
199+ Social Work Research Topics [Updated 2024]
In the vast and dynamic field of social work, research plays a pivotal role in shaping interventions, policies, and practices. Social work research is not just an academic pursuit but a powerful tool for effecting positive change in communities. As aspiring researchers delve into this realm, the journey begins with a crucial decision – selecting the right social work research topic.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of choosing the right social work research topics, provide insights into the selection process, highlight popular research areas, discuss emerging trends, offer tips for conducting research, and share valuable resources for social work researchers.
Significance of Choosing the Right Social Work Research Topics
Table of Contents
Impact on Research Quality
The choice of a research topic significantly influences the quality and relevance of the research conducted. A well-chosen topic enhances the researcher’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge in social work.
Alignment with Personal Interests and Goals
Selecting a topic aligned with personal interests and career goals fosters a sense of passion and commitment. This alignment not only sustains the researcher’s enthusiasm throughout the process but also increases the likelihood of producing impactful research.
Contribution to the Field of Social Work
The right research topic has the potential to contribute to the broader field of social work by addressing pressing issues, proposing innovative solutions, and advancing our understanding of complex social dynamics.
How to Select Social Work Research Topics?
- Understanding the Scope of Social Work: Social work is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses various domains such as mental health, child welfare, community development, and more. Prospective researchers should explore the diverse scopes within social work to identify areas that resonate with their interests and expertise.
- Identifying Personal Interests and Passion: Passion fuels research endeavors. Researchers should reflect on their personal experiences, values, and interests to identify areas within social work that evoke a strong sense of commitment.
- Considering Relevance to Current Social Issues: Social work research gains significance when it addresses current societal challenges. Researchers should evaluate potential topics based on their relevance to contemporary issues, ensuring that the findings can contribute meaningfully to ongoing dialogues and efforts for social change.
199+ Social Work Research Topics: Category-Wise
Mental health and social work.
- The impact of community support on mental health outcomes.
- Examining the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in social work.
- Exploring stigma surrounding mental health in diverse populations.
- Integrating technology in mental health counseling: Challenges and opportunities.
- The role of social work in preventing suicide and self-harm.
Diversity and Inclusion in Social Work
- LGBTQ+ inclusivity in social work practice.
- Addressing microaggressions and bias in social work interactions.
- Promoting cultural competence in social work education.
- Exploring challenges faced by immigrants and refugees in accessing social services.
- Intersectionality in social work: Understanding and addressing multiple identities.
Social Work and Community Development
- Evaluating the impact of community gardens on neighborhood well-being.
- The role of social workers in disaster response and recovery.
- Strategies for combating homelessness and housing insecurity.
- Assessing the effectiveness of community-based participatory research in social work.
- Social work’s contribution to sustainable community development.
Social Work and Child Welfare
- Investigating the long-term outcomes of children in foster care.
- The impact of parental substance abuse on child welfare.
- Exploring cultural competence in child welfare services.
- Innovative approaches to supporting kinship care families.
- Assessing the effectiveness of early intervention programs for at-risk children.
Global Perspectives in Social Work Research
- Cross-cultural perspectives on social work ethics.
- Human rights and social work: An international comparison.
- The role of social work in addressing global health disparities.
- Social work responses to forced migration and refugee crises.
- Comparative analysis of social work systems in different countries.
Technology and Social Work
- Ethical considerations in the use of artificial intelligence in social work.
- Online therapy and its implications for the future of social work.
- Integrating telehealth in social work practice: Challenges and benefits.
- Cyberbullying and the role of social workers in prevention and intervention.
- The impact of social media on social work advocacy.
Policy and Advocacy in Social Work
- Analyzing the impact of welfare reform on vulnerable populations.
- Social work advocacy for criminal justice reform.
- The role of social workers in shaping healthcare policies.
- Addressing disparities in access to education through social work policy.
- Environmental justice and the role of social work in sustainability.
Substance Abuse and Addiction in Social Work
- Harm reduction strategies in social work practice.
- Supporting families affected by substance abuse: A social work perspective.
- Exploring the intersection of trauma and addiction in social work.
- Assessing the effectiveness of drug prevention programs in schools.
- The role of social workers in opioid addiction treatment.
Gerontology and Aging in Social Work
- Aging in place: Examining the role of social work in supporting seniors at home.
- Social isolation and mental health in the elderly population.
- Addressing elder abuse: Strategies for prevention and intervention.
- Palliative care and the role of social workers in end-of-life care.
- The impact of dementia on families and the role of social work support.
Education and Social Work
- The role of school social workers in addressing student mental health.
- Inclusive education: Social work interventions for students with disabilities.
- Bullying prevention programs in schools: A social work perspective.
- Examining the impact of teacher-student relationships on academic outcomes.
- Social work support for students experiencing homelessness.
Human Trafficking and Exploitation
- Human trafficking prevention and intervention strategies in social work.
- The role of social workers in supporting survivors of human trafficking.
- Addressing labor exploitation through social work advocacy.
- Intersectionality and human trafficking: A comprehensive approach.
- Assessing the effectiveness of anti-trafficking policies and programs.
Family Dynamics and Social Work
- Impact of divorce and separation on children: Social work interventions.
- Foster care reunification: Challenges and success factors.
- LGBTQ+ parenting and the role of social work in family support.
- Domestic violence prevention programs: A social work perspective.
- Blended families: Navigating challenges and fostering resilience.
Health and Healthcare Disparities
- Social determinants of health and their impact on vulnerable populations.
- Access to healthcare for underserved communities: A social work perspective.
- The role of social workers in supporting individuals with chronic illnesses.
- Reducing health disparities among racial and ethnic minorities through social work interventions.
- Palliative care and the psychosocial aspects of terminal illness.
Human Rights and Social Work
- Social work advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights.
- Promoting gender equality through social work initiatives.
- Indigenous rights and the role of social workers in reconciliation.
- Advocacy for the rights of people with disabilities: A social work perspective.
- Social work responses to human rights violations and social justice issues.
Disability and Inclusion
- Social work interventions for children with developmental disabilities.
- The impact of inclusive employment programs on individuals with disabilities.
- Accessibility and social work advocacy for people with physical disabilities.
- Autism spectrum disorder: Social work support for individuals and families.
- Inclusive recreation programs: Enhancing the lives of people with disabilities.
Veterans and Military Social Work
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the role of social workers in veteran support.
- Social work interventions for military families experiencing deployment stress.
- Transitioning from military to civilian life: Challenges and opportunities.
- The impact of substance abuse on veterans and social work prevention strategies.
- Access to mental health services for veterans: A social work perspective.
Community Mental Health Programs
- Evaluating the effectiveness of community mental health clinics.
- Peer support programs in community mental health: A social work approach.
- Social work interventions for reducing stigma around mental illness in communities.
- Integrating mental health into primary care settings through collaborative care approaches.
- Social workers’ roles in school-based mental health initiatives.
Immigration and Social Work
- Social work responds to populations of immigrants and refugees’ mental health issues.
- The effect of immigration laws on social service accessibility.
- Community integration and social work support for immigrants.
- Advocacy for immigrant rights: A social work perspective.
- Family reunification and the role of social workers in immigration processes.
Social Work in Rural Communities
- Access to healthcare in rural communities: Social work interventions.
- Substance abuse prevention in rural settings: Challenges and solutions.
- Community development strategies for promoting rural well-being.
- Addressing mental health disparities in rural populations: A social work approach.
- Social work support for families facing economic challenges in rural areas.
Trauma-Informed Social Work Practice
- Integrating trauma-informed care into social work practice.
- Addressing childhood trauma through school-based interventions.
- Trauma-focused therapies and their application in social work.
- Vicarious trauma and self-care strategies for social workers.
- The role of social workers in supporting survivors of sexual assault.
Social Work in Schools
- School-based bullying prevention programs: A social work perspective.
- Social work interventions for students with learning disabilities.
- The impact of school social workers on academic success.
- Mental health support for at-risk youth in school settings.
- The role of social workers in addressing the school-to-prison pipeline.
Criminal Justice and Social Work
- Reentry programs for formerly incarcerated individuals: A social work approach.
- Juvenile justice and the role of social workers in rehabilitation.
- Addressing racial disparities in the criminal justice system: A social work perspective.
- The impact of incarceration on families and social work support.
Community-Based Participatory Research (CBPR)
- Principles and applications of community-based participatory research in social work.
- Engaging communities in the research process: A CBPR approach.
- Evaluating the outcomes of community-based interventions using CBPR.
- Challenges and opportunities in implementing CBPR in diverse settings.
- Empowering communities through CBPR: Case studies and best practices.
Social Work and Environmental Justice
- Climate change and its impact on vulnerable populations: A social work perspective.
- Environmental justice and community organizing: Social work interventions.
- Sustainable community development and the role of social workers.
- Access to clean water and sanitation: A social work advocacy approach.
- Indigenous perspectives on environmental justice: A social work lens.
Human Services Administration
- Leadership styles in human services administration: A social work perspective.
- The role of technology in improving human services delivery.
- Strategies for effective human services program evaluation.
- Addressing burnout and promoting self-care in human services organizations.
- Social work ethics and decision-making in human services administration.
Social Work and Artificial Intelligence
- Applications of AI in social work practice: Opportunities and challenges.
- The role of chatbots in mental health support: A social work perspective.
- Bias and fairness in algorithmic decision-making in social work.
- Human-AI collaboration in social work: Enhancing service delivery.
Crisis Intervention and Social Work
- Social work responses to natural disasters: Lessons learned and best practices.
- Crisis intervention strategies for individuals experiencing acute trauma.
- The role of social workers in emergency shelters and disaster recovery.
- Trauma-informed care in crisis intervention: A social work approach.
- Collaborative approaches to crisis intervention in community settings.
Social Work in the LGBTQ+ Community
- LGBTQ+ youth homelessness: Social work interventions and prevention.
- Supporting transgender and non-binary individuals in social work practice.
- Mental health disparities in the LGBTQ+ community: A social work perspective.
- LGBTQ+ inclusive policies in social service organizations.
- Social work advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights and equal access to services.
Social Work and Aging
- Aging in place: Social work interventions for promoting independence.
- Social work support for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their families.
- End-of-life decision-making and the role of social workers.
- Social isolation among older adults: Strategies for prevention and intervention.
- Exploring innovative housing models for aging populations.
Faith-Based Social Work
- The intersection of faith and social work: Ethical considerations.
- Faith-based organizations in community development: A social work perspective.
- Pastoral care and counseling: Social work support in religious communities.
- Addressing religious discrimination in social work practice.
- Interfaith dialogue and its role in fostering social cohesion: A social work approach.
Social Work in Substance Use Prevention
- Social work interventions for preventing substance use among adolescents.
- The impact of early childhood experiences on later substance use: A social work perspective.
- Prevention programs targeting high-risk populations: A social work approach.
- Social work support for families affected by parental substance use.
- Community-based strategies for preventing opioid misuse: A social work lens.
Global Mental Health and Social Work
- Cultural considerations in global mental health: A social work approach.
- Collaborative approaches to addressing mental health stigma globally.
- The role of social workers in disaster mental health response internationally.
- Integrating traditional healing practices into global mental health interventions.
- Comparative analysis of mental health policies and services worldwide.
Social Work and Human-Animal Interaction
- Animal-assisted therapy in social work practice: Applications and benefits.
- The role of therapy animals in reducing stress and promoting well-being.
- Animal cruelty prevention and the role of social workers.
- The impact of pet ownership on mental health: A social work perspective.
- Ethical considerations in incorporating animals into social work interventions.
Refugee Mental Health and Social Work
- Trauma-informed approaches in working with refugee populations.
- Social work support for refugee children in educational settings.
- Addressing mental health disparities among refugee communities.
- Cultural competence in providing mental health services to refugees.
- Resettlement challenges and social work interventions for refugees.
Community Resilience and Social Work
- Building community resilience in the face of adversity: A social work perspective.
- Social work interventions for promoting resilience in vulnerable populations.
- Resilience-based mental health programs in schools: A social work approach.
- The role of social workers in disaster resilience planning.
- Collective trauma and community healing: A social work lens.
Technology and Social Work Ethics
- Ethical considerations in the use of social media in social work practice.
- Privacy and confidentiality in the age of digital record-keeping.
- Ensuring equity in access to technology-based interventions: A social work approach.
- Social work responses to cyberbullying: Prevention and intervention strategies.
- Ethical guidelines for the use of virtual reality in social work practice.
Social Work in Sports
- Sports-based youth development programs: A social work perspective.
- The role of social workers in promoting mental health in athletes.
- Addressing substance use and performance-enhancing drugs in sports: A social work lens.
- Inclusive sports programs for individuals with disabilities: A social work approach.
- Social work interventions for preventing and addressing sports-related violence.
Social Work in the Arts
- Arts-based interventions in social work practice: Applications and outcomes.
- The role of creative expression in trauma recovery: A social work perspective.
- Using theater and performance arts in social work education and therapy.
- Arts programs for at-risk youth: A social work approach.
- The impact of the arts on community well-being: A social work lens.
Social Work and Foster Care Adoption
- Social work interventions for successful foster care reunification.
- Addressing the unique needs of LGBTQ+ youth in foster care.
- The impact of foster care placement on child development: A social work perspective.
- Post-adoption support services: A social work approach.
- Cultural competence in transracial and transcultural foster care and adoption.
Social Work in the Gig Economy
- The Role of Social Work in Addressing Mental Health Challenges in the Gig Economy
- Exploring Social Work Strategies for Supporting Gig Workers’ Financial Stability
- Gig Economy and Social Work Advocacy: Ensuring Fair Labor Practices
- Navigating Occupational Hazards: Social Work Interventions in Gig Work Environments
- Social Work’s Contribution to Promoting Work-Life Balance in the Gig Economy
Emerging Trends in Social Work Research
- The Impact of Technology on Social Work Practice: Examine how technology is influencing social work practices and service delivery, considering both advantages and ethical considerations.
- Ethical Considerations in the Use of Technology in Social Work Research: Discuss the ethical challenges associated with the integration of technology in social work research and propose guidelines for responsible use.
- Cross-Cultural Studies in Social Work: Explore the significance of cross-cultural studies in social work research, promoting a deeper understanding of diverse cultural contexts.
- Addressing Global Social Issues through Research: Investigate how social work research can contribute to addressing global social challenges, such as poverty, migration, and climate change.
Tips for Conducting Social Work Research
Developing a Research Question
Craft a research question for social work research topics that is clear, concise, and aligns with the chosen social work research topic. The question should guide the research process and contribute meaningfully to the existing literature.
Choosing Appropriate Research Methods
Select research methods that align with the nature of the research question and the goals of the study. Consider whether qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approaches are most suitable for addressing the research objectives.
Ethical Considerations in Social Work Research
Prioritize ethical considerations throughout the research process. Ensure informed consent, confidentiality, and respect for the dignity and rights of research participants.
Resources for Social Work Researchers
Journals and Publications
Explore reputable social work journals and publications to stay updated on the latest research, methodologies, and findings. Examples include the “Journal of Social Work” and the “British Journal of Social Work.”
Professional Organizations
Joining professional organizations such as the National Association of Social Workers (NASW) provides access to valuable resources, networking opportunities, and conferences that enhance a researcher’s knowledge and skills.
Online Databases and Research Tools
Utilize online databases like PubMed , Social Work Abstracts, and Google Scholar to access a wide range of social work research articles. Additionally, familiarize yourself with research tools and software that can streamline the research process.
In conclusion, the journey of selecting the social work research topics is a crucial step that requires thoughtful consideration and reflection. The chosen topic should align with personal interests, address current social issues, and contribute meaningfully to the field of social work.
As researchers embark on this journey, they have the opportunity to explore diverse areas, from mental health and child welfare to emerging trends in technology and global perspectives.
By following ethical guidelines, employing appropriate research methods, and leveraging valuable resources, social work researchers can make significant contributions to improving the well-being of individuals and communities.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Find top study documents
Social Work Research Topics & Tips on Finding and Distinguishing Good Ones
Updated 12 Jun 2024
Social work research is the systematic investigation of problems pertaining to the social work field. Alternatively, it can be defined as the application of research methods for addressing/solving problems confronted by social workers in their practice.
Major research areas include studying concepts, theories, principles, underlying methods, employees’ skills and their interaction with individuals and groups as well as internal processes, functioning principles within social entities. For a more specific selection of social work research topics, go to the appropriate section within this article.
Social work is ultimately focused on practical application, hence, the ultimate goal of social work research is understanding the efficacy of various intervention methods aimed at alleviating the conditions of people suffering from social deprivation – this highlights the importance presented by both the field and its associated research. For such difficult topics, you may ask yourself "can I pay someone to write my research paper " - and our professional team is here to help you.

Signs of Good Research Topics
Of all social work research questions, how could one distinguish the ones holding the greatest value or potential? Considering these signs could increase the chances of picking higher quality or more productive social work topics:
- Chosen topics are backed up by one or more published studies by research teams from the US or from abroad with solid article-related citation metrics, typically published in prestigious peer-reviewed academic journals (journals with high impact factor).
- Social work research topics in question are related to practice – theoretical research is very important, but nothing beats practical knowledge and efficient practical intervention methods and strategies. However, this aspect might depend on other circumstances as well (for students, for instance, theoretical topics are fairly acceptable). To ensure a successful research proposal in the field of social work, consider utilizing research proposal writing services .
- Social work research topics are breaking certain stereotypes. People are inclined towards topics that break preconceived notions – such topics naturally receive greater attention. If they bring solid evidence and reasonable arguments while providing/promising real benefits, such topics can simply revolutionize the field.
- Chosen social work research topics match current trends. Don’t understand us wrong – not everything that is trendy deserves attention (many things are overhyped). However, trends do have a sound reason for emerging (there is normally value behind the forces driving them). Moreover, delving into a field/topic that has only been recently established often gives significant advantages (career-wise). So watch out for trends in your research field closely, but always scrutinize them for what they are worth.
Get your paper in 3 hours!
- Customized writing: 100% original, personalized content.
- Expert editing: polished, standout work.
✔️ Zero AI. Guaranteed Turnitin success.
Where Can You Find Perfect Topics?
When exploring education research topics or searching for social worker research topics, it might prove useful to follow a few proven strategies (which are equally valid for many other occasions):
- Skim through your study literature (e.g. handbooks, course notes) – this is material you already studied, but going through it might help you to systematically visualize all studied topics or subtopics (these can suggest new ideas).
- Brainstorming. Access your knowledge base – chances are you have a few interesting topics stored in mind that you’d like to explore in greater detail.
- Browse through published article titles in social work journals or, even better, study newsletters/highlights on journal websites. Alternatively, one could search on platforms aggregating field-related news from multiple journals.– while some articles/topics might be overly complicated or specific, these still offer an immense choice.
- Browse online for ready research topics for a custom research paper from our research paper writing service – skimming through such lists would bombard you with topics of appropriate complexity and scope /broadness or would inspire new related ideas (e.g. by combining elements from different topics).
Yet another way to pick a good topic is to get research paper writing help from our professional writers – they would manage all aspects, including that of choosing an original and solid topic (obviously, you might be willing to confirm it, before proceeding with your writing project).
Need more writing assistance?
Connect with our top writers and receive a paper sample on social work crafted to your needs.
100 Social Work Research Topics
Below is a comprehensive social work research topics list to help get you started with your project.
50 Controversial Research Topics
- Group therapy vs individual therapy for increasing autistic children adaptability
- Impact on parents having children with autism spectrum disorder.
- Role play vs group discussion efficiency in increasing knowledge regarding drug abuse among high-school students.
- Addressing the stigma associated with depression.
- Measures to counteract condemning stereotypes with regard to depression (explaining and highlighting the biological mechanisms underlying it)
- Identifying individuals with suicide predisposition serving in military units.
- Life events role in PTSD onset in veterans.
- Strategies to prevent PTSD onset in US army veterans.
- Social inclusion measures for war veterans.
- Most efficient strategies for suicide prevention in academic setting.
- Categories are most vulnerable to drug abuse.
- Most efficient educational measures to prevent future drug abuse in children
- Myths about substance abuse among adolescents.
- Family support importance for alcohol addicts rehabilitation.
- Workaholics – new type of addicts. Impact on personal and family lives.
- Mental retardation in Alzheimer’s disease – how to cope with it as a family member?
- Promoting integration for children with Down syndrome.
- General considerations for working with children with developmental disabilities.
- Educating society with regard to dyslexic children (all target groups could be considered: parents, classmates, teachers, etc.)
- Dyslexia cases combined with ADHD – how to approach it?
- Dismounting common myths about dyslexia.
- Counteracting bullying aimed at dyslexic children.
- Early intervention benefits to address language difficulties in case of dyslexic children.
- What role should educators, parents, schools, mental health centers, private practice have in addressing dyslexia?
- Key prerequisites for building resilience to adverse life events in children
- Strategies for building resilience in welfare workers.
- Who is responsible for developing resilience in social workers?
- Self-help guidelines for social workers to become resilient.
- Most common problems encountered by LGBT youth in US schools.
- Arming LGBT individuals with coping strategies to face discrimination.
- The situation with juvenile delinquents across various US states.
- Rationale behind separating juvenile delinquents from adult delinquents.
- Factors contributing to high youth incarceration rate in certain US states (Wyoming, Nebraska, South Dakota).
- Most efficient reeducation strategies for juvenile delinquents.
- Society inclusion measures for people that served in prison.
- Coping with the stigma of having served in prison.
- Attitudes of welfare workers towards incarcerated individuals.
- Attitudes of correctional officers towards mental health of incarcerated individuals.
- Gender differences relevance when working with incarcerated people.
- Factors increasing the risk of recidivism in released prisoners.
- Incarceration impacts on parent-child relationships.
- Incarceration effects on mental health.
- Social inclusion role and family support in preventing recidivism by former prisoners.
- Circumstances associated with the highest risk of becoming a human trafficking victim.
- Ethical rules important when working with human trafficking victims.
- Trauma characteristic depiction for human trafficking victims.
- What is considered neglecting a child in child welfare?
- Prerequisites of a safe childhood and a functional family.
- Dealing with child abuse in orphanages.
- Types of child maltreatment/abuse.
Essay Examples Relevant to Social Work Controversial Topics
- Social Work
- Child Abuse
- Discrimination
50 Hot Research Topics for Social Work Students
- Difference in approaching children vs adolescents suffering from domestic violence.
- Success stories in preventing child abuse in certain regions/states.
- Strategies to encourage women to report domestic violence cases.
- Damage to families with ongoing domestic violence.
- Healing steps for victims of domestic violence.
- Effects of child neglect on later academic performance and career.
- Removing a child from a setting – when is it justified?
- Guidelines on providing testimony in court as a social worker
- Peculiarities of social work in health care assistance.
- Grief counseling for families that lost a loved one.
- Understanding the symptoms of grief.
- Risk factors for dangerous grief.
- Conduct/communication rules with persons in grief.
- Types of elder abuse. Which are the most common ones?
- Predictors of elder abuse (related to relationships within families, financial, status).
- The integrative concept of human services.
- The utility of mentoring programs in social care.
- Work with elders experiencing cognitive impairment.
- Peculiarities of working with immigrants in social care.
- Considerations for working with HIV positive people.
- Social research topics about homeless people.
- Primary factors contributing to homelessness.
- Challenges faced by social care assistants in working with sexually exploited clients belonging to the opposite gender.
- Meeting unique needs of sexually exploited children.
- Compassion fatigue experienced by welfare worker.
- Challenges experienced by single parents and support strategies
- Problem of getting medical help when belonging to vulnerable categories
- Is there place for spirituality in welfare worker?
- Religious beliefs obstructing welfare worker.
- Support strategies for low-income families having children with impaired development.
- Retrospective views and youth opinions on foster care facilities they have gone through.
- Key wishes/demands expressed by foster care facility residents
- Strategies employed by welfare worker to avoid burnout.
- Importance of building emotional intelligence as welfare worker.
- Discussing sexual health with mentally ill or retarded clients.
- Spirituality and faith as an essential element in many addiction rehabilitation programs.
- Attitude towards older people among welfare workers.
- Factors responsible for reluctance to benefit from mental health services among certain population groups.
- Differences in working with adolescent and adult drug abusers.
- Factors affecting foster youth that impact their higher education retention rate.
- Language barrier as an obstructing factor for minorities in benefiting from mental health services.
- Cultural competence as social work research topic
- Pre and post birth assistance to surrogate mothers. Evaluating impact on mental health.
- Challenges and issues arising in families with adoptive children.
- Play therapy interventions effectiveness in school-based counseling.
- Mental health in hemodialysis patients and corresponding support strategies.
- Importance presented by recreational activities for patients with Alzheimer’s.
- Intimacy impact on the outcome of group therapy practices for alcohol addiction.
- Mental health care outcomes in pedophilia victims.
- Alternative practices in social work.
Essay Examples Relevant to Hot Research Topics for Social Work
- Domestic Violence
- Elder Abuse
- Homelessness
Read also: Get excellent grades with the help of online research paper maker.
Found Topic But No Time For Writing?
We truly hope that by providing this list of social work topics for research papers we’ve addressed an important challenge many students encounter. Nevertheless, choosing suitable social work research topics is not the only challenge when having to write a paper.
Fortunately, Edubirdie website has a number of other tools like a thesis statement generator, a citation tool, a plagiarism checker, etc. to help with related aspects of writing a research paper. Besides, you can directly hire our professional paper writers to assist you with writing the paper according to instructions, creating a detailed outline, an annotated bibliography, but also with editing, proofreading, creating slides for presentation, etc.
Clients can choose their preferred writers freely by evaluating their ranking and performance on the platform. Later, they can communicate with these writers as their projects progress, being able to request intermediary results and providing feedback, additional guiding. If results are not satisfying and don’t match provided instructions, you can request unlimited revisions – all for free. In the unlikely situation in which revision attempts fail, you are guaranteed to get your money back. Given these low risks and guaranteed outcome, you should definitely give it a try!
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback, related blog posts, 150+ medical research paper topics for students.
Med Research Topics: What Makes a Good One? Several essential attributes characterize an excellent medical research topic. First and foremost, i...
How to conduct research: best tips from experienced EduBirdie writers
Have you ever got your scholarly task and been unsure how to start research? Are you a first-year student beginning your project? Whatever the case...
How to cite a research paper: basic rules and examples
Citing scientific papers is a fundamental skill for every university student engaged in academic pursuits. Proper quotation acknowledges the intell...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- About Social Work
- About the National Association of Social Workers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Editor-in-Chief
Lisa de Saxe Zerden, PhD, MSW
About the journal
Social Work is the premier journal of the social work profession. Widely read by practitioners, faculty, and students, it is the official journal of NASW and is provided to all members as a membership benefit …
Find out more
Latest articles
Latest posts on x.

Content Collections
Explore these curated collections, which feature articles from all four of the NASW journals.
Politics & Social Justice Collection
Immigration & Social Work Collection
Mental Health Collection
2020 Social Work Month Collection
2019 Social Work Month Collection
Featured Article
University of Chicago Professor Matt Epperson discusses the paper he co-authored, “Fostering Community-Engaged Research on Criminal Legal Innovations with Logic Models.”
Read the article
More Videos

Find a home for your paper

Call for papers
The NASW journals are accepting manuscripts for upcoming special issues.

Discover a more complete picture of how readers engage with research in Social Work through Altmetric data. Now available on article pages.

Recommend to your library
Fill out our simple online form to recommend Social Work to your library.
Recommend now

Email alerts
Register to receive table of contents email alerts as soon as new issues of Social Work are published online.
Related Titles
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations

- Online ISSN 1545-6846
- Print ISSN 0037-8046
- Copyright © 2024 National Association of Social Workers
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

225 Social Work Research Topics For College Students – Ideas for College Students
Social work is an important job that helps improve people’s lives, families, and communities. Research is a key part of social work studies. It allows you to look deeply into social issues, understand different views, and contribute to the growing knowledge in this field.
Picking the right research topic can be tough. That’s why we’ve made a list of 225 interesting social work research topics. These topics cover many areas, such as child welfare, mental health, addiction, community development, and social justice.
This list is meant to give you ideas, make you think critically, and provide knowledge to help make a real difference in social work.
Importance of Choosing a Relevant Topic
Table of Contents
Picking a good research topic is super important for a few reasons. First, it makes sure your research fits with current issues and trends in social work. By choosing a topic that deals with challenges happening now or builds on existing knowledge, you can contribute to ongoing talks and help develop effective solutions and rules.
Also, a good topic increases the chances that your research findings will be helpful to social workers, policymakers, and communities. Social work directly impacts people’s lives, and by researching important matters, you can potentially create positive change and inform decision-making.
Furthermore, a well-chosen topic can keep you motivated and involved throughout the research process. When you are truly interested and passionate about the subject, you are more likely to approach the research with enthusiasm and hard work, leading to better results.
It is also important to consider if there are enough resources and data available for your chosen topic. Selecting a topic with plenty of existing writings, reliable data sources, and people to research can make the process smoother and increase the credibility of your findings.
Moreover, a good topic can open up opportunities to collaborate with organizations, agencies, or communities actively working in that area, providing opportunities to apply your research and further explore the subject matter.
Recommended Readings: “ Data Communication And Networking Micro Project Topics: Amazing Guide! “.
Top 225 Social Work Research Topics For College Students
Here is the list of the top 225 social work research topics for college students according to different categories; take a look.
Child Well-being
- How foster care affects child growth
- Adoption and its effect on families
- Ways to prevent child abuse
- Role of social workers in child protection services
- Struggles faced by children in foster care
- Importance of keeping families together
- Impact of parental imprisonment on children
- Strengths of kinship care arrangements
- Role of social workers in addressing child poverty
- Helping strategies for children with special needs
Mental Health
11. How common is depression in teens, and how to treat it
- If cognitive-behavioral therapy works for anxiety issues
- How trauma impacts mental health
- Social workers’ role in suicide prevention
- Reducing stigma around mental illness
- Culturally appropriate mental health services
- Substance abuse treatment and recovery programs
- Impact of social media on mental health
- Addressing the mental health needs of LGBTQ+ individuals
- If group therapy is effective for mental health conditions
Elderly Care
21. Challenges faced by caregivers of older adults
- Impact of loneliness on the elderly
- Addressing elder abuse and neglect
- Role of social workers in long-term care facilities
- Promoting independent living for older adults
- End-of-life care and advance directives
- Caring for those with Alzheimer’s and dementia
- Retirement planning and financial security for seniors
- Benefits of intergenerational programs
- Strategies for aging in place
Disability Services
31. Accessibility and inclusion for disabled individuals
- Job opportunities and challenges for the disabled
- How assistive tech impacts daily living
- Social workers’ role in special education settings
- Advocating for disability rights and awareness
- Housing and community living options for the disabled
- Transition planning for youth with disabilities
- Mental health needs of the disabled
- Inclusive recreation and leisure activities
- Disability and intersectionality (race, gender, economic status)
Substance Abuse
41. If harm reduction approaches are effective
- Addressing the opioid epidemic
- Social workers’ role in addiction treatment centers
- Relapse prevention strategies
- How substance abuse impacts families
- Culturally responsive substance abuse interventions
- Role of peer support groups in recovery
- Addressing co-occurring substance abuse and mental health issues
- Prevention strategies for teen substance abuse
- Impact of harm reduction policies on public health
Community Development
51. Strategies for community empowerment and engagement
- Social workers’ role in urban renewal projects
- Addressing food insecurity and food deserts
- Community-based participatory research methods
- Sustainable development and environmental justice
- Promoting social cohesion and inclusion in diverse communities
- Addressing gentrification and displacement
- Social workers’ role in disaster relief and recovery
- Impact of community-based organizations
- Addressing homelessness and housing insecurity
Criminal Justice
61. If restorative justice practices are effective
- Social Workers’ role in the juvenile justice System
- Prisoner re-entry and reducing repeat offenses
- Impact of incarceration on families and communities
- Addressing racial disparities in criminal justice
- Victim support services and victim-centered approaches
- Diversion programs and alternatives to incarceration
- Needs of incarcerated individuals with mental health issues
- Restorative justice practices in schools
- Impact of criminal records on jobs and housing
Immigration and Refugees
71. Integration challenges for immigrants and refugees
- Social workers’ role in refugee resettlement programs
- Addressing the needs of undocumented immigrants
- Cultural competence when working with immigrants/refugees
- Impact of immigration policies on families and communities
- Addressing trauma and mental health needs of refugees
- Language barriers and service access for immigrants
- Immigrant and refugee youth: Challenges and opportunities
- Promoting inclusion and combating discrimination
- Social workers’ role in immigration detention centers
Health Care
81. Addressing health disparities and social factors affecting health
- Social workers’ role in hospitals
- Patient advocacy and navigating healthcare systems
- Chronic illness management and support services
- Addressing the needs of underserved populations in healthcare
- End-of-life care and palliative services
- Mental health needs of healthcare professionals
- Promoting health literacy and patient education
- COVID-19 impact on vulnerable groups
- Telehealth and its implications for social work
School Social Work
91. Addressing bullying and school violence
- Supporting students with special needs
- Promoting a positive school environment
- How poverty impacts student achievement
- Trauma-informed practices in schools
- Supporting LGBTQ+ students and inclusive environments
- Addressing students’ mental health needs
- Dropout prevention and intervention
- Promoting social-emotional learning in schools
- Collaboration between school social workers and other staff
Human Services
101. Addressing homelessness and housing insecurity
- Social workers’ role in domestic violence shelters
- Poverty reduction and economic empowerment programs
- Addressing the needs of veterans and families
- Natural disaster impact on vulnerable groups
- Promoting financial literacy and self-sufficiency
- Addressing food insecurity and hunger
- Social workers’ role in crisis intervention and emergencies
- Addressing the needs of the developmentally disabled
Social Policy
111. Analyzing the impact of social welfare policies
- Social workers’ role in policy advocacy and lobbying
- Addressing income inequality and wealth gaps
- Evaluating the effectiveness of social programs
- Ethics in Social Policy Development
- Comparing social welfare systems across countries
- Climate change impact on vulnerable groups
- Social workers’ role in sustainable development
- Impact of austerity measures on social services
- Addressing the digital divide and technology access
Human Rights
121. Addressing human trafficking and modern slavery
- Social workers’ role in promoting human rights
- Addressing the needs of refugees and displaced persons
- Promoting the rights of indigenous communities
- Addressing gender-based violence and discrimination
- Promoting the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals
- Impact of armed conflicts on civilians
- Promoting children’s rights and protection
- Environmental degradation impact on human rights
- Social workers promoting human rights education
Aging and Elderly Care
131. Addressing ageism and promoting positive aging
- Social workers’ role in long-term care facilities
- Promoting aging in place and community services
- Addressing the needs of caregivers for the elderly
- Financial security and retirement planning for seniors
- Addressing loneliness among the elderly
- Promoting intergenerational activities
- Addressing dementia and Alzheimer’s impact
- Promoting advance care planning and end-of-life care
Family and Marriage Counseling
141. Addressing domestic violence and partner violence
- Social workers’ role in family/marriage counseling
- Divorce impact on children and families
- Promoting healthy family communication and conflict resolution
- Addressing the needs of blended and non-traditional families
- Promoting positive co-parenting strategies
- Addiction impact on families
- Promoting financial stability for families
- Addressing the needs of military families
- Promoting family resilience and coping
Diversity and Social Justice
151. Addressing racial/ethnic disparities in social services
- Promoting cultural competence in social work
- Addressing discrimination and promoting inclusion
- Promoting social justice and human rights
- Addressing the needs of LGBTQ+ individuals and families
- Promoting intersectional approaches to social work
- Addressing systemic oppression and marginalization impact
- Promoting diversity and inclusion in social work education
- Addressing the needs of the disabled
- Anti-racist and anti-oppressive social work
Community Mental Health
161. Addressing trauma’s impact on communities
- Social workers’ role in community mental health centers
- Promoting mental health literacy and reducing stigma
- Addressing the mental health needs of specific groups
- Promoting community-based mental health services
- Poverty and social factors impact mental health
- Promoting peer support and self-help for mental health
- Addressing youth and teen mental health needs
- Promoting mental health in schools and education
- COVID-19 impact on community mental health
Addictions and Substance Abuse
171. Addressing the opioid crisis and overdose prevention
- Social workers’ role in addiction treatment and recovery
- Promoting harm reduction for substance abuse
- Substance abuse impact on families and communities
- Culturally responsive addiction services
- Co-occurring substance abuse and mental health issues
- Promoting peer support in addiction recovery
- Unique needs of women and substance abuse
- Substance abuse prevention and early intervention
- Impact of cannabis legalization
Social Work with Children & Youth
181. Addressing adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
- Social workers’ role in child welfare and protection
- Promoting positive youth development and resilience
- Addressing the needs of youth in juvenile justice
- Promoting educational success and closing achievement gaps
- Addressing bullying and school violence impact
- Promoting youth empowerment and leadership
- Addressing the needs of LGBTQ+ youth
- Promoting family engagement and support
- Technology and social media impact on youth
Human Behavior & Social Environment
191. Poverty and socioeconomic status impact
- Promoting resilience and coping strategies
- Addressing trauma and adverse experiences impact
- Promoting positive identity and self-esteem
- Discrimination and oppression impact
- Promoting social support and community connections
- Environmental factors impact human behavior
- Promoting positive aging and life transitions
- Technology and social media impact
- Promoting cultural competence and humility
Social Work Practice & Ethics
201. Addressing ethical dilemmas in practice
- Promoting self-care and preventing burnout
- Social media and technology impact on practice
- Promoting evidence-based practice
- Addressing interdisciplinary collaboration challenges
- Promoting culturally responsive practice
- Addressing vicarious trauma and compassion fatigue
- Social justice and human rights in practice
- COVID-19 impact on social work practice
- Promoting professional development
International Social Work
211. Addressing global poverty and inequality
- Promoting sustainable development & environmental justice
- Armed conflicts and humanitarian crises impact
- Promoting human rights and global social justice
- Promoting community development and empowerment
- Globalization and migration impact
- Cultural competence in international social work
- Promoting international collaboration
Research & Evaluation
221. Promoting evidence-based practice
- Developing assessment tools and measures
- Evaluating the effectiveness of interventions
- Challenges in community-based participatory research
- Promoting mixed methods in research
These topics cover a wide range of social work issues, allowing for in-depth exploration and analysis within specific niches.
Tips for Selecting a Research Topic
Picking a topic for research is an important first step. Your topic should be something you truly care about and want to explore deeply. Here are some tips for choosing an engaging and meaningful social work research topic:
Find Areas You Really Like
Make a list of the social issues or groups of people that you are most interested in. Think about personal experiences, volunteer work, internships, or classes that made you curious and want to learn more. Having a real interest will keep you motivated throughout the whole research process.
Look at Current Information
Look through recent journals, books, and reliable websites related to your interests. Note any gaps in knowledge or questions that come up from the existing information. These gaps can point you toward relevant research topics.
Consider Real-World Impact
Choose a topic that has the potential to inform policies, practices, or ways to help that can create positive social change. Research that can be applied in real-world situations is especially valuable in social work.
Make Sure Data Exists
Ensure there is enough data available to support an in-depth study of your chosen topic. This may include access to case studies, survey data, records, or people to participate in your research.
Narrow Your Focus
While social issues are often very broad and complex, a focused research topic is easier to manage and allows for deeper exploration. Narrow your topic to a specific population, geographic area, or part of the larger issue.
Get Input from Others
Talk to professors, professionals in the field, or experienced researchers for their insights and suggestions on potential topics. Their expertise can help you refine your ideas and identify promising areas for research.
Think About Ethics
As a social worker, it’s important to consider the ethical impacts of your research, such as protecting participants’ rights and well-being, addressing potential biases, and being sensitive to cultural differences.
Be Flexible
While it’s important to have a clear research focus, be open to adjusting your topic as you learn more from reading materials or encounter new perspectives during the research process.
Choosing a well-defined and meaningful research topic is the base for producing valuable social work research that can add to knowledge and drive positive change.
Social work covers a wide range of issues and groups of people, making it a rich and diverse area for research. The 225 topics listed here are just a small part of the many important areas ready for exploration.
From child well-being and mental health to criminal justice and human rights, each topic offers a chance to examine complex societal challenges deeply and contribute to developing impactful solutions.
As students start their research journeys, they have the potential to uncover new insights, challenge existing ways of thinking, and ultimately improve the lives of individuals, families, and communities.
With genuine interest, hard work, and a commitment to ethical and rigorous research, social work students can make meaningful contributions that drive positive change in our constantly changing world.
How do I know if a research topic is relevant to social work?
A relevant research topic in social work addresses current societal issues, aligns with the goals of social work practice, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
What are some examples of social work research topics related to social justice?
Examples include investigating disparities in access to healthcare, analyzing the impact of systemic racism on marginalized communities, and evaluating policies aimed at promoting social equity.
How can I narrow down a broad research topic in social work?
You can narrow down a broad research topic by focusing on a specific population, geographic location, or aspect of the issue. Conducting a literature review can also help identify gaps and areas for further exploration.
Similar Articles

Top 100 Research Topics In Commerce Field
The world of commerce is rapidly evolving. With new technologies, globalization, and changing consumer behaviors, many exciting research topics exist…


Top 30+ Mini Project Ideas For Computer Engineering Students
Mini projects are really important for computer engineering students. They help students learn by doing practical stuff alongside their regular…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Social Work Research Methods That Drive the Practice

Social workers advocate for the well-being of individuals, families and communities. But how do social workers know what interventions are needed to help an individual? How do they assess whether a treatment plan is working? What do social workers use to write evidence-based policy?
Social work involves research-informed practice and practice-informed research. At every level, social workers need to know objective facts about the populations they serve, the efficacy of their interventions and the likelihood that their policies will improve lives. A variety of social work research methods make that possible.
Data-Driven Work
Data is a collection of facts used for reference and analysis. In a field as broad as social work, data comes in many forms.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative
As with any research, social work research involves both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Quantitative Research
Answers to questions like these can help social workers know about the populations they serve — or hope to serve in the future.
- How many students currently receive reduced-price school lunches in the local school district?
- How many hours per week does a specific individual consume digital media?
- How frequently did community members access a specific medical service last year?
Quantitative data — facts that can be measured and expressed numerically — are crucial for social work.
Quantitative research has advantages for social scientists. Such research can be more generalizable to large populations, as it uses specific sampling methods and lends itself to large datasets. It can provide important descriptive statistics about a specific population. Furthermore, by operationalizing variables, it can help social workers easily compare similar datasets with one another.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative data — facts that cannot be measured or expressed in terms of mere numbers or counts — offer rich insights into individuals, groups and societies. It can be collected via interviews and observations.
- What attitudes do students have toward the reduced-price school lunch program?
- What strategies do individuals use to moderate their weekly digital media consumption?
- What factors made community members more or less likely to access a specific medical service last year?
Qualitative research can thereby provide a textured view of social contexts and systems that may not have been possible with quantitative methods. Plus, it may even suggest new lines of inquiry for social work research.
Mixed Methods Research
Combining quantitative and qualitative methods into a single study is known as mixed methods research. This form of research has gained popularity in the study of social sciences, according to a 2019 report in the academic journal Theory and Society. Since quantitative and qualitative methods answer different questions, merging them into a single study can balance the limitations of each and potentially produce more in-depth findings.
However, mixed methods research is not without its drawbacks. Combining research methods increases the complexity of a study and generally requires a higher level of expertise to collect, analyze and interpret the data. It also requires a greater level of effort, time and often money.
The Importance of Research Design
Data-driven practice plays an essential role in social work. Unlike philanthropists and altruistic volunteers, social workers are obligated to operate from a scientific knowledge base.
To know whether their programs are effective, social workers must conduct research to determine results, aggregate those results into comprehensible data, analyze and interpret their findings, and use evidence to justify next steps.
Employing the proper design ensures that any evidence obtained during research enables social workers to reliably answer their research questions.
Research Methods in Social Work
The various social work research methods have specific benefits and limitations determined by context. Common research methods include surveys, program evaluations, needs assessments, randomized controlled trials, descriptive studies and single-system designs.
Surveys involve a hypothesis and a series of questions in order to test that hypothesis. Social work researchers will send out a survey, receive responses, aggregate the results, analyze the data, and form conclusions based on trends.
Surveys are one of the most common research methods social workers use — and for good reason. They tend to be relatively simple and are usually affordable. However, surveys generally require large participant groups, and self-reports from survey respondents are not always reliable.
Program Evaluations
Social workers ally with all sorts of programs: after-school programs, government initiatives, nonprofit projects and private programs, for example.
Crucially, social workers must evaluate a program’s effectiveness in order to determine whether the program is meeting its goals and what improvements can be made to better serve the program’s target population.
Evidence-based programming helps everyone save money and time, and comparing programs with one another can help social workers make decisions about how to structure new initiatives. Evaluating programs becomes complicated, however, when programs have multiple goal metrics, some of which may be vague or difficult to assess (e.g., “we aim to promote the well-being of our community”).
Needs Assessments
Social workers use needs assessments to identify services and necessities that a population lacks access to.
Common social work populations that researchers may perform needs assessments on include:
- People in a specific income group
- Everyone in a specific geographic region
- A specific ethnic group
- People in a specific age group
In the field, a social worker may use a combination of methods (e.g., surveys and descriptive studies) to learn more about a specific population or program. Social workers look for gaps between the actual context and a population’s or individual’s “wants” or desires.
For example, a social worker could conduct a needs assessment with an individual with cancer trying to navigate the complex medical-industrial system. The social worker may ask the client questions about the number of hours they spend scheduling doctor’s appointments, commuting and managing their many medications. After learning more about the specific client needs, the social worker can identify opportunities for improvements in an updated care plan.
In policy and program development, social workers conduct needs assessments to determine where and how to effect change on a much larger scale. Integral to social work at all levels, needs assessments reveal crucial information about a population’s needs to researchers, policymakers and other stakeholders. Needs assessments may fall short, however, in revealing the root causes of those needs (e.g., structural racism).
Randomized Controlled Trials
Randomized controlled trials are studies in which a randomly selected group is subjected to a variable (e.g., a specific stimulus or treatment) and a control group is not. Social workers then measure and compare the results of the randomized group with the control group in order to glean insights about the effectiveness of a particular intervention or treatment.
Randomized controlled trials are easily reproducible and highly measurable. They’re useful when results are easily quantifiable. However, this method is less helpful when results are not easily quantifiable (i.e., when rich data such as narratives and on-the-ground observations are needed).
Descriptive Studies
Descriptive studies immerse the researcher in another context or culture to study specific participant practices or ways of living. Descriptive studies, including descriptive ethnographic studies, may overlap with and include other research methods:
- Informant interviews
- Census data
- Observation
By using descriptive studies, researchers may glean a richer, deeper understanding of a nuanced culture or group on-site. The main limitations of this research method are that it tends to be time-consuming and expensive.
Single-System Designs
Unlike most medical studies, which involve testing a drug or treatment on two groups — an experimental group that receives the drug/treatment and a control group that does not — single-system designs allow researchers to study just one group (e.g., an individual or family).
Single-system designs typically entail studying a single group over a long period of time and may involve assessing the group’s response to multiple variables.
For example, consider a study on how media consumption affects a person’s mood. One way to test a hypothesis that consuming media correlates with low mood would be to observe two groups: a control group (no media) and an experimental group (two hours of media per day). When employing a single-system design, however, researchers would observe a single participant as they watch two hours of media per day for one week and then four hours per day of media the next week.
These designs allow researchers to test multiple variables over a longer period of time. However, similar to descriptive studies, single-system designs can be fairly time-consuming and costly.
Learn More About Social Work Research Methods
Social workers have the opportunity to improve the social environment by advocating for the vulnerable — including children, older adults and people with disabilities — and facilitating and developing resources and programs.
Learn more about how you can earn your Master of Social Work online at Virginia Commonwealth University . The highest-ranking school of social work in Virginia, VCU has a wide range of courses online. That means students can earn their degrees with the flexibility of learning at home. Learn more about how you can take your career in social work further with VCU.
From M.S.W. to LCSW: Understanding Your Career Path as a Social Worker
How Palliative Care Social Workers Support Patients With Terminal Illnesses
How to Become a Social Worker in Health Care
Gov.uk, Mixed Methods Study
MVS Open Press, Foundations of Social Work Research
Open Social Work Education, Scientific Inquiry in Social Work
Open Social Work, Graduate Research Methods in Social Work: A Project-Based Approach
Routledge, Research for Social Workers: An Introduction to Methods
SAGE Publications, Research Methods for Social Work: A Problem-Based Approach
Theory and Society, Mixed Methods Research: What It Is and What It Could Be
READY TO GET STARTED WITH OUR ONLINE M.S.W. PROGRAM FORMAT?
Bachelor’s degree is required.
VCU Program Helper
This AI chatbot provides automated responses, which may not always be accurate. By continuing with this conversation, you agree that the contents of this chat session may be transcribed and retained. You also consent that this chat session and your interactions, including cookie usage, are subject to our privacy policy .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

The Pursuit of Quality for Social Work Practice: Three Generations and Counting
Enola proctor.
Shanti K. Khinduka Distinguished Professor and director of the Center for Mental Health Services Research at Washington University in St. Louis
Social work addresses some of the most complex and intractable human and social problems: poverty, mental illness, addiction, homelessness, and child abuse. Our field may be distinct among professions for its efforts to ameliorate the toughest societal problems, experienced by society’s most vulnerable, while working from under-resourced institutions and settings. Members of our profession are underpaid, and most of our agencies lack the data infrastructure required for rigorous assessment and evaluation.
Moreover, social work confronts these challenges as it is ethically bound to deliver high-quality services. Policy and regulatory requirements increasingly demand that social work deliver and document the effectiveness of highest quality interventions and restrict reimbursement to those services that are documented as evidence based. Social work’s future, its very survival, depends on our ability to deliver services with a solid base of evidence and to document their effectiveness. In the words of the American Academy of Social Work and Social Welfare (AASWSW; n.d.) , social work seeks to “champion social progress powered by science.” The research community needs to support practice through innovative and rigorous science that advances the evidence for interventions to address social work’s grand challenges.
My work seeks to improve the quality of social work practice by pursuing answers to three questions:
- What interventions and services are most effective and thus should be delivered in social work practice?
- How do we measure the impact of those interventions and services? (That is, what outcomes do our interventions achieve?)
- How do we implement the highest quality interventions?
This paper describes this work, demonstrates the substantive and methodological progression across the three questions, assesses what we have learned, and forecasts a research agenda for what we still need to learn. Given Aaron Rosen’s role as my PhD mentor and our many years of collaboration, the paper also addresses the role of research mentoring in advancing our profession’s knowledge base.
What Interventions and Services Are Most Effective?
Answering the question “What services are effective?” requires rigorous testing of clearly specified interventions. The first paper I coauthored with Aaron Rosen—“Specifying the Treatment Process: The Basis for Effectiveness Research” ( Rosen & Proctor, 1978 )—provided a framework for evaluating intervention effectiveness. At that time, process and outcomes were jumbled and intertwined concepts. Social work interventions were rarely specified beyond theoretical orientation or level of focus: casework (or direct practice); group work; and macro practice, which included community, agency-level, and policy-focused practice. Moreover, interventions were not named, nor were their components clearly identified. We recognized that gross descriptions of interventions obstruct professional training, preclude fidelity assessment, and prevent accurate tests of effectiveness. Thus, in a series of papers, Rosen and I advocated that social work interventions be specified, clearly labeled, and operationally defined, measured, and tested.
Specifying Interventions
Such specification of interventions is essential to two professional responsibilities: professional education and demonstrating the effectiveness of the field’s interventions. Without specification, interventions cannot be taught. Social work education is all about equipping students with skills to deliver interventions, programs, services, administrative practices, and policies. Teaching interventions requires an ability to name, define, see them in action, measure their presence (or absence), assess the fidelity with which they are delivered, and give feedback to students on how to increase or refine the associated skills.
To advance testing the effectiveness of social work interventions, we drew distinctions between interventions and outcomes and proposed these two constructs as the foci for effectiveness research. We defined interventions as practitioner behaviors that can be volitionally manipulated by practitioners (used or not, varied in intensity and timing), that are defined in detail, can be reliably measured, and can be linked to specific identified outcomes ( Rosen & Proctor, 1978 ; Rosen & Proctor, 1981 ). This definition foreshadowed the development of treatment manuals, lists of specific evidence-based practices, and calls for monitoring intervention fidelity. Recognizing the variety of intervention types, and to advance their more precise definition and measurement, we proposed that interventions be distinguished in terms of their complexity. Interventive responses comprise discrete or single responses, such as affirmation, expression of empathy, or positive reinforcement. Interventive strategies comprise several different actions that are, together, linked to a designated outcome, such as motivational interviewing. Most complex are interventive programs , which are a variety of intervention actions organized and integrated as a total treatment package; collaborative care for depression or community assertive treatment are examples. To strengthen the professional knowledge base, we also called for social work effectiveness research to begin testing the optimal dose and sequencing of intervention components in relation to attainment of desired outcomes.
Advancing Intervention Effectiveness Research
Our “specifying paper” also was motivated by the paucity of literature at that time on actual social work interventions. Our literature review of 13 major social work journals over 5 years of published research revealed that only 15% of published social work research addressed interventions. About a third of studies described social problems, and about half explored factors associated with the problem ( Rosen, Proctor, & Staudt, 2003 ). Most troubling was our finding that only 3% of articles described the intervention or its components in sufficient detail for replication in either research or practice. Later, Fraser (2004) found intervention research to comprise only about one fourth of empirical studies in social work. Fortunately, our situation has improved. Intervention research is more frequent in social work publications, thanks largely to the publication policies of the Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research and Research on Social Work Practice .
Research Priorities
Social work faces important and formidable challenges as it advances research on intervention effectiveness. The practitioner who searches the literature or various intervention lists can find more than 500 practices that are named or that are shown to have evidence from rigorous trials that passes a bar to qualify as evidence-based practices. However, our profession still lacks any organized compendium or taxonomy of interventions that are employed in or found to be effective for social work practice. Existing lists of evidence-based practices, although necessary, are insufficient for social work for several reasons. First, as a 2015 National Academies Institute of Medicine (IOM) report—“Psychosocial Interventions for Mental and Substance Use Disorders: A Framework for Establishing Evidence-Based Standards” ( IOM, 2015 )—concluded, too few evidence-based practices have been found to be appropriate for low-resource settings or acceptable to minority groups. Second, existing interventions do not adequately reflect the breadth of social work practice. We have too few evidence-based interventions that can inform effective community organization, case management, referral practice, resource development, administrative practice, or policy. Noting that there is far less literature on evidence-based practices relevant to organizational, community, and policy practice, a social work task force responding to the 2015 IOM report recommended that this gap be a target of our educational and research efforts ( National Task Force on Evidence-Based Practice in Social Work, 2016 ). And finally, our field—along with other professions that deliver psychosocial interventions—lacks the kinds of procedure codes that can identify the specific interventions we deliver. Documenting social work activities in agency records is increasingly essential for quality assurance and third-party reimbursement.
Future Directions: Research to Advance Evidence on Interventions
Social work has critically important research needs. Our field needs to advance the evidence base on what interventions work for social work populations, practices, and settings. Responding to the 2015 IOM report, the National Task Force on Evidence-Based Practice in Social Work (2016) identified as a social work priority the development and testing of evidence-based practices relevant to organizational, community, and policy practice. As we advance our intervention effectiveness research, we must respond to the challenge of determining the key mechanisms of change ( National Institute of Mental Health, 2016 ) and identify key modifiable components of packaged interventions ( Rosen & Proctor, 1978 ). We need to explore the optimal dosage, ordering, or adapted bundling of intervention elements and advance robust, feasible ways to measure and increase fidelity ( Jaccard, 2016 ). We also need to conduct research on which interventions are most appropriate, acceptable, and effective with various client groups ( Zayas, 2003 ; Videka, 2003 ).
Documenting the Impact of Interventions: Specifying and Measuring Outcomes
Outcomes are key to documenting the impact of social work interventions. My 1978 “specifying” paper with Rosen emphasized that the effectiveness of social work practice could not be adequately evaluated without clear specification and measurement of various types of outcomes. In that paper, we argued that the profession cannot rely only on an assertion of effectiveness. The field must also calibrate, calculate, and communicate its impact.
The nursing profession’s highly successful campaign, based on outcomes research, positioned that field to claim that “nurses save lives.” Nurse staffing ratios were associated with in-hospital and 30-day mortality, independent of patient characteristics, hospital characteristics, or medical treatment ( Person et al., 2004 ). In contrast, social work has often described—sometimes advertised—itself as the low-cost profession. The claim of “cheapest service” may have some strategic advantage in turf competition with other professions. But social work can do better. Our research base can and should demonstrate the value of our work by naming and quantifying the outcomes—the added value of social work interventions.
As a start to this work—a beginning step in compiling evidence about the impact of social work interventions—our team set out to identify the outcomes associated with social work practice. We felt that identifying and naming outcomes is essential for conveying what social work is about. Moreover, outcomes should serve as the focus for evaluating the effectiveness of social work interventions.
We produced two taxonomies of outcomes reflected in published evaluations of social work interventions ( Proctor, Rosen, & Rhee, 2002 ; Rosen, Proctor, & Staudt, 2003 ). They included such outcomes as change in clients’ social functioning, resource procurement, problem or symptom reduction, and safety. They exemplify the importance of naming and measuring what our profession can contribute to society. Although social work’s growing body of effectiveness research typically reports outcomes of the interventions being tested, the literature has not, in the intervening 20 years, addressed the collective set of outcomes for our field.
Fortunately, the Grand Challenges for Social Work (AASWSW, n.d.) now provide a framework for communicating social work’s goals. They reflect social work’s added value: improving individual and family well-being, strengthening social fabric, and helping to create a more just society. The Grand Challenges for Social Work include ensuring healthy development for all youth, closing the health gap, stopping family violence, advancing long and productive lives, eradicating social isolation, ending homelessness, creating social responses to a changing environment, harnessing technology for social good, promoting smart decarceration, reducing extreme economic inequality, building financial capability for all, and achieving equal opportunity and justice ( AASWSW, n.d. ).
These important goals appropriately reflect much of what we are all about in social work, and our entire field has been galvanized—energized by the power of these grand challenges. However, the grand challenges require setting specific benchmarks—targets that reflect how far our professional actions can expect to take us, or in some areas, how far we have come in meeting the challenge.
For the past decade, care delivery systems and payment reforms have required measures for tracking performance. Quality measures have become critical tools for all service providers and organizations ( IOM, 2015 ). The IOM defines quality of care as “the degree to which … services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired … outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge” ( Lohr, 1990 , p. 21). Quality measures are important at multiple levels of service delivery: at the client level, at the practitioner level, at the organization level, and at the policy level. The National Quality Forum has established five criteria for quality measures: They should address (a) the most important, (b) the most scientifically valid, (c) the most feasible or least burdensome, (d) the most usable, and (e) the most harmonious set of measures ( IOM, 2015 .) Quality measures have been advanced by accrediting groups (e.g., the Joint Commission of the National Committee for Quality Assurance), professional societies, and federal agencies, including the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. However, quality measures are lacking for key areas of social work practice, including mental health and substance-use treatment. And of the 55 nationally endorsed measures related to mental health and substance use, only two address a psychosocial intervention. Measures used for accreditation and certification purposes often reflect structural capabilities of organizations and their resource use, not the infrastructure required to deliver high-quality services ( IOM, 2015 ). I am not aware of any quality measure developed by our own professional societies or agreed upon across our field.
Future Directions: Research on Quality Monitoring and Measure Development
Although social work as a field lacks a strong tradition of measuring and assessing quality ( Megivern et al., 2007 ; McMillen et al., 2005 ; Proctor, Powell, & McMillen, 2012 ), social work’s role in the quality workforce is becoming better understood ( McMillen & Raffol, 2016 ). The small number of established and endorsed quality measures reflects both limitations in the evidence for effective interventions and challenges in obtaining the detailed information necessary to support quality measurement ( IOM, 2015 ). According to the National Task Force on Evidence-Based Practice in Social Work (2016) , developing quality measures to capture use of evidence-based interventions is essential for the survival of social work practice in many settings. The task force recommends that social work organizations develop relevant and viable quality measures and that social workers actively influence the implementation of quality measures in their practice settings.
How to Implement Evidence-Based Care
A third and more recent focus of my work addresses this question: How do we implement evidence-based care in agencies and communities? Despite our progress in developing proven interventions, most clients—whether served by social workers or other providers—do not receive evidence-based care. A growing number of studies are assessing the extent to which clients—in specific settings or communities—receive evidence-based interventions. Kohl, Schurer, and Bellamy (2009) examined quality in a core area of social work: training for parents at risk for child maltreatment. The team examined the parent services and their level of empirical support in community agencies, staffed largely by master’s-level social workers. Of 35 identified treatment programs offered to families, only 11% were “well-established empirically supported interventions,” with another 20% containing some hallmarks of empirically supported interventions ( Kohl et al., 2009 ). This study reveals a sizable implementation gap, with most of the programs delivered lacking scientific validation.
Similar quality gaps are apparent in other settings where social workers deliver services. Studies show that only 19.3% of school mental health professionals and 36.8% of community mental health professionals working in Virginia’s schools and community mental health centers report using any evidence-based substance-abuse prevention programs ( Evans, Koch, Brady, Meszaros, & Sadler, 2013 ). In mental health, where social workers have long delivered the bulk of services, only 40% to 50% of people with mental disorders receive any treatment ( Kessler, Chiu, Demler, Merikangas, & Walters, 2005 ; Merikangas et al., 2011 ), and of those receiving treatment, a fraction receive what could be considered “quality” treatment ( Wang, Demler, & Kessler, 2002 ; Wang et al., 2005 ). These and other studies indicate that, despite progress in developing proven interventions, most clients do not receive evidence-based care. In light of the growth of evidence-based practice, this fact is troubling evidence that testing interventions and publishing the findings is not sufficient to improve quality.
So, how do we get these interventions in place? What is needed to enable social workers to deliver, and clients to receive, high-quality care? In addition to developing and testing evidence-based interventions, what else is needed to improve the quality of social work practice? My work has focused on advancing quality of services through two paths.
Making Effective Interventions Accessible to Providers: Intervention Reviews and Taxonomies
First, we have advocated that research evidence be synthesized and made available to front-line practitioners. In a research-active field where new knowledge is constantly produced, practitioners should not be expected to rely on journal publications alone for information about effective approaches to achieve desired outcomes. Mastering a rapidly expanding professional evidence base has been characterized as a nearly unachievable challenge for practitioners ( Greenfield, 2017 ). Reviews should critique and clarify the intervention’s effectiveness as tested in specific settings, populations, and contexts, answering the question, “What works where, and with whom?” Even more valuable are studies of comparative effectiveness—those that answer, “Which intervention approach works better, where, and when?”
Taxonomies of clearly and consistently labeled interventions will enhance their accessibility and the usefulness of research reports and systematic reviews. A pre-requisite is the consistent naming of interventions. A persistent challenge is the wide variation in names or labels for interventive procedures and programs. Our professional activities are the basis for our societal sanction, and they must be capable of being accurately labeled and documented if we are to describe what our profession “does” to advance social welfare. Increasingly, and in short order, that documentation will be in electronic records that are scrutinized by third parties for purposes of reimbursement and assessment of value toward outcome attainment.
How should intervention research and reviews be organized? Currently, several websites provide lists of evidence-based practices, some with links, citations, or information about dissemination and implementation organizations that provide training and facilitation to adopters. Practitioners and administrators find such lists helpful but often note the challenge in determining which are most appropriate for their needs. In the words of one agency leader, “The drug companies are great at presenting [intervention information] in a very easy form to use. We don’t have people coming and saying, ‘Ah, let me tell you about the best evidence-based practice for cognitive behavioral therapy for depression,’” ( Proctor et al., 2007 , p. 483). We have called for the field to devise decision aids for practitioners to enhance access to the best available empirical knowledge about interventions ( Proctor et al., 2002 ; Proctor & Rosen, 2008 ; Rosen et al., 2003 ). We proposed that intervention taxonomies be organized around outcomes pursued in social work practice, and we developed such a taxonomy based on eight domains of outcomes—those most frequently tested in social work journals. Given the field’s progress in identifying its grand challenges, its associated outcomes could well serve as the organizing focus, with research-tested interventions listed for each challenge. Compiling the interventions, programs, and services that are shown—through research—to help achieve one of the challenges would surely advance our field.
We further urged profession-wide efforts to develop social work practice guidelines from intervention taxonomies ( Rosen et al., 2003 ). Practice guidelines are systematically compiled, critiqued, and organized statements about the effectiveness of interventions that are organized in a way to help practitioners select and use the most effective and appropriate approaches for addressing client problems and pursuing desired outcomes.
At that time, we proposed that our published taxonomy of social work interventions could provide a beginning architecture for social work guidelines ( Rosen et al., 2003 ). In 2000, we organized a conference for thought leaders in social work practice. This talented group wrestled with and formulated recommendations for tackling the professional, research, and training requisites to developing social work practice guidelines to enable researchers to access and apply the best available knowledge about interventions ( Rosen et al., 2003 ). Fifteen years later, however, the need remains for social work to synthesize its intervention research. Psychology and psychiatry, along with most fields of medical practice, have developed practice guidelines. Although their acceptance and adherence is fraught with challenges, guidelines make evidence more accessible and enable quality monitoring. Yet, guidelines still do not exist for social work.
The 2015 IOM report, “Psychosocial Interventions for Mental and Substance Use Disorders: A Framework for Establishing Evidence-Based Standards,” includes a conclusion that information on the effectiveness of psychosocial interventions is not routinely available to service consumers, providers, and payers, nor is it synthesized. That 2015 IOM report called for systematic reviews to inform clinical guidelines for psychosocial interventions. This report defined psychosocial interventions broadly, encompassing “interpersonal or informational activities, techniques, or strategies that target biological, behavioral, cognitive, emotional, interpersonal, social, or environmental factors with the aim of reducing symptoms and improving functioning or well-being” ( IOM, 2015 , p. 5). These interventions are social work’s domain; they are delivered in the very settings where social workers dominate (behavioral health, schools, criminal justice, child welfare, and immigrant services); and they encompass populations across the entire lifespan within all sociodemographic groups and vulnerable populations. Accordingly, the National Task Force on Evidence Based Practice in Social Work (2016) has recommended the conduct of more systematic reviews of the evidence supporting social work interventions.
If systematic reviews are to lead to guidelines for evidence-based psychosocial interventions, social work needs to be at the table, and social work research must provide the foundation. Whether social work develops its own guidelines or helps lead the development of profession-independent guidelines as recommended by the IOM committee, guidelines need to be detailed enough to guide practice. That is, they need to be accompanied by treatment manuals and informed by research that details the effect of moderator variables and contextual factors reflecting diverse clientele, social determinants of health, and setting resource challenges. The IOM report “Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust” sets criteria for guideline development processes ( IOM, 2011 ). Moreover, social work systematic reviews of research and any associated evidence-based guidelines need to be organized around meaningful taxonomies.
Advancing the Science of Implementation
As a second path to ensuring the delivery of high-quality care, my research has focused on advancing the science of implementation. Implementation research seeks to inform how to deliver evidence-based interventions, programs, and policies into real-world settings so their benefits can be realized and sustained. The ultimate aim of implementation research is building a base of evidence about the most effective processes and strategies for improving service delivery. Implementation research builds upon effectiveness research then seeks to discover how to use specific implementation strategies and move those interventions into specific settings, extending their availability, reach, and benefits to clients and communities. Accordingly, implementation strategies must address the challenges of the service system (e.g., specialty mental health, schools, criminal justice system, health settings) and practice settings (e.g., community agency, national employee assistance programs, office-based practice), and the human capital challenge of staff training and support.
In an approach that echoes themes in an early paper, “Specifying the Treatment Process—The Basis for Effectiveness Research” ( Rosen & Proctor, 1978 ), my work once again tackled the challenge of specifying a heretofore vague process—this time, not the intervention process, but the implementation process. As a first step, our team developed a taxonomy of implementation outcomes ( Proctor et al., 2011 ), which enable a direct test of whether or not a given intervention is adopted and delivered. Although it is overlooked in other types of research, implementation science focuses on this distinct type of outcome. Explicit examination of implementation outcomes is key to an important research distinction. Often, evaluations yield disappointing results about an intervention, showing that the expected and desired outcomes are not attained. This might mean that the intervention was not effective. However, just as likely, it could mean that the intervention was not actually delivered, or it was not delivered with fidelity. Implementation outcomes help identify the roadblocks on the way to intervention adoption and delivery.
Our 2011 taxonomy of implementation outcomes ( Proctor et al., 2011 ), became the framework for two national repositories of measures for implementation research: the Seattle Implementation Research Collaborative ( Lewis et al., 2015 ) and the National Institutes of Health GEM measures database ( Rabin et al., 2012 ). These repositories of implementation outcomes seek to harmonize and increase the rigor of measurement in implementation science.
We also have developed taxonomies of implementation strategies ( Powell et al., 2012 ; Powell et al., 2015 ; Waltz et al., 2014 , 2015) . Implementation strategies are interventions for system change—how organizations, communities, and providers can learn to deliver new and more effective practices ( Powell et al., 2012 ).
A conversation with a key practice leader stimulated my interest in implementation strategies. Shortly after our school endorsed an MSW curriculum emphasizing evidence-based practices, a pioneering CEO of a major social service agency in St. Louis met with me and asked,
Enola Proctor, I get the importance of delivering evidence based practices. My organization delivers over 20 programs and interventions, and I believe only a handful of them are really evidence based. I want to decrease our provision of ineffective care, and increase our delivery of evidence-based practices. But how? What are the evidence-based ways I, as an agency director, can transform my agency so that we can deliver evidence-based practices?
That agency director was asking a question of how . He was asking for evidence-based implementation strategies. Moving effective programs and practices into routine care settings requires the skillful use of implementation strategies, defined as systematic “methods or techniques used to enhance the adoption, implementation, and sustainability of a clinical program or practice into routine service” ( Proctor et al., 2013 , p. 2).
This question has shaped my work for the past 15 years, as well as the research priorities of several funding agencies, including the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and the World Health Organization. Indeed, a National Institutes of Health program announcement—Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health ( National Institutes of Health, 2016 )—identified the discovery of effective implementation strategies as a primary purpose of implementation science. To date, the implementation science literature cannot yet answer that important question, but we are making progress.
To identify implementation strategies, our teams first turned to the literature—a literature that we found to be scattered across a wide range of journals and disciplines. Most articles were not empirical, and most articles used widely differing terms to characterize implementation strategies. We conducted a structured literature review to generate common nomenclature and a taxonomy of implementation strategies. That review yielded 63 distinct implementation strategies, which fell into six groupings: planning, educating, financing, restructuring, managing quality, and attending to policy context ( Powell et al., 2012 ).
Our team refined that compilation, using Delphi techniques and concept mapping to develop conceptually distinct categories of implementation strategies ( Powell et al., 2015 ; Waltz et al., 2014 ). The refined compilation of 73 discrete implementation strategies was then further organized into nine clusters:
- changing agency infrastructure,
- using financial strategies,
- supporting clinicians,
- providing interactive assistance,
- training and educating stakeholders,
- adapting and tailoring interventions to context,
- developing stakeholder relationships,
- using evaluative and iterative strategies, and
- engaging consumers.
These taxonomies of implementation strategies position the field for more robust research on implementation processes. The language used to describe implementation strategies has not yet “gelled” and has been described as a “Tower of Babel” ( McKibbon et al., 2010 ). Therefore, we also developed guidelines for reporting the components of strategies ( Proctor et al., 2013 ) so researchers and implementers would have more behaviorally specific information about what a strategy is, who does it, when, and for how long. The value of such reporting guidelines is illustrated in the work of Gold and colleagues (2016) .
What have we learned, through our own program of research on implementation strategies—the “how to” of improving practice? First, we have been able to identify from practice-based evidence the implementation strategies used most often. Using novel activity logs to track implementation strategies, Bunger and colleagues (2017) found that strategies such as quality improvement tools, using data experts, providing supervision, and sending clinical reminders were frequently used to facilitate delivery of behavioral health interventions within a child-welfare setting and were perceived by agency leadership as contributing to project success.
Second, reflecting the complexity of quality improvement processes, we have learned that there is no magic bullet ( Powell, Proctor, & Glass, 2013 ). Our study of U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs clinics working to implement evidence-based HIV treatment found that implementers used an average of 25 (plus or minus 14) different implementation strategies ( Rogal, et al., 2017 ). Moreover, the number of implementation strategies used was positively associated with the number of new treatment starts. These findings suggest that implementing new interventions requires considerable effort and resources.
To advance our understanding of the effectiveness of implementation strategies, our teams have conducted a systematic review ( Powell et al., 2013 ), tested specific strategies, and captured practice-based evidence from on-the-ground implementers. Testing the effectiveness of implementation strategies has been identified as a top research priority by the IOM (2009) . In work with Charles Glisson in St. Louis, our 15-agency-based randomized clinical trial found that an organizational-focused intervention—the attachment, regulatory, and competency model—improved agency culture and climate, stimulated more clinicians to enroll in evidence-based-practice training, and boosted clinical effect sizes of various evidence-based practices ( Glisson, Williams, Hemmelgarn, Proctor, & Green, 2016a , 2016b ). And in a hospital critical care unit, the implementation strategies of developing a team, selecting and using champions, provider education sessions, and audit and feedback helped increase team adherence to phlebotomy guidelines ( Steffen et al., in press ).
We are also learning about the value of different strategies. Experts in implementation science and implementation practice identified as most important the strategies of “use evaluate and iterative approaches” and “train and educate stakeholders.” Reported as less helpful were such strategies as “access new funding streams” and “remind clinicians of practices to use” ( Waltz et al., 2015 ). Successful implementers in Veterans Affairs clinics relied more heavily on such strategies as “change physical structures and equipment” and “facilitate relay of clinical data to providers” than did less successful implementers ( Rogal et al., 2017 ).
Many strategies have yet to be investigated empirically, as has the role of dissemination and implementation organizations—organizations that function to promote, provide information about, provide training in, and scale up specific treatments. Most evidence-based practices used in behavioral health, including most listed on the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration National Registry of Promising and Effective Practices, are disseminated and distributed by dissemination and implementation organizations. Unlike drugs and devices, psychosocial interventions have no Federal Drug Administration-like delivery system. Kreuter and Casey (2012) urge better understanding and use of the intervention “delivery system,” or mechanisms to bring treatment discoveries to the attention of practitioners and into use in practice settings.
Implementation strategies have been shown to boost clinical effectiveness ( Glisson et al., 2010 ), reduce staff turnover ( Aarons, Sommerfield, Hect, Silvosky, & Chaffin, 2009 ) and help reduce disparities in care ( Balicer et al., 2015 ).
Future directions: Research on implementation strategies
My work in implementation science has helped build intellectual capital for the rapidly growing field of dissemination and implementation science, leading teams to distinguish, clearly define, develop taxonomies, and stimulate more systematic work to advance the conceptual, linguistic, and methodological clarity in the field. Yet, we continue to lack understanding of many issues. What strategies are used in usual implementation practice, by whom, for which empirically supported interventions? What strategies are effective in which organizational and policy contexts? Which strategies are effective in attaining which specific implementation outcomes? For example, are the strategies that are effective for initial adoption also effective for scale up, spread, and sustained use of interventions? Social workers have the skill set for roles as implementation facilitators, and refining packages of implementation strategies that are effective in social service and behavioral health settings could boost the visibility, scale, and impact of our work.
The Third Generation and Counting
Social work faces grand, often daunting challenges. We need to develop a more robust base of evidence about the effectiveness of interventions and make that evidence more relevant, accessible, and applicable to social work practitioners, whether they work in communities, agencies, policy arenas, or a host of novel settings. We need to advance measurement-based care so our value as a field is recognized. We need to know how to bring proven interventions to scale for population-level impact. We need to discover ways to build capacity of social service agencies and the communities in which they reside. And we need to learn how to sustain advances in care once we achieve them ( Proctor et al., 2015 ). Our challenges are indeed grand, far outstripping our resources.
So how dare we speak of a quality quest? Does it not seem audacious to seek the highest standards in caring for the most vulnerable, especially in an era when we face a new political climate that threatens vulnerable groups and promises to strip resources from health and social services? Members of our profession are underpaid, and most of our agencies lack the data infrastructure required for assessment and evaluation. Quality may be an audacious goal, but as social workers we can pursue no less. By virtue of our code of ethics, our commitment to equity, and our skills in intervening on multiple levels of systems and communities, social workers are ideally suited for advancing quality.
Who will conduct the needed research? Who will pioneer its translation to improving practice? Social work practice can be only as strong as its research base; the responsibility for developing that base, and hence improve practice, is lodged within social work research.
If my greatest challenge is pursuing this quest, my greatest joy is in mentoring the next generation for this work. My research mentoring has always been guided by the view that the ultimate purpose of research in the helping professions is the production and systemization of knowledge for use by practitioners ( Rosen & Proctor, 1978 ). For 27 years, the National Institute of Mental Health has supported training in mental health services research based in the Center for Mental Health Services Research ( Hasche, Perron, & Proctor, 2009 ; Proctor & McMillen, 2008 ). And, with colleague John Landsverk, we are launching my sixth year leading the Implementation Research Institute, a training program for implementation science supported by the National Institute of Mental Health ( Proctor et al., 2013 ). We have trained more than 50 social work, psychology, anthropology, and physician researchers in implementation science for mental health. With three more cohorts to go, we are working to assess what works in research training for implementation science. Using bibliometric analysis, we have learned that intensive training and mentoring increases research productivity in the form of published papers and grants that address how to implement evidence-based care in mental health and addictions. And, through use of social network analysis, we have learned that every “dose” of mentoring increases scholarly collaboration when measured two years later ( Luke, Baumann, Carothers, Landsverk, & Proctor, 2016 ).
As his student, I was privileged to learn lessons in mentoring from Aaron Rosen. He treated his students as colleagues, he invited them in to work on the most challenging of questions, and he pursued his work with joy. When he treated me as a colleague, I felt empowered. When he invited me to work with him on the field’s most vexing challenges, I felt inspired. And as he worked with joy, I learned that work pursued with joy doesn’t feel like work at all. And now the third, fourth, and fifth generations of social work researchers are pursuing tough challenges and the quality quest for social work practice. May seasoned and junior researchers work collegially and with joy, tackling the profession’s toughest research challenges, including the quest for high-quality social work services.
Acknowledgments
Preparation of this paper was supported by IRI (5R25MH0809160), Washington University ICTS (2UL1 TR000448-08), Center for Mental Health Services Research, Washington University in St. Louis, and the Center for Dissemination and Implementation, Institute for Public Health, Washington University in St. Louis.
This invited article is based on the 2017 Aaron Rosen Lecture presented by Enola Proctor at the Society for Social Work and Research 21st Annual Conference—“Ensure Healthy Development for All Youth”—held January 11–15, 2017, in New Orleans, LA. The annual Aaron Rosen Lecture features distinguished scholars who have accumulated a body of significant and innovative scholarship relevant to practice, the research base for practice, or effective utilization of research in practice.
- Aarons GA, Sommerfield DH, Hect DB, Silvosky JF, Chaffin MJ. The impact of evidence-based practice implementation and fidelity monitoring on staff turnover: Evidence for a protective effect. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2009; 77 (2):270–280. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013223 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Academy of Social Work and Social Welfare (AASWSW) Grand challenges for social work (n.d.) Retrieved from http://aaswsw.org/grand-challenges-initiative/
- Balicer RD, Hoshen M, Cohen-Stavi C, Shohat-Spitzer S, Kay C, Bitterman H, Shadmi E. Sustained reduction in health disparities achieved through targeted quality improvement: One-year follow-up on a three-year intervention. Health Services Research. 2015; 50 :1891–1909. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1475-6773.12300 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bunger AC, Powell BJ, Robertson HA, MacDowell H, Birken SA, Shea C. Tracking implementation strategies: A description of a practical approach and early findings. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2017; 15 (15):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-017-0175-y . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans SW, Koch JR, Brady C, Meszaros P, Sadler J. Community and school mental health professionals’ knowledge and use of evidence based substance use prevention programs. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2013; 40 (4):319–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-012-0422-z . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fraser MW. Intervention research in social work: Recent advances and continuing challenges. Research on Social Work Practice. 2004; 14 (3):210–222. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731503262150 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Glisson C, Schoenwald SK, Hemmelgarn A, Green P, Dukes D, Armstrong KS, Chapman JE. Randomized trial of MST and ARC in a two-level evidence-based treatment implementation strategy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2010; 78 (4):537–550. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019160 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glisson C, Williams NJ, Hemmelgarn A, Proctor EK, Green P. Increasing clinicians’ EBT exploration and preparation behavior in youth mental health services by changing organizational culture with ARC. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2016a; 76 :40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2015.11.008 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glisson C, Williams NJ, Hemmelgarn A, Proctor EK, Green P. Aligning organizational priorities with ARC to improve youth mental health service outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2016b; 84 (8):713–725. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000107 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gold R, Bunce AE, Cohen DJ, Hollombe C, Nelson CA, Proctor EK, DeVoe JE. Reporting on the strategies needed to implement proven interventions: An example from a “real-world” cross-setting implementation study. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2016; 91 (8):1074–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.03.014 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greenfield S. Clinical practice guidelines: Expanded use and misuse. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2017; 317 (6):594–595. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.19969. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hasche L, Perron B, Proctor E. Making time for dissertation grants: Strategies for social work students and educators. Research on Social Work Practice. 2009; 19 (3):340–350. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731508321559 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM), Committee on Comparative Effectiveness Research Prioritization. Initial national priorities for comparative effectiveness research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM) Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM) Psychosocial interventions for mental and substance use disorders: A framework for establishing evidence-based standards. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2015. https://doi.org/10.17226/19013 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jaccard J. The prevention of problem behaviors in adolescents and young adults: Perspectives on theory and practice. Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research. 2016; 7 (4):585–613. https://doi.org/10.1086/689354 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2005; 62 (6):617–627. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.617 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohl PL, Schurer J, Bellamy JL. The state of parent training: Program offerings and empirical support. Families in Society: The Journal of Contemporary Social Services. 2009; 90 (3):248–254. http://dx.doi.org/10.1606/1044-3894.3894 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kreuter MW, Casey CM. Enhancing dissemination through marketing and distribution systems: A vision for public health. In: Brownson R, Colditz G, Proctor E, editors. Dissemination and implementation research in health: Translating science to practice. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lewis CC, Stanick CF, Martinez RG, Weiner BJ, Kim M, Barwick M, Comtois KA. The Society for Implementation Research collaboration instrument review project: A methodology to promote rigorous evaluation. Implementation Science. 2015; 10 (2):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-014-0193-x . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lohr KN. Medicare: A strategy for quality assurance. I. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 1990. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luke D, Baumann A, Carothers B, Landsverk J, Proctor EK. Forging a link between mentoring and collaboration: A new training model for implementation science. Implementation Science. 2016; 11 (137):1–12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13012-016-0499-y . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McKibbon KA, Lokker C, Wilczynski NL, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Davis DA, Straus SS. A cross-sectional study of the number and frequency of terms used to refer to knowledge translation in a body of health literature in 2006: A tower of Babel? Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (16) doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-5-16. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McMillen JC, Proctor EK, Megivern D, Striley CW, Cabasa LJ, Munson MR, Dickey B. Quality of care in the social services: Research agenda and methods. Social Work Research. 2005; 29 (3):181–191. doi.org/10.1093/swr/29.3.181. [ Google Scholar ]
- McMillen JC, Raffol M. Characterizing the quality workforce in private U.S. child and family behavioral health agencies. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2016; 43 (5):750–759. doi: 10.1007/s10488-0150-0667-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Megivern DA, McMillen JC, Proctor EK, Striley CW, Cabassa LJ, Munson MR. Quality of care: Expanding the social work dialogue. Social Work. 2007; 52 (2):115–124. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/sw/52.2.115 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merikangas KR, He J, Burstein M, Swendsen J, Avenevoli S, Case B, Olfson M. Service utilization for lifetime mental disorders in U.S. adolescents: Results of the National Comorbidity Survey Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A) Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2011; 50 (1):32–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.10.006 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute of Mental Health. Psychosocial research at NIMH: A primer. 2016 Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/research-priorities/psychosocial-research-at-nimh-a-primer.shtml .
- National Institutes of Health. Dissemination and implementation research in health (R01) 2016 Sep 14; Retrieved from https://archives.nih.gov/asites/grants/09-14-2016/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-16-238.html .
- National Task Force on Evidence-Based Practice in Social Work. Unpublished recommendations to the Social Work Leadership Roundtable 2016 [ Google Scholar ]
- Person SD, Allison JJ, Kiefe CI, Weaver MT, Williams OD, Centor RM, Weissman NW. Nurse staffing and mortality for Medicare patients with acute myocardial infarction. Medical Care. 2004; 42 (1):4–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlr.0000102369.67404.b0 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell BJ, McMillen C, Proctor EK, Carpenter CR, Griffey RT, Bunger AC, York JL. A compilation of strategies for implementing clinical innovations in health and mental health. Medical Care Research and Review. 2012; 69 (2):123–157. https://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1077558711430690 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell BJ, Proctor EK, Glass JE. A systematic review of strategies for implementing empirically supported mental health interventions. Research on Social Work Practice. 2013; 24 (2):192–212. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731513505778 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, Kirchner JE. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: Results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implementation Science. 2015; 10 (21):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0209-1 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Knudsen KJ, Fedoravicius N, Hovmand P, Rosen A, Perron B. Implementation of evidence-based practice in community behavioral health: Agency director perspectives. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2007; 34 (5):479–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-007-0129-8 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Landsverk J, Baumann AA, Mittman BS, Aarons GA, Brownson RC, Chambers D. The Implementation Research Institute: Training mental health implementation researchers in the United States. Implementation Science. 2013; 8 (105):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-8-105 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Luke D, Calhoun A, McMillen C, Brownson R, McCrary S, Padek M. Sustainability of evidence-based healthcare: Research agenda, methodological advances, and infrastructure support. Implementation Science. 2015; 10 (88):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0274-5 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, McMillen JC. Quality of care. In: Mizrahi T, Davis L, editors. Encyclopedia of Social Work. 20. Washington, DC, and New York, NY: NASW Press and Oxford University Press; 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199975839.013.33 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Powell BJ, McMillen CJ. Implementation strategies: Recommendations for specifying and reporting. Implementation Science. 2012; 8 (139):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-8-139 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Rosen A. From knowledge production to implementation: Research challenges and imperatives. Research on Social Work Practice. 2008; 18 (4):285–291. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049731507302263 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Rosen A, Rhee C. Outcomes in social work practice. Social Work Research & Evaluation. 2002; 3 (2):109–125. [ Google Scholar ]
- Proctor EK, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, Hensley M. Outcomes for implementation research: Conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 2011; 38 (2):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-010-0319-7 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rabin BA, Purcell P, Naveed S, Moser RP, Henton MD, Proctor EK, Glasgow RE. Advancing the application, quality and harmonization of implementation science measures. Implementation Science. 2012; 7 (119):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-7-119 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rogal SS, Yakovchenko V, Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Kirchner JE, Proctor EK, Chinman MJ. The association between implementation strategy use and the uptake of hepatitis C treatment in a national sample. Implementation Science. 2017; 12 (60) http://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-017-0588-6 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosen A, Proctor EK. Specifying the treatment process: The basis for effectiveness research. Journal of Social Service Research. 1978; 2 (1):25–43. https://doi.org/10.1300/J079v02n01_04 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosen A, Proctor EK. Distinctions between treatment outcomes and their implications for treatment evaluation. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1981; 49 (3):418–425. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.49.3.418 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosen A, Proctor EK, Staudt M. Targets of change and interventions in social work: An empirically-based prototype for developing practice guidelines. Research on Social Work Practice. 2003; 13 (2):208–233. https://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1049731502250496 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Steffen K, Doctor A, Hoerr J, Gill J, Markham C, Riley S, Spinella P. Controlling phlebotomy volume diminishes PICU transfusion: Implementation processes and impact. Pediatrics (in press) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Videka L. Accounting for variability in client, population, and setting characteristics: Moderators of intervention effectiveness. In: Rosen A, Proctor EK, editors. Developing practice guidelines for social work intervention: Issues, methods, and research agenda. New York, NY: Columbia University Press; 2003. pp. 169–192. [ Google Scholar ]
- Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Chinman MJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, Proctor EK, Kirchner JE. Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC): Protocol for a mixed methods study. Implementation Science. 2014; 9 (39):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-9-39 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Matthieu MM, Damschroder LJ, Chinman MJ, Smith JL, Kirchner JE. Use of concept mapping to characterize relationships among implementation strategies and assess their feasibility and importance: Results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) study. Implementation Science. 2015; 10 (109):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0295-0 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang PS, Lane M, Olfson M, Pincus HA, Wells KB, Kessler RC. Twelvemonth use of mental health services in the United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2005; 62 (6):629–640. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.629. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang PS, Demler O, Kessler RC. Adequacy of treatment for serious mental illness in the United States. American Journal of Public Health. 2002; 92 (1):92–98. http://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/abs/10.2105/AJPH.92.1.92 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zayas L. Service delivery factors in the development of practice guidelines. In: Rosen A, Proctor EK, editors. Developing practice guidelines for social work intervention: Issues, methods, and research agenda. New York, NY: Columbia University Press; 2003. pp. 169–192. https://doi.org/10.7312/rose12310-010 . [ Google Scholar ]

Home > College of Social and Behavioral Sciences > Social Work > Social Work Theses
Social Work Theses, Projects, and Dissertations
Theses/projects/dissertations from 2024 2024.
WHAT IS THE READINESS OF SOCIAL WORK STUDENTS TO WORK WITH AUTISTIC INDIVIDUALS? , Ignacio Aguilar Pelaez
EXAMINING EXPERIENCES AMONG SOCIAL WORKERS WORKING WITH PARENTS WHO SUFFER FROM SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER , Alicia Alvarado and Eleno Zepeda
COVID-19, SOCIAL ISOLATION, AND MSW STUDENTS’ MENTAL HEALTH , Cassandra Barajas
Through the Lens of Families and Staff in Emergency Shelters , Elizabeth Barcenas
MACHISMO: THE IMPACT IT HAS ON HISPANIC MALE COLLEGE STUDENTS RECEIVING MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES , Sara Barillas and Alexander Aguirre
THE DISPROPORTIONATE IMPACTS OF CERTAIN FACTORS THAT DIFFERENTIATE THE AMOUNT OF MENTAL HEALTH REFERRALS OF SCHOOL A COMPARED TO SCHOOL B , Jesus Barrientos
Correlation of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Somatic Symptoms in Adolescents , Shannon Beaumont
Caregivers of Dialysis Patients , Alyssa Bousquet and Amelia Murillo
Self-Care Habits and Burnout Among County Social Workers on the Central Coast of California , Jaclyn Boyd and Denise Ojeda
GENDER DYSPHORIA IN ADOLESCENCE AND THE MODELS OF CARE: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW , Arnold Briseno
THE EFFECTS OF PARENTING STYLES ON COMMUNICATION AMONG ASIAN AMERICAN YOUNG ADULTS , Abigail Camarce
BARRIERS TO AND FACILITATORS OF CARE: EXPLORING HOW LOW-INCOME WOMEN ACCESS REPRODUCTIVE HEALTHCARE IN A RURAL COMMUNITY , Sydney Taylor Casey
CLIENT PERPETRATED VIOLENCE AND SAFETY CULTURE IN CHILD WELFARE: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW , Amber Castro
ACCESSIBILITY OF SERVICES FOR TRANSGENDER ADOLESCENTS FROM A CHILD WELFARE PERSPECTIVE , Eduardo Cedeno
WHAT ARE THE BARRIERS TO SEEKING PSYCHOTHERAPY SERVICES ACROSS DIFFERENT RACIAL AND ETHNIC GROUPS? , Deysee Chavez and Elisa Rodarte
Homelessness In The Coachella Valley , Katrina Clarke
Challenges Veterans Encounter Receiving or Seeking Mental Health Services , Denise D. Contreras and Andrea Ramirez
EXAMINING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PSYCHOSOCIAL INTERVENTIONS FOR OPIOID USE DISORDER: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Elizabeth Ashley Contreras
IS A SOCIAL SUPPORT BASED MODEL BETTER FOR TREATING ALCOHOLISM? A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Jordan Anthony Contreras
SOCIAL WORKERS’ PREPAREDNESS FOR PRACTICE WITH PATIENTS EXPERIENCING PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS , Paula Crespin
INVESTIGATING THE LEVEL OF EVIDENCE OF ADVERSE CHILDHOOD EXPERIENCES AND PARENTING PRACTICES: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Eloisa Deshazer
MENTAL HELP-SEEKING: BARRIERS AMONG AFRICAN AMERICANS: THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY IN ADDRESSING THOSE BARRIERS , Charneka Edwards
Treatment not Punishment: Youth Experiences of Psychiatric Hospitalizations , Maira Ferrer-Cabrera
THE BARRIERS TO NATURAL OUTDOOR SPACES: PERSPECTIVES FROM PEOPLE WITH MOBILITY DISABILITIES , Sierra Fields and Kailah Prince
IMPLEMENTATION OF MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES AND CURRICULUM FOR ELEMENTARY-AGED CHILDREN , Indra Flores Silva and Jason Kwan
POOR ACADEMICS FROM COLLEGE STUDENTS GRIEVING THROUGH COVID 19 , Sarah Frost
COMPASSION FATIGUE IN SHORT TERM RESIDENTIAL THERAPEUTIC PROGRAM SETTINGS , Sandra Gallegos
A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE GUN VIOLENCE RESTRAINING ORDER , Bonnie Galloway and Yasmeen Gonzalez-Ayala
STRESS AND HELP-SEEKING IN FARMWORKERS IN THE COACHELLA VALLEY , Alexis Garcia and Daniela Mejia
THE EFFECTIVNESS OF FEDERAL PELL GRANT PROGRAM , Maria Delcarmen Garcia Arias and Ashley Hernandez
PARENT INVOLVEMENT AND EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES AMONG LATINO FAMILIES , Diana Garcia and Gabriela Munoz
IMPACT OF SCHOOL-BASED MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES ON STUDENT ATTENDANCE AT A SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SCHOOL DISTRICT , Johanna Garcia-Fernandez and Morgan Stokes
BARRIERS TO GENDER-AFFIRMING CARE , Gloria Garcia
THE CONTRIBUTING FACTORS OF PLACEMENT INSTABILITY FOR PREGNANT FOSTER YOUTH , Amanda Garza and Shayneskgua Colen
PROGRESSION OF BLACK WOMEN IN TENURE RANKED POSITIONS , Unique Givens
Child Maltreatment Primary Prevention Methods in the U.S.: A Systematic Review of Recent Studies , Maria Godoy-Murillo
Assessing and Meeting the Needs of Homeless Populations , Mitchell Greenwald
Parity In Higher Education In Prison Programs: Does It Exist? , Michael Lee Griggs and Vianey Luna
SURROGACY AND IT'S EFFECTS ON THE MENTAL HEALTH OF THE GESTATIONAL CARRIER , DayJahne Haywood
SUBSTANCE USE TREATMENT WITHIN THE US PRISON SYSTEM , Timothy Hicks
LGBTQ+ College Students Hopeful Future Expectations , Savannah Hull
EFFECTS OF VOLUNTARY REMOVAL ON AN IMMIGRANT FAMILY , Miriam Jimenez
THE MOTIVATING FACTORS AFFECTING THE CONTINUANCE AND COMPLETION OF SUBSTANCE USE TREATMENT FOR MOTHERS , Jacquetta Johnson
FACTORS AFFECTING THE ENROLLMENT AND GRADUATION RATES AMONGST AFRICAN AMERICAN MALES IN THE UNITED STATES , Tracie Johnson
SUPPORTING FORMERLY INCARCERATED INDIVIDUALS IN HIGHER EDUCATION: A QUANTITATIVE STUDY , Lisa Marie Jones-Wiertz
PROTESTANT CHURCH WORKERS' KNOWLEDGE OF CHILD ABUSE REPORTING AND REPORTING BEHAVIOR , Rachel Juedes
Social Media Told Me I Have A Mental Illness , Kathleen Knarreborg
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ROLE MODELS, SOCIOECONOMIC MOBILITY BELIEFS, AND ACADEMIC OUTCOMES , Christian Koeu and Marisol Espinoza Garcia
CULTURAL AND STRUCTURAL BARRIERS OF UTILIZING MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES IN A SCHOOL-BASED SETTING FOR LATINX POPULATIONS , Silvia Lozano and Bridgette Guadalupe Calderon
EDUCATIONAL OUTCOMES FOR YOUTH THAT PARTICIPATED IN EXTENDED FOSTER CARE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Kassandra Mayorga and Roxana Sanchez
NON-BINARY IDENTITY WITHIN COMPETENCY TRAINING FOR MENTAL/BEHAVIORAL HEALTH PROVIDERS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW , Alexis McIntyre
Childhood Neglect and Incarceration as a Adult , Marissa Mejia and Diana Gallegos
IMPACT OF RESOURCE SCARCITY ON UNDOCUMENTED STUDENTS IN HIGHER EDUCATION , Sebastian Melendez Lopez
STUDY EXPLORING FEELINGS OF SELF-BLAME AND SHAME AMONG INDIVIDUALS RAISED BY SEVERELY MENTALLY ILL CAREGIVERS , Joanie Minion
THE OBSTACLES FACING HOMELESS VETERANS WITH MENTAL ILLNESS WHEN OBTAINING HOUSING , Melissa Miro
STUDENTS OF HIGHER EDUCATION RECEIVING SUPPLEMENTAL NUTRITION ASSISTANCE PROGRAM AND ITS IMPACT ON MENTAL HEALTH , Cristina Palacios Mosqueda
COMMERCIALLY SEXUALLY EXPLOITED CHILDREN TARGETED WITHIN SOCIAL SERVICES , Britny Ragland
ART THERAPY FOR BEREAVED SIBLINGS AFTER PEDIATRIC CANCER DEATH , Daniela Ramirez-Ibarra
HOW DID THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC IMPACT EXTENDED FOSTER CARE SOCIAL WORKERS WHILE PROVIDING SOCIAL SERVICES , Omar Ramirez and Victoria Lopez
A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF BODY MODIFICATION BIASES IN THE MENTAL HEALTH FIELD , Lonese Ramsey
Bridging Training Gaps: Assessing Knowledge and Confidence of Mental Health Interns in Opioid Misuse Intervention for School-Aged Children and Adolescents , Carolina Rodriguez and Gabriela Guadalupe Gonzalez
PERCEPTIONS OF YOUTH ATHLETE SAFETY PARENTS VS DIRECTORS , Nicole Anais Rodriguez
SPIRITUALITY AND RECOVERY FROM ADDICTION: EXPERIENCES OF NARCOTICS ANONYMOUS MEMBERS , Elizabeth Romberger
ADVERSE CHILDHOOD EXPERIENCES AND ALTRUISM: THE IMPACT ON SOCIAL WORK AS A CAREER CHOICE , Nancy Salas and Brittany Altuna
MAJOR FACTORS OF SUSTAINING RECOVERY AFTER RELAPSE FROM A SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER , Amanda Tei Sandhurst
UNDERSTANDING THE PERSPECTIVES AND ATTITUDES OF 12-STEP PARTICIPANTS TOWARDS MEDICATION-ASSISTED TREATMENT , Christopher Scott
THE UTILIZATION OF MUSIC AND AUTONOMOUS SENSORY MERIDIAN RESPONSE IN REDUCING STRESS , Robert Scott
THE AFTERMATH OF THE PANDEMIC’S EFFECT ON COLLEGE STUDENT DEPRESSION , Lorena Sedano
Exploring the Experiences of Minority Former Foster Youths During and Post Care: A Qualitative Study , Caithlyn Snow
Factors that Contribute to Disparities in Access to Mental Health Services within Hispanic Adults , Jasmine Soriano
THE CHALLENGES TO THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ADMINISTRATION FOR CHILDREN AND FAMILIES MEMORANDUM: FOSTER CARE AS A SUPPORT TO FAMILIES , Rebecca Joan Sullivan-Oppenheim
RESILIENCE IN FATHERHOOD: EXPLORING THE IMPACT OF ABSENT FATHERS ON BLACK AMERICAN MEN'S PARENTING NARRATIVES AND PRACTICES , Ericah Thomas
FACTORS THAT IMPACT FOSTER YOUTHS’ HIGH SCHOOL GRADUATION , Esther Thomas
EXAMINING A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SEXUAL SATISFACTION AND CHILD MALTREATMENT , Amanda Titone
THE PRESENT STRUGGLES OF IMMIGRANT FARMWORKERS IN CALIFORNIA , Leslie Torres and Angelica Huerta
PROGRAM EVALUATION OF SCHOOL-BASED MENTAL HEALTH COUNSELING SERVICES , Yvette Torres and Emily Ann Rodriguez
Stressors, Caffeine Consumption, and Mental Health Concerns among College Students , Stacey Trejo
DISPARITIES SURROUNDING THE AVAILABILITY OF FEMININE HYGIENE PRODUCTS IN THE WORKPLACE , Marlene Ventura
MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT HELP SEEKING ATTITUDES AND BEHAVIORS AMONG LATINX COMMUNITY , Nancy Vieyra
JUSTICE-INVOLVED STUDENTS: EFFECTS OF USING SUPPORT SERVICES TO OVERCOME BARRIERS , Gabby Walker and Sofia Alvarenga
MANDATED REPORTERS’ KNOWLEDGE AND REPORTING OF CHILD ABUSE , Alexis Reilly Warye
THE COMMUNITY RESILIENCY MODEL (CRM) APPLIED TO TEACHER’S WELL-BEING , John Waterson
Addressing Rural Mental Health Crises: An Alternative to Police , Faith Ann Weatheral-block
Theses/Projects/Dissertations from 2023 2023
PROLONGED EXPOSURE TO CONGREGATE CARE AND FOSTER YOUTH OUTCOMES , Tiffany Acklin
YOU CALL US TREATMENT RESISTANT: THE EFFECTS OF BIASES ON WOMEN WITH BORDERLINE PERSONALITY DISORDER , Cassidy Acosta
EXAMINING SOCIAL DETERMINANTS OF HEALTH OF FORMERLY INCARCERATED CALIFORNIA STUDENTS WHO GRADUATED FROM PROJECT REBOUND , Ashley C. Adams
ALTERNATIVE APPROACHES TO POLICE INTERVENTIONS WHEN RESPONDING TO MENTAL HEALTH CRISES INCIDENTS , Karen Rivera Apolinar
Understanding Ethical Dilemmas in Social Work Practice , Arielle Arambula
IS THERE A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PROFESSORIAL-STUDENT RACIAL MATCH AND ACADEMIC SATISFACTION OF AFRICAN AMERICAN SOCIAL WORK STUDENTS , Ashlei Armstead
NON-SPANISH SPEAKING LATINOS' EXPERIENCES OF INTRAGROUP MARGINALIZATION AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR ETHNIC IDENTITY , Marissa Ayala
SERVICES AVAILABLE IN THE MIXTEC COMMUNITY AND THE BARRIERS TO THOSE SERVICES , Currie Bailey Carmon
IMPACT OF OUTDOOR ADVENTURE ON THE SELF-ESTEEM, SELF-CONFIDENCE, AND COMFORT LEVEL OF BLACK AND BROWN GIRLS , Nathan Benham
THE ROLE UNDOCUMENTED STUDENT RESOURCE CENTERS PLAY IN SUPPORTING UNDOCUMENTED STUDENTS IN HIGHER EDUCATION , Cynthia Boyzo
Program Evaluation of Teen Parent Support Group , Brianne Yvonne Irene Brophy
THE IMPACT THE JOB STRESS OF A CHILD WELFARE SOCIAL WORKER HAS ON THE QUALITY OF THEIR RELATIONSHIP WITH THEIR INTIMATE PARTNER , Nadine Cazares
Adverse Effects for Siblings Who Witness Child Abuse , Leslie Chaires
ASIAN DISCRIMINATION: IN THE FIELD OF SOCIAL WORK , Sunghay Cho
PERCEIVED FINANCIAL STRAIN AND ITS EFFECTS ON COLLEGE STUDENTS’ WELFARE , Monica Contreras and Clarissa Adrianna Martinez
The Media and Eating Disorders , Diane Corey
INCREASING TEACHER AWARENESS OF MENTAL HEALTH IN CHILDREN , Sarah Alexis Cortes
Page 1 of 17
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
- Department, Program, or Office
- Disciplines
Author Corner
- School of Social Work homepage
A service of the John M. Pfau Library

Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright Acrobat Reader
How to become a research social worker
- How to become a research sw
- What is a research social worker
- What do research social worker do
- Salary and outlook
When people think about social work, research social work is probably not one of the first fields that comes to mind. Nevertheless, research social work actually plays an important role as its findings can dictate not only governmental policy, but also political reform as well as the allocation of funding.
Research social workers need to be methodical, objective, and thorough in their research. As with any other field of research, the goal is not to confirm what you hope to be true, but rather figure out what is true.
For example, suppose that a city program offers a $1 million grant to a local community led organization. Before that money can be spent, the grant stipulates that a study must be completed to find out what groups in the community need the most support.
In this case, although the research social worker might have pre-existing ideas about how the money should be spent, it is their job to put their personal beliefs aside and complete an objective study of the community to determine where resources are lacking.
The preceding example illustrates a case where a research social worker may be polling hundreds of thousands or people, looking at economic and housing data, and otherwise compiling a macro-view of the community. Research social work can also exist at the micro-level.
Individual research
Participatory research refers to research whereby a social worker integrates themselves with a person or family in order to understand the problems they face and, more broadly, what community resources are missing or inadequate. There are both advantages and disadvantages to this “micro-view” participatory research.
Advantages
- It’s possible to gain a very detailed view of a single person’s life and how they interact with the community. Much can be learned that would not otherwise reveal itself through a high level poll or questionnaire.
- Due to the trust that can form between a community member and a research social worker, the “subject” may reveal more than they would with a questionnaire.
Disadvantages
- Participatory research is time consuming and resource heavy. For example, if a research social worker spends two days with a family, that’s time that they could have otherwise spent gathering data from hundreds or thousands of community members via more efficient means.
- It can become very difficult to remain objective as participatory research can lead the researcher to believe that one family’s problems are the most pressing, even if data strongly indicates that other groups are in greater need.
- Relationships can form between the social worker and the subject. While these are not necessarily negative, they may lead to biases in data collection which wouldn’t otherwise be prevalent with more impersonal research methods.
Ultimately both macro and micro (participatory) research have a role to play in data gathering. Throughout their careers a research social worker will most likely conduct both kinds of research, and everything in between.
How research social workers need to conduct themselves
In terms of participatory research it is important for a research social worker to take into account multiple voices from the community. So even if a research social believes they know which groups are most at risk they still need to conduct wide ranging interviews and remain objectively open to the answers that they receive. This really touches upon a key facet of research social work: objectivity. Being open to what the data is saying regardless of whether it confirms or denies existing views held by the research social worker.
Also, it’s important to realize that research social workers may not be able to divulge the purpose of their research as they’re carrying it out. If participants knew the reason that the social worker was conducting a study they may be biased in how they present themselves or answer the social worker’s inquiries. This can actually prove frustrating for research social workers as they may not be able to answer even the most basic questions about what they’re doing.
Why social work research is important
We’ve covered why social research is important in regard to determining needs within a community and how that research can help to allocate funding to the proper areas. But research social work is also important in determining the efficacy of programs that have been implemented in the community. For example, research social workers can,
- Administer before and after surveys to determine how the implementation of a new program has benefitted (or not benefitted) the community.
- They may also conduct individual interviews with community members to find out how they feel about new programs. More specifically, these interviews may also be a chance to learn exactly how community members are benefitting from a program and also their thoughts on how it can be improved.
Research social work is very important in that it helps to determine what programs are needed in a community and after the programs are created it is research social workers who measure their efficacy.
While a “regular” social worker may spend their life seeing the trees (dealing with individual cases) it is the research social worker’s goal to see the forest. That is, understand the broader macro environment and the role that community programs play in it.
Educational requirements to become a research social worker
Most candidates should only consider taking a degree from a CSWE ( Council on Social Work Education ) accredited institution. Educational institutions without this accreditation may lack a rigorous teaching approach and degree holders from non-CSWE universities may find it more difficult to locate a good job.
Research social work typically requires a candidate to have a Ph.D. as they will be expected to have a comprehensive understanding of statistics and how to compile the data that they collect. Thus research social work typically requires a large commitment in terms of schooling.
In some cases, however, a social worker with a masters degree may be able to find work in the research field. Typically this person will handle assignments like distributing questionnaires and doing other data collection tasks in the neighborhood. A Ph.D. social worker will then compile that data and present the findings to local and federal government officials, among others.
Why research social work can be difficult
One of the primary difficulties associated with social work research is that the social research worker’s role isn’t actually to help, but rather to study and gather data. This is not to suggest that the social worker must be robotic and ignore all problems, however, their role isn’t to solve but to observe. A research social worker may suggest that a “regular” social worker get involved but that’s typically the extent of what they can do.
It can also be difficult doing participatory research, getting to know a subject or a family over the course of a day or two and then having to leave that family and move on. A normal social worker may stay with a family for months or even years, and enjoy a greater reward as that family’s situation improves.
Thus social work research is suggested for those who understand their limited intervention role and are truly interested in data and devising the most effective ways to measure the efficacy of programs within the neighborhood. Research social workers can get their satisfaction from seeing community programs succeed, rather than working with individual subjects.
Research social work career outlook
It can be difficult to determine the career outlook specifically in regard to the research social worker. This is a very niche area of social work, all the more so since it typically requires a Ph.D. That being said, we can still gain valuable information by looking at overall trends for the social work field.
The BLS (Bureau of Labor Statistics) estimates that from 2021 to 2031 there will be a 9 percent growth rate in the field of social work. In terms of actual numbers, 64,000 new social work jobs will be created by 2031.
Research social worker salary
Again, when it comes to determining the salary for a research social worker it’s difficult as there is little data available. That being the case we can still make a fairly good estimation of how much research social workers earn.
According to HumanServicesEdu.org , “NASW found that a DSW or PhD can boost your earnings by around $17,000 over the baseline numbers you could expect with a bachelor’s.”
Overall we can see that research social workers tend to earn more than other social workers and their job prospects are very good.
Frequently asked questions
A research social worker conducts research studies and evaluations to gather data and evidence related to social work practice and policies.
They use a range of research methods, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, observation, or experimental designs, to answer research questions and test hypotheses.
A Bachelor’s degree in social work is the minimum requirement for most entry-level social work positions. However, many research social work positions require a Master’s degree in social work. Gain relevant work experience and develop research skills. You can also pursue a DSW or PhD to further your knowledge and expertise.
Research social workers need to be knowledgeable about different research methods, social policies, be able to analyze and interpret complex data.
- Research Paper Guides
- Research Paper Topics
- 300 Social Work Research Topics & Questions for Papers
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
300 Social Work Research Topics & Questions for Papers

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Social work research focuses primarily on studying problems experienced in social work field. The research, in this case, talks about challenges that caseworkers go through in their practice. Social work research topics cover various things, including problems in welfare work, and indicate how research can be used to gain a deep understanding of the issues. Have you been wondering how to develop an intriguing social work topic and possible areas to discuss in your research? Don't worry because this article by our online paper writing service covers all your concerns. The blog post will provide some social work research topic ideas that you can consider for your social work research.
What Are Social Work Research Topics?
Social work research topics are areas of study that involve applying research methodology to comprehend sectors that are challenging for social workers. These topic ideas concentrate on addressing some problems that caseworkers go through both in their lives and their field. Research topics for social work may vary. However, like any other research paper, writing social work research topics deals with application of related theories and concepts, as well as understanding the entire casework aspects. The research involves applying cause and effect, analytic, survey, and experimental procedures to find ways to address welfare challenges. The purpose of welfare work study is to understand the efficiency of various interventions used to address challenges people develop due to welfare deprivation.
Characteristics of Good Social Work Topics
As an individual seeking to conduct research in welfare work areas, you need to know some of the features that make social work topics to be of great value. Below are characteristics that will make topics for social work research incredible.
- A good topic covers modern trends and incorporates the ideas in the social field.
- The topic should break specific stereotypes using reasonable evidence.
- It must also be supported by various studies that are peer-reviewed.
- Topic chosen must be related to practices in the welfare field.
How to Choose a Social Work Topic?
A plan to decide on excellent social work topics to research starts with a general orientation into social work field. Here are some steps involved when choosing a social work research topic.
- Pick a sector with research potential or simply the one you like.
- Start with “why” and “what” questions and expand on them.
- Read data on faculty’s research interests.
- Read a proper research paper that find interesting and focus on literature review and background sections to gain insight into various issues.
- Identify and browse journals that relate to your likes.
- Lastly, you can look online for research topics that are ready and skim through them to gain new knowledge.
Once you pick a topic, don’t hesitate to contact our proficient research paper writers . Our experts are adept in many fields and can complete a research paper on any topic.
Social Work Research Topics List
Social work research topics cover various concepts and challenges related to caseworkers and their fields of practice. Below are comprehensive research topics in social work that are compelling to explore.
- Parenting and how it is affected by drug abuse.
- Hardship and benefits of teenage adoption.
- Dealing with suicidal thoughts.
- Societal view on mental sickness stigma.
- Adverse impact of displacement on street kids.
- Homelessness and associated psychological effects.
- Managing PTSD among veterans.
- Adolescents and associated clinical depression.
- How group therapy helps to better the lives of foster residents.
- Family role in reducing or increasing depression.
- Effectiveness of anti-depressants.
- Impact of death on wellbeing of a family.
- Effects of divorce on lifestyle and health of children.
- Ways to address military troops' suicidal tendencies.
- Causes of suicidal thoughts in society.
- Impact of disability on lives of parents.
- Ways to address stigma associated with disability.
- Children with autism are socially excluded.
- Impacts of bullying on children’s wellbeing.
- Complexities around child labor.
- Debate for and against abortion.
- Maltreatment of children in foster care.
- Change in societal reaction to HIV/AIDS in the 1990s and now.
- Rape and its psychological impact on the victim.
- Ways to reduce human trafficking.
Unique Topics in Social Work
There are scholarly research topics in social work that draw extra attention from readers since they are unique in nature. Such topics often concentrate on issues neglected in society. Below are unique topics for social work research.
- Is wellbeing therapy sustainable?
- Teenage girls’ menstrual experiences in foster homes for the first time.
- Poverty and how it impedes growth in the American Deep South.
- Negative impact of conversion therapy on LGBTQ society.
- Influence of inclusive healthcare system on ensuring good welfare lives of people.
- Interracial marriages and their associated problems.
- Effects of diversity on children with disabilities.
- Effects of physical abuse on spousal intimacy.
- Pornography as a primary contributor of incest in families.
- Increase in violence against children and women.
- Activism role based on culture in Native Americans ’ lives.
- Sexual addiction of women to men.
- Disparity in health services for immigrants.
- Challenges experienced by people diagnosed with fibromyalgia.
- Living with a spouse with memory problem.
- Power issue in divorce mediation.
- Issues related to having many partners.
- Reintegration of those who survive substance abuse into the society.
- Employment initiatives for women.
- Dynamic systems applied to nations in war situations.
- Transracial adoption and identity issue.
- The hidden trauma in young counselors.
- Ensuring access to medical services in villages.
- Lowering the gender pay gap.
- Reducing racism and antisemitism.
Controversial Topics in Social Work
Presently, there are several controversial issues in social work that may give rise to social research topics. Listed below are some controversial social work research topics.
- Societal reaction to euthanasia.
- Myths on adolescents’ substance abuse.
- Societal groups that are most vulnerable to substance abuse.
- Ways to deal with drug abuse in orphanages.
- Ethical issues associated with human trafficking.
- Family support role in reducing recidivism.
- How imprisonment affects mental health.
- Gender difference when dealing with imprisoned individuals.
- Juvenile delinquents and reeducation strategies.
- Whose role is it to develop resilience in social work?
- What are strategies to build resilience among welfare workers?
- Benefits associated with social health education among incarcerated women.
- How unreported cases of abuse propagate violence.
- Does constructivist therapy offer anything new to social work?
- Should caseworkers support hypnosis use?
- Who is responsible for misdiagnosis?
- How does misdiagnosis affect lives of mentally ill individuals?
- Health benefits associated with hypnosis on an individual.
- Should parents be involved in preventing dyslexia?
- Ways to address panic for both adults and adolescents.
- Challenges faced by the LGBTQ community.
- Do traffickers suffer psychological consequences of human trafficking?
- Welfare workers’ roles in civil wars.
- Various strategies to help anti-social students.
- Was confinement sanctioning by the court a good move?
Interesting Social Work Research Questions
Before you start your research, it is essential to develop a social work research question that guides the type of information you will gather. Some of the social work research questions examples that talk about various interesting social work topics are listed below.
- How can the US solve the rise in obesity cases?
- How does taking student loans impact them psychologically?
- How can America curb increasing addiction cases?
- How do we help adults with learning disabilities?
- How can we improve lives of pregnant incarcerated mothers?
- What is America’s racial disparity prevalence?
- How can PTSD patients receive support?
- Does poverty have psychological effects on children?
- What are workplace violence indicators?
- What are strategies to ensure work-family balance?
- What does society believe about divorce and its impact on children?
- Do you think substance abuse can be regulated?
- What are consequences of living with HIV/AIDS?
- Do you feel traumatized living with dyslexia?
- What are causes of bipolar disorder?
- How does society treat those with bipolar disorders?
- Who is more vulnerable to divorce?
- Does the US criminal justice system play its role in reducing juvenile delinquency?
- What are problems minority kids face at their foster homes?
- Does substance misuse lead to alcoholism?
- Role of police brutality in increasing transformative change?
- What is the appropriate strategy to help patients with bipolar?
- How can we avoid re-incarceration?
- What does religion say about LGBTQ community?
- How does ADHD affect children in foster homes?
>> Read more: Criminal Justice Research Paper Topics
Hot Topics in Social Work
There are various topics in social work that a researcher can explore to address current hot issues such as COVID-19 pandemic. These topics are important since they help determine current and future solutions to an issue. Here are some social work issues topics that you can consider.
- What are effects of Russian-Ukraine war on society?
- Impact of COVID-19 on welfare workers’ psychological health.
- Issues that arise in households with adopted children.
- Social workers’ attitude towards older people.
- Importance of religion in reducing stereotypes.
- How building emotional intelligence helps caseworkers.
- Demands that residents in a foster facility make.
- Challenges single parents experience.
- Support strategies for single parents.
- Strategies to help sexually exploited children.
- Factors leading to homelessness in the US.
- Forms of abuse elders experience from young people.
- Media role in shaping antisemitism stereotypes.
- Approaches to working with elderly people who are cognitively impaired.
- Parental role in shaping sexual orientation of their children.
- When should a child be removed from a setting?
- Child neglect and its effects on victim’s academic performance.
- Psychological effects of children watching domestic violence.
- Grief and its associated symptoms.
- Methods for assisting kids who have seen domestic violence.
- Ways to encourage domestic violence reporting.
- Technology and addiction treatment.
- Suicide prevention protocol in different localities.
- Risk factors associated with secondary traumatic stress.
- Ways to increase cancer screening rates.
Human Services Research Topics
Human services topics are important since they deal with human existence and ways to make it better. Human service topics focus on how social workers help to satisfy individuals’ and communities’ needs. Generally, social workers’ primary aim is to ensure people live in the most comfortable way possible. Some of the human service research topics are indicated below.
- Adverse impact of unemployment.
- Ways to deal with anxiety and depression among small children.
- Reducing number of incarcerated individuals.
- Impact of juvenile delinquency in the US.
- Relevant ways to breed love in foster care.
- Integration of dyslexic people into society.
- Government intervention to enhance welfare conditions.
- Importance of food banks for the US citizens.
- High school bullying prevalence and impacts.
- Factors leading to family violence.
- Impact of homophobia on LGBTQ+ community.
- Drawbacks of the US correctional system.
- Effects of mental illness misdiagnosis.
- The move to invalidate bullying in high schools.
- Causes of panicking in kids.
- Interventions to reduce unemployment rates in the US.
- Strategies to show concern for individuals from communities with low income.
- Challenges of homophobia in the UAE.
- Social workers in reducing child abuse cases.
- Strategies to enhance resilience among welfare workers.
- The need for psychological therapy among welfare workers.
- Important household policies that can reduce domestic violence.
- Shortcomings of America’s carceral system.
- Interventions for children raised in abusive homes.
- Ways to improve learning experience for disabled children.
Best Social Work Research Topics Ideas
Social work plays a huge role in our daily lives. Therefore, exploring research topics ideas for social work will help us to understand welfare workers’ role in making our lives better. This section discusses various social work topics for research papers. It is categorized into subsections, starting with research paper topics, thesis topics, and dissertation topics. Here, you will also find social work capstone ideas, topics for discussion, essay, and presentation topics. Details for each subsection are provided below.
Social Work Research Paper Topics
As an individual in social work field, you will write several research papers and essays. Social work paper topics you can cover depend on your interests, trends, or any other factor. Some interesting topics related to social work you can consider include the following.
- Social workers' perspectives on elderly.
- Causes of people's unwillingness to take advantage of mental health care services.
- Problems that foster children face that prevent them from completing their college degrees.
- Welfare workers’ role in drug abuse prevention.
- The significance of cultural awareness in casework.
- Facilitation of prenatal and postpartum care for surrogate moms.
- Assessing how PTSD affects psychological wellbeing.
- Adoptive families face unique difficulties and concerns.
- Benefits of play therapy interventions for school counseling.
- Hemodialysis patients' mental health and the methods used to help them.
- Importance of leisure pursuits for Alzheimer's patients.
- Damages of psychological violence.
- Trauma and adolescent transition among LGBTQ+ kids.
- Understanding the neglect-syndrome of foster kids.
- Understanding trauma for caseworkers.
- Foster parenting's advantages.
- Role of foster parents in violence prevention.
- Domestic violence and its impacts.
- Foster homes’ role in creating a safe space.
- How diversity helps in social works sector.
Social Work Thesis Topics
There are several thesis topics in social work to research during your master’s program or PhD, which can vary depending on your interest or occupation. Below are some of the social work literature review topics that you can look into.
- Effectiveness of group therapy for alcoholics.
- Mental health services’ effectiveness for pedophilia survivors.
- Inaccessibility of mental health care for members of underrepresented groups due to language barriers.
- Prepartum depression and connection to expecting mothers.
- Relationship between codependency and emotional unavailability.
- Strategies to handle fatigue among welfare workers.
- Burnout causes among social workers.
- Challenges associated with child birth and labor.
- Depression and the perception of welfare mothers.
- Prevalence of mental health in the US.
- The use of an integrated system in various foster homes within America.
- Nurses’ commitment level and how it is associated with health outcomes.
- Impact of legalizing abortion in some states.
- Comparison between displacement in foster homes and war sites.
- Analyzing displacement and associated challenges.
- How immigrant families benefit from parenthood?
- Issues that visually disabled students face at school.
- Essence of welfare work sector diversity.
- Learning about depression from the welfare mom's viewpoint.
- Ways to improve healthcare system.
Social Work Dissertation Topics
Dissertation is a crucial part of your education life as a social worker. Therefore, dissertation topics in social work have to be properly framed and specific. Here are some of the dissertation topics for social work to consider.
- Coping strategies of men during violence at home.
- Rape and how it affects victim’s psychological development.
- Acceptance rate of addiction by addicts within the US.
- Vulnerable groups and government’s role in improving their lives.
- Justification of gender pay gap in America.
- Addiction to substance abuse and its role in the contemporary world.
- Prevalence of homosexuality in the US.
- Naturalizing human needs as a way to break down taboo and barriers.
- The association between stigma and drug abuse persistence.
- Drug abuse and how music increases its prevalence.
- Rate at which American citizens care for their forefathers.
- Technological role in shaping our sexual preferences.
- Reasons why men and women commit suicide.
- Existing protection policies for children in New York State.
- Investigating US women who have experienced child sexual abuse.
- Assessment of healing strategies for drug abuse survivors.
- The role of parents in supporting their children’s ambitions.
- Volunteering and its impact on self-satisfaction.
- Therapies used to treat effective disorder in an American youth.
- The need for sexual education among young girls with mental health issues.
Social Work Capstone Project Ideas
As a social worker, you should consider some social work project topics for your capstone project . Capstone project social work research topics are highlighted below.
- Impact of domestic violence on marital satisfaction.
- How does government support minority groups?
- Media role in ensuring public safety.
- Causes of child neglect.
- How juvenile crime affects the US.
- How government ensures food security.
- Enhancing public safety in minority communities.
- Problems associated with criminal justice system.
- Social integration of individuals with Down Syndrome.
- Role of school administration in reducing bullying.
- Bullying and victims’ academic performance.
- Trauma experienced by social workers.
- Parenting and its role in children’s sexual orientation.
- What causes panic in schools.
- How child support is essential in divorced couples.
- Child neglect and its causes.
- Damages caused by psychological violence.
- Trauma of adolescent transitioning in LGBTQ+ children.
- Understanding foster kids’ neglect-syndrome.
- Causes of increase in reincarceration among youths in America.
Social Work Topics for Discussion
Highlighted below are some social work discussion topics to consider.
- Root causes of domectic violence.
- Location-specific suicide prevention and crisis protocols.
- How does drug dependence influence parenting?
- Public policies for and against LGBT community.
- Ways of providing support for bipolar patients.
- Prenatal depression in expectant mothers.
- How to cope with imprisonment stigma.
- Ways to improve living standards in foster homes.
- What are the best community service strategies for refugees?
- How can backyard farming be used to empower women?
- Utilizing gender sensitivity to help the LGBT community.
- Cultural importance of generation gap.
- Secondary traumatic stress: symptoms, risk factors & ways of managing.
- How to motivate women to report family violence.
- Various ways in which unemployment influences immigrants.
- How peer service providers confront reproductive health issues.
- The major problems faced by welfare workers.
- Detrimental influence of alcohol and drug on adolescents.
- Effectiveness of the prohibition of liquor.
- Key reasons for heightened crime rates in modern society.
Social Work Essay Topics
Here are some of social work topics for essays that you should consider in your writing.
- Global challenges faced by deported women.
- Street hawking opportunities for teenagers.
- Main factors that lead to incest.
- Positive and negative effects of health care reforms.
- How environmental welfare work is undertaken.
- Care strategies for immigrants.
- Impact of corporate social responsibility on community wellbeing.
- Does welfare scheme affect worker’s performance?
- The impact of sexual violence on adolescent girls.
- How does diversity affect various communities?
- Effect of play therapy interventions in school counseling.
- Influence of poverty on children’s development and education.
- How should welfare workers deal with pedophilia victims?
- How should caseworkers prevent burnout?
- How to establish a high school service-learning program.
- Elder abuse: most prevalent forms.
- The central issues associated with special education.
- Personal perspective on the obstacles faced by vulnerable populations in search medical help.
- What is the greatest risk of fetal alcohol exposure?
- Ways to enhance caseworkers’ mental health.
Social Work Topics for Presentation
Presentation social work topics for research discuss different aspects of the field of social work. The research topics have to be practical for them to be presented well. Below are some good research topics for social work presentation.
- Strategies to ensure equality during job recruitment.
- Autism and its risk factors.
- Causes of depression in kids.
- What are risk factors of PTSD among victims?
- Ways to reduce suicide cases in society.
- Advantages and disadvantages of rehabilitation centers.
- Community initiatives to cater for the elders.
- Effects of misdiagnosis of mental illness.
- Ethics of abortion.
- Importance of early cancer screening.
- Strategies to reduce unemployment rate among minority communities.
- How foster parents can help in countering youth violence.
- Euthanasia and how various religions view it.
- Compare societal preparation to COVID-19 and HIV/AIDS.
- Contemporary ways to substance abuse.
- Eating disorder and its causes.
Research Topics for Social Work Students
College students also apply social work research topics in their study of related subject, which covers various aspects in the field of social work. Here are some of social work research topics for college students.
- Resident’s experience in long-term care facilities.
- Strategies to handle life when both parents suffer from Alzheimer’s.
- Pregnancy experience among immigrants and how they approach it.
- How does death affect the collective wellbeing of the family?
- Enhancing digital literacy among immigrant students.
- How socioeconomic disparity affects the old.
- Social and mental effects of loans on students.
- Social problems that autistic children face.
- Conversion therapy’s negative effects on the LGBTQ+ community.
- Impact of science on cancer treatment.
You will find a lot of topics in different fields on our platform. If you are looking for topics in laws or mental health research paper topics , just go to our library and find what you need.
Bottom Line on Social Work Research Topic Ideas
Feel free to choose a topic of your choice from the social work research topics examples recommended above. Apply appropriate topic categories during the process of choosing topics depending on your needs, knowledge in the field, and the type of paper you are writing. Practice using the provided examples will make you perfect.
In case you need a personalized research topic, or require a complete social work research paper, you can buy research paper online from StudyCrumb. Particularly, our writers will help you choose social work research paper topics, write papers for you, and proofread the work to ensure there are no grammatical errors.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

- Request Info
- Academic Programs
- Continuing Studies
- Camp Students & Families
- Academy Students & Families
- Faculty & Staff

Social Work Theories in Practice
Social work is a multifaceted profession that uses various theories to guide practice and intervention strategies. These theories provide a framework for understanding complex social issues and facilitating change at individual, community, and societal levels.
This blog post will explore critical theories that inform social work practice, including social learning theory, psychodynamics, psychosocial development theory, systems theory, rational choice theory, contingency theory, cognitive behavioral therapy, conflict theory, and the broader societal context.
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory, pioneered by Albert Bandura, posits that people learn from one another through observation, imitation, and modeling. This theory is crucial in social work as it underscores the importance of role models and environments in shaping behavior. Interventions based on this theory often involve shaping positive behaviors and attitudes through structured programs that promote positive social interactions.
Example : A social worker is helping a teenager who struggles with aggression and has been influenced by violent behavior in his neighborhood. The social worker organizes a mentorship program where the teenager can interact with positive role models, demonstrating effective conflict resolution and communication skills. This exposure helps the teenager learn and adopt healthier behaviors through observation and emulation.
Psychodynamics
Developed from the ideas of Sigmund Freud, psychodynamics explores how unconscious motives and conflicts influence behavior. In social work, psychodynamic theory is used to delve into an individual's past experiences and emotional traumas affecting their current behavior and relationships. This understanding helps social workers address deep-seated emotional issues and foster healing and development.
Example : A social worker encounters a client who exhibits severe trust issues and difficulty forming relationships stemming from early childhood neglect. Using psychodynamic principles, the social worker explores these past experiences with the client, helping them understand and process their unconscious fears and how these impact their current relationships, thereby facilitating emotional healing and development.
Psychosocial Development Theory
Erik Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development emphasizes the impact of social experiences across the lifespan. Each stage of life is associated with specific challenges and tasks that contribute to overall growth. Social workers use this theory to assess and support clients at different developmental stages, ensuring that developmental crises are resolved healthily.
Example : In a case involving an elderly client facing depression after retiring, a social worker uses Erikson's stages of psychosocial development to assess and address the crisis of integrity vs. despair. The social worker encourages the client to reflect on life achievements and develop a sense of fulfillment and purpose, possibly through volunteering or community activities.
Systems Theory
Systems theory views individuals as part of more interconnected systems, including family, community, and society. This approach helps social workers recognize the multiple factors affecting individuals and how changes in one part of the system can influence others. Interventions may focus on altering the environment or interactions within these systems to improve the individual's circumstances.
Example : A social worker assists a family with a child with behavioral problems. Recognizing the interconnectedness of systems, the social worker evaluates the dynamics within the family, school, and peer group. The intervention includes working with the parents to improve their parenting techniques, liaising with teachers for support at school, and facilitating positive peer interactions.
Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory suggests that individuals make decisions based on actions' anticipated costs and benefits. Social workers applying this theory might focus on helping clients weigh the pros and cons of their choices to foster better decision-making processes, particularly in scenarios involving high-risk or significant life changes.
Example : A social worker uses rational choice theory to help a client contemplating leaving a job due to stress but is worried about financial security. The social worker helps the client list the benefits and drawbacks of staying versus leaving the job, considering factors like mental health, economic implications, and long-term career goals, thereby aiding the client in making a well-informed decision.
Contingency Theory
Contingency theory is rooted in the premise that there is no best way to approach management but that the most effective approach depends on the specific circumstances. In social work, this theory can tailor interventions to clients' unique needs and contexts, recognizing that strategies and plans must be flexible and adaptable.
Example : A social worker leading a community outreach program adapts their approach based on each neighborhood’s needs and resources. In one area, the focus might be on job training due to high unemployment, while another might need more youth programs to engage teenagers. The social worker uses contingency theory to assess and apply the most effective strategies in each unique situation.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a structured, hands-on approach that addresses problematic behaviors by identifying and changing negative thinking patterns and beliefs. Social workers use CBT to help clients develop coping strategies and change behaviors detrimental to their well-being. This therapy is particularly effective in treating anxiety, depression, and certain disorders.
Example : A client is dealing with anxiety and panic attacks. The social worker, trained in CBT, works with the client to identify specific thought patterns and beliefs that trigger anxiety. Through techniques such as cognitive restructuring and behavioral experiments, the client learns to manage and reduce anxiety symptoms effectively.
Conflict Theory
Conflict theory, influenced by Karl Marx, explores how power differentials and structural inequalities impact individual and community functioning. Social workers using this theory may focus on advocacy, social justice, and structural change to address poverty, discrimination, and oppression.
Example : A social worker in a low-income urban area recognizes that systemic inequalities affect community health. They use conflict theory to advocate for better healthcare services and organize community groups to lobby for policy changes. This includes challenging the power structures that lead to unequal access to healthcare and supporting community empowerment.
Understanding society and its influence on individuals is fundamental in social work. This broad perspective examines social policies, cultural norms, and economic conditions that affect individual opportunities and quality of life. Social workers strive to bring societal change through policy advocacy and community development to create more equitable conditions.
Example : A social worker is involved in policy development to address homelessness. Understanding the societal impact on this issue, they analyze how economic policies, housing market dynamics, and social services affect the homeless population. The social worker collaborates with policymakers to create more inclusive housing solutions and supportive services that address the root causes of homelessness.
These theories offer a glimpse into the frameworks that inform social work practice. By integrating these theories, social workers are better equipped to understand their clients' needs and foster change that improves individual lives and society. Each theory provides unique insights and tools, allowing social workers to approach problems comprehensively and effectively. Integrating these theories will remain central to addressing the challenges individuals and communities face as the field evolves.
To better make a difference in the lives of diverse and vulnerable populations through social work, consider enrolling in our Masters in Social Work degree .
- For Grad Students
- Graduate Justice Fellowship
- Graduate Student Institute for Engaged Research and Teaching
- Higgins Labor Program
- Common Good Initiative
- Spanish Community-Engaged Learning
- Programs for Education in Prison
- Poverty Studies Interdisciplinary Minor
- SPIRE: The Global Catholic Social Tradition Network
- Just Wage Initiative
- Journal of Poverty and Public Policy
- Virtues and Vocations
- Signs of the Times
- Arts of Dignity
- MVP Fridays
- The Labor Café
- Rev. Bernie Clark, C.S.C., Annual Lecture
- Biennial Catholic Social Tradition Conference
- Social Concerns Fair
University of Notre Dame
South Bend’s Clemente Course graduates reflect on ‘taking that first step’ into college
June 27, 2024.

As a college student in the early 1970s, Oletha Jones started to feel a bit guilty seeing her father, a construction worker, struggle to pay tuition amid the ups and downs of the construction industry.
Even though higher education was a priority in her family, she decided to stop attending Indiana University South Bend to find gainful employment and work for a while before continuing toward her degree. Then she met her husband, and they started a family. “From there, I just really focused on my family,” she said. “But I always had the intention of going back to college.”
Jones had an opportunity to resume her education last fall when the Clemente Course in the Humanities became available locally through a partnership between the IU South Bend Civil Rights Heritage Center and the Center for Social Concerns.
Bard College established the Clemente Course in 1996 out of the recognition that many people from low-income backgrounds and marginalized groups have had limited access to higher education. The program makes college-level courses available to people at no cost, including free books and course materials as well as transportation and child care.
The Center for Social Concerns has promoted the democratization of education through other initiatives, such as Notre Dame Programs for Education in Prison . The partnership to bring the Clemente Course to South Bend is another way to extend the transformative opportunity of a college education to more community members.
In May, Jones and five other students in South Bend’s inaugural cohort of the Clemente Course celebrated their graduation from the program.
During the academic year, the students — who ranged in age from 19 to 75 — took courses in philosophy, U.S. history, literature, art history, and critical thinking and writing. They’re eligible to earn six credits from Bard College for their work and could transfer those credits to another college or university as they continue their education.
“Being part of this program was liberating and allowed me to be creative, which has really intensified my yearning to continue,” Jones said. “It gave me a thirst. It felt good to be in the classroom again.”

Professor Darryl Heller , director of the Civil Rights Heritage Center and a faculty fellow of the Center for Social Concerns, called Jones and her classmates trailblazers for future Clemente students in the South Bend area. The program started small last year, but Heller said the goal is to enroll 25 students this coming fall.
“At heart, Clemente Courses rest on the premise that a liberal arts education is, well, liberatory,” Heller said in May at the graduation ceremony for the South Bend class. “Thus, our premise is grounded on the conviction that reflection in the humanities can create a foundation for people to engage the world around them in new ways.”
Pam Blair, another graduate of the inaugural Clemente class, is an academic programs assistant for Notre Dame’s Kroc Institute for International Peace Studies. She is also a poet and visual artist who hosts South Bend’s monthly Poetry Den.
“I went to art college out of high school, but I only completed three years due to financial difficulties,” Blair said. “The Clemente Course has started something in me where I want to finish that degree.”
Heller, who also served as the academic director for the Clemente Course in South Bend, taught the U.S. history course. The other four courses were taught by two IU South Bend professors and two Notre Dame professors.

“All of our professors were excellent,” Blair said. “They were accommodating to all the individuals. We had older, middle-aged, and young students in there. Our teachers were really good about navigating that diversity in the classroom.”
Blair said the environment in the classroom was conducive to dialogue and learning for its own sake. “There were no bad questions,” she said. “The experience really opens your mind.”
Mark Sanders , a professor of English and Africana studies at Notre Dame and a faculty fellow of the Center for Social Concerns, taught the Clemente Course’s literature class. He said the Clemente Course makes an enormous contribution to the community by providing entry-level college courses for adults finding their way into higher education.
“In my course, this year’s students embraced the challenge of reading William Shakespeare, Rita Dove, and Gabriel García Márquez, among many other authors, to immerse themselves in literary analysis’ intricacies and rewards,” Sanders said. “They developed many of the critical reading and writing skills essential for upper-level classes. And equally as importantly, they read and wrote in pursuit of greater knowledge, understanding, and discernment, indeed an independence of thought crucial for sustaining a democracy.”
Jones said she hopes others in the South Bend region take advantage of the opportunity the Clemente Course offers.
“Take that first step and open yourself up to get out of your comfort zone. At least take that first step. That’s what I did,” she said. “I made up my mind that I was just going to start and see where it would lead.”
Anyone interested in enrolling in the Clemente Course in the Humanities should contact Professor Darryl Heller at [email protected] .
Related Stories

McNeill Common Good Fellows explore issues of justice through summer research

Virtues & Vocations hosts 2024 conference on higher education and human flourishing

Postdoc Geneva Hutchinson uses art as an entry point to conversations about justice

Senior Send-Off celebrates the Class of 2024’s commitment to the common good
Sign up for The Current, our monthly newsletter
Upcoming Events
2024 welcome back bash, mvp fridays: ross douthat, 2024 summer research awards ceremony and reception, mvp fridays: javier zamora, book launch: virtue in virtual spaces, mvp fridays: ilyon woo, mvp fridays (stanford).
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Americans’ Views of Government’s Role: Persistent Divisions and Areas of Agreement
Wide majorities of Biden and Trump supporters oppose cuts to Social Security
Table of contents.
- Views on the efficiency of government
- Views on the government’s regulation of business
- Confidence in the nation’s ability to solve problems
- Views on the effect of government aid to the poor
- Views on government’s role in health care
- Views on the future of Social Security
- Trust in government
- Feelings toward the federal government
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ attitudes about U.S. government, such as its size and role.
This report is based primarily on a survey of 8,709 adults, including 7,166 registered voters, from April 8 to 14, 2024. Some of the analysis in this report is based on a survey of 8,638 adults from May 13 to 19, 2024.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for the report and its methodology .
While the economy, immigration and abortion have emerged as major issues in the 2024 election, Joe Biden and Donald Trump also have dramatically different ideas about the size and role of government.
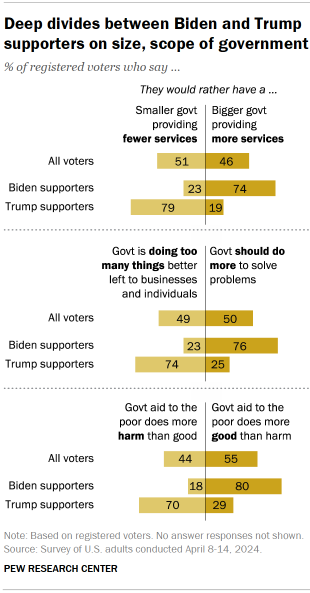
These differences reflect decades-old divisions between Democrats and Republicans over the scope of government.
Among registered voters, large majorities of Biden supporters – roughly three-quarters or more – favor a bigger, more activist government.
- 74% say they would rather have a bigger government providing more services.
- 76% say government should do more to solve problems.
- 80% say government aid to the poor “does more good than harm.”
Trump supporters, by comparable margins, take the opposing view on all three questions.
The Pew Research Center survey of 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – conducted April 8-14, 2024, examines Americans’ views of the role and scope of government , the social safety net and long-term trends in trust in the federal government .
Democratic support for bigger government is little changed in the last five years but remains higher than it was a decade ago. Republicans’ views have shifted less over the last 10 years.
Among all adults, about three-quarters of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents favor a bigger government, up from about six-in-ten in 2014 and 2015. The share of Republicans and Republican leaners who prefer a bigger government has increased only modestly over the same period.
Democratic support for bigger government, while slightly lower than in 2021 (78%), remains at nearly its highest level in five decades. During Bill Clinton’s presidency in the 1990s, fewer than half of Democrats said they preferred a bigger government with more services.
Voters continue to express very different views about government’s role in specific areas than about the government generally.
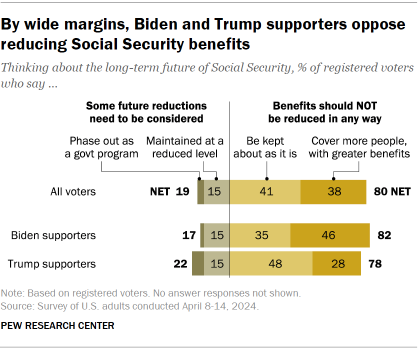
A large majority of voters (80%) – including 82% of Biden supporters and 78% of Trump supporters – say that in thinking about the long-term future of Social Security, benefits should not be reduced in any way.
However, Biden supporters are more likely than Trump supporters to say Social Security should cover more people with greater benefits.
- 46% of Biden supporters favor expanding Social Security coverage and benefits, compared with 28% of Trump supporters.
Most Americans (65%) continue to say the federal government has a responsibility to make sure all Americans have health care coverage.
Democrats overwhelmingly (88%) say the federal government has this responsibility, compared with 40% of Republicans.
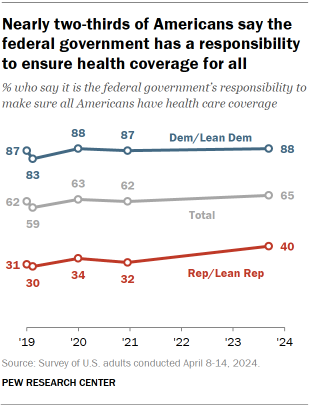
The share of Republicans who say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage has increased 8 percentage points since 2021, from 32% to 40%.
There are wide income differences among Republicans in opinions about the government’s role in health care:
- 56% of Republicans with lower family incomes say the government has a responsibility to provide health coverage for all, compared with 36% of those with middle incomes and 29% of higher-income Republicans.
When asked how the government should provide health coverage, 36% of Americans say it should be provided through a single national program, while 28% say it should be through a mix of government and private programs. These views have changed little in recent years.
Democrats continue to be more likely than Republicans to favor a “single payer” government health insurance program (53% vs. 18%).
Other key findings in this report
- Americans’ trust in the federal government remains low but has modestly increased since last year. Today, 22% of American adults say they trust the government to do what is right always or most of the time, which is up from 16% in June 2023.
- While the public overall is divided over the nation’s ability to solve important problems, young adults are notably pessimistic about the country’s ability to solve problems . About half of Americans (52%) say the U.S. can’t solve many of its important problems, while 47% say it can find a way to solve problems and get what it wants. Roughly six-in-ten adults under age 30 (62%) say the nation can’t solve major problems, the highest share in any age group and 16 points higher than two years ago.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Election 2024
- Federal Government
- Government Spending & the Deficit
- Health Care
- Partisanship & Issues
- Social Security & Medicare
- Trust in Government
Third-party and independent candidates for president often fall short of early polling numbers
6 facts about presidential and vice presidential debates, biden, trump are least-liked pair of major party presidential candidates in at least 3 decades, cultural issues and the 2024 election, more than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Middle school voices help anti-vaping strategies
- June 24, 2024

A team of researchers from the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa and University of California Riverside collaborated with Hawaiʻi Island schools to explore and develop strategies to prevent vape use among middle school students, with input from 69 students helping shape the prevention curriculum.

Researchers from UH Mānoa include the John A. Burns School of Medicine ( JABSOM ) Department of Native Hawaiian Health, UH Cancer Center and the Thompson School of Social Work & Public Health .
“The data on substance use, especially within Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander youth, seem to suggest that the age at which prevention interventions are effective or most needed tends to be in middle school or even earlier,” said Kelsie Okamura, with JABSOM ‘s Department of Native Hawaiian Health.
Okamura and the team took the project to Hawaiʻi Island middle schools and, through interviews or focus groups, got a first-hand glimpse into what middle schoolers encounter when it comes to the temptation to use vapes.
“It’s happening at the backyard paʻina . It’s with friends at the school bus stop, the gym, and the community center. Those are some of the scenarios we are hearing about,” Okamura said.
Resistance skills used by students
The research explores effective resistance skills middle school students use to avoid vaping. Key strategies include:
- Refuse: Firmly saying “no,” especially effective with strangers.
- Explain: Offering explanations or excuses, often used with friends.
- Avoid: Steering clear of places where vaping is common.
- Leave: Exiting situations where vaping offers occur, particularly when the offeror is not a close acquaintance.
The study may be eye-opening to parents, and the successful methods being used by middle schoolers will be built into the curriculum for Hoʻouna Pono, a culturally grounded substance use prevention program.
“You can really hear the student voices in this paper and I think that’s really important,” Okamura said. “We can include some of the resistance skills to help teachers build those skills in students and get practices and rehearsals in school.”
Read more at JABSOM .
Related Posts:
- $2.8M to develop e-cigarette intervention for rural…
- UH Cancer Center researcher receives Hawaiʻi 1st…
- Substance abuse in Hawaiʻi tracked by new dashboard
- previous post: Anxiety, depression a major problem in space science community
- next post: $1.6 M to advance ‘computational thinking’ and respond to emerging technology
If required, information contained on this website can be made available in an alternative format upon request. Get Adobe Acrobat Reader
About Calendar COVID-19 Updates Directory Emergency Information For Media MyUH Work at UH
Gagana Samoa
Kapasen Chuuk
Kajin Majôl
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
- Administrative

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
199+ Social Work Research Topics [Updated 2024] General / By Stat Analytica / 28th November 2023. In the vast and dynamic field of social work, research plays a pivotal role in shaping interventions, policies, and practices. Social work research is not just an academic pursuit but a powerful tool for effecting positive change in communities.
50 Controversial Research Topics. Group therapy vs individual therapy for increasing autistic children adaptability. Impact on parents having children with autism spectrum disorder. Role play vs group discussion efficiency in increasing knowledge regarding drug abuse among high-school students. Addressing the stigma associated with depression.
The Journal of Social Work is a forum for the publication, dissemination and debate of key ideas and research in social work. The journal aims to advance theoretical understanding, shape policy, and inform practice, and welcomes submissions from all … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication ...
About the journal. Social Work Research publishes exemplary research to advance the development of knowledge and inform social work practice. Find out more. "The Air Is Being Sucked Out of the Room": Experiences of Social Work Students of Color with Antiracism Education in the Classroom and Practicum. LGBTQ+ People's Perceptions of ...
Practice research in social work is evolving and has been iteratively defined through a series of statements over the last 15 years ... The group aims to appraise relevant research or policy related to diversity in social work, and may develop practice research questions for further exploration. The papers in this special edition have been ...
Research on Social Work Practice (RSWP), peer-reviewed and published eight times per year, is a disciplinary journal devoted to the publication of empirical research concerning the assessment methods and outcomes of social work practice. Intervention programs covered include behavior analysis and therapy; psychotherapy or counseling with individuals; case management; and education.
Widely regarded as the outstanding journal in the field, it includes analytic reviews of research, theoretical articles pertaining to social work research, evaluation studies, and diverse research studies that contribute to knowledge about social work issues and problems. 2021 Journal Impact Factor™: 1.844. Social Work in the Age of a Global ...
An official journal of the National Association of Social Workers. Publishes papers that strive to improve practice and advance knowledge in social work ... Discover a more complete picture of how readers engage with research in Social Work through Altmetric data. Now available on article pages. Recommend to your library. ... Related Titles.
Abstract This article traces themes over time for conducting social work research to improve social work practice. The discussion considers 3 core themes: (a) the scientific practitioner, including different models for applying this perspective to research and practice; (b) intervention research; and (c) implementation science. While not intended to be a comprehensive review of these themes ...
1948-1955 •. 1933-1947 •. Social Work is the premier journal of the social work profession. Widely read by practitioners, faculty, and students, it is the official journal of NASW and is provided to all members as a membership benefit. Social Work is dedicated to improving practice and advancing knowledge in social work and social welfare.
The history of social work education may have also contributed to making it difficult for those teaching on university social work courses to engage routinely in research (Orme and Powell, 2007).
5.01 (d): Social workers should contribute to the knowledge base of social work and share with colleagues their knowledge related to practice, research, and ethics…. 5.02 (a) Social workers should monitor and evaluate policies, the implementation of programs, and practice interventions. 5.02 (b) Social workers should promote and facilitate ...
The findings revealed that social work continues to lack a clear definition of research and produces research that only minimally influences practice, often due to the pressure for social work academics to research and publish in support of their career trajectory within academia versus writing for practitioners.
Research & Data. > News > Research & Data. Research & Data. NASW's Center for Workforce Studies and the Social Work Policy Institute conducted research that examined the social work workforce and issues that related to the work of social workers, including serving people with multiple and complex needs.
LITERATURE SEARCH METHOD. For this project, research was conducted through a review of the literature, including both books and scholarly articles, on EBP in mental health services in social work as well as other relevant professions and by interviewing a convenience sample of experts currently conducting research related to the development and dissemination of evidence based interventions for ...
Here is the list of the top 225 social work research topics for college students according to different categories; take a look. Child Well-being. How foster care affects child growth. Adoption and its effect on families. Ways to prevent child abuse. Role of social workers in child protection services. Struggles faced by children in foster care.
Social work researchers will send out a survey, receive responses, aggregate the results, analyze the data, and form conclusions based on trends. Surveys are one of the most common research methods social workers use — and for good reason. They tend to be relatively simple and are usually affordable.
Our literature review of 13 major social work journals over 5 years of published research revealed that only 15% of published social work research addressed interventions. About a third of studies described social problems, and about half explored factors associated with the problem ( Rosen, Proctor, & Staudt, 2003 ).
Yet, bridging the gap between research and practice has been a long-standing problem in the social work profession (Thyer, 2015), and social workers lack an organizing framework for how to incorporate social media in addressing this gap.Past approaches to closing this gap have neglected the context realities that shape the use of research in practice settings (Epstein, 2015) as well as the ...
what is the readiness of social work students to work with autistic individuals?, ignacio aguilar pelaez. pdf. examining experiences among social workers working with parents who suffer from substance use disorder, alicia alvarado and eleno zepeda. pdf. covid-19, social isolation, and msw students' mental health, cassandra barajas. pdf
A Bachelor's degree in social work is the minimum requirement for most entry-level social work positions. However, many research social work positions require a Master's degree in social work. Gain relevant work experience and develop research skills. You can also pursue a DSW or PhD to further your knowledge and expertise.
Social work research topics cover various concepts and challenges related to caseworkers and their fields of practice. Below are comprehensive research topics in social work that are compelling to explore. Parenting and how it is affected by drug abuse. Hardship and benefits of teenage adoption.
Social work is a multifaceted profession that uses various theories to guide practice and intervention strategies. These theories provide a framework for understanding complex social issues and facilitating change at individual, community, and societal levels. This blog post will explore critical
Abstract. This study sought to investigate the public perception of social workers in the Eastern Black Sea Region, Turkey. In this research, a questionnaire developed by Bolgün and Şahin (Citation 2019)was employed, and using the convenience sampling method face-to-face interviews were held with a total of 600 participants.Using various statistical tests, normally distributed scores were ...
Application: We suggest that issues related to burnout and compassion fatigue are key aspects that need to be incorporated within the social work curriculum in educational programs in India.A focus on maintaining a healthy work-life balance, and the importance of self-care in maintaining good health and wellbeing are key elements that need to be emphasized.
Professor Darryl Heller, director of the Civil Rights Heritage Center and a faculty fellow of the Center for Social Concerns, called Jones and her classmates trailblazers for future Clemente students in the South Bend area.The program started small last year, but Heller said the goal is to enroll 25 students this coming fall. "At heart, Clemente Courses rest on the premise that a liberal ...
The Pew Research Center survey of 8,709 adults - including 7,166 registered voters - conducted April 8-14, 2024, examines Americans' views of the role and scope of government, the social safety net and long-term trends in trust in the federal government.
Sites most commonly used by temps looking for work: ... Staffing firms and buyers of contingent labor can use this report to better understand which job boards and social networking sites temporary workers use when looking for work, and how those site preferences vary by worker skill sets. ... Related research. Trends in Temp Use of Platforms ...
Reading time: 2 minutes A team of researchers from the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa and University of California Riverside collaborated with Hawaiʻi Island schools to explore and develop strategies to prevent vape use among middle school students, with input from 69 students helping shape the prevention curriculum.. Kelsie Okamura. Researchers from UH Mānoa include the John A. Burns ...