
How Starbucks Uses Pricing Strategy For Profit Maximization
Jun 16, 2020
Price Intelligently
SaaS pricing and monetization experts
Join our newsletter for the latest in SaaS
By subscribing you agree to receive the Paddle newsletter. Unsubscribe at any time.
Last Thursday Starbucks raised their beverage prices by an average of 1% across the U.S, a move that represented the company’s first significant price increase in 18 months. I failed to notice because the price change didn’t affect grande or venti (medium and large) brewed coffees and I don’t mess with smaller sizes, but anyone who purchases tall size (small) brews saw as much as a 10 cent increase.The company’s third quarter net income rose 25% to $417.8 million from $333.1 million a year earlier, and green coffee prices have plummeted, so what gives?
We recently wrote bout Starbucks' expansion struggles over at Paddle Studios . Watch above or check it out after you read this.
Starbucks claims the price increase is due to rising labor and non-coffee commodity costs, but with the significantly lower coffee costs already improving their profit margins, it seems unlikely this justification is the true reason for the hike in prices. In addition, the price hike was applied to less than a third of their beverages and only targets certain regions. Implementing such a specific and minor price increase when the bottom line is already in great shape might seem like a greedy tactic, but the Starbucks approach to pricing is one we can all use to improve our margins. As we’ve said before, it only takes a 1% increase in prices to raise profits by an average of 11% .
Value Based Pricing Can Boost Margins
For the most part, Starbucks is a master of employing value based pricing to maximize profits, and they use research and customer analysis to formulate targeted price increases that capture the greatest amount consumers are willing to pay without driving them off. Profit maximization is the process by which a company determines the price and product output level that generates the most profit. While that may seem obvious to anyone involved in running a business, it’s rare to see companies using a value based pricing approach to effectively uncover the maximum amount a customer base is willing to spend on their products. As such, let’s take a look at how Starbucks introduces price hikes and see how you can use their approach to generate higher profits.
An Overview of the Starbucks Pricing Strategy
The right customers and the right market.
While cutting prices is widely accepted as the best way to keep customers during tough times, the practice is rarely based on a deeper analysis or testing of an actual customer base. In Starbucks’ case, price increases throughout the company’s history have already deterred the most price sensitive customers, leaving a loyal, higher-income consumer base that perceives these coffee beverages as an affordable luxury. In order to compensate for the customers lost to cheaper alternatives like Dunkin Donuts, Starbucks raises prices to maximize profits from these price insensitive customers who now depend on their strong gourmet coffee.
Rather than trying to compete with cheaper chains like Dunkin, Starbucks uses price hikes to separate itself from the pack and reinforce the premium image of their brand and products. Since their loyal following isn’t especially price sensitive, Starbucks coffee maintains a fairly inelastic demand curve , and a small price increase can have a huge positive impact on their margins without decreasing demand for beverages. In addition, only certain regions are targeted for each price increase, and prices vary across the U.S. depending on the current markets in those areas (the most recent hike affects the Northeast and Sunbelt regions, but Florida and California prices remain the same).
Product Versioning & Price Communication
They also apply price increases to specific drinks and sizes rather than the whole lot. By raising the price of the tall size brewed coffee exclusively, Starbucks is able to capture consumer surplus from the customers who find more value in upgrading to grande after witnessing the price of a small drip with tax climb over the $2 mark. By versioning the product in this way, the company can enjoy a slightly higher margin from these customers who were persuaded by the price hike to purchase larger sizes.
Starbucks also expertly communicates their price increases to manipulate consumer perception. The price hike might be based on an analysis of the customer’s willingness to pay, but they associate the increase with what appears to be a fair reason. Using increased commodity costs to justify the price as well as statements that aim to make the hike look insignificant (less than a third of beverages will be affected, for example) help foster an attitude of acceptance.

You know your business, we know pricing
Price Intelligently's team of monetization experts work with you to combine strategy and data to solve complex business problems and accelerate your growth.
What can Your Business Learn From Starbucks?
The profit maximizing tactics Starbucks implements in their pricing strategy are vital components of a process anyone can use. Here are some of the takeaways you can apply to your own business:
1. Study your customer personas. Starbucks understands that the majority of their customer base is fairly insensitive to price, and uses small price increases that everyday consumers barely notice to boost margins. Quantify your buyer personas and the demand for your product or service will help you choose a price that captures the maximum amount your customers are willing to pay.
2. Justify the exchange rate for your product. Communicating price increases effectively is crucial to a successful price hike, and managing customer perception is a key part of the Starbucks strategy. Support your price increases using changes in the market such as higher commodity costs and ease the pain on the consumer by finding an attractive way to publicize the new prices. Starbucks said their beverage prices were increasing by an average of 1%, but that low average probably stemmed from including all of their beverages in the equation, including ones that remained at the same prices.
3. Use product differentiation to put your company in the lead. You can justify maximizing your profits using the fairest of reasons, but if the customers don’t value your service the way they value a delicious cup of coffee, then a decrease in demand is inevitable. Build a service or product that consumers can’t live without, and you’ll be able to implement price hikes without turning off your customers.
4. Don’t increase the prices of the products with the highest margins. Raise the prices of the products surrounding them. As mentioned earlier, Starbucks raised the price of the tall size brew exclusively in order to persuade customers to purchase larger sizes (with slightly higher margins). Price hikes for your lower margin products can entice customers to upgrade to more expensive options, especially with respect to products and services that are tiered based on time usage and features. The goal is to use the price increases to guide the customer towards your most profitable product.
To learn more about pricing specifics, check out our Pricing Strategy ebook , our Pricing Page Bootcamp, or learn more about our price optimization software. We're here to help!
Related reading

- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure

The Strategy Watch
To be the Best Source of Business Strategy & Analysis
Pricing Strategy of Starbucks Coffee Company
Starbucks is an American multinational coffeehouse that was founded in 1971 and thriving ever since. Currently, Starbucks has over 33 thousand stores in 80 countries. People have been loving their coffees for the last five decades. Their pricing strategies have been able to keep their consumer base consistent.
Types of Pricing Strategy Applied by the Company
Starbucks uses multiple strategies, among which value-based pricing has been their go-to choice for profit maximization. Before determining a suitable strategy for the organization, they analyze their consumer’s behavior thoroughly and then formulate the prices according to their target audience. This helps to keep the consumers connected to the brand. They also believe in profit maximization where they determine the price according to their production level to generate the maximum amount of profit. The value-based pricing method is not so common among firms as it’s quite difficult to implement this approach. But Starbucks has been successful with this method.
Details Discussion on the Pricing Strategy of Starbucks
Starbucks is very calculative when it comes to its pricing strategy. When it comes to their branding and promotional activities, they take on the premium approach. But their pricing and branding are quite target-oriented. Their brand identity is very exquisite which helps to boost their sales even though their products are not inexpensive. They focus a lot on their promotional activities, especially during different events and holiday seasons. Here are some of the pricing strategies that are taken by Starbucks.
Menu-based Pricing Strategy
Starbucks offers a specialized menu on which their pricing depends a lot. All the items on their menu are correlated to their pricing strategy. One great thing is, they provide the same menu in every store. As a result, they can supply their raw materials in bulk which eventually reduces their operating cost. They have quite a good number of options for their consumers. All of these products are sold at a reasonable price compared to the other restaurants. As the menu is quite diverse, everyone would be able to find something of their likings.
Selling the Brand
Starbucks has been able to maintain its profitability ratio by keeping its services and menu consistent. The scale of their branding is quite large and they have placed all of their stores strategically looking at the demographic of their target audience.
The amount that Starbucks spends on promotional activities is comparatively less than other existing brands in the market. Even though their prices fall into the premium category, they have still managed to increase the volume of their sales. One of the major reasons behind this is the wide range of their menu. They offer something or the other for every consumer. For instance, recently the popularity of organic products has increased at a significant level. The coffee shop that offers organic cups, costs around $7 whereas Starbucks ‘ large cup of coffee is less the $5. Still, Starbucks is known as a premium brand because a lot of brands offer good coffee at a much lower price. One can say, that the extra pennies are for the brand value. Another important fact is, there has been a time where Starbucks has increased the price of their items when the actual price of coffee has decreased. Therefore, it shows that Starbucks prices their items according to the demand not based on the prices of their raw materials.
Promotional Pricing Strategy
Starbucks doesn’t spend a lot on promotional activities compared to the other brands but their promotions are very strategic. For example, they always bring special drinks during the holiday season. They also add seasonal items to their menu. For example, their pumpkin spiced latte is an all-time favorite of consumers which they only add to their menu during the fall. These seasonal items add extra value to their brand. Items like these don’t need any extra cost as they already have the machines for making a latte. The only additional item they need is the pumpkin spices. Because they only bring this item during the fall, this eliminates the additional cost as pumpkin is widely available during the fall. Their promotional style has certainly increased their brand value without affecting their operating cost.
Demand Strategy
Starbucks also follows a demand-based pricing strategy. They increase the price of certain items according to the demand of the consumers. For instance, when the price of the coffee beans decreased, a lot of coffee shops had decreased their prices in order to increase their sales. But Starbucks had not decreased its prices. This proves that their pricing strategy doesn’t depend on the supply of the raw materials rather it solely depends on the demand of the consumers. Starbucks has created a premium brand value among its consumers. Even if Starbucks increases the price of their americano from $2.25 to $3, people will still buy it for the brand value. Hence, Starbucks doesn’t change its pricing by looking at the prices of its raw materials.
Pricing Strategy of the Competition
The coffeehouse business is not that competitive as the market is quite oligopolistic. 5 different pricing strategies are followed by the existing brands. These are:
- Menu strategy: under this strategy, the pricing is set according to the food offered by the brand. So once a café decides its menu, it can calculate the cost and decide the price accordingly.
- Flexible pricing strategy: some companies prefer this strategy as it gives them the scope to change the pricing of their products according to the situation.
- Bundling strategy: this is one of the common strategies where two or three items are bundled and sold as a combo meal. This is a great way of increasing sales.
Along with these, two other popular strategies are the complimentary strategy and the discounting strategy.
Recommendation
Starbucks can provide occasional bundle offers to consumers. This will increase their sales to a further extend. Recently a lot of people have switched to different coffee shops due to an increase in prices. Offers like holiday discounts, bundle offers, promo codes, etc. will help Starbucks to regain its consumers and increase its sales.
Related Reading
- Pricing Strategy of Airbnb
- Pricing Strategy of Dove
- Pricing Strategy of Ford Motors
- Pricing Strategies of Nike
- Differences between Weaknesses and Threats in SWOT Analysis

Nishat Tarannum Mridula is a contributing writer at The Strategy Watch . She has been contributing for last two years.
Nishat is currently studying at the University of Dhaka . Even though her major is in Banking, she enjoys writing on diverse topics, starting from appliances to blogposts. She is in the middle of completing her BBA from University of Dhaka. Alongside that, she writes different types of business articles for The Strategy Watch .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Demand and Supply
Start up: crazy for coffee.
Starbucks Coffee Company revolutionized the coffee-drinking habits of millions of Americans. Starbucks, whose bright green-and-white logo is almost as familiar as the golden arches of McDonald’s, began in Seattle in 1971. Fifteen years later it had grown into a chain of four stores in the Seattle area. Then in 1987 Howard Schultz, a former Starbucks employee, who had become enamored with the culture of Italian coffee bars during a trip to Italy, bought the company from its founders for $3.8 million. Starbucks went through several CEOs after Shultz left in 2000, and he returned in 2008 and stayed through 2017. Kevin Johnson is the current CEO. In 2019, the average cost of a a cappuccino or a latté in American Starbucks was $3.50 and Starbuck’s had grown to become an international chain, with over 31,000 stores around the world.
The change in American consumers’ taste for coffee and the profits raked in by Starbucks lured other companies to get into the game. Retailers such as Seattle’s Best Coffee and Gloria Jean’s Coffees entered the market, and today there are thousands of coffee bars, carts, drive-throughs, and kiosks in downtowns, malls, and airports all around the country. Even McDonald’s began selling specialty coffees. Since then, Starbucks has purchased Seattle’s Best (2003), Diedrich Coffee (2006), and Teavana (2012).
The price of coffee beans has been quite volatile over the decades. Just as consumers were growing accustomed to their cappuccinos and lattés, in 1997, the price of coffee beans shot up. Excessive rain and labor strikes in coffee-growing areas of South America had reduced the supply of coffee, leading to a rise in its price. In the early 2000s, Vietnam flooded the market with coffee, and the price of coffee beans plummeted. Then, weather conditions in various coffee-growing countries reduced supply, and the price of coffee beans went back up. This caused more investment into coffee beans, and prices dropped again.
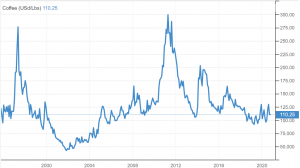
Coffee Prices from 1995 – Present
Markets , the institutions that bring together buyers and sellers, are always responding to events, such as bad harvests and changing consumer tastes that affect the prices and quantities of particular goods. The demand for some goods increases, while the demand for others decreases. The supply of some goods rises, while the supply of others falls. As such events unfold, prices adjust to keep markets in balance. This chapter explains how the market forces of demand and supply interact to determine equilibrium prices and equilibrium quantities of goods and services. We will see how prices and quantities adjust to changes in demand and supply and how changes in prices serve as signals to buyers and sellers.
The model of demand and supply that we shall develop in this chapter is one of the most powerful tools in all of economic analysis. You will be using it throughout your study of economics. We will first look at the variables that influence demand. Then we will turn to supply, and finally we will put demand and supply together to explore how the model of demand and supply operates. As we examine the model, bear in mind that demand is a representation of the behavior of buyers and that supply is a representation of the behavior of sellers. Buyers may be consumers purchasing groceries or producers purchasing iron ore to make steel. Sellers may be firms selling cars or households selling their labor services. We shall see that the ideas of demand and supply apply, whatever the identity of the buyers or sellers and whatever the good or service being exchanged in the market. In this chapter, we shall focus on buyers and sellers of goods and services.
Microeconomics for Managers Copyright © 2020 by Margo Bergman is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Starbucks Case Study - How Starbucks Conquered The Coffee Industry?

Devashish Shrivastava
Starbucks Corporation is an American coffee chain that was established in 1971 in Seattle, Washington. By mid-2019, the organization had a presence in over 30,000 areas around the world. Starbucks has been depicted as the fundamental delegate of "second wave espresso," a reflectively-named development that advanced high-quality espresso and specially simmered coffee. Starbucks now uses robotized coffee machines for proficiency and well-being.
Starbucks serves hot and cold beverages, entire bean espresso, micro-ground moment espresso known as VIA, coffee, caffe latte, full-and free leaf teas such as Teavana tea products, Evolution Fresh squeezes, Frappuccino refreshments, La Boulange baked goods, and bites (for example, chips and wafers); some offerings such as the Pumpkin Spice Latte are explicit to the territory of the store. Numerous Starbucks outlets sell pre-bundled nourishment items, sweltering and cold sandwiches, and drinkware such as cups and tumblers. Furthermore, there are Select "Starbucks Evenings" areas that offer brew, wine, and appetizers.
Starbucks first ended up productive in Seattle in the mid-1980s. Despite an underlying financial downturn with its venture into the Midwest and British Columbia in the late 1980s, the organization experienced rejuvenated success with its entrance into California in the mid-1990s. Starbucks opened an average of two new stores every day between 1987 and 2007. On December 1, 2016, Howard Schultz reported he would leave his position as the CEO and would be supplanted by Kevin Johnson. Johnson accepted the role of the CEO of Starbucks on April 3, 2017, and Howard Schultz resigned to end up as the 'Chairman Emeritus', effective from June 26, 2018. Kevin Johnson is currently serving as the CEO and President of Starbucks.
Starbucks - Company Highlights
Startup Story Of Starbucks Corporation History Of Starbucks Corporation Starbucks - Name and Logo Starbucks Expansion Journey Starbucks Corporation in India Business Strategy Of Starbucks In India Products Of Starbucks Corporation Business Growth Of Starbucks Corporation Over The Years Future Plans Of Starbucks Corporation
Startup Story Of Starbucks Corporation

If you are wondering how did Starbucks start? Then, the story of Starbucks started back in 1971, when the company was a roaster and retailer of whole bean and ground coffee, tea and spices with a single store in Seattle’s Pike Place Market.
Zev Siegel stated that at that time he knew the coffee industry inside and out, he was well-versed, especially with the gourmet end of the industry. Besides, he was also known as the most educated coffee guy in the country at that time. So, the three college friends - Zev Siegel, Jerry Baldwin and Gordon, started out with their coffee bean shop and roastery at Seattle’s famous Pike Place Market in 1971. Eventually, they found a mentor in Alfred Peet, who was the founder of Peet’s Coffee and the man responsible for bringing custom coffee roasting to the U.S. and started with the coffee business in full swing. Starbucks initially began by selling coffee beans that were roasted by Peet's, a gourmet coffee company in Berkeley, California, and later on, started roasting on their own.
History Of Starbucks Corporation

The first Starbucks store was initiated in 1971 in Washington by 3 individuals who met while they were studying at the University of San Francisco: English educator Hun Baldwin, history educator Zev Siegl, and author Gordon Bowker. The trio was encouraged to sell top-notch espresso beans and hardware after businessman Alfred Peet showed them his style of simmering beans.
During this time, the organization sold simmered, entire espresso beans. During its first year of activity, Starbucks bought green espresso beans from Peet's, and then started purchasing legitimately from producers.
Starbucks - Name and Logo

Bowker reviews that Terry Heckler, with whom Bowker claimed a publicizing office, thought words starting with "st" were ground-breaking. The organizers conceptualized a rundown of words starting with "st" and in the long run arrived on "Strabo," a mining town in the Cascade Range. The team then finalized on "Starbuck," the name of the young chief mate in the book "Moby-Dick".
Starbucks has given too many slogans/taglines already among which the most popular one is - " Brewed for those who love coffee".
Starbucks Expansion Journey

In 1984, the first proprietors of Starbucks, driven by Jerry Baldwin, acquired Peet's. During the 1980s, all-out offers of espresso in the US were falling. However, offers of strength espresso expanded, shaping 10% of the market in 1989; it stood at just 3% in terms of market share in 1983. By 1986, the organization worked six stores in Seattle and had just barely started to sell coffee.
In 1987, the first proprietors sold the Starbucks chain to the previous manager Howard Schultz, who rebranded his II Giornale espresso outlets as Starbucks and immediately extended. Starbucks then launched its outlets outside Seattle at Waterfront Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, and Chicago, Illinois. By 1989, 46 stores existed over the Northwest and Midwest, and every year Starbucks was simmering more than 2,000,000 pounds (907,185 kg) of coffee. At the hour of its first sale of stock (IPO) on the financial exchange in June 1992, Starbucks had 140 outlets with an income of $73.5 million, up from $1.3 million in 1987.
The organization's fairly estimated worth was $271 million at this point. The 12% segment of the organization that was sold raised around $25 million for the organization, which encouraged a multiplying of the number of stores throughout the following two years. By September 1992, Starbucks' offer cost had ascended by 70% to more than multiple times the income per portion of the past year. In July 2013, over 10% of in-store buys were made on the client's cell phones utilizing the Starbucks app.
The organization used the versatile social media stage when it propelled the "Tweet-a-Coffee" campaign in October 2013. People had the option to buy a $5 gift voucher for a companion by entering both "@tweetacoffee" and the companion's handle in a tweet. Research firm Keyhole observed the advancement of the event and a media article from December 2013 detailed that Starbucks had discovered that 27,000 individuals had taken an interest and $180,000 of buys were made to date.

As of 2018, Starbucks is positioned 132nd on the Fortune 500 rundown of the biggest United States organizations by revenue. In July 2019, Starbucks announced a "monetary second from last quarter total compensation of $1.37 billion, or $1.12 per share, up from $852.5 million, or 61 pennies for each offer, a year sooner." The organization's fairly estimated worth of $110.2 billion expanded by 41% in the middle of 2019. The income per share in quarter three was recorded at 78 pennies, considerably more than the estimate of 72 cents.
Starbucks Corporation in India

In January 2011, Starbucks Corporation and Tata Coffee reported designs to start opening Starbucks outlets in India. Despite a bogus beginning in 2007, in January 2012, Starbucks declared a 50:50 joint endeavour with Tata Global Beverages, called Tata Starbucks Ltd. , which would possess and work outlets marked "Starbucks, A Tata Alliance". Starbucks had endeavoured to enter the Indian market in 2007. However, it didn't provide any explanation behind its withdrawal of it.
It was on October 19, 2012 that Starbucks opened its first store, a 4,500 sq ft store in Elphinstone Building, Horniman Circle, Mumbai. Starbucks opened its first cooking and bundling plant in Coorg, Karnataka in 2013 to supply its Indian outlets. The company extended its reach to Delhi on 24 January 2013 by opening 2 outlets. Tata Global Beverages declared in 2013 that they would have 50 areas before the end of the year, with a venture of ₹4 billion ($58 million). The organization did open its 50th store in India on July 8, 2014.
The third city of India to get a Starbucks outlet was Pune, where the organization opened an outlet at Koregaon Park on 8 September 2013. Starbucks opened a 3,000-square-foot lead store at Koramangala, Bangalore on 22 November 2013, making it the fourth city to have an outlet. Starbucks opened the biggest espresso-forward store in the nation at Vittal Mallya Road, Bangalore on 18 March 2019. The store is estimated at 3,000 sq ft and is Starbucks' 140th outlet in India.
Tata Starbucks opened 25 stores between 2017 and 2018, which went up to 30 during 2018-19. On 21 February 2019, CEO Navin Gurnaney reported that Tata Starbucks would use only compostable and recyclable bundling materials over the entirety of its stores from June 2020.

Starbucks reported its entrance in Gujarat on 7 August 2019. The organization opened five stores in Surat and Ahmedabad the following day. Starbucks' leader store in the state is situated at Prahlad Nagar, Ahmedabad, and offers more vegan alternatives than other Indian outlets. CEO Navin Gurnaney expressed that the organization would open more than 30 stores in the 2019-20 financial year, of which 11 have already been opened.
Business Strategy Of Starbucks In India
Starbucks' strategies for business in India seemed rock-solid but the brand wasn't completely immune still. In any case, the world's biggest bistro chain is building its position cautiously via a progression of well-picked steps. Numerous worldwide brands have entered India since the 1990s, being pulled in by its developing and optimistic customer base. Yet, not all have succeeded.
Starbucks isn't the primary contestant in India's composed espresso showcase; so it doesn't have any first-participant advantage. Cafe Coffee Day (CCD) is the market head while Barista Lavazza was the main espresso chain to open for business. Both are valued by the white-collar class. Costa Coffee, Coffee Bean and Tea Leaf (CBTL), and Gloria Jean are valued by the rich group in India.
India is customarily a tea-drinking nation, so espresso chains have concentrated on giving a feel where individuals can unwind and invest energy with one another. This setup implies higher capital expenses. It is different from the US, where the vast majority have a liking for espresso. The Indian buyer base has likewise advanced in the recent decade. What can worldwide brands like Starbucks do to augment their odds of achievement in India? Here are a few thoughts:

Picking a Local Partner
Worldwide brands face the difficult choice of either going solo or tying up with a nearby accomplice. Starbucks' choice to team up with India's TATA Global Beverages demonstrates attention to utilizing different advantages. The TATA Group is one of India's morally determined brands, an observation passed on about Starbucks India too.
Given that India produces espresso beans in just a couple of spots, the other sourcing alternative was bringing in the beans. Be that as it may, this would have raised costs fundamentally.
Tata's espresso plant in Karnataka has been contracted to supply beans to Starbucks' universally, making common cooperative energies. It has contracted to take into account TATA's TAJ SATS, which supplies to TATA's top-notch lodging network – The TAJ. The TATAs are put into the retail part with store brands like Westside, Tanishq, Croma, Star Bazaar, and so forth. Starbucks can use them for information sharing on Indian land, territory points of interest, and handling land administrations. This would enable its very own development to outline. This strategy gives scope for store-in-store deals.
Consistency in Store Arrangements
This keeps up the one-of-a-kind selling purpose of customer experience and allows to pick up economies of scale on CAPEX. Starbucks plans to have a similar store group crosswise over India. However, the size can change depending on financial matters. This is how it works all around. Starbucks wants to provide an agreeable 'café' experience. Having a similar organization gives clients the solace of accepting the equivalent 'Starbucks' vibe any place they go throughout the world.
Keeping the store designs steady means it needs to pick and open new areas stringently, to such an extent that the area can yield a throughput by the venture. Its methodology in-store arrangement is different from CCD, which has picked various configurations to tap the potential interest in any region. CCD has opened a couple of premium outlets dependent on the area's customer profile . It has additionally gone for non-store organizations like takeaway booths and candy machines. Be that as it may, Starbucks may expect that such non-store configurations may weaken its image esteem.
Estimating the Pace of Expansion
India is the place where an inability to screen primary concerns has tossed numerous organizations out of the rigging. So, a top-line just approach doesn't work here. Since Starbucks needs to pick new areas stringently by its equivalent configuration approach, it has decided on a deliberate pace of extension. It is concentrating on the budgetary feasibility of every outlet, as opposed to going for an aggressive development plan which may have brought about rehashed calls for capital.
This operational process is different from its system in the USA and China where it has fabricated scale by opening stores in pretty much every area – being the main port-of-call for espresso by basically being all over the place. CCD's methodology behind adaptable store organizations was to guarantee there is a CCD bistro at a simple reach. It is intriguing to check its normal store gainfulness given its scale.
Guaranteeing Top-Authority Backing and Responsibility
Top initiative responsibility from the two sides of the organization, Tata and Starbucks, has been plentifully clear. Starbucks took as much time as is needed to enter the market (6 years), recognizing that India was a mind-boggling market and required cautious passage arranging. The two sides have spoken finally about their dedication and shared their future plans to give their business a new direction toward growth.
Altering Contributions to Suit Indian Market and Client Needs
Being adjusted to Indian culture, tastes, and inclinations conveyed at a suitable "esteem" guarantees customer importance, construct, and continued utilization. Starbucks mirrors this comprehension – as observed through a blend of western staples, a wide scope of intriguing Indian tidbits similar to confined refreshments on the idea. Since its experience ( and item as well, however to a lesser degree) is its image guarantee, its test lies in conveying an all-around steady, yet locally significant brand experience.
The stores, or the "third spot" as Starbucks calls them, have been altered likewise. The stores don't pursue the worldwide layout and appear to have been planned with consideration, with neighbourhood contacts consolidated. Stores in various urban communities have been structured unexpectedly, mirroring the neighbourhood culture – for e.g., New Delhi's store has ropes and chat on the dividers and henna designs on the floor, though the Pune store has a rich showcase of collectables and copper.
There appears to be sufficient utilization of shading – something missing in the US. The stores have been intended to convey a particular, premium café experience, predictable, and in a state of harmony with the one conveyed over the rest of the world.

Making Inventive and Restricted Plan of Action
Starbucks appears to have made a confined plan of action, planned for conveying a universally reliable item and involvement with locally-focused costs. The Tata group conveys a major sourcing advantage (attributable to its quality over the generation chain, developing, broiling, and exchanging espresso), yet it has just gone past that to develop and support associations with nearby espresso cultivators – putting resources into structure economical cultivating rehearses. All of Starbucks' espresso is sourced locally, a first-ever for the organization.
Scaling up using Arrangements and Organizations
The Tata organization is the genuine overthrow in the Starbucks passage story. Having Tata as an accomplice is gigantically profitable, not due to the validity and strength it offers, or because it coordinates the scale and stature of Starbucks as an organization.
It offers numerous advantages catalyzing pretty much every market section achievement variable - for example, The Tata group has involvement in the retail business , a solid reputation in advancing new pursuits, gives a sourcing advantage through Tata espresso, offers access to high traffic areas using its lodgings and other retail outlets, guarantee excellent nourishment and refreshment supply through its F&B business and so forth.
Furthermore, the potential for an effective organization is amazingly high given Starbucks' and Tata's mutual qualities – the two of them have a solid social inner voice and are resolved to "give back" to the general public and network.
Influencing India for Worldwide Items
Not long after it finished its first year, Starbucks reported that it was serving top-quality Indian Arabica espresso as "Indian coffee" in different markets. Another world-class office for cooking and bundling has just been initiated in Coorg, Karnataka; the results of which are to be analyzed in India and abroad.
Overseeing Discernment and Guidelines
This viewpoint is tied in with structure, a solid positive observation and a picture for the business and brand crosswise over key outer partners and crowds – incorporating the administration, corporate accomplices, networks inside the eco-framework, and customers on the loose. Given what Starbucks has figured out how to accomplish in a year and a half since dispatch, it appears to be genuinely evident that its thought combined with the Tata advantage (critical reach and impact) has helped in developing solid connections and a positive picture with key outside partners and voting demographics.
Engage Nearby Association
Starbucks is by all accounts constructing a nation-explicit activity with nearby individuals in charge and overall unmistakable customer interface focuses, giving them the necessary position to coordinate and work. There is overwhelming interest in enlisting the perfect individuals and giving the essential preparation – to install and instil the organization's culture and administration models.
Along these lines, how has Starbucks fared against the McKinsey spread out variables for long-haul India achievement? Its accomplishments against the scorecard look noteworthy. With thorough vigorous passage arranging and brilliant and quick execution, the multi-month-old endeavour appears to have impressive force, making purchaser and network-driven ventures and focused on sustaining its centre business and brand. It appears to be very much set to "win" in India.
Whether Starbucks will collect a huge piece of the overall industry and accomplish its objective of India being among its best 5 markets over the long haul is not yet clear. It's still early days, yet for the organization, this appears to be an incredible beginning and a great globalization model for multinationals looking for an India section.
Products Of Starbucks Corporation
Aside from the typical items offered globally, Starbucks in India has some Indian-style item contributions, for example, Tandoori Paneer Roll, Chocolate Rossomalai Mousse, Malai Chom Tiramisu, Elaichi Mewa Croissant, Chicken Kathi Roll, and Murg Tikka Panini to suit Indian customers. All coffees sold in Indian outlets are produced using Indian broiled espressos by Tata Coffee. Starbucks additionally sells Himalayan packaged mineral water. Free Wi-Fi is accessible at all Starbucks stores.

In January 2017, Tata Starbucks presented Starbucks' tea image "Teavana". Teavana offers 18 unique assortments of tea in India. One of the assortments called the India Spice Majesty Blend was explicitly created for the Indian market and is just accessible in India. India Spice Majesty Blend is a mix of full leaf Assam dark tea injected with entire cinnamon, cardamom, cloves, pepper, star anise, and ginger. On 15 June 2015, Tata Starbucks reported that it was suspending the utilization of fixings that had not been affirmed by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
The organization didn't indicate what the fixings were or which items they were utilized in. The organization additionally expressed that it was applying for FSSAI endorsement for these ingredients.

As per the Latte Index positioning of the expense of a tall hot latte at Starbucks in 44 nations, India was the fifth most costly nation to buy the drink dependent on January 2016 costs. The record distributed by US-based buyer research firm ValuePenguin found that a tall hot latte cost $7.99 in India, far higher than the $2.75 it costs in the least expensive nation, the United States, yet much lower than the $12.32 in the most costly nation, Russia .
Tata Starbucks propelled the Starbucks Delivers program in mid-2019. The administration offers home conveyance from Starbucks outlets through an organization with Swiggy. The administration was first propelled in Mumbai, with designs to turn it out to other cities.
In its menu, the Tata Starbucks company has launched ice-creams as their new products. The frozen delights are available even in flavours like java chip and caramel macchiato among others and will come in takeaway tubs and single scoops. The ice-creams are now available in 50-60% of the Starbucks stores.
Business Growth Of Starbucks Corporation Over The Years

Tata Starbucks, a 50:50 joint endeavour between Tata Global Beverages and Starbucks Coffee of the US, has announced a 30% top-line development in financial 2018-19, driven by new store openings and improved execution. Tata Starbucks, which is hoping to make back the initial investment in the current money, has opened 146 stores to date. Tata Starbucks announced "twofold digit top-line development - 30% for the entire year, driven by new stores and improved store execution," Tata Global Beverages Ltd (TGBL) said in a financial specialists' introduction. Tata Starbuck's income for 2018-19 is required to be approximately INR 450 crores.
TGBL said Tata Starbucks opened 30 outlets in the past financial year, out of which 15 new stores were opened during the last quarter of the money-related year. The organization claimed detailed benefits at the store level; all urban areas were likewise productive, and additionally saw an ascend in nourishment share in general deals.
The Starbucks company has added around 40 stores in FY21 but the company had recorded a 33% Y-O-Y fall in its revenues during the same fiscal. According to the Sushant Dash, CEO of Tata Starbucks, the recovery that the company has seen after the second wave of COVID-19 was better than what it saw after the first wave of the deadly pandemic. The quarterly growth after Q2 FY22 was 120% more than what it saw during the same period in the previous fiscal. The company has hugely focused on home deliveries ever since the pandemic broke out. It has already addressed concerns associated with the spillage and other challenges pertaining to home delivery, which contributed to over 18% of the total sales that the company witnessed this fiscal, as per the reports in November 2021. Furthermore, the company has also added ice-creams to their menu in flavours like java chip and caramel macchiato. The Sanjeev Kapoor menu is another thing that has been freshly launched by Tata Starbucks. Besides, the company also launched a one-litre freshly brewed beverage and at-home coffee.

Future Plans Of Starbucks Corporation
Tata Starbucks Pvt. Ltd. is looking to forcefully grow its impression in the Indian market with its eyes on the quickly spreading "espresso culture" among the twenty to thirty-year-olds and upwardly versatile customers. Tata Starbucks, a JV between US-based Starbucks Coffee Company and Tata Global Beverages Ltd, hopes to set up altogether more number stores this monetary than it did previously.
Starbucks is hopeful about solid business development in India throughout the following year as it means to leave red in monetary numbers after 2020. "Our proceeded with development in topline and reasonable methodology towards extension will enable us to accomplish make back the initial investment by March 2020," Navin Gurnaney, CEO, Tata Starbucks disclosed to Business Line in the wake of declaring five new stores in Gujarat - three in Ahmedabad and two in Surat. Gurney likewise included, "First time in quite a while, we are opening five stores in any state in one go.
Gujarat is a significant market for us. In the wake of opening these five stores on Thursday, the all outnumber of hides away goes up to 157 in India." Starbucks entered India with its first store opened at Mumbai in 2012. Of the 157, the organization has opened all out 11 stores so far in this financial, as against complete 30 stores opened during 2018-19. It takes into account 270,000 clients each week in India. The organization had announced a turnover of INR 442 crores for the monetary 2018-19.
"Espresso business in India is developing significantly. The espresso culture is being initiated by recent college grads, upwardly versatile, and individuals who travel and get brand. Two years back, we set up 25 stores (in a year). During the last financial 2018-19, we included 30 stores.
This year we will beat that number considerably and by end of March 2020, we will have included a lot a greater number of stores than we included in the past," Gurney said. With per store venture prerequisites being evaluated at INR 1.7-2 crores, the complete CAPEX plan by the organization works out in overabundance of INR 50 crores during current monetary on the off chance that it opens more number of stores than a year ago. Be that as it may, Gurnaney ceased from giving venture figures for 2019-20.
The organization is likewise open to different open doors for development including inorganic development through acquisitions. Be that as it may, when tested about any probability of a venture plan in the espresso chain Cafe Coffe Day (CCD), Gurnaney denied estimating any discussions for securing. "We are very hopeful about India. We will be attentively forceful (to extend). (At present) we are not in discussions with anyone for obtaining.
In any case, we are hoping to develop constantly," he included. With an end goal to upgrade the client experience, Starbucks is presenting new nourishment things, taking into account all client needs including breakfast and lunch. The income share from nourishment things is right now around 25%, even as it keeps on developing with new things to meet the client's needs.
Who founded Starbucks?
Starbucks was started by Hun Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker in 1971.
Where was the first Starbucks started?
Starbucks was started in Pike Place Market, Seattle, Washington, United States.
When was Starbucks started in India?
Starbucks was launched in India in 2012.
What is the revenue of Starbucks?
Starbucks revenue was recorded $29.02 billion in 2021.
How many Starbucks stores are there worldwide?
There are 33,830 Starbucks stores in the world as of 2021.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Maximizing Efficiency: 8 Best Productivity Gadgets for Entrepreneurs
According to technology experts, productivity gadgets are devices or innovations that help individuals complete tasks more efficiently and effectively. These devices frequently use technology to automate operations, organize information, or simplify complex activities, eliminating distractions while increasing output. These devices come in various forms, from hardware to software programs, each
AI for Modern Tech Stack Solutions in Business Operations
This article has been contributed by Ms. Karunya Sampath, Co-founder & CEO of Payoda Technologies. When it comes to artificial intelligence, there is always a fear of missing out. However, AI is here to stay. The notion of AI has expanded so much over time that you may already be using
How to Generate Real Estate Leads Using AI
This article has been contributed by Satya S Mahapatra, Chief Brand Custodian and part of the Founder’s office at JUSTO Realfintech. India’s real estate sector is on a growth trajectory with nearly 4.11 lakh residential units sold in 2023, registering a growth of over 33% from 2022.
Magnum Ice Cream Marketing Strategy | Secrets Behind Magnum's Success
Brands like Magnum become instant favorites of people. The credit goes to the public relations team that works behind the scenes and creates mind-boggling marketing strategies and advertisements. These help the brand build its place in the market. And for Magnum, it's Unilever that is responsible for the media spend
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
Economic Characteristics of Starbucks
Introduction, demand and supply, the elasticity of starbucks coffee, market structure of starbucks.
Starbucks is the largest coffee-selling company in the United States. Its brand has grown alongside the economic growth of the company. The particular brand’s strength places the company at the top of the industry. The purpose of this paper is to analyze the economic characteristics of the company. After analyzing the demand and supply, the elasticity of coffee, and Starbucks’ market structure, it is economically stable. The demand and supply of the company are interdependent, and the price elasticity of the demand is elastic. Therefore, the oligopolistic company is at its level among various coffee companies.
Starbucks is a multinational coffee-selling company serving exceptionally delicious coffee. Starbucks coffee is recognized in the United States as one of the best coffee in the country. Indeed, the company is said to have created a coffee-drinking culture in America. High demand for various types of coffee makes the company sell more, thus making more revenue. The demand and supply, the elasticity of the company’s coffee, and the structure of the market illustrate the economic status of Starbucks. The coffee is sold at relatively high prices, yet the firm sells at least 4 billion cups every year (Pandey et al., 2021). As of 2020, Starbucks reported a revenue of $19.16 billion (Pandey et al., 2021). Thus, the economic characteristics of Starbucks coffee indicate the stability of the company.
The demand for coffee is influenced by many factors that affect the price equilibrium. Some of these factors include taste and preferences, population, prices of substitutes, income level, taxes, and consumers’ expectations (“Elasticity,” 2016). However, when the supply influences the demand, it increases when the supply decreases. When one or many of the considered factors change, the level of demand changes; in other words, unless all the factors considered remain constant, the level of demand will change with any change within. The law of demand states that when the prices are high, the demanded quantity is low (Alicke et al., 2017). The supply law provides that when the prices are high, the suppliers will supply more products.
The supply of coffee beans significantly influences the demand for Starbucks coffee. When the prices of coffee go high, the suppliers offer more coffee materials to the company. The suppliers are motivated by the product prices with which the company purchases its raw materials (“Elasticity,” 2016). When the prices go down, the suppliers are less motivated to supply more materials, so they supply less.
On the one hand, demand is influenced by many factors other than the quantity supplied. On the other hand, supply is highly affected by one major factor, the weather on the farm (Alicke et al., 2017). Coffee production involves relying on the weather, which is very unpredictable. Starbucks’ leading coffee bean suppliers are based in South America. Unfortunately, there is a lot of unpredictability in the temperature in the region.
Starbucks’ coffee supply beans depend on how favorable the weather has been in the producing regions. Coffee beans are often destroyed by lousy weather, especially when they are not yet harvested. Bad weather can be caused by either heavy rains or low levels of rainfall. During heavy rains, the coffee beans develop mold, excessive fermentation, and diseases, thus increasing the beans’ defects during harvest (Pandey et al., 2021). During low rains, the size of the coffee beans grows smaller, thus dropping its quality and quantity. During this bad weather, the farmers may not sell enough to the suppliers. Henceforth, with reduced supply, the level of demand for coffee in Starbucks increases.
Demand is affected by various factors that are determined by the economy. The prices of substitute coffee in the US, like Costa Coffee, may affect the demand for Starbucks’ coffee. When Costa Coffee offers lower prices for the same type of coffee, customers will likely go for the cheap coffee. Income and taxes are other significant factors influencing the demand for Starbucks coffee (“Elasticity,” 2016). When the income decreases or is highly taxed, the customers may reduce their spending on coffee. The taste and preferences of US customers could not change from the delicious Starbucks coffee; thus, the factor is less likely to affect demand (Alicke et al., 2017). Other factors that might not significantly affect Starbucks coffee demand are consumers’ expectations and their population.
A product is considered elastic if its quantity in demand changes with a change in prices. Conversely, if the demand changes barely change the prices, then the product is said to be inelastic (“Elasticity,” 2016). In Starbucks, the coffee is elastic, meaning that the change in demand drastically affects prices. The elasticity of coffee demand in the company is not experienced in all types of coffee.
However, so long as the demand is influenced by factors affecting demand, it deems the demand elastic. Latte coffee is one product with substitution; hence more likely to have an elastic demand. For example, various types of latte coffee in Starbucks are sold between 2 and 5 dollars. Costa Coffee latte prices range between 2 and 4 dollars (Pandey et al., 2021). Most types of lattes are sold at standard prices between the two companies. Therefore, if Starbucks increases the costs of lattes, the customers will buy from Costa Coffee.
The price elasticity of demand is determined by the quantity needed over the prices. Elasticity is the responsiveness of one item concerning changes in another economic variable (“Elasticity,” 2016). In this case, the elasticity of demand is determined by a change in the quantity and prices of a product. Therefore, to assess the elasticity of responsiveness of Starbucks coffee’s responsiveness to the costs, there is a need to consider its price elasticity. The magnitude of price elasticity of demand is measured by the quantity demanded by customers when they experience price changes. The more price-elastic the demand is, the more the customers react to prices. Henceforth, the more the customers will adjust their spending behaviors.
In Starbucks, the price elasticity of demand is usually not extreme. It means changes in demand may alter the prices of the coffee, but the customers change their spending behavior slightly. According to Schwartz (2018), Starbucks often raises coffee prices and gets sales. Maintaining the number of sales means that the customers’ spending is barely altered by variation in prices. Thus, the demand for coffee is not much affected by hiking prices. Although the change in prices may make a few customers, for instance, 10 out of 1000 look for alternative coffee, the demand for the same is not much affected.
The general price elasticity of demand in Starbucks may be elastic, but the company experiences inelastic demand from time to time. Schwartz (2018) mentions that Starbucks has inelastic demand customers, and some types of coffee with inelastic demand. Some customers believe that Starbucks does not have a substitute. Therefore, they purchase coffee from Starbucks whether the prices are high or low. Similarly, coffee such as frappuccino is only available in Starbucks: hence, the buyers will purchase it even when the prices go high (Pandey et al., 2021). All in all, the inelasticity of demand in Starbucks is smaller than elasticity. The general price elasticity of demand for Starbucks coffee is elastic.
Starbucks multinational company dominates an oligopoly type of market structure. An oligopoly market structure is whereby a few firms dominate the market (“Elasticity,” 2016). In this type of market structure, a few large firms may dominate the market, but there are also small ones. In the Starbucks coffee market, there is a high concentration of few firms which operate in large sizes. Some of these firms, Starbucks included, are McDonald’s, Maxwell House, Folgers, Dunkin Donuts, Costa Coffee, and Caribou Coffee (Pandey et al., 2021). The first food companies exist in large size, and although some may not be anywhere close to Starbucks, they are its competitors.
Starbucks might be in a highly concentrated market structure but remains at the top. In an oligopoly market structure, large firms have exceptional advantages, making it hard for small firms to enter the concentrated region (“Elasticity,” 2016). Starbucks has several unique benefits, thus making it stay at the top. One of the benefits is having one of the strongest brands. Starbucks has been in operation for many years, and there is no year it recorded reduced growth. According to Schwartz (2018), the company has opened at least 32,938 coffee stores worldwide.
The act of investing worldwide has made the Starbucks brand recognizable by both coffee drinkers and non-drinkers. The company records growth in stores, customers, and loyalty. It also expands its products every year to ensure relevance and innovation. The presence of many stores in various countries contributes to the retention of customers. When a company opens another branch, the customers understand that the product is good, hence more likely to stay loyal.
Starbucks, alongside the big firms, holds the advantage of economies of scale. The firm has a least 14 000 stores in the United States alone (Pandey et al., 2021). Consequently, lowering prices while increasing the level of production will help in achieving increased revenue. The economies of scale prevent a new firm from entering full production. Starbucks holds the benefit of economies of scale for both small and large organizations.
The best coffee-selling company stays at the top of the industry because, unlike its competitors, its revenue is not affected by lowered prices. Starbucks could cut down the costs compared to those of other large firms, but it will make equivalent revenue because its brand is powerful. Therefore, changes in prices barely change the demand for the company, hence maintaining the top position.
As illustrated by its economic characteristics, Starbucks is economically strong. The company’s coffee sales are barely affected by changes in demands and prices. Starbucks holds a strong position in the coffee selling industry because it is an established brand. The general demand and supply of Starbucks are interdependent. An increase in demand increases the supply of coffee beans.
Starbucks may slightly experience inelasticity of price demand, but that does not determine its position in elasticity. In general, the price elasticity of demand is proportionately elastic. The Starbucks Company holds the position of oligopoly market structure. The strength of the brand, customer loyalty, and the advantage of economies and scales are among many reasons why Starbucks stays at the top of the coffee industry.
Alicke, K., Rexhausen, D., & Seyfert, A. (2017). Supply chain 4.0 in consumer goods . Mckinsey & Company , 1-11. Web.
Elasticity: Demand and Supply . (2016). Cengage Learning.
Pandey, R., Ganatra, V., Jamnik, S., Goel, P., Goyal, P., Xuan, C. L. & Zen, L. J. (2021). An empirical study on customer satisfaction, perception, and brand image in Starbucks coffee in India, Asia . International Journal of Tourism and hospitality in the Asia Pacific (IJTHAP) , 4 (1), 53-63. Web.
Schwartz, E. (2018). Who will care about the Starbucks price hike? . Econlife. Web.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2023, August 5). Economic Characteristics of Starbucks. https://business-essay.com/economic-characteristics-of-starbucks/
"Economic Characteristics of Starbucks." BusinessEssay , 5 Aug. 2023, business-essay.com/economic-characteristics-of-starbucks/.
BusinessEssay . (2023) 'Economic Characteristics of Starbucks'. 5 August.
BusinessEssay . 2023. "Economic Characteristics of Starbucks." August 5, 2023. https://business-essay.com/economic-characteristics-of-starbucks/.
1. BusinessEssay . "Economic Characteristics of Starbucks." August 5, 2023. https://business-essay.com/economic-characteristics-of-starbucks/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "Economic Characteristics of Starbucks." August 5, 2023. https://business-essay.com/economic-characteristics-of-starbucks/.
- Google’s Corporate Strategy, Problems and Solutions
- Louis Vuitton Company’s History and Cultural Concepts
- Amazon’s Effectiveness & Supply Chain Management
- Wal-Mart in China and Options for Resolutions
- Theranos Business Relations With Government
- Transformational Leadership in Welcome Aboard Case
- Economic Concept of Elasticity in Netflix Case
- Wells Fargo Firm’s Financial Performance and Success
- OHS Violation Ontario: Summary of the Incident
- Communications Strategy: The Coca-Cola Company Case Study
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

PRICING STRATEGIES AND CONSUMER PERCEPTIONS – A STUDY OF SKIN CARE PRODUCTS

2020, IAEME PUBLICATION
The current research paper proposes to understand the perceptions of the respondents with respect to the prices of the skin care cosmetic products. Price is one of the crucial elements of marketing mix as it the only revenue generating variable for companies. Further, price is the most sensitive area of decision making and any pricing mistake decreases the profitability of the concern. In view of the significance of pricing in determining the profitability of companies, marketers must understand the prerequisites for successful pricing. One of the prerequisites for successful pricing is to understand how price works in the market place and secondly in identifying the consumer perceptions about prices and price changes. Price elasticity is the measure to estimate the extent of variation in the demand due to price variations. Pricing in skin care category is under consideration as skin care segment is not only the leader in the personal product industry but shows immense growth potential with per capita usage of skin care products in India still being low. In an attempt to understand how consumers perceive the value of the products and their prices and the reactions for price variations of skin care products, primary data has been collected. The sample is a convenience sample covering females belonging to Hyderabad and Secunderabad. The college going girls, working population and home makers who are of 18 and above years of age constitute the sample. The impact of the independent variables age, income and occupation on the perceived value, price elasticity and perceptions of the consumers about skin care product prices is analysed. Interestingly, in the skin care category, price elasticity is less for a hike in the price of the products while price elasticity is higher for price reduction. Besides, the skin care products are considered as costly irrespective of whether they are natural products, international brands or national products. Despite the fact that the skin care products are perceived to be costly, respondents buy them as the use of the products is considered to be essential to maintain the skin tone.
Related Papers
IJSRP Journal
The purpose of this study is to investigate internal and external influences on consumers purchasing decisions on cosmetic products in Tamilnadu and Kerala. The questionnaires were given to 500 consumers who are all using cosmetics. Out of 500 consumers contacted, 412 questionnaires were received with required coverage and details. The instruments of this study involved two parts: the first section of the instrument consisted of forced-choice questions about demographic characteristics: gender, marital status, age, occupation, monthly income level.
International Journal in Management and Social Science
Nilesh Anute
The Objective of this research paper is to study consumer buying behaviour towards cosmetic products. This research is conducted in Pune city and a survey method was used to collect the data from 200 respondents. Personal care sector is an integral part of the nation’s economy with its huge potential. The personal care industry is one of the largest consumer sectors in the country. The purchasing power and disposable incomes of the Indian consumer have considerably increased and it has created a niche for leading organizations in this segment in the last decade, resulting in phenomenal growth in this sector.
IAEME PUBLICATION
IAEME Publication
Consumer behavior has changed in recent times because of increased community awareness about environmental problems and has induced them to splurge on green products. The primary objective of this study is to Explore the major factors influencing the purchase pattern of green skincare products among male consumers in India. For the study, a sample of 200 male respondents was taken with a questionnaire having a set of 18 attributes condensed into six factor components influencing the purchasing patterns of green-skincare products. The data received on 6 measured variables and 18 statements were taken through the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA). Principle axis factoring, varimax rotation & eigen values were used to get the total number of factors. Reliability test was done to extract the relevancy of the components. Based on the analysis, five components were extracted namely-Ethical consumerism, Health concern, Brand image & influences, Lifestyle and economic consideration, Promotion techniques. The insights of this study can be used by skincare brands to spread awareness and frame strategies for the promotion of green skincare products among males.
Proceedings of the International Conference on Business and Engineering Management (ICONBEM 2021)
Rifelly Dewi Astuti SE MM 197809112008122002
Vinith Nair
Journal ijmr.net.in(UGC Approved)
The Objective of this research paper is to study consumer buying behaviour towards cosmetic products. This research is conducted in Pune city and a survey method was used to collect the data from 200 respondents. Personal care sector is an integral part of the nation’s economy with its huge potential. The personal care industry is one of the largest consumer sectors in the country. The purchasing power and disposable incomes of the Indian consumer have considerably increased and it has created a niche for leading organizations in this segment in the last decade, resulting in phenomenal growth in this sector. Introduction Understanding behavior of consumers is a key to the success of business organizations. Marketing personnel are constantly analyzing the patterns of buying behavior and purchase decisions to predict the future trends. Consumer behavior can be explained as the analysis of how, when, what and why people buy. According to Global Cosmetic Industry report the advanced education provided by brands about the products' ingredients and benefits have made today's consumer more aware of what they're putting on their bodies, and making them more willing to pay. Consumer behavior can be understood as: "The decision process and physical activity individuals engage in when evaluating, acquiring, using, or disposing of goods and services." (Loudon and Della Bitta, 1980).
Malaysian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities (MJSSH)
Abdullah Sanusi Othman
The cosmetics industry is one of the world's fast-growing sectors. With more and more new cosmetic companies joining the market this beauty industry is booming, resulting in a highly competitive environment. Furthermore, Consumers with rapidly shifting preferences and expectations have created challenges on the market, resulting in a shorter product ’s life cycle, impasse innumerable skin care giants and novice companies. As such, to stay and retain new customers, it is important for the cosmetic companies to continually grow their business activities. In order to achieve that, cosmetic companies need to understand and satisfy their customers by creating values and meet their demands. The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of brand image, perceive product price and perceived quality on intention to purchase cosmetic products. A total of 139 questionnaires were collected from consumers in the Kelang Valley who have experienced purchasing and using cosmetic prod...
Orissa Journal of Commerce
Ritu Narang
Global organic skin care industry is expected to register a phenomenal growth in the next five years due to increasing popularity of healthier lifestyle. Surprisingly, most existing literature is limited to organic food or personal care products. This study is a pioneering attempt to profile Indian users of organic skin care products. Demographic relationship with purchase intention was empirically tested. Employing regression analysis, the findings revealed that personal income and education have significant influence on intention to buy organic beauty/ skin-care products. Results of this study have crucial theoretical and practical implications for marketers of organic skin care industry as it will give them an insight regarding Indian consumers of organic skin care products. Firms can develop effective marketing strategies for organic skin care products focusing on the key demographic influences by pondering over the results of this study.
RELATED PAPERS
Leoncio Cordova
Intan Meliasari R
International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering
TS. DR. RAJESWARI RAJU
Clinical Imaging
Masako Kataoka
The Lancet. Infectious diseases
Hager Abdulaziz
Springer eBooks
jacek jagodzinski
Nigerian Journal of Physics
Michael Onuu
The New England Journal of Medicine
Caroline Whitacre
IEEE Communications Magazine
Manuel Gil Pérez
Quaternary Science Reviews
Peter K. Swart
Ngọc Hải Nguyễn
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950)
MATEC Web of Conferences
Academia Edu
Emory law journal
Robert Ahdieh
The Journal of Chemical Physics
Daniel Codorniu Pujals
Vincent Legat
SciELO Argentina
Graciela Morgade
Environmental Entomology
Marie Bengtsson
Open Forum Infectious Diseases
David Tybor
Revista de Saúde Pública
Olusoji J Daniel
Sustainability
sherif elkholy
Repository Publikasi Ilmiah
suryo widodo
Revista Nacional de Gerenciamento de Cidades
Geise Pasquotto
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Starbucks Corporation, an American company founded in 1971 in Seattle, WA, is a premier roaster, marketer and retailer of specialty coffee around world. Starbucks has about 182,000 employees across 19,767 company operated & licensed stores in 62 countries. Their product mix includes roasted and handcrafted high-
Starbucks has been leveraging its consumer loyalty and lack of elasticity among its consumers by continuously passing on increases in costs, due to wages and coffee prices, to its customers. As a ...
Here are some of the takeaways you can apply to your own business: 1. Study your customer personas. Starbucks understands that the majority of their customer base is fairly insensitive to price, and uses small price increases that everyday consumers barely notice to boost margins. Quantify your buyer personas and the demand for your product or ...
Starbucks also follows a demand-based pricing strategy. They increase the price of certain items according to the demand of the consumers. For instance, when the price of the coffee beans decreased, a lot of coffee shops had decreased their prices in order to increase their sales. But Starbucks had not decreased its prices.
The model of demand and supply that we shall develop in this chapter is one of the most powerful tools in all of economic analysis. You will be using it throughout your study of economics. We will first look at the variables that influence demand. Then we will turn to supply, and finally we will put demand and supply together to explore how the ...
An Increase in Demand. An increase in the quantity of a good or service demanded at each price is shown as an increase in demand. Here, the original demand curve D1 shifts to D2. Point A onD1 corresponds to a price of $6 per pound and a quantity demanded of 25 million pounds of coffee per month.
Even though Starbucks has increased their prices by about 0% per year (Taylor, 2017), (Meyer, 2018) for the last 5 years, it is difficult to provide a typical price vs. demand quantity curve to calculate elasticity from such a small change in price.
Starbucks Case Study - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document analyzes Starbucks' decision to raise drink prices against conventional wisdom during a recession when customers were cutting back. It uses a case study approach and mathematical analysis to argue that when price-sensitive customers leave during a downturn ...
Starbucks Price Increase case study.docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Starbucks decided to raise drink prices by up to 8% despite customers cutting back during the recession, going against the conventional wisdom of lowering prices. Through analyzing their gross margins and estimating price elasticity of demand ...
Price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. Again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more. It is read as an absolute value.
The Elasticity of Starbucks. Sept. 16, 2004 12:01 am ET. Share. Resize. According to your Sept. 2 article " Latte Letdown: Starbucks Set to Raise Prices ," "economics professors often use ...
elasticitycasestudy-160313085509 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Case study about the elasticity of demand and supply
Elasticity Analysis: Factors And Demand Analysis Of Starbucks. Starbucks is an American company that produces tea, coffee beverages, smoothies, baked goods and sandwiches. It was founded on March 30, 1971 in Seattle, Washington. The founders are Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegi and Gordon Bowker. Starbucks locations serve hot and cold drinks, whole ...
Expert-verified. Ans (1)---- Price elasticity of demand for Starbuck …. MICROECONOMICS: CASE STUDY (30 Marks) An Overview of the Starbucks Pricing Strategy While cutting prices is widely accepted as the best way to keep customers during tough times, the practice is rarely based on a deeper analysis or testing of an actual customer base.
Starbucks Case Study. Starbucks Corporation is an American coffee chain that was established in 1971 in Seattle, Washington. By mid-2019, the organization had a presence in over 30,000 areas around the world. Starbucks has been depicted as the fundamental delegate of "second wave espresso," a reflectively-named development that advanced high-quality espresso and specially simmered coffee.
The general price elasticity of demand in Starbucks may be elastic, but the company experiences inelastic demand from time to time. Schwartz (2018) mentions that Starbucks has inelastic demand customers, and some types of coffee with inelastic demand. ... The Coca-Cola Company Case Study; Interested in business strategies? Take a look at ...
Case Study Of Demand And Demand For Starbucks Coffee. Apart of the high demand and cost for petroleum these days, coffee is appointed to be the second most traded product on global markets next to oil. Coffee is nature resources that is cultivated in more than 50 countries and provides living for more than 22 million farmers, altogether up to ...
Coffee is one of the most consumed beverages in the world. From the book Principle of Economics, it is found that the elasticity of coffee demand is about 0.3; that is, a 10% rise in the price of coffee leads to a decline of about 3% in the quantity of coffee consumed. Here, the rise in price offsets the decline in consumption.
In this paper, our main objective is to empirically study. demand for different income groups in China, aimed to provide 3-block residential electricity tariff reform and the evaluation welfare effects of the new pricing system. With Beijing urban micro level data covering 2002 to 2009 from Beijing Statistics.
Price elasticity is the measure to estimate the extent of variation in the demand due to price variations. Pricing in skin care category is under consideration as skin care segment is not only the leader in the personal product industry but shows immense growth potential with per capita usage of skin care products in India still being low ...
A significant shift in demand was found to have occurred subsequent to 1964. The price elasticity was estimated at about −0.63 during 1946-1964 and −0.41 during 1965-1971. These results are consistent with those obtained in other studies of urban water demand in the arid parts of the western United States.
The market for cosmetic products is growing at an average annual rate between 4% and 5%. The total revenue in cosmetic industry in 2018 was over 260 billion euro. Cosmetic market is composed of several categories: skincare, hair care, make-up, perfumes, toiletries and deodorants, and oral cosmetics. Skincare is the leading category, accounting ...
The Elasticity of Demand: Understanding Consumer Responsiveness Price Elasticity of Demand ... Starbucks emphasizes creating a feeling of belonging, ... and cultural norms. The book combines theory with real-world examples and case studies, making it a must-read for marketers aiming to grasp and impact consumer behavior.