
Yearly paid plans are up to 65% off for the spring sale. Limited time only! 🌸
- Form Builder
- Survey Maker
- AI Form Generator
- AI Survey Tool
- AI Quiz Maker
- Store Builder
- WordPress Plugin
HubSpot CRM
Google Sheets
Google Analytics
Microsoft Excel
- Popular Forms
- Job Application Form Template
- Rental Application Form Template
- Hotel Accommodation Form Template
- Online Registration Form Template
- Employment Application Form Template
- Application Forms
- Booking Forms
- Consent Forms
- Contact Forms
- Donation Forms
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Evaluation Surveys
- Feedback Surveys
- Market Research Surveys
- Personality Quiz Template
- Geography Quiz Template
- Math Quiz Template
- Science Quiz Template
- Vocabulary Quiz Template
Try without registration Quick Start
Read engaging stories, how-to guides, learn about forms.app features.
Inspirational ready-to-use templates for getting started fast and powerful.
Spot-on guides on how to use forms.app and make the most out of it.
See the technical measures we take and learn how we keep your data safe and secure.
- Integrations
- Help Center
- Sign In Sign Up Free
- 40+ Hilarious research memes that will make you smile

Şeyma Beyazçiçek
Researches are part of our lives, especially if you are a forever learner. While doing research, we have been through similar difficulties or experienced the same feelings. In order to show these common points, internet memes come to our aid!
In this blog, you will see excellent any kind of material, such as UX research memes, clinical research memes, psychology research memes, and research paper memes. If you want to take a break and enjoy your time, you should definitely take a look at our 40 hilarious Research memes that will make you laugh :
- 1. Tip of the iceberg

#1 Research meme - Source: Facebook - High Impact PhD
In the background of each research, there are nights, days, weeks, and even months spent time and effort for the research. So, the paper itself is just a little concrete form of all the effort and work.

2. There is no destination!

#2 Research meme - Source: Make a meme
Researches are like living. There is no destination, but it is a journey! As you read and see, you will realize the limitless world of knowledge.
3. But it sounds cool, isn’t it?

#3 Research meme - Source: Quick meme
When we need to do research, the first thing to do is to google it, right? We seem to have no better option as the first step in our era.
4. Don’t want to check🫣

#4 Research meme - Source: Ah See it
Before submitting the paper, reading it might feel like it is not good enough. If you do not want to feel like that, all you need to do is submit it without the last check. 🤗
- 5. Memes matter🤨

#5 Research meme - Source: Reddit
When it comes to doing Research about anything not related to the Research topic, everything seems to be worth reading and learning. Especially if it is a meme!
6. They are always one step ahead!

#6 Research meme - Source: Facebook- High Impact PhD Memes
It is undeniable that applied research with sensational findings always gathers more attention and funding. Basic research is always doomed to lose spotlights. 😏
7. Vs the reality

#7 Research meme - Source: Pinterest
When you tell people that you are doing psych research, everybody imagines something different. However, the reality is completely different from their picture. But calm down; at least we know that you are drowning among the papers.
8. Don’t want to be THAT person

#8 Research meme - Source: Illinois
If you are the person who made somebody do psych Research or made them into psychology, you should definitely question yourself and your actions. 👀
9. None can say the opposite!
#9 Research meme - Source: Giphy
If one has never done any research, s/he can assume that you begin a research, develop, and finish it. Nevertheless, of course, the process is way much more complicated than that!
- 10. Welcome to the Research-lover club🫶

#10 Research meme - Source: Imgflip
If you are into research, any topic will be a duty for you. A new phone? A holiday plan? A trip abroad? Considered it done because the necessary research is done!
11. Me trying not to be a square

#11 Research meme - Source: Facebook- High Impact PhD Memes
When you attempt to try a new research method for the first time, you might feel the anxiety of not knowing what you are doing. But as you do, it gets better, we promise.
12. That’s the only smart thing to do 😎

#12 Research meme - Source: Meme-arsenal
Before making an important decision, no matter what, you should definitely do your research because it is how cool people act!
13. UX Research is everything!
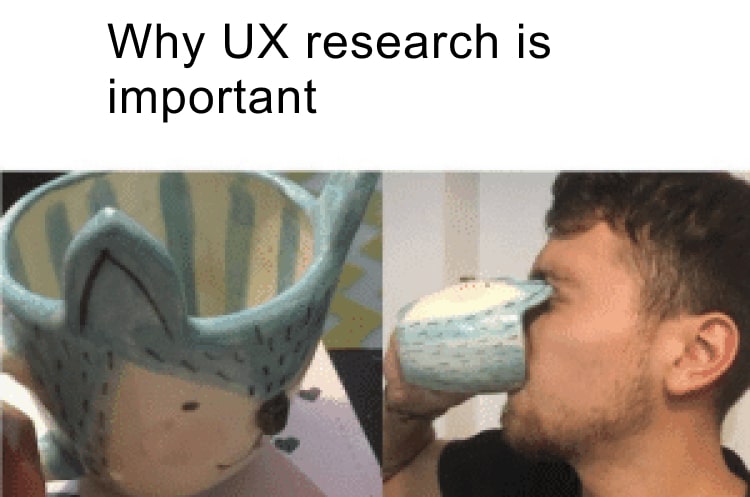

#13 Research meme - Source: Playbook UX
If you are a UX designer, you can share this meme with confidence. The picture given above summarizes the importance of UX research very well.
14. Watch me, then 😈

#14 Research meme - Source: Pinterest
Yes, probably it is not a paper that can be written the night before; we know that. But if there is no other option left, it is possible turning into a writing machine. ⌨️
- 15. It is a serious job🧐

#15 Research meme - Source: Memes
While doing research, the most significant part is to collect data related to your topic in your most serious mood. It is essential but hard to keep this mood for a long time.
16. Am I just perfect or bad at self-feedback?

#16 Research meme - Source: Tumblr
It seems like it is easier to find somebody else’s errors or criticize it. But when it comes to ours, our mistakes come suddenly invisible. Science needs to explain this!
17. I want to break free🎶

#17 Research meme - Source: McGill
While working on our research papers, we know that you do not completely feel free and work as you wish. Practicum supervisors are like a limit for research.
18. Above the clouds☁️

#18 Research meme - Source: Imgflip
While doing the research, there is always a crowd of tabs that we cannot dare close. But, when we complete the research, it is the most satisfying feeling to close all the tabs finally.
19. So am I…

#19 Research meme - Source: Make a meme
This process is challenging both physically and psychologically, for sure. So, finishing a research paper might feel like someone who survived a battle scene.
- 20. Look, I am famous!

#20 Research meme - Source: Twitter-High Impact PhD Memes
It is a really really satisfactory feeling to see your work online! Also, reading your work from someone else’s perspective is quite fun.
21. It is hard to keep your energy stable 📉

#21 Research meme - Source: Meme-arsenal
At the beginning of the semester, we have big energy and motivation to start our paper. However, at the end of the semester, it is hard to feel the same enthusiasm and energy.
22. Why would they?😭

#22 Research meme
Yes, we know that the question is optional, but still, it hurts us… When the respondents skip the question, we feel the rejection of the bone. 💔
23. So, what a medical researcher does?

#23 Research meme - Source: Mosio
When you tell people that you are a medical researcher, everybody might assume or imagine your work differently. This meme given above is a good illustration of the situation.
24. The hardest part is done 👍

#24 Research meme - Source: Quick meme
Sometimes, it is hard to understand the topic or instructions of the research. When you understand it, it gets easier. However, when you complete your research and realize that you did wrong from the beginning, it is like a nightmare!
- 25. No kid, just no.

#25 Research meme - Source: Memes happen
Yes, Wikipedia is also a source of information. But when the data is taken as copy and paste, it is an unacceptable mistake that a professional never ever does!
26. It is worthy ✨

#26 Research Meme
Looking at your final work and being able to be proud of the paper feels like a real victory! Is the paper good? Yes. Am I okay? Doesn’t matter. 🤝
27. Hard to tell🤔

#27 Research meme - Source: Make a meme
Both quantitive research and qualitative research have pros. But it is like a dilemma to make a decision between these two.
28. But I googled it 😏

#28 Research meme - Source: Quick meme
Yes, it is not possible to do our research in libraries. Instead, we google our questions and topics. Still, it is research, isn’t it?😇
29. Do not confuse me, please🙏

#29 Research meme - Source: Twitter - Iopsyche Memes
Sometimes, our research does not give us what we want. However, we can turn these opposite ideas into the next work. Looking on the bright side is our job!
- 30. Which one are you?

#30 Research meme - Source: 9GAG
If you want to be the muscled dog, take your job seriously. Otherwise, you will be the weak dog if you do not work like a professional!
31. 🥁Drum rolls🥁

#31 Research meme - Source: Memes happen
Imagine that you have already prepared the 15 pages of your research, and your PI tells you to start over. The pain🤡
32. It is time to be serious

#32 Research meme - Source: Cheezburger
Yes, the research is important. There should not be any spelling errors. But memes never allow spelling eros. Check it once, twice, three times, four times, five times….
33. That critical decision

#33 Research meme - Source: Meme-arsenal
It is essential to read the important papers related to the topic. But when it takes too much time and delays the time of starting your own research, it might feel anxious.😶
34. Let’s calm down

#34 Research meme - Source: Joey deVilla
One cannot deny that Google is a source of information today. But still, simply scrolling through pages on Google does not give you a good research paper.
- 35. Let your confidence speak!
#35 Research meme - Source: Giphy
When you are well-equipped for a topic that you have done your research before, and you witness that someone is talking totally wrong about it, you can let your self-confidence speak!
36. A product without UX Research?!

#36 Research meme - Source: Twitter - Doug Collins
The importance of UX research can be fully understood when a product is launched without UX research.
37. Let’s make it spicy🪩
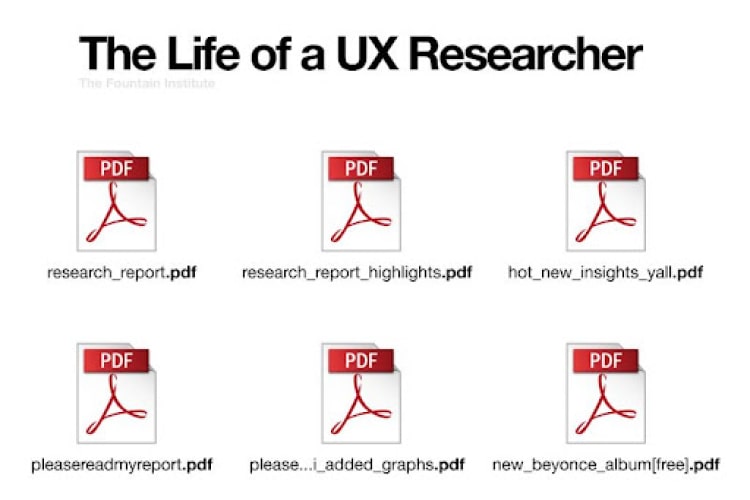
#37 Research meme - Source: LinkedIn
If your cries for help are ignored, all you need to do is to name the docs in a fun way, just like the example given above. 😊
38. The moment of confusion
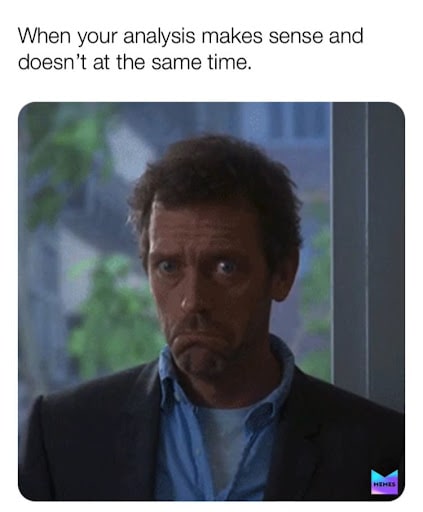

#38 Research meme - Source: Memes
When you think about too much of your research, it starts to seem wrong and correct at the same time. So, not to feel burn-out, avoid thinking about too much.
39. Social media and research?

#39 Research meme - Source: Ah See It
Digital culture has changed many things. When we witness someone on social media mention their research, it does not sound reassuring, right?
- 40. It is what it is

#40 Research meme - Source: Make a meme
I have not slept, and I have not eaten properly lately. I am also not socializing in these last days. But it does not matter because I finished my research. 👍
In this post, we have collected funny research paper memes, UX research memes, funny clinical research memes, or research memes in gif forms to make you smile. Memes are an excellent form of common feelings, and if these memes were able to help you have a great time, we are even happier than you!
Şeyma is a content writer at forms.app. She loves art and traveling. She is passionate about reading and writing. Şeyma has expertise in surveys, survey questions, giveaways, statistics, and online forms.
- Form Features
- Data Collection
Table of Contents
Related posts.
22+ Best form builders to create exquisite-looking forms in 2024

20 Great computer security survey questions to ask in your questionnaire
Eren Eltemur

5 powerful tricks to use for your research questionnaire
forms.app Team
27 Hilarious Peer Review Memes for Academics and Researchers 🤓🔬
Welcome to our latest blog post! If you’re part of the academic or research community, you know that the peer review process, while essential, can be a rollercoaster of emotions. That’s why we’ve compiled a collection of 27 side-splitting peer review memes that perfectly capture the ups, downs, and quirky moments of academic life . From the endless cycle of revisions to the mysterious vanishing reviewer, these memes offer a light-hearted look at the challenges and idiosyncrasies we all face in the world of research. So, take a break from your scholarly endeavors, and let’s dive into some academic humor that’s sure to bring a smile to your face! 📚😂
Top 27 Hilarious Peer Review Memes:
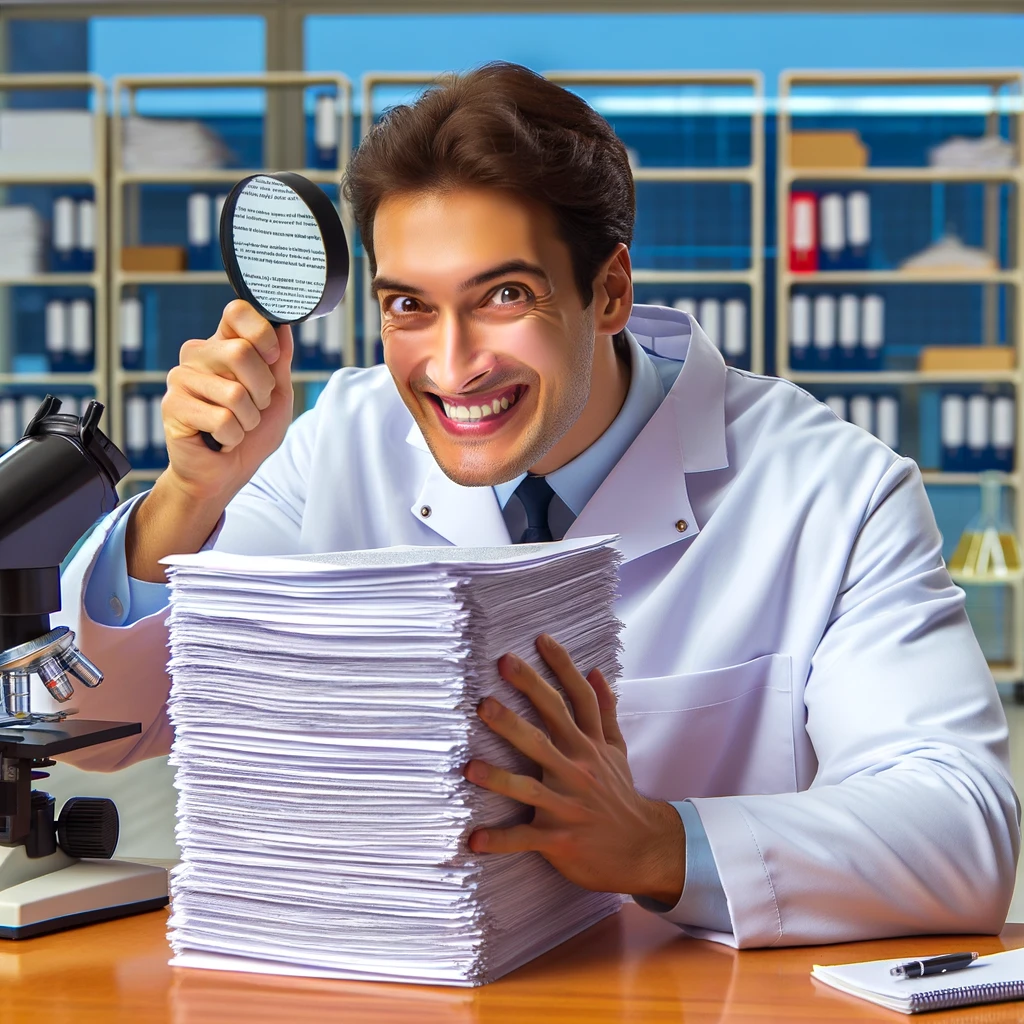
“Finding a Minor Error” : A scientist triumphantly holding a magnifying glass over a stack of research papers, with the caption: “When you spot a minor error in a well-written paper .”

“Reviewer 2 Strikes Again” : A trio of superheroes labeled “Reviewer 1,” “Reviewer 3,” and a villain labeled “Reviewer 2,” with the caption: “The never-ending battle in peer review.”

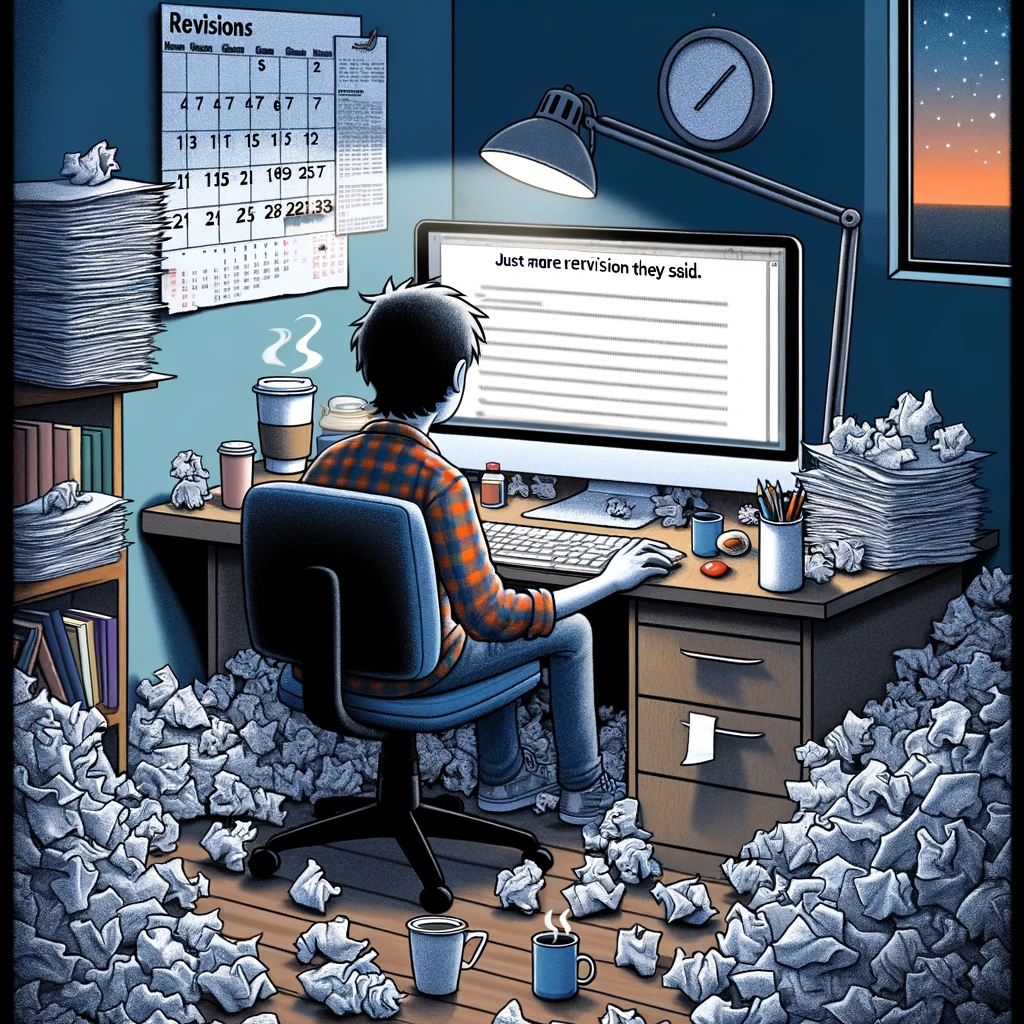
“Endless Revisions” : A researcher sitting at a computer , surrounded by piles of crumpled paper and coffee cups , with a calendar showing months passing by. Caption: “Just one more revision they said.”

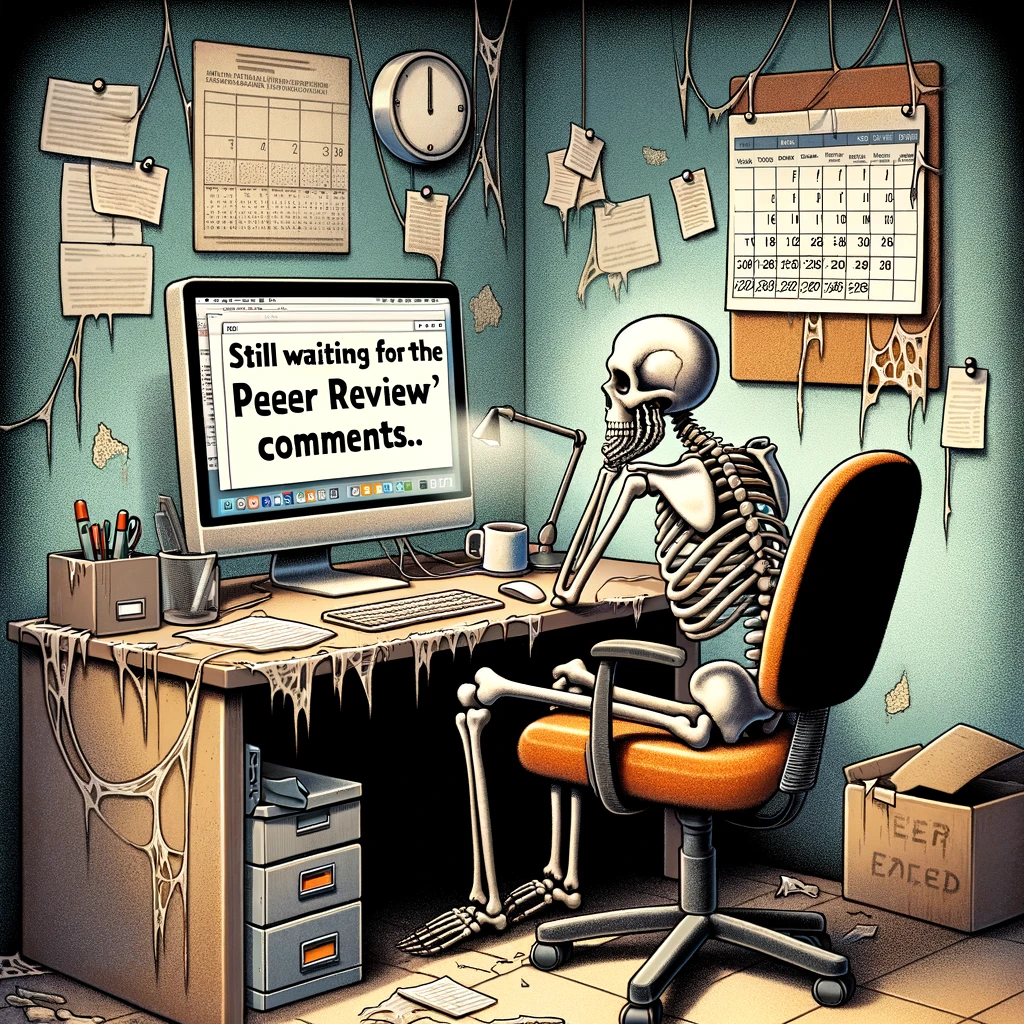
“The Waiting Game” : A skeleton sitting at a computer with an inbox still waiting for peer review feedback, captioned: “Still waiting for the reviewers’ comments.”

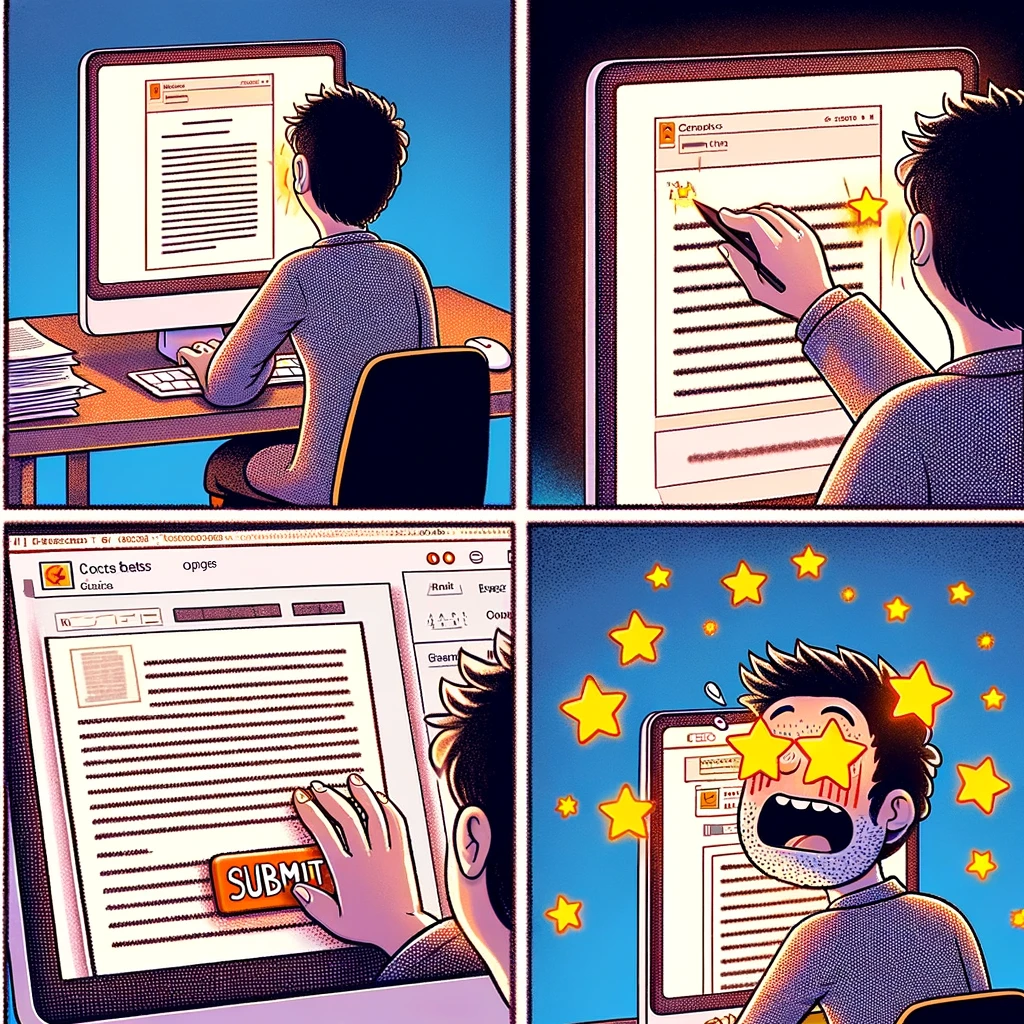
“The Optimistic Author” : An author submitting a paper with stars in their eyes , dreaming of acceptance. Next panel shows them receiving revision requests, with a caption: “Reality hits hard.”

“Citation Overload” : An overstuffed sandwich with each layer labeled as a different citation, captioned: “When reviewers ask for more citations.”

“Lost in Translation” : A researcher looking confused at a screen showing review comments that are vague and contradictory, captioned: “Trying to decipher reviewer feedback.”

“Data Juggling” : A scientist juggling multiple charts and graphs, with the caption: “When reviewers ask for additional data analysis.”

“The Perfect Match” : Two researchers finding each other on a dating app, only to realize they are reviewer and author of a contentious paper, captioned: “When your peer review is too close to home.”

“The Methodology Maze” : An image of a researcher looking perplexed at a complex maze, with each turn labeled with different research methods. Caption: “Navigating the methodology section as per reviewer’s suggestions.”
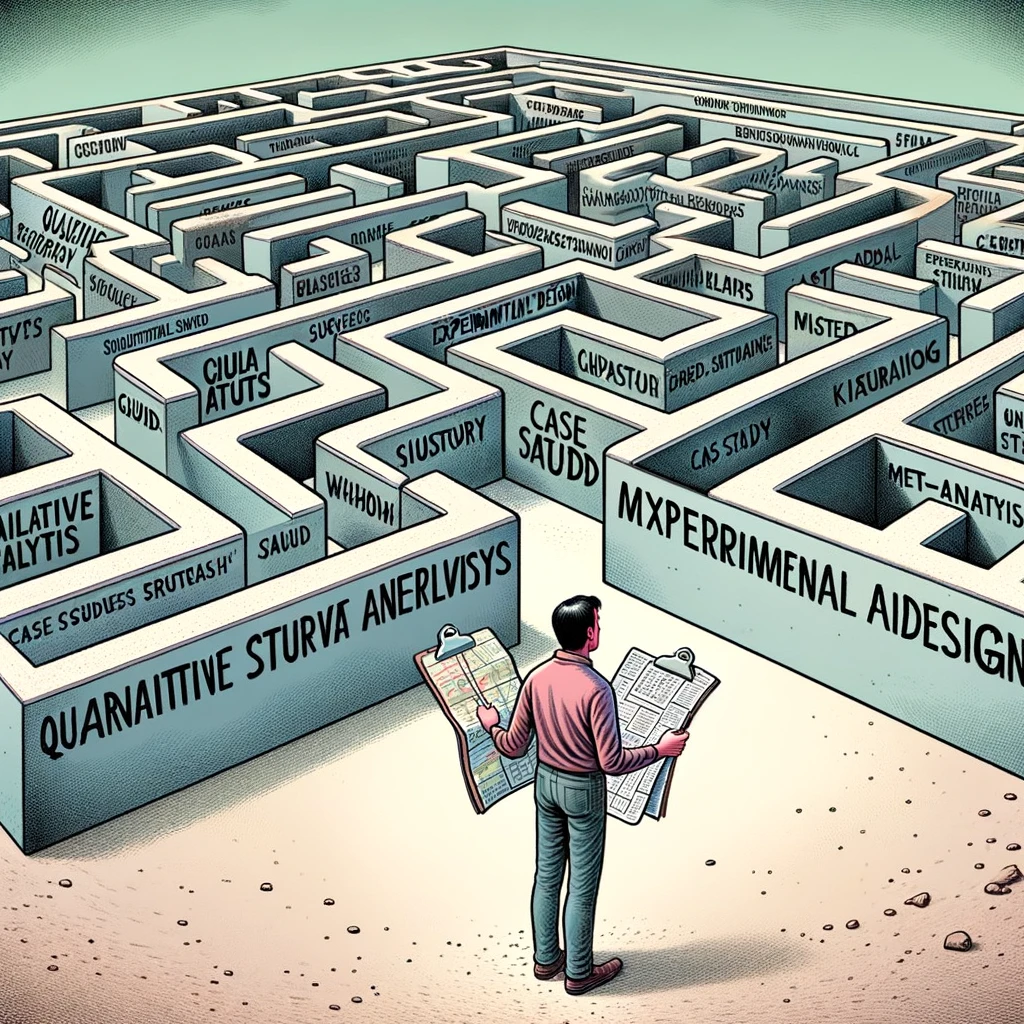
“Infinite Edits Loop” : A flowchart looping endlessly between “Submit Revision” and “Receive More Edits”. Caption: “The never-ending cycle of peer review.”
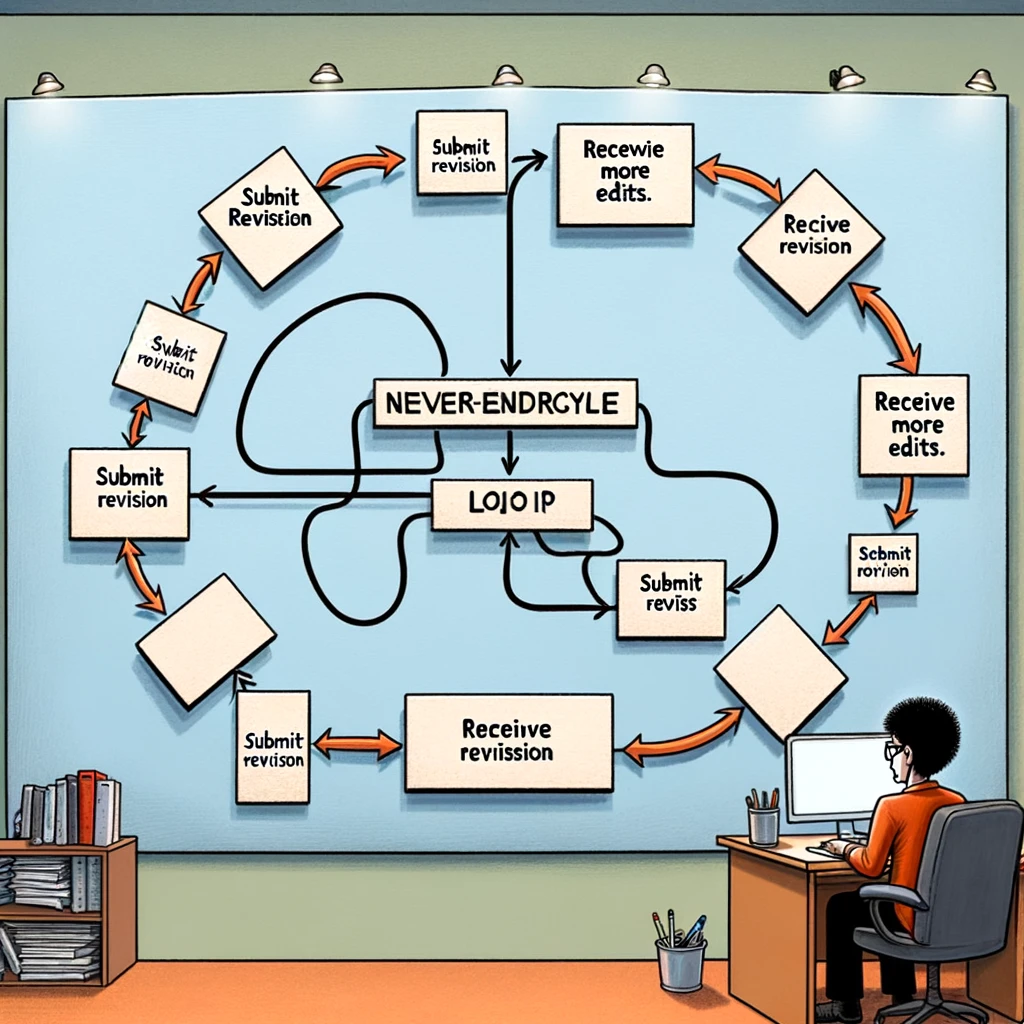
“Reviewer’s Crystal Ball” : A mystic crystal ball with the words “Future Studies” inside it. Caption: “When reviewers expect you to predict and address future research outcomes.”

“The Jargon Jungle” : A researcher hacking through a dense jungle, where each plant is labeled with complex scientific jargon. Caption: “Trying to simplify language as suggested by reviewers.”

“Expectation vs. Reality: Results Section” : Two panels; the first showing a neat, straightforward graph (Expectation), and the second showing a messy, complicated graph (Reality). Caption: “What reviewers expect vs. what you have.”
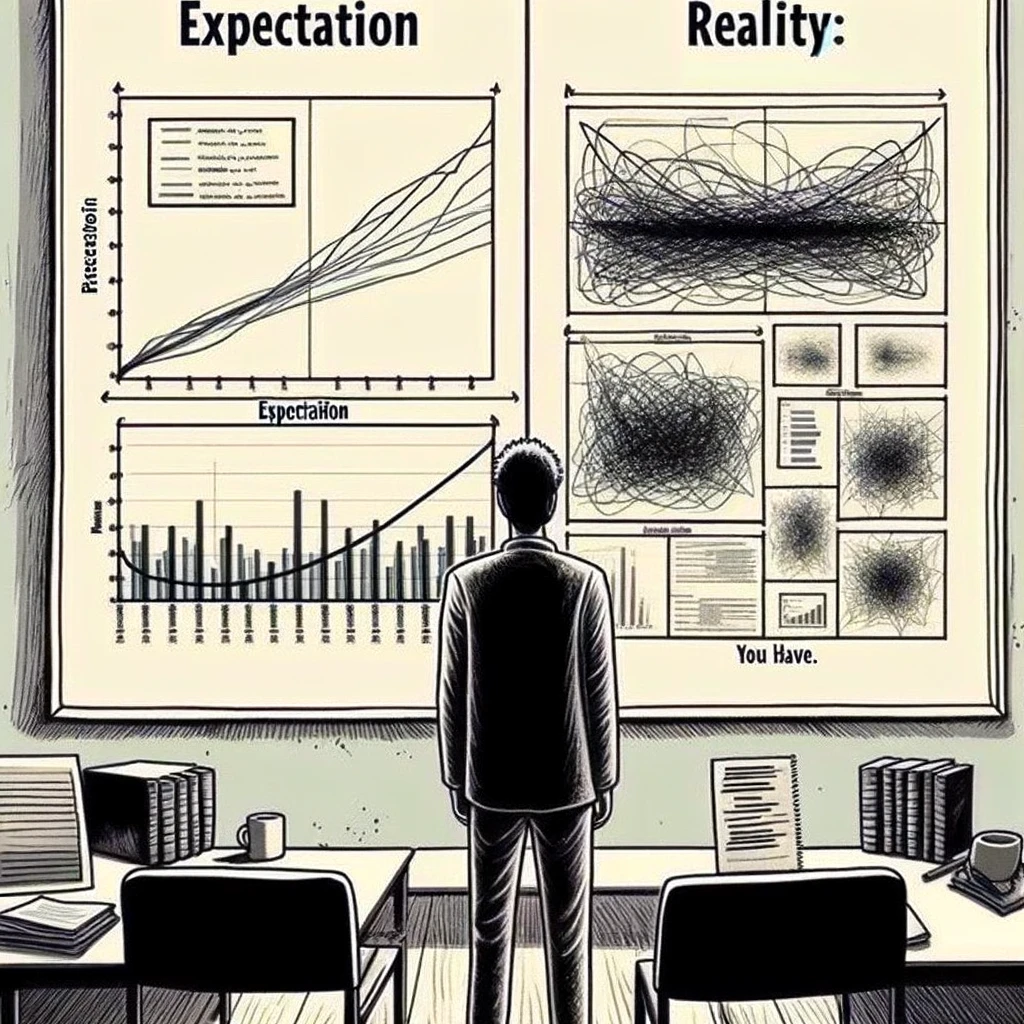
“The Ghost Reviewer” : A ghost hovering over a computer, ignoring the email reminders. Caption: “The mysterious case of the disappearing reviewer.”

“Conference Call Confusion” : A group of confused researchers on a video call, with speech bubbles of contradictory comments. Caption: “When every reviewer has a different opinion.”

“The Lengthy Literature Review” : A researcher buried under a mountain of books and papers. Caption: “When reviewers ask for a ‘brief’ literature review update.”

“Graphs Galore” : A researcher surrounded by an overwhelming number of graphs and charts, looking bewildered. Caption: “When one reviewer asks for more data visualization.”

“The Keyword Conundrum” : A researcher looking at a thesaurus with a confused expression, surrounded by a cloud of keywords. Caption: “When reviewers suggest using ‘more specific’ keywords.”

“Revision Rollercoaster” : A rollercoaster ride with highs labeled “Acceptance” and lows labeled “Major Revisions.” Caption: “The emotional rollercoaster of manuscript revisions.”

“The Citation Detective” : A detective with a magnifying glass inspecting a citation, with the caption: “When reviewers question every single reference.”

“Reviewer Roulette” : A roulette wheel with sections labeled as different reviewer personalities (e.g., “The Nitpicker,” “The Over-Enthusiast,” “The Ghost”). Caption: “Spinning the wheel to see what kind of reviewer you’ll get this time .”

“Conference Deadline Panic” : A researcher frantically typing on a laptop with a calendar showing a looming conference date . Caption: “Trying to incorporate last-minute review comments before the conference deadline.”

“The Abstract Abyss” : A researcher staring into a swirling vortex labeled “Abstract.” Caption: “When you have to summarize years of work in 250 words.”

“Data Dive” : An image of a diver surrounded by a sea of data points and graphs. Caption: “Exploring the depths of data analysis after reviewer feedback.”

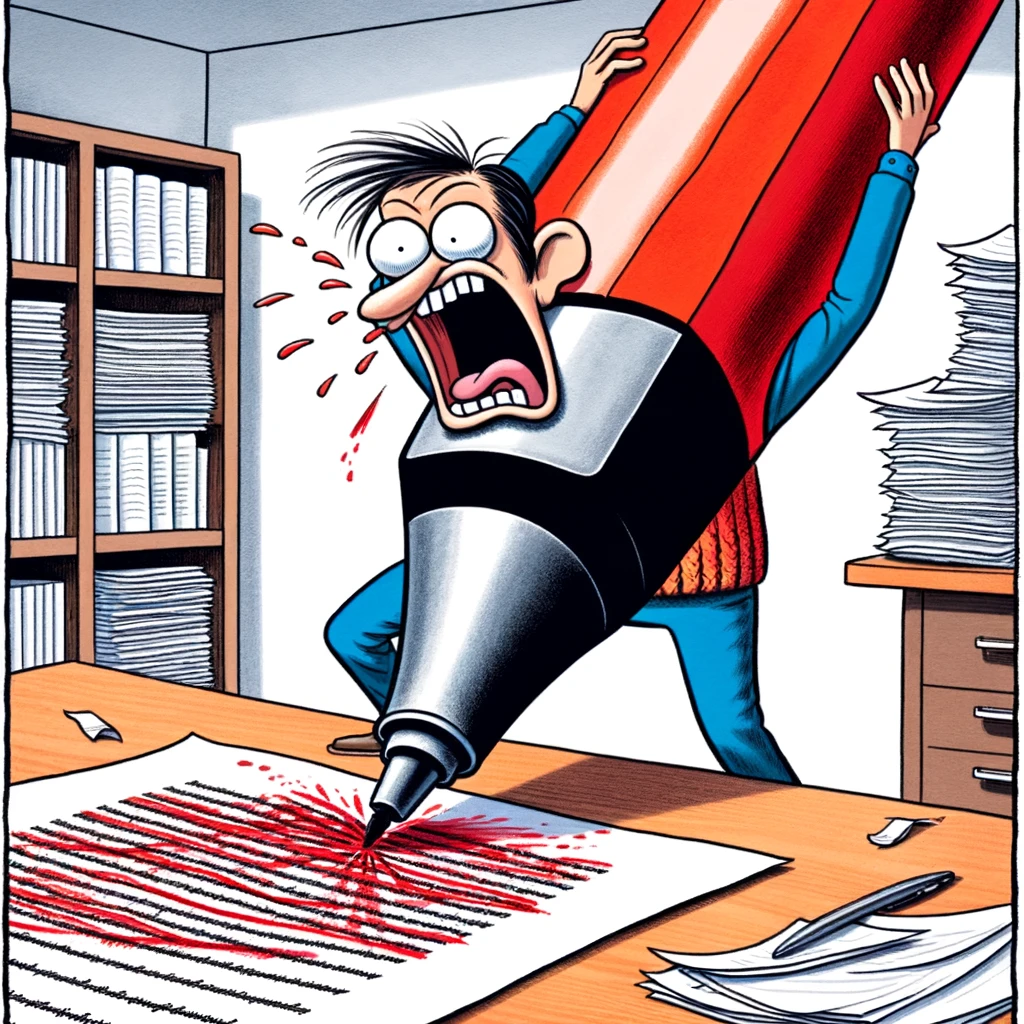
“The Overzealous Editor” : A cartoon of an editor with a giant red pen , crossing out huge sections of a manuscript. Caption: “When the editor gets a little too enthusiastic with revisions.”

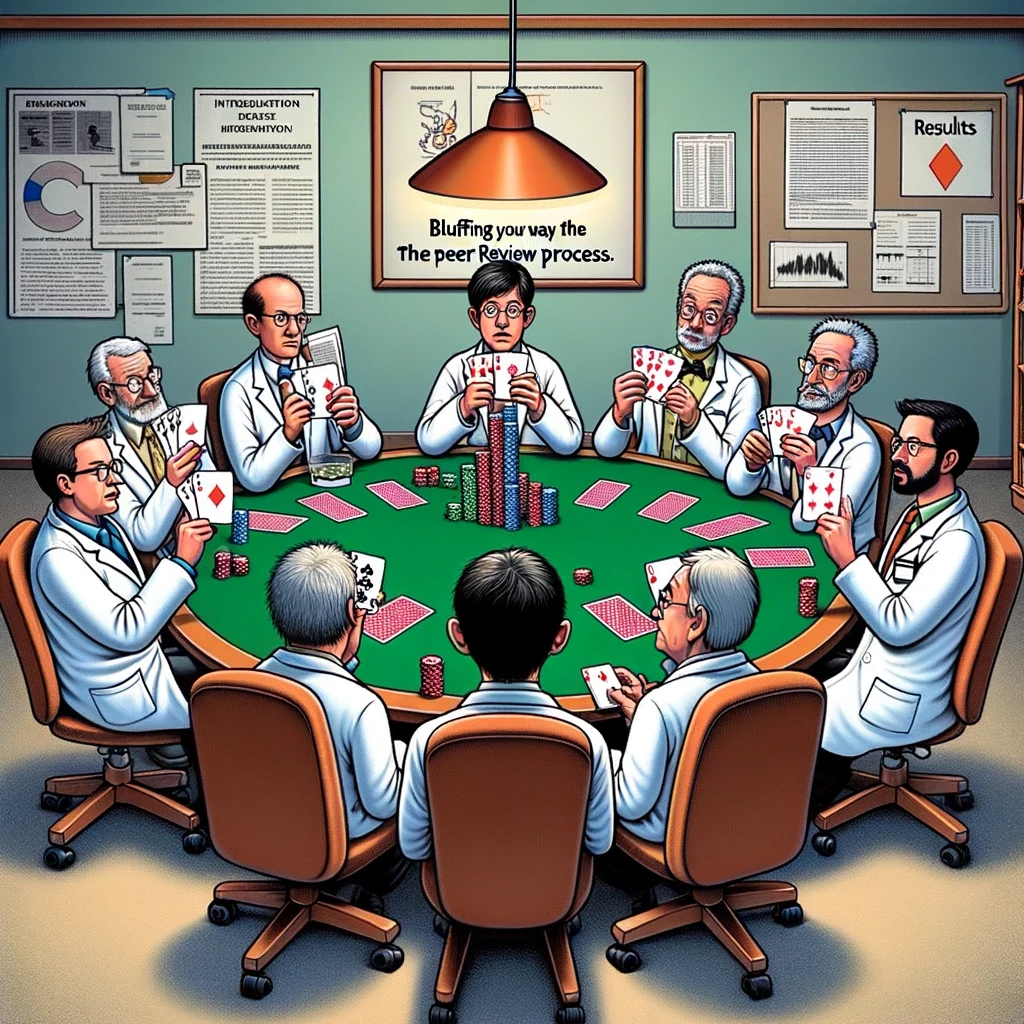
“Peer Review Poker” : Researchers sitting around a poker table, holding cards with different sections of a manuscript. Caption: “Bluffing your way through the peer review process.”

And there you have it – 27 hilariously relatable peer review memes that every academic and researcher will understand and appreciate. Whether you’ve faced the enigmatic Reviewer 2, endured the endless revisions, or navigated the complex maze of methodology, these memes are a humorous reminder that you’re not alone in this journey. Share these with your colleagues to spread some laughter in your lab or library . Remember, a little humor goes a long way in making the rigorous journey of research a bit more enjoyable. Stay tuned for more academic insights and light-hearted content! 🌟📉
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


77 Funny Book Writing Memes for Authors and Writers
Hey, writers. It’s good to see you here instead of hard at work on your current writing project. Of course, we know that it’s important to have some downtime and to have a bit of a laugh, which is why we’ve collected these 77 fun memes that do a rather good job of poking fun at the truth of what it is to be a writer. Have fun checking them out. You might just see a bit of yourself in them.
“Why Can’t You Just Get Your Book Published?”
Just tell a publisher to publish the book…. You beautiful genius, why didn’t we writers think of that?

Writers When They’re Determined to Do Anything
Why finish a book when there are so many other important things to do, like, well, anything except finish? After all, the crevices in the keyboard don’t clean themselves, do they?

Getting Those Thoughts Down on Paper
It always feels like the best characters are trapped inside our big brains, but we aren’t quite smart enough to help them get out and on the page.

How I Tell a Story
Does this sound familiar? It’s not our fault. What some may see as scatterbrained, we can tell ourselves, is simply a mad genius at work.

When You Find a Typo in a Published Book
Ah, yes, the dichotomy of typos. It feels so good when you find a typo in someone else’s published book, but so bad when you see one in your own.

Red Pill or Blue Pill?
Overcomplicating things and spending hours creating the perfect Spotify playlist for a story that will never see the light of day hits close to home, doesn’t it?

Respond to Bad Reviews
All publicity’s good publicity, right? While bad reviews aren’t going to do you any favors, lashing out against a reviewer will hurt your brand… no matter how good it might feel.

Picking Between Past and Present Tenses
Few things make writers tenser than talking about tenses.

I Just Hope I Find It Along the Way
This is how a lot of great stories start . It’s also how a lot of manifestos tend to start, so be careful.

Rewriting the Beginning 50 Times
The middle is where many writers fear to tread. Surely, if you just tweak the beginning another one or fifty times, the middle will be easier.

Who’s Been Keeping Me From Writing
Writing isn’t easy, but it’s a lot harder when your biggest obstacle to getting things done is the weirdo staring back at you from the mirror.

The World Right Now
The real world can be a bummer. It’s no wonder writers spend so much time in their own heads. It’s often the best place to be.

Writing vs. Editing the First Draft
It appears you even threw the kitchen sink into the first draft. Sounds good now, but just wait until you have to edit.

Two Kinds of People
Want to make a writer curse like Yosemite Sam and fight like a Spartan? Go ahead and dogear the pages in their favorite books.

Most Difficult Things About Writing
Admit it. We’ve all gone down the rabbit hole of character names for hours and days on end, searching for that perfect name with meaning, history, and gravitas. And then we wind up using Jack or Kate because it’s easier to type.

The Present Tense
With this type of tense problem, it might just be easier to give up and learn a completely new skill. Maybe basketweaving.

“Your Parents Are Dead”
Seriously, how many characters have one or more dead parents to give them “character”? In literature and pop culture, from Bambi to Batman, parents have it rough.

My First Draft
Your brain is a wonderful, powerful tool, but that first draft always comes out like a child’s first finger painting. It’s messy, it might be a dog or a dinosaur, but it can be turned into something special. Probably.

When Someone Finds Your First Draft
The only thing worse than cringing when reading your first draft is finding out that someone else has seen your first draft.

“I Trusted You”
Just keep telling yourself that it’s only a fictional death. Tell your therapist and your tissue box the same thing.

Being a Good Writer
And here you are… reading these memes and telling yourself that it’s still “writing work” because you are “getting ready”.

A Day in the Life of a Writer
Hey, this is rather accurate, except we’re missing the parts about feeling like an imposter and wondering whether that new show you want to stream is out yet.

Genius Level of an Author
Even worse is the location where you tend to have those great ideas. We all know that it’s usually in the bathroom.

I Think I Did a Pretty Good Job
If only we all had this kind of confidence in ourselves as writers! Honestly, though, don’t write reviews for yourself… the Internet will find you and make sure you know how wrong you are.

I Wonder if…
Well, this is a great way to start a horror story . Now what happens when they start trying to get in touch with you?

How I Feel When I Write a Plot Twist
Oh, that plot twist feels so great when you come up with it… until you realize that you confused twist with a trope.

Trying to Work Out if the Plot Ties Together
Plot seems easy, but we all know it’s not. It’s like doing long division in your head while walking barefoot across a floor filled with Legos.

The List of Books That I’ve Actually Finished Writing
Yeah… but at least you have a list.

Writing in the Middle of the Night
Honestly, there’s not much of a difference between vampires and writers, except that vampires tend to be more organized and better dressers.

I Will Find You
It’s not a lack of ideas that plagues most writers. It’s the lack of a pen and paper to write them down while on the toilet.

Brace Yourself and Kill the Character
Yes, kill the character, but make sure you wear gloves and bury the body deep.

I Have No Memory of This Place
This is where you convince yourself that you never really liked the story, so you can start that new idea.

If we’re being honest, most of us are actually some combination of the first and the sixth image here. I mean, we sometimes look at a sheet of paper.

When You Write Something Really Dark
And then you start to worry about the authorities checking your online search history.

Me Listening to Music While Writing
We all know that we have those ideal “theme songs” for everything we write. Don’t pretend you’re any different.

The Reality of My Writing
With a little massaging and edits even this could work… or not.

When People Try to Read Your Unfinished Writing
This is when it’s time to start poking at some eyes and smacking hands.

New Project vs. Unfinished Projects
There’s nothing sweeter than the kernel of a new idea. Until you’ve actually thought about it and played around a bit. Then there’s that next new idea.

My Creativity
Creativity is like the friend who tries to hype you up to do something dangerous and then just leaves you standing alone in the middle of the restaurant in your underwear.

20 More Words for a Paper
And here’s why writing toward word counts can be a problem. I mean, “here is”.

Writers have more excuses than a kid who wants to get out of gym class on dodgeball day.

Finding Your First Typo in Your Published Book
If you’ve ever wanted to know what it feels like to have your heart drop into a bucket of ice water and embarrassment, here it is.

I Wrote a Novel in Second Person
To be honest, the writer deserves to be there. Second person for a novel is an abomination.

How to Be Successful
“Here’s what you need, kid. You need a little luck, a little talent, and a couple of those plot things from Jersey Jim down on 52nd Street. Yeah, that’s how you do it.”

A Famous Writer
You would probably be better off with a career in just about anything else aside from venomous snake wrangler. And even then…

Time to Get to Work
So, this is what it’s like when people feel called out about something. Not cool, Padme. Not cool.

A Serial Killer’s Google Search History
Seriously, if there’s a serial killer in the city and the authorities started looking at search histories, writers are screwed.

The Main Villain
This is a little like turning a raging wolf into a tiny lap dog wearing a jaunty hat. It doesn’t always work, and it can take away some of the allure and mystery from your original Big Bad.

A Character With Living Parents
Well, that’s impossible. Characters don’t have living parents. Time to pack it up and become a full-time blueberry farmer.

A Total Emotional Hellscape
Sure, it makes us sad. Yet, we continue to do it. We writers are sadistic gods of our created worlds, and we like the power.

Writers After Killing Your Favorite Character
Writers have a heart. Honest. We just keep ours in a little jar in the cabinet.

When You Write 200 Years of World History
Worldbuilding is nature’s way to keep the population of fantasy writers in check.

Adverbs Everywhere
Think of adverbs as characters you don’t like. Kill them with impunity and smile while doing it.

Story Idea vs. First Draft
At least you recognize that the first draft is a little goofy… some writers just press submit.

It’s Called an Oughtobiography
Instead of reading this clever meme, you “ought to be” writing.

Delete Charakter
When you have a character that doesn’t fit… just pluck them out of the story like aliens beaming up a farmer in Indiana. Find another story for them.

Manuscript Evolution
I’d like to say that it gets easier with time, but I don’t like to lie.

All the Random Subplots Without Cohesion
Don’t worry. No one will notice. Honest. Wait, I don’t like to lie.

When I Finally Write the End
Honestly, there’s no better feeling. So, to get that good feeling faster, start your books backwards.

Something Useless and Unpractical
It’s a good feeling. All that worldbuilding is great. You aren’t getting any further on your story, but hey, you do you.

Where Does It Hurt
Everyone says technology is the way of the future. This happens too often, and everyone starts looking for stone tablets and chisels.

When Only 10 People Read Your Book
It’s not the size of your audience that counts, it’s the journey. You’ll grow stronger, and maybe some fresh “eyes” to see where you can do better.

I’m Going to Become a Writer
This is disturbingly accurate. Of course, it would’ve been nice if the guidance counselor had actually told me this. At least then, I could’ve made an informed decision.

Alright… “Chapter 1”
You laugh, but how many would-be writers are slowly decaying in front of the blank page right now. Not so funny now is it?

At the Third and Last Act of Editing
Editing has to be some sort of karmic retribution we’re all suffering because of the transgressions of some writer from the past, right?

Some Sort of Bullshit Energy
If you use enough fancy high-tech-sounding words and have people with lab coats and clipboards in scenes, no one will notice.

How I Speak vs. How I Write
Writers have two creatures living in us. One is refined, charming, and intelligent. It doesn’t get out much. The other creature is rabid, weird, and always present.

What Gives People Feelings of Power
It doesn’t seem like it takes much to please a writer. Just finish a chapter… just finish a chapter. Little do people know that’s like milking a cobra.

Villain vs. Mentor Character
Sometimes, we do get attached to the characters. We don’t want to let them go. But our villains have to be villainous. They can’t just shake their fist at the sky.

After a Character Runs Out of Meaning
Of course, for fantasy, urban fantasy, and horror authors, the coffin just ends up adding more character meaning.

Am I Researching or Just Procrastinating
To the untrained eye, it appears as though I’m procrastinating. But am I researching? No, I’m procrastinating!

It’s Free Character Development
Well, it’s part of humanity, so it can be part of a character. Of course, this often serves as a dark mirror for many writers.

Finishing the Current Chapter
Yes, this is procrastinating, but it’s also writing… so, we should probably come up with another word for it. Procrastin-writing?

Very Little Overlap
These little circles show the truth. But when you hit that sliver in the middle, it’s like magic.

That Plot Twist
This is like a surprise fart, but one that you and others will enjoy because it doesn’t stink.

The Tone I Wanted to Write the Story in
Honestly, this might say a lot about you and what you have inside. Not that it’s a bad thing.

Killing New Characters, You’re Attached to
Sometimes killing makes us sad, sometimes it makes us happy. If we weren’t writers, we’d be in prison.

How many times did you see yourself in these memes? Let’s be honest. Writers who have been at it for more than a couple of days are sure to find a lot of humor and a lot of truth in the memes. Hope you had fun with them and even more importantly, isn’t it time you got back to that work in progress?
Yves Lummer
As the founder of BookBird, Yves Lummer has pioneered a thriving community for authors, leading more than 100,000 of them towards their dreams of self-publishing. His expertise in book marketing has become a catalyst for multiple best-sellers, establishing his reputation as an influential figure in the publishing world.

Elements of a Story: 8 Story Elements Explained
February 6, 2024

170 Book Puns: Funny Puns & Jokes You’ll Never Forget
February 4, 2024

Side Character: Definition, Examples & Writing Tips

How to Start a Story: 10 Secret Writing Tips

Inciting Incident: Definition, Purpose & Examples
January 23, 2024

Biography vs. Autobiography vs. Memoir: Art of Life Stories
November 22, 2023
Privacy Overview

Want to sell more Books?
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
PhD Memes About Research Life | High Impact PhD memes
ilovephd phd memes
Explore the world of “High Impact PhD Memes,” where humor meets academia. This collection of memes delves into the unique challenges and relatable moments of the PhD journey. From battling writer’s block to celebrating small victories, these memes capture the essence of research life. Join fellow doctoral candidates in sharing a laugh and finding solace in shared experiences. Get ready to dive into the comical side of academia!
Check this impact meme, interesting and funny PhD memes about research life from iLovePhD Memes Facebook Page
This is how I Run my PhD Life with Research Problems and Life Problems

Research Gap Identified

A Night Before Thesis Defense

When My Supervisor Shouts At Me

Position to Read Article in PDF

References and Review Paper

I heard he’s doing PhD in stress management

ILovePhD’s Meme Presented in the Final Thesis Defense

How deadlines chsing me

Motivation During First and Final year of the PhD

Can you Proof Read my Article

Cofee with First Publication Motivate a lot

Ph.D. Couple Goals | We Love PhD

Forget Princess I Want to be a Scientist – PhD Memes

Difference between First and Fifth year in LAB


PhD Scholar after Thesis Defence

Graphical Abstract vs. Abstract – PhD Memes

Welcome to PhD – Memes

When you notice people reading your research work but no one citing it.

Where is the novelty

PhD advisor before and after PhD admission

What if someone had published your idea

Eat and Innovate

Difference between Theory and Practice

Procrastination to write a research paper

Advisor with new project ideas

What I am doing in Life | Why I joined PhD

Show the difference between existing vs proposed work

Before deadline vs after deadline
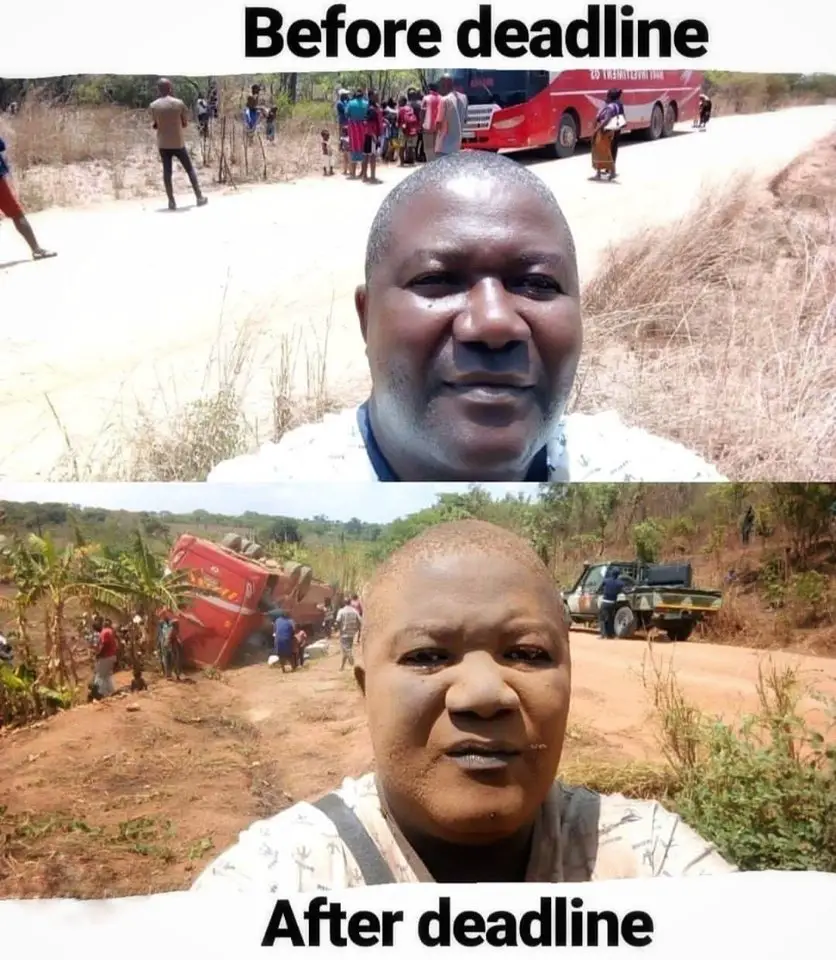

When your experiment gives outstanding result but you don’t know how

The idea of graduating and having to write my thesis

When scholar says he/she will submit manuscript draft tomorrow, but it’s been 6 months now

When everything is going wring in your life but you’re used to it

Study vs Stress Meme

Lab on Sunday

When you start thinking about your research during dinner

“High Impact PhD Memes” offers a humorous and relatable glimpse into the world of research and academia. These memes resonate with the experiences of doctoral candidates, highlighting the challenges, victories, and moments of camaraderie that define the PhD journey. As we explore this collection, it becomes evident that humor can be a powerful tool for coping with the rigors of research life. So, whether you’re in the midst of your own PhD adventure or simply curious about the world of academia, these memes provide a lighthearted and insightful perspective that brings a smile to your face and a sense of connection to the scholarly community.
- getting a phd memes
- High impact PhD memes
- high impact phd memes twitter
- interstellar phd memes
- latest phd memes
- love phd memes
- md phd memes
- Peer Reviewer
- phd dissertation memes
- phd doctor memes
- phd humor memes
- phd jokes memes
- phd memes facebook
- phd memes funny
- phd memes instagram
- phd memes jokes tamil
- phd memes postdoc
- phd memes reddit
- phd memes tamil
- phd memes twitter
- phd research memes
- phd student memes
- phd student phd memes
- phd supervisor memes
- phd thesis on memes
- phd thesis writing memes
How to Check Scopus Indexed Journals 2024
List of open access sci journals in computer science, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, leave a reply cancel reply, most popular, apply for the dst-jsps indo-japan call 2024, india-eu partner up for explainable and robust ai research, scopus indexed journals list 2024, 5 free data analysis and graph plotting software for thesis, the hrd scheme india 2024-25, 6 best online chemical drawing software 2024, imu-simons research fellowship program (2024-2027), best for you, what is phd, popular posts, how to write a research paper in a month, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 258
- Journals 234
- Fellowship 130
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 92
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence

Scientific Publishing Is a Joke
An XKCD comic—and its many remixes—perfectly captures the absurdity of academic research.

A real scientific advance, like a successful date, needs both preparation and serendipity. As a tired, single medical student, I used to feel lucky when I managed two good dates in a row. But career scientists must continually create this kind of magic. Universities judge their research faculty not so much by the quality of their discoveries as by the number of papers they’ve placed in scholarly journals, and how prestigious those journals happen to be. Scientists joke (and complain) that this relentless pressure to pad their résumés often leads to flawed or unoriginal publications. So when Randall Munroe, the creator of the long-running webcomic XKCD , laid out this problem in a perfect cartoon last week, it captured the attention of scientists—and inspired many to create versions specific to their own disciplines. Together, these became a global, interdisciplinary conversation about the nature of modern research practices.
The cartoon is, like most XKCD comics, a simple back-and-white line drawing with a nerdy punch line. It depicts a taxonomy of the 12 “Types of Scientific Paper,” presented in a grid. “The immune system is at it again,” one paper’s title reads. “My colleague is wrong and I can finally prove it,” declares another. The gag reveals how research literature, when stripped of its jargon, is just as susceptible to repetition, triviality, pandering, and pettiness as other forms of communication. The cartoon’s childlike simplicity, though, seemed to offer cover for scientists to critique and celebrate their work at the same time.
The concept was intuitive—and infinitely remixable. Within a couple of days, the sociologist Kieran Healy had created a version of the grid for his field; its entries included “This seems very weird and bad but it’s perfectly rational when you’re poor,” and “I take a SOCIOLOGICAL approach, unlike SOME people.” Epidemiologists got on board too—“We don’t really have a clue what we’re doing: but here are some models!” Statisticians , perhaps unsurprisingly, also geeked out: “A new robust variance estimator that nobody needs.” (I don’t get it either.) You couldn’t keep the biologists away from the fun (“New microscope!! Yours is now obsolete”), and—in their usual fashion—the science journalists soon followed (“Readers love animals”). A doctoral student cobbled together a website to help users generate their own versions. We reached Peak Meme with the creation of a meta-meme outlining a taxonomy of academic-paper memes. At that point, the writer and internet activist Cory Doctorow lauded the collective project of producing these jokes as “an act of wry, insightful auto-ethnography—self-criticism wrapped in humor that tells a story.”
Put another way: The joke was on target. “The meme hits the right nerve,” says Vinay Prasad, an associate epidemiology professor and a prominent critic of medical research . “Many papers serve no purpose, advance no agenda, may not be correct, make no sense, and are poorly read. But they are required for promotion.” The scholarly literature in many fields is riddled with extraneous work; indeed, I’ve always been intrigued by the idea that this sorry outcome was more or less inevitable, given the incentives at play. Take a bunch of clever, ambitious people and tell them to get as many papers published as possible while still technically passing muster through peer review … and what do you think is going to happen? Of course the system gets gamed: The results from one experiment get sliced up into a dozen papers, statistics are massaged to produce more interesting results, and conclusions become exaggerated . The most prolific authors have found a way to publish more than one scientific paper a week. Those who can’t keep up might hire a paper mill to do (or fake) the work on their behalf.
In medicine, at least, the urgency of COVID-19 only made it easier to publish a lot of articles very quickly. The most prestigious journals— The New England Journal of Medicine , the Journal of the American Medical Association , and The Lancet —have traditionally reserved their limited space for large, expensive clinical trials. During the pandemic, though, they started rapidly accepting reports that described just a handful of patients. More than a few CVs were beefed up along the way. Scientists desperate to stay relevant began to shoehorn COVID-19 into otherwise unrelated research, says Saurabh Jha, an associate radiology professor and a deputy editor of the journal Academic Radiology .
A staggering 200,000 COVID-19 papers have already been published, of which just a tiny proportion will ever be read or put into practice. To be fair, it’s hard to know in advance which data will prove most useful during an unprecedented health crisis. But pandemic publishing has only served to exacerbate some well-established bad habits, Michael Johansen, a family-medicine physician and researcher who has criticized many studies as being of minimal value, told me. “COVID publications appear to be representative of the literature at large: a few really important papers and a whole bunch of stuff that isn’t or shouldn’t be read,” he said. Peer-reviewed results confirming that our vaccines really work, for example, could lead to millions of lives being saved. Data coming out of the United Kingdom’s nationwide RECOVERY trial have provided strong evidence for now-standard treatments such as dexamethasone. But that weird case report? Another modeling study trying to predict the unpredictable? They’re good for a news cycle, maybe, but not for real medical care. And some lousy studies have even undermined the treatment of COVID-19 patients ( hydroxychloroquine has entered the chat).
I should pause here to acknowledge that I’m a hypocrite. “Some thoughts on how everyone else is bad at research” is listed as one of the facetious article types in the original XKCD comic, yet here I am rehashing the same idea, with an internet-culture angle. Unfortunately, because The Atlantic isn’t included in scientific databases, publishing this piece will do nothing to advance my academic career. “Everyone recognizes it’s a hamster-in-a-wheel situation, and we are all hamsters,” says Anirban Maitra, a physician and scientific director at MD Anderson Cancer Center. (He created a version of the “12 Types” meme for my own beloved field: “A random pathology paper with the phrase ‘artificial intelligence’ in the title.”) Maitra has built a successful career by running in the publication wheel—his own bibliography now includes more than 300 publications —but he says he has no idea how to fix the system’s flaws. In fact, none of the scientists I talked with could think of a realistic solution. If science has become a punch line, then we haven’t yet figured out how to get rid of the setup.
While the XKCD comic can be read as critical of the scientific enterprise, part of its viral appeal is that it also conveys the joy that scientists feel in nerding out about their favorite topics. (“Hey, I found a trove of old records! They don’t turn out to be particularly useful, but still, cool!”) Publication metrics have become a sad stand-in for quality in academia, but maybe there’s a lesson in the fact that even a webcomic can arouse so much passion and collaboration across the scientific community. Surely there’s a better way to cultivate knowledge than today’s endless grid of black-and-white papers.

"research paper" Memes & GIFs
Imgflip pro.
- AI creation tools & better GIFs
- Custom 6x6 profile icon and new colors
- Your images are featured instantly in auto-approve-sfw streams
- Your images jump to the top of approval queues
Research Paper
Research Paper | image tagged in gifs,research paper,pulp fiction,writing | made w/ Imgflip video-to-gif maker
College Memes: The Ultimate Study Break

Did you know that the term 'meme' was coined by British evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins in his 1976 book 'The Selfish Gene'? While he originally used it to describe the spread of cultural ideas and behaviors, today, memes take on a whole new form in the context of college life. These digital nuggets of humor and satire have evolved into a unique way for students to bond over shared experiences and challenges, all while providing a good chuckle.
Whether it's a meme about a last-minute essay idea or a witty take on a professor's quirks, these humorous images and captions have become an integral part of college culture, offering a sense of camaraderie among students as they navigate the often tumultuous waters of higher education.
College Memes: Short Description
Get ready for a rollercoaster of emotions as we delve into the world of university memes that will have you laughing and crying at the same time. These humorous digital gems capture the ups and downs of student life, from the hilarious antics of roommates to the stress-induced moments during finals week. Join us as we explore the lighter side of higher education, one meme at a time, and discover the relatable moments that make you both chuckle and shed a tear of recognition. Whether you're a seasoned essay writer or a student juggling multiple deadlines, these school memes offer a humorous break from the academic grind.
15 College Memes That Perfectly Capture Student Life
College life presents a series of challenges that can leave even our high school selves scratching their heads in bewilderment. The transition is nothing short of an obstacle course, filled with days spent in a sleep-deprived frenzy, racing to complete assignments, constantly running late to classes, and pondering existential questions like 'Why am I doing this?' or 'Should I just drop out?' It's a journey that can leave you questioning your sanity, and it's during these moments that the real transformation occurs.
After four years of trials and tribulations, it becomes abundantly clear that humor is the lifeblood that sustains us through the ups and downs of college. In addition to finding humor in the college journey, students also turn to valuable resources like books for college students and the best educational podcasts to aid in their academic pursuits and personal development. But here, we've curated a collection of the finest memes about school that are guaranteed to evoke both hearty laughter and moments of shared despair.
These funny college memes are intended to show off some of our favorite moments and a bit of fun. Colleges have many wonderful experiences – learning academic passion and friendships—as well as downsides such as stress and student debt. Thankfully, college students enjoy satirizing unis, as these wacky memes prove.
Ready to Conquer Your College Challenges with Confidence?
Just like the humorous twists in our article, let us help you navigate your coursework with ease!
- Attempting to break the world record for 'Most Repetitive Page Turner' as you struggle to stay focused on the text.

- Preparing for tomorrow's test like a professional procrastinator, because anxiety makes for great company.

- Sitting in class, nodding along like an expert bobblehead, while your inner monologue sings the 'Lost in Lecture' anthem.

- Exhausted but victorious, as you finally put to rest the assignment that's drained you for weeks.

- As the teacher fires off questions like missiles, you find yourself in full 'Stealth Mode,' transforming your focus into an intense examination of the table's profound table-ness, desperately hoping to avoid the dreaded spotlight.

- When you ghost Duolingo for just 48 hours, the Duolingo bird levels up from an app mascot to a multilingual mob boss, demanding you beg for mercy in Spanish – porque tu español es muy malo!

- While you anxiously clicked your pen during the test, that one Morse code expert in the class couldn't help but wonder why you seemed so determined to conquer Cuba, one pen click at a time.

- When the teacher mercilessly erases your uproarious Kahoot nickname, you're left feeling like a cartoon character stripped of their goofy charm in a room full of seriousness.

- Even if you granted me a whopping 67 years to complete my homework, I'd still somehow manage to procrastinate until the eleventh hour.

- As you hand your paper to the professor, you think to yourself: ‘Well, it may not be perfect, but it's a testament to my dedication and struggle to understand the subject matter.’

- You on a lazy Sunday night, blissfully unaware that the impending Monday test is lurking like a ninja, ready to pounce from around the corner.

- Your homework, initially presented as three questions, suddenly morphs into a complex trilogy with each part unraveling into a, b, and c, making you question if you've unwittingly stepped into a mathematically twisted parallel universe.

- The teacher's stern countdown echoes in the classroom, granting you a mere 5 minutes to transcribe the whiteboard's contents, while your fellow students lounge in their seats, slyly capturing the information on their phones with a nonchalant finesse.

- Teachers in regular classes, wielding their 'stop talking!' authority like seasoned bodybuilders, versus teachers in the current era, who implore with puppy-dog eyes, 'Please, someone, say something,' as they navigate the challenges of remote learning.

- Prepared to absorb the entire semester's worth of knowledge in just 12 hours, you channel your inner Eleven from Stranger Things, ready to unleash your supernatural cramming abilities.

Summing It Up
From the chaotic rush of assignments to moments of shared laughter and despair, these memes serve as a humorous reflection of the college journey. College life may be a rollercoaster, but with humor and valuable companions by your side, the ride becomes all the more enjoyable! And if you're looking to make those college connections last a lifetime, take a look at our guide on how to make new friends in college for some practical advice.
So, don't hesitate to post these relatable memes or share them with your friends. They capture the essence of college life in a way that resonates with anyone who has ever experienced the ups and downs of writing stuff for classes or trying to make sense of the academic whirlwind. Embrace the humor and camaraderie that these posts bring to your college experience!
Want to Experience a Stress-Free Academic Journey?
With our college essay writing service , you can focus on enjoying the memorable moments of laughter and learning that college has to offer!

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

Related Articles
.webp)

Adapting Memes for Qualitative Research
Filed Under: Market Research , Tools & Techniques , Focus Groups , Qualitative Research

Shaili Bhatt
Alum, Online Qualitative Research
When writing a discussion guide, it’s wonderful to be able to tap into resources that already exist in order to craft a well-rounded discussion.
A treasure trove of creative activities to elicit people’s thoughts and feelings beyond a surface level already exist. They are readily available to moderators of all experience levels, so it’s a big research-geek thrill when inspiration sparks for a projective activity with a new angle!
Our online qual team here at C+R enjoys passing around new links, for information or sheer entertainment. Twitter searches, Pinterest, and social publishers like Mashable, BuzzFeed and Reddit are some of our current sources for inspiration. In fact, when I came across the “What I Really Do” storyboard meme in 2012, one of the Top Memes for 2012, with all of its visual glory and bite-size insights, I was very excited!
The sharing fad around this meme, “What I Really Do,” which you probably saw last year, surreptitiously inspired me to transfer the basic visual layout of the meme to adapt it for use in online qualitative research.
This meme consists of a stylish comic montage of people’s thoughts related to the author/participant and his or her occupation, and boils down to a self-aware confession of “what I really do.”
The visuals are compelling connotations of their perceptions when the author spends time to find just the right pictures. The honesty in that last frame is often insightful, and exudes just the right magic that we qualitative researchers like to capture. In short, this new projective gives us a multi-angle lens into consumers’ lives.
The “What I Really Do” meme works well for research in its multi-frame storyboard layout (usually six frames). For a lighter exercise, I like this twist for the meme-theme:
Participants individually select an image for each of the three buckets. As a flexible, thought-provoking format, it’s easy to change out the “What” to a “Where” or “How,” such as, “Where I Vacationed” or “How I Cooked”, even ask about group perceptions–just change the “I” to “We” (like “What We Watched” or “What We Played”) and refer to friend or family connections in the instructions.
The stories and depictions that people generate through these activities are almost always entertaining and insightful for all involved, and early results suggest these activities would float well across a variety of category discussions.
explore featured Case studies
Collaborative, iterative, immersive, and agile creative…, the power of dining missions and live look-ins to deep…, from taste to emotion: how multi-modal research with….

Hey, get our newsletter
Join 5,000+ market research professionals who “emerge smarter” with our insights, what’s new & coming up, smartpulse: our neuroscience tool for assessing experiences, shopper segmentation.
Discover how our Shopper Segmentation can help understand shoppers’ mindsets.
WEBINAR NOW On-Demand
Empowering Your Strategies with Shopper Segmentation
Hear from our shopper insights expert, Kathleen Blum as she unveils our new proprietary Shopper Segmentation. Gain valuable insights into shoppers’ thoughts, needs, and behaviors in the food, beverage, and household categories. In this webinar:
- Learn the difference between a shopper and a consumer segmentation.
- Meet some of the shopper segments and gain a deeper understanding of their mindset, preferences, and motivations.
- Learn how our typing tool can be incorporated in targeted shopper projects and custom consumer segmentations for a comprehensive view of how your consumer and shopper segments intertwine.
- Discover how our shopper segmentation can help inform decisions about your product offerings, marketing strategies, and customer engagement initiatives.
Register Now
Search this site

Chapter 6: 21st-century media and issues
6.4.4 Messages through memes (research essay)
Alexander Caldwell
English 102, April 2021
The simple fact is that humans are social animals. With that in mind, anything social should be studied and learned about to ensure that humanity has an understanding of itself. Memes, without question, play a role in modern society and will likely do so for some time to come. While it is difficult trying to turn a topic that is not serious at all into an academic study, I find it most rewarding to know more about those short and humorous texts or videos. Memes make many people, I included, share a laugh and can be enjoyed by almost everyone.
Understanding A Meme
To get a closer look at memes, I decided to conduct a survey. The survey asked three questions. The first question, “What is your favorite meme?” Each respondent had a different favorite meme. Some of the memes were more popular, like doge memes, others were lesser-known. In theory, this question was not needed. Memes are memes regardless of how one likes or dislikes them. The real purpose of this question was to give clarity to the respondent. This question allowed the respondent to think more specifically about one meme. This is important for the next question that was asked. The next question intended to find out why memes are funny but asking that question directly would be too vague. By adding the previous question about what meme they favored, the participants could go into detail and have context for what meme they favor and would like to describe. That brings the next question where the survey asked, “What do you think makes this meme funny to you?” This question was what I was truly trying to get at. This question helps the understanding of why people enjoy memes in the first place. Many results came for this question, all interesting none the least. One of the respondents replied, “It’s straight to the point and the text catches you off guard” in reference to the “Mom I threw up” meme. This shows that the respondent enjoys the element of surprise and the simplicity of the meme. This respondent was not the only one who likes memes due to surprise. Others also answered in a similar fashion stating, “The randomness of it.” Another respondent answered this question in a different manner. Their meme is related to a popular figure, like Burnie Sander memes or Kermit the Frog memes. These responses followed the lines of liking the meme because they like the image or the entity that was in the meme. The final noticeable response was related to dark humor. The respondent answered, “It makes fun of something damn near cringeworthy out of people who like being “Positive” … in a way which is dank… It hits a lot of the checkmarks all in one package.” This type of response shows that dark humor reaches the viewer by making fun of ordinary objects in life and turns them into something that contradicts the original object. This information says that while people enjoy memes for different reasons, memes are successful at humor because of their relatability and their unexpected nature. The last question I asked was how people share or find memes. These responses were to be expected, many find them online and through social media. Popular platforms include Discord, Instagram, Twitter, through text messaging. With that in mind, memes appear to have a part in modern-day social life as they are a part of humor, social media, and texting.
While a survey is an adequate way of getting close to the understanding of what a meme is, a rhetorical analysis of a meme might also help introduce some perspective on what a meme is. The meme I choose for the analysis is one selected from one of the respondents’ responses and can be seen as posted on Reddit . This meme appears to have first been posted on Reddit in 2019, under the community of “me_irl,” which means ‘me in real life.’ The meme is by no means formal writing and was posted on Reddit to share a piece of humor created by the author. Therefore, the audience of the meme is others online, in particular, people on Reddit. The author appears to relate to the audience by stating that they were up late and wanted something to eat. It uses a sort of shadow-demon to relate to what would normally just be a human eating a late-night snack. This invokes humor because it creates emotion for an unexpected connection between the shadow demons and the consumption of beans. What makes the image even funnier is the blur and the laser-red eyes. This adds humor because it makes the image look as if it is out of a horror film. Yet, the topic at hand is only about eating beans contradicting the horror-movie-like setup. This analysis lightly suggests there are more to memes than one might initially think. It is clear that the creators of memes can relate to their audience and can invoke emotions by using memes. This leads to the need to understand what memes can be used for outside the limits of just entertainment.
One final aspect that is important to observe memes is finding out where memes come from. As the survey suggests, memes appear to be shared throughout social networks quite a bit. This still leaves the answer of where they originate from unknown. Luckily, an organization by the name of Emerging Technology, from arXiv, is capable of answering this question in their article “This Is Where Internet Memes Come From.” The study found out that a large sum of memes is being actively created in 4chan communities. The study suggests that these communities are mass-producing memes, many of which are politically charged. This goal was accomplished by sifting through millions of memes and tracking their origins (Emerging Technology). Knowing where the majority of memes come from can be handy. To elaborate, in my survey, not a single person mentioned that they used 4chan as a meme source. While it is possible that people withheld information, I do not think it is likely. Rather, it could suggest that if 4chan is in fact a major meme producer, social media plays as a powerful tool for disseminating memes. Furthermore, it could be implying that the typical meme off of a social media other than 4chan has been copied over from one platform to another.
Memes Used in the Real World
In the world at large, memes are beginning to be realized as an affluent force in human society. With that said, it is not hard to realize that memes are being used for different purposes, one of the areas in specific is advertising and marketing. In the article “We “Meme” Business: Exploring Malaysian Youths’ Interpretation of Internet Memes In Social Media Marketing” authors Kee-Man Chuah et. al. surveyed with the intent to help the marketing world. The survey was composed of fifty Malaysian youths. The goal of the survey was to get an understanding of what the youths would understand and consider funny. The results showed that memes with shorter text and text more related to the image of the meme were more understood. Chuah describes this relationship between the meme and the individual’s understanding as “iconicity” (932-941). Iconicity plays an important role in marketing as the more iconicity a meme has, the better off the meme will be at achieving the business’s goal for product awareness. The next step then would be to find out if memes can actually be used for marketing. Fortunately, in Harshit Sharma’s “Memes in Digital Culture and Their Role in Marketing and Communication: A Study in India” the answer is found. Sharma looks at a few examples. One example is where a business generates a meme for their products, and another is where the public generates memes on their own which gives the product publicity. Sharma first alludes to an old spice commercial. The commercial involved a short, quick-pasted, humorous scene with football celebrity Isaiah Mustafa. This commercial acted as a meme and was even spread like a meme, going through a multitude of social media. In short, Old Spice’s commercial meme was a success, boosting sales to 207 percent (305). It goes without saying that the meme generated by Old Spice must have had a high iconicity, which explains its success. The other use of memes the article goes over is public-generated memes. This example examines the two Indian drink brands that are complements to each other, Thumbs Up, a cola, and Old Monk, a rum. The situation proceeded when the inventor of Old Monk died. An image of a glass half empty started to circulate on social media with the text “This glass is half empty” (Sharma 312). An example of this image can be seen here . This publicly generated meme offered both products free advertising and publicity that undoubtedly helped the companies in the long run. From here, I must allude to the fact that marketing is nothing but the effective and clever use of communication to convince a consumer to buy a product. This hints at a greater picture of what memes are.
Another, even more, noticeable than ever, use of memes is in politics. It is quite obvious that memes are a part of modern politics, but it still begs the question of how memes are used in politics and what memes mean to the realm of political engagement. As it turns out, Vera Zakem’s et. al. article “Exploring the utility of memes for US government influence campaigns” has a few comments to share on the matter. Zakem writes that politicians have three primary uses for memes, to inoculate, to infect, and to treat. Inoculate refers to the action of sharing memes that try to convince the audience to have a lighter judgment on an issue that negatively affects a politician. Infect is the spreading of memes that support a politician’s ideas. Treat is the category that describes memes that try to rebuttal any negative information that is against a politician (15-16). While appearing to relate to a disease, the actual relationship memes seem to have is a tie to communicating to the audience. Politicians can use memes to advance or defend what they stand for. Zakem then provides an example of infection and treatment via memes as seen in figure 3. The article goes over a situation where a United States ambassador in Russia was accused, falsely, of attending a political movement that would negatively impact the ambassador. This was the infection. The embassy responded with a meme that inoculated the situation, thereby treating it. The meme used the same image the accuser used, and re-photodoped the ambassador in different places, including the moon (4-5). The situation itself is humorous, but it only goes to show the power memes hold. For the ambassador’s case, memes proved to be a useful tool for publicly defending his reputation. See this website for examples of the memes.
Continuing with the relationship between memes and politics, it is quite obvious that younger generations are taking part in political memes. Emma Axelrod agrees with this statement in her article “The Role of Memes in Politics.” Axelrod then adds that people are starting to view politics more like sports teams. These teams are then influenced by memes. The example that she brings up, among others, is the meme about Ted Cruz being the zodiac killer (Axelrod). Despite the fact that Cruz was not actually a zodiac killer of any kind, a negative demagogue formed around him. During this time, circa the 2016 election, even I noticed the zodiac killer memes and could not help but connect Cruz to those memes. Denying the power memes have over politics is futile. However, this is all the more reason to study political memes and their effects on people. Fortunately, the insight needed for looking deeper into political memes is provided by Heidi E. Huntington’s “Affect and effect of Internet memes: assessing perceptions and influence of online user-generated political discourse as media.” The article by Huntington follows a study on how political and non-political memes influence an individual. The political memes were generally found to be easily identifiable by the subject. The subjects viewed these memes as a vehicle for political stances rather than simple jokes. In response to this, if the meme did not follow their political ideology, it was contested by the viewer. In other words, the memes that were identified as political fail to bring in understanding, rather they brought adversity from the viewers (Huntington 186-187). This statement implies heavily that political memes share a message, a message that will be rejected by viewers of a different opinion. The study also talks about what happens to non-political memes as well. As it turns out, memes that appear to be non-political have an easier time persuading the viewer. This is in spite of the fact that people only saw these memes as jokes and not actual arguments (Huntington iii). Huntington’s research hints that people are able to interpret and respond to a meme. The implications here are that while political memes do not always achieve their goal, they are still able to elicit a response. Interestingly enough, non-political memes seem to hold a coinciding power, only in the case of non-political memes, people do not reject the message being sent.
Memes’ Meaning to Human Communication
It is clear now that memes have many different purposes. Memes play a role in politics, business, and general entertainment. A linking trait between all three topics is that memes seem to serve as a sort of medium for communication. One might even be so bold as to conclude that memes and communication have direct relevance to one another. Think about it, memes are capable of sending a variety of messages for their viewers, whether it’s to advocate a politician, products, or simply to share a laugh. For these reasons, I believe it is safe to say that memes play a role in human communication.
To understand what memes have to do with communication, it is crucial to understand the original definition of a meme. As it turns out, the term “meme” did not start as a reference to internet jokes and humorous comments. In James Gleick’s “What Defines a Meme?” the term meme was crafted by a man named Richard Dawkins in the year 1986. Dawkin’s definition of a meme was an idea, behavior, or culture and its ability to spread through people. These memes are comparable to genetics and can even evolve. Dawkin’s memes also have the ability to latch on to physical items as well. An example that Gleick uses is the hula hoop. In the late fifties, the hula hoop became popular. While the hula hoop was not a meme itself, it was an object that was used by the meme. Therefore, a meme’s survival is dependent on the success of the object the meme is associated with (Gleick). With that in mind, Dawkin’s memes are not really all that different from the modern understanding of a meme. It is logical to conclude that modern memes fall under Dawkin’s definition of meme. This makes sense since internet memes are humorous ideas and messages that get spread throughout the wide web. Internet memes also evolve and change with current events. As funny as it sounds, memes can be considered to be one of Dawkin’s memes. A final note on Dawkin’s meme can be found in “Memes as Speech Acts,” by L. Grundlingh. The term for Dawkin’s meme comes from the Greek word “mīmēma” which translated to “something imitated” (Grundlingh 147). This can, again, be tied into memes as memes are shared, copied, and remade all the time. Grundlingh continues by then adding the idea of semiotics. Semiotics is defined in Grundlingh’s article by T. A. Sebeok “Signs: An Introduction to Semiotics” as being an apparent link between nonverbal and verbal communication (qtd. 148). Memes share verbal and nonverbal pieces of the semiotic definition. This is noteworthy because semiotics describes or categorizes how memes communicate. Grundlingh even presses so far as to say that memes are a speech act, the communication, and understanding between two people (148). This makes sense knowing full-well that memes can advocate politicians, advertise products, and share humor with other people. Another approach to tying memes in with communication is the notion that memes are basically a language of their own. Patrick Davison wrote about this idea in his article “The Language of Internet Memes.” Memes, like any language, follow a set of formulas and branch out similar to how a language has accents and slang. The overarching meme is what is called an image macro. Variants and remakes of this meme are then called submemes (Davison 127). Anyone that has indulged themself with memes before can understand the comparisons that are being made. Davison’s comparison was ideal for introducing the concept that memes supplement as a language of their own. In the article by Opspe titled “Memetic Communication” the author explains how memes can be used in place of verbal communication. The writer elaborates with the idea that people send each other gifs, images, or videos. The content is usually considered a meme by nature and can be understood by the recipient of the meme. The author refers to these texts as reaction images (Opspe). This makes sense, I personally, have also used memes to express my thoughts and feelings. An example of this is the “sector is clear” meme as shown in figure 4.
This meme came from a Star War video game and implied that everything is calm, for the moment. This meme also implies another message. It also implies that this calm might be very temporary as the next text plane usually continues with the clone trooper say “not clear, not clear” with sparks flying in the background. I have no doubt that others have also shared a meme in place of text or verbal words. Going back to the article, the author also makes reference to words, mainly slang, that have their origin thanks to memes. The author references 4chan and other meme-based social media as a source of many slang terms like “lol” “derp” and “yolo.” These slang terms were created due to their close relationship with memes (Opspe). It is quite clear that memes are a part of communication and in some cases even play as a medium of communication.
Personal Experience With Memes
Memes are an item produced by the public and for the public, mostly that is. I have seen many opinions shared through my experience through memes. I have even gone to lengths to make my own opinion through the use of memes once or twice. I, like many others my age, became something of a meme connoisseur. The effect I believe memes had on me was that I slowly became more apathetic to politics. The issue that I noticed with political memes was that they created something of a demagogue. They seem to create a mentality of “my political candidate is pure, and the other candidate is literally Hitler or a witch.” I came to this conclusion on my own years before reading about how Axelrod’s finding in “The Role of Memes in Politics” which basically described a similar scenario. For that reason, I nowadays only try to use memes for general entertainment. Another purpose that I personally use memes for is to keep up to date with current events. While trying to abstain from the political realm, I find that memes can be quite enlightening for current events in science, economics, and society as a whole. My favorite example of this is the black hole memes that were produced in light of the first live image of a black hole. Another, more recent, example is the Suez Canal memes. Regardless of where memes venture to talk about, I will continue to enjoy them.
Concluding Statements
It is a matter of fact that memes are a part of communication at large. With that said noting how humanity uses memes should be important. The power in memes can be seen in a multitude of areas including and not limited to politics, advertising, and general entertainment. Memes can be used against people and can harm just as easily as they can be used to share a laugh. For that reason, when one shares a meme, they should be conscious of what they are actually communicating by posting the meme. Some will be eager to judge other’s memes, and some turn a blind eye to ill-willed memes. I say, for the best or worse, let memes be memes. In the end, humans are social animals and memes are just another form of human communication.
Works Cited
Axelrod, Emma. “The Role of Memes in Politics.” Brown Political Review, 20 Mar. 2016, brownpoliticalreview.org/2016/03/role-memes-politics/.
Caldwell, Alexander W. “Meme Survey for College Writing.” Google Forms, Mar. 2021, https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1xU3q6dkuZWweZAr7LT-pUA-v8-lqpvQMJv7vzt-to8E/edit#question=2144072070&field=1932620711.
Chuah, Kee-Man, Yumni Musfirah Kahar, and Looi-Chin Ch’ng. “We “Meme” Business: Exploring Malaysian Youths’interpretation Of Internet Memes In Social Media Marketing.” International Journal of Business and Society , Vol. 21 No. 2, 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kee-Man-Chuah/publication/343098924_We_meme_business_Exploring_Malaysian_Youths%27_Interpretation_of_Internet_Memes_in_Social_Media_Marketing/links/5f16abec92851cd5fa39b280/We-meme-business-Exploring-Malaysian-Youths-Interpretation-of-Internet-Memes-in-Social-Media-Marketing.pdf.
Davison, Patrick. “The Language of Internet Memes.” The Social Media Reader , edited by Michael Mandiberg, New York University Press, 2012. ProQuest Ebook Central , https://ebookcentral-proquest-com.proxy.ulib.csuohio.edu/lib/clevelandstate-ebooks/detail.action?docID=865738.
EA Star Wars. “Star Wars Battlefront II: Official Gameplay Trailer” YouTube, 10 Jun. 2017. https://youtu.be/_q51LZ2HpbE
Emerging Technology from the arXiv. “This Is Where Internet Memes Come From.” MIT Technology Review, MIT Technology Review, 11 June 2018, www.technologyreview.com/2018/06/11/142394/this-is-where-internet-memes-come-from/.
Gleick, James. “What Defines a Meme?.” Smithsonian.com, Smithsonian Institution, May 2011, www.smithsonianmag.com/arts-culture/what-defines-a-meme-1904778/.
Grundlingh, L. “Memes as Speech Acts.” Social Semiotics , vol. 28, no. 2, Apr. 2018, pp. 147–168. EBSCOhost , doi:10.1080/10350330.2017.1303020.
Huntington, Heidi E. “Affect and effect of Internet memes: assessing perceptions and influence of online user-generated political discourse as media,” Colorado State University, 2017.https://mountainscholar.org/bitstream/handle/10217/183936/Huntington_colostate_0053A_14303.pdf.
Opspe. “Memetic Communication.” Know Your Meme, 5 March 2013, knowyourmeme.com/memes/memetic-communication.
Sharma, Harshit. “Memes in Digital Culture and Their Role in Marketing and Communication: A Study in India.” Interactions: Studies in Communication & Culture , vol. 9, no. 3, Nov. 2018, pp. 303–318. EBSCOhost , doi:10.1386/iscc.9.3.303_1.
Srivastawa, Vandana “Twitter User Pays Fitting Tribute Through Picture to Kapil Mohan, the Creator of Old Monk, Takes Jibe at Thums Up.” 10 Jan. 2018. https://www.india.com/viral/twitter-user-pays-fitting-tribute-through-picture-to-kapil-mohan-the-creator-of-old-monk-takes-jibe-at-thums-up-2837691/.
Zakem, Vera, Megan K. McBride, and Kate Hammerberg. “Exploring the utility of memes for US government influence campaigns.” Center for Naval Analyses Arlington United States, 2018. https://www.cna.org/cna_files/pdf/DRM-2018-U-017433-Final.pdf.
ZestfulHydra. “me irl.” Reddit, Apr. 2019. https://www.reddit.com/r/me_irl/comments/bgjrj8/me_irl/.
Understanding Literacy in Our Lives by Alexander Caldwell is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Why Submit?
- About Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication
- About International Communication Association
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Memes in a digital world: reconciling with a conceptual troublemaker, memes: from academic to public discourse (and back), memes' promises and pitfalls for analyzing digital culture, unpacking internet memes, leave britney alone, acknowledgments, about the authors.
- < Previous
Memes in a Digital World: Reconciling with a Conceptual Troublemaker
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Limor Shifman, Memes in a Digital World: Reconciling with a Conceptual Troublemaker, Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , Volume 18, Issue 3, 1 April 2013, Pages 362–377, https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12013
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This paper re-examines the concept of “meme” in the context of digital culture. Defined as cultural units that spread from person to person, memes were debated long before the digital era. Yet the Internet turned the spread of memes into a highly visible practice, and the term has become an integral part of the netizen vernacular. After evaluating the promises and pitfalls of memes for understanding digital culture, I address the problem of defining memes by charting a communication-oriented typology of 3 memetic dimensions: content, form, and stance. To illustrate the utility of the typology, I apply it to analyze the video meme “Leave Britney Alone.” Finally, I chart possible paths for further meme-oriented analysis of digital content.
Memes are a pain. Or so at least a glance into the world of academic literature would suggest. Ever since Richard Dawkins coined the term in 1976 to describe gene-like infectious units of culture that spread from person to person, memes have been the subject of constant academic debate, derision, and even outright dismissal. Recently, however, the concept once kicked out the door by many academics is coming back through the Windows (and other operating systems) of Internet users. In the vernacular discourse of netizens, the phrase “Internet meme” is commonly applied to describe the propagation of content items such as jokes, rumors, videos, or websites from one person to others via the Internet. According to this popular notion, an Internet meme may spread in its original form, but it often also spawns user-created derivatives.
The uptick in vibrant popular discourse about memes in an era increasingly defined by Internet communication is not coincidental. While memes were conceptualized long before the digital era, the unique features of the Internet turned their diffusion into a ubiquitous and highly visible routine. Memes, since at least as early as the 1990s, have been said to “replicate at rates that make even fruit flies and yeast cells look glacial in comparison” ( Dennett, 1993 , p. 205). In what follows, I explore the utility of memes for understanding digital culture, positing throughout the following two premises: First, that the intense emotions and dramatic statements characterizing both sides of the memes debate need to be toned down. While enthusiastic advocators argue that the meme explains everything and their opponents assert it explains and changes absolutely nothing, it might be worth asking whether the meme concept may be useful for something . In this endeavor I follow the footsteps of researchers such as Johnson ( 2007 ), Knobel and Lankshear ( 2007 ), Jones and Schieffelin ( 2009 ), Benett (2003), and Burgess ( 2008 ), who used the meme as a prism for understanding certain aspects of contemporary culture without embracing the whole set of implications and meanings ascribed to it over the years.
The second premise is that we should look at memes from a communication-oriented perspective. Coined by a biologist, the term meme has been widely adapted (and disputed) in many disciplines, to include psychology, philosophy, anthropology, folklore, and linguistics. For the most part, however, it was utterly ignored in the field of communication. Until the twenty-first century, mass communication researchers felt comfortable overlooking memes. As units that propagate gradually through interpersonal contact, they were considered unsuitable for exploring content that is transmitted simultaneously from a single institutional source to the masses. But this is no longer the case in an era of blurring boundaries between interpersonal and mass, professional and amateur, bottom-up and top-down communications. In a time marked by a convergence of media platforms ( Jenkins, 2006 ), when content flows swiftly from one medium to another, memes have become more relevant than ever to communication scholarship.
The questions I address in what follows are rather straightforward: How, if at all, is the meme concept useful for understanding digital culture? What important obstacles stand in the way of its being accepted in research, and how can these barriers be overcome? The answers to these questions unfold serially in five parts. In the first section, I interpret the meme concept and its controversial status in academia, as well as its revival in the vernacular discourse of Internet users. I then look at the promises and pitfalls of memes for understanding Internet culture, suggesting that some previous premises about the concept should be put aside. In the third part of this essay I delve into the problem of defining meme units, charting a communication-oriented typology of memetic dimensions. To illustrate the utility of this typology, I provide a detailed analysis of Chris Crocker's video meme “Leave Britney Alone” and its various imitations, as well as a short corroborative analysis of the more recent “Pepper-Spraying Cop” meme. Finally, I offer some thoughts about the potential meaning and relevance of this paper to the field of diffusion studies, charting possible paths for further meme-oriented analysis of new media.
The term meme was introduced by the biologist Richard Dawkins in his book The Selfish Gene (1976). As part of his larger effort to apply evolutionary theory to cultural change, Dawkins defined memes as small cultural units of transmission, analogous to genes, which are spread from person to person by copying or imitation. Examples of memes in his pioneering text include specific signifiers such as melodies, catchphrases, and clothing fashions, as well as abstract beliefs (for instance, the concept of God). Like genes, memes are defined as replicators that undergo variation, competition, selection, and retention. At any given moment, many memes are competing for the attention of hosts; however, only memes suited to their sociocultural environment spread successfully, while others become extinct ( Chielens & Heylighen, 2005 ).
The word meme derives from the Greek mimema , signifying “something which is imitated,” which Dawkins shortened to rhyme with gene. Interestingly, a similar term to signify cultural evolution had appeared a century earlier. In 1870 the Austrian sociologist Ewald Hering coined the phrase Die Mneme (from the Greek mneme , meaning memory), which the German biologist Richard Semon used as a title for his 1904 book Die Mnemischen Empfindungen in ihren Beziehungen zu den Originalempfindungen ( Hull, 2000 ). Unaware of this existing terminology ( Dawkins, 2004 ), Dawkins' expression proved an accidental but successful imitation in itself: His concept survived and proliferated in the scientific world.
After more than a decade of sporadic and stuttering growth, memetics —understood as “the theoretical and empirical science that studies the replication, spread and evolution of memes” ( Heylighen & Chielens, 2009 , p. 1)—began to take shape as an active research program, drawing scientists from many fields in the 1990's ( Hull, 2000 ). Important landmarks on this path included contributions made by the prominent philosophers Douglas Hofstadter (1985) and Daniel C. Dennett ( 1990 , 1993 , 1995 ), the emergence of the Journal of Memetics between 1997 and 2005, and the publication of several meme-oriented books ( Boyd & Richardson, 2005 ; Brodie, 1996 ; Distin, 2005 ; Lynch, 1996 ). Of this stream, Susan Blackmore's The Meme Machine (1999) may well be the most influential, yet also the most disputed.
Since its early days, memetics has drawn constant fire. Among the criticisms raised against it, four positions are particularly relevant to our context. The first is the concept's ambiguity: There is disagreement about what precisely a meme is, which leads to difficulties in quantifying and measuring it. Second, the analogy between nature and culture feeding the field has been criticized as reductive, materialistic, and ineffective in describing complex human behaviors. Third, the conscious selection and mutation of memes has generated heated debates over human agency and memetic control. Finally, some critics claim that memetics has no added value: It does not offer tools or insights beyond those employed in traditional disciplines such as cultural anthropology or linguistics ( Benitez-Bribiesca, 2001 ; Chesterman, 2005 ; Rose, 1998 ). We shall return to these four quandaries—and to possible ways of addressing them.
While widely disputed in academia, the meme concept has enthusiastically been picked up by Internet users. A search of Google Trends suggests a spurt of interest on the subject since data collection began in 2008, and a quick Google query of the term “Internet meme” yielded around 1,550,000 hits (January 4, 2012), many of them leading to large interactive depositories of memetic content. For example, on the popular website Know your meme , “resident Internet scientists” appropriately dressed in white coats provide various explanations for the success of certain videos in generating wide attention ( http://knowyourmeme.com ). According to Knobel and Lankshear ( 2007 ), the word meme is employed by Internet users mainly to describe the rapid uptake and spread of a “particular idea presented as a written text, image, language 'move,' or some other unit of cultural 'stuff''” (p. 202). This vernacular use, the authors submit, is utterly different from the one prevalent in the academic study of memetics: If the former tends to describe recent, often short-lasting fads, longevity is the key of “serious” memetics, since successful memes are defined as the ones that survive in the longue durée . Another difference relates to the object of analysis: Whereas in memetics the unit of analysis itself is abstract and controversial, Internet users tend to ascribe the meme tag to concrete phenomena such as particular YouTube videos that lure many derivatives. “Leave Britney Alone,” the “Star War Kid,” Hitler's “Downfall” parodies, and the “Numa Numa guy” are particularly famous drops in a memetic ocean.
The yawning gap between popular and academic uses of memes may serve as a fertile site for an improved meme theory. Here I follow Johnson's ( 2007 ) assertion that memes may be of particular relevance for cultural analysis that is interested in deciphering the meaning of “seemingly superficial and trivial elements of popular culture” (p. 27). Thus, a promising starting point for this exploration would be in identifying and mapping memetic dimensions of texts previously crowned as successful Internet memes, with an eye toward examining whether Internet memes enrich our understanding of this controversial concept.
But before such an expedition begins, we need to get rid of some excess baggage. During its 25 years of existence, the term meme accumulated many meanings. Some of them seem very useful for understanding contemporary digital culture; others somewhat less. In the next section I will catalog and differentiate between them.
Three main attributes ascribed to memes are of particular relevance to the analysis of contemporary digital culture. First, memes may best be understood as cultural information that passes along from person to person, yet gradually scales into a shared social phenomenon . 1 Although they spread on a micro basis, memes' impact is on the macro: They shape the mindsets, forms of behavior, and actions of social groups ( Knobel & Lankshear, 2007 ). This attribute is highly compatible to the way culture is formed in the so-called era of Web 2.0, which is marked by application platforms for facilitating user-generated content. YouTube, Twitter, Facebook, Wikipedia, and other similar applications are based on propagation of content, to paraphrase Lincoln, of users by users for users. Such sites represent “express paths” for meme diffusion: content spread by individuals can scale up to mass levels within hours. More broadly, this decentralized, nonhierarchical, and user-based model also drives new mindsets and social norms occupying media use ( Baym & Burnett, 2009 ; boyd, 2008 ; Jenkins, 2006 ; O'Reilly, 2007 ).
A second attribute of memes is that they reproduce by various means of imitation . In oral communication, people become aware of memes through their senses, process them in their minds, and then “repackage” them in order to pass them along to others ( Dawkins, 1982 ). In the digital age, however, people do not have to repackage memes: They can spread content as is by forwarding, linking, or copying. Yet a quick look at any Web 2.0 application would reveal that people do choose to create their own versions of Internet memes, in startling volumes. Two main repackaging strategies of memes are prevalent on the web: mimicry and remix. There is nothing new about mimicry —people have always been engaged in impersonating others. However in the web 2.0 era everyday mimetic praxis have turned into a highly visible phenomenon in the public sphere. Websites such as YouTube are flooded with imitations—almost any user-generated video that passes a certain threshold of views inspires a stream of emulations ( Shifman, 2012 ). The second strategy of memetic repackaging, remixing , is also extremely prevalent, as digital technology and a plethora of user-friendly applications enable people to download, re-edit, and distribute content very easily ( Lessig, 2008 ; Manovich, 2005 ). User-driven imitation and remix have become highly valued pillars of contemporary participatory culture, to the extent that one may argue that we live in an era driven by a hyper-memetic logic. 2 The term “meme” is particularly suitable to describe this glut of re-works, as the concept —deliberately connoting “mimesis”—is flexible enough to capture a wide range of communicative intentions and actions, spanning all the way from naïve copying to scornful imitation.
A third attribute of memes that makes them appealing for scholars interested in digital culture is their diffusion through competition and selection . Memes vary greatly in their degree of fitness, that is, their level of adaptiveness to the sociocultural environment in which they propagate ( Aunger, 2000 ). While processes of cultural selection are ancient, digital media have afforded researchers with the ability to trace the spread and evolution of memes ( Shifman & Thelwall, 2009 ). But it is not only experts who can now analyze digital traces on the Web—in many Web 2.0-friendly websites, metadata about viewing preferences, choices, and responses is constantly aggregated and displayed for all users to view ( Benkler, 2006 ; Burgess & Green, 2009 ). Thus, metainformation about competition and selection processes is increasingly becoming a visible part of the process itself.
The analysis so far presents memes and digital culture as a match made in heaven: The Internet is not only saturated with memetic activity, but also allows for its investigation in unprecedented ways. However, some controversies surrounding memes—in particular those I shall refer to as “biological analogies” and “who's the boss”—have hindered the wide uptake of the concept in studying digital culture.
Two biological analogies are especially prevalent in the discourse about memes: viruses and genes. The meme-as-virus analogy sees the similarity between memes and disease agents. Taking epidemiology as its model, it considers memes the cultural equivalents of flu bacilli, transmitted through the communicational equivalents of sneezes ( Alvarez, 2004 ). In Internet culture, this metaphor is prevalent in the highly visible discourse on “viral” content. Yet Jenkins et al. ( 2009 ) rightfully assert that this metaphor has been used in a problematic way, conceptualizing people as helpless and passive creatures, susceptible to the domination of meaningless media “snacks” that infect their minds.
The second prevalent biological metaphor for memes —deriving directly from Dawkins' work—takes evolutionary genetics as its model. However, some works have “pushed the analogy with the gene to its logical extremes” by seeking cultural equivalents for all principal evolutionary genetic concepts, including genotype, phenotype, transcription, and code ( Alvarez, 2004 , p. 25). This effort was criticized not only because memes behave very differently than genes ( Atran, 2001 ), but also since the reduction of culture to biology narrows and simplifies complex human behaviors. The prevalent notion is thus that the meme-gene analogy should be taken with many grains of salt ( Blackmore, 1999 ). Put differently, it is not necessary to think of biology when analyzing memes. The ideas of replication, adaptation, and “fitness” to a certain environment can be analyzed from a purely social/cultural perspective.
Another fundamental controversy in memetics, tagged here as “who's the boss,” relates to the issue of human agency in the process of meme diffusion. On one end of the spectrum, we find scholars such as Blackmore ( 1999 ), who claims that people are “meme machines” operated by the numerous memes they host and constantly spread. Nonetheless, I contend here that the undermining of human agency is not inherent to the meme concept itself—only to one strain of its interpretation. A number of works within the field of memetics are clearly opposed to it. Most important to this essay is Rosaria Conte's ( 2000 ) suggestion to treat people not as vectors of cultural transmission, but as actors behind this process. The dissemination of memes, she submits, is based on intentional agents with decision-making powers: Social norms, perceptions, and preferences are crucial in memetic selection processes. This conceptualization of people as active agents is highly appropriate for understanding how memes travel on the digital highway, particularly when examining cases in which the initial meaning of a meme is dramatically altered in the course of its diffusion.
If the biology-driven and power-driven controversies hinder the wide scholarly usage of memes, a third site of struggle—around the meme concept itself—may provide a path forward.
A core problem of memetics, maybe the core quandary, is the exact meaning of the term. The jury is still out on what is meant by “meme.” As mentioned above, Dawkins' ( 1976 ) initial definition of meme was quite ambiguous: He referred to it as “a unit of cultural transmission, or a unit of imitation” (p. 206). His set of meme examples spanned ideas (God), texts (nursery rhymes and jokes), and practices (Christian rituals). Ever since, the study of memes has been subject to disputes centering on the mind/body or genotype/phenotype dichotomy, yielding three positions regarding the nature of memes: mentalist-driven, behavior-driven, and inclusive.
Mentalist-driven memetics, represented by leading scholars in the field such as Dawkins himself (in his 1982 clarification of the theory), Dennett ( 1995 ), and Lynch ( 1996 ), is based on the differentiation between memes and meme vehicles. According to this school of thought, memes are ideas or pieces of information that reside in our brain. They are not simple ideas such as red, round, or cold, but complex ones that “form themselves into distinct memorable units” such as the ideas of alphabet, chess, or Impressionism ( Dennett, 1995 , p. 344). In order to be passed along from one person to another, memes are “loaded” on various vehicles: images, texts, artifacts or rituals. According to this view, those observable meme vehicles are equivalent to phenotypes—the visible manifestation of genes. In other words, memes are idea complexes and meme vehicles, their tangible expressions.
In contrast, the stream of thought surrounding behavior-driven memetics sees memes as behaviors and artifacts rather than ideas ( Gatherer, 1998 ). In the behaviorist vocabulary, the meme vehicle and meme are inseparable: The meme has no existence outside the events, practices, and texts in which it appears; that is, it is always experienced as encoded information. Moreover, this approach claims that if memes were indeed only abstract units of information, it would be impossible to identify them separately from their manifestation in the outside world. Defining memes as concrete units enables their evolution and diffusion to be studied empirically. This brand of memetics is closely related to the scholarly approach known as “diffusion studies” (Aungar, 2000). Many studies in this rich tradition focus on the diffusion of “innovations,” occasionally adapting the term meme and the general memetic framework (For recent overviews of the field, see Rogers, 2003 and Katz, 1999 ). However, as detailed in the concluding section, diffusion studies tend to cling to narrow definitions of memes, thus overlooking the complexity and richness that may be ascribed to the concept.
Whereas members of the mentalist- and behavior-driven schools see memes as either ideas or practices, what I tag as the inclusive memetic approach , represented by Susan Blackmore, uses the term “indiscriminately to refer to memetic information in any of its many forms; including ideas, the brain structures that initiate those ideas, the behaviors these brain structures produce, and their versions in books, recipes, maps and written music” (p. 66); that is, any type of information that can be copied by imitation should be called a meme.
But this inclusive approach may lack analytical power, as it assembles very different elements under its big conceptual tent. I therefore suggest a fourth approach: moving forward by looking at diffused units as incorporating several memetic dimensions . Since this paper focuses on digital culture, I will demonstrate this approach through the analysis of memes that spread via the Internet. Internet memes are defined here as units of popular culture that are circulated, imitated, and transformed by individual Internet users, creating a shared cultural experience in the process. I suggest looking at Internet memes not as single ideas or formulas that propagated well, but as groups of content items that were created with awareness of each other and share common characteristics. Going back to Dawkins' original idea—that memes are units of imitation —I find it useful to isolate three dimensions of cultural items that people can potentially imitate: content, form, and stance .
The first dimension relates mainly to the content of a specific text, referencing to both the ideas and the ideologies conveyed by it. The second dimension relates to form : This is the physical incarnation of the message, perceived through our senses. It includes both visual/audible dimensions specific to certain texts, as well as more complex genre-related patterns organizing them (such as lip-synch or animation). While ideas and their expression have been widely discussed in relation to the meme concept, the third—communication-related dimension—is presented here for the first time. This dimension—which relates to the information memes convey about their own communication—is labeled here as stance . Expanding Englebertson's (2007) definitions, I use “stance” to depict the ways in which addressers position themselves in relation to the text, its linguistic codes, the addressees, and other potential speakers. Like form and content, stance is potentially memetic; when re-creating a text, users can decide to imitate a certain position that they find appealing or use an utterly different discursive orientation.
Since I use stance in this context as a very broad category, I wish to clarify it by breaking it into three subdimensions, drawing on concepts from discourse and media studies: (1) participation structures -- who is entitled to participate and how, as conceptualized by Phillips ( 1972 ), (2) keying -- the tone and style of communication, as defined by Goffman ( 1974 ) and further developed by Blum-Kulka et al. ( 2004 ), and (3) communicative functions , as conceptualized by Roman Jakobson (1960). Jakobson identified six fundamental functions of human communication, concisely presented as follows: (a) Referential communication, which is oriented toward the context, or the “outside world”; (b) emotive, oriented toward the addresser and his/her emotions; (c) conative, oriented toward the addressee and available paths of actions (e.g. imperatives); (d) phatic, which serves to establish, prolong, or discontinue communication; (e) metalingual, which is used to establish mutual agreement on the code (for example, a definition); and (f) poetic, focusing on the aesthetic or artistic beauty of the construction of the message itself.
This analytic framework, consistent with the three memtic dimensions (content, form, and stance), as well as the three subdimensions of the latter dimension (participation structures, keying, and communicative functions) will be developed and applied in the following section to the analysis of a successful YouTube meme, featuring one somewhat upset fan.
On September 10, 2007, a young gay blogger and actor named Chris Crocker uploaded a YouTube video in which he reacted to the harsh criticism following pop star Britney Spears' lackluster performance on the MTV Music video awards. Crying and shouting throughout most of the clip, Crocker implored his viewers to “Leave Britney Alone”:
And how fucking dare anyone out there make fun of Britney, after all she's been through! She lost her aunt, she went through a divorce, she had two fucking kids, Her husband turned out to be a user, a cheater, and now she's going through a custody battle. All you people care about is readers and making money off of her. SHE'S A HUMAN! What you don't realize is that Britney is making you all this money and all you do is write a bunch of crap about her. She hasn't performed on stage in years. Her song is called “give me more” for a reason because all you people want is MORE, MORE, MORE, MORE, MORE!. LEAVE HER ALONE! You're lucky she even performed for you BASTARDS! LEAVE BRITNEY ALONE! […] Leave Britney Spears alone right NOW! I mean it. Anyone that has a problem with her you deal with me! because she's not well right now. Leave her alone…
The video gained over 2 million views within 24 hours, and many more in the following days and months (current view count is over 42 million). The Crocker sensation was reported on various mainstream media stages and generated worldwide attention ( Salvato, 2009 ). The video soon spawned a stream of derivatives: imitation-based memes (in which known actors and ordinary users impersonated Crocker), as well as remix-based memes (in which music, graphic elements, or dubbing were re-edited with the original).
In exploring “Leave Britney Alone” as a meme, we need to examine the distribution of the original video, but perhaps more importantly, we should investigate the structure and meaning of the new variations created of this video. People may share a certain video with others for many different reasons (spanning from identification to scornful ridicule), but when they create their own versions of it they inevitably reveal their interpretations of the text. The conceptualization of Internet memes as trinities of content, form and stance suggests that we need to follow separately the uptake—or rejection—of each memetic dimension by the text's imitators. In what follows, I will implement this strategy to evaluate the ways in which Crocker's video-meme was transformed in the course of its digital lifespan. The main dimensions embedded in the original video and their alternations by users are summarized in Table 1 .
Memetic Dimensions and Their Manifestation
Crocker's 2007 video was a complex potage of ideas, textual practices, and communicative strategies. While in practice these dimensions are importantly intertwined, feeding off each other in multifaceted ways, I attempt to disentangle them here for analytical purposes. Our starting point is the video's content, namely the ideas and ideologies that it conveys. The text includes, among other things, facts about Britney Spears' life (e.g., her two children) and castigation of people criticizing fallen celebrities. More broadly, in this video and others, Crocker wishes to convey the ideological message that being gay and effeminate is a legitimate practice. In terms of form, or textual construction, the video's layout includes one talking head, filmed in close up and in one-shot and situated in front a white cloth. It further includes repetitions of certain phrases, raised voice pitch, tears, and distraught hair-hand gestures.
The most complex dimension for analysis in Crocker's video relates to the dimension of stance. In relation to the subdimension of participation structure , the video, by virtue of its existence, reminds the viewer that a gay, overtly effeminate individual is openly expressing his opinion in the public sphere. Keying , as noted above, is the tone, or modality, of the internal framing of discursive events as formed by their participants. People can key their communication as funny, ironic, mocking, pretend, or serious ( Blum-Kulka et al., 2004 ). In the case of “Leave Britney Alone,” Crocker keys his utterances as extremely serious and as ultraemotional—sometimes so serious that, at a remove, it can even appear comical and ambiguously parodic. While some commentators questioned the sincerity of the video, Crocker insisted it was utterly genuine ( Christian, 2010 ). In an illuminating analysis of Crocker's video as a case for examining the borders between amateurism and professionalism in contemporary culture, Salvato ( 2009 ) describes it not only as being serious and emotional, but also marked by lack of self-control. Crocker embodies the allegedly amateur avocation to “lose it,” his body “deemed so wholly out of control in its production of fluids, movements and sounds” (p. 11). In relation to the communication functions defined by Jakobson (1960), of the six described above, the ones that seem most prominent in the video are the referential (Crocker provides us with facts about Britney's life), the conative (viewers are indulged to change their behavior), and above all the emotive, as this video is all about the addresser and his emotional state. In addition, a contextual examination of this video may lead to the identification of a certain phatic function to it. “Leave Britney Alone” is one of a stream of videos uploaded by Crocker on his YouTube channel. Through these frequent feeds, Crocker aspires to maintain the communicative path between himself, his budding acting career, and his faithful YouTube (and MySpace) viewers.
So far, I have charted the memetic dimensions embedded in Crocker's initial video. The question to be addressed now is: Which of these dimensions was taken up and imitated with accuracy by Internet users in their derivatives, and which ones were altered? In other words, which of these dimensions succeeded in the memetic competitive selection process? Since it is virtually impossible to track and examine all of this meme's offsprings, I compiled a sample of 20 highly viewed derivative videos. To create the sample, two queries where used in YouTube's internal search engine: the string “Leave Britney Alone,” and the words “leave” “alone” “Crocker.” I then sorted the results according to their view count, and selected the 20 most viewed videos (above 100,000 views) in which people were seen imitating Crocker. Analyzing them qualitatively, I aimed at identifying patterns of memetic uptake.
Among the three memetic dimensions, the one that viewers imitated with a high level of accuracy is the video's form. The mise-en-scène of one person in front of a white cloth filmed in one-shot was evident in virtually all texts. Men were featured in 16 videos out of 20, often bearing feminine markers similar to Crocker's (such as a wig or eyeliner). In addition, the composition of Crocker's sentences, as well as key phrases such as “leave X alone” and “s/he is a human,” were repeated throughout the sample.
In contrast to the relative accuracy in the imitation of the videos' form, radical changes take place on both the content and stance dimensions. These alternations are related, to a large extent, to the construction of all the videos in our sample as parodies . A major feature of parody is its construction with a critical difference from a source text that it mimics ( Hutcheon, 1985 ). While all parody includes some kind of imitation, it is important to note that not all imitations are parodies. Many YouTube videos are emulated without mocking their protagonists. For instance, the “Evolution of Dance” hit—itself capturing an openly self-parodying event—has spawned numerous imitations in which people copy the performer's dance movements in various contexts, without lampooning him. This is distinctly not the case in “Leave Britney Alone,” where the parodic intentions of the original are at best ambiguous and highly exploitable. As I demonstrate below, parody targets both the ideological and communicative aspects of the original meme.
To begin with, hardly any of the ideas conveyed by the original video were further circulated by its imitators: In only 2 texts out of 20 did speakers repeat Crocker's words; in all other cases, imitation involved a significant alternation of the original utterances. Videos divide evenly between two types. The first (commonly labeled “Leave Chris Crocker Alone”) includes clips mocking Britney Spears and Chris Crocker. In these clips, Crocker's message about the legitimacy of being an overtly effeminate homosexual is lampooned in various ways. Thus, for instance, the comedian Seth Green, in a heavily viewed parody, shouts and “implores” the audience to leave Chris Crocker alone, pausing occasionally to fix his black eyeliner: “You can't talk about someone when you are not willing to do what they do! You have not spent a mile walking in his sneakers, or, platform pumps…I don't know what he wears… BUT I BET IT'S STYLISH!” The second type of parody videos includes clips that mock a battery of other pop stars and celebrities. In such videos—including, for instance, “Leave Justin Bieber Alone,” “Leave Miley (Cyrus) Alone,” and “Leave Rebecca Black Alone”—the presenters mock Crocker's outcry to pity celebrities by performing the opposite: they publicly bash these celebs. Thus, for example, in one video the protagonist implores his viewers to “Leave Michael Jackson Alone”: “He had sex with a few people, who turned out to be under 13… He's only a human! I think […] And so what if he dangled his child off a balcony. You bastards are even lucky he bothered to show him to you…”
A radical alternation of meaning also takes place in the communication-oriented dimension of stance. In relation to participation roles, the notion that users who upload videos may be overtly effeminate gays is disdained through scornful imitations of Crocker's effeminate traits. Another major shift is related to keying (the tone and style of communication): User-generated derivatives abandon Crocker's overtly emotional performance in favor of a cynical and ironic one. No one says what s/he means in those videos. When a speaker “pleads” with his audiences to “leave Michael Jackson alone” because he “loves his monkey,” it is quite clear that the words spoken are not those meant. The same is true for the clip that implores “Leave Miley [Cyrus] Alone,” praising her with the following words: “She made you guys a movie in 3-D. She didn't have to do that. We would have been OK with 2-D, but she went the extra mile.” In all these cases the humorous effect derives from the gap between the uttered words and their diminishing meaning, or intention. Interestingly, the vast majority of the sampled videos employ common ironic keying: These videos are more similar to each other than to Crocker's original.
Regarding the communicative functions, I found that the most prominent ones in the original video—emotive and conative—are marginal in its derivatives. While imitators do convey a certain feeling (scornful amusement), and seem to want to generate a similar amused reaction, both the emotive and the conative components are not as explicit and strong as in the original video. Rather, imitations stress a different communicative role: They draw attention to the communication process itself, thus performing more closely to the metalinguistic function. This analysis follows Hariman's ( 2008 ) description of parody as “talk beside itself,” a mode of communication in which subtle communicative strategies become manifest. In our case, imitations draw attention to the communicative codes and strategies Crocker uses. Shouting, dramatization, and repetitions are all exaggerated and thus scorned as artificial and inappropriate. On a broader level, Crocker's imitations may also be fulfilling the phatic function. In an environment characterized by the rapid propagation and diversification of content, producing a takeoff of a popular and well known YouTube video such as “Leave Britney Alone” helps the person who uploads it stay in touch with the wider YouTube community. Uploading such videos may thus serve as another way to maintain the links underscoring a huge and highly heterogenic crowd.
My analysis so far yields a complex web of imitations and memetic dimensions. While users emulate the forms manifested in Crocker's video, they imitate the other imitators to construct opposing memes at the content and stance dimensions. In other words, the process of imitation combines overt copying and reversals of aspects of the original event. It may be that the most powerful communication-oriented meme spread by users in this process—one that has been replicated in almost all the videos we examined—is that of ironic communication: communication that veers from a definite commitment to one's uttered words, using language in a playful and nonobliging way.
So far I have demonstrated the utility of the threefold meme typology through a video-based example. I wish to further illustrate its applicability to other formats, such as image and text. To this end, I'll briefly look into the recent example of the “Pepper-Spraying Cop” meme. On 18 November 2011, students from the University of California - Davis campus gathered as part of the Occupy Wall Street protest. When they refused police orders to evacuate the area, two officers reacted by pepper-spraying a row of still-sitting students directly in their faces. Shortly after the incident, videos documenting it were uploaded to YouTube, generating uproar against the excessive use of force by American police officers (Dearen, 22.2. 2011 ). A photograph in which one of the cops, John Pike, was shown spraying the students quickly evolved into an Internet meme. Users Photoshopped the so-called casually pepper-spraying cop into an endless array of contexts, spanning historical; artistic; and pop-culture-oriented backgrounds (Jardin, 23.11. 2011).
The plethora of images constituting the “Pepper-Spraying Cop” meme can be analyzed through the lens of the three dimensional model of content, form and stance. Such an exercise reveals that while most versions share a similar Photoshop-based form, they vary greatly in terms of content. Content-wise, two main groups of meme versions were identified. The first group focuses on political contexts: Pike is shown pepper-spraying iconic American symbols such as George Washington crossing the Delaware; the former U.S. presidents on Mount Rushmore; and the Constitution itself, as well as freedom fighters across the globe (e.g., in Tiananmen Square). These political versions share a clear idea: that the officer brutally violated the basic values of justice and freedom as represented by the protestors. A second group of user-generated images is pop-culture oriented. In these versions, Pike is pepper-spraying icons such as Snoopy and Marilyn Monroe, as well as a battery of stars identified with other Internet memes, such as little baby panda and Keyboard Cat. The ideas conveyed by this group of pop-culture oriented memes are often polysemic. In one case, in which Pike is portrayed as spraying Rebecca Black—a widely scorned teen singer and Internet phenomenon—the original meaning of the photo as criticism of Pike seems to be almost reversed.
This differentiation between two types of memetic content can be further associated with alternations in stance. For instance, the utterly serious keying of the original photograph has been transformed in the process of memetic uptake, which involves explicit playfulness. Yet if in the politically oriented versions of the meme the keying is mainly sardonic, in the pop-culture-oriented ones the main tone is amused and humorous. The analysis of the “Pepper-Spraying Cop” meme according to the three memetic dimensions thus reveals that in contrast to the unified pattern of memetic uptake characterizing “Leave Britney Alone,” other memes might encompass a more divergent mode of diffusion and evolution. And this differentiation, as elaborated below, should be subjected to further empirical analysis.
This article is essentially about matchmaking. While memes and digital culture seem like an ideal fit, scholars—particularly in the field of communication—have so far been timid about coupling them. The forgoing essay thus both identifies and explores a fledgling field of knowledge. As such, it addresses three basic questions: (a) how, if at all, is the meme concept useful for understanding digital culture; (b) What important obstacles stand in the way of its being accepted in research; and (c) How can these obstacles be overcome?
Three attributes ascribed to the meme concept were highlighted here as particularly useful for exploring digital culture: Memes diffuse at the micro level but shape the macro structure of society; they reproduce by various means of imitation; and they follow the rules of competitive selection. These features were discussed here not only as apt descriptions of the technological affordances of the Internet in the Web 2.0 era, but also as key logics and perhaps even highly valued ideological pillars of a so called “participatory culture.” Yet two different features identified with the meme concept—close linkage with the biological metaphor and the undermined role of human agents—have hindered its uptake by media scholars. Two possible paths to overcoming these barriers were suggested: Forsaking the aspiration to find biological equivalents to all things cultural and conceptualizing humans in a more active way.
Another stumbling block to wider interest in memes relates to the ambiguity surrounding the concept. Since there is still dispute over what memes are, it is virtually impossible to study them empirically. Responding to this lacuna, I suggest in this article to define memes as complex systems incorporating three dimensions: content, form, and stance. When scrutinizing the propagation of memes, we should therefore examine them as trinities rather than as unified entities: The embracement—or rejection—of each dimension must be followed separately.
This distinction between memetic dimensions may serve as an invaluable tool for tracing the ways memes promulgate and shape digital culture. For instance, in the aforementioned “Leave Britney Alone” case, users chose to systematically undermine the ideological and communicative memes conveyed by Crocker's video, while simultaneously constructing and spreading opposing memes entailing ironic communication. Thus, while each user-generated video is ostensibly discrete and free to take its own form, a closer look reveals that Crocker's imitators chose to follow similar ideological and communicative routes, emulating each other's imitations. This pattern suggests that the ostensibly chaotic world (wide web) may in fact follow more organized cultural trajectories than meets the eye.
The differentiation between memetic dimensions may also advance our ability to create distinctions and draw borders between Internet memes. If we think of Internet memes as groups of interconnected content units that share common characteristics, we may further posit that such shared features may include content; form; and stance, and various combinations thereof. Therefore, the definition of a certain meme's scope may rely on the memetic dimension through which it is examined. For instance, if our prism is that of content, or ideas, we may argue that the same memetic content can be expressed in a video, a text, or a Photoshop image. In this case, what we define as a particular “Internet meme” will incorporate various formats. Alternatively, we may identify memetic formats, such as Image Macros or Lip-Sync, which are used for conveying various ideas. This differentiation thus allows for a nuanced, flexible, and dynamic account of what constitutes an Internet meme.
In providing a close reading of only two cases, this article implicitly suggests the need for further studies charting a large-scale map of Internet memes. Such works could ask what ideologies, textual conventions, and communication forms are conveyed by popular Internet memes, and what are the webs of relationships between these memetic dimensions. Eventually, this line of research will provide a comprehensive overview of prevalent assumptions, norms, and ideologies behind the memetic construction of digital culture.
As a concluding note, I wish to offer some preliminary thoughts about the potential meaning and relevance of this paper to the field of diffusion studies. At the turn of the century, Elihu Katz ( 1999 ), one of the founding fathers of the field, claimed that although questions about “how things get from here to there” (p.145) are at the heart of all disciplines in the social sciences and humanities, the field of diffusion studies has gone significantly undertheorized. He describes a gulf between the skyrocketing numbers of diffusion case studies and the lack of substantial efforts to theorize across discrete case studies and fields 3 One of the reasons Katz mentions for this impasse is the fact that “the items themselves refuse to hold still” (p.145). Another problem he hints at but does not articulate explicitly relates to the definition of the diffused unit. The study of diffusion until now has tended to focus on specific entities: In most text books, diffusion is defined as the propagation of “an idea, practice, or object” (e.g. Rogers, 2003 , p. 12). The “thing” itself which is diffused is always a well-defined entity, with clear boundaries. It is unchanging; its constant nature is what makes diffusion analysis possible.
This paper suggests a different route. Its three-dimension typology for analyzing Internet memes highlights the fact that, in diffusion or other types of communication research, the cultural object itself is a composite. In many cases, an item is at the same time an idea, a practice, and an object. Diffusion studies may therefore benefit from exploring the degree to which these dimensions work in cooperation or competition with each other. Indeed, looking at the diffused unit as an amalgam may also provide a key for a more nuanced account of cultural change. So far, the focus of diffusion studies has been mainly on the diffusion of innovation . But if we differentiate between content-, form-, and stance- based memes, we might discover that so-called “innovations” are sometimes old ideas or communicative practices in new textual gowns. This framework may therefore allow us to think about the delicate balance the between diffusion of innovation and the diffusion of tradition . Such a trajectory seems to fall in line with Benjamin Peters' ( 2009 ) recent suggestion to reconceptualize “new media” as “renewable media”: Rather than just asking if a medium is new or not, it might be more rewarding to trace the various forms that certain technological ideas take in the course of history. 4
To provisionally conclude, the meme is a natural for studying Internet and digital culture. Memetic behavior is not novel, but its scale, scope, and global visibility in contemporary digital environments are unprecedented. In this hyper-memetic era, user-driven circulation of copies and derivatives is a prevalent logic, or as Henry Jenkins (2009) aptly puts it: “if you don't spread, you are dead.” Copies become, in this sense, more important than the “original”: They are the raison d'etre of digital communication. It is clear that much more work is needed in excavating the wealth deriving from the coupling of the meme concept and digital communication. The fit between the two displays all the reluctance, enthusiasm, and pragmatic negotiation that one might expect of the marriage of an odd couple. Like it, it may be messy and complicated, but continuously interesting.
I am indebted to Menahem Blondheim, Benjamin Peters and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on this manuscript. I would also like to thank Elihu Katz, Paul Frosh, and Zohar Kampf for their useful advice.
In this sense, one might argue that memes are equivalent to signs. Indeed, signs have much in common with memes, to the extent that it has been argued that memes are no more than newly labeled signs ( Kilpinen, 2008 ). Yet two fundamental differences between the concepts justify their discrete existence. First, as described above, the meme is not just a sign, but a complex sign: Whereas “god” is a meme, “red” is not ( Dennett, 1995 ). Second, while each meme is comprised of signs, not all signs are memes. For instance, Beethoven's Fifth Symphony is composed of many signs, but only its first four notes have evolved as a meme. Over time, these notes were replicated as a discrete entity, separate from the symphony, thriving in contexts in which Beethoven's works were utterly unknown ( Dennett, 1995 ). To put it differently: A meme is a sign—or a set of signs—that gets replicated by many individuals. Borrowing from Simone de Beauvoir, we can thus argue: “One is not born a meme, but rather becomes one.”
This “hyper-memetic” existence may be related to new modes of thinking about copies, and copying. In his recent In Praise of Copying , Marcus Boon ( 2010 ) addresses the pervasive presence of copying in contemporary culture, claiming that it should first be celebrated as an integral and fundamental part of being human, and only then be thought of as something that should—or should not—be regulated. For a rich analysis of the concept see also Schwartz, 1996 .
In the decade following Katz's article, diffusion studies where reenergized by the ascent of the World Wide Web. “Diffusion of innovations” has so far been cited in a startling number of 31,598 works, according to Google Scholar. Some of these new studies strive to retheorize the field (e.g. Peres et. al, 2010), yet to the best of my knowledge, they still do not account for the problems of defining the propagated unit—and the changes it undergoes—more sensitively.
This mode of thinking of media as renewable, or as re-mediating well entrenched social structures, is evident in some historical works about the emergence of particular media, such as the telegraph ( Blondheim, 1994 ).
Alvarez , A . ( 2004 ). Memetics: An evolutionary theory of cultural transmission . Sorites , 15 , 24 – 28 . Retrieved from http://www.sorites.org/Issue_15/alvarez.htm
Google Scholar
Atran , S. ( 2001 ). The trouble with memes: Inference versus imitation in cultural creation . Human Nature , 12 ( 4 ), 351 – 381 . doi: 10.1007/s12110-001-1003-0
Aunger R. ( 2000 ). Introduction . In R. Aunger (Ed.) Darwinizing culture: The status of memetics as a science (pp. 1 – 24 ). Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Google Preview
Baym , N., & Burnett , R. ( 2009 ). Amateur experts: International fan labor in Swedish independent music . International Journal of Cultural Studies 12 ( 5 ), 433 – 449 . doi: 10.1177/1367877909337857
Benitez-Bribiesca , L. ( 2001 ). Memetics: A dangerous idea . Interciecia 26 , 29 – 31 . Retrieved from http://redalyc.uaemex.mx/pdf/339/33905206.pdf
Benkler , Y. ( 2006 ). The wealth of networks: How social production transforms markets and freedom . New Haven, CT : Yale University Press .
Bennett , W. L. ( 2003 ). New media power: The Internet and global activism . In N. Couldry and J. Curran (Eds.) Contesting media power (pp. 17 – 37 ). Lanham, MD : Rowman & Littlefield .
Blackmore , S. ( 1999 ). The meme machine . Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Blondheim , M. ( 1994 ). When bad things happen to good technologies: Three phases in the diffusion and perception of American telegraphy . In Y. Ezrahi and E. Mendelsohn (Eds.) Technology, pessimism, and postmodernism (pp. 77 – 114 ). Dordrecht, Netherlands : Kluwer Academic Publishers .
Blum-Kulka , S. , Huck-Taglicht , D. , & Avni , H. ( 2004 ). The social and discursive spectrum of peer talk . Discourse Studies 6 ( 3 ), 307 – 328 . doi: 10.1177/1461445604044291
Boon , M. ( 2010 ). In praise of copying . Cambridge, MA : Harvard University Press .
boyd , d . ( 2008 ). Taken out of context: American teen sociality in networked publics . PhD Dissertation. University of California-Berkeley, School of Information.
Boyd , R., & Richerson , P.J. ( 2005 ). Not by genes alone: How culture transformed human evolution . Chicago, IL : University of Chicago Press .
Brodie , R. ( 1996 ). Virus of the mind: The new science of the meme . Seattle, WA : Integral Press .
Burgess , J. ( 2008 ). All your chocolate rain are belong to us? Viral video, YouTube and the dynamics of participatory culture . In G. Lovink and S. Niederer (Eds.), Video vortex reader: Responses to YouTube (pp. 101 - 109 ). Amsterdam, Netherlands : Institute of Network Cultures .
Burgess , J., & Green JB. ( 2009 ). YouTube: Online video and participatory culture . Cambridge, England : Polity Press .
Christian , A. J . ( 2010 ). Camp 2.0: A queer performance of the personal . Communication, Culture & Critique , 13 ( 3 ), 352 – 376 . doi: 0.1111/j.1753-9137.2010.01075.x
Chesterman, A . ( 2005 ). The memetics of knowledge . In H.V. Engberg and H. Gerzymisch-Arbogast (Eds.), Knowledge systems and translation (pp. 17 – 30 ). Berlin, Germany and New York, NY : Mouton de Gruyter .
Chielens , K., & Heylighen , F . ( 2005 ). Operationalization of meme selection criteria: Procedures to empirically test memetic hypotheses . Proceedings AISB . Retrieved from http://www.aisb.org.uk/publications/proceedings/aisb05/9_Soc_Final.pdf
Conte , R. ( 2000 ). Memes through (social) minds . In R. Aunger (Ed.), Darwinizing culture: The status of memetics as a science (pp. 83 – 120 ). Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Dawkins , R. ( 1976 ). The selfish gene . Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Dawkins , R. ( 1982 ). The extended phenotype . Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Dawkins , R. ( 2004 ). A devil's chaplain: Reflections on hope, lies, science, and love . Boston, MA : Mariner Books .
Dennett , D.C. ( 1990 ). Memes and the exploitation of the imagination . Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , 48 , 127 – 13 . retrieved from http://ase.tufts.edu/cogstud/papers/memeimag.htm
Dennett , D.C. ( 1993 ). Consciousness explained . Boston, MA : Little, Brown and Co .
Dennett , D.C. ( 1995 ). Darwin's dangerous idea : Evolution and the meanings of life . New York, NY : Touchstone .
Dearen , J. (November 20, 2011 ). UC Davis Pepper Spray Incident Prompts Suspension Of Officers . The Huffington Post . Retrieved November 21, 2011 from http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2011/11/20/uc-davis-pepper-spray-inc_n_1104104.html
Distin , K. ( 2005 ). The selfish meme: A critical reassessment . Cambridge, England : Cambridge University Press .
Englebretson , R. ( 2007 ). Stancetaking in discourse: An introduction . In R. Englebretson (Ed.) . Stancetaking in discourse (pp. 1 – 26 ). Amsterdam, Netherlands : Benjamins .
Gatherer , D. ( 1998 ). Why the “thought contagion” metaphor is retarding the progress of memetics . Journal of Memetics – Evolutionary Models of Information Transmission . Retrieved from http://www.cpm.mmu.ac.uk/jom-emit/1998/vol1992/gatherer_d.html
Goffman , E. ( 1974 ). Frame analysis . Cambridge, MA : Harvard University Press .
Hariman , R. ( 2008 ). Political parody and public culture . Quarterly Journal of Speech , 94 , 247 – 272 . doi: 10.1080/00335630802210369
Heylighen F., & Chielens K. ( 2009 ). Cultural evolution and memetics . In B. Meyers (Ed.), Encyclopedia of complexity and system science . Retrieved from http://pespmc1.vub.ac.be/Papers/Memetics-Springer.pdf
Hull , D.L. ( 2000 ). Taking memetics seriously: Memetics will be what we make it . In R. Aunger (Ed.), Darwinizing culture: The status of memetics as a science (pp. 43 – 168 ). Oxford, England : Oxford University Press .
Hutcheon , L. ( 1985 ). A theory of parody: The teachings of twentieth-century art forms . London, England : Methuen .
Jenkins , H. ( 2006 ). Convergence culture: Where old and new media collide . New York, NY : New York University Press .
Jenkins, H. , Li , X , Krauskopf , A.D., & Grean , J. (Feb 2009 ). If it doesn't spread, it's dead (part one): Media viruses and memes . Retrieved from http://henryjenkins.org/2009/02/if_it_doesnt_spread_its_dead_p.html .
Johnson , D. ( 2007 ). Mapping the meme: A geographical approach to materialist rhetorical criticism . Communication & Critical/Cultural Studies , 4 ( 1 ), 27 – 50 . doi: 10.1080/14791420601138286
Jones , G. M. & Schieffelin , B. B. ( 2009 ). Talking text and talking back: “My BFF Jill” from boob tube to YouTube . Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 14 ( 4 ), 1050 – 1079 . doi: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2009.01481.x
Katz , E. ( 1999 ). Theorizing diffusion: Tarde and Sorokin revisited . Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science , 566 , 144 – 55 . doi: 10.1177/000271629956600112
Kilpinen , E. ( 2008 ). Memes versus signs: On the use of meaning concepts about nature and culture . Semiotica . 171 ( 1–4 ), 215 – 237 . doi: 10.1515/SEMI.2008.075
Knobel , M., & Lankshear , C. ( 2007 ). A new literacies sampler . New York, NY : Peter Lang .
Lessig , L. ( 2008 ). Remix: Making art and commerce thrive in the hybrid economy . New York, NY : Penguin .
Lynch , A. ( 1996 ). Thought contagion: How belief spreads through society . New York, NY : Basic Books .
Manovich , L. ( 2005 ). Remixing and remixability . Retrieved from http://www.manovich.net/DOCS/Remix_modular.doc .
O'Reilly , T . ( 2007 ). What is Web 2.0: Design patterns and business models for the next generation of software . International Journal of Digital Economics , 65 , 17 – 37 . Retrieved from http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/4578/
Peters , B. ( 2009 ). And lead us not into thinking the new is new: A bibliographic case for new media history . New Media and Society , 11 ( 1–2 ), 13 – 30 . doi: 10.1177/1461444808099572
Peres , R. , Muller , E., & Mahajan , V. ( 2010 ). Innovation diffusion and new product growth models: A critical review and research directions . International Journal of Research in Marketing , 27 , 91 – 106 . Retrieved from http://renanaperes.homestead.com/files/PeresMullerMahajan2010.pdf
Phillips , S. ( 1972 ). Participant structures and communicative competence: Warm Springs children in community and classroom . In C. Cazden , V.P. John , & D. Hymes (Eds.), Functions of language in the classroom (pp. 370 – 394 ). New York, NY : Teachers College Press .
Rogers , E.M. ( 2003 ). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). New York : Free Press .
Rose , N. ( 1998 ). Controversies in meme theory . Journal of Memetics - Evolutionary Models of Information Transmission , 2. Retrieved from http://cfpm.org/jom-emit/1998/vol2/rose_n.html
Salvato , N . ( 2009 ). Out of hand: YouTube amateurs and professionals . The Drama Review , 53 ( 3 ), 67 – 83 . Retrieved from http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/the_drama_review/v053/53.3.salvato.html
Schwartz , H. ( 1996 ). The culture of the copy: Striking likenesses, unreasonable facsimiles . New York : Zone Books .
Shifman , L. & Thelwall , M. ( 2009 ). Assessing global diffusion with web memetics: The spread and evolution of a popular joke . Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 60 ( 12 ), 2567 – 2576 . doi: 10.1002/asi.21185
Shifman , L. ( 2012 ). An anatomy of a YouTube meme . New Media and Society , 14 ( 2 ), 187 – 203 . doi:10.1177/1461444811412160
Limor Shifman is a Senior Lecturer at the Department of Communication and Journalism, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Her main research interests are new media, popular culture, and the social construction of humor.
Addresss: Department of Communication and Journalism, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, 91905, Israel
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Advertising and Corporate Services
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1083-6101
- Copyright © 2024 International Communication Association
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1937 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,867 quotes across 1937 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

Figures in Research Paper – Examples and Guide
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?

Do you encounter writer’s block during the first draft of a research paper? Crafting a clear outline from your initial ideas and notes can feel like a daunting first hurdle. Many researchers and students struggle with the initial stages of research paper writing. Uncertainties about content structure, information selection, and weaving complex findings into a cohesive narrative can lead to staring at a blank page.
Table of Contents
- AI-generated outlines with a personalized approach
- Identify gaps to strengthen your research paper
- Step 1: Creating a research paper outline
- Step 2: Breaking down the outline into sections
- Step 3: Drafting the research paper
A glimpse into academic forums and social media gives a clear picture that many researchers across the world go through similar problems while writing the first draft of a research paper. Where to begin? What should I write? How to begin? How to compile 2-3+ years of research into a 2500 or 5000-word research paper? If you’re grappling with these concerns, do not worry. You’re not alone.

Researchers face a mountain of work when it comes to writing papers. Paperpal decided to tackle this challenge and, in the process, discovered some fascinating writing habits:
- Start verbally: Some researchers find their flow by talking through their ideas first. They record themselves or brainstorm with a friend, then use these spoken notes as a springboard for their draft.
- Write on the go: Others prioritize keeping their thoughts flowing freely. They write in bursts, leaving the structuring and editing for later.
- Divide and Conquer: For some, especially new researchers, a structured approach works best. They break the paper into sections, focusing on building each one in detail before assembling the final draft.
- Outlines: Many researchers swear by outlines. Outlines provide a roadmap, complete with headings, subheadings, and key points. This saves time in the long run by eliminating the need for major restructuring later. You can focus on polishing the language and adding academic vocabulary during the final edit .
Inspired by the outline method, Paperpal set out to create a tool that would give researchers a head start. This led to the development of Paperpal’s AI-generated outlines, which build a rough skeleton for your draft, allowing you to flesh out each section with confidence.
How do Paperpal’s AI-generated outlines help you write the first draft 2x faster?
Unlike traditional outlining methods, Paperpal doesn’t just provide a generic structure. Paperpal’s AI-generated outlines identify the key topics that form the backbone of your draft, providing a clear structure without sacrificing crucial elements.
AI-generated outlines with a personalized approach
Paperpal goes beyond just suggesting topics. It seamlessly integrates your input, including notes, ideas, and research findings. This ensures the generated outline reflects your unique perspective and aligns perfectly with your project goals. This personalized approach not only streamlines the drafting process but also fosters a sense of ownership, keeping you engaged and motivated.
Identify gaps to strengthen your research paper
After creating an outline based on your notes, Paperpal takes things a step further by helping you flesh out each section with content suggestions. Let’s say you’re working on the introduction of your research paper . Paperpal not only analyzes your notes to generate an outline, but it also identifies potential gaps in your research. It can then suggest content additions like knowledge gaps, research questions, and rationale statements to address those weaknesses. This comprehensive support streamlines the writing process for your first draft, making it smoother and more effortless.
Researchers who have incorporated Paperpal into their workflow, have achieved higher levels of academic writing productivity . The result? Producing the first draft of a research paper in a shorter time frame, without making it completely AI-driven.
How to write the first draft of a research paper with Paperpal?
Paperpal redefines the way researchers approach academic writing, transforming the once-daunting task of drafting into a breeze. Here’s a walkthrough of writing the first draft of a research paper with Paperpal.
Step 1: Creating a research paper outline
- Sign- up to Paperpal and open a new or existing document.
- Navigate to Templates , select Outlines and choose Research Article to begin.
- Fill out the necessary details in the required fields according to your needs. Add your research notes to the Brief Description section and click on Generate .
Paperpal gets you started on the right foot by analyzing your information and generating a comprehensive outline. This roadmap for your draft breaks down the content into clear, logical sections:
- Background: Sets the context for your research.
- Topic Importance: Highlights the significance of your research area.
- Existing Knowledge: Summarizes what’s already known about the topic.
- Knowledge Gap: Identifies areas where further research is needed.
- Rationale: Explains why your research is important to address the gap.
- Research Question: Formulates the specific question your research aims to answer.
- Aim/Objective: Defines the overall goals and desired outcomes of your research.
- Hypothesis: Makes a prediction about the expected results of your study (optional, not all research papers require a hypothesis).
Paperpal’s outline provides a head-start to structure and write your research paper. This process helps in laying a strong foundation for your writing and refining it effortlessly.
Step 2: Breaking down the outline into sections
Once you have the initial outline, you can further refine it by dividing it into subsections. This helps you explore each aspect of your research in detail, ensuring thorough coverage of your topic. You can choose from pre-built sections like Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion and start developing one by one.
Step 3: Drafting the research paper
Start your research paper’s draft based on the outline and custom section enhancements. During the writing phase, Paperpal also offers insights into using its features:
- Incorporating references and additional content as required
- Rephrasing, shortening sentences, and refining language and structure using Paperpal’s Edit and Rewrite options
- Refining your draft by adding citations and specific information relevant to the topic via Paperpal Research. This ensures originality, and clarity, and adds value to your writing.
By streamlining the journey from raw research to a polished draft, Paperpal helps students, researchers, and academics overcome common writing hurdles and achieve greater productivity. Whether you are a seasoned researcher or a student, Paperpal serves as a trusted companion, guiding you through each stage of the drafting process. Unlock academic writing potential with Paperpal. Get your free Paperpal account today!
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
MLA Works Cited Page: Format, Template & Examples
You may also like, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 27 May 2024
Evidence of ongoing volcanic activity on Venus revealed by Magellan radar
- Davide Sulcanese ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5472-3197 1 , 2 ,
- Giuseppe Mitri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8390-458X 1 , 2 &
- Marco Mastrogiuseppe ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9902-8115 3 , 4
Nature Astronomy ( 2024 ) Cite this article
716 Accesses
1102 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Geomorphology
- Volcanology
The surface of Venus has undergone substantial alterations due to volcanic activity throughout its geological history, and some volcanic features suggest that this activity persisted until as recently as 2.5 million years ago. Recent evidence of changes in the surface morphology of a volcanic vent has been interpreted as a potential indication of ongoing volcanic activity. To investigate more widespread alterations that have occurred over time in the planet’s surface morphology, we compared radar images of the same regions observed from 1990 to 1992 with the Magellan spacecraft. We found variations in the radar backscatter from different volcanic-related flow features on the western flank of Sif Mons and in western Niobe Planitia. We suggest that these changes are most reasonably explained as evidence of new lava flows related to volcanic activities that took place during the Magellan spacecraft’s mapping mission with its synthetic-aperture radar. This study provides further evidence in support of a currently geologically active Venus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
111,21 € per year
only 9,27 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
The Egyptian pyramid chain was built along the now abandoned Ahramat Nile Branch
Underwater acoustic analysis reveals unique pressure signals associated with aircraft crashes in the sea: revisiting MH370

2023 summer warmth unparalleled over the past 2,000 years
Data availability.
The Venus Magellan SAR F-BIDRs used in this work are available from the PDS geosciences node ( https://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/magellan/fbidr/index.htm ). Magellan altimetry data were extrapolated using the Altimeter and Radiometry Composite Data Record, which is also available from the PDS geosciences node ( https://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/Magellan/arcdr/index.htm ). Magellan Stereo-Derived Topography used in this work is also available from the PDS geosciences node ( https://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/magellan/stereo_topography.htm ). The source data images used for this paper can be found at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10875314 (ref. 47 ).
Code availability
The data have been processed using Matlab. Codes are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Truong, N. & Lunine, J. Volcanically extruded phosphides as an abiotic source of Venusian phosphine. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , e2021689118 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Esposito, L. W. Sulfur dioxide: episodic injection shows evidence for active Venus volcanism. Science 223 , 1072–1074 (1984).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Smrekar, S. E. et al. Recent hotspot volcanism on Venus from VIRTIS emissivity data. Science 328 , 605–608 (2010).
Bondarenko, N., Head, J. & Ivanov, M. Present‐day volcanism on Venus: evidence from microwave radiometry. Geophys. Res. Lett . https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL045233 (2010).
D’Incecco, P. et al. Geologically recent areas as one key target for identifying active volcanism on Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49 , e2022GL101813 (2022).
Gülcher, A. J., Gerya, T. V., Montési, L. G. & Munch, J. Corona structures driven by plume–lithosphere interactions and evidence for ongoing plume activity on Venus. Nat. Geosci. 13 , 547–554 (2020).
D’Incecco, P., López, I., Komatsu, G., Ori, G. G. & Aittola, M. Local stratigraphic relations at Sandel crater, Venus: possible evidence for recent volcano-tectonic activity in Imdr Regio. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 546 , 116410 (2020).
Herrick, R. R. & Hensley, S. Surface changes observed on a Venusian volcano during the Magellan mission. Science 379 , 1205–1208 (2023).
Van Zelst, I. Comment on ‘Estimates on the frequency of volcanic eruptions on Venus’ by Byrne and Krishnamoorthy (2022). J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 127 , e2022JE007448 (2022).
Byrne, P. K. Reply to Comment by I. van Zelst on ‘Estimates on the frequency of Volcanic eruptions on Venus’ (2022). J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 127 , e2022JE007666 (2022).
Byrne, P. K. & Krishnamoorthy, S. Estimates on the frequency of volcanic eruptions on Venus. J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 127 , e2021JE007040 (2022).
Ford, J. P. Guide to Magellan Image Interpretation (NASA, 1993).
Saunders, R. et al. Magellan mission summary. J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 97 , 13067–13090 (1992).
Copp, D. L. & Guest, J. E. Geologic Map of the Sif Mons Quadrangle (V-31), Venus . Report No. 2898 (US Geological Survey, 2007).
Hansen, V. L. Geologic Map of the Niobe Planitia Quadrangle (V-23), Venus . Report (US Geological Survey, 2009).
Herrick, R. R. & Sharpton, V. L. Implications from stereo‐derived topography of Venusian impact craters. J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 105 , 20245–20262 (2000).
Ford, P. G. & Pettengill, G. H. Venus topography and kilometer‐scale slopes. J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 97 , 13103–13114 (1992).
Herrick, R. R. Stereo-derived Topography for Venus from Cycle 1 and Cycle 3 Magellan FMAP Mosaics (PDS, 2020); https://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/mgn/urn-nasa-pds-magellan_stereo_topography/document/magellan_stereo_topography_description.pdf
Pettengill, G. H., Ford, P. G. & Chapman, B. D. Venus: surface electromagnetic properties. J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 93 , 14881–14892 (1988).
Campbell, B. A. Use and Presentation of Magellan Quantitative Data in Venus Mapping . Report 95-519 (US Geological Survey, 1995).
Muhleman, D. Symposium on radar and radiometric observations of Venus during the 1962 conjunction: radar scattering from Venus and the Moon. Astron. J. 69 , 34 (1964).
Tyler, G. L. et al. Magellan: electrical and physical properties of Venus’ surface. Science 252 , 265–270 (1991).
Theilig, E., Wall, S. & Saunders, R. Radar interpretation of lava fields as a function of incidence angle: implications for interpretation of Magellan SAR data on Venus. In Proc. 19th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (eds Ryder, G. & Sharpton, V. L.) 323–333 (Cambridge Univ. Press and Lunar and Planetary Institute, 1989).
Weitz, C. M., Plaut, J. J., Greeley, R. & Saunders, R. S. Dunes and microdunes on Venus: why were so few found in the Magellan data? Icarus 112 , 282–295 (1994).
Greeley, R. et al. Wind-related features and processes on Venus: summary of Magellan results. Icarus 115 , 399–420 (1995).
Danklmayer, A., Doring, B. J., Schwerdt, M. & Chandra, M. Assessment of atmospheric propagation effects in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 47 , 3507–3518 (2009).
Duan, X., Moghaddam, M., Wenkert, D., Jordan, R. L. & Smrekar, S. E. X band and model of Venus atmosphere permittivity. Radio Sci. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009RS004169 (2010).
Hensley, S., Martin, J., Oveisgsharan, S., Duan, X. & Campbell, B. Radar performance modeling for Venus missions. In Proc. 16th VEXAG Meeting 2018 (eds Gilmore, M. S. et al.) 39 (LPI, 2018).
Hofgartner, J. et al. Transient features in a Titan sea. Nat. Geosci. 7 , 493–496 (2014).
Malin, M. C. Mass movements on Venus: preliminary results from Magellan cycle 1 observations. J. Geophys. Res.: Planets 97 , 16337–16352 (1992).
Meyer, F. J. & Sandwell, D. T. SAR interferometry at Venus for topography and change detection. Planet. Space Sci. 73 , 130–144 (2012).
Rowland, S. K., Smith, G. A. & Mouginis-Mark, P. J. Preliminary ERS-1 observations of Alaskan and Aleutian volcanoes. Remote Sens. Environ. 48 , 358–369 (1994).
Schaefer, L. N., Lu, Z. & Oommen, T. Post-eruption deformation processes measured using ALOS-1 and UAVSAR InSAR at Pacaya Volcano, Guatemala. Remote Sens. 8 , 73 (2016).
Fegley, B. Jr & Prinn, R. G. Estimation of the rate of volcanism on Venus from reaction rate measurements. Nature 337 , 55–58 (1989).
Papale, P., Garg, D. & Marzocchi, W. Global rates of subaerial volcanism on Earth. Front. Earth Sci. 10 , 922160 (2022).
Crisp, J. A. Rates of magma emplacement and volcanic output. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 20 , 177–211 (1984).
Hensley, S. et al. VISAR: bringing radar interferometry to Venus. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts , P32D-03 (American Geophysical Union, 2021).
Ghail, R. C. et al. VenSAR on EnVision: taking Earth observation radar to Venus. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 64 , 365–376 (2018).
ADS Google Scholar
Smrekar, S. et al. VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy): a discovery mission. In 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO) 1–20 (IEEE, 2022).
Hensley, S. et al. Planned differential interferometric SAR observations at Venus by the Veritas mission. In IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 12–15 (IEEE, 2022).
Widemann, T. et al. Venus evolution through time: key science questions, selected mission concepts and future investigations. Space Sci. Rev. 219 , 56 (2023).
Kittler, J. & Illingworth, J. Minimum error thresholding. Pattern Recognit. 19 , 41–47 (1986).
Lee, J.-S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2 , 165–168 (1980).
Pettengill, G. H., Ford, P. G., Johnson, W. T., Raney, R. K. & Soderblom, L. A. Magellan: radar performance and data products. Science 252 , 260–265 (1991).
USGS EROS Archive - Digital Elevation - Global 30 Arc-Second Elevation (GTOPO30) (US Geological Survey, 2018); https://doi.org/10.5066/F7DF6PQS
Kilburn, C. R. in Encyclopedia of Volcanoes (eds Sigurdsson, H. et al.) 291–305 (Academic, 2000).
Sulcanese, D., Mitri, G. & Mastrogiuseppe, M. Source data files of ‘Evidence of ongoing volcanic activity on Venus revealed by Magellan radar’ by Sulcanese, D., et al. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10875314 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We want to thank our collaborator G. Alberti for helping in processing Magellan radar products. G.M., D.S. and M.M. acknowledge support from the Italian Space Agency (Grant No. 2022-15-HH.0).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
International Research School of Planetary Sciences, Università d’Annunzio, Pescara, Italy
Davide Sulcanese & Giuseppe Mitri
Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Geologia, Università d’Annunzio, Pescara, Italy
Dipartimento di Ingegneria dell’Informazione, Elettronica e Telecomunicazioni, Università La Sapienza, Rome, Italy
Marco Mastrogiuseppe
Link Campus University, Rome, Italy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.S. led the writing of the paper, conducted all the analyses and interpreted the geological and geomorphological results presented in this article. G.M. was responsible for the conceptualization of the project and the manuscript, provided support in manuscript writing and assisted in the geological interpretation of the data. M.M. provided support in the analysis of the data, particularly in the radar and altimeter data analysis, and the interpretation of the results pertaining to the radar part. He also contributed to manuscript writing, specifically in the sections related to the electromagnetic models and alternative hypotheses regarding the radar section.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Davide Sulcanese .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Astronomy thanks Paul Byrne and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Figs. 1–13 and Tables 1–4.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Sulcanese, D., Mitri, G. & Mastrogiuseppe, M. Evidence of ongoing volcanic activity on Venus revealed by Magellan radar. Nat Astron (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-024-02272-1
Download citation
Received : 21 March 2023
Accepted : 11 April 2024
Published : 27 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-024-02272-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this blog, you will see excellent any kind of material, such as UX research memes, clinical research memes, psychology research memes, and research paper memes. If you want to take a break and enjoy your time, you should definitely take a look at our 40 hilarious Research memes that will make you laugh : 1. Tip of the iceberg.
"The Perfect Match": Two researchers finding each other on a dating app, only to realize they are reviewer and author of a contentious paper, captioned: "When your peer review is too close to home." "The Methodology Maze": An image of a researcher looking perplexed at a complex maze, with each turn labeled with different research methods.. Caption: "Navigating the methodology ...
It's good to see you here instead of hard at work on your current writing project. Of course, we know that it's important to have some downtime and to have a bit of a laugh, which is why we've collected these 77 fun memes that do a rather good job of poking fun at the truth of what it is to be a writer. Have fun checking them out.
It's a free online image maker that lets you add custom resizable text, images, and much more to templates. People often use the generator to customize established memes , such as those found in Imgflip's collection of Meme Templates . However, you can also upload your own templates or start from scratch with empty templates.
Search the Imgflip meme database for popular memes and blank meme templates. Create. Make a Meme Make a GIF Make a Chart Make a Demotivational research Meme Templates. Search. NSFW GIFs Only. ... Research paper. Add Caption. Neil Degrasse Tyson - Jerk Research. Add Caption. Surrounded by books. Add Caption. So you need to do research. Add ...
32666. Explore the world of "High Impact PhD Memes," where humor meets academia. This collection of memes delves into the unique challenges and relatable moments of the PhD journey. From battling writer's block to celebrating small victories, these memes capture the essence of research life. Join fellow doctoral candidates in sharing a ...
The paper concludes with the cultural significance of employing memes in qualitative work as innovative approaches in data collection and research representation. ... The meme is also a form of communication that continues to write itself, literally. Memes are adapted and reformed by the millions of people who participate in the writing and ...
"The meme hits the right nerve," says Vinay Prasad, an associate epidemiology professor and a prominent critic of medical research. "Many papers serve no purpose, advance no agenda, may not ...
Embark on a meme-filled rollercoaster ride with PhD and Masters students! Watch as they tackle the challenges of research, writing, and thesis preparation, s...
Make a memeMake a gifMake a chart. Research Paper. Research Paper | image tagged in gifs,research paper,pulp fiction,writing | made w/ Imgflip video-to-gif maker. by RebekahBuchanan. 800 views, 3 upvotes.
College Memes: Short Description. Get ready for a rollercoaster of emotions as we delve into the world of university memes that will have you laughing and crying at the same time. These humorous digital gems capture the ups and downs of student life, from the hilarious antics of roommates to the stress-induced moments during finals week.
This meme consists of a stylish comic montage of people's thoughts related to the author/participant and his or her occupation, and boils down to a self-aware confession of "what I really do.". The visuals are compelling connotations of their perceptions when the author spends time to find just the right pictures.
6.4.4 Messages through memes (research essay) 6.5.1 Literacy in video games (argument from experience) 6.5.2 How video games affect literacy (synthesis) ... The meme is by no means formal writing and was posted on Reddit to share a piece of humor created by the author. Therefore, the audience of the meme is others online, in particular, people ...
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
Outline Your Paper: Organize your thoughts and ideas by creating an outline before you start writing. This will help you maintain a logical flow and ensure that all relevant points are covered. Write Clear and Concise Sentences: Avoid overly complex sentences and jargon that may confuse your readers. Aim for clarity and precision in your ...
This guide explains the merits of each method and lays out ways to approach ethical issues involved in meme research. SAGE Research Methods: Doing Research Online. Written by . Sulafa Zidani. As a scholar of digital culture, Sulafa Zidani writes on global creative practices in online civic engagement across geopolitical contexts and languages ...
This paper re-examines the concept of "meme" in the context of digital culture. Defined as cultural units that spread from person to person, memes were debated long before the digital era. Yet the Internet turned the spread of memes into a highly visible practice, and the term has become an integral part of the netizen vernacular.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Create a research paper outline. Paragraph structure. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write an research paper introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the research paper conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research Paper Writing Service - UKessay is a professional academic writing service for busy students ...
What follows is a step-by-step guide on how you can make your research paper a good read and improve the chances of your paper's acceptance: CONTENTS. 1. How to dive into the process of writing. Outline of a research paper. Keep sub-topics and references ready. 2. Getting the title of your research paper right. 3.
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
A research paper is an expanded essay that presents your own interpretation or evaluation or argument. In fact, this guide is designed to help you navigate the research voyage, through developing a research question and thesis, doing the research, writing the paper, and correctly documenting your sources. Research Paper Writing Service is one ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Write a Python script to automate sending daily email reports (opens in a new window) Create a personal webpage for me after asking me three questions (opens in a new window) Create a morning routine to boost my productivity (opens in a new window)
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes) or at the end of a paper (endnotes). The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but ...
Step 1: Creating a research paper outline. Step 2: Breaking down the outline into sections. Step 3: Drafting the research paper. A glimpse into academic forums and social media gives a clear picture that many researchers across the world go through similar problems while writing the first draft of a research paper.
The steps of the research process are detailed below to help guide you through developing your ideas into a feasible research project. Table of contents. Step 1: Choose a topic. Step 2: Identify a problem. Step 3: Develop research questions. Step 4: Create a research design. Step 5: Write a research proposal.
Research Findings: Results showed that Chinese preschool children could independently generate a variety of writing samples without adult support. Early Chinese writing skills represent two factors, namely (a) the ability to transcribe recognizable characters (transcription skill), and (b) the ability to generate meaningful ideas (composing skill).
Legal research and writing instructors are pivotal in this endeavor. They have the unique opportunity to introduce tribal law within the core first-year curriculum. ... Challenges, and Strategies (May 28, 2024). Univ. of Wisconsin Legal Studies Research Paper No. 1806, 31 Perspectives (Forthcoming 2024)., Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com ...
According to a recent study 8, an ~2.2 km 2 volcanic vent that changed shape during an 8 month period between two radar images taken by the Magellan spacecraft has been interpreted as evidence of ...