
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes
Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

What happens to your baby right after birth

How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next

Appointments at Mayo Clinic
- Pregnancy week by week
- Fetal presentation before birth
The way a baby is positioned in the uterus just before birth can have a big effect on labor and delivery. This positioning is called fetal presentation.
Babies twist, stretch and tumble quite a bit during pregnancy. Before labor starts, however, they usually come to rest in a way that allows them to be delivered through the birth canal headfirst. This position is called cephalic presentation. But there are other ways a baby may settle just before labor begins.
Following are some of the possible ways a baby may be positioned at the end of pregnancy.
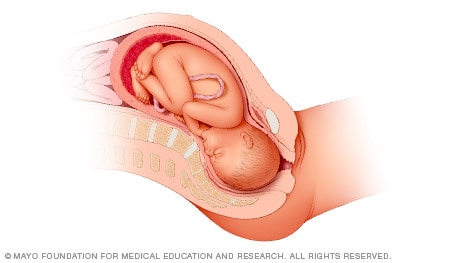
Head down, face down
When a baby is head down, face down, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput anterior position. This the most common position for a baby to be born in. With the face down and turned slightly to the side, the smallest part of the baby's head leads the way through the birth canal. It is the easiest way for a baby to be born.
Head down, face up
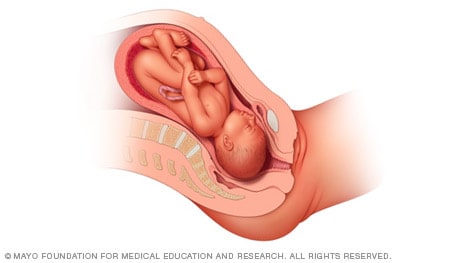
When a baby is head down, face up, the medical term for it is the cephalic occiput posterior position. In this position, it might be harder for a baby's head to go under the pubic bone during delivery. That can make labor take longer.
Most babies who begin labor in this position eventually turn to be face down. If that doesn't happen, and the second stage of labor is taking a long time, a member of the health care team may reach through the vagina to help the baby turn. This is called manual rotation.
In some cases, a baby can be born in the head-down, face-up position. Use of forceps or a vacuum device to help with delivery is more common when a baby is in this position than in the head-down, face-down position. In some cases, a C-section delivery may be needed.
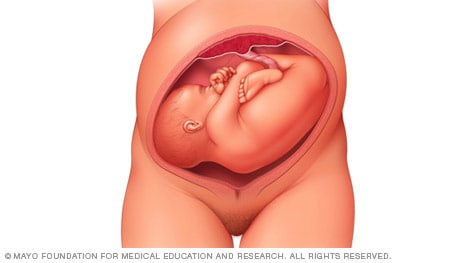
Frank breech
When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a frank breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Most babies in a frank breech position are born by planned C-section.

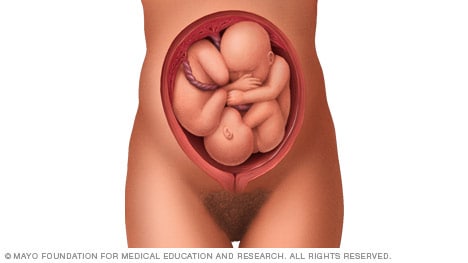
Complete and incomplete breech
A complete breech presentation, as shown below, is when the baby has both knees bent and both legs pulled close to the body. In an incomplete breech, one or both of the legs are not pulled close to the body, and one or both of the feet or knees are below the baby's buttocks. If a baby is in either of these positions, you might feel kicking in the lower part of your belly.
If you are more than 36 weeks into your pregnancy and your baby is in a complete or incomplete breech presentation, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. It involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a breech position, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies in a complete or incomplete breech position are born by planned C-section.

When a baby is sideways — lying horizontal across the uterus, rather than vertical — it's called a transverse lie. In this position, the baby's back might be:
- Down, with the back facing the birth canal.
- Sideways, with one shoulder pointing toward the birth canal.
- Up, with the hands and feet facing the birth canal.
Although many babies are sideways early in pregnancy, few stay this way when labor begins.
If your baby is in a transverse lie during week 37 of your pregnancy, your health care professional may try to move the baby into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of your health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
If the procedure isn't successful, or if the baby moves back into a transverse lie, talk with a member of your health care team about the choices you have for delivery. Many babies who are in a transverse lie are born by C-section.
If you're pregnant with twins and only the twin that's lower in the uterus is head down, as shown below, your health care provider may first deliver that baby vaginally.
Then, in some cases, your health care team may suggest delivering the second twin in the breech position. Or they may try to move the second twin into a head-down position. This is done using a procedure called external cephalic version. External cephalic version involves one or two members of the health care team putting pressure on your belly with their hands to get the baby to roll into a head-down position.
Your health care team may suggest delivery by C-section for the second twin if:
- An attempt to deliver the baby in the breech position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to have the baby delivered vaginally in the breech position.
- An attempt to move the baby into a head-down position is not successful.
- You do not want to try to move the baby to a head-down position.
In some cases, your health care team may advise that you have both twins delivered by C-section. That might happen if the lower twin is not head down, the second twin has low or high birth weight as compared to the first twin, or if preterm labor starts.
- Landon MB, et al., eds. Normal labor and delivery. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Holcroft Argani C, et al. Occiput posterior position. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 19, 2023.
- Frequently asked questions: If your baby is breech. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/if-your-baby-is-breech. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Hofmeyr GJ. Overview of breech presentation. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Strauss RA, et al. Transverse fetal lie. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Chasen ST, et al. Twin pregnancy: Labor and delivery. https://www.updtodate.com/contents/search. Accessed May 22, 2023.
- Cohen R, et al. Is vaginal delivery of a breech second twin safe? A comparison between delivery of vertex and non-vertex second twins. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2021; doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005569.
- Marnach ML (expert opinion). Mayo Clinic. May 31, 2023.
Products and Services
- A Book: Obstetricks
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy
- 3rd trimester pregnancy
- Fetal development: The 3rd trimester
- Overdue pregnancy
- Pregnancy due date calculator
- Prenatal care: 3rd trimester
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
- Opportunities
Mayo Clinic Press
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press .
- Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence
- The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book
- Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance
- FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment
- Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book
- Healthy Lifestyle
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.

- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Original Author(s): Minesh Mistry Last updated: 12th November 2018 Revisions: 7
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Preparation
- 3 General Inspection
- 4 Abdominal Inspection
- 5.1 Fundal Height
- 5.3 Presentation
- 5.4 Liquor Volume
- 5.5 Engagement
- 6 Fetal Auscultation
- 7 Completing the Examination
The obstetric examination is a type of abdominal examination performed in pregnancy.
It is unique in the fact that the clinician is simultaneously trying to assess the health of two individuals – the mother and the fetus.
In this article, we shall look at how to perform an obstetric examination in an OSCE-style setting.
Introduction
- Introduce yourself to the patient
- Wash your hands
- Explain to the patient what the examination involves and why it is necessary
- Obtain verbal consent
Preparation
- In the UK, this is performed at the booking appointment, and is not routinely recommended at subsequent visits
- Patient should have an empty bladder
- Cover above and below where appropriate
- Ask the patient to lie in the supine position with the head of the bed raised to 15 degrees
- Prepare your equipment: measuring tape, pinnard stethoscope or doppler transducer, ultrasound gel
General Inspection
- General wellbeing – at ease or distressed by physical pain.
- Hands – palpate the radial pulse.
- Head and neck – melasma, conjunctival pallor, jaundice, oedema.
- Legs and feet – calf swelling, oedema and varicose veins.
Abdominal Inspection
In the obstetric examination, inspect the abdomen for:
- Distension compatible with pregnancy
- Fetal movement (>24 weeks)
- Surgical scars – previous Caesarean section, laproscopic port scars
- Skin changes indicative of pregnancy – linea nigra (dark vertical line from umbilicus to the pubis), striae gravidarum (‘stretch marks’), striae albicans (old, silvery-white striae)
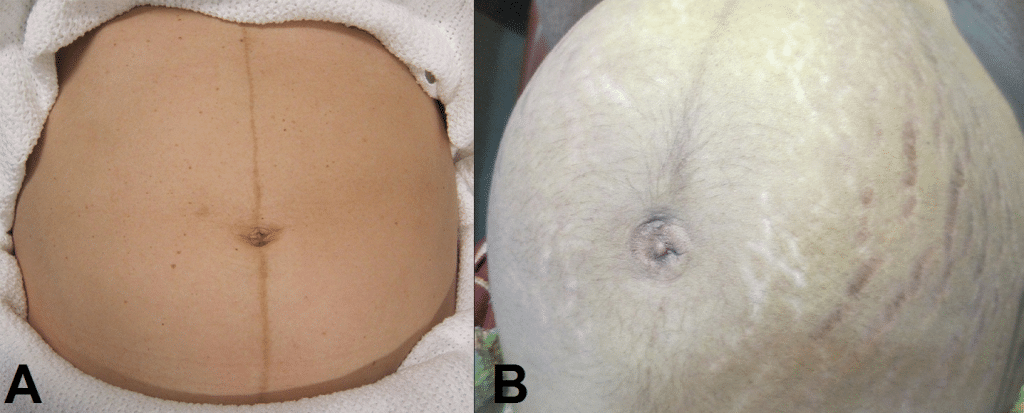
Fig 1 – Skin changes in pregnancy. A) Linea nigra. B) Striae gravidarum and albicans.
Ask the patient to comment on any tenderness and observe her facial and verbal responses throughout. Note any guarding.
Fundal Height
- Use the medial edge of the left hand to press down at the xiphisternum, working downwards to locate the fundus.
- Measure from here to the pubic symphysis in both cm and inches. Turn the measuring tape so that the numbers face the abdomen (to avoid bias in your measurements).
- Uterus should be palpable after 12 weeks, near the umbilicus at 20 weeks and near the xiphisternum at 36 weeks (these measurements are often slightly different if the woman is tall or short).
- The distance should be similar to gestational age in weeks (+/- 2 cm).
- Facing the patient’s head, place hands on either side of the top of the uterus and gently apply pressure
- Move the hands and palpate down the abdomen
- One side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back. Fetal limbs may be palpable on the opposing side
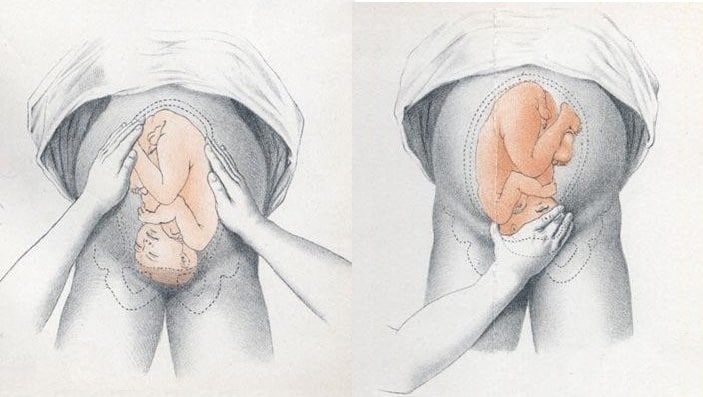
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (below the umbilicus) to find the presenting part.
- Firm and round signifies cephalic, soft and/or non-round suggests breech. If breech presentation is suspected, the fetal head can be often be palpated in the upper uterus.
- Ballot head by pushing it gently from one side to the other.
Liquor Volume
- Palpate and ballot fluid to approximate volume to determine if there is oligohydraminos/polyhydramnios
- When assessing the lie, only feeling fetal parts on deep palpation suggests large amounts of fluid
- Fetal engagement refers to whether the presenting part has entered the bony pelvis
- Note how much of the head is palpable – if the entire head is palpable, the fetus is unengaged.
- Engagement is measured in 1/5s
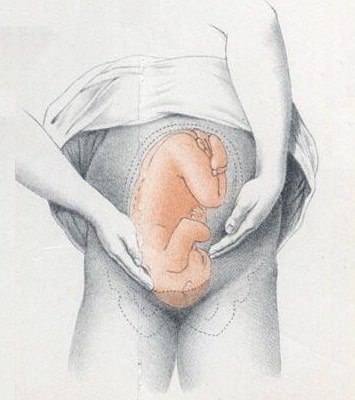
Fig 3 – Assessing fetal engagement.
Fetal Auscultation
- Hand-held Doppler machine >16 weeks (trying before this gestation often leads to anxiety if the heart cannot be auscultated).
- Pinard stethoscope over the anterior shoulder >28 weeks
- Feel the mother’s pulse at the same time
- Should be 110-160bpm (>24 weeks)
Completing the Examination
- Palpate the ankles for oedema and test for hyperreflexia (pre-eclampsia)
- Thank the patient and allow them to dress in private
- Summarise findings
- Blood pressure
- Urine dipstick
- Hands - palpate the radial pulse.
- Skin changes indicative of pregnancy - linea nigra (dark vertical line from umbilicus to the pubis), striae gravidarum ('stretch marks'), striae albicans (old, silvery-white striae)
- One side will feel fuller and firmer - this is the back. Fetal limbs may be palpable on the opposing side
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Breech presentation.
Caron J. Gray ; Meaghan M. Shanahan .

Affiliations
Last Update: November 6, 2022 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
- Describe the pathophysiology of breech presentation.
- Review the physical exam of a patient with a breech presentation.
- Summarize the treatment options for breech presentation.
- Explain the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by breech presentation.
- Introduction
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the fetus sitting with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position. Finally, the incomplete breech can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended). [1] [2] [3]
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4] [5] These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
- Epidemiology
Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech.
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10%, and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
- Pathophysiology
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6] [7]
Conditions that change the vertical polarity or the uterine cavity, or affect the ease or ability of the fetus to turn into the vertex presentation in the third trimester include:
- Mullerian anomalies: Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and didelphys uterus
- Placentation: Placenta previa as the placenta is occupying the inferior portion of the uterine cavity. Therefore, the presenting part cannot engage
- Uterine leiomyoma: Mainly larger myomas located in the lower uterine segment, often intramural or submucosal, that prevent engagement of the presenting part.
- Prematurity
- Aneuploidies and fetal neuromuscular disorders commonly cause hypotonia of the fetus, inability to move effectively
- Congenital anomalies: Fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Polyhydramnios: Fetus is often in unstable lie, unable to engage
- Oligohydramnios: Fetus is unable to turn to vertex due to lack of fluid
- Laxity of the maternal abdominal wall: Uterus falls forward, the fetus is unable to engage in the pelvis.
The risk of cord prolapse varies depending on the type of breech. Incomplete or footling breech carries the highest risk of cord prolapse at 15% to 18%, while complete breech is lower at 4% to 6%, and frank breech is uncommon at 0.5%.
- History and Physical
During the physical exam, using the Leopold maneuvers, palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breech in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation.
During a cervical exam, findings may include the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted. If the patient has been laboring, caution is warranted as the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex.
Any of these findings should raise suspicion and ultrasound should be performed.
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
On ultrasound, the fetal lie and presenting part should be visualized and documented. If breech presentation is diagnosed, specific information including the specific type of breech, the degree of flexion of the fetal head, estimated fetal weight, amniotic fluid volume, placental location, and fetal anatomy review (if not already done previously) should be documented.
- Treatment / Management
Expertise in the delivery of the vaginal breech baby is becoming less common due to fewer vaginal breech deliveries being offered throughout the United States and in most industrialized countries. The Term Breech Trial (TBT), a well-designed, multicenter, international, randomized controlled trial published in 2000 compared planned vaginal delivery to planned cesarean delivery for the term breech infant. The investigators reported that delivery by planned cesarean resulted in significantly lower perinatal mortality, neonatal mortality, and serious neonatal morbidity. Also, there was no significant difference in maternal morbidity or mortality between the two groups. Since that time, the rate of term breech infants delivered by planned cesarean has increased dramatically. Follow-up studies to the TBT have been published looking at maternal morbidity and outcomes of the children at two years. Although these reports did not show any significant difference in the risk of death and neurodevelopmental, these studies were felt to be underpowered. [8] [9] [10] [11]
Since the TBT, many authors since have argued that there are still some specific situations that vaginal breech delivery is a potential, safe alternative to planned cesarean. Many smaller retrospective studies have reported no difference in neonatal morbidity or mortality using these specific criteria.
The initial criteria used in these reports were similar: gestational age greater than 37 weeks, frank or complete breech presentation, no fetal anomalies on ultrasound examination, adequate maternal pelvis, and estimated fetal weight between 2500 g and 4000 g. In addition, the protocol presented by one report required documentation of fetal head flexion and adequate amniotic fluid volume, defined as a 3-cm vertical pocket. Oxytocin induction or augmentation was not offered, and strict criteria were established for normal labor progress. CT pelvimetry did determine an adequate maternal pelvis.
Despite debate on both sides, the current recommendation for the breech presentation at term includes offering external cephalic version (ECV) to those patients that meet criteria, and for those whom are not candidates or decline external cephalic version, a planned cesarean section for delivery sometime after 39 weeks.
Regarding the premature breech, gestational age will determine the mode of delivery. Before 26 weeks, there is a lack of quality clinical evidence to guide mode of delivery. One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Face and brow presentation
- Fetal anomalies
- Fetal death
- Grand multiparity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Oligohydramnios
- Pelvis Anatomy
- Preterm labor
- Primigravida
- Uterine anomalies
- Pearls and Other Issues
In light of the decrease in planned vaginal breech deliveries, thus the decrease in expertise in managing this clinical scenario, it is prudent that policies requiring simulation and instruction in the delivery technique for vaginal breech birth are established to care for the emergency breech vaginal delivery.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12] [13] [14]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Caron Gray declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Meaghan Shanahan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation. [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. [Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997] [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. Krause M, Fischer T, Feige A. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997 Jul-Aug; 201(4):128-35.
- The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. [Early Hum Dev. 1993] The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. Sival DA, Prechtl HF, Sonder GH, Touwen BC. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Mar; 32(2-3):161-76.
- The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. [PLoS One. 2019] The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. Jennewein L, Allert R, Möllmann CJ, Paul B, Kielland-Kaisen U, Raimann FJ, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0225546. Epub 2019 Dec 2.
- Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. [Semin Perinatol. 2003] Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. Tunde-Byass MO, Hannah ME. Semin Perinatol. 2003 Feb; 27(1):34-45.
- Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. Mattuizzi A. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020 Jan; 48(1):70-80. Epub 2019 Nov 1.
Recent Activity
- Breech Presentation - StatPearls Breech Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic
RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
● The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented downward (also called "back down" or dorsoinferior), and the fetal shoulder presents at the cervix ( figure 1 ).
● The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented upward (also called "back up" or dorsosuperior), and the fetal small parts and umbilical cord present at the cervix.
(Note: Lie refers to the long axis of the fetus relative to the longitudinal axis of the uterus; the long axis of the fetus can be transverse to, oblique to, or parallel to [longitudinal lie] the longitudinal axis of the uterus. Presentation refers to the fetal part that directly overlies the pelvic inlet; it is usually cephalic [head] or breech [buttocks] but can be a shoulder, compound [eg, head and hand], or funic [umbilical cord]. Position is the relationship of a nominated site of the presenting part to a denominating location on the maternal pelvis [eg, right occiput anterior].)
- MSD careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

Obstetric and Newborn Care I
10.02 key terms related to fetal positions.
a. “Lie” of an Infant.
Lie refers to the position of the spinal column of the fetus in relation to the spinal column of the mother. There are two types of lie, longitudinal and transverse. Longitudinal indicates that the baby is lying lengthwise in the uterus, with its head or buttocks down. Transverse indicates that the baby is lying crosswise in the uterus.
b. Presentation/Presenting Part.
Presentation refers to that part of the fetus that is coming through (or attempting to come through) the pelvis first.
(1) Types of presentations (see figure 10-1). The vertex or cephalic (head), breech, and shoulder are the three types of presentations. In vertex or cephalic, the head comes down first. In breech, the feet or buttocks comes down first, and last–in shoulder, the arm or shoulder comes down first. This is usually referred to as a transverse lie.
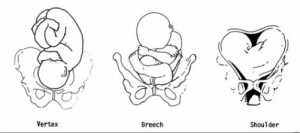
(2) Percentages of presentations.
(a) Head first is the most common-96 percent.
(b) Breech is the next most common-3.5 percent.
(c) Shoulder or arm is the least common-5 percent.
(3) Specific presentation may be evaluated by several ways.
(a) Abdominal palpation-this is not always accurate.
(b) Vaginal exam–this may give a good indication but not infallible.
(c) Ultrasound–this confirms assumptions made by previous methods.
(d) X-ray–this confirms the presentation, but is used only as a last resort due to possible harm to the fetus as a result of exposure to radiation.
c. Attitude.
This is the degree of flexion of the fetus body parts (body, head, and extremities) to each other. Flexion is resistance to the descent of the fetus down the birth canal, which causes the head to flex or bend so that the chin approaches the chest.
(1) Types of attitude (see figure 10-2).
(a) Complete flexion. This is normal attitude in cephalic presentation. With cephalic, there is complete flexion at the head when the fetus “chin is on his chest.” This allows the smallest cephalic diameter to enter the pelvis, which gives the fewest mechanical problems with descent and delivery.
(b) Moderate flexion or military attitude. In cephalic presentation, the fetus head is only partially flexed or not flexed. It gives the appearance of a military person at attention. A larger diameter of the head would be coming through the passageway.
(c) Poor flexion or marked extension. In reference to the fetus head, it is extended or bent backwards. This would be called a brow presentation. It is difficult to deliver because the widest diameter of the head enters the pelvis first. This type of cephalic presentation may require a C/Section if the attitude cannot be changed.
(d) Hyperextended. In reference to the cephalic position, the fetus head is extended all the way back. This allows a face or chin to present first in the pelvis. If there is adequate room in the pelvis, the fetus may be delivered vaginally.
(2) Areas to look at for flexion.
(a) Head-discussed in previous paragraph, 10-2c(1).
(b) Thighs-flexed on the abdomen.
(c) Knees-flexed at the knee joints.
(d) Arches of the feet-rested on the anterior surface of the legs.
(e) Arms-crossed over the thorax.
(3) Attitude of general flexion. This is when all of the above areas are flexed appropriately as described.
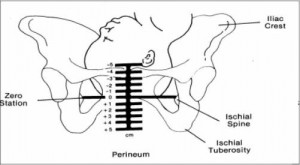
d. Station.
This refers to the depth that the presenting part has descended into the pelvis in relation to the ischial spines of the mother’s pelvis. Measurement of the station is as follows:
(1) The degree of advancement of the presenting part through the pelvis is measured in centimeters.
(2) The ischial spines is the dividing line between plus and minus stations.
(3) Above the ischial spines is referred to as -1 to -5, the numbers going higher as the presenting part gets higher in the pelvis (see figure10-3).
(4) The ischial spines is zero (0) station.
(5) Below the ischial spines is referred to +1 to +5, indicating the lower the presenting part advances.
e. Engagement.
This refers to the entrance of the presenting part of the fetus into the true pelvis or the largest diameter of the presenting part into the true pelvis. In relation to the head, the fetus is said to be engaged when it reaches the midpelvis or at a zero (0) station. Once the fetus is engaged, it (fetus) does not go back up. Prior to engagement occurring, the fetus is said to be “floating” or ballottable.
f. Position.
This is the relationship between a predetermined point of reference or direction on the presenting part of the fetus to the pelvis of the mother.
(1) The maternal pelvis is divided into quadrants.
(a) Right and left side, viewed as the mother would.
(b) Anterior and posterior. This is a line cutting the pelvis in the middle from side to side. The top half is anterior and the bottom half is posterior.
(c) The quadrants never change, but sometimes it is confusing because the student or physician’s viewpoint changes.
NOTE: Remember that when you are describing the quadrants, view them as the mother would.
(2) Specific points on the fetus.
(a) Cephalic or head presentation.
1 Occiput (O). This refers to the Y sutures on the top of the head.
2 Brow or fronto (F). This refers to the diamond sutures or anterior fontanel on the head.
3 Face or chin presentation (M). This refers to the mentum or chin.
(b) Breech or butt presentation.
1 Sacrum or coccyx (S). This is the point of reference.
2 Breech birth is associated with a higher perinatal mortality.
(c) Shoulder presentation.
1 This would be seen with a transverse lie.
2. Scapula (Sc) or its upper tip, the acromion (A) would be used for the point of reference.
(3) Coding of positions.
(a) Coding simplifies explaining the various positions.
1 The first letter of the code tells which side of the pelvis the fetus reference point is on (R for right, L for left).
2 The second letter tells what reference point on the fetus is being used (Occiput-O, Fronto-F, Mentum-M, Breech-S, Shoulder-Sc or A).
3 The last letter tells which half of the pelvis the reference point is in (anterior-A, posterior-P, transverse or in the middle-T).

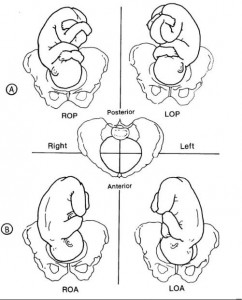
(b) Each presenting part has the possibility of six positions. They are normally recognized for each position–using “occiput” as the reference point.
1 Left occiput anterior (LOA).
2 Left occiput posterior (LOP).
3 Left occiput transverse (LOT).
4 Right occiput anterior (ROA).
5. Right occiput posterior (ROP).
6 Right occiput transverse (ROT).
(c) A transverse position does not use a first letter and is not the same as a transverse lie or presentation.
1 Occiput at sacrum (O.S.) or occiput at posterior (O.P.).
2 Occiput at pubis (O.P.) or occiput at anterior (O.A.).
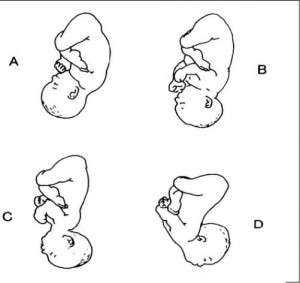
(4) Types of breech presentations (see figure10-4).
(a) Complete or full breech. This involves flexion of the fetus legs. It looks like the fetus is sitting in a tailor fashion. The buttocks and feet appear at the vaginal opening almost simultaneously.
A–Complete. B–Frank. C–Incomplete.
(b) Frank and single breech. The fetus thighs are flexed on his abdomen. His legs are against his trunk and feet are in his face (foot-in-mouth posture). This is the most common and easiest breech presentation to deliver.
(c) Incomplete breech. The fetus feet or knees will appear first. His feet are labeled single or double footing, depending on whether 1 or 2 feet appear first.
(5) Observations about positions (see figure 10-5).
(a) LOA and ROA positions are the most common and permit relatively easy delivery.
(b) LOP and ROP positions usually indicate labor may be longer and harder, and the mother will experience severe backache.
(c) Knowing positions will help you to identify where to look for FHT’s.
1 Breech. This will be upper R or L quad, above the umbilicus.
2 Vertex. This will be lower R or L quad, below the umbilicus.
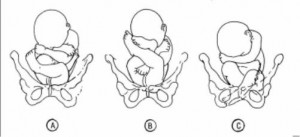
(d) An occiput in the posterior quadrant means that you will feel lumpy fetal parts, arms and legs (see figure 10-5 A). If delivered in that position, the infant will come out looking up.
(e) An occiput in the anterior quadrant means that you will feel a more smooth back (see figure 10-5 B). If delivered in that position, the infant will come out looking down at the floor.
Distance Learning for Medical and Nursing Professionals
7.6 Transverse lie and shoulder presentation
A transverse lie constitutes an absolute foeto-pelvic disproportion, and vaginal delivery is impossible.
This is an obstetric emergency, because labour is obstructed and there is a risk of uterine rupture and foetal distress.
7.6.1 Diagnosis
- The uterus is very wide: the transverse axis is virtually equivalent to the longitudinal axis; fundal height is less than 30 cm near term.
- On examination: head in one side, breech in the other (Figures 7.1a and 7.1b). Vaginal examination reveals a nearly empty true pelvis or a shoulder with—sometimes—an arm prolapsing from the vagina (Figure 7.1c).
Figures 7.1 - Transverse lie and shoulder presentation
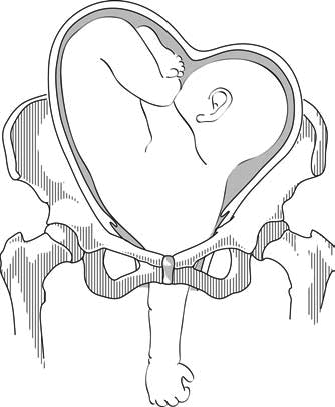
7.6.2 Possible causes
- Grand multiparity (5 deliveries or more)
- Uterine malformation
Twin pregnancy
- Prematurity
- Placenta praevia
- Foeto-pelvic disproportion
7.6.3 Management
This diagnosis should be made before labour begins, at the last prenatal visit before the birth.
At the end of pregnancy
Singleton pregnancy.
- External version 4 to 6 weeks before delivery, in a CEmONC facility ( Section 7.7 ).
- If this fails, delivery should be carried out by caesarean section, either planned or at the beginning of labour (Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1 ).
- External version is contra-indicated.
- If the first twin is in a transverse lie (unusual): schedule a caesarean section.
- If the second twin is in a transverse lie: there is no indication for caesarean section, but plan delivery in a CEmONC facility so that it can be performed if necessary. Deliver the first twin and then, assess the foetal position and give a few minutes for the second twin to adopt a longitudinal lie. If the second twin stays in a transverse lie, and depending on the experience of the operator, perform external version ( Section 7.7 ) and/or internal version ( Section 7.8 ) on the second twin.
During labour, in a CEmONC facility
Foetus alive and membranes intact.
- Gentle external version, between two contractions, as early as possible, then proceed as with normal delivery.
- If this fails: caesarean section.
Foetus alive and membranes ruptured
- Multipara with relaxed uterus and mobile foetus, and an experienced operator: internal version and total breech extraction.
- Primipara, or tight uterus, or immobile foetus, or engaged arm, or scarred uterus or insufficiently-experienced operator: caesarean section.
- Incomplete dilation: caesarean section.
Caesarean section can be difficult due to uterine retraction. Vertical hysterotomy is preferable. To perform extraction, grasp a foot in the fundus (equivalent to a total breech extraction, but by caesarean section).
Foetus dead
Embryotomy for transverse lie (Chapter 9, Section 9.7.7 ).
During labour, in remote settings where surgery is not available
Try to refer the patient to a CEmONC facility. If not feasible:
- Attempt external version as early as possible.
- If this fails, wait for complete dilation.
- Perform an external version ( Section 7.7 ) combined with an internal version ( Section 7.8 ), possibly placing the woman in various positions (Trendelenburg or knee-chest).
- Put the woman into the knee-chest position.
- Between contractions, push the foetus back and try to engage his head.
- Vacuum extraction (Chapter 5, Section 5.6.1 ) and symphysiotomy (Chapter 5, Section 5.7 ) at the slightest difficulty.
- Incomplete dilation: Trendelenburg position and watchful waiting until complete dilation.
Try to refer the patient, even if referral takes some time. If not feasible, embryotomy for transverse lie (Chapter 9, Section 9.7.7 ).

An expert resource for medical professionals Provided FREE as a service to women’s health
The Global Library of Women’s Medicine EXPERT – RELIABLE - FREE Over 20,000 resources for health professionals
The Alliance for Global Women’s Medicine A worldwide fellowship of health professionals working together to promote, advocate for and enhance the Welfare of Women everywhere

An Educational Platform for FIGO
The Global Library of Women’s Medicine Clinical guidance and resourses
A vast range of expert online resources. A FREE and entirely CHARITABLE site to support women’s healthcare professionals
The Global Academy of Women’s Medicine Teaching, research and Diplomates Association
- Expert clinical guidance
- Safer motherhood
- Skills videos
- Clinical films
- Special textbooks
- Ambassadors
- Can you help us?
- Introduction
- Definitions
- Complications
- External Cephalic Version
- Management of Labor And Delivery
- Cesarean Delivery
- Perinatal Outcome
- Practice Recommendations
- Study Assessment – Optional
- Your Feedback
This chapter should be cited as follows: Okemo J, Gulavi E, et al , Glob. libr. women's med ., ISSN: 1756-2228; DOI 10.3843/GLOWM.414593
The Continuous Textbook of Women’s Medicine Series – Obstetrics Module
Common obstetric conditions
Volume Editor: Professor Sikolia Wanyonyi , Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi, Kenya

Abnormal Lie/Presentation
First published: February 2021
Study Assessment Option
By completing 4 multiple-choice questions (randomly selected) after studying this chapter readers can qualify for Continuing Professional Development awards from FIGO plus a Study Completion Certificate from GLOWM See end of chapter for details
INTRODUCTION
The mechanism of labor and delivery, as well as the safety and efficacy, is determined by the specifics of the fetal and maternal pelvic relationship at the onset of labor. Normal labor occurs when regular and painful contractions cause progressive cervical dilatation and effacement, accompanied by descent and expulsion of the fetus. Abnormal labor involves any pattern deviating from that observed in the majority of women who have a spontaneous vaginal delivery and includes:
- Protraction disorders (slower than normal progress);
- Arrest disorders (complete cessation of progress).
Among the causes of abnormal labor is the disproportion between the presenting part of the fetus and the maternal pelvis, which rather than being a true disparity between fetal size and maternal pelvic dimensions, is usually due to a malposition or malpresentation of the fetus.
This chapter reviews how to define, diagnose, and manage the clinical impact of abnormalities of fetal lie and malpresentation with the most commonly occurring being the breech-presenting fetus.
DEFINITIONS
At the onset of labor, the position of the fetus in relation to the birth canal is critical to the route of delivery and, thus, should be determined early. Important relationships include fetal lie, presentation, attitude, and position .
Fetal lie describes the relationship of the fetal long axis to that of the mother. In more than 99% of labors at term, the fetal lie is longitudinal . A transverse lie is less frequent when the fetal and maternal axes may cross at a 90 ° angle, and predisposing factors include multiparity, placenta previa, hydramnios, and uterine anomalies. Occasionally, the fetal and maternal axes may cross at a 45 ° angle, forming an oblique lie .
Fetal presentation
The presenting part is the portion of the fetal body that is either foremost within the birth canal or in closest proximity to it. Thus, in longitudinal lie, the presenting part is either the fetal head or the breech, creating cephalic and breech presentations , respectively. The shoulder is the presenting part when the fetus lies with the long axis transversely.
Commonly the baby lies longitudinally with cephalic presentation. However, in some instances, a fetus may be in breech where the fetal buttocks are the presenting part. Breech fetuses are also referred to as malpresentations. Fetuses that are in a transverse lie may present the fetal back (or shoulders, as in the acromial presentation), small parts (arms and legs), or the umbilical cord (as in a funic presentation) to the pelvic inlet. When the fetal long axis is at an angle to the bony inlet, and no palpable fetal part generally is presenting, the fetus is likely in oblique lie. This lie usually is transitory and occurs during fetal conversion between other lies during labor.
The point of direction is the most dependent portion of the presenting part. In cephalic presentation in a well-flexed fetus, the occiput is the point of direction.
The fetal position refers to the location of the point of direction with reference to the four quadrants of the maternal outlet as viewed by the examiner. Thus, position may be right or left as well as anterior or posterior.
Unstable lie
Refers to the frequent changing of fetal lie and presentation in late pregnancy (usually refers to pregnancies >37 weeks).
Fetal position
Fetal position refers to the relationship of an arbitrarily chosen portion of the fetal presenting part to the right or left side of the birth canal. With each presentation there may be two positions – right or left. The fetal occiput, chin (mentum) and sacrum are the determining points in vertex, face, and breech presentations. Thus:
- left and right occipital presentations
- left and right mental presentations
- left and right sacral presentations.
Fetal attitude
The fetus instinctively forms an ovoid mass that corresponds to the shape of the uterine cavity towards the third trimester, a characteristic posture described as attitude or habitus. The fetus becomes folded upon itself to create a convex back, the head is flexed, and the chin is almost in contact with the chest. The thighs are flexed over the abdomen and the legs are bent at the knees. The arms are usually parallel to the sides or lie across the chest while the umbilical cord fills the space between the extremities. This posture is as a result of fetal growth and accommodation to the uterine cavity. It is possible that the fetal head can become progressively extended from the vertex to face presentation resulting in a change of fetal attitude from convex (flexed) to concave (extended) contour of the vertebral column.
The categories of frank, complete, and incomplete breech presentations differ in their varying relations between the lower extremities and buttocks (Figure 1). With a frank breech, lower extremities are flexed at the hips and extended at the knees, and thus the feet lie close to the head. With a complete breech, both hips are flexed, and one or both knees are also flexed. With an incomplete breech, one or both hips are extended. As a result, one or both feet or knees lie below the breech, such that a foot or knee is lowermost in the birth canal. A footling breech is an incomplete breech with one or both feet below the breech.
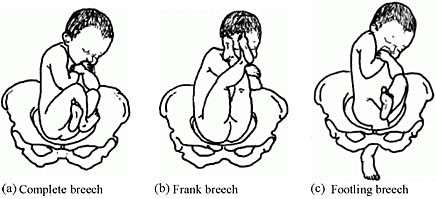
Types of breech presentation. Reproduced from WHO 2006, 1 with permission.
The relative incidence of differing fetal and pelvic relations varies with diagnostic and clinical approaches to care.
About 1 in 25 fetuses are breech at the onset of labor and about 1 in 100 are transverse or oblique, also referred to as non-axial. 2
With increasing gestational age, the prevalence of breech presentation decreases. In early pregnancy the fetus is highly mobile within a relatively large volume of amniotic fluid, therefore it is a common finding. The incidence of breech presentation is 20–25% of fetuses at <28 weeks, but only 7–16% at 32 weeks, and only 3–4% at term. 2 , 3
Face and brow presentation are uncommon. Their prevalence compared with other types of malpresentations are shown below. 4
- Occiput posterior – 1/19 deliveries;
- Breech – 1/33 deliveries;
- Face – 1/600–1/800 deliveries;
- Brow – 1/500–1/4000 deliveries;
- Transverse lie – 1/833 deliveries;
- Compound – 1/1500 deliveries.
Transverse lie is often unstable and fetuses in this lie early in pregnancy later convert to a cephalic or breech presentation.
The fetus has a relatively larger head than body during most of the late second and early third trimester, it therefore tends to spend much of its time in breech presentation or in a non-axial lie as it rotates back and forth between cephalic and breech presentations. The relatively large volume of amniotic fluid present facilitates this dynamic presentation.
Abnormal fetal lie is frequently seen in multifetal gestation, especially with the second twin. In women of grand parity, in whom relaxation of the abdominal and uterine musculature tends to occur, a transverse lie may be encountered. Prematurity and macrosomia are also predisposing factors. Distortion of the uterine cavity shape, such as that seen with leiomyomas, prior uterine surgery, or developmental anomalies (Mullerian fusion defects), predisposes to both abnormalities in fetal lie and malpresentations. The location of the placenta also plays a contributing role with fundal and cornual implantation being seen more frequently in breech presentation. Placenta previa is a well-described affiliate for both transverse lie and breech presentation.
Fetuses with congenital anomalies also present with abnormalities in either presentation or lie. It is possibly as a cause (i.e. fitting the uterine cavity optimally) or effect (the fetus with a neuromuscular condition that prevents the normal turning mechanism). The finding of an abnormal lie or malpresentation requires a thorough search for fetal abnormalities. Such abnormalities could include chromosomal (autosomal trisomy) and structural abnormalities (hydrocephalus), as well as syndromes of multiple effects (fetal alcohol syndrome).
In most cases, breech presentation appears to be as a chance occurrence; however, up to 15% may be owing to fetal, maternal, or placental abnormalities. It is commonly thought that a fetus with normal anatomy, activity, amniotic fluid volume, and placental location adopts the cephalic presentation near term because this position is the best fit for the intrauterine space, but if any of these variables is abnormal, then breech presentation is more likely.
Factors associated with breech presentation are shown in Table 1.
Risk factors for breech presentation.
Spontaneous version may occur at any time before delivery, even after 40 weeks of gestation. A prospective longitudinal study using serial ultrasound examinations reported the likelihood of spontaneous version to cephalic presentation after 36 weeks was 25%. 5
In population-based registries, the frequency of breech presentation in a second pregnancy was approximately 2% if the first pregnancy was not a breech presentation and approximately 9% if the first pregnancy was a breech presentation. After two consecutive pregnancies with breech presentation at delivery, the risk of another breech presentation was approximately 25% and this rose to 40% after three consecutive breech deliveries. 6 , 7
In addition, parents who themselves were delivered at term from breech presentation were twice as likely to have their offspring in breech presentation as parents who were delivered in cephalic presentation. This suggests a possible heritable component to fetal presentation. 8
Leopold’s maneuvers
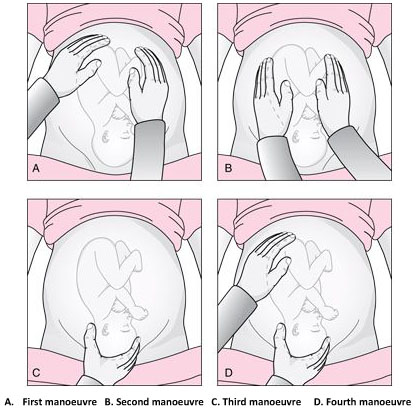
The Leopold’s maneuvers: palpation of fetus in left occiput anterior position. Reproduced from World Health Organization, 2006, 1 with permission.
Abdominal examination can be conducted systematically employing the four maneuvers described by Leopold in 1894. 9 , 10 In obese patients, in polyhydramnios patients or those with anterior placenta, these maneuvers are difficult to perform and interpret.
The first maneuver is to assess the uterine fundus. This allows the identification of fetal lie and determination of which fetal pole, cephalic or podalic – occupies the fundus. In breech presentation, there is a sensation of a large, nodular mass, whereas the head feels hard and round and is more mobile.
The second maneuver is accomplished as the palms are placed on either side of the maternal abdomen, and gentle but deep pressure is exerted. On one side, a hard, resistant structure is felt – the back. On the other, numerous small, irregular, mobile parts are felt – the fetal extremities. By noting whether the back is directed anteriorly, transversely, or posteriorly, fetal orientation can be determined.
The third maneuver aids confirmation of fetal presentation. The thumb and fingers of one hand grasp the lower portion of the maternal abdomen just above the symphysis pubis. If the presenting part is not engaged, a movable mass will be felt, usually the head. The differentiation between head and breech is made as in the first maneuver.
The fourth maneuver helps determine the degree of descent. The examiner faces the mother’s feet, and the fingertips of both hands are positioned on either side of the presenting part. They exert inward pressure and then slide caudad along the axis of the pelvic inlet. In many instances, when the head has descended into the pelvis, the anterior shoulder or the space created by the neck may be differentiated readily from the hard head.
According to Lyndon-Rochelle et al ., 11 experienced clinicians have accurately identified fetal malpresentation using Leopold maneuvers with a high sensitivity 88%, specificity 94%, positive-predictive value 74%, and negative-predictive value 97%.
Vaginal examination
Prelabor diagnosis of fetal presentation is difficult as the presenting part cannot be palpated through a closed cervix. Once labor begins and the cervix dilates, and palpation through vaginal examination is possible. Vertex presentations and their positions are recognized by palpation of the various fetal sutures and fontanels, while face and breech presentations are identified by palpation of facial features or the fetal sacrum and perineum, respectively.
Sonography and radiology
Sonography is the gold standard for identifying fetal presentation. This can be done during antenatal period or intrapartum. In obese women or in women with muscular abdominal walls this is especially important. Compared with digital examinations, sonography for fetal head position determination during second stage labor is more accurate. 12 , 13
COMPLICATIONS
Adverse outcomes in malpresented fetuses are multifactorial. They could be due to either underlying conditions associated with breech presentation (e.g., congenital anomalies, intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth) or trauma during delivery.
Neonates who were breech in utero are more at risk for mild deformations (e.g., frontal bossing, prominent occiput, upward slant and low-set ears), torticollis, and developmental dysplasia of the hip.
Other obstetric complications include prolapse of the umbilical cord, intrauterine infection, maldevelopment as a result of oligohydramnios, asphyxia, and birth trauma and all are concerns.
Birth trauma especially to the head and cervical spine, is a significant risk to both term and preterm infants who present breech. In cephalic presenting fetuses, the labor process prepares the head for delivery by causing molding which helps the fetus to adapt to the birth canal. Conversely, the after-coming head of the breech fetus must descend and deliver rapidly and without significant change in shape. Therefore, small alterations in the dimensions or shape of the maternal bony pelvis or the attitude of the fetal head may have grave consequences. This process poses greater risk to the preterm infant because of the relative size of the fetal head and body. Trauma to the head is not eliminated by cesarean section; both intracranial and cervical spine trauma may result from entrapment in either the uterine or abdominal incisions.
In resource-limited countries where ultrasound imaging, urgent cesarean delivery, and neonatal intensive care are not readily available, the maternal and perinatal mortality/morbidity associated with transverse lie in labor can be high. Uterine rupture from prolonged labor in a transverse lie is a major reason for maternal/perinatal mortality and morbidity.
EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSION
External cephalic version (ECV) is the manual rotation of the fetus from a non-cephalic to a cephalic presentation by manipulation through the maternal abdomen (Figure 3).
External version of breech presentation . Reproduced from WHO 2003 , 14 with permission .
This procedure is usually performed as an elective procedure in women who are not in labor at or near term to improve their chances of having a vaginal cephalic birth. ECV reduces the risk of non-cephalic presentation at birth by approximately 60% (relative risk [RR] 0.42, 95% CI 0.29–0.61) and reduces the risk of cesarean delivery by approximately 40% (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.40–0.82). 7
In a 2008 systematic review of 84 studies including almost 13,000 version attempts at term, the pooled success rate was 58%. 15
A subsequent large series of 2614 ECV attempts over 18 years reported a success rate of 49% and provided more details): 16
- The success rate was 40% in nulliparous women and 64% in parous women.
- After successful ECV, 97% of fetuses remained cephalic at birth, 86% of which were delivered vaginally.
- Spontaneous version to a cephalic presentation occurred after 4.3% of failed attempts, and 2.2% of successfully vertexed cases reverted to breech.
Factors associated with lower ECV success rates include nulliparity, anterior placenta, lateral or cornual placenta, decreased amniotic fluid volume, low birth weight, obesity, posteriorly located fetal spine, frank breech presentation, ruptured membranes.
The following factors should be considered while managing malpresentations: type of malpresentation, gestational age at diagnosis, availability of skilled personnel, institutional resources and protocols and patient factors and preferences.
Breech presentation
According to a term breech trial, 17 planned cesarean delivery carries a reduced perinatal mortality and early neonatal morbidity for babies with breech presentation at term compared to vaginal breech delivery. When planning a breech vaginal birth, appropriate patient selection and skilled personnel in breech delivery are key in achieving good neonatal outcomes. In appropriately selected patients and skilled personnel in vaginal breech deliveries, perinatal mortality is between 0.8 and 1.7/1000 for planned vaginal breech birth and between 0 and 0.8/1000 for planned cesarean section. 18 , 19 The choice of the route of delivery should therefore be made considering the availability of skilled personnel in conducting breech vaginal delivery; providing competent newborn care; conducting rapid cesarean delivery should need arise and performing ECV if desired; availability of resources for continuous intrapartum fetal heart rate and labor monitoring; patient clinical features, preferences and values; and institutional policies, protocols and resources.
Four approaches to the management of breech presentation are shown in Figure 4: 8
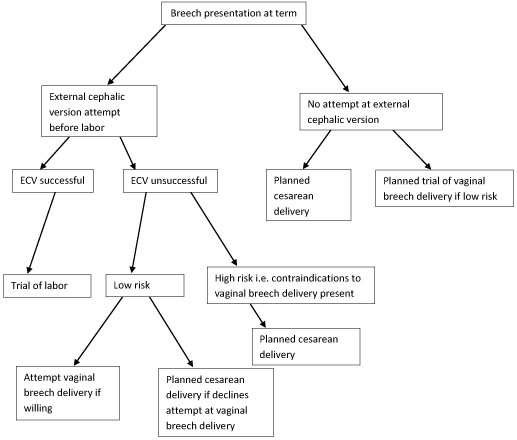
Management of breech presentation. ECV, external cephalic version.
The options available are:
- Attempting external cephalic version (ECV) before labor with a trial of labor if successful and conducting cesarean delivery if unsuccessful.
- Footling or kneeling breech presentation;
- Fetal macrosomia;
- Fetal growth restriction;
- Hyperextended fetal neck in labor;
- Previous cesarean delivery;
- Unavailability of skilled personnel in breech delivery;
- Other contraindications to vaginal delivery like placenta previa, cord prolapse;
- Fetal anomaly that may interfere with vaginal delivery like hydrocephalus.
- Planned cesarean delivery without an attempt at ECV.
- Planned trial of vaginal breech delivery in patients with favorable clinical characteristics for vaginal delivery without an attempt at ECV.
All the four approaches should be discussed in detail with the patient, and in light of all the considerations highlighted above, a safe plan of care agreed upon by both the patient and the clinician in good time.
Transverse and oblique lie
If a diagnosis of transverse/oblique fetal lie is made before onset of labor and there are no contraindications to vaginal birth or ECV, ECV can be attempted at 37 weeks' gestation. If the malpresentation recurs, further attempts at ECV can be made at 38–39 weeks with induction of labor if successful.
ECV can also be attempted in early labor with intact fetal membranes and no contraindications to vaginal birth.
If ECV is declined or is unsuccessful, then planned cesarean section should be arranged after 39 weeks' gestation.
MANAGEMENT OF LABOR AND DELIVERY
Skills to conduct vaginal breech delivery are very important as there are women who may opt for planned vaginal breech birth and even among those who choose planned cesarean delivery, about 10% may go into labor and end up with a vaginal breech delivery. 17 Some implications of cesarean delivery such as need for repeat cesarean deliveries, placental attachment disorders and uterine rupture make vaginal birth more desirable to some individuals. In addition, vaginal birth has advantages such as affordability, quicker recovery, shorter hospital stay, less complications and is more favorable for resource poor settings.
In appropriately selected women, planned vaginal breech birth is not associated with any significant long-term neurological morbidity. Regardless of planned mode of birth, cerebral palsy occurs in approximately 1.5/1,000 breech births, and abnormal neurological development occurs in approximately 3/100. 18 Careful patient selection is very important for good outcomes and it is generally agreed that women who choose to undergo a trial of labor and vaginal breech delivery should be at low risk of complications from vaginal breech delivery. Some contraindications to vaginal breech delivery have been highlighted above.
Women with breech presentation near term, pre- or early-labor ultrasound should be performed to assess type of breech presentation, flexion of the fetal head and fetal growth. If a woman presents in labor and ultrasound is unavailable and has not recently been performed, cesarean section is recommended. Vaginal breech deliveries should only take place in a facility with ability and resources readily available for emergency cesarean delivery should the need arise.
Induction of labor may be considered in carefully selected low-risk women. Augmentation of labor is controversial as poor progress of labor may be a sign of cephalo-pelvic disproportion, however, it may be considered in the event of weak contractions. A cesarean delivery should be performed if there is poor progress of labor despite adequate contractions. Labor analgesia including epidural can be used as needed.
Vaginal breech delivery should be conducted in a facility that is able to carry out continuous electronic fetal heart rate monitoring sufficient personnel to monitor the progress of labor. From the term breech trial, 17 the commonest indications for cesarean section are poor progress of labor (50%) and fetal distress (29%). There is an increased risk of cord compression which causes variable decelerations. Since the fetal head is at the fundus where contractions begin, the incidence of early decelerations arising from head compression is also higher. Due to the irregular contour of the presenting part which presents a high risk of cord prolapse, immediate vaginal examination should be undertaken if membranes rupture to rule out cord prolapse. The frequency of cord prolapse is 1% with frank breech and more than 10% in footling breech. 8
Fetal blood sampling from the buttocks is not recommended. A passive second stage of up to 90 minutes before active pushing is acceptable to allow the breech to descend well into the pelvis. Once active pushing commences, delivery should be accomplished or imminent within 60 minutes. 18
During planned vaginal breech birth, a skilled clinician experienced in vaginal breech birth should supervise the first stage of labor and be present for the active second stage of labor and delivery. Staff required for rapid cesarean section and skilled neonatal resuscitation should be in-hospital during the active second stage of labor.
The optimum maternal position in second stage has not been extensively studied. Episiotomy should be undertaken as needed and only after the fetal anus is visible at the vulva. Breech extraction of the fetus should be avoided. The baby should be allowed to deliver spontaneously with maternal effort only and without any manipulations at least until the level of the umbilicus. A loop of the cord is then pulled to avoid cord compression. After this point, suprapubic pressure can be applied to facilitate flexion of the fetal head and descent.
Delay of arm delivery can be managed by sweeping them across the face and downwards towards in front of the chest or by holding the fetus at the hips or bony pelvis and performing a 180° rotation to deliver the first arm and shoulder and then in the opposite direction so that the other arm and shoulder can be delivered i.e., Lovset’s maneuver (Figure 5).
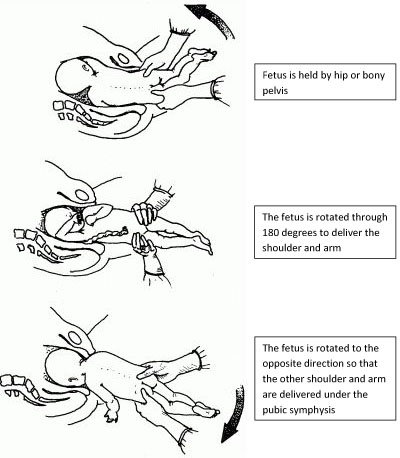
Lovset’s maneuver. Reproduced from WHO 2006 , 1 with permission .
The fetal head can deliver spontaneously or by the following maneuvers:
- Turning the body to the floor with application of suprapubic pressure to flex the head and neck.
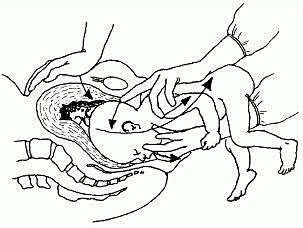
Mauriceau-smellie-veit maneuver . Reproduced from WHO 2003, 14 with permission.
- By use of Piper’s forceps.
- Burns-Marshall maneuver where the baby’s legs and trunk are allowed to hang until the nape of the neck is visible at the mother’s perineum so that its weight exerts gentle downwards and backwards traction to promote flexion of the head. The fetal trunk is then swept in a wide arc over the maternal abdomen by grasping both the feet and maintaining gentle traction; the aftercoming head is slowly born in this process.
If the above methods fail to deliver the fetal head, symphysiotomy and zavanelli maneuver with cesarean section can be attempted. Duhrssen incisions where 1–3 full length incisions are made on an incompletely dilated cervix at the 6, 2 and 10 o’clock positions can be done especially in preterm.
Face presentation
The diagnosis of face presentation is made during vaginal examination where the presenting portion of the fetus is the fetal face between the orbital ridges and the chin. At diagnosis, 60% of all face presentations are mentum anterior, 26% are mentum posterior and 15% are mentum transverse. Since the submentobregmatic (face presentation) and suboccipitobregmatic (vertex presentation) have the same diameter of 9.5 cm, most face presentations can have a successful vaginal birth and not necessarily require cesarean section delivery. 6 The position of a fetus in face presentation helps in guiding the management plan. Over 75% of mentum anterior presentations will have a successful vaginal delivery, whereas it is impossible to have a vaginal birth in mentum posterior position unless it converts spontaneously to mentum anterior position. In mentum posterior position the neck is maximally extended and cannot extend further to deliver beneath the symphysis pubis (Figure 7).
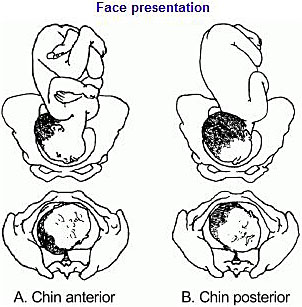
Face presentation. Reproduced from WHO 2003, 14 with permission.
As in breech management, face presentation also requires continuous fetal heart rate monitoring, since abnormalities of fetal heart rate are more common. 5 , 6 In one study , 20 only 14% of pregnancies had normal tracings, 29% developed variable decelerations and 24% had late decelerations. Internal fetal heart rate monitoring with an electrode is not recommended, as it may cause facial and ophthalmic injuries if incorrectly placed. Labor augmentation and cesarean sections are performed as per standard obstetric indications. Vacuum and midforceps delivery should be avoided, but an outlet forceps delivery can be attempted. Attempts to manually convert the face to vertex or to rotate a posterior position to a more favorable anterior mentum position are rarely successful and are associated with high fetal morbidity and mortality, and maternal morbidity, including cord prolapse, uterine rupture, and fetal cervical spine injury with neurological impairment.
Brow presentation
The diagnosis of brow presentation is made during vaginal examination in second stage of labor where the presenting portion of the fetal head is between the orbital ridge and the anterior fontanel.
Brow presentation may be encountered early in labor, but is usually a transitional state and converts to a vertex presentation after the fetal neck flexes. Occasionally, further extension may occur resulting in a face presentation. The majority of brow presentations diagnosed early in labor convert to a more favorable presentation and deliver vaginally. Once brow presentation is confirmed, continuous fetal heart rate monitoring is necessary and labor progress should be monitored closely in order to pick any signs of abnormal labor. Since the brow diameter is large (13.5 cm), persistent brow presentation usually results in prolonged or arrested labor requiring a cesarean delivery. Labor augmentation and instrumental deliveries are therefore not recommended.
CESAREAN DELIVERY
This is an option for women with breech presentation at term to choose cesarean section as their preferred mode of delivery, for those with unsuccessful ECV who do not want to attempt vaginal breech delivery, have contraindications for vaginal breech delivery or in the event that there is no available skilled personnel to safely conduct a vaginal breech delivery. Women should be given enough and accurate information about pros and cons for both planned cesarean section and planned vaginal delivery to help them make an informed decision.
Since the publication of the term breech trial, 17 , 19 there has been a dramatic global shift from selective to planned cesarean delivery for women with breech presentation at term. This study revealed that planned cesarean section carried a reduced perinatal mortality and early neonatal morbidity for babies with breech presentation at term compared to planned vaginal birth (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.19–0.56). The cesarean delivery rate for breech presentation is now about 70% in European countries, 95% in the United States and within 2 months of the study’s publication, there was a 50–80% increase in rates of cesarean section for breech presentation in The Netherlands.
A planned cesarean delivery should be scheduled at term between 39–41 weeks' gestation to allow maximum time for spontaneous cephalic version and minimize the risk of neonatal respiratory problems. 8 Physical exam and ultrasound should be performed immediately prior to the surgery to confirm the fetal presentation. A detailed consent should be obtained prior to surgery and should include both short- and long-term complications of cesarean section and the alternatives of care that are available. The abdominal and uterine incisions should be sufficiently large to facilitate easy delivery. Thereafter, extraction of the fetus is similar to what is detailed above for vaginal delivery.
Cesarean section for face presentation is indicated for persistent mentum posterior position, mentum transverse and some mentum anterior positions where there is standard indication for cesarean section.
Persistent brow presentation usually necessitates cesarean delivery due to the large presenting diameter that causes arrest or protracted labor.
Transverse/oblique lie
Cesarean section is indicated for patients who present in active labor, in those who decline ECV, following an unsuccessful ECV or in those with contraindications to vaginal birth.
For dorsosuperior (back up) transverse lie, a low transverse incision is made on the uterus and an attempt to grasp the fetal feet with footling breech extraction is made. If this does not succeed, a vertical incision is made to convert the hysterotomy into an inverted T incision.
Dorsoinferior (back down) transverse lie is more difficult to deliver since the fetal feet are hard to grasp. An attempt at intraabdominal version to cephalic or breech presentation can be done if membranes are intact before the uterine incision is made. Another option is to make a vertical uterine incision; however, the disadvantage of this is the risk of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies.
PERINATAL OUTCOME
Availability of skilled neonatal care at delivery is important for good perinatal outcomes to facilitate resuscitation if needed for all fetal malpresentations. 8 All newborns born from fetal malpresentations require a thorough examination to check for possible injuries resulting from birth or as the cause of the malpresentation.
Neonates who were in face presentation often have facial edema and bruising/ecchymosis from vaginal examinations that usually resolve within 24–48 hours of life and low Apgar scores. Trauma during labor may cause tracheal and laryngeal edema immediately after delivery, which can result in neonatal respiratory distress and difficulties in resuscitative efforts.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
- Diagnosis of unstable lie is made when a varying fetal lie is found on repeated clinical examination in the last month of pregnancy.
- Consider external version to correct lie if not longitudinal.
- Consider ultrasound to exclude mechanical cause.
- Inform woman of need for prompt admission to hospital if membranes rupture or when labor starts.
- If spontaneous rupture of membranes occurs, perform vaginal examination to exclude the presence of a cord or malpresentation.
- If the lie is not longitudinal in labor and cannot be corrected perform cesarean section.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Author(s) statement awaited.
Publishers’ note: We are constantly trying to update and enhance chapters in this Series. So if you have any constructive comments about this chapter please provide them to us by selecting the "Your Feedback" link in the left-hand column.
Online Study Assessment Option All readers who are qualified doctors or allied medical professionals can now automatically receive 2 Continuing Professional Development credits from FIGO plus a Study Completion Certificate from GLOWM for successfully answering 4 multiple choice questions (randomly selected) based on the study of this chapter. Medical students can receive the Study Completion Certificate only.
(To find out more about FIGO’s Continuing Professional Development awards programme CLICK HERE )
I wish to proceed with Study Assessment for this chapter
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience from our website. By using the website or clicking OK we will assume you are happy to receive all cookies from us.

COMMENTS
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie) Neck bent forward with chin tucked. Arms folded across the chest . If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible. Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse. Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position. Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with. Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. ... In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than ...
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
Frank breech. When a baby's feet or buttocks are in place to come out first during birth, it's called a breech presentation. This happens in about 3% to 4% of babies close to the time of birth. The baby shown below is in a frank breech presentation. That's when the knees aren't bent, and the feet are close to the baby's head.
This presentation occurs when your baby's head is up near your ribs, and both feet are up by their head (like they're bent perfectly in half). Baby's buttocks points down towards the cervix. ... Lying Sideways (Transverse Lie) When baby is positioned horizontally—or side to side—across the uterus, it's known as a transverse lie ...
The fetal presentation describes the fetal part that is lowest in the maternal abdomen. In case of labor, it is the lowest fetal part in the birth canal. Many fetal presentations are possible: Cephalic presentation: the fetal head is the lowest fetal part. This is by far the most common presentation at term of pregnancy and in labor.
Fetal lie, position, and presentation are noted. Lie describes the relationship of the long axis of the fetus to that of the mother (longitudinal, oblique, transverse). Position describes the relationship of the presenting part to the maternal pelvis (eg, occiput left anterior for cephalic, sacrum right posterior for breech).
During routine prenatal care, clinicians assess fetal lie and presentation with physical examination in the late third trimester. Ultrasonography can also be done. If breech presentation is detected, external cephalic version can sometimes move the fetus to vertex presentation before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.
Lie. Facing the patient's head, place hands on either side of the top of the uterus and gently apply pressure. Move the hands and palpate down the abdomen. One side will feel fuller and firmer - this is the back. Fetal limbs may be palpable on the opposing side. Fig 2 - Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Fetal presentation means the part of the fetus that is "presenting" at the cervix: Cephalic presentation means head first. ... Whenever a fetal transverse lie is encountered near term or in labor, evaluate the patient carefully with ultrasound to determine if there are any predisposing factors, such as a placenta previa or pelvic kidney that ...
Presentation. After the lie of the fetus is assessed, the clinician has to detail the fetus further by describing the lowermost structure of the fetus in the maternal pelvis. This is referred to as the fetal presentation. In a vertical (or longitudinal) lie, the fetal presentation can be either cephalic or breech. In the transverse lie, the ...
Presentation of twins in Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden"), a standard medical text for midwives published in 1513. In obstetrics, the presentation of a fetus about to be born specifies which anatomical part of the fetus is leading, that is, is closest to the pelvic inlet of the birth canal. According to the leading part, this is identified as a cephalic, breech, or shoulder presentation.
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position.
Transverse lie refers to a fetal presentation in which the fetal longitudinal axis lies perpendicular to the long axis of the uterus. It can occur in either of two configurations: The curvature of the fetal spine is oriented downward (also called "back down" or dorsoinferior), and the fetal shoulder presents at the cervix ( figure 1 ).
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part (the part that first enters the birth canal). All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations ...
Fetal presentation is a reference to the part of the fetus that is overlying the maternal pelvic inlet. The most common relationship between fetus and mother is the longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. A breech fetus also is a longitudinal lie, with the fetal buttocks as the presenting part.
A normal fetal lie is an ideal position for labor and baby delivery in which the baby is head-down with the chin tucked into its chest. The back of the head is positioned so that it is ready to enter the pelvis. The fetus faces the mother's back, called cephalic presentation, and the babies mostly settle in this position by 32 to 36 weeks of ...
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion). The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids Uterine Fibroids A fibroid is a noncancerous tumor of the uterus that is composed of muscle and fibrous tissue.
This is usually referred to as a transverse lie. Figure 10-1. Typical types of presentations. (2) Percentages of presentations. (a) Head first is the most common-96 percent. (b) Breech is the next most common-3.5 percent. (c) Shoulder or arm is the least common-5 percent. (3) Specific presentation may be evaluated by several ways.
7.6.1 Diagnosis. The uterus is very wide: the transverse axis is virtually equivalent to the longitudinal axis; fundal height is less than 30 cm near term. On examination: head in one side, breech in the other (Figures 7.1a and 7.1b). Vaginal examination reveals a nearly empty true pelvis or a shoulder with—sometimes—an arm prolapsing from ...
The incidence of breech presentation is 20-25% of fetuses at <28 weeks, but only 7-16% at 32 weeks, and only 3-4% at term. 2, 3. Face and brow presentation are uncommon. Their prevalence compared with other types of malpresentations are shown below. 4. Occiput posterior - 1/19 deliveries;