History Thesis Topics: List of 69 Outstanding Ideas

Unless you plan to go for a Ph.D. in history, a thesis will be the most significant academic writing of your life. It shows your in-depth knowledge of a subject, your ability to think logically, creatively, and originally. Besides, it’s a great way to demonstrate how good your writing is.
But finding an appropriate title for your thesis is a challenging task. You may feel unsure about any idea until you see the rest of them. So, what can help you?
A history thesis topics list, of course. In this article, you’ll consider a wide variety of ideas about historical events and figures. There are some tips on picking the right one for you. With a little explanation of the basics, you’ll differentiate the Bachelor’s thesis from the Master’s one in a second.
- ☝️ How to Choose?
- ⭐ Top-12 Thesis Ideas
- 🚀 American History
- ⚔️ European History
- 🎨 Art History
- 📚 MA Thesis Topics
- 🦉 MPhil Thesis Ideas
- 👨🏫 Thesis vs. Dissertation

☝ How to Choose a History Thesis Topic?
Before picking a topic about history, you have to understand what you’re looking for. Take into account that you’re going to spend plenty of time writing your thesis. So, you need to find an idea that engages you and is worthy of your time. Don’t go for a random history topic that you do not feel passionate about.
Searching for an idea, follow the tips below:
- Find a topic that interests you . You’ll most probably write your thesis for a whole semester or even longer. That’s why you should determine something that doesn’t bore easily. At least those countless hours in the library will be spent with pleasure. The more the idea challenges and intrigues you, the less you’ll procrastinate and suffer from writing. No one can tell you what to write about. Your advisor can help you specify the topic, but it is up to you what to write about.
- Look for a topic that creates a trajectory for further research . You may not pursue it later, but having an opportunity to do so is a significant advantage. If you decide to pursue a further degree, you will already be familiar with the topic well. Take a look at available works in a free essays database to get a clearer picture of what can be further explored.
- Find a professor who will become your thesis advisor . Bring some thesis ideas up and see what your instructor suggests. It’s a good thing to have several research topics in mind—the instructor can help you determine the best one.
- Think beyond the graduation date . Whether you are going to start a career or continue your studies, your thesis should help you in achieving your goals. What may your employer look for in your paper? What do you need to be successful in your job or further research? It’s good to approach the issue with some level of practicality. See if you can apply the skills and information you’ve acquired to your professional life.
- Strive for originality but stay within your studies context . Try to make your title unique to grasp attention and intrigue from the get-go. At the same time, don’t fall outside the scope of your field. Before picking a topic, do some research to understand the field deeper. This way, you’ll see what exactly you would like to address.
- Make sure your title fits the requirements . Open your university guidelines for the thesis work and find this out before anything else. Ask your thesis advisor as well to give you honest feedback.

⭐ Top-12 History Thesis Ideas
- Civil War — the role of women.
- The Watergate Scandal.
- Contemporary art history.
- The Napoleonic Wars.
- Causes of World War 2.
- Impact of the Black Plague.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis.
- Japanese-American conflict.
- The Vietnam anti-war protests.
- Origins of the Great Famine in Ireland.
- The French Revolution.
- The rule of Elizabeth I.
📝 History Thesis Topics for Bachelor’s Degree
Usually, American Universities don’t require students to write a Senior Thesis. However, you still have an option to choose one. You can write a thesis as a part of your program completion. It will take a lot of time, energy, and effort. But, in the end, you will be able to produce a prime piece of academic writing.
Strive to write anywhere from 60 to 100 pages. You will also dedicate a lot of time writing and polishing it afterward. Make sure to leave enough time for that too.
What’s the first step?
Look for a thesis advisor you know you will enjoy working with. Consider all the professors you’ve interacted with at your university and pick several. Approach them and see if they are accepting new students for thesis supervision.
Make sure to choose a history thesis paper topic that your advisor knows a lot about. At some point, you will become very knowledgeable about the history thesis topic you chose. It will be crucial to have someone who can direct you.
There are several reasons why you should consider writing a thesis for a Bachelor’s Degree in history:
- It provides you with essential experience in writing, researching, and brainstorming ideas. It can later help you in your academic or professional life.
- You can deeply understand a subject that interests you.
- You can improve your reading skills.
- If you have to use foreign sources, you can also increase your foreign language skills.

Are you still wondering what historical thesis ideas are appropriate? Then, this list is perfect for you.
🚀 American History Thesis Topics
- African American history in the United States : disfranchisement and segregation in 1890-1900
- Early American History and the lost colony of Roanoke
- The construction of race in American culture and history. It’s not a secret that race is a social construct. In American culture and history, it plays a critical role. In the thesis, you will have a chance to research the mechanisms through which the race was constructed. Movies, literary representations, articles, what else? It’s up to you to find out what can be relevant.
- World War 2 through personal letters and diaries . This thesis can be personal and will not leave people indifferent. Examination of diaries, notes, and personal accounts can be fascinating. You won’t be bored doing historical research. Maybe you even have some in your own family? Worth checking it out.
- Guilt over Slavery in the United States: a historical examination
- Gender equality in American education . A comparative study of Germany, Russia, The United States
- New York City and its historical geography. NYC is one of the captivating American cities. Writing a thesis about its historical geography is not an easy task. Gladly, you have tons of information available to you.

- Rocket Science as one of the most significant innovations of the 20th century
- Examining the Role of Privilege within the Ivy League Universities
- Role of American Public Health in a Post-9/11 World
⚔ European History Thesis Topics
- Formation and development of the European Union during the 20th century
- Feminist perspective on the representation of women in Roman Art
- Religion and Nation in Europe in the 19th century
- Construction of National Identity in Post-Soviet Latvia. What did contribute to developing a national identity of post-soviet Latvia? First of all, its independence and belonging to the European Union. In this thesis, talk about colonization and colonial identity. Consider the policies Latvian government implemented to build a Latvian character. What is it? What are the essential characteristics of it?
- Composition and religious hierarchy in The Last Supper by Leonardo Da Vinci
- Representation of Jews in Late Medieval Period in Europe
- Problems of political leadership in Athens of 404-355 BCE
- The French Renaissance Court and its structural hierarchy. This topic is interesting yet complex. Its complexity comes not from the name but the nature of the French Renaissance Court. You need to have a clear idea of how the royal court is built and is operating. Find relevant historians of that time, and, hopefully, you can speak some French.
- Immigrational Politics of the United Kingdom. The problem of multiculturism at the beginning of 1960-1980.
- Orientalism or the Middle East through the prism of Western scholars in the XIX century. In this thesis, start by exploring the notion of Orientalism. Edward Said will be a good point of departure and one of the most fundamental works to cite and read. You can agree with his argument or disagree with it. Nevertheless, find the relevant evidence for your point of view.
🎨 Art History Thesis Topics
- Medicine in Ancient Rome with a focus on surgeries through paintings. This thesis topic is rich. Numerous Ancient Roman paintings depict surgeries and medical treatments. Find the most interesting ones and talk about innovations in medicine. What was the point of recording medical procedures in art? Truly a topic that can captivate anyone.
- Vincent Van Gogh: A phycological analysis of the artist’s last years . In this thesis, examine his artworks together with the personal letters. Look at the words he used, as well as the images he painted. You need it to comprehend what was happening in Vincent’s life in his last years. Some art therapists claim that the artist had bipolar disorder. Examine those views. However, be careful not to give any medical diagnosis yourself.

- Plato on Punishment and Vice: the notion of punishment in The Republic. You cannot get a degree without reading the most fundamental text of the Western Academy, The Republic . In this thesis, you should simply focus on the ideas of punishment and vice. Plato wrote a lot regarding the morals and the laws. Try to discern what exactly he meant. Extract his views regarding capital punishment and punitive justice.
- Modern Art in Europe, with a specific focus on Italy
- Trade in Medieval Europe with a focus on Africa through art
- The erotism of art of Ancient Rome
- Synthesis of sculpture and paintings in Spanish art of the 17th century
- Neoclassicism in French art of the 1900s-1910s
- Surrealism in Art as the quintessence between realism and hyper-realism
📋 History Thesis Topics for Master’s Degree
In the United States, to enter a graduate degree in history, a bachelor’s degree is required. Most of the time, students will have to submit several recommendation letters. Plus, they need GRE scores and writing samples. Add to this several essays explaining the purpose of going to university again, and there you have it.

It is common to have several completion requirements. They can include basic courses, language tests, and a master’s thesis at the end of the program. However, it depends on the department and the university.
Keep in mind that there are several credits that students should obtain to get a degree. It differs from university to university as well. In most of the programs throughout the United States, they are required to complete 30-32 credits to get an M.A. degree. This number usually corresponds to 8-9 classes.
If you are pursuing an M.A., you’re in luck. There is an excellent chance that you will be able to choose if you would like to write a thesis or not. If you are pursuing an M.Phil., then you will have to write your thesis because it’s a research degree.
No matter if you are pursuing an M.A. or an M.Phil., this historical thesis ideas can help you find a title:
📚 MA Thesis Topics in History
- Apotheosis of the Philippine Historical Political Tradition
- Kerala History: Syrian Christians in the region in the 18th century
- History of Modern India with a focus on women’s rights
- The history of theater in the American South and the main characteristics of the Southern Drama. This thesis includes a lot of aspects starting from playwriting in Charleston to drama in New Orleans. Then there are War Drama, Black Drama, etc. Try to find a good balance to fit all of the main characteristics of the Southern Drama and theater.
- New Deal and its impacts on events leading to the Great Depression
- Mistakes of the Soviet side in WW2. WWII was the deadliest military conflict of the 20th century. In this thesis, talk about the biggest mistakes the Red Army made during the war. Some of those can include signing to the Non-Aggression Pact with Hitler. Plus, there were anti-tank dogs and the Molovot-Ribbentrop Pact.

- Military strategies that allowed Napoleon to win crucial battles
- Mussolini & Hitler : connection along with its consequences for Italy
- Queen Victoria’s politics and the way it has changed British history
- The Development of Strategic Bombing Doctrine Between the World Wars
- Historical Creation of a Black Elite in the United States
- Through Imperial Eyes: Race and British Reactions to the American Slavery Question
- Gertrude Bell’s Influence in the Formation of Iraq. Gertrude Bell is a crucial figure in Islamic studies. She contributed a lot to the formation of Iraq. In this thesis, explore her unique contribution and approach to building a modern state of the country. She was highly trusted by British politicians and by Arab leaders.
- Baptist church history as a way to escape slavery
🦉 MPhil Thesis Topics in History
- Investigating the impact of WWI on trade blocks. A case study of the European Union
- Women in WWII: sexual objectification of women through magazines and advertisement. Women played an integral part in WWII. In this thesis, explore the role of sexual imagery in the advertising industry during the war.
- Sudan-American relationships in 1989-2000: US Foreign Policy and Genocide in Sudan
- Criticism of the war on drugs during the Ronald Reagan administration
- The political evolution of the Southern States during the Reconstruction Era
- Everest Expeditions in British Popular Culture, 1920-1960. Explore how Everest Expeditions were depicted in British movies. Analyze the subject via comics, journals, and visual art in the first part of the 20th century.
- Impact of Otto von Bismarck on German Liberalism

- Discrimination of German immigrants in the USA during WW2
- The Fourth International and the Spanish Civil War
- Political and economic aspects of the crisis in Venetian Diplomacy in the 1500s
- The connection between institutionalized racism and police violence in the United States. There are several dimensions to racism. In this thesis, look for a connection between structural racism and police violence in the US. Compare the numbers, look at the stories. See if this data exposes any hidden bias.
- An image of the Medieval Period in Post Modern Art
- A comparative analysis of the Four Quran English Translation. In this thesis, discuss why and how the Quran can be translated. Also, you should look at the four translations. Try to determine which one is the closest. To do that, you need to have an advanced level of Arabic.
- The psychological effect of war on American soldiers in Vietnam
👨🏫 Differences between a Thesis and Dissertation
Understanding the difference between a thesis and a dissertation is essential. Would you like to obtain a master’s and a doctoral degree? Then read attentively. In the United States, both thesis and dissertation are vital for this purpose.
The prominent differences that you have to realize are the following:
- A dissertation is required to graduate with a doctoral degree. A thesis is a culmination of a master’s program.
- A dissertation is written to add a new piece of knowledge to the field. A thesis is to show that you have enough knowledge about the field.
- A dissertation usually takes several semesters, sometimes even years, to complete. A thesis does not require this amount of time. It can be finished within months.
- A dissertation can be seen as an academic book. A master’s thesis is a long research paper.

Let’s see the main characteristics of a bachelor’s thesis, a master’s thesis, an MPhil’s thesis, and a dissertation:
- A Bachelor’s Thesis (honors thesis). It’s a research-based paper that allows undergraduate students to put their knowledge into practice. The paper is usually 40-60 pages long. It includes an introduction, main body, conclusion, and bibliography.
- A Master’s Thesis. It’s a piece of original scholarly work. A mater’s thesis is written under the close supervision of an academic advisor. It attempts to bring some fresh look or a new perspective to a field of study. The length of a master’s thesis can vary. Usually, it doesn’t go beyond 100 pages.
- An MPhil’s Thesis (Master of Philosophy). It’s a specific type of thesis. As it was stated earlier, most American Universities don’t grant this degree. A few schools give it under specific circumstances. Doctoral students should accomplish all the course work and pass their exams. Then, this degree can be granted to them. A more colloquial way to call this degree is “all but dissertation.” In other cases, this degree is granted to students who are doing their postgraduate research.
- A Dissertation. It’s a major piece of academic writing. It’s independent, shows critical and thinking ability. A dissertation is meant to illustrate academic knowledge, originality of work, and research skills. The length usually stays within 200-300 pages.

Any thesis or dissertation is a monumental work. Choose a topic that you are passionate about. Make sure it’s researchable and clear, but at the same time memorable. Spend time writing, proofreading, editing, and talking to your advisor about your ideas and academic goals.
Remember that it is okay to get frustrated and tired at times. If it happens to you, stop working for a bit and relax. Good luck and congratulations on your soon to be graduation! We hope this article was helpful. Share it with those who may need a history thesis topic or a piece of advice.
🔗 References
- MPhil in History: University of Oxford
- How to Pick a Masters Thesis Topic: Peter Campbell for Medium
- How Do I Choose A Thesis Topic: Grad School Hub
- Writing a Senior Thesis: Undergraduate Program, Department of History, Brandeis University
- The Bachelor’s Thesis, Bachelor EE: University of Twente
- Guidelines for the Preparation of Your Master’s Thesis: the Office of Graduate Studies and Research: University of Nebraska at Kearney
- Guidelines for Writing a Master’s Thesis for MA Degree: Jeremy Bailey, Susan Scarrow, University of Houston
- What is a dissertation? How it is different from an essay: The Royal Literary Fund
- What is the Difference Between a Thesis and a Dissertation: The Best Master’s Degrees
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Twitter
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via email
Department of History
Yale history dissertations.

During the late 1800’s, only a trickle of dissertations were submitted annually, but today, the department averages about 25 per year. See who some of those intrepid scholars were and what they wrote about by clicking on any of the years listed below.
History PhD
First awarded by the University of Maryland in 1937, the Doctorate in History is conferred for superior achievement in historical research, writing, and interpretation.
Additional Information
- Forms and Resources
- Funding and Awards
- People (Department Directory)
PhD Program Overview
The Doctorate in History (PhD) is an essential component in the training of professional historians. The most significant requirement of the PhD degree program is the dissertation, an original and noteworthy contribution to historical knowledge. In anticipation of dissertation research, students spend several years mastering bibliographical tools, research and writing methods, and general, special, and minor fields of study.
Admission to the PhD program is offered to highly qualified applicants holding at least a Bachelor's (BA) degree, normally in History or a related discipline. Application and admissions procedures are described on the Department of History's graduate admissions page .
The length of time required to complete the PhD varies by field of study and student. Students admitted with a Bachelor's (BA) degree might expect to complete the program in five to six years of full-time study. Students entering with a Master of Arts (MA) degree might expect to complete the program in four to five years of full-time study. The degree must be completed in no more than nine years. Students typically take two years of course work, prepare for and take language exams (if required for their field) and comprehensive exams, and then research and write the dissertation.
Program Requirements and Policies
General program requirements.
- Course work in the major and minor fields
- Language examinations if required by field
- Comprehensive examinations
- Dissertation prospectus
- Advancement to candidacy
- The dDssertation
Each of these program requirements must be met before the PhD can be conferred.
Course Requirements
All PhD students entering with a Bachelor's (BA) degree (or equivalent) must take, at a minimum, the following courses (total 30 credits, not including 12 credits of “Dissertation Research”):
- Contemporary Theory (HIST 601; 3 credits)
- Major Field General Seminar (HIST 608; 3 credits)
- Readings courses in the major field (HIST 6XX and 7XX; 9 credits)
- Readings courses in the minor field (HIST 6XX and 7XX; 9 credits)
- Research seminars (HIST 8XX; 6 credits)
- Dissertation Research (HIST 898/899; 12 credits)
Special Notes:
- Courses completed during previous post-baccalaureate degree programs and/or at other institutions may be considered to satisfy course requirements. However, students entering the PhD program with a Master's (MA) degree or equivalent in History or a related discipline must take a minimum of two 600-800 level courses in the major field, one of which should be with the major advisor.
- Requests for course requirement waivers, equivalency, and credit transfers should be directed to the Director of Graduate Studies. A request must include the course syllabus and transcripts showing the final grade. The endorsement of the advisor is typically sought.
- Up to nine credit hours of major and minor field readings courses may be taken at the 400 level. Students seeking to take a 400 level course for graduate credit should consult the instructor of record to discuss course expectations before registering.
- HIST 708/709: “Directed Independent Reading for Comprehensive Examinations” does not count toward the nine-credit readings seminar requirement.
- Students in the U.S. and Latin America fields are expected to take two major field seminars (HIST 608)–in this case, one of these 608s will be counted toward the “Readings courses in the major field” requirement.
- Students must complete the entire program for the doctoral (PhD) degree, including the dissertation and final examination, during a four-year period after admission to candidacy, but no later than nine years after admission to the doctoral (PhD) program. Students must be advanced to candidacy within five years of admission to the doctoral (PhD) program.
Fields of Study
Doctoral students should choose one of the following as their “major field” of study:
Global Interaction and Exchange
- Jewish History (Classical Antiquity to the Present)
Latin America
Middle East
- Technology, Science, and Environment
United States
Learn more about fields of study and faculty work produced in each field by visiting the research fields page .
The Minor Field
All doctoral students are required to complete a minor field of study outside the major field of study. This requirement is typically met through nine credit hours of coursework. However, a student may opt to satisfy the requirement by written examination.
A minor field is usually a field of history outside the student's major field of concentration. For example, a student in the U.S. field may select a minor field in Latin American history; a student in the Women & Gender field may select a minor field in European history. The minor field may be a standard national-chronological field (e.g., 19th-century United States; Imperial Russia; Postcolonial India), or it may be a cross-cultural, cross-regional thematic field (e.g., the Atlantic in the era of the slave trade; gender and Islam). Or, it might be taken in a department or program outside of History (e.g., Women's Studies, English, Government & Politics, Classics and Comparative Literature).
For students opting to satisfy the minor field requirement via coursework, all courses must be approved by the student's advisor and must, to the satisfaction of the advisor and the Graduate Committee, form a coherent field of historical inquiry distinct from the general field. Courses taken at the master's level may count towards fulfillment of the minor field requirements, subject to the approval of the advisor and, in the case of courses taken at outside institutions, of the director of graduate studies.
Language Requirements
Language requirements must be fulfilled before a student is admitted to candidacy. While no MA degree requires language examinations, students will often have to learn one or more foreign languages in their field of study to successfully complete their research. They will also need to learn these languages if they wish to continue on towards a PhD. When applying for either program, preference will be given to students with prior experience with languages in their fields of study.
Language requirements differ across the varying fields within history.
No foreign language requirements for the PhD. If a student’s dissertation topic requires research in foreign language materials, the advisor will decide if the student needs to show proficiency by taking an examination in the language in question.
Spanish and Portuguese. For admission, applicants will be evaluated on their language abilities, and preference will be given to applicants with a strong command of Spanish and/or Portuguese. All PhD students must show proficiency by examination in both languages by the time they are admitted to candidacy. Exceptions to one of those languages (typically Portuguese) if the student’s dissertation requires the use of indigenous languages or documents produced by ethnic minorities. In such cases, students must be proficient in those languages.
One language (in addition to English). Depending on the field, the adviser may determine that the student needs to show proficiency in an additional language.
For admission, students must have proficiency at the advanced intermediate level in at least one major Middle Eastern language (Arabic, Persian or Turkish). All PhD students must acquire advanced proficiency in their chosen language either by course work or exam by the time they are admitted to candidacy. In addition, students must demonstrate proficiency in one European language by the time of their comprehensive exams.
Ancient Mediterranean
For admission, students should present knowledge of classical Greek and Latin at the intermediate level and reading knowledge of either French or German. Knowledge of classical Greek, Latin, French and German is required for the PhD. Other language skills, eg. Italian, Spanish, Modern Greek or Hebrew, may prove to be necessary for dissertation research but are not formal program requirements. Students satisfy the requirement in Latin and Greek in one of two ways: either by completing three upper level or graduate courses (400-600 level) in each language and obtaining at least a B in all courses and an A- or better in at least two of the courses; or by passing a departmental sight translation exam. This exam consists of translating (with the help of a dictionary) three passages of three sentences each (roughly one-fourth to one-third OCT page) selected from prose authors of average difficulty. Students show proficiency in French and German through the regular departmental language exams.
Medieval Europe
For admission, proficiency in either Latin, French or German and familiarity with a second of those languages. All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in Latin, French and German. They can satisfy the Latin requirement in one of two ways: either by taking three upper level or graduate courses (400-600 level) and obtaining at least a B in all courses and an A- or better in at least two of the courses; or by passing a departmental sight translation exam. This exam consists of translating (with the help of a dictionary) three passages of three sentences each (roughly one-fourth to one-third OCT page) selected from medieval prose authors of average difficulty. Students show proficiency in French and German through the regular departmental language exams. Depending on the field, students may have to know an additional national/regional language like Spanish or Italian.
Early Modern Europe
For admission, proficiency in one foreign language related to the field. All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in two foreign languages. Depending on the field, students may also have to know Latin.
Modern Europe
For admission, students must know the language of the country or region in which they are interested. All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in the language of the country/region in which they are interested plus another European language.
Russia/Soviet Union
For admission, three years of Russian or the equivalent. All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in Russian plus either French or German. Depending on the area of interest, the adviser may require an additional language.
For admission, advanced intermediate-level proficiency in modern Hebrew. All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in modern Hebrew and one other language necessary for their fields. The advisor may require other languages as necessary.
Chinese History
For admission, students must have had at least two years of university-level Chinese language courses. All PhD students must acquire advanced proficiency in Chinese since they will be using Chinese documents for their dissertations. Before admission to candidacy students must pass a Chinese language exam in which they will translate about 30 lines of modern, scholarly Chinese into English. As with all departmental language exams, students will be able to use a dictionary, and they will have four hours to complete the translation.
Language Examinations
Except as specified for Latin and ancient Greek, the typical language proficiency examination includes a summary and translation of a passage from a work of modern scholarship in the student’s field. The director of graduate studies appoints a faculty member, typically the student’s advisor, to coordinate the exam and select an excerpt from a published work of historical scholarship in the student’s field. Students write a 200-300 word summary of this five-to-seven page excerpt from the scholarly literature in their fields, and then they do a direct translation of an indicated 30-line passage within that excerpt. The direct translation must be accurate and rendered in idiomatic English. Students have four hours to complete the exam, and they may use a language dictionary that they themselves provide.
Language exams can be taken at any time before candidacy. The exams are read by two members of the faculty: typically, the student’s advisor, who chooses the passage and serves as chair of the exam committee, and one other member of the faculty chosen by the D\director of graduate studies in consultation with the advisor. Faculty from outside the department who have the necessary expertise are eligible to serve as evaluators. The two possible grades are pass and fail. If the two readers do not agree, the director of graduate studies will appoint a third faculty member to read the exam. Students who do not pass on the first attempt may retake the examination without prior approval. After a second failure, the student must petition for reexamination. The chair of the language exam committee will notify the director of graduate studies about the results of the exam within one week after the exam, and the graduate coordinator will notify the student in writing about the results, which will then be inserted into the student’s records. All students should normally pass their language examinations during their third year of the program, though given the complexity of the language requirements in different fields of study, the department recognizes the need to exercise some flexibility in the timing of this requirement.
- Comprehensive Examinations
Comprehensive examinations (comps) are a standard feature of historical training in the United States. The examinations require the examinee to demonstrate mastery of historical scholarship and historiography in a major field, including specialized mastery of the authors, themes, works and topics most relevant to the intended dissertation topic. All students register for HIST 708/709: “Directed Independent Reading for Comprehensive Examinations” for two semesters, once in the semester prior to the one in which they are scheduled to take the examinations (normally the fifth semester of the student’s program) and the second in the same semester as their examinations (normally the sixth semester of the student’s program). As noted above, these courses do not count towards the nine-credit readings seminar requirement.
Comprehensive examinations include the following:
- A special field examination in the form of an essay. Students prepare an essay of 4,000 to \5,000 words in length, 16-20 pages, double-spaced in a 12-point font. The special field is a subfield of the major field in which the dissertation is centered.
- A take-home major field examination administered in written format. Students have 48 hours to complete the exam, which should be 5,000 to 6,000 words, 20-24 pages, double-spaced in a 12-point font in length.
- A two-hour oral examination by the examination committee, including coverage of both the take-home major field exam and the essay that comprises the special field exam.
Timeline : The comprehensive examinations are administered during the first half of the student’s sixth semester in the program. The special field essay has to be submitted to the graduate coordinator before the student takes the major field examination. The oral examination follows within two weeks of passing the major field examination and the special field essay. Students entering the program with an MA in history might be expected to complete their comprehensive examinations during their fifth semester in the program. (Also see the “Combined Timeline for Comprehensive Examinations and the Prospectus” at the end of this document.)
Reading Lists : The format, content and length of the reading lists for the comprehensive examinations vary by field but the list should normally be in the range of 200 to 250 books. Of these, about two-thirds should be in the major field and one-third in the special field. In all fields, students develop their reading lists in consultation with their advisors and other members of the examination committee. The reading list must be compiled and approved by the examination committee by the end of their second-year summer (after the student’s fourth semester in the program). For students coming in with an MA in history who would like to take their examinations during their fifth semester in the program, the list must be ready by the end of the student’s third semester. After approval, limited changes may be made solely by mutual agreement of the student and his/her advisor.
The examination committee : The examination committee consists of three or four members of the Graduate Faculty, typically all members of the history faculty. The director of graduate studies designates the committee members and chair, in consultation with the major advisor and the student. The committee chair shall not be the student's advisor. All committee members contribute questions to the written and oral examinations. Most or all of these same committee members are normally also on the student’s dissertation committee but the composition of the examination and prospectus committees do not need to be the same.
Grading : Comprehensive examinations will be graded pass, pass with distinction or fail.
Combined Timeline for Comprehensive Exams and Prospectus
- Both the initial version of the prospectus and the special field essay are due before the major field take-home examination during the first half of the sixth semester of the student's program.
- The major field take-home examination should be completed also during the first half of the sixth semester of the student's program after the initial version of the prospectus and the special field essay are submitted.
- The two-hour oral examination on both the take-home major field exam and the essay that comprises the special field exam follows within two weeks of passing the major field examination and the special field exam. This oral exam can take place during the second half of the sixth semester of the student’s program.
- The one-hour oral examination based on the initial version of the prospectus also takes place during the second half of the sixth semester of the student’s program but only after successful completion of the two-hour oral examination (#3 above).
- The final version of the prospectus as approved by the advisor is due on the first day of the academic semester that immediately follows the comprehensive examinations, which is normally the seventh semester of the student’s program.
Prospectus & Candidacy
Dissertation Prospectus
The dissertation prospectus is a written précis of the proposed dissertation research, its significance, the sources and methods to be used, the relevant bibliography including primary source materials and the plan of completion. It is intended to form the substance of grant proposals students will write in order to apply for both internal and external grants and fellowships. Each field of study has its own expectations for the length of the prospectus, but normally these should be concise documents not to exceed 10-12 pages in length, followed by a bibliography. In all fields, the prospectus is developed by the student in close collaboration with the advisor and other members of the examination committee.
The preparation of the prospectus includes the following stages :
- An initial version of the prospectus.
- A one-hour oral examination based on that initial version.
- A final version incorporating any revisions suggested by members of the dissertation committee and approved by the advisor submitted to the graduate coordinator.
Timeline : The initial draft version of the prospectus should be submitted to the graduate coordinator during the first half of the student’s sixth semester before the student takes the major field examination, normally at the same time as the special field essay. The one-hour oral examination of the prospectus based on the initial version is scheduled during the second half of the student’s sixth semester in the program following satisfactory completion of the comprehensive examinations. The final version of the prospectus as approved by the advisor is due on the first day of the academic semester that immediately follows the comprehensive examination. (Also see the “Combined Timeline for Comprehensive Examinations and the Prospectus” at the end of this document.)
The relationship between the prospectus and the special field Essay: The special field essay normally covers the historiography of the entire subfield within the major field in which the dissertation is anchored, while the prospectus is more narrowly concerned with the specific research topic of the dissertation.
The examination committee: The prospectus oral examination committee consists of the advisor and at least two other members of the Graduate Faculty, who are normally also members of the student’s dissertation committee. The advisor chairs the examination. All committee members contribute questions to the oral examination and make suggestions for revisions. Upon passing the oral examination, the student will complete any revisions requested (as determined by the advisor and the committee) and submit the final prospectus approved by the advisor to the graduate program coordinator.
MA “Along the Way”
When a student receives a pass or pass with distinction and the endorsement to continue on in the PhD program, the student has the option to request that the Master of Arts degree be conferred "along the way," subject to fulfillment of the standard requirements of the MA degree.
In some instances, the examination committee may recommend that a PhD student taking comprehensive examinations be given a pass at the MA level, sufficient for the conferral of a terminal master's degree. Such a recommendation will be made with the expectation that the student not continue on towards doctoral candidacy.
Petition for Reexamination
In the case of failure of a language examination taken for the second time or one or more components of the comprehensive examinations and the prospectus preparation process (special field essay, take-home major field examination, two-hour oral examination and prospectus oral examination), the student may petition the director of graduate studies to take the whole examination or the relevant component(s) a second time. If the petition is approved, the student may retake the examination as soon as possible. A student may petition only once to retake all or part of the comprehensive examinations and the prospectus preparation process.
Successful completion of the prospectus is typically the last step before application for advancement to candidacy.
- Advancement to Candidacy
A doctoral student advances to candidacy when all degree requirements (i.e., course work, demonstrated competence in languages or special skills, comprehensive examinations and the dissertation prospectus) have been satisfied, with the exception of the dissertation.
Formal admission to candidacy (sometimes known as "All but Dissertation" or "ABD" status) is granted by the dean of the Graduate School. The application is routed through the director of graduate studies.
Advising & Committees
Each student admitted to the PhD program will choose an advisor who is a member of the Graduate Faculty and whose intellectual interests are compatible with the student's plan of study. All graduate students are required to choose an advisor by November 1 of their first semester. If they do not choose an advisor by that date, the director of graduate studies will appoint one for them. The faculty advisor will be responsible for advising the student on all aspects of their academic program, for approving the student's course of study each semester, for monitoring their progress through the program,and for notifying the student of the nature and timing of examinations and other evaluative procedures. The advisor, in consultation with the student and the director of graduate studies, will be responsible for constituting the Comprehensive Examination and Dissertation Examination committees. The advisor will also represent the student to the Graduate Committee, as appropriate.
At the conclusion of the first year of study, all students will make available to their advisor a transcript of coursework and major written work completed during the first year. Upon review of the appropriate materials, the advisor will then recommend to the director of graduate studies continuation, modification or, as appropriate, termination of the student's program. All recommendations for termination require discussion and approval of the Graduate Committee.
Students may change advisors. The director of graduate studies and the new faculty advisor shall approve changes in advisors before a student advances to candidacy. After advancement to candidacy, changes shall be approved only by petition to the Graduate Committee. A change of advisor must be recorded in the student's electronic file.
Registration and Degree Progress
Continuous Registration
All graduate students must register for courses and pay associated tuition and fees each semester, not including summer and winter sessions, until the degree is awarded.
Pre-candidacy doctoral students who will be away from the university for up to one year may request a waiver of continuous registration and its associated tuition and fees. Waivers shall be granted only if the student is making satisfactory progress toward the degree and can complete all the degree requirements within the required time limits. Interruptions in continuous registration cannot be used to justify an extension to time-to-degree requirements.
Once advanced to candidacy, a student is no longer eligible for Waivers of Continuous Registration. Doctoral candidates must maintain continuous registration in HIST 899: “Doctoral Dissertation Research” until the degree is awarded.
The Graduate School makes available an official leave absence for childbearing, adoption, illness and dependent care. The dean of the Graduate School must approve the leave. The time-to-degree clock is suspended during an approved leave of absence.
Additional information on continuous registration and leave absence policies is published online in the Graduate Catalog.
Time-to-Degree
All students admitted to the doctoral program are expected to
- advance to candidacy within three years from initial enrollment in the Ph.D. program, and
- complete all degree requirements within six years of entering the program.
Progress-to-Degree
All students in the doctoral program will be expected to demonstrate steady progress toward the completion of degree requirements. At a minimum, the Graduate School requires students to maintain a B average in all graduate courses. However, the Department of History expects a higher level of performance, with the great majority of a student’s grades at the level of an A- or above.
Students in major fields that require lengthy language or special skill acquisition might be granted a one-year extension to progress-to-degree expectations. Additional extensions will require the approval of the Graduate Committee.
In order to meet progress-to-degree expectations :
- 800-level research seminar work should normally be completed by the end of the fourth semester in the program.
- The major field reading list must be compiled and approved by the examination committee by the end of the summer after the student’s fourth semester in the program.
- Students should complete their comprehensive examinations by the end of their sixth semester in the program. Students coming in with an M.A. in history should normally complete their comprehensive examinations by the end of their fifth semester in the program.
- Each student will be expected to submit a copy of the final dissertation prospectus approved by the advisor to the graduate program coordinator at the beginning of their seventh academic semester in the program.
- All students should normally pass their language examinations during the third year of their program.
- The director of graduate studies will review fully each student's progress-to-degree as well as the overall progress-to-degree by degree cohort at least once a year.
Failure to make satisfactory progress-to-degree or to maintain the expected grade point average may result in the suspension or loss of departmental funding, the denial of a petition for extensions, and in extreme cases, a recommendation for dismissal.
NOTE : The above guidelines on continuous registration, time-to-degree and progress-to-degree guidelines are for students matriculating in fall 2018 or thereafter. Students entering the graduate program in prior semesters are subject to guidelines at time of matriculation.
Extensions and Waivers
The Graduate Committee will consider petitions for waivers to departmental guidelines. Petitions for waivers to Graduate School requirements must be submitted to the dean of the Graduate School, using the appropriate form. In most instances, the petitioning student will be required to provide a rationale for the waiver request, and, as appropriate, a convincing plan of study. The advice of the student's advisor may be sought. The advisor will be required to endorse any waiver request that involves extensions to overall time-to-degree as well as the major benchmarks of progress-to-degree.
All petitions should be directed to the director of graduate studies. The director of graduate studies, and in some cases the dean of the Graduate School, will notify the student of their disposition of petitions for extensions.
Sample Program of Study
Introduction.
The program of study often varies by field and many factors may extend or reorder the sequence and length of the program of study.
The following program of study assumes that the doctoral student will be assigned a teaching assistantship in the second, third and fourth years of study. Students coming in with an MA in history will be expected to complete the program in five or five and a half years.
Foreign language study is not incorporated into this program.
First Year (Departmental Fellowship)
- Major Field General Seminar (608) or Contemporary Theory (HIST 601)
- Major Field Readings Seminar
- Minor Field Course
- Research Seminar OR Minor Field Course
- Exploratory Research
Second Year (Teaching Assistantship)
- 2 courses out of the following three categories:
- Research Seminar
- Research Seminar
- Reading for Comprehensive Examinations
- Initial Prospectus Preparation
Third Year (Teaching Assistantship)
- HIST 708: Readings for Comprehensives”
- Prospectus Preparation
- Grant Applications
- HIST 709: “Readings for Comprehensive Examinations”
- Prospectus Oral Examination
- Final Version of Prospectus
- Dissertation Research
Fourth Year (Teaching Assistantship)
- Dissertation Research (HIST 899)
Fifth Year (Departmental or External Fellowship)
- Grant Applications
Spring & Summer
- Dissertation Writing
Sixth Year (Departmental or External Fellowship)
- Job applications
- Job applications
Graduate Placement
Learn more about the career and life paths of our PhD alumni.
Graduate Coordinator, History
2131 Francis Scott Key Hall College Park MD, 20742
Department of History
Ph.d. program outline.
- Ph.D. Program
The Ph.D. program in History is designed to train students in the skills of conducting original historical research and crafting unique historical arguments.
In the course of their work as historians, Brown scholars draw on a wide range of methods and engage with a variety of audiences. Thus although we begin with the core skills of academic research and writing and teaching at the college and university levels, we do not end there. Many Brown doctoral students explore teaching in and writing for different settings, and prepare for a breadth of careers that value the skills that a obtaining a Ph.D. in history entails.
The Brown Ph.D. program is intimate and rigorous, and students are expected to complete in five to seven years. One of the program's hallmarks is a series of required courses in which an entire cohort is trained in core professional skills. This series is composed of: (1) a methodology colloquium that introduces the students to a wide range of theory and historical practice; (2) an advanced writing workshop in which students write an article-quality paper; (3) a professionalization seminar in which students are trained in the habits of mind and skills of the profession; and (4) a dissertation prospectus seminar. Critically, students in an entering cohort proceed through these courses together, so that discussions across fields, geographies, and chronologies are built into the doctoral program.
The program is divided into two stages
- During the first and second years students take seminars that introduce the major historiographical questions and methodologies of various fields and that develop their research skills; they write an article-length paper based on original archival research; they take a professionalization course that introduces them to the principal tasks and cultures of the profession (grant writing, for instance, and conference presentations); and they form an exam committee and begin preparation for the preliminary examinations.
- After passing the examinations by the end of their fifth semester, students develop a prospectus for and research and write their dissertation. The dissertation is typically completed in the fifth or sixth year (though some students take longer).
The department offers four types of Ph.D. seminars:
- Field Seminars (2970s) offer students a broad overview of a field, typically an exam field.
- Required Seminars are the four seminars required of all Ph.D. students: Colloquium, Writing Workshop, Professionalization, and Prospectus.
- Special Topics Seminars focus on the historiography of a particular nation or region, for example, a particular historical “event,” or historiographical debate. They allow for focused, close training, including specialized skills (e.g. paleography), readings in languages other than English, or extensive examination of the scholarship on a particular problem.
- Thematic Seminars (2980s) offer students the opportunity to explore a particular theoretical/methodological frame in a transnational and transtemporal perspective.
The First and Second Years
In their first year, students take 3 seminars in the fall (2 plus the colloquium) and 3 seminars in the spring. Ideally, the courses should be a mix of Field and Thematic seminars, with the inclusion of a Special Topics seminar where appropriate. The colloquium is required of all first-year Ph.D. students and constitutes the basic introductory methodology and theory course for the degree.
Any student who wishes to do so may, after consultation with her or his advisor, substitute an independent reading course offered by a member of the department or a graduate-level course outside of the department.
Research Paper
During the spring semester of the first year, each student begins work on their research paper. Production of the paper is a year-long process that begins in a spring-semester Thematic seminar and concludes in the subsequent fall in the Graduate Workshop. Students designate one of their Thematic seminars as the foundation for the paper and compose a research prospectus as the final project in the course (the prospectus should include a literature review and a discussion of archival sources). Students engage in archival research during the summer and enroll in the Graduate Workshop in the fall, in which they write the final paper.
By the end of the first year, students are expected to have assembled a three-member exam committee.
Second Year
In their second year, students will serve as teaching assistants and will continue to take a mix of Field, Special Topics, and Thematic seminars. In addition, each semester they take one required course: in the fall, the Graduate Workshop, in which they write their research paper, and in the spring Professionalization, which focuses on the principal professionals tasks and expectations they will encounter in a career as a professional historian.
The First Two Summers
Students are required to make progress toward the completion of their degree during the summer months. The department recognizes that for some students progress will take the form of language training, while for others archival work or other research-related projects might be appropriate, along with reading for preliminary exams. During their first summer, all students are expected to complete significant archival research for their research paper.
During the third year, students must pass their preliminary examinations by the end of the fifth (fall) semester. Exams are typically scheduled for early December.
Preliminary Exams
By the end of the first year of study the student submit a departmental form that lists three fields in which she/he will be examined. The student will indicate the field in which her/his dissertation will be written. This will be the major field. The others will be minor fields. No more than two fields may be in the history of the same national culture. Normally, all three examiners will be members of the Department of History, and the fields will be chosen based on consultation with the examiners and the Director of Graduate Studies. A student may petition the department to prepare one field in another department or program.
Based on the foregoing, the first three years of the Ph.D. program for a typical student would look schematically like this
Fourth Year
The fourth year is typically a fellowship year, during which students conduct dissertation research wherever their work takes them.
The fifth year is typically funded as a teaching assistantship, during which time students continue research and writing of the dissertation.
Students in the fourth year and beyond register for HIST 2990, Thesis Preparation.
Additional Ph.D. Information
Doctoral dissertation, fields of study, funding and financial aid.
Ph.D. in World History
World history concentration.
The Doctoral Program in history, with a core focus on world history, trains research historians who plan to teach at the college and university levels. Emphasizing global approaches to historical study, the program encourages students to think beyond national boundaries, comparatively, and in terms of themes that span geographically dispersed areas of the world-trade, migration, disease, religion, state formation, colonialism, and post-colonialism. Studies also include long-term historical processes, major global transformations, and interactions between states and colonial societies. Candidates for the Ph.D. in history may examine African, Asian, European, Latin American, or U.S. history in a world historical context. The program emphasizes mentoring of students in their courses, supervised teaching, and in the doctoral dissertation.
Systematic training in theory and methodology and preparation for college teaching are distinctive features of the Northeastern program. All doctoral students undertake intensive reading in the theoretical literature that informs historical analysis, as well as in global historiography. Each student develops a deliberate methodological focus in an area such as cultural history, social history, environmental and biological history, or public history. Students are mentored in the practice of teaching and are encouraged to lecture and lead discussion sections under the supervision of faculty.
A mix of reading courses and research seminars in area studies and comparative or transnational history provide students with the bedrock of training in the literature and research methods of history. Students may also take a limited number of courses outside the department.
The Department of History maintains close ties with interdisciplinary programs such as Asian Studies; Latino, Latin American, and Caribbean Studies; Law and Public Policy; Women Gender and Sexuality Studies, and with the Departments of African American Studies; Art and Architecture; English; Sociology and Anthropology; and Political Science. Graduate students may obtain a certificate in Women’s, Gender & Sexuality Studies .
All doctoral candidates must develop and demonstrate a strong reading knowledge of the languages in which they will undertake research. In cases where students require training in languages not offered at Northeastern, the department helps them arrange to take courses at nearby institutions.
The doctoral dissertation presents an original interpretation of a topic of historical significance based on detailed research into primary sources, a survey of the relevant literature, and skilled application of the theoretical and methodological apparatus germane to the topic.
In recent years, the Department of History has been able to provide funding to Ph.D. students for five years.
The GRE will not be required as part of graduate admissions to any certificate, master’s, or doctoral program in CSSH or across the university for matriculation in 2022-2023
Applicants and admitted students are invited and encouraged to join one of our Welcome Days. Please click here for more information and to RSVP.
Type of Program
- PhD Program
Get more information about this graduate program.
More programs, bachelor of arts (b.a.) in environmental studies & history, bachelor of arts (b.a.) in history & philosophy, bachelor of arts (b.a.) in history, bachelor of arts (b.a.) in history & asian studies, bachelor of arts (b.a.) in history & cultural anthropology.
PhD in History
You are here: american university college of arts & sciences history phd in history.

- Request Info
Are you interested in…
Explore more.
Are you interested in...
Contact: Gautham Rao Graduate Director
Battelle-Tompkins Memorial Building on a map
Back to top
Study History Where It Is Made
AU’s PhD in History will prepare you for a career as an educator, researcher, analyst, and writer working in academia, public and institutional history, and other fields requiring investigative and analytical skills. In this program, you will develop a deeper understanding of how historians investigate and interpret the past while you explore the past with your own original research .
You will receive a high level of mentorship and develop close working relationships with your professors. Under the guidance of our award-winning faculty , our students complete strong dissertations and present work at top conferences while making valuable connections and gaining experience in the Washington, DC, area.
This program is ideal for students interested in American and modern European history, including Russian history. Our department also has strengths in a variety of subfields , including public history, African American history, women’s/gender history, politics and foreign relations, and Jewish history. This diversity will open your options for research and allow for specialization without sacrificing breadth of study.
Rigorous Study with a Degree of Flexibility
Our program combines rigorous training in scholarship with the flexibility to pursue your intellectual interests. Our coursework will give you a solid foundation in historical theory and methodology, research methods, and United States or modern European history. Together with your academic advisor, you will design a program of study to match your academic goals . You will acquire and demonstrate mastery of tools of research , such as foreign languages, quantitative research methods, oral history, new media, and other methodologies. Your doctoral examinations will be tailored to fit your individual fields of study. You will then pursue your own research in writing your doctoral dissertation.
The Department will supervise PhD dissertations in the history of Modern Europe (normally for the period 1789 to the present), United States history (including the colonial period), US foreign relations, and modern Jewish history.
See all admissions and course requirements .
Cutting-Edge Faculty Dedicated to Your Success
Our history faculty makes national news, uncovers under-represented areas of history, and guides doctoral students , helping them generate innovative and influential research . From predicting presidential elections to publishing award-winning books and articles, our distinguished professors produce relevant historical scholarship and will train you do the same. With academic and professional mentorship from our faculty, you will you will enter the field as a thoroughly prepared and well-connected scholar.
Endless Opportunities in a Historic City
Pursuing your doctorate in the nation’s capital provides you with unparalleled access to renowned museums, archives, institutions, and resources . From the Library of Congress, Smithsonian Institution and National Archives to the DC Historical Society, our students are only a metro ride away from exceptional local and national repositories. As part of the Washington Consortium , students at American University are able to take courses at colleges and universities throughout the DC metropolitan area, providing the opportunity to work with a variety of faculty in diverse programs and fields of study.
A truly global city, DC, contains hundreds of embassies, cultural organizations, and enclave communities. Brimming with history , the DC area offers Civil War battlefields, the Capitol, Mount Vernon, the White House, and countless landmarks of the colonial period, Revolutionary War, Civil War, and more recent American history. The city is also home to smaller historical organizations like the DC Historical Society and the DC Preservation League. Whether your interest is global, national, or local, this historic city undoubtedly has something for you.
Explore the Possibilities
Our students go on to become university and college faculty and administrators or work in federal and state governments, for museums and archives, and in other exciting fields. Our alumni teach at universities around the world , from the University of Houston in Texas to University of Prince Edward Island in Canada and Ludwig Maximilians Universität in Munich. Our PhDs hold positions with the nation’s most important institutions , including the Library of Congress, Department of State, National Archives and Records Administration, American Historical Association, National Endowment for the Humanities, US Holocaust Memorial Museum, and the National Museum of African American History and Culture.
Recent and Current PhD Dissertation topics
- Auketayeva, Laura : "Gender and Jewish Evacuees in the Soviet Union during the Holocaust"
- Barry, Michael : "Islamophobic & Anti-Islamophobic Ideas in America"
- Brenner, Rebecca : "When Mail Arrived on Sundays, 1810-1912"
- Boose, Donelle : "Black Power and the Organizing Tradition: Work-ing Women of Washington, DC. 1965-1990"
- Chatfield, Andrew : "American Support for India’s Self-Determination from 1915-1920: Progressives, Radicals, and Anti-Imperialists"
- Duval, Lauren : "Landscapes of Allegiance: Space, Gender, and Mili-tary Occupation in the American Revolution"
- Englekirk, Ryan : "The Third Team: Unmasking Fraternity and Mascu-linity Among Major League Baseball Umpires 1970-2010"
- Estess, Jonah : "The People’s Money: The American Revolution, Cur-rency, and the Making of Political Economic Culture in American Life, 1775-1896"
- Frome, Gavin : "American Protestant Service Workers in Viet Nam, 1954-1975"
- Gabor, Ruth : "'Moda' for the Masses: Moscow Fashion’s Appeal at Home and Abroad during the Cold War"
- Gibson, Laura : "It’s Love that Counts: The History of Non-Nuclear Families in American Domestic Sitcoms"
- Grant, Jordan : "Catchers and Kidnappers: Slave Hunting in Early America"
- Grek, Ivan : "Illiberal Civil Society in Russia, 1992-2000"
- Harris, Curtis : "Hardwood Revolution: The NBA's Growth & Player Revolt, 1950-1976"
- Hawks, Julie : "Capital Investments: Engineering American Cold War Culture"
- Jobe, Mary "Allison" : "'We Remember Him for His Character': The Life of James W. Ford and the Communist Party USA"
- Kaplan, Anna : "Left by the Wayside: Memories and Postmemories of the Integration of the University of Mississippi"
- Killian, Linda : "Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Paine: The Shared Political Ideology at the Heart of American Democracy"
- Kitterman, Katherine : "'No Ordinary Feelings': Mormon Women’s Political Activism, 1870-1896"
- Langford, Amy : "Creating a Body Politic: Boundary Crossings and the (Re) Making of Latter-Day Saints on the U.S. Border, 1885-1920"
- Levin, Jeffrey : "Felix Warburg and the Establishment of the Hebrew University"
- MacNeill, Lindsay : "Policing Politics in Austria, 1918-1955"
- Milwicki, Alon : "Baptizing Nazism: An Analysis of the Religious Roots of American Neo-Nazism"
- Rafferty-Osaki, Terumi : "'Strictly Masculine': Reforming and Per-forming Manhood at Tule Lake, 1942-1946"
- Recordati, Maurizio : "Russia Turns Inward: Russian Grand Strategy in the Post-Crimean War Period (1856-78)"
- Sowry, Nathan : "Museums, Native American Representation, & the Public: The Role of Museum Anthropology in Public History, 1873-1929"
- Styrna, Pawel : "Polish-Russian Relations, 1904-1921"
- Vehstedt, Scott : "'Lets Help Finland': The Return of American Relief Aid in the Winter War, 1939-1940"
- Weixelbaum, Jason : "At the Crossroads of Fascism: The Decision of Ford, General Motors, and IBM to do Business with Nazi Germany"
Alumni Job Placements
Graduates of the history PhD program are working as professors, researchers, and directors across the US and at international locations. Here is a list of where select graduates have or are currently working:
- Director, National Coalition for History
- Assistant Professor, University of Prince Edward Island
- Assistant Professor, Towson University
- Assistant Professor of History and Director of American Studies, West Chester University
- Independent historian
- Senior Archivist, National Archives
- Associate Professor, Ryerson University
- Assistant Professor, University of Arkansas at Little Rock
- Historian, US Army
- Senior policy adviser and special assistant to the president of the Humane Society
- Historian, Office of the Historian, Department of State
- Museum Director, Renton History Museum, Oregon
- Public History Coordinator, American Historical Association
- Assistant Professor, Bridgewater State University
- Lecturer in Sociology, California State University at Bakersfield
- Assistant Professor, Delaware State University
- Historian, Global Classroom, US Holocaust Museum
- Director, Digital Archive, Woodrow Wilson Presidential Library
- Assistant Professor, Illinois State University
- Adjunct Professor, University of Maryland at College Park
- Senior Fellow, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
- Assistant Professor, University of West Florida
- Independent historian and filmmaker
- Adjunct Assistant Professor of History, US Naval Academy
- Administrative Support Specialist at FEMA
- Senior editor and writer, National Endowment for the Humanities
- Instructor, Religion Dept., National Cathedral School (earned Master of Divinity after PhD)
- Curriculum and Publications Coordinator, AU Registrar's Office
- Assistant Professor, Seminole State College
News & Notes
PhD candidate Reza Akbari presented at the Middle East Studies Association's annual conference in Montreal, Canada. His presentation, Etched in Mistrust: Continuity and Change in US-Iran Nuclear Negotiations (1969-1978), argued that America's drive to keep Iran's nuclear program peaceful began decades before the establishment of the Islamic Republic.
PhD candidate Andrew Sperling published " A Halloween Party in Boston Turned Ugly when a Gang Hurled Antisemetic Slurs and Attacked Jewish Teenagers ," detailing the events of an antisemetic attack on Jewish teens at a Halloween party in 1950.
Theresa Runstedtler 's new book on Black ballplayers of the 1970s and '80s setting the NBA up for success: Black Ball: Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Spencer Haywoof, and the Generation that Saved the Soul of the NBA (2023) .
Doctoral student Maurizio Recordati Koen won first prize in the 2022 Trench Gascoigne Essay Competition for "The Stuff of Strategy: How Sublime Strategics Turned into a Real Thing" in RUSI Journal.
John Schmitz (CAS/PhD '07) published Enemies among Us: The Relocation, Internment, and Repatriation of German, Italian, and Japanese Americans during the Second World War .
Doctoral student Jonah Estess presented his paper, "Mo’ Money, Mo’ Problems: The American Revolution and the National Origins of the Politicization of Money" as part of the panel at this year's Business History Conference.
Andrew Demshuk published Three Cities after Hitler: Redemptive Reconstruction across Cold War Borders .
PhD candidate Katherine Kitterman wrote on women's voting rights in Utah for the Washington Post.

Inaugural Postdoctoral Fellow
Nguyet Nguyen brings new perspective to the Vietnam War.
Discover CAS: The Humanities
Explore our community.
Video Take a Video Tour .
Please send me information about PhD in History
It looks like you already used that name and address to request information for one or more AU graduate program(s).
If you have not previously requested AU graduate program information, create a new request
FACULTY OF HUMANITIES

- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Our Community
- Request Info
PhD Program in History

The programs offered by the Department of History emphasize the modern world in a global framework. A range of approaches to history, from political and cultural through social and intellectual, to environment and medicine, find representation in our program.
The humanities teach a breadth of soft skills that graduates need to succeed in the job market.
Katarina Todić '15
Bachelor of Arts Honours French and History

I strongly believe that a foundation in the Humanities helps develop the strong leaders, thinkers, and doers we need in the future.
Alex Piccini '16
Honours History

The experience of a Humanities degree is the preparation for life’s skills and opportunities
Mark Giavedoni '01
Combined Honours English and History
About the Program
The History PhD program involves the completion of 2 minor fields by course work and one major field of readings by September 15th of the second year of doctoral study. Thereafter candidates will devote their full time to research and writing their doctoral thesis.
The Department offers full and part-time PhD degrees to candidates.
Areas of Research offered include:
- Animal History
- Atlantic World
- Britain 1688-2000
- Canada 1791-2000
- Environmental History
- Medieval Europe
- Modern Europe
- Science & Technology
- Urban History
- War and Society

Admission Requirements
The Department supervises doctoral research in a variety of areas of specialization. Prospective applicants are directed to consult the Department’s website which details research specializations. Candidates must contact individual faculty for guidance on appropriate thesis topics.
Application Process
Completed applications consisting of the following:
- How to Apply
- Departmental Application Form (This is equivalent to the required study plan). Once you’ve completed your Departmental Application Form, save it as a PDF and upload as an attachment to your online application. You can also send it as an attachment via email to: [email protected]
- Two Confidential Reports from referees most familiar with your academic studies (These can be found on McMaster University Graduate Studies Online Application – the online application process).
- Transcripts from all post-secondary academic institutions attended (When applying online your transcripts are listed under “Academic History Checklist”).
- Writing Sample.
- The above should be submitted by 1 February for consideration by our graduate studies committee for admission and funding (September admission only). Transcripts and confidential report forms should be sent directly to the Department under separate cover. We may still consider applications after the February 1 deadline.
Program Timelines
When admission to PhD work has been granted, a candidate will, in consultation with his or her prospective supervisor and the Graduate Studies Chair of the Department, select two Minor Fields and one Major Specialization. Minor Fields and Major Specialization will cover the principal literature in the areas of concentration.
Minor fields normally consist of two half-year 700‐level graduate reading seminars in each of which a major historiographical essay is required. The grade for a minor field will consist of the grades for the in- course requirements and the historiographical essay, in combination as indicated by the minor field supervisor. One minor field course will be taken in the fall term, the second in the winter term. Instructors may opt to set a written exam.
While some overlap may be deemed beneficial, the Minor Fields should not duplicate Major Specialization reading. All doctoral candidates must have a minimum of three, and usually four, instructors supervising the combination of their Minor Fields and Major Specialization.
Major Specialization preparation begins in September and takes the form of a reading course that will run normally until the following May. The reading for the course will be determined by the course instructors with oversight from the department’s Graduate Studies Committee to ensure appropriate breadth and depth of the reading list. As part of the reading course, candidates will complete a significant historiographical paper or papers. Instructors may opt to set a written exam.
Successful completion of 6 units of Minor‐Field coursework and 6 units of Major Specialization coursework, fulfill the course requirements of the School of Graduate Studies for doctoral candidates. Satisfactory performance in doctoral Minor Field and Major Specialization courses is a minimum grade of B‐. A single grade of F on any course in the PhD program, or two B- grades, entails automatic withdrawal from the program.
Finally, all History PhD candidates will write a dissertation research proposal by the end of their first year in the PhD programme. Each candidate’s proposal, of 10-15 pages in length, is defended on a Pass/Fail basis with the candidate’s PhD committee no later than the third week of September. This defence will constitute the required PhD comprehensive examination (written and oral). In order to attain a passing mark, the dissertation proposal and its oral defense must satisfactorily demonstrate breadth of knowledge and the integration of key ideas and methods related to the student’s thesis area. Successful passage of the comprehensive examination along with successful completion of the coursework is required before a candidate may proceed in programme.
Tuition & Program Fees
Visit Graduate Studies to learn more about tuition, supplementary fees and everything you need to know about being paid as a Teaching or Research Assistant. Tuition fees are assessed on a term by term basis, depending on the number of courses a student takes or if they are paying by term.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much is tuition?
For the 2023-2024 academic year, tuition fees are as follows:
Please note, these costs are exclusive of supplementary fees and are subject to change on an annual basis.
When is tuition due?
Tuition is usually due in mid-September. Dates will change on an annual basis and will be communicated via departmental communication channels.
What does the course load look like for an MA student?
MA students in the Department of History are required to take 3 level-700 courses in the fall and winter terms. Each class is approximately 3 hours in length based on course offerings and student interest. Courses are offered one day per week. Unless otherwise specified, courses are offered in-person and students are expected to be present in class on campus. Course scheduling and registration takes place in the spring/summer.
Does the Department require scholarly work?
Both the MA and the PhD require completion of the supplemental application, which can be found on the respective application websites. The PhD application requires a writing sample.
How is graduate funding decided? Is it guaranteed?
Within the Department of History, there is a graduate committee which is composed of History faculty members. For MA students, each individual faculty member reviews the applications and ranks the students. Each student receives an average ranking. The student’s GPA is then used as a further ranking tool to determine graduate scholarships. The application and the student’s GPA has equal weighting in determining their final rank. Top students are likely, but not guaranteed, to receive scholarship funding. In addition to scholarship funding, there are multiple teaching assistant positions which offer students an opportunity to study and work. No funding is guaranteed and is subject to change on an annual basis.
For PhD students, minimum funding is guaranteed. As of September 1, 2023, all full-time PhD students admitted to the program are guaranteed a minimum of $17,500 which may be composed of multiple different sources of funding. This is guaranteed for 4 years.
Does the department offer any scholarships?
The department offers the following internal scholarships for graduate students:
Is it necessary to consult a potential supervisor?
For an MA student, you will connect with a potential supervisor by the end of your first term.
For a PhD student, it is highly recommended that you consult with a potential supervisor before applying into the program. Supervision requires a heavy commitment from faculty members, and some faculty members may not be able to provide the necessary support required. The department cannot guarantee a supervisor for incoming PhD students.
Can the application fee be waived?
No, the fee is mandatory to apply into the program.
How are my international grades calculated?
The university uses the Ontario University Registrars’ Association guides to calculating international grades. These vary from country to country. If you are interested, you may reach out to [email protected] for clarification.
What testing is required if English is not my first language? What is the minimum score required?
Applicants whose first language is not English will be required to provide an official record of the Test of English as a Foreign Language. A minimum TOEFL score of 92 (iBT), 580 on the regular test and a score of 237 on the computerized test are required. If you are submitting the IELTS test, a minimum score of 7 is required.
Faculty Scholarship Adjustments Guidelines
The McMaster Graduate Scholarship (MGS) is the most common form of scholarship support available to graduate students in our program. The MGS ensures that students receive a guaranteed minimum level of scholarship support. Adjustments to the MGS will depend on other available scholarships.
The Faculty of Humanities Adjustments guidelines policy is available for review.
REVIEW THE POLICY
Apply to the PhD Program in History

LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR GRADUATE SUPERVISORS
Research your passion in History with supervision from our world-class faculty.

SEE OUR CURRENT AND FORMER GRAD STUDENTS
Supplemental information.
2023-2024 Graduate Courses Term 1 Seminars (September – December 2023)
- History 702 War and American Society since 1898| Dr. Stephen Streeter
- History 741 Historiography | Dr. Tracy McDonald
- History 756 The World Wars| Dr. Martin Horn
- History 767 War and Society in East Asian History| Dr. Jaeyoon Song
Term 2 Seminars (January – April 2024)
- History 717 Topics in Early Modern European History| Dr. Megan Armstrong
- History 721 Modern British History| Dr. Stephen Heathorn
- History 725 Canadian Environmental History| Dr. Ken Cruikshank
- History 757 The British Empire and Global Integration, 1815-1960| Dr. John Weaver
- History 776 History of Sexualities in the Western World, 1750 to the present| Dr. Michael Gauvreau
Winter – Summer 2024 (January – August 2024)
- History 798 PhD Major Specialization
Summer 2024 (May – August 2024)
- History 797 MA Research Paper
2022-2023 Graduate Courses Term 1 Seminars (September – December 2022)
- History 708 Research in European International Relations 1890-1956 | Dr. Martin Horn
- History 741 Historiography | Dr. Michael Gauvreau
- History 754 Social and Environmental History of Modern America | Dr. Ken Cruikshank
- History 767 War and Society in East Asian History | Dr. Jaeyoon Song
Term 2 Seminars (January – April 2023)
- History 743 Topics in Soviet History | Dr. Tracy McDonald
- History 757 The British Empire and Global Integration, 1815-1960 | Dr. John Weaver
- History 766 Comparative Perspectives on Health and Medicine in the Colonial World | Dr. Juanita De Barros
- History 776 History of Sexualities in the Western World, 1750 to the present | Dr. Michael Gauvreau
- History 777 Decolonizing Indigenous History | Dr. Allan Downey
2021-2022 Graduate Courses Term 1 Seminars (September – December 2021) In- Person
- History 728 American Foreign Relations | Dr. S. Streeter | Tuesday 9:30 – 12:20
- History 741 Historiography (required for MA’s) | Dr. T. McDonald | Thursday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 766 Comparative Perspectives on Health and Medicine in the Colonial World | Dr. J. De Barros | Wednesday 14:30 – 17:20
- History 775 The Canadian Left in the Twentieth Century | Dr. I. McKay | Monday 9:00 – 12:00
Term 2 Seminars (January – April 2022)
- History 757 The British Empire and Global Integration, 1815-1960 | Dr. J. Weaver | Wednesday 13:30 – 16:20
- History 764 Global Power, Local Cultures: Comparative Colonialisms in Africa | Dr. B. Ibhawoh | Tuesday 12:30 – 15:30
- History 767 War and Society in East Asian History | Dr. J. Song | Thursday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 776 History of Sexualities in the Western World 1750 to the present | Dr. M. Gauvreau | Friday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 780 Historical Perspectives on Women and Biography | Dr. A. McQueen | Monday 9:00 – 12:00
Winter – Summer 2022 (January – August 2022)
Summer 2022 (May – August 2022)
2020-2021 Graduate Courses
Term 1 Seminars (September – December 2020) (Virtual)
- History 717 Topics in Early Modern European History | Megan Armstrong | Friday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 741 Historiography | Michael Gauvreau | Thursday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 766 Comparative Perspectives on Health and Medicine in the Colonial World | Juanita De Barros | Wednesday 13:00 – 16:00
- History 769 Historical Representations of Cities | Alison McQueen | Tuesday 9:30 – 12:30
- History 775 The Canadian Left in the Twentieth Century | Ian McKay | Monday 13:00 – 16:00
Term 2 Seminars (January – April 2021)
- History 725 Environmental History: Canada in International Perspective | Ken Cruikshank | Wednesday 13:00 – 16:00
- History 756 The World Wars | Martin Horn | Wednesday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 765 Canadian Sport History | Nancy Bouchier | Monday 9:30 – 12:30
- History 767 War and Society in East Asian History | Jaeyoon Song | Thursday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 776 History of Sexualities in the Western World, 1750 to the Present | Michael Gauvreau | Friday 9:00 – 12:00
- History 779 History of Indigenous Manifestos | Allan Downey | Tuesday 13:00 – 16:00
Winter – Summer 2021 (January – August 2021)
Summer 2021 (May – August 2021)
2019-2020 Graduate Courses
Term 1 Seminars (September – December 2019)
- History 702 War and American Society in 1898 – Stephen Streeter
- History 741 Historiography – Tracy McDonald
- History 772 State & Civil Society in Canada, 1948-2000 – Ian McKay
- History 775 The Canadian Left in the Twentieth Century- Ian McKay
- History 790 MA Independent Study
Term 2 Seminars (January – April 2020)
- History 717 Topics in Early Modern History- Megan Armstrong
- History 743 Topics in Soviet History – Tracy McDonald
- History 757 ( Cross-listed as GLOBALST 757 ) The British Empire and Global Integration, 1815-1960 – John Weaver
- History 776 History of Sexualities in the Western World, 1750 to the present- Michael Gauvreau
- History 779 History of Indigenous Manifestos – Allan Downey
Summer 2020 (May – August 2020)
Winter 2020 – Summer 2020 (January – August 2020)
Funding is available through a large number of available scholarships. McMaster’s School of Graduate Studies maintains a list of available scholarships available as well as details on how to apply.
In addition to McMaster scholarships, the School of Graduate Studies also maintains a list of external scholarships.
- Program Handbook
- Thesis Defence
- Graduate Calendar
- School of Graduate Studies Graduate Resources
- Graduate Associations
- Where to find jobs
Department Life
Graduate students are fully incorporated into the intellectual and social life of the Department.
UPCOMING EVENTS
Graduate History Society
Our graduate students have their own organization

Thursday Speaker Series
See out past and future guest speakers
Find a Humanities Expert

Research-focused and student-centered. Humanities researchers promote interdisciplinary approaches to local and global leadership. Learn more about our researchers by searching by name or keyword.
HIST6390 - Topics in History
HIST 6390 Topics in History (3 semester credit hours) The study of specific themes and/or periods in history. May be repeated for credit as topics vary (9 semester credit hours maximum). (3-0) R

PhD Program
The UCLA Department of Art History offers a two-stage graduate program toward the PhD. Students are not admitted for a terminal master’s (MA) degree. The MA is awarded in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the PhD and is granted with the successful completion of the first stage of the program, typically at the end of the second year, 6th quarter, in residence. Normative time to degree for the PhD is seven years from the term of admission. For students entering with a MA in hand, the normative time to degree is five years from the term of admission.
All students are required to complete the M.A. requirements in the department. The Graduate Review Committee may waive the M.A. requirements, at the time of admission, for students matriculating with a M.A. degree in Art History or adjacent discipline from another institution. Following Academic Senate policy on duplication of degrees, a student who enters the program with a M.A. degree in Art History from another institution is not eligible to receive a second M.A. degree in Art History from UCLA.
Please see here for the official UCLA Art History Graduate Program Requirements published on the Graduate Division website.
- The student is assigned a faculty mentor upon admission to the program. The mentor is responsible for the student’s course of study and must be consulted at least once each quarter. A change of faculty supervision and/or change in field(s) must be approved by the Graduate Review Committee.
- The Director of Graduate Studies (DGS) offers intellectual guidance, approves any exceptions to the program requirements, and adjudicates disputes between a student and his/her faculty mentor. The DGS further serves as Chair of the Graduate Review Committee, which governs the admissions process.
- The Student Affairs Officer (SAO) assists students with all the administrative aspects of moving through the program.
- Each spring quarter, the entire faculty reviews the status of each graduate student to ensure appropriate time-to-degree progress.
Toward the MA
Requirements for the MA
- Satisfaction of the first language requirement.
- Successful completion of AH 200 with a grade of “B+” or better.
- Nine graduate and upper division courses (36 units) completed while in the program. At least six of those courses (24 units) must be at the graduate level, including four graduate seminars. AH 200 may be counted towards the required six courses.
- Successful completion of a qualifying paper (approximately 30 pages) according to the standards and procedures outlined below.
* Typically the above requirements are completed within the first two years of study (6 quarters).
Distribution of Coursework
The nine required courses must include at least two courses from Group A and two courses from Group B noted below.
Qualifying Paper for the MA
- The qualifying paper is a revised and expanded version of a paper written for a class from the first year of coursework. It should be approximately 30 pages in length (excluding footnotes, images, and bibliography) and should demonstrate the student’s ability 1) to formulate a thesis, 2) to present an extended argument, and 3) to conduct original research. Quality of the writing will also be evaluated.
- By the end of the fall quarter of the second year, student selects a class paper from the first year in consultation with his or her advisor to revise and expand as the qualifying paper.
- In the following winter quarter, student enrolls for 4 units of 598 (RSRCH-MASTER THESIS) to work on the paper under the supervision of advisor.
- Director of Graduate Studies (DGS) will contact each student during the winter quarter (usually early February) to appoint a committee of three faculty readers for the qualifying paper, one of which is the student’s advisor. At least one of the faculty readers will have had no classroom contact with the student. All students may suggest potential readers; however, the DGS will balance the student’s request against equity of faculty workload.
- On the first day of instruction of the spring quarter, students submits three copies of the qualifying paper to the Student Affairs Officer (SAO) along with a list of the three readers assigned to review the paper.
- The qualifying papers will be distributed to the three assigned faculty readers and each reader will complete an evaluation form and submit it to the SAO within three weeks of receipt of the paper.
- By the fourth week of the spring quarter, the SAO will make available the papers with reader’s comments to the student and these papers will be added to the student’s permanent file.
- The Graduate Review Committee, taking into consideration the faculty reader evaluations, will determine whether the student will be awarded the MA and permitted to proceed into the PhDprogram. In some cases, the Committee may recommend that the student receive the MA degree but discontinue further graduate study. It is also possible (although very rare) that the student’s work may not be judged adequate to receive the MA.
Completion of the MA
- Prior to the third week of the spring quarter in the second year, the student should complete the “Petition for Advancement to Candidacy for the Master’s Degree” (provided by and returned to the SAO).
- Once the Department has accepted the qualifying paper, the student must file it with Graduate Division by the Monday of the tenth week of the spring quarter, formatted as a thesis.
- Graduate Division guidelines for formatting MA theses are available here . Workshops on thesis formatting are offered at the beginning of each fall and winter quarters. See the Grad Division website for more information.
- Following the Department’s annual spring review of graduate students, the student must submit a completed form for transfer from the MA to the PhD program (provided by and returned to the SAO).
Toward the PhD
Upon the completion of the MA or starting with a MA from another institution, the student begins the PhD program having chosen a major field of study within art history, often known at the time of application. By the end of the second quarter of residence at the PhD stage, the student also selects a minor field, which may be outside the department (e.g. Architecture, History, Anthropology, Comparative Literature, Archaeology, etc.). The major and minor advisors are responsible for the student’s course of study and completion of requirements within the selected field. Graduate Review Committee must approve any change of advisor(s) or the major and minor fields.
Requirements for the PhD
- Satisfaction of language requirements (minimum 2, including 1 from MA stage; more may be required depending on field of study)
- Completion of 8 graduate and upper division courses (32 units)
- Written comprehensive exams in major and minor fields
- Dissertation prospectus and oral qualifying exam
- Doctoral dissertation
- A total of 8 graduate and upper division courses are required, of which at least 4 must be art history courses at the graduate level.
- Of the nine courses (36 units) required for the MA, students may use a maximum of two of these (8 units) to count towards Ph.D. coursework. Students may also apply courses taken in excess of MA requirements towards fulfilling Ph.D. course requirements. (This does not apply to students who received their MA from other institutions/departments.)
- 5 courses in one field are required to claim it as the major field; 3 courses in one field are required to claim it as the minor field. The minor can also be from outside the department (e.g. Architecture, History, Anthropology, Comparative Literature, Archaeology, etc.).
- Students entering the PhD stage deficient in Art History 200 (Art Historical Theories and Methodologies) or its equivalent must add this to the total requirements. In some cases, Art History 201 (Topics in Historiography of Art History) may be required by faculty/advisor recommendation. Any additional coursework required by the Graduate Review Committee at time of admission must be completed during the first two quarters of residence and may not count toward the minimum course requirements for either the MA or PhD degree.
Written Comprehensive Examinations
- Upon completion of coursework and fulfillment of language requirements, the student takes the PhD written comprehensive examinations in the major and minor fields of study, designed and evaluated by the student’s major and minor advisors respectively.
- The purpose of the examinations is to test the student’s breadth and depth of knowledge in his/her fields of study. If a student fails to pass the examination or part thereof, the failed portion may be repeated once no later than the subsequent quarter of residence. No further repetition will be allowed. The written comprehensive examinations may be taken during any two-week period of the Fall, Winter, and Spring quarters. Typically, students take these exams during the winter quarter of the second year in residence, 5th quarter, in the PhD program.
- The Department offers two formats for the major and minor written exams, the details of which must be worked out in advance between the student and the examiner. Format A: Take-home. 2-3 essay questions to be completed in 1 week (for the minor exam, 1-2 questions to be completed in 3 days). Format B: Sit-down. 2-3 essay questions to be completed in 6 hours (for the minor exam, 1-2 questions to be completed in 3 hours). Many faculty incorporate designing of a syllabus as an exam question and the formats above do not preclude this possibility. Such an assignment would count as one question/essay.
- The specific format and dates for the major and minor exams must be submitted to the Student Affairs Officer at least three weeks in advance using the appropriate departmental form.
Doctoral Committee
- Upon passing the written comprehensive examinations in major and minor fields of study, the student selects a dissertation topic and nominates the members of his/her Doctoral Committee in consultation with his/her advisor.
- This committee minimally consists of the major advisor, now serving as committee chair, two additional members of the art history faculty (normally, but not necessarily, including the student’s minor advisor), and one member from another UCLA department. For details on the acceptable status of these members and for minimum university standards of the doctoral committee, please see page 14-17 in the Standards and Procedures for Graduate Study manual .
- The student and committee chair must agree on all committee members. Any changes in committee constitution after formal nomination must be reported to and approved by the Graduate Division; replacing the committee chair can only occur by consent or if the faculty member leaves UCLA.
- Please note that the Graduate Division generally approves Committee nominations within 2-3 weeks, and the oral qualifying exam may not be taken before official approval has been received.
Dissertation Prospectus and Oral Qualifying Examination
- The dissertation topic should be identified in discussions with the advisor. These discussions usually evolve organically through the course of study and are highly individualized. Typically, the oral examination is scheduled during the quarter following the successful completion of the written examinations.
- Once the Doctoral Committee has been officially approved by Graduate Division, and after having conducted considerable exploratory research and preparation for his/her dissertation, the student submits to each member of the Doctoral Committee a dissertation prospectus. The prospectus should not be distributed to the full committee without the approval of the student’s committee chair.
- The dissertation prospectus should not exceed 20 pages and include a statement of purpose regarding the art historical topic/problem being addressed (what is at stake in the study), tentative chapter outlines, working bibliography, research plan, methodological strategies, and preliminary schedule for completion.
- Students should submit the prospectus to committee members 2-3 weeks before the oral examination date to allow sufficient time for the prospectus to be reviewed. If any member of the Doctoral Committee finds the prospectus inadequate, he or she must notify the committee chair at least one week prior to the oral examination date. In some cases, the prospectus must be revised and/or the examination date postponed.
- The student is responsible for scheduling the oral exam, consulting with committee members well in advance regarding the date and time of availability of each faculty member. The SAO helps the student reserve an appropriate space for the exam.
- The purpose of the oral examination is to assess the validity and feasibility of the proposed dissertation topic and its methodologies, as well as the soundness of the student’s projected approach to completing the project.
- At the end of the examination, each committee member reports the examination as “passed” or “not passed.” A student may not pass and may not be advanced to candidacy if more than one member votes “not passed” regardless of the size of the committee, or if the major advisor so votes. Upon majority vote of the committee, the oral qualifying examination may be repeated once. Students upon passing the oral examination are formally advanced to candidacy by the Graduate Division.
- At the time of the exam, the Doctoral Committee decides, by unanimous agreement, whether or not to waive the final oral examination (not normally required) and selects, again by unanimous agreement, a minimum of three members, two from the art history faculty and one from an outside department, who will read, approve, and certify the final draft of the dissertation. For details regarding the acceptable status of these certifying members, consult the publication, Standards and Procedures for Graduate Study at UCLA.
- Upon passing the oral examination, the student is officially Advanced to Candidacy (ATC).
Dissertation and Final Oral Examination (if required)
- After advancing to candidacy, the student works on the dissertation in consultation with his/her advisor, committee chair, as well as Doctoral Committee certifying members according to the rules laid out in the above named publication. Upon completion of the dissertation or individual chapters thereof, and with approval of the committee chair, the student circulates a copy of the dissertation in Week 1 of the quarter for comments and suggestions from the certifying members of the Doctoral Committee. Each reader is allowed four weeks in which to read it and make corrections and comments, and the student is allowed three weeks in which to respond and revise the dissertation. It is incumbent upon the student to communicate in a timely manner with all certifying members of the Doctoral Committee to ensure adequate time for review. Committee members must be consulted as each reader may require more time. PLEASE REVIEW the timeline for dissertation completion which clearly outlines the schedule for submission during the student’s final quarter.
- After incorporating into the final draft of the dissertation the recommended changes, the student will circulate the dissertation again among the certifying members of the Doctoral Committee. This draft should be circulated sufficiently in advance of the deadline for filing the dissertation so that each reader is allowed at least two weeks in which to reread it (see quarterly Schedule of Classes for filing deadlines).
- Each certifying member of the committee then decides whether or not to approve the dissertation. In cases where less than the entire committee acts as certifying members, approval of the dissertation must be unanimous. If the entire committee acts as certifying members, the dissertation is considered approved with one negative decision so long as that negative decision is not that of the committee chair. After final approval by the Dean of the Graduate Division, the student files the required number of copies of the dissertation with the Manuscript Advisor of the Office of University Archives. Deadlines for filing the dissertation fall approximately two weeks before the date the degree is to be awarded.
- Note: A final oral examination is not normally required for Art History, but in some cases it may be requested by the Doctoral Committee (determined at the oral qualifying exam), and is held prior to filing the dissertation. All members of the committee must attend and vote. A student may pass with one negative vote so long as that vote is not that of the committee chair. In case of failure, the Doctoral Committee decides, by unanimous agreement, whether or not the candidate may be re-examined.
- Upon filing the dissertation, the student receives the Ph.D.
Language Requirements
The completion of the PhD requires reading knowledge of a minimum of two foreign languages relevant to the student’s field of study (more than two may be required in some cases and must be determined in consultation with the faculty advisor). Applicants are expected to already possess reading proficiency in at least one of the two languages for which they will be responsible. New students shall sit for at least one language exam upon arrival at UCLA.
Students at the MA stage are expected to satisfy their first foreign language requirement by the end of the 3rd quarter in residence. It is highly recommended that they complete the second language requirement by the end of the 6th quarter in residence.
Students at the PhD stage are expected to satisfy their second foreign language requirement by the end of the 1st quarter and any additional languages by the end of the 3rd quarter in residence (or in consultation with the major advisor).
Fulfilling the Language Requirement
Option 1: Pass the Departmental Foreign Language Exam.
The language exam consists of translation of a text of 300-700 words chosen by the examiner to be translated into English in three hours (use of a non-electronic dictionary is allowed). Specific qualities of the language and expected level of proficiency in the field will impact the choice and length of the selected text. The Department expects accurate rendition in English rather than a strict translation, word for word, and values the quality of the translation over the completion of the exam.
Language exams are scheduled four times a year, approximately three weeks prior to finals week during the regular academic quarters. Entering students must sit for the first language exam in the first week of the fall quarter. Exam results will be sent out by email within three weeks of the exam date. If feedback on the exam is desired after the results have been announced, students are welcome to contact the examiner. If a student fails the exam and wants to appeal, he or she should contact the Chair of the Language Committee or Director of Graduate Studies.
Option 2: Complete UCLA courses French 6, German 6, Italian 6, Spanish 25, or other relevant language classes with a minimum grade of “B”.
The following is a general guideline for language requirements in relation to specific fields of study. The final selection and number of languages is to be determined in consultation with the primary advisor.
African Indigenous African languages, Arabic, French, German, Portuguese Ancient/Mediterranean/Near East Akkadian, Sumerian, Egyptian, Greek, Latin Chinese/Korean/Japanese Two East Asian languages, for pre-modern studies additionally literary Chinese or Japanese Byzantine/Western Medieval French, German, Greek, Latin, Italian, Slavic Languages, Turkish, Spanish Indigenous Americas One European language, one indigenous language (e.g., Quechua, Nahuatl, Maya), one other language (depending on topic) Islamic Arabic, Turkish/Ottoman, Persian, French, German Latin America Spanish (mandatory), French, German, Portuguese Modern & Contemporary Europe & America French, German, Spanish, Italian, Russian Renaissance/Baroque/Early Modern Italian, French, Spanish, German, Latin, Dutch, Slavic Languages, Latin and/or Greek (depending on topic) South Asia Sanskrit, Hindi/Urdu, Persian Southeast Asia Thai, Vietnamese, Indonesian
History, PHD
On this page:, at a glance: program details.
- Location: Tempe campus
- Second Language Requirement: No
Program Description
Degree Awarded: PHD History
The PhD program in history offers outstanding opportunities for graduate study in North American, European, public and global-comparative history.
The School of Historical, Philosophical and Religious Studies' world-class faculty members deliver courses and individualized mentoring in a wide range of historical topics, such as urban history, environment and sustainability studies, politics and policy, immigration, gender, race and ethnicity, and comparative history. In addition, doctoral history students are strongly encouraged to take advantage of the numerous collaborative opportunities that exist throughout the university in ASU's many innovative schools and centers.
Degree Requirements
84 credit hours, a written comprehensive exam, an oral comprehensive exam, a prospectus and a dissertation
Required Core (16 credit hours) HST 502 Public History Methodology (3) HST 640 Historical Methods (3) HST 641 North American History (3) HST 643 Global History (3) HST 644 Area Studies in History (3) HST 682 Advanced Research Skill (1)
Electives and Research (44 credit hours)
Other Requirement (12 credit hours) HST 591 Seminar (6) HST 792 Research (6)
Culminating Experience (12 credit hours) HST 799 Dissertation (12)
Additional Curriculum Information In general, all credit hours must be at the 500 level or above. Graduate credit may be awarded for 400-level courses; it must be approved in advance and documented in the student's file.
The doctoral program requires a minimum of 84 credit hours and may be completed in four to five years. Students with a master's degree may apply 30 credit hours toward the 84 required credit hours with approval of the academic unit and the Graduate College. If the student does not already have a master's degree in a related field, then the remaining 30 credit hours are made up of electives and research to reach the 84 credit hours required for the doctoral program.
Admission Requirements
Applicants must fulfill the requirements of both the Graduate College and The College of Liberal Arts and Sciences.
Applicants are eligible to apply to the program if they have earned a bachelor's or master's degree, in any field, from a regionally accredited institution.
Applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in the last 60 hours of their first bachelor's degree program, or applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in an applicable master's degree program. The most competitive applicants have a GPA of 3.30 or higher.
All applicants must submit:
- graduate admission application and application fee
- official transcripts
- statement of purpose
- resume or curriculum vitae
- writing sample
- three letters of recommendation
- proof of English proficiency
Additional Application Information An applicant whose native language is not English must provide proof of English proficiency regardless of their current residency. The history program requires a TOEFL iBT score of at least 90. A student whose native language is not English also must submit a copy of an article or research paper in the student's native or principal research language in addition to the English writing sample required of all students.
Students are required to submit a minimum of three email addresses of faculty or others qualified to speak to the student's suitability for graduate study in history. Letters of reference should be submitted by the recommenders in addition to the electronic reference form they are asked to complete.
The statement of purpose is to be addressed to the history admission committee and should explain the applicant's scholarly background and training, career goals, the primary field the applicant wishes to pursue, the proposed research specialization, and why the applicant wants to pursue graduate study at ASU; it should be about 500 words in length.
The writing sample, either published or unpublished, may be an article, a research paper, or any other extended sample of expository skill, and it must be no longer than 35 pages in length. Longer writing samples should not be submitted without first consulting the graduate director. Documents and files should not be password protected. Acceptable file types are .rtf, .pdf and .doc.
Next Steps to attend ASU
Learn about our programs, apply to a program, visit our campus, application deadlines, learning outcomes.
- Identify and complete applications for funding opportunities that can support their research
- Demonstrate mastery of three domains of historical knowledge as well as display expertise in their proposed topic of study
- Accomplish meaningful contributions to the profession through accepted publications and presentations
Career Opportunities
Graduates possess the foundational skills in research, writing, and communication and fundamental training needed for careers in research, archival work, higher education, teaching, public history, government service, and a host of other areas in the public, private and nonprofit sectors.
They serve as first-rate historians, highly qualified instructors at two-year schools and universities, researchers and consultants for business and government, archivists, foreign service officers, management professionals, community organizers and public servants. Other career examples include:
- editorial and publishing professional
- K-12 school teacher
- museum director and staff
- nonprofit director
- university professor
Global Experience
With over 250 programs in more than 65 countries (ranging from one week to one year), study abroad is possible for all ASU students wishing to gain global skills and knowledge in preparation for a 21st-century career. Students earn ASU credit for completed courses, while staying on track for graduation, and may apply financial aid and scholarships toward program costs. https://mystudyabroad.asu.edu
Program Contact Information
If you have questions related to admission, please click here to request information and an admission specialist will reach out to you directly. For questions regarding faculty or courses, please use the contact information below.
- [email protected]
- 480/965-5778

- How to Choose a PhD Research Topic
- Finding a PhD
Introduction
Whilst there are plenty of resources available to help prospective PhD students find doctoral programmes, deciding on a research topic is a process students often find more difficult.
Some advertised PhD programmes have predefined titles, so the exact topic is decided already. Generally, these programmes exist mainly in STEM, though other fields also have them. Funded projects are more likely to have defined titles, and structured aims and objectives.
Self funded projects, and those in fields such as arts and humanities, are less likely to have defined titles. The flexibility of topic selection means more scope exists for applicants to propose research ideas and suit the topic of research to their interests.
A middle ground also exists where Universities advertise funded PhD programmes in subjects without a defined scope, for example: “PhD Studentship in Biomechanics”. The applicant can then liaise with the project supervisor to choose a particular title such as “A study of fatigue and impact resistance of biodegradable knee implants”.
If a predefined programme is not right for you, then you need to propose your own research topic. There are several factors to consider when choosing a good research topic, which will be outlined in this article.
How to Choose a Research Topic
Our first piece of advice is to PhD candidates is to stop thinking about ‘finding’ a research topic, as it is unlikely that you will. Instead, think about developing a research topic (from research and conversations with advisors).
Consider several ideas and critically appraise them:
- You must be able to explain to others why your chosen topic is worth studying.
- You must be genuinely interested in the subject area.
- You must be competent and equipped to answer the research question.
- You must set achievable and measurable aims and objectives.
- You need to be able to achieve your objectives within a given timeframe.
- Your research question must be original and contribute to the field of study.
We have outlined the key considerations you should use when developing possible topics. We explore these below:
Focus on your interests and career aspirations
It is important to choose a topic of research that you are genuinely interested in. The decision you make will shape the rest of your career. Remember, a full-time programme lasts 3-4 years, and there will be unforeseen challenges during this time. If you are not passionate about the study, you will struggle to find motivation during these difficult periods.
You should also look to your academic and professional background. If there are any modules you undertook as part of your Undergraduate/Master degree that you particularly enjoyed or excelled in? These could form part of your PhD research topic. Similarly, if you have professional work experience, this could lead to you asking questions which can only be answered through research.
When deciding on a PhD research topic you should always consider your long-term career aspirations. For example, as a physicist, if you wish to become an astrophysicist, a research project studying black holes would be more relevant to you than a research project studying nuclear fission.
Read dissertations and published journals
Reading dissertations and published journals is a great way to identify potential PhD topics. When reviewing existing research ask yourself:
- What has been done and what do existing results show?
- What did previous projects involve (e.g. lab-work or fieldwork)?
- How often are papers published in the field?
- Are your research ideas original?
- Is there value in your research question?
- Could I expand on or put my own spin on this research?
Reading dissertations will also give you an insight into the practical aspects of doctoral study, such as what methodology the author used, how much data analysis was required and how was information presented.
You can also think of this process as a miniature literature review . You are searching for gaps in knowledge and developing a PhD project to address them. Focus on recent publications (e.g. in the last five years). In particular, the literature review of recent publications will give an excellent summary of the state of existing knowledge, and what research questions remain unanswered.
If you have the opportunity to attend an academic conference, go for it! This is often an excellent way to find out current theories in the industry and the research direction. This knowledge could reveal a possible research idea or topic for further study.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Discuss research topic ideas with a PhD supervisor
Discuss your research topic ideas with a supervisor. This could be your current undergraduate/masters supervisor, or potential supervisors of advertised PhD programmes at different institutions. Come to these meetings prepared with initial PhD topic ideas, and your findings from reading published journals. PhD supervisors will be more receptive to your ideas if you can demonstrate you have thought about them and are committed to your research.
You should discuss your research interests, what you have found through reading publications, and what you are proposing to research. Supervisors who have expertise in your chosen field will have insight into the gaps in knowledge that exist, what is being done to address them, and if there is any overlap between your proposed research ideas and ongoing research projects.
Talking to an expert in the field can shape your research topic to something more tangible, which has clear aims and objectives. It can also find potential shortfalls of your PhD ideas.
It is important to remember, however, that although it is good to develop your research topic based on feedback, you should not let the supervisor decide a topic for you. An interesting topic for a supervisor may not be interesting to you, and a supervisor is more likely to advise on a topic title which lends itself to a career in academia.
Another tip is to talk to a PhD student or researcher who is involved in a similar research project. Alternatively, you can usually find a relevant research group within your University to talk to. They can explain in more detail their experiences and suggest what your PhD programme could involve with respect to daily routines and challenges.
Look at advertised PhD Programmes
Use our Search tool , or look on University PhD listing pages to identify advertised PhD programmes for ideas.
- What kind of PhD research topics are available?
- Are these similar to your ideas?
- Are you interested in any of these topics?
- What do these programmes entail?
The popularity of similar PhD programmes to your proposed topic is a good indicator that universities see value in the research area. The final bullet point is perhaps the most valuable takeaway from looking at advertised listings. Review what similar programmes involve, and whether this is something you would like to do. If so, a similar research topic would allow you to do this.
Writing a Research Proposal
As part of the PhD application process , you may be asked to summarise your proposed research topic in a research proposal. This is a document which summarises your intended research and will include the title of your proposed project, an Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography. If you are required to submit this document then read our guidance on how to write a research proposal for your PhD application.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Boston University Academics
Boston University
- Campus Life
- Schools & Colleges
- Degree Programs
- Search Academics
- PhD in History
The Department of History at Boston University admits students to its PhD program who have majored in history or a closely related academic field, who have strong academic records, and who are interested in working in the fields of African, American, Asian, or European history. The department trains PhD students to develop and execute original research designs that will lead to scholarly publications intended to make original and important contributions to the historical discipline and its subfields. At the same time, the department also prepares students to become the next generation of effective history teachers, able to instruct on a wide range of topics. Our expectation is that our PhDs will become professors at research universities, colleges, community colleges, and staff members at research libraries and archives.
Learning Outcomes
- Demonstrate mastery of chosen subfield of history and related fields. The candidate should understand the major interpretive schools in their field and related fields, contemporary trends within the historiography, and the position of their own work in relation to these.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the archive system essential to their research.
- Produce and defend publishable original research.
- Conduct all research in an ethical manner.
- Be able to teach effectively at the undergraduate and graduate levels.
Course Requirements
Students in the program must take 64 credits, 56 of which should be taken in seminars, lecture courses, directed research, and directed study, preferably over a period of four or five semesters. The remaining 8 credits are reserved for four semesters of a two-credit Dissertation Workshop (GRS HI 900) taken after the oral exam. Required courses include:
- GRS HI 800 European Historiography
- GRS HI 801 The Historian’s Craft
- GRS HI 850 American Historiography
- GRS HI 870 African Historiography
- Four semesters GRS HI 900 Dissertation Writing
Students must take the historiography courses in their first year, alongside HI 801, which will be offered every year in the spring semester. Students are allowed to take up to two graduate-level courses in a single discipline other than history that is related to their interests. Candidates for the PhD may count only 16 credits in courses designed primarily for undergraduates (these courses are offered at the 600 or 700 level and ordinarily have 200- or 300-level equivalents) for the degree.
Research Paper
Every doctoral student must write at least two major research papers and submit them to the Graduate Studies Committee. The paper completed in GRS HI 801 The Historian’s Craft counts as one of the research papers. Students entering the program with a master’s degree may petition the Director of Graduate Studies to transfer credit for one research paper.
Language Requirements
The department aims to graduate world-class scholars capable of conducting research in languages other than English. Students working in African, Asian, and European history must conduct primary research in languages other than English. But given that significant secondary literature is produced outside the English-speaking world, the department believes that it is important for all of our doctoral students, including Americanists, to demonstrate a genuine ability to read research in foreign languages. To this end, we require that doctoral candidates in United States history demonstrate a graduate-level reading knowledge in one relevant foreign language, and doctoral candidates in Asian, European, and African history demonstrate a graduate-level reading knowledge in two relevant foreign languages. In exceptional circumstances, doctoral candidates in European history may petition for exemption from the two-language requirement.
Language proficiency can be demonstrated either through a departmental language examination or through successful completion of a noncredit graduate-level foreign language reading course offered by Boston University. If a student has passed a reading examination at another accredited graduate school and submits evidence to the Director of Graduate Studies, the departmental requirement will be considered satisfied in most cases. Students may not schedule their qualifying examination without having completed this requirement. For more information on when language requirements need to be fulfilled, please see the department website .
Qualifying Examination
Each candidate for the doctoral degree must pass an oral examination in a major field of history as well as a one minor field of history. The examination must be taken no later than one year after the completion of coursework. The examination shall be comprehensive and cover any and all phases of the subject. A unanimous vote of the examining committee is required to pass the qualifying oral examination. Qualifying examinations are scheduled only during the two regular semesters of the academic year.
Dissertation and Final Oral Examination
Candidates shall demonstrate their abilities for independent study in a dissertation representing original research or creative scholarship. A prospectus for the dissertation must be completed and approved by the readers, the Director of Graduate Studies, and the Department Chair/Program Director within twelve months of the successful completion of the qualifying oral examination. This prospectus may be prepared in a directed study with the prospective dissertation advisor during the last semester of coursework, or it may be prepared after all coursework has been completed. Candidates must undergo a final oral examination in which they defend their dissertation as a valuable contribution to knowledge in their field and demonstrate a mastery of their field of specialization in relation to their dissertation. All portions of the dissertation and final oral examination must be completed as outlined in the GRS General Requirements for the Doctor of Philosophy Degree .
Any PhD student who has fulfilled the requirements of the master’s degree program, as stated here , can be awarded a master’s degree.
Related Bulletin Pages
- Graduate School of Arts & Sciences Departments
- Graduate School of Arts & Sciences Courses
- Abbreviations and Symbols
Beyond the Bulletin
- Graduate Program in History
- Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Graduate Admissions
- Graduate Financial Aid
- BA/MA Program
- Master’s Degree Requirements
- PhD Degree Requirements
- African American Studies
- American & New England Studies
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Bioinformatics
- Biostatistics
- Classical Studies
- Cognitive & Neural Systems
- Computer Science
- Creative Writing
- Earth & Environment
- Editorial Studies
- MA in History
- History of Art & Architecture
- Latin American Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary Translation
- Mathematics & Statistics
- Molecular Biology, Cell Biology & Biochemistry
- Neuroscience
- Pardee School of Global Studies
- Playwriting
- Political Science
- Preservation Studies
- Religious Studies
- Romance Studies
- Sociology & Social Work
- Statistical Practice
- African Studies Certificate
- Asian Studies Certificate
- Advanced Biogeoscience Certificate
- Holocaust, Genocide & Human Rights Studies Certificate
- Latin American Studies Certificate
- Linguistics Certificate
- Museum Studies Certificate
- Muslim Studies Certificate
- Teaching Language, Literature & Film Certificate
- Teaching Writing Certificate
- Women’s, Gender & Sexuality Studies Certificate
- Departments
- Research Centers & Institutes
Terms of Use
Note that this information may change at any time. Read the full terms of use .
related websites
Accreditation.
Boston University is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education (NECHE).

- © Copyright
- Mobile Version

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Department of History of Art
- About Us overview
- Slade Visiting Professors
- Recent Staff Publications
- Alumni overview
- Distinguished Alumni
- Keeping in Touch
- Equality Diversity Inclusivity (EDI)
- Athena SWAN
- Privacy Policy
- People overview
- Directors of Studies
- Head of Department
- University Teaching Officers
- Emeritus and Honorary Professors
- Affiliated Lecturers
- Research and other Fellows
- Associated Academic Staff
- Slade Professors
- MSt Building History
- Professional Staff
- Graduate Students - PhD in History of Art
- Admissions overview
- Undergraduate study overview
- Why study Art History?
- The Course overview
- Years 2 and 3
- Teaching and Learning
- Studying in Cambridge
- What Our Students Say
- Careers in Art History overview
- Destinations of recent alumni
- Alumni Profiles
- Postgraduate Courses overview
- MPhil in the History of Art and Architecture overview
- How to apply for the MPhil in History of Art & Architecture
- MSt in Building History
- PhD in History of Art overview
- How to apply for the PhD in History of Art
- Language Centre
- Research overview
- Medieval and Renaissance Visual Culture
- Eighteenth- and Nineteenth-Century Art and Architecture
- Modern and Contemporary Art and Theory
- Cambridge Visual Culture
- The Ax:son Johnson Centre for the Study of Classical Architecture
- The Cambridge Courtauld Russian Art Centre (CCRAC) overview
- The People’s Art School and Unovis in Vitebsk: An international conference organised by the Cambridge Courtauld Russian Art Centre (CCRAC) in collaboration with the Van Abbemuseum, Eindhoven overview
- About the Conference
- Organisers and Sponsors
- Conference Programme
- Current PhD Topics in the Department overview
- Francesca Aimi: Domenico Veneziano in Context: Reassessing Florentine Visual Culture in the 1440s
- Anneke de Bont: The Christian Epistemic Image in Northern European Print, c.1570–c.1700
- Helen Bremm: Surrealist Tempera Paintings in Mexico and the United States, c.1940–1970
- Thomas Cooper: May Morris, Making, Textiles, c. 1880 – 1938
- Frankie Dytor: Reanimating the Renaissance, 1873 – 1914
- Research Collaborations
- Visiting Scholars
- Visiting Students
- Leverhulme Early Career Fellowships
- Seminar Series overview
- Graduate Research Seminars
- The Medieval Art Seminar Series
- The Cambridge Modern and Contemporary Art Seminar Series
- KUNST: German Theoretical Approaches to Art (1750-2000)
- The Cambridge Architectural History Seminars
- The Ax:son Johnson Centre for the Study of Classical Architecture Seminar Series
- The Renaissance and Early Modern Seminar Series
- Outreach overview
- Masterclasses
- Sutton Trust Summer School
- Resources and Other Programmes
- Events overview
- Past Events
Current PhD Topics in the Department
- The Cambridge Courtauld Russian Art Centre (CCRAC)
The Secretary The Department of History of Art 1-5 Scroope Terrace Cambridge CB2 1PX Tel: 01223 332975 Fax: 01223 332960
Contact: [email protected] [email protected]
Site privacy & cookie policies, how to find us.
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

History Dissertation Topics
Published by Grace Graffin at January 9th, 2023 , Revised On May 29, 2024
Choosing the most appropriate topic for a history dissertation can be tricky. Before selecting a topic, it is imperative to have an in-depth knowledge of the historical events or phenomena you wish to evaluate. Complete comprehension of a topic area is necessary before you can go about the task of completing your dissertation.
To help you get started with brainstorming for history topic ideas, we have developed a list of the latest topics that can be used for writing your history dissertation.
PhD qualified writers of our team have developed these topics, so you can trust to use these topics for drafting your dissertation.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives , literature review, along with the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics here.
2024 History Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: who was responsible for the european civil wars an exploratory study identifying the determinants of the 1870 franco-prussian war.
Research Aim: This research aims to determine various political, social, and economic factors which caused European civil wars. It will use the 1870 Franco-Prussian War as a case study to analyse which political, social, or economic forces played their part in exaggerating this war. Moreover, it will use various historical lenses to evaluate the available evidence in this area to determine the factors objectively. Lastly, it will recommend ways through a historical viewpoint that could’ve saved lives in these wars.
Topic 2: What were the Socio-Economic Discontents of the Second Industrial Revolution? A Marx-Engels Perspective
Research Aim: This study identifies various socioeconomic discontents of the Second Industrial Revolution through the Marx-Engels communist lens. It will analyse how the second industrial revolution brought undesirable socio-economic changes in Europe and the rest of the world. It will develop a socio-economic framework by using Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels’s critique of capitalism and social class theory to show the second industrial revolution divided the entire world into two classes. Moreover, it will show how imperialist powers used the Second Industrial Revolution to change the world order.
Topic 3: Did Mongols Bring Social Change in Ancient Arab? Impact of Mongol Invasion on Ancient Arab Culture and Traditions
Research Aim: This research intends to analyse the social change brought by Mongols in ancient Arab. It will find the impact of the Mongols’ invasion on ancient Arab culture and traditions by identifying channels such as slavery, forced marriages, etc., through which Mongols brought a cultural change. Moreover, it will find whether Arabs could come back to their original state or whether modern Arabs have their traits. And through which ways did ancient Arabs resist those changes?
Topic 4: What is Common among the United States’ Iraq, Japan, Afghanistan, and Cuba Invasions? A Comparative Study Finding the United States Common Political and Economic Motives
Research Aim: This study compares the United States’ Iraq, Japan, Korea, Afghanistan, and Cuba invasions. It will identify the United States’ common political and economic motives among these invasions, which gave it an incentive to pursue. It will be a multidisciplinary study exploring geopolitical, geo-economic, geo-strategic, and historical aspects of the invasions. Moreover, it will also compare the post-invasion situation of these countries to show how these countries dealt with it.
Topic 5: The Life and Work of William Shakespeare: His Influence on The Modern Theater- A Critique of Dr. Johnson
Research Aim: This study sheds light on the life and work of William Shakespeare by analysing his role in modern theatre. It will try to highlight his contribution to the field of literature and theatre but through the approach of Dr Johnson. Johnson’s works will be evaluated to see whether William Shakespeare has done something significant for modern theatre or it is just a one-sided view of William Shakespeare’s followers. It will analyse various works of William Shakespeare from Johnson’s critical lens to provide an objective assessment.
COVID-19 History Research Topics
Topic 1: the history of coronavirus..
Research Aim: This study will explore the historical facts and theories related to the coronavirus pandemic.
Topic 2: History of Spanish flu
Research Aim: In 1918, a deadly pandemic called Spanish flu hit the world, and many people lost their lives. This study will highlight the history of the disease, its symptoms, and similarities with the present crisis of COVID-19.
Topic 3: The history of various types of pandemics and their consequences
Research Aim: This study will investigate the history of various types of pandemics and their consequences on people’s health, the economy, and the world’s transformation after it.
History Research Topics 2024
Topic 1: types of communications in history.
Research Aim: This research aims to identify the types of communications in history
Topic 2: Terrorism and its impact on people's life
Research Aim: This research aims to address terrorism’s impact on people’s life
Topic 3: Treaty of Lausanne and the world's predictions about Turkey in 2023
Research Aim: This research aims to conduct a study on the Treaty of Lausanne and the world’s predictions about Turkey in 2023
Topic 4: Mythological stories and their impact on the youth
Research Aim: This research aims to study the impact of mythological stories on the youth.
Dissertation Topics from the Nineteenth Century
Topic 1: analysis of church wealth expropriation and political conflict in 19th-century colombia..
Research Aim: The research will explore the events of political violence after independence in Colombia regarding the redefinition of the Catholic Church’s property rights. The study primarily focuses on the country after 1850 to measure the influence of that expropriation of the Church’s assets on political violence.
Topic 2: Exploring the impact of the 19th-century development of refrigeration on The American meatpacking industry.
Research Aim: The city of Chicago in the United States is known to be the centre of modern refrigeration development due to it being the hub of the meatpacking industry. The proposed research will analyse Chicago’s meatpacking sector’s development and its significant role in developing critical technologies such as refrigeration. The study will examine the development of refrigerated transport and cold storage units to comprehend the city’s meatpacking industry’s local and later global success throughout the 19th century.
Topic 3: Examining the impact of the telegraph in the United States of America
Research Aim: The research uses document analysis to examine the influence of the invention of the telegraph in the United States of America. Specifically, the study will analyse how the telegraph revolutionised communication and news broadcasting to newspapers over national and international networks.
Topic 4: The impact of industrial conflict and technology on the development of technical education in 19th-century England.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the role that 19th-century employers played in training and educating young industrial workers in England. The purpose of the study is to comprehend the various factors that influenced the development of technical education while discovering the reason for antagonistic relations with skilled workers, which may have caused the Great Strike and Lockout of 1897.
Topic 5: The impact of changing gender relations on childbearing populations in the 19th-century Netherlands.
Research Aim: The research will look to comprehend the changes in childbearing patterns using a sequence analysis approach. The study will also try to understand the association between gender relations, historical fertility records, and women’s reproductive patterns in the 19th-century Netherlands.
Topic 6: Examining the shift of hierarchical and ethnocentric foreign relations to the Western model of international relations in 19th-century Japan.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the 19th century, a period of transition in Japanese foreign policy. The study will mainly focus on Russo-Japanese relations using document analysis to assess the four stages of shift that led Japan from an ethnocentric foreign policymaker to the Western type without colonisation and defeat in war.
History and Religious Dissertations
Topic 1: the impact of popular culture on evangelical christians in america..
Research Aim: The research uses document analysis to examine the impact that popular culture has had in shaping Evangelical Christian thought in the United States from the 1960s to the 2000s. The study focuses on analysing the variables that have allowed Evangelicalism to become a middle-class populist movement.
Topic 2: Fertility, feminism, and the American revolution
Research Aim: The research using document analysis, analyses the impact of the American Revolution on declining birth rates in the colonies and the increase of family limitation among white free women. The research will investigate the intentions of founding American women in their rejection of abundant fertility and a patriarchal family and the existent or non-existent role that colonial Christians played.

Topic 3: The decline of irrational and magical ideologies in England 1500-1600.
Research Aim: The research analyses how the introduction of religion, specifically early Christianity, had an impact on declining the conventional thought processes that used irrationality or magic as their basis. The research will use document analysis as its research method.
Topic 4: The impact of religion on innovation, 1604.
Research Aim: The research examines how Sir Frances Bacon’s epistle “Of Innovations” argues for the positive potential of innovation from the understanding of the Biblical scriptures. The study will also explore the relationship between Bacon and the English Protestant Church.
Topic 5: The role of churches and religion in World War II.
Research Aim: The research looks to examine the role of churches in Europe during WWII. The study will also analyse their religious ideologies and their deeds as institutions to impact the perceptions of World War II. The research will be conducted using document analysis.
History and Sociology Dissertations
Topic 1: race, poverty, and food deserts in cardiff, 1980-2016..
Research Aim: The research examines the demographic and spatial patterns that have shaped access to supermarkets in low-income neighbourhoods in Cardiff from 1980 to 2016. The research methods used will be quantitative.
Topic 2: Impact of World War II rationing on British cuisine
Research Aim: The research analyses the impact of rationing items by the British Ministry of Food on the specific culture from the 1940s to the 1980s. The research uses variables of socio-economic classes and geographic locations of the country to examine the cultural impacts it had on the British palate during the time. The research methods will include quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Topic 3: Impact of religious doctrines and ideologies on racism and racist factions in the USA.
Research Aim: The research analyses the relationship between different Christian sects and racial prejudice among groups of Christians based on geographic location (North or South) in the United States after the 2016 presidential elections. The research will be quantitative in nature but will incorporate qualitative techniques of historical document analysis to examine how racism in the country has changed since the Civil Rights Era of the United States.
Topic 4: The historical development and impact of public transportation in Shanghai, China, 1843-1937.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the impact of public transportation on the development of Shanghai’s urban landscape using the variables of tradition vs modernity, state and social relationships, and technology and society relations. The research will provide a historical analysis of the city from the British and the Opium Wars’ colonisation to the 20th century. The study will use qualitative document analysis and quantitative techniques as research methods.
Topic 5: The impact of water resource management, technological solutions, and urban growth after World War II on Atlanta, Georgia.
Research Aim: The purpose of the dissertation is to examine the origins of water-related issues in Atlanta by discovering the challenges that public officials, activists, and engineers faced in the area in terms of planning and enacting an effective environmental policy after World War II in the metropolitan area of Atlanta. The research will use historical document analysis as its methodology.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service !
Historical People and Events Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: examining the events and people giving rise to winston churchill.
Research Aim: The research examines the network of friends and colleagues of former Prime Minister Winston Churchill on how they influenced the primer’s reputation after his retirement and death. The study will analyse the history of the Churchill Archives Centre, Cambridge, and the influence that Sir John Colville had on shaping Churchill’s image.
Topic 2: The rise of the right-wing woman in 20th-century Britain- Analysing Margaret Thatcher and Mary Whitehouse
Research Aim: The relationship between conservative powerhouses Margaret Thatcher and Mary Whitehouse was well known to the public for its traditional undertones. The research will examine the relationship between the two women using document analysis, particularly the public presentation relationship, to better understand the importance of conservative women in Britain. The research will analyse the twentieth-century political and cultural contexts that gave rise to these two women.
Topic 3: Examining the cooperative transformational leadership of Nelson Mandela and F. W. de Klerk.
Research Aim: The research will study the transfer of power in South Africa by focusing on the cooperative leadership strategies, policies, and personal characteristics of leaders such as Nelson Mandela and F. W. de Klerk. The research will examine how these two leaders could bring systematic revolution through democratic and peaceful means.
Topic 4: Pablo Picasso- The making of “Guernica” and its historical context.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the history of paintings of people suffering from the convulsion of war, explicitly focusing on Goya. The paper will examine the factors and influences on Pablo Picasso that led to the development of “Guernica.” The research will analyse how Picasso depicted real history snatches with symbolism that resonated with people.
Topic 5: Analysing the role of women in the Crusade Movement.
Research Aim: The research examines women’s contribution to the Crusades and its impact on propaganda, recruitment, organisation of the crusades, and financing of the campaigns. The study will also survey their roles in looking after families and properties while also giving liturgical support at home for those on the crusade campaigns.
Topic 6: The impact of the Harlem Renaissance on urban landscaping, Jazz music, and literature.
Research Aim: The research will examine the Great Migration of the 1910s in the United States, where a concentration of African American population moved North, causing demographic shifts. The study will analyse Toni Morrison’s Jazz, Persia Walker’s Black Orchid Blues, and other works regarding music and urbanisation.
Topic 23: John F. Kennedy- Rise of American foreign power and South Vietnam.
Research Aim: The research will analyse John F. Kennedy’s foreign policy strategies’ central themes. The paper examines the themes of counterinsurgency, credibility, and commitment in South Asia, particularly South Vietnam, to improve his credibility after the Bay of Pigs incident. The paper will observe the president’s fascination regarding psychological warfare, military forces, and countering ‘communism’ aggression in Southeast Asia.
Italian Unification History Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the preservation of italy- analysing the fragility of italian unity 1866-68..
Research Aim: The research analyses the impact of the Austro-Prussian War at its conclusion in July 1866. The paper analyses factors such as the fall of the Liberal government in Britain that impacted the fragility of the Italian Unification. The paper examines the historical event through the bilateral relationship between a newly rising Italy and Britain.
Topic 2: Analysing the Italian post-unification period- Racial and colonial factors influencing modern Italians.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the rise of Italian fascism with the premise that it rose from the failures of previous liberal governments. The study particularly examines the first Liberal period after unification, which led to the explosion of civil war in the South of Italy. The study will analyse the racial and colonial factors that influenced the competition with Western European nations for imperialistic endeavours.
Topic 3: Prison system management in 19th-century Italian prisons after unification.
Research Aim: The research analyses accounting practices in prisons using documentation analysis of the prison management system of major Italian States in the early 19th century. The study aims to use various accounting methods to uncover the potentially socially damaging tools of accounting in prison reforms to discipline individuals of lesser status.
Topic 4: The impact of the mafia on Italian education after unification.
Research Aim: The research will use historical point data to analyse the impact the Mafia had on the level of education between 1874 and 1913. The particular geographic constraint of the study will be restricted to Sicily, Italy, after the unification of the Italian Kingdom in 1861.
German Unification History Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: examining the parties and problems of governance in the german empire..
Research Aim: The research will examine, using document analysis, the various processes for political restructuring that caused the founding of many political parties, interest groups, and civic associations. The research analyses how the Federal Republic strategised to transfer German Democratic Republic citizens’ sovereign rights to international institutions and the Federal Republic institutions.
Topic 2: Analysing the collapse of the GDR and the reunification of Germany.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the factors and influences surrounding the collapse of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from 1898 to 1990 and the reunification of East and West Germany. The research will also analyse the role of businesses with regard to the collapse, particularly the German business elites and their relationship with the Soviet Union.
Topic 3: Analysing the impact of Bismarck on the capitulation of German liberalism.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the impact the German National Liberal party of 1866 to 1867 had on supporting Otto von Bismarck’s policy of German unification. The study will examine the political stakes involved and the philosophy of Realpolitik in the Unification of the German Empire.
Topic 4: The impact of radical nationalism and political change after Bismarck.
Research Aim: The research will examine the factors that gave rise to the radicalisation of the German right under the politics of Otto von Bismarck. The study looks to find evidence of German fascism prior to World War II. To conduct the research, a thorough document analysis will be done with an extensive literature review.
World War I Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the response of german immigrants to discrimination in the usa during world war i.
Research Aim: The research will examine the impact of caste-based discrimination on assimilation patterns of immigrant minorities, specifically German immigrants in the United States during WWI. The study will understand if discriminated minority groups increase their assimilation efforts to avoid discrimination and public harassment. The research will use naming patterns of children and records of petitions of naturalisations to conduct the study empirically.
Topic 2: Analysing the impact of affective experience and popular emotion on WWI International Relations.
Research Aim: The research will examine the factors of communal emotion and mass emotion during the outbreak of WWI to demonstrate the political significance of widespread sentiment. The research looks to study the factors with regard to contemporary populism.
Topic 3: The impact of military service in WWI on the economic status of American Veterans?
Research Aim: The research will analyse the different registration regimes during the WWI draft to find their impact on economic outcomes. The research will use empirical from 1900 to 1930 United States to study short-term impact of military service, while the United States census of 1960 is used to determine the long-term impacts. The data collected will be of household income and draft population of the time in WW1.
Topic 4: Examining the Impact of Quarrying Companies Royal Engineers in WWI to support British armies on the Western Front.
Research Aim: The research will examine the history of the Quarrying Companies unit within the Royal Engineers in WWI. The study will analyse the impact that the group had on British armies on the Western Front, particularly for the aid of the British Expeditionary Forces until its disbandment in 1919.
The Great Depression (Britain 1918-1939) Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the impact of the great depression on labour productivity..
Research Aim: The research will examine the labour productivity of the UK manufacturing industry during the Great Depression. The research will be of empirical methodology and collect data on actual hours of work, real output, and employment statistics. The study will prove that during the Great Depression, output per work hour was counter-cyclical between 1929 and 1932.
Topic 2: Analysing the discourse of British newspapers during the Great Depression.
Research Aim: The research will use document analysis and text analysis to examine the rhetoric of British newspapers when unemployment rises. The study will accurately analyse the Great Depression in Britain by determining how the stigmatisation of poverty changes in the rhetoric of newspapers when discussing unemployment.
Topic 3: The Impact of the Great Depression on British Women Migration 1925-1935.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the impact that the Great Depression had on the migration of women out of Britain to the rest of its empire. The study will use empirical data to analyse the Society for Overseas Settlement of British Women (SOSBW). The research will assess if the society’s training programme influenced the employment and migration of women.
Topic 4: The Great Depression and British industrial growth- Analysing economic factors contributing to the Great Depression in Britain.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the British deceleration of industrial growth and the percentage rate of growth as the cause of the Great Depression in Britain. The research will examine the contribution of the Industrial Revolution and its initial rapid percentage of rate of growth causing ‘retardation.’ The study will be empirical and analyse historical patterns of Britain’s national economy.
Second World War Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: analysing brazilian aviation in world war ii.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the extent to which Brazilians were actively engaged in combat on the Brazilian coast and in the European theatre. The study will primarily focus on the global conflict through the Forca Aerea Brasileira, FAB, or the Brazilian Air Force development before participation in the Second World War.
Topic 2: The impact of invention secrecy in World War II.
Research Aim: The research will examine the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) patent secrecy orders which put over 11,000 US patent applications given secrecy orders. The study will analyse how this policy impacted keeping technology from the public during the war effort, specifically radar, electronics, and synthetic materials.
Topic 3: Analysing aerial photographic intelligence in WWII by British geologists.
Research Aim: The research will examine the period of WWII from 1939 to 1945 when intelligence was collected from aerial photographs by the Allied Central Interpretation Unit. The study will assess the history of aerial photographic information based on geology contributing to the Allied landings in Normandy in 1944.
Topic 4: Analysing British propaganda in the United States during WWII.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the strategies that British propagandists used to understand the American opinion of WWII during the war and for post-war relationships. The study will investigate the policies and factors that contributed to keeping the wartime alliance and creating an acceptable political climate in the United States for post-war cooperation.
Order a Proposal
Worried about your dissertation proposal? Not sure where to start?
- Choose any deadline
- Plagiarism free
- Unlimited free amendments
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Completed to match exact requirements
History of Nazi Germany Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the impact of discrimination against jewish managers on firm performance in nazi germany..
Research Aim: The research will examine the large-scale increase in discrimination in Nazi Germany to cause the dismissal of qualified Jewish managers in large firms. The study will analyse the persistent stock prices of firms, dividend payments, and return on assets after the discriminatory removal of Jewish managers.
Topic 2: Examining children’s literature in Nazi Germany
Research Aim: The research will analyse children’s literature which was propagandised between 1933 and 1945 under the National Socialists party. The paper will examine the various themes, specifically the Nordic German worldview, and how German values were distorted to produce a homogenous folk community.
Topic 3: Shifting from liberal education of the Weimar Republic to Nazi educational reforms- Analysing educational reforms under the Nazi government.
Research Aim: The research will examine education reform that the National Socialist government implemented in elementary education. The research will look to accumulate personal accounts of families and students who experienced the era to better comprehend the educational reforms. The study seems to under how these educational reforms moulded student ideologies.
Topic 4: The effects of antisemitism in film comedy in Nazi Germany.
Research Aim: The research will explore the themes of antisemitism in film comedy produced during the reign of the Nazi party in Germany. The research will study how themes impacted the perceptions of people living in Germany post-war. The research will use document analysis and empirical analysis to document and examine the themes and attitudes.
History of Cinema Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: analysing the history and politics of bollywood..
Research Aim: The research will explore the various events in Indian film history that have allowed it to become a global sensation. The paper will analyse its market-driven triumph against Hollywood imports starting from the 1930s. The paper will also examine the nationalist social views of films produced in Bollywood during the 1950s.
Topic 2: The role of cinematic depictions influencing popular understanding of the Spanish Civil War.
Research Aim: The research will examine the role that cinema played in shaping the understanding of the Spanish Civil War. The study will focus on fictional films that were produced in Spain and Hollywood between the 1940s and the early years of the 21st century.
Topic 3: Analysing distinctive characteristics of Korean films.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the characteristics of Korean films and examine their historical development. The research will focus on the eras of the Japanese colonial period to 1945 when the American army occupied South Korea. The study will analyse the role of censorship throughout this time period in producing Korean films.
Topic 4: Examining the history of cinema in Britain since 1896.
Research Aim: The research will explore the development of cinema exhibitions and cinema-going in Britain in 1896. They will analyse various factors that led to the rapid growth of cinema in Britain just before WWI. The study will examine factors such as the position of cinema, the development of modern spaces, artistic respectability, the invention of sound, and cinema as individual entertainment.
History of Racism Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: analysing the factors influencing institutional racism in america..
Research Aim: The research will explore the complicated history of racism in the United States. It will analyse how racism has become embedded throughout American society, from land ownership, education, healthcare, employment, and the criminal justice system. The research will use a mixed-methods research approach to gather data.
Topic 2: Examining the relationship between racism and environmental deregulation in the Trump Era.
Research Aim: The research will analyse the possible relationship between environmental deregulation and racism between 2016 and 2017 under the Trump Administration. The study will primarily collect data from executive actions, ecological events, and tweets from the President during this time period. The study will document racist events that were targeted at people of colour, Asians, Arabs, South Asians, Muslims, and indigenous persons.
Topic 3: Analysing the experience of racism in English schools towards Eastern European Migrants.
Research Aim: The research will use qualitative design to analyse the experience of racism faced by students of Eastern European descent. The research will use the framework proposed by the Critical Race Theory and Critical Conceptions of Whiteness to conduct the study. The research will focus on the racism experienced by these students as marginal whiteness for their various linguistic accents.
Topic 4: The impact of racism on Afro-Italian entrepreneurship.
Research Aim: The research will use qualitative data to analyse the participation of Afro-Italian women entrepreneurs in start-ups relating to beauty, style, and hair care lines. The study explores the obstacles that young black women entrepreneurs face in Italian due to racism and how their inclusion in small economies changes the perception of Blackness and Black womanhood related to Italian material culture.
Also Read: Religion, Theology and Philosophy Dissertation Topics
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

History of Spanish Civil War Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: examining the role of international nurses during the spanish civil war..
Research Aim: The research will use document analysis, primarily memoirs, to explore the life and work of international nurse participation during the Spanish Civil War. The study will examine their role with regard to contributions made to Spanish nursing during the war.
Topic 2: Examining republican propaganda during the Spanish Civil War.
Research Aim: The research will explore the propaganda used by the Republicans of the Spanish Civil War from 1936 to 1939 to support their ideology of the war. The paper will focus on three primary forms of media – newspapers, cinema, and music. The study will conduct the analysis using historical context to examine its effectiveness in propagating the Republican messages.
Topic 3: The history of British Battalions in the International Brigades of the Spanish Civil War.
Research Aim: The research will examine the role, experiences, and contributions of British volunteers to the Spanish Republic through the British Battalion of the 15th International Brigade. The study will accurately analyse the motivations of the volunteers to join the International Brigades and participate in the Spanish Civil War.
Topic 4: British cultural perspectives on the Spanish Civil War.
Research Aim: The research will explore the cultural perspectives of the political understanding of the British responses to the Spanish Civil War. The study will examine the mass culture and personal experiences of British visitors to Spain in the 1930s.
History of the United States Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the impact of ‘the frontier’ on american expansion and imperialism..
Research Aim: The research explores the idea of ‘manifest destiny, its connection to the American frontier, and its impact on imperialism. The study focuses on how the American perception of savagery and civilisation is related to expanding the American frontier.
Topic 2: Analysing the American public opinion on the War in Vietnam.
Research Aim: The research uses empirical data to analyse the American public attitude with regard to the Vietnam War. The data will be analysed using demographic groups and perception studies. The study will investigate how these perceptions eventually shaped government policy preferences during the Vietnam War.
Topic 3: Analysing the inaugural speeches of re-elected US presidents since WWII.
Research Aim: The research identifies, analyses, and assesses the use of individual style in inaugural speeches of re-elected US presidents since WWII. The research will be conducted using document analysis of lexical and semantic levels. The study will assess how the inaugural addresses are shaped to reflect the public policy of re-elected presidents.
Topic 4: Analysing the rise of white power and paramilitary groups in the United States.
Research Aim: The research analyses the rise and expansion of white nationalists and racist far-right groups using government publications, journalistic accounts, and archival records. The research focuses on the failure in Vietnam, giving rise to white power movements. The study will examine various events to assess the factors and significance that caused an increase in paramilitary groups in the United States.
Topic 5: Examining the rise of new white nationalism in America.
Research Aim: The research will use data acquired from speeches, books, and internet sources written by white nationalists to assess the shift of white nationalist ideas of oppression of other races to a view of victimhood of white nationalists. The research will use an extensive literature review to document the development of white nationalism in American history while also considering the development of social media.
Historic Events of Early Twentieth-Century Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the creation of uniquely american musical sounds; changes in classical music from the 19th to 20th century..
Research Aim: The research explores the changes in American classical music, shifting from its traditional European origins to a more defined American sound. The study will contend that historical events such as the upheaval and shifts of society during the American Civil War were the main factors in the creation of new American classical music.
Topic 2: The influence of political parties on democracy and party-state relations in the 20th-century.
Research Aim: The research will analyse institutional reforms of party-state relations, including constitutions, electoral laws, and party laws in France and Italy during the 20th century. The study will examine the impact of party entanglement on contributing to democratisation in Europe.
Topic 3: The impact of suspicion and distrust on conflict coverage- A case study of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Research Aim: The research will use inductive-qualitative analysis to examine the journalistic narratives of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. To do so, the factors of suspicion of information sources, awareness of being under suspicion, and distrust of peer journalists are used to examine the trust of journalists and the dilemmas they face in hostile environments.
Also Read: Project Management Dissertation Topics
List Of Top Trending Dissertation Topics For History Students
- Decolonisation Movements and the Reshaping of Global Power Dynamics
- The Rise of Social Media and Its Influence on Historical Narratives
- Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Historical Research
- The Cold War’s Legacy in the Context of Contemporary Geopolitical Tensions
- Redefining National Identity in a Globalised World
- A Long-Term Analysis of The Environmental Consequences of Industrialization
- The Representation of Race and Gender in Historical Film and Television
- The Ethics of Cultural Appropriation in Museums and Historical Sites
- Space and its Influence on International Cooperation
- Cyberwarfare and its Implications for Global Security
- The Role of Technology in Shaping Revolutions Throughout History
- The Power of Propaganda and its Role in Shaping Public Opinion
- The Interconnectedness of Global Trade Routes and Historical Exchange
- The Black Death’s Devastating Impact and its Long-Term Social Repercussions
- The Rise of Populism and its Challenges to Democratic Institutions
- The History of Censorship and its Impact on Freedom of Expression
- The New World and its Devastating Consequences on Indigenous Populations
- The Scientific Revolution and its Challenges to Religious Authority
- The French Revolution’s Legacy: Liberty, Equality, Fraternity, and Their Unfinished Business
- The Unintended Consequences of Technological Advancements Throughout History
- The Power of Social Movements in Driving Political and Social Change
- The History of Espionage and its Influence on International Relations
- The Role of Diplomacy in Resolving International Conflicts
- The Vietnam War’s Legacy and its Enduring Impact on American Society
- The Civil Rights Movement in the United States and its Global Influence
- The History of LGBTQ+ Rights and the Ongoing Fight for Equality
- The Challenges and Opportunities of Urbanisation Throughout History
- The History of Mental Health and the Changing Attitudes Towards Treatment
- The Role of Religion in Shaping Historical Events and Social Development
- The History of Education and its Impact on Social Mobility
- The Power of Literature and Art in Reflecting and Influencing Historical Change
- The Role of Espionage in Shaping the Outcomes of Major Historical Events
- The Challenges of Preserving and Interpreting Historical Artifacts for Future Generations
Important Notes:
As a student of history looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment with existing history theories – i.e., to add value and interest to your research topic.
The field of history is vast and interrelated to so many other academic disciplines like literature , linguistics , politics , international relations , and more. That is why it is imperative to create a history dissertation topic that is particular, sound, and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic; it is the basis of your entire research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your topic wrong; your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation as you may end up in a cycle of rejection at the very initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
While developing a research topic, keeping our advice in mind will allow you to pick one of the best history dissertation topics that fulfils your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalising your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and can also be practically implemented. Take a look at some of our sample history dissertation topics to get an idea for your own dissertation.
How to Structure Your History Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes the project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems to be addressed. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review : This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analysing published and unpublished literature available on the chosen research topic, in light of research questions to be addressed. The purpose is to highlight and discuss the relative weaknesses and strengths of the selected research area while identifying any research gaps. Break down of the topic, and key terms can have a positive impact on your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology : The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter, which usually includes research design , research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods, and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis : Findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs, charts, and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion : The researcher presents his interpretation of the results in this chapter, and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section is to establish the link between the results and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regard to the implications of the findings and directions for the future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References : Make sure to complete this in accordance with your University’s requirements
- Bibliography
- Appendices : Any additional information, diagrams, or graphs that were used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is a UK based academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing , Ph.D. Proposal Writing , Dissertation Writing , Dissertation Editing, and Improvement .
Our team of writers is highly qualified. They are experts in their respective fields. They have been working for us for a long time. Thus, they are well aware of the issues and the trends of the subject they specialise in.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find dissertation topics about history.
- History era or event that excites you!
- Look for the historical roots of modern issues.
- Seek guidance from professors with research areas you like.
- Consider the availability of research materials for your topic.
- Narrow a broad topic into a specific research question.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable science dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending science dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
If you are a student of sports law at a university, you are familiar with the tension that comes with writing a dissertation due to the difficulty of choosing a topic.
Top 25 interesting recent dissertation topics on web development to score exceptional grades in your web development dissertation.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Skip to main content
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Apply Apply
- Follow Us

What Can You Do with a PhD in History?

You’re a history buff — the person everyone wants on their trivia team. You can rattle off the dates, facts, and names of the world’s most significant events and periods. If you’re considering using your powers for good, getting a PhD in history is a great option.
People with a passion for being stuck in the past have options once they’ve completed their history doctoral program. Beyond history jobs in academia, there’s a spot for a historian around the table in nearly every industry. The skill set required to complete a PhD opens up a variety of doors in whichever direction you choose to pursue. Here’s an idea of some things you can do with a PhD in History .
If you see yourself leading the nation’s young people through their own historical journeys, a PhD prepares you to teach at almost any level, though going the professor route could be more lucrative than teaching high school. On average history professors make between $80,000-$164,000 per year.
You’ll select your focus and spend your days sharing your passion with undergraduate and master’s level students. Along with teaching, if you pursue a history career in academia, you’ll likely spend some time researching topics within your wheelhouse. Re: your passion!
If spending your days in front of the class, hosting debates, and leading young minds excites you, there might be even more time on a college campus in your future. However, tenured history professor roles may take some time to find and the salaries can range based on the type of university and location.
Future Planning
Those studying the past usually have some insights into the future. If you’re looking to explore the world outside of strictly history, you might use your skills to find a career in future planning. No, not retirement planning (though that’s an option too).
Historians have a knack for identifying themes and patterns in culture, politics, and the world. A history PhD program allows you to use your historical knowledge to contribute to the modern world by making an impact on the community around you. Many politicians, inclusion officers, grant writers, and even human resource managers use their history PhDs to influence their worlds.
Your ability to think critically about the past and lend your knowledge to the future makes you an asset to any organization looking to excel into the modern world. Be prepared to market yourself as someone who can best set the organization up for success in an ever-changing world.
Business/Technology
In the business and technology world, it’s all about understanding the customer. Who are you selling to? What is their day-to-day life like? How do you best understand their needs and wants?
As a historian, your ability to communicate with a diverse population and understand the context of their lives makes you especially valuable on a sales, marketing, development, or innovation team. As a PhD, employers know you are well-read, have strong research skills and have spent many, many, many hours writing. It’s no surprise that Historians make excellent copywriters, marketers, and editors.
We won’t lie to you, there aren’t many Fortune 500 CEOs that can claim a doctorate in history. Most CEOs have MBAs or degrees in engineering. But there should be more historians up at the top — maybe you have what it takes.
Intelligence Analysis
You may not be the next Indiana Jones, but you might cut it as a secret agent. The ability to analyze and synthesize information from various sources is crucial for intelligence analysts — and history PhDs have that in spades.
Skilled at recognizing biases, evaluating the reliability of sources, and making informed judgments based on incomplete or uncertain information, historians have a strong ability to think critically and evaluate evidence.
Additionally, historians have a deep understanding of the historical, cultural and social context in which events occur. This understanding can help you identify underlying factors and motivations that may not be immediately apparent to others.
Archivist/Historian
If you’ve always dreamed about a career in history, this is likely what you’ve pictured. Spending days dusting off old newspapers and curating the perfect collection of artifacts — historians and archivists are often hired by governments or organizations to collect, analyze, organize, and preserve important documents and artifacts.
Companies may hire a historian to reflect on the organization’s past in order to better inform their future choices or to maintain an existing collection of artifacts. We get it. We saw National Treasure, too. This would be a pretty amazing career.
The salary for historian jobs can vary based on size of the organization and unfortunately, the importance they place on preserving their history. For reference, the average PhD in history salary is $75,000 in the U.S.
Become a Historian at SMU
So, what can you do with a PhD in history? You can make sense of the past to inform the future, you can write exceptionally well, and you can excel in nearly any industry. Simply holding your doctoral degree in history shows employers the determination you have. There should be a seat saved for you at every company, college, and organization looking to succeed.
Ready to get started?
Explore what you can do with a PhD in History, read the guide Reanalyzing Our World, PhDs in The Humanities at SMU !

Request more
Information.
Complete the form to reach out to us for more information
Published On
More articles, recommended articles for you, spotlight: ph.d. alumnus matthew babcock.
Prof. Matthew Babcock is an Assistant Professor of History at UNT Dallas, where he has worked as a...
Is a PhD in Humanities Worth It?
If you’ve recently completed an undergraduate degree in a field like English, History or Religious...
How to Compare History PhD Programs
So, you've set your sights on pursuing a PhD in History. As a prospective History PhD student, you...
Browse articles by topic
Subscribe to.
Department of History

Ph.D. Admissions
With more than 40 full-time faculty members, the Department of History trains graduate students in a wide range of fields and methodological approaches, covering periods from antiquity to the present.
Graduate students in history benefit from a high faculty-to-student ratio, which enables us to provide more individual attention than many other programs. The size of each entering class varies slightly from year to year, with eight to 10 students being typical. In all, we have approximately 50 students, a talented and diverse group who come from many parts of the United States and the world.
Vanderbilt University offers many opportunities for interdisciplinary engagement. The Robert Penn Warren Center for the Humanities houses on-going seminars in areas ranging from Circum-Atlantic studies to postcolonial theory, science studies, and pre-modern cultural studies. Other centers and programs whose activities would be of interest to history graduate students include the Center for Latin American, Caribbean, and Latinx Studies ; the Department of Medicine, Health, and Society ; the Max Kade Center for European and German Studies ; the Department of African American and Diaspora Studies ; the Department of Gender and Sexuality Studies ; and the programs in Asian Studies Program , American Studies , and Jewish Studies . The Department of History strongly encourages interdisciplinary work.
Please note: The Department of History does not accept external applications for a terminal master’s degree. The M.A. is usually earned en route to the Ph.D. It is also available to Vanderbilt undergraduates who enroll in the 4+1 program in history.
Director of Graduate Studies and Admissions: Ari Bryen Graduate Administrator: Madeline Trantham
If you have any questions regarding the graduate application process that are not answered here, please email us .
Application
The Vanderbilt history department offers the Ph.D. degree. Students normally earn the M.A. following two years of coursework, fulfillment of the research paper requirement, and satisfactory performance on language examinations. The department does not offer a free-standing terminal M.A. degree.
The application deadline for Fall 2025 admission is December 1, 2024. Applicants for whom the $95 application fee presents a financial hardship are encouraged to apply for a fee waiver from the Graduate School.
Foreign applicants or applicants who do not qualify for a fee waiver from the Graduate School should contact [email protected] . These applicants should explain briefly in their email why the fee presents a financial hardship. Requests for a fee waiver will be assessed and forwarded to the College of Arts & Science. If a fee waiver is granted, the applicant will be notified.
Applicants should have an undergraduate degree from an accredited institution, domestic or international.
Application Components
As part of the online application, candidates will provide:
- Statement of Purpose (please be specific about your research goals and provide names of faculty members with whom you would like to work, and why. In addition, please explain how your interests and goals may connect with our Areas of Excellence ).
- A minimum of three letters of recommendation (and no more than five).
- An unofficial, scanned college transcript(s) and graduate transcript(s) if applicable. Admitted applicants will be instructed to submit official and final transcripts as a condition of enrollment at Vanderbilt.
- TOEFL and IELTS scores are accepted for international students whose native language is not English. For more information, read the Graduate School’s Language Proficiency policy.
- Candidates are required to upload a writing sample of no more than 25 pages as part of the online application process. The option to upload the writing sample is made available immediately after entering your test scores into the online application. Please note that until this writing sample has been uploaded, your application will be considered incomplete. Research papers and theses, especially those that explore a historical topic and show facility in using original and/or archival materials, are of most use to the admissions committee in making their decisions. Co-authored writing samples are not accepted.
- GRE scores are not required for admission.
Return to top
Areas of Excellence
Graduate students will select an area of excellence from a drop-down menu in the online application; prospective advisers will submit a note to the admissions committee explaining the candidate’s fit. Therefore, applicants are strongly encouraged to reach out to prospective advisors to figure out how their interests could connect with our areas of excellence initiative and to explain in their Statement of Purpose how they envision benefitting from it.
Economics: Labor, Business, Capitalism:
The Vanderbilt History Department offers a rich setting for the study of the history of economy, widely conceived, including labor and business history, the history of capitalism, trade networks, and general questions of economic development as they connect with politics, culture, religion, and social history. Ranging temporally from the classical/medieval era to the modern world, and geographically from the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, Europe and the United States, the Vanderbilt History faculty is interested in the study of commodities, thought, empire, trade, free and unfree labor, finance, cultures, and the global development of capitalism. Our view is capacious, with wide interest in legal, political, and regulatory regimes that influence such processes. Working with faculty across the department, we encourage comparative and transnational forms of historical inquiry. Vanderbilt also offers connections with a robust team of formal economic historians in the Economic Department and a strong undergraduate Economics-History major.
Legal History
Vanderbilt is home to a thriving community of legal historians. We range chronologically from the ancient Mediterranean to the twenty-first century, and our faculty and graduate students have written on topics as diverse as ancient violence, the history of prostitution, racial passing, citizenship, Islamic law, policing, capital punishment, sovereignty and state building, privacy law, American slavery, and the intersections of religion and law.
Our community is centered on the Legal History Colloquium, a trans-institutional seminar that brings together faculty and students from the Law School, the Divinity School, and the College of Arts & Sciences working on legal historical themes. The colloquium strives to be international and comparative in methods and scope. Students in Legal History take a graduate seminar on Methods in Legal History, which introduces them to the wide-range of work done by legal historians. Working in consultation with their adviser, students of legal history write one of their two graduate seminar papers on a legal topic; they also have opportunities to serve as teaching assistant to faculty in diverse areas of legal history.
Race & Diaspora
Vanderbilt’s History Department focuses on complex histories of racial formation, as well as race and migration. The unique history of African peoples dispersed by the Atlantic and Indian Ocean slave trades is of particular interest. Deploying local, national, transnational, and transdisciplinary approaches, students work closely with accomplished scholars in the History Department—as well as other academic departments, such as African American & Diaspora Studies—to study a wide array of interrelated topics.
These include race as a concept, ideology, and system, as well as the role of race in shaping identity and culture in the Americas and other parts of the world. Likewise, students examine theories of race & diaspora, encompassing historical phenomena such as settler colonialism, racial enslavement, labor migrations, deportation, colonialism, and post-colonialism. In addition, research can extend to the analysis of subsequent mass demographic movements and the creation of “new” racialized peoples, homelands, communities, cultures, and ideologies as historical groups responded to upheaval and sought opportunities. Therefore, scholarship on race and diaspora also attends to manifestations of social, religious, economic, and political oppression and social control, and the attendant struggles of resistance and adaptation. This, in turn, leads us to scrutinize race alongside state formation, racialized citizenship, capitalism, state-building, and surveillance. As with all work on race, centering analyses of gender and sexuality is a priority in order to provide a deeper understanding of racial identities and structures. In addition, examining race and diaspora from the ancient world through the 20th Century and in relationship to Native American, Asian, and Jewish diasporas is also possible.
Research Areas
Ancient/medieval.
Vanderbilt boasts a dynamic group of scholars in Ancient and Medieval history. The faculty represent a range of geographic and chronological periods, including the Roman Empire, Ancient/Medieval Syria, medieval Europe, Judaism, Islam and Asia. The faculty share a mutual interest in reconstructing past through rigorous, source-driven historical reconstruction, with specializations in legal, religious, economic, cultural and military history. They work closely with a distinguished cohort of early modern historians, and in collaboration with the programs in Classical and Mediterranean Studies, the Legal History Seminar, Jewish Studies, Women and Gender Studies, the Pre-Modern Cultural Studies seminar (Robert Penn Warren Center); the departments of English, French & Italian, German, Russian and East European Studies, History of Art, and the Graduate Department of Religion.
We welcome applications from potential graduate students interested both in particular subject areas, but also in the questions and methods shared by all historians of pre-modern societies – how to work with patchy or fragmentary evidence, how to reconstruct the world of culture and symbols, how to push beyond the learned texts that predominate in our records, and how to ask meaningful questions about the past.
There is no prescribed graduate curriculum; students are invited to craft their own program within the framework of the History Department Ph.D. requirements during coursework. Particular scrutiny is given, in evaluating applications, to a candidate’s prior preparation (including knowledge of languages necessary to undertake Ph.D. level research) and a candidate’s writing sample. Applicants are encouraged to contact potential supervisors in advance.
Vanderbilt University's History Department continues to diversify geographically and thematically, with African history being the latest doctoral field to be added to our offerings. Our doctoral program in African history is designed to produce scholars and teachers who possess a simultaneously broad and deep knowledge of the African past. We train academic historians of Africa who are grounded in the historiographies, methodologies, and debates that animate the field, but who also recognize and account for Africa's connections to the rest of the world and to global events.
We welcome applications from prospective graduate students who desire rigorous training in the core historical methodologies as well as in ethnographic approaches to the African past. Graduate students will be trained to mine and make sense of archival, oral, ethnographic, linguistic, and other unconventional sources as well as to utilize clues offered by Africa's vast material culture to reconstruct and interrogate the past. The goal is to develop our students into producers of new knowledge about Africa and effective teachers of African history.
Students can expect to be trained in the social, economic, and political histories of the continent while exploring themes as diverse as gender, technology, trade, religion, colonialism, nationalism, healing practices, slavery, intellectual production, among others. Students will be trained to appreciate the dominant dynamics of Africa's precolonial, colonial, and postcolonial histories while recognizing the parallels and overlaps between these periods. Our courses explore trans-regional patterns but also cover the peculiar historical features of particular regions.
The small number of our Africanist faculty means that we are able to devote considerable time to independent studies, collaborative learning, and mentorship. We perform traditional mentoring tasks, but we are also able to provide consistent support as students identify research fields, apply for research grants, and apply for jobs during the dissertation phase of their training.
Vanderbilt hosts an accomplished faculty in Asian history and is particularly strong in the twentieth century, early modern, and medieval periods. We emphasize global interconnections and broad comparative approaches both within the department and in affiliated programs across campus.
With a small cohort admitted each year, students benefit from close mentorship with Asia faculty, including one-on-one independent study and directed research. Students will be expected to take history department courses in other regions (Europe, US, Latin America, Middle East, Africa) and methodologies (including Visual Culture, Spatial Histories, Empire, and History of Science). Students can also explore related topics with Asia faculty in History of Art, languages and literature (Asian Studies), Religious Studies, Sociology, English, and Political Science.
South Asia: Vanderbilt is emerging as an important location for the study of early modern and modern South Asia, especially in the fields of political history, religious history, and the history of western India ( Samira Sheikh ). Graduate students admitted to study South Asian history may be supported by faculty in related fields, such as Indian Ocean history ( Tasha Rijke-Epstein ), the history of the British empire ( Catherine Molineux ), and the Islamic world ( Leor Halevi , David Wasserstein ). Distinguished South Asia specialists elsewhere at Vanderbilt include Tony K. Stewart, Adeana McNicholl and Anand Vivek Taneja in Religious Studies, Tariq Thachil in Political Science, Akshya Saxena in English, and Heeryoon Shin in History of Art. Those interested in premodern links between India and east Asia may benefit from scholars of Buddhism and Chinese architecture (Robert Campany/Tracy Miller).
Nineteenth and Twentieth-Century Northeast Asia: With specialists in the cultural and intellectual history of modern/contemporary Japan ( Gerald Figal , Yoshikuni Igarashi ) and modern China/Northeast Asia ( Ruth Rogaski ), Vanderbilt is an excellent place to train in topics such as colonialism and empire, war, history and memory, contemporary culture, and history of the body and medicine. Faculty in U.S. History ( Tom Schwartz , Paul Kramer ) also maintain strong interests in Sino-U.S. relations. Associated faculty include Guojun Wang in Chinese literature, Lijun Song in Chinese medical sociology, and Brett Benson in contemporary Chinese politics.
Early and Middle-period Imperial China: Vanderbilt hosts a strong faculty in the political organization, military history, and material culture of the Song dynasty ( Peter Lorge ), with the capacity for comparative study in other medieval societies (Europe, Middle East, South Asia). Students can also explore topics as diverse as sacred landscapes, regional networks, and religious identities with affiliated faculty in History of Art (Tracy Miller) and Chinese religions (Rob Campany).
Atlantic World
Vanderbilt ranks among the nation's top twenty research universities and boasts a diverse and dynamic History Department. One of the newest and most exciting areas of faculty research and graduate training at Vanderbilt is Atlantic World History. Graduate students who choose to complete a major or minor field in Atlantic World history at Vanderbilt will be introduced to a wide range of literature addressing the interactions among European, Native American, and African peoples. Working closely with our Atlantic World historians, students develop a dissertation topic and prospectus during their fifth and sixth semesters.
From their first semester, we encourage doctoral students in our field to become actively engaged in the profession through field research, networking, collaborative projects, grant writing and publishing. We also encourage training in digital humanities and our students have worked on projects such as the Slave Societies Digital Archive , the Manuel Zapata Olivella Collection and Enslaved: Peoples of the Historic Slave Trade .
Our students have presented their research at numerous national and international conferences including the American Historical Association, the Conference on Latin American History, the Brazilian Studies Association, the Forum on European Expansion and Global Interaction, the Omohundro Institute of Early American History, the African History Association, and the Association of Caribbean History, among others. Over the last decade our students have won many prestigious research awards, including the Fulbright, Social Science Research Council, American Council for Learned Societies, and Rotary fellowships. Our students have conducted research in areas as diverse as Angola, Barbados, Brazil, Colombia, Cuba, Germany, Ghana, Jamaica, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and Sweden.
Graduates of our Atlantic World History program have earned tenure-track positions in history departments at the University of Wisconsin, the University of Florida, Michigan State University, the University of West Florida, the University of Birmingham, UK, the University of Arkansas, Queens College, Georgia Gwinnett College and the University of Texas-Arlington.
Early Modern
Vanderbilt has a vibrant group of scholars in Early Modern history. Faculty research and teaching interests include geographic specialists in England/Britain, France, Germany, Italy, eastern Europe, India, and China. Among the areas of inquiry are legal, religious, economic, cultural, and gender/sexuality history. The Early Modern faculty work closely with historians of antiquity and medieval history, and in collaboration with the programs in Classical and Mediterranean Studies, Jewish Studies, Women’s and Gender Studies, the departments of English, French and Italian, and German, Russian and East European Studies, History of Art, and the Pro-Modern Cultural Studies Seminar (Robert Penn Warren Center.)
We welcome applications from potential graduate students interested in particular subject areas as well as in the questions and methods shared by all historians of early modern societies, including how to work with incomplete, fragmentary, or (deliberately) misleading evidence, how to reconstruct the world of culture and symbols, how to push beyond the learned texts that predominate in the historical record, and how to ask meaningful questions about the past.
There is no prescribed graduate curriculum; students are invited to craft their own program within the framework of the History Department Ph.D. requirements during coursework, but an applicant’s prior preparation, including knowledge of languages necessary to undertake Ph.D. level research, and the writing sample, are particularly important factors. Applicants are encouraged to contact potential supervisors in advance.
Vanderbilt University trains graduate students in all periods of Islam's history, from its origins in late antiquity to modernity, and in various regional settings.
Our faculty works in multiple fields, including law, business, religion, imperialism, and nationalism. They have written on topics as diverse as early Islamic death rituals; politics and society in al-Andalus; Jewish-Muslim trade in the medieval Mediterranean; the political, religious and economic landscape of early modern Gujarat; Jewish identity in the Ottoman Empire; Islam in the modern Balkans; Nigerian responses to colonialism; and the rise of ISIS.
Latin America
Vanderbilt University has one of the oldest programs in Latin American studies in the United States. Our doctoral program focuses on developing scholars and teachers with both a broad knowledge of Latin American and Caribbean history and intensive training in research and writing in their specialty. Doctoral students normally do four semesters of classes, then take their qualifying exams at the end of their fourth semester or the beginning of their fifth semester. Working closely with our historians of Latin America and the Caribbean, students develop a dissertation topic and prospectus during their fifth semester. From their first semester, we encourage our doctoral students to become actively engaged in the profession through field research, networking, publishing, collaborative projects, and grant applications. Our students have presented their research at numerous national and international conferences including the American Historical Association, Conference on Latin American History, Latin American Studies Association, Brazilian Studies Association, Association of Caribbean Historians, and the Southern Historical Association. Over the last decade our students have won many prestigious internal and external research awards (ACLS, Mellon, Boren, SSRC, and Fulbright). Since 1989, 39 students have entered our doctoral program. Twenty-three have completed their dissertations, and ten students are currently in the program. The average time to completion of dissertation has been six years. Close individual supervision of our students has been key to the timely and successful progress of our students.
Vanderbilt University has a distinguished tradition in Latin American and Caribbean history beginning with the hiring of Alexander Marchant (and four other Brazil specialists) and the creation of an Institute of Brazilian Studies in 1947. Among other noted historians of Latin America who have taught at Vanderbilt are Simon Collier, Robert Gilmore, J. León Helguera, and Barbara Weinstein. Close individual supervision of our students has been key to the timely and successful progress of our students.
Vanderbilt is home to a thriving community of legal historians. Our faculty expertise ranges from ancient Rome to the contemporary United States, and we place a strong emphasis on comparative and thematic inquiry. Faculty have written on topics as diverse as ancient violence, the history of prostitution, racial passing, Islamic law, American slavery, and law in early modern empires.
Our community is centered on the Legal History Workshop, an invited speaker series that runs throughout the year. The workshop features some of the most exciting new perspectives on legal history and strives to be international and comparative in methods and scope.
In addition to coursework in their geographic and chronological areas of expertise, students are encouraged to take the Methods in Legal History seminar, which runs every other year. This team-taught seminar introduces students to the range of work done by legal historians and runs in conjunction with the workshop.
Modern Europe
Vanderbilt's doctoral program in Modern Europe focuses on developing scholars and teachers with a broad knowledge of European history and its relationship to the world. Graduate students are rigorously trained in both the national historiographies of their regional and linguistic specializations, as well as in related transnational and thematic fields, such as environmental history, nationalism and nation-building, law and empire, the history of music, minority politics, history of religion, mass violence, and the history of science and technology.
With a small, competitive cohort accepted each year, doctoral students in Modern Europe at Vanderbilt benefit from close mentor relationship with their advisors and other senior faculty, both through small seminar-style coursework and close individual supervision during the dissertation process. Mentorship extends beyond the classroom to include support in grant-writing, preparation for the job market, and opportunities for teaching assistantships in related fields. Collectively, the department's European faculty has supervised more than 40 theses in modern Europe and helped to place students in prestigious fellowships and tenure-track jobs in the United States and Europe.
Science, Technology, and Medicine
Vanderbilt is home to a robust and diverse community of historians engaged in the study of Science, Technology, and Medicine (STM). Students in STM are exposed to both the intensive historiographies of STM fields as well as a broad and deep training in the relevant historical locations and periods. Vanderbilt STM students are encouraged to imagine themselves as both scholars and as historians.
Our faculty expertise ranges across time, place, and topic; from material culture in Africa, to medicine in China, to intellectual and cultural history in the West. Faculty have written on topics as diverse as modern privacy, the young Darwin, Diabetes, Albert Einstein, Qi, clinical trials—even the future of technology.
Our community is centered on two workshops, one designed by graduate students for the STM scholars within the department, and the other designed to engage the broader Vanderbilt community, recognizing the inherently interdisciplinary nature of STM studies.
United States
Students in our doctoral program are trained broadly in the historiography of the United States in the nineteenth, twentieth, and now twenty-first centuries. They also have ample opportunities to work in transnational and thematic fields, including African American history, diplomatic history, environmental history, intellectual history, legal history, political history, and religious history as well as the history of capitalism, gender and sexuality, popular culture, race and racism, and science, medicine, and technology. The department has a strong profile in the field of U.S. and the world, and offers students training in transnational approaches. Graduate students and faculty meet regularly as a group to discuss research work in progress in the department's informal Americanist Seminar.
With a small, diverse cohort accepted each year, doctoral students in U.S. history at Vanderbilt benefit from expert supervision and guidance. Our faculty is committed to excellent mentoring in both research and teaching. Graduate students enjoy close working relationships with their advisors and other faculty inside and outside the department, whether in the Law School or Peabody College of Education or in the departments of medicine, health and society, sociology, philosophy, or religious studies. Faculty assist students as well with grant-writing, conference presentations, article drafting, and preparation for the job market. The department has helped to place students in prestigious fellowships and tenure-track jobs as well as significant research and policy positions outside the academy.
Return to top
The Geography of History PhDs
Dylan Ruediger | May 7, 2018
The AHA’s “ Where Historians Work ” is an ambitious research project designed to track the career outcomes of everyone who earned a PhD in history from 2004–13 in the United States. Last year, we launched a beta version of “Where Historians Work” showing initial results from 34 PhD programs. Since then, we have gathered information on the remaining 127 PhD programs, locating some 8,000 individuals using publicly available information. We are now in a position to truly understand the national landscape of employment for history PhDs.
Later this spring we’ll publish a series of interactive visualizations that highlight what we have learned about historians and their careers, while allowing users to ask research questions about the data. As we’ve gathered data, we’ve published several blog posts on our findings, focused on describing the incredible range of careers we have discovered in the data. This post focuses on the geography of historians with a PhD, bringing a new and more literal sense of where historians work into the mix.
Fig. 1. Geographical dispersal of history PhDs, 2004–13
Unsurprisingly, perhaps, the geography of history PhDs closely replicates population patterns in the United States, making “the same places everyone else does” the most straightforward answer to the question of where historians work. History PhDs congregate in high population states: of the 15 most populous states, only Washington and Arizona are not also among the top 15 for employing PhDs from our cohort. (For state population, visit census.gov .)
Another clear pattern is that states that award the largest numbers of history PhDs, many of which have high populations overall, tend to also employ them in the largest numbers. Fifteen states and 98 PhD programs account for 72 percent of all history PhDs earned from 2004–13. These 15 states also employed 50 percent of those historians, a big number to be sure, but one that left room for them to “export” large numbers of PhDs to other states. California, for example, is home to over 600 historians, but awarded over 1,100 PhDs in the discipline. The states that “export” PhDs appear to send them to the Southeast and West, both regions that are home to more PhDs than were trained within their borders.
Fig. 2. States home to the largest number of history PhDs
As you might expect, the careers historians build differ depending on where they live. Sometimes, it seems possible to speculate about why this might be. In California, for instance, only 38 percent of historians work in four-year tenure-track positions, while in South Dakota, over 80 percent do. South Dakota is one of the few states that does not host a PhD program, and it seems that few historians move there except for those who land tenure-track positions. In contrast, California’s high quality of life and diversified economy seem to attract them in large numbers. However, numbers at the state level vary significantly and often are complicated by small samples (as in the case of South Dakota, home to only 12 history PhDs in our cohort), making it difficult to draw firm conclusions.
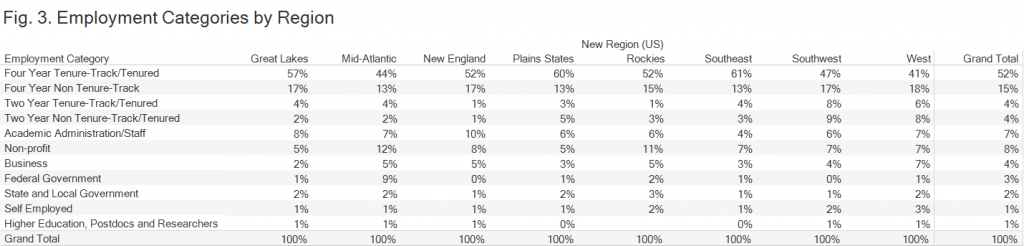
Fig. 3. Employment categories by region
Seen regionally, PhD employment patterns begin to even out, though not without suggesting subtle variations in the regional economies. Tenure-track employment is most common in the Southeast, Great Plains, and Great Lakes, and least common in the far West. In contrast, non-tenure-track rates are relatively stable across regions, except in the West and Southwest, where over a quarter of history PhDs are employed in contingent positions. Outside the professoriate, historians disperse in slightly different directions as they take advantage of regional economic opportunities. In New England, PhDs find more opportunities in academic administration, while those out West are most likely to be employed in the private sector.
In general, PhDs working in large urban areas seem to be employed in more diverse jobs than those living in rural areas and college towns. Large cities tend to have lower rates of employment on the tenure track and are hubs for those working in the nonprofit and business sector. Cities also tend to have high rates of historians teaching off the tenure track.
No major city is more distinctive, though, than the District of Columbia. DC is home to only 700,000 residents and is a mere 68 square miles, but only five states employ more historians than the city. The 295 history PhDs we have located working here are remarkable not only for their density, but for their employment patterns, which look like nowhere else in the country. Over 75 percent of all historians employed by the federal government work in the District. Even so, fewer than half of DC’s history PhDs work for the federal government because the District is also a national hub for historians in the nonprofit and business sectors. Nine percent of all history PhDs employed by nonprofits work in in DC; only the State of New York employs more. Likewise, only California and New York employ more historians in the private sector than DC. In another dramatic departure from national averages, only 18 percent of DC historians work as postsecondary teachers compared to 75 percent who do so nationally.
Knowing where historians live raises important questions about the relationship between mobility and careers, a perennial, controversial, and poorly understood aspect of PhD culture. PhD candidates have long been told that their ability to find employment rests on their willingness to move anywhere in pursuit of a tenure-track job. Without question, many history PhDs appear to follow this path. However, department-level data (available in the forthcoming version of Where Historians Work) shows that in many departments, graduates cluster in the cities and regions where they receive their degrees. These geographies no doubt reflect hierarchies of prestige within the discipline: earlier studies of historical careers done by the AHA have found that graduates from high-prestige programs scatter more widely than those from ones with regional reputations, a pattern that seems to still hold true. The geographical data also highlights the existence of regional employment patterns that complicate our sense of a single national academic job market. More importantly, they suggest that many PhDs have ties of family, friendship, and circumstance in the regions where they earn their degrees, and build careers that reflect those roots. Our data speak to outcomes rather than motivations, but knowing more about where historians live is a crucial step towards untangling the question of why.
This post first appeared on AHA Today .
Tags: AHA Today Career Diversity for Historians Graduate Education
The American Historical Association welcomes comments in the discussion area below, at AHA Communities , and in letters to the editor . Please read our commenting and letters policy before submitting.
Please read our commenting and letters policy before submitting.

In This Section
History of Medicine, PhD
School of medicine.
The PhD program in the History of Medicine is part of the broader Program on the History of Science, Medicine, and Technology jointly run by the Department of the History of Medicine (SOM) and the Department of the History of Science and Technology (KSAS).
The work of the PhD program extends over all phases and dimensions of the development of medicine and related sciences, the history of disease, and the historical analysis of related conceptual, cultural, and social problems. Students acquire facility in the methods of historical research and gain a wide acquaintance with the available literature in the history of medicine, science, and related fields of history. Departmental offerings are particularly strong in the history of medicine and science in early modern Europe and the Islamic world; medicine, science, and technology in the United States in the 19th and 20th centuries, including genetics; history of disease and public health; and studies of health and society in Latin America and Africa. The program offers coverage of racism and gender in the history of medicine, how medical and scientific knowledge is created, and medical practices of the body.
Students enter the PhD program with diverse backgrounds including medicine, science, and history. The PhD program prepares students for scholarly careers in teaching, research, and in non-academic fields. For further information, see our website . Students interested in the history of medicine should apply to the Program through the School of Medicine. Those interested in the history of science and technology should apply through the History of Science and Technology Department of the Krieger School of Arts and Sciences.
Students who wish to combine medical training with academic training in the history of medicine may also inquire about the M.D.-PhD program by visiting the MD/PhD admissions website: https://mdphd.johnshopkins.edu/admissions/
Financial Aid
The regular department fellowships include tuition, stipend, research allowance and medical insurance.
Admission Requirements
Candidates must be at the post-baccalaureate level. Preference will be given to applicants with training in some aspect of the health sciences or history. For further information applicants should access the following website for contact information: Contact – Department of the History of Medicine (hopkinshistoryofmedicine.org) .
Program Requirements
The student must satisfy the requirements of the University, the School of Medicine, and the Program.
The principal requirement for the PhD degree in the history of medicine is the writing of a dissertation based upon original research and of publishable quality. Prior to embarking on full-time dissertation research, candidates will prepare themselves by a variety of courses, seminars, and guided reading. During the first year of study, students receive a general introduction to historical research and complete a year-long survey in the history of medicine. In their second and third years, candidates prepare three fields of study: one in the Department of the History of Medicine; one in the History Department; and a third field to be determined by the student and the advisor. The specific requirements for such fields are set by the faculty member directing the field, in consultation with the student. These fields entail both broad and intensive reading, and the passing of a comprehensive examination and/or preparation of several historiographic essays. Towards the end of the third year, students must prepare and defend a dissertation prospectus. Candidates must also demonstrate a reading knowledge of two foreign languages before being admitted to formal candidacy for the degree. The final requirement for the PhD degree is completion of a dissertation that is an original contribution to historical knowledge and of a standard suitable for publication. More detailed information can be found on the department website .

Spring 2024 PhD Student Spotlight, Juan Ignacio Wilson

Thank you so much for taking the time for this interview. To begin, how does your dissertation, “The Many Foundations: Reform, Revolution, and the Transformation of Law and Politics in Mexico, 1867-1940,” help us better understand Mexico's legal and political structures?
I think it helps us understand what a revolution, which ended with a new constitution, can and cannot do in terms of transforming ingrained structures of power. I am looking at very local institutions and trying to understand how those local structures shape more general forms of rule. They are the essential building blocks of the state order but act with relative independence of the central state. The revolution and the constitution changed many aspects of the Mexican state on paper, but as long as the founding blocks at the local level remained untouched, the continuities were much stronger than the ruptures. There was people who saw this at the moment and who tried to make the revolution’s legacy all about the transformation of local forms of government, conflict solving, resource administration, etc., but those attempts were ultimately not successful.
In terms of Mexico, I believe studying the continuity in local forms of governance before and after the revolution goes a long way in explaining the stability of the PRI (The Party of the Institutionalized Revolution, which governed Mexico until the year 2000) and some authoritarian aspects of the country’s politics even today. In addition, I think the dissertation is also useful for understanding the concept of revolution and what revolutionary action—of which there was a lot in Latin America during the 20th century—can achieve, especially when it needs to deal with the creation of new legal institutions in order to stay in power and produce the promised changes. No revolutionary movement can escape that uncomfortable moment of legalization and institutionalization. Yet in Latin America, those moments have been less theorized and studied than the romantic moments of violent government overthrow, maybe because those moments of everyday politics and rule are much more boring than the “event” of a revolution yet they are inextricably tied together.
Where have you traveled to conduct your research? Have you found anything particularly surprising or compelling?
I have traveled through Mexico, moving from Mexico City to Guanajuato, Oaxaca, and especially Veracruz, which I adopted as my main research site. In the case of Veracruz, one of the things that strikes me is how one of the richest states within Mexico, the seat of the country’s main Atlantic port, the cradle of the Mexican oil industry in the early 20th century, the most populated state at that time, an area of large sugar and coffee plantations and the largest textile factories, the birthplace of very radical agrarian and labor movements in Mexico, etc., transformed from the richest to one of the poorest areas of the country. That in itself requires an explanation.
What drew your interest to Latin American legal and social history? The simple answer to that question is biographical. I was born in Chile and trained as a lawyer, so the question of the interaction between law and social change in the region in which I grew up seemed like the natural outcome of my studies. In a much deeper sense, however, I have always been curious, not only about the extent to which law can actually produce social change—a fact that policymakers and bureaucrats tend to take for granted—but more importantly, how that change is produced. What are the mechanisms through which law intervenes in social practices, how does it interact with established customs, how does it transform the language through which we describe our political conflicts, etc.? Laws—legal institutions generally—are very complex mediators between political aspirations and social conduct. The question of how change is produced is the point where history comes in, when you ask not just what happened, but how it happened.
Are there differences in the way legal history in Latin America and legal history in the US are practiced? How and why?
Several, some of which make writing legal history in a Latin American context particularly challenging. First, there is an atavistic and deep-seated skepticism about the law’s effectiveness in Latin America. Many social scientists—historians, sociologists, anthropologists—have put more effort into studying economic inequality, religion, family structure, etc., than trying to understand the law, partly because they don’t see it as having any explanatory power. The field of legal history has then been taken by lawyers with little concern for social dynamics, who have developed the field as a form of antiquarianism. Within Latin America's historical profession, legal history is, with few honorable exceptions, one of the most conservative fields of study, practiced mainly by lawyers within law schools, and completely uninterested in questions of social conflict and social change.
This is not the case in the US. At least since the advent of critical legal studies, if not before, legal history has sometimes been able to adopt a subversive role. It has been used to question accepted historical narratives and simple explanations for social change. The basis for that kind of history is an understanding that law is a partially autonomous system. While it is influenced by economics, politics, religion, etc., it also influences those systems in turn and, therefore, has an independent explanatory power when trying to understand social change. That influence is not easily described though it has to do with changes in political narratives, the quotidian use of judicial institutions by people previously excluded from the systems of power, and forms of empowerment or cooptation of social movements. Law’s impact is not a simple mechanic of passion of the law + punishment = change in behavior, the sort of “felicific calculus” that Jeremy Bentham wanted. Historians, however, have found and keep finding sophisticated ways to explain laws impact on social practice.
Aside from your research, I believe you are quite involved with the Forum on Law and Legalities, housed in the Law, Letters, and Society program at UChicago. What is your role and can you tell me a little about it?
Together with a colleague in the history department, Benjamín Montaño, also a Latin Americanist, also working on legal history, we both had a role in its foundation, and as coordinators during the Forum’s first four quarters of existence. We saw that stemming from different geographical contexts and working with various methodologies, many faculty and graduate students were interested in questions about law and its role in social change. We thought that we could all benefit from more interdisciplinary discussion, seeing how our projects are read by people outside our own field. Moreover, this is a topic that has gained a lot of traction in other universities, under the umbrella of the Law and Political Economy project, born and housed at Yale Law School. Having a space like a Forum on Law and Legalities will help us connect with that project and invite scholars from other universities working on similar issues.
At first we thought structuring this as a workshop under the Council for Advanced Studies, but sadly there were very little resources for such an initiative. So, we talked to Jon Levy and he came up with the idea of housing the project under the Law, Letters, and Society program, which has been great for flexibility and to attract faculty to it. I believe the Forum is operating successfully. The current coordinators, Natalia Niedmann and Nahomi Esquivel, have been doing a fantastic job of putting together a roster of great presentations. Attendance has been good and the discussions have been really stimulating, precisely the type of debate we envisioned when the project started.
What other organizations or projects are you involved in at UChicago?
I am in my final years of the program, so I have been cutting back on some of my obligations. However, I have been constantly affiliated with the Center for Latin American Studies and the Center for International Social Science Research. I was also a fellow at the Pozen Family Center for Human Rights, which was another great experience of interdisciplinary discussion about legal topics. In a more casual vein, I have been participating in a Gramsci reading group that meets regularly to discuss the Prison Notebooks. It is mostly people from history, but some people from political science have joined us. We also have the good luck of having people who read Italian in the group, so we don’t get lost on translation issues. I would say, jokingly, that it’s like reading with an arbiter.
This Website Uses Cookies.
This website uses cookies to improve user experience. By using our website you consent to all cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
The Department of History offers a full range of courses and programs in the fields of American, British and European, East Asian, Latin American, and Ottoman and Middle Eastern history. It offers exceptionally strong training in the fields of environmental history, science, technology and medicine, as well as women’s and gender history. While concentrating on the history of one nation or geographic area, students are encouraged to develop a comparative or global perspective in their work. To facilitate this, the department cooperates closely with a wide variety of interdisciplinary programs and departments to offer students additional instruction in comparative and world history perspectives.
Admission Requirements
Applicants for admission to graduate work in history are required to submit their college transcripts, scores on the Graduate Record Examination, an example of their written work (e.g., a paper submitted in an advanced undergraduate or graduate course), two letters of reference (preferably from professors), and a statement of their research interests and career goals.
Students who are not citizens or permanent residents of the United States must also submit proof of English proficiency (such as TOEFL, IELTS or PTE Academic scores). International students who have received a college or university degree from an institution in the United States, United Kingdom (England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales), Ireland, Australia, New Zealand or some Canadian provinces are not required to submit TOEFL, IELTS or PTE Academic scores. Additionally, all international students must provide immigration forms guaranteeing financial support.
Admission to the PhD program is determined by the department when the student has completed work for the MA degree or its equivalent. All students who enter the program with an MA degree in history from another institution have their work reviewed by the department at the end of their first semester to confirm their admission to the doctoral program. Students entering with MA degrees in history from outside institutions are required to take an additional eight credits beyond the additional 24 credits needed for the PhD degree.
Program Requirements
Course requirements.
Students pursuing the PhD in History must complete a minimum of 56 graduate credits (excluding credit for the dissertation but including credits earned toward the MA) with an average of B+, which includes:
- HIST 592 Historiography*
- HIST 591 Teaching of College History (mandatory only for funded students)
- Two 600-level research seminars (one of which must have been taken at the master’s level)
- Elective courses in the major field (X credits)
- Elective courses in the minor field (X credits)
*Students are encouraged to fulfill this requirement in their first year.
A student’s coursework should be closely correlated with the proposed major and minor fields, and should include a balance between general colloquia and specialized research seminars. Students are encouraged to work with a number of different professors to broaden their exposure to different historical styles, methods and theories. In addition to the work completed for their courses, students are expected to pursue a coherent program of readings in preparation for their comprehensive examinations. Independent reading courses may be arranged with individual instructors to cover special topics, but must not be used to satisfy more than one-third of a student’s degree requirements. At the doctoral level, only four (additional) credits of independent study taken under the S/U grading option will count toward the minimum number of course credits required for the degree. All graduate seminars counted toward the history degree must be taken for a letter grade.
Choosing Advisors
Students are advised by a faculty member in their fields of concentration during their first semester in the graduate program. Before the beginning of the second semester, the student selects an appropriate member of the faculty as principal advisor (sponsor) and chair of a guidance committee. The student, in consultation with the principal advisor, solicits two additional faculty members to serve on the guidance committee. The chairperson of the guidance committee, with the assistance of colleagues and the director of graduate studies, aids students in their choices of courses, advises them on the fulfillment of other academic requirements and, in general, guides them through the graduate program. Normally, the guidance committee forms the core of the student’s comprehensive examination committee. In most cases, too, a student’s guidance committee serves as a three-person dissertation committee.
No faculty member is required to accept a particular student as an advisee. A student may, for reasonable cause, petition the director of graduate studies for a change of principal advisor or guidance committee.
Foreign Language Requirements
All PhD students must demonstrate proficiency in a foreign language chosen by the student in consultation with his or her guidance committee. Students for whom English is not their native language must demonstrate proficiency in English. The guidance committee may also require additional languages necessary for scholarship in the student’s field.
Exam Requirements
The comprehensive examination consists of two examinations, one written and one oral, in the major and minor fields and a dissertation prospectus. Doctoral candidates must take a comprehensive examination in either a) one major and two minor fields; OR b) in two major and one minor fields. Every major field has a written component, either a one-day exam of six to eight hours or a take-home exam completed over a period of two weeks. The student will be examined on the written answers in the subsequent oral portion of the examination, which also tests the student’s knowledge in the minor field(s), includes a defense of the prospectus, and lasts three hours. Detailed lists of both major and minor fields are available from the department and in the departmental Graduate Student Handbook.
Students are officially admitted to candidacy for the PhD degree upon satisfactory completion of the comprehensive examination. Candidates for the PhD degree must maintain registration (dissertation or continuous registration credits) until all the degree requirements are completed. (See also the Graduate School policy statement.)
Dissertation Prospectus Requirement
Presentation of an acceptable prospectus is assumed to be part of the PhD comprehensive examination. Students may, in consultation with their guidance committees, separate their prospectus presentation from the comprehensive examination; in such cases, they must have a colloquium on the prospectus within three months of the PhD oral comprehensive examination. If necessary, revisions to the prospectus may be made following the comprehensive examination or prospectus colloquium. The final prospectus must, in any case, be on file in the department within six months of passing the comprehensive examination.
Dissertation Requirement
At least two semesters must elapse between admission to candidacy and the granting of the degree. The PhD in history is granted, after admission to candidacy, on successful completion of the following requirements:
- Submission of a dissertation approved by the candidate’s dissertation committee. The dissertation must present a new interpretation of a familiar subject, or an investigation of a subject hitherto neglected and must be written under the supervision of a member of the graduate faculty.
- Successful defense of the dissertation in an oral examination.
Additional Information About the Program
The department reserves the right to alter these regulations and requirements without notice, pending the publication of the next scheduled issue of this publication.
For more information on the History PhD program, please refer to the History Department website . To apply to the History PhD program, please visit the University Admissions website .
History PhD Alum, John Eicher releases 10-part Lecture Series
John P. R. Eicher, Associate Professor of European History at Penn State University and a 2023-24 National Endowment for the Humanities Fellow, has released a ten-part YouTube lecture series titled, "Western Civilization (1500-Present): From Dawn, to Decadence, to Disillusionment."
The series argues that the growth of bureaucratic thinking in "the West '' created a world where [a]bstractions eclipse reality, which grants [b]ureaucracies [c]ontrol of the modern world. Along the way, the series examines the fate of nineteenth-century Western "Progress" and its implications for our postmodern, twenty-first-century world. The series follows a 500-year narrative "arc," but each 40-50 minute lecture may be viewed as a "stand alone" presentation, complete with its own set of arguments. Delivered in a warm but lively style, the lectures are interactive, engaging, and media-rich. They are aimed at a general audience but they may also be useful in the classroom as a video "textbook" of modern Western civilization or modern European history.
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCXIDNsry_OMooCULA1rakCA
Promotional Music Video (500 images of 500 years in under 5 minutes!):
" (Music: Handsome Furs, "Repatriated." Video: John Eicher.)
1) " The ABCs of Modern Western Civilization: Abstraction, Bureaucracy, Control "
2) " What Physics Do You Believe In? Renaissance, Reformation, and the Rise of the Scientific Worldview "
3) " What Goes Up Must Come Down: From the Rise of the Enlightenment to the Fall of Napoleon "
4) " Nationalism: An "Invented Tradition" of "Imagined Communities "
5) " The 19th Century Industrial Revolutions: A Vast, Uncontrolled and Unscientific Experiment or The Reason Why you Brush Your Teeth, Know the Time, and Don't Know Who Made Everything You Own "
6) " Nineteenth-Century Imperialism: The Sun Never Sets on the British Empire Because the Lights Are Always on at the Foreign Office "
6.5) " Interlude: Modernism: The Greater the Circle of Understanding, the Greater the Circumference of Ignorance "
7) " The First World War (1914-18) & The Interwar Period (1918-39): The Beginning. Of the End. Of History. "
8) " WWII, the Holocaust, and the A-Bomb: Everything not Forbidden is Compulsory... and Postwar 'Progress' "
9) " C:\Postmodernism (A History of Now): A Unified World, Divided. A Divided World, Managed. A Managed World, Unified. C:\Continue. "
Asian American & Pacific Islander Heritage Month
Rice university phd graduate defies the odds after being diagnosed with muscular dystrophy.

HOUSTON, Texas (KTRK) -- Doctors predicted he wouldn't make it past his 20s after being diagnosed with muscular dystrophy. Not only has Dr. Felix Wu defied the odds, but he's also been thriving after graduating from Rice University . Now, he's working towards making the world a better place for people with disabilities.
It was a day Lisa Hu and Gang Wu will never forget. Felix Wu was only about 3 years old when his family visited different doctors to find out what was impacting his mobility and causing him to fall frequently.
Finally, they got an answer from one of their physicians. It was Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). They grappled in shock when they were given a grim prognosis that their son would likely only live to be between 18 and 25 years old.
"Our world turned upside down. The landscape suddenly became something we didn't know. At the time, treatment was very limited, and there's no cure. So it was very tough for us. Our focus became to slow the progression of the disease," Hu said.
According to the Muscular Dystrophy Association , muscle weakness is the primary symptom of DMD.
It can begin as early as 2 years old, first affecting the muscles close to the core of the body and then later impacting the limbs. Children with the condition may have difficulty jumping, running, and walking.
READ MORE: Teacher refuses to let muscular dystrophy slow him down
Felix Wu shared that it was tough as a child when he couldn't participate in the same physical activities as his classmates or when he had to navigate in and out of buildings that weren't very accessible for people with disabilities. However, he said what affected him the most was how others perceived him.
"I've been questioned about what I'm able to achieve, and it's taken opportunities away from me. There's been assumptions that I'm not intelligent or mature enough to handle certain things. When I did succeed, sometimes people would assume I took some type of shortcut, and that's how I got here," Felix Wu said.
Felix Wu's condition was something his parents couldn't control. So they started focusing on what they could control, taking their son to see the world and supporting him in whatever he wanted to do.
"All we can do is give him our love and educate him as much as we can about DMD. We let him make his own decisions about his health and tell us what he wants or doesn't want to do," Hu said.
One of their favorite activities to do together as a family is visit national parks around the country, and they have been to more than 70 so far.
Felix Wu also loves playing video and board games in his spare time, such as Pokemon and Magic: The Gathering.
But Felix Wu has also always been extremely studious. To Hu and Gang Wu's surprise, he committed to doing well academically and ranking at the top of his class, pointing out that his parents never pressured him to get good grades.
"He's very self-driving, and on top of that, he's very smart. He learns things very fast. We're happy that he has been doing so good. But sometimes, we have to remind him to slow down and take care of his health," Gang Wu said.
SEE ALSO: A unique concert for boy battling muscular dystrophy
As Felix Wu reflected during Asian American Pacific Islander (AAPI) Heritage Month, he said his parents, who are originally from China and came to the U.S. in the 1980s for college, are the inspiration behind his success.
"I think about how lucky I am for the resources I have to this day that they didn't have. That's definitely motivated me to keep moving forward," Felix Wu said.
For the last nine years, Gang Wu has made the hour-long drive between Katy and Rice University to get Felix to class.
But this month, they took their last ride to campus. Felix Wu graduated with a PhD in psychological sciences focusing on industrial-organizational and quantitative psychology, making him a "triple owl" for earning his bachelor's and master's degrees at the prestigious institution.
"No matter what the stakes are for his future, we know Felix is going to fight. It doesn't matter if he's going to win or not, he's going to fight," Gang Wu said.
Felix Wu, who is now 26, is taking a short break before starting his new job at a consulting firm.
He told ABC13 he plans to continue using his research and data to help improve workplace conditions for people with disabilities.
"People with disabilities are employed at a far lower rate than everybody else. That's important because, economically, you need a job to actually be able to survive and thrive. This is an important area where I can bring my own experience and show that there are still a lot of things that people with disabilities can do," Felix Wu said.
For stories on Houston's diverse communities, follow Rosie Nguyen on Facebook , X and Instagram .
SEE ALSO: AAPI domestic violence survivor recalls her abusive relationship: 'I was living in survival mode'
Related Topics
- ASIAN AMERICAN & PACIFIC ISLANDER HERITAGE MONTH
- RICE UNIVERSITY
- RACE & CULTURE

AAPI domestic violence survivor shares story to empower others

Best AANHPI businesses 2024

Learn more about Houston's diverse community with We Belong

Speaking her truth
Top stories.

Majority of I-45 N. Freeway SB main lanes open after truck fire: TxDOT

Congresswoman Sheila Jackson Lee announces she has pancreatic cancer

Fewer storms and hotter temps starting Monday

Woman found dead in East Harris County apartment after welfare check
- 36 minutes ago

2 men found dead in trailer with high level of carbon monoxide: HCSO
Woman points gun at family, deputies, causing Tomball standoff: HCSO
Man hit, killed by driver after exiting car in Atascocita: sheriff
18 cars burglarized at upscale apartment has residents concerned
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Renowned historian of modern social science Dorothy Ross dies at 87
The first woman to be named chair of the history department, ross's research focused on historical writing in the social sciences, revealing insights that transformed scholars' understanding of the past.
By Rachel Wallach
Dorothy Ross, pioneering historian of the origins of modern social science and a professor emerita in the Johns Hopkins University Department of History , died last week. She was 87.
Ross's research focused on historical writing in the social sciences, revealing insights from the history of fields including psychology, economics, political science, and sociology that transformed scholars' understanding of the past. The depth of her dedication to graduate education was illustrated by her 2023 establishment of the New Directions Fund in the History Department to support graduate student research and conference travel.
Image caption: Dorothy Ross
"Dorothy was an exemplary scholar, a generous mentor, and a kind colleague," said Tobie Meyer-Fong , professor and chair of the Department of History. "She was incredibly supportive of me when I first joined the department and continued to offer wise counsel as recently as this past semester. She was a role model both professionally and personally: She was an ambitious and brilliant historian, an outstanding teacher of graduate students, a loving wife, a devoted mother and grandmother, and a kind and caring friend. She made it seem possible and desirable to have both professional and family commitments."
In her 1991 book, The Origins of American Social Science , Ross examined how American social science modeled itself on natural science and liberal politics, arguing that the field was informed by the ideology of American exceptionalism, and tracing how each discipline responded to change in historical consciousness, political needs, professional structures, and available conceptions of science. As editor of Modernist Impulses in the Human Sciences, 1870-1930 (1994), she explored modernism in the human sciences, philosophy, and natural sciences in the context of the debate at that time—generated by the advent of postmodernism—about modernism in intellectual history and throughout the humanities.
"Dorothy's work was authoritative, wide-ranging, and scrupulously fair, even as she revealed all the problems that emerged as the social sciences became increasingly ahistorical and individualistic," said Angus Burgin , associate professor in the Department of History. "As a teacher and colleague she wore her extraordinary depth of learning lightly, approaching everyone she encountered with respect, honesty, and a seriousness of purpose. Spending time with her was always a reminder of why we chose to become historians." In his role at the SNF Agora's Center for Economy and Society, Burgin recently had the opportunity to name a foundation-funded endowed chair, which he named in Ross's honor.
"Her scholarship was formidable. The sheer erudition in her work is breathtaking," said François Furstenberg , A&S '03 (PhD), professor in the Department of History, who earned his doctorate under Ross's guidance. "Her scholarship was theoretically and indeed philosophically informed and empirically rich. I have read and re-read her work and now, nearly 30 years after first reading it, I still find more to learn and admire."
Deeply committed to outstanding graduate education, Ross was known for intensely engaging with her students' research and for the example of her powerful and questioning intellect. Her ferocious intellect and exacting questions were balanced by her intellectual and personal generosity and wry sense of humor.
"Dorothy was a smart, generous, and very patient person," said Motoe Sasaki, A&S '01 (MA), '09 (PhD), who is now associate professor on the Faculty of Intercultural Communication at Hosei University in Tokyo. "She was not the type of professor who just explained things to students. I recall many times she let students find their own way to make sense of specific academic issues or problems. When I was unsure of things, Dorothy would bombard me with questions from a number of perspectives so that I could realize the direction in which to proceed. This always brought me to a new place."
In 2002, Kenneth Moss met Ross when he presented a paper to the history department as a candidate for a faculty position, quickly learning the level of precise thinking she demanded. "She pointed to a single word in the paper and demanded (in a friendly tone but one that brooked no evasion) that I unpack exactly what I meant to say with it," he said. "The word was 'visceral.' This was in no way a picayune or trivial question, nor an unfair one; in fact, she had zeroed in on the pivotal moment in the paper's argument, and indeed a central moment in the argument of what became my first book."
Moss got the job, serving as a professor of modern Jewish history from 2003 to 2021 and becoming Ross's friend as well as colleague. He is now a professor of Jewish history in the Department of History at the University of Chicago.
"Dorothy had an unfailingly friendly and gracious manner with people," Moss said, "but I think that everyone who met her saw from the very first that she had a razor-sharp mind, demanded intellectual precision—and had a finely tuned bull**** detector. Her acuity, precision, and love of careful thinking will be missed."
Earlier this year, Louis Hyman was named the history department's inaugural Dorothy Ross Professor of Political Economy and Professor at the Agora Institute. In his remarks, he highlighted how Ross's research—especially in The Origins of American Social Science —showed that separating history from social science drastically inhibits what policy is able to accomplish.
Image caption: From left, Louis Hyman, Dorothy Ross, and Angus Burgin on Feb. 22 at Hyman's installation as the inaugural Dorothy Ross Professor of Political Economy in History and Professor at the SNF Agora Institute
"Her work remains as a touchstone because it centered the texts (so many texts!) in her analysis. She didn't celebrate or denounce, for instance, the rise of marginalism in economic thought, but explained it in ways that restored happenstance and social structure to a narrative that had, to that point, just treated its rise as a scientific inevitability," Hyman said. "She historicized. In a time when it was easy to slip into fashionable theories, her combination of close and wide reading created in Origins an enduring classic of American intellectual history, that showed just how American our intellectual history was."
At the same time that she was knocking down barriers in social thinking and blazing historiographic trails, Ross was also doing those things within academia. Having joined the history department in 1990, she was the first woman, in 1993, to be named its chair, serving in that position until 1996. She and several other women hired as full professors at that time had a profound effect on the department, Meyer-Fong said.
A native of Milwaukee, Wisconsin, Ross earned a bachelor's degree at Smith College in 1958, and master's and doctoral degrees at Columbia University in 1959 and 1965, respectively. Before coming to Hopkins, she served as assistant professor of history at Princeton from 1972 to 1978, including a stint as Philip and Beulah Rollins Bicentennial Preceptor from 1973 to 1976; and as associate professor and then professor at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, from 1978 to 1990.
She previously served as a fellow in history and psychiatry at Cornell University Medical College-Payne Whitney Clinic from 1965 to 1967, and as special assistant to the Committee on Women Historians at the American Historical Association from 1971 to 1972.
Ross was a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in Behavioral Sciences, the Society of American Historians, and the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars; and a member of the American Studies Association, History of Science Society, American History Association, and Organization of American Historians, where she also served on the executive board. She edited the Johns Hopkins University Press series called New Studies in American Intellectual and Cultural History. She served on the editorial boards of the Journal of the History of Ideas , Rethinking History , Modern Intellectual History , and Cambridge University Press's Ideas in Context series. She was a delegate to the American Historical Association to the Consortium of Social Science Associations, and chaired the Organization of American Historians' Ellis Hawley Prize Committee.
Posted in Arts+Culture , Politics+Society
Tagged history , krieger school , obituary
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
🎨 Art History Dissertation Topics. Art comes in all shapes and forms. To grasp it better, we can explore each kind separately. Here's a list of art history dissertation ideas: 🎶 Topics on Performing Arts. History and Development of Ballet. Ballet is an art form with a long history. Initially, a specific dance originated in Medieval Italy.
History Thesis Topics: List of 69 Outstanding Ideas. by IvyPanda®. 11 min. 21,459. Unless you plan to go for a Ph.D. in history, a thesis will be the most significant academic writing of your life. It shows your in-depth knowledge of a subject, your ability to think logically, creatively, and originally.
The dissertation represents the culmination of years of graduate training. For many, the pages of the dissertation are stained with blood, sweat and tears. And coffee. And more tears. Since 1882, when the first dissertation was presented to the history department for doctoral qualification at Yale, hundreds of scholars have since followed that same path, dedicating themselves
The Doctorate in History (PhD) is an essential component in the training of professional historians. The most significant requirement of the PhD degree program is the dissertation, an original and noteworthy contribution to historical knowledge. ... works and topics most relevant to the intended dissertation topic. All students register for ...
The Ph.D. program in History is designed to train students in the skills of conducting original historical research and crafting unique historical arguments. In the course of their work as historians, Brown scholars draw on a wide range of methods and engage with a variety of audiences. Thus although we begin with the core skills of academic ...
In recent years, the Department of History has been able to provide funding to Ph.D. students for five years. The GRE will not be required as part of graduate admissions to any certificate, master's, or doctoral program in CSSH or across the university for matriculation in 2022-2023. Applicants and admitted students are invited and encouraged ...
1 / 2. ︎. The Program in History of Science at Princeton University trains students to analyze science, medicine, and technology in historical and cultural context. We are a community of scholars including roughly a dozen core and affiliated faculty members and about twenty graduate students, in addition to undergraduate concentrators and ...
AU's PhD in History will prepare you for a career as an educator, ... Recent and Current PhD Dissertation topics. The Department will supervise PhD dissertations in the history of Modern Europe (normally for the period 1789 to the present), United States history (including the colonial period), US foreign relations, and modern Jewish history. ...
History 798 PhD Major Specialization; Summer 2022 (May - August 2022) History 797 MA Research Paper . 2020-2021 Graduate Courses. Term 1 Seminars (September - December 2020) (Virtual) History 717 Topics in Early Modern European History | Megan Armstrong | Friday 9:00 - 12:00; History 741 Historiography | Michael Gauvreau | Thursday 9:00 ...
HIST6390 - Topics in History. HIST 6390 Topics in History (3 semester credit hours) The study of specific themes and/or periods in history. May be repeated for credit as topics vary (9 semester credit hours maximum). (3-0) R. UT Dallas 2024 Graduate Catalog.
10 Good History Research Topics that are Easy to Adapt. Conditions for Slaves During the Building of the Great Pyramid. Three Events from the First Greek Olympiad. How, Where, and When Rome was Founded. The Battle of Marathon: How the Greeks Defeated Persia.
Students entering the PhD stage deficient in Art History 200 (Art Historical Theories and Methodologies) or its equivalent must add this to the total requirements. In some cases, Art History 201 (Topics in Historiography of Art History) may be required by faculty/advisor recommendation.
The Department of History offers doctoral degrees in African, American, Asian, and European history. The PhD program is distinguished by the strength of its faculty and by its commitment to training students broadly and as a community. Through guided steps of coursework, preparation for the comprehensive oral examination, archival research, and ...
The PhD program in history offers outstanding opportunities for graduate study in North American, European, public and global-comparative history. The School of Historical, Philosophical and Religious Studies' world-class faculty members deliver courses and individualized mentoring in a wide range of historical topics, such as urban history ...
How to Choose a Research Topic. Our first piece of advice is to PhD candidates is to stop thinking about 'finding' a research topic, as it is unlikely that you will. Instead, think about developing a research topic (from research and conversations with advisors). Did you know: It took Professor Stephen Hawking an entire year to choose his ...
PhD in History. The Department of History at Boston University admits students to its PhD program who have majored in history or a closely related academic field, who have strong academic records, and who are interested in working in the fields of African, American, Asian, or European history. ... able to instruct on a wide range of topics. Our ...
Current PhD Topics in the Department. Francesca Aimi. Domenico Veneziano in mid-15th-century Florence. ( Dr Cooper) Ilaria Bernocchi. Italian heroic portraits in the Sixteenth Century. ( Prof Marr) Aisha Bornø. Scandinavian women artists in and beyond the Parisian avant-garde.
The AHA's Career Diversity for Historians initiative is leading a national conversation to better align the purpose of doctoral education with the varying skills, values, and interests of graduate students and the changing professional opportunities for historians within and beyond the academy. In the spring of 2018, 20 PhD-granting history departments were awarded Career Diversity ...
History of Cinema Dissertation Topics. Topic 1: Analysing the history and politics of Bollywood. Topic 2: The role of cinematic depictions influencing popular understanding of the Spanish Civil War. Topic 3: Analysing distinctive characteristics of Korean films. Topic 4: Examining the history of cinema in Britain since 1896.
Studying a PhD in History is a rigorous and intellectually stimulating experience. As a doctoral student, you will have the opportunity to conduct original research, contribute to historical scholarship, and engage in critical analysis of primary and secondary sources. You will work closely with your supervisor, who will guide and support you ...
A history PhD program allows you to use your historical knowledge to contribute to the modern world by making an impact on the community around you. Many politicians, inclusion officers, grant writers, and even human resource managers use their history PhDs to influence their worlds. Your ability to think critically about the past and lend your ...
The Vanderbilt history department offers the Ph.D. degree. Students normally earn the M.A. following two years of coursework, fulfillment of the research paper requirement, and satisfactory performance on language examinations. The department does not offer a free-standing terminal M.A. degree. The application deadline for Fall 2025 admission ...
The AHA's "Where Historians Work" is an ambitious research project designed to track the career outcomes of everyone who earned a PhD in history from 2004-13 in the United States. Last year, we launched a beta version of "Where Historians Work" showing initial results from 34 PhD programs. Since then, we have gathered information on the remaining 127 PhD programs, locating some ...
The principal requirement for the PhD degree in the history of medicine is the writing of a dissertation based upon original research and of publishable quality. Prior to embarking on full-time dissertation research, candidates will prepare themselves by a variety of courses, seminars, and guided reading.
Several, some of which make writing legal history in a Latin American context particularly challenging. First, there is an atavistic and deep-seated skepticism about the law's effectiveness in Latin America. Many social scientists—historians, sociologists, anthropologists—have put more effort into studying economic inequality, religion ...
History, PhD. The Department of History offers a full range of courses and programs in the fields of American, British and European, East Asian, Latin American, and Ottoman and Middle Eastern history. It offers exceptionally strong training in the fields of environmental history, science, technology and medicine, as well as women's and gender ...
John P. R. Eicher (PhD, 2015), Associate Professor of European History at Penn State University and a 2023-24 National Endowment for the Humanities Fellow, has released a ten-part YouTube lecture series titled, "Western Civilization (1500-Present): From Dawn, to Decadence, to Disillusionment."
12:30-3:30 pm -- DH Research Fellows' Showcase. 12:30 - 1:50 PM : The Meaning and Measurement of Place. with presentations from: Matt Randolph (PhD Candidate in History): "Bringing AI to Archibald Grimké's Archive: A Case Study of Artificial Intelligence for Histories of Race and Slavery". This digital project builds upon two years of research ...
Felix Wu, a 26-year-old man diagnosed with muscular dystrophy, beats the odds by graduating from Rice University with a PhD. Dr. Felix Wu defied the odds since doctors predicted he'd live a short ...
Dorothy Ross, pioneering historian of the origins of modern social science and a professor emerita in the Johns Hopkins University Department of History, died last week. She was 87. Ross's research focused on historical writing in the social sciences, revealing insights from the history of fields including psychology, economics, political ...