Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article

A guiding framework for needs assessment evaluations to embed digital platforms in partnership with Indigenous communities
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft
Affiliation School of Occupational and Public Health, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft
Affiliation School of Public Health Sciences, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Île-à-la-Crosse School Division, The Northern Village of Île-à-la-Crosse, Île-à-la-Crosse, SK, Canada
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Supervision
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations DEPtH Lab, Faculty of Health Sciences, Western University, London, ON, Canada, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, Western University, London, ON, Canada, Lawson Health Research Institute, London, Ontario, Canada
- Jasmin Bhawra,
- M. Claire Buchan,
- Brenda Green,
- Kelly Skinner,
- Tarun Reddy Katapally

- Published: December 22, 2022
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282
- Reader Comments
Introduction
In community-based research projects, needs assessments are one of the first steps to identify community priorities. Access-related issues often pose significant barriers to participation in research and evaluation for rural and remote communities, particularly Indigenous communities, which also have a complex relationship with academia due to a history of exploitation. To bridge this gap, work with Indigenous communities requires consistent and meaningful engagement. The prominence of digital devices (i.e., smartphones) offers an unparalleled opportunity for ethical and equitable engagement between researchers and communities across jurisdictions, particularly in remote communities.
This paper presents a framework to guide needs assessments which embed digital platforms in partnership with Indigenous communities. Guided by this framework, a qualitative needs assessment was conducted with a subarctic Métis community in Saskatchewan, Canada. This project is governed by an Advisory Council comprised of Knowledge Keepers, Elders, and youth in the community. An environmental scan of relevant programs, three key informant interviews, and two focus groups (n = 4 in each) were conducted to systematically identify community priorities.
Through discussions with the community, four priorities were identified: (1) the Coronavirus pandemic, (2) climate change impacts on the environment, (3) mental health and wellbeing, and (4) food security and sovereignty. Given the timing of the needs assessment, the community identified the Coronavirus pandemic as a key priority requiring digital initiatives.
Recommendations for community-based needs assessments to conceptualize and implement digital infrastructure are put forward, with an emphasis on self-governance and data sovereignty.
Citation: Bhawra J, Buchan MC, Green B, Skinner K, Katapally TR (2022) A guiding framework for needs assessment evaluations to embed digital platforms in partnership with Indigenous communities. PLoS ONE 17(12): e0279282. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282
Editor: Stephane Shepherd, Swinburne University of Technology, AUSTRALIA
Received: June 1, 2022; Accepted: December 2, 2022; Published: December 22, 2022
Copyright: © 2022 Bhawra et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: Data are co-owned by the community and all data requests should be approved by the Citizen Scientist Advisory Council and the University of Regina Research Office. Citizen Scientist Advisory Council Contact: Mr. Duane Favel, Mayor of Ile-a-lacrosse, email: [email protected] ; [email protected] University of Regina Research Office contact: Ara Steininger, Research Compliance Officer; E-mail: [email protected] . Those interested can access the data in the same manner as the authors.
Funding: TRK received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Canada Research Chairs Program to conduct this research. The funding organization had no role to play in any part of the study implementation of manuscript generation.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Community engagement has been the cornerstone of participatory action research in a range of disciplines. Every community has a unique culture and identity, hence community members are the experts regarding their diverse histories, priorities, and growth [ 1 – 3 ]. As a result, the successful uptake, implementation, and longevity of community-based research initiatives largely depends on meaningful community engagement [ 4 – 9 ]. There is a considerable body of evidence establishing the need for ethical community-research partnerships which empower citizens and ensure relevant and sustainable solutions [ 1 – 3 , 10 ]. For groups that have been marginalized or disadvantaged, community-engaged research that prioritizes citizens’ control in the research process can provide a platform to amplify citizens’ voices and ensure necessary representation in decision-making [ 11 ]. Such initiatives must be developed in alignment with a community’s cultural framework, expectations, and vision [ 12 ] to support continuous and meaningful engagement throughout the project. In particular, when partnering with Indigenous communities, a Two-Eyed Seeing approach can provide valuable perspective to combine the strengths of Indigenous and Western Knowledges, including culturally relevant methods, technologies, and tools [ 13 – 15 ].
Many communities have a complicated relationship with research as a result of colonialism, and the trauma of exploitation and discrimination has continued to limit the participation of some communities in academic partnerships [ 16 ]. Indigenous Peoples in Canada experience a disproportionate number of health, economic, and social inequalities compared to non-Indigenous Canadians [ 17 ]. Many of these health (e.g., elevated risk of chronic and communicable diseases) [ 18 – 21 ]), socioeconomic (e.g., elevated levels of unemployment and poverty) [ 19 , 22 – 24 ], and social (e.g., racism and discrimination) [ 19 , 22 – 24 ]) inequities can be traced back to the long-term impacts of assimilation, colonization, residential schools, and a lack of access to healthcare [ 19 , 20 , 22 – 24 ]. To bridge this gap, and more importantly, to work towards Truth and Reconciliation [ 25 ], work with Indigenous Peoples must be community-driven, and community-academia relationship building is essential before exploring co-conceptualization of initiatives [ 26 ].
One of the first steps in building a relationship is to learn more about community priorities by conducting a needs assessment [ 27 , 28 ]. A needs assessment is a research and evaluation method for identifying areas for improvement or gaps in current policies, programs, and services [ 29 ]. When conducted in partnership with a specific community, needs assessments can identify priorities and be used to develop innovative solutions, while leveraging the existing knowledge and systems that communities have in place [ 30 ]. Needs assessments pave the path for understanding the value and applicability of research for community members, incorporating key perspectives, and building authentic partnerships with communities to support effective translation of research into practice.
For rural, remote, and northern communities within Canada, issues related to access (e.g., geographic location, transportation, methods of communication, etc.) pose significant barriers to participation in research and related initiatives [ 31 ]. Digital devices, and in particular, the extensive usage of smartphones [ 32 ] offers a new opportunity to ethically and equitably engage citizens [ 33 ]. Digital platforms (also referred to as digital tools) are applications and software programs accessible through digital devices. Digital platforms can be used for a variety of purposes, ranging from project management, to healthcare delivery or mass communication [ 34 ]. Digital infrastructure–the larger systems which support access and use of these digital platforms, including internet, satellites, cellular networks, and data storage centres [ 34 ]. The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has catalyzed the expansion of digital technology, infrastructure and the use of digital devices in delivering essential services (e.g., healthcare) and programs to communities [ 35 , 36 ].
While digital platforms have been used in Indigenous communities for numerous initiatives, including environmental mapping initiatives (e.g., research and monitoring, land use planning, and wildlife and harvest studies) [ 37 , 38 ] and telehealth [ 39 ], there has largely been isolated app development without a corresponding investment in digital infrastructure. This approach limits the sustainability of digital initiatives, and importantly does not acknowledge an Indigenous world view of holistic solutions [ 39 ].
Thus given the increasing prominence of digital devices [ 39 , 40 ], it is critical to evaluate the conceptualization, implementation, and knowledge dissemination of digital platforms. To date, there is little guidance on how to evaluate digital platforms, particularly in partnership with rural and remote communities [ 41 ]. A review of recent literature on community-based needs assessments uncovered numerous resources for conducting evaluations of digital platforms, however, a key gap is the lack of practical guidance for conducting needs assessments in close collaboration with communities in ways that acknowledge existing needs, resources, supports and infrastructure that also incorporates the potential role of digital platforms in addressing community priorities.
This paper aims to provide researchers and evaluators with a framework (step-by-step guide) to conduct needs assessments for digital platforms in collaboration with Indigenous communities. To achieve this goal, a novel needs assessment framework was developed using a Two-Eyed Seeing approach [ 13 – 15 ] to enable the identification of community priorities, barriers and supports, as well as existing digital infrastructure to successfully implement digital solutions. To demonstrate the application of this framework, a community-engaged needs assessment conducted with a subarctic Indigenous community in Canada is described and discussed in detail.
Framework design and development
This project commenced with the design and development of a new framework to guide community-based needs assessments in the digital age.
Needs assessments
Needs assessments are a type of formative evaluation and are often considered a form of strategic or program planning, even more than they are considered a type of evaluation. Needs assessments can occur both before and during an evaluation or program implementation; however, needs assessments are most effective when they are conducted before a new initiative begins or before a decision is made about what to do (e.g., how to make program changes) [ 29 ]. Typically, a needs assessment includes: 1) collecting information about a community; 2) determining what needs are already being met; and 3) determining what needs are not being met and what resources are available to meet those needs [ 42 ].
Framework development
Based on existing literature, community consultation, and drawing expertise from our team of evaluation experts who have over a decade of experience working with Indigenous communities on a range of research and evaluation projects, a novel framework was developed to guide community-based needs assessments focused on the application of digital platforms.
This framework (see Fig 1 ) is driven by core questions necessary to identify community priorities that can be addressed by developing and implementing digital platforms. Through team discussion and community consultation, five key topic areas for the assessment of community needs were identified: i) current supports; ii) desired supports; iii) barriers; iv) community engagement; and v) digital access and connectivity. A series of general questions across the five needs assessment topic areas were developed. Thereafter, a set of sub-questions were embedded in each key topic area.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282.g001
The Guiding Framework outlines an approach for conducting community needs assessments which can be adapted across communities and jurisdictions. This framework offers a flexible template that can be used iteratively and applied to various community-engaged needs assessments in a range of areas, including but not limited to community health and wellness projects. The questions assigned to each topic area can be used to guide needs assessments of any priority identified by community stakeholders as suitable for addressing with digital platforms.
Needs assessment methods
The Guiding Framework was implemented in collaboration with a subarctic Indigenous community in Canada, and was used to identify key community priorities, barriers, supports, and existing digital infrastructure which could inform the design and implementation of tailored digital platforms.
Using an environmental scan of relevant documents and qualitative focus groups and interviews, a needs assessment was conducted with the Northern Village of Île-à-la-Crosse, Saskatchewan, Canada between February and May 2020.
This project is governed by a Citizen Scientist Advisory Council which included researchers, Knowledge Keepers, Elders, and youth from Île-à-la-Crosse. The study PI (TRK) and Co-Investigator (JB) developed a relationship with key decision-makers in Île-à-la-Crosse in 2020. Through their guidance and several community visits, the decision-makers introduced the research team to Elders, youth, and other community members to gain a better understanding of current priorities and needs in Île-à-la-Crosse. The research team developed relationships with these community members and invited them to join the Council to formally capture feedback and plan ongoing projects to promote health and wellbeing in the community. The Council represents the needs and interests of the community, and guides the project development, implementation, and evaluation. Council members were provided with Can $150 (US $119.30) as honoraria for each meeting to respect their time, knowledge, and contributions.
Written consent was obtained from all focus group participants and verbal consent was obtained from all key informants participating in interviews. This study received ethics clearance from the research ethics boards of the University of Regina and the University of Saskatchewan through a synchronized review protocol (REB# 2017–29).
Established in 1776, Île-à-la-Crosse is a northern subarctic community with road access in northwest Saskatchewan. Sakitawak, the Cree name for Île-à-la-Crosse, means “where the rivers meet,” hence the community was an historically important meeting point for the fur trade in the 1800s [ 43 , 44 ] The community lies on a peninsula on the Churchill River, near the intersections with the Beaver River and Canoe River systems. Île-à-la-Crosse has a rich history dating back to the fur trade. Due to its strategic location, Montreal-based fur traders established the first trading point in Île-à-la-Crosse in 1776, making the community Saskatchewan’s oldest continually inhabited community next to Cumberland House [ 45 ]. In 1821, Île-à-la-Crosse became the headquarters for the Hudson’s Bay Company’s operations in the territory. In 1860, the first convent was established bringing Western culture, medical services, and education to the community.
Île-à-la-Crosse has a population of roughly 1,300 people [ 19 ]. Consistent with Indigenous populations across Canada, the average age of the community is 32.7 years, roughly 10 years younger than the Canadian non-Indigenous average [ 19 ]. Census data report that just under half (44%) of the community’s population is under the age of 25, 46.3% are aged 25–64, and 9.3% aged 65 and over [ 19 ]. Members of the community predominantly identify as Métis (77%), with some identifying as First Nations (18%), multiple Indigenous responses (1.2%), and non-Indigenous (2.7%) [ 19 ]. Many community members are employed in a traditional manner utilizing resources of the land (e.g., hunting, fishing, trapping), others in a less traditional manner (e.g., lumbering, tourism, wild rice harvesting), and some are employed through the hospital and schools. The community currently has one elementary school with approximately 200 students from preschool to Grade 6, and one high school serving Grades 7–12 with adult educational programming. Île-à-la-Crosse has a regional hospital with Emergency Services, which includes a health services centre with a total of 29 beds. Other infrastructure of the community includes a Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) station, a village office, volunteer fire brigade, and a catholic church [ 46 ].
Needs assessment approach
Île-à-la-Crosse shared their vision of integrating digital technology and infrastructure as part of its growth, thus the needs assessment was identified as an appropriate method to provide the formative information necessary to understand what the needs are, including who (i.e., players, partners), and what (i.e., information sources) would need to be involved, what opportunities exist to address the needs, and setting priorities for action with key community stakeholders [ 47 ]. As a starting point and rationale for this needs assessment, the community of Île-à-la-Crosse values the potential of technology for improving health communication, information reach, access to resources, and care, and was interested in identifying priorities to begin building digital infrastructure. Given the timing of the COVID-19 pandemic, being responsive to community health needs were key priorities that they wanted to start addressing using a digital platform. This needs assessment facilitated and enabled new conversations around key priorities and next steps.
The evaluation approach was culturally-responsive and included empowerment principles [ 48 – 50 ]. Empowerment evaluation intends to foster self-determination. The empowerment approach [ 50 ] involved community members–represented through the Citizen Scientist Advisory Council–engaging in co-production of the evaluation design and implementation by establishing key objectives for the evaluation, informing evaluation questions, building relevant and culturally responsive indicators, developing focus group guides, leading recruitment and data collection, and interpreting results [ 51 ]. In this way, the approach incorporated local community and Indigenous Knowledges as well as Western knowledge, in a similar approach to Two-Eyed Seeing [ 13 – 15 ]. Using these needs assessment evaluation results, the community will identify emerging needs and potential application issues, and work with the researchers to continue shaping project development and implementation.
Two-Eyed Seeing to embed digital platforms
Two-Eyed Seeing as described by Elder Albert Marshall [ 13 , 14 ], refers to learning to see with the strengths of Indigenous and Western Knowledges. Our engagement and overall approach to working with the community of Île-à-la-Crosse takes a Two-Eyed Seeing lens, from co-conceptualization of solutions, which starts with understanding the needs of the community. All needs are a result of direct Indigenous Knowledge that was provided by the Advisory Council. Indigenous Knowledge is not limited to the knowledge of Elders and Traditional Knowledge Keepers; however, they play a critical role in guiding that knowledge through by providing historical, geographic, and cultural context. Moreover, the Knowledge Keepers can be key decision-makers in the community, and in our case, they were key informants who participated in this needs assessment. Every aspect of needs assessment was dependent on the Advisory Council and Key informants providing the Indigenous Knowledge that the research team needed to tailor digital solutions. As a result, Two-Eyed Seeing approach informed all aspects of the research process.
As we are working to develop, and bring digital platforms and technologies (i.e., Western methods) to address key community priorities, Indigenous Knowledge is central to the overall project. Indigenous Elders, decision-makers, and Advisory Council members are bringing both their historical and lived experience to inform project goals, key priority areas, target groups, and methods. Île-à-la-Crosse is a predominantly Metis community, which differs in culture from other Indigenous communities in Canada—First Nations and Inuit communities. Ceremony is not a key part of community functioning; thus, specific cultural ceremonies were not conducted upon advice of the Advisory Council. Instead, the knowledge of historical issues, challenges, and success stories in the community is considered Indigenous Knowledge for this needs assessment, and more importantly, this Indigenous Knowledge informed the focus areas and next steps for this project. Overall, the spirit of collaboration and co-creation which combined Western research methods/technology with Indigenous Knowledge and expertise is considered Two-Eyed Seeing in this project. This lens was taken at all phases, from the engagement stage to Advisory Council meetings, to planning and executing the needs assessment and next steps.
Data collection
In order to obtain an in-depth understanding of the key priorities and supports within the community of Île-à-la-Crosse, this needs assessment used a qualitative approach. An environmental scan was conducted in February 2020 of current school and community policies and programs. Published reports, meeting memos, community social media accounts, and the Île-à-la-Crosse website were reviewed for existing policies and programs. The Citizen Scientist Advisory Council identified appropriate data sources for the document review and corroborated which programs and initiatives were currently active in the community.
Qualitative data were collected from key decision-makers and other members within the community. A purposeful convenience sampling approach was employed to identify members of the community who could serve on the Council and participate in focus group discussions. Key decision makers and existing Council members recommended other community members who could join the focus group discussions to provide detailed and relevant information on community priorities, digital infrastructure, supports, and challenges. Two focus groups were conducted by members of the research team in Île-à-la-Crosse with the Council in May 2020. Focus group participants were asked to describe community priorities, supports, and barriers, as well as experience and comfort with digital platforms. Each focus group had four participants, were two-hours in length, and followed an unstructured approach. Three key informant interviews were conducted in Île-à-la-Crosse between February and April 2020. One-hour interviews were conducted one-on-one and followed a semi-structured interview format. The focus groups and key informant interviews were led by the study PI, TRK, and Co-Investigator, JB, who have extensive training and experience with qualitative research methods, particularly in partnership with Indigenous communities. Focus groups and key informant interviews were conducted virtually using Zoom [ 52 ]. The key informant interviews and focus groups were audio-recorded and transcribed. All data were aggregated, anonymized, and securely stored in a cloud server. Data are owned by the community. Both the Council and the research team have equal access to the data.
Data analysis
All documents identified through the environmental scan were reviewed for key themes. A list of existing school and community programs was compiled and organized by theme (i.e., education-focused, nutrition-focused, health-focused, etc.). Follow-up conversations with key informants verified the continued planning and provision of these programs.
Following the 6-step method by Braun and Clarke (2006), a thematic analysis was conducted to systematically identify key topic areas and patterns across discussions [ 53 ]. A shortlist of themes was created for the key informant interviews and focus groups, respectively. A manual open coding process was conducted by two reviewers who reached consensus on the final coding manual and themes. Separate analyses were conducted for key informant interviews and focus group discussions; however, findings were synthesized to identify key themes and sub-themes in key priorities for the community, community supports and barriers, as well as digital connectivity and infrastructure needs.
Needs assessment findings
The needs assessment guiding framework informed specific discussions of key issues in the community of Île-à-la-Crosse. Key informant interviews and focus group discussions commenced by asking about priorities–“what are the key areas of focus for the community?” In all conversations–including a document review of initiatives in Île-à-la-Crosse–health was highlighted as a current priority; hence, questions in the guiding framework were tailored to fit a needs assessment focused on community health. The following five overarching evaluation questions were used to guide the evaluation: i) What are the prominent health issues facing residents of Île-à-la-Crosse?; ii) What supports are currently available to help residents address prominent health issues in the community?; iii) What types of barriers do community members face to accessing services to manage their health?; iv) How is health-related information currently shared in the community?; and v) To what extent are health services and information currently managed digitally/electronically? The evaluation questions were kept broad to capture a range of perspectives. An evaluation matrix linking the proposed evaluation questions to their respective sub-questions, indicators, and data collection tools is outlined in Table 1 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282.t001
Feedback on each needs assessment topic area is summarized in the sections below. Sample quotes supporting each of the key topic areas is provided in Table 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282.t002
Key priorities
Four priorities were identified through the focus groups, key informant interviews, and document review ( Fig 2 ). Given the timing of the discussion, the primary issue of concern was the COVID-19 pandemic. Many community members were worried about contracting the virus, and the risk it posed to Elders in the community. Of greater concern, however, was how COVID-19 exacerbated many existing health concerns including diabetes and hypertension in the community. For example, routine procedures were postponed and community members with other health conditions were not receiving routine healthcare during the height of the pandemic. The St. Joseph’s Hospital and Health Centre services Île-à-la-Crosse and bordering communities, hence maintaining capacity for COVID-19 patients was a priority. COVID-19 exposed existing barriers in the healthcare system which are described in greater detail in the barriers to community health section.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282.g002
Another priority discussed by many community members was climate change and the environment. Community members noted that changes in wildlife patterns, land use, and early winter ice road thaw were areas of concern, particularly due to the impact these factors have on traditional food acquisition practices (i.e., hunting) and food access. For instance, the geographic location of Île-à-la-Crosse is surrounded by a lake, and the main highway which connects the community to the land has experienced increased flooding in the past few years.
In addition to posing immediate danger to community members, food security and sovereignty are also closely linked to road access. While the community produces some of its own food through the local fishery and greenhouses, Île-à-la-Crosse is still dependent on a food supply from the south (i.e., Saskatoon). During COVID-19, food access was further restricted due to limited transport and delivery of food products, which increased the risk of food insecurity for community members. Food insecurity was believed to be of bigger concern for Elders in the community compared to younger members. Younger community members expressed having the ability to source their own food in a variety of capacities (e.g., fishing in the lake), whereas Elders rely more heavily on community resources and support (e.g., grocery stores, friends, and family).
Community members also discussed issues surrounding mental health and wellbeing. This topic was of particular concern for youth and Elders in the community. Community members discussed the importance of identifying covert racism (vs. discrimination) that exists within health services that exacerbated mental health issues and care, as well as developing coping strategies, resilience, and supports to prevent mental health crises. Key informants emphasized the need to minimize the stigma around mental health and focus on holistic wellbeing as they work to develop strategies to improve community wellness.
Community health supports
Île-à-la-Crosse has been working on developing supports to improve community health through various initiatives. A document review identified a community-specific wellness model which has informed program development and planning over the past few years. The key components of the Île-à-la-Crosse wellness model are: i) healthy parenting; ii) healthy youth; iii) healthy communities; iv) Elders; v) healing towards wellness; and vi) food sovereignty. The Elders Lodge in the community provides support for holistic wellbeing by promoting intergenerational knowledge transmission, guidance to youth and community members, as well as land-based activities which improve bonding, cultural awareness, and mental and spiritual well-being among community members. The Elders Lodge hosts both drop-in and organized events.
Several initiatives have been developed to support food sovereignty in the community, including a greenhouse program where fruits and vegetables are grown and shared locally. This program is run in partnership with the school to increase food knowledge and skills among youth. In addition, after-school programs including traditional food education (i.e., cooking classes) and land-based activities (i.e., berry picking) led by Elders support the goals of the wellness model. The community is currently working on developing additional programs dedicated to improving mental wellness among adults, youth, and Elders.
Barriers to community health
When key informants were asked to identify barriers to community health, they described delays in access to timely health information. For example, daily COVID-19 tests conducted at the regional health centre in Île-à-la-Crosse were relayed to the provincial health authority; however, information about the total number of COVID-19 cases could take up to one week to be sent back to the community. This time lag restricted community decision-makers’ ability to enact timely policy (i.e., contact tracing) and rapidly respond to managing cases.
A second barrier that was raised by community members was a delay in access to timely healthcare. The Île-à-la-Crosse hospital is a regional health service centre serving the community as well as surrounding areas. Community members noted that the load often exceeded the capacity of the single hospital, and some patients and procedures were relocated to hospitals and clinics in the larger city of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. This was reported to be challenging for many community members as it was associated with longer wait times, long commutes, and sometimes required time off work. Many of these challenges were exacerbated during the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result of the pandemic, many medical centres and hospitals postponed routine and elective medical procedures in an attempt to accommodate the overwhelming influx of patients who contracted COVID-19. In addition, community members were advised to avoid spending time in health centres to limit risk of exposure to the virus. These COVID-related changes further delayed access to timely healthcare for many community members of Île-à-la-Crosse.
Several community members reported experiencing institutional racism in healthcare and social service settings outside of Île-à-la-Crosse. This was particularly exacerbated during the COVID-19 movement restrictions, where community members faced significant difficulties in accessing services and care in larger urban centres, and experienced further discrimination due to the stigma of COVID-19-related rumours about communities in the north.
Lastly, community members discussed a lack of awareness about some health topics, including where and how to access reliable health information. Some community members attributed this lack of awareness to a general distrust in government health information due to a history of colonialism and exploitation in Canada, which likely contributed to increased misinformation about COVID-19 risk and spread.
Health communication
The primary modes of communication within Île-à-la-Crosse are radio and social media. These platforms were used throughout the pandemic to communicate health information about COVID-19 case counts and trends. Community members also reported obtaining health information from healthcare practitioners (i.e., for those already visiting a healthcare provider), Elders, and the internet. Key informants indicated an interest in improving digital infrastructure to enable sharing of timely and accurate health information with community members and minimize misinformation. Key informants also reported room for improvement in the community’s digital health infrastructure, particularly in improving timely communication with community members, and to inform decision-making in crisis situations.
Digital infrastructure and connectivity
Île-à-la-Crosse has its own cell tower which offers reliable access to cellular data. The community also has access to internet via the provincial internet provider–SaskTel, as well as a local internet provider—Île-à-la-Crosse Communications Society Inc. Key informants and community members confirmed that most individuals above 13 years of age have access to smartphones, and that these mobile devices are the primary mode of internet access. However, it was unclear whether everyone who owns smartphones also has consistent data plans or home internet connections. Key informants described the great potential of digital devices like smartphones to increase the speed and accuracy of information sharing. Discussions with both key informants and community members suggested the need for a community-specific app or platform which could provide timely health information that was tailored to the community’s needs.
Community members noted that expanding digital infrastructure had to be paired with efforts to improve digital literacy–particularly as it relates to data security, privacy, and online misinformation. A separate initiative was discussed which could work to improve digital literacy among youth and Elders, as this would improve both the uptake of digital health platforms, as well as their usefulness and application. Key informants discussed the importance of building digital infrastructure that would enable data sovereignty, self-governance, and determination. The key informants, who are also primary decision-makers in the community, described opportunities for ethical development of digital platforms that would ensure that data is owned by the community.
Needs assessments are commonly the first step in understanding specific community needs, [ 27 , 28 ]; however, few evaluation frameworks provide practical guidance on how to engage communities in needs assessments [ 41 ]. This paper provides a step-by-step guide for conducting needs assessments in collaboration with communities in the digital age. Using the series of questions outlined in the Guiding Framework, researchers and evaluators can gain an in-depth understanding of a community’s priorities, needs, existing capacity, and relevant solutions.
The Guiding Framework was critical to establishing a partnership with the community of Île-à-la-Crosse, as it enabled the research team to obtain detailed insight into their priorities–in this case, community health–as well as community capacity. Taking a Two-Eyed Seeing approach [ 15 ], conversations with the community highlighted strengths of Western digital technology and the diversity of Indigenous Knowledges for addressing priorities [ 13 ]. This approach was also important to establishing trust and respect for the variety of perspectives that could be used to address community priorities. The resulting partnership also enabled the conceptualization of tangible action items that were aligned with current and future priorities–a key factor in the sustainability and feasibility of community-based initiatives [ 4 – 8 , 54 ].
Challenges and opportunities for using digital platforms for priorities identified by needs assessment
Many rural and remote communities face similar challenges and share common priorities with Île-à-la-Crosse. For example, resource and service access, including food and other essential supplies, healthcare, and internet connectivity are issues faced by many rural and remote communities across Canada [ 55 – 60 ]. Key informants and community members from our partner community corroborated these access issues, particularly in relation to public health. Given the potential for digital technology to bridge access gaps, it has become pertinent to invest in digital infrastructure and platform development.
Research has shown that in many rural and remote communities, smartphone ownership is not the limiting factor–it is internet inequity, which is defined as differential internet access based on wealth, location (urban, rural, or remote), gender, age, or ethnicity [ 61 ]. The United Nations has declared internet access a human right [ 10 ], which makes it imperative to develop digital infrastructure such as internet connectivity to improve digital accessibility. Île-à-la-Crosse has its own cell tower which offers reliable access to cellular data. The community of Île-à-la-Crosse also has access to consistent and dedicated internet service through a provincial internet provider and local internet provider. The needs assessment showed that the universality of smartphone ownership combined with good internet connectivity lays the foundation for the development of tailored, culturally appropriate digital health platforms in communities like Île-à-la-Crosse.
In particular, the needs assessment revealed that smartphone apps, which most citizens are well-versed with, can be used to provide local services and access to resources. For example, a locally developed app can connect the Mayor’s office with community members in real-time to provide updates on COVID-19 outbreaks. Apps also have the potential to connect communities to resources within and outside of the community [ 35 , 57 ]. For example, advanced artificial intelligence algorithms can be used to anticipate community needs prior to urgent crises like COVID-19, environmental disasters, or food crises [ 35 , 62 – 65 ]. To date, the issue has not been the lack of technology or ability to bridge this gap for rural and remote communities. Instead, larger systemic inequities have limited our ability to co-create local solutions for global problems by decentralizing technology that is widely available [ 35 , 66 ], which highlights upstream inequities in developing digital platforms.
Recommendations for inclusive digital needs assessments
Given the widespread adoption of digital technology, digital platforms can provide rich data to identify and address community crises [ 2 , 3 , 35 ]. Importantly, co-created digital platforms can be used to share knowledge in real-time with community members and other stakeholders to enable remote engagement, which is especially important during crisis situations such as a pandemic [ 2 , 3 , 35 ]. As we implement creative digital platforms in varied programs or research projects, we must also integrate this digital perspective into the evaluation process. Research and evaluation literature has well established approaches to needs assessment evaluations [ 29 , 42 , 67 ]; however, in the 21st century, we need to account for the use and application of digital platforms in community-focused initiatives. To identify how and where digital platforms can play a role in addressing community priorities, we propose several recommendations for inclusive community-based needs assessments.
First, at the crux of all community-based needs assessments is relationships. A relationship built on respect, reciprocity, mutual understanding, and prioritizing the needs and vision of communities is essential for sustainable impact. The First Nations OCAP® principles [ 68 ] informed conversations between the research team and community about data ownership and control. These principles include ownership of knowledge and data, control over all aspects of research, access to information about one’s own community, and possession or control of data [ 68 ]. The OCAP® principles ensure First Nations and other Indigenous Peoples the right to their own information, and also reflect commitments to use and share information in a way that maximizes the benefit to a community, while minimizing harm. Some communities may choose to lead a project, or work closely in collaboration with experts for specific projects. Irrespective of the project dynamics, needs assessments rely on detailed information and context about a community for a project to succeed.
Second, it is important for researchers and evaluators to gain an understanding of the current digital infrastructure and connectivity in the community. The needs assessment framework ( Fig 1 ) includes relevant questions for identifying data and WIFI access in a community, penetration of digital devices, and existing digital infrastructure. Even for community-based initiatives that are not focused on a digital platforms, digital technologies will inevitably be a part of the solution, a barrier, or both. Hence the digital landscape has become part of the context that we must capture and understand in a needs assessment to better design and develop programming, policies, and other initiatives.
Third, it is important to ask the question of where and how a digital tool or platform could help. Are there gaps that digital platforms can help address or fill? In rural and remote communities, in particular, digital platforms can provide access to real-time information and services not otherwise available. For example, Telehealth [ 69 , 70 ] in the Canadian north offers citizens access to essential healthcare services, including video appointments with medical specialists. Prior to Telehealth, many residents would need to fly into bigger cities in the nearest province to access health care [ 55 ].
Lastly, an understanding of the broader context which affects a community’s ability to adopt digital platforms is critical to the success of digital initiatives. This includes, but is not limited to, capturing data on socioeconomic status and the accessibility of internet-connected digital devices. Digital platforms should help to bridge the divide in resource, service, and information access–not widen the gap. For some communities, this may require working on building digital infrastructure and obtaining dedicated funds to expand access prior to implementing digital initiatives. In addition, digital literacy cannot be taken for granted. Digital literacy refers to individuals’ ability to not only use digital devices, but according to Eshet-Alkalai [ 71 ], “includes a large variety of complex cognitive, motor, sociological, and emotional skills, which users need in order to function effectively in digital environments.” In its simplest form, digital literacy may include the ability to navigate digital platforms, download apps, and communicate electronically. Other more specific skills include ability to read and understand instructions, terms and services, as well as data privacy and security statements [ 72 – 74 ] As part of a needs assessment, identifying digital literacy within a community is an important step to safe, ethical, and relevant digital tool development.
Considering the challenges, immense potential, and learnings from applying the Guiding Framework, a tailored digital platform was conceptualized called Sakitawak Health.
Development of Sakitawak Health
Sakitawak Health is a culturally-responsive digital epidemiological platform to monitor, mitigate, and manage COVID-19 outbreaks. The needs assessment concluded that digital platforms can be used for emerging or other existing population health crises within Île-à-la-Crosse and potentially other Indigenous communities. Moreover, to co-create digital platforms, the Île-à-la-Crosse Citizen Scientist Advisory Council identified key features to embed in CO-Away, including free virtual care for citizens via a smartphone app at the frontend, and access to anonymized community data on the backend for decision-makers.
The app will provide three key precision medicine services that are specific to each citizen: 1) continuous risk assessment of COVID-19 infection; 2) evidence-based public health communication; and 3) citizen reporting of food availability, access to public services, and COVID-19 symptoms and test results. These culturally-responsive features have been co-created with Métis decision-makers in Île-à-la-Crosse based on imminent community needs and preferences. CO-Away will enable real-time data collection through continuous citizen engagement to inform municipal jurisdictional policies.
There are three guiding principles for developing Sakitawak Health: I) Citizen empowerment and data ownership: Active engagement is enabled through app features such as visualizing community risk. More importantly, the community owns the data to ensure data sovereignty; II) Privacy: Utilizing a cutting-edge methodology called federated machine learning, we will develop artificial intelligence algorithms that stores sensitive data such as participant location on mobile devices itself (i.e., sensitive data are not stored in external servers); III) Security and scalability: The backend server will be located in Cloud in Canada, which allows for horizontal and vertical scalability (i.e., the potential for developing multiple frontend apps and decision-making dashboards).
Recognizing the importance of data sovereignty and Indigenous self-governance
Data sovereignty and social justice are important aspects of community-based work, particularly for communities that have experienced discrimination or systemic inequities [ 2 , 75 ]. Data sovereignty refers to meaningful control and ownership of one’s data [ 76 ]. For Indigenous communities in Canada, self-determination and self-governance are of paramount importance given the colonial history of oppression, trauma, and disenfranchisement [ 77 ], and data sovereignty and ownership of digital platforms can promote that independence. In conducting digital community-based needs assessments, the application of a Two-Eyed Seeing lens enables us to leverage strengths of both Indigenous and Western Ways of Knowing to help focus on key priorities and develop solutions.
The engagement and overall approach to working with the community of Île-à-la-Crosse applied a Two-Eyed Seeing lens. In the needs assessment with Île-à-la-Crosse, Two-Eyed Seeing involved incorporation of Métis Knowledge during team engagements, which ensured that any digital platforms developed would incorporate Indigenous Knowledge to promote data sovereignty. All priorities identified within this manuscript are a result of direct Indigenous Knowledge that was provided by the Council. Indigenous Knowledge is not limited to the knowledge of Elders and Traditional Knowledge Keepers; however, they play a critical role in guiding that knowledge through by providing historical, geographic, and cultural context. Discussions with Île-à-la-Crosse about data sovereignty centered around citizen ownership of data, community access, and ensuring data privacy and security. The ultimate goal of this approach to data sovereignty is to facilitate decreased dependence on external systems and use digital solutions for Indigenous self-determination and self-governance.
The needs assessment represents the first phase of a larger evaluation strategy to develop and implement culturally appropriate digital platforms for community health. Phase 1 involved identifying core health priorities and desired supports in the community of Île-à-la-Crosse. Based on the needs assessment findings, Phase 2 of this project will involve the development of tailored digital health platforms and programming to support digital literacy. As part of Phase 2, digital literacy programs and tailored digital health platforms will be pilot tested and adapted prior to their implementation. In Phase 3, a process evaluation will be conducted to assess the reach, uptake, and use of digital health platforms and digital literacy programming. Integrated knowledge translation will be conducted during all phases to ensure continuous feedback, communication, and knowledge sharing with all relevant stakeholder groups.
Conclusions
Needs assessments can facilitate important conversations in community-based research and evaluation to learn about key priorities, challenges, and opportunities for growth. The Guiding Framework for Community-Based Needs Assessments to Embed Digital Platforms details a step-by-step approach to begin a conversation with communities to better understand their needs, and to tailor research and evaluation projects focused on embedding digital platforms. In Île-à-la-Crosse, the needs assessment framework has propelled the launch of a timely, community-engaged digital initiative to address key priorities, starting with COVID-19. Overall, tailored platforms can help bridge existing gaps in resource, program, and service access in Indigenous communities, irrespective of their location across the world.
Supporting information
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0279282.s001
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of community members of Île-à-la-Crosse. The Elders, youth, and key decision-makers who are part of the Île-à-la-Crosse Citizen Scientist Advisory Council have been invaluable in providing support, guidance, and cultural training to the research team. The authors also acknowledge the support of the Canadian Internet Registration Authority in advancing the uptake of digital health applications.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. Smith LT. Decolonizing Methodologies: Research and Indigenous Peoples. London; New York; Dunedin: Zed Books Ltd; University of Otago Press; Distributed in the USA exclusively by St Martin’s Press; 2021. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315597843-10 .
- 7. Narayan D. Empowerment and Poverty Reduction: A Sourcebook. Washington, D.C.; The World Bank; 2002.
- 8. Cairncross L, Morrell C, Drake J, Brownhill S. Tenants Managing: An Evaluation of Tenant Management Organisations in England. London: Office of the Deputy Prime Minister; 2002.
- 9. Pratchett L, Durose C, Lowndes V, Smith G, Stoker G, Wales C. Empowering communities to influence local decision making: systematic review of the evidence. London: 2009.
- 10. La Rue F. Report of the Special Rapporteur on the Promotion and Protection of the Right to Freedom of Opinion and Expression, Frank La Rue: addendum. 2011.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 19. Statistics Canada. Île-à-la-Crosse, NV [Census subdivision], Saskatchewan and Saskatchewan [Province] (table). Ottawa: 2017. https://doi.org/Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 98-316-X2016001.
- 20. Waldram JB, Herring A, Young TK. Aboriginal Health in Canada: Historical, Cultural, and Epidemiological Perspectives. 2nd editio. Toronto: University of Toronto Press; n.d.
- 22. Central Urban Métis Federation Inc., Kinistin Saulteaux Nation, Saskatoon Health Region. Strengthening the Circle: Partnering for Improved Health for Aboriginal People. Saskatoon, SK: 2010.
- 28. Pavlish CP, Pharris MD. Community-based collaborative action research : a nursing approach. Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2012.
- 42. Stufflebeam DL, Shinkfield AJ. Evaluation theory, models, and applications. 1st ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 2007.
- 43. McLennan D. Sakitawak Development’s Facebook Page n.d.
- 44. Cameco Corp. Patuanak—English River First Nation—Community Profiles—Community. Cameco North Saskatchewan 2020.
- 45. McLennan D. The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan: Île-à-la-Crosse n.d. https://esask.uregina.ca/entry/ile-a-la-crosse.jsp .
- 52. Zoom Video Communications Inc. Security guide 2016.
- 68. The First Nations Information Governance Centre. The First Nations Principles of OCAP TM Training Course 2021:1–6. https://fnigc.ca/ocap-training .
- 69. Telehealth 2021. North Heal 2021. https://www.northernhealth.ca/services/digital-health/telehealth .
- 75. Kukutai T, Taylor J, editors. Indigenous Data Sovereignty: Toward an Agenda. The Australian National University Press; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPDPSW.2014.214 .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

An ESP Needs Analysis: Addressing the Needs of English for Informatics Engineering

JEES (Journal of English Educators Society)
English for specific purposes (ESP) have different needs of English language use. These needs will be the fundamental indicators to develop appropriate ESP syllabus. In order to find those needs, a need analysis research is necessary to conduct. This qualitative study addresses the result of ESP needs analysis for 95 Informatics Engineering of Muhammadiyah University of Ponorogo students. Brief reviews of ESP, needs analysis, and current learners’ situation of ESP classroom for Informatics Engineering are described as theoretical frameworks. A needs analysis questionnaire is utilized as an approach to find specific needs and to evaluate the current class situation. The results address 10 areas of English language use for Informatics Engineering major.
Related Papers
Rafika Farah
This present study aims at investigating the students’ target needs in learning ESP Speaking of Law department students. The adapted version of Aliakbari & Boghayeri’s (2014) and Alsamadani’s (2017) questionnaire was used as the main instrument of this study to understand the 45 students’ perception about their needs in learning ESP speaking course. A mixed-method research design was implemented in this present research. Students’ responses were analyzed statistically using SPSS 16.0 by calculating the mean, frequency and percentage. To elicit more understanding on the topic, interview was implemented to senior students in order to get deeper investigation about students’ target needs. The interview data were then analyzed using NVivo 12 Plus. This study reveals that most of the students’ needs are concerned with their professional job in the future so they are able to use English in their fields. Thus, this study provides some highlighting points on what to include in course develo...
Mohd Hilmi Hamzah
This study aims to identify the difficulties of pronunciation and conversation faced by EFL learners who undertook a Preparatory Year Program (PYP) in Saudi Arabia, It highlights the main issues in pronunciation and conversations (e.g., textbooks, teaching methods, and students' attitude and motivation) and techniques to address these problems. The instruments used in the study were classroom observations and teachers' discussions. The results revealed that firstly, students did not have a sound knowledge of grammar. Secondly, students' outside environment was influenced by their mother tongue. Thirdly, the teaching methods did not suit their proficiency levels. Finally, they were demotivated and thought that they have an impossible mission to improve their English pronunciation and conversation.
Ririn Pusparini
Pre-service teachers’ (PST) beliefs and practices have been agreed as an initially vital basis to continue maintaining a qualified learning process. This article reviews the research on PSTs’ beliefs and practices concerning teaching and learning English as a foreign language (EFL) and the exploration of the complex relationship between EFL PSTs’ beliefs and practices. It encompasses a discussion about the nature of teachers’ beliefs, an overview of PSTs’ belief formation, and some previous studies on PSTs’ beliefs. The review of related literature summarizes the empirical studies on PSTs’ beliefs and practices from 2011 up to 2020, which reveal the diversity and similarity of the studies on EFL PSTs’ beliefs. The result obtained in this study depicts that PSTs’ beliefs about EFL teaching and learning are affected by prior language learning experiences, teacher education, and teaching practices. Besides, some constraints in the classroom setting can trigger the beliefs change coveri...
Journal of English Educators Society
Mega Safitri
This study investigated predominant learning style of 3rd semester students of English Language Education Program in Faculty of Cultural Studies at Universitas Brawijaya according to gender. Purposive sampling was used for this research and the sampling in this research was 100 students consist of 34 male students and 66 female students taken from 3rd semester English Department students of Faculty of Cultural Studies at Universitas Brawijaya. All participants were administered an Indonesian translated version of Reid’s (1984) Perceptual Learning Style Preference Questionnaire consisting of Visual, Auditory, Kinesthetic, Tactile, Group, and Individual, included 30 items. This study used quantitative survey design and Microsoft Excel 2007 as the analysis software. The validity and the reliability of this research were calculated by SPSS v.21. The result indicated that predominant male’s learning style was Kinesthetic and estimated by 14 male students (41%) while female students becom...
Choiril Anwar
This research was about the analysis of EFL teacher and students in using classroom language. The aim of this study was to find the errors in using classroom language. A descriptive research was used in this research. The samples of this research were the English teacher and science class students of a state senior high school. The researchers collected the data by using field note and voice recording. Then, the data findings were analyzed in using four steps. They are: identifying error, describing error, explaining error, and error evaluation. While data collection techniques were adapted from Mayring (2014). They are coding, revision, final coding, and result. From the result of the research, the researchers concluded that the errors found from respondents could be classified as local errors. It implies that those errors only affect a single element of sentence, but do not prevent a message from being hard.
Mohamad Fadhili Yahaya
Amalul Umam
Changes in Curriculum lead to changes in teaching and learning processes as well as new ways to demonstrate best practices for increasing students’ achievement. The Curriculum 2013 suggests teachers to use authentic materials and requires them to apply authentic assessments. It is quite challenging for English teachers because this condition creates problems especially for novice teachers. Therefore, they need to have prior knowledge and personal experience related to teaching practice and situation. In this study, authentic materials and authentic assessments were implemented in pre-service-English-teacher classroom at a university in Bogor, specifically in listening class, in order to familiarize them to the kind of materials and assessments. Action research was employed where documentation, observation, questionnaire, and interview were used to collect the data. The result shows that the integration of authentic materials and authentic assessment in EFL classroom helped the stude...
Over the years, the quality and effectiveness of teaching have been the priority of the Indian government in improving the education sector, particularly the teaching reading comprehension skill among teachers. This paper investigates the relationship between self-efficacy on teaching reading comprehension skills among secondary school teachers in Telangana State, India. The study is a quantitative research of the survey type. The total of 2019 teachers of government owned secondary schools constituted the population, simple random sampling technique was used to select 192 teaching English language across all secondary schools in the state. Two sets of questionnaire title Teacher self-efficacy Scale (TSES) and Teaching Reading Comprehension Skills which was adapted from Progress International Literacy Study (PIRLS) were used to seek information from English teachers. Pearson product moment correlation statistics was used to analysis the data and the results of the findings reve...
eko suhartoyo
Deriving from the postulation that learning strategies are shaped from a learning situation, which is inseparable from its socio-cultural context. A paradigm has shifted language learning strategies (LLSs) studies in the new perspective of situational-based research. Using a narrative approach, this study examined one female pre-service teacher of an English education major in occupying strategies to fulfill the learning needs. To meet with the data, semi-structured interviews were carried out for the participant through a series of interconnected questions. The results marked that the use of learning strategies varied in a distinct learning situation, including the strategies to achieve the learning goal as well as to encounter the obstacles in English learning. Thus, this study has emphasized the feasibility of LLSs in context. Suggestions were also presented at the end of this paper. HIGHLIGHTS: The use of strategies is varied in changing learning situation. The appropriate strat...
yuli astutik
This research article described the interactional strategies used by low learners in public qualitative study on whether or not low learners used the aspects of interactional strategies was the main focus. This paper also aimed to know what aspects mostly used and the factors that cause this problem. Observing and interviewing to six subjects regarding on the use of interactional strategies; exemplification, confirmation checks, comprehension checks, repetition, clarification requests, repetition requests, exemplification requests, and assistance appeal were carried out. Finding interactional strategies in all situations. Four students have applied 3 were as the speaker. In another side, when they were the listeners, they The result showed that repetition was the interactional strategy mostly used by low learners. Nevertheless, the reason of using it was not proper reason. The further finding indicated some factors cause low lear use four interactional strategies such as fluency, grammar, lack of vocabulary and pronunciation in addition to the English practice merely in the formal situation.
RELATED PAPERS
JEELS (Journal of English Education and Linguistics Studies)
JEELS (Journal of English Education and Linguistics Studies) , rif_elbarz mahbub
Andi Susilo
mas darul ihsan
Feny Martina,M.Pd
Dedi Rahman Nur
Indah Ayu Widuna
Social and Management Research Journal
Mohd Effendi Ewan Mohd Matore
Jamie Wallin
The Asian ESP Journal
Asmara Shafqat
Kartika Marta Budiana
sri rachmajanti
Armeria Wijaya
Dr. Lestari Setyowati , M.Pd
AMATUL HAFEEZ ALVI , Ash Alvi
Nuria Setiarini
Journal of Language and Education
DR. PRODHAN MAHBUB IBNA SERAJ
JOPR IAIN Salatiga
PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences
FAIZAL RISDIANTO
putri anisa
Journal of English Language Teaching and Linguistics
sugirin sugirin
Inayati Fitriyah Asrimawati inayati0017pasca.2018
YUSUP SUPRIYONO
IJET (Indonesian Journal of English Teaching)
Arif Nugroho
Dr. Hussam Rajab
International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM)
Muhammad Ashar
Elsya : Journal of English Language Studies
Mohammad Naim Rahim
KnE Social Sciences
COUNS-EDU: The International Journal of Counseling and Education
yenni rozimela
Arif Husein Lubis
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology
Dr. Kashif Ishaq , Qasim Ali
diani nurhajati
EduLite: Journal of English Education, Literature and Culture
Dedi Irwansyah
Farid Rokhman
International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research
Nurul Binti Azlan
English Language Teaching
Panna Chaturongakul
sebastianus menggo
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Conditions for approaching shared value creation management in the Japanese rice flour-related business: application of mixed methods research
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024

Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Lily Kiminami ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1784-6283 1 ,
- Shinichi Furuzawa 1 &
- Akira Kiminami 2
This is the second paper on creating shared value (CSV) management in Japanese rice flour-related businesses conducted by the same authors. In the first study, the relationships among business philosophies, business strategies and business outcomes of rice flour-related corporates in Japan were clarified using structural equation modeling (SEM) and cognitive mapping of questionnaire survey results. The management philosophy, effective altruism, influences business strategies (potential head market, tail market, organizational learning, and proposals from stakeholders) of rice flour-related corporates, inducing innovation and determining current business performance and future prospects for shared value creation. The business performance reflects their expectations for the rice flour market, and influences the direction of market development. In addition, we showed a need for policy innovations that strengthen effective altruism and create shared value through organizational learning of the stakeholders in rice flour-related businesses. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to clarify conditions for approaching CSV management in domestic rice flour-related businesses by applying mixed methods research (MMR). Specifically, a latent class analysis (LCA) was introduced to classify the management characteristics of rice flour-related businesses with survey results, and a qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) conducted on the CSV management entities extracted from the LCA to clarify the necessary and sufficient conditions for achieving CSV management. The results revealed that there are very few rice flour-related businesses in Japan that have approached CSV management, and sufficient conditions for approaching CSV management in rice flour-related businesses are a combination of effective altruism and various management strategies (long tail/organizational learning/innovation/stakeholder proposals). Therefore, we conclude that to achieve a sustainable regional development of rice flour-related businesses, policy innovations that integrate pull-type and push-type strategies are important.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The production volume of rice for rice flour (a part of new demand rice) in 2022 reached 45,903 tons in Japan. The top five prefectures of Niigata (12,731 tons; 27.7%), Tochigi (8035 tons; 17.5%), Saitama (4395 tons; 9.6%), Akita (2569 tons; 5.6%), and Ishikawa (2176 tons; 4.7%) account for 65.1% of the whole country (MAFF 2023 ). The reason why the production of rice for rice flour is concentrated in specific regions is that it is necessary to develop actual users and to collaborate with primary processors, secondary processors, and distributors to receive subsidies (Kinoshita 2012 ). On the other hand, a survey report on the use of rice flour by food manufacturers conducted by the NPO Domestic Rice Flour Promotion Network ( 2017 ) pointed out that the characteristics of consumers targeted by companies that sell domestically produced rice flour products are those with high health consciousness and allergies, and insisting on `domestic production' and `local production for local consumption'; the high price of rice flour is the most important issue in expanding its usage.
However, through an interview survey, Takahashi ( 2012 ) revealed that the formation of a self-sustaining industrial cluster in Kumamoto Prefecture is contributing to the development of a rice flour-related business aimed at solving social issues. In particular, by collaborating with producers, distributors, processing companies, and related research institutions, flour milling companies have succeeded in reducing costs and creating demand by introducing high-yield rice.
As an empirical study on the CSV management of rice flour-related corporates in Japan, Kiminami et al. ( 2024 ) clarified the relationships among business philosophy, business strategy, and business outcome of rice flour-related corporates by introducing structural equation modeling (SEM) and cognitive map analysis to the results of a questionnaire survey. The results revealed that the management philosophy (Effective Altruism, and member of the Rice Flour Association) of rice flour-related corporates influences their business strategies (potential head market, tail market, organizational learning, and proposals from stakeholders) which induce innovation and determine business performance (current performance and future prospects for shared value creation), and the business performance reflects their expectations for the rice flour market and influences the direction of market development. Based on the analytical results, the research suggested a policy innovation that strengthens effective altruism and creating shared value through organizational learning of stakeholders in rice flour-related businesses.
Therefore, the purpose of our study is to clarify the conditions for approaching CSV management in the domestic rice flour-related businesses following up the results of previous study. The methodology of this research is unique in that latent class analysis (LCA) was introduced to the survey results for classifying the management characteristics of rice flour-related businesses, and a qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) was conducted on the CSV management entities extracted from the LCA to clarify the necessary and sufficient conditions for approaching CSV management. Based on the empirical analysis results, we will derive policy implications of regional science.
2 Literature review
2.1 creating shared value.
Creating shared value (CSV) is the idea that companies create social value by working to solve social needs and problems, and as a result, economic value is created (Porter and Kramer 2011 ). CSV is often criticized as being vague in its differences from corporate social responsibility (CSR). According to Dembek et al. ( 2016 ), the definition of CSV is roughly divided into those that emphasize conceptual theory and those that emphasize the relationship with real society. The former includes Porter and Kramer, and the later includes Maltz et al. ( 2011 ). These different positions on the definition of CSV are also reflected in different views on the relationship between CSV and sustainability. In addition, as pointed out by Horings ( 2015 ), there are three ways to understand regional value: economic, intentional, and symbolic approaches. In terms of sustainable regional development, it is thought that the companies introducing CSV have a formation process with management philosophy and market strategy that is different from the companies without introducing CSV.
Although there are no studies targeting the rice industry or rice flour, there are some empirical analyses on shared value creation in the agriculture and food sectors. Wiśniewska-Paluszak and Paluszak ( 2019 ) found that companies engaged in CSV in Polish agribusiness are gaining new competitive advantages through solving social issues and redefining business models through cooperation with stakeholders. Additionally, Saraswati ( 2021 ) pointed out that Indonesian food companies create value by placing the highest priority on consumers, while also creating shared value with society, employees, the environment, and business partners. Furthermore, using mixed methods research, Kiminami et al. ( 2022 ) found that social entrepreneurs as the creative class in Japanese urban agriculture are approaching shared value creation while generating cognitive innovation through organizational learning with stakeholders.
2.2 Effective altruism
Effective altruism (EA) is an evidence- and theory-based philosophy or movement that seeks to maximize the improvement of the world, with particular emphasis on the areas of global poverty, human existential risk, and animal welfare (MacAskill 2015 ). EA is particularly useful for maximizing social impact with limited resources when the scale is large (social problems that can be solved), the visibility is low (niche), and there are no other viable alternatives. The idea of EA enables impact assessment and prioritization of projects that solve social problems, and many efforts are already being put into practice. As a practical initiative in the agriculture and food sectors, there is a movement to promote the production of alternative proteins (Good Food Institute), as well as R&D and market entry by private companies. In addition, research is being conducted to focus on the awareness and behavior of individuals who engage in donation behavior based on EA, and to analyze the factors that promote and inhibit it (e.g., Jaeger and van Vugt 2022 ). However, there are no examples of empirically analyzing the decision-making and actions of existing businesses and companies from the perspective of EA.
2.3 Social innovation in rice market
Kiminami et al. ( 2021a ) pointed out that the bottleneck in creating innovation in Japan’s rice cultivation to date is that agricultural policies (push policies), including rice policies, have not had the expected effects. Although rice production adjustment has been officially abolished, it still exists as a game equilibrium and customary system, and even if there are structural reforms in the economic realm, cultural belief systems (peasantism) dominate the political and social realm of the system.
On the other hand, Christensen et al. ( 2019 ) classify innovation into three types: sustaining innovation, efficiency innovation, and market-creating innovation, and point out the following: market-creating innovations create new markets that serve people for whom products either did not exist or where existing products were not affordable for a variety of reasons, making complex and expensive products far more affordable. Market-creating innovation is a strong foundation for sustained economic prosperity; for markets to be created and sustained, they must be profitable, or at least have the prospect of producing profits in the future. It is also important to create jobs and, most importantly, to change the culture through new markets. On the other hand, it is pointed out that because a society’s institutions reflect the culture and values of its people, a pull strategy is needed, rather than simply pushing effective institutions.
Social innovation (SI) is a new solution to meet social needs. It also leads to new or better capabilities and relationships, and better utilization of resource assets, increasing a society's ability to act (Murray et al. 2010 ). Europe explicitly incorporated SI in its food and agricultural innovation policies in 2010 (European Commission 2010 ). In 2020, the "Farm to Fork Strategy (F2F)" was launched with the aim of creating a sustainable food system, and it is introducing policies that place particular emphasis on addressing environmental and climate change issues (European Commission 2020 ). These can be said to be policy innovations that combine push and pull strategies to promote SI in the food and agriculture sector by popularizing the CSV-type management.
2.4 Long tail theory and corporate strategy
Traditionally, sales at brick-and-mortar stores focused on best-selling products, which accounted for about 20% of the total sales, based on the Pareto principle (80% of sales are generated by 20% of good customers). However, consumer choice theory in economics has been extended to accept considerations, such as the cost of information gathering, the incompleteness of information, and the limitations of consumers’ cognitive abilities in gathering and processing information.
As Anderson ( 2008 ) has argued, e-commerce and other new technologies improve efficiency by facilitating the entry of new producers and innovations, creating a “long tail” of niche products. And reducing the market share of previously popular products. However, the development of a long-tail market requires not only an efficient distribution system for a wide variety of products and services, but also the ability to meet consumers with diverse niche needs and provide products and services that meet their needs. Salvador et al. ( 2020 ) found that business success in long-tail markets requires reducing the cost of creating and maintaining large assortments on the supply side and exploring large assortments on the demand side.
However, the characteristics of a company’s long-tail strategy differ depending on the characteristics of the business (e.g., online retailer, brick-and-mortar retailer, manufacturer, etc.). Therefore, to establish a long-tail market, promotions that increase latent demand in the tail, a system that can supply many niche products at low prices, mechanization, and mass customization to efficiently produce a wide variety of products in small quantities are necessary (Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2019 ). Furthermore, Kiminami et al. ( 2021b ) explicitly used the long-tail market concept to study the Japanese rice market. The results showed that rice consumption can be expanded through market-creating innovation to expand the head portion by satisfying latent needs for rice, and expand the tail potion by doing business that leverages consumers’ internal motivation.
2.5 Organizational learning
There are various theories on organizational learning, each with different learning subjects, purposes, processes, and styles. Huber ( 1991 ) describes organizational learning as a process by which an organization acquires new information and knowledge, periodically modifies that knowledge, and changes the organization’s potential scope of action. Senge ( 2006 ) considers an organization that continuously develops its ability to adapt and change to be a learning organization, with growth in five areas: systems thinking, personal mastery, mental models, building a shared vision, and team learning. According to Iriyama ( 2019 ), in business administration, innovation is a part of organizational learning in a broad sense, and it is common to acquire new knowledge through learning and reflect it in organizational outcomes.
Tippins and Sohi ( 2003 ) used structural equation modeling to evaluate the introduction of organizational learning in IT companies using four indicators (knowledge acquisition, knowledge diffusion, knowledge interpretation, and organizational memory), and found that organizational learning has an impact on corporate performance. Furthermore, Attia and Eldin ( 2018 ) analyzed the impact of knowledge management capabilities, organizational learning, and supply chain management on organizational performance of food companies in Saudi Arabia, and found that organizational learning improves corporate performance. Furthermore, Kiminami et al. ( 2024 ) clarified the relationship between a company’s management philosophy, management strategy, and management performance.
3 Analytical framework and methods
3.1 analytical framework.
Based on the results of the literature review above, we frame our research questions as follows: What is the current situation of CSV-type management in rice flour-related businesses in Japan? What are the conditions for approaching CSV management under the circumstances? If policy innovation is required for rice flour-related businesses? The analytical framework for this study is shown in Fig. 1 . To achieve the research purpose, we formulate the following hypotheses for verification. In addition, in this study, latent class analysis (LCA) will be applied to verify Hypothesis 1 and qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) will be applied to verify Hypothesis 2.
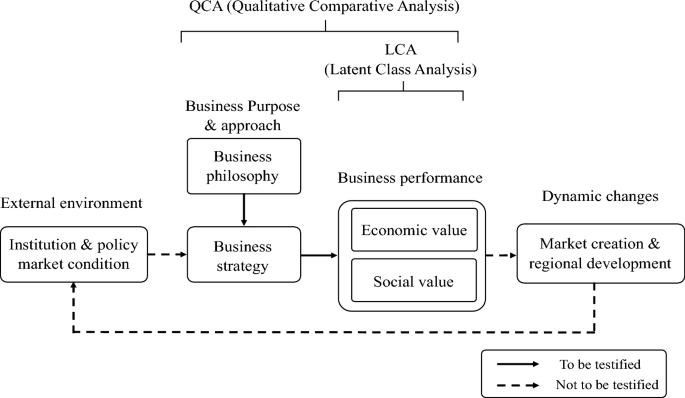
Analytical framework
Hypothesis 1: There are very few rice flour-related businesses in Japan that have approached CSV-type management.
Hypothesis 2: A sufficient condition for approaching CSV-type management in rice flour-related businesses is the combination of the management philosophy of effective altruism and various management strategies (long tail/organizational learning/innovation/stakeholder proposals).
3.2 Data and analysis methods
3.2.1 questionnaire survey.
The questionnaire was distributed to retailers and stores listed on each Agricultural Administration Bureau website, members of the National Rice Flour Association (only those listed on the website), companies supporting the R10 Project, Footnote 1 and rice flour distributors. The survey was conducted by mail in September 2022, and the final distributed number was 974 (excluding those to unknown addresses), and the returned number was 240. The main asked questions include basic attributes (industry classification, number of employees, sales), effective altruism, market potential, organizational learning, innovation, and management performance. Table 1 is a summary of surveyed attributes. Looking at the industries, “food manufacturing” accounts for more than half, followed by “agriculture, forestry and fisheries”, “food distribution”, and “restaurant”. In terms of sales, “10 million yen to less than 30 million yen” was the most common, followed by “100 million yen to less than 500 million yen” and “less than 10 million yen”. The percentage of companies with sales of 500 million or more is about 24.3%, and large companies account for a certain number. In terms of number of employees, “0 to 5 or less” was the highest, followed by “6 to 20 or less” and “21 to 50 or less”. In addition, 231 samples were used in the analysis, excluding samples whose basic attributes were not answered (Appendix 1 ).
3.2.2 Mixed methods research
Traditional research has adopted either the “qualitative method”, which understands phenomena by describing them in detail and accurately, or the “quantitative method”, which captures phenomena quantitatively and understands them through statistical analysis. However, to elucidate complex phenomena and problems, the data to be collected and analysis methods may become complex. For this reason, a mixed methods approach that integrates qualitative and quantitative research is currently attracting attention as a research method.
Creswell and Plano Clark ( 2017 ) summarized mixed methods approaches into three types: convergent designs, explanatory sequential designs, and exploratory sequential designs. In a convergent design, quantitative and qualitative data are collected and analyzed separately, and the results of the analyses are combined or compared. In an explanatory sequential design, quantitative data are collected and analyzed first, then qualitative data are collected and analyzed to explain the results. An exploratory sequential design first explores an issue through qualitative data collection and analysis, followed by quantitative data collection and analysis to develop measurements and interventions based on the findings. The mixed methods approach used in this study collects quantitative data from a questionnaire survey to extract CSV-type management through latent class analysis (LCA), and analyses the conditions for realizing CSV-type management through QCA (qualitative comparative analysis). Therefore, it is a mixed methods approach with an explanatory sequential design.
3.2.2.1 Latent class analysis (LCA)
Latent class analysis is a method that identifies the latent types (= latent classes) that a population of respondents consists of and reveals the structure of each (Bollen 2002 ; Magidson 2020 ). In recent years, researches applying LCA have been increasing in those such as consumer knowledge and environmentally conscious behavior in food selection (Peschel et al. 2016 ), joint venture decision-making in agriculture (Kragt et al. 2019 ), and farmers' willingness to pay for animal welfare investments (Peden et al. 2019 ). Therefore, it is also effective in analyzing long-tail markets, where diversity of preferences and behavioral patterns of economic agents is important.
3.2.2.2 Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA)
QCA is a standard method for drawing causal relationships from a small number of cases. QCA is innovative in that it uses set theory and Boolean algebra to systematize formal procedures for inferring causal relationships from case comparisons. Research results using QCA have increased rapidly since the 2010s, and have been published mainly in business administration, political science, environmental studies, sociology, etc. (Oana et al. 2021 ). The method characteristics of QCA are that small data can be analyzed, even fuzzy concepts can be analyzed, integrated analysis with cases is easy, and causal complexity (inferring complex causal paths from cause to effect) can be revealed from cases.
QCA is effective in bridging quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis, so it is effective to use it as one of the analysis methods in mixed methods research. For example, in an empirical study that combines SEM and QCA, Torres et al. ( 2021 ) used SEM and fsQCA to clarify the process and necessary and sufficient conditions for the influence of gamification on consumer brand loyalty.
4 Analytical results
4.1 results of latent class analysis (lca).
Here, we use the technique of latent class analysis (LCA) to classify rice flour-related businesses. As a result of searching for the optimal number of classes using Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), the optimal number was two for the BIC standard and four for the AIC standard (Appendix 2 ). Considering interpretability, the number of classes was finally set to four (AIC = 2661.833, BIC = 2947.554, Chi-square value = 1010.19). Table 2 shows the analysis results when the number of classes is specified as four, and shows the proportion of each class and the expected probability for each question item.
Class 1 businesses selected many items for “current performance'' and many answered “Strongly agree'' to all items for “future prospects'', so these businesses can be interpreted as CSV-type managements (attribution probability:18.3%). Among Class 2 businesses, those who answered "no selection" for "current performance" and "strongly disagree" or "somewhat disagree" for all items of "future prospects" were the most likely, and they can be interpreted as non-CSV type I managements (attribution probability 13.4%). On the other hand, Class 3 businesses have "1" or "4" selections for "current performance" and answered "somewhat agree" to all items for "business prospects", and they can be interpreted as a weak CSV or CSR type managements (attribution probability: 39.3%). Finally, Class 4 businesses have the second highest percentage of respondents who answered “no selection” for “current performance” and the largest number of respondents responded “neither agree nor disagree” for all items of “future prospects”, they can be interpreted as non-CSV type II managements (attribution probability: 29.0%).
Next, we performed a cross-tabulation analysis based on the above LCA results, and found that CSV-type management is characterized by "secondary processing", "membership of the Rice Flour Association", and a “management philosophy” of effective altruism (Table 3 ).
On the other hand, regarding management strategy, it was found that CSV-type management emphasizes “latent demand'' (market potential), organizational learning, potential head markets, tail markets, and proposals from stakeholders (Table 4 ). Furthermore, regarding innovation, CSV-type management emphasizes all four innovation types (Table 5 ), and regarding management results, it emphasizes both "current performance" and “future prospects” (Table 6 )
To summarize the results of LCA and cross-tabulation analysis, CSV-type rice flour-related businesses have following characteristics: secondary processing and sales, members of related associations, and a high level of effective altruism as management philosophy. This means that CSV-type companies place the highest priority on effectively resolving social issues through rice flour-related businesses and are striving for sustainable business development. In addition, the companies’ management strategy for realizing this goal is to view the rice flour market as a niche market with high potential, and to stimulate multifaceted innovation related to rice flour through organizational learning and collaboration with stakeholders. As a result, the business performances are improving. However, there are very few corporates that have approached CSV management in rice flour-related businesses (Class 1: 18.3%). Our Hypothesis 1 is supported.
4.2 Results of qualitative comparative analysis (QCA)
The QCA in this study is performed with reference to previous research (Tamura 2015 ; Yokoyama and Azuma 2022 ). The flow of analysis is: (1) setting up and coding of causal conditions and outcome, (2) analysis of necessary conditions, and (3) analysis of sufficient conditions. The analysis used the software packages of R and SetMethods for QCA (Oana et al. 2021 ; Mori 2017 , 2018 ).
Based on the literature review and analysis results of previous research, we set and coded the following five factors as the cause conditions for the success of rice flour-related businesses in creating shared value (Table 7 ). In this research, we set "future business prospects" as an outcome and conduct analysis. The data matrix after coding is shown in Appendix 3 .
First, we conduct a necessary condition analysis for approaching CSV management in rice flour-related businesses. The results of the analysis are shown in Table 8 , with "future prospects" as the business outcome. In general, the standard for the degree of consistency in necessary condition analysis is high, with a value of 0.9 or higher being considered as a guideline. Among the analysis results of this research, there are no causal conditions for which the degree of consistency is 0.9 or higher. Therefore, there are no factors that can be said to be necessary conditions for approaching CSV management in rice flour-related businesses. However, among the positive groups, the one with the highest degree of consistency is stakeholders (0.71), followed by innovation (0.70) and effective altruism (0.66).
Second, we complete a truth table to explore the sufficient conditions for CSV success in rice flour-related businesses. Footnote 2 In standard QCA analysis, there are three solutions: “complex solution”, “simplest solution”, and “intermediate solution”, each with different assumptions regarding logical residuals. Since it is generally recommended to use an “intermediate solution”, the results of the intermediate solution are used here as well. The completed truth table is shown in Appendix 4 .
Table 9 and Fig. 2 show the results of the “intermediate solution” regarding future prospects. The logical formula are derived from I to V as follows. The consistency level of the results was set at 0.8. All directional predictions of causal conditions were assumed to be “present”. The consistency of solution is 0.851 and the coverage is 0.857, so the results are generally good. The inherent coverage is all less than 0.1. There are four relevant combinations: effective altruism and stakeholders; organizational learning and innovation; long tail and innovation; and effective altruism and long tail. It can be said that an appropriate combination of these causal conditions is necessary to improve the business prospects of CSV-type companies.
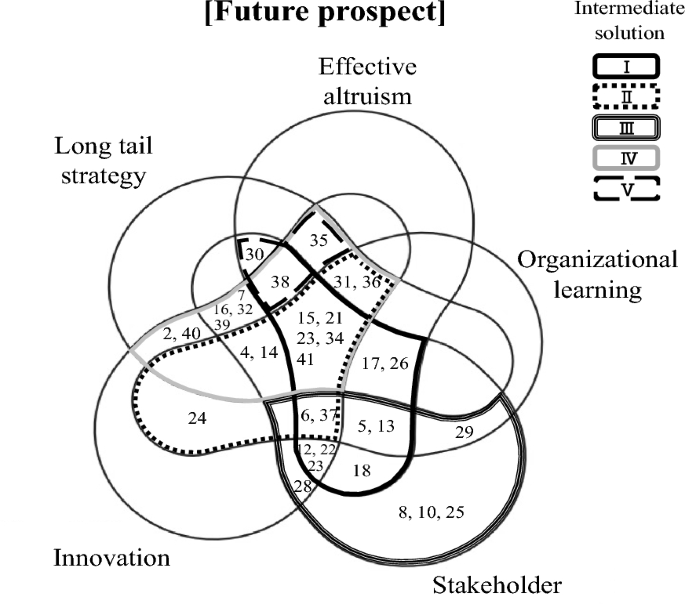
Venn diagram of intermediate solution for sufficiency conditions
FuzEfAltru2*FuzStHold (I)
+ FuzOL*FuzInno (II)
+ ~ FuzLongTail*FuzStHold (III)
+ FuzLongTail*FuzInno (IV)
+ FuzEfAltru2* ~ FuzOL*FuzLongTail (V)
To summarize the results of QCA, there are no factors that can be said to be necessary conditions, and the relative importance of stakeholders, innovation, and effective altruism was confirmed. On the other hand, regarding sufficient conditions, it has been revealed that the combinations of the management philosophy of effective altruism and various management strategies (innovation, long-tail, stakeholder, and organizational learning) are important. Companies that carry out CSV-type management related to rice flour are causing SI through businesses that aim to solve social issues. Our Hypothesis 2 is supported.
5 Conclusions and policy implications
In this study, we conducted an analysis using mixed methods research (MMR) with the aim of clarifying the conditions for approaching CSV management in domestic rice flour-related businesses. Based on the above-mentioned analysis, we obtained the following results.
Table 10 shows the types of policies based on the strengths and weaknesses of push-type strategies and pull-type strategies. Japan's rice policy to date has focused on a push-type strategy (Policy B) in the absence of a pull-type strategy, and production has been promoted in a direction that does not match the latent needs of consumers or social needs. There was a lack of perspective on fostering and expressing the entrepreneurship of producers. As a result, market-creating innovations that can increase both economic and social value have not been realized. In general, the development of the rice flour-related business is strongly determined by the regional supply structure of raw material rice both in terms of price and quality, and is influenced by overall rice policy. Like the overall rice policy, the policy for rice flour-related business emphasizes a push-type strategy at the production stage of raw material rice (Policy B), and some pull-type strategies in the distribution, processing, and sales stages. Under the circumstances, only some of the rice flour-related businesses that engaged in distribution, processing, and sales are approaching CSV management. Therefore, CSV-type managements in rice flour-related business are in the infant stage. Considering the situation at the regional level, Kumamoto Prefecture (type C) has a strong tendency toward a pull-type strategy, and Niigata Prefecture has a push-type strategy (type B). Footnote 3
To promote rice flour-related businesses to approach CSV management in the future, it is necessary to have policy innovation that integrates pull-type and push-type strategies (Policy A). First, there is a need to form clusters for rice flour-related businesses crossing boundaries of industries and regions. The current push-type strategy emphasizes the formation of food system for rice flour within the regions without rationality. Second, it is important not only to respond to consumers' latent needs and increase consumption, but also to bring about a change in stakeholders’ awareness in the form of a cultural change regarding rice flour (both consumer side and producer/supply side). Thirdly, it is important for each rice flour-related business to evolve the management philosophy of effective altruism and constantly review and explore management strategies through systematic triple-loop learning (Barbat et al. 2011 ). Finally, rice flour-related businesses are expected to expand from micro-level SI activities to macro-level activities that transcend industries, regions, and national borders, and have an impact on social structures. By facing the issues that have been neglected in the food system such as social needs (food safety and health, etc.) and social value (food security and climate change, etc.), a shared vision can be built through organizational learning.
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
The R10 project is an initiative implemented in Niigata Prefecture as a movement to replace 10% or more of wheat flour consumption with domestically produced rice flour. Efforts are underway to develop large-scale users, develop demand in new fields, and spread the use of the product in household consumption. Companies that support the project will be registered as supporting companies.
In a complete truth table, when there are five causal conditions, there are 2 5 = 32 possible combinations of existence/absence of the causal conditions.
Niigata Prefecture is the region with the highest production of rice as well as raw material rice for flour. Most of the rice flour-related businesses have been a response to the adjustment of rice production. On the other hand, Kumamoto Prefecture is not a major rice-producing prefecture, but its rice flour-related businesses have been promoted through private initiatives. This has led to the development of popular varieties for rice flour such as Mizuho no Chikara. Additionally, a council made up of rice flour-related businesses has become a platform for innovation creation.
Anderson C (2008) The longer long tail: How endless choice is creating unlimited demand, Hyperion
Attia A, Eldin IE (2018) Organizational learning, knowledge management capability and supply chain management practices in the Saudi food industry. J Knowl Manag 22(69):1217–1242. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-09-2017-0409
Article Google Scholar
Barbat G, Boigey P, Jehan I (2011) Triple-loop learning: theoretical framework, methodology and illustration (an example from the railway sector). Projectics 8(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3917/proj.008.0129
Bollen K (2002) Latent variables in psychology and the social science. Annu Rev Psychol 53:605–634. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135239
Christensen CM, Ojomo E, Dillon K (2019) The prosperity paradox: how innovation can lift nations out of poverty. Harper Business, New York
Google Scholar
Creswell JW, Plano Clark V (2017) Designing and conducting mixed methods research, 3rd edn. SAGE Publications, New York
DembekK SP, Bhakoo V (2016) Literature review of shared value: a theoretical concept or a management buzzword? J Bus Ethics 137:231–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-015-2554-z
European Commission (2020) Farm to fork stratgy: for a fair, healthy and environmentall-friendly food system. European Union. https://food.ec.europa.eu/document/download/472acca8-7f7b-4171-98b0-ed76720d68d3_en . Accessed 5 Apr 2024
European Commission (2010) Europe 2020: a strategy for smart, sustainable and inclusive growth. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=COM:2010:2020:FIN:en:PDF . Accessed 5 Apr 2024
Horlings LG (2015) Values in place: a value-oriented apporach toward sustainable place-shaping regional studies. Regional Science 2(1):257–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681376.2015.1014062
Huber GP (1991) Organizational learning: the contributing processes and literatures. Organ Sci 2(1):88–115
Iriyama A (2019) Management theories of the global standard. Diamond Inc, Tokyo ( in Japanese )
Jaeger B, van Vugt M (2022) Psychological barriers to effective altruism: an evolutionary perspective. Curr Opin Psychol 44:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.008
Kiminami L, Furuzawa S, Kiminami A (2021a) Transformation of Japan’s rice policy toward innovation creation for a sustainable development. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci 5:351–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-020-00175-3
Kiminami L, Furuzawa S, Kiminami A (2021b) Rice policies for long-tail market-creating innovations: empirical study on consumers’ cognition and behavior in Japan. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci 5:909–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-021-00209-4
Kiminami L, Furuzawa S, Kiminami A (2022) Exploring the possibilities of creating shared value in Japan’s urban agriculture: using a mixed methods approach. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci 6:541–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-022-00233-y
Kiminami L, Furuzawa S, Kiminami A (2024) Empirical study on the rice flour business in Japan: introducing structural equation modeling (SEM) and cognitive mapping. Jpn Jo Agric Econ 26:1–22
Kinoshita K (2012) Towards the diffusion of rice flour. Bull Toyohashi Sozo Jr Coll 29:31–38 ( in Japanese )
Kragt ME, Lynch B, Llewellyn RS, Umberger WJ (2019) What farmer types are most likely to adopt joint venture farm business structures? Aust J Agric Resour Econ 63:881–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12332
MacAskill W (2015) Doing good better: a radical new way to make a difference. Guardian Faber Publishing, London
MAFF (2019) Interview with experts in the Japanese food manufacturing industry. Commissioned project survey of comparative analysis for industrial structure in the food manufacturing industry in 2019 ( in Japanese ) https://www.maff.go.jp/j/budget/yosan_kansi/sikkou/tokutei_keihi/R1itaku/R1ippan/attach/pdf/index-43.pdf . Accessed 18 Oct 2023
MAFF (2023) Production volume of newly demanded rice produced in 2022 ( in Japanese ). https://www.maff.go.jp/j/seisan/jyukyu/komeseisaku/ . Accessed 14 Sept 2023
Magidson J, Vermunt JK, Madura JP (2020) Latent class analysis: foundation entries. SAGE Publications, SAGE Research Methods Foundations
Maltz E, Thompson F, Ringold DJ (2011) Assessing and maximizing corporate social initiatives: a strategic view of corporate social responsibility. J Public Aff 11(4):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.384
Mori D (2017) How to use software for qualitative comparative analysis (QCA): fs/QCA and R (1). Kumamoto Law Rev 140:250–209 ( in Japanese )
Mori D (2018) How to use software for qualitative comparative analysis (QCA): fs/QCA and R (2). Kumamoto Law Rev 141:388–348 ( in Japanese )
Murray R, Caulier-Grice J, Mulgan G (2010) The open book of social innovation. The Young Foundation
NPO Domestic Rice Flour Promotion Network (2017) Survey for companies regarding rice flour ( in Japanese ). https://www.maff.go.jp/j/seisan/keikaku/komeko/attach/pdf/index-74.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2023
Oana IE, Schneider CQ, Thomann E (2021) Qualitative comparative analysis using R: a beginner’s guide. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Peden RSE, Akaichi F, Camerlink I, Simon LAB (2019) Pig farmers’ willingness to pay for management strategies to reduce aggression between pigs. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0224924. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224924
Peschel AO, Grebitus G, Steiner B, Veeman M (2016) How does consumer knowledge affect environmentally sustainable choices? Evidence from a cross-country latent class analysis of food labels. Appetite 106:78–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.02.162
Porter ME, Kramer MR (2011) The big idea: creating shared value (How to reinvent capitalism-and unleash a wave of innovation and growth). Harv Bus Rev 89(1–2):62–77
Salvador F, Piller FT, Aggarwal S (2020) Surviving on the long tail: an empirical investigation of business model elements for mass customization. Long Range Plan 53(4):101886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2019.05.006
Saraswati E (2021) Analysis of creating shared value in the food and beverage industry. Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi Dan Bisnis 16(1):154–162. https://doi.org/10.24843/JIAB.2021.v16.i01.p10
Senge PM (2006) The fifth discipline: the art and practice of the learning organization. Doubleday, New York
Takahashi M (2012) The development of the Kumamoto food industry cluster. Yokohama Bus Rev 33(1):71–85 ( in Japanese )
Tamura M (2015) Qualitative Comparative Analysis of business cases: exploring cause and effect using small data, Hakuto-shobo, Tokyo ( in Japanese )
Tippins MJ, Sohi RS (2003) IT competency and firm performance: is organizational learning a missing link? Strateg Manag J 24(8):745–761. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.337
Torres P, Augusto M, Neves C (2021) Value dimensions of gamification and their influence on brand loyalty and word-of-mouth: relationships and combinations with satisfaction and brand love. Psychol Mark 39(1):59–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21573
Wiśniewska-Paluszak J, Paluszak G (2019) Examples of creating shared value (CSV) in agribusiness in Poland. Ann Pol Assoc Agric Agribus Econ XXI 2:297–306. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0013.2198
Yokoyama N, Azuma S (2022) Towards formalization of analytical approaches to tackle issues of retail business models: exploring the methodological strengths of process tracing method and qualitative comparative analysis (QCA). Jpn Mark J 41(4):53–64. https://doi.org/10.7222/marketing.2022.021 . ( in Japanese )
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI under Grant No. 20K06256 (Analysis of social entrepreneurship in urban agriculture: Creating shared value through social business), No. 20H03089 (Comprehensive study on structure and process of entrepreneurship in agriculture and rural sector), and No. 20K12280 (Analysis on innovation of social enterprise for sustainable agriculture and food systems). The authors wish to express our gratitude for the support.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Niigata University, Niigata, Japan
Lily Kiminami & Shinichi Furuzawa
The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Akira Kiminami
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lily Kiminami .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 11 .
See Fig. 3 .
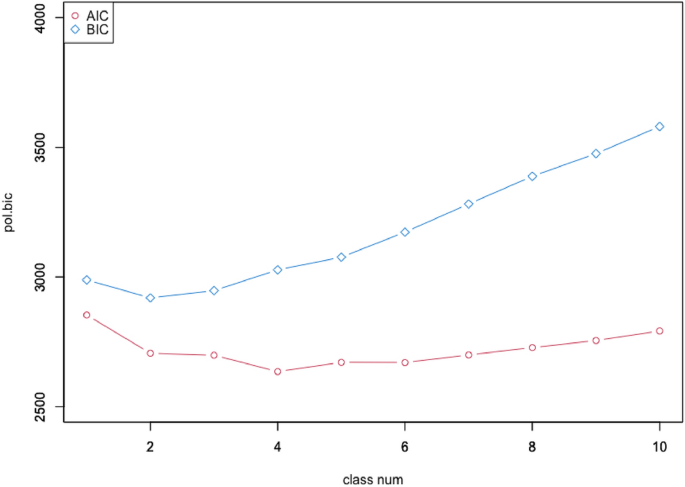
Scree plot of AIC and BIC versus number of latent classes
See Table 12 .
See Table 13 .
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team .
About this article
Kiminami, L., Furuzawa, S. & Kiminami, A. Conditions for approaching shared value creation management in the Japanese rice flour-related business: application of mixed methods research. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-024-00342-w
Download citation
Received : 18 December 2023
Accepted : 18 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-024-00342-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Rice flour-related business
- Creating shared value (CSV)
- Latent class analysis (LCA)
- Qualitative comparative analysis (QCA)
- Mixed methods research (MMR)
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Analysis and research on mechanical stress and multiobjective optimization of synchronous reluctance motor
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Target Situation Analysis (TSA) Needs analysis was firmly established in the mid-1970s (West, 1998). In the earlier periods needs analysis was mainly concerned with. linguistic and register ...
Research Article . From needs analysis to development of a vocational English language curriculum: A practical guide for practitioners . Suat Kaya . 1. Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen University, Turkey . This study was conducted to examine the needs of the students of cabin services program regarding English in order to guide the design of a ...
The aim of this study is to analyze research methods, data collection tools, and data analysis methods of the needs assessment studies conducted in the language education and teaching process. In ...
Grammatical needs analysis is related to the frequency in which grammatical forms are used in certain communicative situations (Çelik, 2003). Needs analysis in the language education process devel-ops within the scope of certain objectives depending on the purpose of the research. Objectives of the needs analysis in
Needs analysis is important because the results are relevant for specifying objectives, procedures, content, materials, methods, and outcomes assessment at the task, course, or program level (Flowerdew & Peacock, 2001).Hyland's definition highlighted the distinctive approach of ESP (English for specific purposes) to language teaching as "identification of the specific language features ...
Needs analysis can help in making a language program more suitable to the needs of the learners. It can also help in establishing a sense of ownership and motivation among teachers and learners. ... This paper is part of a Ph.D. research project on Learners' Needs Analysis for EAP in Ethiopian Higher Education. Tamene Kitila. Tamene Kitila is ...
The needs analysis suggests directions for future research on improving the related skills. Next Article in Journal. Graduates' Competencies and Employability: A Conceptual Framework. Previous Article in Journal. ... Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper ...
Penelitian analisis kebutuhan dan rekomendasi pembelajaran ini menerapkan protocol Needs Analysis oleh Hutchinson & Waters (2010) dan Dudley-Evans & St. John (1998) dengan melibatkan mahasiswa ...
These and many other language-learning goals will require different levels of proficiency, different strengths in receptive and productive skills, knowledge of different genres, registers, vocabulary, and collocations, and different pragmatic abilities. A needs analysis (NA) will identify learner goals and communicative language needs, and ...
A needs analysis also involves an examination of the causes, so as to set the right priorities - real and practical solutions - for the future. ... Ferguson, this resource discusses research design, sample survey and methodologies to conduct a needs assessment. It also includes case studies on topics like AIDS, Maternal Health. Case Study:
Abstract. This study aimed to conduct a need analysis to examine the university students' needs for the innovation of the ELT curriculum of the preparatory-school of an English medium university in Istanbul. A triangulation research method was followed in the present study. The educational approach underpinning this method is constructivism.
Needs Analysis of English for Specific Purposes for Tourism Personnel in Ayutthaya. LEARN Journal: Language Education and Acquisition Research Network, 15(1), 409-439. Received 15/09/2021 Received in ... Harding, 2009). This research, thus, aims to investigate the problems that tourism personnel in Ayutthaya have and what they need when
Mehmet (2015) stated that needs analysis is an important means of conducting research prior to designing and evaluating lessons/materials/syllabus and it helps draw a profile of students/course in order to determine and prioritize the needs for which students require English (Richards et al:1992). However, in this study bearing in
Introduction In community-based research projects, needs assessments are one of the first steps to identify community priorities. Access-related issues often pose significant barriers to participation in research and evaluation for rural and remote communities, particularly Indigenous communities, which also have a complex relationship with academia due to a history of exploitation. To bridge ...
DOI: 10.1016/J.SBSPRO.2010.03.136 Corpus ID: 144564722; A language needs analysis research at an English medium university in Turkey @article{Akyel2010ALN, title={A language needs analysis research at an English medium university in Turkey}, author={Ayse Akyel and Yesim Ozek}, journal={Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences}, year={2010}, volume={2}, pages={969-975}, url={https://api ...
In order to find those needs, a need analysis research is necessary to conduct. This. ... and writing abstract and research paper in English. Based on the result, 54% students agree and 24% students strongly agree that there should be additional higher level of English. They understand that English cannot be mastered at a glance, so they have ...
To see where the business predicament lies, managers must first conduct a thorough needs analysis. Needs analysis will make it clear whether employee skills or a thorough knowledge of tasks are at the heart of the question, not some specific hiring problems, understaffing, or inadequate equipment. ... How To Cite a Research Paper in 2024 ...
Abstract. Needs Analysis can provide an insight into the beliefs, opinions and views of the learners and teachers and can help in making a language programme more attuned to the needs of the ...
A Research Paper Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Master of Science Degree m Training and Development ... & Kazanas, 2004). This leads to a needs analysis to determine the cause of the performance problem and the appropriate solution that will close the gap in performance,
It focuses on the organizational analysis, task analysis, and individual analysis (Horng & Lin, Citation 2013; Khan and Masrek, Citation 2017; Sahoo & Mishra, Citation 2019). As a result, TNA can play a vital role in motivating the employees by identifying their actual training needs which ultimately leads to higher performance.
The analysis used the software packages of R and SetMethods for QCA (Oana et al. 2021; Mori 2017, 2018). Based on the literature review and analysis results of previous research, we set and coded the following five factors as the cause conditions for the success of rice flour-related businesses in creating shared value (Table 7). In this ...
Work on the "double empathy problem" (DEP) is rapidly growing in academic and applied settings (e.g., clinical practice). It is most popular in research on conditions, like autism, which are characterized by social cognitive difficulties. Drawing from this literature, we propose that, while research on the DEP has the potential to improve understanding of both typical and atypical social ...
The present paper discusses the importance of needs analysis in ESP. By delving into different theories, the author's overall objective is to scrutinize a wide spectrum of existing frameworks ...
The mechanical strength of the synchronous reluctance motor (SynRM) has always been a great challenge. This paper presents an analysis method for assessing stress equivalence and magnetic bridge stress interaction, along with a multiobjective optimization approach. Considering the complex flux barrier structure and inevitable stress concentration at the bridge, the finite element model ...
Using a systematic literature review (SLR) analysis, the research examines peer-reviewed papers from the Web of Science database from 2018 to 2024, with an emphasis on digital literacy and technological integration. The initial search included 130 publications, which were filtered down from a list of criteria to 35 relevant research.
The construction of new towns is one of the main measures to evacuate urban populations and promote regional coordination and urban-rural integration in China. Mining the spatio-temporal pattern of new town hot spots based on multivariate data and analyzing the influencing factors of new town construction hot spots can provide a strategic basis for new town construction, but few researchers ...
The research about ESP, especially the topic of need analysis still needs to be explored. Thus, this research aims to identify language skills needed and develop English teaching materials at ...
It's also a people and operational challenge in need of thoughtful and intelligent response. You can be the AI leader your organization needs," Ann says. ... Almost as many (51%) names thought leadership e-books or white papers, 47% short articles, and 43% research reports. Click the image to enlarge. Popular content distribution channels ...
Abstract: This paper explores the reasons for the existence of a needs analysis questionnaire and attempts to de ne. the needs of the learners in a speci c teaching context. The aim is to clearly ...