Java Coding Practice


What kind of Java practice exercises are there?
How to solve these java coding challenges, why codegym is the best platform for your java code practice.
- Tons of versatile Java coding tasks for learners with any background: from Java Syntax and Core Java topics to Multithreading and Java Collections
- The support from the CodeGym team and the global community of learners (“Help” section, programming forum, and chat)
- The modern tool for coding practice: with an automatic check of your solutions, hints on resolving the tasks, and advice on how to improve your coding style

Click on any topic to practice Java online right away
Practice java code online with codegym.
In Java programming, commands are essential instructions that tell the computer what to do. These commands are written in a specific way so the computer can understand and execute them. Every program in Java is a set of commands. At the beginning of your Java programming practice , it’s good to know a few basic principles:
- In Java, each command ends with a semicolon;
- A command can't exist on its own: it’s a part of a method, and method is part of a class;
- Method (procedure, function) is a sequence of commands. Methods define the behavior of an object.
Here is an example of the command:
The command System.out.println("Hello, World!"); tells the computer to display the text inside the quotation marks.
If you want to display a number and not text, then you do not need to put quotation marks. You can simply write the number. Or an arithmetic operation. For example:
Command to display the number 1.
A command in which two numbers are summed and their sum (10) is displayed.
As we discussed in the basic rules, a command cannot exist on its own in Java. It must be within a method, and a method must be within a class. Here is the simplest program that prints the string "Hello, World!".
We have a class called HelloWorld , a method called main() , and the command System.out.println("Hello, World!") . You may not understand everything in the code yet, but that's okay! You'll learn more about it later. The good news is that you can already write your first program with the knowledge you've gained.
Attention! You can add comments in your code. Comments in Java are lines of code that are ignored by the compiler, but you can mark with them your code to make it clear for you and other programmers.
Single-line comments start with two forward slashes (//) and end at the end of the line. In example above we have a comment //here we print the text out
You can read the theory on this topic here , here , and here . But try practicing first!
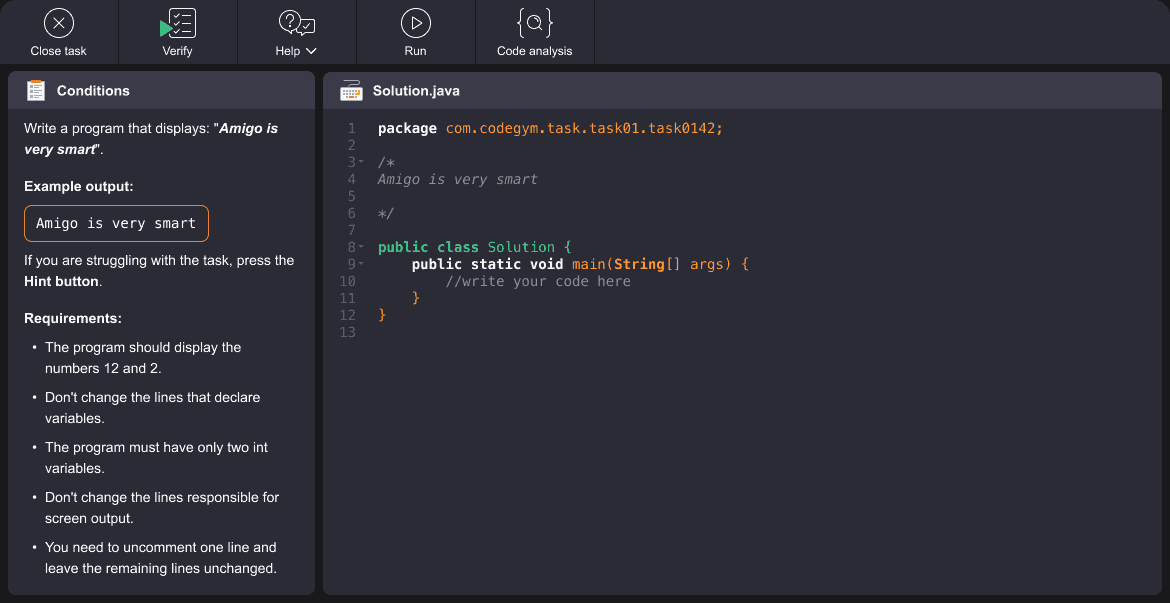
Explore the Java coding exercises for practicing with commands below. First, read the conditions, scroll down to the Solution box, and type your solution. Then, click Verify (above the Conditions box) to check the correctness of your program.
The two main types in Java are String and int. We store strings/text in String, and integers (whole numbers) in int. We have already used strings and integers in previous examples without explicit declaration, by specifying them directly in the System.out.println() operator.
In the first case “I am a string” is a String in the second case 5 is an integer of type int. However, most often, in order to manipulate data, variables must be declared before being used in the program. To do this, you need to specify the type of the variable and its name. You can also set a variable to a specific value, or you can do this later. Example:
Here we declared a variable called a but didn't give it any value, declared a variable b and gave it the value 5 , declared a string called s and gave it the value Hello, World!
Attention! In Java, the = sign is not an equals sign, but an assignment operator. That is, the variable (you can imagine it as an empty box) is assigned the value that is on the right (you can imagine that this value was put in the empty box).
We created an integer variable named a with the first command and assigned it the value 5 with the second command.
Before moving on to practice, let's look at an example program where we will declare variables and assign values to them:
In the program, we first declared an int variable named a but did not immediately assign it a value. Then we declared an int variable named b and "put" the value 5 in it. Then we declared a string named s and assigned it the value "Hello, World!" After that, we assigned the value 2 to the variable a that we declared earlier, and then we printed the variable a, the sum of the variables a and b, and the variable s to the screen
This program will display the following:
We already know how to print to the console, but how do we read from it? For this, we use the Scanner class. To use Scanner, we first need to create an instance of the class. We can do this with the following code:
Once we have created an instance of Scanner, we can use the next() method to read input from the console or nextInt() if we should read an integer.
The following code reads a number from the console and prints it to the console:
Here we first import a library scanner, then ask a user to enter a number. Later we created a scanner to read the user's input and print the input out.
This code will print the following output in case of user’s input is 5:
More information about the topic you could read here , here , and here .
See the exercises on Types and keyboard input to practice Java coding:
Conditions and If statements in Java allow your program to make decisions. For example, you can use them to check if a user has entered a valid password, or to determine whether a number is even or odd. For this purpose, there’s an 'if/else statement' in Java.
The syntax for an if statement is as follows:
Here could be one or more conditions in if and zero or one condition in else.
Here's a simple example:
In this example, we check if the variable "age" is greater than or equal to 18. If it is, we print "You are an adult." If not, we print "You are a minor."
Here are some Java practice exercises to understand Conditions and If statements:
In Java, a "boolean" is a data type that can have one of two values: true or false. Here's a simple example:
The output of this program is here:
In addition to representing true or false values, booleans in Java can be combined using logical operators. Here, we introduce the logical AND (&&) and logical OR (||) operators.
- && (AND) returns true if both operands are true. In our example, isBothFunAndEasy is true because Java is fun (isJavaFun is true) and coding is not easy (isCodingEasy is false).
- || (OR) returns true if at least one operand is true. In our example, isEitherFunOrEasy is true because Java is fun (isJavaFun is true), even though coding is not easy (isCodingEasy is false).
- The NOT operator (!) is unary, meaning it operates on a single boolean value. It negates the value, so !isCodingEasy is true because it reverses the false value of isCodingEasy.
So the output of this program is:
More information about the topic you could read here , and here .
Here are some Java exercises to practice booleans:
With loops, you can execute any command or a block of commands multiple times. The construction of the while loop is:
Loops are essential in programming to execute a block of code repeatedly. Java provides two commonly used loops: while and for.
1. while Loop: The while loop continues executing a block of code as long as a specified condition is true. Firstly, the condition is checked. While it’s true, the body of the loop (commands) is executed. If the condition is always true, the loop will repeat infinitely, and if the condition is false, the commands in a loop will never be executed.
In this example, the code inside the while loop will run repeatedly as long as count is less than or equal to 5.
2. for Loop: The for loop is used for iterating a specific number of times.
In this for loop, we initialize i to 1, specify the condition i <= 5, and increment i by 1 in each iteration. It will print "Count: 1" to "Count: 5."
Here are some Java coding challenges to practice the loops:
An array in Java is a data structure that allows you to store multiple values of the same type under a single variable name. It acts as a container for elements that can be accessed using an index.
What you should know about arrays in Java:
- Indexing: Elements in an array are indexed, starting from 0. You can access elements by specifying their index in square brackets after the array name, like myArray[0] to access the first element.
- Initialization: To use an array, you must declare and initialize it. You specify the array's type and its length. For example, to create an integer array that can hold five values: int[] myArray = new int[5];
- Populating: After initialization, you can populate the array by assigning values to its elements. All elements should be of the same data type. For instance, myArray[0] = 10; myArray[1] = 20;.
- Default Values: Arrays are initialized with default values. For objects, this is null, and for primitive types (int, double, boolean, etc.), it's typically 0, 0.0, or false.
In this example, we create an integer array, assign values to its elements, and access an element using indexing.
In Java, methods are like mini-programs within your main program. They are used to perform specific tasks, making your code more organized and manageable. Methods take a set of instructions and encapsulate them under a single name for easy reuse. Here's how you declare a method:
- public is an access modifier that defines who can use the method. In this case, public means the method can be accessed from anywhere in your program.Read more about modifiers here .
- static means the method belongs to the class itself, rather than an instance of the class. It's used for the main method, allowing it to run without creating an object.
- void indicates that the method doesn't return any value. If it did, you would replace void with the data type of the returned value.
In this example, we have a main method (the entry point of the program) and a customMethod that we've defined. The main method calls customMethod, which prints a message. This illustrates how methods help organize and reuse code in Java, making it more efficient and readable.
In this example, we have a main method that calls the add method with two numbers (5 and 3). The add method calculates the sum and returns it. The result is then printed in the main method.
All composite types in Java consist of simpler ones, up until we end up with primitive types. An example of a primitive type is int, while String is a composite type that stores its data as a table of characters (primitive type char). Here are some examples of primitive types in Java:
- int: Used for storing whole numbers (integers). Example: int age = 25;
- double: Used for storing numbers with a decimal point. Example: double price = 19.99;
- char: Used for storing single characters. Example: char grade = 'A';
- boolean: Used for storing true or false values. Example: boolean isJavaFun = true;
- String: Used for storing text (a sequence of characters). Example: String greeting = "Hello, World!";
Simple types are grouped into composite types, that are called classes. Example:
We declared a composite type Person and stored the data in a String (name) and int variable for an age of a person. Since composite types include many primitive types, they take up more memory than variables of the primitive types.
See the exercises for a coding practice in Java data types:
String is the most popular class in Java programs. Its objects are stored in a memory in a special way. The structure of this class is rather simple: there’s a character array (char array) inside, that stores all the characters of the string.
String class also has many helper classes to simplify working with strings in Java, and a lot of methods. Here’s what you can do while working with strings: compare them, search for substrings, and create new substrings.
Example of comparing strings using the equals() method.
Also you can check if a string contains a substring using the contains() method.
You can create a new substring from an existing string using the substring() method.
More information about the topic you could read here , here , here , here , and here .
Here are some Java programming exercises to practice the strings:
In Java, objects are instances of classes that you can create to represent and work with real-world entities or concepts. Here's how you can create objects:
First, you need to define a class that describes the properties and behaviors of your object. You can then create an object of that class using the new keyword like this:
It invokes the constructor of a class.If the constructor takes arguments, you can pass them within the parentheses. For example, to create an object of class Person with the name "Jane" and age 25, you would write:
Suppose you want to create a simple Person class with a name property and a sayHello method. Here's how you do it:
In this example, we defined a Person class with a name property and a sayHello method. We then created two Person objects (person1 and person2) and used them to represent individuals with different names.
Here are some coding challenges in Java object creation:
Static classes and methods in Java are used to create members that belong to the class itself, rather than to instances of the class. They can be accessed without creating an object of the class.
Static methods and classes are useful when you want to define utility methods or encapsulate related classes within a larger class without requiring an instance of the outer class. They are often used in various Java libraries and frameworks for organizing and providing utility functions.
You declare them with the static modifier.
Static Methods
A static method is a method that belongs to the class rather than any specific instance. You can call a static method using the class name, without creating an object of that class.
In this example, the add method is static. You can directly call it using Calculator.add(5, 3)
Static Classes
In Java, you can also have static nested classes, which are classes defined within another class and marked as static. These static nested classes can be accessed using the outer class's name.
In this example, Student is a static nested class within the School class. You can access it using School.Student.
More information about the topic you could read here , here , here , and here .
See below the exercises on Static classes and methods in our Java coding practice for beginners:

Java Tutorial for Beginners: Learn Core Java Programming
Java Tutorial Summary
This Java tutorial for beginners is taught in a practical GOAL-oriented way. It is recommended you practice the code assignments given after each core Java tutorial to learn Java from scratch. This Java programming for beginners course will help you learn basics of Java and advanced concepts.
What is Java?
Java is a class-based object-oriented programming language for building web and desktop applications. It is the most popular programming language and the language of choice for Android programming.
Java Syllabus
First Steps in Java Basics
Basics Concepts of Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs)
Java Basics Language Constructs
Learn Java String Tutorial
Most Misunderstood Topics!
Java Memory Management
Abstract Class & Interface in Java
Better Late than Never
Exception Handling in Java
Conditional Loops in Java
Java Advance Stuff!
Java Programs
Java Differences
Java Interview Questions, Tools & Books
What will you learn in this Java Tutorial for Beginners?
In this Java tutorial for beginners, you will learn Java programming basics like What is Java platform, JVM, how to install Java, OOPS concepts, variables, class, object, arrays, strings, command-line arguments, garbage collection, inheritance, polymorphism, interface, constructor, packages, etc. You will also learn advanced concepts like switch-case, functions, multithreading, swing, files, API, Java Spring, etc., in this Java basics for beginners guide.
Prerequisites for learning Java Tutorial?
This free Java for beginners tutorial is designed for beginners with little or no Java coding experience. These Java notes for beginners will help beginners to learn Java online for free.
Why Learn Java Programming?
Here are the reasons why you should learn Java:
- Java is very easy to learn.
- Java developers are in demand, and it easy to get a job as a Java programmer.
- It has a good collection of open-source libraries.
- Java is free.
What are the Benefits of Java?
Here are the benefits of Java:
- Java is object-oriented.
- It is platform-independent.
- You can effortlessly write, compile, and debug programs compare to other programming languages.
Applications of Java Programming
Following are the major applications of Java Programming language:
- Mobile Applications
- Web Applications
- Web and Application servers
- Enterprise Applications
- Embedded Applications
- Desktop GUI Applications
What are the types of Java programs?
Here are the types of Java Program:
- Stand-alone applications.
- Web Applications using JSP , Servlet, Spring, Hibernate, JSF, etc.
How do I get real-time exposure to Java?
You can get real-time exposure to Java by coding in live projects. You can join our Live Java Project to get your hands dirty in Java.
- C Program Transpose of a Matrix 2 Ways | C Programs
- C Program : To Find Maximum Element in A Row | C Programs
- C Program Patterns of 0(1+)0 in The Given String | C Programs
- C Program : Rotate the Matrix by K Times | C Porgrams
- C Program : Check if An Array Is a Subset of Another Array
- C Program To Check Upper Triangular Matrix or Not | C Programs
- C Program : To Find the Maximum Element in a Column
- C Program : Rotate a Given Matrix by 90 Degrees Anticlockwise
- C Program : Non-Repeating Elements of An Array | C Programs
- C Program Sum of Each Row and Column of A Matrix | C Programs
- C Program : Remove Vowels from A String | 2 Ways
- C Program : Remove All Characters in String Except Alphabets
- C Program : Sorting a String in Alphabetical Order – 2 Ways
- C Program To Check If Vowel Or Consonant | 4 Simple Ways
- C Program To Check Whether A Number Is Even Or Odd | C Programs
- C Program To Count The Total Number Of Notes In A Amount | C Programs
- C Program To Print Number Of Days In A Month | Java Tutoring
- C Program To Input Any Alphabet And Check Whether It Is Vowel Or Consonant
- C Program To Find Reverse Of An Array – C Programs
- C Program To Check A Number Is Negative, Positive Or Zero | C Programs
- C Program To Find Maximum Between Three Numbers | C Programs
- C Program Inverted Pyramid Star Pattern | 4 Ways – C Programs
- C Program To Check If Alphabet, Digit or Special Character | C Programs
- C Program To Check Whether A Character Is Alphabet or Not
- C Program To Check Character Is Uppercase or Lowercase | C Programs
- C Program To Check Whether A Year Is Leap Year Or Not | C Programs
- C Program To Calculate Profit or Loss In 2 Ways | C Programs
- C Program Area Of Triangle | C Programs
- C Program To Check If Triangle Is Valid Or Not | C Programs
- C Program Find Circumference Of A Circle | 3 Ways
- C Program Area Of Rectangle | C Programs
- X Star Pattern C Program 3 Simple Ways | C Star Patterns
- C Program Area Of Rhombus – 4 Ways | C Programs
- C Program To Check Number Is Divisible By 5 and 11 or Not | C Programs
- C Program Hollow Diamond Star Pattern | C Programs
- Mirrored Rhombus Star Pattern Program In c | Patterns
- C Program Area Of Isosceles Triangle | C Programs
- C Program To Find Area Of Semi Circle | C Programs
- C Program Area Of Parallelogram | C Programs
- C Program Area Of Trapezium – 3 Ways | C Programs
- C Program Area Of Square | C Programs
- C Program Check A Character Is Upper Case Or Lower Case
- C Program To Find Volume of Sphere | C Programs
- C Program to find the Area Of a Circle
- C Program Area Of Equilateral Triangle | C Programs
- Hollow Rhombus Star Pattern Program In C | Patterns
- C Program To Count Total Number Of Notes in Given Amount
- C Program To Calculate Volume Of Cube | C Programs
- C Program To Find Volume Of Cone | C Programs
- C Program To Calculate Perimeter Of Rectangle | C Programs
- C Program To Calculate Perimeter Of Rhombus | C Programs
- C Program Volume Of Cuboid | C Programs
- C Program To Calculate Perimeter Of Square | C Programs
- C Program Count Number Of Words In A String | 4 Ways
- C Program To Search All Occurrences Of A Character In String | C Programs
- C Program To Copy All Elements From An Array | C Programs
- C Program To Left Rotate An Array | C Programs
- C Program To Delete Duplicate Elements From An Array | 4 Ways
- C Program Volume Of Cylinder | C Programs
- C Program To Compare Two Strings – 3 Easy Ways | C Programs
- C Mirrored Right Triangle Star Pattern Program – Pattern Programs
- C Program To Toggle Case Of Character Of A String | C Programs
- C Program To Count Occurrences Of A Word In A Given String | C Programs
- C Square Star Pattern Program – C Pattern Programs | C Programs
- C Program To Remove First Occurrence Of A Character From String
- C Program To Search All Occurrences Of A Word In String | C Programs
- C Program Inverted Right Triangle Star Pattern – Pattern Programs
- C Programs – 500+ Simple & Basic Programming Examples & Outputs
- C Program To Reverse Words In A String | C Programs
- C Program To Delete An Element From An Array At Specified Position | C Programs
- Hollow Square Pattern Program in C | C Programs
- C Program To Find Reverse Of A string | 4 Ways
- C Program To Remove Last Occurrence Of A Character From String
- C Program To Remove Repeated Characters From String | 4 Ways
- C Plus Star Pattern Program – Pattern Programs | C
- Rhombus Star Pattern Program In C | 4 Multiple Ways
- C Program To Check A String Is Palindrome Or Not | C Programs
- C Program Replace First Occurrence Of A Character With Another String
- C Pyramid Star Pattern Program – Pattern Programs | C
- C Program To Sort Even And Odd Elements Of Array | C Programs
- C Program To Search An Element In An Array | C Programs
- C Program To Remove Blank Spaces From String | C Programs
- C Program To Trim Leading & Trailing White Space Characters From String
- C Program Number Of Alphabets, Digits & Special Character In String | Programs
- C Program Replace All Occurrences Of A Character With Another In String
- C Program To Copy One String To Another String | 4 Simple Ways
- C Program To Find Maximum & Minimum Element In Array | C Prorams
- C Program To Find Last Occurrence Of A Word In A String | C Programs
- Merge Two Arrays To Third Array C Program | 4 Ways
- C Program Right Triangle Star Pattern | Pattern Programs
- C Program To Count Frequency Of Each Character In String | C Programs
- C Program To Find Last Occurrence Of A Character In A Given String
- C Program To Find First Occurrence Of A Word In String | C Programs
- C Program To Concatenate Two Strings | 4 Simple Ways
- C Program Find Maximum Between Two Numbers | C Programs
- C Program To Trim White Space Characters From String | C Programs
- C Program Count Number Of Vowels & Consonants In A String | 4 Ways
- C Program To Sort Array Elements In Ascending Order | 4 Ways
- Highest Frequency Character In A String C Program | 4 Ways
- C Program To Count Number Of Even & Odd Elements In Array | C Programs
- C Program To Count Frequency Of Each Element In Array | C Programs
- C Program To Remove First Occurrence Of A Word From String | 4 Ways
- C Program To Count Occurrences Of A Character In String | C Programs
- C Program To Trim Trailing White Space Characters From String | C Programs
- C Program To Put Even And Odd Elements Of Array Into Two Separate Arrays
- C Program To Print All Unique Elements In The Array | C Programs
- C Program To Convert Lowercase String To Uppercase | 4 Ways
- C Program To Print Number Of Days In A Month | 5 Ways
- Diamond Star Pattern C Program – 4 Ways | C Patterns
- C Program To Insert Element In An Array At Specified Position
- C Program To Convert Uppercase String To Lowercase | 4 Ways
- C Program Hollow Inverted Right Triangle Star Pattern
- C Program To Count Number Of Negative Elements In Array
- C Program To Find Sum Of All Array Elements | 4 Simple Ways
- C Program To Sort Array Elements In Descending Order | 3 Ways
- C Program Count Number of Duplicate Elements in An Array | C Programs
- C Program To Remove All Occurrences Of A Character From String | C Programs
- C Program Hollow Inverted Mirrored Right Triangle
- C Program To Input Week Number And Print Week Day | 2 Ways
- C Program To Read & Print Elements Of Array | C Programs
- C Program To Right Rotate An Array | 4 Ways
- C Program To Replace Last Occurrence Of A Character In String | C Programs
- C Program Hollow Mirrored Rhombus Star Pattern | C Programs
- 8 Star Pattern – C Program | 4 Multiple Ways
- C Program To Find Lowest Frequency Character In A String | C Programs
- C Program Half Diamond Star Pattern | C Pattern Programs
- C Program To Find First Occurrence Of A Character In A String
- C Program To Find Length Of A String | 4 Simple Ways
- C Program Hollow Mirrored Right Triangle Star Pattern
- Hollow Inverted Pyramid Star Pattern Program in C
- Right Arrow Star Pattern Program In C | 4 Ways
- C Program To Print All Negative Elements In An Array
- C Program Hollow Right Triangle Star Pattern
- C Program : Check if Two Strings Are Anagram or Not
- C Program : Capitalize First & Last Letter of A String | C Programs
- C Program : Check if Two Arrays Are the Same or Not | C Programs
- Left Arrow Star Pattern Program in C | C Programs
- C Program Inverted Mirrored Right Triangle Star Pattern
- C Program Mirrored Half Diamond Star Pattern | C Patterns
- Hollow Pyramid Star Pattern Program in C
- C Program : Non – Repeating Characters in A String | C Programs
- C Program : Sum of Positive Square Elements in An Array | C Programs
- C Program : To Reverse the Elements of An Array | C Programs
- C Program : Find Longest Palindrome in An Array | C Programs
- C Program Lower Triangular Matrix or Not | C Programs
- C Program : Maximum Scalar Product of Two Vectors
- C Program Merge Two Sorted Arrays – 3 Ways | C Programs
- C Program : Check If Arrays are Disjoint or Not | C Programs
- C Program : Convert An Array Into a Zig-Zag Fashion
- C Program : Minimum Scalar Product of Two Vectors | C Programs
- C program : Find Median of Two Sorted Arrays | C Programs
- C Program : Find Missing Elements of a Range – 2 Ways | C Programs
Learn Java Java Tutoring is a resource blog on java focused mostly on beginners to learn Java in the simplest way without much effort you can access unlimited programs, interview questions, examples
Java programs – 500+ simple & basic programs with outputs.
in Java Programs , Java Tutorials April 20, 2024 Comments Off on Java Programs – 500+ Simple & Basic Programs With Outputs
Java programs: Basic Java programs with examples & outputs. Here we covered over the list of 500+ Java simple programs for beginners to advance, practice & understood how java programming works. You can take a pdf of each program along with source codes & outputs.
In case if you are looking out for C Programs , you can check out that link.
We covered major Simple to basic Java Programs along with sample solutions for each method. If you need any custom program you can contact us.
All of our Sample Java programs with outputs in pdf format are written by expert authors who had high command on Java programming. Even our Java Tutorials are with rich in-depth content so that newcomers can easily understand.
1. EXECUTION OF A JAVA PROGRAM
Static loading : A block of code would be loaded into the RAM before it executed ( i.e after being loaded into the RAM it may or may not get executed )
Dynamic loading: A block of code would be loaded into the RAM only when it is required to be executed.
Note: Static loading took place in the execution of structured programming languages. EX: c- language
Java follows the Dynamic loading
– JVM would not convert all the statements of the class file into its executable code at a time.
– Once the control comes out from the method, then it is deleted from the RAM and another method of exe type will be loaded as required.
– Once the control comes out from the main ( ), the main ( ) method would also be deleted from the RAM. This is why we are not able to view the exe contents of a class file.
Simple Hello Word Program
Out of 500+ Simple & Basic Java Programs: Hello world is a first-ever program which we published on our site. Of course, Every Java programmer or C programmer will start with a “Hello World Program”. Followed by the rest of the programs in different Categories.
Basic Java Programs – Complete List Here
Advanced simple programming examples with sample outputs, string, array programs.
Sort Programs
Conversion Programs:
Star & Number Pattern Programs
Functions of JVM:
- It converts the required part if the bytecode into its equivalent executable code.
- It loads the executable code into the RAM.
- Executes this code through the local operating system.
- Deletes the executable code from the RAM.
We know that JVM converts the class file into its equivalent executable code. Now if a JVM is in windows environment executable code that is understood by windows environment only.
Similarly, same in the case with UNIX or other or thus JVM ID platform dependent.
Java, With the help of this course, students can now get a confidant to write a basic program to in-depth algorithms in C Programming or Java Programming to understand the basics one must visit the list 500 Java programs to get an idea.
Users can now download the top 100 Basic Java programming examples in a pdf format to practice.
But the platform dependency of the JVM is not considered while saying Java is platform independent because JVM is supplied free of cost through the internet by the sun microsystems.
Platform independence :
Compiled code of a program should be executed in any operating system, irrespective of the as in OS in which that code had been generated. This concept is known as platform independence.
- The birth of oops concept took place with encapsulation.
- Any program contains two parts.
- Date part and Logic part
- Out of data and logic the highest priority we have given to data.
- But in a structured programming language, the data insecurity is high.
- Thus in a process, if securing data in structured prog. lang. the concept of encapsulation came into existence.
Note: In structured programming lang programs, the global variable play a vital role.
But because of these global variables, there is data insecurity in the structured programming lang programs. i.e functions that are not related to some variables will have access to those variables and thus data may get corrupted. In this way data is unsecured.
“This is what people say in general about data insecurity. But this is not the actual reason. The actual concept is as follows”.
Let us assume that, we have a ‘C’ program with a hundred functions. Assume that it is a project. Now if any upgradation is required, then the client i.e the user of this program (s/w) comes to its company and asks the programmers to update it according to his requirement.
Now we should note that it is not guaranteed that the programmers who developed this program will still be working with that company. Hence this project falls into the hands of new programmers.
Automatically it takes a lot of time to study. The project itself before upgrading it. It may not be surprising that the time required for writing the code to upgrade the project may be very less when compared to the time required for studying the project.
Thus maintenance becomes a problem.
If the new programmer adds a new function to the existing code in the way of upgrading it, there is no guarantee that it will not affect the existing functions in the code. This is because of global variables. In this way, data insecurity is created.
- To overcome this problem, programmers developed the concept of encapsulation .
- For example, let us have a struc.prog.lang. program with ten global variables and twenty functions.
- It is sure that all the twenty functions will not use all the global variables .
Three of the global variables may be used only by two functions. But in a structured prog. Lang like ‘C’ it is not possible to restrict the access of global variables by some limited no of functions.
Every function will have access to all the global variables.
To avoid this problem, programmers have designed a way such that the variables and the functions which are associated with or operate on those variables are enclosed in a block and that bock is called a class and that class and that class is given a name, Just as a function is given a name.
Now the variables inside the block cannot be called as the local variable because they cannot be called as global variables because they are confined to a block and not global.
Hence these variables are known as instance variables
_______________________________________________________________
Example 2 :
Therefore a class is nothing but grouping data along with its functionalities.
Note 1: E ncapsulation it’s the concept of binding data along with its corresponding functionalities.
Encapsulations came into existence in order to provide security for the data present inside the program.
Note 2: Any object oriental programming language file looks like a group of classes. Everything is encapsulated. Nothing is outside the class.
- Encapsulation is the backbone of oop languages.
- JAVA supports all the oop concepts ( i.e. encapsulation, polymorphism, inheritance) and hence it is known as an object-oriented programming language.
- C++ breaks the concept of encapsulation because the main ( ) method in a C++ program is declared outside a class. Hence it is not a pure oop language, in fact, it is a poor oop language.
Related Posts !

Java Program To Find Perimeter Of Rectangle | 3 Ways
May 31, 2024

Java Program Calculate Perimeter Of Square | Programs
May 28, 2024
Java Program To Calculate Perimeter Of Rhombus | 3 Ways
May 25, 2024

VPN Blocked by Java Security on PC? Here’s How to Fix That
Hcf of two & n numbers java program | 3 ways.
May 22, 2024
LCM Of Two Numbers Java Program | 5 Ways – Programs
May 19, 2024

Java Program Convert Fahrenheit To Celsius | Vice Versa
Java Program to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius – Here we discuss the various methods to ...

Programming in Java · Computer Science · An Interdisciplinary Approach
Online content. , introduction to programming in java., computer science., for teachers:, for students:.
{{ activeMenu.name }}
- Python Courses
- JavaScript Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Courses
- Data Science Courses
- React Courses
- Ethical Hacking Courses
- View All Courses
Fresh Articles

- Python Projects
- JavaScript Projects
- Java Projects
- HTML Projects
- C++ Projects
- PHP Projects
- View All Projects

- Python Certifications
- JavaScript Certifications
- Linux Certifications
- Data Science Certifications
- Data Analytics Certifications
- Cybersecurity Certifications
- View All Certifications

- IDEs & Editors
- Web Development
- Frameworks & Libraries
- View All Programming
- View All Development
- App Development
- Game Development
- Courses, Books, & Certifications
- Data Science
- Data Analytics
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning (ML)
- View All Data, Analysis, & AI
- Networking & Security
- Cloud, DevOps, & Systems
- Recommendations
- Crypto, Web3, & Blockchain
- User-Submitted Tutorials
- View All Blog Content
- JavaScript Online Compiler
- HTML & CSS Online Compiler
- Certifications
- Programming
- Development
- Data, Analysis, & AI
- Online JavaScript Compiler
- Online HTML Compiler
Don't have an account? Sign up
Forgot your password?
Already have an account? Login
Have you read our submission guidelines?
Go back to Sign In
10 Best Java Projects for Beginners 2024 [With Source Code]
If I could go back in time to help my younger self learn Java, I'd tell him to build more Java projects!
That's exactly why I wrote this article: to share 10 Java projects to help beginners like you.
Whether you’re looking to start a career in Java development or enhance your portfolio, these Java projects are perfect for leveling up your Java skills.
I’ve also personally designed the first three Java projects to be step-by-step tutorials so you can follow along with me to get hands-on and code some cool stuff.
You can think of these tutorial projects as taking a free Java course while growing your Java portfolio!
I'm also regularly adding new Java projects with step-by-step tutorials, so make sure you bookmark this page and check back for the latest Java projects to grow your skills.
Without further ado, let’s dive in and start building with Java!
- 10 Best Java Projects for Beginners in 2024
1. Java Chat Application
What is this Java project?
In this Java project, you'll build a chat application, a dynamic and engaging tool that facilitates real-time communication between users
I've also designed this project to be a step-by-step tutorial so you can follow along with me to build something very cool and very practical.
This project also goes beyond merely creating a functional application; it serves as an excellent example of utilizing Java's networking capabilities and Swing framework to create interactive and responsive desktop applications.
It's a perfect addition to your portfolio, particularly if you're looking to demonstrate your proficiency in Java development, as it showcases essential programming concepts within a context that is both interactive and practically valuable.
So get ready and fire up your favorite Java IDE , and let's get building!
Java Skills Covered:
- Networking Logic: Develop the core logic for establishing client-server connections, including handling multiple client connections simultaneously.
- Dynamic UI Updates: Utilize the Swing framework to dynamically update the chat interface, reflecting messages and user actions in real-time, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
- Event Handling: Manage action and window events to capture user inputs such as sending a message or exiting the chat.
- User Interface Design: Apply principles of Swing GUI design to create a clean, user-friendly interface for the chat application, demonstrating skills in creating appealing desktop applications.
- Multithreading: Implement multithreading to handle concurrent tasks, such as listening for incoming messages while allowing the user to type new messages.
- Best Practices in Java: Write clean, efficient, and well-structured Java code, adhering to best practices for readability, maintainability, and performance.
Build This Java Project Here
2. Java Chess Game
In this project, you will create a fully interactive chess game, a classic strategy game that brings to life the timeless battle between two opposing forces on a checkered board.
I've also designed this Java project to be a step-by-step tutorial so you can follow along with me to build something fun, challenging, and very impressive!
This project also goes beyond creating a basic application; it's about mastering the intricacies of Java's Swing framework to create a visually appealing and user-interactive gaming experience.
It's also a perfect addition to your portfolio, particularly if you want to demonstrate your ability to handle complex logic and state management, problem-solving skills, and an understanding of GUI development.
So, warm up those coding fingers, and let’s get started with this exciting project!
- Game Logic Implementation: Craft the fundamental logic for chess, including piece movements, capturing mechanics, and game-ending conditions like checkmate.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) Design: Utilize the Swing framework to design and implement a user-friendly and visually appealing interface for the chess game.
- Event-Driven Programming: Manage user interactions through event listeners, enabling players to move pieces, respond to game states, and interact with the game dynamically.
- Advanced State Management: Develop sophisticated game state management to handle the various states of a chess game, including tracking turns, game status, and special moves.
- Problem-Solving: Demonstrate advanced problem-solving abilities in implementing chess rules, strategizing piece movements, and validating legal moves.
- Best Practices in Java: Write clean, efficient, and well-structured Java code, following best practices for software design, maintainability, and GUI development.
3. Java Email Client
In this Java project, you're going to build an email client application, allowing users to interact with their emails through a desktop interface.
This is another Java project that I've designed to be a step-by-step tutorial, so you can follow along with me to build something practical, challenging, and quite cool! I'll also guide you on how to setup your email client to connect with Gmail.
This tutorial is not just about coding; it's about applying Java's powerful capabilities in networking and the Swing framework to craft applications that are both interactive and efficient.
So, stretch out those digits and get started with this exciting project!
- Email Protocols: Learn to use JavaMail API for handling SMTP and IMAP protocols, enabling the sending and receiving of emails.
- Dynamic UI Updates: Utilize the Swing framework to dynamically update the email client interface, reflecting changes in real-time and improving the user experience.
- Event Handling: Implement action listeners to capture user interactions like composing emails, adding attachments, and authenticating users.
- User Interface Design: Employ Swing GUI design to develop a clean, intuitive interface for the email client, showcasing your ability to craft appealing and functional desktop applications.
- Session Management: Handle email session management efficiently, ensuring secure and persistent connections to email servers.
- Best Practices in Java: Write clean, effective, and well-organized Java code, adhering to best practices for code readability, maintainability, and application performance.
4. Brick Breaker Game
This brick breaker game is one of many fun Java projects that has you trying to break bricks at the top of the screen. The player controls a tiny ball placed on a small platform at the bottom of the screen, which can be moved around from left to right using the arrow keys. The goal is to break the bricks without missing the ball with your platform. The project makes use of Java swing and OOPS concepts , among other things.
Source Code
5. Data Visualization Software
Data Visualization has become important as it displays data visually using statistical graphics and scientific visualization, to the point where data visualization software has been created. This project displays the node connectivity in networking in data visualization form. This node connectivity can be located at different locations via mouse or trackpad.
6. ATM Interface
This somewhat complex Java project consists of five different classes and is a console-based application. When the system starts the user is prompted with a user id and user pin. After entering the details successfully, the ATM functionalities are unlocked.
7. Web Server Management System
This web server management system project deals with the information, maintenance, and information management of the web server. It covers several concepts, including tracing the physical location of an entity, and identifying URL authorities and names.
8. Airline Reservation System
The project is a web-based one featuring open architecture that keeps up with the dynamic needs of the airline business by the addition of new systems & functionality. The project includes online transactions, fares, inventory, and e-ticket operations.
The software consists of four key modules, i.e., user registration, login, reservation, and cancellation. The app allows communication through a TCP/IP network protocol thereby facilitating the usage of internet & intranet communication globally.
9. Online Book Store
This project is mainly developed for bookstores and shops to digitize the book-purchasing process. The aim is to create an efficient and reliable online bookselling platform. It also records sold and stock books automatically in the database.
10. Snake Game in Java
If you are a ’90s kid or an adult you have probably played this game on your phone. The goal of this game is to make the snake eat the tokens without the snake being touched to the boundary on the screen. Every time the snake eats the token the score is updated. The player loses when the snake touches the boundary and the final score is displayed.
- How To Setup Your Java Environment
Before you start coding in Java, it's essential to have your coding environment properly set up and ready for action.
Being a compiled language that runs on a wide range of devices through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Java requires a bit more setup compared to interpreted languages like JavaScript that run directly in web browsers.
Here's how to set up a Java development environment on most operating systems.
Install a Java Development Kit (JDK)
First and foremost, you need the JDK, which includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and the compilers and tools needed to compile and run Java applications.
- Download the JDK: Visit AdoptOpenJDK or Oracle's official Java site to download the JDK. I recommend choosing the LTS (Long-Term Support) version for stability.
- Install the JDK: Run the installer and follow the instructions. Make sure to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to the JDK installation path and add the JDK's bin directory to your system's PATH . This is crucial for making Java commands accessible from your command line or terminal.
Verify Installation
After setting up, verify that everything is working correctly.
To begin, open a terminal or command prompt and run these commands to check the installed Java and Java compiler versions, respectively:
Then, try creating a simple Java program and compile it using:
Then run it with:
This should confirm your JDK is correctly set up.
Install a Java IDE or Code Editor
You'll need an IDE or code editor that supports Java syntax highlighting and potentially IntelliSense for code completion.
Eclipse, NetBeans, and IntelliJ IDEA are some of the most popular choices and three of my personal favorites.
That said, I'd also consider Visual Studio Code (VSCode) as this is a hugely popular choice among developers for various languages thanks to its extensive and lightweight feature set and vast library of extensions.
If you do go the VSCode route, head to the VSCode extension marketplace and install the ‘Extension Pack for Java’ from Microsoft, and you’ll be good to go.
Install Git [Optional but Recommended]
If you're really new to coding, you might want to skip this step, but even then, I'd really recommend becoming familiar with Git as soon as you can.
If you want the TL-DR, Git is a version control system that lets you track changes in your code and collaborate with others.
While this step is not strictly necessary for Java development, it's a best practice, especially for larger projects or when working in a team.
Simply download Git from the official Git website , and during installation, you can accept most default settings. That said, you might want to choose your preferred text editor and ensure that Git is added to your system's PATH.
- Wrapping Up
And there we have it! If you've taken the time to build these 10 Java projects, you should be feeling much more competent and confident with Java.
You'll also have a burgeoning Java portfolio that's packed full of interesting and practical Java projects, each demonstrating your dedication and abilities.
I also hope you enjoyed following along with my step-by-step tutorial on the first three Java projects!
My motivation with these Java tutorials is to guide you through the nuances of Java development while also giving you hands-on experience that you'd usually only get when taking a Java course.
Here at hackr.io , we're huge fans of project-based learning, so I hope these Java projects have bolstered your confidence and sparked a deeper interest in web development or any other form of Java development.
Remember, the journey doesn't end here!
With new projects and step-by-step tutorials regularly added to this page, be sure to check back often for new opportunities to refine your Java skills and expand your portfolio.
Happy coding!
Want to sharpen up your Java development skills in 2024? Check out:
Udemy's Top Rated Course: Java 17 Masterclass: Start Coding in 2024
People are also reading:
- Top Java Certifications
- Best Java Books
- Top Java Programming Interview Questions
- Core Java Cheatsheet
- Top Java Frameworks
- Best Way to Learn Java
- Constructor in java
- Prime Number Program in Java
- Difference between Java vs Javascript

Technical Editor for Hackr.io | 15+ Years in Python, Java, SQL, C++, C#, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP, .NET, MATLAB, HTML & CSS, and more... 10+ Years in Networking, Cloud, APIs, Linux | 5+ Years in Data Science | 2x PhDs in Structural & Blast Engineering
Subscribe to our Newsletter for Articles, News, & Jobs.
Disclosure: Hackr.io is supported by its audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
In this article
- How To Create A Professional Portfolio Page Using HTML HTML Projects Web Development
- How To Create A Product Landing Page Using HTML HTML Projects Web Development
- How To Create An Interactive Photo Gallery Using HTML HTML Projects Web Development
Please login to leave comments
Always be in the loop.
Get news once a week, and don't worry — no spam.
{{ errors }}
{{ message }}
- Help center
- We ❤️ Feedback
- Advertise / Partner
- Write for us
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Change Privacy Settings
- Disclosure Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Refund Policy
Disclosure: This page may contain affliate links, meaning when you click the links and make a purchase, we receive a commission.
Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to, java reference, java examples.
Java is a popular programming language.
Java is used to develop mobile apps, web apps, desktop apps, games and much more.
Examples in Each Chapter
Our "Try it Yourself" editor makes it easy to learn Java. You can edit Java code and view the result in your browser.
Try it Yourself »
Click on the "Run example" button to see how it works.
We recommend reading this tutorial, in the sequence listed in the left menu.
Java is an object oriented language and some concepts may be new. Take breaks when needed, and go over the examples as many times as needed.
Java Exercises
Test yourself with exercises.
Insert the missing part of the code below to output "Hello World".
Start the Exercise
Advertisement
Test your Java skills with a quiz.
Start Java Quiz
Learn by Examples
Learn by examples! This tutorial supplements all explanations with clarifying examples.
See All Java Examples
My Learning
Track your progress with the free "My Learning" program here at W3Schools.
Log in to your account, and start earning points!
This is an optional feature. You can study at W3Schools without using My Learning.

Java Keywords
Java String Methods
Java Math Methods
Download Java
Download Java from the official Java web site: https://www.oracle.com
Java Exam - Get Your Diploma!
Kickstart your career.
Get certified by completing the course

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
Object-Oriented Programming in Java – A Beginner's Guide

Hi, folks! Today we are going to talk about object-oriented programming in Java.
This article will help give you a thorough understanding of the underlying principles of object-oriented programming and its concepts.
Once you understand these concepts, you should have the confidence and ability to develop basic problem-solving applications using object-oriented programming principles in Java.
What is Object-Oriented Programming?
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a fundamental programming paradigm based on the concept of “ objects ” . These objects can contain data in the form of fields (often known as attributes or properties) and code in the form of procedures (often known as methods).
The core concept of the object-oriented approach is to break complex problems into smaller objects.
In this article, we will be looking at the following OOP concepts:
What is Java?
- What is a class?
- What is an object?
- What is a Java Virtual Machine (JVM)?
- How access modifiers work in Java.
- How constructors work in Java.
- How methods work in Java.
- Key principles of OOP.
- Interfaces in Java.
Java is a general-purpose, class-based, object-oriented programming language, which works on different operating systems such as Windows, Mac, and Linux.
You can use Java to develop:
- Desktop applications
- Web applications
- Mobile applications (especially Android apps)
- Web and application servers
- Big data processing
- Embedded systems
And much more.
In Java, every application starts with a class name, and this class must match the file name. When saving a file, save it using the class name and add “ .java ” to the end of the file name.
Let's write a Java program that prints the message “ Hello freeCodeCamp community. My name is ... ” .
We are going to start by creating our first Java file called Main.java, which can be done in any text editor. After creating and saving the file, we are going to use the below lines of code to get the expected output.
Don't worry if you don't understand the above code at the moment. We are going to discuss, step by step, each line of code just below.
For now, I want you to start by noting that every line of code that runs in Java must be in a class.
You may also note that Java is case-sensitive. This means that Java has the ability to distinguish between upper and lower case letters. For example, the variable “ myClass ” and the variable “ myclass ” are two totally different things.
Alright, let's see what that code's doing:
Let's first look at the main() method: public static void main(String[] args) .
This method is required in every Java program, and it is the most important one because it is the entry point of any Java program.
Its syntax is always public static void main(String[] args) . The only thing that can be changed is the name of the string array argument. For example, you can change args to myStringArgs .
What is a Class in Java?
A class is defined as a collection of objects. You can also think of a class as a blueprint from which you can create an individual object.
To create a class, we use the keyword class .
Syntax of a class in Java:
In the above syntax, we have fields (also called variables) and methods, which represent the state and behavior of the object, respectively.
Note that in Java, we use fields to store data, while we use methods to perform operations.

Let's take an example:
We are going to create a class named “ Main ” with a variable “ y ” . The variable “ y ” is going to store the value 2.
Note that a class should always start with an uppercase first letter, and the Java file should match the class name.
What is an Object in Java?
An object is an entity in the real world that can be distinctly identified. Objects have states and behaviors. In other words, they consist of methods and properties to make a particular type of data useful.
An object consists of:
- A unique identity: Each object has a unique identity, even if the state is identical to that of another object.
- State/Properties/Attributes: State tells us how the object looks or what properties it has.
- Behavior: Behavior tells us what the object does.
Examples of object states and behaviors in Java:
Let's look at some real-life examples of the states and behaviors that objects can have.
- Object: car.
- State: color, brand, weight, model.
- Behavior: break, accelerate, turn, change gears.
- Object: house.
- State: address, color, location.
- Behavior: open door, close door, open blinds.
Syntax of an object in Java:
What is the java virtual machine (jvm).
The Java virtual machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs.
The JVM has two primary functions, which are:
- To allow Java programs to run on any device or operating system (this is also known as the "Write once, run anywhere" principle).
- And, to manage and optimize program memory.
How Access Modifiers Work in Java
In Java, access modifiers are keywords that set the accessibility of classes, methods, and other members.
These keywords determine whether a field or method in a class can be used or invoked by another method in another class or sub-class.
Access modifiers may also be used to restrict access.
In Java, we have four types of access modifiers, which are:
Let's look at each one in more detail now.
Default Access Modifier
The default access modifier is also called package-private. You use it to make all members within the same package visible, but they can be accessed only within the same package.
Note that when no access modifier is specified or declared for a class, method, or data member, it automatically takes the default access modifier.
Here is an example of how you can use the default access modifier:
Now let's see what this code is doing:
void output() : When there is no access modifier, the program automatically takes the default modifier.
SampleClass obj = new SampleClass(); : This line of code allows the program to access the class with the default access modifier.
obj.output(); : This line of code allows the program to access the class method with the default access modifier.
The output is: Hello World! This is an Introduction to OOP - Beginner's guide. .
Public Access Modifier
The public access modifier allows a class, a method, or a data field to be accessible from any class or package in a Java program. The public access modifier is accessible within the package as well as outside the package.
In general, a public access modifier does not restrict the entity at all.
Here is an example of how the public access modifier can be used:
Now let's see what's going on in that code:
In the above example,
- The public class Car is accessed from the Main class.
- The public variable tireCount is accessed from the Main class.
- The public method display() is accessed from the Main class.
Private Access Modifier
The private access modifier is an access modifier that has the lowest accessibility level. This means that the methods and fields declared as private are not accessible outside the class. They are accessible only within the class which has these private entities as its members.
You may also note that the private entities are not visible even to the subclasses of the class.
Here is an example of what would happen if you try accessing variables and methods declared private, outside the class:
Alright, what's going on here?
- private String activity : The private access modifier makes the variable “activity” a private one.
- SampleClass task = new SampleClass(); : We have created an object of SampleClass.
- task.activity = "We are learning the core concepts of OOP."; : On this line of code we are trying to access the private variable and field from another class (which can never be accessible because of the private access modifier).
When we run the above program, we will get the following error:
This is because we are trying to access the private variable and field from another class.
So, the best way to access these private variables is to use the getter and setter methods.
Getters and setters are used to protect your data, particularly when creating classes. When we create a getter method for each instance variable, the method returns its value while a setter method sets its value.
Let's have a look at how we can use the getters and setters method to access the private variable.
When we run the above program, this is the output:
As we have a private variable named task in the above example, we have used the methods getTask() and setTask() in order to access the variable from the outer class. These methods are called getter and setter in Java.
We have used the setter method ( setTask() ) to assign value to the variable and the getter method ( getTask() ) to access the variable.
To learn more about the this keyword, you can read this article here .
Protected Access Modifier
When methods and data members are declared protected , we can access them within the same package as well as from subclasses.
We can also say that the protected access modifier is somehow similar to the default access modifier. It is just that it has one exception, which is its visibility in subclasses.
Note that classes cannot be declared protected. This access modifier is generally used in a parent-child relationship.
Let's have a look at how we can use the protected access modifier:
What's this code doing?
In this example, the class Test which is present in another package is able to call the multiplyTwoNumbers() method, which is declared protected.
The method is able to do so because the Test class extends class Addition and the protected modifier allows the access of protected members in subclasses (in any packages).
What are Constructors in Java?
A constructor in Java is a method that you use to initialize newly created objects.
Syntax of a constructor in Java:
So what's going on in this code?
- We have started by creating the Main class.
- After that, we have created a class attribute, which is the variable a .
- Third, we have created a class constructor for the Main class.
- After that, we have set the initial value for variable a that we have declared. The variable a will have a value of 9. Our program will just take 3 times 3, which is equal to 9. You are free to assign any value to the variable a . (In programming, the symbol “*” means multiplication).
Every Java program starts its execution in the main() method. So, we have used the public static void main(String[] args) , and that is the point from where the program starts its execution. In other words, the main() method is the entry point of every Java program.
Now I'll explain what every keyword in the main() method does.
The public keyword.
The public keyword is an access modifier . Its role is to specify from where the method can be accessed, and who can access it. So, when we make the main() method public, it makes it globally available. In other words, it becomes accessible to all parts of the program.
The static keyword.
When a method is declared with a static keyword, it is known as a static method. So, the Java main() method is always static so that the compiler can call it without or before the creation of an object of the class.
If the main() method is allowed to be non-static, then the Java Virtual Machine will have to instantiate its class while calling the main() method.
The static keyword is also important as it saves unnecessary memory wasting which would have been used by the object declared only for calling the main() method by the Java Virtual Machine.
The Void keyword.
The void keyword is a keyword used to specify that a method doesn’t return anything. Whenever the main() method is not expected to return anything, then its return type is void. So, this means that as soon as the main() method terminates, the Java program terminates too.
Main is the name of the Java main method. It is the identifier that the Java Virtual Machine looks for as the starting point of the java program.
The String[] args .
This is an array of strings that stores Java command line arguments.
The next step is to create an object of the class Main. We have created a function call that calls the class constructor.
The last step is to print the value of a , which is 9.
How Methods Work in Java
A method is a block of code that performs a specific task. In Java, we use the term method, but in some other programming languages such as C++, the same method is commonly known as a function.
In Java, there are two types of methods:
- User-defined Methods : These are methods that we can create based on our requirements.
- Standard Library Methods : These are built-in methods in Java that are available to use.
Let me give you an example of how you can use methods in Java.
Java methods example 1:
In the above example, we have created a method named divideNumbers() . The method takes two parameters x and y, and we have called the method by passing two arguments firstNumber and secondNumber .
Now that you know some Java basics, let's look at object-oriented programming principles in a bit more depth.
Key Principles of Object-Oriented Programming.
There are the four main principles of the Object-Oriented Programming paradigm. These principles are also known as the pillars of Object-Oriented Programming.
The four main principles of Object-Oriented Programming are:
- Encapsulation (I will also touch briefly on Information Hiding)
- Inheritance
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
Encapsulation and Information Hiding in Java
Encapsulation is when you wrap up your data under a single unit. In simple terms, it is more or less like a protective shield that prevents the data from being accessed by the code outside this shield.
A simple example of encapsulation is a school bag. A school bag can keep all your items safe in one place, such as your books, pens, pencils, ruler, and more.
Information hiding or data hiding in programming is about protecting data or information from any inadvertent change throughout the program. This is a powerful Object-Oriented Programming feature, and it is closely associated with encapsulation.
The idea behind encapsulation is to ensure that " sensitive " data is hidden from users. To achieve this, you must:
- Declare class variables/attributes as private .
- Provide public get and set methods to access and update the value of a private variable.
As you remember, private variables can only be accessed within the same class and an external class cannot access them. However, they can be accessed if we provide public get and set methods.
Let me give you an additional example that demonstrates how the get and set methods work:
Inheritance in Java
Inheritance allows classes to inherit attributes and methods of other classes. This means that parent classes extend attributes and behaviors to child classes. Inheritance supports reusability.
A simple example that explains the term inheritance is that human beings (in general) inherit certain properties from the class "Human" such as the ability to speak, breathe, eat, drink, and so on.
We group the "inheritance concept" into two categories:
- subclass (child) - the class that inherits from another class.
- superclass (parent) - the class being inherited from.
To inherit from a class, we use the extends keyword.
In the below example, the JerryTheMouse class is created by inheriting the methods and fields from the Animal class.
JerryTheMouse is the subclass and Animal is the superclass.
Abstraction in Java
Abstraction is a concept in object-oriented programming that lets you show only essential attributes and hides unnecessary information in your code. The main purpose of abstraction is to hide unnecessary details from your users.
A simple example to explain abstraction is to think about the process that comes into play when you send an email. When you send an email, complex details such as what happens as soon as it is sent and the protocol that the server uses are hidden from you.
When you send an e-mail, you just need to enter the email address of the receiver, the email subject, type the content, and click send.
You can abstract stuff by using abstract classes or interfaces .
The abstract keyword is a non-access modifier, used for classes and methods:
- Abstract class: is a restricted class that cannot be used to create objects. To access it, it must be inherited from another class.
- Abstract method: A method that doesn't have its body is known as an abstract method. We use the same abstract keyword to create abstract methods.
The body of an abstract method is provided by the subclass (inherited from).
Polymorphism in Java
Polymorphism refers to the ability of an object to take on many forms. Polymorphism normally occurs when we have many classes that are related to each other by inheritance.
Polymorphism is similar to how a person can have different characteristics at the same time.
For instance, a man can be a father, a grandfather, a husband, an employee, and so forth – all at the same time. So, the same person possesses different characteristics or behaviors in different situations.
We are going to create objects Cow and Cat, and call the animalSound() method on each of them.
Inheritance and polymorphism are very useful for code reusability. You can reuse the attributes and methods of an existing class when you create a new class.
Interfaces in Java
An interface is a collection of abstract methods. In other words, an interface is a completely " abstract class " used to group related methods with empty bodies.
An interface specifies what a class can do but not how it can do it.
We have looked at some of the main object-oriented programming concepts in this article. Having a good understanding of these concepts is essential if you want to use them well and write good code.
I hope this article was helpful.
My name is Patrick Cyubahiro, I am a software & web developer, UI/UX designer, technical writer, and Community Builder.
Feel free to connect with me on Twitter: @ Pat_Cyubahiro , or to write to: ampatrickcyubahiro[at]gmail.com
Thanks for reading and happy learning!
Community Builder, Software & web developer, UI/IX Designer, Technical Writer.
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Adam Marcus
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
- Software Design and Engineering
Learning Resource Types
Introduction to programming in java, assignments.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- Java Arrays
- Java Strings
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
- Java Multithreading
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
- Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
- Java Tutorial
Overview of Java
- Introduction to Java
- The Complete History of Java Programming Language
- C++ vs Java vs Python
- How to Download and Install Java for 64 bit machine?
- Setting up the environment in Java
- How to Download and Install Eclipse on Windows?
- JDK in Java
- How JVM Works - JVM Architecture?
- Differences between JDK, JRE and JVM
- Just In Time Compiler
- Difference between JIT and JVM in Java
- Difference between Byte Code and Machine Code
- How is Java platform independent?
Basics of Java
- Java Basic Syntax
- Java Hello World Program
- Java Data Types
- Primitive data type vs. Object data type in Java with Examples
- Java Identifiers
Operators in Java
- Java Variables
- Scope of Variables In Java
Wrapper Classes in Java
Input/output in java.
- How to Take Input From User in Java?
- Scanner Class in Java
- Java.io.BufferedReader Class in Java
- Difference Between Scanner and BufferedReader Class in Java
- Ways to read input from console in Java
- System.out.println in Java
- Difference between print() and println() in Java
- Formatted Output in Java using printf()
- Fast I/O in Java in Competitive Programming
Flow Control in Java
- Decision Making in Java (if, if-else, switch, break, continue, jump)
- Java if statement with Examples
- Java if-else
- Java if-else-if ladder with Examples
- Loops in Java
- For Loop in Java
- Java while loop with Examples
- Java do-while loop with Examples
- For-each loop in Java
- Continue Statement in Java
- Break statement in Java
- Usage of Break keyword in Java
- return keyword in Java
- Java Arithmetic Operators with Examples
- Java Unary Operator with Examples
Java Assignment Operators with Examples
- Java Relational Operators with Examples
- Java Logical Operators with Examples
- Java Ternary Operator with Examples
- Bitwise Operators in Java
- Strings in Java
- String class in Java
- Java.lang.String class in Java | Set 2
- Why Java Strings are Immutable?
- StringBuffer class in Java
- StringBuilder Class in Java with Examples
- String vs StringBuilder vs StringBuffer in Java
- StringTokenizer Class in Java
- StringTokenizer Methods in Java with Examples | Set 2
- StringJoiner Class in Java
- Arrays in Java
- Arrays class in Java
- Multidimensional Arrays in Java
- Different Ways To Declare And Initialize 2-D Array in Java
- Jagged Array in Java
- Final Arrays in Java
- Reflection Array Class in Java
- util.Arrays vs reflect.Array in Java with Examples
OOPS in Java
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concept in Java
- Why Java is not a purely Object-Oriented Language?
- Classes and Objects in Java
- Naming Conventions in Java
- Java Methods
Access Modifiers in Java
- Java Constructors
- Four Main Object Oriented Programming Concepts of Java
Inheritance in Java
Abstraction in java, encapsulation in java, polymorphism in java, interfaces in java.
- 'this' reference in Java
- Inheritance and Constructors in Java
- Java and Multiple Inheritance
- Interfaces and Inheritance in Java
- Association, Composition and Aggregation in Java
- Comparison of Inheritance in C++ and Java
- abstract keyword in java
- Abstract Class in Java
- Difference between Abstract Class and Interface in Java
- Control Abstraction in Java with Examples
- Difference Between Data Hiding and Abstraction in Java
- Difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in Java with Examples
- Difference between Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Dynamic Method Dispatch or Runtime Polymorphism in Java
- Difference between Compile-time and Run-time Polymorphism in Java
Constructors in Java
- Copy Constructor in Java
- Constructor Overloading in Java
- Constructor Chaining In Java with Examples
- Private Constructors and Singleton Classes in Java
Methods in Java
- Static methods vs Instance methods in Java
- Abstract Method in Java with Examples
- Overriding in Java
- Method Overloading in Java
- Difference Between Method Overloading and Method Overriding in Java
- Differences between Interface and Class in Java
- Functional Interfaces in Java
- Nested Interface in Java
- Marker interface in Java
- Comparator Interface in Java with Examples
- Need of Wrapper Classes in Java
- Different Ways to Create the Instances of Wrapper Classes in Java
- Character Class in Java
- Java.Lang.Byte class in Java
- Java.Lang.Short class in Java
- Java.lang.Integer class in Java
- Java.Lang.Long class in Java
- Java.Lang.Float class in Java
- Java.Lang.Double Class in Java
- Java.lang.Boolean Class in Java
- Autoboxing and Unboxing in Java
- Type conversion in Java with Examples
Keywords in Java
- Java Keywords
- Important Keywords in Java
- Super Keyword in Java
- final Keyword in Java
- static Keyword in Java
- enum in Java
- transient keyword in Java
- volatile Keyword in Java
- final, finally and finalize in Java
- Public vs Protected vs Package vs Private Access Modifier in Java
- Access and Non Access Modifiers in Java
Memory Allocation in Java
- Java Memory Management
- How are Java objects stored in memory?
- Stack vs Heap Memory Allocation
- How many types of memory areas are allocated by JVM?
- Garbage Collection in Java
- Types of JVM Garbage Collectors in Java with implementation details
- Memory leaks in Java
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Stack Area
Classes of Java
- Understanding Classes and Objects in Java
- Singleton Method Design Pattern in Java
- Object Class in Java
- Inner Class in Java
- Throwable Class in Java with Examples
Packages in Java
- Packages In Java
- How to Create a Package in Java?
- Java.util Package in Java
- Java.lang package in Java
- Java.io Package in Java
- Java Collection Tutorial
Exception Handling in Java
- Exceptions in Java
- Types of Exception in Java with Examples
- Checked vs Unchecked Exceptions in Java
- Java Try Catch Block
- Flow control in try catch finally in Java
- throw and throws in Java
- User-defined Custom Exception in Java
- Chained Exceptions in Java
- Null Pointer Exception In Java
- Exception Handling with Method Overriding in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- Lifecycle and States of a Thread in Java
- Java Thread Priority in Multithreading
- Main thread in Java
- Java.lang.Thread Class in Java
- Runnable interface in Java
- Naming a thread and fetching name of current thread in Java
- What does start() function do in multithreading in Java?
- Difference between Thread.start() and Thread.run() in Java
- Thread.sleep() Method in Java With Examples
- Synchronization in Java
- Importance of Thread Synchronization in Java
- Method and Block Synchronization in Java
- Lock framework vs Thread synchronization in Java
- Difference Between Atomic, Volatile and Synchronized in Java
- Deadlock in Java Multithreading
- Deadlock Prevention And Avoidance
- Difference Between Lock and Monitor in Java Concurrency
- Reentrant Lock in Java
File Handling in Java
- Java.io.File Class in Java
- Java Program to Create a New File
- Different ways of Reading a text file in Java
- Java Program to Write into a File
- Delete a File Using Java
- File Permissions in Java
- FileWriter Class in Java
- Java.io.FileDescriptor in Java
- Java.io.RandomAccessFile Class Method | Set 1
- Regular Expressions in Java
- Regex Tutorial - How to write Regular Expressions?
- Matcher pattern() method in Java with Examples
- Pattern pattern() method in Java with Examples
- Quantifiers in Java
- java.lang.Character class methods | Set 1
- Java IO : Input-output in Java with Examples
- Java.io.Reader class in Java
- Java.io.Writer Class in Java
- Java.io.FileInputStream Class in Java
- FileOutputStream in Java
- Java.io.BufferedOutputStream class in Java
- Java Networking
- TCP/IP Model
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- Differences between IPv4 and IPv6
- Difference between Connection-oriented and Connection-less Services
- Socket Programming in Java
- java.net.ServerSocket Class in Java
- URL Class in Java with Examples
JDBC - Java Database Connectivity
- Introduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
- JDBC Drivers
- Establishing JDBC Connection in Java
- Types of Statements in JDBC
- JDBC Tutorial
- Java 8 Features - Complete Tutorial
Operators constitute the basic building block of any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provide.
Types of Operators:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Ternary Operator
- Bitwise Operators
- Shift Operators
This article explains all that one needs to know regarding Assignment Operators.
Assignment Operators
These operators are used to assign values to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable, and the right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data type of the operand on the left side. Otherwise, the compiler will raise an error. This means that the assignment operators have right to left associativity, i.e., the value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left. Therefore, the right-hand side value must be declared before using it or should be a constant. The general format of the assignment operator is,
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are:
1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the “=” sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
2. Compound Assignment Operator: The Compound Operator is used where +,-,*, and / is used along with the = operator.
Let’s look at each of the assignment operators and how they operate:
1. (=) operator:
This is the most straightforward assignment operator, which is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. This is the basic definition of an assignment operator and how it functions.
Syntax:
Example:
2. (+=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘+’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by adding the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
Note: The compound assignment operator in Java performs implicit type casting. Let’s consider a scenario where x is an int variable with a value of 5. int x = 5; If you want to add the double value 4.5 to the integer variable x and print its value, there are two methods to achieve this: Method 1: x = x + 4.5 Method 2: x += 4.5 As per the previous example, you might think both of them are equal. But in reality, Method 1 will throw a runtime error stating the “i ncompatible types: possible lossy conversion from double to int “, Method 2 will run without any error and prints 9 as output.
Reason for the Above Calculation
Method 1 will result in a runtime error stating “incompatible types: possible lossy conversion from double to int.” The reason is that the addition of an int and a double results in a double value. Assigning this double value back to the int variable x requires an explicit type casting because it may result in a loss of precision. Without the explicit cast, the compiler throws an error. Method 2 will run without any error and print the value 9 as output. The compound assignment operator += performs an implicit type conversion, also known as an automatic narrowing primitive conversion from double to int . It is equivalent to x = (int) (x + 4.5) , where the result of the addition is explicitly cast to an int . The fractional part of the double value is truncated, and the resulting int value is assigned back to x . It is advisable to use Method 2 ( x += 4.5 ) to avoid runtime errors and to obtain the desired output.
Same automatic narrowing primitive conversion is applicable for other compound assignment operators as well, including -= , *= , /= , and %= .
3. (-=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘-‘ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by subtracting the variable’s value on the right from the current value of the variable on the left and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
4. (*=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘*’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by multiplying the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
5. (/=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘/’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by dividing the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigning the quotient to the operand on the left.
6. (%=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘%’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by dividing the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigning the remainder to the operand on the left.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Java-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The best way we learn anything is by practice and exercise questions. Here you have the opportunity to practice the Java programming language concepts by solving the exercises starting from basic to more complex exercises. A sample solution is provided for each exercise. It is recommended to do these exercises by yourself first before checking ...
Write a Java program to compute the area of a polygon. Area of a polygon = (n*s^2)/ (4*tan (π/n)) where n is n-sided polygon and s is the length of a side Input Data: Input the number of sides on the polygon: 7 Input the length of one of the sides: 6 Expected Output. The area is: 130.82084798405722.
1. How to do Java projects for beginners? To do Java projects you need to know the fundamentals of Java programming. Then you need to select the desired Java project you want to work on. Plan and execute the code to finish the project. Some beginner-level Java projects include: Reversing a String; Number Guessing Game; Creating a Calculator
Explore the Java coding exercises for practicing with commands below. First, read the conditions, scroll down to the Solution box, and type your solution. Then, click Verify (above the Conditions box) to check the correctness of your program. Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3. Start task.
Get certified by completing the JAVA course. Track your progress - it's free! Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more.
10 Java code challenges to practice your new skills. 1. Word reversal. For this challenge, the input is a string of words, and the output should be the words in reverse but with the letters in the original order. For example, the string "Dog bites man" should output as "man bites Dog.".
Popular for its versatility and ability to create a wide variety of applications, learning Java opens up your possibilities when coding. With it, you'll be able to develop large systems, software, and mobile applications — and even create mobile apps for Android. Learn important Java coding fundamentals and practice your new skills with ...
The course is designed to introduce the Java programming language to beginners. It covers the basics of Java, including syntax, data types, and operators. The course dives deeper into exception handling, file I/O, working with arrays, and object-oriented programming concepts. ... To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will ...
Learn Java: Object-Oriented Programming Explore classes and objects in this introduction to object-oriented programming with Java. Beginner Friendly. 3 hours. Free course. Learn Java: Loops and Arrays Take your programming skills to the next level by learning about arrays and loops. Beginner ...
Java Tutorial Summary. This Java tutorial for beginners is taught in a practical GOAL-oriented way. It is recommended you practice the code assignments given after each core Java tutorial to learn Java from scratch. This Java programming for beginners course will help you learn basics of Java and advanced concepts.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: The final local variable age cannot be assigned. It must be blank and not using a compound assignment at variables.Main.main(Main.java:9) However, if you leave the variable uninitialized while declaring, the code will work:
How Edabit Works. This is an introduction to how challenges on Edabit work. In the Code tab above you'll see a starter function that looks like this: public static boolean returnTrue () { } All you have to do is type return true; between the curly braces { } and then click the Check button. If you did this correctly, the button will turn re ...
This java tutorial would help you learn Java like a pro. I have shared 1000+ tutorials on various topics of Java, including core java and advanced Java concepts along with several Java programming examples to help you understand better. All the tutorials are provided in a easy to follow systematic manner. It is for everyone, whether you are a ...
This course is an introduction to software engineering, using the Java™ programming language. It covers concepts useful to 6.005. Students will learn the fundamentals of Java. The focus is on developing high quality, working software that solves real problems. The course is designed for students with some programming experience, but if you have none and are motivated you will do fine.
Out of 500+ Simple & Basic Java Programs: Hello world is a first-ever program which we published on our site. Of course, Every Java programmer or C programmer will start with a "Hello World Program". Followed by the rest of the programs in different Categories. 1. Area Of Circle Java Program. 2.
LEARN JAVA PROGRAMMING WRITING 200+ JAVA PROGRAMS, PUZZLES & EXERCISES. RECOMMENDED for absolute beginners to Java and Programming!. BONUS - Learn to Build REST API with Spring, Spring Boot, and JPA. 7 Things YOU need to know about this JAVA PROGRAMMING Course #1: 150,000+ Learners - One of the highest-rated Java Courses on Udemy! #2: Designed for ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS to Java Programming (Core ...
7. Library Management System. Learning Management System, this project build on Java is a great way to update the record, monitor and add books, search for the required ones, taking care of the issue date and return date. It comes with basic features like creating a new record and updating and deleting it.
Programming assignments. Creative programming assignments that we have used at Princeton. You can explore these resources via the sidebar at left. Introduction to Programming in Java. Our textbook Introduction to Programming in Java [ Amazon · Pearson · InformIT] is an interdisciplinary approach to the traditional CS1 curriculum with Java. We ...
Best Practices in Java: Write clean, effective, and well-organized Java code, adhering to best practices for code readability, maintainability, and application performance. Build This Java Project Here. 4. Brick Breaker Game. This brick breaker game is one of many fun Java projects that has you trying to break bricks at the top of the screen.
Example Get your own Java Server. Click on the "Run example" button to see how it works. We recommend reading this tutorial, in the sequence listed in the left menu. Java is an object oriented language and some concepts may be new. Take breaks when needed, and go over the examples as many times as needed.
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a fundamental programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects ". These objects can contain data in the form of fields (often known as attributes or properties) and code in the form of procedures (often known as methods). The core concept of the object-oriented approach is to break complex problems ...
This section provides the assignments for the course, supporting files, and a special set of assignment files that can be annotated. Assignments | Introduction to Programming in Java | Electrical Engineering and Computer Science | MIT OpenCourseWare
Note: The compound assignment operator in Java performs implicit type casting. Let's consider a scenario where x is an int variable with a value of 5. int x = 5; If you want to add the double value 4.5 to the integer variable x and print its value, there are two methods to achieve this: Method 1: x = x + 4.5. Method 2: x += 4.5.