
The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources


Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
APA Results Section – Explanation & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The APA results section summarizes data and includes reporting statistics in a quantitative research study. The APA results section is an essential part of your research paper and typically begins with a brief overview of the data followed by a systematic and detailed reporting of each hypothesis tested. The interpreted results will then be presented in the discussion sections. Ensure you adhere to APA style guidelines consistently throughout the paper.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 APA Results Section – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: APA results section
- 3 What’s included in the APA results section?
- 4 APA results section: Introducing the data
- 5 APA results section: Summarizing the data
- 6 APA results section: Reporting the results
- 7 APA results section: Formatting numbers
- 8 APA results section: Don’t include these
APA Results Section – In a Nutshell
- The APA results section of empirical manuscripts reports the quantitative results of a study conducted on a data set.
- The APA results section provides concrete evidence to disprove or confirm the hypothesis.
Definition: APA results section
The American Psychological Association recommends the APA style guide for presenting results in a manuscript. A research manuscript’s APA results section describes the researcher’s findings following a thorough data analysis and interpretation of the results. It uses obtained data to test or refute the theory of a research study.
What’s included in the APA results section?
The APA results section includes preliminary details on the data, participants, statistics , and the results of the explanatory analysis , as discussed below.
- Participants – The number of participants is reported at every study stage
- Missing data – Identifying the amount of data excluded from the final analysis.
- Adverse effects – Report any unforeseen events for clinical studies
- Descriptive statistics – Summarize the secondary and primary outcomes of a study
- Inferential statistics – Helps researchers draw conclusions and make predictions from the data.
- Confidence interval and effect size – Confidence intervals are a range of possible values for the data set mean.
- Results of explanatory analysis – An exploratory research investigates data to test a hypothesis, check assumptions, and find anomalies.
APA results section: Introducing the data
Before you discuss your research findings, start by clearly describing the participants at each study stage. If any data was excluded from the eventual analysis, indicate that too.
Participants
Recruitment, participant flow, and attrition should be reported. Attrition bias affects external and internal validity and produces erroneous results.
A flow chart is often the best way to report the number of participants per group per stage and their reasons for attrition. Below is an example of how to report participant flow.
- 25% of the 400 participants who signed up and completed the first survey were eliminated for not fitting the research criteria.
- 15% didn’t use fiber optics internet exclusively.
- 10% did not have internet access.
- 300 participants progressed to the final survey round for a gift bag.
- 52 people didn’t complete the survey.
This resulted in 248 research participants.
Missing data & adverse effects
In any study, missing data must be reported. Unexpected events, poor storage, and equipment failures can cause missing data. In any instance, clearly explain why you couldn’t use the data.
Data outliers can be excluded from the final study, but you must explain why. Include how you handled missing data. Standard procedures include mean-value imputation, interpolation, extrapolation, and substitution.
- Results of 33 participants were excluded from the study as they did not meet the research criteria.
- The data for another 4 participants were lost due to human error.
APA results section: Summarizing the data
It is important to note that you should provide a summary of your study’s results. However, you can create a supplemental archive for other researchers to access raw data. 2
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are concise coefficients that summarize a specific data collection , such as a population sample or APA results section. APA results section can include descriptive statistics such as:
- Central tendency measures describe a data set by identifying the center of the data set. ( mode , median, mean )
- Measures of variability describe the score dispersion within a data set. ( standard deviation , range, variance , and interquartile range )
- Sample sizes
- Variables of interest, which are measured, changing quantities in experimental studies. Be sure to explain how you operationalized any variable of interest you use.
- 20 athletes in five trials were given 400 mg of a performance-enhancing substance to measure their speed (m/s ) and reaction time(s).
- After averaging each athlete’s speed and response time, the group’s averages were calculated.
The group that used the performance-enhancing drug had a higher speed (m/s) than the group that did not use the drug ( M = 4, SD=1.25 )
APA results section: Reporting the results
APA journal standards require all the appropriate hypothesis tests, confidence intervals, and effect size estimates to be reported in the APA results section.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics help researchers draw conclusions and make predictions based on the data.
When you are reporting the inferential statistics in the APA results section, use the following:
- Degrees of freedom
- Test statistic (includes the z-score, t-value, and f-ratio )
- Error term (if needed, though it is not included in correlations and non-parametric tests.)
- The exact p-value (unless . 001)
In keeping with the hypotheses, athletes who take performance-enhancing drugs have increased reaction times, and speeds, t (20) = 1s , p .001
Confidence intervals & effect sizes
A confidence interval can be described as a range of possible values for the mean derived from the sample data. It helps show the variability that is around point estimates. You should include confidence intervals any time you report estimates for population parameters.
Night guards consume an average of 600 mg of caffeine weekly, 93% CI [90, 200}
Effect size measures an experiment’s magnitude. It explains the research’s significance. Since effect size is an estimate, confidence intervals should be included.
Moderate amounts of performance-enhancing drugs increase speed significantly, Cohen’s d =1.4, 93% CI [0.92, 1.57]
Subgroup & exploratory analyses
Exploratory analysis tests a hypothesis, checks assumptions , and finds patterns and anomalies in data . If you find notable results, report them as exploratory, not confirming, to avoid overstating their value.
APA results section: Formatting numbers
Use figures, text, and tables to show numbers in APA results sections properly.
✓ For three or fewer numbers, use a sentence, a table for 4 and 20 numbers, and a figure for more than 20 .
✓ Number and title the APA tables and figures , as well as relevant notes. If you have already presented the data in a table, do not repeat it in a figure and vice versa.
✓ Statistics in your APA results section must be abbreviated, capitalized, and italicized.
✓ Use APA norms for reporting statistics and writing numbers.
✓ Look up these guidelines if you are unsure how to present certain symbols.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
APA results section: Don’t include these
Besides knowing what to include in an APA results section, it is just as important to know what not to have. Below is an outline of what you should exclude from an APA results section.
What should be included in the APA results section?
The APA results section should include details on the participants, descriptive statistics and inferential statistics , missing data , and the results of any exploratory analysis.
What tense should I use to write my results?
Write the APA results section in the past tense.
When should I include tables and figures?
Include tables and figures if you will discuss them in the body text of the APA results section.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Method section
Your method section provides a detailed overview of how you conducted your research. Because your study methods form a large part of your credibility as a researcher and writer, it is imperative that you be clear about what you did to gather information from participants in your study.
With your methods section, as with the sections above, you want to walk your readers through your study almost as if they were a participant. What happened first? What happened next?
The method section includes the following sub-sections.
I. Participants: Discuss who was enrolled in your experiment. Include major demographics that have an impact on the results of the experiment (i.e. if race is a factor, you should provide a breakdown by race). The accepted term for describing a person who participates in research studies is a participant not a subject.
II. Apparatus and materials: The apparatus is any equipment used during data collection (such as computers or eye-tracking devices). Materials include scripts, surveys, or software used for data collection (not data analysis). It is sometimes necessary to provide specific examples of materials or prompts, depending on the nature of your study.
III. Procedure: The procedure includes the step-by-step how of your experiment. The procedure should include:
- A description of the experimental design and how participants were assigned conditions.
- Identification of your independent variable(s) (IV), dependent variable(s) (DV), and control variables. Give your variables clear, meaningful names so that your readers are not confused.
- Important instructions to participants.
- A step-by-step listing in chronological order of what participants did during the experiment.
Results section
The results section is where you present the results of your research-both narrated for the readers in plain English and accompanied by statistics.
Note : Depending on the requirements or the projected length of your paper, sometimes the results are combined with the discussion section.
Organizing Results
Continue with your story in the results section. How do your results fit with the overall story you are telling? What results are the most compelling? You want to begin your discussion by reminding your readers once again what your hypotheses were and what your overall story is. Then provide each result as it relates to that story. The most important results should go first.
Preliminary discussion: Sometimes it is necessary to provide a preliminary discussion in your results section about your participant groups. In order to convince your readers that your results are meaningful, you must first demonstrate that the conditions of the study were met. For example, if you randomly assigned subjects into groups, are these two groups comparable? You can't discuss the differences in the two groups until you establish that the two groups can be compared.
Provide information on your data analysis: Be sure to describe the analysis you did. If you are using a non-conventional analysis, you also need to provide justification for why you are doing so.
Presenting Results : Bem (2006) recommends the following pattern for presenting findings:
- Remind readers of the conceptual hypotheses or questions you are asking
- Remind readers of behaviors measured or operations performed
- Provide the answer/result in plain English
- Provide the statistic that supports your plain English answer
- Elaborate or qualify the overall conclusion if necessary
Writers new to psychology and writing with statistics often dump numbers at their readers without providing a clear narration of what those numbers mean. Please see our Writing with Statistics handout for more information on how to write with statistics.
Discussion section
Your discussion section is where you talk about what your results mean and where you wrap up the overall story you are telling. This is where you interpret your findings, evaluate your hypotheses or research questions, discuss unexpected results, and tie your findings to the previous literature (discussed first in your literature review). Your discussion section should move from specific to general.
Here are some tips for writing your discussion section.
- Begin by providing an interpretation of your results: what is it that you have learned from your research?
- Discuss each hypotheses or research question in more depth.
- Do not repeat what you have already said in your results—instead, focus on adding new information and broadening the perspective of your results to you reader.
- Discuss how your results compare to previous findings in the literature. If there are differences, discuss why you think these differences exist and what they could mean.
- Briefly consider your study's limitations, but do not dwell on its flaws.
- Consider also what new questions your study raises, what questions your study was not able to answer, and what avenues future research could take in this area.
Example: Here is how this works.
References section
References should be in standard APA format. Please see our APA Formatting guide for specific instructions.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.
Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
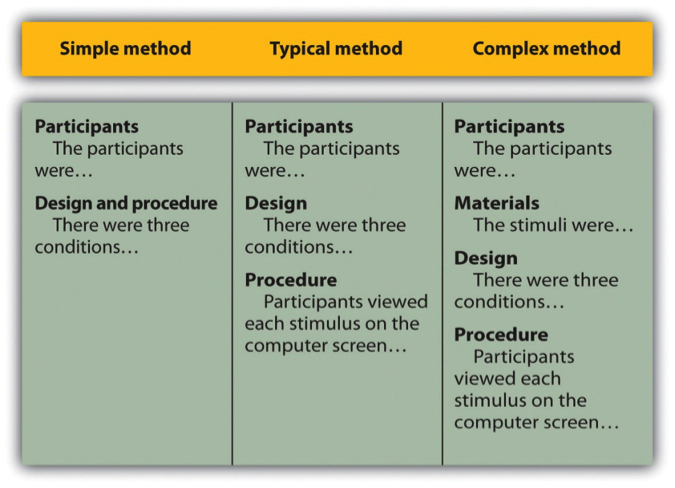
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write an APA Research Paper
Psychology/neuroscience 201, v iew in pdf format.
An APA-style paper includes the following sections: title page, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references. Your paper may also include one or more tables and/or figures. Different types of information about your study are addressed in each of the sections, as described below.
General formatting rules are as follows:
Do not put page breaks in between the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections.
The title page, abstract, references, table(s), and figure(s) should be on their own pages. The entire paper should be written in the past tense, in a 12-point font, double-spaced, and with one-inch margins all around.
(see sample on p. 41 of APA manual)
- Title should be between 10-12 words and should reflect content of paper (e.g., IV and DV).
- Title, your name, and Hamilton College are all double-spaced (no extra spaces)
- Create a page header using the “View header” function in MS Word. On the title page, the header should include the following: Flush left: Running head: THE RUNNING HEAD SHOULD BE IN ALL CAPITAL LETTERS. The running head is a short title that appears at the top of pages of published articles. It should not exceed 50 characters, including punctuation and spacing. (Note: on the title page, you actually write the words “Running head,” but these words do not appear on subsequent pages; just the actual running head does. If you make a section break between the title page and the rest of the paper you can make the header different for those two parts of the manuscript). Flush right, on same line: page number. Use the toolbox to insert a page number, so it will automatically number each page.
Abstract (labeled, centered, not bold)
No more than 120 words, one paragraph, block format (i.e., don’t indent), double-spaced.
- State topic, preferably in one sentence. Provide overview of method, results, and discussion.
Introduction
(Do not label as “Introduction.” Title of paper goes at the top of the page—not bold)
The introduction of an APA-style paper is the most difficult to write. A good introduction will summarize, integrate, and critically evaluate the empirical knowledge in the relevant area(s) in a way that sets the stage for your study and why you conducted it. The introduction starts out broad (but not too broad!) and gets more focused toward the end. Here are some guidelines for constructing a good introduction:
- Don’t put your readers to sleep by beginning your paper with the time-worn sentence, “Past research has shown (blah blah blah)” They’ll be snoring within a paragraph! Try to draw your reader in by saying something interesting or thought-provoking right off the bat. Take a look at articles you’ve read. Which ones captured your attention right away? How did the authors accomplish this task? Which ones didn’t? Why not? See if you can use articles you liked as a model. One way to begin (but not the only way) is to provide an example or anecdote illustrative of your topic area.
- Although you won’t go into the details of your study and hypotheses until the end of the intro, you should foreshadow your study a bit at the end of the first paragraph by stating your purpose briefly, to give your reader a schema for all the information you will present next.
- Your intro should be a logical flow of ideas that leads up to your hypothesis. Try to organize it in terms of the ideas rather than who did what when. In other words, your intro shouldn’t read like a story of “Schmirdley did such-and-such in 1991. Then Gurglehoff did something-or-other in 1993. Then....(etc.)” First, brainstorm all of the ideas you think are necessary to include in your paper. Next, decide which ideas make sense to present first, second, third, and so forth, and think about how you want to transition between ideas. When an idea is complex, don’t be afraid to use a real-life example to clarify it for your reader. The introduction will end with a brief overview of your study and, finally, your specific hypotheses. The hypotheses should flow logically out of everything that’s been presented, so that the reader has the sense of, “Of course. This hypothesis makes complete sense, given all the other research that was presented.”
- When incorporating references into your intro, you do not necessarily need to describe every single study in complete detail, particularly if different studies use similar methodologies. Certainly you want to summarize briefly key articles, though, and point out differences in methods or findings of relevant studies when necessary. Don’t make one mistake typical of a novice APA-paper writer by stating overtly why you’re including a particular article (e.g., “This article is relevant to my study because…”). It should be obvious to the reader why you’re including a reference without your explicitly saying so. DO NOT quote from the articles, instead paraphrase by putting the information in your own words.
- Be careful about citing your sources (see APA manual). Make sure there is a one-to-one correspondence between the articles you’ve cited in your intro and the articles listed in your reference section.
- Remember that your audience is the broader scientific community, not the other students in your class or your professor. Therefore, you should assume they have a basic understanding of psychology, but you need to provide them with the complete information necessary for them to understand the research you are presenting.
Method (labeled, centered, bold)
The Method section of an APA-style paper is the most straightforward to write, but requires precision. Your goal is to describe the details of your study in such a way that another researcher could duplicate your methods exactly.
The Method section typically includes Participants, Materials and/or Apparatus, and Procedure sections. If the design is particularly complicated (multiple IVs in a factorial experiment, for example), you might also include a separate Design subsection or have a “Design and Procedure” section.
Note that in some studies (e.g., questionnaire studies in which there are many measures to describe but the procedure is brief), it may be more useful to present the Procedure section prior to the Materials section rather than after it.
Participants (labeled, flush left, bold)
Total number of participants (# women, # men), age range, mean and SD for age, racial/ethnic composition (if applicable), population type (e.g., college students). Remember to write numbers out when they begin a sentence.
- How were the participants recruited? (Don’t say “randomly” if it wasn’t random!) Were they compensated for their time in any way? (e.g., money, extra credit points)
- Write for a broad audience. Thus, do not write, “Students in Psych. 280...” Rather, write (for instance), “Students in a psychological statistics and research methods course at a small liberal arts college….”
- Try to avoid short, choppy sentences. Combine information into a longer sentence when possible.
Materials (labeled, flush left, bold)
Carefully describe any stimuli, questionnaires, and so forth. It is unnecessary to mention things such as the paper and pencil used to record the responses, the data recording sheet, the computer that ran the data analysis, the color of the computer, and so forth.
- If you included a questionnaire, you should describe it in detail. For instance, note how many items were on the questionnaire, what the response format was (e.g., a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree)), how many items were reverse-scored, whether the measure had subscales, and so forth. Provide a sample item or two for your reader.
- If you have created a new instrument, you should attach it as an Appendix.
- If you presented participants with various word lists to remember or stimuli to judge, you should describe those in detail here. Use subheadings to separate different types of stimuli if needed. If you are only describing questionnaires, you may call this section “Measures.”
Apparatus (labeled, flush left, bold)
Include an apparatus section if you used specialized equipment for your study (e.g., the eye tracking machine) and need to describe it in detail.
Procedure (labeled, flush left, bold)
What did participants do, and in what order? When you list a control variable (e.g., “Participants all sat two feet from the experimenter.”), explain WHY you did what you did. In other words, what nuisance variable were you controlling for? Your procedure should be as brief and concise as possible. Read through it. Did you repeat yourself anywhere? If so, how can you rearrange things to avoid redundancy? You may either write the instructions to the participants verbatim or paraphrase, whichever you deem more appropriate. Don’t forget to include brief statements about informed consent and debriefing.
Results (labeled, centered, bold)
In this section, describe how you analyzed the data and what you found. If your data analyses were complex, feel free to break this section down into labeled subsections, perhaps one section for each hypothesis.
- Include a section for descriptive statistics
- List what type of analysis or test you conducted to test each hypothesis.
- Refer to your Statistics textbook for the proper way to report results in APA style. A t-test, for example, is reported in the following format: t (18) = 3.57, p < .001, where 18 is the number of degrees of freedom (N – 2 for an independent-groups t test). For a correlation: r (32) = -.52, p < .001, where 32 is the number of degrees of freedom (N – 2 for a correlation). For a one-way ANOVA: F (2, 18) = 7.00, p < .001, where 2 represents the between and 18 represents df within Remember that if a finding has a p value greater than .05, it is “nonsignificant,” not “insignificant.” For nonsignificant findings, still provide the exact p values. For correlations, be sure to report the r 2 value as an assessment of the strength of the finding, to show what proportion of variability is shared by the two variables you’re correlating. For t- tests and ANOVAs, report eta 2 .
- Report exact p values to two or three decimal places (e.g., p = .042; see p. 114 of APA manual). However, for p-values less than .001, simply put p < .001.
- Following the presentation of all the statistics and numbers, be sure to state the nature of your finding(s) in words and whether or not they support your hypothesis (e.g., “As predicted …”). This information can typically be presented in a sentence or two following the numbers (within the same paragraph). Also, be sure to include the relevant means and SDs.
- It may be useful to include a table or figure to represent your results visually. Be sure to refer to these in your paper (e.g., “As illustrated in Figure 1…”). Remember that you may present a set of findings either as a table or as a figure, but not as both. Make sure that your text is not redundant with your tables/figures. For instance, if you present a table of means and standard deviations, you do not need to also report these in the text. However, if you use a figure to represent your results, you may wish to report means and standard deviations in the text, as these may not always be precisely ascertained by examining the figure. Do describe the trends shown in the figure.
- Do not spend any time interpreting or explaining the results; save that for the Discussion section.
Discussion (labeled, centered, bold)
The goal of the discussion section is to interpret your findings and place them in the broader context of the literature in the area. A discussion section is like the reverse of the introduction, in that you begin with the specifics and work toward the more general (funnel out). Some points to consider:
- Begin with a brief restatement of your main findings (using words, not numbers). Did they support the hypothesis or not? If not, why not, do you think? Were there any surprising or interesting findings? How do your findings tie into the existing literature on the topic, or extend previous research? What do the results say about the broader behavior under investigation? Bring back some of the literature you discussed in the Introduction, and show how your results fit in (or don’t fit in, as the case may be). If you have surprising findings, you might discuss other theories that can help to explain the findings. Begin with the assumption that your results are valid, and explain why they might differ from others in the literature.
- What are the limitations of the study? If your findings differ from those of other researchers, or if you did not get statistically significant results, don’t spend pages and pages detailing what might have gone wrong with your study, but do provide one or two suggestions. Perhaps these could be incorporated into the future research section, below.
- What additional questions were generated from this study? What further research should be conducted on the topic? What gaps are there in the current body of research? Whenever you present an idea for a future research study, be sure to explain why you think that particular study should be conducted. What new knowledge would be gained from it? Don’t just say, “I think it would be interesting to re-run the study on a different college campus” or “It would be better to run the study again with more participants.” Really put some thought into what extensions of the research might be interesting/informative, and why.
- What are the theoretical and/or practical implications of your findings? How do these results relate to larger issues of human thoughts, feelings, and behavior? Give your readers “the big picture.” Try to answer the question, “So what?
Final paragraph: Be sure to sum up your paper with a final concluding statement. Don’t just trail off with an idea for a future study. End on a positive note by reminding your reader why your study was important and what it added to the literature.
References (labeled, centered, not bold)
Provide an alphabetical listing of the references (alphabetize by last name of first author). Double-space all, with no extra spaces between references. The second line of each reference should be indented (this is called a hanging indent and is easily accomplished using the ruler in Microsoft Word). See the APA manual for how to format references correctly.
Examples of references to journal articles start on p. 198 of the manual, and examples of references to books and book chapters start on pp. 202. Digital object identifiers (DOIs) are now included for electronic sources (see pp. 187-192 of APA manual to learn more).
Journal article example: [Note that only the first letter of the first word of the article title is capitalized; the journal name and volume are italicized. If the journal name had multiple words, each of the major words would be capitalized.]
Ebner-Priemer, U. W., & Trull, T. J. (2009). Ecological momentary assessment of mood disorders and mood dysregulation. Psychological Assessment, 21, 463-475. doi:10.1037/a0017075
Book chapter example: [Note that only the first letter of the first word of both the chapter title and book title are capitalized.]
Stephan, W. G. (1985). Intergroup relations. In G. Lindzey & E. Aronson (Eds.), The handbook of social psychology (3 rd ed., Vol. 2, pp. 599-658). New York: Random House.
Book example: Gray, P. (2010). Psychology (6 th ed.). New York: Worth
Table There are various formats for tables, depending upon the information you wish to include. See the APA manual. Be sure to provide a table number and table title (the latter is italicized). Tables can be single or double-spaced.
Figure If you have more than one figure, each one gets its own page. Use a sans serif font, such as Helvetica, for any text within your figure. Be sure to label your x- and y-axes clearly, and make sure you’ve noted the units of measurement of the DV. Underneath the figure provide a label and brief caption (e.g., “Figure 1. Mean evaluation of job applicant qualifications as a function of applicant attractiveness level”). The figure caption typically includes the IVs/predictor variables and the DV. Include error bars in your bar graphs, and note what the bars represent in the figure caption: Error bars represent one standard error above and below the mean.
In-Text Citations: (see pp. 174-179 of APA manual) When citing sources in your paper, you need to include the authors’ names and publication date.
You should use the following formats:
- When including the citation as part of the sentence, use AND: “According to Jones and Smith (2003), the…”
- When the citation appears in parentheses, use “&”: “Studies have shown that priming can affect actual motor behavior (Jones & Smith, 2003; Klein, Bailey, & Hammer, 1999).” The studies appearing in parentheses should be ordered alphabetically by the first author’s last name, and should be separated by semicolons.
- If you are quoting directly (which you should avoid), you also need to include the page number.
- For sources with three or more authors, once you have listed all the authors’ names, you may write “et al.” on subsequent mentions. For example: “Klein et al. (1999) found that….” For sources with two authors, both authors must be included every time the source is cited. When a source has six or more authors, the first author’s last name and “et al.” are used every time the source is cited (including the first time).
Secondary Sources
“Secondary source” is the term used to describe material that is cited in another source. If in his article entitled “Behavioral Study of Obedience” (1963), Stanley Milgram makes reference to the ideas of Snow (presented above), Snow (1961) is the primary source, and Milgram (1963) is the secondary source.
Try to avoid using secondary sources in your papers; in other words, try to find the primary source and read it before citing it in your own work. If you must use a secondary source, however, you should cite it in the following way:
Snow (as cited in Milgram, 1963) argued that, historically, the cause of most criminal acts... The reference for the Milgram article (but not the Snow reference) should then appear in the reference list at the end of your paper.
Tutor Appointments
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Results
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Results Section in Research
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions.
In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings of the study. It is important to be objective and not interpret the data in this section. Instead, the researcher should report the data as accurately and objectively as possible.
Structure of Research Results Section
The structure of the research results section can vary depending on the type of research conducted, but in general, it should contain the following components:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the study, its aims, and its research questions. It should also briefly explain the methodology used to conduct the study.
- Data presentation : This section presents the data collected during the study. It may include tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help readers better understand the data. The data presented should be organized in a logical and coherent way, with headings and subheadings used to help guide the reader.
- Data analysis: In this section, the data presented in the previous section are analyzed and interpreted. The statistical tests used to analyze the data should be clearly explained, and the results of the tests should be presented in a way that is easy to understand.
- Discussion of results : This section should provide an interpretation of the results of the study, including a discussion of any unexpected findings. The discussion should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Limitations: This section should acknowledge any limitations of the study, such as sample size, data collection methods, or other factors that may have influenced the results.
- Conclusions: The conclusions should summarize the main findings of the study and provide a final interpretation of the results. The conclusions should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Recommendations : This section may provide recommendations for future research based on the study’s findings. It may also suggest practical applications for the study’s results in real-world settings.
Outline of Research Results Section
The following is an outline of the key components typically included in the Results section:
I. Introduction
- A brief overview of the research objectives and hypotheses
- A statement of the research question
II. Descriptive statistics
- Summary statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation) for each variable analyzed
- Frequencies and percentages for categorical variables
III. Inferential statistics
- Results of statistical analyses, including tests of hypotheses
- Tables or figures to display statistical results
IV. Effect sizes and confidence intervals
- Effect sizes (e.g., Cohen’s d, odds ratio) to quantify the strength of the relationship between variables
- Confidence intervals to estimate the range of plausible values for the effect size
V. Subgroup analyses
- Results of analyses that examined differences between subgroups (e.g., by gender, age, treatment group)
VI. Limitations and assumptions
- Discussion of any limitations of the study and potential sources of bias
- Assumptions made in the statistical analyses
VII. Conclusions
- A summary of the key findings and their implications
- A statement of whether the hypotheses were supported or not
- Suggestions for future research
Example of Research Results Section
An Example of a Research Results Section could be:
- This study sought to examine the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.
- Hypothesis : College students who report better sleep quality will have higher GPAs than those who report poor sleep quality.
- Methodology : Participants completed a survey about their sleep habits and academic performance.
II. Participants
- Participants were college students (N=200) from a mid-sized public university in the United States.
- The sample was evenly split by gender (50% female, 50% male) and predominantly white (85%).
- Participants were recruited through flyers and online advertisements.
III. Results
- Participants who reported better sleep quality had significantly higher GPAs (M=3.5, SD=0.5) than those who reported poor sleep quality (M=2.9, SD=0.6).
- See Table 1 for a summary of the results.
- Participants who reported consistent sleep schedules had higher GPAs than those with irregular sleep schedules.
IV. Discussion
- The results support the hypothesis that better sleep quality is associated with higher academic performance in college students.
- These findings have implications for college students, as prioritizing sleep could lead to better academic outcomes.
- Limitations of the study include self-reported data and the lack of control for other variables that could impact academic performance.
V. Conclusion
- College students who prioritize sleep may see a positive impact on their academic performance.
- These findings highlight the importance of sleep in academic success.
- Future research could explore interventions to improve sleep quality in college students.
Example of Research Results in Research Paper :
Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables and a binary churn outcome variable.
Our analysis revealed that all three algorithms performed well in predicting customer churn, with an overall accuracy of 85%. However, the Random Forest algorithm showed the highest accuracy (88%), followed by the Support Vector Machine (86%) and the Neural Network (84%).
Furthermore, we found that the most important predictor variables for customer churn were monthly charges, contract type, and tenure. Random Forest identified monthly charges as the most important variable, while Support Vector Machine and Neural Network identified contract type as the most important.
Overall, our results suggest that machine learning algorithms can be effective in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company, and that Random Forest is the most accurate algorithm for this task.
Example 3 :
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
Abstract : This study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use, body image, and self-esteem among young adults. A total of 200 participants were recruited from a university and completed self-report measures of social media use, body image satisfaction, and self-esteem.
Results: The results showed that social media use was significantly associated with body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem. Specifically, participants who reported spending more time on social media platforms had lower levels of body image satisfaction and self-esteem compared to those who reported less social media use. Moreover, the study found that comparing oneself to others on social media was a significant predictor of body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem.
Conclusion : These results suggest that social media use can have negative effects on body image satisfaction and self-esteem among young adults. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media use and to recognize the potential negative impact it can have on their mental health. Furthermore, interventions aimed at promoting positive body image and self-esteem should take into account the role of social media in shaping these attitudes and behaviors.
Importance of Research Results
Research results are important for several reasons, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research results can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field, whether it be in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, or humanities.
- Developing theories: Research results can help to develop or modify existing theories and create new ones.
- Improving practices: Research results can inform and improve practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and public policy.
- Identifying problems and solutions: Research results can identify problems and provide solutions to complex issues in society, including issues related to health, environment, social justice, and economics.
- Validating claims : Research results can validate or refute claims made by individuals or groups in society, such as politicians, corporations, or activists.
- Providing evidence: Research results can provide evidence to support decision-making, policy-making, and resource allocation in various fields.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper
Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper:
- Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
- Present the findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data and make the presentation more engaging.
- Describe the data: Describe the data in detail, including the sample size, response rate, and any missing data. Provide relevant descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and ranges.
- Interpret the findings: Interpret the findings in light of the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of the findings and the extent to which they support or contradict existing theories or previous research.
- Discuss the limitations : Discuss the limitations of the study, including any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that may have affected the results.
- Compare the results : Compare the results with those of previous studies or theoretical predictions. Discuss any similarities, differences, or inconsistencies.
- Avoid redundancy: Avoid repeating information that has already been presented in the introduction or methods sections. Instead, focus on presenting new and relevant information.
- Be objective: Be objective in presenting the results, avoiding any personal biases or interpretations.
When to Write Research Results
Here are situations When to Write Research Results”
- After conducting research on the chosen topic and obtaining relevant data, organize the findings in a structured format that accurately represents the information gathered.
- Once the data has been analyzed and interpreted, and conclusions have been drawn, begin the writing process.
- Before starting to write, ensure that the research results adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the intended audience, such as a scientific journal or academic conference.
- Begin by writing an abstract that briefly summarizes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Follow the abstract with an introduction that provides context for the research, explains its significance, and outlines the research question and objectives.
- The next section should be a literature review that provides an overview of existing research on the topic and highlights the gaps in knowledge that the current research seeks to address.
- The methodology section should provide a detailed explanation of the research design, including the sample size, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Present the research results in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and figures to illustrate the findings.
- Discuss the implications of the research results, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the topic and what further research is needed.
- Conclude the paper by summarizing the main findings, reiterating the significance of the research, and offering suggestions for future research.

Purpose of Research Results
The purposes of Research Results are as follows:
- Informing policy and practice: Research results can provide evidence-based information to inform policy decisions, such as in the fields of healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. They can also inform best practices in fields such as business, engineering, and social work.
- Addressing societal problems : Research results can be used to help address societal problems, such as reducing poverty, improving public health, and promoting social justice.
- Generating economic benefits : Research results can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that can create economic value and improve quality of life.
- Supporting academic and professional development : Research results can be used to support academic and professional development by providing opportunities for students, researchers, and practitioners to learn about new findings and methodologies in their field.
- Enhancing public understanding: Research results can help to educate the public about important issues and promote scientific literacy, leading to more informed decision-making and better public policy.
- Evaluating interventions: Research results can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as treatments, educational programs, and social policies. This can help to identify areas where improvements are needed and guide future interventions.
- Contributing to scientific progress: Research results can contribute to the advancement of science by providing new insights and discoveries that can lead to new theories, methods, and techniques.
- Informing decision-making : Research results can provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This can include decision-making at the individual, organizational, or governmental levels.
- Fostering collaboration : Research results can facilitate collaboration between researchers and practitioners, leading to new partnerships, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Research Results
Some Advantages of Research Results are as follows:
- Improved decision-making: Research results can help inform decision-making in various fields, including medicine, business, and government. For example, research on the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease can help doctors make informed decisions about the best course of treatment for their patients.
- Innovation : Research results can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. For example, research on renewable energy sources can lead to the development of new and more efficient ways to harness renewable energy.
- Economic benefits: Research results can stimulate economic growth by providing new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. For example, research on new materials or manufacturing techniques can lead to the development of new products and processes that can create new jobs and boost economic activity.
- Improved quality of life: Research results can contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals and society as a whole. For example, research on the causes of a particular disease can lead to the development of new treatments and cures, improving the health and well-being of millions of people.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Formatting Guides
APA Results Section: Full Guide + Tips + Example
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker

Emma Flores knows all about formatting standards. She shares with StudyCrumb readers tips on creating academic papers that will meet high-quality standards.
You may also like

The APA results section is a part of a research paper where the findings and statistical analyses are presented. You should briefly summarize the research outcomes stivking to specific APA style guidelines.
By now you probably have conducted your research and all that’s left is to share your findings in APA Results section. American Psychological Association has established multiple rules for designing your research outcomes. Chances are that you have numerous questions regarding this part of a paper, but only a limited time to find any sound answers. That’s why we have prepared this quick guide. Keep reading and find out what goes in the Result section and how to properly format it in APA writing style .
APA Results Section: Basics
APA Results section is a part of a research paper where scientists share their findings. After all, it is impossible to tell otherwise about the work’s significance. There is no need to elaborate on your research topic. Rather it just focuses on statistics and numerical data. APA Results section should provide data that answers your research question. Here’s what you should include in this part of a paper:
- Number of participants
- Descriptive statistical data
- Inferential statistical data
- Missing details
- Side effects
- Written reports.
You should maintain a consistent structure and offer an easy-to-follow flow of ideas. It’s usually written using the past tense. You must present the outcomes of a study that has already been finished.
How to Write Results Section: APA
When designing an APA format Results section, you should work out each block step by step. Let us walk you through each stage of the writing process:
- Preliminary discussion
- Analysis of obtained data
- Presenting your research findings.
Note that these details should only be summarized. Keep interpretations for your Discussion section.
Preliminary Discussion in Your APA Results Section
APA Results section of a research paper should start with a brief reminder. Briefly restate your main goal and hypotheses that you wanted to test. (We have the whole blog on how to write a hypothesis .) Then, you should mention a number of participants, excluded data (if there is any) and adverse effects. Report how many people participated in your research. A number of participants may vary depending on each stage of your study. This being said, you should explain the reasons for attrition to ensure internal validity. Your research depends much on how complete your data is. But sometimes, you might lack some necessary equipment or have things going the way you don’t expect. That’s why you should inform your readers about any missing data and reasons behind this. If it’s a clinical research, you should also report any side effects that have happened. Pay extra attention to reporting style, as you must convince readers that your research was conducted according to set conditions. Without this, it won’t be possible to achieve a desired result. Wonder how to cite a report APA ? We have a special blog that contains all rules with every detail.
APA Results Section: Summarize Your Data Analysis
Writing the APA results section relies on preparing an explanation of your outcomes. Dry statistics isn’t your best option. Instead, you should make a descriptive analysis of data that you have collected. Introduce descriptive statistics for each type of analysis – preliminary, secondary and subgroup one. Make sure you properly report descriptive statistics in your APA Results section. The means of reporting may vary depending on the nature of your data and conditions.
Means of reporting data
Besides, you should also include such elements:
- Sample sizes
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability (for point estimate).
Provide verified information from trusted sources. Losing your readers’ trust is easy. APA recommends using citations in cases when rare statistics is integrated. However, you shouldn’t bother citing common knowledge.
Presenting Outcomes in Your APA Results Section
To introduce outcomes in your APA results section, report hypothesis tests. Then, mention if it was confirmed by presenting numbers. Make sure you specify such information:
- Test statistic
- Degree of freedom
- Your p -value
- Magnitude and direction.
Readers don’t have to guess what details you have omitted and should be able to draw conclusions based on real data. Besides, you should estimate effect sizes and provide information on confidence intervals. There is one good way to organize your statistical results – moving from the most important to the least important. First, you should focus on the primary questions and then address secondary research questions until you cover subgroups. Follow this structure and provide information in stages. Your work formatting is one of the most important steps to success. So, follow American Psychological statistics to cope with numbers.
APA Results Section: How to Format
After having decided on the format of an APA results section, you should consider the general requirements. The manual contains information about such details:
- Font: Times New Roman.
- Size: 12 pt. font size.
- Spacing: Double-spaced.
- Margins: 1 inch on all sides.
You might also want to integrate visual elements to enhance your research. For example, you can use figures, graphs, charts or tables to present numerical data. According to APA 7th edition, you should create an appendix and make respective references. Number figures and graphs in the order they appear in your APA results section.
APA Results Section: Writing Tips
Before writing the APA results section, make sure that the data is meaningful and can potentially contribute to further research. Academic writing is peculiar as the presentation of information should be carried out according to all rules and requirements. However, this is not the end. A few tips will help to write a worthwhile Results section. Consider the following:
- Tense All outcomes of a study must be described in the past tense, because the objective is to describe the obtained results.
- Brevity Any deviation from a topic is unacceptable, nor the provision of useless information is. Staying on point and being concise is the right decision.
- Objectivity Present an unbiased synopsis of outcomes, as this will allow you to present information in a convenient and useful format. Readers will be grateful.
Preparing a paper takes a lot of effort and this is a good reason to take advantage of the advice from academic professionals.
Example of APA Results Section
Sometimes, all you need to get started is an APA results section example. A decent sample is easy to find here. Pay attention to the key points and keep them in mind as you write. Moreover, you can use this template to format this paper’s part with APA requirements in mind.
APA Results Section: Final Thoughts
The APA results section requires a special attention from students. Hypothesis and presentation of evidence are the basis for project development. Reporting your main findings in this section will help you prove your hypothesis and enhance your stuy.
Delegate this tedious task to StudyCrumb and get skilled writers to write paper . Our experts have got a solid track record in delivering high-quality research papers in a timely manner and will be eager to help you, too.
Frequently Asked Questions About APA Results Section
1. how many words should an apa results section contain.
An APA results section is presented in a concise style, so the number of words is limited. It shouldn’t exceed 1000 words, which is 2-3 pages of double spaced text. Be specific and don’t deviate from your main point.
2. What’s the difference between APA Results section and APA Discussion section?
APA results section presents the outcomes of research. Here, you should focus on the results, statistical and other data as proof of your hypothesis. A Discussion section, in turn, involves an analysis of findings. In this part of your study, you should evaluate hypotheses and interpret your results.
3. When should I use tables or figures to present numbers in my APA results section?
APA results section includes not only textual information about your research outcomes, but also other ways of presenting information. Create tables, figures and archives to present your findings. Here are several rules you should keep in mind before using visual elements:
- Use sentences to talk about numbers up to 3 components;
- As for converting numbers greater than 20, use a table;
- Charts are worth saving for when there are more than 20 figures.
4. What tense should I use in my results section?
Writing the Results section requires another rule one must follow. Everything should be written in past tense. This way, you will indicate that your research project is complete and that all presented findings are obtained empirically.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen . Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean – any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs discussion vs conclusion, checklist: research results, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like ‘appears’ or ‘implies’.
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe shop: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the trainers, boots, sandals, etc.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualise trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarise or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organisations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
‘I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.’
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Swaen, B. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/results-section/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
What is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
General Research Paper Guidelines: Discussion
Discussion section.
The overall purpose of a research paper’s discussion section is to evaluate and interpret results, while explaining both the implications and limitations of your findings. Per APA (2020) guidelines, this section requires you to “examine, interpret, and qualify the results and draw inferences and conclusions from them” (p. 89). Discussion sections also require you to detail any new insights, think through areas for future research, highlight the work that still needs to be done to further your topic, and provide a clear conclusion to your research paper. In a good discussion section, you should do the following:
- Clearly connect the discussion of your results to your introduction, including your central argument, thesis, or problem statement.
- Provide readers with a critical thinking through of your results, answering the “so what?” question about each of your findings. In other words, why is this finding important?
- Detail how your research findings might address critical gaps or problems in your field
- Compare your results to similar studies’ findings
- Provide the possibility of alternative interpretations, as your goal as a researcher is to “discover” and “examine” and not to “prove” or “disprove.” Instead of trying to fit your results into your hypothesis, critically engage with alternative interpretations to your results.
For more specific details on your Discussion section, be sure to review Sections 3.8 (pp. 89-90) and 3.16 (pp. 103-104) of your 7 th edition APA manual
*Box content adapted from:
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: 8 the discussion . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/discussion
Limitations
Limitations of generalizability or utility of findings, often over which the researcher has no control, should be detailed in your Discussion section. Including limitations for your reader allows you to demonstrate you have thought critically about your given topic, understood relevant literature addressing your topic, and chosen the methodology most appropriate for your research. It also allows you an opportunity to suggest avenues for future research on your topic. An effective limitations section will include the following:
- Detail (a) sources of potential bias, (b) possible imprecision of measures, (c) other limitations or weaknesses of the study, including any methodological or researcher limitations.
- Sample size: In quantitative research, if a sample size is too small, it is more difficult to generalize results.
- Lack of available/reliable data : In some cases, data might not be available or reliable, which will ultimately affect the overall scope of your research. Use this as an opportunity to explain areas for future study.
- Lack of prior research on your study topic: In some cases, you might find that there is very little or no similar research on your study topic, which hinders the credibility and scope of your own research. If this is the case, use this limitation as an opportunity to call for future research. However, make sure you have done a thorough search of the available literature before making this claim.
- Flaws in measurement of data: Hindsight is 20/20, and you might realize after you have completed your research that the data tool you used actually limited the scope or results of your study in some way. Again, acknowledge the weakness and use it as an opportunity to highlight areas for future study.
- Limits of self-reported data: In your research, you are assuming that any participants will be honest and forthcoming with responses or information they provide to you. Simply acknowledging this assumption as a possible limitation is important in your research.
- Access: Most research requires that you have access to people, documents, organizations, etc.. However, for various reasons, access is sometimes limited or denied altogether. If this is the case, you will want to acknowledge access as a limitation to your research.
- Time: Choosing a research focus that is narrow enough in scope to finish in a given time period is important. If such limitations of time prevent you from certain forms of research, access, or study designs, acknowledging this time restraint is important. Acknowledging such limitations is important, as they can point other researchers to areas that require future study.
- Potential Bias: All researchers have some biases, so when reading and revising your draft, pay special attention to the possibilities for bias in your own work. Such bias could be in the form you organized people, places, participants, or events. They might also exist in the method you selected or the interpretation of your results. Acknowledging such bias is an important part of the research process.
- Language Fluency: On occasion, researchers or research participants might have language fluency issues, which could potentially hinder results or how effectively you interpret results. If this is an issue in your research, make sure to acknowledge it in your limitations section.
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: Limitations of the study . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/limitations
In many research papers, the conclusion, like the limitations section, is folded into the larger discussion section. If you are unsure whether to include the conclusion as part of your discussion or as a separate section, be sure to defer to the assignment instructions or ask your instructor.
The conclusion is important, as it is specifically designed to highlight your research’s larger importance outside of the specific results of your study. Your conclusion section allows you to reiterate the main findings of your study, highlight their importance, and point out areas for future research. Based on the scope of your paper, your conclusion could be anywhere from one to three paragraphs long. An effective conclusion section should include the following:
- Describe the possibilities for continued research on your topic, including what might be improved, adapted, or added to ensure useful and informed future research.
- Provide a detailed account of the importance of your findings
- Reiterate why your problem is important, detail how your interpretation of results impacts the subfield of study, and what larger issues both within and outside of your field might be affected from such results
University of Southern California (n.d.). Organizing your social sciences research paper: 9. the conclusion . https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/conclusion
- Previous Page: Results
- Next Page: References
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields of psychology, education, and other social sciences.
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
The APA results section summarizes data and includes reporting statistics in a quantitative research study. The APA results section is an essential part of your research paper and typically begins with a brief overview of the data followed by a systematic and detailed reporting of each hypothesis tested. The interpreted results will then be presented in the discussion sections.
The results section is where you present the results of your research-both narrated for the readers in plain English and accompanied by statistics. Note: Depending on the requirements or the projected length of your paper, sometimes the results are combined with the discussion section. Organizing Results. Continue with your story in the results ...
How to write an APA results section ... In the methods section of an APA research paper, you report in detail the participants, measures, and procedure of your study. 263. APA format for academic papers and essays Learn how to set up APA format for your paper. From the title page and headings to references and citations.
This document is specifically about how to report statistical results. Refer to our handout "Writing an APA Empirical (lab) Report" for details on writing a results section. Every statistical test that you report should relate directly to a hypothesis. Begin the results section by restating each hypothesis, then state whether your results ...
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report, an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. ... For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are ...
General formatting rules are as follows: Do not put page breaks in between the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections. The title page, abstract, references, table (s), and figure (s) should be on their own pages. The entire paper should be written in the past tense, in a 12-point font, double-spaced, and with one-inch margins ...
Writing up your results - Guidelines based on APA style. In a results section, your goal is to report the results of the data analyses used to test your hypotheses. To do this, you need to identify your data analysis technique, report your test statistic, and provide some interpretation of the results. Each analysis you run should be related ...
Use one-inch margins on all sides of the paper. 3. The text should be left-justified (a straight line), and the right side should be "ragged" (do not justify on both sides) 4. Paragraphs should be indented at the beginning (please use paragraphs!) 5.
To build trust in your analysis, Morrow recommends keeping your results section separate from your discussion, as in quantitative studies, so that readers can distinguish "data-based interpretations" from your own conclusions. STAY FOCUSED. While complex analyses and formatting guidelines can seem like formidable barriers to writing up your ...
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions. In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings ...
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
APA Results section of a research paper should start with a brief reminder. Briefly restate your main goal and hypotheses that you wanted to test. ... Before writing the APA results section, make sure that the data is meaningful and can potentially contribute to further research. Academic writing is peculiar as the presentation of information ...
Chapters 4 through 7 consider the typical sections of a qualitative research paper— the introductory sections, Method, Results, and Discussion. These chapters emphasize aspects of reporting that are unique to qualitative research. They describe the general elements that should be reported in qualitative papers and can assist authors in devel-
Papers usually end with a concluding section, often called the "Discussion.". The Discussion is your opportunity to evaluate and interpret the results of your study or paper, draw inferences and conclusions from it, and communicate its contributions to science and/or society. Use the present tense when writing the Discussion section.
Here are a few best practices: Your results should always be written in the past tense. While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible. Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions.
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
Discussion Section. The overall purpose of a research paper's discussion section is to evaluate and interpret results, while explaining both the implications and limitations of your findings. Per APA (2020) guidelines, this section requires you to "examine, interpret, and qualify the results and draw inferences and conclusions from them ...
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
An APA-style paper includes the following sections: title page, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references. Your paper may also include one or more tables and/or figures. Different types of information about your study are addressed in each of the sections, as described below. General formatting rules are as follows:
For student papers, the title (in bold), byline, affiliations, course number and name, instructor, and assignment due date should be centered on the title page. section labels: Section labels (e.g., "Abstract," "References") should be centered (and bold). abstract: The first line of the abstract should be flush left (not indented).