How to write an engaging and effective presentation script?
Explore expert tips and techniques to elevate your script, ensuring it resonates with your audience and enhances your message.
Bharti Jain
Delivering presentations

In today's world, presentations are a crucial part of professional communication, whether for pitching a new idea, educating an audience, or persuading potential clients. However, the backbone of any successful presentation is its script. A well-crafted presentation script can captivate your audience and deliver your message effectively. In this blog, we’ll explore the intricacies of crafting such a presentation that not only delivers information but also engages your audience, drawing insights from the tools and strategies provided by Prezent.

What is a presentation script?
It is much more than a mere set of words to be read or spoken; it is a strategic narrative designed to communicate ideas effectively. It’s the roadmap of your presentation content, detailing every turn of your story, every fact you want to highlight, and every emotion you wish to evoke. A well-written script aligns with your visuals and delivery, creating a harmonious and impactful presentation.
Here’s an example of presentation script containing key points only:

What are the key elements of a compelling presentation script?
When we talk about crafting a presentation script that captivates and engages, it's essential to focus on the following elements.
1. Write a script with a clear objective
It's a common misconception that the sole purpose is just to relay whatever is on your mind. Every presentation has a specific goal, and it's crucial to identify this goal right from the start. Are you looking to inform, persuade, inspire, or motivate your audience?
For example, if your goal is to persuade your audience, you need an approach as if you're a lawyer making a closing argument. This means your script should be filled with strong, convincing evidence and delivered in a tone that's persuasive and compelling. On the other hand, if your aim is to inform, it should resemble a teacher's lesson plan: well-organized, clear, and educational. Here, the focus is on clarity and thoroughness.
2. Audience-centric approach
Tailoring your content to resonate with your audience's interests and level of understanding is crucial. It’s similar to a chef knowing his diners' preferences before crafting a menu.
For example, If your audience comprises young entrepreneurs, using startup success stories and Silicon Valley anecdotes can make your content more relatable and engaging.
Ignoring the audience’s background and interests is like serving a steak to a vegetarian – it just won’t connect. So you need to ensure that you get your audience to listen.
3. Need to write a strong narrative
A strong narrative structure in your script is essential – consider it the spine of your presentation. It should have a compelling introduction (like the opening scene of a gripping movie), an informative body (similar to the plot development of a novel), and a memorable conclusion (the final scene that leaves the audience thinking).
For instance, Steve Jobs’ iconic iPhone launch presentation in 2007 masterfully followed this structure in his presentation speech, captivating the audience from start to finish.
4. Emotional engagement
Creating an emotional connection with the audience can be achieved through storytelling , anecdotes, or humor.
Take, for instance, the iconic "I Have a Dream" speech by Martin Luther King Jr. His powerful storytelling and emotional appeal transformed statistical data about racial injustice into a palpable narrative that moved an entire nation.
Similarly, humor can play a significant role in keeping the audience engaged. Ellen DeGeneres' commencement speech at Tulane University in 2009 is a prime example. She skillfully blended humor with her personal life story, especially her struggles and achievements.

5. Simplicity and clarity
Conveying your ideas in a straightforward and understandable manner is vital. Think of it as the principle of KISS (Keep It Simple, Stupid). Your presentation should be like clear, concise instructions, not a complex, hard-to-decipher manual. Avoid jargon and technical terms unless absolutely necessary.
Remember, Albert Einstein once said,
If you can't explain it simply, you don't understand it well enough.
Your script should reflect clarity of thought and simplicity of expression.
How to write a presentation script that is effective?
Crafting an engaging presentation script is a multifaceted process that requires attention to detail, a deep understanding of your subject, and a keen sense of audience engagement. Here are some crucial strategies that you should know:
1. In-depth research
To lay a solid foundation for your presentation, start with comprehensive research. Dive deep into your topic to ensure every aspect of your script is well-informed and accurate. This doesn't mean just skimming through the top Google search results. Explore various sources, from scholarly articles to industry reports, to gather a rich array of information.
This depth of understanding not only boosts the credibility of your presentation but also prepares you to confidently handle any questions that might arise during or after your presentation.
2. Conversational tone
A key aspect of a good script is its tone. Aim for a conversational style – as if you're talking to a friend over coffee rather than memorising & lecturing in a formal setting. This approach makes your presentation more relatable and engaging. Avoid complex jargon and technical terms unless necessary, and instead, opt for simple language that flows smoothly. Think of it like storytelling with data.
Check this example to understand better:
Without conversational tone
“In today's discourse, we shall examine the multifaceted and intricate ramifications of digital transformation on global business paradigms."
With conversational tone
"Let's talk about how digital transformation is changing the way we do business around the world. It's pretty fascinating stuff!"
In the first sentence, the formal tone and complex language create a barrier, making the content feel distant and academic. The second sentence, conversational in nature, uses simple language and a friendly approach, inviting the audience into an engaging discussion.
3. Proper visual integration
Visuals are not just decorations; they are integral to reinforcing your message. While scripting, think about how each segment of your speech can be accompanied by relevant visual aids, whether it's a slide, an infographic, or a short video clip. For instance, when discussing a complex process, a diagram can make it easier for your audience to grasp. The key is to ensure that your visuals complement your words, adding clarity and keeping the audience visually engaged.
4. Interactive elements
Engaging your audience is crucial, and interactive elements can significantly boost this engagement. Incorporate rhetorical questions to provoke thought or invite audience participation at certain junctures. You might include a quick poll, a show of hands, or even a brief Q&A session. These elements transform your presentation from a monologue into a dialogue, making it a two-way interaction that keeps your audience actively involved.
5. Rehearse and practice your presentation
The final and perhaps most critical step for the presenter is to refine and rehearse the script several times . This is where you fine-tune your pacing, adjust your tone, and smooth out any rough edges. Rehearsing out loud, ideally in front of a mirror or a test audience, helps identify parts of the script that may need reworking. Pay attention to timing, pauses, and emphasis on key points. Remember, practice doesn’t just make perfect; it builds confidence, ensuring that when it's showtime, you deliver with poise and impact.
How to enhance the effectiveness of a powerpoint presentation through engaging designs?
The integration of engaging presentation designs in your presentation can significantly boost it's effectiveness. Thoughtfully chosen visuals and layout strategies not only grab attention but also make your message more impactful. Let’s delve into how to achieve this synergy:
1. Slide with complementary visuals
Utilize design elements like relevant images, charts, and infographics that reinforce your script’s message. For example, if you're discussing market growth, a well-designed graph can visually represent the data you're talking about, making complex information more accessible and engaging. The key is to choose visuals that directly support and enhance what you're saying.

2. Consistent theme
Maintaining a consistent design theme throughout your presentation helps in creating a visually cohesive experience and makes your brand image stronger. This includes consistent use of color schemes, fonts, and graphic styles that align with the tone and content of your presentation. A uniform theme not only looks professional but also helps in keeping the audience’s attention focused on your message.
3. Focus on readability
Ensure that any text on your visuals is clear and easy to comprehend. Overloading slides with text can overwhelm your audience. Instead, opt for key phrases or bullet points that complement your spoken words. The text should be large enough to be easily readable from a distance, and the color contrast should make it stand out against the background.

4. Balanced layout
Achieving a balance between visual elements and white space is crucial for a clean and effective slide design. A cluttered slide can distract and confuse your audience, while too much white space may lead to a lack of visual interest. Aim for a layout that emphasizes key elements, using white space to highlight important information without making the slide feel overcrowded.

Expert tips for great presentation speech
Delivering a strong presentation is more than just writing; it involves a nuanced blend of delivery techniques, audience interaction, and adaptability. Here are some expert tips presentation style:
1. Dynamic pacing
Varying the pace of your delivery keeps your audience engaged. For example, slow down during complex topics for better understanding, and speed up during familiar or lighter segments to maintain energy. This dynamic pacing ensures that important points are emphasized and the audience remains attentive throughout.
2. Feedback loop
Gathering feedback on your script and presentation style can offer invaluable insights. It’s like holding a mirror to your performance. Present it to a small group or a trusted colleague and solicit a honest feedback from your audience. Pay attention to their responses and suggestions - they can help you identify areas for improvement that you might not have noticed on your own.
3. Body language and voice modulation
Being conscious of your non-verbal cues and voice modulation can dramatically enhance the effectiveness of your delivery. Your body language should complement the tone of your message.
For instance, use open gestures for welcoming or inclusive points, and firmer gestures for strong, decisive statements. Similarly, modulate your voice to match the content - a softer tone for sensitive topics, or a stronger, more assertive tone for key arguments. This congruence between your words and your delivery makes your presentation more convincing and engaging.
4. Stay adaptable
Adaptability is crucial in presentations. Sometimes, despite all the planning, the audience's reaction may not be what you expected, or technical issues may arise. Be prepared to improvise your approach on the fly.
For instance, if a particular part of your presentation isn't resonating as expected, be ready to shift gears, perhaps by moving to an interactive Q&A earlier than planned.
Staying adaptable ensures that you maintain control of the presentation, no matter the circumstances.
What are the benefits of a good presentation script?
It enhances your ability to connect with the audience. It serves as a guide, ensuring that you deliver your message in a clear, engaging, and relatable way. When you have a well-crafted script, it's easier to explain complex topics in a way that's easy for everyone to understand. This not only keeps your audience attentive but also makes your presentation more memorable.
Additionally, as the presenter, you get confidence boost. Knowing that you have a solid foundation for your presentation helps reduce anxiety and allows you to focus on delivery. As a result, your message doesn't just get heard; it resonates with the audience, leaving them informed, inspired, and often impressed by the clarity and effectiveness of your communication.
How can Prezent help with great presentation scripts?
Prezent, the communication productivity platform for enterprise teams, can significantly enhance the process of writing and delivering presentation scripts in various ways:
1. Efficiency in slide creation: Prezent's AI capabilities streamline slide creation. With a library of over 35,000 slides , presenters can quickly find and customize them, allowing more time to focus on writing a script with great content and delivery.
2. Consistency and brand alignment: Prezent ensures that all slides adhere to brand guidelines , maintaining a professional and cohesive look throughout the presentation. This consistency is crucial for the visual elements.
3. Enhanced storytelling through visuals: The AI-driven slide creation tools in Prezent suggest visual storytelling elements relevant to the script. This enhances audience engagement and understanding, particularly when complex points need to be conveyed.
4. Best practice examples and learning: Prezent offers a feature of best practice examples – a curated collection of exemplary presentations. These examples showcase industry norms and creative approaches, providing valuable insights into effective presentation styles and structures.
5. Personalized insights with fingerprints: The ' Fingerprints ' feature in helps understand your and your audience's strengths, preferences, and areas for growth. This leads to personalized insights, enhancing communication skills and ensuring that the presentation resonates with the audience. Create your Fingerprint today !.
6. Adaptability to content: Prezent adapts slide design based on the script's content, suggesting appropriate charts for analytical sections or illustrative visuals for narrative parts, ensuring the slides are in perfect harmony.
7. Feedback and improvement suggestions: With its advanced AI capabilities, Prezent can offer feedback and improvement suggestions on both the content and design of the presentation, based on communication and design best practices.
Overall, Prezent acts as a comprehensive tool for enhancing presentation scripts, ensuring that the visual components effectively support and elevate the spoken content, while also offering insights and suggestions for continuous improvement. To see Prezent in action you can sign up for our free trial or book a demo today!
More zenpedia articles

Speak to their minds: Understand the psychology of the audience

The ultimate and effective presentation checklist: From planning to applause!

Best practices to create and deliver effective presentations
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
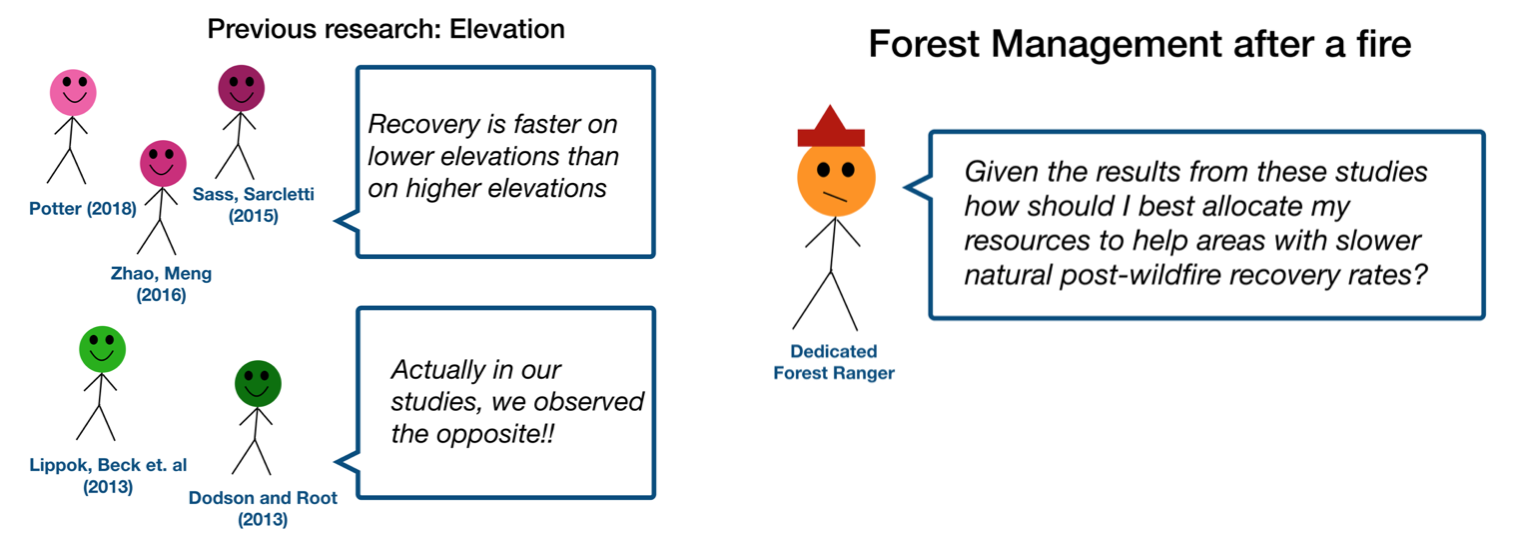
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation
How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation

Every research endeavor ends up with the communication of its findings. Graduate-level research culminates in a thesis defense , while many academic and scientific disciplines are published in peer-reviewed journals. In a business context, PowerPoint research presentation is the default format for reporting the findings to stakeholders.
Condensing months of work into a few slides can prove to be challenging. It requires particular skills to create and deliver a research presentation that promotes informed decisions and drives long-term projects forward.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Presentation
Key slides for creating a research presentation, tips when delivering a research presentation, how to present sources in a research presentation, recommended templates to create a research presentation.
A research presentation is the communication of research findings, typically delivered to an audience of peers, colleagues, students, or professionals. In the academe, it is meant to showcase the importance of the research paper , state the findings and the analysis of those findings, and seek feedback that could further the research.
The presentation of research becomes even more critical in the business world as the insights derived from it are the basis of strategic decisions of organizations. Information from this type of report can aid companies in maximizing the sales and profit of their business. Major projects such as research and development (R&D) in a new field, the launch of a new product or service, or even corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives will require the presentation of research findings to prove their feasibility.
Market research and technical research are examples of business-type research presentations you will commonly encounter.
In this article, we’ve compiled all the essential tips, including some examples and templates, to get you started with creating and delivering a stellar research presentation tailored specifically for the business context.
Various research suggests that the average attention span of adults during presentations is around 20 minutes, with a notable drop in an engagement at the 10-minute mark . Beyond that, you might see your audience doing other things.
How can you avoid such a mistake? The answer lies in the adage “keep it simple, stupid” or KISS. We don’t mean dumbing down your content but rather presenting it in a way that is easily digestible and accessible to your audience. One way you can do this is by organizing your research presentation using a clear structure.
Here are the slides you should prioritize when creating your research presentation PowerPoint.
1. Title Page
The title page is the first thing your audience will see during your presentation, so put extra effort into it to make an impression. Of course, writing presentation titles and title pages will vary depending on the type of presentation you are to deliver. In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include:
- The full title of the report
- The date of the report
- The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report
- The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended
When writing the title of your research presentation, it should reflect the topic and objective of the report. Focus only on the subject and avoid adding redundant phrases like “A research on” or “A study on.” However, you may use phrases like “Market Analysis” or “Feasibility Study” because they help identify the purpose of the presentation. Doing so also serves a long-term purpose for the filing and later retrieving of the document.
Here’s a sample title page for a hypothetical market research presentation from Gillette .

2. Executive Summary Slide
The executive summary marks the beginning of the body of the presentation, briefly summarizing the key discussion points of the research. Specifically, the summary may state the following:
- The purpose of the investigation and its significance within the organization’s goals
- The methods used for the investigation
- The major findings of the investigation
- The conclusions and recommendations after the investigation
Although the executive summary encompasses the entry of the research presentation, it should not dive into all the details of the work on which the findings, conclusions, and recommendations were based. Creating the executive summary requires a focus on clarity and brevity, especially when translating it to a PowerPoint document where space is limited.
Each point should be presented in a clear and visually engaging manner to capture the audience’s attention and set the stage for the rest of the presentation. Use visuals, bullet points, and minimal text to convey information efficiently.

3. Introduction/ Project Description Slides
In this section, your goal is to provide your audience with the information that will help them understand the details of the presentation. Provide a detailed description of the project, including its goals, objectives, scope, and methods for gathering and analyzing data.
You want to answer these fundamental questions:
- What specific questions are you trying to answer, problems you aim to solve, or opportunities you seek to explore?
- Why is this project important, and what prompted it?
- What are the boundaries of your research or initiative?
- How were the data gathered?
Important: The introduction should exclude specific findings, conclusions, and recommendations.

4. Data Presentation and Analyses Slides
This is the longest section of a research presentation, as you’ll present the data you’ve gathered and provide a thorough analysis of that data to draw meaningful conclusions. The format and components of this section can vary widely, tailored to the specific nature of your research.
For example, if you are doing market research, you may include the market potential estimate, competitor analysis, and pricing analysis. These elements will help your organization determine the actual viability of a market opportunity.
Visual aids like charts, graphs, tables, and diagrams are potent tools to convey your key findings effectively. These materials may be numbered and sequenced (Figure 1, Figure 2, and so forth), accompanied by text to make sense of the insights.

5. Conclusions
The conclusion of a research presentation is where you pull together the ideas derived from your data presentation and analyses in light of the purpose of the research. For example, if the objective is to assess the market of a new product, the conclusion should determine the requirements of the market in question and tell whether there is a product-market fit.
Designing your conclusion slide should be straightforward and focused on conveying the key takeaways from your research. Keep the text concise and to the point. Present it in bullet points or numbered lists to make the content easily scannable.

6. Recommendations
The findings of your research might reveal elements that may not align with your initial vision or expectations. These deviations are addressed in the recommendations section of your presentation, which outlines the best course of action based on the result of the research.
What emerging markets should we target next? Do we need to rethink our pricing strategies? Which professionals should we hire for this special project? — these are some of the questions that may arise when coming up with this part of the research.
Recommendations may be combined with the conclusion, but presenting them separately to reinforce their urgency. In the end, the decision-makers in the organization or your clients will make the final call on whether to accept or decline the recommendations.

7. Questions Slide
Members of your audience are not involved in carrying out your research activity, which means there’s a lot they don’t know about its details. By offering an opportunity for questions, you can invite them to bridge that gap, seek clarification, and engage in a dialogue that enhances their understanding.
If your research is more business-oriented, facilitating a question and answer after your presentation becomes imperative as it’s your final appeal to encourage buy-in for your recommendations.
A simple “Ask us anything” slide can indicate that you are ready to accept questions.
1. Focus on the Most Important Findings
The truth about presenting research findings is that your audience doesn’t need to know everything. Instead, they should receive a distilled, clear, and meaningful overview that focuses on the most critical aspects.
You will likely have to squeeze in the oral presentation of your research into a 10 to 20-minute presentation, so you have to make the most out of the time given to you. In the presentation, don’t soak in the less important elements like historical backgrounds. Decision-makers might even ask you to skip these portions and focus on sharing the findings.
2. Do Not Read Word-per-word
Reading word-for-word from your presentation slides intensifies the danger of losing your audience’s interest. Its effect can be detrimental, especially if the purpose of your research presentation is to gain approval from the audience. So, how can you avoid this mistake?
- Make a conscious design decision to keep the text on your slides minimal. Your slides should serve as visual cues to guide your presentation.
- Structure your presentation as a narrative or story. Stories are more engaging and memorable than dry, factual information.
- Prepare speaker notes with the key points of your research. Glance at it when needed.
- Engage with the audience by maintaining eye contact and asking rhetorical questions.
3. Don’t Go Without Handouts
Handouts are paper copies of your presentation slides that you distribute to your audience. They typically contain the summary of your key points, but they may also provide supplementary information supporting data presented through tables and graphs.
The purpose of distributing presentation handouts is to easily retain the key points you presented as they become good references in the future. Distributing handouts in advance allows your audience to review the material and come prepared with questions or points for discussion during the presentation.
4. Actively Listen
An equally important skill that a presenter must possess aside from speaking is the ability to listen. We are not just talking about listening to what the audience is saying but also considering their reactions and nonverbal cues. If you sense disinterest or confusion, you can adapt your approach on the fly to re-engage them.
For example, if some members of your audience are exchanging glances, they may be skeptical of the research findings you are presenting. This is the best time to reassure them of the validity of your data and provide a concise overview of how it came to be. You may also encourage them to seek clarification.
5. Be Confident
Anxiety can strike before a presentation – it’s a common reaction whenever someone has to speak in front of others. If you can’t eliminate your stress, try to manage it.
People hate public speaking not because they simply hate it. Most of the time, it arises from one’s belief in themselves. You don’t have to take our word for it. Take Maslow’s theory that says a threat to one’s self-esteem is a source of distress among an individual.
Now, how can you master this feeling? You’ve spent a lot of time on your research, so there is no question about your topic knowledge. Perhaps you just need to rehearse your research presentation. If you know what you will say and how to say it, you will gain confidence in presenting your work.
All sources you use in creating your research presentation should be given proper credit. The APA Style is the most widely used citation style in formal research.
In-text citation
Add references within the text of your presentation slide by giving the author’s last name, year of publication, and page number (if applicable) in parentheses after direct quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
The alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (Smith, 2020, p. 27).
If the author’s name and year of publication are mentioned in the text, add only the page number in parentheses after the quotations or paraphrased materials. As in:
According to Smith (2020), the alarming rate at which global temperatures rise directly impacts biodiversity (p. 27).
Image citation
All images from the web, including photos, graphs, and tables, used in your slides should be credited using the format below.
Creator’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Image.” Website Name, Day Mo. Year, URL. Accessed Day Mo. Year.
Work cited page
A work cited page or reference list should follow after the last slide of your presentation. The list should be alphabetized by the author’s last name and initials followed by the year of publication, the title of the book or article, the place of publication, and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. New York, NY: ABC Publications.
When citing a document from a website, add the source URL after the title of the book or article instead of the place of publication and the publisher. As in:
Smith, J. A. (2020). Climate Change and Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Study. Retrieved from https://www.smith.com/climate-change-and-biodiversity.
1. Research Project Presentation PowerPoint Template

A slide deck containing 18 different slides intended to take off the weight of how to make a research presentation. With tons of visual aids, presenters can reference existing research on similar projects to this one – or link another research presentation example – provide an accurate data analysis, disclose the methodology used, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Research Presentation Scientific Method Diagram PowerPoint Template

Whenever you intend to raise questions, expose the methodology you used for your research, or even suggest a scientific method approach for future analysis, this circular wheel diagram is a perfect fit for any presentation study.
Customize all of its elements to suit the demands of your presentation in just minutes.
3. Thesis Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

If your research presentation project belongs to academia, then this is the slide deck to pair that presentation. With a formal aesthetic and minimalistic style, this research presentation template focuses only on exposing your information as clearly as possible.
Use its included bar charts and graphs to introduce data, change the background of each slide to suit the topic of your presentation, and customize each of its elements to meet the requirements of your project with ease.
4. Animated Research Cards PowerPoint Template

Visualize ideas and their connection points with the help of this research card template for PowerPoint. This slide deck, for example, can help speakers talk about alternative concepts to what they are currently managing and its possible outcomes, among different other usages this versatile PPT template has. Zoom Animation effects make a smooth transition between cards (or ideas).
5. Research Presentation Slide Deck for PowerPoint

With a distinctive professional style, this research presentation PPT template helps business professionals and academics alike to introduce the findings of their work to team members or investors.
By accessing this template, you get the following slides:
- Introduction
- Problem Statement
- Research Questions
- Conceptual Research Framework (Concepts, Theories, Actors, & Constructs)
- Study design and methods
- Population & Sampling
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
Check it out today and craft a powerful research presentation out of it!
A successful research presentation in business is not just about presenting data; it’s about persuasion to take meaningful action. It’s the bridge that connects your research efforts to the strategic initiatives of your organization. To embark on this journey successfully, planning your presentation thoroughly is paramount, from designing your PowerPoint to the delivery.
Take a look and get inspiration from the sample research presentation slides above, put our tips to heart, and transform your research findings into a compelling call to action.

Like this article? Please share
Academics, Presentation Approaches, Research & Development Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Design • May 22nd, 2024
Exploring the 12 Different Types of Slides in PowerPoint
Become a better presenter by harnessing the power of the 12 different types of slides in presentation design.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.
Leave a Reply
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to make a scientific presentation

Scientific presentation outlines
Questions to ask yourself before you write your talk, 1. how much time do you have, 2. who will you speak to, 3. what do you want the audience to learn from your talk, step 1: outline your presentation, step 2: plan your presentation slides, step 3: make the presentation slides, slide design, text elements, animations and transitions, step 4: practice your presentation, final thoughts, frequently asked questions about preparing scientific presentations, related articles.
A good scientific presentation achieves three things: you communicate the science clearly, your research leaves a lasting impression on your audience, and you enhance your reputation as a scientist.
But, what is the best way to prepare for a scientific presentation? How do you start writing a talk? What details do you include, and what do you leave out?
It’s tempting to launch into making lots of slides. But, starting with the slides can mean you neglect the narrative of your presentation, resulting in an overly detailed, boring talk.
The key to making an engaging scientific presentation is to prepare the narrative of your talk before beginning to construct your presentation slides. Planning your talk will ensure that you tell a clear, compelling scientific story that will engage the audience.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to make a good oral scientific presentation, including:
- The different types of oral scientific presentations and how they are delivered;
- How to outline a scientific presentation;
- How to make slides for a scientific presentation.
Our advice results from delving into the literature on writing scientific talks and from our own experiences as scientists in giving and listening to presentations. We provide tips and best practices for giving scientific talks in a separate post.
There are two main types of scientific talks:
- Your talk focuses on a single study . Typically, you tell the story of a single scientific paper. This format is common for short talks at contributed sessions in conferences.
- Your talk describes multiple studies. You tell the story of multiple scientific papers. It is crucial to have a theme that unites the studies, for example, an overarching question or problem statement, with each study representing specific but different variations of the same theme. Typically, PhD defenses, invited seminars, lectures, or talks for a prospective employer (i.e., “job talks”) fall into this category.
➡️ Learn how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The length of time you are allotted for your talk will determine whether you will discuss a single study or multiple studies, and which details to include in your story.
The background and interests of your audience will determine the narrative direction of your talk, and what devices you will use to get their attention. Will you be speaking to people specializing in your field, or will the audience also contain people from disciplines other than your own? To reach non-specialists, you will need to discuss the broader implications of your study outside your field.
The needs of the audience will also determine what technical details you will include, and the language you will use. For example, an undergraduate audience will have different needs than an audience of seasoned academics. Students will require a more comprehensive overview of background information and explanations of jargon but will need less technical methodological details.
Your goal is to speak to the majority. But, make your talk accessible to the least knowledgeable person in the room.
This is called the thesis statement, or simply the “take-home message”. Having listened to your talk, what message do you want the audience to take away from your presentation? Describe the main idea in one or two sentences. You want this theme to be present throughout your presentation. Again, the thesis statement will depend on the audience and the type of talk you are giving.
Your thesis statement will drive the narrative for your talk. By deciding the take-home message you want to convince the audience of as a result of listening to your talk, you decide how the story of your talk will flow and how you will navigate its twists and turns. The thesis statement tells you the results you need to show, which subsequently tells you the methods or studies you need to describe, which decides the angle you take in your introduction.
➡️ Learn how to write a thesis statement
The goal of your talk is that the audience leaves afterward with a clear understanding of the key take-away message of your research. To achieve that goal, you need to tell a coherent, logical story that conveys your thesis statement throughout the presentation. You can tell your story through careful preparation of your talk.
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient.
Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
- Outline your presentation
- Plan your presentation slides
- Make the presentation slides
- Practice your presentation

Writing an outline helps you consider the key pieces of your talk and how they fit together from the beginning, preventing you from forgetting any important details. It also means you avoid changing the order of your slides multiple times, saving you time.
Plan your talk as discrete sections. In the table below, we describe the sections for a single study talk vs. a talk discussing multiple studies:
The following tips apply when writing the outline of a single study talk. You can easily adapt this framework if you are writing a talk discussing multiple studies.
Introduction: Writing the introduction can be the hardest part of writing a talk. And when giving it, it’s the point where you might be at your most nervous. But preparing a good, concise introduction will settle your nerves.
The introduction tells the audience the story of why you studied your topic. A good introduction succinctly achieves four things, in the following order.
- It gives a broad perspective on the problem or topic for people in the audience who may be outside your discipline (i.e., it explains the big-picture problem motivating your study).
- It describes why you did the study, and why the audience should care.
- It gives a brief indication of how your study addressed the problem and provides the necessary background information that the audience needs to understand your work.
- It indicates what the audience will learn from the talk, and prepares them for what will come next.
A good introduction not only gives the big picture and motivations behind your study but also concisely sets the stage for what the audience will learn from the talk (e.g., the questions your work answers, and/or the hypotheses that your work tests). The end of the introduction will lead to a natural transition to the methods.
Give a broad perspective on the problem. The easiest way to start with the big picture is to think of a hook for the first slide of your presentation. A hook is an opening that gets the audience’s attention and gets them interested in your story. In science, this might take the form of a why, or a how question, or it could be a statement about a major problem or open question in your field. Other examples of hooks include quotes, short anecdotes, or interesting statistics.
Why should the audience care? Next, decide on the angle you are going to take on your hook that links to the thesis of your talk. In other words, you need to set the context, i.e., explain why the audience should care. For example, you may introduce an observation from nature, a pattern in experimental data, or a theory that you want to test. The audience must understand your motivations for the study.
Supplementary details. Once you have established the hook and angle, you need to include supplementary details to support them. For example, you might state your hypothesis. Then go into previous work and the current state of knowledge. Include citations of these studies. If you need to introduce some technical methodological details, theory, or jargon, do it here.
Conclude your introduction. The motivation for the work and background information should set the stage for the conclusion of the introduction, where you describe the goals of your study, and any hypotheses or predictions. Let the audience know what they are going to learn.
Methods: The audience will use your description of the methods to assess the approach you took in your study and to decide whether your findings are credible. Tell the story of your methods in chronological order. Use visuals to describe your methods as much as possible. If you have equations, make sure to take the time to explain them. Decide what methods to include and how you will show them. You need enough detail so that your audience will understand what you did and therefore can evaluate your approach, but avoid including superfluous details that do not support your main idea. You want to avoid the common mistake of including too much data, as the audience can read the paper(s) later.
Results: This is the evidence you present for your thesis. The audience will use the results to evaluate the support for your main idea. Choose the most important and interesting results—those that support your thesis. You don’t need to present all the results from your study (indeed, you most likely won’t have time to present them all). Break down complex results into digestible pieces, e.g., comparisons over multiple slides (more tips in the next section).
Summary: Summarize your main findings. Displaying your main findings through visuals can be effective. Emphasize the new contributions to scientific knowledge that your work makes.
Conclusion: Complete the circle by relating your conclusions to the big picture topic in your introduction—and your hook, if possible. It’s important to describe any alternative explanations for your findings. You might also speculate on future directions arising from your research. The slides that comprise your conclusion do not need to state “conclusion”. Rather, the concluding slide title should be a declarative sentence linking back to the big picture problem and your main idea.
It’s important to end well by planning a strong closure to your talk, after which you will thank the audience. Your closing statement should relate to your thesis, perhaps by stating it differently or memorably. Avoid ending awkwardly by memorizing your closing sentence.
By now, you have an outline of the story of your talk, which you can use to plan your slides. Your slides should complement and enhance what you will say. Use the following steps to prepare your slides.
- Write the slide titles to match your talk outline. These should be clear and informative declarative sentences that succinctly give the main idea of the slide (e.g., don’t use “Methods” as a slide title). Have one major idea per slide. In a YouTube talk on designing effective slides , researcher Michael Alley shows examples of instructive slide titles.
- Decide how you will convey the main idea of the slide (e.g., what figures, photographs, equations, statistics, references, or other elements you will need). The body of the slide should support the slide’s main idea.
- Under each slide title, outline what you want to say, in bullet points.
In sum, for each slide, prepare a title that summarizes its major idea, a list of visual elements, and a summary of the points you will make. Ensure each slide connects to your thesis. If it doesn’t, then you don’t need the slide.
Slides for scientific presentations have three major components: text (including labels and legends), graphics, and equations. Here, we give tips on how to present each of these components.
- Have an informative title slide. Include the names of all coauthors and their affiliations. Include an attractive image relating to your study.
- Make the foreground content of your slides “pop” by using an appropriate background. Slides that have white backgrounds with black text work well for small rooms, whereas slides with black backgrounds and white text are suitable for large rooms.
- The layout of your slides should be simple. Pay attention to how and where you lay the visual and text elements on each slide. It’s tempting to cram information, but you need lots of empty space. Retain space at the sides and bottom of your slides.
- Use sans serif fonts with a font size of at least 20 for text, and up to 40 for slide titles. Citations can be in 14 font and should be included at the bottom of the slide.
- Use bold or italics to emphasize words, not underlines or caps. Keep these effects to a minimum.
- Use concise text . You don’t need full sentences. Convey the essence of your message in as few words as possible. Write down what you’d like to say, and then shorten it for the slide. Remove unnecessary filler words.
- Text blocks should be limited to two lines. This will prevent you from crowding too much information on the slide.
- Include names of technical terms in your talk slides, especially if they are not familiar to everyone in the audience.
- Proofread your slides. Typos and grammatical errors are distracting for your audience.
- Include citations for the hypotheses or observations of other scientists.
- Good figures and graphics are essential to sustain audience interest. Use graphics and photographs to show the experiment or study system in action and to explain abstract concepts.
- Don’t use figures straight from your paper as they may be too detailed for your talk, and details like axes may be too small. Make new versions if necessary. Make them large enough to be visible from the back of the room.
- Use graphs to show your results, not tables. Tables are difficult for your audience to digest! If you must present a table, keep it simple.
- Label the axes of graphs and indicate the units. Label important components of graphics and photographs and include captions. Include sources for graphics that are not your own.
- Explain all the elements of a graph. This includes the axes, what the colors and markers mean, and patterns in the data.
- Use colors in figures and text in a meaningful, not random, way. For example, contrasting colors can be effective for pointing out comparisons and/or differences. Don’t use neon colors or pastels.
- Use thick lines in figures, and use color to create contrasts in the figures you present. Don’t use red/green or red/blue combinations, as color-blind audience members can’t distinguish between them.
- Arrows or circles can be effective for drawing attention to key details in graphs and equations. Add some text annotations along with them.
- Write your summary and conclusion slides using graphics, rather than showing a slide with a list of bullet points. Showing some of your results again can be helpful to remind the audience of your message.
- If your talk has equations, take time to explain them. Include text boxes to explain variables and mathematical terms, and put them under each term in the equation.
- Combine equations with a graphic that shows the scientific principle, or include a diagram of the mathematical model.
- Use animations judiciously. They are helpful to reveal complex ideas gradually, for example, if you need to make a comparison or contrast or to build a complicated argument or figure. For lists, reveal one bullet point at a time. New ideas appearing sequentially will help your audience follow your logic.
- Slide transitions should be simple. Silly ones distract from your message.
- Decide how you will make the transition as you move from one section of your talk to the next. For example, if you spend time talking through details, provide a summary afterward, especially in a long talk. Another common tactic is to have a “home slide” that you return to multiple times during the talk that reinforces your main idea or message. In her YouTube talk on designing effective scientific presentations , Stanford biologist Susan McConnell suggests using the approach of home slides to build a cohesive narrative.
To deliver a polished presentation, it is essential to practice it. Here are some tips.
- For your first run-through, practice alone. Pay attention to your narrative. Does your story flow naturally? Do you know how you will start and end? Are there any awkward transitions? Do animations help you tell your story? Do your slides help to convey what you are saying or are they missing components?
- Next, practice in front of your advisor, and/or your peers (e.g., your lab group). Ask someone to time your talk. Take note of their feedback and the questions that they ask you (you might be asked similar questions during your real talk).
- Edit your talk, taking into account the feedback you’ve received. Eliminate superfluous slides that don’t contribute to your takeaway message.
- Practice as many times as needed to memorize the order of your slides and the key transition points of your talk. However, don’t try to learn your talk word for word. Instead, memorize opening and closing statements, and sentences at key junctures in the presentation. Your presentation should resemble a serious but spontaneous conversation with the audience.
- Practicing multiple times also helps you hone the delivery of your talk. While rehearsing, pay attention to your vocal intonations and speed. Make sure to take pauses while you speak, and make eye contact with your imaginary audience.
- Make sure your talk finishes within the allotted time, and remember to leave time for questions. Conferences are particularly strict on run time.
- Anticipate questions and challenges from the audience, and clarify ambiguities within your slides and/or speech in response.
- If you anticipate that you could be asked questions about details but you don’t have time to include them, or they detract from the main message of your talk, you can prepare slides that address these questions and place them after the final slide of your talk.
➡️ More tips for giving scientific presentations
An organized presentation with a clear narrative will help you communicate your ideas effectively, which is essential for engaging your audience and conveying the importance of your work. Taking time to plan and outline your scientific presentation before writing the slides will help you manage your nerves and feel more confident during the presentation, which will improve your overall performance.
A good scientific presentation has an engaging scientific narrative with a memorable take-home message. It has clear, informative slides that enhance what the speaker says. You need to practice your talk many times to ensure you deliver a polished presentation.
First, consider who will attend your presentation, and what you want the audience to learn about your research. Tailor your content to their level of knowledge and interests. Second, create an outline for your presentation, including the key points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support those points. Finally, practice your presentation several times to ensure that it flows smoothly and that you are comfortable with the material.
Prepare an opening that immediately gets the audience’s attention. A common device is a why or a how question, or a statement of a major open problem in your field, but you could also start with a quote, interesting statistic, or case study from your field.
Scientific presentations typically either focus on a single study (e.g., a 15-minute conference presentation) or tell the story of multiple studies (e.g., a PhD defense or 50-minute conference keynote talk). For a single study talk, the structure follows the scientific paper format: Introduction, Methods, Results, Summary, and Conclusion, whereas the format of a talk discussing multiple studies is more complex, but a theme unifies the studies.
Ensure you have one major idea per slide, and convey that idea clearly (through images, equations, statistics, citations, video, etc.). The slide should include a title that summarizes the major point of the slide, should not contain too much text or too many graphics, and color should be used meaningfully.

- Program Design
- Peer Mentors
- Excelling in Graduate School
- Oral Communication
- Written communication
- About Climb
Creating a 10-15 Minute Scientific Presentation
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation
Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions
Two additional videos should prove useful:
Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation walks you through the key principles in designing powerful, easy to read slides.
Delivering a Presentation provides tips and approaches to help you put your best foot forward when you stand up in front of a group.
Other resources include:
Quick Links
Northwestern bioscience programs.
- Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Chemical and Biological Engineering (ChBE)
- Driskill Graduate Program in the Life Sciences (DGP)
- Interdepartmental Biological Sciences (IBiS)
- Northwestern University Interdepartmental Neuroscience (NUIN)
- Campus Emergency Information
- Contact Northwestern University
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- University Policies
- Northwestern Home
- Northwestern Calendar: PlanIt Purple
- Northwestern Search
Chicago: 420 East Superior Street, Rubloff 6-644, Chicago, IL 60611 312-503-8286
Newly Launched - World's Most Advanced AI Powered Platform to Generate Stunning Presentations that are Editable in PowerPoint

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Research Presentation Templates with Examples and Samples

Simran Shekhawat
Research organizes all your thoughts, suggestions, findings and innovations in one area that postulates to determining the future applicability. A crucial part of strategic planning is research. It aids organizations in goal setting, decision-making, and resource allocation. Research allows us to uncover and discover many segments of society by establishing facts and generating data that effectively determine future outcomes and progress.
Here's an ultimate guide to conduct market research! Click to know more!
Research primarily comprises gathering and analysing information about consumer behaviour, industry dynamics, economic conditions, and other elements that affect how markets and businesses behave in the context of understanding market trends. Understanding market trends requires market research, which is likely to be successful. Research can reveal prospective market dangers and difficulties, enabling organizations to create backup plans and decide on market entry or expansion with more excellent knowledge. By understanding market trends, businesses can create marketing and advertising efforts that resonate with their target audience.
Learn about product market research templates. Click here .
Additionally, it aids in determining the best customer-reach methods. Businesses can better satisfy market demands by customizing their products or services by studying consumer behaviours, preferences, and feedback. Assessing Market Size and Potential research can shed light on a market's size, potential for expansion, and competitive environment. Businesses aiming to expand or enter new markets need to know this information.
SlideTeam introduces you with their newly launch research templates that has been extensively built to enhance the quality of company’s research and development area by forging to bring answers related to every ‘how’ and ‘why’. The sole purpose of these is to inform, gather information and contributes towards the development and knowledge about the field of study. These templates are professionally design to disseminate knowledge to provide better judgements.
Template 1: Clinical Research Trial PowerPoint Template

Use this premium PPT template to captivate your audience. Download this well-created template to raise your presenting threshold. Establish your milestones with workflows designed to ease the overburdening of tasks. State clear-cut objectives to specify your aim and deliver a timeline. Use these 58-page PowerPoint slides to launch your product success and deliver a presentation that awakes the audience with your research performance and goals.
Click here!

Template 2: Company Stock Analysis and Equity Research Report Slide

Uncover impacts about the stock markets and analyze company-related specific and general equity design using this ready-made template. Understanding the technicality of maintenance and presentation of stocks and equity research, we at SlideTeam have designed an equity research PowerPoint slide to ease your presentation load. This presentation aims to analyze the target company's financial performance, ratios, and financial model to welcome investment in the company. Provide an extensive company summary, income statement, balance sheet, vertical and horizontal analysis, organization shareholding structure, SWOT analysis, and share price performance throughout history through this template.
Download Now!
Template 3: IT Services Research and Development Template

Showcase the power of your company's services, expertise achievement and future goals using this PPT template. This PPT slide provides you with a summary, key statistics, targets, and overview of your IT service Company. Allow this template to lay out values mission, categorize solutions, and enlist a range of services provided along with expenditure incurred on Research development. The deck also includes a business model canvas that depicts the company's historical development, global reach, management team, organizational structure, employee breakdown, and ownership structure.
Template 4: Research Proposal Steps PowerPoint Template

If you are looking to learn how to draft a research proposal, this slide is the ultimate fit for a newbie to comprehend about - 'what', 'where', and 'how' of research. Download this slide to learn about the format and structure of the research proposal. Use this template to illustrate the goal of the research proposal. Furthermore, our PPT sample file aids in instructing students on how to write a research proposal. Furthermore, you may quickly persuade the audience about the proposal's limitations, objectives, and research gap.
Template 5: Research Proposal for Thesis Template

Provide a clear idea and concise summary of your research with the help of this premium template. A well-written thesis statement frequently paves the way for discussion and debate. It can be the foundation for academic dialogue, enabling others to interact with and challenge your ideas—essential for developing knowledge across all disciplines. Your thesis statement will determine the depth of your study and conclusion while enabling you to attract your targeted audience.
Template 6: Market Research PowerPoint Template

To understand the trends and techniques of market structure, companies need to be aware of the trends and to enable that, and market research is one such profitable asset to invest in to allow numerous investments from companies across. Use this template to highlight the key drivers of growth that define the ultimate indicators of market trends. Use this PPT slide to solve marketing issues and make company decisions, incorporating polished business analysis PPT visuals. Get this template to connect business operations with your company's strategic goals.
Template 7: Establish Research Objective Template

For an effective and meaningful research, clarity is essential. Deploy this template to facilitate that research objectives should specify the precise goals and targets of the study to assist in limiting its scope. To ensure the study's readability and comprehensibility, SlideTeam has crafted a flowchart template design to help you elucidate the study's objective, providing a basis for measuring and evaluating the success of well-defined research. Define and design your research with the help of this four-stage design pattern.
Template 8: A Company Research Venn Chart Presentation
Establish relationships between the sets and groups of data while comparing and contrasting the company's research analysis. This template is helpful as it helps to understand the abstract, objectives, limitations, methodologies, research gap, etc., of the research effectively while focusing on postulating future recommendations and suggestions.
Template 9: Sample Research Paper Outline in a One-Pager Summary Presentation

How effortless it is to study a research paper without turning several pages? Grab this PPT template to research any topic and jot down your findings in a simple and concise format. Most importantly, a significant amount of their precious time can now be dedicated to critical tasks, aiding them in accelerating the research process. This incredibly well-curated one-pager template includes information about the introduction, problem, literature review, suggestions, and conclusions.
Template 10: Big Data Analytics Market Research Template
Deploy this template to introduce your company's extensive data analysis to understand the industry landscape, identify objectives, and make informed business decisions. Use this template slide to determine the current market size and growth rate. Consider the variables influencing this expansion, such as the rising volume of data produced and the demand for data-driven insights. Give information about the big data analysis market's prospects for the future. Over the coming few years, forecast growth trajectories, rising technologies, and market dynamics. Recognize the intended client base's demographics. Summarize your research and include suggestions for companies wishing to enter or grow in the big data analysis market.
PS: Provide an extensive statistical analysis for your research with this template. Check out now!
Refine your Research with SlideTeam.
SlideTeam introduces to its extensively built research templates that not only refines your search capability but also contributes towards the authenticity and development of your organization. It helps you to uncover veils of possibilities of growth while determining the bottlenecks and deriving appropriate solutions for future deliverables.
One of the attractive features about SlideTeam’s template are they are 100% customisable and editable as per the needs.
Download now!
PS: Provide an extensive statistical analysis for your research with this template . Check out now!
FAQs on Research Presentation
What is a research presentation.
Research Presentation is a visual representation of an individual or a team's observational findings or invocation in a particular subject.
What are the steps in research presentation?
To effectively convey your research findings to your audience, various phases are involved in creating a research presentation. Whether you're giving a presentation at a conference or a business meeting,
- Define your audience - Identify your audience's interests and level of knowledge. Make sure to adjust your presentation to fit their wants and needs.
- Outline What You Present - Create a clear structure with an introduction, three main ideas, and a conclusion. Choose the most essential points you want your audience to remember.
- Research and Data Collection - Gather and arrange the pertinent information, facts, and proof. Make sure your sources are reliable and current.
- Develop Visuals - To improve understanding, create visual aids like slides, charts, graphs, and photographs. Keep visuals straightforward, clutter-free, and with a distinct visual hierarchy.
- Get Your Audience Active - Take advantage of storytelling, anecdotes, or pertinent instances to draw in your audience. If appropriate, encourage audience participation and questions during the lecture.
- Present your argument - Start with a compelling introduction. Follow your outline while ensuring a logical and obvious flow.
- Keep an open line of communication, communicate clearly, and change your tone and pace. Improve your communication by making gestures and using body language. Respond to comments and questions as they come up or after the presentation.
- Recap and Draw a Conclusion - Summarize the core ideas and principal conclusions. Reiterate the importance of your study and its consequences.
How do you research a topic for a presentation?
To begin with, the idea of research presentation, choosing topics that align with your expertise and knowledge is the first and foremost. After understanding the topic, collect core factual and empirical data for proper understanding. After gauging information, it creates a place for every subtopic that must be introduced.
Related posts:
- Must-have Business Analyst Resume Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 10 Data Processing Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Data Mapping Document Templates with Samples and Examples
- Must-have Power BI Templates with Samples and Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Business Model Templates with Samples and Examples
Top 7 Introduction Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 April, 2024 • 11 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation
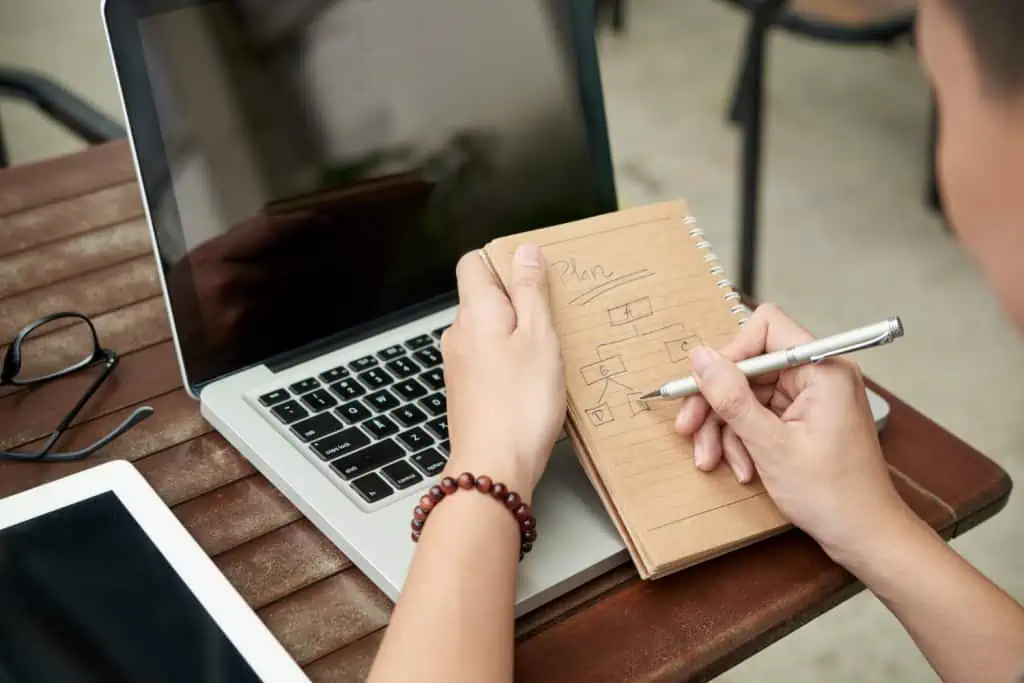

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?” Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?” Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….” Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….” Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

- Slidesgo School
- Presentation Tips
How to Start a Thesis Defense Presentation

After months and years of hard work, the moment to wrap things all up is finally here—your thesis defense presentation.
Whether you’re pursuing a master’s degree or doctorate, it’s the final step to that much-deserved achievement.
A thesis defense requires a lot of prior research and preparation. And as important as its content is, so is how you present it because a stunning design with clear data and text hierarchy plays an immense role in comprehension.
In this article, we’ll explore how you make your thesis defense .
The organization is the key to success. Establishing some previous steps before any project or work is essential for the result to be very positive. And the defense of a thesis could not be less.
Below, we will develop all the necessary steps to make a thesis defense presentation and we will give you some tips on how to carry them out.
How to Make an Amazing Presentation
Defining the concept of your thesis presentation, structuring your thesis defense presentation, how do you welcome the audience, tell them why you did this thesis, go into the content by explaining your thesis part by part, how to end the defense of the thesis.
After a long time of research and study, the content of your thesis is ready. Now, you have to find the best way to reflect all that effort behind your work. The information comes across more clearly if you use a visual format, as it attracts the attention of the audience. To present your thesis information in a clear, concise, and ultimately amazing way, you can use one of our unique thesis defense templates , available at Slidesgo.
As an example, in this article, we are going to use the Ecology Thesis template . With it, we will show you what to include in your presentation and how to make an attractive design.
After choosing the Google Slides and PowerPoint template that best suits the needs and subject matter of your thesis, it is time to define an overarching concept.
This is the main theme on which your designs are based. It must be relevant to your thesis as its purpose is to guide your selection of colors, typography, images, style, etc.
These must be portrayed in a way that supports the main message of your slides and should be aligned with your concept both visually and sociologically.
Once you have defined the concept, you will have to move on to the next step: structuring the content of your thesis. A good structure will show that there is a good organization behind the work, but most importantly: it will highlight your content.
In this article, we are going to show you a structure that could be a good example of how to structure a thesis, but you can adapt it to what your specific content requires.
Before you begin your thesis defense, you should welcome your audience. A good presentation will make you connect with your audience, which will result in more general interest in your work.
Use an appropriate language register (avoid informal language), but be approachable and natural.
"Welcome to the thesis defense on [the title of your thesis]". Next, introduce yourself with your name and give a short description of your background and occupation.
Don't forget to say “thank you for attending!”
To continue establishing that connection with your audience, explain the reasons that led you to do this thesis. Tell the professional reasons, and you can even say some personal ones, which will denote closeness, and your audience will appreciate it.
Now it's time to go into the content of the thesis ! After these preliminary steps, which are just as important as the thesis itself, it is time to explain part by part the structure (which you had previously established). We are going to propose a structure for your project, but the final decision is always yours!

First impressions are very important. Because your title page is the very first thing viewers see, it must be striking and impactful. It also sets the stage for the rest of your slides.
In one glance, the following should be established:
- Thesis defense topic
- Design style
For instance, the ecology thesis’s title page uses illustrations of a natural landscape to represent the topic of nature and a striking shade of blue to set the tone.
The sans serif font used depicts clean-cut typography and style and the thesis topic is written in large and bold typography, which draws attention to it immediately.
.jpg)
Right after your title page, include an introduction slide to provide more details about your topic.
This means explaining what you hope to answer with your research, its importance to your field, and why you chose it.
Continue to incorporate design elements relevant to your concept. This example has done just that by using a different natural landscape and including animals. For coherence, stick to the same typography and style throughout your presentation.
.jpg)
The aim of the literature review slide is to illustrate your knowledge of your thesis topic and any relevant theories.
Walls of text kill a design. For clarity, we recommend presenting this with bullet points. Each one should be short and sweet and only touch on the basics; you can elaborate on them in your speech.
Don’t forget to be consistent with your design. In our example, we’ve maintained the tone of blue chosen and added illustrations of leaves in the far corners of the slide.
Also, address similar research that has been done. This is to showcase your topic’s originality and, if relevant, how it’s different and/or an improvement from previously done research.
.jpg)
This is one of the most important parts of a thesis defense presentation.
It allows your viewers to assess the rationality and validity of your approach and consequently, the accuracy of your results.
A great methodology slide explains the what , how, and why :
- What method did you use for your research
- Why did you choose it
- How did you conduct it
Because this part of your thesis will be rather technical, the most effective way to aid understanding is by using graphics like charts and tables.
.jpg)
Keep text to a minimum to avoid drawing attention away from the graphics. If there is a text that must absolutely be included, consider using bullet points and keep them short.
Don’t forget to maintain color, style, and typography coherence.
.jpg)
The results slides are easily the most quantitative part of a thesis defense.
Here, your aim is to simply introduce your findings. Select the most impactful data and highlight them here.
Just as with methodology, use graphics like charts, tables, and graphs to portray the data in a clear way. And, once again, try not to write too much text. Let the visual content do the talking .
.jpg)
After you’ve introduced your data, the next step would be to help your audience make sense of it. That means understanding what it means in the context of your thesis research topic and your discipline.
Simply put, you should answer the question: What do the numbers mean?
The best way to approach this would be to do it as if you were creating an infographic .
Illustrations like icons are a quick and simple way to represent your message. It also reduces the amount of text on your slide, which makes the information much more digestible.
For a balanced thesis presentation, you should also address any outliers and anomalies.
To quote bestselling author Robin Sharma, “Starting strong is good. Finishing strong is epic.”
That’s exactly what to aim for in your conclusion.
Provide an overview of your thesis topic and remind your audience what you set out to answer with your research. In our example, we’ve used three icons accompanied by a short title and text.
.jpg)
Following that, reiterate the important points of your research results you want your audience to take away from your thesis defense presentation.
You can do so by expanding the next slide to have more icons and points, for example.
.jpg)
Don’t forget to address any shortcomings and limitations in your approach and extra points for suggesting possible improvements for future research.
We are going to give you a little tip to make your thesis defense a success. You can combine your defense with good public speaking techniques. Take a look at our article "How to become a great speaker" .
We hope this article has been of great help, have you already seen our templates to make the presentation of your thesis ? Choose the one that best suits your needs, we are sure that one of them will go perfectly with your thesis presentation!
Good luck from Slidesgo.

Do you find this article useful?
Related tutorials.

Slidesgo for Education: How to use it being a school district
Education is always on the move, and the integration of technology into classrooms is revolutionizing the way we teach and learn. In this way, Slidesgo has come in handy for teachers worldwide, but… did you know we have more than just slides? Now is your chance to redefine the educational scene in your school district. However, to do so, a flashy presentation alone won’t cut it—you need the right approach and the proper set of tools to truly change the way educators and students connect. By streamlining teaching and ramping up engagement, you can make a real, tangible difference. Let’s explore how Slidesgo for Education can inspire and...

Lesson plan generator: AI-mazing classes that empower minds
Teaching is an art, but even the most creative educators need a little help streamlining their planning. With just 24 hours in a day, it often feels like we need days with 37 hours to get everything done. That’s where we at Slidesgo come in, tackling this issue head-on and developing a practical, simple, and—most importantly—fast solution for educators.Our brand-new AI lesson plan generator is not just another digital tool; it’s your new teaching assistant that will transform your lesson planning process. With just a few details—your lesson topic, classroom level, and setting—you’ll get within seconds a fully formed lesson plan tailored to engage...

Why do you need Slidesgo if you are a student?
Being a student can be a bit tough— juggling deadlines to absorbing heaps of new information, students face many challenges on a daily basis.Fortunately, technology has tackled some of the most time-consuming aspects of learning, giving students room to develop complex skills. Even if traditional education is still catching up with some of these advancements, students are finding and using helpful educational tools to streamline their study routines.Slidesgo is one of these tools, making the learning experience more rewarding. Let’s find out why!

Entrepreneurship and Personal Development Hackathon: The magic of learning by doing
The new generations show us that the way of learning has completely changed. Now more than ever, it is key to encourage and support the development of social and entrepreneurial skills in children so that they can become more actively involved in their learning. Participating in creative projects and collaborative activities allows them to explore and learn on their own about topics that interest them, solve their problems with more autonomy, and work better in teams.This idea was the motivation behind the Junior Entrepreneurship and Personal Development Hackathon organized by Slidesgo in collaboration with Genyus School. At this event, more than 150 children had...
Sample Presentation Script
This section provides a sample script for delivering a half-day to full-day presentation covering all of the topics listed in the outline. Tailor the script to your chosen program length, content and audience.
Presentation Outline
Introduction
- Success stories
- Legal issues
- Definitions and statistics
General Library Access
- Building and physical environment
Adaptive Technology
- Hearing and speech impairments
- Specific learning disabilities
- Mobility impairments
- Health impairments
- Beginning the process of planning for adaptive technology
- Getting started: a list of adaptive technology devices
Electronic Resources
- Universal design principles
- General page design
- Graphical features
- Special features
- Web pages test
Distribute handouts .
- Making Library Resources Accessible to People with Disabilities
- Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
- Meet the Speakers in the Videotape: Working Together: People with Disabilities and Computer Technology
- World Wide Access: Accessible Web Design
- Meet the Speakers in the Videotape: World Wide Access
Put up overhead transparency.
Universal Access: Electronic Information in Libraries
I'm here today to share with you information and issues related to people with disabilities, electronic resources, and libraries.
Put up overhead transparency .
Recent advances in adaptive computer technology, greater reliance on computers, and increased availability and networking of electronic information resources have resulted in life-changing opportunities for many people with disabilities. In combination, these technologies provide many people with disabilities better access to education, careers, and other life experiences.
Libraries play an important role in ensuring equitable access to information for all members of our society. In addition, federal legislation mandates that public institutions, including libraries, provide accommodations for people with disabilities so that they can utilize the same services and resources as other people.
What are some of the electronic resources currently in your library?
Presenter Note: Solicit audience input to list items such as CD-ROM encyclopedias and indexes, online catalogs, WWW pages, and full-text databases.
The information covered in this presentation will provide you with tools and insights that will help ensure that these electronic resources are accessible to the broadest audience. As an extra benefit, you will find that being sensitive to the needs of people with disabilities can often make access easier for everyone.
Program Outline
- Legal issues statistics
- General library access
- Adaptive technology
- Electronic resources
Our program today will cover these five topics. To begin I will share some success stories or examples of the impact that adaptive technology for computers and electronic resources has had for people with disabilities. Then we will consider the most important legislative directives on the issue and look at some statistics about people with disabilities. We will then consider the bigger picture of access to libraries and library services for people with disabilities. With that background, a videotape presentation and discussion of adaptive technology for computers will bring our focus to electronic resources in libraries. The last segment of the program will include the second videotape presentation and a discussion of universal design of electronic resources applied to the development of World Wide Web pages.
Today's presentation will help you understand the impact of these technologies for people with disabilities while giving you the tools to begin implementing them in your library. Your packet of handouts is one of the tools that will help you apply the ideas presented. Let's walk through it.
The following handouts are in your packet.
Much of the information presented today is provided in these handouts. I will let you know which handout covers the information we are focusing on as we go through the presentation. Keep the handouts handy to save from taking duplicative notes.
Success Stories
I'm going to start out today by sharing with you a few stories of people with disabilities who are able to access information resources thanks to the availability of adaptive technology and accessible electronic resources. You'll meet them in the videotape we'll view shortly.
- Ben cannot use his hands, but muscular dystrophy doesn't interfere with his use of the Internet; he uses a voice input program that allows him to talk his way through the Net - six hours a day!
- Sarah uses her library's online catalog and the Internet to research and write papers for school. Her learning disability makes it difficult for her to read so she uses a speech output system to read the screen.
- Anna is blind. She uses a screen reader and speech output system to access her library's full-text databases and CD-ROMs. Her system works well until she runs into programs not designed according to universal design principles.
- Shane surfs the Net with a small tube in his mouth. The computer obeys his every command as he inputs Morse code - sip for a dot, puff for a dash. His cerebral palsy is only a minor inconvenience as he researches information on his special interest, naval communication.
- Sherri is legally blind, but has enough sight to use enlarged screen images as she uses governmental resources on the World Wide Web in pursuing her master's degree in public administration.
- Katie is hearing impaired. She often uses a sign language interpreter. On the Internet, however, Katie communicates with the reference librarian quickly and easily through electronic mail.
These stories provide examples of people with disabilities who are successfully pursuing avocations, education, and careers thanks to adaptive technology and electronic resources. During our presentation today, we will be learning how to ensure that there will be many more success stories like these for people with disabilities.
Legal Issues
According to Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (504) and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA), "no otherwise qualified individual with a disability shall, solely by reason of his/her disability, be excluded from the participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity of a public entity." Footnote 1
The ADA and the regulations promulgated to implement it have stressed that people with disabilities should be provided the same services as others, unless this would be less effective. The Department of Justice has stated that "Integration is fundamental to the purpose of the American with Disabilities Act." If accommodation, or an adjustment is needed to make a resource, program or facility accessible to a person with a disability, the individual's preference of accommodation must be given primary consideration. Footnote 2
In short, libraries must assure that people with disabilities can participate in library programs and utilize library resources as independently as possible. And this includes electronic information resources. As legal questions about the implications of the ADA for access to electronic information resources are tested, libraries are being required to provide access to these services.
According to decisions in recent cases on access to electronic resources, libraries in academic institutions must proactively and deliberately plan for accessibility. A recent letter from the U.S. Department of Education Office for Civil Rights noted:
Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act requires a public college to take appropriate steps to ensure that communications with persons with disabilities "are as effective as communications with others" [28 C.F.R. ss 35.160(a)]. OCR has repeatedly held that the term "communication" in this context means the transfer of information, including (but not limited to) the verbal presentation of a lecture, the printed text of a book, and the resources of the Internet.
The letter continues:
"Title II further states that, in determining what type of auxiliary aid and service is necessary, a public college shall give primary consideration to requests of the individual with a disability" [28 C.F.R. ss 35.106(b)(2)]. Footnote 3
In providing guidance on expectations for libraries in providing access to electronic resources, the letter states:
Modern adaptive technology has radically affected the degree to which it is economically feasible to make printed materials and computer based information systems accessible to blind patrons. The larger and more financially endowed the library, the higher the expectation that a greater volume of information will be made available within a shorter amount of time, particularly when reasonably priced adaptive technology is available to replace tasks that previously required personnel. An important indicator regarding the extent to which a public library is obligated to utilize adaptive technology is the degree to which it is relying on technology to serve its non-disabled patrons. The more technology that has been purchased by a public library to serve non-disabled patrons, the more reasonable the expectation that it will employ technology such as scanners to serve its patrons with disabilities. Footnote 4
As libraries increasingly provide electronic resources, they are legally obligated to ensure accessibility for people with disabilities.
Definitions and Statistics
So, what exactly does "person with a disability" mean?
"Person with a disability" means "any person who has a physical or mental impairment which substantially limits one or more major life activities including walking, seeing, hearing, speaking, breathing, learning, and working; has a record of such an impairment; or is regarded as having such an impairment."
Examples of qualifying disabilities covered by legislation may include, but are not limited to, spinal cord injuries, loss of limbs, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, hearing impairments, visual impairments, speech impairments, specific learning disabilities, head injuries, psychiatric disorders, diabetes, cancer, and AIDS.
The examples listed here are conditions which limit people's abilities to perform specific tasks. Some of these conditions are readily apparent; some are invisible. Some require that we provide special accommodations in the library; some do not. Additionally, some people who have conditions with the same label may have very different abilities when it comes to performing specific tasks. For example, one student who has cerebral palsy may have difficulty walking. For another student, cerebral palsy may result in no functional use of her/his hands or voice.
Now that we discussed the definition of disability according to the ADA, let's consider some statistics to gain a better understanding of this service population.
According to surveys conducted in 1991-1992, 9.6% or 1 in 10 Americans has a severe disability that substantially limits at least one major life activity. 19.4 % or 1 in 5 Americans has a disability. Footnote 5
In addition, we can expect the number of library patrons with disabilities to increase. Some reasons for this increase include:
Advances in medical technology and techniques result in greater numbers of people who survive traumatic accidents and problematic births.
Improvements in technology make it possible for more people with disabilities to live independently and have productive lives for which they will want and need library resources.
Increased awareness of people with disabilities' rights to accommodations and equal opportunities in education and employment, guaranteed by 504 and the ADA, has, and will continue to encourage more people to pursue these activities and request accommodations.
The creation of federal and state mandated K-12 and higher education academic support programs helps more students with disabilities complete high school and enter college and careers. The number of students with disabilities enrolled in universities and colleges has already increased. In 1994, 9.2% of all full-time, first-time entering freshman reported a disability, up from 2.6% in 1978.6 This trend will create a greater demand for accessible information resources in academic libraries.
The aging of the baby boomer generation will cause a significant demographic shift in our society, increasing the number of people with low vision, hearing impairments, and other disabilities related to the aging process.
Among people aged 18-44, 5% have a severe disability; among people aged 65-74, 25% have a severe disability; and among people aged 75-84, 42% have a severe disability. Footnote 7
All of these factors are leading to increased numbers of people with disabilities who are and will be requesting services at libraries.
The purpose of this introduction is to help you understand why libraries need to be prepared to serve people with disabilities. The legal imperatives of the ADA and other laws and the expected increase of people with disabilities in our constituencies and argue strongly for immediate action. Libraries will be best prepared to serve patrons with disabilities if they strive to include them in regularly provided services. This is best achieved by using universal design principles when designing facilities, equipment, services and resources; by providing a base level of adaptive technology; and by developing a policy and procedures for handling requests for accommodation. By taking these steps the library will be better able to respond quickly to more specialized requests for accommodation.
The rest of today's presentation will help you develop an understanding of adaptive technology and of universal design principles so that you can help develop accessible services and resources for your library.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Crafting an engaging presentation script is a multifaceted process that requires attention to detail, a deep understanding of your subject, and a keen sense of audience engagement. Here are some crucial strategies that you should know: 1. In-depth research. To lay a solid foundation for your presentation, start with comprehensive research.
Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling. Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story.
The #1 reason you should have a script and practice it isn't so you have a smooth delivery—it's so your presentation is organized, comprehensive, and easy to follow. 💡. Okay. Time to finally reveal my unique approach to scripting and practicing your presentation! 4.
2. Know Your Audience. Most people give their thesis defense presentation to an academic panel. This panel will look to see if you've developed a thorough understanding of your topic and thesis. They'll also be looking to see if you've got a solid foundation for your argument.
Cut out waffle words, limiting content to the essentials. To avoid cognitive overload, combine text and images. Add animated graphics, icons, characters and gestures to bring your research presentation to life and capture your audience's attention. 2. Split up the Content Onto Multiple Slides.
In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include: The full title of the report. The date of the report. The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report. The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended.
A clearly stated research question when visually presented helps. Be sure that the visuals are not too complicated. Include only the information you will be discussing. Be sure the visual is large enough to be clearly seen by the listener. Point to the visuals during the presentation. Leave the visual up long enough so that the listener can ...
Instructions: This grid offers you a simple way to begin to connect and categorize the sources you have found so far. 1. Write your research question in the space provided at the top of your grid. 2. In the first column, list the papers/sources that are most relevant to your research. question. 3.
Related Articles. This guide provides a 4-step process for making a good scientific presentation: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slide outlines, constructing slides, and practicing the talk. We give advice on how to make effective slides, including tips for text, graphics, and equations, and how to use rehearsals of your talk to ...
Writing a Research Report: Presentation. Tables, Diagrams, Photos, and Maps. - Use when relevant and refer to them in the text. - Redraw diagrams rather than copying them directly. - Place at appropriate points in the text. - Select the most appropriate device. - List in contents at beginning of the report.
AP® Research — Presentation and Oral Defense 2021 Scoring Guidelines. NOTE: To receive the highest performance level presumes that the student also achieved the preceding performance levels in that row. ADDITIONAL SCORES: In addition to the scores represented on the rubric, teachers can also assign scores of 0 (zero). A score of. A score of.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation. Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation. Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions. Two additional videos should prove useful: Designing PowerPoint Slides for a ...
Template 1: Clinical Research Trial PowerPoint Template. Use this premium PPT template to captivate your audience. Download this well-created template to raise your presenting threshold. Establish your milestones with workflows designed to ease the overburdening of tasks.
Keeping your defense simple will cut through all the other noise. Work on narrowing the focus of each slide to cover one point. Just one. Condensing ideas is tough, especially when you're discussing a complex issue. But taking your presentation one slide at a time ensures the audience can follow your argument clearly.
Introduction - The introduction script for presentations should be a welcome and personal connection to the topic. Main Points - Benefits of "topic". Transitions - Use phrases like "Now let's move on to," or "Next, we'll discuss.". Conclusion - Recap key points and call to action.
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience's attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding ...
This is to showcase your topic's originality and, if relevant, how it's different and/or an improvement from previously done research. Methodology. This is one of the most important parts of a thesis defense presentation. It allows your viewers to assess the rationality and validity of your approach and consequently, the accuracy of your ...
The anatomy of a research findings presentation by Deirdre Lyon. We've put together a collection of over 30 templates and examples to help you present your user research findings in a way that stakeholders will actually use. Alternative ways to share UX research findings Slide deck. Slides decks are a popular way to report user research findings.
Electronic Information in Libraries Computers + Adaptive Technology + Electronic Resources = Opportunities. This section provides a sample script for delivering a half-day to full-day presentation covering all of the topics listed in the outline. Tailor the script to your chosen program length, content and audience. Presentation Outline.
Sample Presentation Script. Printer-friendly version. Universal Access: Electronic Resources in Libraries Sample Presentation Script.pdf. This section provides a sample script for delivering a half-day to full-day presentation covering all of the topics listed in the outline. Tailor the script to your chosen program length, content and audience.
Master's Thesis Defense Script Moderator Introduces the Defense Process Thank you for joining us today, for [Name's] thesis defense. I'm [Name] from [Dept.] and I will be moderating the proceedings. In the School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, we ask that you hold questions until after the candidate's presentation.
5. Tell a story with your presentation script. Relate how the product or brand started and where the idea originated. Example: " I started this company as a broke college student with a dream. Today, that dream has become a team of 500 in national offices. 6. Use humor and personal anecdotes.
RESEARCH SCRIPT Good Afternoon Panelist! Aejay Alexia Nicole D. Under the advisory of Engineer Crispin Licataoa. Today be discussing the study that we did in regards to the Assessment of Green Technology Application on Commercial Buildings using the Philippine Green Building Rating System To express our views in a clearer manner, we created this visual presentation.