10 Other Ways to Say “In This Essay, I Will” (With Examples)
In academic writing , there is a tendency to overuse common phrases like “In this essay, I will.” While this phrase clearly outlines what the essay will cover, using it repeatedly can make your writing boring and repetitive.
In this article, I aim to provide readers with 10 effective synonyms for “In this essay, I will” to add variety to their essays and papers. Using different languages keeps the reader engaged and demonstrates a more advanced writing style.
This post aims to expand your options when introducing the topics covered in an essay. You can craft a strong opening that draws readers in by avoiding overused phrases and incorporating more creative language.
Whether writing for school, work, or your blog, having alternate ways to say “In this essay, I will” will improve the flow of your writing. The examples provided will help you replace the standard phrase in your work.
I hope you find these tips useful for taking your essay introductions to the next level.

Is It Wrong to Say “In This Essay, I Will”?
It is wrong to overuse the phrase “In this essay, I will” in academic writing. Though this phrase clearly outlines the topics that will be covered, relying on it too heavily can make your writing repetitive and boring for the reader.
Here are a few reasons why it’s best to avoid overusing “In this essay, I will”:
- It’s formulaic and overused. This phrase has become a tired cliché in essays, so finding alternatives makes your writing come across as more original and sophisticated.
- It can make your introduction seem mechanical. Leading with “In this essay, I will” repeatedly makes the opening sound detached rather than engaging the reader’s interest from the start.
- It’s a missed opportunity for more creative language. Varying your introduction keeps readers attentive and demonstrates a more skilled writing style.
- It hinders smooth transitions between ideas. Overusing this repetitive phrase prevents your essay from flowing logically from one point to the next.
- It’s redundant. Usually, the topics covered are outlined elsewhere like in the title or abstract, so repeatedly stating “In this essay, I will” is unnecessary.
While “In this essay, I will” can be useful when used sparingly, relying on this phrase too much results in monotonous writing . Keeping introductions lively and avoiding repetition makes a paper more appealing to read. With some thought and creativity, there are many engaging ways to smoothly introduce the key points in an academic essay.
What to Say Instead of “In This Essay, I Will”
- The purpose of this essay is to
- This essay aims to
- In the following pages, I intend to
- The goal of this piece is to
- Throughout this essay, I plan to
- In this document, my objective is to
- The focus of this composition will be to
- Throughout this paper, I intend to
- The ambition of this work is to
- Within this text, I aspire to
1. The purpose of this essay is to…
This directly states the intended goal of your essay and informs the reader of its primary aim.
Example: The purpose of this essay is to ignite a national conversation about the alarming decline of bee populations and its potential consequences for our food security.
2. This essay aims to…
Similar to the first option, it suggests a more focused exploration of the chosen topic.
Example: This essay aims to delve into the psychological motivations behind historical figures often labeled as “villains,” uncovering the complexities that shaped their actions.
3. In the following pages, I intend to…
This creates a sense of anticipation and informs the reader about the specific areas you’ll be covering.
Example: In the following pages, I intend to dissect the intricate power dynamics within Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice,” unveiling the societal norms and hidden agendas that fuel the characters’ interactions.
4. The goal of this piece is to…
Similar to “aims to,” but emphasizes the desired outcome you hope to achieve with your essay.
Example: The goal of this piece is to empower individuals to recognize and combat microaggressions in their daily lives, fostering a more inclusive and respectful society.
5. Throughout this essay, I plan to…
Highlights the journey of exploration your essay will take, suggesting a more dynamic reading experience.
Example: Throughout this essay, I plan to embark on a literary safari through the captivating world of Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s “One Hundred Years of Solitude,” unraveling its magical realism and timeless themes.
6. In this document, my objective is to…
Emphasizes a clear and objective approach to the topic, suitable for informative essays.
Example: In this document, my objective is to provide a balanced overview of the pros and cons of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), equipping readers with the information needed to form their own informed opinions.
7. The focus of this composition will be to…
Narrows down the specific aspect of the topic you’ll be concentrating on.
Example: The focus of this composition will be to analyze the stylistic innovations and recurring themes within the poetry of Sylvia Plath, exploring her unique contribution to the confessionalist movement.
8. Throughout this paper, I intend to…
Similar to “focus,” but emphasizes your intent and guiding principle throughout the essay.
Example: Throughout this paper, I intend to critically examine the portrayal of mental illness in mainstream media, challenging harmful stereotypes and advocating for accurate representation .
9. The ambition of this work is to…
Conveys a strong and aspirational goal for your essay, highlighting its potential impact.
Example: The ambition of this work is to reimagine the future of education, promoting personalized learning experiences that ignite students’ curiosity and foster lifelong adaptability.
10. Within this text, I aspire to…
Expresses a personal desire to achieve something meaningful with your essay, adding a touch of emotional engagement.
Example: Within this text, I aspire to illuminate the hidden beauty and resilience of overlooked communities, fostering empathy and inspiring action for positive change.
In summary, using more varied language to introduce the topics covered adds creativity and enhances the flow of an essay. The alternatives provided in this article, such as “The purpose of this essay is to” or “Throughout this paper, I intend to,” demonstrate more lively ways to articulate what the essay will examine.
Avoiding repetition and employing these different options will make an essay introduction stand out while still effectively framing the forthcoming discussion. With some thoughtful language choices and succinct presentation , writers can craft dynamic essay openings without overly relying on the dull, ubiquitous phrase “In this essay, I will.”
Related Posts:
10 Better Ways To Write “In This Essay, I Will…”
“In this essay, I will” is a common way for people to talk about what they will write in their essays. However, it’s often overused, which is why it might be wise to look into a few available alternatives. This article will share the best ones with you.
What Can I Write Instead Of “In This Essay, I Will…”?
The preferred versions do not reference the “essay” at all. Instead, the best options are “you will learn about” and “you will find out about.” These work well because they save time and words in the essay, and they don’t seem like wasted space for the reader.
You Will Learn About
“You will learn about” works well because it shows the reader straight away what they will learn. We do not have to use the phrase “In this essay” or anything similar because they’re already aware that they are reading an essay.
You Will Find Out About
Check out some of these examples to see how it works:
I Find… Really Interesting…
You can see how it works in the following examples:
This Essay Demonstrates
“This essay demonstrates” is a good phrase to start an essay if you want to include the phrase. There is nothing fundamentally wrong with starting essays with a phrase like this; it mostly depends on personal choice and writing style.
This Essay Will Discuss
“This essay will discuss” is another way to share the overall point of your essay. The sooner we can convey the overall meaning, the more interested the reader will be. It helps them to know what they are reading about before they begin.
Here are a few examples to show you how it works:
In This Essay, You Will Learn
Check out some examples of how it might work:
I Will Show Both Sides Of The Argument
This essay will analyze.
Some examples will help you to understand it better:
I Strongly Agree/Disagree, And This Essay Will Explore Why
This paper will explore.
Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here .
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What is an equivalent to saying "for the purpose of this essay"? [closed]
I cannot think of another formal way to say "for the purpose of this essay." The following sentence shows some context:
For the purpose of this essay, it is not necessary to dwell any further on particular conditions...
- expressions
4 Answers 4
I agree the phrase is worth avoiding; but avoiding it does not require any substitute. The sample sentence of which you offer the first part almost certainly deserves to be deleted entirely during revision. Resist temptations to talk about your essay within your essay. (One exception might be a partitio or divisio section offering an advance road-map to a particularly complicated argument.)
You could use a phrase similar to "outside the scope of this essay"
- Welcome to English Language & Usage @Anon. When you have enough rep such a short post could be made as a comment. – user63230 Commented Dec 1, 2014 at 1:04
The English adverb herein may serve. From en.wiktionary , it means “Within this content, context, or thing”. You could say:
it is not necessary to dwell herein any further on particular conditions
or could say
Those conditions need not be considered here
but for brevity might instead say “I'll say no more of this now” or use an old standby, “But I digress”.
Of course, as Brian Donovan has noted in an answer, there's little need in an essay – a fairly short work – for such a sentence at all.
I sometimes say:
For present purposes
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged expressions synonyms or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
Hot Network Questions
- Could two moons orbit each other around a planet?
- Transparent Glass Material Eevee Blender version 4.2
- What is the "closest approximation" to fields by an equational variety?
- Does Justice Sotomayor's "Seal Team 6" example, in and of itself, explicitly give the President the authority to execute opponents? If not, why not?
- Evil God Challenge: What if an evil god is just trolling humanity and that explains why there's good in the world?
- What's the history of Spell Slots in D&D?
- How to read chainline specs for crankset and bottom bracket compatibility?
- Mathematical expression of controlled Ry gate
- Why does Paul's fight with Feyd-Rautha take so long?
- Switch loop light convert to ceiling fan
- Reversing vowels in a string
- Sci-fi book series about a teenage detective, possibly named Diamond, with a floating AI assistant
- Source impedance-trace impedance - load termination impedance confusion
- Can the US president kill at will?
- Why do some JFETs oscillate and others don't?
- How much damage does my Hexblade Warlock deal with their Bonus Action attack?
- What is 切り抜きが怖い言い方?
- Guessing whether the revealed number is higher
- Is "able to find related code by searching keyword 'MyClass '(variable declaration)" a reason to avoid using auto in c++?
- Error handling for singly linked list in C
- Can a country refuse to deliver a person accused of attempted murder?
- confidence intervals for proportions containing a theoretically impossible value (zero)
- Did any attendees write up accounts of pre-1980 Homebrew Computer Club meetings?
- Hourly pay rate calculation between Recruiting and Payroll Systems
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

16 Synonyms for “In This Essay I Will”

If you’re unsure how to introduce what you will be talking about in an essay, you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ll discuss whether it’s okay to use the phrase “in this essay I will” as an introduction. Moreover, we’ve provided a list of alternative phrases you can use instead!
“In This Essay I Will” Synonyms
- The following essay will
- The purpose of this paper is
- In the following essay, I will
- This essay will
- This paper will
- The following paper will
- The aim of this paper is
- The aim of this essay is
- The purpose of this essay is
- This paper aims
- In this paper, I intend to
- The following paper shall
- In this paper, I will
- This study will
- The following dissertation will
- This thesis will
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- It is not bad to introduce a paper with “in this essay I will,” but you should ask your teacher whether they prefer a paper without personal pronouns in it.
- “The following essay” is a great alternative that uses similar words while removing the personal pronoun “I.”
- You can use “the purpose of this paper is” if you want to completely change your phrasing from the original.
Keep reading to see how we use our choice of alternatives for “in this essay I will” in a couple of helpful examples.
After that, we’ll talk about whether it’s a bad idea to use the phrase “in this essay I will” in an academic paper.
The Following Essay Will
Another way to say “in this essay I will” is to say “the following essay will.” This alternative is great for when you’re writing a particularly formal essay.
After all, many academics urge against the use of personal pronouns like “I” in some academic essays. This synonym uses similar words to the original but removes the controversial “I”!
“The following essay will” isn’t an inherently better phrase than “In this essay I will.” However, it is a fact that most markers warn against the use of personal pronouns. Therefore, it’s a safer option if you’re unsure!
Let’s see a couple of examples making use of this alternative:
The following essay will discuss the sociological impacts of neocolonialism in former British colonies.
While both Clapton and Hendrix were self-taught, the following essay will illustrate that both possessed skills that were equal to, if not surpassing, their classically trained counterparts.
The Purpose of This Paper Is
If you’re wondering what to say instead of “in this essay I will,” we’d go with the phrase “the purpose of this paper is.”
This alternative is great if you want to completely alter your choice of words in your introduction. It replaces “essay” with “paper” and removes the personal pronoun “I” to boot!
This makes this synonym a better option than “in this essay I will” if you are unsure whether the marker will penalize you for using personal pronouns.
Finally, consider the following examples to see this phrase in action:
The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the link between patriarchy and capitalism.
With the following questions in mind, the purpose of this paper is to theoretically unpack Kant’s notion of a “universal and objective law” in light of globalization and arguments for moral relativism.
Is It Bad to Say “In This Essay I Will”?
The phrase “in this essay I will” is not inherently bad . For example, this may be a perfectly acceptable way to start an essay at a high school level.
There are even some higher academic papers that start this way. In general, how one goes about introducing their topic is a matter of preference .
That being said, it’s always a good idea to talk to the person who will be grading your paper before you start. Ask them if it’s okay to use personal pronouns. In recent times, some professors prefer papers written in an accessible way that’s easy for everyone to understand!
Likewise, some teachers would prefer a more formal tone, so using personal pronouns like “I” should be avoided. That’s why we recommend that you always ask before you start!
So, if you’ve found out that “in this essay I will” is acceptable according to your teacher, here are a few variations of this phrase you might try:
- In this essay I will discuss
- in this essay I will be discussing
- in this essay I will argue
It would also be correct to add a comma after “in this essay.” Whether or not you add a comma is a stylistic choice , and some people choose not to for a smoother read. Nonetheless, the following variations would also be correct:
- In this essay, I will show
- In this essay, I will demonstrate
In conclusion, it isn’t necessarily bad to say “in this essay I will” to introduce your paper. However, it’s always good to check with your teacher or professor and find out how formal they want your paper to sound.
If you found our list of synonyms helpful, feel free to bookmark this page!
- 19 Gender-Neutral Alternatives to “Dear Sir or Madam”
- 15 Other Ways to Say “If I Can Be of Further Assistance”
- 15 Other Ways to Say “At Your Earliest Convenience”
- 15 Other Ways to Say “No Need to Apologize”
We are a team of experienced communication specialists.
Our mission is to help you choose the right phrase or word for your emails and texts.
Choosing the right words shouldn't be your limitation!
© WordSelector
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
How to write a research paper like a pro.
- Academic Integrity vs. Academic Dishonesty: Understanding the Key Differences
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your Thesis
- Guide to Structuring Your Narrative Essay for Success
- How to Hook Your Readers with a Compelling Topic Sentence
- Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
- How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

17 academic words and phrases to use in your essay
(Last updated: 20 October 2022)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
For the vast majority of students, essay writing doesn't always come easily. Writing at academic level is an acquired skill that can literally take years to master – indeed, many students find they only start to feel really confident writing essays just as their undergraduate course comes to an end!
If this is you, and you've come here looking for words and phrases to use in your essay, you're in the right place. We’ve pulled together a list of essential academic words you can use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essays .
Whilst your ideas and arguments should always be your own, borrowing some of the words and phrases listed below is a great way to articulate your ideas more effectively, and ensure that you keep your reader’s attention from start to finish.
It goes without saying (but we'll say it anyway) that there's a certain formality that comes with academic writing. Casual and conversational phrases have no place. Obviously, there are no LOLs, LMFAOs, and OMGs. But formal academic writing can be much more subtle than this, and as we've mentioned above, requires great skill.
So, to get you started on polishing your own essay writing ability, try using the words in this list as an inspirational starting point.
Words to use in your introduction
The trickiest part of academic writing often comes right at the start, with your introduction. Of course, once you’ve done your plan and have your arguments laid out, you need to actually put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard) and begin your essay.
You need to consider that your reader doesn’t have a clue about your topic or arguments, so your first sentence must summarise these. Explain what your essay is going to talk about as though you were explaining it to a five year old – without losing the formality of your academic writing, of course! To do this, use any of the below words or phrases to help keep you on track.
1. Firstly, secondly, thirdly
Even though it sounds obvious, your argument will be clearer if you deliver the ideas in the right order. These words can help you to offer clarity and structure to the way you expose your ideas. This is an extremely effective method of presenting the facts clearly. Don’t be too rigid and feel you have to number each point, but using this system can be a good way to get an argument off the ground, and link arguments together.
2. In view of; in light of; considering
These essay phrases are useful to begin your essay. They help you pose your argument based on what other authors have said or a general concern about your research. They can also both be used when a piece of evidence sheds new light on an argument. Here’s an example: The result of the American invasion has severely impaired American interests in the Middle East, exponentially increasing popular hostility to the United States throughout the region, a factor which has proved to be a powerful recruitment tool for extremist terrorist groups (Isakhan, 2015). Considering [or In light of / In view of] the perceived resulting threat to American interests, it could be argued that the Bush administration failed to fully consider the impact of their actions before pushing forward with the war.
3. According to X; X stated that; referring to the views of X
Introducing the views of an author who has a comprehensive knowledge of your particular area of study is a crucial part of essay writing. Including a quote that fits naturally into your work can be a bit of a struggle, but these academic phrases provide a great way in.
Even though it’s fine to reference a quote in your introduction, we don’t recommend you start your essay with a direct quote. Use your own words to sum up the views you’re mentioning, for example:
As Einstein often reiterated, experiments can prove theories, but experiments don’t give birth to theories.
Rather than:
“A theory can be proved by experiment, but no path leads from experiment to the birth of a theory.” {Albert Einstein, 1954, Einstein: A Biography}.
See the difference?
And be sure to reference correctly too, when using quotes or paraphrasing someone else's words.

Adding information and flow
The flow of your essay is extremely important. You don’t want your reader to be confused by the rhythm of your writing and get distracted away from your argument, do you? No! So, we recommend using some of the following ‘flow’ words, which are guaranteed to help you articulate your ideas and arguments in a chronological and structured order.
4. Moreover; furthermore; in addition; what’s more
These types of academic phrases are perfect for expanding or adding to a point you’ve already made without interrupting the flow altogether. “Moreover”, “furthermore” and “in addition” are also great linking phrases to begin a new paragraph.
Here are some examples: The dissociation of tau protein from microtubules destabilises the latter resulting in changes to cell structure, and neuronal transport. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to further oxidative stress causing increased levels of nitrous oxide, hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxidases.
On the data of this trial, no treatment recommendations should be made. The patients are suspected, but not confirmed, to suffer from pneumonia. Furthermore, five days is too short a follow up time to confirm clinical cure.
5. In order to; to that end; to this end
These are helpful academic phrases to introduce an explanation or state your aim. Oftentimes your essay will have to prove how you intend to achieve your goals. By using these sentences you can easily expand on points that will add clarity to the reader.
For example: My research entailed hours of listening and recording the sound of whales in order to understand how they communicate.
Dutch tech companies offer support in the fight against the virus. To this end, an online meeting took place on Wednesday...
Even though we recommend the use of these phrases, DO NOT use them too often. You may think you sound like a real academic but it can be a sign of overwriting!
6. In other words; to put it another way; that is; to put it more simply
Complement complex ideas with simple descriptions by using these sentences. These are excellent academic phrases to improve the continuity of your essay writing. They should be used to explain a point you’ve already made in a slightly different way. Don’t use them to repeat yourself, but rather to elaborate on a certain point that needs further explanation. Or, to succinctly round up what just came before.
For example: A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between phenomena. In other words, there is no treatment effect.
Nothing could come to be in this pre-world time, “because no part of such a time possesses, as compared with any other, a distinguishing condition of existence rather than non-existence.” That is, nothing exists in this pre-world time, and so there can be nothing that causes the world to come into existence.
7. Similarly; likewise; another key fact to remember; as well as; an equally significant aspect of
These essay words are a good choice to add a piece of information that agrees with an argument or fact you just mentioned. In academic writing, it is very relevant to include points of view that concur with your opinion. This will help you to situate your research within a research context.
Also , academic words and phrases like the above are also especially useful so as not to repeat the word ‘also’ too many times. (We did that on purpose to prove our point!) Your reader will be put off by the repetitive use of simple conjunctions. The quality of your essay will drastically improve just by using academic phrases and words such as ‘similarly’, ‘as well as’, etc. Here, let us show you what we mean:
In 1996, then-transport minister Steve Norris enthused about quadrupling cycling trips by 2012. Similarly, former prime minister David Cameron promised a “cycling revolution” in 2013…
Or Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) aims to bridge the gap of access to electricity across the continent (...). Another key fact to remember is that it must expand cost-efficient access to electricity to nearly 1 billion people.
The wording “not only… but also” is a useful way to elaborate on a similarity in your arguments but in a more striking way.

Comparing and contrasting information
Academic essays often include opposite opinions or information in order to prove a point. It is important to show all the aspects that are relevant to your research. Include facts and researchers’ views that disagree with a point of your essay to show your knowledge of your particular field of study. Below are a few words and ways of introducing alternative arguments.
8. Conversely; however; alternatively; on the contrary; on the other hand; whereas
Finding a seamless method to present an alternative perspective or theory can be hard work, but these terms and phrases can help you introduce the other side of the argument. Let's look at some examples:
89% of respondents living in joint families reported feeling financially secure. Conversely, only 64% of those who lived in nuclear families said they felt financially secure.
The first protagonist has a social role to fill in being a father to those around him, whereas the second protagonist relies on the security and knowledge offered to him by Chaplin.
“On the other hand” can also be used to make comparisons when worded together with “on the one hand.”
9. By contrast; in comparison; then again; that said; yet
These essay phrases show contrast, compare facts, and present uncertainty regarding a point in your research. “That said” and “yet” in particular will demonstrate your expertise on a topic by showing the conditions or limitations of your research area. For example:
All the tests were positive. That said, we must also consider the fact that some of them had inconclusive results.
10. Despite this; provided that; nonetheless
Use these phrases and essay words to demonstrate a positive aspect of your subject-matter regardless of lack of evidence, logic, coherence, or criticism. Again, this kind of information adds clarity and expertise to your academic writing.
A good example is:
Despite the criticism received by X, the popularity of X remains undiminished.
11. Importantly; significantly; notably; another key point
Another way to add contrast is by highlighting the relevance of a fact or opinion in the context of your research. These academic words help to introduce a sentence or paragraph that contains a very meaningful point in your essay.
Giving examples
A good piece of academic writing will always include examples. Illustrating your essay with examples will make your arguments stronger. Most of the time, examples are a way to clarify an explanation; they usually offer an image that the reader can recognise. The most common way to introduce an illustration is “for example.” However, in order not to repeat yourself here are a few other options.
12. For instance; to give an illustration of; to exemplify; to demonstrate; as evidence; to elucidate
The academic essays that are receiving top marks are the ones that back up every single point made. These academic phrases are a useful way to introduce an example. If you have a lot of examples, avoid repeating the same phrase to facilitate the readability of your essay.
Here’s an example:
‘High involvement shopping’, an experiential process described by Wu et al. (2015, p. 299) relies upon the development of an identity-based alliance between the customer and the brand. Celebrity status at Prada, for example, has created an alliance between the brand and a new generation of millennial customers.

Concluding your essay
Concluding words for essays are necessary to wrap up your argument. Your conclusion must include a brief summary of the ideas that you just exposed without being redundant. The way these ideas are expressed should lead to the final statement and core point you have arrived at in your present research.
13. In conclusion; to conclude; to summarise; in sum; in the final analysis; on close analysis
These are phrases for essays that will introduce your concluding paragraph. You can use them at the beginning of a sentence. They will show the reader that your essay is coming to an end:
On close analysis and appraisal, we see that the study by Cortis lacks essential features of the highest quality quantitative research.
14. Persuasive; compelling
Essay words like these ones can help you emphasize the most relevant arguments of your paper. Both are used in the same way: “the most persuasive/compelling argument is…”.
15. Therefore; this suggests that; it can be seen that; the consequence is
When you’re explaining the significance of the results of a piece of research, these phrases provide the perfect lead up to your explanation.
16. Above all; chiefly; especially; most significantly; it should be noted
Your summary should include the most relevant information or research factor that guided you to your conclusion. Contrary to words such as “persuasive” or “compelling”, these essay words are helpful to draw attention to an important point. For example:
The feasibility and effectiveness of my research has been proven chiefly in the last round of laboratory tests.
Film noir is, and will continue to be, highly debatable, controversial, and unmarketable – but above all, for audience members past, present and to come, extremely enjoyable as a form of screen media entertainment.
17. All things considered
This essay phrase is meant to articulate how you give reasons to your conclusions. It means that after you considered all the aspects related to your study, you have arrived to the conclusion you are demonstrating.
After mastering the use of these academic words and phrases, we guarantee you will see an immediate change in the quality of your essays. The structure will be easier to follow, and the reader’s experience will improve. You’ll also feel more confident articulating your ideas and using facts and examples. So jot them all down, and watch your essays go from ‘good’ to ‘great’!

Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’

How to write a master’s essay

- academic writing
- writing a good essay
- writing essays
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- How it works

How to Write the Dissertation Aims and Objectives – Guide & Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information regarding aims and objectives, their differences, writing tips , and the common mistakes you should avoid while writing them.
The aim is often a single sentence or a short paragraph that describes your dissertation’s main goal and intent. It tells what you hope to achieve at the end. You should write the aim so that it becomes identifiable when it is achieved with the completion of your dissertation .
The aim is written in a subsection of the introduction to clarify the overall purpose of the dissertation .
Example: It is often observed that employees in culturally diverse workplaces struggle to work effectively in a team. A probable cause of this issue is bullying at the workplace. This research investigates the impact of bullying on employee job satisfaction at culturally diverse workplaces and the resulting loss of employee productivity. This research will use surveys and case study analysis to analyze the impact of bullying on employees.
The objectives in a dissertation describe the ways through which you intend to achieve the research aim. They are specific statements that break down the aim into several smaller key sections of the overall research. Suitable objectives can help you stay focused and conduct research in the direction of your aim.
The number of objectives should be realistic; usually, between three to six, and each one should be possible to achieve. The following example shows the objectives for the previously-mentioned dissertation aim.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace
The objectives of a dissertation should be SMART.
- Specific: should be precise, focused, and well-defined
- Measurable: the progress should be measurable, and you should be able to determine when you have achieved an objective.
- Achievable: you should be able to carry out the required action within your available resources
- Relevant: should be related to the dissertation aim
- Time-bound: should be possible within the available time
Differences between aims and objectives
Aims and objectives are often mixed, but there are clear differences between them.
| Aims | Objectives |
|---|---|
| describes “what” you intend to achieve through your research | focus on “how” you will achieve the aim |
| usually written in broad terms covering the entire dissertation | are specific statements describing steps through which the research aim will be achieved |
| is written as a single sentence or a small paragraph | should be written as a numbered list. |
| focuses on long-term outcomes | focus on short-term and immediate outcomes. |
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

How to write aims and objectives?
There is no particular way or standard to write the aims and objectives. Different researchers have different writing styles, and often it can be influenced by your research supervisor. However, you should follow certain basic principles while writing aims and objectives in a dissertation.
Writing the aim statement
The aim statement should cover the following essential elements.
- Why is the research necessary? (covers the underlying problem on which the study is to be conducted)
- What is the research about? (description of the research title)
- How are you going to conduct it? (a brief statement of intended research methods)
An appropriate aim clearly defines the research purpose without confusing the reader. If you struggle to explain your research and its importance in simpler terms, you should consider refining your research to clarify it further.
Writing objectives
The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps,
- The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review . (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study)
- One objective can be applied to the methodology portion. (Verbs to be used: collect, select, demonstrate, estimate)
- Two to three objectives can cover the critical evaluation or discussion chapters (Verbs to be used: analyze, compare, evaluate)
- The final objective will cover the conclusion or recommendation portion. (Verbs to be used: conclude, recommend)
Instead of writing like a paragraph, the objectives should be written as a numbered list to give them more clarity.
How many aims and objectives should be there?
It depends upon the topic of your research and mainly upon your supervisor’s requirements. Generally, a dissertation has a single broad statement as the research aim. However, it is acceptable to include a main aim along with two to three subsidiary aims.
Similarly, the number of objectives should be realistic and sufficient to measure the progress regarding the achievement of the research aim. Their number can generally vary from three to six depending upon the aim.
Common mistakes to avoid while writing research aims and objectives
- Writing a broad research aim
Writing a broad research aim is a common mistake, and it often becomes difficult to achieve. It may create a problem when you are asked to prove how you have achieved your aims during your viva defense . It would be best to narrow your study to a specific area in the early stages of the dissertation.
- Formulating overlapping research objectives
The objectives should be written such that they are measurable and distinct from each other. If they overlap, it makes it difficult to structure your dissertation properly in specific chapters.
- Setting unrealistic aims
Students often get over-ambitious while describing the research aim and face problems afterward in achieving those aims. You should avoid this mistake and be realistic about what you can achieve in the available time and resources.
Aims and objectives are the sections that require significant time and attention to avoid future hassles while conducting research and writing your dissertation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to set dissertation aims and objectives.
To set dissertation aims and objectives, define your research goals clearly. Aims state what you want to achieve, while objectives outline specific, measurable steps to reach those goals. Ensure they align with your research question and contribute to your study’s significance.
You May Also Like
Explore the top 4 AI essay writer tools of 2024 – Writeressay.ai, Aiessaybot.org, Essayrewriter.io, and Aiarticlespinner.com.
We have identified the most common dissertation questionnaire mistakes made by researchers that need to be avoided for good dissertations and thesis
The best language for a thesis depends on the audience and field. English is common for global reach, but local languages may suit specific contexts better.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

9 Examples: How to Write a Purpose Statement
By Status.net Editorial Team on September 30, 2023 — 15 minutes to read
- Key Elements of a Purpose Statement Part 1
- How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step Part 2
- Identifying Your Goals Part 3
- Defining Your Audience Part 4
- Outlining Your Methods Part 5
- Stating the Expected Outcomes Part 6
- Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper Part 7
- Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals Part 8
- Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives Part 9
- Purpose Statement Example For an Essay Part 10
- Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal Part 11
- Purpose Statement Example For a Report Part 12
- Purpose Statement Example For a Project Part 13
- Purpose Statement Templates Part 14
A purpose statement is a vital component of any project, as it sets the tone for the entire piece of work. It tells the reader what the project is about, why it’s important, and what the writer hopes to achieve.
Part 1 Key Elements of a Purpose Statement
When writing a purpose statement, there are several key elements that you should keep in mind. These elements will help you to create a clear, concise, and effective statement that accurately reflects your goals and objectives.
1. The Problem or Opportunity
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing.
2. The Target Audience
The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement. This should be a clear and specific description of the group of people who will benefit from your work.
3. The Solution
The third element is the solution that you are proposing. This should be a clear and specific description of the action that you will take to address the problem or pursue the opportunity.
4. The Benefits
The fourth element is the benefits that your solution will provide. This should be a clear and specific description of the positive outcomes that your work will achieve.
5. The Action Plan
The fifth element is the action plan that you will follow to implement your solution. This should be a clear and specific description of the steps that you will take to achieve your goals.
Part 2 How to Write a Purpose Statement Step-by-Step
Writing a purpose statement is an essential part of any research project. It helps to clarify the purpose of your study and provides direction for your research. Here are some steps to follow when writing a purpose statement:
- Start with a clear research question: The first step in writing a purpose statement is to have a clear research question. This question should be specific and focused on the topic you want to research.
- Identify the scope of your study: Once you have a clear research question, you need to identify the scope of your study. This involves determining what you will and will not include in your research.
- Define your research objectives: Your research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with your research question and the scope of your study.
- Determine your research design: Your research design will depend on the nature of your research question and the scope of your study. You may choose to use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach.
- Write your purpose statement: Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes the purpose of your study. It should include your research question, the scope of your study, your research objectives, and your research design.
Research question: What are the effects of social media on teenage mental health?
Scope of study: This study will focus on teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States.
Research objectives: To determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.
Research design: This study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals.
Purpose statement: The purpose of this study is to examine the effects of social media on teenage mental health among teenagers aged 13-18 in the United States. The study will use a mixed-methods approach, including a survey and interviews with teenagers and mental health professionals. The research objectives are to determine the prevalence of social media use among teenagers, to identify the types of social media used by teenagers, to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health, and to provide recommendations for parents, educators, and mental health professionals.

Part 3 Section 1: Identifying Your Goals
Before you start writing your purpose statement, it’s important to identify your goals. To do this, ask yourself the following questions:
- What do I want to achieve?
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What impact do I want to make?
Once you have a clear idea of your goals, you can start crafting your purpose statement. Your purpose statement should be a clear and concise statement that outlines the purpose of your work.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to provide high-quality products and services that improve the lives of our customers and contribute to the growth and success of our company.”
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a non-profit organization, your statement might look something like this:
“Our purpose is to improve the lives of underserved communities by providing access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.”
Remember, your purpose statement should be specific, measurable, and achievable. It should also be aligned with your values and goals, and it should inspire and motivate you to take action.
Part 4 Section 2: Defining Your Audience
Once you have established the purpose of your statement, it’s important to consider who your audience is. The audience for your purpose statement will depend on the context in which it will be used. For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper, your audience will likely be your professor or academic peers. If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal, your audience may be potential investors or clients.
Defining your audience is important because it will help you tailor your purpose statement to the specific needs and interests of your readers. You want to make sure that your statement is clear, concise, and relevant to your audience.
To define your audience, consider the following questions:
- Who will be reading your purpose statement?
- What is their level of knowledge or expertise on the topic?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What do they hope to gain from reading your purpose statement?
Once you have a clear understanding of your audience, you can begin to craft your purpose statement with their needs and interests in mind. This will help ensure that your statement is effective in communicating your goals and objectives to your readers.
For example, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a research paper on the effects of climate change on agriculture, your audience may be fellow researchers in the field of environmental science. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is clear and concise, using technical language that is familiar to your audience.
Or, if you’re writing a purpose statement for a business proposal to potential investors, your audience may be less familiar with the technical aspects of your project. In this case, you would want to make sure that your purpose statement is written in a way that is easy to understand, using clear and concise language that highlights the benefits of your proposal.
The key to defining your audience is to put yourself in their shoes and consider what they need and want from your purpose statement.
Part 5 Section 3: Outlining Your Methods
After you have identified the purpose of your statement, it is time to outline your methods. This section should describe how you plan to achieve your goal and the steps you will take to get there. Here are a few tips to help you outline your methods effectively:
- Start with a general overview: Begin by providing a brief overview of the methods you plan to use. This will give your readers a sense of what to expect in the following paragraphs.
- Break down your methods: Break your methods down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make it easier for you to stay organized and for your readers to follow along.
- Use bullet points: Bullet points can help you organize your ideas and make your methods easier to read. Use them to list the steps you will take to achieve your goal.
- Be specific: Make sure you are specific about the methods you plan to use. This will help your readers understand exactly what you are doing and why.
- Provide examples: Use examples to illustrate your methods. This will make it easier for your readers to understand what you are trying to accomplish.
Part 6 Section 4: Stating the Expected Outcomes
After defining the problem and the purpose of your research, it’s time to state the expected outcomes. This is where you describe what you hope to achieve by conducting your research. The expected outcomes should be specific and measurable, so you can determine if you have achieved your goals.
It’s important to be realistic when stating your expected outcomes. Don’t make exaggerated or false claims, and don’t promise something that you can’t deliver. Your expected outcomes should be based on your research question and the purpose of your study.
Here are some examples of expected outcomes:
- To identify the factors that contribute to employee turnover in the company.
- To develop a new marketing strategy that will increase sales by 20% within the next year.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of a new training program for improving customer service.
- To determine the impact of social media on consumer behavior.
When stating your expected outcomes, make sure they align with your research question and purpose statement. This will help you stay focused on your goals and ensure that your research is relevant and meaningful.
In addition to stating your expected outcomes, you should also describe how you will measure them. This could involve collecting data through surveys, interviews, or experiments, or analyzing existing data from sources such as government reports or industry publications.
Part 7 Purpose Statement Example for a Research Paper
If you are writing a research paper, your purpose statement should clearly state the objective of your study. Here is an example of a purpose statement for a research paper:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of social media on the mental health of teenagers in the United States.
This purpose statement clearly states the objective of the study and provides a specific focus for the research.
Part 8 Purpose Statement Example For Personal Goals
When writing a purpose statement for your personal goals, it’s important to clearly define what you want to achieve and why. Here’s a template that can help you get started:
“I want to [goal] so that [reason]. I will achieve this by [action].”
Example: “I want to lose 10 pounds so that I can feel more confident in my body. I will achieve this by going to the gym three times a week and cutting out sugary snacks.”
Remember to be specific and realistic when setting your goals and actions, and to regularly review and adjust your purpose statement as needed.
Part 9 Purpose Statement Example For Business Objectives
If you’re writing a purpose statement for a business objective, this template can help you get started:
[Objective] [Action verb] [Target audience] [Outcome or benefit]
Here’s an example using this template:
Increase online sales by creating a more user-friendly website for millennial shoppers.
This purpose statement is clear and concise. It identifies the objective (increase online sales), the action verb (creating), the target audience (millennial shoppers), and the outcome or benefit (a more user-friendly website).
Part 10 Purpose Statement Example For an Essay
“The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and consequences of climate change, with a focus on the role of human activities, and to propose solutions that can mitigate its impact on the environment and future generations.”
This purpose statement clearly states the subject of the essay (climate change), what aspects will be explored (causes, consequences, human activities), and the intended outcome (proposing solutions). It provides a clear roadmap for the reader and sets the direction for the essay.
Part 11 Purpose Statement Example For a Proposal
“The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding and support for the establishment of a community garden in [Location], aimed at promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh, healthy produce.”
Why this purpose statement is effective:
- The subject of the proposal is clear: the establishment of a community garden.
- The specific goals of the project are outlined: promoting sustainable urban agriculture, fostering community engagement, and improving local access to fresh produce.
- The overall objective of the proposal is evident: securing funding and support.
Part 12 Purpose Statement Example For a Report
“The purpose of this report is to analyze current market trends in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, assess consumer preferences and buying behaviors, and provide strategic recommendations to guide [Company Name] in entering this growing market segment.”
- The subject of the report is provided: market trends in the electric vehicle industry.
- The specific goals of the report are analysis of market trends, assessment of consumer preferences, and strategic recommendations.
- The overall objective of the report is clear: providing guidance for the company’s entry into the EV market.
Part 13 Purpose Statement Example For a Project
“The purpose of this project is to design and implement a new employee wellness program that promotes physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace.”
This purpose statement clearly outlines the objective of the project, which is to create a new employee wellness program. The program is designed to promote physical and mental wellbeing in the workplace, which is a key concern for many employers. By implementing this program, the company aims to improve employee health, reduce absenteeism, and increase productivity. The purpose statement is concise and specific, providing a clear direction for the project team to follow. It highlights the importance of the project and its potential benefits for the company and its employees.
Part 14 Purpose Statement Templates
When writing a purpose statement, it can be helpful to use a template to ensure that you cover all the necessary components:
Template 1: To [action] [target audience] in order to [outcome]
This template is a straightforward way to outline your purpose statement. Simply fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- The purpose of […] is
- To [action]: What action do you want to take?
- [Target audience]: Who is your target audience?
- In order to [outcome]: What outcome do you hope to achieve?
For example:
- The purpose of our marketing campaign is to increase brand awareness among young adults in urban areas, in order to drive sales and revenue growth.
- The purpose of our employee training program is to improve customer service skills among our frontline staff, in order to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- The purpose of our new product launch is to expand our market share in the healthcare industry, by offering a unique solution to the needs of elderly patients with chronic conditions.
Template 2: This [project/product] is designed to [action] [target audience] by [method] in order to [outcome].
This template is useful for purpose statements that involve a specific project or product. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate information:
- This [project/product]: What is your project or product?
- Is designed to [action]: What action do you want to take?
- By [method]: What method will you use to achieve your goal?
- This app is designed to provide personalized nutrition advice to athletes by analyzing their training data in order to optimize performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of a purpose statement.
A purpose statement should clearly communicate the main goal or objective of your writing. It should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your work. The key elements of a purpose statement include the topic or subject matter, the intended audience, and the overall goal or objective of your writing.
How can a purpose statement benefit your writing?
A purpose statement can help you stay focused and on track when writing. It can also help you to avoid going off-topic or getting bogged down in unnecessary details. By clearly identifying the main goal or objective of your writing, a purpose statement can help you to stay organized and ensure that your writing is effective and impactful.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a purpose statement?
One common mistake is being too vague or general in your purpose statement. Another mistake is making your purpose statement too long or complex, which can make it difficult to understand. Additionally, it’s important to avoid including unnecessary information or details that are not directly relevant to your main goal or objective.
How can you tailor your purpose statement to your audience?
When writing a purpose statement, it’s important to consider your audience and their needs. You should tailor your purpose statement to your audience by using language and terminology that they will understand. You should also consider their level of knowledge or expertise on the subject matter and adjust your purpose statement accordingly.
What are some effective templates for writing a purpose statement?
There are many effective templates for writing a purpose statement, but one common approach is to use the following structure: “The purpose of this writing is to [insert goal or objective] for [insert audience] regarding [insert topic or subject matter].”
Can you provide examples of successful purpose statements?
- “The purpose of this report is to provide an analysis of the current market trends and make recommendations for future growth strategies for our company.”
- “The purpose of this essay is to explore the impact of social media on modern communication and its implications for society.”
- “The purpose of this proposal is to secure funding for a new community center that will provide educational and recreational opportunities for local residents.”
- 20 Inspiring Examples: How to Write a Personal Mission Statement
- 5 Examples: How to Write a Letter of Employment
- 6 Example Emails: How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation
- 2 Templates and Examples: Individual Development Plan
- 5 Effective Examples: How to Write a Two-Week Notice
- 3 Examples: Job Application Email (with Tips)

Essay on My Purpose in Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on My Purpose in Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on My Purpose in Life
Introduction.
Life is a journey filled with lessons and experiences. My purpose in life is to learn, grow, and contribute to the world.
I believe that learning is a lifelong process. I strive to gain knowledge every day, which helps me to become a better person.
Personal growth is important to me. I aim to improve myself continuously, overcoming challenges and growing stronger.
Contribution
I want to make a positive impact in the world. I aim to help others, and through this, fulfill my purpose in life.
250 Words Essay on My Purpose in Life
Life is a journey of self-discovery and purpose. It is a voyage that leads one to the realization of their significance in the grand scheme of existence. My purpose in life, as I perceive it, is to contribute positively to the world, continually learn and grow, and inspire others.
Positive Contribution
In the vast expanse of the universe, our individual existences may seem insignificant. However, I believe that each one of us has the capacity to make a positive impact. My purpose is to contribute to society’s welfare, be it through volunteer work, professional endeavors, or simply spreading kindness and understanding in my daily interactions.
Continuous Learning and Growth
Life is a continuous learning process. Each day presents new opportunities to grow, learn, and evolve. I am committed to lifelong learning, not just in the academic or professional sense, but in personal development. This involves embracing challenges, cultivating resilience, and fostering a growth mindset.
Inspiring Others
Lastly, I aspire to inspire. I believe that one of the most profound ways to make a difference is to inspire others to discover their own purpose and pursue it with passion. This could be through sharing experiences, leading by example, or providing support and encouragement.
In conclusion, my purpose in life is to contribute positively to the world, continually learn and grow, and inspire others. This purpose is not static but evolves as I journey through life, constantly shaped by experiences, insights, and personal growth. It serves as a compass, guiding my decisions and actions, and giving meaning to my existence.
500 Words Essay on My Purpose in Life
Contributing to the world.
I believe that each of us has a responsibility to make the world a better place. This does not necessarily mean grand, sweeping changes. Even small actions can have a profound impact. For me, contributing to the world means using my skills and talents to help others. As a college student, I have the opportunity to acquire knowledge and expertise in a particular field. My aim is to use this expertise to solve problems and create solutions that can improve people’s lives. Whether it’s through research, innovation, or direct service, I want to leave a positive mark on the world.
Another aspect of my purpose in life is to inspire others. I believe that we all have the power to influence those around us, to encourage them to strive for their dreams and to become the best versions of themselves. This can be achieved through leading by example, sharing our experiences, and showing empathy and understanding. I strive to be a source of inspiration for my peers, not by being perfect, but by demonstrating resilience in the face of challenges, and by showing that it’s okay to make mistakes and learn from them.
Personal Growth and Evolution
In conclusion, my purpose in life is a multifaceted one. It involves contributing positively to the world, inspiring others, and continuously growing and evolving. This purpose is not fixed; it is dynamic and will likely evolve as I journey through life. Nonetheless, it serves as a guiding light, helping me make decisions and navigate through life’s complexities. I believe that by living in alignment with this purpose, I can lead a fulfilling life and make a positive impact on the world.
This is my purpose, but each person’s purpose is unique to them. It is up to each of us to discover our own purpose, to find that unique path that leads us to fulfillment and allows us to contribute to the world in our own unique way.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Life Life Goals
My Vision and Mission in Life: the Purpose of My Journey
Table of contents, defining my vision, embracing my mission, the interplay between vision and mission.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Volunteering
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Sentence examples for the aim of this essay from inspiring English sources
Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig. Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig.
Is your sentence correct in English?
Login and get your AI feedback from Ludwig.
review of the articles to identify those with high relation with the aim of this essay and (ii).
The aim of this essay is to develop a theoretical background feasible in defining an optimal experience.
The aim of this essay is to describe commonly encountered neoplastic and non-neoplastic entities involving the perinephric space and to describe their key imaging characteristics.
The aim of this essay is to orient Internet users to three sites providing access to the work of Charles Darwin.
Since the aim of this essay is to review the issues concerning whether genuine moral knowledge is possible, we need to assess the merits of this debunking argument, paying close attention to how the ideal of objectivity is understood in this context.
The aim of this essay was to determine the antibiotic susceptibilities of the Brucella isolates identified in the Laboratory of Clinical Bacteriology, Parasitology, Zoonoses, and Geographical medicine of the University of Crete.
Write in English at your best, with Ludwig
Used by millions of students, scientific researchers, professional translators and editors from all over the world.

Simone Ivan Conte
Be a smart writer
Most frequent sentences:, write in english at your best with ludwig.
Essay On My Aim In Life

Table of Contents
Short Essay On My Aim In Life
My aim in life is a question that everyone asks themselves at some point. It is a crucial decision that shapes our future and determines the path we take in life.
Personally, my aim in life is to become a successful professional in my chosen field and make a positive impact on society. I believe that success can be measured in various ways, including financial stability, personal growth, and the ability to make a difference in the lives of others.
To achieve my aim, I know that I need to work hard, be disciplined, and remain focused on my goals. This means putting in the effort to gain the necessary education and skills, as well as staying motivated and determined even when faced with challenges and obstacles.
In addition, I believe that it is important to give back to my community and contribute to the well-being of others. I want to use my skills and knowledge to help people and make a positive impact on their lives.
In conclusion, my aim in life is to achieve success and fulfillment through hard work, dedication, and the desire to make a difference in the world. I believe that by pursuing my goals with determination and a sense of purpose, I can achieve my aim and live a life that is both meaningful and rewarding.
Long Essay On My Aim In Life
Everyone has a different aim in life. Some want to be a doctor, some an engineer, and some a teacher. But what is your aim in life? In this essay, I will explain my ambition and the steps I am taking to reach it. Read on to find out how I am striving to make my dreams come true!
Introduction
It is very important to have an aim in life. A life without an aim is like a ship without a rudder. A man without an aim cannot succeed in life. He wanders like a lost sheep in the wilderness. Therefore, every young man should fix his aim in life and work hard to achieve it.
I have made up my mind to become a doctor and serve humanity. I know it is not an easy task but I am determined to achieve it. I have set my goals and I am working hard towards them. My parents are also very supportive and they are helping me achieve my dream.
I know that becoming a doctor requires a lot of dedication, hard work and sacrifice but I am ready for all of it. I am confident that I will be able to achieve my goal and make my parents proud.
Understanding the Meaning of Aim in Life
It is often said that everyone has an aim in life. An aim or a goal is what drives us to do better in life. It motivates us to work hard and gives us a sense of purpose.
A lot of people think that having an aim in life is not important. They believe that as long as they are happy and content with what they have, that is all that matters. While it is true that being happy and content are important, it is also important to have an aim in life.
An aim gives our lives direction and helps us focus on what we want to achieve. It gives us something to strive for and keeps us motivated. Without an aim, we may not be as successful as we could be and we may not live up to our full potential.
Some people know from a young age what their aim in life is, while others take longer to figure it out. There is no right or wrong answer when it comes to figuring out your aim in life. What matters is that you find something that you are passionate about and that will make you happy.
If you are still trying to figure out your aim in life, don’t worry – there is plenty of time! Just keep exploring different options and eventually you will find something that feels right for you.
Reasons for Having an Aim
It is very important to have an aim in life. A life without an aim is like a boat without a rudder. On the other hand, if our life has some purpose, we can feel more confident and happier. Here are some of the reasons why it is important to have an aim in life:
1) Having an aim gives us a sense of direction and helps us to focus on what is important.
2) It motivates us to work hard and achieve our goals.
3) It helps us to overcome difficulties and setbacks.
4) It gives meaning to our life and makes us feel more fulfilled.
5) It makes us better people as we strive to achieve our goals.
Different Types of Aims in Life
A person’s aim in life is the goal that they want to achieve. It is what they hope to accomplish with their lives. There are many different types of aims in life, and each person has their own unique goals. Some people want to make a difference in the world, while others simply want to be happy and successful. No matter what your aim is, it is important to set goals and work towards them.
One of the most common types of aims in life is to be successful. Many people want to achieve success in their careers, whether it is becoming a CEO or starting their own business. Others may want to be financially successful, such as becoming a millionaire. Whatever your definition of success is, setting goals and working towards them can help you achieve it.
Another type of aim in life is to be happy. This could mean different things for different people. Some people may want to find a partner and settle down, while others may simply want to enjoy their hobbies and activities. Whatever makes you happy, Pursuing it can help you lead a fulfilling life.
There are many other types of aims in life, such as helping others or making a difference in the world. No matter what your aim is, remember to set goals and work towards them. Pursuing your dreams can help you lead a happy and successful life.
Importance or Need for Setting an Aim in Life
My aim in life.
My Aim in Life Everyone has some ambitions in life. It is always good to have an aim in life. A man without an aim is like a ship without a rudder. A fixed goal enables a man to draw strength from adversity, and progress towards it with unswerving determination. My aim in life is to be a doctor. I know that it is not easy to become a doctor. It needs years of hard work and continuous study. I am prepared to make all the sacrifices that are necessary to achieve my goal.
I want to serve humanity by alleviating their sufferings and providing them with the best possible medical care. I have always been inspired by the doctors who have served humanity selflessly and I hope to emulate their example. I know that becoming a doctor is not going to be easy but I am prepared for the challenges that lie ahead. I am confident that with hard work and dedication I will be able to achieve my dream of becoming a doctor and serving humanity.
Ways to Achieve My Aim
There are many ways to achieve one’s aim in life. One can achieve their aim by working hard and determination towards their goal. Another way to achieve one’s aim is to have a positive attitude and be optimistic about achieving their goals. Finally, another way to achieve success is by networking and making connections with people who can help you reach your goals.
In conclusion, my aim in life is to become a successful entrepreneur. I know that it won’t be easy and there will be many challenges along the way but I believe that with hard work, dedication and some luck, I can achieve this goal. With an entrepreneurial mindset and a clear vision of where I want to go in life, nothing can stop me from achieving my dreams.
Manisha Dubey Jha is a skilled educational content writer with 5 years of experience. Specializing in essays and paragraphs, she’s dedicated to crafting engaging and informative content that enriches learning experiences.
Related Posts
Essay on importance of yoga, essay on cow, climate change essay, essay on slaver, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Essay on Aim in Life
Here we have shared the Essay on Aim in Life in detail so you can use it in your exam or assignment of 150, 250, 400, 500, or 1000 words.
You can use this Essay on Aim in Life in any assignment or project whether you are in school (class 10th or 12th), college, or preparing for answer writing in competitive exams.
Topics covered in this article.
Essay on Aim in Life in 150-300 words
Essay on aim in life in 400 words, essay on aim in life in 500-1000 words.
Having a clear aim in life is crucial for personal growth, motivation, and success. It provides a sense of direction and purpose, guiding our actions and decisions. An aim gives us something to strive for, inspiring us to work hard and overcome obstacles.
My aim in life is to become a successful entrepreneur. I have always been fascinated by the idea of creating something meaningful and making a positive impact on the world. I want to build a business that solves real-world problems, offers innovative solutions, and creates job opportunities for others.
To achieve my aim, I am committed to continuous learning and personal development. I am pursuing a degree in business administration to gain the necessary knowledge and skills. I am also actively involved in entrepreneurship-related activities and networking events to expand my knowledge and connect with like-minded individuals.
Alongside my entrepreneurial journey, I believe in giving back to society. I aim to create a socially responsible business that contributes to environmental sustainability and social welfare.
While the path to achieving my aim may be challenging, I am determined to persevere. I understand that success requires dedication, hard work, and resilience. I am prepared to embrace failure as a learning opportunity and adapt my strategies to overcome obstacles.
In conclusion, having an aim in life provides us with a sense of purpose and motivation. My aim is to become a successful entrepreneur who makes a positive impact on society. I am committed to continuous learning, personal growth, and contributing to the betterment of others. With determination and hard work, I believe I can turn my aim into a reality.
Having a clear aim in life is essential for personal fulfillment and success. It provides direction, motivation, and a sense of purpose. An aim serves as a guiding force, helping us make decisions and prioritize our efforts toward achieving our goals.
My aim in life is to become a doctor. From a young age, I have been deeply passionate about the field of medicine and the opportunity it presents to serve and make a positive impact on people’s lives. I want to dedicate my skills and knowledge to improving the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
To pursue my aim, I am focusing on my education and acquiring the necessary qualifications. I am studying diligently, maintaining good grades, and actively participating in extracurricular activities related to the medical field. I am also seeking opportunities to gain practical experience through internships and volunteering in healthcare settings.
Becoming a doctor requires lifelong learning and continuous professional development. I am committed to staying updated with the latest advancements in medical science and technologies to provide the best possible care to my patients. I aim to specialize in a specific area of medicine that aligns with my interests and allows me to make a significant impact.
Beyond the technical skills, I believe in the importance of compassion, empathy, and effective communication in the medical profession. I aim to develop strong interpersonal skills to establish trust and build meaningful connections with my patients. I want to provide them with not only medical treatment but also emotional support and reassurance.
As a doctor, my aim goes beyond individual patient care. I aspire to contribute to public health initiatives, promote preventive healthcare, and raise awareness about important health issues. I want to be actively involved in medical research and contribute to advancements in the field to improve healthcare outcomes on a larger scale.
While the journey to becoming a doctor may be demanding and challenging, I am prepared to put in the hard work and dedication required. I understand the responsibility and commitment that comes with the profession, and I am ready to embrace it.
In conclusion, having a clear aim in life is crucial for personal and professional growth. My aim to become a doctor is driven by my passion for helping others and making a positive impact on society. I am committed to continuous learning, empathy, and excellence in my pursuit of this aim. I believe that by dedicating myself to this noble profession, I can contribute to the well-being of individuals and communities, and fulfill my purpose in life.
Title: Aim in Life – Pursuing Passion, Purpose, and Personal Fulfillment
Introduction :
Having a clear aim in life is essential for personal growth, motivation, and a sense of purpose. It gives us a direction to follow, sets goals to strive for, and provides a framework for decision-making. In this essay, I will discuss the importance of having an aim in life, the process of discovering and refining one’s aim, and the impact it can have on personal fulfillment and success.
The Significance of Having an Aim
Having an aim in life gives us a sense of purpose and direction. It provides meaning and structure to our lives, guiding our actions and decisions. An aim serves as a source of motivation, helping us overcome challenges and stay focused on our goals. It instills a sense of determination and resilience, pushing us to pursue our passions and overcome obstacles along the way.
Discovering and Refining One’s Aim
Discovering one’s aim in life is a journey of self-discovery. It involves reflecting on personal interests, values, and strengths to identify areas that align with one’s passions and aspirations. It requires introspection, exploration, and a willingness to explore various paths before finding the right fit. Refining one’s aim involves setting specific goals, breaking them down into actionable steps, and continuously reassessing and adjusting as one progresses.
The Power of Passion
Passion is a driving force that fuels motivation and perseverance. When our aim aligns with our passions, we are more likely to invest time, effort, and dedication to achieve our goals. Passion ignites enthusiasm and a deep sense of fulfillment in what we do, enhancing our overall satisfaction and happiness. It helps us overcome setbacks and challenges, as our passion propels us forward, even in the face of adversity.
The Impact on Personal Fulfillment
Having a clear aim in life contributes to personal fulfillment. When we are aligned with our purpose, we experience a sense of satisfaction and contentment. We find meaning in our actions and a deep sense of accomplishment as we work towards our goals. Personal fulfillment comes from the journey of pursuing our aim, the growth and self-improvement we undergo along the way, and the positive impact we make on others and society.
Success and Achievement
Having an aim in life sets the stage for success and achievement. It provides a roadmap for progress and growth, helping us set goals and take steps towards their attainment. With a clear aim, we can channel our efforts and focus on the necessary skills, knowledge, and experiences required to succeed. It enables us to make informed decisions, seize opportunities, and persist in the face of challenges. By achieving our aims, we build a sense of accomplishment and create a legacy that reflects our values, passions, and contributions.
Conclusion :
Having an aim in life is instrumental in personal growth, motivation, and fulfillment. It guides our actions, sets goals, and gives us a sense of purpose and direction. It is through pursuing our aims that we can tap into our passions, overcome obstacles, and achieve success. Discovering and refining one’s aim is an ongoing process of self-discovery, reflection, and adaptation. It is through this journey that we find personal fulfillment and make a positive impact on ourselves and the world around us. Therefore, it is important to embrace our aims, follow our passions, and work towards the realization of our goals.
Related Posts
- Essay on Pollution
- Essay on “Impact of Social Media on Youth”

Essential Elements of Valid Contract (Explained With Examples)

What is World Population? Main Causes, Effects, Top 20 Countries
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
My Aim in Life Essay For Students: 100, 200 & 500 Words Essay
Writing an essay is equal to exploring your inner self. Teachers have a very straightforward justification for requesting you to write an essay. Writing an essay makes it simple for you to communicate yourself more rationally.
The lecturers are attempting to assist you in developing your writing abilities, vocabulary, and distinctive writing style by giving you essay assignments. Essays are a required component of many academic and scholastic tests, including the UPSC and SAT. It is also an essential evaluation component of English proficiency exams, such as the TOEFL, Duolingo, and IELTS.
Table of Content
Essay on My Aim in Life in 100 words
Essay on my aim in life in 200 words, essay on my aim in life in 500 words, what is the aim, importance of aim in life, how to find your aim, types of aim, how to choose the right aim of life, how to achieve the aim in life.
My aim in life is to become a doctor. I want to serve humanity by providing medical care to those in need. Healing the sick and alleviating their suffering is my passion. I aspire to make a positive impact on society and contribute to the well-being of others. Becoming a doctor requires dedication, hard work, and compassion, qualities that I am committed to cultivating. I believe that pursuing this noble profession will not only fulfill my personal aspirations but also allow me to make a meaningful difference in the lives of others.
My aim in life is to become a successful entrepreneur. I envision myself creating innovative solutions to address societal challenges and make a positive impact on the world. As an entrepreneur, I aspire to build a business that not only generates profits but also contributes to the greater good. I am passionate about entrepreneurship because it allows me to exercise creativity, take risks, and pursue my vision for a better future. I am committed to acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed in the business world, including leadership, problem-solving, and adaptability. By pursuing my aim of becoming an entrepreneur, I hope to leave a lasting legacy and inspire others to pursue their dreams.
My aim in life is to become a teacher. I believe that education is the key to unlocking opportunities and empowering individuals to reach their full potential. As a teacher, I aspire to inspire and motivate students to excel academically and personally. I want to create a nurturing and supportive learning environment where students feel valued and encouraged to explore their interests and passions. By instilling a love for learning and fostering critical thinking skills, I hope to prepare students for success in life and contribute to building a brighter future for society. Becoming a teacher requires patience, empathy, and dedication, qualities that I am committed to cultivating. I am passionate about making a positive difference in the lives of others and believe that education is the most powerful tool for driving social change. Through my work as a teacher, I aim to empower future generations to become compassionate, responsible, and engaged members of society.
An aim in life is like a guiding star that directs our efforts and shapes our journey towards success and fulfillment. It is the beacon that illuminates our path, providing clarity and purpose to our endeavors.
Having a clear aim in life is crucial for personal development and growth. It gives us a sense of direction, motivating us to strive harder and overcome obstacles. An aim provides focus, helps in prioritizing tasks, and ensures that our efforts are aligned with our aspirations. Without a defined aim, we may wander aimlessly, lacking purpose and satisfaction in life.
Discovering one’s aim in life is a process of self-reflection and exploration. It involves identifying our passions, interests, and values, as well as understanding our strengths and weaknesses. Engaging in activities that resonate with us and seeking guidance from mentors can also help in clarifying our aim.
Primary Aim in life
Our primary aim in life is the overarching goal that defines our purpose and drives our actions. It encompasses our long-term aspirations and reflects what we ultimately strive to achieve. Whether it’s pursuing a career, making a difference in society, or achieving personal fulfillment, our primary aim serves as the cornerstone of our life’s journey.
Aims can vary greatly from person to person, depending on individual values, aspirations, and circumstances. They can be categorized into various types such as career goals, educational aspirations, personal development objectives, and societal contributions. Each type of aim contributes to different aspects of our lives, shaping our overall growth and fulfillment.
Choosing the right aim in life requires careful consideration and introspection. It involves aligning our aspirations with our talents, passions, and values, ensuring that our aim is both meaningful and achievable. Assessing our strengths and weaknesses, seeking advice from mentors, and exploring different options can help in making an informed decision about our life’s aim.
Achieving our aim in life requires dedication, perseverance, and resilience. It involves setting clear goals, formulating action plans, and consistently working towards them. Staying focused, overcoming setbacks, and adapting to challenges are essential in the pursuit of our aim. Seeking support from mentors, acquiring relevant skills, and remaining adaptable to change can also facilitate our journey towards achieving our aim.
In conclusion, having a clear aim in life is essential for personal fulfillment, growth, and success. It provides direction, purpose, and motivation, guiding us through life’s journey and helping us realize our full potential. By identifying our aim, setting goals, and striving towards them with determination, we can chart a path towards a meaningful and fulfilling life. Let us embrace the power of aim-setting and embark on a journey towards realizing our dreams and aspirations.
Similar Reads: 500+Words Essay on My Hobby in English Essay on My House in English: Check 300, 500 & 800 Words Essay My Village Essay in English For Students
My Aim In Life Essay- FAQs
What is the best answer for aim in life.
The best answer for aim in life varies for each individual but generally involves a combination of personal passion, societal contribution, and self-fulfillment. It should reflect one’s aspirations, values, and long-term goals, guiding their actions and decisions towards a purposeful and meaningful life.
How do I write an essay about my aim in life?
To write an essay about your aim in life, start by reflecting on your passions, interests, and long-term goals. Define your aim clearly and concisely, explaining why it is important to you and how you plan to achieve it. Organize your essay with an introduction, body paragraphs discussing your aim and its significance, and a conclusion summarizing your main points.
What is the biggest aim in life?
The biggest aim in life is subjective and varies from person to person. It could be achieving personal fulfillment, making a positive impact on society, or leaving a lasting legacy. Ultimately, the biggest aim in life is one that brings a sense of purpose and fulfillment, guiding individuals towards their highest aspirations and deepest desires.
Why is aim important in life?
Aim is important in life because it provides direction, motivation, and purpose. It gives individuals a sense of clarity about their goals and aspirations, guiding their actions and decisions towards achieving them. Aim also helps in prioritizing tasks, staying focused, and overcoming obstacles, leading to personal growth and fulfillment. Without a clear aim, individuals may feel lost or directionless, lacking motivation and meaning in their lives.
What is full form of AIM?
The full form of AIM varies depending on the context. In the context of messaging and communication technology, AIM stands for AOL Instant Messenger, a popular instant messaging service. However, in the broader sense, AIM can stand for “Ambition, Inspiration, Motivation,” reflecting key elements of goal-setting and personal development.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- English Blogs
- School English
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
My Aim In Life Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on my aim in life .
It is a well-known fact that a person without an aim is a person without a life. All the creatures in this universe have one or another specific aim. It is common for all things. As the human is the best creature among them all, he has been given a right to select what he wants to do in his life. The mindset of each and every person is of its own type. Therefore, his aim in life will also be different from others.
Life is God’s greatest blessing; nevertheless, if there is no purpose and aim, life is useless and meaningless. Every one of us is born with a mission. It is essential to have a goal in life. If you want to pursue something in your life, you must have a goal. Student life is the ideal time to set goals. A person with a defined objective outperforms someone who does not have a goal in life. And if you don’t know what you want, you’ll never be motivated to work hard. To live a good life and deal with challenges, we need a proper plan. As a result, it is critical for everyone to have a life goal.

What is the Aim?
In a generic term purpose or goal is an aim. A person in his childhood might want to be a famous astronaut or a movie star or a police officer or something like that. Aim means to intend, to try, or to aspire. Each aim generally starts with a declaration of setting the goal, then breaking it into smaller pieces over a set timeline. Thus to achieve it one has to overcome many obstacles and setbacks from time to time.
Importance of aim in life:
There is a popular saying that a man without an aim is like an aim without a rudder. It means a ship without a rudder faces danger. Thus similarly a man without aim cannot reach towards his goal of life. He stumbles in his way of life.
So every person must have a definite aim. So, the aim of life is to give your life a purpose and meaning. Certainly, it is done by finding out what truly matters to you. Your purpose is to create more joy in life or to show others how you can live your life in the best possible manner.
How to find your Aim?
If you try to accomplish things that aren’t meant for you, that doesn’t offer you a sense of belonging and don’t provide you inner peace and happiness, you’re not in the correct field. You are not pursuing your goals and passions.
Everyone is unique in their own way. One may excel in academics while the other may be skilled in photography. Some people are born to aid the needy, others with bright brains, still others to pursue art and architecture, and still others simply write their way through life and become authors.
Simply close your eyes and think about something you appreciate the most on a larger scale, and that’s all there is to it. That is your life’s passion and goal. All you have to do is get closer to the part and shoot at it. By just following your passion, you can make your goal a reality.
Primary Aim in life:
A person can set the aim of his life by applying various parameters in life. Some of these maybe –
- To live with a specific purpose and passion every day
- To live for others by helping them.
- To become a great father, mother, son or daughter.
- To become a wildly successful entrepreneur and businessman
- To live a healthy, active and fit life
- To live with financial freedom in life.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Types of Aim:
Different people have different aims. Some people may want to become a doctor while others may want to start their own business. Likewise if engineering appeals, to some, the army may be the attraction for others. Some aim at becoming a teacher while social service or politics suits others. So different people adopt different aims according to their inclination or taste or perception about life.
How to Choose the right Aim of life?
It is the responsibility of the parents and the teachers to persuade their wards to select a profession according to their aptitude. Thus one can say that the right aim means right life and the wrong aim means wrong life. So, we should be very cautious while deciding on our aim.
Certainly, this is the most difficult problem that a young man faces is the selection of a profession. If a person does not choose his aim rightly, he will be always misfitted in his life. Thus, the best aim would be for one in which one feels happy always and he can do something worthwhile. Also at the same time, he assures about bright prospects in life.
Everyone should set a goal that is personal to them and will always inspire them to reach new heights. Therefore, don’t follow the mob and mimic the ambitions of friends.
How to Achieve the Aim in Life?
We should never make wealth or power the end of our existence, whether we succeed or fail in accomplishing our aim. We must never chase the celebrity bubble. Our goal should be to achieve our set aim solely for our own good, for our own enjoyment and satisfaction.
Some non-avoidable points which must be remembered are-
- Be Proactive
- No More Negativity
- Always be balanced
- Fully Focused
- Break it down
- Embrace failure
- Tell everyone
- Get help and guidance
- Track your progress
- Visualize the end result
- Reset the action plan based on feedback
We should also jot down and make a list of all our aims to be achieved. This activity will help you in a lot many ways. A few of them are:
- It may help you live longer and be healthier.
- If others ask, you will be an inspiration to them.
- It will be a guide to the best version of yourself.
- Your aim preferences will be prioritised based on your requirements.
- It will serve as a progress tracker as you work your way up the achievement ladder.
Conclusion:
Thus it is a fact that setting an aim and acting to achieve it is very important for a successful life. Everyone must start working towards it. The timely execution of an action plan with a proactive attitude is the key to success. One of the best ways to stay motivated is by visualizing the change and likewise by achieving step by step milestones.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Photo by Peter Turnley/Corbis/Getty
Philosophy was once alive
I was searching for meaning and purpose so i became an academic philosopher. reader, you might guess what happened next.
by Pranay Sanklecha + BIO
‘Why did you decide to study philosophy?’ asked the Harvard professor, sitting in the park in his cream linen suit.
‘Because I want to find out how to live,’ I said. ‘I want to find out what matters and I want to live my life accordingly.’
He smiled affectionately, leaning forward in his deck chair.
‘If you want to find meaning, Pranay, don’t study philosophy. Go fish, become a carpenter, do anything. But don’t expect to find it by studying philosophy.’
If by ‘philosophy’ we refer to the played-out game of academic analytic philosophy, he was right. But if by philosophy we refer to the mysterious human activity of searching for truth, to processes of thought and perception, to communal seeking, to genuine dialogue and true encounter, to the moment when our minds open and something true rushes in – if we refer to any of these things, then the professor from Harvard was about as wrong as one could be.
A few years later, I finished my doctorate at the University of Graz in Austria and embarked on life as a post-doc. Someone in that position usually has to churn out paper after paper on arcane aspects of philosophy for journals that no one reads. She has to attend conferences on subtle disputes, esoteric matters, where even the people attending look bored. She has to waste the best years of her life involving herself in intricate disputes that make no difference to her or anyone else’s life.
I had to do some of these things myself, but less than average, because I had lucked into a tenure-track position at Graz. Relative to the usual post-doc, I was free. And, as with so many kinds of freedom, to have it was also to be confronted by a question: how should I use it?
The natural option for my post-doc work would have been to find ever more pedantic things to say about John Rawls
In Austria, philosophy departments are funded by the state, which is to say that they are funded by the people of Austria through their taxes. Many academics were even officially contracted to the state as civil servants. I wasn’t, but the fact remained: people, many of them worse off than I was, were paying me to do philosophy. I felt like I owed them something.
The natural option for my post-doc work would have been to plough the departmental furrow and find ever more pedantic things to say about John Rawls. But Austria, I somehow felt, had heard enough about what people thought about the difference principle. Fine. Not that, then. But what instead?
The longer I spent trying to figure out what would be valuable to other people, the more lost I became. Eventually I decided to approach it from the other angle. I would find something that I really cared about – not intellectually, but existentially. That way, at least one person would find my post-doc work valuable.
F or a long time, I had been enduring a crisis of meaning. I wanted to live a life that mattered, to do things that were valuable – and I was increasingly haunted by the suspicion that nothing really mattered, that everything was ultimately meaningless. I decided that my new research project would be on the meaning of life.
I worked in a tradition of philosophy that people still call ‘analytic’. The basic idea of analytic philosophy when it was first propagated was simple. At its core, it consisted of G E Moore’s favourite question. Someone would say something like: ‘Being is indivisible’, and Moore would ask, ‘But what on earth does that mean ?’ To put this in more theoretical terms, the big idea behind analytic philosophy was to replace metaphysics with linguistic analysis. Advocates of this ‘linguistic turn’ believed, in Richard Rorty ’s words, that ‘philosophical problems are problems which may be solved (or dissolved) either by reforming language, or by understanding more about the language we presently use.’ The way to make progress on the question of God’s existence was not to find more arguments for and against Her existence. Rather, one made progress by investigating what it meant to say ‘God exists’.
Today, it’s hard to fully inhabit the excitement felt by the pioneers of analytic philosophy and their immediate descendants, but it’s impossible to doubt that there was considerable excitement at the time. Michael Dummett, a Wykeham Professor of Logic at the University of Oxford, and not therefore a man given to emotional pronouncements, claimed that:
Only with Frege [ie analytic philosophy] was the proper object of philosophy finally established: namely, first, that the goal of philosophy is the analysis of the structure of thought ; secondly, that the study of thought is to be sharply distinguished from the study of the psychological process of thinking ; and, finally, that the only proper method for analysing thought consists in the analysis of language .
While it remains usual to speak of analytic philosophy, nobody nowadays can say what it really means
Bliss it must have been in that dawn to be alive! But the French Revolution went from equality to tyranny, and in time, it turned out that Dummett had been too optimistic about analytic philosophy. The programme was revised and ultimately abandoned.
But the term ‘analytic philosophy’ has outlasted the historical movements of analytic philosophy. While it remains usual to speak of analytic philosophy and analytic philosophers, nobody nowadays can say what it really means.
Some people associate it with clarity, which is hilarious if you actually read analytic philosophy. Here, for instance, is Robert Nozick in Philosophical Explanations (1981):
We have said that W is a whole relative to parts p 1 , … , p n when the closest continuer of W need not be the sum of the closest continuers of the parts p i , when (a) it is possible that the closest continuer of W exists yet does not contain as a part some existing closest continuer of one of the p i ’s; or (b) it is possible that the closest continuer of W exists and contains some part q that is not a closest continuer of any of the p i (nor a sum or other odd carving up of these); or (c) it is possible that at some later time no continuer of W is close enough to be it, even though each of the p i then has a continuer close enough to be it – the parts exist at the later time but the whole does not.
That sentence has many properties. I’m not sure clarity is one of them.
O thers say it has something to do with ‘rigour’. This may be closer to the truth, but only if you take it as something to do with rigor mortis . Consider Susan Wolf writing on meaning in life. She has just expressed the idea that the ‘best sort of life is one that is involved in, or contributes to something “larger than oneself”.’ But as soon as Wolf has said this, she realises she has not been rigorous, that the thought has not been properly explained. She immediately tells us that: ‘[c]ontemplation of the case of Sisyphus should, however, be enough to show that this “larger” must be understood metaphorically. We may, after all, imagine the rock Sisyphus is endlessly pushing uphill to be very large.’
I think we can all agree that this is very rigorous. The thought has been pursued until there is no more thought possible. The lemon has been squeezed dry. Sisyphus could have been pushing a very large rock up that hill. The largeness of rocks, we now see, is not the type of largeness that Wolf had in mind. It is a different type of largeness. One might almost venture to call it… metaphorical.
‘The meaning of life’ has actually been a very marginal topic in analytic philosophy
Another way people have tried picking out analytic philosophy is to base it on a geo-linguistic criterion and call it Anglophone philosophy. But this is very unfair to the poor German professors churning out pages of turgid prose in what Bernard Williams called the ‘style [that] tries to remove in advance every conceivable misunderstanding or misinterpretation or objection, including those that would occur only to the malicious or the clinically literal-minded.’
No, nowadays – and ironically for a tradition that prides itself on ruthless thought and hard-edged precision – analytic philosophy is basically just a vibe. And as with all vibes, it’s clear who belongs and who doesn’t. As someone working in the analytic tradition, I knew exactly what ‘the literature’ was and what kind of stuff I should be reading for my research.
Despite ‘the meaning of life’ being the topic that non-philosophers think philosophers work on, it’s actually been a very marginal topic in analytic philosophy. Sure, interest in the issue was never fully extinguished, and every so often an older philosopher – it was almost always an older philosopher, who had a secure professional position and reputation and could therefore afford to write about the meaning of life – would write a little paper about it. But for pretty much all of the past century, it was not the sort of thing that anyone worked on before getting tenure.
However, lately there has been something of a revival of interest in the topic in analytic philosophy. Over the past 15 to 20 years, more and more papers and books have been published. The work has begun to coalesce into something approaching a recognisable sub-field of the discipline. One of the foundations of the analytic work is a distinction between the meaning of life and meaning in life. Questions about the meaning of life refer to the question of whether human life as such has a meaning, or whether the universe does. It’s a holistic kind of question. Meaning in life, on the other hand, refers to the ‘individualistic’ question of how and where and whether individuals can find meaning in their own lives.
The consensus view is that the two questions are fundamentally distinct and theoretically separate – you can have a meaningful life in a meaningless universe, and vice versa. How robust this separation is I’m not entirely sure, but that doesn’t matter for our current purposes. The point for now is that on this distinction, we can say that my crisis of meaning and my research project were both about meaning in life – the very thing that analytic philosophers wrote and talked about.
T here’s a Sherlock Holmes story in which the plot turns on a dog that doesn’t bark when it should have. And as I read more and more analytic philosophy on meaning in life, I kept stumbling into this non-barking dog. I spent a long time reading, taking notes, straining to figure out what I was struggling with. The more I tried, the less I understood.
Eventually, I realised that there was no there there. I had been trying to understand an absence. In the analytic literature on meaning in life, there is remarkably little sustained engagement with nihilist or sceptical worries about value. The basic version of this worry is very simple: it’s the worry that nothing is valuable. You’d think that this was quite an important worry to consider when thinking about the meaning of life – nihilism is very much a thing. It’s not that you had to endorse nihilism, but you at least had to engage seriously with the reasons people have for being nihilists. Analytic philosophers dealt with this worry by assuming it away.
For instance, Wolf, the doyenne of the field, proposes the theory that ‘meaningfulness consists in active engagement in projects or activities of worth’. She recognises the threat of nihilism and accepts that her theory ‘would be utterly destroyed if it turned out there were no such things as projects or activities of worth at all’. Her response is to call it ‘an article of faith’ that there is a distinction between worthwhile and worthless projects. And like all articles of faith, that only speaks to someone who already believes.
This view assumes that meaning in life is a realisable and sometimes actually realised property of an individual life
Here is another example. Aaron Smuts argues in Welfare, Meaning, and Worth (2017) that: ‘one’s life is meaningful to the extent that it promotes the good’. He sees, naturally, that nihilists might have problems with this account but he dismisses this issue right away: ‘I will merely note that I see no compelling reasons to take nihilism seriously … Nothing more can be said in favour of objective value here. I acknowledge that the good cause account is off the table for nihilists. So be it.’
These examples are suggestive, nothing more. But there is an explanation behind them that is important. The neglect of sceptical and nihilist worries about meaning in life is no accident. Rather, it is a necessary expression of the debate as it is framed and conducted.
Philosophers working on meaning in life love cases . They identify paradigmatic examples of meaningful lives, and then use them to draw conclusions about the necessary and sufficient conditions for living a meaningful life. Thaddeus Metz is explicit about this at the beginning of his book Meaning in Life (2013): ‘I, like most in the field, take specific exemplary instances of great meaning to have been realised by the likes of Mandela, Mother Teresa, Einstein, Darwin, Picasso, and Dostoyevsky.’ Wolf, too, speaks of ‘Gandhi, perhaps, or Mother Theresa, or Einstein, or Cézanne’ as ‘paradigms of meaningful lives’, and uses these cases to make arguments and claims about meaning in life.
This method of using paradigmatic cases is closely linked to one of the foundational assumptions of the analytic project. Wolf states the assumption clearly when she describes what she accurately calls the ‘standard view’ about meaning in life. As she puts it, the standard view holds ‘that meaningfulness is an intelligible feature to be sought in a life, and that it is at least sometimes attainable but not everywhere assured.’ The view assumes, in other words, that meaning in life is a realisable and sometimes actually realised property of an individual life.
We can see why the method and the assumption go together. When you use paradigmatic cases of meaningful lives to think about meaning, you’ve made a commitment to the claim that people can and sometimes do live meaningful lives. From this perspective, the method generates the assumption.
And if we look at it from the other angle, the use of the method is an expression of the assumption, and an explanation of why the former is so widely accepted. If you assume that meaning in life is something that is sometimes actually realised in individual lives, it makes perfect sense to try to find examples of those lives in which it is realised so that you can then start identifying some general features of meaningful lives.
The problem is that the method and the assumption are deeply flawed. To see why, consider Leo Tolstoy’s own crisis of meaning:
In the middle of my concern with the household, which at the time kept me quite busy, a question would suddenly come into my head: ‘Very well, you will have 6,000 desyatins [unit of land] in the Samara province, as well as 300 horses; what then?’ And I was completely taken aback and didn’t know what to think. As soon as I started to think about the education of my children, I would ask myself, ‘Why?’ Or I would reflect on how the people might attain prosperity, and I would suddenly ask myself, ‘What concern is it of mine?’ Or in the middle of thinking about the fame that my works were bringing me I would say to myself, ‘Very well, you will be more famous than Goethe, Pushkin, Shakespeare, Molière, more famous than all the writers in the world – so what?’ And I could find absolutely no reply.
Let us now imagine that a well-meaning friend of Tolstoy’s introduces him to the present-day literature on meaning in life. The literature would tell him: ‘Leo, it’s alright. We got you. Your life, you see, is a paradigmatically meaningful life. So, first of all, don’t worry that it’s meaningless. It’s actually the very model of a meaningful life. And then, if you want to know some more, well, from your life, and from other paradigmatic cases of meaningful lives, we can tell you (at some level of abstraction) what is required to live a meaningful life.’
Tolstoy is hardly going to find any of this of much use. His problem is precisely that he thinks his life is meaningless, so a theory of meaning that is built on the assumption that his life is meaningful is at best a joke to him.
I speak of Tolstoy, but I am speaking of myself too. I had turned to analytic philosophy with a hope born of desperation. I longed for something that would help me with my crisis, something that would relieve the pain. I found nothing. The assumption that allowed the analytic philosopher to proceed was the exact locus of my crises.
Does anything really matter? That’s what Tolstoy and I both want to know. And analytic philosophers don’t just refuse to answer this question – they couldn’t even ask it, because their project only got started on the assumption that things did matter. What use was this to us?
This is a problem for the analytic debate. Philosophers working in this tradition of questions of life’s meaning explicitly aim to address existential questions about life’s meaning, and to be capturing and addressing the human experience of searching for meaning. So even purely on their terms, the fact that they assume away sceptical and nihilist concerns and experiences is a problem.
Philosophy programmes are being cut, and I am willing to bet a tenured professor’s salary that more cuts are coming
The analytic debate takes something of existential concern – a question that was for many people literally a matter of life and death – and managed to be blind to much of their experience. It takes one of the most profound questions that human beings can ask and has turned it into a discussion of the private prejudices and contingent beliefs (also called ‘intuitions’) of a bunch of people who have been similarly socialised. And in doing these things, it’s not exceptional. It’s actually a symptom and an illustration of something much bigger and more important than a bunch of academics getting something wrong in one local debate.
Consider the temples of ancient Greece. Once they were thick with blood and smoke. They were places where living creatures were sacrificed, where novices were initiated by frightening esoteric rituals, where strange chants mingled with cries of pain and ecstasy. Today, they are tourist attractions.
The discipline of academic philosophy is like those Greek temples. Its practitioners are caretakers wandering around empty rooms, painting the walls, and washing the floor while the entire edifice collapses around them.
There are many signs of declining vitality at the general level. Daily Nous, a popular professional philosophy blog, has a category called ‘Cuts and Threats to Philosophy Programs’, which is instructive in itself – it wouldn’t have been necessary in 1960. The entries in this category testify that philosophy programmes across the United Kingdom and the United States are regularly threatened with closure. Increasing numbers are being cut, and I am willing to bet a tenured professor’s annual salary that there are significantly more cuts coming.
The cutting of programmes is a natural reflection of the fact that people don’t want to study philosophy. Philosophy degrees in the US are either modestly up or stable relative to 2017, but significantly down relative to 2010. If you extend the period out to roughly the past 20 years, then philosophy majors as a percentage of bachelor’s degrees have stayed roughly stable – but only because it was already low, between 0.4-0.6 per cent. These are important pieces of evidence, but they are secondary. They are symptoms and manifestations of something much more important, namely an internal decline and an inner death.
Look at the words that professional philosophers produce. Look, for however long you can bear, into the pages of arcane journals filled with intricate disputes about how many trolleys can dance on the head of a pin. Peek into classrooms that are filled with the atmosphere of boredom and futility. Speak to young philosophers, young practitioners of the discipline, the ones who should be filled with love and excitement for philosophy and see instead their disappointment and their cynicism.
I was once one of those young philosophers. I came to philosophy as so many other young people, as so many of my contemporaries, as so many of my students over the years came to it. We were driven by deep and authentic need, by the needs that human beings have always had – the need to make sense of our lives, the need to be consoled for our suffering, the need to be awed by things greater than ourselves, the need to experience the true, the good, and the beautiful. We yearned for wisdom, for glimpses of ideas and people that allowed us to believe that there was something very fine in human beings and that we might legitimately strive to live in ways that cultivated and expressed it.
That is what we yearned for. What we found was something rather different. Geoff Dyer put it well in Out of Sheer Rage (1997):
Walk around a university campus and there is an almost palpable smell of death about the place because hundreds of academics are busy killing everything they touch. I recently met an academic who said that he taught German literature. I was aghast: to think, this man who had been in universities all his life was teaching Rilke. Rilke! Oh, it was too much to bear. You don’t teach Rilke, I wanted to say, you kill Rilke! You turn him to dust and then you go off to conferences where dozens of other academic-morticians gather with the express intention of killing Rilke and turning him to dust. Then, as part of the cover-up, the conference papers are published, the dust is embalmed and before you know it literature is a vast graveyard of dust, a dustyard of graves.
I recognise that anger. It still makes me angry now, to think of the depth and the beauty and the pain of the human need, and of how it is met by dusty professors playing their little games. But anger is not an easy place to live from; nor is it the most fertile. Over time, the anger receded, and it was replaced by something that felt like a moral challenge. If academic philosophy really was so awful (and it was), then shouldn’t I try to offer an alternative?
P hilosophy was once alive too, almost terrifyingly so. Why else would a man called Socrates choose to cheerfully go to his death rather than betray it? Can we make it alive again by going back to a vision of how the Greeks did philosophy?
No. Philosophy was alive for the ancients because it was the form – which they needed to invent – that authentically expressed some very deep and constant human needs. The way to reanimate philosophy, to fill it again with life and vitality and urgency, is not to copy an old form. For philosophy to become a living thing, for a form to be invented that speaks to human beings today, it needs to go back to the needs that the form once contained and satisfyingly expressed.
I left academia in the summer of 2022. Since then, I do philosophy in the world
How? I have no suggestions about which I am certain. I am suspicious of any grand programme here because the whole thing about a live form – about life itself, possibly – is that its growth must be – to a large extent – unplanned, it must evolve organically, it must grow and change as a response to the needs and the context in which it first comes into being at all.
Instead of programmes or manifestos, then, let me offer two basic principles that have guided my own experiments.
- Principle 1: If we are trying to create (or rediscover) a philosophy that is a vital response to authentic human need, then let us go wherever the human need is. Let us go back to the world, to the modern equivalents of the Greek agora, let us do philosophy in places and with people where we are not protected – and mummified – by the sophisticated conventions and intricate rules of the institution of academic philosophy.
- Principle 2: If we are trying to create (or rediscover) a form of philosophy and an activity of philosophising that is alive, then we need to be alive ourselves, and our life needs to be in the form. This does not mean confessional or autobiographical philosophy (though it can be that too, if it wants). It means rather… actually, no. You need to decide what it means.
I’ve put my money where my mouth is. I left academia in the summer of 2022. Since then, I do philosophy in the world. I do it with people and for people who really are grappling with philosophical questions – not as theoretical puzzles, but as things that matter in their lives. In this activity, I have glimpses of philosophical activity that is alive, and these glimpses are sufficient for a lifetime.

History of technology
Learning to love monsters
Windmills were once just machines on the land but now seem delightfully bucolic. Could wind turbines win us over too?
Stephen Case

Global history
The route to progress
Anticolonial modernity was founded upon the fight for liberation from communists, capitalists and imperialists alike
Frank Gerits

Thinkers and theories
Paper trails
Husserl’s well-tended archive has given him a rich afterlife, while Nietzsche’s was distorted by his axe-grinding sister
Peter Salmon

Philosophy of mind
The problem of erring animals
Three medieval thinkers struggled to explain how animals could make mistakes – and uncovered the nature of nonhuman minds

Moral progress is annoying
You might feel you can trust your gut to tell right from wrong, but the friction of social change shows that you can’t
Daniel Kelly & Evan Westra

The disruption nexus
Moments of crisis, such as our own, are great opportunities for historic change, but only under highly specific conditions
Roman Krznaric
20: What is the Additional Information Essay? The College Essay Advisors Podcast
Join Stacey and Becca as they discuss the role of the Additional Information Essay in the college application. They cover the purpose of this text box and the kinds of circumstances that warrant an essay, as well as the dangers of submitting a superfluous essay.Watch some of our YouTube videos:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0MaLsIu1vdEhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a6VxiKDeqQcAccess our Supplemental Essay Guides:https://www.collegeessayadvisors.com/supplemental-essay-guide-2024-25/Work one-...
- More Episodes
- © 2024 The College Essay Advisors Podcast
A Tale of Two Commanders
One found purpose in the world, the other in his own megalomaniacal vision of what the world ought to be.
Why do nations go to war? Why do young men fight and die over the causes that normally occupy the minds of aged statesmen? These are age-old questions, but I didn’t think about them in my youth. I served for two years in the Peace Corps (in Uzbekistan), but gave no thought at all to a military career. Now that I have youth, these questions recur often, in my mind and at my dinner table. This can happen when one lives in a house full of males (my husband and five sons), in an age when Great Power conflict seems to loom on the horizon.
We talk about current events and what they mean in the context of history. This is uncomfortable because I don’t know exactly what they mean, which is the kind of reality that can be gracefully massaged in conversation with a talk radio host but not with your own kids. I’m frequently tempted to change the subject. (Dessert, anyone?) But I’ve come to understand that there are good reasons why military history is fascinating to boys. It raises crucial questions about virtue, self-sacrifice, civic duty, and manhood. I’d like to think that a nuanced exploration of the subject may make them less susceptible to empty, jingoistic rhetoric—while deepening their understanding of honor in ways that apply to more than war. At the same time, these conversations remind me that I am truly proud to be an American. In the Peace Corps, I remember sparring amicably with Uzbek friends about Soviet military history, and realizing how hard it would be to get perspective on the (harrowing) losses they suffered in the brutal conflict between Hitler and Stalin. On patriotic holidays, I’m grateful to be able to talk to my sons about George Washington, not Georgy Zhukov .
This point was vividly underscored when we recently read The Mask of Command , by the late John Keegan, as family read-aloud. Keegan is a British military historian whose earlier classic, The Face of Battle , explored the experience of the common soldier through the lens of three famous battles (Agincourt, Waterloo, and the Somme). The sequel considers the psychology and vocation of military commanders through profiles of four defining figures: Alexander the Great, the Duke of Wellington, Ulysses S. Grant, and Adolf Hitler. All of them are interesting, but I submit that the final two essays, on Grant and Hitler, teach certain lessons far better than a thousand warnings against “toxic masculinity” or “Christian nationalism.”
A Place in History
Why does Keegan, a Brit, choose Grant for the hero of his book? The selection is not shocking, but neither is it an obvious choice. He was a victorious general and a US president, and his face appears on the $50 bill. But he’s not someone we regularly commemorate in story or song. Nobody I know has ever named a son “Ulysses,” and we tend to remember Grant’s defects as much as his strengths. People tend to know him as a high-functioning alcoholic who, from a military-historical perspective, won his war mainly by taking proper advantage of the Union’s enormous advantages. The Southern generals (especially Stonewall Jackson and Robert E. Lee) are remembered for their military brilliance, while Grant is frequently cast as just the man who managed to be competent where feckless predecessors had failed.
Keegan doesn’t agree with this assessment. Lee had a gift for Napoleonic strategizing, but in Keegan’s view, Grant was the one who truly grasped the nature of modern warfare. It’s not surprising that epic storytelling has focused more on the tragic romance of the South’s defeated Napoleons, but Grant’s “unheroic leadership” (Keegan’s term), prosaic and practical as it was, had its own peculiar excellence. He had an extraordinary ability to distill the strategically and morally essential features of a situation, and to focus unwaveringly on what needed to be done. And he didn’t much care whether anyone composed anthems about it.
Hitler’s selection as villain is utterly unsurprising; he is surely the most universally reviled human being on the planet today. That (dis)honor is merited. He started the world’s deadliest war, and orchestrated genocidal war crimes on an unprecedented scale. Hitler was a bad person. Given the obviousness of that starting point, though, the portrait Keegan paints of him is arresting and in some ways startling. The reader may actually be moved to a bit of sympathy for the alienated young striver who, in the First World War, managed at last to break into the social class where he had always felt he belonged, only to see his new friends promptly slaughtered at Flanders. Everyone knows what Hitler hated, but Keegan fills out the picture by telling us what he loved, which is ultimately more revealing. Both Hitler and Grant were patriots, and both thrived on meaningful activity and a sense of purpose. Grant found those things in the world. Hitler found them in his own megalomaniacal vision of what the world ought to be.
That difference would not have been obvious, however, in Hitler’s early life, when he might have seemed more prepared than Grant to embrace commitment and self-sacrifice. It would in some ways be comforting to see the young Hitler as a budding sadomasochist or psychopath, on his way to becoming a Caligula or a Saddam Hussein. Even in his awful maturity, however, he doesn’t seem to have reveled in rape or torture. His motives are disturbingly comprehensible, and even familiar: at the start of the First World War, he threw himself into a cause with full patriotic fervor and conviction, believing (not unreasonably at the time) that Germany was the world’s elite military power, destined to stand astride Europe. As a Meldegänger (messenger), Hitler regularly placed himself in mortal peril to deliver crucial information that, among other things, prevented advancing German troops from being obliterated by friendly fire. His superiors were unstinting in their praise. The young Grant, by contrast, attended West Point but graduated in the lower-middle end of his class. He served with some distinction in the Mexican-American war, but a bad conscience over that war (which he saw as unjust), and severe homesickness (especially for his wife) sent him into a spiral of heavy drinking, and he ended up resigning his commission and returning to the Midwest. The outbreak of the Civil War found him scratching out a bare living as a store clerk to keep his children fed. It’s not entirely surprising that George McClellan refused to renew his commission at the start of the war.
There’s a curious symmetry to the two men’s biographies: the young Hitler fighting on the losing side of a war he supported passionately, while the young Grant fought on the winning side of a war he regarded as wrong. Both then moved into some years of obscurity, when no one would have guessed at their ultimate place in history. Grant, however, spent those years trying to live decently as a husband, father, and upstanding citizen. Hitler spent them developing his delusions of grandeur, mastering the art of propaganda, and considering how to channel his rage and resentment into a rematch of the war Germany had lost. He muscled his way into the annals of history. Grant allowed a world-historical role to find him.
A Clarity of Purpose
Grant was neither charismatic nor charming. He detested pomp, speechmaking, and all forms of ostentation. He lived simply while on campaign, mostly preferring minimal furniture and simple fare. (But he did apparently have a taste for oysters. As a fellow oyster-lover, I enjoyed that eclectic detail.) Everything about Grant’s unassuming minimalism spoke to an individual who was self-directed, comfortable in his skin, and so aware of the extent of his abilities that there was no need to embellish. He also knew his own mind, and was able to hold that clarity even in the midst of tremendous tumult. America’s bloodiest conflict was, in his view, a detestable necessity, but unlike the previous war, it was in fact necessary and just.
Grant inspired respect in friends, enemies, his soldiers, and the broader public. Hitler used cake and fear to manufacture the social acceptance he continued to crave.
So he won it. He did it because he could, and because he understood why it needed to be done. That ruthless efficiency and clarity of purpose permeated everything Grant did as a general, from his communications to his officers (always concise, clear, and delivering exactly the needed details) to his strategic decisions. He was a master of logistics. He had a spectacular memory for terrain and troop movements, and a shrewd ability to read both his own subordinates and enemy commanders. He seemed impervious to the psychological games that Robert E. Lee played so successfully with his predecessors. He understood, too, that he commanded a democratic army. Draconian efforts to deter desertion were impractical for Grant, so it was necessary to factor his soldiers’ moods and wishes into his strategic calculations.
In the midst of such an ugly and emotional conflict, this extraordinary focus enabled him to win the trust and admiration of both his subordinates and his enemies. His compass was not clouded by the fog of war. Then, at Appomattox and beyond, Grant’s magnanimity made it clear that he had never been motivated by a hunger for domination or a thirst for revenge. Not for nothing did he name his favorite horse “Cincinnatus.”
Against that backdrop, the grotesque dimensions of Hitler’s demagoguery are particularly glaring. Though he was masterful at inspiring devotion in the distant masses, the people in his immediate orbit were constantly managing him, struggling to keep him on task and scrambling to adapt to his mercurial moods. He had fractious relationships with his generals. Quite often he would ignore their advice and then blame them when his orders went awry in predictable ways. Lower-ranking underlings were less likely to be fired, but their jobs were not enviable. Keegan tells of late nights at his headquarters in Rastenberg and Vinnitsa (far from the battlefields where his soldiers were killing and dying) where he forced his subordinates to sit awake at all hours, eating excessive quantities of cake and laboring to feign interest while he held forth with sophomoric opinions on everything under the sun. A number of young women were stationed at headquarters, ostensibly as secretaries but mainly because he enjoyed being flattered and fawned over. His war councils frequently degenerated into tangential rambles; although he was obsessed with victory, Hitler found it increasingly difficult as the war went on to focus on significant practical details. At the same time, he was unwilling to recognize his limits and delegate authority to men of greater ability.
Grant, in short, inspired respect in friends, enemies, his soldiers, and the broader public. Hitler used cake and fear to manufacture the social acceptance he continued to crave.
A Noble Fight
One hesitates to reduce two such complicated men to a simplistic aphorism, and yet one immediately springs to mind. A man’s gotta do what a man’s gotta do. Grant lived that truth, won his war, became the 18th US president, and died at 68, surrounded by loving children and grandchildren. Hitler failed utterly to achieve any of his life’s objectives. He lost his war, incurred the hatred of the entire world, and died alone by his own hand. (Oddly, he had a vegetarian spaghetti lunch served immediately before going off to shoot himself in the head.)
That failure was not merely moral. Hitler failed by every metric that mattered to him personally. How do angry and alienated neo-Nazis manage to overlook this point? His strategic military choices were erratic at best. His personal life was pathetic. He presented himself as the savior of Germany, but ended up subjecting her to even worse humiliations than the ones that had scarred his own youth. To his beloved homeland, he delivered yet another lost generation.
Near the end of his life, Keegan believes, he realized the awful extent of this failure. Over just a few months, he deteriorated to an astonishing degree, reaching the point where he could hardly walk across the yard without stopping to rest. In the daytime he was distracted and puffy-eyed; insomnia plagued his nights.
For Hitler’s supreme command had been—and may have appeared to him as he passed it in retrospect—no more than a charade of false heroics. It had been based, as he himself has trumpeted in his days of power, on the concept of lonely suffering, on his internalizing of his soldiers’ risks and hardships in the fastness of Rastenburg and Vinnitsa, on the equation of their physical ordeal with his psychological resistance, on the substitution of ”nerve” for courage, ultimately on the ritual of suicide as the equivalent of death in the face of the enemy.
No earthly punishment could be adequate for crimes as monstrous as Hitler’s, but it’s terrible nevertheless to imagine such a grim moment of truth. Who could possibly want to be Hitler?
Grant, for his part, has the rare distinction of being a successful military leader who was inadequately appreciated by later countrymen. It seems unlikely he would have minded. He knew what he did, and he was the sort of man who always valued his wife’s good opinion more than any journalist’s or historian’s. For our sake, however, it is worth looking back and remembering, particularly because there is something distinctively American about Ulysses S. Grant. Even in midst of war, he distinguished himself as a republican leader, and a lover of ordered liberty. He drew his strength from his natural connections to family, friends, and the Midwestern soil, and from a nuanced appreciation of what was best in the American political tradition. Autocracy was completely foreign to his nature, and that made him a better man, and a better military leader.
For boys especially, the lessons are crucial. It’s not wrong to love one’s country, but that love needs to be tempered by other loves, and by a recognition of moral constraints on what can be done in pursuit of national greatness. It’s not “toxic” to aspire to manliness, but great men are guided by a prudent appraisal of what a given moment requires. All boys, perhaps, are on some level spoiling for a noble fight. But noble fights are earned, not demanded, and certainly not chosen on one’s own preferred terms.
This is not a uniquely American truth, but Americans have been more successful than some at living it. If a British historian can see that, then surely we can too.
Essay Can the Republic Survive Corrupt Presidents? Richard Samuelson
Essay Molière’s Medicine for Wayward Youth Reuven Brenner
Essay J. K. Rowling and the Hate Monster Helen Dale
Essay Rebooting Market Liberalism in a Populist Age Samuel Gregg
Essay The World We Have Lost James Hankins
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Americans’ Views of Government’s Role: Persistent Divisions and Areas of Agreement
Wide majorities of Biden and Trump supporters oppose cuts to Social Security
Table of contents.
- Views on the efficiency of government
- Views on the government’s regulation of business
- Confidence in the nation’s ability to solve problems
- Views on the effect of government aid to the poor
- Views on government’s role in health care
- Views on the future of Social Security
- Trust in government
- Feelings toward the federal government
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role.
This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a survey of 8,638 adults from May 13 to 19, 2024.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
While the economy, immigration and abortion have emerged as major issues in the 2024 election, Joe Biden and Donald Trump also have dramatically different ideas about the size and role of government.
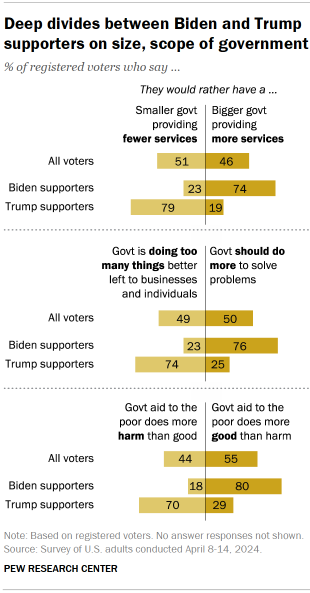
These differences reflect decades-old divisions between Democrats and Republicans over the scope of government.
Among registered voters, large majorities of Biden supporters – roughly three-quarters or more – favor a bigger, more activist government.
- 74% say they would rather have a bigger government providing more services.
- 76% say government should do more to solve problems.
- 80% say government aid to the poor “does more good than harm.”
Trump supporters, by comparable margins, take the opposing view on all three questions.
The Pew Research Center survey of 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – conducted April 8-14, 2024, examines Americans’ views of the role and scope of government , the social safety net and long-term trends in trust in the federal government .
Democratic support for bigger government is little changed in the last five years but remains higher than it was a decade ago. Republicans’ views have shifted less over the last 10 years.
Among all adults, about three-quarters of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents favor a bigger government, up from about six-in-ten in 2014 and 2015. The share of Republicans and Republican leaners who prefer a bigger government has increased only modestly over the same period.
Democratic support for bigger government, while slightly lower than in 2021 (78%), remains at nearly its highest level in five decades. During Bill Clinton’s presidency in the 1990s, fewer than half of Democrats said they preferred a bigger government with more services.
Voters continue to express very different views about government’s role in specific areas than about the government generally.
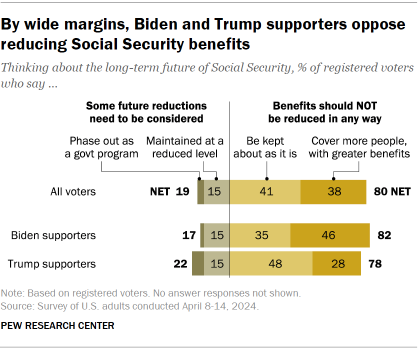
A large majority of voters (80%) – including 82% of Biden supporters and 78% of Trump supporters – say that in thinking about the long-term future of Social Security, benefits should not be reduced in any way.
However, Biden supporters are more likely than Trump supporters to say Social Security should cover more people with greater benefits.
- 46% of Biden supporters favor expanding Social Security coverage and benefits, compared with 28% of Trump supporters.
Most Americans (65%) continue to say the federal government has a responsibility to make sure all Americans have health care coverage.
Democrats overwhelmingly (88%) say the federal government has this responsibility, compared with 40% of Republicans.
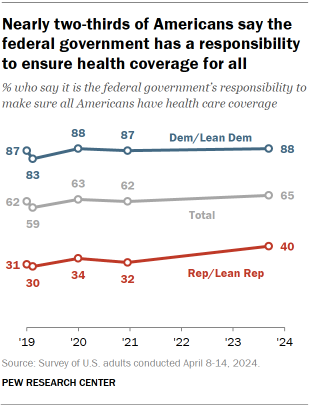
The share of Republicans who say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage has increased 8 percentage points since 2021, from 32% to 40%.
There are wide income differences among Republicans in opinions about the government’s role in health care:
- 56% of Republicans with lower family incomes say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage for all, compared with 36% of those with middle incomes and 29% of higher-income Republicans.
When asked how the government should provide health coverage, 36% of Americans say it should be provided through a single national program, while 28% say it should be through a mix of government and private programs. These views have changed little in recent years.
Democrats continue to be more likely than Republicans to favor a “single payer” government health insurance program (53% vs. 18%).
Other key findings in this report
- Americans’ trust in the federal government remains low but has modestly increased since last year. Today, 22% of American adults say they trust the government to do what is right always or most of the time, which is up from 16% in June 2023.
- While the public overall is divided over the nation’s ability to solve important problems, young adults are notably pessimistic about the country’s ability to solve problems . About half of Americans (52%) say the U.S. can’t solve many of its important problems, while 47% say it can find a way to solve problems and get what it wants. Roughly six-in-ten adults under age 30 (62%) say the nation can’t solve major problems, the highest share in any age group and 16 points higher than two years ago.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Election 2024
- Federal Government
- Government Spending & the Deficit
- Health Care
- Partisanship & Issues
- Social Security & Medicare
- Trust in Government
Third-party and independent candidates for president often fall short of early polling numbers
6 facts about presidential and vice presidential debates, biden, trump are least-liked pair of major party presidential candidates in at least 3 decades, cultural issues and the 2024 election, more than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Advertisement
Justices Limit Power of Federal Agencies, Imperiling an Array of Regulations
A foundational 1984 decision had required courts to defer to agencies’ reasonable interpretations of ambiguous statutes, underpinning regulations on health care, safety and the environment.
- Share full article

By Adam Liptak
Reporting from Washington
- June 28, 2024
The Supreme Court on Friday reduced the power of executive agencies by sweeping aside a longstanding legal precedent, endangering countless regulations and transferring power from the executive branch to Congress and the courts.
The precedent, Chevron v. Natural Resources Defense Council , one of the most cited in American law, requires courts to defer to agencies’ reasonable interpretations of ambiguous statutes. There have been 70 Supreme Court decisions relying on Chevron, along with 17,000 in the lower courts.
The decision is all but certain to prompt challenges to the actions of an array of federal agencies, including those regulating the environment, health care and consumer safety.
The vote was 6 to 3, dividing along ideological lines.
“Chevron is overruled,” Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. wrote for the majority. “Courts must exercise their independent judgment in deciding whether an agency has acted within its statutory authority.”
In dissent, Justice Elena Kagan said the ruling amounted to a judicial power grab. “A rule of judicial humility,” she wrote, “gives way to a rule of judicial hubris.”
Justice Kagan summarized her dissent from the bench, a rare move and a sign of profound disagreement. “Courts, in particular this court, will now play a commanding role” in setting national policy, she said.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. The purpose of this essay is to… This directly states the intended goal of your essay and informs the reader of its primary aim. Example: The purpose of this essay is to ignite a national conversation about the alarming decline of bee populations and its potential consequences for our food security. 2. This essay aims to…
This Paper Will Explore. "This paper will explore" is the last alternative we want to cover. It's possible to replace "essay" in all cases with "paper," and many readers prefer to see this because it does not sound as wasteful or as obvious. The idea behind both "this essay" and "this paper" is the same.
For the purpose of this essay, it is not necessary to dwell any further on particular conditions... expressions; synonyms; Share. Improve this question. Follow edited Nov 30, 2014 at 16:30. James Waldby - jwpat7. 66.8k 11 11 gold badges 110 110 silver badges 208 208 bronze badges.
"The aim of this paper is to . . .," and "The purpose of this essay is to . . ." A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn. A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement ...
In an argumentative essay, your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning. In an expository essay, you'll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn't have to include a strong opinion in this case ...
If you're wondering what to say instead of "in this essay I will," we'd go with the phrase "the purpose of this paper is.". This alternative is great if you want to completely alter your choice of words in your introduction. It replaces "essay" with "paper" and removes the personal pronoun "I" to boot! This makes this ...
Argumentative essays. An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement—a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations) and analysis.. Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic.
4. Moreover; furthermore; in addition; what's more. These types of academic phrases are perfect for expanding or adding to a point you've already made without interrupting the flow altogether. "Moreover", "furthermore" and "in addition" are also great linking phrases to begin a new paragraph. Here are some examples:
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Writing objectives. The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps, The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review. (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study) One objective can be applied to the methodology portion.
The first element of a purpose statement is the problem or opportunity that you are addressing. This should be a clear and specific description of the issue that you are trying to solve or the opportunity that you are pursuing. 2. The Target Audience. The second element is the target audience for your purpose statement.
Most essays follow a similar structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, as shown in the diagram below. Click on the plus icons for more information. ... The purpose of the introduction is to give your reader a clear idea of what your essay will cover. It should provide some background information on the specific ...
The primary aim of this essay is to advocate for a broader receiver psychology paradigm that more explicitly includes a research focus on receivers' psychological landscapes. 6. Animal Behaviour. Since the aim of this essay is to review the issues concerning whether genuine moral knowledge is possible, we need to assess the merits of this ...
250 Words Essay on My Purpose in Life Introduction. Life is a journey of self-discovery and purpose. It is a voyage that leads one to the realization of their significance in the grand scheme of existence. My purpose in life, as I perceive it, is to contribute positively to the world, continually learn and grow, and inspire others. ...
In this essay, I will delve into the intricacies of my personal vision and mission, exploring the aspirations that drive me and the principles that ... overarching purpose, my mission delineates the steps I must take to realize that purpose. My mission keeps me grounded, reminding me that every action, no matter how small, contributes to the ...
The part of a sentence "the aim of this essay" is correct and usable in written English. You can use it as the opening line of an essay. For example: The aim of this essay is to explore the social and economic impacts of gentrification in low-income neighborhoods. The aim of this essay is not to compare Hume and Kant on all matters ethical.
Short Essay On My Aim In Life. My aim in life is a question that everyone asks themselves at some point. It is a crucial decision that shapes our future and determines the path we take in life. Personally, my aim in life is to become a successful professional in my chosen field and make a positive impact on society. I believe that success can ...
Essay on Aim in Life in 150-300 words. Having a clear aim in life is crucial for personal growth, motivation, and success. It provides a sense of direction and purpose, guiding our actions and decisions. An aim gives us something to strive for, inspiring us to work hard and overcome obstacles.
However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic. The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
Essay on My Aim in Life in 100 words. My aim in life is to become a doctor. I want to serve humanity by providing medical care to those in need. Healing the sick and alleviating their suffering is my passion. I aspire to make a positive impact on society and contribute to the well-being of others. Becoming a doctor requires dedication, hard ...
500+ Words Essay on My Aim in Life. It is a well-known fact that a person without an aim is a person without a life. All the creatures in this universe have one or another specific aim. It is common for all things. As the human is the best creature among them all, he has been given a right to select what he wants to do in his life.
The operational plan 1.1Detailed Target market 1.2Market positionning 1.3Management implications CONCLUSION INTRODUCTION The aim of this essay is to analyse and explain the Blackberry's launching in France. Indeed, mobile email access has been a …show more content…. France joined 10 other European Union countries in adopting the euro as its ...
Syndicate this essay ... Philosophers working in this tradition of questions of life's meaning explicitly aim to address existential questions about life's meaning, and to be capturing and addressing the human experience of searching for meaning. So even purely on their terms, the fact that they assume away sceptical and nihilist concerns ...
Join Stacey and Becca as they discuss the role of the Additional Information Essay in the college application. They cover the purpose of this text box and the kinds of circumstances that warrant an essay, as well as the dangers of submitting a superfluous essay.Watch some of our YouTube videos:https…
A Clarity of Purpose. Grant was neither charismatic nor charming. He detested pomp, speechmaking, and all forms of ostentation. He lived simply while on campaign, mostly preferring minimal furniture and simple fare. (But he did apparently have a taste for oysters. As a fellow oyster-lover, I enjoyed that eclectic detail.)
Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans' attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role. This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a ...
A foundational 1984 decision had required courts to defer to agencies' reasonable interpretations of ambiguous statutes, underpinning regulations on health care, safety and the environment.