastically different semantics. Thus this proposal uses := to clarify the distinction.
The two forms have different flexibilities. The := operator can be used inside a larger expression; the = statement can be augmented to += and its friends, can be chained, and can assign to attributes and subscripts.
Previous revisions of this proposal involved sublocal scope (restricted to a single statement), preventing name leakage and namespace pollution. While a definite advantage in a number of situations, this increases complexity in many others, and the costs are not justified by the benefits. In the interests of language simplicity, the name bindings created here are exactly equivalent to any other name bindings, including that usage at class or module scope will create externally-visible names. This is no different from for loops or other constructs, and can be solved the same way: del the name once it is no longer needed, or prefix it with an underscore.
(The author wishes to thank Guido van Rossum and Christoph Groth for their suggestions to move the proposal in this direction. [2] )
As expression assignments can sometimes be used equivalently to statement assignments, the question of which should be preferred will arise. For the benefit of style guides such as PEP 8 , two recommendations are suggested.
- If either assignment statements or assignment expressions can be used, prefer statements; they are a clear declaration of intent.
- If using assignment expressions would lead to ambiguity about execution order, restructure it to use statements instead.
The authors wish to thank Alyssa Coghlan and Steven D’Aprano for their considerable contributions to this proposal, and members of the core-mentorship mailing list for assistance with implementation.
Appendix A: Tim Peters’s findings
Here’s a brief essay Tim Peters wrote on the topic.
I dislike “busy” lines of code, and also dislike putting conceptually unrelated logic on a single line. So, for example, instead of:
instead. So I suspected I’d find few places I’d want to use assignment expressions. I didn’t even consider them for lines already stretching halfway across the screen. In other cases, “unrelated” ruled:
is a vast improvement over the briefer:
The original two statements are doing entirely different conceptual things, and slamming them together is conceptually insane.
In other cases, combining related logic made it harder to understand, such as rewriting:
as the briefer:
The while test there is too subtle, crucially relying on strict left-to-right evaluation in a non-short-circuiting or method-chaining context. My brain isn’t wired that way.
But cases like that were rare. Name binding is very frequent, and “sparse is better than dense” does not mean “almost empty is better than sparse”. For example, I have many functions that return None or 0 to communicate “I have nothing useful to return in this case, but since that’s expected often I’m not going to annoy you with an exception”. This is essentially the same as regular expression search functions returning None when there is no match. So there was lots of code of the form:
I find that clearer, and certainly a bit less typing and pattern-matching reading, as:
It’s also nice to trade away a small amount of horizontal whitespace to get another _line_ of surrounding code on screen. I didn’t give much weight to this at first, but it was so very frequent it added up, and I soon enough became annoyed that I couldn’t actually run the briefer code. That surprised me!
There are other cases where assignment expressions really shine. Rather than pick another from my code, Kirill Balunov gave a lovely example from the standard library’s copy() function in copy.py :
The ever-increasing indentation is semantically misleading: the logic is conceptually flat, “the first test that succeeds wins”:
Using easy assignment expressions allows the visual structure of the code to emphasize the conceptual flatness of the logic; ever-increasing indentation obscured it.
A smaller example from my code delighted me, both allowing to put inherently related logic in a single line, and allowing to remove an annoying “artificial” indentation level:
That if is about as long as I want my lines to get, but remains easy to follow.
So, in all, in most lines binding a name, I wouldn’t use assignment expressions, but because that construct is so very frequent, that leaves many places I would. In most of the latter, I found a small win that adds up due to how often it occurs, and in the rest I found a moderate to major win. I’d certainly use it more often than ternary if , but significantly less often than augmented assignment.
I have another example that quite impressed me at the time.
Where all variables are positive integers, and a is at least as large as the n’th root of x, this algorithm returns the floor of the n’th root of x (and roughly doubling the number of accurate bits per iteration):
It’s not obvious why that works, but is no more obvious in the “loop and a half” form. It’s hard to prove correctness without building on the right insight (the “arithmetic mean - geometric mean inequality”), and knowing some non-trivial things about how nested floor functions behave. That is, the challenges are in the math, not really in the coding.
If you do know all that, then the assignment-expression form is easily read as “while the current guess is too large, get a smaller guess”, where the “too large?” test and the new guess share an expensive sub-expression.
To my eyes, the original form is harder to understand:
This appendix attempts to clarify (though not specify) the rules when a target occurs in a comprehension or in a generator expression. For a number of illustrative examples we show the original code, containing a comprehension, and the translation, where the comprehension has been replaced by an equivalent generator function plus some scaffolding.
Since [x for ...] is equivalent to list(x for ...) these examples all use list comprehensions without loss of generality. And since these examples are meant to clarify edge cases of the rules, they aren’t trying to look like real code.
Note: comprehensions are already implemented via synthesizing nested generator functions like those in this appendix. The new part is adding appropriate declarations to establish the intended scope of assignment expression targets (the same scope they resolve to as if the assignment were performed in the block containing the outermost comprehension). For type inference purposes, these illustrative expansions do not imply that assignment expression targets are always Optional (but they do indicate the target binding scope).
Let’s start with a reminder of what code is generated for a generator expression without assignment expression.
- Original code (EXPR usually references VAR): def f (): a = [ EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation (let’s not worry about name conflicts): def f (): def genexpr ( iterator ): for VAR in iterator : yield EXPR a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Let’s add a simple assignment expression.
- Original code: def f (): a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def f (): if False : TARGET = None # Dead code to ensure TARGET is a local variable def genexpr ( iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Let’s add a global TARGET declaration in f() .
- Original code: def f (): global TARGET a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def f (): global TARGET def genexpr ( iterator ): global TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Or instead let’s add a nonlocal TARGET declaration in f() .
- Original code: def g (): TARGET = ... def f (): nonlocal TARGET a = [ TARGET := EXPR for VAR in ITERABLE ]
- Translation: def g (): TARGET = ... def f (): nonlocal TARGET def genexpr ( iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for VAR in iterator : TARGET = EXPR yield TARGET a = list ( genexpr ( iter ( ITERABLE )))
Finally, let’s nest two comprehensions.
- Original code: def f (): a = [[ TARGET := i for i in range ( 3 )] for j in range ( 2 )] # I.e., a = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2]] print ( TARGET ) # prints 2
- Translation: def f (): if False : TARGET = None def outer_genexpr ( outer_iterator ): nonlocal TARGET def inner_generator ( inner_iterator ): nonlocal TARGET for i in inner_iterator : TARGET = i yield i for j in outer_iterator : yield list ( inner_generator ( range ( 3 ))) a = list ( outer_genexpr ( range ( 2 ))) print ( TARGET )
Because it has been a point of confusion, note that nothing about Python’s scoping semantics is changed. Function-local scopes continue to be resolved at compile time, and to have indefinite temporal extent at run time (“full closures”). Example:
This document has been placed in the public domain.
Source: https://github.com/python/peps/blob/main/peps/pep-0572.rst
Last modified: 2023-10-11 12:05:51 GMT
The Assignment Statement
Assignment is fundamental to Python; it is how the objects created by an expression are preserved. We'll look at the basic assignment statement, plus the augmented assignment statement. Later, in Multiple Assignment Statement , we'll look at multiple assignment.
Basic Assignment
We create and change variables primarily with the assignment statement. This statement provides an expression and a variable name which will be used to label the value of the expression.
variable = expression
Here's a short script that contains some examples of assignment statements.
Example 6.1. example3.py
We have an object, the number 150 , which we assign to the variable shares . We have an expression 3+5.0/8.0 , which creates a floating-point number, which we save in the variable price . We have another expression, shares * price , which creates a floating-point number; we save this in value so that we can print it. This script created three new variables.
Since this file is new, we'll need to do the chmod +x example3.py once, after we create this file. Then, when we run this progam, we see the following.
Augmented Assignment
Any of the usual arithmetic operations can be combined with assignment to create an augmented assignment statement.
For example, look at this augmented assignment statement:
This statement is a shorthand that means the same thing as the following:
Here's a larger example
Example 6.2. portfolio.py
First, we'll do the chmod +x portfolio.py on this file. Then, when we run this progam, we see the following.
The other basic math operations can be used similarly, although the purpose gets obscure for some operations. These include -=, *=, /=, %=, &=, ^=, |=, <<= and >>=.
Here's a lengthy example. This is an extension of Craps Odds in the section called “Numeric Types and Expressions” .
In craps, the first roll of the dice is called the “ come out roll ”. This roll can be won immediately if one rolls 7 or 11. It can be lost immediately if one roll 2, 3 or 12. The remaining numbers establish a point and the game continues.
Example 6.3. craps.py
There's a 22.2% chance of winning, and a 11.1% chance of losing. What's the chance of establishing a point? One way is to figure that it's what's left after winning or loosing. The total of all probabilities always add to 1. Subtract the odds of winning and the odds of losing and what's left is the odds of setting a point.
Here's another way to figure the odds of rolling 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 or 10.
By the way, you can add the statement print win + lose + point to confirm that these odds all add to 1. This means that we have defined all possible outcomes for the come out roll in craps.
Tracing Execution
We can trace the execution of a program by simply following the changes of value of all the variables in the program. Here's an example for Example 6.3, “craps.py”
- win: 0 , 0.16 , 0.22
- list: 0 , 0.027 , 0.083 , 0.111
- point: 1 , 0.77 , 0.66
As with many things Python, there is some additional subtlety to this, but we'll cover those topics later. For example, multiple-assignment statement is something we'll look into in more deeply in Chapter 13, Tuples .
CS105: Introduction to Python
Variables and assignment statements.
Computers must be able to remember and store data. This can be accomplished by creating a variable to house a given value. The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command:
in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a . Next, type the command:
in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. This variable will remember the value 3.45 until it is assigned a different value. To see this, type these two commands:
You should see the new value contained in the variable a echoed to the screen. The new value has "overwritten" the old value. We must be careful since once an old value has been overwritten, it is no longer remembered. The new value is now what is being remembered.
Although we will not discuss arithmetic operations in detail until the next unit, you can at least be equipped with the syntax for basic operations: + (addition), - (subtraction), * (multiplication), / (division)
For example, entering these command sequentially into the command line window:
would result in 12.32 being echoed to the screen (just as you would expect from a calculator). The syntax for multiplication works similarly. For example:
would result in 35 being echoed to the screen because the variable b has been assigned the value a * 5 where, at the time of execution, the variable a contains a value of 7.
After you read, you should be able to execute simple assignment commands using integer and float values in the command window of the Repl.it IDE. Try typing some more of the examples from this web page to convince yourself that a variable has been assigned a specific value.
In programming, we associate names with values so that we can remember and use them later. Recall Example 1. The repeated computation in that algorithm relied on remembering the intermediate sum and the integer to be added to that sum to get the new sum. In expressing the algorithm, we used th e names current and sum .
In programming, a name that refers to a value in this fashion is called a variable . When we think of values as data stored somewhere i n the computer, we can have a mental image such as the one below for the value 10 stored in the computer and the variable x , which is the name we give to 10. What is most important is to see that there is a binding between x and 10.
The term variable comes from the fact that values that are bound to variables can change throughout computation. Bindings as shown above are created, and changed by assignment statements . An assignment statement associates the name to the left of the symbol = with the value denoted by the expression on the right of =. The binding in the picture is created using an assignment statemen t of the form x = 10 . We usually read such an assignment statement as "10 is assigned to x" or "x is set to 10".
If we want to change the value that x refers to, we can use another assignment statement to do that. Suppose we execute x = 25 in the state where x is bound to 10.Then our image becomes as follows:
Choosing variable names
Suppose that we u sed the variables x and y in place of the variables side and area in the examples above. Now, if we were to compute some other value for the square that depends on the length of the side , such as the perimeter or length of the diagonal, we would have to remember which of x and y , referred to the length of the side because x and y are not as descriptive as side and area . In choosing variable names, we have to keep in mind that programs are read and maintained by human beings, not only executed by machines.
Note about syntax
In Python, variable identifiers can contain uppercase and lowercase letters, digits (provided they don't start with a digit) and the special character _ (underscore). Although it is legal to use uppercase letters in variable identifiers, we typically do not use them by convention. Variable identifiers are also case-sensitive. For example, side and Side are two different variable identifiers.
There is a collection of words, called reserved words (also known as keywords), in Python that have built-in meanings and therefore cannot be used as variable names. For the list of Python's keywords See 2.3.1 of the Python Language Reference.
Syntax and Sema ntic Errors
Now that we know how to write arithmetic expressions and assignment statements in Python, we can pause and think about what Python does if we write something that the Python interpreter cannot interpret. Python informs us about such problems by giving an error message. Broadly speaking there are two categories for Python errors:
- Syntax errors: These occur when we write Python expressions or statements that are not well-formed according to Python's syntax. For example, if we attempt to write an assignment statement such as 13 = age , Python gives a syntax error. This is because Python syntax says that for an assignment statement to be well-formed it must contain a variable on the left hand side (LHS) of the assignment operator "=" and a well-formed expression on the right hand side (RHS), and 13 is not a variable.
- Semantic errors: These occur when the Python interpreter cannot evaluate expressions or execute statements because they cannot be associated with a "meaning" that the interpreter can use. For example, the expression age + 1 is well-formed but it has a meaning only when age is already bound to a value. If we attempt to evaluate this expression before age is bound to some value by a prior assignment then Python gives a semantic error.
Even though we have used numerical expressions in all of our examples so far, assignments are not confined to numerical types. They could involve expressions built from any defined type. Recall the table that summarizes the basic types in Python.
The following video shows execution of assignment statements involving strings. It also introduces some commonly used operators on strings. For more information see the online documentation. In the video below, you see the Python shell displaying "=> None" after the assignment statements. This is unique to the Python shell presented in the video. In most Python programming environments, nothing is displayed after an assignment statement. The difference in behavior stems from version differences between the programming environment used in the video and in the activities, and can be safely ignored.
Distinguishing Expressions and Assignments
So far in the module, we have been careful to keep the distinction between the terms expression and statement because there is a conceptual difference between them, which is sometimes overlooked. Expressions denote values; they are evaluated to yield a value. On the other hand, statements are commands (instructions) that change the state of the computer. You can think of state here as some representation of computer memory and the binding of variables and values in the memory. In a state where the variable side is bound to the integer 3, and the variable area is yet unbound, the value of the expression side + 2 is 5. The assignment statement side = side + 2 , changes the state so that value 5 is bound to side in the new state. Note that when you type an expression in the Python shell, Python evaluates the expression and you get a value in return. On the other hand, if you type an assignment statement nothing is returned. Assignment statements do not return a value. Try, for example, typing x = 100 + 50 . Python adds 100 to 50, gets the value 150, and binds x to 150. However, we only see the prompt >>> after Python does the assignment. We don't see the change in the state until we inspect the value of x , by invoking x .
What we have learned so far can be summarized as using the Python interpreter to manipulate values of some primitive data types such as integers, real numbers, and character strings by evaluating expressions that involve built-in operators on these types. Assignments statements let us name the values that appear in expressions. While what we have learned so far allows us to do some computations conveniently, they are limited in their generality and reusability. Next, we introduce functions as a means to make computations more general and reusable.

Python Tutorial
File handling, python modules, python numpy, python pandas, python matplotlib, python scipy, machine learning, python mysql, python mongodb, python reference, module reference, python how to, python examples, python assignment operators.
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables:
Related Pages

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]

Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries
Python Operators
Precedence and associativity of operators in python.
- Python Arithmetic Operators
- Difference between / vs. // operator in Python
- Python - Star or Asterisk operator ( * )
- What does the Double Star operator mean in Python?
- Division Operators in Python
- Modulo operator (%) in Python
- Python Logical Operators
- Python OR Operator
- Difference between 'and' and '&' in Python
- not Operator in Python | Boolean Logic
Ternary Operator in Python
- Python Bitwise Operators
Python Assignment Operators
Assignment operators in python.
- Walrus Operator in Python 3.8
- Increment += and Decrement -= Assignment Operators in Python
- Merging and Updating Dictionary Operators in Python 3.9
- New '=' Operator in Python3.8 f-string
Python Relational Operators
- Comparison Operators in Python
- Python NOT EQUAL operator
- Difference between == and is operator in Python
- Chaining comparison operators in Python
- Python Membership and Identity Operators
- Difference between != and is not operator in Python
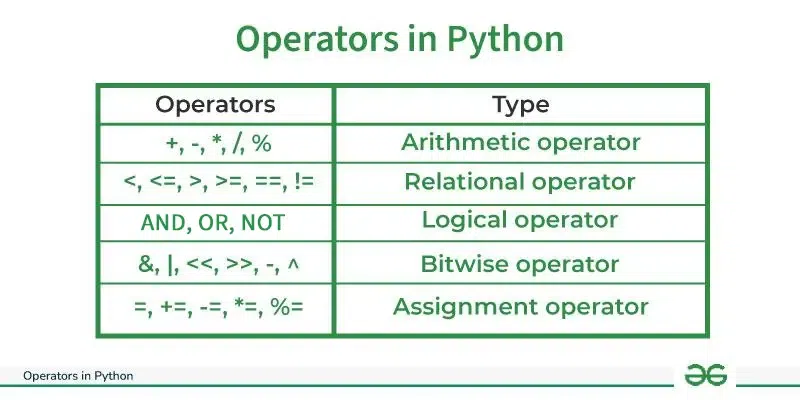
In Python programming, Operators in general are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for logical and arithmetic operations. In this article, we will look into different types of Python operators.
- OPERATORS: These are the special symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc.
- OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator is applied.
Types of Operators in Python
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Identity Operators and Membership Operators
Arithmetic Operators in Python
Python Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication , and division .
In Python 3.x the result of division is a floating-point while in Python 2.x division of 2 integers was an integer. To obtain an integer result in Python 3.x floored (// integer) is used.
Example of Arithmetic Operators in Python
Division operators.
In Python programming language Division Operators allow you to divide two numbers and return a quotient, i.e., the first number or number at the left is divided by the second number or number at the right and returns the quotient.
There are two types of division operators:
Float division
- Floor division
The quotient returned by this operator is always a float number, no matter if two numbers are integers. For example:
Example: The code performs division operations and prints the results. It demonstrates that both integer and floating-point divisions return accurate results. For example, ’10/2′ results in ‘5.0’ , and ‘-10/2’ results in ‘-5.0’ .
Integer division( Floor division)
The quotient returned by this operator is dependent on the argument being passed. If any of the numbers is float, it returns output in float. It is also known as Floor division because, if any number is negative, then the output will be floored. For example:
Example: The code demonstrates integer (floor) division operations using the // in Python operators . It provides results as follows: ’10//3′ equals ‘3’ , ‘-5//2’ equals ‘-3’ , ‘ 5.0//2′ equals ‘2.0’ , and ‘-5.0//2’ equals ‘-3.0’ . Integer division returns the largest integer less than or equal to the division result.
Precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python
The precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python is as follows:
- P – Parentheses
- E – Exponentiation
- M – Multiplication (Multiplication and division have the same precedence)
- D – Division
- A – Addition (Addition and subtraction have the same precedence)
- S – Subtraction
The modulus of Python operators helps us extract the last digit/s of a number. For example:
- x % 10 -> yields the last digit
- x % 100 -> yield last two digits
Arithmetic Operators With Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Modulo and Power
Here is an example showing how different Arithmetic Operators in Python work:
Example: The code performs basic arithmetic operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It adds (‘+’) , subtracts (‘-‘) , multiplies (‘*’) , computes the remainder (‘%’) , and raises a to the power of ‘b (**)’ . The results of these operations are printed.
Note: Refer to Differences between / and // for some interesting facts about these two Python operators.
Comparison of Python Operators
In Python Comparison of Relational operators compares the values. It either returns True or False according to the condition.
= is an assignment operator and == comparison operator.
Precedence of Comparison Operators in Python
In Python, the comparison operators have lower precedence than the arithmetic operators. All the operators within comparison operators have the same precedence order.
Example of Comparison Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Comparison Operators in Python.
Example: The code compares the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ using various comparison Python operators and prints the results. It checks if ‘a’ is greater than, less than, equal to, not equal to, greater than, or equal to, and less than or equal to ‘b’ .
Logical Operators in Python
Python Logical operators perform Logical AND , Logical OR , and Logical NOT operations. It is used to combine conditional statements.
Precedence of Logical Operators in Python
The precedence of Logical Operators in Python is as follows:
- Logical not
- logical and
Example of Logical Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Logical Operators in Python:
Example: The code performs logical operations with Boolean values. It checks if both ‘a’ and ‘b’ are true ( ‘and’ ), if at least one of them is true ( ‘or’ ), and negates the value of ‘a’ using ‘not’ . The results are printed accordingly.
Bitwise Operators in Python
Python Bitwise operators act on bits and perform bit-by-bit operations. These are used to operate on binary numbers.
Precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python
The precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python is as follows:
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise Shift
- Bitwise AND
- Bitwise XOR
Here is an example showing how Bitwise Operators in Python work:
Example: The code demonstrates various bitwise operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It performs bitwise AND (&) , OR (|) , NOT (~) , XOR (^) , right shift (>>) , and left shift (<<) operations and prints the results. These operations manipulate the binary representations of the numbers.
Python Assignment operators are used to assign values to the variables.
Let’s see an example of Assignment Operators in Python.
Example: The code starts with ‘a’ and ‘b’ both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on ‘b’ . The results of each operation are printed, showing the impact of these operations on the value of ‘b’ .
Identity Operators in Python
In Python, is and is not are the identity operators both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical.
Example Identity Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Identity Operators in Python.
Example: The code uses identity operators to compare variables in Python. It checks if ‘a’ is not the same object as ‘b’ (which is true because they have different values) and if ‘a’ is the same object as ‘c’ (which is true because ‘c’ was assigned the value of ‘a’ ).
Membership Operators in Python
In Python, in and not in are the membership operators that are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence.
Examples of Membership Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Membership Operators in Python:
Example: The code checks for the presence of values ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the list. It prints whether or not each value is present in the list. ‘x’ is not in the list, and ‘y’ is present, as indicated by the printed messages. The code uses the ‘in’ and ‘not in’ Python operators to perform these checks.
in Python, Ternary operators also known as conditional expressions are operators that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It was added to Python in version 2.5.
It simply allows testing a condition in a single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
Syntax : [on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]
Examples of Ternary Operator in Python
The code assigns values to variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ (10 and 20, respectively). It then uses a conditional assignment to determine the smaller of the two values and assigns it to the variable ‘min’ . Finally, it prints the value of ‘min’ , which is 10 in this case.
In Python, Operator precedence and associativity determine the priorities of the operator.
Operator Precedence in Python
This is used in an expression with more than one operator with different precedence to determine which operation to perform first.
Let’s see an example of how Operator Precedence in Python works:
Example: The code first calculates and prints the value of the expression 10 + 20 * 30 , which is 610. Then, it checks a condition based on the values of the ‘name’ and ‘age’ variables. Since the name is “ Alex” and the condition is satisfied using the or operator, it prints “Hello! Welcome.”
Operator Associativity in Python
If an expression contains two or more operators with the same precedence then Operator Associativity is used to determine. It can either be Left to Right or from Right to Left.
The following code shows how Operator Associativity in Python works:
Example: The code showcases various mathematical operations. It calculates and prints the results of division and multiplication, addition and subtraction, subtraction within parentheses, and exponentiation. The code illustrates different mathematical calculations and their outcomes.
To try your knowledge of Python Operators, you can take out the quiz on Operators in Python .
Python Operator Exercise Questions
Below are two Exercise Questions on Python Operators. We have covered arithmetic operators and comparison operators in these exercise questions. For more exercises on Python Operators visit the page mentioned below.
Q1. Code to implement basic arithmetic operations on integers
Q2. Code to implement Comparison operations on integers
Explore more Exercises: Practice Exercise on Operators in Python
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- python-basics
- Python-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- précédent |
- Python »
- 3.14.0a0 Documentation »
- La référence du langage Python »
- 10. Spécification complète de la grammaire
- Theme Auto Light Dark |
10. Spécification complète de la grammaire ¶
Ceci est la grammaire complète de Python, issue directement de la grammaire utilisée pour générer l'analyseur syntaxique CPython (voir Grammar/python.gram ). La version ci-dessous ne comprend pas les détails relatifs à la génération de code et la reprise sur erreur.
The notation is a mixture of EBNF and PEG . In particular, & followed by a symbol, token or parenthesized group indicates a positive lookahead (i.e., is required to match but not consumed), while ! indicates a negative lookahead (i.e., is required not to match). We use the | separator to mean PEG's "ordered choice" (written as / in traditional PEG grammars). See PEP 617 for more details on the grammar's syntax.
Sujet précédent
9. Composants de plus haut niveau
Sujet suivant
La bibliothèque standard
- Signalement de bogue
- Voir la source

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An assignment statement evaluates the expression list (remember that this can be a single expression or a comma-separated list, the latter yielding a tuple) and assigns the single resulting object to each of the target lists, from left to right. ... All historical features enabled by the future statement are still recognized by Python 3. The ...
Multiple- target assignment: x = y = 75. print(x, y) In this form, Python assigns a reference to the same object (the object which is rightmost) to all the target on the left. OUTPUT. 75 75. 7. Augmented assignment : The augmented assignment is a shorthand assignment that combines an expression and an assignment.
Here, variable represents a generic Python variable, while expression represents any Python object that you can provide as a concrete value—also known as a literal—or an expression that evaluates to a value. To execute an assignment statement like the above, Python runs the following steps: Evaluate the right-hand expression to produce a concrete value or object.
In this tutorial, you used assignment expressions to make compact sections of Python code that assign values to variables inside of if statements, while loops, and list comprehensions. For more information on other assignment expressions, you can view PEP 572—the document that initially proposed adding assignment expressions to Python.
A variable is a name for a value. An assignment statement associates a variable name on the left of the equal sign with the value of an expression calculated from the right of the equal sign. Enter. Once a variable is assigned a value, the variable can be used in place of that value. The response to the expression width is the same as if its ...
Variables and Assignment¶. When programming, it is useful to be able to store information in variables. A variable is a string of characters and numbers associated with a piece of information. The assignment operator, denoted by the "=" symbol, is the operator that is used to assign values to variables in Python.The line x=1 takes the known value, 1, and assigns that value to the variable ...
Learn about assignment statements in Python. We'll cover the following. Syntax; Assignment shortcuts; Walrus operator; Syntax. Assignment statements consist of a variable, an equal sign, and an expression. Here's an example: Get hands-on with 1200+ tech skills courses.
Assignment Statements# We have already seen that Python allows you to evaluate expressions, for instance 40 + 2. It is very convenient if we are able to store the calculated value in some variable for future use. The latter can be done via an assignment statement. An assignment statement creates a new variable with a given name and assigns it a ...
Variable Assignment. Think of a variable as a name attached to a particular object. In Python, variables need not be declared or defined in advance, as is the case in many other programming languages. To create a variable, you just assign it a value and then start using it. Assignment is done with a single equals sign ( = ).
Expression statements in Python are lines of code that evaluate and produce a value. They are used to assign values to variables, call functions, and perform other operations that produce a result. x = 5. y = x + 3. print(y) In this example, we assign the value 5 to the variable x, then add 3 to x and assign the result ( 8) to the variable y.
00:00 Since Python's argument passing mechanism relies so much on how Python deals with assignment, the next couple of lessons will go into a bit more depth about how assignment works in Python.. 00:12 Recall some things I've already mentioned: Assignment is the process of binding a name to an object. Parameter names are also bound to objects on function entry in Python.
A statement is an instruction that a Python interpreter can execute. So, in simple words, we can say anything written in Python is a statement. Python statement ends with the token NEWLINE character. It means each line in a Python script is a statement. For example, a = 10 is an assignment statement. where a is a variable name and
Learn the basics of assignment statements in Python in this tutorial. We'll cover the syntax and usage of the assignment operator, including multiple assignm...
Unparenthesized assignment expressions are prohibited at the top level of the right hand side of an assignment statement. Example: y0 = y1 := f(x) # INVALID y0 = (y1 := f(x)) # Valid, though discouraged. Again, this rule is included to avoid two visually similar ways of saying the same thing.
This statement provides an expression and a variable name which will be used to label the value of the expression. variable = expression. Here's a short script that contains some examples of assignment statements. Example 6.1. example3.py. #!/usr/bin/env python. # Computer the value of a block of stock. shares= 150. price= 3 + 5.0/8.0.
We use Python assignment statements to assign objects to names. The target of an assignment statement is written on the left side of the equal sign (=), and the object on the right can be an arbitrary expression that computes an object. There are some important properties of assignment in Python :- Assignment creates object references instead of co
The Assignment Statement and Types Topics: Python's Interactive Mode Variables Expressions Assignment Strings, Ints, and Floats . The Python Interactive Shell Python can be used in a way that reminds you of a calculator. In the ``command shell ... In Python, "=" prescribes an action, "evaluate
In this lesson, you'll learn about the biggest change in Python 3.8: the introduction of assignment expressions.Assignment expression are written with a new notation (:=).This operator is often called the walrus operator as it resembles the eyes and tusks of a walrus on its side.. Assignment expressions allow you to assign and return a value in the same expression.
The assignment operator = is used to associate a variable name with a given value. For example, type the command: a=3.45. in the command line window. This command assigns the value 3.45 to the variable named a. Next, type the command: a. in the command window and hit the enter key. You should see the value contained in the variable a echoed to ...
Python Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables: Operator. Example. Same As. Try it. =. x = 5. x = 5.
Note that in Python, unlike C, assignment cannot occur inside expressions. C programmers may grumble about this, but it avoids a common class of problems encountered in C programs: typing = in an expression when == was intended. ... No. Assignment in Python is a statement, not an expression. Share. Improve this answer. Follow
Assignment Operators in Python. Let's see an example of Assignment Operators in Python. Example: The code starts with 'a' and 'b' both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on 'b'.
In the U.S. and Canada, Coursera charges $49 per month after the initial 7-day free trial period. The Google IT Automation with Python Certificate can be completed in less than 6 months at under 10 hours per week of part-time study, so most learners can complete the certificate for less than $300 USD.
To create a variable, you just assign it a value and then start using it. Assignment is done with a single equals sign ( = ): Python. >>> n = 300. This is read or interpreted as " n is assigned the value 300 .". Once this is done, n can be used in a statement or expression, and its value will be substituted: Python.
Spécification complète de la grammaire — Documentation Python 3.14.0a0. 10. Spécification complète de la grammaire ¶. Ceci est la grammaire complète de Python, issue directement de la grammaire utilisée pour générer l'analyseur syntaxique CPython (voir Grammar/python.gram ). La version ci-dessous ne comprend pas les détails relatifs ...