- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

How the Experimental Method Works in Psychology
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amanda Tust is an editor, fact-checker, and writer with a Master of Science in Journalism from Northwestern University's Medill School of Journalism.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Amanda-Tust-1000-ffe096be0137462fbfba1f0759e07eb9.jpg)
sturti/Getty Images
The Experimental Process
Types of experiments, potential pitfalls of the experimental method.
The experimental method is a type of research procedure that involves manipulating variables to determine if there is a cause-and-effect relationship. The results obtained through the experimental method are useful but do not prove with 100% certainty that a singular cause always creates a specific effect. Instead, they show the probability that a cause will or will not lead to a particular effect.
At a Glance
While there are many different research techniques available, the experimental method allows researchers to look at cause-and-effect relationships. Using the experimental method, researchers randomly assign participants to a control or experimental group and manipulate levels of an independent variable. If changes in the independent variable lead to changes in the dependent variable, it indicates there is likely a causal relationship between them.
What Is the Experimental Method in Psychology?
The experimental method involves manipulating one variable to determine if this causes changes in another variable. This method relies on controlled research methods and random assignment of study subjects to test a hypothesis.
For example, researchers may want to learn how different visual patterns may impact our perception. Or they might wonder whether certain actions can improve memory . Experiments are conducted on many behavioral topics, including:
The scientific method forms the basis of the experimental method. This is a process used to determine the relationship between two variables—in this case, to explain human behavior .
Positivism is also important in the experimental method. It refers to factual knowledge that is obtained through observation, which is considered to be trustworthy.
When using the experimental method, researchers first identify and define key variables. Then they formulate a hypothesis, manipulate the variables, and collect data on the results. Unrelated or irrelevant variables are carefully controlled to minimize the potential impact on the experiment outcome.
History of the Experimental Method
The idea of using experiments to better understand human psychology began toward the end of the nineteenth century. Wilhelm Wundt established the first formal laboratory in 1879.
Wundt is often called the father of experimental psychology. He believed that experiments could help explain how psychology works, and used this approach to study consciousness .
Wundt coined the term "physiological psychology." This is a hybrid of physiology and psychology, or how the body affects the brain.
Other early contributors to the development and evolution of experimental psychology as we know it today include:
- Gustav Fechner (1801-1887), who helped develop procedures for measuring sensations according to the size of the stimulus
- Hermann von Helmholtz (1821-1894), who analyzed philosophical assumptions through research in an attempt to arrive at scientific conclusions
- Franz Brentano (1838-1917), who called for a combination of first-person and third-person research methods when studying psychology
- Georg Elias Müller (1850-1934), who performed an early experiment on attitude which involved the sensory discrimination of weights and revealed how anticipation can affect this discrimination
Key Terms to Know
To understand how the experimental method works, it is important to know some key terms.
Dependent Variable
The dependent variable is the effect that the experimenter is measuring. If a researcher was investigating how sleep influences test scores, for example, the test scores would be the dependent variable.
Independent Variable
The independent variable is the variable that the experimenter manipulates. In the previous example, the amount of sleep an individual gets would be the independent variable.
A hypothesis is a tentative statement or a guess about the possible relationship between two or more variables. In looking at how sleep influences test scores, the researcher might hypothesize that people who get more sleep will perform better on a math test the following day. The purpose of the experiment, then, is to either support or reject this hypothesis.
Operational definitions are necessary when performing an experiment. When we say that something is an independent or dependent variable, we must have a very clear and specific definition of the meaning and scope of that variable.
Extraneous Variables
Extraneous variables are other variables that may also affect the outcome of an experiment. Types of extraneous variables include participant variables, situational variables, demand characteristics, and experimenter effects. In some cases, researchers can take steps to control for extraneous variables.
Demand Characteristics
Demand characteristics are subtle hints that indicate what an experimenter is hoping to find in a psychology experiment. This can sometimes cause participants to alter their behavior, which can affect the results of the experiment.
Intervening Variables
Intervening variables are factors that can affect the relationship between two other variables.
Confounding Variables
Confounding variables are variables that can affect the dependent variable, but that experimenters cannot control for. Confounding variables can make it difficult to determine if the effect was due to changes in the independent variable or if the confounding variable may have played a role.
Psychologists, like other scientists, use the scientific method when conducting an experiment. The scientific method is a set of procedures and principles that guide how scientists develop research questions, collect data, and come to conclusions.
The five basic steps of the experimental process are:
- Identifying a problem to study
- Devising the research protocol
- Conducting the experiment
- Analyzing the data collected
- Sharing the findings (usually in writing or via presentation)
Most psychology students are expected to use the experimental method at some point in their academic careers. Learning how to conduct an experiment is important to understanding how psychologists prove and disprove theories in this field.
There are a few different types of experiments that researchers might use when studying psychology. Each has pros and cons depending on the participants being studied, the hypothesis, and the resources available to conduct the research.
Lab Experiments
Lab experiments are common in psychology because they allow experimenters more control over the variables. These experiments can also be easier for other researchers to replicate. The drawback of this research type is that what takes place in a lab is not always what takes place in the real world.
Field Experiments
Sometimes researchers opt to conduct their experiments in the field. For example, a social psychologist interested in researching prosocial behavior might have a person pretend to faint and observe how long it takes onlookers to respond.
This type of experiment can be a great way to see behavioral responses in realistic settings. But it is more difficult for researchers to control the many variables existing in these settings that could potentially influence the experiment's results.
Quasi-Experiments
While lab experiments are known as true experiments, researchers can also utilize a quasi-experiment. Quasi-experiments are often referred to as natural experiments because the researchers do not have true control over the independent variable.
A researcher looking at personality differences and birth order, for example, is not able to manipulate the independent variable in the situation (personality traits). Participants also cannot be randomly assigned because they naturally fall into pre-existing groups based on their birth order.
So why would a researcher use a quasi-experiment? This is a good choice in situations where scientists are interested in studying phenomena in natural, real-world settings. It's also beneficial if there are limits on research funds or time.
Field experiments can be either quasi-experiments or true experiments.
Examples of the Experimental Method in Use
The experimental method can provide insight into human thoughts and behaviors, Researchers use experiments to study many aspects of psychology.
A 2019 study investigated whether splitting attention between electronic devices and classroom lectures had an effect on college students' learning abilities. It found that dividing attention between these two mediums did not affect lecture comprehension. However, it did impact long-term retention of the lecture information, which affected students' exam performance.
An experiment used participants' eye movements and electroencephalogram (EEG) data to better understand cognitive processing differences between experts and novices. It found that experts had higher power in their theta brain waves than novices, suggesting that they also had a higher cognitive load.
A study looked at whether chatting online with a computer via a chatbot changed the positive effects of emotional disclosure often received when talking with an actual human. It found that the effects were the same in both cases.
One experimental study evaluated whether exercise timing impacts information recall. It found that engaging in exercise prior to performing a memory task helped improve participants' short-term memory abilities.
Sometimes researchers use the experimental method to get a bigger-picture view of psychological behaviors and impacts. For example, one 2018 study examined several lab experiments to learn more about the impact of various environmental factors on building occupant perceptions.
A 2020 study set out to determine the role that sensation-seeking plays in political violence. This research found that sensation-seeking individuals have a higher propensity for engaging in political violence. It also found that providing access to a more peaceful, yet still exciting political group helps reduce this effect.
While the experimental method can be a valuable tool for learning more about psychology and its impacts, it also comes with a few pitfalls.
Experiments may produce artificial results, which are difficult to apply to real-world situations. Similarly, researcher bias can impact the data collected. Results may not be able to be reproduced, meaning the results have low reliability .
Since humans are unpredictable and their behavior can be subjective, it can be hard to measure responses in an experiment. In addition, political pressure may alter the results. The subjects may not be a good representation of the population, or groups used may not be comparable.
And finally, since researchers are human too, results may be degraded due to human error.
What This Means For You
Every psychological research method has its pros and cons. The experimental method can help establish cause and effect, and it's also beneficial when research funds are limited or time is of the essence.
At the same time, it's essential to be aware of this method's pitfalls, such as how biases can affect the results or the potential for low reliability. Keeping these in mind can help you review and assess research studies more accurately, giving you a better idea of whether the results can be trusted or have limitations.
Colorado State University. Experimental and quasi-experimental research .
American Psychological Association. Experimental psychology studies human and animals .
Mayrhofer R, Kuhbandner C, Lindner C. The practice of experimental psychology: An inevitably postmodern endeavor . Front Psychol . 2021;11:612805. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.612805
Mandler G. A History of Modern Experimental Psychology .
Stanford University. Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt . Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
Britannica. Gustav Fechner .
Britannica. Hermann von Helmholtz .
Meyer A, Hackert B, Weger U. Franz Brentano and the beginning of experimental psychology: implications for the study of psychological phenomena today . Psychol Res . 2018;82:245-254. doi:10.1007/s00426-016-0825-7
Britannica. Georg Elias Müller .
McCambridge J, de Bruin M, Witton J. The effects of demand characteristics on research participant behaviours in non-laboratory settings: A systematic review . PLoS ONE . 2012;7(6):e39116. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039116
Laboratory experiments . In: The Sage Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods. Allen M, ed. SAGE Publications, Inc. doi:10.4135/9781483381411.n287
Schweizer M, Braun B, Milstone A. Research methods in healthcare epidemiology and antimicrobial stewardship — quasi-experimental designs . Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol . 2016;37(10):1135-1140. doi:10.1017/ice.2016.117
Glass A, Kang M. Dividing attention in the classroom reduces exam performance . Educ Psychol . 2019;39(3):395-408. doi:10.1080/01443410.2018.1489046
Keskin M, Ooms K, Dogru AO, De Maeyer P. Exploring the cognitive load of expert and novice map users using EEG and eye tracking . ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf . 2020;9(7):429. doi:10.3390.ijgi9070429
Ho A, Hancock J, Miner A. Psychological, relational, and emotional effects of self-disclosure after conversations with a chatbot . J Commun . 2018;68(4):712-733. doi:10.1093/joc/jqy026
Haynes IV J, Frith E, Sng E, Loprinzi P. Experimental effects of acute exercise on episodic memory function: Considerations for the timing of exercise . Psychol Rep . 2018;122(5):1744-1754. doi:10.1177/0033294118786688
Torresin S, Pernigotto G, Cappelletti F, Gasparella A. Combined effects of environmental factors on human perception and objective performance: A review of experimental laboratory works . Indoor Air . 2018;28(4):525-538. doi:10.1111/ina.12457
Schumpe BM, Belanger JJ, Moyano M, Nisa CF. The role of sensation seeking in political violence: An extension of the significance quest theory . J Personal Social Psychol . 2020;118(4):743-761. doi:10.1037/pspp0000223
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
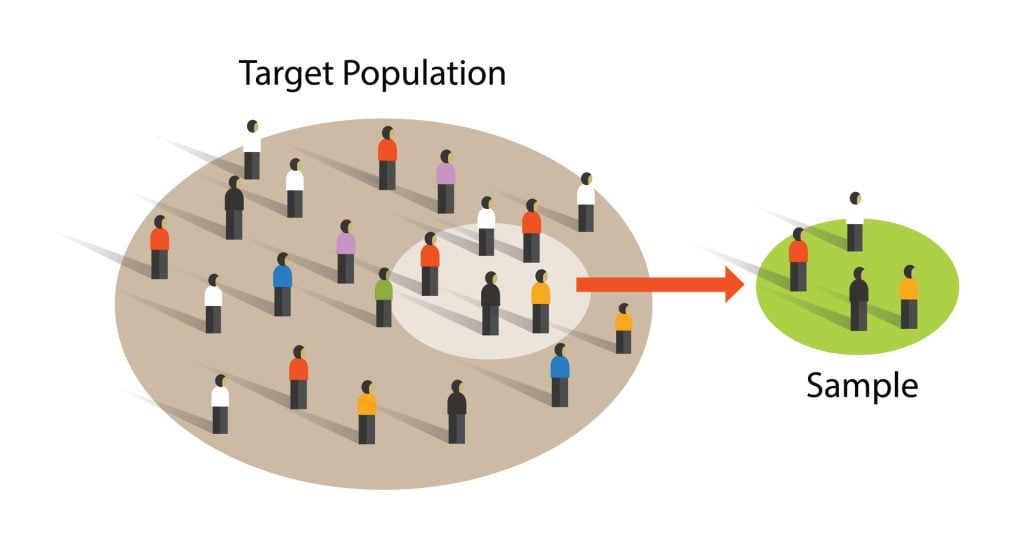
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
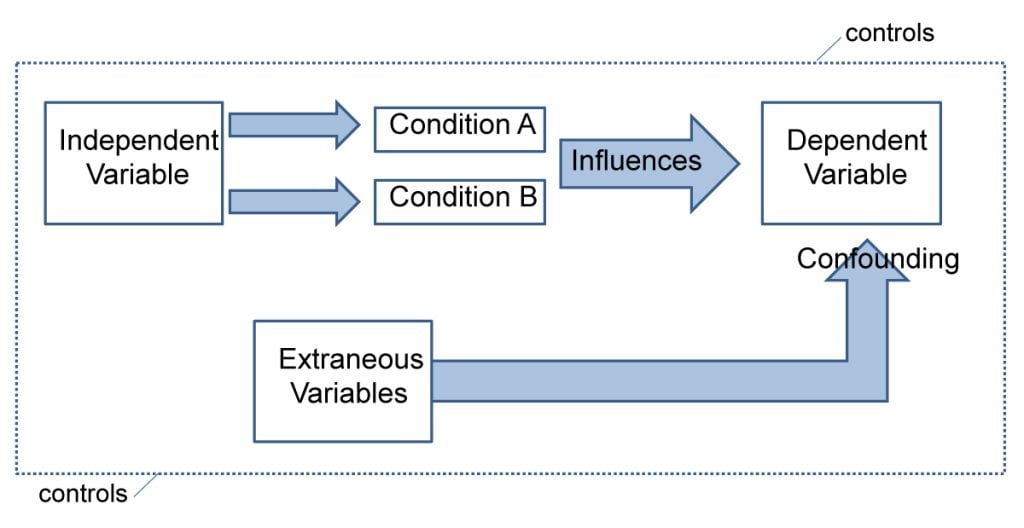
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
The researcher decides where the experiment will take place, at what time, with which participants, in what circumstances, using a standardized procedure.
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
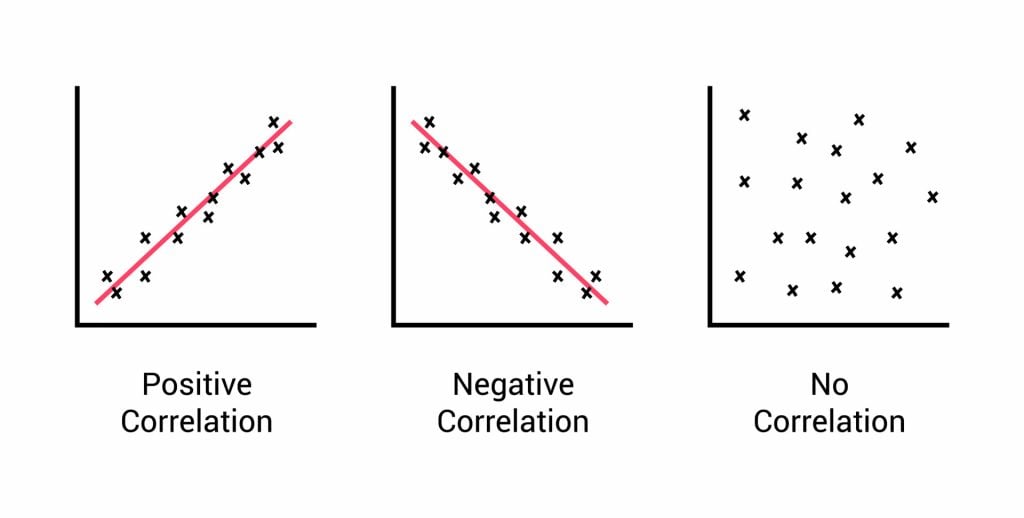
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
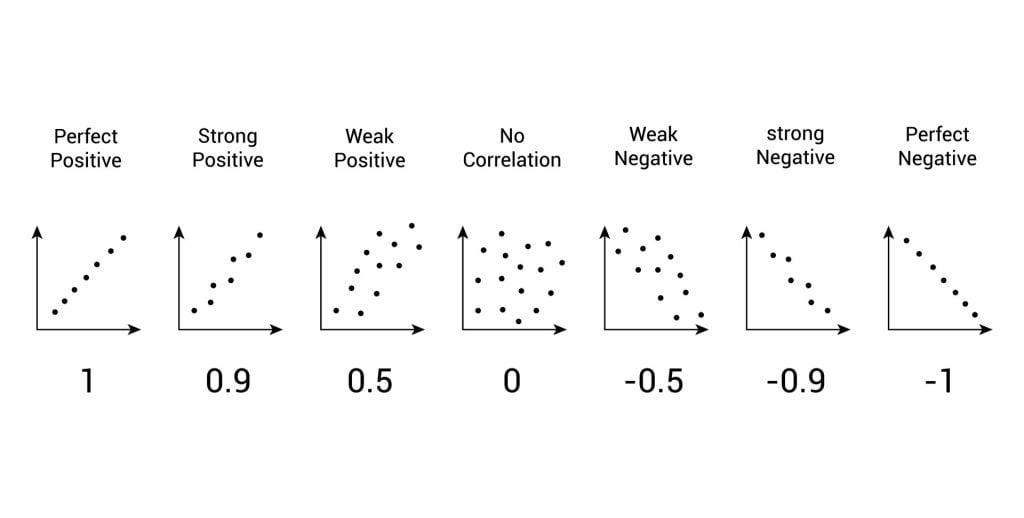
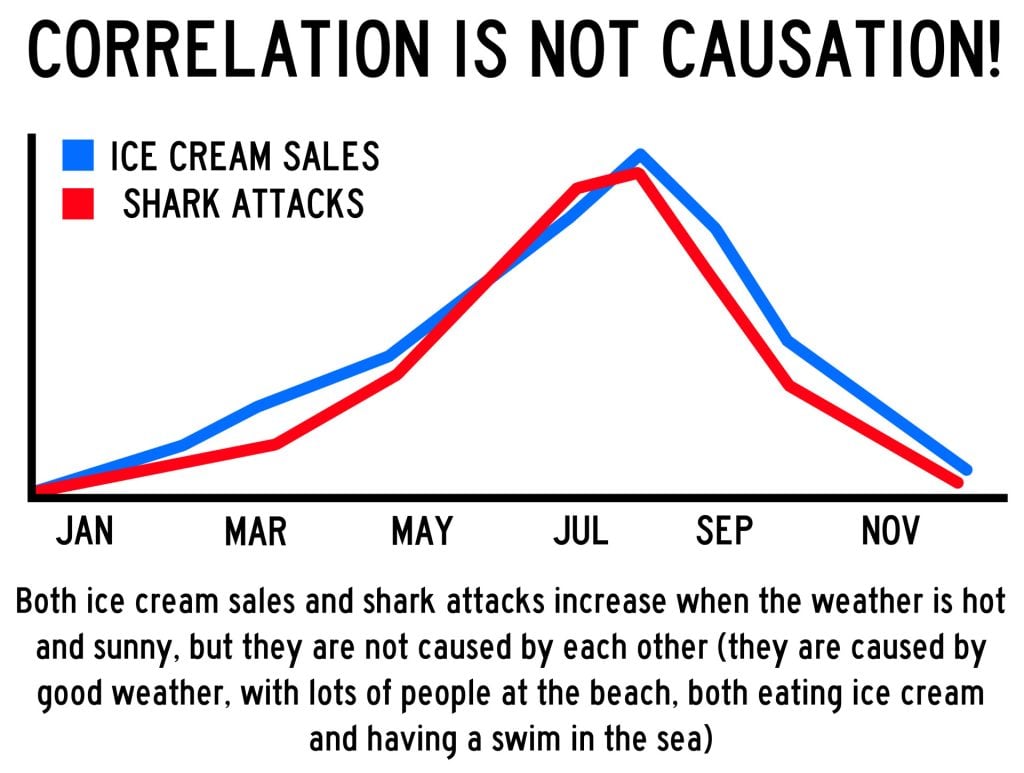
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.

Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
Meta-analysis is a statistical procedure used to combine and synthesize findings from multiple independent studies to estimate the average effect size for a particular research question.
Meta-analysis goes beyond traditional narrative reviews by using statistical methods to integrate the results of several studies, leading to a more objective appraisal of the evidence.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
- Strengths : Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
- Weaknesses : Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.

- General Categories
- Mental Health
- IQ and Intelligence
- Bipolar Disorder

Field Experiments in Psychology: Real-World Research Techniques
Stepping out of the controlled confines of the laboratory, psychologists venture into the unpredictable and fascinating world of field experiments, where the complexities of human behavior unfold in their most authentic form. It’s a thrilling journey that takes researchers from the sterile environment of white coats and clipboards to the bustling streets, crowded classrooms, and vibrant workplaces where real life happens.
Imagine, if you will, a psychologist perched on a park bench, surreptitiously observing how people interact with a strategically placed piece of litter. Or picture another researcher, clipboard in hand, wandering through a bustling shopping mall, noting how store layouts influence purchasing decisions. These scenarios aren’t just figments of imagination; they’re real examples of field experiments in action.
The Great Outdoors of Psychological Research
Field experiments in psychology are like taking the lab coat off and putting on a pair of hiking boots. They’re all about studying human behavior in its natural habitat, where the unpredictability of real life adds a dash of excitement (and a pinch of chaos) to the scientific process. Unlike their more buttoned-up cousins, laboratory experiments, field experiments embrace the messiness of the real world.
But why bother leaving the comfort of the lab? Well, as any seasoned psychologist will tell you, human behavior isn’t always at its most authentic when people know they’re being watched. It’s like trying to study wild animals in a zoo – you’ll learn something, sure, but you’re not getting the full picture. Field study psychology: Exploring real-world behavior and cognition allows researchers to observe people in their natural habitats, warts and all.
The importance of field experiments in psychological research can’t be overstated. They bridge the gap between theory and practice, allowing researchers to test their hypotheses in the real world where it really counts. It’s one thing to predict how people might behave in a controlled setting, but it’s another thing entirely to see how those predictions hold up when faced with the chaos of everyday life.
Defining Field Experiments: More Than Just People-Watching
So, what exactly is a field experiment? Well, it’s not just hanging out at the mall food court and taking notes (though that might be part of it). A field experiment is a research study conducted in a real-world setting where the researcher manipulates one or more variables to observe their effect on behavior. It’s like setting up a tiny laboratory in the middle of everyday life.
The key characteristics of field experiments are what set them apart from other research methods. First and foremost, they take place in natural settings – no white walls or one-way mirrors here. Secondly, they involve the manipulation of variables, just like in a laboratory experiment. The difference is that these manipulations are designed to blend seamlessly into the environment, like a chameleon in a rainforest.
Field experiments have some significant advantages over other research designs. They offer high ecological validity – fancy researcher-speak for “it’s like real life.” Experimental realism psychology: Bridging the gap between lab and life is at its peak in field experiments, as participants are often unaware they’re part of a study, behaving as they naturally would.
But it’s not all sunshine and rainbows in the world of field experiments. They come with their own set of challenges. Controlling variables in the real world is about as easy as herding cats – possible, but not without its difficulties. And then there’s the ethical consideration of studying people without their knowledge. It’s a delicate balance between scientific pursuit and respecting privacy.
The Art and Science of Field Experimentation
Conducting a field experiment is a bit like planning a surprise party – it requires careful preparation, perfect timing, and a dash of creativity. The process begins with identifying research questions that are best answered outside the lab. These are often questions about how people behave in specific real-world contexts, like how pedestrians react to a person in distress or how the presence of security cameras affects shoplifting rates.
Selecting the right field setting is crucial. It’s like choosing the perfect canvas for a masterpiece. The setting needs to provide opportunities to observe the behavior of interest while also allowing for the subtle manipulation of variables. A busy city street might be perfect for studying helping behavior, while a retail store could be ideal for researching consumer decision-making.
Participant recruitment in field experiments often happens without the participants even knowing it. It’s a bit like being an extra in a movie without realizing you’re on camera. This naturalistic approach is what gives field experiments their power, but it also raises important ethical considerations. Researchers must carefully balance the need for authentic behavior with respect for individual privacy and autonomy.
Designing and implementing experimental manipulations in the field is where the creativity of psychology really shines. It might involve strategically placing objects, altering environmental cues, or even using confederates – actors who are in on the experiment. The key is to make these manipulations subtle enough that they don’t disrupt the natural flow of behavior.
Data collection in field experiments can be as varied as the experiments themselves. It might involve direct observation, hidden cameras, or even collecting physical evidence left behind by participants. Field research in psychology: Methods, applications, and challenges often requires researchers to be quick on their feet, adapting their methods to the unpredictable nature of real-world settings.
The Many Flavors of Field Experiments
Field experiments come in various types, each with its own unique flavor. Natural field experiments are like finding a ready-made experiment in the wild. Researchers stumble upon situations where natural variations in the environment create experimental-like conditions. It’s like nature doing the experimenting for you!
Artifactual field experiments, on the other hand, involve bringing elements of the laboratory into the field. Imagine a researcher setting up a mobile lab in a park or a shopping center. It’s a bit like having your cake and eating it too – you get the control of a lab with the realism of a field setting.
Framed field experiments are where things get really interesting. These involve creating a controlled environment within a natural setting, often without participants realizing they’re part of an experiment. It’s like setting up an invisible stage in the middle of everyday life and watching how people react to the unseen script.
Let’s look at some examples to bring these types to life. A natural field experiment might involve studying how different weather conditions affect people’s moods by analyzing social media posts. An artifactual field experiment could involve setting up a booth in a mall to test people’s reaction times under different levels of background noise. A framed field experiment might involve altering the layout of grocery store aisles to see how it affects purchasing behavior.
Field Experiments Across the Psychology Spectrum
Field experiments have found their way into various subfields of psychology, each adapting the method to suit its unique needs. In social psychology, field experiments have been instrumental in studying real-world behavior. Social psychology experiments: Groundbreaking studies that shaped our understanding of human behavior often rely on field settings to observe how people interact in authentic social situations.
Developmental psychologists use field experiments to observe natural growth and change over time. These studies might involve observing children’s play behaviors in different playground designs or tracking how adolescents’ social media use evolves in response to different online environments.
In the world of industrial-organizational psychology, field experiments are used to test workplace interventions. Imagine a study where different management styles are subtly implemented in different departments of a company to see their effects on employee productivity and satisfaction. It’s like A/B testing, but with people’s careers!
Environmental psychology is another area where field experiments shine. These studies examine how people interact with their surroundings, from urban planning to conservation behaviors. A field experiment in this area might involve altering the design of recycling bins in a public space to see how it affects recycling rates.
Navigating the Choppy Waters of Field Experimentation
While field experiments offer a unique window into human behavior, they’re not without their challenges. Maintaining experimental control in uncontrolled environments is like trying to conduct an orchestra in the middle of a hurricane – possible, but requiring exceptional skill and adaptability.
One of the biggest hurdles is addressing potential confounding variables. In the real world, there are countless factors that could influence behavior beyond the variables being studied. It’s like trying to isolate a single voice in a crowded room – tricky, but not impossible with the right techniques.
Ensuring internal and external validity in field experiments is a delicate balancing act. Internal validity asks whether the experiment accurately measures what it intends to measure, while external validity questions whether the results can be generalized to other situations. It’s like trying to hit a bullseye while riding a unicycle – challenging, but oh so rewarding when you get it right.
Ethical issues in field experiments require careful consideration. True experiments in psychology: Definition, components, and applications often involve informed consent, but field experiments sometimes operate in a grey area. Researchers must navigate the fine line between scientific inquiry and respecting individual rights and privacy.
Balancing scientific rigor with real-world applicability is the ultimate challenge in field experimentation. It’s about finding that sweet spot where the research is both academically sound and practically useful. After all, what good is knowledge if it can’t be applied to improve people’s lives?
The Future is Field
As we wrap up our journey through the world of field experiments, it’s clear that this method of research is more than just a tool in the psychologist’s toolkit – it’s a window into the authentic human experience. Field experiments allow us to step out of the sterile laboratory and into the messy, complex, and utterly fascinating world of real human behavior.
The future of field experiments in psychology is bright and full of possibilities. As technology advances, new tools for data collection and analysis will open up even more opportunities for studying behavior in natural settings. Imagine wearable devices that can track physiological responses in real-time, or AI-powered systems that can analyze vast amounts of behavioral data collected in the field.
Natural experiments in psychology: Unveiling real-world insights will likely play an increasingly important role as researchers seek to understand complex social phenomena that can’t be easily replicated in controlled settings. From studying the psychological impacts of major societal events to understanding how new technologies shape human interaction, field experiments will be at the forefront of psychological discovery.
The role of field experiments in advancing psychological knowledge cannot be overstated. They provide a crucial bridge between theory and practice, allowing researchers to test and refine their understanding of human behavior in the crucible of real-world experience. As psychology continues to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of human experience, field experiments will undoubtedly remain a vital tool in our quest to understand the endlessly fascinating puzzle of the human mind and behavior.
So, the next time you’re out and about, take a moment to look around. You might just be an unwitting participant in a field experiment, contributing to our collective understanding of what makes us tick. And isn’t that a thrilling thought?
References:
1. Levitt, S. D., & List, J. A. (2009). Field experiments in economics: The past, the present, and the future. European Economic Review, 53(1), 1-18.
2. Gneezy, U. (2005). Deception: The role of consequences. American Economic Review, 95(1), 384-394.
3. Harrison, G. W., & List, J. A. (2004). Field experiments. Journal of Economic Literature, 42(4), 1009-1055.
4. Gerber, A. S., & Green, D. P. (2012). Field experiments: Design, analysis, and interpretation. WW Norton.
5. Paluck, E. L. (2010). The promising integration of qualitative methods and field experiments. The ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 628(1), 59-71.
6. Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Houghton Mifflin.
7. Cialdini, R. B. (2009). We have to break up. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4(1), 5-6.
8. Lewin, K. (1951). Field theory in social science: Selected theoretical papers. Harper & Brothers.
9. Bronfenbrenner, U. (1977). Toward an experimental ecology of human development. American Psychologist, 32(7), 513-531.
10. Barker, R. G. (1968). Ecological psychology: Concepts and methods for studying the environment of human behavior. Stanford University Press.
Was this article helpful?
Would you like to add any comments (optional), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Related Resources
Brain Samples: Unlocking the Secrets of Neuroscience

Discover Psychology Impact Factor: Exploring the Journal’s Influence and Significance

Confidence Intervals in Psychology: Enhancing Statistical Interpretation and Research Validity

Control Condition in Psychology: Definition, Purpose, and Applications

Dependent Variables in Psychology: Definition, Examples, and Importance

Debriefing in Psychology: Definition, Purpose, and Techniques

Correlation in Psychology: Definition, Types, and Applications

Data Collection Methods in Psychology: Essential Techniques for Researchers
Histogram in Psychology: Definition, Applications, and Significance

Dimensional vs Categorical Approach in Psychology: Comparing Methods of Classification

IMAGES