129 Human Trafficking Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
📝 key points to use to write an outstanding human trafficking essay, 🏆 best human trafficking topic ideas & essay examples, ⭐ simple & easy human trafficking essay titles, 📌 most interesting human trafficking topics to write about, 👍 good research topics about human trafficking.
- ❓ Research Questions about Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is one of the most challenging and acute assignment topics. Students should strive to convey a strong message in their human trafficking essays.
They should discuss the existing problems in today’s world and the ways to solve them. It means that essays on human trafficking require significant dedication and research. But do not worry, we are here to help you write an outstanding essay.
Find the issue you want to discuss in your paper. There are many titles to choose from, as you can analyze the problem from various perspectives. The examples of human trafficking essay topics include:
- The problem of child trafficking in today’s world
- The causes of human trafficking
- Human trafficking: The problem of ethics and values
- The role of today’s society in fostering human trafficking
- Human trafficking as a barrier to human development
- The rate of human trafficking victims in the world’s countries
- How to prevent and stop human trafficking
Remember that you can select other human trafficking essay titles if you want. Search for them online or ask your professor for advice.
Now that you are ready to start working on your paper, you can use these key points for writing an outstanding essay:
- Study the issue you have selected and do preliminary research. Look for news articles, scholarly papers, and information from reputable websites. Do not rely on Wikipedia or related sources.
- Work on the outline for your paper. A well-developed outline is a key feature of an outstanding essay. Include an introductory and a concluding paragraph along with at least three body paragraphs. Make sure that each of your arguments is presented in a separate paragraph or section.
- Check out human trafficking essay examples online to see how they are organized. This step can also help you to evaluate the relevance of the topic you have selected. Only use online sources for reference and do not copy the information you will find.
- Your introductory paragraph should start with a human trafficking essay hook. The hooking sentence or a phrase should grab the reader’s attention. An interesting fact or a question can be a good hook. Hint: make sure that the hooking sentence does not make your paper look overly informal.
- Do not forget to include a thesis statement at the end of your introductory section. Your paper should support your thesis.
- Define human trafficking and make sure to answer related questions. Is it common in today’s world? What are the human trafficking rates? Help the reader to understand the problem clearly.
- Discuss the causes and consequences of human trafficking. Think of possible questions you reader would ask and try to answer all of them.
- Be specific. Provide examples and support your arguments with evidence. Include in-text citations if you refer to information from outside sources. Remember to use an appropriate citation style and consult your professor about it.
- Discuss the legal implications of human trafficking in different countries or states. What are the penalties for offenders?
- Address the ethical implications of the problem as well. How does human trafficking affect individuals and their families?
- A concluding paragraph should be a summary of your arguments and main ideas of the paper. Discuss the findings of your research as well.
Check out our samples (they are free!) and get the best ideas for your paper!
- Human Trafficking: Process, Causes and Effects To make the matters worse they are abused and the money goes to the pockets of these greedy people as they are left empty handed after all the humiliation they go through.
- Trafficking of Children and Women: A Global Perspective The scale of women and children trafficking is very large but difficult to put a figure on the actual number of women and children trafficked all over the world. The demand for people to work […]
- Human Trafficking in the United States The paper also discusses the needs of the victims of human trafficking and the challenges faced in the attempt to offer the appropriate services.
- Human Trafficking in Africa Therefore, Africa’s human trafficking can be primarily attributed to the perennial political instability and civil unrest as the root causes of the vice in the continent. Some traditions and cultural practices in Africa have significantly […]
- Human Trafficking: Slavery Issues These are the words to describe the experiences of victims of human trafficking. One of the best places to intercept human trafficking into the US is at the border.
- Reflection on Human Trafficking Studies When researching and critically evaluating the global issue of human trafficking, I managed to enrich my experience as a researcher, a professional, and an individual due to the facts and insights gained through this activity.
- Human Trafficking Through the General Education Lens First and foremost, the numerous initiatives show that the regional governments are prepared to respond to the problem of human trafficking in a coordinated manner.
- Discussion: Human Trafficking of Adults Human trafficking of adults is one of the most essential and significant issues of modern times, which affects the lives of millions of people in almost every corner of the globe.
- Human Trafficking and Related Issues and Tensions In the business sector, therefore, discrimination leads to the workload of the trafficked employee to make a huge lot of work to be done at the right time required.
- Doctor-Patient Confidentiality and Human Trafficking At the same time, it is obligatory to keep the records of all the patients in the healthcare settings while Dr. To conclude, the decision in the case of an encounter with human trafficking should […]
- Three Ethical Lenses on Human Trafficking As a result of the issue’s illegality, a deontologist will always observe the law and, as a result, will avoid or work to eradicate human trafficking.
- Policy Issues on Human Trafficking in Texas The challenge of preventing human trafficking in Texas and meeting the needs of its victims is complicated by the multifaceted nature of the problem.
- Dark Window on Human Trafficking: Rhetorical Analysis In this essay, Ceaser utilized his rhetorical skills to dive into the dark world of human trafficking, which severely hits Latin America and the USA, through the usage of images and forms of different societal […]
- Human Trafficking: Giving a Fresh Perspective One question I find reoccurring is, “Are all victims of human trafficking being dishonest?” Throughout my career and law enforcement, I met the cases in which victims were dishonest, and I wanted to discover why.
- Human Trafficking and Variety of Its Forms The types of human trafficking that harshly break human rights are sex trafficking, forced labor, and debt bondage. To conclude, it is essential to say that human trafficking has been the worst type of crime […]
- Child Welfare and Human Trafficking Young people and children that live in “out-of-home care” due to reasons of abuse or lack of resources are at higher risk of becoming subjects of trafficking.
- Human Trafficking and Healthcare Organizations Human Trafficking, which is a modern form of slavery, is a critical issue nowadays since it affects many marginalized people around the world.
- Human Trafficking Is a Global Affair It refers to the unlawful recruitment, harboring and transportation of men, women and children for forced labor, sex exploitation, forced marriages, through coercion and fraud.
- Human Trafficking and Nurses’ Education Therefore, there is a need to educate nurses in understanding human trafficking victims’ problems and learning the signs or ared flags’ of human trafficking.
- Intelligence Issues in Human Trafficking To begin with, the officer is to examine the social groups of migrants and refugees, as they are the most vulnerable groups in terms of human trafficking.
- Intelligence Issues in Border Security, Human Trafficking, and Narcotics Trafficking This paper aims to emphasize drug trafficking as the main threat for the nation and outline intelligence collecting methods on drug and human trafficking, border security, and cybersecurity.
- Human Trafficking in the UK: Examples and References The bureaucracy and lack of flexibility pose quite significant threats to the success of the UK anti-trafficking strategies. An illustration of this lack of flexibility and focus is the case of the Subatkis brothers.
- Criminology: Human Trafficking However, the UAE clearly has admitted that there is a high level of rights infringement against women by the ISIS in Iraq and Syria.
- Human Trafficking: Labor Facilitators and Programs Labor trafficking is a significant issue in the modern world because it refers to people who are forced to engage in labor through the use of coercion, fraud, and force.
- Human Trafficking: Solution to Treat Survivors And A Public Health Issues Ultimately, this led to the child’s lack of a sense of security, to the presence of a strong desire to be loved and important to someone.
- Human Trafficking and Its Social and Historical Significance Human trafficking is a type of crime that involves kidnapping and transporting of women, men, and children out of the country with the purposes of slave labor, prostitution, organ harvesting, and other nefarious purposes.
- Egypt and Sudan Refugees and Asylum Seekers Face Brutal Treatment and Human Trafficking In this report by Amnesty International, the issue of the security of refugees and asylum seekers in Shagarab refugee camps, which are located in the eastern parts of Sudan, is raised.
- Stephanie Doe: Misyar Marriage as Human Trafficking in Saudi Arabia In this article, the author seeks to highlight how the practice of temporary marriages by the wealthy in Saudi Arabia, commonly known as misyar, is a form of human trafficking.
- Effects of Human Trafficking in Teenagers: The Present-Day Situation In this case, the inclusion of the additional factor, the type of human trafficking, will contribute to a better understanding of the problem and develop a solution.
- Aftermath of Human Trafficking in Children and Teenagers The major part of the available research is concentrated on the victims of sex abuse and the applied means of their treatment.
- Human Trafficking of Illegal Immigrants People perceive II not as a vulnerable demographic but as a part of the problem, thus causing the target population to develop the behaviors that complicate the process of preventing and addressing the instances of […]
- Human Trafficking in the USA However, the development of the society and rise of humanism resulted in the reconsideration of the attitude towards this phenomenon and the complete prohibition of all forms of human trafficking.
- Human Trafficking and Exploitation in Modern Society It is necessary to determine the essence of human trafficking to understand the magnitude of the problem of slavery in the modern world.
- Child Welfare: Human Trafficking in San Diego The paper consists of an introduction, the consecutive sections addressing the definition of the issue, its legal background, the occurrence of child trafficking, and the interventions initiated by the authorities to fight the threat.
- Human Trafficking as an Issue of Global Importance Being a threat to global safety and well-being, the phenomenon of human trafficking has to be managed by reconsidering the existing policy statements of organizations responsible for monitoring the levels of human trafficking and preventing […]
- Psychotherapy for Victims of Human Trafficking The use of different dependent variables is the primary feature that differs a single-subject design from a program evaluation the essence of which is to cover a range of questions and evaluate them all without […]
- Human Trafficking: Enforcing Laws Worldwide This essay focuses on the issue of enforcement of laws concerning human trafficking, the influence of country prosperity on the approaches to solving this problem, the vulnerable categories at high risk of becoming victims, and […]
- Social Work: Human Trafficking and Trauma Theory One of the theoretical frameworks is trauma theory that focuses on the traumatic experiences victims are exposed to as well as the influence of these traumas on their further life.
- Human Trafficking Problems in Canada The authors describe the government’s influence on the level of human trafficking and argue that the concept of slavery is almost the same as modern human trafficking.
- Terrorism, Human Trafficking, and International Response One of the key positive results of the global counter-terrorism efforts was the reduction of Al Qaeda’s presence both globally and in the Middle East, and the enhancement of travel safety.
- Human Trafficking in Mozambique: Causes and Policies “Human Trafficking in Mozambique: Root Causes and Recommendations” is a policy paper developed by the research team of UNESCO as a powerful tool in order to analyze the situation with human trafficking in Mozambique and […]
- Human Trafficking as a Terrorist Activity The biggest problem that is worth mentioning is that it is believed that the number of such activities is growing at an incredibly fast rate, and it is important to take necessary measures to limit […]
- Human Trafficking: Healthcare and Globalization Aspects The first study conducts a literature review on articles in the year 2011 and 2012 based on the handing of human trafficking by healthcare professionals.
- Human Trafficking and Modern-day Slavery One of the biggest challenges in addressing modern slavery and human trafficking is the fact that the vice is treated as a black market affair where facts about the perpetrators and the victims are difficult […]
- Combating Human Trafficking in the USA It is necessary to note, however, that numerous researchers claim that the number of human trafficking victims is quite difficult to estimate due to the lack of effective methodology.
- The Fight Against Human Trafficking Human trafficking constitutes a gross violation of the human rights of the individual as he/she is reduced to the status of a commodity to be used in any manner by the person who buys it.
- Criminal Law: Human Trafficking Promises of a good life and the absence of education opportunities for women have led to the increased levels of human trafficking.
- Human Trafficking: Definition, Reasons and Ways to Solve the Problem That is why, it becomes obvious that slavery, which is taken as the remnant of the past, prosper in the modern world and a great number of people suffer from it.
- Human Trafficking and the Trauma It Leaves Behind According to Snajdr, in the United States, most of the Black immigrants who came to the country during the colonial era were actually victims of human trafficking.
- Mexican Drug Cartels and Human Trafficking Reports from Mexico says that due to the pressure exerted on the drug cartels by the government, they have resolved in other means of getting revenue and the major one has been human trafficking alongside […]
- Human Trafficking in Eastern Europe The fall of communism in Eastern Europe has led to a long-term issue of human trafficking in some of the nations in the region.
- Human Trafficking between Africa and Europe: Security Issues This situation is usually made possible by the fact that the traffickers are usually criminal groups that have a potential to do harm to the victims and to the family of the victims.
- Tackling the Issue of Human Trafficking In Europe, prevention of human trafficking is interpreted to mean both awareness raising and active prevention activities that ideally look into the primary causes of human trafficking.
- Human trafficking in Mozambique The reason for this goes back to the fact the government in place has failed to put the interests of its people as a priority.
- “Not For Sale: End Human Trafficking and Slavery”: Campaign Critique To that extent, Not for Sale campaign attempts to enhance the ability of the people in vulnerable countries to understand the nature and form of trafficking and slavery.
- The Human Trafficking Problem Another way is through employment and this involves the need to create more jobs within the community that is at a higher risk of facing human trafficking.
- Human Trafficking in the United States: A Modern Day Slavery The question of the reasons of human trafficking is a complex one to answer since there are various causes for it, but the majors causes include; Poverty and Inequality: It is evident that human trafficking […]
- Definition of Human Rights and Trafficking One of the infamous abuses of human rights is the practice of human trafficking, which has become prevalent in the current society.
- How Prostitution Leads to Human Trafficking This is a form of a business transaction that comes in the name of commercial sex either in the form of prostitution or pornography.
- Criminal Enforcement and Human Trafficking
- Combating Human Trafficking Should Go Towards the Recovery of The Victim
- Connections Between Human Trafficking and Environmental Destruction
- The Problems of Human Trafficking and Whether Prostitution Should Be Legal
- The Issue of Human Trafficking, a Criminal Business in the Modern Era
- The Problem of Human Trafficking in America
- Ways You Can Help Fight Human Trafficking
- Assignment on Human Trafficking and Prostitution
- The Plague of Human Trafficking in Modern Society
- Critical Thinking About International Adoptions: Saving Orphans or Human Trafficking
- The Issue of Human Trafficking and the Backlash of Saving People
- The Role of Corruption in Cambodia’s Human Trafficking
- A Theoretical Perspective on Human Trafficking and Migration-Debt Contracts
- Conditions That Allow Human Trafficking
- Understanding Human Trafficking Using Victim-Level Data
- Evaluation of the International Organization for Migration and Its Efforts to Combat Human Trafficking
- Causes and Consequences of Human Trafficking in Haiti
- Fishing in Thailand: The Issue of Overfishing, Human Trafficking and Forced Labor
- Differences Between Definitions of Human Trafficking
- Banks and Human Trafficking: Rethinking Human Rights Due Diligence
- The World Are Victims of Human Trafficking
- Understandings and Approaches to Human Trafficking in The Middle East
- The Issue of Human Trafficking, Child Prostitution and Child Soldiers
- Human Trafficking and the Trade in Sexual Slavery or Forced
- The Protection of Human Trafficking Victims by the Enforcement Bodies in Malaysia
- The Remnants of Human Trafficking Still Exists Today
- The Issue of Human Trafficking and Its Connection to Armed Conflict, Target Regions, and Sexual Exploitation
- Causes Effects of Human Trafficking
- The Issue of Human Trafficking and Forced Child Prostitution Around the World
- Assessing the Extent of Human Trafficking: Inherent Difficulties and Gradual Progress
- The Unknown About Human Trafficking
- Trafficking: Human Trafficking and Main Age
- The Issue of Human Trafficking in Thailand and South Africa
- The Tragedy of Human Trafficking
- Vertex Connectivity of Fuzzy Graphs with Applications to Human Trafficking
- Child Pornography and Its Effects on Human Trafficking

Human Trafficking Essay Topics, Outline, & Example [2024]
“People for sale” is a phrase that describes exactly what human trafficking is. It also makes for an attention-grabbing title for an essay on this subject. You are going to talk about a severe problem, so it’s crucial to hook the reader from the get-go.
A human trafficking essay is an assignment where you discuss causes, effects, or potential solutions to the problem of modern slavery. A well-written essay can help raise awareness of this complicated issue.
In this article by our custom writing experts, you will find:
- 220 human trafficking essay topics;
- a writing guide;
- an essay sample;
- helpful info on human trafficking.
- 🔝 Top 10 Topics
- ❓ What Is Human Trafficking?
- ✍️ Topics for Any Essay Type
- 📝 Essay Outline
- 📑 Essay Sample
- ✏️ Frequent Questions
🔝 Top 10 Human Trafficking Essay Topics
- History of slavery.
- Slavery in literature.
- Human trafficking awareness.
- Modern slavery: legislation.
- Cultural background of traffickers.
- Globalization and human trafficking.
- Human trafficking vs. human rights.
- Modern slavery and kidnapping.
- Human trafficking rates by country.
- Human trafficking effects on the economy.
❓ What Is Human Trafficking?
The United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime determines human trafficking as the recruitment, transportation, harboring, or receipt of persons for the purpose of sexual slavery, exploitation, forced labor, organs removal, etc.

According to the recent reports of the Council of Europe, human trafficking rates have reached epidemic proportions . Millions of people are being trafficked for different reasons, primarily for sexual exploitation and forced labor. Women and children are the primary victims of human trafficking , which makes the problem especially acute.
One of the most worrying factors that directly impact the increase in trafficking rates is the growing number of refugees and migrants. It’s the largest seen since WWII, and it has intensified during the last years.
Types of Human Trafficking
Before you start writing your essay, it’s essential to review the forms of human trafficking. Knowing them will help you see the bigger picture. Here are the most common ones.
| The status of a person who is considered the property of someone else. | |
| Involuntary servitude usually maintained by the use of force or threats. | |
| A situation in which one is forced to perform commercial sex acts. | |
| The form of servitude which usually occurs in private households. | |
| Marriages arranged without one’s consent, often for material gain. | |
| A situation in which one is sold into marriage as a slave. | |
| Harvesting of one’s organs, such as the kidney, to sell them. | |
| A form of servitude in which one is forced to work to pay for one’s debt. |
Additionally, victims of human smuggling and child trafficking are often involved in various kinds of labor. While sexual exploitation is one of the major reasons for trafficking, it’s not the only one. These are also serious problems that you can focus on in your essay.
According to Polaris Project, there are 25 types of modern slavery . Among them are:
- Manufacturing in sweatshops;
- Agricultural work;
- Food and cleaning services;
- Beauty and massage salons.
Note that each of these practices has unique traits. It means there are specific methods of recruitment and control associated with them. Make sure to take all essential features of human trafficking into account when writing your essay.
The History of Human Trafficking
If we go back in time, we can see that human trafficking has a long history. Here are some of its milestones:
| During the wars of conquest in ancient Egypt, Rome, and Greece, the defeated peoples were made slaves. Their children were brought up for military service, and women were either sent to slavery or forced to prostitute. | |
| In the Middle Ages, slavery and human trafficking took several different forms. After the Christianization of Europe, the church tried to stop this practice. However, it still flourished in the Islamic world. | |
| Church bans didn’t stop Christian slavers. They engaged in human trafficking from non-Christianized countries to African and Muslim Spain. The beginning of America’s colonization also contributed to the slave trade. | |
| Unfortunately, these phenomena still exist. If you think that slavery only concerns developing countries, you are wrong. In its report, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime . It’s true even for the most progressive countries of North America, Western Europe, and Australia. |
As you now know, human trafficking is inextricably linked to other crimes against human rights. And the eradication of this phenomenon depends on both governments and ordinary citizens.
What Is Being Done to Stop Human Trafficking
In recent decades, a lot has been done to curb slavery. The United Nations General Assembly has established the World Day against Trafficking in Persons on July 30 . It was done to raise awareness of the situation and promote and protect victims’ rights.
One of the essential frameworks used to combat human trafficking is the 3P: prosecution, protection, and prevention .
| Criminalization of all human trafficking forms. Holding traffickers accountable by imposing prison sentences. | ||
| Identification of victims. Provision of support and safety to victims and their families. | ||
| Protection of at-risk populations. Engaging the private sector in fighting against human trafficking. |
Sometimes “ partnership ” is added as the fourth P. Since human trafficking became a pandemic, it requires a combined effort of people working together to overcome this problem. You can learn more about the 3P paradigm from this article by the US Department of State .
You may ask, “What can I do?” Here are some ways in which anyone can help fight human trafficking:
- In each country, there is a hotline where you can report on a known case of human trafficking or an attempt at recruiting.
- Be attentive to various kinds of controversial proposals and promises of a better life.
- Try to avoid bad company.
These recommendations may seem simple, but they can help you stay away from danger, spread awareness, and even save lives.
Before you start writing a human trafficking essay, you need to find a compelling topic. Check out the following list of topics and prompts and choose a subject that interests you.
✍️ Human Trafficking Topics for Any Essay Type
Human Trafficking Argumentative Essay Topics
- We should let survivors inform the public about the dangers of trafficking.
- State laws should protect the rights of trafficking survivors.
- Victim behavior is not the reason for the actions of criminals.
- Present medical facts about the ability of humans to survive a trauma.
- What psychological techniques do criminals use to lure victims?
- School is a safe haven for children from disadvantaged families.
- High social status is not a guarantee of protection against traffickers.
- Deception as a tool for controlling victims of modern slavery.
- Family can provide significant support to a victim of human trafficking.
- Physical violence and threats are the chief tools for controlling traffickers.
- Health workers should follow safety rules when rescuing trafficking victims .
- Countries providing financial advantages for anonymous economic activities should be held accountable.
- Psychologists should comply with ethical standards when assisting victims of trafficking.
- Countries with high trafficking rates should develop maps showing hotspots.
- Victims of modern slavery are not to blame: justification from the criminal perspective.
- Whom should we hold responsible for what happens to the victims in captivity?
- Will economic support for vulnerable groups help reduce the level of human trafficking?
- Prolonged captivity reduces the chances of adaptation after release.
- Exercise and physical activity help victims of trafficking to overcome trauma.
- Medication alone is ineffective in combating PTSD among trafficking victims.
Human Trafficking Argumentative Essay Prompts & Tips
- Who is responsible for human trafficking—the government, police, or society? There is no sufficient progress in stopping human trafficking. This is mainly due to the absence of an unequivocal opinion about who is responsible for the situation. Give your own ideas in this essay.
- The need to inform the public about human trafficking. Demonstrate the necessity to convey this information to the masses. You can also suggest ways of doing it.
- Immediate assistance for the victims of modern slavery. Show why it is important to provide psychological aid to rescued victims. What is the role of nurses and community organizations in it?
- Psychological help to victims of human trafficking: group therapy. Group therapy is based on awareness and acceptance of trauma. These actions are the basis of PTSD treatment. Decide whether it’s the optimal solution for victims’ psychological rehabilitation.
- Countries with widespread human trafficking should develop appropriate laws. Legislation changes are a crucial element of an integrated approach. In this essay, provide a list of existing laws and possible new regulations.
- The devastating impact of modern slavery. Describe the disastrous consequences that victims of human trafficking face. Find stories describing their lives in various media. How did they become victims? What happened to them after release from captivity?
- Tightening police measures as a way to stop human trafficking. Women and children are especially vulnerable targets for traffickers. Demonstrate the need to enable the police to protect them better.
- The high rate of trafficking indicates a high crime rate in a country. Determine which countries have the highest human trafficking rates. What are the related crimes observed there? Is there a correlation?
- The use of technology to catch criminals and traffickers. In this essay, discuss technologies that can help officials stop traffickers. For instance, satellite imagery allows identifying places of victims’ detention.
- International financial law is one of the best ways to stop human trafficking. Would the right to disclose anonymous bank accounts help reduce such crimes? What new laws and agreements are required to allow this?
For an argumentative essay, you need to conduct extensive research and present evidence to support your claim (check out our argumentative essay guide to learn more.) Here are the main steps:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. Identify the sides of the argument. | |
| ✔️ | State which side you support and why. | |
| ✔️ | Provide evidence and give reasons why your claim is correct. Additionally, present an opposing viewpoint. Show its drawbacks as well as aspects that you agree with. | |
| ✔️ | Restate your thesis and mention that other viewpoints are also valid. |
Human Trafficking Persuasive Essay Topics
- An anti-trafficking tax will help decrease the modern slavery rates.
- Is preventing new cases of slavery more critical than saving victims?
- Modern slavery is a serious problem that the CIA should address.
- Ignoring human trafficking is the same as neglecting Nazism.
- Forced labor is an economic problem as it is caused by poverty.
- Border control no longer solves the problem of forced labor.
- Should producers of weapons pay an anti-trafficking tax?
- Imprisonment for paying for escort services will stop human trafficking.
- Will stricter gun control laws help stop human trafficking?
- Victims of human trafficking should receive lifetime financial compensation.
- Human trafficking is a national problem that requires coordination of efforts.
- Treatment of human trafficking victims is a responsibility of society as well as psychologists.
- Two-year state-funded hospital treatment will help survivors to cope with the trauma.
- Are social networks a determining factor in the spread of human trafficking?
- Assess gender disparity in using the labor of human trafficking victims.
- Did the political polarization of society lead to an increase in people smuggling?
- Immigration laws are an effective means of combating modern slavery.
- Human traffickers’ family members capable of domestic violence should share responsibility with criminals.
- Civil and human rights protection laws do not sufficiently address human trafficking.
- People smuggling is not a crime from the criminals’ perspective: is this statement true?
Tips & Persuasive Essay Prompts Related to Human Trafficking
- The President must take personal responsibility. The problem of human trafficking is more acute than ever. It requires the immediate intervention of the President and Vice President. For example, they can declare the upcoming year the year of the fight against human trafficking.
- Criminals guilty of human trafficking should be kept in special prisons. The government should create special jails for rapists and human traffickers with a stricter regime. Moreover, we should prevent these criminals from becoming part of society again. Is this proposal fair?
- Trafficking should be punished with life imprisonment . Today, life imprisonment is mainly reserved for murder. Should human trafficking be penalized to the fullest extent?
- Can self-defense lessons help to avoid the risk of being captured by traffickers? Do you agree that schools should introduce a martial arts training system?
- State laws should permit surveillance in regions with high trafficking rates. Debate whether security is more important than the right to anonymity. Should the government allow the police to access people’s data?
- Public organizations that help the survivors should take official responsibility. If non-governmental associations take it, they can receive financial support. It will help them cooperate more effectively with the police. Do you agree?
- The existence of human trafficking in a country: deontology, utilitarianism and egoism. The United States is officially a democracy. However, the human trafficking rates show that America is close to a feudal society. Criminal ties among the upper class also enforce it.
- Fines as a way to motivate social workers and patrol officers to fight human trafficking. Many activists and police officers work in areas with high human trafficking rates. Do you agree that governments should fine them? Would a system of moderate fines motivate them to be more responsible?
- People who cannot pay rent are easy targets for traffickers. The government should prevent homelessness to combat human trafficking. For instance, it can compensate for the rent of vulnerable demographics.
- Homelessness as the main reason for being captured by traffickers. Homelessness deprives a person of protection. States with the highest human trafficking rates should start building shelters for the homeless. The state should provide them with food, clothing, jobs, and education. This way, traffickers won’t capture them into slavery.
A persuasive essay aims to convince the reader to share your opinion. You can do it by citing facts and statistics (check out our persuasive essay guide for more info.) Here’s how to write it:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. State which side you’re on. | |
| ✔️ | Summarize your claim in one sentence. Say why the readers should agree with your viewpoint. | |
| ✔️ | Give reasons why your claim is correct. Make use of facts as well as emotions. | |
| ✔️ | Restate your thesis and finish your essay with a statement appealing to readers’ feelings. |
Human Trafficking Informative Essay Topics
- How do international organizations fight modern slavery?
- Human trafficking in developed African countries.
- Outline the demography of human trafficking in the US .
- How does society stigmatize trafficking survivors?
- Fair trade as a way to combat modern slavery.
- Sex trafficking from a feminist perspective.
- The role of photography in the fight against forced labor.
- Fighting human trafficking on the dark web.
- Media coverage of human trafficking: ethical aspects.
- Review how anyone can help combat human trafficking.
- Association of human trafficking with social insecurity.
- How can medical institutions provide safety to victims of trafficking?
- Review the political and economic effects of human trafficking in the US.
- What lessons can the US learn from the trafficking situation in Eastern Europe?
- Forced labor and higher education in the US: programs for survivors.
- What US laws protect victims of slavery and define criminal activities?
- Review government statistics on forced labor in the US over the last five years.
- Which American states have the highest human trafficking rates?
- Modern slavery in the Arab world: from ancient times to modern days.
- Using technology to combat forced labor: the latest solutions.
Tips & Informative Writing Prompts for Human Trafficking Essays
- Measures that governments can take to reduce human trafficking. Review legal and informative measures to combat modern slavery. You can base this essay on reports from official government agencies.
- Human trafficking: types, symptoms , and effects. For this essay, present the kinds of trafficking according to the official categorization. It includes divisions according to age, gender, and type of forced labor. You can also describe the symptoms commonly found in victims.
- The history of human trafficking: from ancient times to the 21 st century. Start by describing ancient cultures that used forced labor. Alternatively, you may focus on the history of slavery in the US. Include the latest statistics on reported cases of human trafficking.
- Human trafficking and fundamental humanistic values. Outline humanistic values that are violated by forced labor. Back it up with arguments drawn from the works of famous humanists.
- What are the consequences of human trafficking for victims? Describe the trauma that people develop while in captivity. Use reports from national and global organizations. What physiological symptoms are associated with adaptation after release?
- How does the US deal with the problem of reporting on forced labor? Present ways of communicating the risks of human trafficking. Base this essay on government anti-trafficking reports. Include a list of trafficker indicators and other red flags.
- Environments that put a person in danger of becoming a victim of human trafficking. These include unemployment , homelessness, and the absence of immigration status. You can base this essay on data from governmental reports.
- Informing the population as means of reducing human trafficking rates. Does informing people actually reduce the number of potential victims? Review the best informing strategies used by community organizations.
- Why are migrants the most vulnerable population group in terms of human trafficking? In this essay, provide information on migrants’ life circumstances. Mention the aspects that make them the most vulnerable demographic. Examples include unemployment and insecurity before the law. You can also present the most common schemes by which traffickers capture migrants.
- New approaches to mitigating the effects of modern slavery in psychotherapy. Describe what methods therapists use to help slavery victims. You can present a list of optimal practices for restoring the integrity of survivors’ personalities. For this essay on human trafficking, use scientific articles and reports from practicing therapists.
An informative essay should educate the reader on something they didn’t know before. Have a look at this outline:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. | |
| ✔️ | Explain your topic in one sentence. | |
| ✔️ | Present facts, statistics, and other evidence necessary to explain the topic in detail. Don’t include your personal opinion. | |
| ✔️ | Synthesize your essay’s main points. |
Topics for an Expository Essay on Human Trafficking
- Assess social adaptation methods for victims of sexual slavery.
- Social adaptation of men who worked for traffickers in captivity.
- Police memo: evidence sufficient to detain a trafficker.
- Describe how to identify a trafficker based on 7 criteria.
- Power of the image: photo reports on human trafficking.
- Anonymous story of a sexual slavery survivor.
- Present a psychological and demographic portrait of a trafficker.
- Describe the conditions of human traffickers’ detention.
- Dealing with trauma in children who have been in labor slavery.
- Human trafficking in the Southern and Northern states.
- How to restore citizenship and documents after release from captivity.
- How can human trafficking survivors get free medical care?
- Who is more effective in stopping human trafficking: government agencies or community organizations?
- Being in captivity during the war, in forced labor, or sexual slavery: psychological consequences.
- Gender differences in human trafficking victims’ labor.
- Modern slavery’s connection to the criminal underworld in the Northern states.
- Enumerate the reasons why homeless people can end up in captivity.
- How many years does adaptation take for human trafficking survivors?
- Explore the modern meaning of the word “slavery.”
- Discuss ways of psychological support for the families of slavery victims.
Modern Day Slavery Writing Prompts & Tips for Expository Essays
- Human trafficking and modern slavery: real stories told by the media. Review several articles about falling into slavery. You can focus on press coverage from the 2010s. The stories of survivors will speak for themselves.
- Non-governmental organizations of the USA assisting victims: the power of community . Present five influential organizations from California, Texas, Florida, Ohio, and Nevada. Assess the personal contributions of staff. What is the role of local communities?
- How to help a friend if they’ve become a victim of human trafficking. In this essay, list tactics and strategies for assisting forced labor victims. Pay particular attention to compliance with safety regulations.
- What is it like to be a forced labor victim? A more creative task is to describe the situation from the inside. Can victims try to escape and free themselves from slavery? What is the role of psychological pressure from traffickers? How can an ordinary person cope with such a monstrous challenge?
- Prostitution, forced labor, and organ trafficking: a comparison. In addition, describe what forms of modern slavery prevail in different countries.
- Therapy methods in human trafficking survivors. Review what therapy practices are the most suitable for working with the survivors.
- An overview of common human trafficking schemes. These often involve vulnerable demographics, including illegal immigrants and adolescents from underprivileged communities.
- In what conditions do human trafficking victims live? In this paper, explain how life in captivity affects one’s mental health. Determine the connections between trauma and the body’s response to it.
- Ways of integration of human trafficking survivors. Review the best strategies for their adaptation to everyday life. Give examples of social adaptation that include education and employment.
- Human trafficking in the Southern and Border States. Study the situation in Texas, California, Florida, Georgia, and Arizona. Then, describe how to solve the problem. Don’t forget to emphasize the role of social work with illegal migrants.
An expository essay includes a thesis statement, evidence, and a logical conclusion. You can also use elements of creative writing in your paper (feel free to read our expository essay guide for more info.) Here are the main steps:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. | |
| ✔️ | Identify the main problem or points of comparison that you will discuss in your essay. | |
| ✔️ | Present statistics, facts, and other evidence necessary to describe the main issue, its causes, effects, or solutions. | |
| ✔️ | Synthesize your essay’s main points. |
Human Trafficking Research Paper Topics
- Survival in an unfamiliar city: is an escape from slavery possible?
- What prevents citizens from recognizing victims of human trafficking?
- Are monthly payments for human trafficking survivors justified?
- Dietary adaptation for malnourished forced labor survivors.
- How do the police investigate slavery markets?
- Economic levers to combat human trafficking: practical approaches.
- Describe global criminal connections that lead to modern slavery.
- Being in captivity leads to psychological trauma inherited by victims’ children.
- The use of figureheads on social media is a successful tactic against traffickers.
- Five app projects that will help avoid becoming a human trafficking victim.
- We should ban goods produced by forced labor worldwide.
- Human trafficking transportation problems as an opportunity to catch criminals.
- Research the use of symbolic language in informing victims of human trafficking.
- Funding for the installation of video surveillance systems to catch traffickers.
- People from what socio-economic background are the most vulnerable to child labour and exploitation?
- How can we combat human trafficking during a pandemic?
- Ethics of business and economic relations as a way to combat slavery.
- Informing vulnerable groups about human trafficking and attracting them to cooperation.
- Coordinated interaction of police departments is the key to success in combating people smuggling.
Human Trafficking Research Paper Prompts & Tips
- Deficiencies in US law determine success or failure in the fight against human trafficking. US legislation on human trafficking includes several rules. International acts and agreements also guide it. Nonetheless, the US laws, especially in the leading states, require urgent revision.
- Human trafficking as modern slavery: history repeating itself. Draw analogies between the trends and schemes from the past and the present. What historical practices can be effective in combating slavery? In particular, this concerns the anti-slavery movement and public awareness.
- Domestic human trafficking in the US shows increasing tendencies. Here, analyze the growth of domestic human trafficking cases. Demonstrate the need to create new approaches to catch criminals.
- Technology companies can stop human trafficking. The luring of victims often occurs on social media. Should social networking companies be penalized for failing to act against criminals?
- Can social media campaigns help protect potential victims? It’s necessary to create a program that will inform users about the dangers of trafficking. This method of targeted communication can be very effective.
- City officials should be ready to engage in the fight against modern slavery. Provide examples of American cities that are actively fighting human trafficking. What approaches and practices can be adopted throughout the US?
- Medical institutions are the main asset in combating human trafficking. More than three-quarters of victims receive medical care while in captivity. Health workers have the legal right to place a patient in a hospital and protect them from contact with criminals. This approach has been successful in many states.
- The police have insufficient funding to combat human trafficking. The police are conducting successful investigations, and there are many cases of solved human trafficking crimes. The state can grant more money to the police to uncover more trafficking schemes. It will allow using more advanced technologies in search of criminals.

- Hotlines should be more accessible to victims of trafficking. Hotlines are highly effective in combating human trafficking. They are easy to find on the Internet, but captive victims rarely have access to the network. How can we improve this situation?
- Families of trafficking victims and their participation in the search. Demonstrate the need to establish a format for families’ closer cooperation with the police. Would it help to conduct police investigations more effectively? Should we allow families to conduct their own investigations?
- The US is responsible for the success of international cooperation against human trafficking.
To write a research paper, you study the available information, analyze it, and make conclusions. Here’s a human trafficking research paper outline:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. Define the terms that you will use throughout the paper. | |
| ✔️ | State the main focus and purpose of your research. | |
| ✔️ | Analyze the sources and evaluate them. Present your own findings and back them up with evidence. | |
| ✔️ | Synthesize your paper’s main arguments. State whether further research is needed. |
Causes of Human Trafficking Essay Topics
- Discuss psychological factors of human trafficking.
- What personal reasons make people become traffickers?
- Greed as a major reason for human trafficking.
- What are the major causes of sex trafficking?
- Substantial profit as one of the human trafficking root causes.
- Explore the reasons for forced marriages.
- How does social media promote people trafficking?
- Commercialized sex and its contribution to human trafficking.
- Does authoritarianism promote human trafficking?
- Compare the cases of human trafficking in the United States and Thailand.
- Explore the court cases of traffickers. Does the judicial system cope with its duties?
- Why are weak anti-trafficking policies the primary cause of people’s exploitation?
- Discuss the role of government in human trafficking.
- Investigate the reforms on human trafficking. How effective are these measures?
- Lack of relevant laws leads to more trafficking cases. Do you agree?
- Should legal punishments apply to victims as well as traffickers?
- Why is ethnicity one of the main factors of people trafficking?
- Explore the connection between drug addiction and slavery.
- Violent force and threats as major leverages of traffickers.
- Naivety leads to becoming a victim of traffickers. Provide your arguments.
Causes of Human Trafficking Essay Prompts & Tips
- What are the leading causes of human trafficking? Your essay may start with the definition of people trafficking. Think about social and economic factors. Dig into history to find the reasons. Most importantly, look at this issue from various angles.
- Explore poverty as one of the reasons for human trafficking. How does poverty influence people? Can it force them to behave illegally? What are people ready to do for money?
- Migration: is it a cause or a consequence of human trafficking? Some people are so eager to immigrate to developed countries that they can do anything. They are even ready to sell their children to get money or sell themselves into slavery. At the same time, others become traffickers to move to another country.
- Discuss the connection between human trafficking and education. Think about the following: If a person lacks education, they lack knowledge about their rights. They can be deluded more easily. Following this logic, these individuals can become desired prey for traffickers.
- What is the role of war in human trafficking? Do armed conflicts provoke or prevent the spread of slavery? How do they facilitate the development of this problem? Is smuggling flourishing in countries that are at war? These are excellent questions to start with.
- What are the effects of cheap labor demand? Supply and demand are two pillars of economics. If there were no need for a cheap working force, traffickers wouldn’t exploit people so easily. They force their victims to work almost for free while selling the goods at a high price.
- Investigate institutional racism as a root cause of people trafficking. Who is the most vulnerable social class? Naturally, these are marginalized groups. They lack protection at a constitutional level. That’s why they can become victims of traffickers.
- Cultural and social causes of human trafficking. For some nations, selling children, slavery, smuggling, and bonded labor are commonplace. In some countries, such as Uzbekistan, people are forced to work in the cotton fields by the authorities. If you do research, you will see many similar examples worldwide.
- How do natural disasters facilitate human trafficking? The consequences of some natural disasters force people to migrate and find alternative ways to earn money. Some of them have no other option but to let themselves be exploited.
- How does the absence of safe migration conditions assist people trafficking? Many people from developing countries want to move to the United States to achieve their American Dream. Traffickers delude fortune seekers, promising well-paid jobs and help in crossing the border.
Discussing human trafficking in a cause-and-effect essay is an excellent way to investigate this issue in detail. You can learn how to write it from our article on cause-and-effect essays . Here’s a recap:
| ✔️ | Give some background information regarding your topic. | |
| ✔️ | Point out one or several causes of the issue in question. | |
| ✔️ | In each paragraph, show how different phenomena affect one another. Or, enumerate the causes first and then discuss the effects. | |
| ✔️ | Synthesize your paper’s main points. |
Solutions to Human Trafficking Essay Topics
- How can employers help stop human trafficking?
- Producing films about slavery : is it a problem solution?
- How can we stop human trafficking by learning the indicators?
- How can people protect themselves from traffickers when going abroad?
- Why should employers stop using cheap labor?
- Compare and contrast solutions to labor and sex trafficking.
- The role of parents and caregivers in preventing forced labor.
- How can civic awareness stop human trafficking?
- What is more important: to persecute traffickers or to protect victims?
- In what ways can attorneys help stop people smuggling?
- Can creating a reliable online platform for job searching help reduce slavery?
- Educational curriculum : should students be taught how to indicate and prevent human trafficking?
- Investigate the list of goods produced by child exploitation as a form of human trafficking. How does this information influence people’s choices?
- Forewarned is forearmed: discuss the effectiveness of anti-trafficking non-profit websites.
- How can stricter validity checks on job-searching websites solve the issue of modern slavery?
- Can the implementation of severe punishments for human trafficking help to curb the problem?
- Legalization of prostitution as a way of preventing sex trafficking.
- How can timely identification of human trafficking indicators save the lives of the victims?
- Fighting against poverty and unemployment as a means of preventing people smuggling.
- Watching documentaries about modern slavery as a problem solution.
Solutions to Human Trafficking Essay Prompts & Tips
- What are the primary solutions to human trafficking? Think about the following: How can this problem be solved on personal and national levels? It’s crucial to mention self-awareness , education, volunteering, and the role of charity organizations. You may also address the necessity to change the law.
- Human trafficking: an international approach. The issue of modern slavery is a global problem. That’s why it should be dealt with at the international level. The authorities all over the world should unite to fight against people trafficking.
- Compare and contrast the effectiveness of volunteering and adopting new policies. On the one hand, volunteers attract public attention to the issue of human trafficking. On the other hand, we should protect marginalized groups at the constitutional level. Otherwise, human trafficking will remain flourishing in the future.
- Coverage of human trafficking cases in social media. Is it a good idea for the victims to share their stories on Instagram, Twitter, or Facebook? How can it help prevent this issue? Could it lead to the stigmatization of these people by others? You can start by brainstorming these ideas.
- Discuss whether fundraising is an effective solution to human trafficking. Ponder on how holding a fundraiser helps bring awareness to the problem of modern slavery. What are some other benefits of fundraising, such as financial assistance?
- Donations help prevent human trafficking. Do you agree? Every person can donate some money, clothes, or even shelter for the victims of human trafficking. Business owners may ensure employment opportunities, giving these people a chance for a better future. Focus on the importance of psychological and legal assistance.
- How does the media help prevent human trafficking? The media attracts people’s attention to the problem. They become more aware and careful. The cases of victims are widely discussed, leading to more fundraising and volunteering .
- Explore the anti-trafficking legislation in the United States. Discuss its strengths and drawbacks. What could be changed or done better? Is it effective? How are the rights of marginalized groups protected? These ideas are only the tip of the iceberg.
- Education opportunities for disadvantaged groups as a way of preventing human trafficking. Should the government provide marginalized people with free education? How can it affect human trafficking? Discuss it in your essay.
- Why is a boycott an effective way of preventing human trafficking? If others start rejecting the goods produced by the victims of human trafficking, traffickers won’t get such huge profits. Everyone can make their contribution to the fight against this issue.
A problem-solution essay is particularly suitable for discussing modern slavery. Explore the facts and suggest how to stop this inhumane practice. Here’s how to write about problems and their solutions:
| ✔️ | Describe the problem that needs to be solved. Show why your topic is important. | |
| ✔️ | Introduce a solution to the problem. | |
| ✔️ | Use evidence to illustrate the solution’s effectiveness. | |
| ✔️ | Synthesize your paper’s main points. Show what would happen if your proposed solution is implemented. |
If you haven’t found a suitable topic, feel free to use our topic generator .
📝 Human Trafficking Essay Outline
Before you start writing, let’s have a look at some aspects to consider in your college essay on human trafficking. Here’s the basic template:
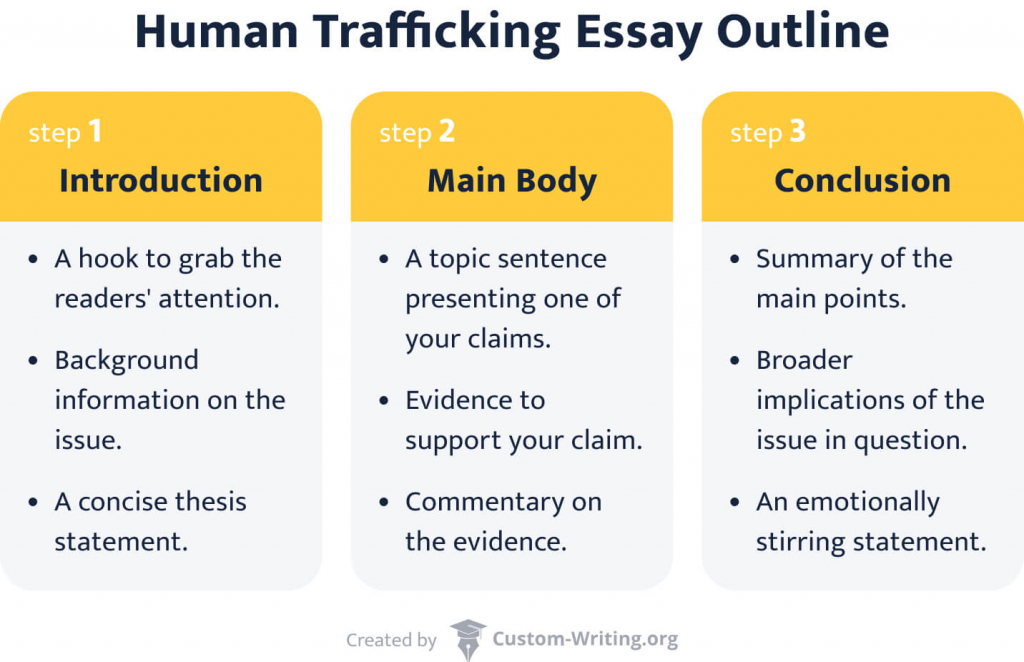
Human Trafficking Essay Introduction: How to Write
The most important part of an essay introduction is a hook. A perfect attention grabber for a human trafficking paper would demonstrate the seriousness of the problem right away. It, in turn, would make your audience eager to read on.
Have a look at some of the ideas for your essay’s hook:
- Cite statistical data related to the current situation with human trafficking.
- Start with a stirring quote to appeal to readers’ emotions.
- Pose a question related to your essay’s topic. Make the reader want to learn the answer.
Besides the hook, it’s logical to start your essay with some background information. This way, even an unprepared reader will understand your essay’s thesis. Think of what your audience may not know about your topic. It will help you determine what to include in this part of the introduction.
Here are some strategies:
- Tell about the countries and regions with the highest trafficking rates—for example, Thailand, the Philippines, India, South Africa, and Eastern Europe.
- Mention reasons behind this problem: unemployment, social discrimination, political instability, armed conflicts, etc.
- Give a solid definition of human trafficking or its specific type. It’s better to formulate your own one rather than take it from a dictionary.
It’s important to notice that your hook and background information should be relevant to your topic. Make sure these elements help to further the understanding of your essay’s main point.
Human Trafficking Essay Thesis
A thesis statement is your essay’s main point formulated in one sentence. It outlines the paper’s direction and provides an answer to the problem stated in the title. You place it at the end of the introduction.
A good thesis statement for a human trafficking essay usually presents the solution to a problem. However, the thesis’ contents depend on your essay’s type. For example, in an informative essay, you don’t need to prove or suggest anything. Instead, you say what you’re going to explain and how you’ll do it.
Once you’ve written the thesis statement, how do you determine whether it’s strong? Well, one way is to answer the questions from the following checklist.
| ✔️ | Make sure it’s not too vague or broad. Alternatively, if it’s too narrow, try clarifying it. | |
| ✔️ | Even if the title is phrased as a statement, it still implies a question that you should answer. | |
| ✔️ | A good thesis statement makes an argument that can be challenged. |
If your answer to all three questions is “yes,” you can be sure of your thesis’s effectiveness.
Finally, don’t forget that the rest of your essay should support your thesis. If necessary, you can rework your statement to better suit the body paragraphs, or vice versa.
Human Trafficking Essay: Main Body
How do you make your essay on human trafficking credible and persuasive? Naturally, you want to add evidence. Here’s how to incorporate it into your paper:
- It’s better to start collecting your evidence before you start writing. Once you’ve found all the necessary information, it will be easier for you to structure the paragraphs. The point is to focus each section on a single aspect.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence. It should present the main idea that you will then support with evidence. Ideally, your audience should be able to follow your logic by reading the topic sentences alone.
- Finally, add your evidence. It can be statistics, facts from scholarly articles, quotes, or even anecdotes. Follow it with your explanation of this information. Say how it relates to the topic and supports your thesis.
Human Trafficking Essay Conclusion: Dos & Don’ts
A strong conclusion is a crucial part of any writing. In this final part, you synthesize your essay in a few sentences while adding a twist to it. If a conclusion is done right, it can leave a lasting impression on your readers.
This dos and don’ts list will help you write a perfect conclusion for a human trafficking essay. Check it out:
| ✔️ | It will inspire your readers and may even prompt them to take action. However, avoid making it sound too sentimental compared with the rest of your essay. |
| ✔️ | For example, you can give some advice on how anyone can help fight human trafficking. |
| ✔️ | For example, in the case of human trafficking, you can point out how fighting it will help solve global human rights problems. |
| ❌ | Instead, show how everything you’ve written fits together. |
| ❌ | Discuss all the critical points in the body paragraphs. |
| ❌ | Clichés such as these make your writing trite. |
Don’t forget to introduce statistics in your essay on human trafficking. It’s available on numerous websites of governmental and non-governmental organizations dealing with the problem. You can find more ideas for your paper in our article about writing a child labor essay.
📑 Human Trafficking Essay Examples
We’ve prepared an outstanding sample essay on human trafficking that you can use as inspiration. You’re welcome to download the PDF file below:
Human trafficking is a global problem. It deprives millions worldwide of their freedom and dignity. Traffickers use various tactics to lure children, men, and women into the trap. For that reason, precaution measures should be taken. It is crucial to educate as many people as possible on the issue to ensure everyone’s safety.
Share your thoughts about human trafficking with us! Why do you think slavery is still in demand? If you were a politician, what would you do to prevent it? Tell us your suggestion in comments below!
Learn more on this topic:
- Canadian Identity Essay: Essay Topics and Writing Guide
- Nationalism Essay: An Ultimate Guide and Topics
- Essay on Corruption: How to Stop It. Quick Guide
- Murder Essay: Top 3 Killing Ideas to Complete your Essay
- World Peace Essay in Simple English: How-to + 200 Topic Ideas
- Gun Control Essay: How-to Guide + 150 Argumentative Topics [2024]
- Student Exchange Program (Flex) Essay Topics [2024]
✏️ Human Trafficking Essay FAQ
Human trafficking is a topical issue in society because it’s an inhumane practice that affects millions of people worldwide. Writing on that topic helps understand why it is happening and what can be done about it.
Human trafficking is a very complex phenomenon driven by various economic, social, cultural, and other causes. Factors of a high human trafficking risk are poverty, social instability, exclusion, and lack of education and awareness (e.g., in South Africa.)
Pretty much every fact connected with human trafficking is horrifying. Nearly everything about this phenomenon can be considered a danger. As human trafficking is a form of slavery, it would be naive to presume there are any positive effects whatsoever.
Human trafficking is a serious problem, and you should be able to express your opinion on it. For example, it can be done in the form of an argumentative essay. It is vital to avoid using too many emotionally charged words. Remember to stay objective and provide facts and examples.
🔗 References
- Tips for Organizing an Argumentative Essay: Judith L. Beumer Writing Center
- Human Trafficking Essay: Bartleby
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment: NHS
- Embrace AI, Technology to Beat Human Traffickers: Reuters
- Essay Writing: Purdue University
- What Is Human Trafficking: Anti-Slavery International
- Human Trafficking: Encyclopedia Britannica
- End Human Trafficking: United Way
- Human Trafficking Facts: CRS
- OSCE Resource Police Training Guide: Trafficking in Human Beings: OSCE
- Study on the Economic, Social and Human Costs of Trafficking in Human Beings Within the EU: Europa.eu
- Writing a Research Paper: University of Wisconsin-Madison
- Human Trafficking: FBI
- Human Trafficking: Causes and Implications: Research Gate
- Writing a Persuasive Essay: Hamilton College
- Parts of an Informative Essay: Pen and the Pad
- Expository Essay Outline: Columbus City Schools
- Introductions & Conclusions: University of Arizona
- Writing the Introduction: Monash University
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Indiana University Bloomington
- Writing a Thesis Statement: Piedmont University
- 4 Ways Anyone Can Fight Human Trafficking: The Muse
- What Fuels Human Trafficking?: UNISEF USA
- What Is Human Trafficking?: Homeland Security
- Psychological Tactics Used by Human Traffickers: Psychology Today
- Psychological Coercion in Human Trafficking: An Application of Biderman’s Framework: NIH
- Warning Signs of Human Trafficking: State of Nevada
- Human Trafficking: US Immigration and Customs Enforcement
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![thesis statement on human trafficking 256 Advantages and Disadvantages Essay Topics [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiling-young-woman-284x153.jpg)
Is globalization a beneficial process? What are the pros and cons of a religious upbringing? Do the drawbacks of immigration outweigh the benefits? These questions can become a foundation for your advantages and disadvantages essay. And we have even more ideas to offer! There is nothing complicated about writing this...

This time you have to write a World War II essay, paper, or thesis. It means that you have a perfect chance to refresh those memories about the war that some of us might forget. So many words can be said about the war in that it seems you will...
![thesis statement on human trafficking 413 Science and Technology Essay Topics to Write About [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/scientist-working-in-science-and-chemical-for-health-e1565366539163-284x153.png)
Would you always go for Bill Nye the Science Guy instead of Power Rangers as a child? Were you ready to spend sleepless nights perfecting your science fair project? Or maybe you dream of a career in science? Then this guide by Custom-Writing.org is perfect for you. Here, you’ll find...
![thesis statement on human trafficking 256 Satirical Essay Topics & Satire Essay Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/classmates-learning-and-joking-at-school-e1565370536154-284x153.jpg)
A satire essay is a creative writing assignment where you use irony and humor to criticize people’s vices or follies. It’s especially prevalent in the context of current political and social events. A satirical essay contains facts on a particular topic but presents it in a comical way. This task...
![thesis statement on human trafficking 267 Music Essay Topics + Writing Guide [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/lady-is-playing-piano-284x153.jpg)
Your mood leaves a lot to be desired. Everything around you is getting on your nerves. But still, there’s one thing that may save you: music. Just think of all the times you turned on your favorite song, and it lifted your spirits! So, why not write about it in a music essay? In this article, you’ll find all the information necessary for this type of assignment: And...

Not everyone knows it, but globalization is not a brand-new process that started with the advent of the Internet. In fact, it’s been around throughout all of human history. This makes the choice of topics related to globalization practically endless. If you need help choosing a writing idea, this Custom-Writing.org...

In today’s world, fashion has become one of the most significant aspects of our lives. It influences everything from clothing and furniture to language and etiquette. It propels the economy, shapes people’s personal tastes, defines individuals and communities, and satisfies all possible desires and needs. In this article, Custom-Writing.org experts...

Early motherhood is a very complicated social problem. Even though the number of teenage mothers globally has decreased since 1991, about 12 million teen girls in developing countries give birth every year. If you need to write a paper on the issue of adolescent pregnancy and can’t find a good...

Human rights are moral norms and behavior standards towards all people that are protected by national and international law. They represent fundamental principles on which our society is founded. Human rights are a crucial safeguard for every person in the world. That’s why teachers often assign students to research and...

Global warming has been a major issue for almost half a century. Today, it remains a topical problem on which the future of humanity depends. Despite a halt between 1998 and 2013, world temperatures continue to rise, and the situation is expected to get worse in the future. When it...

Have you ever witnessed someone face unwanted aggressive behavior from classmates? According to the National Center for Educational Statistics, 1 in 5 students says they have experienced bullying at least once in their lifetime. These shocking statistics prove that bullying is a burning topic that deserves detailed research. In this...

Recycling involves collecting, processing, and reusing materials to manufacture new products. With its help, we can preserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and save energy. And did you know that recycling also creates jobs and supports the economy? If you want to delve into this exciting topic in your...
Amazing information, ladies and gentlemen.
Thank you so much for your help. I really appreciate.

Hi, Thank you very much indeed for stopping by and leaving this kind comment. Don’t hesitate to browse our blog for even more useful materials or even subscribe to our bi-monthly newsletter to receive valuable info directly to your inbox. Kindest regards. Have a nice day!
You have a fantastic website! I’ve found here lots of helpful posts. This post on writing essays on human trafficking is my salvation. Thanks for the tips!
Perfect tips on writing essays on human trafficking! Thank you so much for your help! I really appreciate what you do!
Human Trafficking - Essay Samples And Topic Ideas For Free
Human trafficking, a grievous global issue, involves the trade of humans for forced labor, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation. Essays might delve into the mechanisms, global networks, and the socio-economic or political conditions enabling human trafficking. Moreover, discussions could extend to international and local efforts to combat human trafficking, support victims, and the legal frameworks surrounding human trafficking and modern slavery. A vast selection of complimentary essay illustrations pertaining to Human Trafficking you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.

Illegal Immigration and Human Trafficking
Human trafficking comes in many different forms such as sex trafficking for the purpose of sexual exploitation. Sex exploitation is based on the interaction between a trafficker selling an individual, victim being smuggled to customers for sexual services. Labor trafficking includes situations of debt bondage, forced labor, and involuntary child labor. Labor trafficking uses violence, threats, lies, and other forms of coercion to force people to work against their will in which most cases have no knowledge on the activities […]
Human Trafficking in the Age of Social Media
Human trafficking is an everyday recurrence. Lots of people have heard about Human trafficking, but aren't sure how much of a global issue it truly is. The average age a teen enters the sex trade in the U.S. is 12 to 14-year-old(Do something-Human Trafficking), better known as your teenage or adolescent years. Human trafficking is a problem that must be solved for people at any age, though it starts with adolescents as a result of social media platforms and vulnerability […]
Modern-day Slavery in the United States
Human trafficking is a global issue and is often referred as modern-day slavery, in the United States there is an estimate of 244,000 to 325,000 minors that are at risk for sexual exploitation, with an estimated 199,000 incidents of sexual exploitation of a minor. (In Our Backyard) These victims come from all walks of life, looking for love or hopes of a new life. Minor victims are vulnerable and considered an easy target by their traffickers. (Carpenter) As one trafficker […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Preventing Individuals from the Dangers of Human Trafficking
A topic that most people probably go through their day without paying much attention to is that of human trafficking. Many individuals do not think that human trafficking will ever affect them nor their families. However, the reality is that such a tragic event could happen to anyone regardless of age, race, or gender, it could occur at any given place or time, and the perpetrator could be absolutely anyone. Human trafficking has become a prominent problem in the United […]
Human Trafficking in the Philippines
What if you were given the most appealing chance to escape poverty and took it, just to find out your efforts landed you into the hands of human traffickers? Human trafficking is a large issue dealt with by countries all over the world, including the Philippines, a tier 1 country that is actively changing their methods of the battle against it. For example, one instance of this took place in 2003 where the country passed the "Anti-Trafficking in Persons Act, […]
Modern Slavery – Prostitution, Labor, and Debt Bondage
Human trafficking is a form of modern slavery that serves involuntary solitude, forced prostitution, labor, and debt bondage that happens in the shadows of Charlotte, NC. Involuntary solitude takes away the personal freedom that you have a right as a person. Out of all crimes, Human Trafficking is the fastest growing business of organized crime which can include transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises. It happens through fraud; initiating false promises and/or working conditions, being forced; any […]
Human Trafficking in the United States
Some people have a fear of heights, spiders, or even the dark but in America, the level of fear is far greater. Lions, tigers, and bears are the least of the worries for Americans due to the multiplicative issue of sex trafficking. Sex trafficking includes the purchase of women, children, and in some cases men to be used as sex slaves. Instead of recognizing victims and giving them proper assistance, United States citizens and lawmakers disavow human trafficking. Among the […]
What is Human Trafficking?
Well, human trafficking is any form of recruiting, transporting, or kidnapping, in which the intent is to be held against will, threat, or coercion with payments or benefits to control another person for exploitation. Human trafficking can be practiced in various ways, such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, slavery of different forms, and organ trafficking (1). One issue the U.S. has with this topic is that there is such a small number of victims and their traffickers, which creates contradicting […]
The Impact of Slavery
The participation of England in the slave-trade began in the early 16th century, with the country, on par with Portugal, being the most successful in the trading business until the abolishment of Slavery in the UK in 1807. The original interest of the British traders was more-so with the produce from within Africa, such as ivory and gold, rather than the people of Africa itself. The interest shifted however when the demand for labourers increased and rich British figures became […]
What is Human Trafficking
When people bring up the topic of crimes, the first thing that comes to their mind is gun violence, theft, rape, and murder. A major crime that is not discussed enough is Human trafficking and many people do not recognize that it is not only happening in the middle east, but also in South America and other third world countries. This misdeed can happen to anyone no matter their race, financial background, gender, or sexual orientation and still goes on […]
Human Trafficking and its Relationship with Sex Trafficking
This paper is about Human Trafficking and its relationship with Sex Trafficking. The best way to understand what Human Tracking is would be to define Human Trafficking and give a brief history of Human Trafficking and how long it has actually been going on and what has changed since the early days of Human Trafficking and who is affected by it. This paper will cover which states are the worst for Human trafficking and if there is clearly one state […]
Illegal Immigration and Crime
The United States border is always a topic when the subject is the illegal entry ( entering into a country ) in the United States. Some people defend that building a wall will reduce the criminal activities in the country, while others defend that to stop illegal entry, ( entering into a country) could lapse the United States economy (the process of people making, selling, and buying things). To state that whether criminal activities increases by illegal ( entering into […]
The Construction of Human Trafficking as a Big Social Issue
Specific Purpose: Cognitive, To inform my audience about what is human trafficking and its importance, how human trafficking works, and the statistics on human trafficking. Thesis: Human trafficking is a big social issue, so today, I will explain my knowledge about what is human trafficking and why is it serious, how human trafficking works, and the statistics on human trafficking. Preview: In today's society, It is very scary to be going out anywhere because you never know what is going […]
Human Trafficking in Venezuela
Abstract This research examines the injustices and dehumanization of Latina/os in Venezuela, focusing on its phenomenon of human trafficking. The nation has become a victim of its own economic, social, and political corruption. The trafficking of persons is believed to be the third-largest organized crime worldwide, encompassing many demographics. Human trafficking has plagued Venezuela for many years. This paper ultimately concludes and exposes the extent of the dilemma. The sources used for our research were found through the databases of […]
Societies Role in Human Trafficking
Human Trafficking is defined as the action/practice of illegally transporting people from one country/area to another, typically for the purpose of forced labor or sexual exploitation. Human trafficking is a $32 billion-a-year industry, with 300,000 Americans that are under the age of 18 being allured into the commercial sex trade every year. Society should begin educating the signs of a trafficked victim, go through trainings of how to help a victim, figure out where their products that they use come […]
Celebrity Influences on Human Trafficking
For years human trafficking has been an ongoing problem that people have been unaware of and now many celebrities stepping up to bring awareness to the cause, like Jada Pinkett Smith. Pinkett Smith, displayed in the image on the right, is an American actress who is married to actor Will Smith. In the image we can see Pinkett Smith at an event where her media influence is large. She heard about human trafficking through her daughter who had recently become […]
Spain Criminal Justice
Spain, one of the oldest and most successful countries in the world. One of the biggest countries in all of Europe, and one of the biggest tourist attractions in the world. The history of Spain can be traced back hundreds of years when monarchs ruled the country. Of course, over time many things have changed. The economy, politics, tourism, etc. But, one thing that obviously changed over time is there criminal justice system. How it has developed from the past […]
Human Trafficking in the Tampa Bay Area
The City of Tampa our beloved home where we should feel safe and together as one community. No matter which gender, race or age you are, living in Tampa overall portrays to be a peaceful city where families can stabilize their life and grow with successful opportunity. Tampa is home to multiple suburban communities where kids are raised with their neighbors and play together in their parks. However, when you sit on the park bench and lose sight on your […]
Human Trafficking and Child Welfare
Child victims of human trafficking are more likely to suffer from long term affects rather than adults due to the critic stages of development they may be going through. As time persists after the abuse occurred, strong defensive emotions, like anger and fear, can be associated within relationships the individual has that have no correlation to the abusive event (McCammon, McCammon, & Ramby, 2006). Children who have been abused or trafficked can begin to develop a sense of hypervigilance in […]
Inside the World of Human Trafficking
Have you ever been in a situation where you felt like an object being forced to do things you don't like or feel comfortable? Human trafficking is a big problem in the US and all over the world. Older women, even young girls, are being slaved to participate in a sex labor, labor trafficking, and even forced marriage. In the article, Human Trafficking: A Call for Counselor Awareness and Action it mentions Human Trafficking described as a form of modern-day […]
Human Trafficking in Arizona
Human trafficking is happening here Arizona, right in front of our noses. Let's start off by telling you a little bit more about human trafficking. Human trafficking is criminalized under the United States law, also under federal law, it is a crime to compel another person to provide labor, services, or commercial sex. Human trafficking is a form of modern slavery that is happening in every state, including Arizona. NHTH (National Human Trafficking Hotline), has been working with providers, law […]
How did Slavery Shape Modern Society?
Slavery has never been abolished from America's way of thinking. (Nina Simone) Slavery still exist till this day, from forced labor, sex trafficking, debt bondage, child soldiers, and domestic servitude. Although slavery was abolished in 1865 in the United States, slavery continues to be a worldwide issue from forced child labor, sex trafficking, and debt bondage. Thousands of people suffer every year resulting in injury, kidnapping, and even death so the question remains does slavery still exist to this day? […]
Combating Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is a problem that affects every country in the world, big or small. This practice has become very popular throughout the world because of labor needs and the want to have sex. People are frequently needed to perform labor and a lot of people struggle to meet their sexual needs and as a result they turn to human trafficking to get their fix. While the majority of people in the world recognize that this is a serious global […]
Victims of Human Trafficking and their Access to Healthcare
Access to healthcare has been a dilemma for many years in underdeveloped countries and communities. One reason is the feeble economical dynamics that people are faced with in that territory. However, one of the big issues that tends to hide in the shadows is the global epidemic of human trafficking around the world. There is an inadequacy of access to healthcare for the millions of victims where many of which are frequently predisposed of due to the horrendous conditions they […]
Confronting Human Trafficking in Bulgaria
Overview Human trafficking is a substantial issue in Bulgaria because Bulgaria is a country of transit for migrants who are leaving Eastern Europe to seek a better life and better socioeconomic conditions in wealthier countries in Western Europe (Central Intelligence Agency, 2018). Migrants are the most commonly targeted group for human traffickers in Bulgaria (Petrunov, Weitzer, & Zhang, 2014). Promoting just, peaceful and inclusive societies is a sustainable development goal established by the United Nations (United Nations, 2018). Addressing human […]
The Effects of Human Trafficking and Healthcare Providers
Freedom is inarguably the most treasured right in the United States. But each year, roughly 18,000 men, women and children are trafficked in the United States. Human trafficking is a public health concern that affects individuals, families and entire communities across generations. The health care system plays an important role in identifying and treatment victims of human trafficking; however, how trained are the medical professionals on how to identify and properly treat the victims to ensure a successful recovery? What […]

Why does Drug Trafficking Cause Gun Violence
There is a strong relationship between drug trafficking, drug use, and gun violence. The research attempts to come up with a solution for the research question why does drug trafficking cause gun violence. Most youths have been involved in the use of drugs like marijuana, stimulants, hallucinogens, crack cocaine, heroin, and cocaine hence being involved in violence including gun violence (Johnson, Golub, Dunlap, 2000) This research will play a major role in improving academic research, sow the existing causal effect […]
Victims of Human Trafficking
Limiting victimisation of human trafficking only to the period of traffic or transit of the victim would narrow the true essence of anti-trafficking laws. A sex worker, who was abducted/kidnapped, then trafficked and finally forced into the flesh trade, continues to be a victim of human trafficking and prosecuting him/her under prostitution laws would be penalising a victim of human trafficking. A criminal record for charges such as prostitution, disorderly conduct etc., under general criminal laws as well as specific […]
Human Trafficking in the Textile World
For thousands of years forms of slavery and human trafficking have existed; however, the it was noted best in the 1400s when the European slave trading industry began in Africa (""Timeline of Human Trafficking ). Slavery is defined as a condition in which individuals are owned by others, who control where they live and at what they work (What is Slavery?; the Abolition of Slavery Project ). Many argue that slavery does not exist today because it has been globally […]
Heinous Crime and Global Problem – Human Trafficking
Human trafficking, one of the most heinous crimes, is a global problem that is flourishing in many areas of the world including our local college campuses. The problem has infiltrated Arizona State University (ASU ) as female students have reported exploitation and coercion at university events by traffickers promoting prostitution. Aside from prostitution, students could be at risk of being abducted and exploited for other human trafficking crimes such as drug trafficking, enslavement, organ transplants, or forced labor. Human trafficking […]
Additional Example Essays
- Gender Inequality in Education
- The Oppression And Privilege
- Discrimination in Workplace
- Gender Inequality in the Medical Field
- Gender Inequality in the Workplace
- Essay About Theme for English B
- The Gender Pay Gap and the Equality
- Compare And Contrast In WW1 And WW2
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- How the Roles of Women and Men Were Portrayed in "A Doll's House"
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- Substance Abuse and Mental Illnesses
How To Write an Essay About Human Trafficking
Introduction to the complex issue of human trafficking.
Writing an essay on human trafficking requires a comprehensive understanding of its multifaceted nature. Human trafficking, a form of modern-day slavery, involves the illegal trade of humans for exploitation or commercial gain. In your introduction, outline the various forms of human trafficking, including labor trafficking, sex trafficking, and child trafficking. Acknowledge the global scope of this crime and its impact on individuals and societies. This introductory section should provide a clear foundation for your essay, highlighting the significance of the issue and the necessity of addressing it through various lenses, including legal, social, and human rights perspectives.
Analyzing the Causes and Consequences
The body of your essay should delve into the complex causes and consequences of human trafficking. Explore the various factors that contribute to human trafficking, such as poverty, lack of education, political instability, and demand for cheap labor and sexual exploitation. Discuss how human trafficking violates basic human rights and results in severe psychological, physical, and social consequences for victims. This part of your essay should be supported with facts, statistics, and real-life examples to provide a thorough understanding of the issue. It's crucial to maintain a respectful and sensitive tone, considering the severity and personal nature of the crimes involved.
Addressing Legal Frameworks and Global Responses
In this section, focus on the legal frameworks and global responses to human trafficking. Analyze the international laws and treaties, such as the Palermo Protocol, and national legislations that have been implemented to combat human trafficking. Discuss the roles of various international and non-governmental organizations in prevention, protection, and prosecution. Additionally, consider the challenges in enforcing these laws and the gaps that still exist in the global fight against human trafficking. This part of your essay should highlight the importance of a coordinated international response and the ongoing efforts to strengthen legal and practical measures.
Concluding with a Call to Action
Conclude your essay by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the critical need for continued attention and action against human trafficking. Highlight the importance of raising awareness, improving legal frameworks, and supporting victim rehabilitation. Encourage readers to consider their role in combating human trafficking, whether through education, advocacy, or supporting relevant organizations. A strong conclusion will not only provide closure to your essay but also inspire a sense of responsibility and urgency in addressing this global issue.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

5 Essays On Human Trafficking You Can Access Freely Online
Every country faces specific human rights issues, but human trafficking is a problem for every place on the planet. Wherever there’s poverty, conflict, a lack of education, or political instability, vulnerable people are at risk. Human trafficking is the world’s fastest-growing criminal industry. Sexual exploitation brings in most of the billions of dollars of profit, but forced labor also generates wealth. The universality of human trafficking doesn’t negate the fact that the issue is multi-faceted and as a multitude of root causes . Certain countries are more dangerous than others and certain people groups are more vulnerable. To learn more about specific human trafficking issues and solutions, here are five essays you can read or download for free:
“Human Trafficking and Exploitation: A Global Health Concern”
By: Cathy Zimmerman and Ligia Kiss
While labor migration can be beneficial to workers and employers, it’s also a hotbed for exploitation. In this essay from PLOS, the authors argue that human trafficking and the exploitation of low-wage workers have significant negative health impacts. Because of the magnitude of human trafficking, health concerns constitute a public health problem. Thanks to certain business models that depend on disposable labor, exploitation is allowed to flourish while protections are weakened. The essay states that trafficking initiatives must focus on stopping exploitation within each stage of labor migration. This essay introduces a special collection from PLOS on human trafficking and health. It’s the first medical journal collection on this topic. It includes pieces on child sex trafficking in the United States and the slavery of sea workers in South East Asia. Cathy Zimmerman and Ligia Kiss, the guest editors and authors of the first essay, are from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“Introducing The Slave Next Door”
By: Jen Birks and Alison Gardner
Published in a special issue of the Anti-Trafficking Review on public perceptions and responses to human trafficking, this essay focuses on Great Britain. According to the essay, there’s been a shift in what the public thinks about trafficking based on local reporting and anti-slavery campaigns. British communities are starting to realize how prevalent human trafficking is in their own backyards. The essay takes a closer look at the media and campaigns, how they’re representing cases, and what people are doing with the information. While specific to Britain, it’s a good example of how people can perceive trafficking within their borders.
Jen Birks is an Assistant Professor in media at the Department of Cultural, Media, and visual Studies at the University of Nottingham. Alison Gardner is at the School of Sociology and Social Policy at the University of Nottingham with a Nottingham Research Fellowship. She is part of the university’s Rights Lab.
“My Family’s Slave”
By: Alex Tizon
One of The Atlantic’s biggest stories of 2017, this essay tells a personal story of modern slavery. At 18-years old, Lola was given to the writer’s mother and when they moved to the United States, Lola came with them. On the outside, Tizon’s family was, in his words, “a poster family.” The truth was much darker. The essay sparked countless reader responses, including those of people who were once slaves themselves. Reading both the criticism and praise of the essay is just as valuable as the essay itself.
Alex Tizon died at age 57 years old before his essay was published. He had a successful career as a writer and reporter, sharing a Pulitzer Prize while a staff member at The Seattle Times. He also published a 2014 memoir Big Little Man: In Search of My Asian Self.
“Vietnam’s Human Trafficking Problem Is Too Big To Ignore”
By: Thoi Nguyen
In November 2019, 39 Vietnamese people were found dead in a truck container. They were identified as victims of a human trafficking ring. In Nguyen’s article, he explores the facts about the severity of human trafficking in Vietnam. For years, anti-slavery groups have warned the UK about a rise in trafficking, but it took a tragedy for people to start paying attention. Nguyen discusses who is vulnerable to trafficking, how trafficking functions, and Vietnam’s response.
Freelance journalist Thoi Nguyen is a member of Chatham House and a member of Amnesty International UK. In addition to human trafficking, he writes about the economy, finance, and foreign affairs. He’s a specialist in South East Asian geopolitics.
“History Repeats Itself: Some New Faces Behind Sex Trafficking Are More Familiar Than You Think”
By: Mary Graw Leary
This essay highlights how human trafficking isn’t only a criminal enterprise, it’s also an economic one. Leary looks specifically at how businesses that benefit (directly or indirectly) from slavery have always fought against efforts to end it. The essay focuses on government efforts to disrupt online sex trafficking and how companies are working to prevent that from happening. Human trafficking is a multi-billion dollar industry, so it makes sense that even legitimate businesses benefit. Knowing what these businesses are is essential to ending trafficking.
Mary Graw Leary is a former federal prosecutor and currently a professor of law at The Catholic University of America. The Chair of the United States Sentencing Commission’s Victim Advocacy Group, she’s an expert in exploitation, missing persons, human trafficking, and technology.
You may also like

15 Political Issues We Must Address

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for LGBTQ+ Rights

16 Inspiring Civil Rights Leaders You Should Know

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Housing Rights

15 Examples of Gender Inequality in Everyday Life

11 Approaches to Alleviate World Hunger

15 Facts About Malala Yousafzai

12 Ways Poverty Affects Society

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Memorable Human Trafficking Essay: Topics & Outline [2024]
![thesis statement on human trafficking Memorable Human Trafficking Essay: Topics & Outline [2024]](https://studycorgi.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/woman-working-office-1-792x528.jpg)
Human trafficking is a controversial and highly disputed topic. If your task is to write a text about this serious problem, we will help you! This article will look at essential tips for a well-written human trafficking argumentative essay. Also, you will get a comprehensive list of 75 topics for your research paper or essay on human trafficking. For even more content, you can take a look at our database of essays .
Let’s start!
What Is Human Trafficking?
How to write essay on human trafficking.
- Research Topics
Human trafficking is the process of forcing people to work or have sex against their will. Every year, millions of people worldwide become victims of criminals. No one can be sure that this will not affect them. Traffickers are not interested in the victim’s age, gender, or race — anyone is nothing more than a commodity.

Causes of Human Trafficking
Now, for better writing of human trafficking essay, it is worth understanding the topic’s causes. Here are the most common of them:
✔️ Poverty and lack of stability. The primary victims of traffickers are migrants and the population suffering from wars, disasters, etc. They simply do not have the opportunity to defend their rights and protect themselves. This makes them potential crime victims .
✔️ Devaluation of women and children rights. Some societies have specific cultural norms about women and children. Examples include early forced marriage or lack of birth registration. This further compromises the rights of vulnerable groups of the population and leads to dire consequences. USAID states that 27.6 million people, including children, are trafficked and bought for criminal purposes. Moreover, 98% of victims of sexual exploitation are women and young girls. You should definitely investigate this information in your essay. Causes of human trafficking could be different, but that`s one of the most common.
✔️ Cheap labor. A stable job with a good salary can be a tempting proposition for the poor. Traffickers are well aware of this when they offer employment in restaurants, in the fields, etc. Unfortunately, some employers do not prevent human rights violations and cooperate with criminals.
✔️ Big profit. Human trafficking is the second largest industry in the underworld, with a turnover of $150 billion. Naturally, some do not hesitate to commit a crime for the sake of such earnings. To get more information, you could check more essays about organ trafficking .
✔️ The complexity of detecting crimes. Of course, criminals have learned to hide their actions well, but there are other reasons. It should be understood that victims often do not report violations of their rights. A report from the Canadian Center to End Human Trafficking lists more than five main reasons for this behavior, including a warped perception of the judicial system and fear.
Next, we will look at the types of human trafficking you may encounter in your research of this topic.
Types of Human Trafficking
Let’s delve deeper into the issue and find out about the kinds of trafficking:
🔥 Sexual exploitation
Sexual exploitation is one of the most common and lucrative types of human trafficking. About two-thirds of crimes are committed in this direction. In pursuit of a better life, women and children from all over the world fall into the traps of criminals. The victims are issued with forged documents and forced to live and work in inhuman conditions.
🔥 Forced labor
Often, scammers guarantee their victims a stable job in another city or country, promising good conditions and security. But as soon as people get to traffickers, they are immediately sold for slave labor . They can be sent to plantations, mines, construction sites, or to do other hard work.
🔥 Ilegal orders
In this case, the victims, being captured, become forced executors of the plans of the of criminal gangs’ leaders. Due to the constant terror and threats, they have no other choice. For example, victims may be involved in drug cultivation, begging, or selling counterfeit goods.
Human Trafficking Awareness Month
There is no reliable way to protect yourself from crime or stop human trafficking at the moment. That is why every January, a human trafficking awareness month takes place in the United States. During this period, the U.S. Department of State raises awareness of human trafficking at home and abroad. Also, many international organizations hold seminars and workshops aimed at helping people identify crimes.
What does this mean for you?
It should be understood that knowledge in this topic is essential not only for writing an essay but also in everyday life. After all, everyone can help the world to get rid of human trafficking.
Human Trafficking Movies
How about watching a movie? We have compiled a list of 5 human trafficking movies to help you finalize your thoughts on the topic. Sure, some of them have a share of fiction, but they fully reflect the actual situation.
Here`s the list:
The Whistleblower (2010)
The Whistleblower is a crime drama based on actual events. The main character, as part of the U.N. peacekeeping mission, arrives in Bosnia. In the process of completing the assignment, she discovers an illegal network selling people. Katherine Bolkovats, played by Rachel Weisz, will not sit idly by and will arrest the intruders. However, not everyone shares her enthusiasm. Corruption and apathy become the reasons for the dismissal of the human rights defender.
Tricked (2013)
Tricked is a documentary film about the fight against trafficking in large cities in the United States. You have the opportunity to observe the activities of the Denver human trafficking police squad, which persecute criminals. However, budget cuts and poor court performance make their work meaningless. This movie can help you before writing an essay on human trafficking.
I am Jane Doe (2017)
A Netflix documentary shows the story of the lawsuit against Backpage.com. This site has been displaying ads for the sale of people for sexual slavery for years. After a private screening of the film in Congress, the FBI blocked Backpage’s activities. This story could become a good research topic for a human trafficking essay.
Girl Model (2011)
Girl Model is a documentary focusing on the Japanese human trafficking markets. In this film, one can observe how traffickers lure victims in. The authors also raise the burning topic of the relationship between the modeling business and the human trafficking industry.
Priceless (2016)
Priceless is a romantic drama from the director of “For King and Country,” sheding light on the role of conventional transporters in human trafficking. Priceless is a romantic drama from For King and Country sheds light on the role of conventional transporters in human trafficking . In this film, the fictional character of James Stevens is carrying a load of people without knowing anything about it.
We hope our selection will help you, but we will go directly to learning how to write a human trafficking essay for now!
Human trafficking college essays are similar to other academic papers. However, if you have no idea where to start, don’t worry! We have prepared a detailed plan, following which will help you remember the procedure once and for all.
The human trafficking essay outline is an essential preparatory step before writing the main body of an essay. It is crucial to organize your arguments and evidence and write a short structure of the academic work at this stage. It will not be superfluous to think in advance what you will write in each section and paragraph.
Here’s an example of a possible structure:
Now let’s move on to the analysis of each element!
Human Trafficking Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
After choosing a topic and preparing a plan, it’s time to formulate the essay’s main idea. The human trafficking essay thesis is a clear statement, mainly at the end of the introduction. The introduction should smoothly lead to this thesis, and the rest of the article should prove or refute it.
Here are some examples of what a thesis statement for human trafficking paper might look like:
“Trafficking in human beings violates the basic rights of victims so that it can be equated with a crime against humanity.”
“Trafficking in human beings is a problem that has not been addressed in the past, so it still has an impact on the international community.”
“The condemnation of the international community has not helped solve the problem of human trafficking in recent decades.”
If you would like more examples of thesis statements, there are dozens of 500 words human trafficking essays on our site.
Human Trafficking Essay Introduction
As mentioned earlier, the entire human trafficking essay introduction should lead the reader to your main point. Therefore, don’t add new and important information here. A good option would be to tell a little about the term’s history or provide general statistics. In addition, you can write a couple of introductory phrases to hook the reader and acquaint them with your thoughts on this issue. At the end of the introduction paragraph, you should insert your thesis statement. After that, you can move on to the next section.
Human Trafficking Argumentative Essay Body
You should put all the vital information obtained during the research in this section. The reader will appreciate it if you refer to sources or even quote famous people!
The main section also has some unspoken rules. It will be much better if, after the introduction, you immediately show your main argument. It should be followed by evidence based on other research, statistics, etc. This cycle can be repeated until you run out of ideas. By adhering to this structure, you’ll make the essay more understandable for the reader.
Essay on Human Trafficking: Conclusion
A human trafficking essay conclusion is an equally important part of the whole work. At this point, you should consider everything you have written and restate a thesis. A competent conclusion will allow the reader to understand that you know the topic.
75 Human Trafficking Research Topics
Now you can confidently say that you have a well-written, well-reasoned human trafficking essay almost ready. To give you some inspiration, we have compiled a selection of 75 human trafficking essay topics. Read them, and feel free to start writing!
If you want more ideas, read other human trafficking essay examples on our website.
- The main reasons why human trafficking is still relevant today.
- How can you fight illegal human trafficking ?
- Explore the history of child labor in America.
- How can we prevent human trafficking ?
- Which countries are most affected by illegal human trafficking ?
- What are the three types of human trafficking in the modern world?
- How does prostitution relate to human trafficking?
- Which organizations are successful in fighting trafficking ?
- What is human trafficking awareness month?
- The problem of using child labor by big companies.

- How is the international community fighting human trafficking ?
- How is human trafficking related to modern slavery ?
- Investigate terrorists as subjects of human trafficking .
- How has globalization affected human trafficking?
- How is the film industry helping to combat human trafficking?
- Human trafficking problems in China.
- Will human trafficking ever end?
- What is the situation with human trafficking in the Philippines?
- What are the possible solutions to human trafficking ?
- Analyze the trafficking situation in Mexico.
- How Mexican cartels are involved in human trafficking.
- What are security issues on the border between Africa and Europe?
- Which segments of the population are most affected by traffickers?
- Does international legislation help to combat human trafficking ?
- How does the human psyche change after slavery ?
- Is human trafficking a problem for all humanity?
- Why are children and women vulnerable to traffickers?
- Why are migrants often victims of slave traders?
- The moral side of the problem of human trafficking.
- How to understand that a person is in bondage?

- The role of corruption in human trafficking .
- How to protect yourself from human traffickers?
- Countries that actively use forced labor .
- Assess organs trafficking as a component of human trafficking.
- How does the war affect the situation with human trafficking ?
- How do natural disasters affect the human trafficking situation?
- The Impact of the Internet on the human trafficking industry.
- How is the modeling business related to human trafficking ?
- Linking child pornography to the human trafficking industry.
- Who are major buyers in captive markets?
- What is the reason for the popularity of illegal human trafficking ?
- Who is interested in the prosperity of human trafficking ?
- Are the government’s anti-trafficking campaigns effective?
- How has technology affected the sexual exploitation situation?
- How does community culture influence the spread of human trafficking?
- Is human trafficking a problem for each country or the world as a whole?
- How does poverty affect the trafficking situation?
- Human trafficking as a national security risk.
- What modern slavery looks like, or what is human trafficking?
- Does the U.S. government succeed in combating human trafficking ?
- The role of regular cargo transportation in human trafficking.
- How does human trafficking interfere with human development ?
- How does international police fight human trafficking ?
- The history of human trafficking in Europe.
- The role of social security in the anti-trafficking process.
- Why do victims of human trafficking not talk about their problems?
- What are the main causes of human trafficking?
- How psychotherapy helps victims of slavery?
- The problem of child slavery in the United States.
- How is drug addiction related to human trafficking?
- Why are children an easy target for traffickers?
- Human trafficking and modern society.
- Why can’t society fight human trafficking?
- How is the practice of early marriage linked to human trafficking?
- Consequences of human trafficking for the economy.
- How human trafficking affects the demographics of countries?
- How human trafficking relates to the practice of international adoption ?
- The problem of human trafficking in Thailand .
- The problem of human trafficking in Eastern Europe.
- Human trafficking as a manifestation of antisocial behavior.
- How do the police identify criminal networks for the sale of people?
- The phenomenon of slave markets on the Internet.
- What is the tragedy of human trafficking?
- How the economic situation in the country affects human trafficking?
- Why is it so difficult to identify trafficking networks?
It’s time to choose one of the human trafficking research topics and get started. Remember all the nuances mentioned in the article and share them with your friends!
- What Is Human Trafficking? Homeland Security .
- 5 Prevailing causes of human trafficking. The Borgen Project .
- Types of human trafficking. Interpol .
- National Slavery and Human Trafficking Prevention Month. U.S Department of State .
- 10 Movies About Human Trafficking. Human Rights Careers .
- Writing a Paper: Outlining. Walden University .
- Human Trafficking and Migrant Smuggling. United Nations .
- The Worst Countries For Human Trafficking. RadioFreeEurope .
- Child Labour. International Labour Organisation .
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter X
- Share to LinkedIn
Exploring the Role and Impacts of Digital Technology on Human Trafficking
In today’s rapidly evolving world, technology is often a double-edged sword. While technology has provided innovative solutions to preventing and addressing human trafficking, it has also prompted complex ethical questions and created new opportunities for criminals, including human traffickers, to be increasingly sophisticated in exploiting individuals for profit. Traffickers use technology to recruit, control, market and exploit vulnerable individuals while also evading detection. Traffickers do this, for example, by using the Internet to advertise and sell children online for sex, advertise false jobs on social media platforms that are actually human trafficking schemes, transfer cryptocurrency to other traffickers, and perpetuate online scam operations. At the same time, anti-trafficking stakeholders are using technological innovations to prevent human trafficking, protect victims, and prosecute traffickers. The 2024 Trafficking in Persons Report (TIP Report) introduction explores the challenges associated with digital technology in the fight against human trafficking and highlights how it can be used effectively by the anti-trafficking community.
Defining “Digital Technology”
Digital technology refers to an ever-expanding set of electronic systems and resources that facilitate learning, communication, entertainment, and more. Examples include hardware, such as computers, smartphones and mobile devices, and robotics; software, including mobile applications, geolocation, online games, financial databases, web-based and cloud-based systems, and artificial intelligence (AI); and other online services, such as websites, video streaming, blogs, and social media. For the purposes of this report, digital technologies are explored through their use by traffickers as well as by key anti-trafficking stakeholders and beneficiaries.
The Intersection between Digital Technology and Human Trafficking
One way digital technology and human trafficking can intersect occurs when traffickers use online platforms to exploit victims. While not a novel phenomenon, renewed attention was brought to the issue because many people shifted their daily activities online at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Reports from several countries demonstrated drastic increases in online commercial sexual exploitation and sex trafficking, including online sexual exploitation of children (OSEC), and demand for and distribution of child sexual abuse material (CSAM). Traffickers have continued to advance schemes to exploit individuals using digital tools to groom, deceive, control, and exploit victims. Some of these schemes lure individuals hundreds of miles away, including across borders, while others do not require them to leave their homes. Increasingly, victims and survivors of human trafficking have shared that they first connected with their traffickers online. While traffickers continue to refine and advance their use of digital technologies, governments and other anti-trafficking stakeholders must do the same to combat human trafficking.
How Traffickers Use Technology to Facilitate Trafficking
Human traffickers use a wide range of tactics to manipulate and exploit victims—using technology at every stage of their criminal activities, from the initial planning and execution of the scheme to the way in which they coerce, monitor, and maintain individuals to further their exploitative purpose and increase their profits.
Traffickers use the Internet to facilitate the identification and grooming of potential victims. Traffickers often target and victimize individuals in vulnerable situations such as those experiencing conflict, natural disasters, poverty, challenging home lives, systemic oppression, or a combination of hardships. The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) identified “hunting” and “fishing” as two common strategies perpetrators use to deceive and recruit victims. According to UNODC, online platforms help traffickers search proactively and anonymously for a specific type of individual who they believe is particularly susceptible to further their scheme (the hunting process), or passively attract potential victims by posting online and waiting for a response (the fishing process). Perpetrators may use social media, online advertisements, websites, dating apps, and gaming platforms – or fraudulent or deceptive duplications of such tools – to hide their true identity through fake accounts and profiles while interacting with potential victims. Once potential victims are identified and contact is established, communication through the Internet serves as a powerful tool to deceive individuals with false promises of education, employment, housing, or romantic relationships only to lure them into labor and sex trafficking situations. For example, a trafficker may create an online business website, perhaps posing as a talent recruiter, on which they often include realistic photos to gain a victim’s trust and make them believe the opportunity is authentic and will help advance their career or improve their life. In these cases, traffickers trick the victim into believing they can legitimately earn income not only for themselves, but for their families as well. As trust is established, the trafficker manipulates and traps the individual in an exploitative situation through force, fraud, or coercion. Tactics such as threatening physical abuse or harm to an individual, their reputation, future employment, financial prospects, or their loved ones, are used by traffickers to foster fear. The internet can also serve as a platform to escalate the exploitative scheme further, including via sextortion.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) defines sextortion as a serious crime that occurs when a perpetrator threatens to distribute private and sensitive material if the victim does not provide images of a sexual nature, sexual favors, or money. The perpetrator, who often poses as a love interest, entices individuals to send sensitive images, which the victim believes are being shared privately, but the perpetrator then uses the images to control and coerce their victims to produce more images, perform sexual favors, or give money in cases involving sex trafficking or forced labor. In addition to blackmailing the victims for large sums of money, traffickers may also use the content to generate additional revenue by selling the sensitive material on illicit platforms.
Additionally, traffickers can use the Internet to facilitate forced criminality, an increasingly common mechanism involving traffickers coercing their victims to engage in or support criminal activities ranging from working as part of online scam operations to commercial sex. In online scam operations, traffickers largely recruit victims through deceitful job listings online, confine them in gated compounds, and force them to engage in online criminal activity under threat of serious harm. Online scam operations include illegal online gambling, cryptocurrency investment schemes, and romance scams, all of which involve the victim of trafficking forming relationships with individuals in order to defraud them of significant sums. Some traffickers compel victims to continue to work by threatening that if they seek help, they will be prosecuted for the unlawful acts committed as a direct result of being trafficked; while others are simply unaware that they are trafficking victims.
In sum, traffickers use digital tools like the Internet to amplify the reach, scale, and speed of their trafficking operations. While the methods and means may have evolved with technological developments, the exploitation at the heart of trafficking persists, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive and innovative approaches to investigate and combat this crime.
Challenges and Risks Technology Presents for the Anti-trafficking Community
Digital technology has broadened the scope and scale of operations for traffickers as it allows the flexibility to target and exploit victims across the world while remaining hidden and more difficult to trace. Traffickers adapt their schemes to take advantage of the obscurity available with new online tools, such as hiding behind anonymization tools or software, and benefiting from loose regulations of online platforms. These challenges make it increasingly difficult for law enforcement and anti-trafficking stakeholders to identify and implement coordinated solutions fast enough to effectively combat technology-facilitated human trafficking. Constant evolution in digital technology and the ways in which it is being used also makes it difficult to concentrate efforts or decipher trafficking indicators on a given platform, because law enforcement agencies must continuously adapt their tactics, develop technical expertise, and collaborate with technology companies to effectively combat trafficking. Additionally, NGOs and service providers with data relevant to the field may struggle with how to effectively share information while considering data ownership and ensuring privacy is being maintained and protected.
Cross-Sector Coordination Challenges
Traffickers have widened their reach by communicating with and recruiting victims globally, which has created a need for greater global coordination among anti-trafficking stakeholders and technology experts. These stakeholders face several challenges to coordinating a global response, including navigating diverse legal frameworks to address technology-facilitated human trafficking that transcends borders. It is often difficult to determine which jurisdiction has authority to investigate and prosecute perpetrators and coordinate international investigation efforts involving multiple countries. Even when the jurisdiction is established, the necessary evidence gathering and coordination often results in lengthier processes, causing further strain on law enforcement agencies. Traffickers also take advantage of and operate with impunity due to gaps, inadequacies, or loopholes in laws and regulations to address technology-facilitated trafficking and associated activities.
The lack of sufficient funding for research and training on traffickers’ exploitation of digital tools can leave the anti-trafficking field responding reactively rather than proactively. Capacity and resources are particularly acute challenges for law enforcement in regions with limited access to advanced technology. Several technology-based anti-trafficking tools exist for data mining; however, many regions are unable to take advantage of these resources due to a lack of technological infrastructure and digital literacy. Victims may also find themselves isolated and unable to easily seek help in geographical areas with limited technological capabilities, and poor internet connectivity or coverage may affect their ability to receive information and services from anti-trafficking NGOs in a timely manner.
Data Privacy, Protection, and Access
Data protection, data analysis, and data sharing are crucial methods of using digital technologies to prevent, identify, and reduce instances of human trafficking, but practitioners must consider potential negative effects on the safety and well-being of victims and survivors. Collecting and sharing data on human trafficking cases, including victims’ personally identifiable information (PII) can be essential for law enforcement and victim support efforts, but could raise serious data privacy concerns for victims and survivors should their information be inadvertently released to the public through data breaches, which has become a common issue with digital technology in general. NGOs and technology companies often use data mining techniques to support law enforcement in investigating offenses but may lack appropriate security protocols to properly safeguard the data and protect victims’ PII from bad actors. Different standards for ensuring data privacy and protections across countries and concerns around national security hinder effective information sharing between governments. Frameworks for data collection, storage, and sharing of personal data are often different, complicating international cooperation. Governments should consider strengthening digital literacy and infrastructure, where possible, to improve data security standards and procedures, while listening to the recommendations from anti-trafficking stakeholders, including those with lived experiences of trafficking, to assess the best mechanisms for gathering, analyzing, and sharing data related to victims and survivors.
Encryption & Anonymity
Encryption systems are one way to safeguard data in digital interactions including in web browsing, messaging apps, and financial transactions. Such systems prevent third parties from accessing data by turning readable data into a scrambled code that can only be recovered by the receiver’s system, ensuring that only authorized parties can access the original data. Anonymizing technology provides a high level of privacy and obscures the connection between an individual’s online activity and their real identity. Encryption systems found in many online platforms are designed to protect the privacy and security of all online users; however, these systems and anonymizing technologies such as virtual private networks (VPNs), can also offer protection to bad actors, allowing them to avoid detection and accountability.
As with any crime, heightened anonymity may pose a major challenge for law enforcement and anti-trafficking stakeholders in identifying traffickers and their co-conspirators, whether it is the creator of a fraudulent social media account or author of an online advertisement scam. Traffickers increasingly benefit from and rely on the protection that digital tools offer as it amplifies an offender’s ability to anonymize themselves through the entire transactional process – from the recruitment and the solicitation to the management of the transactions and relationships to the payment. Virtual currency has even enabled a distance between those making and receiving payments and the movement of the money. Traffickers may also hide their IP addresses and encrypt their communications, such as emails, chat messages, and file transfers. Together this allows greater physical separation between the offender and the offense, impacting the crime itself and law enforcement’s ability to intercede.
Media or Misinformation
The proliferation of social media and online forums have increased the potential for false narratives and misinformation about human trafficking to circulate online and skew public perceptions of the crime. Even accurate reporting on human trafficking cases and issues may unintentionally minimize the wide range of potential trafficking experiences. Unfortunately, the most sensationalized and misleading stories tend to attract the most attention and mispresent what human trafficking is while also shifting focus away from more prevalent forms of trafficking and from marginalized populations whose exploitation may not receive the same coverage. Such reports may also create a singular or limited perception within communities of what human trafficking looks like, perpetuating stereotypes and interfering with prevention efforts or victims’ ability to self-identify.
The Promise of Technology in Monitoring and Combating Human Trafficking
Technology also plays an important role in investigating and countering human trafficking. Digital technology, including mobile applications, social media campaigns, and online hubs, can be used to further share information, resources, and training on human trafficking. It can also be used to improve access to online support services for victims, survivors, and vulnerable populations. Organizations are using data analytic tools to help identify current trends in fraudulent recruitment, map complex supply chains for links to forced labor, and detect emerging human trafficking schemes. These tools help support information sharing used to bolster identification, investigation, and prosecution efforts by providing means to integrate and analyze data from multiple sources.
Enhancing Education and Outreach Efforts
Digital technology and literacy expand the reach of prevention efforts to raise awareness and educate the public on human trafficking globally. Given the increase in online activity among children, governments and parents should even further prioritize education around online safety for children and youth, and could take advantage of online tools to inform children of the risks related to the internet. Fortunately, there are already a number of beneficial training tools for young people using social media and mobile applications, as well as for parents and guardians, that help support early interventions to prevent technology-facilitated trafficking of youth. One example of how technology is being used for public awareness is through online campaigns including the Can You See Me? campaign administered by A21, a global anti-trafficking organization in the United States, aimed at informing the general public on how to spot signs of human trafficking and where to report it.
Technology is also being used to improve awareness and outreach efforts to support worker engagement and empowerment. Commonly used messaging apps and social media platforms, as well as specially designed worker engagement and empowerment platforms, are used to educate workers on their labor rights, including the right to organize; access legal and social services; and connect with legitimate employers and jobs. Some tools also offer responsible employment training for managers, provide secure grievance mechanisms for workers, aggregate worker survey responses, and provide feedback opportunities, allowing workers to share information about their recruitment and work experiences. One promising example comes from Polaris, an NGO based in the United States. Through its Nonechka project, Polaris collaborated with technology partner Ulula on a platform that allows farmworkers in Mexico and now in the United States to share their experiences, including information on risky recruitment and employment processes. This information also helps Polaris formulate prevention strategies, as well as inform workers about their rights, wages, and working conditions and how to access general services locally including emergency, transitional, or long-term services.
Victim Services
Digital technology tools can aid victims during the exit and recovery phases of a human trafficking experience. Technology can play a pivotal role in victim identification, employing various methods and platforms for finding victims online and allowing for self-reporting exploitation. For example, the Canadian NGO Center for Child Protection (C3P) operates Project Arachnid , a web crawler that searches for known CSAM. When such material is detected, C3P sends a notice to the provider asking that the material be removed. The NGO Thorn also has an AI-powered tool that detects CSAM and tools that aid law enforcement in child sex trafficking investigations. While digital investigative techniques, including those that make use of AI, can assist in trafficking detection, investigation, and successful prosecutions, basic communication tools such as messaging apps, SMS and text, and phone channels also offer lower-tech and straightforward avenues for victims to communicate with service providers in real time. Successful tools to advance victim services include those that facilitate and increase access to victim resource hotlines, virtual peer community spaces, and financial inclusion resources. There are also online tools to bolster training and technical assistance for professionals who wish to support victims and survivors during the aftermath of victimization and to navigate the criminal justice system. Most of these tools are mobile applications and leverage web- and cloud-based solutions for victim services. The GraceCity App, for example, developed by anti-trafficking advocates in Sacramento, California, is a mobile application that offers victims and survivors details on the community resources in their area. The app can canvass thousands of first responders and provide users with useful resources including nearby NGOs, medical professionals, social workers, and therapists. Technologically enhanced interventions can be instrumental in overcoming challenges to victim identification, outreach, and intervention, providing real-time communication channels that are accessible, secure, and more efficient in providing immediate assistance tailored to the individual’s situation and unique needs.
Data Collection and Sharing Efforts
As mentioned earlier, data collection, data analysis, and data sharing are crucial components of using digital technologies to prevent, identify, and reduce instances of human trafficking. Anti-trafficking stakeholders have created tools and established new initiatives to improve their data collection and sharing to support investigation and prosecution efforts. For example, social media and communication platforms are rich sources of information for law enforcement investigations, but combing through large-scale datasets can be time consuming and labor intensive. A diverse group of stakeholders, including governments, international organizations, civil society organizations, private sector businesses, and information technology professionals developed technology tools to assist in anti-trafficking efforts. These tools help anti-trafficking stakeholders collect and analyze vast amounts of qualitative and quantitative data through techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and natural language processing. These digital tools not only enhance the utility and speed of traditional data collection methods used for case management and investigative purposes, but also make it easier for anti-trafficking actors to analyze the data to share real-time insights that better equip the field to address and combat trafficking. Despite this potential, reports show that NGOs have traditionally underutilized such tools due to lack of knowledge, access, expertise, and funding, and more information is needed to better understand barriers to use.
Anti-trafficking applications can help investigators perform pattern analyses from big-data searches encompassing structured and unstructured data from sources including social media. These analyses allow investigators to understand traffickers’ online activities as well as their most frequently used platforms and profiles used to target and mislead victims. For example, the Counter Trafficking Data Collaborative (CTDC), developed by the International Organization for Migration, brings together anti-trafficking organizations from around the world to make human trafficking data publicly available in a central, accessible online platform. The goal of CTDC is to break down information sharing barriers and equip the anti-trafficking community with reliable data. CTDC offers primary, individual-level data scrubbed of personally identifiable information on victims of human trafficking that can be used to track human trafficking trends globally.
From identifying trafficking patterns to increasing accountability within supply chains to prevent forced labor, the multifaceted nature of data collection and sharing requires multidisciplinary partnerships for the benefits of data-related solutions to fully materialize. Data collection and sharing among several anti-trafficking stakeholders is key to effectively developing anti-trafficking policies, identifying victims, prosecuting the perpetrators, and mapping where and how traffickers and transnational criminal networks operate. Collaboration on data collection and sharing should particularly be encouraged between sectors and stakeholders equipped with capabilities to collect data and gather intelligence and insights. Such stakeholders should include NGOs, survivor-led organizations, individuals with lived experience of human trafficking, and intelligence or investigative agencies. The Traffik Analysis Hub is another example of a global solution that supports joint analysis of large AI-generated data sets, providing partners with the ability to pool data assets to generate new insights into patterns and hotspots of trafficking incidents. Information from the Traffik Analysis Hub, which was developed with the support of IBM, is also shared with law enforcement so actions can be taken to disrupt trafficking operations. The ability to use large quantities of data and data analytics also helps to minimize the use of individual victim information and victim testimony to support trafficking prosecutions.
However, the collection and analysis of large data sets present several significant risks and challenges including privacy and data security concerns, misuse of data, and bias and inaccuracies that could result from reliance on large data collections. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement data protection measures to ensure ethical data collection practices and protect individual’s right to privacy.
- Lessons Learned and Looking Ahead
The Role of Government
Governments have the responsibility to regulate the use of technology, including in anti-trafficking efforts, such as disincentivizing the abuse of online resources for trafficking. Efforts to legislate and regulate tech companies to better prevent and address human trafficking will have broader impacts in areas such as privacy, security, and innovation, so careful consideration with a wide range of stakeholders will be needed.
Right now, government approaches to addressing emerging issues in the digital era continue to be fragmented, in part due to the scale and speed at which digital technology evolves. Inconsistent policies make it difficult to combat tech-facilitated crimes due to their transnational and multi-jurisdictional elements. Some governments are recognizing the importance of regulating digital platforms to protect and further national security, economic development, and human rights priorities and many have begun developing policies around the production, deployment, and use of digital technologies. Collaboration and coordination at the international and national level will make it harder for perpetrators to continue their illicit activities.
Globally, government investment in digital technologies for anti-trafficking efforts remains low, despite significant potential. Private sector and civil society stakeholders, including those with lived experience, will be critical to identifying additional government-funded research and development necessary to channel the positive aspects of technology and protect those who use it. An OSCE and Tech Against Trafficking analysis found that out of 305 technology tools readily available to combat human trafficking, only 9 percent were developed through government investments. Consideration should also be given as to how best to develop and share existing tech tools in regions of the world that lack such tools.
The Role of Law Enforcement
Law enforcement agencies are tasked with combating technology-facilitated human trafficking by monitoring online platforms, investigating suspicious activity, and prosecuting perpetrators. Law enforcement agencies can continuously look for new ways to proactively investigate trafficking cases by harnessing technological innovations to collect evidentiary material. For proactive investigations, agencies can focus on increasing internal capacity to integrate data analytics and artificial intelligence tools into casework, as well as collaborate and coordinate with NGOs and technology companies in tool development, training, and information sharing – with due regard to privacy safeguards.
Law enforcement agencies have found ways to leverage technology to help identify, track, and monitor illicit activity by following its digital footprint. A digital footprint could include online activity, from websites visited to social media posts published, and can help paint a clearer picture of a trafficker’s identity, location, and criminal activity. Such publicly available digital evidence is often helpful in building a trafficking case.
Examples of law enforcement leveraging online data to support criminal investigations include:
- In September 2023, The Netherlands, supported by EUROPOL, coordinated a 3-day investigation targeting online criminal activities that enable human trafficking. Law enforcement from 26 countries alongside representatives from European Labor Authority, European Police College (CEPOL), INTERPOL, OSCE, and International Justice Mission, focused on identifying online platforms and social media to recruit victims for sexual and labor exploitation. This led to identifying 11 suspected human traffickers and 45 potential victims.
- In 2023, Operation Synergia led by INTERPOL, targeted human trafficking rings linked to cyber scam centers. Partnering with a leading creator of cybersecurity technology, Group-IB’s Threat Intelligence and High-Tech Crime Investigation teams collected and shared information with INTERPOL and other law enforcement agencies to locate over 2,400 IP addresses associated with cybercrime, leading to the removal of the servers. Over 60 law enforcement agencies from 50 countries participated in the search and seizure of 1,300 malicious servers and electronic devices, shutting down 70 percent of identified cybercrime command servers while the remaining 30 percent are under investigation.
Law enforcement agencies must be better resourced to combat technology-facilitated human trafficking or use technology for human trafficking investigations. This can be achieved through greater investment in staff, training, and software. Law enforcement officers must be trained on monitoring and evaluating online platforms and developing technical knowledge. Law enforcement agencies can deepen their capabilities by establishing cybercrime units tasked with data analysis and decryption technology. Cooperation protocols with NGO and private sector partners will further data sharing and the design and deployment of new tools that are victim-centric and trauma- and survivor-informed. Multilateral knowledge exchange should also be considered when developing technology tools to prevent traffickers from exploiting the gaps in capacity and legislation between law enforcement agencies. Governments should also focus on implementation of the UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime and its Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children to address legislation gaps. Lastly, law enforcement agencies with access to victims’ personal data must have protection standards in place on the collection and storage of such personal data.
The Role of the Financial Sector
The financial sector also plays a vital role in combating human trafficking. According to the International Labour Organization, human trafficking is responsible for an estimated $236 billion in illicit profits annually. All forms of currency, including both traditional and digital assets (e.g. cryptocurrency), can be laundered, requiring a multidimensional approach involving legislative measures, collaboration between justice and financial sectors, technological innovations, and ethical considerations to detect their use in criminal enterprises. The financial sector’s role extends beyond upholding regulatory frameworks, often guided by promising practices in the area of corporate responsibility. As illicit proceeds from human trafficking can intersect with formal financial systems at any stage of a human trafficking crime, it is essential that financial institutions proactively manage the risk of technology-facilitated human trafficking and train staff on the financial indicators and techniques used by human traffickers to launder money. Coordination in this area should also include financial institutions working with law enforcement, technology companies, and survivors to inform their efforts, including on the development of training programs to enhance the ability of frontline staff and other industry professionals to detect transactions connected to human trafficking, how and when to intervene, and how to determine when a third party is benefitting from the exploitation of another.
Globally, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the standard-setting body for anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism and weapons proliferation. More than 200 countries have agreed to implement FATF recommendations, which provide guidance for member countries to identify, assess, and understand money laundering and illicit finance risks and to mitigate those risks. Since 2019, the FATF has included guidance on how to assess and mitigate risks associated with digital assets and digital asset service providers, including recommendations on how member jurisdictions should regulate cryptocurrency transactions. Countries are encouraged to adapt FATF recommendations to their specific context to establish or enhance efforts to tackle illicit financial transactions.
Following digital financial transactions human traffickers leave behind can identify broader criminal networks and make it more difficult to profit from human trafficking. For this reason, responsible innovation in technology and proactive partnerships between governments, financial institutions, law enforcement, and civil society experts, including those with lived experiences are an important part of identifying illicit financial activity associated with human trafficking and safeguarding financial systems against human trafficking, money laundering, terrorist financing, and other serious financial crimes.
The Role of NGOs
NGOs are one of the primary users and drivers of the development of anti-trafficking technological tools, algorithms, and programs and use digital technology to provide survivors easier access to resources and support services such as online counseling and helplines. NGOs are also well-positioned to build strong partnerships with and bridge the gap between technology companies, governments, survivors, and community organizations to enhance the creation and broaden the use of essential anti-trafficking application services. NGOs can use these relationships to advocate for and consult on the creation of standardized response frameworks, data privacy for victims when using anti-trafficking technology tools, and solutions to other emerging concerns around technology.
A result of a partnership between NGOs and international organizations (IOs) to advance work under the UN’s Global Compact on Decent Work in Global Supply Chains, the Interactive Map for Businesses of Anti-Human Trafficking Organizations was developed to be a user-friendly repository database that tracks global and local initiatives and organizations that businesses can partner with on anti-trafficking efforts. The map provides NGOs an opportunity to optimize coordination, research, awareness, and prevention efforts through the ability to identify specific industry initiatives to combat human trafficking via a filter tool that organizes data based on industry, geography, or issue, among others.
The Role of the Technology Industry
The technology industry, while providing many benefits can also inadvertently create environments that facilitate trafficking and other crimes, including by creating a space that facilitates unsupervised access to children. Many companies acknowledge that the popularity and simplicity of user-friendly application services contribute to unsafe environments by providing traffickers with easy access to communicate, advertise, and coordinate illicit activity. Some technology companies have taken steps to address these challenges, but ongoing efforts are needed to enhance security measures, improve content moderation, and collaborate with law enforcement to prevent technology from being used by bad actors for illicit activities. Technology can play several roles to include using data and algorithm tools to detect human trafficking patterns, identify suspicious and illicit activity, and report such activity to law enforcement. Technology companies play a pivotal role in protecting victims and vulnerable individuals from being exploited through the use of their online platforms and must be part of the solution to combat human trafficking.
Some technology companies are increasingly investing in better language models and machine learning to allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data trends. These tools are a useful resource as they may provide law enforcement agencies with powerful tools to more efficiently target illicit activity and possible cases for investigation, but they are not required. Language models can detect, translate, and categorize key words used by traffickers to identify trafficking communication patterns. It can be used to aid international investigations and target traffickers since they often recruit individuals in different countries primarily communicating through technology and internet platforms in the victims’ native language. Alongside language models, other machine learning tools have the ability to cross reference various data sets, such as combining law enforcement data and transit trends, to help stakeholders formulate specific algorithms that can trace traffickers’ patterns. These tools can enhance collaboration between law enforcement agencies and other stakeholders, as well as quickly close the gap for countries that may not have established effective tools to track or investigate human trafficking. As developers continue to build and enhance anti-trafficking applications for protection, prevention, or prosecution functions, they must be designed to tackle the unique challenges and scenarios that arise in the context of human trafficking.
Regardless of the progress provided by technology tools, it is crucial that anti-trafficking stakeholders be cautious of becoming overly reliant on using AI and facial recognition technology to identify victims of human trafficking and the traffickers. These tools should enhance, not replace, existing methods. Developers, policymakers, and anti-trafficking leaders seeking to improve anti-trafficking efforts with AI and facial recognition tools should prioritize establishing data privacy rights and ensuring individuals’ information is protected throughout data-sharing processes.
Taking Action: Considerations for Anti-Trafficking Stakeholders
Harnessing technology to advance the shared goal of governments, law enforcement actors, technology companies, and civil society to eliminate human trafficking will require proactive efforts by all actors to resolve the complex, often contradictory byproducts of technological progress. Governments can adopt policies and legislation that recognize human traffickers’ use of technology and incentivize the positive use of technology tools to investigate and counter human trafficking, and must coordinate implementation of these policies through collaboration with the technology sector, the financial sector, anti-trafficking NGOs, and lived experience experts who can help build capacity to monitor online spaces, train staff, develop technology tools, and cultivate technical expertise. Law enforcement entities can use technology to conduct data analytics on traffickers, their connections, and their modus operandi to inform human trafficking investigations and related money laundering activities, bolster the identification of victims online, and enhance safety nets. Governments can also strengthen data security from unauthorized access to better protect victims and investigations and find technology-based solutions that further privacy, safety, and trust. Multilateral forums offer important venues for governments to share best practices and develop new policies and standards that uphold current international frameworks but are also tailored to regional and local trafficking situations and existing technological capabilities.
NGOs can advocate for policies and tech solutions that empower vulnerable individuals, strengthen access to services, advance digital learning, and further privacy protections. Local communities, NGOs, and those with lived experience know current trafficking trends and how technology is being used to facilitate crimes, and thus can recommend ways to enhance trauma-informed and victim-centric tech solutions and ways to get tech tools in the hands of those who most need them. The technology sector should work to ensure their online platforms are being used for legitimate purposes and ensure privacy and safety for users. The technology sector can also invest in new technologies that include detecting and countering child sexual abuse material, livestreaming trafficking offenses, and fraudulent cyber scams or job offers among other crimes occurring on their platforms. Governments, anti-trafficking NGOs, companies, and innovators can also employ routine audits of technology tools as digital technologies evolve to limit negative consequences and better guarantee efficient, sustainable means to address human trafficking.
Collaborative efforts allow all relevant parties to inform and promote best practices for the responsible and safe use of technology by a variety of actors, including individuals vulnerable to technology-facilitated trafficking. The challenge is immense, but political will, resource investments, innovation, and partnerships will help prevent traffickers’ use of technology for exploitation, and instead amplify and scale the best applications that assist all anti-trafficking stakeholders in meeting our obligations to combat the newest continuously evolving aspects of this pernicious crime.
- Understanding Human Trafficking
“Trafficking in persons” and “human trafficking” are umbrella terms—often used interchangeably—to refer to a crime whereby traffickers exploit and profit at the expense of adults or children by compelling them to perform labor or engage in commercial sex. When a person younger than 18 is used to perform a commercial sex act, it is a crime regardless of whether there is any force, fraud, or coercion involved.
The United States recognizes two primary forms of trafficking in persons: forced labor and sex trafficking. The basic meaning of these forms of human trafficking and some unique characteristics of each are set forth below, followed by several key principles and concepts that relate to all forms of human trafficking.
More than 180 nations have ratified or acceded to the UN Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons (the UN TIP Protocol), which defines trafficking in persons and contains obligations to prevent and combat the crime.
The United States’ TVPA and the UN TIP Protocol contain similar definitions of human trafficking. The elements of both definitions can be described using a three-element framework focused on the trafficker’s 1) acts; 2) means; and 3) purpose. All three elements are essential to form a human trafficking violation.
Forced Labor
Forced Labor, sometimes also referred to as labor trafficking, encompasses the range of activities involved when a person uses force, fraud, or coercion to exploit the labor or services of another person.
The “acts” element of forced labor is met when the trafficker recruits, harbors, transports, provides, or obtains a person for labor or services.
The “means” element of forced labor includes a trafficker’s use of force, fraud, or coercion. The coercive scheme can include threats of force, debt manipulation, withholding of pay, confiscation of identity documents, psychological coercion, reputational harm, manipulation of the use of addictive substances, threats to other people, or other forms of coercion.
The “purpose” element focuses on the perpetrator’s goal to exploit a person’s labor or services. There is no limit on the location or type of industry. Traffickers can commit this crime in any sector or setting, whether legal or illicit, including but not limited to agricultural fields, factories, restaurants, hotels, massage parlors, retail stores, fishing vessels, mines, private homes, or drug trafficking operations.
All three elements are essential to constitute the crime of forced labor.
There are certain types of forced labor that are frequently distinguished for emphasis or because they are widespread:
Domestic Servitude
“Domestic servitude” is a form of forced labor in which the trafficker requires a victim to perform work in a private residence. Such circumstances create unique vulnerabilities. Domestic workers are often isolated and may work alone in a house. Their employer often controls their access to food, transportation, and housing. What happens in a private residence is hidden from the world – including from law enforcement and labor inspectors – resulting in barriers to victim identification. Foreign domestic workers are particularly vulnerable to abuse due to language and cultural barriers, as well as a lack of community ties. Some perpetrators use these types of conditions as part of their coercive schemes to compel the labor of domestic workers with little risk of detection.
Forced Child Labor
The term “forced child labor” describes forced labor schemes in which traffickers compel children to work. Traffickers often target children because they are more vulnerable. Although some children may legally engage in certain forms of work, forcing or coercing children to work remains illegal. Forms of slavery or slavery-like practices – including the sale of children, forced or compulsory child labor, and debt bondage and serfdom of children – continue to exist, despite legal prohibitions and widespread condemnation. Some indicators of forced labor of a child include situations in which the child appears to be in the custody of a non-family member and the child’s work financially benefits someone outside the child’s family; or the denial of food, rest, or schooling to a child who is working.
Sex Trafficking
Sex trafficking encompasses the range of activities involved when a trafficker uses force, fraud, or coercion to compel another person to engage in a commercial sex act or causes a child to engage in a commercial sex act.
The crime of sex trafficking is also understood through the “acts,” “means,” and “purpose” framework. All three elements are required to establish a sex trafficking crime (except in the case of child sex trafficking where the means are irrelevant).
The “acts” element of sex trafficking is met when a trafficker recruits, harbors, transports, provides, obtains, patronizes, or solicits another person to engage in commercial sex.
The “means” element of sex trafficking occurs when a trafficker uses force, fraud, or coercion. Coercion in the case of sex trafficking includes the broad array of means included in the forced labor definition. These can include threats of serious harm, psychological harm, reputational harm, threats to others, and debt manipulation.
The “purpose” element is a commercial sex act. Sex trafficking can take place in private homes, massage parlors, hotels, or brothels, among other locations, as well as on the internet.
Child Sex Trafficking
In cases where an individual engages in any of the specified “acts” with a child (under the age of 18), the means element is irrelevant regardless of whether evidence of force, fraud, or coercion exists. The use of children in commercial sex is prohibited by law in the United States and most countries around the world.
Key Principles and Concepts
These key principles and concepts relate to all forms of trafficking in persons, including forced labor and sex trafficking.
Human trafficking can take place even if the victim initially consented to providing labor, services, or commercial sex acts. The analysis is primarily focused on the trafficker’s conduct and not that of the victim. A trafficker can target a victim after a victim applies for a job or migrates to earn a living. The trafficker’s exploitative scheme is what matters, not a victim’s prior consent or ability to meaningfully consent thereafter. Likewise, in a sex trafficking case, an adult victim’s initial willingness to engage in commercial sex acts is not relevant where a perpetrator subsequently uses force, fraud, or coercion to exploit the victim and cause them to continue engaging in the same acts. In the case of child sex trafficking, the consent of the victim is never relevant as a child cannot legally consent to commercial sex.
Neither U.S. law nor international law requires that a trafficker or victim move across a border for a human trafficking offense to take place. Trafficking in persons is a crime of exploitation and coercion, and not movement. Traffickers can use schemes that take victims hundreds of miles away from their homes or exploit them in the same neighborhoods where they were born.
Debt Bondage
“Debt bondage” is focused on human trafficking crimes in which the trafficker’s primary means of coercion is debt manipulation. U.S. law prohibits perpetrators from using debts as part of their scheme, plan, or pattern to compel a person to work or engage in commercial sex. Traffickers target some individuals with an initial debt assumed willingly as a condition of future employment, while in certain countries traffickers tell individuals they “inherited” the debt from relatives. Traffickers can also manipulate debts after the economic relationship begins by withholding earnings or forcing the victim to assume debts for expenses like food, housing, or transportation. They can also manipulate debts a victim owes to other people. When traffickers use debts as a means to compel labor or commercial sex, they have committed a crime.
The Non-Punishment Principle
A victim-centered and trauma-informed approach is key to successful anti-trafficking efforts. A central tenet of such an approach is that victims of trafficking should not be inappropriately penalized solely for unlawful acts they committed as a direct result of being trafficked. Effective implementation of the “non-punishment principle,” as it is increasingly referred to, not only requires recognizing and embracing the principle in regional and national laws, but also increasing proactive victim identification.
State-Sponsored Human Trafficking
While the TVPA and UN TIP Protocol call on governments to proactively address trafficking crimes, some governments are part of the problem, directly compelling their citizens into sexual slavery or forced labor schemes. From forced labor in local or national public work projects, military operations, and economically important sectors, or as part of government-funded projects or missions abroad, officials use their power to exploit their nationals. To extract this work, governments coerce by threatening the withdrawal of public benefits, withholding salaries, failing to adhere to limits on national service, manipulating the lack of legal status of stateless individuals and members of minority groups, threatening to punish family members, or conditioning services or freedom of movement on labor or sex. In 2019, Congress amended the TVPA to acknowledge that governments can also act as traffickers, referring specifically to a “government policy or pattern” of human trafficking, trafficking in government-funded programs, forced labor in government-affiliated medical services or other sectors, sexual slavery in government camps, or the employment or recruitment of child soldiers.
Unlawful Recruitment or Use of Child Soldiers
Another manifestation of human trafficking occurs when government forces or any non-state armed group unlawfully recruits or uses children – through force, fraud, or coercion – as soldiers or for labor or services in conflict situations. Children are also used as sex slaves. Sexual slavery, as referred to here, occurs when armed groups force or coerce children to “marry” or be raped by commanders or combatants. Both male and female children are often sexually abused or exploited by members of armed groups and suffer the same types of devastating physical and psychological consequences associated with sex trafficking.
Accountability in Supply Chains
Forced labor is well documented in the private economy, particularly in agriculture, fishing, manufacturing, construction, and domestic work; but no sector is immune. Sex trafficking occurs in several industries as well. Most well-known is the hospitality industry, but the crime also occurs in connection with extractive industries where activities are often remote and lack meaningful government presence. Governments should hold all entities, including businesses, accountable for human trafficking. In some countries, the law provides for corporate accountability in both the civil and criminal justice systems. U.S. law provides such liability for any legal person, including a business that benefits financially from its involvement in a human trafficking scheme, provided that the business knew or should have known of the scheme.
Topics of Special Interest
- Trafficking in Persons for the Purpose of Organ Removal
Trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal is one of the least reported and least understood forms of trafficking – but one that experts believe may be growing. Like sex trafficking and labor trafficking, it is ultimately a crime that exploits human beings for economic profit. Trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal is “a form of trafficking in which an individual is exploited for their organ, including by coercion, deception and abuse of a position of vulnerability.” The crime is sometimes confused with organ trafficking; however, organ trafficking refers more broadly to the illicit trade or exchange of organs for financial or other material gain. In organ trafficking, the focus is on the organ itself; conversely, with trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal, the focus is on the individual. The key global anti-trafficking instrument, the Palermo Protocol, defines exploitation to include at a minimum “the removal of organs,” alongside sexual exploitation, forced labor, and slavery or slavery-like practices.
Often, in cases of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal, would-be donors are tricked into organ donation. Common deceptions include being told human beings have three kidneys or that kidneys regenerate after being removed, or being falsely told they will experience no negative side effects from a kidney removal (in fact, kidney donors may face serious lifelong medical challenges and be unable to work). Although kidneys are the most common organ involved, other organs and tissues, such as livers, corneas, or skin, are also sought, although notably the Palermo Protocol’s definition covers only exploitation for the removal of organs, not of tissues or cells. Victims may not be paid at all, or they may receive some payment; importantly, an individual can still be a victim of trafficking in persons or other human rights abuses even if they received some form of payment.
The 2022 UNODC Global Report on Trafficking in Persons noted trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal constituted only 0.2 percent of detected victims of trafficking compared to the much higher numbers for sex trafficking and forced labor. UNODC has warned “existing barriers to reporting suggest that the full scale of this phenomenon is not yet known.” The report also noted an uptick in cases (from 25 in 2017 to 40 in 2018), though the overall numbers are small. Between 2008 and 2022, UNODC reported 700 victims of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal while noting “the scale of the problem is likely to be much larger.”
Trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal is difficult to detect for several reasons. Data-collection efforts are scarce, and some instances of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal may be mistakenly classified or prosecuted as organ trafficking. Moreover, unlike sex trafficking and labor trafficking, which can take place over months or years, trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal usually involves a brief, often one-time, interaction. Like other forms of trafficking, transactions have increasingly shifted online and become more sophisticated, facilitating the emergence of smaller networks, and even independent brokers and suppliers, which may be more difficult to track.
Both the 2020 and 2022 UNODC Global Report on Trafficking in Persons and a 2021 INTERPOL report suggest North Africa and the Middle East have the highest share of detected victims, in part due to the prevalence of large vulnerable communities, limited access to medical care, and corruption. The media and some NGOs have also reported instances of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal for ritual purposes. However, instances of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal can occur worldwide. In a case recently prosecuted in the United Kingdom, the victim was recruited in Nigeria and brought to London, where the organ removal was to take place (see inset box for additional information). In another case reported by the BBC in late 2023, revealing the connection between organ trafficking and trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal, Pakistani police arrested eight members of an organ-trafficking ring that “lure[d] vulnerable patients from hospitals” and conducted transplants “often without the patient knowing;” several people died from these procedures.
The government of the People’s Republic of China, in particular, has been accused of systematically forcibly removing organs from political prisoners. For example, a group of UN human rights experts noted in 2021:
Forced organ harvesting in China appears to be targeting specific ethnic, linguistic, or religious minorities held in detention, often without being explained the reasons for arrest or given arrest warrants, at different locations. We are deeply concerned by reports of discriminatory treatment of the prisoners or detainees based on their ethnicity and religion or belief.
(Note: forced organ harvesting is not a term defined in the Palermo Protocol, but the phrase is commonly used to describe trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal.)
While there is a need for additional studies and reporting to thoroughly assess the geographic and numeric scope of trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal, stakeholders are taking steps to attempt to address the issue. A number of regional instruments, including the Council of Europe Convention against Trafficking in Human Organs, the Council of Europe Convention on Action against Trafficking in Human Beings, and the ASEAN Convention against Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children, recognize organ removal as a form of trafficking-related exploitation.
Experts have also proposed ideas to increase the supply of legally donated organs, with the intention of making trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal and organ trafficking less lucrative. These ideas include transitioning deceased organ donation from an opt-in to an opt-out system; implementing paired exchanges matching donors and patients; creating awareness campaigns targeted at potential donors, including addressing barriers to altruistic organ donation and providing guidance on how to prevent trafficking in persons for the purpose of organ removal; building the capacity of law enforcement to detect and investigate these cases; and improving transparency and reporting around transplantation.
Twenty-one-year-old “Daniel” (not his real name) scraped out a living selling mobile-phone accessories at an outdoor street market in Lagos, Nigeria, but he thought his luck took a turn when he was offered a “life-changing opportunity” to work in the United Kingdom. The people he believed were his employers instructed him to take a blood test, which he thought was required to secure a visa. The people he had been working with put him on a flight and confiscated his passport. Within days of arriving in London, Daniel was taken to the Royal Free Hospital, where doctors discussed the risks of the upcoming “operation” – something Daniel knew nothing about. Seeing his confusion, the doctors sent Daniel away – but did not notify authorities. Later, Daniel overheard a conversation among those who had brought Daniel to the UK speaking about sending him back to Nigeria to remove his kidney. Scared, Daniel escaped, sleeping on the streets for several days until walking into a police station and telling his story. Daniel’s bravery eventually led to the UK’s first prosecution of – and convictions for – human trafficking for the purpose of organ removal. A prominent Nigerian politician and his wife who had arranged the trafficking scheme to provide their daughter with a kidney transplant, as well as a Nigerian doctor, were convicted in 2023.
This story was published by the BBC, Organ Harvesting: Trafficked for His Kidney and Now Forced into Hiding , June 26, 2023 ( https://www.bbc.com/news/65960515 ); for additional details, see the Crown Prosecution Service, Updated with Sentence: Senior Nigerian Politician Jailed Over Illegal UK Organ-Harvesting Plot , May 5, 2023 ( https://www.cps.gov.uk/cps/news/updated-sentence-senior-nigerian-politician-jailed-over-illegal-uk-organ-harvesting-plot ).
- Connecting the Dots: Preventing Forced Labor by Empowering Workers
Forced labor, a form of human trafficking, is universally condemned yet prevalent in nearly every industry globally. The International Labour Organization (ILO) reports forced labor has grown in recent years – with no region of the world or private sector industry spared – and the majority of forced labor takes place in the private economy, meaning forced labor is connected to global supply chains. These facts demand a re-examination of current efforts to prevent and address forced labor, including the need to elevate the voice and agency of workers and place them at the center of prevention efforts through strategic partnerships. In addition, particular focus should be placed on vulnerable populations, such as migrant workers. ILO research shows the rates of forced labor among migrant workers are higher if migration is irregular or poorly governed, or where recruitment practices are unfair or unethical.
Although prosecuting specific traffickers and assisting individual victims are critical for governments combating forced labor, successful interventions to prevent forced labor require a range of stakeholders willing to visualize and address broader systemic issues centered on worker’s labor rights, including those of migrant workers, as well as supply chain power imbalances. For governments, this may require additional resources and oversight of workplaces, especially in key sectors where forced labor is often present; better monitoring of the labor recruitment industry; increased outreach to and protections for migrant workers; and improved screening measures by well-trained officials targeting populations at greater risk of exploitation. For the private sector, it will mean proactively supporting workers and their ability to advocate for themselves, setting clear expectations of suppliers, and rooting out practices that create environments ripe for exploitation.
Worker-led Approaches to Prevent Forced Labor
Over time, policymakers, academics, and other stakeholders have expanded their thinking to encompass worker-led approaches to address the vulnerabilities of workers and prevent forced labor. Such approaches include advancing labor rights and standards – including freedom of association, collective bargaining, and the remediation of labor rights abuses – as well as worker-driven approaches that include migrants. Research has demonstrated workers are most vulnerable to forced labor if they do not know their rights, are excluded from labor protection laws, and lack access to grievance mechanisms. Workers in the informal sector and women and girls, who often face gender-based violence and harassment in the workplace, can be particularly vulnerable. One of the most effective ways to prevent worker exploitation is to guarantee workers’ full rights to freedom of association and collective bargaining. Independent and democratic labor unions, led by workers, are best able to represent workers’ collective interests at multiple levels, including at the national, subnational, regional, and international levels. Collaborating with local workers, regional international organizations, and global union federations, these unions can reach the most vulnerable workers, organize across a labor sector, and advocate for key policy changes, including responsible migration management. As a result, they are well positioned to engage powerful transnational companies to address forced labor in their supply chains.
According to ILO’s Director of the Bureau for Workers’ Activities, there have been positive developments over time with unions reaching outside of their traditional base to include the unionization of self-employed workers. Many unions have also expanded to include more informal economy, migrant, and domestic workers, which is key as many of these workers are governed by a variety of working arrangements, including fixed-term and temporary contracts.
This diversification of representation is important as unions allow workers to negotiate for better working conditions, influence the laws and policies that impact them, and remediate labor rights abuses. Unions play a pivotal role in securing legislated labor protections and rights, such as legally entitled wages and benefits, occupational safety and health protections, overtime pay, and medical leave. Union-led efforts help raise the wages for the lowest paid and least skilled workers and lead to fewer hours of unpaid overtime work. Unions play crucial roles in identifying labor rights abuses and enforcing rights on the job. One of the most effective ways to prevent the exploitation of migrant workers is by guaranteeing their right to join unions in destination countries. The multiplier impact is notable, as industries with strong union representation tend to have lower levels of labor rights abuse, the worst forms of child labor, and forced labor.
Where there is an absence of unions, there at least should be effective, secure mechanisms for worker communication and grievances. Governments should strongly encourage employers to provide mechanisms so workers can advocate for their rights, discuss workplace issues of concern and interest, and communicate grievances, even if that takes place outside a formal union mechanism. Such mechanisms are essential to preventing forced labor, as they position workers, including migrant workers, to better protect themselves against coercion, deception, discrimination, and other forms of exploitation.
Promising Practices in Improving Labor Conditions
Several examples stand out as raising labor conditions for workers.
Dindigul Agreement, India
Indian women and the Dalit-worker led union Tamil Nadu Textile and Common Labor Union (TTCU) signed in April 2022 a historic agreement with clothing and textile manufacturers and major fashion companies to end gender-based violence and harassment at factories in the southern state of Tamil Nadu. This enforceable brand agreement resulted in multinational companies committing to support a worker- or union-led program at certain factories or worksites. An assessment a year later by the multi-stakeholder oversight committee found that the workers are now effectively able to detect, remediate, and prevent gender-based violence and harassment. In addition, the TTCU has conducted peer education training of more than 2,000 workers and management, held more than 30 meetings with management to resolve grievances, and recruited 58 workers as monitors to help remediate gender-based violence and harassment throughout the factory units.
Freedom of Association for Garment Workers, Honduras
In the decade that has followed Honduran workers signing an agreement with major brand Fruit of the Loom, close to 50 percent of all Honduran garment workers are now employed at a factory where an independent union represents the workforce. As a result of this signed collective bargaining agreement, workers have won increased wages and benefits and witnessed a reduction in verbal harassment and gender-based violence.
While unionization rates vary considerably across the globe, the ILO notes other encouraging examples. In Uzbekistan, trade unions have organized seasonal workers and facilitated dual affiliation to different unions in other countries. In Moldova, unions have begun to establish agreements with unions in destination countries so that migrants have protection when working abroad . In Benin, Botswana, and Mauritius, trade unions have set up Joint Trade Union Councils, which have drawn up joint declarations, charters, and protocols on the modalities of working together in national social dialogue fora. In Lithuania and Ukraine, unions have established structures of cross-border collaboration to improve the recruitment and representation of truck drivers in both countries.
Overall, research has also shown that unionization has spillover effects that extend beyond union workers. Competition means workers at nonunionized firms also often see increased wages and improved workplace safety norms. Union members improve communities through heightened civic engagement and increased voter rates. Unions can also boost business’ productivity by giving experienced workers more input into decisions that design better, more cost-effective workplace procedures.
Milestones, Momentum, and Motivation
Over the last several years, government and private sector attention has become focused on resilient supply chains, and there are increasing supply chain transparency and due diligence policies, regulations, and laws globally. In addition, various initiatives have been developed to raise the importance of workers’ agency. It is notable that flower-sector leader Bloomia’s entire cut-flower supply chain, which encompasses farms in the United States, Chile, and South Africa, will now be certified for human rights protections by the Fair Food Program, pioneers in the worker-driven social responsibility model with its partnerships among retailers, growers, and workers. Combined, the Partnership for Workers‘ Rights, launched by the United States and Brazil at the 2023 UN General Assembly; the Multilateral Partnership for Worker Organizing, Empowerment, and Rights (M-POWER), which is part of the U.S. Presidential Initiative for Democratic Renewal; and the 2023 U.S. Presidential Memorandum on Advancing Worker Empowerment, Rights, and High Labor Standards present a unique opportunity to proactively advance worker empowerment in the short and long term while simultaneously preventing labor rights violations and abuses, especially forced labor. The independent UN Special Rapporteur on Contemporary Forms of Slavery made a key theme for 2024 the role of trade unions and worker organizations in preventing contemporary forms of slavery.
The timing is ideal for all stakeholders committed to preventing forced labor to fully embrace the importance of supporting, elevating, and improving labor standards, bringing workers’ voices to the policy formulation and decision-making table, and working to help the public and private sector enforce rules against unfair labor practices. Governments should take every step to use a whole-of-government approach to advance worker rights and address gaps in labor rights protection and compliance, including for migrant workers; the private sector should see free and fair unions as critical partners in competing in the global economy while protecting workers; and other civil society stakeholders should ensure that workers’ voices are incorporated early and often, especially when their equities are at stake.
- Human Trafficking in Cuba’s Labor Export Program
Each year, the Cuban government sends tens of thousands of workers around the globe under multi-year cooperation agreements negotiated with receiving countries. While medical missions remain the most prevalent, the Cuban government also profited from other similarly coercive labor export programs, including those involving teachers, artists, athletes and coaches, engineers, forestry technicians, and nearly 7,000 merchant mariners worldwide. According to a report published by the Cuban government, by the end of 2023, there were more than 22,000 government-affiliated Cuban workers in over 53 countries, and medical professionals composed 75 percent of its exported workforce. The COVID-19 pandemic increased the need for medical workers in many places around the world, and the Cuban government used the opportunity to expand its reach by increasing the number of its medical personnel abroad through the Henry Reeve Brigades, which Cuba first initiated in 2005 to respond to natural disasters and epidemics. Experts estimate the Cuban government collects $6 billion to $8 billion annually from its export of services, which includes the medical missions. The labor export program remains the largest foreign revenue source for the Cuban government.
There are serious concerns with Cuba’s recruitment and retention practices surrounding the labor export program. While the conditions of each international labor mission vary from country to country, the Cuban government subjects all government-affiliated workers to the same coercive laws. Cuba has a government policy or pattern to profit from forced labor in the labor export program, which includes foreign medical missions. The Cuban government labels workers who leave the program without completing it as “deserters,” a category that under Cuban immigration law deems them as “undesirable.” The government bans workers labeled as “deserters” and “undesirables” from returning to Cuba for eight years, preventing them from visiting their families in Cuba. It categorizes Cuban nationals who do not return to the country within 24 months as having “emigrated.” Individuals who emigrate lose all their citizen protections, rights under Cuban law, and any property they left behind. These government policies and legal provisions, taken together, coerce workers and punish those seeking to exercise freedom of movement. According to credible sources, by 2021, the Cuban government had sanctioned 40,000 professionals under these provisions, and by 2022, there were approximately 5,000 children forcibly separated from their parents due to the government’s policies surrounding the program.
Complaints filed with the International Criminal Court and the UN indicate most workers did not volunteer for the program, some never saw a contract or knew their destination, many had their passports confiscated by Cuban officials once they arrived at their destination, and almost all had “minders” or overseers. According to the complaints and survivors, Cuban heads of mission in the country subjected workers to surveillance, prevented them from freely associating with locals, and imposed a strict curfew. Cuba also confiscated between 75 and 90 percent of each worker’s salary. As a result of the well-founded complaints and information about the exploitative nature of Cuba’s labor export program, at the end of 2023, the UN Special Rapporteur for Contemporary Forms of Slavery filed a new communication outlining the persistent concerns with the program, particularly for Cuban workers in Italy, Qatar, and Spain.
While exploitation, including forced labor, of workers remains the primary concern with the program, Cuba’s practices can also negatively impact a host country’s healthcare system. Survivors of the program have reported being forced by the Cuban in-country mission director to falsify medical records and misrepresent critical information to justify their presence and need to local authorities. Some individuals reported discarding medications, fabricating names, and documenting medical procedures that never occurred. When medical workers refused to comply with the demands of the Cuban in-country mission director, they faced punishment and retaliation. While the Cuban government promotes workers as highly skilled medical professionals and specialists, these workers often lack adequate medical training to treat complex conditions. These practices are unethical, negligent, exploitative, and risk the lives of those they serve.
Governments should make efforts to combat human trafficking, and this includes not purchasing goods or services made or provided with forced labor. Governments that utilize Cuba’s labor export programs despite the serious concerns with the program should at a minimum conduct frequent and unannounced labor inspections to screen these workers for trafficking indicators and employ victim-centered interviewing techniques. These host governments should ensure all Cuban workers are subject to the same laws, regulations, and protections as for other migrant workers and that they are not brought via a negotiated agreement with the Government of Cuba that limits these protections or exempts Cuban workers from Wage Protections Systems or other tools designed to strengthen transparency. Officials should ensure workers maintain complete control of their passports and medical certifications and can provide proof of full salary payment to bank accounts under the workers’ control. They should scrutinize medical reports produced by these workers, offer protection for those who face retaliation and punishment for terminating their employment, and raise awareness of trafficking risks for all foreign workers, including government-affiliated Cuban workers.
- Nothing About Us Without Us: Human Trafficking and Persons with Disabilities
Human traffickers often take advantage of persons in vulnerable situations including individuals who lack access to services and programs or rely on the assistance of others. Among this group of potential targets are persons with disabilities, who represent about 16 percent of the world’s population, or 1.3 billion people, according to the World Health Organization.
Of course, these 1.3 billion people are not monolithic. Some people have a disability from birth; others experience disability later in their lifetime. Some disabilities are life-long, and others may be temporary. A disability can be visible, such as a physical disability, or non-apparent, such as an intellectual or psychosocial disability. People with disabilities are of every age, race, sex and sex characteristics, sexual orientation, gender identity and expression, economic status, and nationality.
Professors Andrea Nichols and Erin Heil have noted the “heightened risk as well as heightened prevalence” of human trafficking involving persons with disabilities, although the authors acknowledged the paucity of existing research. Even when research about persons with disabilities is conducted, it rarely addresses additional intersecting identities, such as race, ethnicity, age, gender, religion, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, or migratory status, that can exacerbate marginalization.
The intersection between disability and human trafficking can be cyclical. On the one hand, persons with disabilities are more likely to be targeted by traffickers; on the other hand, the experience of being trafficked can lead to or exacerbate existing disabilities through physical injuries or emotional trauma that in turn could heighten vulnerability.
Even with access to support, persons with disabilities face increased risk of exploitation. A caregiver may exploit their position to victimize the person they are assisting. Persons with disabilities who receive financial assistance may be exploited for those benefits. As the Human Trafficking Legal Center has explained with respect to the situation in the United States: “While persons with disabilities may be trafficked into sex or labor, many cases include one additional element: the theft of Social Security or disability benefits. The opportunity to steal government benefits provides an added incentive for traffickers to target persons with disabilities.” Persons with disabilities across the globe who receive benefits face similar challenges.
In light of this situation, it is perhaps not surprising that the centerpiece of the United States’ statutory framework to combat trafficking, the Trafficking Victims Protection Act (TVPA), was promulgated in part as a reaction to the Supreme Court’s decision in United States v. Kozminski , 487 U.S. 931 (1988), a case involving two men with intellectual disabilities held in what justices referred to as “slave-like” conditions on a farm. In the case, the Court held that the law banning “involuntary servitude” was limited to circumstances involving “the compulsion of services by the use or threatened use of physical or legal coercion.” However, Congress subsequently passed the TVPA, which recognized that psychological coercion and threats of nonviolent coercion can be every bit as powerful as physical force in overcoming the will of targeted individuals.
In 2009, the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission brought a case involving Henry’s Turkey Service, which exploited 32 intellectually disabled men at a farm in Atalissa, Iowa. For more than 30 years, the men endured physical and mental abuse and received virtually no pay. The jury awarded the men what at the time was the largest-ever award in an employment-discrimination case – $240 million – although it was later reduced to $1.6 million due to a federal cap in the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Not only did the TVPA arise in part from trafficking crimes involving persons with disabilities, one of the first major trafficking prosecutions in the United States involved persons with disabilities. In that case, dozens of immigrants with hearing disabilities, including young children, were forced to work 18-hour days as trinket vendors in New York City. Traffickers targeted persons with disabilities who were also young migrants and did not speak English, exemplifying how disability can intersect with other forms of vulnerability. Sadly, this form of exploitation of persons with disabilities continues to this day.
The TIP Report enhanced its coverage of the intersection of disability and trafficking, with the 2023 TIP Report referencing persons with disabilities in 65 country narratives, up from about 50 in the 2022 TIP Report. These references also highlighted the existence or lack of specialized services for persons with disabilities who are victims of trafficking, and the particular challenges faced by persons with physical or intellectual disabilities.
The U.S. Department of State’s disability rights work is led by Special Advisor on International Disability Rights Sara Minkara. In this appointed position, Ms. Minkara leads the comprehensive strategy to promote and protect the rights of persons with disabilities across U.S. foreign policy. Special Advisor Minkara embodies the slogan “nothing about us without us,” which is often used by disability rights advocates to insist that persons with disabilities participate fully in policies affecting them. The role of Special Advisor on International Disability Rights was first held by Judy Heumann, who served in the position from 2010 to 2017 and is widely regarded as the “mother of the disability rights movement.” Sadly, Ms. Heumann passed away in March 2023, leaving behind an indelible legacy of disability advocacy in the United States and around the world.
From left: Former Special Advisor on International Disability Rights (SAIDR) Judy Heumann, SAIDR Sara Minkara, and Special Assistant to the Special Advisor Hanah Nasri attend a celebration of the anniversary of the Americans with Disabilities Act at the official residence of the Vice President of the United States in July 2022. Photo courtesy of Hanah Nasri. (Photo was published in State Magazine in March 2023: https://statemag.state.gov/2023/05/0523office/ ) .
- Key Trafficking Issues in the Western Hemisphere Region
Human trafficking manifests itself differently around the world. In the Western Hemisphere – North, Central, and South America and the Caribbean – there are broad commonalities in trafficking trends countries face and how their governments and authorities approach the crime. Below is an overview of shared issues in the region to illustrate the overall situation and coordinate the anti-trafficking efforts of governments and other stakeholders . These regional issues are extrapolated from the individual narratives for the countries in the region, including the United States.
Unprecedented irregular migration in the region affects all Western Hemisphere countries. Migrants and asylum seekers are especially vulnerable to sex trafficking and forced labor, including by large and small organized criminal groups. Migrants who rely on migrant smugglers are at particularly high risk of exploitation as many assume debt to pay migrant smugglers. Irregular migration may also include individuals already exploited by traffickers, as victims may be motivated to migrate and seek protection elsewhere. While some countries enacted policies aimed at reducing migrants’ vulnerability to trafficking by providing temporary residency and access to formal employment, education, healthcare, and other services, we encourage all countries faced with irregular migration challenges to prevent trafficking and prioritize screening among migrants.
Countries across the region generally have a good understanding of and response to sex trafficking, especially in identification of women who are victims. Governments also undertake and emphasize the importance of law enforcement and criminal justice approaches to address trafficking, even if implementation is uneven. Many governments seek to tackle both internal and transnational human trafficking. In broad terms, there is political will in many countries to address human trafficking, particularly sex trafficking.
Weak efforts targeting forced labor remain a concern in the Western Hemisphere. Governments generally focus on addressing sex trafficking and have weaker, poorly enumerated procedures to prosecute labor traffickers and protect victims of forced labor. Labor inspectorates are underfunded and understaffed and typically have limited or no authority to inspect informal sector worksites where many victims are exploited, especially along changing migration routes. Governments’ lack of attention to labor trafficking leaves victims unprotected in multiple sectors, including agriculture , mining , logging, maritime, and service .
Traffickers also exploit many victims in forced criminality . Organized crime groups, including gangs and illegal armed groups, exploit girls in child sex trafficking, force children into street begging, forcibly recruit or use child soldiers, and coerce and threaten young men and women to transport drugs, commit extortion, act as lookouts, or commit acts of violence, including murder. Organized crime groups target groups of migrants unable to enter a country due to border restrictions or awaiting asylum decisions, including at the U.S.-Mexico border. State-sponsored forced labor is also a concern, specifically Cuba’s labor export program, including its medical missions – which the Cuban government continues to profit from by subjecting workers to forced labor and exploitation.
Gaps in trafficking victim protection are another broad concern in the Western Hemisphere. For years governments have lacked (or failed to provide the necessary) financial and human resources to screen for and identify trafficking victims and provide them trauma-informed services. Some governments have developed policies and protocols for screening victims and referring them to care, but implementation has been inconsistent or ineffective. In addition, governmental interagency coordination is weak, with working groups often disjointed and disempowered, which is particularly detrimental to the cross-sectoral collaboration needed for victim protection efforts. These problems are particularly notable among migrants, whom governments rarely screen for trafficking indicators.
Furthermore, governments make weak screening and identification efforts even with underserved populations and marginalized groups recognized as at high risk to trafficking, including Afro-descendant, Indigenous, and LGBTQI+ persons, as well as members of other ethnic and linguistic minorities, migrants, refugees, and displaced persons. These populations also frequently experience discrimination from authorities, often making them fearful to report crimes or access care and justice. Finally, there are insufficient trafficking-specific services for victims, particularly for men and boys, in most countries across the region. Governments refer identified trafficking victims to support systems designed to serve other populations, such as migrants, individuals experiencing homelessness, or victims of gender-based violence, which do not meet the specific needs of trafficking victims. Similarly, access to justice and services is concentrated in large urban areas, while the most vulnerable individuals frequently live in rural areas with limited government presence. Lack of victim-centered and trauma-informed services can hinder victim identification, prevent healing, increase risk of re-trafficking, and fuel impunity by making survivors less likely to participate in the case against their traffickers.
Criminal justice responses and definitions of trafficking are concerning across the region. Many governments have weaknesses in their legal systems and uneven judicial application of trafficking laws, including levying fines in lieu of imprisonment for trafficking crimes, imposing penalties not commensurate with those for other crimes, and failing to criminalize all forms of child sex trafficking. Judges, in particular, may lack adequate training in applying trafficking laws and coercive methods traffickers use, which impacts their decisions and sentences. Impunity for trafficking crimes fosters misperceptions about trafficking among both policymakers and the public. Inadequate law enforcement efforts and insufficient capacity-building for law enforcement and other first responders hinders or impacts efforts in low-capacity countries , especially in the Caribbean. Governments with limited resources often do not recognize or implement low-cost/high-impact anti-trafficking policies. Official complicity within law enforcement, the prison system, and local government facilitates trafficking crimes across some governments, but criminal prosecution of complicit officials lags behind the already low number of convictions of other traffickers. Child sex trafficking and extraterritorial commercial child sexual exploitation and abuse are also pervasive concerns, particularly due to the increased use of social media and online platforms to recruit victims. Many officials conflate human trafficking with other crimes, including migrant smuggling, child labor, sexual violence against children, illegal commercial sex, and illegal adoption. Because of this confusion, governments may misidentify trafficking victims, fail to give them adequate support, and therefore underreport trafficking crimes. These problems lead to inadequate data collection and reporting on human trafficking and, therefore, an incomplete understanding of the extent of the crime in the hemisphere.
- A Framework for Balancing Prosecution, Prevention, and Victim Protection Priorities in Criminal Justice Systems
Holding human traffickers accountable is an essential component of the Palermo Protocol’s “3P” paradigm of prosecuting traffickers, protecting victims, and preventing the crime. Prosecutions make powerful statements that human trafficking will not be tolerated, and perpetrators will be held accountable, and because it is important to recognize that prosecution, protection, and prevention efforts are all inextricably intertwined. Victims are better able to assist in investigations and prosecutions when they have access to robust protections, and successful prosecutions protect individual victims from revictimization in addition to preventing the convicted trafficker from exploiting others.
Supporting victims throughout the criminal justice process is critical. Cases often move slowly, leaving victims anxious about the uncertainty of the outcome, fearful of retaliation, re-traumatized by having to recount traumatic events, frustrated by proceedings that can disrupt their lives, and embarrassed, ashamed, or ostracized when information about their victimization becomes public. These feelings of anxiety, uncertainty, trauma, frustration, and fear can be further intensified by the distrust of authorities that traffickers often instill and manipulate to compel victims’ silence and their compliance with the traffickers’ commands. Victims often experience conflicting pressures from authorities encouraging them to cooperate, traffickers seeking to silence them, and their own efforts to put traumatic events behind them. For some survivors, the opportunity to speak out, be believed, and play an active role in bringing traffickers to justice can be empowering and vindicating. Yet for many, the process can be harrowing, especially when they do not receive sufficient services and support.
The difficulties victims often experience during investigations and prosecutions can further intensify the challenges authorities face when seeking to hold perpetrators accountable, protect their communities, and prevent traffickers from harming others. In striving to bring traffickers to justice without unduly burdening, re-traumatizing, or endangering victims, prosecutors continually balance the interests of justice, public safety, and protection of the community with the rights and interests of individual victims. Successful strategies for navigating these challenges will inevitably vary to some extent according to the relevant laws and criminal justice systems across various jurisdictions but the promising practices highlighted below can aid in effectively balancing these complex considerations in a wide range of contexts. The end goal is to enhance support for victims and decrease the burdens they experience during the criminal justice process regardless of whether they are testifying — while also strengthening investigations and prosecutions to increase accountability for traffickers.
Vigorous Victim Protections at All Stages of the Criminal Justice Process
The best way for authorities to support human trafficking survivors is to ensure the provision and continuity of comprehensive services at all stages of the criminal justice process, including in coordination with civil society organizations who specialize in victim services. Children survivors require specialized care and interventions. Robust victim protections, including comprehensive victim-centered, trauma-informed services, are essential to support victims in rebuilding their lives, providing the security and stability they need to safely participate in the criminal justice process, and enabling them to recall and recount their experience. Such services should include access to identity documents, mental health and medical services, housing, and other forms of relief to support physical and mental healing. In addition, survivors should have access to legal support and services, ideally through an independent legal advocate. This support should be tailored to assist the survivor with a range of legal needs, whether related to navigating the investigation and prosecution of the criminal case against the trafficker, to immigration relief, or other legal matters.
Investigators, prosecutors, and victim service providers should collaborate closely to ensure that the victim is stabilized and supported before expecting meaningful participation in the criminal justice process. Trauma can impede a victim’s ability to recall and recount relevant events, so investigators and prosecutors should develop advanced expertise in victim-centered, trauma-informed, culturally appropriate methods for stabilizing survivors, building rapport, and conducting effective interviews. Effective interviewing may entail consistent use of professional interpreters to ensure clarity of communication and often benefits from the use of specialized techniques that incorporate the expertise of survivor leaders. These practices can make the victim’s participation in the process less burdensome and traumatic. They can also strengthen prosecutions by eliciting more accurate statements, minimizing discrepancies that could later be used to attack the victim’s credibility, and enabling the victim to provide more detailed information that could lead to other sources of evidence.
Protection and services for trafficking victims should not be conditioned on whether the trafficker is charged or convicted. In cases where a foreign victim chooses to return to their home country, relocation assistance should be provided and authorities should proceed with prosecutions involving repatriated victims when possible, by having them present evidence virtually where authorized by law or by funding their return travel for court proceedings as necessary. Access to comprehensive support is not only in the best interest of survivors- it also increases the likelihood they will feel sufficiently safe and empowered to assist in the investigation and prosecution. Whether survivors testify against the trafficker or provide more limited assistance to law enforcement, support for their long-term well-being should be a priority even after the case is closed.
Developing Evidence to Decrease Reliance on Victim Testimony
Another best practice in prosecuting trafficking cases is the use of strategic investigative processes to develop evidence that supports the statements or testimony of trafficking survivors. In human trafficking prosecutions, every piece of evidence counts because each piece of corroborating evidence is important to reduce reliance on victim testimony, preventing undue credibility attacks, and to increase the likelihood of conviction.
All human trafficking victims who provide statements, declarations, or testimony are inevitably subjected to credibility challenges, whether by jurists in inquisitorial systems that decide whether the victim’s statements are sufficiently reliable or by the defense in adversarial systems. Victims’ credibility is often scrutinized based on issues such as delays in reporting their victimization, trauma-related inconsistencies in recalling and recounting certain details, or involvement in unlawful acts related to their victimization. Corroborating evidence can be essential to countering such credibility attacks, increasing the likelihood of the victim’s statements or testimony being believed, and leading to higher rates of convictions. Investigators and prosecutors should engage in early and continuous collaboration to assess ways to pursue other sources of evidence beyond victim testimony and to corroborate available statements and evidence through sources such as electronic records, physical evidence, and other potential witnesses.
In some cases, other admissible evidence uncovered during a thorough investigation may minimize the need for victim testimony and can become essential to enabling a prosecution to proceed even if the victim is not able to participate in the trial. Even evidence that provides only limited circumstantial corroboration of one small aspect of a trafficker’s conduct can, when combined with other evidence, provide significant substantiation of a survivor’s account. Investigators and prosecutors should clearly communicate to survivors that they are not “responsible” for the successful investigation and prosecution, that services and protections are not dependent on the outcome of the criminal case, and that authorities are responsible for gathering relevant evidence from all available sources. Such evidence can also significantly reduce the burdens felt by the victim and the risks of re-traumatization associated with participating as a witness.
Victim-Centered, Trauma-Informed Charging and Prosecution Practices
One of a prosecutor’s most serious responsibilities is to utilize all available avenues to protect the victim and prevent witness intimidation efforts that could compromise both the victim’s sense of safety and the integrity of the investigation. Such avenues include seeking court orders, including restraining orders, orders of protection, and no-contact orders to prohibit the defendant from attempting to contact the victim either directly or indirectly. They also include working with law enforcement and victim advocates to prepare a safety plan and document any attempted contact. Prosecutors should encourage survivors to seek help from a trusted point of contact with the police or other authorities and to immediately disclose to the prosecutor or advocate any attempt by the traffickers to contact them. Documented attempts to contact or intimidate the victim should be used in appropriate instances to bring additional obstruction-of-justice or witness tampering charges and may be relevant to explain a victim’s reluctance to cooperate as a witness or recant earlier statements. Proof of the trafficker’s efforts to contact the victim may also allow the prosecutor to introduce otherwise inadmissible evidence.
Even if the survivor is able and willing to testify, the prosecutor should introduce corroborating evidence to bolster and support their testimony, which is especially important when a survivor’s trauma has caused inconsistency in their statements or memory. Prosecutors may also consider using expert testimony in appropriate instances to explain the impacts of trauma on memory and recall. Admissible evidence may include the survivor’s medical records, testimony from first responders or other witnesses to relevant incidents, certain statements made by the accused, electronic messages, physical evidence recovered from relevant locations, and video recordings. Additional evidence gathered using well-designed and implemented strategic investigative processes can in some instances serve, when possible, as a substitute for the victim’s critical testimony, either completely or on select issues, if the victim becomes unavailable or has difficulty testifying effectively.
Unfortunately, despite all efforts to develop other evidence, some cases of the underlying trafficking offenses cannot proceed without the testimony of the victim. In those instances, certain practices can be used to pursue prosecutions and accountability while minimizing undue burdens and adverse impacts on survivors. Prosecutors can strategically focus charges on the most readily provable aspects of the criminal conduct such as assaults, threats, financial crimes, possession of illicit images, or witness tampering, which may be less reliant on victim testimony but may still provide significant opportunities to hold offenders accountable. Prosecutors can also seek to resolve cases through guilty pleas in appropriate instances to secure substantial justice without the need for victim testimony at trial.
When a victim does need to testify, prosecutors should file all applicable motions to limit the scope of their testimony to relevant facts and preclude inappropriate cross-examination about the victim’s prior bad acts or sexual history. When allowed by law, prosecutors should consider seeking the court’s permission to present the victim’s testimony virtually or in any other manner that preserves the defendant’s right to confront the accuser while physically separating the victim from the defendant. Victim services and security should be provided throughout all stages of trial preparation, trial, and sentencing.
Human trafficking survivors with lived experience are uniquely positioned to provide insight, guidance, and expertise on establishing appropriate support systems, strategic investigative processes, and prosecutorial practices that allow victims to be heard and supported at all stages of investigations and prosecutions. Incorporating survivor-informed expertise is essential to providing the security, stability, and support survivors need to participate safely and effectively as witnesses, while reducing the burdens and risks of re-traumatization often associated with the criminal justice process and strengthening efforts to hold traffickers accountable.
- The Intersection of Forced Marriage and Human Trafficking
The question of whether forced marriage constitutes a human trafficking crime is complex, and the answer can vary depending on the circumstances of the forced marriage and the applicable national laws.
Governments around the world have taken different approaches to the issue, both in terms of the laws they have enacted and of the way those laws are implemented in practice. While the governing international law on trafficking in persons, the UN TIP Protocol, allows for flexibility in how State Parties criminalize human trafficking under domestic legislation, establishing exploitative intent is critical to considering whether the conduct constitutes trafficking in persons.
What is forced marriage?
The 2022 update to the U.S. Strategy to Prevent and Respond to Gender-Based Violence Globally defines forced marriage as a marriage at any age that occurs without the free and full consent of both parties, including anyone under the age of 18 who is not able to give full consent. Forced marriage may occur when family members or others use physical or emotional abuse, threats, fraud, or deception to obtain an individual’s agreement. In such cases, an individual cannot be considered to have consented to the marriage. The terms “early marriage” and “child marriage” are often used interchangeably to refer to any marriage in which at least one of the parties has not attained the age of 18. There is overwhelming evidence that child, early, and forced marriages can increase individuals’ vulnerability to future exploitation and abuse – with long-term consequences for their health, wellbeing, safety, and opportunities.
Is Forced Marriage a Form of Trafficking under International Law?
Article 3 of the UN TIP Protocol defines “trafficking in persons” to require three essential elements—an act, conducted using one or more means, for an exploitative purpose. Article 3 does not list forced marriage explicitly as a form of exploitation; instead, it provides that “exploitation shall include, at a minimum, the exploitation of the prostitution of others or other forms of sexual exploitation, forced labor or services, slavery or practices similar to slavery, servitude or the removal of organs.” Accordingly, when a forced marriage involves any of the acts, means, and purposes of exploitation listed in Article 3, it would be considered trafficking under the UN TIP Protocol. For example, forced marriages that also involve forced labor or services, or slavery or practices similar to slavery would also be trafficking in persons if the relevant acts and means are present. However, the non-exhaustive list of forms of exploitation in Article 3 allows State Parties to decide to expand the list of forms of exploitation within their own domestic definition of trafficking in line with the purpose and scope.
While the UN TIP Protocol does not explicitly include forced marriage within the definition of trafficking, many stakeholders argue that if all the elements of trafficking are present (i.e., there is an act, a prohibited means, done for the purpose of exploiting another person), it should not matter that the exploitation takes the form of a forced marriage. These stakeholders point to the identical practices used by unscrupulous recruiters who are paid by business owners or prospective husbands to deceive and obtain the consent of individuals to marry “loving wealthy husbands” or accept “lucrative job offers,” in both instances only to leave victims trapped and exploited.
Countries that have chosen to include forced marriage within their domestic definitions of trafficking, either explicitly or implicitly, have taken three common approaches:
Forced Marriage Included as a Form of Exploitation
By leaving the list of forms of exploitation under Article 3 open-ended, the UN TIP Protocol allows State Parties to choose to expand the list of forms of exploitation included under domestic anti-trafficking laws. As such, some countries have chosen to include forced marriage as an exploitative purpose under their respective anti-trafficking laws. Several countries have taken this approach, including, but not limited to: Argentina, Australia, Botswana, Cambodia, Chad, Costa Rica, Croatia, Ecuador, El Salvador, Haiti, Kenya, Lithuania, Nicaragua, North Macedonia, Seychelles, and Uganda.
“Practices Similar to Slavery” Interpreted to Include Some Forms of Forced Marriage
Other countries interpret the inclusion of “practices similar to slavery” within Article 3 of the UN TIP Protocol to include certain forms of forced marriage. “Practices similar to slavery” is defined in the Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery, the Slave Trade, and Institutions and Practices Similar to Slavery. Under Article 1(c) of this convention, “practices similar to slavery” refers to, inter alia, “Any institution or practice whereby: (i) A woman, without the right to refuse, is promised or given in marriage on payment of a consideration in money or in kind to her parents, guardian, family or any other person or group; or (ii) The husband of a woman, his family, or his clan, has the right to transfer her to another person for value received or otherwise; or (iii) A woman on the death of her husband is liable to be inherited by another person …” For countries that use this definition of “practices similar to slavery” to interpret the scope of the definition of trafficking in persons under the UN TIP Protocol, some, but not all, forms of forced marriage could constitute trafficking in persons.
Forced Marriage and Trafficking in Persons as Distinct Crimes .
It is also worth mentioning that there are many countries that choose to address forced marriage and trafficking in persons as separate offenses. In its 2020 Issue Paper “Interlinkages Between Trafficking in Persons and Marriage,” the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) acknowledges the viability of these different approaches and explains that there is “no one-size-fits-all approach to most effectively counter cases involving interlinkages between trafficking in persons and marriage.”
Establishing Exploitative Intent is Critical in All Approaches
At the heart of the question of whether a forced marriage constitutes a human trafficking crime is the question of whether the intention was to exploit a person or persons through the marriage. Recently, the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union recognized the gravity of and increasing linkages between forced marriages and human trafficking. They formally adopted a directive noting that the exploitation of forced marriages “fall[s] within the scope of offenses concerning trafficking in human beings…to the extent that all the criteria constituting those offenses are fulfilled.”
While States that choose explicitly to include forced marriage within their definition of exploitation, or implicitly, through the inclusion of “practices similar to slavery,” consider “forced marriage as inherently exploitative,” such an interpretation is neither required nor shared by all States. As UNODC explains,
…cultural and national contexts are relevant in determining exploitation, especially in relation to forced and servile marriage. Cultural and other context-specific factors can play a role in shaping perception of what constitutes exploitative conduct for the purposes of establishing that trafficking has occurred.
Marriages generally involve domestic work and sexual relations between spouses, neither of which is generally understood to constitute abuse or exploitation. However, there are circumstances in which individuals may be exploited in connection with each of these under the guise of marital obligations. Taking into consideration the cultural and national contexts in which marriages transpire is a complex but necessary task when determining whether all three elements of a human trafficking offense are present in a case involving forced marriage.
While it is understood forced marriage is inherently harmful, rooted in gender inequality, and can often dramatically increase the risks of individuals to trafficking in persons, gender-based violence (GBV), and other abuses or crimes, it is important to acknowledge there may be circumstances in which a forced marriage has occurred, but the offense of human trafficking has not, because the purpose of the marriage was not to exploit another individual. For example, in some communities, even an untruthful allegation of sexual indiscretion or promiscuity can irreparably damage a girl’s prospects of marriage or place her in physical danger. Parents in these communities may attempt to protect their daughters by marrying them at a young age to avoid such allegations and safeguard their reputations. Similarly, families who live in refugee camps or other unstable situations where there is high prevalence of multiple forms of violence, including GVB, may view marriage as a protective mechanism that will prevent their daughters from being victims of physical or sexual violence or offer them greater economic security. In these instances, such marriages commonly occur without an individual giving their full, free, and informed agreement to marry. By definition, such an arrangement would constitute a forced marriage and depending on the country, potentially a violation of domestic criminal laws. However, if no one involved in arranging the marriage (not the spouse, parents, matchmaker, etc.) is participating for the purpose of exploiting the individual , then the necessary elements of trafficking in persons are not met. Other crimes or human rights abuses may have occurred and should be addressed, but the specific crime of human trafficking has not occurred because the marriage was not for the purpose of exploitation. To the contrary, taking into account the relevant cultural and social norms, these actors may believe they are acting in the best interest of the individual. As in all criminal cases, the knowledge and intent of the individual matters and therefore, in the case of forced marriages as a potential trafficking crime, one must consider if an individual intended to exploit someone, or whether they intended, even misguidedly and mistakenly, to do what was believed to be in the individual’s best interest. These complicated dynamics must be determined in other trafficking contexts as well.
Therefore, when allegations of forced marriage are presented, they must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis to determine whether they constitute trafficking in persons. Such an assessment neither legitimizes forced marriage nor detracts from serious concerns around such practices. Rather, it simply ensures the appropriate criminal prosecution, protection, and prevention responses are utilized to address the conduct in question because, as UNODC explains, “….qualifying a particular type of conduct as trafficking in persons has extensive consequences for both the alleged perpetrators and victims of the crime.”
* NOTE: U.S. law does not explicitly recognize forced marriage as a “severe form of trafficking in persons” or reference it in criminal trafficking laws. Therefore, forced marriage, per se, is not automatically considered a form of trafficking in persons under U.S. law. The facts and circumstances of the forced marriage must be considered to determine whether the conduct falls under a relevant definition or legal provision. Generally, if the person forced to marry is also compelled to work or to engage in commercial sex, then the forced marriage would likely fall within the definition of trafficking in persons and be a crime under U.S. law. Because the definition of “severe forms of trafficking in persons” established under the Trafficking Victims Protection Act governs the Department’s minimum standard assessments for the purposes of the TIP Report, the Department accordingly includes governments’ efforts to combat forced marriage if there is credible evidence that those efforts address forced marriage in which the objective of the marriage was to exploit another person for labor or services or commercial sex.
An Example of When a Forced Marriage Involved Human Trafficking: United States of America v. Zahida Aman, et al.
In United States of America v. Zahida Aman, et al., the United States successfully prosecuted and convicted three individuals for trafficking crimes relating to a forced marriage. On January 24, 2023, the traffickers were sentenced to five, ten, and 12 years of imprisonment, respectively, and ordered to pay restitution to the victim. The case serves as an example of how forced marriage and human trafficking can intersect and result in complex and devastating exploitation of vulnerable individuals, as abuse often goes undetected for long periods of time due to its hidden nature within the confines of familial relationships.
A federal jury sitting in Richmond, Virginia, found defendants Zahida Aman, Mohammad Nauman Chaudhri, and Mohammad Rehan Chaudhri guilty of conspiracy to commit forced labor for compelling the domestic labor of a Pakistani woman for 12 years. The jury further found defendant Aman guilty of forced labor and document servitude, and defendant Rehan Chaudhri guilty of forced labor.
According to the evidence presented in court, defendant Zahida Aman arranged for her son’s marriage to the victim in 2001. The victim moved to the United States and lived in a house in Midlothian, Virginia, with her husband and the three defendants (the husband’s mother and his two brothers). The defendants compelled the victim to serve the family as a domestic servant, using physical and verbal abuse, restricting communication with her family in Pakistan, confiscating her immigration documentation and money, and eventually threatening to separate her from her children by deporting her to Pakistan.
The defendants slapped, kicked, and pushed the victim, even beat her with wooden boards, and on one occasion hog-tied her hands and feet and dragged her down the stairs in front of her children. Even after the victim’s husband moved away, the defendants kept the victim in their Virginia home, often forcing her to perform increasingly laborious tasks…
The evidence further showed that the defendants required the victim to work every day, beginning early each morning. They restricted her food, forbade her from learning to drive or speaking to anyone except the defendants’ family members and prohibited her from calling her family in Pakistan.
Press Release, U.S. Department of Justice
- 2024 TIP REPORT HEROES
This year marks a major milestone—the 20th anniversary of the TIP Report Heroes awards program. Each year, the Department of State honors individuals around the world who have devoted their lives to the fight against human trafficking. These individuals include NGO workers, lawmakers, government officials, survivors of human trafficking, and concerned citizens. They are recognized for their tireless efforts—despite some working in challenging environments where human trafficking concerns remain pervasive and facing resistance, opposition, or threats to their lives—to protect victims, punish offenders, and mitigate the underlying factors that cause vulnerabilities traffickers often target.
For more information about current and past TIP Report Heroes, please visit the TIP Report Heroes Global Network at www.tipheroes.org .
Al Amin Noyon Manager BRAC Migration Centre
Md. Al-Amin, or Noyon, is a welcoming first face to trafficking survivors and migrants as they return to Bangladesh. As a fellow trafficking survivor, Noyon is uniquely qualified and motivated to help them rebuild their lives. In his capacity as manager of the BRAC Migration Welfare Centre onsite at the Dhaka airport, Noyon has supported more than 34,000 Bangladeshi trafficking survivors and migrants over the last 15 years.
Born to a family of modest means, Noyon’s dream of a better life turned into a nightmare when he was exploited in trafficking in Malaysia in 2007, beaten, tortured, and held captive in the jungle. But as the 41-year-old now shares, that is not how his story ends. His motivation to support fellow survivors has long motivated him to serve as a member of ANIRBAN (‘the flame that will not fade ‘ ), a trafficking support platform made up of survivors who raise awareness about human trafficking and advocate for survivors and their rights.
Noyon believes education is one of the best ways to insulate Bangladesh’s next generation from the perils of human trafficking. He assists with safe migration campaigns at schools across Bangladesh and has supported thousands of students whose families are migrants or trafficking survivors secure academic scholarships.
Known by anti-trafficking stakeholders in the Bangladesh government, multilateral organizations, and likeminded partners, Noyon steadfastly supports others despite very real risks to his own safety.
Marcela Martinez Activist/Lawyer
Ms. Martinez is an accomplished Bolivian lawyer from La Paz and a leading anti-trafficking activist, who has demonstrably changed the direction of Bolivian and regional efforts to combat trafficking in persons, providing hope for families affected by human trafficking in Bolivia.
In 2017, Ms. Martinez formed the Social Responsibility Area of her law firm, from which the #RedAlertTempranaZar 🦋 hashtag operates. This hashtag is modeled after the Amber Alert system in the United States to help activate searches for victims in Bolivia. They also provide training, talks, workshops, and prevention webinars to schools, universities, neighborhood associations, and other civil society organizations. To date, more than 18,000 volunteers participate in the network and have helped authorities locate more than 150 victims.
Ms. Martinez’s work has been instrumental in the prosecution of traffickers, protection of survivors, and prevention of victims. She helped draft and lobbied for the passage of the first comprehensive Bolivian national law that gives law enforcement and prosecutors new tools and resources to combat trafficking in persons. She also created the National Trafficking in Persons Council to coordinate all Bolivian government efforts to fight human trafficking.
She was part of the NinaSonko Heart of Fire Women’s Circle, which provides support and holistic and business coaching to survivors of trafficking and violence and supports social reintegration. She has also served as a trainer through UNODC, training judges, prosecutors, and police officers on victim care at the national level. Through her tireless efforts, Ms. Martinez has reduced human trafficking in Bolivia.
Maria Werlau Founder/Executive Director Free Society Project
Maria Werlau is co-founder and Executive Director of Free Society Project, also known as Cuba Archive, a non-profit think tank that defends human rights through information. She began in 2009 researching, documenting, and denouncing exploitation and forced labor in Cuba’s labor export program and advocating for its victims and survivors. In 2010, she published her first academic work on the issue and authored an opinion piece in The Wall Street Journal denouncing the labor export program as a trafficking scheme benefiting the Cuban government. At the time, Cuba’s “internationalism” was mostly known from the slanted narrative of altruistic solidarity.
Since then, Maria has interviewed dozens of Cuban workers, mostly doctors coerced to work across the globe. Through her work at Cuba Archive, she has exposed the dark aspects of Cuba’s medical missions, emphasizing the abuses faced by the workers: violence, sexual harassment, family separation, exploitation, forced labor, wage confiscation, restriction of movement, passport retention, repression, forced exile, psychological trauma, loss of life, and more. She has also documented and exposed the labor export program’s lesser-known impact on the public health systems of Cuba and host countries, as well as its economic, political, and geostrategic value to the Cuban regime.
Maria has authored numerous works on Cuba in English and Spanish, including on healthcare, and provided expert testimony on Cuban labor trafficking to the U.S. Congress and at the OAS and the European Parliament.
Mustafa Ridha Mustafa al-Yasiri Director – Anti-Human Trafficking Directorate Ministry of Interior
Brigadier General Mustafa Ridha Mustafa al-Yasiri has courageously worked in Iraq’s Ministry of Interior (MOI) to combat trafficking in persons throughout a career dedicated to defending Iraq’s most vulnerable. Brigadier General Mustafa vastly improved the Government of Iraq’s efforts to combat trafficking in persons and enhanced services for women trafficking victims, only months after being appointed in March 2023 as the Director of MOI’s Anti-Human Trafficking Directorate. With support from the Minister of Interior, Brigadier General Mustafa immediately increased government resources dedicated to fighting trafficking in persons; appointed women Trafficking in Persons officers and employees to better assist trafficking victims; and appointed new investigative officers and officials knowledgeable on trafficking in persons, victim identification, and violence against women. Together with the Iraqi judiciary, Mustafa established a strategy to identify victims more accurately and better address sexual exploitation and other forms of trafficking.
In addition, Brigadier General Mustafa worked with hiring companies to ensure they publish and display signs detailing Iraqi workers’ rights and the MOI’s Trafficking in Persons hotline. On a weekly basis, he visited shelters to speak with victims, compile lists of needed food and hygienic and medical supplies, and help victims make calls to their families. He also personally accompanied trafficking victims to court to help with their hearings and legal procedures. Every day, motivated by personal conviction, Brigadier General Mustafa is realizing a professional goal to serve and protect many of the most vulnerable citizens of Iraq.
Edith Murogo Founder/Chief Executive Officer Centre for Domestic Training and Development
Edith Murogo is a beacon of hope on the frontlines of the fight against human trafficking and labor exploitation. When Edith started training domestic workers more than two decades ago, she met victims of human trafficking and gender-based violence. This experience prompted her to pioneer initiatives that transformed anti-trafficking efforts in Kenya.
After establishing the Centre for Domestic Training and Development (CDTD) in 2001, Edith became a leading advocate for domestic workers’ rights and lobbied the government for strengthened protections of migrant workers. Edith initiated training to professionalize domestic workers and convinced the government to develop the curriculum and establish a certificate program for domestic workers seeking employment abroad. Since opening, CDTD has assisted over 50,000 domestic workers with advocacy, skills, and knowledge to prevent them from becoming victims of trafficking.
In 2012, Edith opened the Talia Agler Girls Shelter (TAGS) – a safe house providing comprehensive assistance to girls and young women, especially for survivors of sexual and gender-based violence exploited in human trafficking. TAGS has assisted over 1,000 girls with removal from trafficking situations, recovery, and reintegration support services as well as education, mentorship, and leadership opportunities.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Edith established Kenya’s National Shelters Network to coordinate shelter services across Kenya and ensure all survivors receive crucial protection services. Edith is a tireless advocate working with government and civil society to strengthen anti-trafficking laws and responses. The Department of Labor and BBC have highlighted her work in several documentaries about human trafficking.
Oumou Elkhairou Niaré Samaké Coordinator National Integrated Program for the Fight Against Drug Trafficking and Organized Crime; National Committee for the Fight Against Trafficking in Persons and Similar Practices
Oumou Elkhairou Niaré Samaké (Oumou), a well-known Malian magistrate, currently serves as the coordinator of Mali’s National Integrated Program for the Fight against Drug Trafficking and Organized Crime and as Coordinator of the National Committee for the Fight Against Trafficking in Persons and Similar Practices. Oumou is a fierce advocate for human rights, gender-based violence, and trafficking in persons issues. She has spearheaded Mali’s recent adoption of a new Action Plan to Combat Trafficking in Persons; championed the development of Mali’s new draft penal code to criminalize trafficking in persons; and fought to increase prosecutions over the past year of hereditary slavery cases.
In 2020 and 2021, the Trafficking in Persons Committee became relatively inactive. However, upon her appointment in 2022, Oumou reinvigorated Mali’s anti-trafficking efforts. First, she reestablished regular coordination meetings and published the Trafficking in Persons Committee’s overdue 2021 and 2022 annual reports. Next, she spearheaded the development, drafting, and adoption of Mali’s new National Action Plan to Combat Trafficking in persons, launched in October 2023. She has maintained high level standard of contacts with partners, donors, and national and international stakeholders in the fight against trafficking in persons and hereditary slavery.
Samson Inocencio Jr. Vice President International Justice Mission Philippines Program Against Online Sexual Exploitation of Children
Samson “Sam” Inocencio has dedicated over 20 years to combating trafficking in persons through his work with the International Justice Mission (IJM) Philippines. He has contributed to 147 convictions for commercial sexual exploitation and 220 for online sexual exploitation (OSEC) crimes since 2005. After becoming National Director of IJM in 2016, Sam assisted in the removal of 544 children from situations of commercial sexual exploitation and 1,237 children who were at risk of OSEC.
Sam led IJM’s efforts under the U.S.-Philippine Child Protection Compact (CPC) Partnership to combat OSEC crimes and advocated for a 347 percent budget increase for the Philippine National Police – Women and Children Protection Center. As IJM’s representative to the Government of the Philippines’ Interagency Council Against Trafficking, Sam has assisted the Philippines in its efforts to combat the commercial sexual exploitation of children and OSEC related crimes, to hold offenders accountable in courts of law, and to safeguard Filipino children.
He collaborated with the Government of the Philippines in 2016 to develop a “roadmap to Tier 1” in the U.S. Department of State Trafficking in Persons Report. The Philippines has been ranked Tier 1 for eight years due to the merits of its efforts. Sam’s leadership and dedicated service have strengthened the government and civil society’s response to trafficking and protected thousands, especially children, from exploitation.
Marijana Savić Founder/Director Atina
Marijana Savić, the founder and director of NGO Atina, is an activist dedicated to advancing women’s and girls’ rights. For over two decades, she has provided vital support and recovery programs for survivors of trafficking and gender-based violence in Serbia. Her efforts have led to important progress in policy reform to combat human trafficking and support women and girls, who were victims of commercial sexual exploitation.
Under Marijana’s guidance, Atina has become a pivotal organization in Serbia’s anti-trafficking sector. Marijana also actively contributes by helping integrates survivor experiences into law and human rights policies, in Serbia and abroad. Her commitment extends to economic empowerment through the social enterprise Bagel Bejgl, which she founded in 2015. This initiative – which provides employment to trafficking survivors – supports Atina’s sustainability by directing its profits to anti-trafficking programming.
Marijana works with international bodies, including the Council of Europe, as an expert in combating trafficking, especially labor exploitation. An alumnus of the Human Rights Advocates Program at Columbia University, Marijana is also involved in global advocacy as a member of the Global Fund for Children’s board, Canada’s Equality Fund Investment Advisory Council, and the UN Voluntary Trust Fund for Victims of Human Trafficking board.
Marijana’s relentless activism and leadership have earned widespread acclaim and numerous awards for Atina, highlighting her role in shaping a safer, more equitable society for women and girls across Serbia and globally. Her work exemplifies a profound commitment to human rights and the empowerment of the most vulnerable groups.
Rosa Cendón Advisor – Human Trafficking and Gender-based Violence Catalonia Regional Ministry for Equality and Feminism
Rosa Cendón has devoted her life to assisting victims, raising awareness, and combating human trafficking in Spain.
As a social worker and educator based in Barcelona, Rosa has led advocacy and institutional relations for SICARcat, the largest anti-trafficking NGO in the Catalonia region, for 20 years. SICARcat offers assistance to women and children survivors of trafficking by providing them with shelter and legal, psychological, medical, and social support. Since 2022, Rosa has served as an expert advisor for combating human trafficking and gender-based violence at the Catalonia regional Ministry of Equality and Feminism. She continues to promote change by raising awareness of human trafficking and designing public policy.
Rosa is at the forefront of anti-trafficking efforts in Catalonia. Her victim-centered approach has influenced regional and national anti-trafficking and victim protection policies. She contributed to designing the regional Catalonian and Barcelona city protocols for victim protection. Under her leadership, SICARcat developed tools for the detection and intervention of human trafficking cases working closely with law enforcement agencies. She regularly conducts specialized training for key actors.
During the height of the European migration crisis, Rosa helped found the ASIL.CAT network of human rights NGOs that coordinated shelter, protection, and services for the influx of refugees. She worked to ensure that anti-trafficking efforts were included in the asylum reception system. As a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Spain has received over 200,000 Ukrainian refugees and Rosa has been at the forefront in providing support to the refugees arriving to Barcelona.
Letitia Pinas Inspector of Police – Head of the Trafficking in Persons Unit Suriname Police Force
Inspector Letitia Pinas launched her career with the Suriname Police Force in 1998. After serving in the Youth Affairs Department and the Public Relations Department, she was assigned the role of Acting Head of the 14-person Trafficking in Persons Unit in November 2020, to determine its continued usefulness. Inspector Pinas overhauled the underperforming unit by drafting a strategic plan that improved the unit’s ability to investigate suspects and identify and serve victims, its presence in and outreach to the community, and the public’s trust in it.
With no NGOs working on human trafficking, Inspector Pinas assumed a disproportionate burden not only to investigate cases properly and effectively but also ensured efforts continued in the areas of protection and prevention, including expanded awareness. Despite the government facing a multi-year financial crisis, she successfully lobbied for funds from the police to establish an emergency shelter within her office to house victims in the initial stages of an investigation. She closely collaborated with the Prosecutors’ Office for funding to create a long-term shelter for both male and female victims. Through improved collaboration with the Maritime Police and the Military Police, the Trafficking in Persons Unit actively participates in inspections of incoming vessels, while also checking for potential victims amongst incoming travelers at the airport. These efforts have led to increased numbers of identified victims, including many who have trusted the police enough to self-report. Her collaboration with senior police officials resulted in the development of a website that raises awareness on human trafficking and provides society with a tool to anonymously report suspected cases of trafficking.
- Child Soldiers Prevention Act List
Section 402 of the Child Soldiers Prevention Act, as amended (CSPA) requires publication in the annual TIP Report of a list of foreign governments identified during the previous year as having governmental armed forces, police, or other security forces, or government-supported armed groups that recruit or use child soldiers, as defined in the CSPA. These determinations cover the reporting period beginning April 1, 2023 and ending March 31, 2024.
For the purpose of the CSPA, and generally consistent with the provisions of the Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the involvement of children in armed conflict, the term “child soldier” means:
- any person under 18 years of age who takes a direct part in hostilities as a member of governmental armed forces, police, or other security forces;
- any person under 18 years of age who has been compulsorily recruited into governmental armed forces, police, or other security forces;
- any person under 15 years of age who has been voluntarily recruited into governmental armed forces, police, or other security forces; or
- any person under 18 years of age who has been recruited or used in hostilities by armed forces distinct from the armed forces of a state.
The term “child soldier” includes any person described in clauses (ii), (iii), or (iv) who is serving in any capacity, including in a support role, such as a “cook, porter, messenger, medic, guard, or sex slave.”
Governments identified on the list are subject to restrictions, in the following fiscal year, on certain security assistance and commercial licensing of military equipment. The CSPA prohibits assistance to governments that are identified in the list under the following authorities: International Military Education and Training, Foreign Military Financing, Excess Defense Articles, and Peacekeeping Operations, with exceptions for some programs undertaken pursuant to the Peacekeeping Operations authority. The CSPA also prohibits the issuance of licenses for direct commercial sales of military equipment to such governments. Beginning October 1, 2024, and effective throughout Fiscal Year 2025, these restrictions will apply to the listed countries, absent a presidential waiver, applicable exception, or reinstatement of assistance pursuant to the terms of the CSPA. The determination to include a government in the CSPA list is informed by a range of sources, including first-hand observation by U.S. government personnel and research and credible reporting from various UN entities, international organizations, local and international NGOs, and international and domestic media outlets.
The 2024 CSPA List includes governments of the following countries: Please note that 2024 Child Soldiers Prevention Act-related determinations were not final at the time of releasing the 2024 TIP Report. This section will be updated as soon as possible.
- When the Government is the Trafficker: State-Sponsored Trafficking in Persons
While the TVPA Minimum Standards for the Elimination of Trafficking In Persons and the UN TIP Protocol call on governments proactively to address trafficking crimes, some governments are part of the problem, directly compelling their citizens or other individuals into sex trafficking or forced labor. Some governments exploit individuals in forced labor in local or national public works projects, military operations, economically important sectors, as part of government-funded projects or missions abroad, or in sexual slavery on government compounds. Governments extract this work or service by threatening the withdrawal of public benefits; withholding salaries; intentionally failing to adhere to limits on national service; manipulating the lack of legal status of stateless individuals and other minority groups; threatening to punish family members; or conditioning services, food, or freedom of movement on labor or sex.
In 2019, Congress amended the TVPA to acknowledge that governments can also act as traffickers, referring specifically to a “government policy or pattern” of human trafficking; human trafficking in government-funded programs; forced labor (in government-affiliated medical services, agriculture, forestry, mining, construction, or other sectors); sexual slavery in government camps, compounds, or outposts; or employing or recruiting child soldiers. While the TVPA already directs the Secretary to consider the extent to which “officials or employees of the government have participated in, facilitated, condoned, or were otherwise complicit in” trafficking when determining whether the government is making significant efforts to meet the minimum standards, this section directly links a government’s “policy or pattern” of trafficking to a Tier 3 ranking.
The 2024 TIP Report includes the following 13 countries with a documented “policy or pattern” of human trafficking, trafficking in government-funded programs, forced labor in government-affiliated medical services or other sectors, sexual slavery in government camps, or the employment or recruitment of child soldiers:
- Afghanistan*
- China, People’s Republic of
- Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of
- South Sudan
- Turkmenistan
* The TIP Report describes the state of human trafficking within a country and with respect to Afghanistan, assesses the actions of Afghan ministries, as well as the Taliban, without implying recognition of the Taliban or another entity as the government of Afghanistan.
- Methodology
The Department of State prepared this report using information from U.S. embassies, government officials, nongovernmental and international organizations, published reports, news articles, academic studies, consultations with authorities and organizations in every region of the world, and information submitted to [email protected] . This email address provides a means by which organizations and individuals can share information with the Department of State throughout the year on government progress in addressing human trafficking.
U.S. diplomatic posts and domestic agencies reported on the human trafficking situation and governmental action to fight trafficking based on thorough research that included meetings with a wide variety of government officials, local and international NGO representatives, officials of international organizations, journalists, academics, and survivors. U.S. missions overseas are dedicated to covering human trafficking issues year-round. The 2024 Trafficking in Persons Report covers government efforts undertaken from April 1, 2023 through March 31, 2024, to the extent concurrent reporting data is available.
Tier Placement
The Department places each country in this report onto one of four categories. This placement is based not on the size of a country’s problem but on the extent of government efforts to meet the Trafficking Victims Protection Act’s (TVPA) minimum standards for the elimination of human trafficking (see page XX), which are generally consistent with the Palermo Protocol.
While Tier 1 is the highest ranking, it does not mean that a country has no human trafficking problem or that it is doing enough to address the crime. Rather, a Tier 1 ranking indicates that a government has made efforts to address the problem that meet the TVPA’s minimum standards. To maintain a Tier 1 ranking, governments need to demonstrate appreciable progress each year in combating trafficking. Tier 1 represents a responsibility rather than a reprieve.
Tier rankings and narratives in the 2024 Trafficking in Persons Report reflect an assessment of the following:
- enactment of laws prohibiting severe forms of trafficking in persons, as defined by the TVPA, and provision of criminal punishments for trafficking crimes;
- criminal penalties prescribed for human trafficking crimes which are sufficiently stringent and commensurate with those prescribed for other grave crimes;
- implementation of human trafficking laws through vigorous prosecution of the prevalent forms of trafficking in the country and adequate sentencing of traffickers;
- proactive victim identification measures with systematic procedures to guide law enforcement and other government-supported front-line responders in the process of victim identification;
- government funding and partnerships with NGOs to provide victims with access to primary health care, counseling, and shelter, allowing them to recount their trafficking experiences to trained counselors and law enforcement in an environment of minimal pressure;
- victim protection efforts that include access to services and shelter without detention and with legal alternatives to removal to countries in which victims would face retribution or hardship;
- the extent to which a government ensures victims are provided with legal and other assistance and that, consistent with domestic law, proceedings are not prejudicial to victims’ rights, dignity, or psychological well-being;
- the extent to which a government ensures the safe, humane, and, to the extent possible, voluntary repatriation and reintegration of victims;
- governmental measures to prevent human trafficking, including efforts to curb practices identified as contributing factors to human trafficking, such as employers’ confiscation of foreign workers’ passports and allowing labor recruiters to charge fees to prospective migrants; and
- governmental efforts to reduce the demand for commercial sex acts and extraterritorial sexual exploitation and abuse.
Tier rankings and narratives are NOT affected by the following:
- efforts, however laudable, undertaken exclusively by nongovernmental actors in the country;
- general public awareness events—government-sponsored or otherwise—lacking concrete ties to the prosecution of traffickers, protection of victims, or prevention of trafficking; and
- broad-based law enforcement or developmental initiatives.
A Guide to the Tiers
Countries whose governments fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking.
Countries whose governments do not fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards but are making significant efforts to bring themselves into compliance with those standards.
Tier 2 Watch List
Countries whose governments do not fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards but are making significant efforts to bring themselves into compliance with those standards, and for which:
- the estimated number of victims of severe forms of trafficking is very significant or is significantly increasing and the country is not taking proportional concrete actions;
- there is a failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat severe forms of trafficking in persons from the previous year, including increased investigations, prosecutions, and convictions of trafficking crimes, increased assistance to victims, and decreasing evidence of complicity in severe forms of trafficking by government officials.
Countries whose governments do not fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards and are not making significant efforts to do so.
The TVPA, as amended, lists additional factors to determine whether a country should be on Tier 2 (or Tier 2 Watch List) versus Tier 3:
- the extent to which the country is a country of origin, transit, or destination for severe forms of trafficking;
- the extent to which the country’s government does not meet the TVPA’s minimum standards and, in particular, the extent to which officials or government employees have been complicit in severe forms of trafficking;
- reasonable measures that the government would need to undertake to be in compliance with the minimum standards in light of the government’s resources and capabilities to address and eliminate severe forms of trafficking in persons;
- the extent to which the government is devoting sufficient budgetary resources to investigate and prosecute human trafficking, convict and sentence traffickers; and obtain restitution for victims of human trafficking; and
- the extent to which the government is devoting sufficient budgetary resources to protect victims and prevent the crime from occurring.
In addition, the TVPA directs the Secretary of State to consider, as proof of a country’s failure to make significant efforts to fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards, a government policy or pattern of: human trafficking; human trafficking in government-funded programs; forced labor (in government-affiliated medical services, agriculture, forestry, mining, construction, or other sectors); sexual slavery in government camps, compounds, or outposts; or employing or recruiting child soldiers.
The TVPA also provides that any country that has been ranked Tier 2 Watch List for two consecutive years and that would otherwise be ranked Tier 2 Watch List for the next year will instead be ranked Tier 3 in that third year. The Secretary of State is authorized to waive the automatic downgrade only once, in that third year, based on credible evidence that a waiver is justified because the government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to meet the TVPA’s minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is devoting sufficient resources to implement the plan. The following year, a country must either go up to Tier 2 or down to Tier 3. Additionally, the TVPA limits a country to one year on Tier 2 Watch List after that country received a waiver to stay on Tier 2 Watch List and was subsequently downgraded to Tier 3.
Funding Restrictions for Tier 3 Countries
Pursuant to the TVPA, governments on Tier 3 may be subject to certain restrictions on foreign assistance, whereby the President may determine not to provide U.S. government nonhumanitarian, nontrade-related foreign assistance as defined in the TVPA. In addition, the President may determine to withhold funding for government official or employee participation in educational and cultural exchange programs in the case of certain Tier 3 countries. Consistent with the TVPA, the President may also determine to instruct the U.S. Executive Director of each multilateral development bank and the International Monetary Fund to vote against and use their best efforts to deny any loans or other uses of the institutions’ funds to a designated Tier 3 country for most purposes (except for humanitarian, trade-related, and certain development-related assistance). Alternatively, the President may waive application of the foregoing restrictions upon a determination that the provision to a Tier 3 country of such assistance would promote the purposes of the TVPA or is otherwise in the national interest of the United States. The TVPA also authorizes the President to waive these restrictions if necessary to avoid significant adverse effects on vulnerable populations, including women and children.
Applicable assistance restrictions apply for the next Fiscal Year, which begins October 1, 2024.
- TVPA Minimum Standards for the Elimination of Trafficking in Persons
Trafficking Victims Protection Act of 2000, Div. A of Pub. L. No. 106-386, § 108, as amended.
(1) The government of the country should prohibit severe forms of trafficking in persons and punish acts of such trafficking.
(2) For the knowing commission of any act of sex trafficking involving force, fraud, coercion, or in which the victim of sex trafficking is a child incapable of giving meaningful consent, or of trafficking which includes rape or kidnapping or which causes a death, the government of the country should prescribe punishment commensurate with that for grave crimes, such as forcible sexual assault.
(3) For the knowing commission of any act of a severe form of trafficking in persons, the government of the country should prescribe punishment that is sufficiently stringent to deter and that adequately reflects the heinous nature of the offense.
(4) The government of the country should make serious and sustained efforts to eliminate severe forms of trafficking in persons.
Indicia of “Serious and Sustained Efforts”
1. Whether the government of the country vigorously investigates and prosecutes acts of severe forms of trafficking in persons, and convicts and sentences persons responsible for such acts, that take place wholly or partly within the territory of the country, including, as appropriate, requiring incarceration of individuals convicted of such acts. For purposes of the preceding sentence, suspended or significantly reduced sentences for convictions of principal actors in cases of severe forms of trafficking in persons shall be considered, on a case-by-case basis, whether to be considered an indicator of serious and sustained efforts to eliminate severe forms of trafficking in persons. After reasonable requests from the Department of State for data regarding investigations, prosecutions, convictions, and sentences, a government which does not provide such data, consistent with a demonstrably increasing capacity of such government to obtain such data, shall be presumed not to have vigorously investigated, prosecuted, convicted or sentenced such acts.
2. Whether the government of the country protects victims of severe forms of trafficking in persons and encourages their assistance in the investigation and prosecution of such trafficking, including provisions for legal alternatives to their removal to countries in which they would face retribution or hardship, and ensures that victims are not inappropriately incarcerated, fined, or otherwise penalized solely for un-lawful acts as a direct result of being trafficked, including by providing training to law enforcement and immigration officials regarding the identification and treatment of trafficking victims using approaches that focus on the needs of the victims.
3. Whether the government of the country has adopted measures to prevent severe forms of trafficking in persons, such as measures to inform and educate the public, including potential victims, about the causes and consequences of severe forms of trafficking in persons, measures to establish the identity of local populations, including birth registration, citizenship, and nationality, measures to ensure that its nationals who are deployed abroad as part of a diplomatic, peacekeeping, or other similar mission do not engage in or facilitate severe forms of trafficking in persons or exploit victims of such trafficking, a transparent system for remediating or punishing such public officials as a deterrent, measures to pre-vent the use of forced labor or child labor in violation of international standards, effective bilateral, multilateral, or regional information sharing and cooperation arrangements with other countries, and effective policies or laws regulating foreign labor recruiters and holding them civilly and criminally liable for fraudulent recruiting.
4. Whether the government of the country cooperates with other governments in the investigation and prosecution of severe forms of trafficking in persons and has entered into bilateral, multilateral, or regional law enforcement cooperation and coordination arrangements with other countries.
5. Whether the government of the country extradites persons charged with acts of severe forms of trafficking in persons on substantially the same terms and to substantially the same extent as persons charged with other serious crimes (or, to the extent such extradition would be inconsistent with the laws of such country or with international agreements to which the country is a party, whether the government is taking all appropriate measures to modify or replace such laws and treaties so as to permit such extradition).
6. Whether the government of the country monitors immigration and emigration patterns for evidence of severe forms of trafficking in persons and whether law enforcement agencies of the country respond to any such evidence in a manner that is consistent with the vigorous investigation and prosecution of acts of such trafficking, as well as with the protection of human rights of victims and the internationally recognized human right to leave any country, including one’s own, and to return to one’s own country.
7. Whether the government of the country vigorously investigates, prosecutes, convicts, and sentences public officials, including diplomats and soldiers, who participate in or facilitate severe forms of trafficking in persons, including nationals of the country who are deployed abroad as part of a diplomatic, peacekeeping, or other similar mission who engage in or facilitate severe forms of trafficking in persons or exploit victims of such trafficking, and takes all appropriate measures against officials who condone or enable such trafficking. A government’s failure to appropriately address public allegations against such public officials, especially once such officials have returned to their home countries, shall be considered inaction under these criteria. After reasonable requests from the Department of State for data regarding such investigations, prosecutions, convictions, and sentences, a government which does not provide such data, consistent with a demonstrably increasing capacity of such government to obtain such data, shall be presumed not to have vigorously investigated, prosecuted, convicted, or sentenced such acts.
8. Whether the percentage of victims of severe forms of trafficking in the country that are non-citizens of such countries is insignificant.
9. Whether the government has entered into effective, transparent partnerships, cooperative arrangements, or agreements that have resulted in concrete and measurable outcomes with –
a. domestic civil society organizations, private sector entities, or international nongovernmental organizations, or into multilateral or regional arrangements or agreements, to assist the government’s efforts to prevent trafficking, protect victims, and punish traffickers; or
b. the United States toward agreed goals and objectives in the collective fight against trafficking.
10. Whether the government of the country, consistent with the capacity of such government, systematically monitors its efforts to satisfy the criteria described in paragraphs (1) through (8) and makes available publicly a periodic assessment of such efforts.
11. Whether the government of the country achieves appreciable progress in eliminating severe forms of trafficking when compared to the assessment in the previous year.
12. Whether the government of the country has made serious and sustained efforts to reduce the demand for –
a. commercial sex acts; and
b. participation in international sex tourism by nationals of the country.
- Countries in the 2024 TIP Report that are not Party to the Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking In Persons, Especially Women and Children, supplementing the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime
- Congo, Republic of the
- Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of the
- Marshall Islands
- Papua New Guinea
- Solomon Islands
Between April 2023 and March 2024, Uganda became a State Party to the Protocol.
- Global Law Enforcement Data
The 2003 reauthorization of the TVPA added to the original law a new requirement that foreign governments provide the Department of State with data on trafficking investigations, prosecutions, convictions, and sentences in order to fully meet the TVPA’s minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking (Tier 1). The 2004 TIP Report collected this data for the first time. The 2007 TIP Report showed for the first time a breakout of the number of total prosecutions and convictions that related to labor trafficking, placed in parentheses.
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only |
LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 17,471 | 869 | 7,135 | 332 | 96,960 | 23,906 | 5 |
| 2018 | 11,096 | 457 | 7,481 | 259 | 85,613 | 11,009 | 5 |
| 2019 | 11,841 | 1,024 | 9,548 | 498 | 118,932 | 13,875 | 7 |
| 2020 | 9,876 | 1,115 | 5,011 | 337 | 109,216 | 14,448 | 16 |
| 2021 | 10,572 | 1,379 | 5,260 | 374 | 90,354 | 21,219 | 15 |
| 2022 | 15,159 | 2,670 | 5,577 | 528 | 115,324 | 24,340 | 27 |
| 2023 | 18,774 | 3,684 | 7,115 | 1,256 | 133,943 | 42,098 | 14 |
The above statistics are estimates derived from data provided by foreign governments and other sources and reviewed by the Department of State. Aggregate data fluctuates from one year to the next due to the hidden nature of trafficking crimes, dynamic global events, shifts in government efforts, and a lack of uniformity in national reporting structures.
“As we work to help people disproportionately affected by human trafficking, including members of racial and ethnic minorities, women and girls, the LGBTQI+ community, and migrants, we remain committed to learning from and partnering with survivors to support their recoveries and to recruit their help in better spotting and preventing these too often overlooked crimes.”
President Joseph R. Biden Jr. President
“I believe history will show that this was the moment when we had the opportunity to lay the groundwork for the future of AI. And the urgency of this moment must then compel us to create a collective vision of what this future must be. A future where AI is used to advance the public interest.”
Vice President Kamala Harris, United States
“Combating trafficking requires a strong coalition of local and global partners to share resources and information, better equip front-line workers, and track and respond to evolving trafficking trends.”
Antony Blinken, Secretary of State
“The Intelligence Community in close partnership with law enforcement has been improving its production of detailed data analysis and reporting to better discern patterns and trends in human trafficking of migrants. And with the help of new tools for conducting such analysis, we’re investing in these efforts, we think to good effect, as we also work to continually improve our connection to both local and federal law enforcement as well as the Department of Homeland Security to assist them in their work to countering the problem.”
Avril Haines, Director of National Intelligence
“Survivors are the real experts. Their experiences and their perspectives can help inform and motivate our policies so that we will do more, not less, and accelerate our efforts to combat this heinous cruelty.”
U.S. Representative Chris Smith (R-NJ)
“Yet traffickers continue to operate with impunity. Their crimes are receiving not nearly enough attention. This must change. We must invest much more in detection and protection. We must strengthen law enforcement to bring criminals that commodify human beings to justice. And we must do more to help survivors rebuild their lives.”
A ntonio Guterres, UN Secretary-General
“We need to step up our efforts to reach every trafficking victim, by strengthening detection, investigating cases, and prosecuting the criminals involved. We also need to proactively identify, assist, and support survivors of this crime to truly leave no one behind. This requires support from all sectors of society, from healthcare to social services to law enforcement.”
Ghada Waly, Executive Director of UNODC
“The scourge of human trafficking continues to evolve. Civil unrest and war across the globe, natural disasters, climate change, and the advent and increasing reach of social media all pose significant challenges.”
Sameer Jain, Member of U.S. Advisory Council on Human Trafficking
“If we are to ever defeat trafficking, and this undoubtedly must be our shared ambition, effective approaches to prevention must be the bedrock upon which our anti-trafficking efforts are built. Preventing trafficking in human beings from taking place is the best way to truly protect vulnerable groups and deprive traffickers of the illicit proceeds the crime generates.”
OSCE Secretary General Helga Maria Schmid
“Traffickers prey on the marginalized and most vulnerable. But we are witnessing an emerging trend where the demographic profile of trafficking victims is also expanding, at pace with the digital developments in which we are living.”
Dr. Kari Johnstone , OSCE Special Representative and Co-ordinator for Combating Human Trafficking
“We have to talk about those things that make us uncomfortable, especially if we want to work for an end to human trafficking. Part of that is acknowledging that when we say nothing and do nothing in the face of many of these issues we are perpetuating the same violence that was done to us.”
Rafael Bautista, Member of the U.S. Advisory Council on Human Trafficking
“Building consensus around an affirmative vision is the first line of our tech diplomacy. But the rules, the standards, the norms that societies follow are going to determine whether this technology is used for good or whether it’s used for ill.”
- Tier Placements List
| Argentina | Estonia | Poland |
| Australia | Finland | Seychelles |
| Austria | France | Singapore |
| The Bahamas | Georgia | Spain |
| Bahrain | Germany | Suriname |
| Belgium | Guyana | Sweden |
| Canada | Iceland | Taiwan |
| Chile | Korea, Republic of | United Kingdom |
| Colombia | Lithuania | United States of America |
| Cyprus | Luxembourg | |
| Czech Republic | The Netherlands | |
| Denmark | Philippines |
| Albania | Hungary | Panama |
| Antigua & Barbuda | India | Paraguay |
| Armenia | Indonesia | Peru |
| Aruba | Iraq | Portugal |
| Azerbaijan | Ireland | Qatar |
| Bangladesh | Israel | Romania |
| Barbados | Italy | Saudi Arabia |
| Belize | Jamaica | Senegal |
| Bhutan | Japan | Sierra Leone |
| Bolivia | Jordan | Slovakia |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Kazakhstan | Slovenia |
| Botswana | Kenya | South Africa |
| Brazil | Kosovo | Sri Lanka |
| Bulgaria | Latvia | St. Lucia |
| Burundi | Lesotho | St. Vincent and Grenadines |
| Cabo Verde | Malawi | Switzerland |
| Cameroon | Malaysia | Tanzania |
| Comoros | Mauritania | Thailand |
| Costa Rica | Mauritius | Timor-Leste |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of | Mexico | Togo |
| Cote d’Ivoire | Micronesia | Tonga |
| Croatia | Moldova | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Ecuador | Mongolia | Tunisia |
| Egypt | Montenegro | Türkiye |
| El Salvador | Morocco | Uganda |
| Eswatini | Mozambique | Ukraine |
| Ethiopia | Namibia | United Arab Emirates |
| The Gambia | New Zealand | Uzbekistan |
| Ghana | Nigeria | Vietnam |
| Greece | North Macedonia | Zambia |
| Guatemala | Norway | |
| Guinea | Oman | |
| Honduras | Palau |
| Algeria | Guinea Bissau | Marshall Islands |
| Benin | Hong Kong | Nepal |
| Burkina Faso | Kuwait | Niger |
| Central African Republic | Kyrgyz Republic | Rwanda |
| Chad | Laos | Serbia |
| Congo, Republic of | Lebanon | Solomon Islands |
| Curacao | Liberia | Tajikistan |
| Dominican Republic | Madagascar | Uruguay |
| Equatorial Guinea | Maldives | Vanuatu |
| Fiji | Mali | Zimbabwe |
| Gabon | Malta |
| Afghanistan | Djibouti | Russia |
| Belarus | Eritrea | Sint Maarten |
| Brunei | Iran | South Sudan |
| Burma | Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of | Sudan |
| Cambodia | Macau | Syria |
| China, People’s Republic of | Nicaragua | Turkmenistan |
| Cuba | Papua New Guinea | Venezuela |
| Haiti |
| Libya |
| Somalia |
| Yemen |
A note on Kiribati: Reports during the 2024 reporting period indicated human trafficking crimes may have occurred in Kiribati. However, information on anti-trafficking efforts from the Government of Kiribati and the nature and scope of trafficking in persons in Kiribati were insufficient to undertake a full assessment for the 2024 Report. The Department of State will continue gathering information in the coming year and assess appropriate reporting for the 2025 TIP Report.
- Regional Maps
The Regional Maps will be included in the PDF accessible online version. Below includes the region-specific Global Law Enforcement Data.
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 1,325 | 98 | 551 | 34 | 26,517 | 5,902 | 2 |
| 2018 | 1,253 | 37 | 1,190 | 29 | 24,407 | 3,749 | 2 |
| 2019 | 955 | 71 | 2,122 | 32 | 42,517 | 1,284 | 2 |
| 2020 | 1,493 | 251 | 382 | 107 | 28,538 | 6,947 | 8 |
| 2021 | 1,686 | 265 | 659 | 68 | 11,450 | 3,643 | 3 |
| 2022 | 2,477 | 388 | 904 | 139 | 21,790 | 5,436 | 5 |
| 2023 | 2,551 | 460 | 758 | 200 | 21,877 | 8,148 | 2 |
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2,949 | 77 | 3,227 | 72 | 4,915 | 669 | 0 |
| 2018 | 2,351 | 63 | 1,275 | 16 | 5,466 | 291 | 1 |
| 2019 | 3,276 | 86 | 3,662 | 20 | 14,132 | 7,687 | 2 |
| 2020 | 1,838 | 70 | 1,502 | 12 | 2,884 | 691 | 1 |
| 2021 | 1,440 | 73 | 1,066 | 60 | 3,348 | 859 | 0 |
| 2022 | 4,570 | 708 | 1,607 | 63 | 4,635 | 2,037 | 3 |
| 2023 | 3,390 | 398 | 1,802 | 97 | 6,543 | 1,161 | 2 |
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2,548 | 179 | 1,257 | 53 | 12,750 | 3,330 | 0 |
| 2018 | 2,394 | 234 | 1,379 | 80 | 16,838 | 2,675 | 1 |
| 2019 | 2,896 | 106 | 1,346 | 41 | 17,383 | 1,369 | 2 |
| 2020 | 2,355 | 101 | 1,291 | 33 | 18,173 | 1,082 | 2 |
| 2021 | 3,285 | 86 | 1,905 | 92 | 21,347 | 2,124 | 5 |
| 2022 | 2,932 | 169 | 1,668 | 67 | 24,528 | 2,497 | 6 |
| 2023 | 3,147 | 201 | 1,667 | 93 | 32,996 | 4,448 | 4 |
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 974 | 112 | 104 | 11 | 1,834 | 53 | 0 |
| 2018 | 738 | 10 | 155 | 7 | 2,675 | 83 | 0 |
| 2019 | 788 | 44 | 419 | 22 | 3,619 | 35 | 0 |
| 2020 | 533 | 106 | 414 | 84 | 3,461 | 1,827 | 0 |
| 2021 | 869 | 356 | 353 | 88 | 3,440 | 1,127 | 1 |
| 2022 | 644 | 173 | 545 | 85 | 2,980 | 1,790 | 0 |
| 2023 | 2,258 | 1,344 | 770 | 390 | 3,450 | 1,596 | 2 |
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 8,105 | 264 | 1,063 | 48 | 40,857 | 11,813 | 2 |
| 2018 | 3,102 | 41 | 2,465 | 9 | 24,544 | 1,841 | 1 |
| 2019 | 2,602 | 616 | 1,156 | 349 | 28,929 | 3,227 | 1 |
| 2020 | 2,747 | 532 | 834 | 74 | 45,060 | 3,275 | 3 |
| 2021 | 1,910 | 479 | 438 | 17 | 38,426 | 12,426 | 2 |
| 2022 | 3,304 | 1,118 | 597 | 104 | 49,715 | 11,161 | 1 |
| 2023 | 6,041 | 1,101 | 1,245 | 368 | 50,815 | 23,089 | 0 |
| YEAR | PROSECUTIONS | Prosecutions – Labor Only | CONVICTIONS | Convictions – Labor Only | VICTIMS IDENTIFIED | Victims Identified – Labor Only | LEGISLATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 1,571 | 139 | 969 | 114 | 10,011 | 2,139 | 1 |
| 2018 | 1,252 | 72 | 1,017 | 177 | 11,683 | 2,370 | 0 |
| 2019 | 1,324 | 101 | 843 | 34 | 12,352 | 273 | 0 |
| 2020 | 910 | 55 | 588 | 27 | 11,100 | 626 | 2 |
| 2021 | 1,382 | 120 | 794 | 49 | 12,343 | 1,040 | 4 |
| 2022 | 1,232 | 114 | 256 | 70 | 11,676 | 1,419 | 12 |
| 2023 | 1,387 | 180 | 873 | 108 | 18,292 | 3,656 | 4 |
- Stopping Human Trafficking and Sexual Exploitation and Abuse (SEA) by International Peacekeepers and Civilian Personnel
This section summarizes actions taken by the United Nations (UN), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) to prevent trafficking in persons or the exploitation of victims of trafficking during calendar year 2023.
| Total Number of Peacekeeping and Support Personnel | 63,170
| 2,264 | 4,477 |
| Total Number of Missions | 11 | 14 | 2 |
| Prevention Policy | “Special Measures for Protection from Sexual Exploitation and Sexual Abuse” (2003) | “Code of Conduct for Staff and Mission Members” “Staff Instruction No. 33/2023: Whistleblowing and Protection against Retaliation” (adopted 3 October 2023) “Staff Instructions No. 0032/2022: Prevention of Sexual Exploitation and Abuse” (adopted 20 June 2022) “Staff Instruction No. 11/2004: Preventing the Promotion/Facilitation of Trafficking in Human Beings” (adopted 22 January 2004)
| Human Security Unit (political) International Military Staff – Gender Advisor (Military Advice) Heads of NATO Military Bodies (e.g. SACEUR, SACT) |
| Lead Office Responsible for Implementation | The Conduct and Discipline Service (CDS) The Office of Internal Oversight Services (OIOS) | Secretary General Department of Human Resources Office of Internal Oversight
| For preventing human trafficking, conflict-related sexual violence and SEA, training is done via pre-deployment and during any missions or operations. Nations are responsible for the provision of pre-deployment training of their personnel in accordance with NATO standards. Heads of NATO Bodies are responsible for providing training to their personnel. |
| Prevention Training | Pre-deployment and at mission, including an e-learning program | Pre-deployment OSCE Prevention of Sexual Exploitation and Abuse (PSEA) mandatory online training launched in October 2023. Introductory workshop for the PSEA Focal Points held on 15 September 2023.
| None reported |
| Number of Allegations in 2023 | 101 allegations were made against military, police, and civilian personnel. Ninety percent of the allegations were in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Central African Republic. This is only the second time in the past 10 years that 100 or more allegations were recorded in one year. 22 of the allegations affected children. | The OSCE Department for Human Resources had no record of any reported allegations of sexual exploitation or sexual abuse in 2023. The OSCE Office of Internal Oversight did not receive any allegations of SEA in 2023.
| No reported allegations – NATO relies on contributing countries to report allegations. |
| New Initiatives | UNHCR is piloting its participation in the Misconduct Disclosure Scheme (MDS), which facilitates the sharing of misconduct data between employers and prevents the rehiring of perpetrators across NGOs and other participating agencies. UNHCR uses MDS as a complement to its use of ClearCheck. UNOPS planned to pilot its participation in MDS in early 2024. In accordance with General Assembly resolution 77/278, the Secretariat is exploring “whether ClearCheck database and the Misconduct Disclosure Scheme can complement each other.” The World Food Program (WFP) and IOM are developing a multilingual multimedia package of accessible information on protection from SEA for beneficiaries. In 2023, the UN Secretariat piloted a reinforcement training package for uniformed commanders, in cooperation with Member States. It provides targeted training support for commanders on conduct and discipline, with a focus on the prohibition of SEA. The package will be rolled out in 2024. | The OSCE appointed PSEA focal points in April 2023 to raise awareness of Staff Instruction 32 and provide guidance on how to prevent and respond to incidents. In May 2023, the OSCE revised its contractual arrangements with external providers, including the General Conditions of Contract for both goods and services, as well as the standard Implementing Partner Agreement. These revisions now incorporate clauses mandating contractors to implement suitable measures for preventing and addressing SEA by their employees or any individuals engaged in providing services to the OSCE.
| In July 2023, NATO adopted its new policy on combating trafficking in human beings. The aim of this new policy was to provide a coherent, consistent, and integrated political framework for NATO’s role in combating trafficking in human beings. This policy applies to all NATO personnel in all Alliance operations, missions, and activities, wherever NATO operates, from peacetime to crisis and conflict, including stabilization and post-conflict, and should be considered within the broader framework policies and guidance within NATO, including the wider Human Security Approach and Guiding Principles. This Security Approach allows for a more comprehensive view of the human environment, consequently enhancing operational effectiveness and contributing to lasting peace and security.
|
| Links for Additional Information |
|
- Relevant International Conventions
The chart below shows the Ratification, Accession (a), or Acceptance (A) of relevant international conventions for those countries that have ratified, acceded to, or accepted any such conventions between April 2023 and March 2024. A complete list that includes the status of all of the countries covered by the Trafficking in Persons Report is available at: https://www.state.gov/international-conventions-relevant-to-combating-trafficking-in-persons/
| Country | UN Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons (2000) | Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution and Child Pornography (2000) | Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict (2000) | ILO Convention 29, Forced Labour (1930) | ILO Protocol of 2014 to the Forced Labour Convention | ILO Convention 105, Abolition of Forced Labour (1957) | ILO Convention 182, Elimination of Worst Forms of Child Labour (1999) | ILO Convention 189, Domestic Workers (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brunei-Darussalam | 2020 (a) | 2006 | 2016 | 2024 | _
| _
| 2008 | _
|
| Mexico | 2003 | 2002 | 2002 | 1934 | 2024 | 1959 | 2000 | 2020 |
| Seychelles | 2004 | 2012 | 2010 | 1978 | _
| 1978 | 1999 | 2024 |
| Uganda | 2024 | 2001 | 2002 | 1963 | _
| 1963 | 2001 | _
|
- International, Regional, and Sub-Regional Organizations Combating Trafficking in Persons
For the 2024 Trafficking in Persons Report, the Framework Documents and other Relevant Guidance section has been consolidated to show only documents published during the reporting year: April 1, 2023 – March 31, 2024. If you would like to review documents from previous years, please refer to the 2023 Trafficking in Persons Report .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
| (2023) UN General Assembly Resolution on Improving the coordination of efforts against trafficking in persons (A/RES/78/228) (2023) (A/78/119) (2023) HRC Resolution on Trafficking in Persons, especially women and children (A/HRC/RES/53/9) (2023)
(2023) (2023) (2024)
| UN Special Rapporteur on Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children UN Special Rapporteur on Contemporary Forms of Slavery UN Special Rapporteur on the Sale of Children, Child Prostitution, and Child Pornography
|
|
https://www.ilo.org
| (2023) (2023) (2024) (2024) (2024) (2024)
|
|
|
| (2023) |
|
| (EU/Horn of Africa Migration Route Initiative)
| (2023) (2024) |
|
|
| (2023) (2023) (2023) (2023) (2024)
| ASEAN Senior Officials Meeting on Transnational Crime
|
|
| (2023) (2023) (2023) (2023) | Bali Process Working Group on Trafficking in Persons |
|
| No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period. |
|
|
(in Russian only) | No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period.
|
|
|
| No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period.
| United Nations Action for Cooperation against Trafficking in Persons Regional COMMIT Task Force |
|
| (2023) (2023) (2024) (2024)
| Task Force against Trafficking in Human Beings Expert Group on Children at Risk Task Force Against Trafficking in Human Beings |
|
| (2023) (2023) (2023) (2024) (2024) (2024) (2024)
| Group of Experts on Action Against Trafficking in Human Beings
|
|
| (2023) (2023) (2023)
| The ECOWAS Regional Network of National Focal Institutions Against Trafficking in Persons Plus Anti-Trafficking Unit |
|
| (2024) (2024) | EU Anti-Trafficking Coordinator EU Network of National Rapporteurs and Equivalent Mechanisms EU Civil Society Platform against Trafficking in Human Beings Coordination Group of the EU agencies working against trafficking in human beings |
|
| (updated in 2023) (2024) (2024) |
|
|
| No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period.
|
|
|
| (2023) (2023) (2024) (2024)
| Department of Public Security and Department against Transnational Organized Crime |
|
| (2023) (2024) (2024)
| OECD Task Force on Countering Illicit Trade |
|
| No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period.
|
|
|
| (2023) (2023) (2023) (2023) (2023) (2023) (2024) (2024) (2024) (2024)
| Special Representative and Co-ordinator for Combating Trafficking in Human Beings Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights International Survivors of Trafficking Advisory Council |
|
| No relevant Framework Documents or other Relevant Guidance were published during the reporting period.
| The Liaison Officers Network to Combat Migrant Smuggling and Trafficking in Persons |
|
| (2023) (2023)
|
|
- Annual Report to Congress on the Use of Child Soldiers under Section 405(c) of the Child Soldiers Prevention Act of 2008
This report is submitted in accordance with section 405(c) of the Child Soldiers Prevention Act of 2008 (22 U.S.C. 2370c-2(c)) (CSPA). Section 1 lists the countries identified as being in violation of the standards under the CSPA in 2023. Section 2 provides a description and the amounts of assistance withheld pursuant to section 404(a) of the CSPA. Section 3 provides a list of waivers or exceptions exercised under the CSPA. Section 4 contains the justifications for such waivers. Section 5 provides a description and the amounts of assistance provided to countries pursuant to such waivers.
Section 1. Countries in Violation of the Standards Under the CSPA in 2023.
The Secretary of State identified the following countries as having governmental armed forces, police, or other security forces or government-supported armed groups that recruited or used child soldiers within the meaning of section 404(a) of the CSPA during the reporting period of April 1, 2022 – March 31, 2023: Afghanistan, Burma, Central African Republic (CAR), Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Egypt, Eritrea, Iran, Libya, Mali, Russia, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Syria, Türkiye, Venezuela, and Yemen.
Section 2. Description and Amount of Assistance Withheld Pursuant to Section 404(a).
No security assistance subject to section 404(a) of the CSPA was planned to be provided to Afghanistan, Burma, Eritrea, Iran, Mali, Russia, Rwanda, South Sudan, Syria, or Venezuela in fiscal year (FY) 2024.
Section 3. List of Waivers or Exceptions Exercised under Section 404(a).
On September 15, 2023, the President determined that it is in the national interest of the United States to waive the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Egypt; to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Türkiye for International Military Education and Training (IMET) and Peacekeeping Operations (PKO) assistance, issuance of direct commercial sales (DCS) licenses, and support provided pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333, to the extent that the CSPA would restrict such assistance or support; to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Libya and Somalia to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance, and support provided pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333, to the extent that the CSPA would restrict such assistance or support; to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to the Democratic Republic of the Congo to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance and issuance of DCS licenses in connection with the reexport of transport aircraft, to the extent that the CSPA would restrict such assistance; to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to the Central African Republic and Yemen to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance, to the extent that the CSPA would restrict such assistance; and to waive the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA to allow for the issuance of DCS licenses related to other U.S. government assistance for the above countries and, with respect to the Russian Federation, solely for the issuance of DCS licenses in connection with the International Space Station (ISS). The President has further certified that the governments of the above countries are taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
Section 4. Justifications for Waivers and Exceptions.
Pursuant to section 404(c) of the Child Soldiers Prevention Act of 2008 (CSPA) (22 U.S.C. 2370c-1(c)), the President has determined that it is in the national interest of the United States to waive the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Egypt; to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition with respect to the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Libya, Somalia, Türkiye, and Yemen, including to allow for the issuance of direct commercial sales (DCS) licenses related to other U.S. government assistance for these countries that is not subject to the prohibition in section 404(a); and, with respect to Russia, to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition solely for DCS licenses in connection with the International Space Station. The President has further certified that the governments of the above countries are taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers. The justification for this determination and certification with respect to each country is set forth in this Memorandum.
The Central African Republic (CAR)
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to CAR to allow for the provision of International Military Education and Training (IMET) and Peacekeeping Operations (PKO) assistance and has certified that the CAR Government (CARG) is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
Armed groups in CAR continue to threaten civilians and pose a longstanding risk to stability. The waiver for PKO and IMET assistance for CAR will support the professionalization of the military to better provide security to the people of CAR while respecting human rights and international humanitarian law (IHL). Additionally, IMET programming allows the United States to invest in CAR military officers to promote professional military education and foster relationships with foreign military personnel rooted in democratic values.
The CARG is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers through meaningful engagement with U.S. and UN officials in seeking assistance to eradicate trafficking in persons, including the recruitment or use of child soldiers by CAR security forces and armed groups. Recent efforts have included the adoption of a national plan to counter trafficking in children, government directives prohibiting the presence of children around military bases, and collaboration with the UN and implementing partners to reintegrate children affected by conflict.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to DRC to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance and issuance of licenses for DCS in connection with the reexport of transport aircraft and has certified that the Government of the DRC (GDRC) is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
The proliferation of armed groups amidst ongoing conflict in eastern DRC continues to threaten security and stability for the people of the DRC. IMET and PKO assistance for the DRC enables the United States to continue professionalization efforts of the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC) by enhancing its capacity to provide security within its territory while respecting human rights and IHL. IMET and PKO assistance provide mechanisms to support security sector governance reforms and training in areas such as military justice, civil-military relations, respect for human rights and IHL, military engineering, and resource management and logistics, which enhance security and help make the FARDC a more transparent, accountable institution.
The GDRC is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers through sustained commitment to implement its 2012 Action Plan to end and prevent the recruitment and use of child soldiers in partnership with the UN. Additionally, in 2022 the GDRC adopted a national strategy for the implementation of the Demobilization, Disarmament, Community Recovery and Stabilization Program, which signals an important step in prioritizing children affected by armed conflict, particularly in eastern DRC.
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United State to waive, in full, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Egypt and has certified that the Government of Egypt is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
Egypt is an important U.S. partner in counterterrorism, anti-trafficking, and regional security operations, which advance both U.S. and Egyptian security. The decades-long defense partnership is a pillar for regional stability and key to securing peace with Israel, supporting the Multinational Force and Observers missions, and enhancing security of the Suez Canal. Since 1978, the United States has provided more than $54 billion in military assistance for Egypt, which has contributed to Egypt’s capabilities to protect and defend its land, air, and maritime borders and to confront an evolving terrorist threat, including in the Sinai Peninsula.
The Government of Egypt is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers, even as the scope and intensity of the counterterrorism fight in the Sinai continues to see a significant downturn; 2023 is on track to report the lowest levels of violence in the Sinai since the conflict began in 2011. The U.S. government is not aware of the Egyptian military, police, or other security forces recruiting or using child soldiers. Consistent with Egypt’s domestic laws and its obligations under the Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict, the Egyptian government effectively prohibits persons under the age of 18 from being forcibly recruited into the armed forces. The Government of Egypt provides critical influence in addressing the recruitment or use of child soldiers by tribal militias, and the U.S. government will continue to engage the Egyptian government regarding reports of recruitment of child soldiers by government-supported Sinai tribal forces.
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Libya to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance and DoD support provided pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333 and has certified that the Government of National Unity (GNU) in Libya is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
The U.S. government selected Libya as a priority country for implementation of the U.S. Strategy to Prevent Conflict and Promote Stability. The Department of State further assesses that in Libya the most durable solution to the unlawful recruitment of child soldiers, including by GNU-aligned units and the self-styled Libyan National Army, is a negotiated political settlement that ends Libya’s instability and the cycles of conflict. IMET assistance will facilitate English language proficiency to improve interoperability and promote civil-military relations, including civilian control of a unified military. PKO assistance will build upon the October 2020 ceasefire and support U.N. efforts to advance Libya’s transition to a unified, democratically elected, and inclusive political system based on respect for human rights. PKO provides the U.S. government a tool to support UNSMIL in its ceasefire monitoring function. Department of Defense support will build the capacity of Libyan military institutions in support of progress towards civilian-controlled, accountable, defense institutions that uphold human rights, combat terrorism, and address security challenges.
The GNU is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers through engagement with the UN and the U.S. government in the context of our recurring bilateral Security Dialogue. Through cooperation with UNSMIL, representatives of the Libyan 5+5 Joint Military Commission, comprised of senior military officers from both the east and west, engage with UNICEF on preventing child soldier recruitment. The U.S. government is not aware of the GNU’s military, police, or other governmental security forces recruiting or using child soldiers. Further, GNU security sector leaders provide critical influence to prevent and end the recruitment or use of child soldiers by armed groups in Libya and mitigate the reliance on external forces or groups for internal security.
Russian Federation
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United State to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to the Russian Federation to allow for issuance of licenses for DCS solely in connection with the International Space Station (ISS) and has certified that the Government of the Russian Federation is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
It is in the U.S. national interest to work with Russia to maintain the safety of ISS operations. Maintaining longstanding U.S.-Russia ISS operations requires the ability to issue DCS licenses for defense articles and defense services in support of the ISS until the planned termination of its operation, which the National Aeronautics and Space Administration estimates will be in 2030. This waiver will allow such activities to continue and will enable the issuance of licenses necessary to support the safe operation of the ISS, U.S.-Russia integrated crew missions to the ISS, and the safety of U.S. and other personnel onboard the ISS.
The Russian Federation is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers. In accordance with the Russian Federation’s Law on the Ratification of the Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict of 2008, the Government of the Russian Federation effectively prohibits persons under the age of 18 from being forcibly recruited into the armed forces.
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Somalia to allow for the provision of IMET and PKO assistance, and DoD support provided pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333 and has certified that the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS) is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
Foreign terrorist organizations including al-Shabaab continue to threaten security and stability for the people of Somalia. The waiver for IMET and PKO assistance for Somalia enables the United States to continue professionalization efforts of the Somali National Army (SNA) by enhancing their capacity to provide security within their territory while respecting human rights and IHL. Further, a waiver for support provided by the Department of Defense pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333 will allow for U.S. government assistance to build the Somali military’s capacity to conduct effective, sustained counterterrorism operations against al-Shabaab and help reinforce U.S. values, including those related to preventing and ending the unlawful recruitment or use of child soldiers.
The FGS is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers through sustained commitment to implement its 2019 “road map” to accelerate progress on its 2012 Action Plan on ending the recruitment and use of children by the Somali National Armed Forces in partnership with the UN. The SNA’s Child Protection Unit continued to make progress in implementing screening procedures, training, and disseminating media to prevent the recruitment and use of child soldiers. The FGS also continued implementation of standard operating procedures for the handover of children allegedly associated with armed groups.
The President has determined it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Türkiye for IMET and PKO assistance, issuance of DCS licenses, and DoD support provided pursuant to 10 U.S.C. 331 and 10 U.S.C. 333 and has certified that the Government of Türkiye is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
Türkiye has been an important U.S. security partner and valued NATO Ally since 1952, regulating passage, in accordance with international law, through the straits of the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, which link the Black Sea with the Mediterranean. Further, Türkiye’s military capability and geographic location are vital to the United States’ integrated deterrence strategy and ability to respond to regional events including with respect to counterterrorism, humanitarian assistance, and disaster relief operations. Türkiye’s support, including defense and security cooperation, to NATO Allies and partners deters malign influence in the region. This waiver will assist in maintaining NATO cohesion and continued interoperability, bolster regional security, and advance bilateral cooperation.
The Government of Türkiye is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers, including those present in elements of the Syrian National Army receiving support from the Government of Türkiye. The United States is not aware of the Turkish military, police, or other security forces recruiting or using child soldiers. Consistent with Türkiye’s domestic laws and its obligations under the Optional Protocol to the Convention on the Rights of the Child on the Involvement of Children in Armed Conflict, the Turkish military effectively prohibits persons under the age of 18 from being forcibly recruited into the armed forces. Further, the Government of Türkiye provides critical influence in addressing the problem of child soldiers with respect to the Syrian National Army.
The President has determined that it is in the national interest of the United States to waive, in part, the application of the prohibition in section 404(a) of the CSPA with respect to Yemen to allow for provision of IMET and PKO assistance and has certified that the Government of the Republic of Yemen (ROYG) is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers.
It is in the U.S. national interest to support UN-led efforts to achieve an inclusive negotiated political resolution to the conflict in Yemen. The waiver for IMET assistance for Yemen enables the United States to continue to support professionalization and interoperability efforts of the Yemeni Armed Forces (YAF) by enhancing their capacity to provide inclusive security within their territory while respecting human rights and IHL. Further, this waiver will improve the YAF’s capacity to conduct effective, sustained counterterrorism operations, ensuring freedom of navigation through the Bab Al-Mandeb Strait, and securing the space for restoring effective governance institutions.
The ROYG is taking effective and continuing steps to address the problem of child soldiers through sustained commitment to implement its 2018 “road map” to accelerate progress on its 2014 Action Plan to end and prevent the recruitment of children by Yemeni Armed Forces in partnership with the UN. The ROYG established child protection units within all military regions, issued directives banning child recruitment, and conducted numerous senior government field visits to monitor the implementation of screening procedures to prevent child recruitment and remove children from military units.
Section 5. Description and Amount of Assistance Provided Pursuant to a Waiver.
The information provided below only includes assistance obligated as of April 20, 2024. Additional assistance will be obligated during FY 2024.
Central African Republic
International Military Education Training $101,124
As of April 20, 2024, IMET funding was obligated for the following activity: professional military education and training.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
International Military Education Training $177,238
International Military Education Training $1,352,782
International Military Education Training $31,284
Peacekeeping Operations $31,917,530.44
As of April 20, 2024, PKO funding was obligated for Somali National Army and Somali Ministry of Defense for the following activities:
logistical support; advisory support; equipment; and program oversight.
10 U.S.C. 333 $4 ,668,640.56
As of April 20, 2024, 333 funding was obligated for the following activities: training and equipment.
International Military Education Training $182,098
International Military Education Training $339,662
As of April 20, 20, 2024, IMET funding was obligated for the following activity: professional military education and training.
- GLOSSARY OF ABBREVIATIONS
| ASEAN | Association of Southeast Asian Nations |
| GBV | Gender-based Violence |
| ECOWAS | Economic Community of West African States |
| EU | European Union |
| EUROPOL | European Union Agency for Law Enforcement Cooperation |
| FARC | Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia |
| GRETA | Council of Europe’s Group of Experts on Action against Trafficking in Human Beings |
| IDP | Internally displaced person |
| ILO | International Labour Organization |
| INTERPOL | International Criminal Police Organization |
| IOM | International Organization for Migration |
| ISIS | Islamic State of Iraq and Syria |
| IUU | Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated |
| LGBTQI+ | Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer, and Intersex |
| MOU | Memorandum of Understanding |
| NAP | National Action Plan |
| NGO | Nongovernmental organization |
| NRM | National Referral Mechanism |
| SOPs | Standard Operating Procedures |
| OAS | Organization of American States |
| OSCE | Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe |
| UN | United Nations |
| UNHCR | United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees |
| UNICEF | United Nations Children’s Fund |
| UNODC | United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime |
| UN TIP Protocol (Palermo Protocol) | Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children, supplementing the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime |
Notes: Local currencies have been converted to U.S. dollars ($) using the currency exchange rates reported by the U.S. Department of the Treasury on December 31, 2023.
- Acknowledgments
The Staff of the Office to Monitor and Combat Trafficking in Persons Is:
Mekhribon Abdullaeva
Sylvia Amegashie
Katrina Askew-Alston
Andrea Balint Garza
Shonnie R. Ball
Suzanne Balson
Matt Becker
Getoria Berry
Brooke Beyer
Caris Boegl
Michelle C. Bloom
Alexandria Boling
Katherine Borgen
Gregory Borgstede
Kelsey Brennan
Joshua Bull
Carla M. Bury
Renée Callender
Jessica Cisneros
Kate Cooper
Camila Crowley
Reena Dalwadi
Sarah Davis
Steven Davis
Ana DiGiacomo
Daniel Evensen
Anna Fraser
Lauren Frey
Mark Forstrom
Lucia Gallegos
Beatriz Garcia Velazquez
Brianna Gehring
Chauna Gibson
Natasha Greenberg
Andrew Grimmer
Takiyah Golden
Denise Harrison
Jocelyn Harrison
Emmanuel Hector
Caitlin B. Heidenreich
Ashley Hernandez
J. Brett Hernandez
Matthew Hickey
Crystal Hill
Megan Hjelle-Lantsman
Jennifer M. Ho
Marta Hoilman
Ariana Holly
Moira Honohan
Renee Huffman
Veronica Jablonski
Harold Jahnsen
Sarah Jennings
Devin Johnson
Maurice W. Johnson
Kari A. Johnstone
Chelsea Kaser
Patrick Kelly
Emily Korenak
Kendra L. Kreider
Mary Lagdameo
Valery Lavigne
James Lensen-Callas
Rebecca Lesnak
Abigail Long
Samantha Lord
Jean McAnerney
Cameron Malcom
Bryan Marcus
LaTina Marsh
Sunny Massa
Kerry McBride
Rendi McCoy
Tamara McCoy
Maura K. McManus
Leah F. Meyer
Rebecca Morgan
Ericka Moten
Ryan Mulvenna
Dan Muncaster
Cristina Narvaez
Amy O’Neill Richard
Zury Palencia
Lauren Parnell
Ashlei Perry
Marissa Pietrobono
Sanjana Polapragada
Justin D. Pollard
David Rabinovich
Patrick Read
Andrea E. Reed
Casey Risko
Angie Rivas
Amy Rustan Haslett
Manith Sarik
Aram Schvey
Tori Jamese Scott-Senghor
Adrienne Sgarlato
Jessica Singh
Stephen Shade
Kaela Shear
Soumya Silver
Cornelius Slayton
Susan Snyder
Megan Stalder
Latoshae Summers
Desirée Suo Weymont
Jamie Sutter
Francesca J. Tadle
Atsuki Takahashi
James Taylor
Anna Thiessen
Cecilia Thompson
Juan Jose Tierjo
Wanda Toney
Andrea Ugolini
Melissa Verlaque
Matthew Villemain
Myrna E. Walch
Frances Wallman
Bianca Washington
Pauline Werner
Danielle (Nikki) Wetsel
Terry Whenry
Sharifa White
Joshua Williams
Willow Williamson
Joshua Youle
Salia Zouande
Special thanks to Brian Piaquadio, Julia Maruszewski, LeGrand Latney, Kimberly Ross, and the creative services team at Global Publishing Solutions. Special thanks also to the ECA Bureau and technical project managers Tasha Wilkinson and Ed Williams.
Special thanks to Bukola Oriola, Dawn Schiller, Christine Cesa, Jeri Moomaw, Harold D’Souza, Jessa Crisp, Jill Brogdon, Megan Lundstrom, Rafael Bautista, Tanya Gould, and other subject matter experts with lived experience of human trafficking from the Department of State’s Human Trafficking Expert Consultant Network for their contributions to the TIP Report.
On This Page
U.s. department of state, the lessons of 1989: freedom and our future.
Summer internships lead to research wins
For students like Tiffany Roach, Daniel Capelluto's research lab provided a place free of distractions with an academic family and mentorship to help students stay focused and have the best chances of being successful.
- Jenise L. Jacques
24 Jun 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Copy address link to clipboard

The spirit Tiffany Roach found as a summer intern in one of Virginia Tech's research labs helped bring her future into focus.
As part of the Office of Undergraduate Academic Affairs, the Multicultural Academic Opportunities Program offers a 10-week summer research internship during which students both internal and external to Virginia Tech are matched with a faculty member in the areas of research they are interested in pursuing. In addition to a monthly stipend, the program also provides a housing and meal plan.
“Daniel’s lab is a beautiful example of what it means to be a mentor and how collaboration can improve discovery,” Roach said of the Protein Signaling Domains Laboratory led by Daniel Capelluto, associate professor of biological sciences.
Roach was a candidate for the summer research internship as the university she attended as an undergraduate did not offer STEM research opportunities.
Without the summer internship experience, Roach said she would have never envisioned that she would be working on projects that have profound implications for health and helping humans. “The professional development seminars, graduation exam prep class, and genuine desire to encourage and support me helped smooth the way for a productive summer in research and successful graduate school applications,” Roach said.
The Capelluto lab was also the perfect intersection of molecular work that uncovered potential mechanisms for disease, while the summer internship served as a catalyst by providing a platform and support group that made it possible.
Inspiring research
“The research itself was also a point of inspiration for me, as my interests and passion were in molecular mechanisms and how something in the cell worked,” Roach said. “I loved working and thinking on the molecular level, but also felt this need to be involved in human health research.”
Upon returning to her home university after the summer in 2016 to complete her undergraduate degree, Roach knew that wanted to attend Virginia Tech for graduate school. In 2018, she was accepted and found herself back in her happy place as a lab assistant in Capelluto's lab.
For Roach, pursuing the STEM field was also deeply personal. After watching her father lose the battle with cancer, she was not satisfied with the “there is nothing more we can do” response from doctors.
“It bothered me that we didn’t have the knowledge necessary to keep fighting, so I knew I wanted to study science and contribute to our understanding of how the body and disease works,” she said.
Now six years later, Roach has successfully defended a Ph.D. in biological sciences while also helping Capelluto’s research team better understand dysentery, a gastrointestinal disease. The latter effort recently was bolstered by a National Science Foundation (NSF) grant.
Better understanding dysentery – an unresolved disease caused by a bacterial infection – was one of the lingering questions for Roach and Capelluto, researchers both affiliated with the Fralin Life Sciences Institute . Its symptoms include diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and stomach pain.
To help advance their research, the NSF awarded a $840,000 grant to the team. Capelluto, who will serve as principal investigator, will partner with Anne Brown, associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry who specializes in computational modeling, and Carla Finkielstein, professor of biological sciences and director of the Molecular Diagnostics Lab at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC who will use molecular tools to study how the protein TOM1 works under different cell settings.

Breakthroughs in disease research
According to Roach, previous research conveyed that Shigella, a type of bacteria, can infect a human cell more easily by shutting down the cell’s ability to degrade cell surface receptors, but it did not expand on the mechanism of how this actually happens.
“Our research uncovers how the degradative process is shut down, which is essential knowledge to then design a way to prevent or fix this invasion strategy,” Roach said. “Furthermore, we are unveiling a strategy that other bacteria may be using as well, so this research is providing the foundational stones for major breakthroughs in disease research for the future.”
Cells are dynamic and have the ability to modify protein functions based on their necessities.
“One such process, known as ubiquitination, can lead to multiple outcomes, by not only changing protein function, but also their ability to be relocated or integrated within a cellular compartment,” Capelluto said.
Roach likens the relationship between TOM1 binding to ubiquitin with that of making responsible choices for one's own health.
“This is what we should be doing in a healthy environment when we're doing our job properly and taking care of our body, but then when the bacterium enters, it knows our weaknesses, such as the temptation of cookies and treats when the afternoon slump hits,” Roach said. “So in a similar sense, the bacteria is producing a different metabolite that then draws — or hijacks — TOM1 away from its job. And it's binding to that rather than ubiquitin.”
Accelerating summer undergraduate experience
With the new NSF funding comes the opportunity to bring in a new intern from Bennett College to engage in research this summer under the auspices of the newly formed AccelerateSTEM program.
By creating the AccelerateSTEM program, Capelluto's idea was to expand upon the summer undergraduate research internship by allowing the opportunity for students -- including its first student Simidele Rogers -- to stay at Virginia Tech and continue her research during the full academic year.
Following the completion of the summer internship, Rogers will have the opportunity to continue her research in Capelluto’s lab while concurrently taking online courses from her home institutions until graduation. During the following fall semester, she plans to apply for a one-year accelerated master’s degree at Virginia Tech.
Rogers will continue working in Capelluto’s lab through her senior year and then complete the one-year master’s degree training program offered through Virginia Tech.
“Programs such as AccelerateSTEM open up opportunities for students at historically Black colleges and universities to have access to state-of- the-art labs, world-renowned faculty mentors and possibly consider graduate education at Virginia Tech,” said Monica Hunter, director of the Multicultural Academic Opportunities Program.
Bennett College and Virginia Tech are part of the Virginia-North Carolina Alliance for Minority Participation, a NSF-funded grant that supports STEM students as well as encourages undergraduate research and attendance in graduate or professional school post undergraduate. Capelluto will collaborate with Shenna Shearin, assistant professor of chemistry at Bennett College.
Lindsey Haugh
- Biochemistry
- Biological Sciences
- College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- College of Science
- Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC
- Fralin Life Sciences Institute
- Graduate Education
- Graduate Research
- Inclusion and Diversity
- Molecular Diagnostics Lab
- National Science Foundation
- Reduce Inequalities
- Undergraduate Academic Affairs
- Undergraduate Research
Related Content


COMMENTS
Thesis Statement for Human Trafficking. Human trafficking is a heinous crime that violates the fundamental human rights of individuals across the globe. This essay aims to explore the various aspects of human trafficking, including its prevalence, causes, impact on victims, and measures to combat this abhorrent practice.
A Thesis in the Field of International Relations. for the Degree of Master of Liberal Arts in Extension Studies. Harvard University. November 2021 2021 Alisa Gbiorczyk Abstract. It has to be recognized that human trafficking is a problem in all American states. Small towns do, in fact, face this international problem.
A thesis statement on human trafficking should explore how human trafficking exploits vulnerable people and exposes them to a ruthless cycle of abuse and mistreatment. Each of the main points that ...
The examples of human trafficking essay topics include: The problem of child trafficking in today's world. The causes of human trafficking. Human trafficking: The problem of ethics and values. The role of today's society in fostering human trafficking. Human trafficking as a barrier to human development.
Sex trafficking. is defined as "a commercial sex act that is induced by force, fraud, or coercion, or in which the. person induced to perform sex acts is under 18 years of age" (Trafficking Victims Protection Act. of 2000). Measures have been implemented to help combat and prevent human trafficking.
Human Trafficking Essay Thesis . A thesis statement is your essay's main point formulated in one sentence. It outlines the paper's direction and provides an answer to the problem stated in the title. You place it at the end of the introduction. A good thesis statement for a human trafficking essay usually presents the solution to a problem.
Human trafficking is not a problem unique to the United States, so it is necessary to examine how another country addresses trafficking from a legislative standpoint. The second chapter explores what role the international community and the media have played in potentially restricting Canadian human trafficking policy. A review of media
Thesis Statement for Human Trafficking. 1 page / 612 words. Human trafficking is a heinous crime that violates the fundamental human rights of individuals across the globe. This essay aims to explore the various aspects of human trafficking, including its prevalence, causes, impact on victims, and measures to combat this abhorrent practice.
60 essay samples found. Human trafficking, a grievous global issue, involves the trade of humans for forced labor, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation. Essays might delve into the mechanisms, global networks, and the socio-economic or political conditions enabling human trafficking. Moreover, discussions could extend to ...
With an estimated 24.9 million victims of human trafficking around the world, trafficking in persons is increasingly one of the most pressing issues of our time (International Labor Organization, 2017). While human trafficking is not a new phenomenon, it was not until 2000 that the first federal human trafficking legislation was enacted in the U.S.
One of The Atlantic's biggest stories of 2017, this essay tells a personal story of modern slavery. At 18-years old, Lola was given to the writer's mother and when they moved to the United States, Lola came with them. On the outside, Tizon's family was, in his words, "a poster family.". The truth was much darker.
Human trafficking is a rising international issue that has become a key concern for human rights organizations and governments throughout the world. As such, new policies are being developed and implemented to combat the problem. A guiding standard for these policies is the United ... the entire thesis process, including guiding me through ...
The Global Initiative to Fight Human Trafficking "The United Nations Global Initiative to Fight Human Trafficking (UN.GIFT) aims to mobi-lize state and non-state actors to eradicate human trafficking by: (a) reducing both the vulner-ability of potential victims and the demand for exploitation in all its forms; (b) ensuring adequate
Human Trafficking Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips. After choosing a topic and preparing a plan, it's time to formulate the essay's main idea. The human trafficking essay thesis is a clear statement, mainly at the end of the introduction. The introduction should smoothly lead to this thesis, and the rest of the article should prove or ...
Argumentative Thesis Statement on Human Trafficking - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Human trafficking is a complex issue that requires an in-depth thesis to properly address. Producing a high-quality thesis on human trafficking involves meticulous research exploring the root causes, societal impacts, legal frameworks, and ethics of this crime.
In an introduction to an essay, the most important element is the thesis statement. You should also include a definition of human trafficking.
Human trafficking remains one of the most pervasive criminal activities worldwide, including in the United States. Much of the research on human trafficking in the U.S. has been limited, focusing primarily on individual-level factors, providing victim assistance, or with a few exceptions, examining the role of structural characteristics on ...
ygenerating ne. work maps, social network analysis allows the role and influence of net. ork actorsto be analyzed. Social network analysis is also used to identify, describe, and m. relationships in a network, or analyze the structure of a system (Blanchet and James, 2012). system andtheorize about c.
Thesis Statement for Child Trafficking. Child trafficking is a heinous crime that continues to plague our society, robbing innocent children of their childhood and basic human rights. From forced labor to sexual exploitation, the trafficking of children remains a pressing global issue that demands our attention and action.
The document discusses the challenges students face when crafting a thesis statement for an essay on human trafficking. It notes that human trafficking is a complex issue with many dimensions, requiring extensive research on topics like causes, impacts, and counter-trafficking efforts. Students must also consider ethical issues and balance factual accuracy with sensitivity. The document ...
Thesis Statement On Human Trafficking. Human trafficking is illegal trading in people for various forms of modern-day slavery such as forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation (Lee, 2007, p. 56). Thesis statement: technological transformation plays a crucial role in the facilitation of processes and practices that surround human trafficking.
Thesis Statement Human Trafficking - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
combatting human trafficking. As non-governmental organisations develop capacity and knowledge to combat human trafficking they have often become key stakeholders in the field. In this dissertation, I examine to what extent the efforts of NGOs are aligned with the South African Government policy and legislative agenda in dealing with human
All human trafficking victims who provide statements, declarations, or testimony are inevitably subjected to credibility challenges, whether by jurists in inquisitorial systems that decide whether the victim's statements are sufficiently reliable or by the defense in adversarial systems. ... Advisor - Human Trafficking and Gender-based ...
The spirit Tiffany Roach found as a summer intern in one of Virginia Tech's research labs helped bring her future into focus. As part of the Office of Undergraduate Academic Affairs, the Multicultural Academic Opportunities Program offers a 10-week summer research internship during which students both internal and external to Virginia Tech are matched with a faculty member in the areas of ...