An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- SAGE Open Med

Grounded theory research: A design framework for novice researchers
Ylona chun tie.
1 Nursing and Midwifery, College of Healthcare Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, QLD, Australia
Melanie Birks
Karen francis.
2 College of Health and Medicine, University of Tasmania, Australia, Hobart, TAS, Australia
Background:
Grounded theory is a well-known methodology employed in many research studies. Qualitative and quantitative data generation techniques can be used in a grounded theory study. Grounded theory sets out to discover or construct theory from data, systematically obtained and analysed using comparative analysis. While grounded theory is inherently flexible, it is a complex methodology. Thus, novice researchers strive to understand the discourse and the practical application of grounded theory concepts and processes.
The aim of this article is to provide a contemporary research framework suitable to inform a grounded theory study.
This article provides an overview of grounded theory illustrated through a graphic representation of the processes and methods employed in conducting research using this methodology. The framework is presented as a diagrammatic representation of a research design and acts as a visual guide for the novice grounded theory researcher.
Discussion:
As grounded theory is not a linear process, the framework illustrates the interplay between the essential grounded theory methods and iterative and comparative actions involved. Each of the essential methods and processes that underpin grounded theory are defined in this article.
Conclusion:
Rather than an engagement in philosophical discussion or a debate of the different genres that can be used in grounded theory, this article illustrates how a framework for a research study design can be used to guide and inform the novice nurse researcher undertaking a study using grounded theory. Research findings and recommendations can contribute to policy or knowledge development, service provision and can reform thinking to initiate change in the substantive area of inquiry.
Introduction
The aim of all research is to advance, refine and expand a body of knowledge, establish facts and/or reach new conclusions using systematic inquiry and disciplined methods. 1 The research design is the plan or strategy researchers use to answer the research question, which is underpinned by philosophy, methodology and methods. 2 Birks 3 defines philosophy as ‘a view of the world encompassing the questions and mechanisms for finding answers that inform that view’ (p. 18). Researchers reflect their philosophical beliefs and interpretations of the world prior to commencing research. Methodology is the research design that shapes the selection of, and use of, particular data generation and analysis methods to answer the research question. 4 While a distinction between positivist research and interpretivist research occurs at the paradigm level, each methodology has explicit criteria for the collection, analysis and interpretation of data. 2 Grounded theory (GT) is a structured, yet flexible methodology. This methodology is appropriate when little is known about a phenomenon; the aim being to produce or construct an explanatory theory that uncovers a process inherent to the substantive area of inquiry. 5 – 7 One of the defining characteristics of GT is that it aims to generate theory that is grounded in the data. The following section provides an overview of GT – the history, main genres and essential methods and processes employed in the conduct of a GT study. This summary provides a foundation for a framework to demonstrate the interplay between the methods and processes inherent in a GT study as presented in the sections that follow.
Glaser and Strauss are recognised as the founders of grounded theory. Strauss was conversant in symbolic interactionism and Glaser in descriptive statistics. 8 – 10 Glaser and Strauss originally worked together in a study examining the experience of terminally ill patients who had differing knowledge of their health status. Some of these suspected they were dying and tried to confirm or disconfirm their suspicions. Others tried to understand by interpreting treatment by care providers and family members. Glaser and Strauss examined how the patients dealt with the knowledge they were dying and the reactions of healthcare staff caring for these patients. Throughout this collaboration, Glaser and Strauss questioned the appropriateness of using a scientific method of verification for this study. During this investigation, they developed the constant comparative method, a key element of grounded theory, while generating a theory of dying first described in Awareness of Dying (1965). The constant comparative method is deemed an original way of organising and analysing qualitative data.
Glaser and Strauss subsequently went on to write The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research (1967). This seminal work explained how theory could be generated from data inductively. This process challenged the traditional method of testing or refining theory through deductive testing. Grounded theory provided an outlook that questioned the view of the time that quantitative methodology is the only valid, unbiased way to determine truths about the world. 11 Glaser and Strauss 5 challenged the belief that qualitative research lacked rigour and detailed the method of comparative analysis that enables the generation of theory. After publishing The Discovery of Grounded Theory , Strauss and Glaser went on to write independently, expressing divergent viewpoints in the application of grounded theory methods.
Glaser produced his book Theoretical Sensitivity (1978) and Strauss went on to publish Qualitative Analysis for Social Scientists (1987). Strauss and Corbin’s 12 publication Basics of Qualitative Research: Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques resulted in a rebuttal by Glaser 13 over their application of grounded theory methods. However, philosophical perspectives have changed since Glaser’s positivist version and Strauss and Corbin’s post-positivism stance. 14 Grounded theory has since seen the emergence of additional philosophical perspectives that have influenced a change in methodological development over time. 15
Subsequent generations of grounded theorists have positioned themselves along a philosophical continuum, from Strauss and Corbin’s 12 theoretical perspective of symbolic interactionism, through to Charmaz’s 16 constructivist perspective. However, understanding how to position oneself philosophically can challenge novice researchers. Birks and Mills 6 provide a contemporary understanding of GT in their book Grounded theory: A Practical Guide. These Australian researchers have written in a way that appeals to the novice researcher. It is the contemporary writing, the way Birks and Mills present a non-partisan approach to GT that support the novice researcher to understand the philosophical and methodological concepts integral in conducting research. The development of GT is important to understand prior to selecting an approach that aligns with the researcher’s philosophical position and the purpose of the research study. As the research progresses, seminal texts are referred back to time and again as understanding of concepts increases, much like the iterative processes inherent in the conduct of a GT study.
Genres: traditional, evolved and constructivist grounded theory
Grounded theory has several distinct methodological genres: traditional GT associated with Glaser; evolved GT associated with Strauss, Corbin and Clarke; and constructivist GT associated with Charmaz. 6 , 17 Each variant is an extension and development of the original GT by Glaser and Strauss. The first of these genres is known as traditional or classic GT. Glaser 18 acknowledged that the goal of traditional GT is to generate a conceptual theory that accounts for a pattern of behaviour that is relevant and problematic for those involved. The second genre, evolved GT, is founded on symbolic interactionism and stems from work associated with Strauss, Corbin and Clarke. Symbolic interactionism is a sociological perspective that relies on the symbolic meaning people ascribe to the processes of social interaction. Symbolic interactionism addresses the subjective meaning people place on objects, behaviours or events based on what they believe is true. 19 , 20 Constructivist GT, the third genre developed and explicated by Charmaz, a symbolic interactionist, has its roots in constructivism. 8 , 16 Constructivist GT’s methodological underpinnings focus on how participants’ construct meaning in relation to the area of inquiry. 16 A constructivist co-constructs experience and meanings with participants. 21 While there are commonalities across all genres of GT, there are factors that distinguish differences between the approaches including the philosophical position of the researcher; the use of literature; and the approach to coding, analysis and theory development. Following on from Glaser and Strauss, several versions of GT have ensued.
Grounded theory represents both a method of inquiry and a resultant product of that inquiry. 7 , 22 Glaser and Holton 23 define GT as ‘a set of integrated conceptual hypotheses systematically generated to produce an inductive theory about a substantive area’ (p. 43). Strauss and Corbin 24 define GT as ‘theory that was derived from data, systematically gathered and analysed through the research process’ (p. 12). The researcher ‘begins with an area of study and allows the theory to emerge from the data’ (p. 12). Charmaz 16 defines GT as ‘a method of conducting qualitative research that focuses on creating conceptual frameworks or theories through building inductive analysis from the data’ (p. 187). However, Birks and Mills 6 refer to GT as a process by which theory is generated from the analysis of data. Theory is not discovered; rather, theory is constructed by the researcher who views the world through their own particular lens.
Research process
Before commencing any research study, the researcher must have a solid understanding of the research process. A well-developed outline of the study and an understanding of the important considerations in designing and undertaking a GT study are essential if the goals of the research are to be achieved. While it is important to have an understanding of how a methodology has developed, in order to move forward with research, a novice can align with a grounded theorist and follow an approach to GT. Using a framework to inform a research design can be a useful modus operandi.
The following section provides insight into the process of undertaking a GT research study. Figure 1 is a framework that summarises the interplay and movement between methods and processes that underpin the generation of a GT. As can be seen from this framework, and as detailed in the discussion that follows, the process of doing a GT research study is not linear, rather it is iterative and recursive.

Research design framework: summary of the interplay between the essential grounded theory methods and processes.
Grounded theory research involves the meticulous application of specific methods and processes. Methods are ‘systematic modes, procedures or tools used for collection and analysis of data’. 25 While GT studies can commence with a variety of sampling techniques, many commence with purposive sampling, followed by concurrent data generation and/or collection and data analysis, through various stages of coding, undertaken in conjunction with constant comparative analysis, theoretical sampling and memoing. Theoretical sampling is employed until theoretical saturation is reached. These methods and processes create an unfolding, iterative system of actions and interactions inherent in GT. 6 , 16 The methods interconnect and inform the recurrent elements in the research process as shown by the directional flow of the arrows and the encompassing brackets in Figure 1 . The framework denotes the process is both iterative and dynamic and is not one directional. Grounded theory methods are discussed in the following section.
Purposive sampling
As presented in Figure 1 , initial purposive sampling directs the collection and/or generation of data. Researchers purposively select participants and/or data sources that can answer the research question. 5 , 7 , 16 , 21 Concurrent data generation and/or data collection and analysis is fundamental to GT research design. 6 The researcher collects, codes and analyses this initial data before further data collection/generation is undertaken. Purposeful sampling provides the initial data that the researcher analyses. As will be discussed, theoretical sampling then commences from the codes and categories developed from the first data set. Theoretical sampling is used to identify and follow clues from the analysis, fill gaps, clarify uncertainties, check hunches and test interpretations as the study progresses.
Constant comparative analysis
Constant comparative analysis is an analytical process used in GT for coding and category development. This process commences with the first data generated or collected and pervades the research process as presented in Figure 1 . Incidents are identified in the data and coded. 6 The initial stage of analysis compares incident to incident in each code. Initial codes are then compared to other codes. Codes are then collapsed into categories. This process means the researcher will compare incidents in a category with previous incidents, in both the same and different categories. 5 Future codes are compared and categories are compared with other categories. New data is then compared with data obtained earlier during the analysis phases. This iterative process involves inductive and deductive thinking. 16 Inductive, deductive and abductive reasoning can also be used in data analysis. 26
Constant comparative analysis generates increasingly more abstract concepts and theories through inductive processes. 16 In addition, abduction, defined as ‘a form of reasoning that begins with an examination of the data and the formation of a number of hypotheses that are then proved or disproved during the process of analysis … aids inductive conceptualization’. 6 Theoretical sampling coupled with constant comparative analysis raises the conceptual levels of data analysis and directs ongoing data collection or generation. 6
The constant comparative technique is used to find consistencies and differences, with the aim of continually refining concepts and theoretically relevant categories. This continual comparative iterative process that encompasses GT research sets it apart from a purely descriptive analysis. 8
Memo writing is an analytic process considered essential ‘in ensuring quality in grounded theory’. 6 Stern 27 offers the analogy that if data are the building blocks of the developing theory, then memos are the ‘mortar’ (p. 119). Memos are the storehouse of ideas generated and documented through interacting with data. 28 Thus, memos are reflective interpretive pieces that build a historic audit trail to document ideas, events and the thought processes inherent in the research process and developing thinking of the analyst. 6 Memos provide detailed records of the researchers’ thoughts, feelings and intuitive contemplations. 6
Lempert 29 considers memo writing crucial as memos prompt researchers to analyse and code data and develop codes into categories early in the coding process. Memos detail why and how decisions made related to sampling, coding, collapsing of codes, making of new codes, separating codes, producing a category and identifying relationships abstracted to a higher level of analysis. 6 Thus, memos are informal analytic notes about the data and the theoretical connections between categories. 23 Memoing is an ongoing activity that builds intellectual assets, fosters analytic momentum and informs the GT findings. 6 , 10
Generating/collecting data
A hallmark of GT is concurrent data generation/collection and analysis. In GT, researchers may utilise both qualitative and quantitative data as espoused by Glaser’s dictum; ‘all is data’. 30 While interviews are a common method of generating data, data sources can include focus groups, questionnaires, surveys, transcripts, letters, government reports, documents, grey literature, music, artefacts, videos, blogs and memos. 9 Elicited data are produced by participants in response to, or directed by, the researcher whereas extant data includes data that is already available such as documents and published literature. 6 , 31 While this is one interpretation of how elicited data are generated, other approaches to grounded theory recognise the agency of participants in the co-construction of data with the researcher. The relationship the researcher has with the data, how it is generated and collected, will determine the value it contributes to the development of the final GT. 6 The significance of this relationship extends into data analysis conducted by the researcher through the various stages of coding.
Coding is an analytical process used to identify concepts, similarities and conceptual reoccurrences in data. Coding is the pivotal link between collecting or generating data and developing a theory that explains the data. Charmaz 10 posits,
codes rely on interaction between researchers and their data. Codes consist of short labels that we construct as we interact with the data. Something kinaesthetic occurs when we are coding; we are mentally and physically active in the process. (p. 5)
In GT, coding can be categorised into iterative phases. Traditional, evolved and constructivist GT genres use different terminology to explain each coding phase ( Table 1 ).
Comparison of coding terminology in traditional, evolved and constructivist grounded theory.
Adapted from Birks and Mills. 6
Coding terminology in evolved GT refers to open (a procedure for developing categories of information), axial (an advanced procedure for interconnecting the categories) and selective coding (procedure for building a storyline from core codes that connects the categories), producing a discursive set of theoretical propositions. 6 , 12 , 32 Constructivist grounded theorists refer to initial, focused and theoretical coding. 9 Birks and Mills 6 use the terms initial, intermediate and advanced coding that link to low, medium and high-level conceptual analysis and development. The coding terms devised by Birks and Mills 6 were used for Figure 1 ; however, these can be altered to reflect the coding terminology used in the respective GT genres selected by the researcher.
Initial coding
Initial coding of data is the preliminary step in GT data analysis. 6 , 9 The purpose of initial coding is to start the process of fracturing the data to compare incident to incident and to look for similarities and differences in beginning patterns in the data. In initial coding, the researcher inductively generates as many codes as possible from early data. 16 Important words or groups of words are identified and labelled. In GT, codes identify social and psychological processes and actions as opposed to themes. Charmaz 16 emphasises keeping codes as similar to the data as possible and advocates embedding actions in the codes in an iterative coding process. Saldaña 33 agrees that codes that denote action, which he calls process codes, can be used interchangeably with gerunds (verbs ending in ing ). In vivo codes are often verbatim quotes from the participants’ words and are often used as the labels to capture the participant’s words as representative of a broader concept or process in the data. 6 Table 1 reflects variation in the terminology of codes used by grounded theorists.
Initial coding categorises and assigns meaning to the data, comparing incident-to-incident, labelling beginning patterns and beginning to look for comparisons between the codes. During initial coding, it is important to ask ‘what is this data a study of’. 18 What does the data assume, ‘suggest’ or ‘pronounce’ and ‘from whose point of view’ does this data come, whom does it represent or whose thoughts are they?. 16 What collectively might it represent? The process of documenting reactions, emotions and related actions enables researchers to explore, challenge and intensify their sensitivity to the data. 34 Early coding assists the researcher to identify the direction for further data gathering. After initial analysis, theoretical sampling is employed to direct collection of additional data that will inform the ‘developing theory’. 9 Initial coding advances into intermediate coding once categories begin to develop.
Theoretical sampling
The purpose of theoretical sampling is to allow the researcher to follow leads in the data by sampling new participants or material that provides relevant information. As depicted in Figure 1 , theoretical sampling is central to GT design, aids the evolving theory 5 , 7 , 16 and ensures the final developed theory is grounded in the data. 9 Theoretical sampling in GT is for the development of a theoretical category, as opposed to sampling for population representation. 10 Novice researchers need to acknowledge this difference if they are to achieve congruence within the methodology. Birks and Mills 6 define theoretical sampling as ‘the process of identifying and pursuing clues that arise during analysis in a grounded theory study’ (p. 68). During this process, additional information is sought to saturate categories under development. The analysis identifies relationships, highlights gaps in the existing data set and may reveal insight into what is not yet known. The exemplars in Box 1 highlight how theoretical sampling led to the inclusion of further data.
Examples of theoretical sampling.
Thus, theoretical sampling is used to focus and generate data to feed the iterative process of continual comparative analysis of the data. 6
Intermediate coding
Intermediate coding, identifying a core category, theoretical data saturation, constant comparative analysis, theoretical sensitivity and memoing occur in the next phase of the GT process. 6 Intermediate coding builds on the initial coding phase. Where initial coding fractures the data, intermediate coding begins to transform basic data into more abstract concepts allowing the theory to emerge from the data. During this analytic stage, a process of reviewing categories and identifying which ones, if any, can be subsumed beneath other categories occurs and the properties or dimension of the developed categories are refined. Properties refer to the characteristics that are common to all the concepts in the category and dimensions are the variations of a property. 37
At this stage, a core category starts to become evident as developed categories form around a core concept; relationships are identified between categories and the analysis is refined. Birks and Mills 6 affirm that diagramming can aid analysis in the intermediate coding phase. Grounded theorists interact closely with the data during this phase, continually reassessing meaning to ascertain ‘what is really going on’ in the data. 30 Theoretical saturation ensues when new data analysis does not provide additional material to existing theoretical categories, and the categories are sufficiently explained. 6
Advanced coding
Birks and Mills 6 described advanced coding as the ‘techniques used to facilitate integration of the final grounded theory’ (p. 177). These authors promote storyline technique (described in the following section) and theoretical coding as strategies for advancing analysis and theoretical integration. Advanced coding is essential to produce a theory that is grounded in the data and has explanatory power. 6 During the advanced coding phase, concepts that reach the stage of categories will be abstract, representing stories of many, reduced into highly conceptual terms. The findings are presented as a set of interrelated concepts as opposed to presenting themes. 28 Explanatory statements detail the relationships between categories and the central core category. 28
Storyline is a tool that can be used for theoretical integration. Birks and Mills 6 define storyline as ‘a strategy for facilitating integration, construction, formulation, and presentation of research findings through the production of a coherent grounded theory’ (p. 180). Storyline technique is first proposed with limited attention in Basics of Qualitative Research by Strauss and Corbin 12 and further developed by Birks et al. 38 as a tool for theoretical integration. The storyline is the conceptualisation of the core category. 6 This procedure builds a story that connects the categories and produces a discursive set of theoretical propositions. 24 Birks and Mills 6 contend that storyline can be ‘used to produce a comprehensive rendering of your grounded theory’ (p. 118). Birks et al. 38 had earlier concluded, ‘storyline enhances the development, presentation and comprehension of the outcomes of grounded theory research’ (p. 405). Once the storyline is developed, the GT is finalised using theoretical codes that ‘provide a framework for enhancing the explanatory power of the storyline and its potential as theory’. 6 Thus, storyline is the explication of the theory.
Theoretical coding occurs as the final culminating stage towards achieving a GT. 39 , 40 The purpose of theoretical coding is to integrate the substantive theory. 41 Saldaña 40 states, ‘theoretical coding integrates and synthesises the categories derived from coding and analysis to now create a theory’ (p. 224). Initial coding fractures the data while theoretical codes ‘weave the fractured story back together again into an organized whole theory’. 18 Advanced coding that integrates extant theory adds further explanatory power to the findings. 6 The examples in Box 2 describe the use of storyline as a technique.
Writing the storyline.
Theoretical sensitivity
As presented in Figure 1 , theoretical sensitivity encompasses the entire research process. Glaser and Strauss 5 initially described the term theoretical sensitivity in The Discovery of Grounded Theory. Theoretical sensitivity is the ability to know when you identify a data segment that is important to your theory. While Strauss and Corbin 12 describe theoretical sensitivity as the insight into what is meaningful and of significance in the data for theory development, Birks and Mills 6 define theoretical sensitivity as ‘the ability to recognise and extract from the data elements that have relevance for the emerging theory’ (p. 181). Conducting GT research requires a balance between keeping an open mind and the ability to identify elements of theoretical significance during data generation and/or collection and data analysis. 6
Several analytic tools and techniques can be used to enhance theoretical sensitivity and increase the grounded theorist’s sensitivity to theoretical constructs in the data. 28 Birks and Mills 6 state, ‘as a grounded theorist becomes immersed in the data, their level of theoretical sensitivity to analytic possibilities will increase’ (p. 12). Developing sensitivity as a grounded theorist and the application of theoretical sensitivity throughout the research process allows the analytical focus to be directed towards theory development and ultimately result in an integrated and abstract GT. 6 The example in Box 3 highlights how analytic tools are employed to increase theoretical sensitivity.
Theoretical sensitivity.
The grounded theory
The meticulous application of essential GT methods refines the analysis resulting in the generation of an integrated, comprehensive GT that explains a process relating to a particular phenomenon. 6 The results of a GT study are communicated as a set of concepts, related to each other in an interrelated whole, and expressed in the production of a substantive theory. 5 , 7 , 16 A substantive theory is a theoretical interpretation or explanation of a studied phenomenon 6 , 17 Thus, the hallmark of grounded theory is the generation of theory ‘abstracted from, or grounded in, data generated and collected by the researcher’. 6 However, to ensure quality in research requires the application of rigour throughout the research process.
Quality and rigour
The quality of a grounded theory can be related to three distinct areas underpinned by (1) the researcher’s expertise, knowledge and research skills; (2) methodological congruence with the research question; and (3) procedural precision in the use of methods. 6 Methodological congruence is substantiated when the philosophical position of the researcher is congruent with the research question and the methodological approach selected. 6 Data collection or generation and analytical conceptualisation need to be rigorous throughout the research process to secure excellence in the final grounded theory. 44
Procedural precision requires careful attention to maintaining a detailed audit trail, data management strategies and demonstrable procedural logic recorded using memos. 6 Organisation and management of research data, memos and literature can be assisted using software programs such as NVivo. An audit trail of decision-making, changes in the direction of the research and the rationale for decisions made are essential to ensure rigour in the final grounded theory. 6
This article offers a framework to assist novice researchers visualise the iterative processes that underpin a GT study. The fundamental process and methods used to generate an integrated grounded theory have been described. Novice researchers can adapt the framework presented to inform and guide the design of a GT study. This framework provides a useful guide to visualise the interplay between the methods and processes inherent in conducting GT. Research conducted ethically and with meticulous attention to process will ensure quality research outcomes that have relevance at the practice level.
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Grounded Theory – Methods, Examples and Guide
Grounded Theory – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

Grounded Theory
Definition:
Grounded Theory is a qualitative research methodology that aims to generate theories based on data that are grounded in the empirical reality of the research context. The method involves a systematic process of data collection, coding, categorization, and analysis to identify patterns and relationships in the data.
The ultimate goal is to develop a theory that explains the phenomenon being studied, which is based on the data collected and analyzed rather than on preconceived notions or hypotheses. The resulting theory should be able to explain the phenomenon in a way that is consistent with the data and also accounts for variations and discrepancies in the data. Grounded Theory is widely used in sociology, psychology, management, and other social sciences to study a wide range of phenomena, such as organizational behavior, social interaction, and health care.
History of Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory was first introduced by sociologists Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss in the 1960s as a response to the limitations of traditional positivist approaches to social research. The approach was initially developed to study dying patients and their families in hospitals, but it was soon applied to other areas of sociology and beyond.
Glaser and Strauss published their seminal book “The Discovery of Grounded Theory” in 1967, in which they presented their approach to developing theory from empirical data. They argued that existing social theories often did not account for the complexity and diversity of social phenomena, and that the development of theory should be grounded in empirical data.
Since then, Grounded Theory has become a widely used methodology in the social sciences, and has been applied to a wide range of topics, including healthcare, education, business, and psychology. The approach has also evolved over time, with variations such as constructivist grounded theory and feminist grounded theory being developed to address specific criticisms and limitations of the original approach.
Types of Grounded Theory
There are two main types of Grounded Theory: Classic Grounded Theory and Constructivist Grounded Theory.
Classic Grounded Theory
This approach is based on the work of Glaser and Strauss, and emphasizes the discovery of a theory that is grounded in data. The focus is on generating a theory that explains the phenomenon being studied, without being influenced by preconceived notions or existing theories. The process involves a continuous cycle of data collection, coding, and analysis, with the aim of developing categories and subcategories that are grounded in the data. The categories and subcategories are then compared and synthesized to generate a theory that explains the phenomenon.
Constructivist Grounded Theory
This approach is based on the work of Charmaz, and emphasizes the role of the researcher in the process of theory development. The focus is on understanding how individuals construct meaning and interpret their experiences, rather than on discovering an objective truth. The process involves a reflexive and iterative approach to data collection, coding, and analysis, with the aim of developing categories that are grounded in the data and the researcher’s interpretations of the data. The categories are then compared and synthesized to generate a theory that accounts for the multiple perspectives and interpretations of the phenomenon being studied.
Grounded Theory Conducting Guide
Here are some general guidelines for conducting a Grounded Theory study:
- Choose a research question: Start by selecting a research question that is open-ended and focuses on a specific social phenomenon or problem.
- Select participants and collect data: Identify a diverse group of participants who have experienced the phenomenon being studied. Use a variety of data collection methods such as interviews, observations, and document analysis to collect rich and diverse data.
- Analyze the data: Begin the process of analyzing the data using constant comparison. This involves comparing the data to each other and to existing categories and codes, in order to identify patterns and relationships. Use open coding to identify concepts and categories, and then use axial coding to organize them into a theoretical framework.
- Generate categories and codes: Generate categories and codes that describe the phenomenon being studied. Make sure that they are grounded in the data and that they accurately reflect the experiences of the participants.
- Refine and develop the theory: Use theoretical sampling to identify new data sources that are relevant to the developing theory. Use memoing to reflect on insights and ideas that emerge during the analysis process. Continue to refine and develop the theory until it provides a comprehensive explanation of the phenomenon.
- Validate the theory: Finally, seek to validate the theory by testing it against new data and seeking feedback from peers and other researchers. This process helps to refine and improve the theory, and to ensure that it is grounded in the data.
- Write up and disseminate the findings: Once the theory is fully developed and validated, write up the findings and disseminate them through academic publications and presentations. Make sure to acknowledge the contributions of the participants and to provide a detailed account of the research methods used.
Data Collection Methods
Grounded Theory Data Collection Methods are as follows:
- Interviews : One of the most common data collection methods in Grounded Theory is the use of in-depth interviews. Interviews allow researchers to gather rich and detailed data about the experiences, perspectives, and attitudes of participants. Interviews can be conducted one-on-one or in a group setting.
- Observation : Observation is another data collection method used in Grounded Theory. Researchers may observe participants in their natural settings, such as in a workplace or community setting. This method can provide insights into the social interactions and behaviors of participants.
- Document analysis: Grounded Theory researchers also use document analysis as a data collection method. This involves analyzing existing documents such as reports, policies, or historical records that are relevant to the phenomenon being studied.
- Focus groups : Focus groups involve bringing together a group of participants to discuss a specific topic or issue. This method can provide insights into group dynamics and social interactions.
- Fieldwork : Fieldwork involves immersing oneself in the research setting and participating in the activities of the participants. This method can provide an in-depth understanding of the culture and social dynamics of the research setting.
- Multimedia data: Grounded Theory researchers may also use multimedia data such as photographs, videos, or audio recordings to capture the experiences and perspectives of participants.
Data Analysis Methods
Grounded Theory Data Analysis Methods are as follows:
- Open coding: Open coding is the process of identifying concepts and categories in the data. Researchers use open coding to assign codes to different pieces of data, and to identify similarities and differences between them.
- Axial coding: Axial coding is the process of organizing the codes into broader categories and subcategories. Researchers use axial coding to develop a theoretical framework that explains the phenomenon being studied.
- Constant comparison: Grounded Theory involves a process of constant comparison, in which data is compared to each other and to existing categories and codes in order to identify patterns and relationships.
- Theoretical sampling: Theoretical sampling involves selecting new data sources based on the emerging theory. Researchers use theoretical sampling to collect data that will help refine and validate the theory.
- Memoing : Memoing involves writing down reflections, insights, and ideas as the analysis progresses. This helps researchers to organize their thoughts and develop a deeper understanding of the data.
- Peer debriefing: Peer debriefing involves seeking feedback from peers and other researchers on the developing theory. This process helps to validate the theory and ensure that it is grounded in the data.
- Member checking: Member checking involves sharing the emerging theory with the participants in the study and seeking their feedback. This process helps to ensure that the theory accurately reflects the experiences and perspectives of the participants.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple sources of data to validate the emerging theory. Researchers may use different data collection methods, different data sources, or different analysts to ensure that the theory is grounded in the data.
Applications of Grounded Theory
Here are some of the key applications of Grounded Theory:
- Social sciences : Grounded Theory is widely used in social science research, particularly in fields such as sociology, psychology, and anthropology. It can be used to explore a wide range of social phenomena, such as social interactions, power dynamics, and cultural practices.
- Healthcare : Grounded Theory can be used in healthcare research to explore patient experiences, healthcare practices, and healthcare systems. It can provide insights into the factors that influence healthcare outcomes, and can inform the development of interventions and policies.
- Education : Grounded Theory can be used in education research to explore teaching and learning processes, student experiences, and educational policies. It can provide insights into the factors that influence educational outcomes, and can inform the development of educational interventions and policies.
- Business : Grounded Theory can be used in business research to explore organizational processes, management practices, and consumer behavior. It can provide insights into the factors that influence business outcomes, and can inform the development of business strategies and policies.
- Technology : Grounded Theory can be used in technology research to explore user experiences, technology adoption, and technology design. It can provide insights into the factors that influence technology outcomes, and can inform the development of technology interventions and policies.
Examples of Grounded Theory
Examples of Grounded Theory in different case studies are as follows:
- Glaser and Strauss (1965): This study, which is considered one of the foundational works of Grounded Theory, explored the experiences of dying patients in a hospital. The researchers used Grounded Theory to develop a theoretical framework that explained the social processes of dying, and that was grounded in the data.
- Charmaz (1983): This study explored the experiences of chronic illness among young adults. The researcher used Grounded Theory to develop a theoretical framework that explained how individuals with chronic illness managed their illness, and how their illness impacted their sense of self.
- Strauss and Corbin (1990): This study explored the experiences of individuals with chronic pain. The researchers used Grounded Theory to develop a theoretical framework that explained the different strategies that individuals used to manage their pain, and that was grounded in the data.
- Glaser and Strauss (1967): This study explored the experiences of individuals who were undergoing a process of becoming disabled. The researchers used Grounded Theory to develop a theoretical framework that explained the social processes of becoming disabled, and that was grounded in the data.
- Clarke (2005): This study explored the experiences of patients with cancer who were receiving chemotherapy. The researcher used Grounded Theory to develop a theoretical framework that explained the factors that influenced patient adherence to chemotherapy, and that was grounded in the data.
Grounded Theory Research Example
A Grounded Theory Research Example Would be:
Research question : What is the experience of first-generation college students in navigating the college admission process?
Data collection : The researcher conducted interviews with first-generation college students who had recently gone through the college admission process. The interviews were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Data analysis: The researcher used a constant comparative method to analyze the data. This involved coding the data, comparing codes, and constantly revising the codes to identify common themes and patterns. The researcher also used memoing, which involved writing notes and reflections on the data and analysis.
Findings : Through the analysis of the data, the researcher identified several themes related to the experience of first-generation college students in navigating the college admission process, such as feeling overwhelmed by the complexity of the process, lacking knowledge about the process, and facing financial barriers.
Theory development: Based on the findings, the researcher developed a theory about the experience of first-generation college students in navigating the college admission process. The theory suggested that first-generation college students faced unique challenges in the college admission process due to their lack of knowledge and resources, and that these challenges could be addressed through targeted support programs and resources.
In summary, grounded theory research involves collecting data, analyzing it through constant comparison and memoing, and developing a theory grounded in the data. The resulting theory can help to explain the phenomenon being studied and guide future research and interventions.
Purpose of Grounded Theory
The purpose of Grounded Theory is to develop a theoretical framework that explains a social phenomenon, process, or interaction. This theoretical framework is developed through a rigorous process of data collection, coding, and analysis, and is grounded in the data.
Grounded Theory aims to uncover the social processes and patterns that underlie social phenomena, and to develop a theoretical framework that explains these processes and patterns. It is a flexible method that can be used to explore a wide range of research questions and settings, and is particularly well-suited to exploring complex social phenomena that have not been well-studied.
The ultimate goal of Grounded Theory is to generate a theoretical framework that is grounded in the data, and that can be used to explain and predict social phenomena. This theoretical framework can then be used to inform policy and practice, and to guide future research in the field.
When to use Grounded Theory
Following are some situations in which Grounded Theory may be particularly useful:
- Exploring new areas of research: Grounded Theory is particularly useful when exploring new areas of research that have not been well-studied. By collecting and analyzing data, researchers can develop a theoretical framework that explains the social processes and patterns underlying the phenomenon of interest.
- Studying complex social phenomena: Grounded Theory is well-suited to exploring complex social phenomena that involve multiple social processes and interactions. By using an iterative process of data collection and analysis, researchers can develop a theoretical framework that explains the complexity of the social phenomenon.
- Generating hypotheses: Grounded Theory can be used to generate hypotheses about social processes and interactions that can be tested in future research. By developing a theoretical framework that explains a social phenomenon, researchers can identify areas for further research and hypothesis testing.
- Informing policy and practice : Grounded Theory can provide insights into the factors that influence social phenomena, and can inform policy and practice in a variety of fields. By developing a theoretical framework that explains a social phenomenon, researchers can identify areas for intervention and policy development.
Characteristics of Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is a qualitative research method that is characterized by several key features, including:
- Emergence : Grounded Theory emphasizes the emergence of theoretical categories and concepts from the data, rather than preconceived theoretical ideas. This means that the researcher does not start with a preconceived theory or hypothesis, but instead allows the theory to emerge from the data.
- Iteration : Grounded Theory is an iterative process that involves constant comparison of data and analysis, with each round of data collection and analysis refining the theoretical framework.
- Inductive : Grounded Theory is an inductive method of analysis, which means that it derives meaning from the data. The researcher starts with the raw data and systematically codes and categorizes it to identify patterns and themes, and to develop a theoretical framework that explains these patterns.
- Reflexive : Grounded Theory requires the researcher to be reflexive and self-aware throughout the research process. The researcher’s personal biases and assumptions must be acknowledged and addressed in the analysis process.
- Holistic : Grounded Theory takes a holistic approach to data analysis, looking at the entire data set rather than focusing on individual data points. This allows the researcher to identify patterns and themes that may not be apparent when looking at individual data points.
- Contextual : Grounded Theory emphasizes the importance of understanding the context in which social phenomena occur. This means that the researcher must consider the social, cultural, and historical factors that may influence the phenomenon of interest.
Advantages of Grounded Theory
Advantages of Grounded Theory are as follows:
- Flexibility : Grounded Theory is a flexible method that can be used to explore a wide range of research questions and settings. It is particularly well-suited to exploring complex social phenomena that have not been well-studied.
- Validity : Grounded Theory aims to develop a theoretical framework that is grounded in the data, which enhances the validity and reliability of the research findings. The iterative process of data collection and analysis also helps to ensure that the research findings are reliable and robust.
- Originality : Grounded Theory can generate new and original insights into social phenomena, as it is not constrained by preconceived theoretical ideas or hypotheses. This allows researchers to explore new areas of research and generate new theoretical frameworks.
- Real-world relevance: Grounded Theory can inform policy and practice, as it provides insights into the factors that influence social phenomena. The theoretical frameworks developed through Grounded Theory can be used to inform policy development and intervention strategies.
- Ethical : Grounded Theory is an ethical research method, as it allows participants to have a voice in the research process. Participants’ perspectives are central to the data collection and analysis process, which ensures that their views are taken into account.
- Replication : Grounded Theory is a replicable method of research, as the theoretical frameworks developed through Grounded Theory can be tested and validated in future research.
Limitations of Grounded Theory
Limitations of Grounded Theory are as follows:
- Time-consuming: Grounded Theory can be a time-consuming method, as the iterative process of data collection and analysis requires significant time and effort. This can make it difficult to conduct research in a timely and cost-effective manner.
- Subjectivity : Grounded Theory is a subjective method, as the researcher’s personal biases and assumptions can influence the data analysis process. This can lead to potential issues with reliability and validity of the research findings.
- Generalizability : Grounded Theory is a context-specific method, which means that the theoretical frameworks developed through Grounded Theory may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the research findings.
- Lack of structure : Grounded Theory is an exploratory method, which means that it lacks the structure of other research methods, such as surveys or experiments. This can make it difficult to compare findings across different studies.
- Data overload: Grounded Theory can generate a large amount of data, which can be overwhelming for researchers. This can make it difficult to manage and analyze the data effectively.
- Difficulty in publication: Grounded Theory can be challenging to publish in some academic journals, as some reviewers and editors may view it as less rigorous than other research methods.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) –...

Documentary Analysis – Methods, Applications and...

ANOVA (Analysis of variance) – Formulas, Types...

Graphical Methods – Types, Examples and Guide
Grounded Theory Methodology: Principles and Practices
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
- Cite this reference work entry

- Linda Liska Belgrave 2 &
- Kapriskie Seide 2
2661 Accesses
20 Citations
Since Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss’ (The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research. New York: Adline De Gruyter, 1967) publication of their groundbreaking book, The Discovery of Grounded Theory , grounded theory methodology (GTM) has been an integral part of health social science. GTM allows for the systematic collection and analysis of qualitative data to inductively develop middle-range theories to make sense of people’s actions and experiences in the social world. Since its introduction, grounded theorists working from diverse research paradigms have expanded the methodology and developed alternative approaches to GTM. As a result, GTM permeates multiple disciplines and offers a wide diversity of variants in its application. The availability of many options can, at times, lead to confusion and misconceptions, particularly among novice users of the methodology. Consequently, in this book chapter, we aim to acquaint readers with this qualitative methodology. More specifically, we sort through five major developments in GTM and review key elements, from data collection through writing. Finally, we review published research reflecting these methods, to illustrate their application. We also note the value of GTM for elucidating components of culture that might otherwise remain hidden.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Grounded Theory Methods
Ahmad F, Hudak PL, Bercovitz K, Hollenberg E, Levison W. Are physicians ready for patients with internet-based health information? J Med Internet Res. 2006;8(3):e22.
Article Google Scholar
Aita K, Kai I. Physicians’ psychosocial barriers to different modes of withdrawal of life support in critical care: a qualitative study in Japan. Soc Sci Med. 2010;70(4):616–22.
Bateman J, Allen M, Samani D, Kidd J, Davies D. Virtual patient design: exploring what works and why. A grounded theory study. Med Educ. 2013;47:595–606.
Beard RL, Fetterman DJ, Wu B, Bryant L. The two voices of Alzheimer’s: attitudes toward brain health by diagnosed individuals and support persons. Gerontologist. 2009;49:S40–9.
Belgrave LL, Seide K. Coding for grounded theory. In: Bryant A, Charmaz K, editors. The SAGE handbook of current developments in grounded theory. London. Forthcoming.
Google Scholar
Brown B. Shame resilience theory: a grounded theory study on women and shame. Fam Soc. 2006;87(1):43–52.
Bryant A. Re-grounding grounded theory. J Inf Technol Theory Appl. 2002;4:25–42.
Bryant A. Grounded theory and grounded theorizing: pragmatism in research practice. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Bryant A, Charmaz K. Grounded theory in historical perspective: an epistemological account. In: Bryant A, Charmaz K, editors. The handbook of grounded theory. London: Sage; 2007a. p. 31–57.
Chapter Google Scholar
Bryant A, Charmaz K. Introduction. In: Bryant A, Charmaz K, editors. The handbook of grounded theory. London: Sage; 2007b. p. 31–57.
Charmaz K. Body, identity and self: adapting to impairment. Sociol Q. 1995;36:657–80.
Charmaz K. Constructivist and objectivist grounded theory. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln Y, editors. Handbook of qualitative research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2000. p. 509–35.
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory: a practical guide through qualitative analysis. London: Sage; 2006.
Charmaz K. Constructionism and grounded theory. In: Holstein JA, Gubrium JF, editors. Handbook of constructionist research. New York: Guilford; 2007. p. 35–53.
Charmaz K. Shifting the grounds: constructivist grounded theory methods for the twenty-first century. In: Morse J, Stern P, Corbin J, Bowers B, Charmaz K, Clarke A, editors. Developing grounded theory: the second generation. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press; 2009. p. 127–54.
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2014.
Charmaz K, Belgrave LL. Qualitative interviewing and grounded theory analysis. In: Gubrium JF, Holstein JA, Marvasti AB, McKinney KD, editors. The sage handbook of interview research: the complexity of the craft. 2nd ed. Los Angeles: Sage; 2012. p. 347–65.
Clarke A. From grounded theory to situational analysis: what’s new? Why? How? In: Morse J, Stern P, Corbin J, Bowers B, Charmaz K, Clarke A, editors. Developing grounded theory: the second generation. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press; 2009. p. 194–233.
Clarke A. Feminisms, grounded theory, and situational analysis revisited. In: Clarke AE, Friese C, Washburn R, editors. Situational analysis in practice: mapping research with grounded theory. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press; 2015. p. 84–154.
Clarke A, Friese C. Grounded theory using situational analysis. In: Bryant A, Charmaz K, editors. The sage handbook of grounded theory. London: Sage; 2007. p. 363–97.
Corbin J, Strauss A. Basics of qualitative research: techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 4th ed. Los Angeles: Sage; 2015.
Cresswell JW. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2009.
Cresswell JW. Qualitative inquiry & research design: choosing among five approaches. 3rd ed. Los Angeles: Sage; 2013.
Cresswell JW. Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. 5th ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2018.
Creswell JW, Poth CN. Qualitative inquiry & research design: choosing among five approaches. 4th ed. Los Angeles: Sage; 2018.
Denzin NK, Giardina MD. Qualitative inquiry and social justice: towards a politics of hope. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press; 2009.
Erol M. Melting bones: the social construction of postmenopausal osteoporosis in Turkey. Soc Sci Med. 2011;73(10):1490–7.
Fielding N. Analytic density, postmodernism, and applied multiple methods research. In: Bergman MM, editor. Advances in mixed methods research: theories and applications. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2008. p. 37–52.
Glaser BG. Theoretical sensitivity. Mill Valley: The Sociology Press; 1978.
Glaser BG, Strauss AL. Awareness of dying. Chicago: Aldine Pub; 1965.
Glaser BG, Strauss AL. The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research. New York: Adline De Gruyter; 1967.
Kononowicz AA, Zary N, Edebring S, Hege I. Virtual patients – what are we talking about? A framework to classify the meanings of the term in healthcare education. BMC Med Educ. 2015;15:11.
Larsson IE, Sahlsten MJ, Sjöström B, et al. Patient participation in nursing care from a patient perspective: a grounded theory study. Scand J Caring Sci. 2007;21:313–20.
Liamputtong P. Performing qualitative cross-cultural research. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
Liamputtong P. Culture as social determinant of health. In: Liamputtong P, editor. Social determinants of health: individual, community and healthcare. Melbourne: Oxford University Press; 2018.
Lindsay K, Vanderpyl J, Logo P, Dalbeth N. The experience and impact of living with gout: a study of men with chronic gout using a qualitative grounded theory approach. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17:1–6.
Nagel DA, Burns VF, Tilley C, Augin D. When novice researchers adopt constructivist grounded theory: Navigating the less traveled paradigmatic and methodological paths in Ph.D. dissertation work. Int J Doctoral Stud. 2015;10:365–83.
Poteat T, German D, Kerrigan D. Managing uncertainty: a grounded theory of stigma in transgender health care encounters. Soc Sci Med. 2013;84:22–9.
Quah S. Health and culture. In: Blackwell encyclopedia of sociology. 2007. Retrieved from http://www.blackwellreference.com/subscriber/tocnode.html?id=g9781405124331_chunk_g978140512433114_ss1-7 .
Schnitzer G, Loots G, Escudero V, Schechter I. Negotiating the pathways into care in a globalizing world: help-seeking behavior of ultra-orthodox Jewish parents. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2011;57(2):153–65.
Seide K. In the midst of it all: a qualitative study of the everyday life of Haitians during an ongoing cholera epidemic. Unpublished Master’s Thesis. University of Miami; 2016.
Stern PN. On solid ground: essential properties for growing grounded theory. In: Bryant A, Charmaz K, editors. The sage handbook of grounded theory. London: Sage; 2007. p. 114–26.
Strauss A, Corbin J. Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Newbury Park: Sage; 1990.
Ulysse GA. Papa, patriarchy, and power: snapshots of a good Haitian girl, feminism, & diasporic dreams. J Haitian Stud. 2006;12(1):24–47.
Wertz FJ, Charmaz K, McMullen L, Josselson R, Anderson R, McSpadden E. Five ways of doing qualitative analysis. New York: Guilford Press; 2011.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Sociology, University of Miami, Coral Gables, FL, USA
Linda Liska Belgrave & Kapriskie Seide
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Linda Liska Belgrave .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Belgrave, L.L., Seide, K. (2019). Grounded Theory Methodology: Principles and Practices. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_84
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_84
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Grounded theory research: A design framework for novice researchers
Affiliations.
- 1 Nursing and Midwifery, College of Healthcare Sciences, James Cook University, Townsville, QLD, Australia.
- 2 College of Health and Medicine, University of Tasmania, Australia, Hobart, TAS, Australia.
- PMID: 30637106
- PMCID: PMC6318722
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312118822927
Background: Grounded theory is a well-known methodology employed in many research studies. Qualitative and quantitative data generation techniques can be used in a grounded theory study. Grounded theory sets out to discover or construct theory from data, systematically obtained and analysed using comparative analysis. While grounded theory is inherently flexible, it is a complex methodology. Thus, novice researchers strive to understand the discourse and the practical application of grounded theory concepts and processes.
Objective: The aim of this article is to provide a contemporary research framework suitable to inform a grounded theory study.
Result: This article provides an overview of grounded theory illustrated through a graphic representation of the processes and methods employed in conducting research using this methodology. The framework is presented as a diagrammatic representation of a research design and acts as a visual guide for the novice grounded theory researcher.
Discussion: As grounded theory is not a linear process, the framework illustrates the interplay between the essential grounded theory methods and iterative and comparative actions involved. Each of the essential methods and processes that underpin grounded theory are defined in this article.
Conclusion: Rather than an engagement in philosophical discussion or a debate of the different genres that can be used in grounded theory, this article illustrates how a framework for a research study design can be used to guide and inform the novice nurse researcher undertaking a study using grounded theory. Research findings and recommendations can contribute to policy or knowledge development, service provision and can reform thinking to initiate change in the substantive area of inquiry.
Keywords: Framework; grounded theory; grounded theory methods; novice researcher; study design.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Grounded Theory Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your complete guide to grounded theory research.
11 min read If you have an area of interest, but no hypothesis yet, try grounded theory research. You conduct data collection and analysis, forming a theory based on facts. Read our ultimate guide for everything you need to know.
What is grounded theory in research?
Grounded theory is a systematic qualitative research method that collects empirical data first, and then creates a theory ‘grounded’ in the results.
The constant comparative method was developed by Glaser and Strauss, described in their book, Awareness of Dying (1965). They are seen as the founders of classic grounded theory.
Research teams use grounded theory to analyze social processes and relationships.
Because of the important role of data, there are key stages like data collection and data analysis that need to happen in order for the resulting data to be useful.
The grounded research results are compared to strengthen the validity of the findings to arrive at stronger defined theories. Once the data analysis cannot continue to refine the new theories down, a final theory is confirmed.
Grounded research is different from experimental research or scientific inquiry as it does not need a hypothesis theory at the start to verify. Instead, the evolving theory is based on facts and evidence discovered during each stage.Also, grounded research also doesn’t have a preconceived understanding of events or happenings before the qualitative research commences.
Free eBook: Qualitative research design handbook
When should you use grounded theory research?
Grounded theory research is useful for businesses when a researcher wants to look into a topic that has existing theory or no current research available. This means that the qualitative research results will be unique and can open the doors to the social phenomena being investigated.
In addition, businesses can use this qualitative research as the primary evidence needed to understand whether it’s worth placing investment into a new line of product or services, if the research identifies key themes and concepts that point to a solvable commercial problem.
Grounded theory methodology
There are several stages in the grounded theory process:
1. Data planning
The researcher decides what area they’re interested in.
They may create a guide to what they will be collecting during the grounded theory methodology. They will refer to this guide when they want to check the suitability of the qualitative data, as they collect it, to avoid preconceived ideas of what they know impacting the research.
A researcher can set up a grounded theory coding framework to identify the correct data. Coding is associating words, or labels, that are useful to the social phenomena that is being investigated. So, when the researcher sees these words, they assign the data to that category or theme.
In this stage, you’ll also want to create your open-ended initial research questions. Here are the main differences between open and closed-ended questions:
These will need to be adapted as the research goes on and more tangents and areas to explore are discovered. To help you create your questions, ask yourself:
- What are you trying to explain?
- What experiences do you need to ask about?
- Who will you ask and why?
2. Data collection and analysis
Data analysis happens at the same time as data collection. In grounded theory analysis, this is also known as constant comparative analysis, or theoretical sampling.
The researcher collects qualitative data by asking open-ended questions in interviews and surveys, studying historical or archival data, or observing participants and interpreting what is seen. This collected data is transferred into transcripts.
The categories or themes are compared and further refined by data, until there are only a few strong categories or themes remaining. Here is where coding occurs, and there are different levels of coding as the categories or themes are refined down:
- Data collection (Initial coding stage): Read through the data line by line
- Open coding stage: Read through the transcript data several times, breaking down the qualitative research data into excerpts, and make summaries of the concept or theme.
- Axial coding stage: Read through and compare further data collection to summarize concepts or themes to look for similarities and differences. Make defined summaries that help shape an emerging theory.
- Selective coding stage: Use the defined summaries to identify a strong core concept or theme.
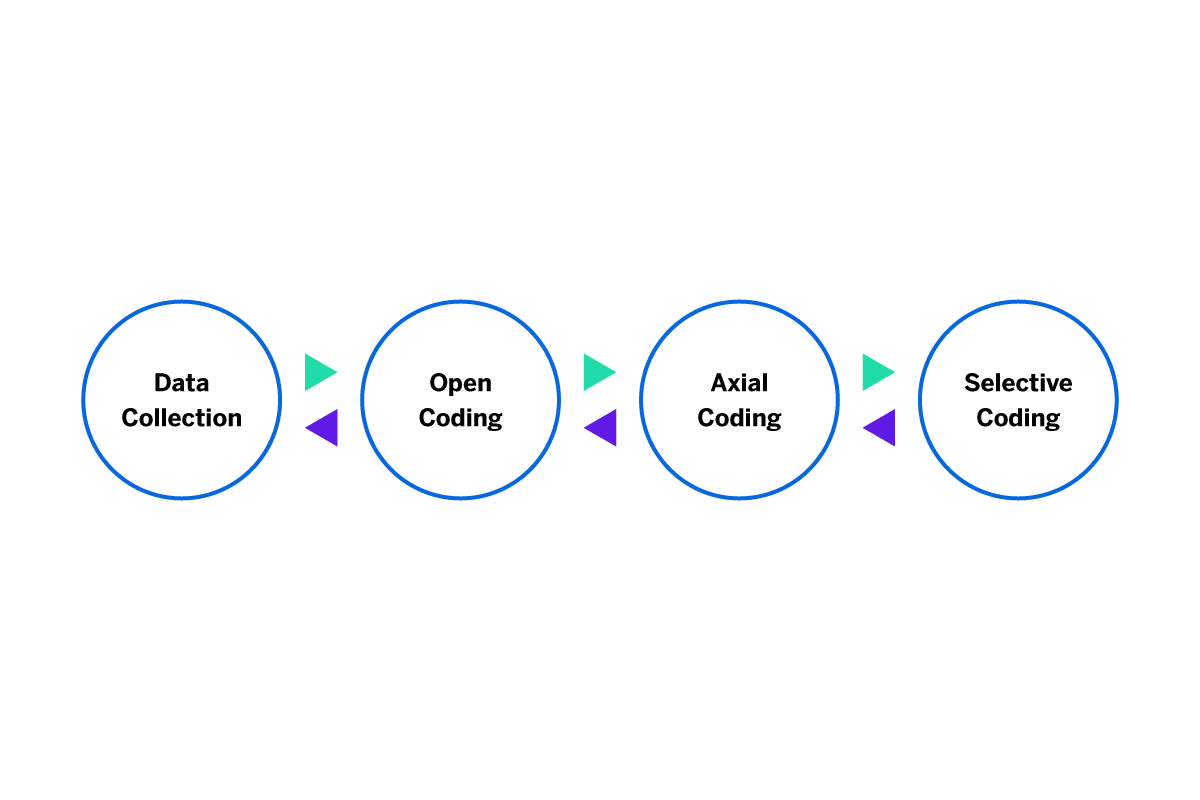
During analysis, the researcher will apply theoretical sensitivity to the collected data they uncover, so that the meaning of nuances in what they see can be fully understood.
This coding process repeats until the researcher has reached theoretical saturation. In grounded theory analysis, this is where all data has been researched and there are no more possible categories or themes to explore.
3. Data analysis is turned into a final theory
The researcher takes the core categories and themes that they have gathered and integrates them into one central idea (a new theory) using selective code. This final grounded theory concludes the research.
The new theory should be a few simple sentences that describe the research, indicating what was and was not covered in it.
An example of using grounded theory in business
One example of how grounded theory may be used in business is to support HR teams by analyzing data to explore reasons why people leave a company.
For example, a company with a high attrition rate that has not done any research on this area before may choose grounded theory to understand key reasons why people choose to leave.
Researchers may start looking at the quantitative data around departures over the year and look for patterns. Coupled with this, they may conduct qualitative data research through employee engagement surveys , interview panels for current employees, and exit interviews with leaving employees.
From this information, they may start coding transcripts to find similarities and differences (coding) picking up on general themes and concepts. For example, a group of excepts like:
- “The hours I worked were far too long and I hated traveling home in the dark”
- “My manager didn’t appreciate the work I was doing, especially when I worked late”
- There are no good night bus routes home that I could take safely”
Using open coding, a researcher could compare excerpts and suggest the themes of managerial issues, a culture of long hours and lack of traveling routes at night.
With more samples and information, through axial coding, stronger themes of lack of recognition and having too much work (which led people to working late), could be drawn out from the summaries of the concepts and themes.
This could lead to a selective coding conclusion that people left because they were ‘overworked and under-appreciated’.
With this information, a grounded theory can help HR teams look at what teams do day to day, exploring ways to spread workloads or reduce them. Also, there could be training supplied to management and employees to engage professional development conversations better.
Advantages of grounded theory
- No need for hypothesis – Researchers don’t need to know the details about the topic they want to investigate in advance, as the grounded theory methodology will bring up the information.
- Lots of flexibility – Researchers can take the topic in whichever direction they think is best, based on what the data is telling them. This means that exploration avenues that may be off-limits in traditional experimental research can be included.
- Multiple stages improve conclusion – Having a series of coding stages that refine the data into clear and strong concepts or themes means that the grounded theory will be more useful, relevant and defined.
- Data-first – Grounded theory relies on data analysis in the first instance, so the conclusion is based on information that has strong data behind it. This could be seen as having more validity.
Disadvantages of grounded theory
- Theoretical sensitivity dulled – If a researcher does not know enough about the topic being investigated, then their theoretical sensitivity about what data means may be lower and information may be missed if it is not coded properly.
- Large topics take time – There is a significant time resource required by the researcher to properly conduct research, evaluate the results and compare and analyze each excerpt. If the research process finds more avenues for investigation, for example, when excerpts contradict each other, then the researcher is required to spend more time doing qualitative inquiry.
- Bias in interpreting qualitative data – As the researcher is responsible for interpreting the qualitative data results, and putting their own observations into text, there can be researcher bias that would skew the data and possibly impact the final grounded theory.
- Qualitative research is harder to analyze than quantitative data – unlike numerical factual data from quantitative sources, qualitative data is harder to analyze as researchers will need to look at the words used, the sentiment and what is being said.
- Not repeatable – while the grounded theory can present a fact-based hypothesis, the actual data analysis from the research process cannot be repeated easily as opinions, beliefs and people may change over time. This may impact the validity of the grounded theory result.
What tools will help with grounded theory?
Evaluating qualitative research can be tough when there are several analytics platforms to manage and lots of subjective data sources to compare. Some tools are already part of the office toolset, like video conferencing tools and excel spreadsheets.
However, most tools are not purpose-built for research, so researchers will be manually collecting and managing these files – in the worst case scenario, by pen and paper!
Use a best-in-breed management technology solution to collect all qualitative research and manage it in an organized way without large time resources or additional training required.
Qualtrics provides a number of qualitative research analysis tools, like Text iQ , powered by Qualtrics iQ, provides powerful machine learning and native language processing to help you discover patterns and trends in text.
This also provides you with research process tools:
- Sentiment analysis — a technique to help identify the underlying sentiment (say positive, neutral, and/or negative) in qualitative research text responses
- Topic detection/categorisation — The solution makes it easy to add new qualitative research codes and group by theme. Easily group or bucket of similar themes that can be relevant for the business and the industry (eg. ‘Food quality’, ‘Staff efficiency’ or ‘Product availability’)
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Grounded Theory: What It Is + Approach in Qualitative Research

In the realm of qualitative research, the grounded theory approach stands as a stalwart methodology that has reshaped how researchers unravel the complexities of the human experience.
This approach, developed by Barney G. Glaser and Anselm L. Strauss in the 1960s, provides a systematic framework for generating theories from empirical data.
Grounded theory methods involve systematically deriving theories from qualitative data, facilitating a deep understanding of complex phenomena. The grounded theory method empowers researchers to construct concepts and theories directly from the data they collect, fostering a comprehensive and contextually rich analysis.
In this blog, we delve into the core principles of the grounded theory approach and explore how platforms like QuestionPro can enhance its application in qualitative research.
Understanding the Grounded Theory Approach
Grounded theory is a qualitative research methodology that involves developing theories directly from the data collected during the research process instead of relying on pre-existing theories or hypotheses.
This approach aims to generate insights and understanding about a particular phenomenon by systematically analyzing and coding the data to uncover patterns, relationships, and concepts.
It emphasizes research’s iterative and inductive nature, allowing theories to emerge organically from the data rather than being imposed on it. This methodology is commonly used in social sciences and other fields to explore complex social processes and generate new theories from empirical observations and interviews.
The Importance of Grounded Theory Research?
Grounded theory research is particularly well-suited for situations where you want to develop a new theory or gain a deeper understanding of a complex phenomenon that hasn’t been extensively studied before. Here are some scenarios where such theory research can be valuable:
Exploratory Studies
When you’re exploring a new area of research where little prior theory exists, it can help you generate theories and concepts directly from the data.
Complex Social Processes
It can provide insights into the underlying dynamics if you’re studying complex social processes, behaviors, interactions, or cultural phenomena.
Emergent Phenomena
When examining a relatively new or rapidly evolving phenomenon, grounded theory can help you uncover the underlying structures and trends driving its emergence.
Theory Building
If you aim to develop a new theoretical framework based on empirical evidence, it provides a systematic approach to theory building grounded in data.
Contextual Understanding
When you want to deeply understand a phenomenon within its specific context, it allows you to capture the nuances and intricacies that more hypothesis-driven methods might miss.
Understanding Participant Perspectives
It effectively captures participants’ perspectives and experiences in a detailed and nuanced manner.
Diverse Data Types
It’s useful when you’re working with diverse types of qualitative data, such as interviews, observations, field notes, or textual documents.
Challenging Assumptions
Grounded theory allows you to develop insights that contradict or expand upon established knowledge to challenge existing assumptions or theories.

Interdisciplinary Research
This can be valuable in interdisciplinary research, where you’re attempting to integrate perspectives from multiple disciplines to develop new insights.
Theory Development in Practical Fields
In fields like education, healthcare, or social work, where practical solutions are needed, it can help in developing theories that inform real-world applications.
Key steps of the grounded theory approach
The grounded theory process involves several key steps researchers follow to generate theories from empirical data systematically. While there might be variations and adaptations in different researchers’ approaches, the following steps are commonly associated with the grounded theory methodology:
Data Collection
The foundation of the constructivist grounded theory approach lies in collecting data through methods such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. This raw data serves as the bedrock for theory construction.
Open Coding
Researchers meticulously dissect the data, assigning initial codes to capture the fundamental concepts present. This stage facilitates unbiased exploration, as researchers do not force-fit data into pre-existing categories.
Axial Coding
Building upon the initial codes, researchers start categorizing and interlinking them to form more comprehensive themes. The aim is to identify connections and relationships between these categories.
Selective Coding
The process evolves further as a core category central to the phenomenon under study emerges. Researchers refine and establish links between this core category and other concepts.
Constant Comparison
Throughout the journey, researchers consistently compare new data with existing codes and categories, refining their understanding and allowing the theory to evolve organically.
Theoretical Sampling
Researchers strategically select new data sources or participants to enrich the theory’s development and validation, ensuring that the existing theory resonates with diverse perspectives.
The journey reaches its zenith with theoretical sensitivity saturation, where new data ceases to alter the theory significantly. This signifies a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon.
Writing the Theory
Researchers compile their insights into a coherent narrative that encapsulates emerging relationships, patterns, and concepts. This narrative becomes the tangible outcome of the grounded theory study.
Advantages and disadvantages of grounded theory
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of using grounded theory:
Advantages:
- Emergent Theory: Theories are developed from data, allowing for fresh insights.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various research contexts and dynamic phenomena.
- Holistic Understanding: In-depth immersion in data leads to comprehensive insights.
- Conceptualization: Generates new concepts and theoretical frameworks.
- Contextual Insight: Focuses on understanding phenomena within their social and cultural context.
Disadvantages:
- Time-Consuming: Iterative process requires significant time and effort.
- Subjectivity: Interpretation influenced by researcher bias.
- Lack of Reproducibility: Lack of standardized procedure can hinder replication.
- Initial Data Collection Challenges: Open-ended data collection may need clearer stopping criteria.
- Theory Ambiguity: Generated theories might be open to varied interpretations.
- Less Quantitative Emphasis: Not suitable for producing quantitative or statistical results.
QuestionPro’s role in enhancing the grounded theory approach
In their study of online community dynamics, the researchers employed grounded theory analysis to uncover emergent patterns of interaction and collaboration among participants. Platforms like QuestionPro offer a range of tools that complement and enhance the grounded theory Approach in qualitative research:
- Survey Design: Design your survey in QuestionPro to collect open-ended responses. These could be in the form of text answers, comments, or even multimedia content.
- Data Collection: Distribute the survey to your participants. You can target specific groups or populations based on your research objectives.
- Data Analysis: Once you collect the qualitative data, you can export the responses from QuestionPro. Then, you can follow the steps of the grounded theory procedures, including open coding, axial coding, and selective coding, using specialized qualitative analysis software like NVivo, Dedoose, or even manual methods.
- Theory Development: Analyze the data and identify emergent concepts and patterns. Through iterative coding and constant comparative method, you can develop grounded theory research that explains the phenomenon you’re investigating.
The grounded theory Approach remains a cornerstone in qualitative research, fostering a dynamic interplay between data and emerging theory construction.
QuestionPro’s suite of tools lends a helping hand to researchers embarking on this journey, providing support across data collection, analysis, collaboration, and visualization.
As the landscape of research evolves, the synergy between methodologies like the grounded theory approach and innovative platforms like QuestionPro paves the way for deeper insights into the tapestry of human experiences.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 8 Data Trends to Understand the Future of Data
May 30, 2024

Top 12 Interactive Presentation Software to Engage Your User
May 29, 2024

Trend Report: Guide for Market Dynamics & Strategic Analysis

Cannabis Industry Business Intelligence: Impact on Research
May 28, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- Supplements
- Patient Perspectives
- Methods Corner
- Science for Patients
- Invited Commentaries
- ESC Content Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Instructions for reviewers
- Submission Site
- Why publish with EJCN?
- Open Access Options
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Read & Publish
- About European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing
- About ACNAP
- About European Society of Cardiology
- ESC Publications
- Editorial Board
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- War in Ukraine
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, distinguishing features of grounded theory, the role and timing of the literature review.
- < Previous
Grounded theory: what makes a grounded theory study?
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Carley Turner, Felicity Astin, Grounded theory: what makes a grounded theory study?, European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing , Volume 20, Issue 3, March 2021, Pages 285–289, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjcn/zvaa034
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Grounded theory (GT) is both a research method and a research methodology. There are several different ways of doing GT which reflect the different viewpoints of the originators. For those who are new to this approach to conducting qualitative research, this can be confusing. In this article, we outline the key characteristics of GT and describe the role of the literature review in three common GT approaches, illustrated using exemplar studies.
Describing the key characteristics of a Grounded theory (GT) study.
Considering the role and timing of the literature review in different GT approaches.
Qualitative research is a cornerstone in cardiovascular research. It gives insights in why particular phenomena occur or what underlying mechanisms are. 1 Over the past 2 years, the European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing published 20 qualitative studies. 2–21 These studies used methods such as content analysis, ethnography, or phenomenology. Grounded theory (GT) has been used to a lesser extent.
Grounded theory is both a methodology and a method used in qualitative research ( Table 1 ). It is a research approach used to gain an emic insight into a phenomenon. In simple terms, this means understanding the perspective, or point of view, of an ‘insider’, those who have experience of the phenomenon. 22 Grounded theory is a research approach that originated from the social sciences but has been used in education and health research. The focus of GT is to generate theory that is grounded in data and shaped by the views of participants, thereby moving beyond description and towards theoretical explanation of a process or phenomenon. 23
Grounded theory as a method and methodology
One of the key issues with using GT, particularly for novices, is understanding the different approaches that have evolved as each specific GT approach is slightly different.
The tradition of GT began with the seminal text about classic GT written by Glaser and Strauss, 24 but since then GT has evolved into several different types. The approach to GT chosen by the researcher depends upon an understanding of the epistemological underpinnings of the different approaches, the match with the topic under investigation and the researcher’s own stance. Whilst GT is frequently used in applied health research, very few studies detail which GT approach has been used, how and why. Sometimes published studies claim to use GT methodology but the approaches that form the foundation of GT are not reported. This may be due to the word limit in academic journals or because legitimate GT approaches have not been followed. Either way, there is a lack of clarity about the practical application of GT. The purpose of this article is to outline the distinguishing characteristics of GT and outline practical considerations for the novice researcher regarding the place of the literature review in GT.
There are several distinguishing features of GT, as outlined by Sbaraini et al. 25 The first is that GT research is conducted through an inductive process. This means that the researcher is developing theory rather than testing it and must therefore remain ‘open’ throughout the study. In essence, this means that the researcher has no preconceived ideas about the findings. Taking an inductive approach means that the focus of the research may evolve over time as the researchers understand what is important to their participants through the data collection and analysis process.
With regards to data analysis, the use of coding is initially used to break down data into smaller components and labelling them to capture the essence of the data. The codes are compared to one another to understand and explain any variation in the data before they are combined to form more abstract categories. Memos are used to record and develop the researcher’s analysis of the data, including the detail behind the comparisons made between categories. Memos can stimulate the researcher’s thinking, as well as capturing the researcher’s ideas during data collection and analysis.
A further feature for data analysis in a GT study is the simultaneous data analysis and sampling to facilitate theoretical sampling. This means that as data analysis progresses participants are purposefully selected who may have characteristics or experiences that have arisen as being of interest from data collection and analysis so far. Questions in the topic guide may also be modified to follow a specific line of inquiry, test ideas and interpretations, or fill gaps in the analysis to build an emerging substantive theory. This evolving and non-linear methodology is to allow the evolution of the study as indicated by data, rather than analysing at the end of data collection. This approach to data analysis supports the researcher to take an inductive approach as discussed above.
Theoretical sampling facilitates the construction of theory until theoretical saturation is reached. Theoretical saturation is when all the concepts that form the theory being developed are well understood and grounded in data. Finally, the results are expressed as a theory where a set of concepts are related to one another and provide a framework for making predictions. 26 These key features of GT are summarized in Table 2 .
Distinguishing features of a GT study (adapted from Sbaraini et al. 25 )
The identification of a gap in the published literature is typically a requirement of successful doctoral studies and grant applications. However, in GT research there are different views about the role and timing of the literature review.
For researchers using classic Glaserian GT, the recommended approach is that the published literature should not be reviewed until data collection, analysis and theory development has been completed. 24 The rationale for the delay of the literature review is to enable the researcher to remain ‘open’ to discover theory emerging from data and free from contamination by avoiding forcing data into pre-conceived concepts derived from other studies. Furthermore, because the researcher is ‘open’ to whichever direction the data takes they cannot know in advance which aspects of the literature will be relevant to their study. 27
In Glaserian GT, the emerging concepts and theory from data analysis inform the scope of the literature review which is conducted after theory development. 24 This approach to the literature review aligns with the rather positivist stance of Glaser in which the researcher aims to remain free of assumptions so that the theory that emerges from the data is not influenced by the researcher. Reviewing the literature prior to data analysis would risk theory being imposed on the data. Perhaps counterintuitively, Glaser does recommend reading literature in unrelated fields to understand as many theoretical codes as possible. 28 However, it is unclear how this is different to reading literature directly related to the topic and could potentially still lead to the contamination of the theory arising from data that delaying the literature review is intended to avoid. It is also problematic regarding the governance processes around research, whereby funders and ethics committees would expect at least an overview of the existing literature as part of the justification for the study.
A study by Bergman et al. 29 used a classic Glaserian GT approach to examine and identify the motive of power in myocardial infarction patients’ rehabilitation process. Whilst the key characteristics of GT were evident in the way the study was conducted, there was no discussion about how the literature review contributed to the final theory. This may have been due to the word limit but illustrates the challenges that novice researchers may have in understanding where the literature review fits in studies using GT approaches.
In Straussian GT, a more pragmatic approach to the literature view is adopted. Strauss and Corbin 30 recognized that the researcher has prior knowledge, including that of the literature, before starting their research. They did not recommend dissociation from the literature, but rather that the literature be used across the various stages of the research. Published literature could identify important areas that could contribute to theory development, support useful comparisons in the data and stimulate further questions during the analytical process. According to Strauss and Corbin, researchers should be mindful about how published work could influence theory development. Whilst visiting the literature prior to data collection was believed to enhance data analysis, it was not thought necessary to review all the literature beforehand, but rather revisit the literature at later stages in the research process. 30
A study published by Salminen-Tuomaala et al. 31 used a Straussian GT approach to explore factors that influenced the way patients coped with hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction. The authors described a reflexive process in which the researcher noted down their preconceived ideas about the topic as part of the data analysis process. The literature review was conducted after data analysis.
The most recent step in the evolution of GT is the move towards a constructivist epistemological stance advocated by Charmaz. 32 In simple terms, this means that the underlying approach reflects the belief that theories cannot be discovered but are instead constructed by the researcher and their interactions with the participants and data. As the researcher plays a central role in the construction of the GT, their background, personal views, and culture will influence this process and the way data are analysed. For this reason, it is important to be explicit about these preconceptions and aim to maintain an open mind through reflexivity. 32 Therefore, engaging in a preliminary literature review and using this information to compare and contrast with findings from the research undertaken is desirable, alongside completing a comprehensive literature review after data analysis with a specific aim to present the GT.
A study published by Odell et al. 33 used the modified GT approach recommended by Charmaz 32 to study patients’ experiences of restenosis after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. The authors described the different GT approaches and key features of GT methodology which clearly informed the conduct of the study. However, there was no detail about how the literature review was used to shape the data analysis process and findings.
A solution: be clear on the approach taken to the literature review and why
Despite the clear differences in the approach to the literature review in GT, there appears to be a lack of precise guidance for novice researchers regarding how in depth or exhaustive a preliminary literature review should be. This lack of guidance can lead to a variety of different approaches as evidenced in the GT studies we have cited as examples, which is a challenge for the novice researcher. This uncertainty is further compounded by the concurrent approach to data collection and analysis which allows for the research focus to evolve as the study progresses. The complexity of the research process and the role and timing of the literature review is summarized in Figure 1 .

Literature review in Grounded Theory.
Taking a pragmatic approach, researchers will need to familiarize themselves with the literature to receive funding and approval for their study. This preliminary literature review can be followed up after data analysis by a more comprehensive review of the literature to help support the theory that was developed from the data. The key is to ensure transparency in reporting how the literature review has been used to develop the theory. The preliminary literature review can be used to set the scene for the research as part of the introduction, and the more extensive literature review can then be used during the discussion section to compare the theory developed from the data with existing literature, as per Probyn et al. 34
Whilst this pragmatic approach aligns with Straussian GT and Charmaz’s constructivist GT, it is at odds with Glaserian GT. Therefore, if Glaserian GT is chosen, the researcher should be explicit about deviation and provide a rationale.
Word count for journal articles is often a limiting factor in how much detail is included in why certain methodologies are used. Submitting detail about the methodology and rationale behind it can be presented as online supplementary material, thereby allowing interested readers to access further information about how and why the research was executed.
The use of GT as a methodology and method can shed light on areas where little knowledge is already known, generating theory directly from data. The traditional format of a published article does not always reflect the iterative approach to the literature review and data collection and analysis in GT. This can generate tension between how the research is presented in relation to how it was conducted. However, one simple way to ensure clarity in reporting is to be transparent in how the literature review is used.
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest : The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Greenhalgh T , Taylor R. Papers that go beyond numbers (qualitative research) . Br Med J 1997 ; 315 : 740 – 743 .
Google Scholar
Wilson RE , Rush KL , Reid RC , et al. The symptom experience of early and late treatment seekers before an atrial fibrillation diagnosis . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2021 ; 20 :231--242.
Lauck SB , Achtem L , Borregaard B , et al. Can you see frailty? An exploratory study of the use of a patient photograph in the transcatheter aortic valve implantation programme . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2021 ; 20 :252--260.
Sundelin R , Bergsten C , Tornvall P , Lyngå, P. et al. Self-rated stress and experience in patients with Takotsubo syndrome: a mixed methods study . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; doi: 10.1177/1474515120919387.
Janssen DJ , Ament SM , Boyne J , et al. Characteristics for a tool for timely identification of palliative needs in heart failure: the views of Dutch patients, their families and healthcare professionals . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; doi: 10.1177/1474515120918962.
Steffen EM , Timotijevic L , Coyle A. A qualitative analysis of psychosocial needs and support impacts in families affected by young sudden cardiac death: the role of community and peer support . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; doi: 10.1177/1474515120922347.
Molzahn AE , Sheilds L , Bruce A , Schick-Makaroff K , Antonio M , Clark AM. Life and priorities before death: a narrative inquiry of uncertainty and end of life in people with heart failure and their family members . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; 19 : 629 – 637 .
Wistrand C , Nilsson U , Sundqvist A-S. Patient experience of preheated and room temperature skin disinfection prior to cardiac device implantation: a randomised controlled trial . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; 19 : 529 – 536 .
Widell C , Andréen S , Albertsson P , Axelsson ÅB. Octogenarian preferences and expectations for acute coronary syndrome treatment . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; 19 : 521 – 528 .
Ferguson C , George A , Villarosa AR , Kong AC , Bhole S , Ajwani S. Exploring nursing and allied health perspectives of quality oral care after stroke: a qualitative study . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2020 ; 19 : 505 – 512 .
Sutantri S , Cuthill F , Holloway A. ‘ A bridge to normal’: a qualitative study of Indonesian women’s attendance in a phase two cardiac rehabilitation programme . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 , doi: 10.1177/1474515119864208.
Liu X-L , Willis K , Fulbrook P , Wu C-J(J) , Shi Y , Johnson M. Factors influencing self-management priority setting and decision-making among Chinese patients with acute coronary syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 700 – 710 .
Wingham J , Frost J , Britten N , Greaves C , Abraham C , Warren FC , Jolly K , Miles J , Paul K , Doherty PJ , Singh S , Davies R , Noonan M , Dalal H , Taylor RS. Caregiver outcomes of the REACH-HF multicentre randomized controlled trial of home-based rehabilitation for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 611 – 620 .
Olsson K , Näslund U , Nilsson J , Hörnsten Å. Hope and despair: patients’ experiences of being ineligible for transcatheter aortic valve implantation . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 593 – 600 .
Heery S , Gibson I , Dunne D , Flaherty G. The role of public health nurses in risk factor modification within a high-risk cardiovascular disease population in Ireland – a qualitative analysis . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 584 – 592 .
Brännström M , Fischer Grönlund C , Zingmark K , Söderberg A. Meeting in a ‘free-zone’: clinical ethical support in integrated heart-failure and palliative care . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 577 – 583 .
Haydon G , van der Riet P , Inder K. Long-term survivors of cardiac arrest: a narrative inquiry . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 458 – 464 .
Freysdóttir GR , Björnsdóttir K , Svavarsdóttir MH. Nurses’ Use of Monitors in Patient Surveillance: An Ethnographic Study on a Coronary Care Unit . London, England : SAGE Publications ; 2019 . p 272 – 279 .
Google Preview
Pokorney SD , Bloom D , Granger CB , Thomas KL , Al-Khatib SM , Roettig ML , Anderson J , Heflin MT , Granger BB. Exploring patient–provider decision-making for use of anticoagulation for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: results of the INFORM-AF study . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 280 – 288 .
Instenes I , Fridlund B , Amofah HA , Ranhoff AH , Eide LS , Norekvål TM. ‘ I hope you get normal again’: an explorative study on how delirious octogenarian patients experience their interactions with healthcare professionals and relatives after aortic valve therapy . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 224 – 233 .
Palmar-Santos AM , Pedraz-Marcos A , Zarco-Colón J , Ramasco-Gutiérrez M , García-Perea E , Pulido-Fuentes M. The life and death construct in heart transplant patients . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2019 ; 18 : 48 – 56 .
De Chesnay M , Banner D. Nursing Research Using Grounded Theory: Qualitative Designs and Methods . New York, NY : Springer Publishing Company ; 2015 .
Corbin J , Strauss A. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory . 3rd ed. California : SAGE ; 2007 .
Glaser BG , Strauss AL. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . New York : Aldine ; 1967 .
Sbaraini A , Carter SM , Evans RW , Blinkhorn A. How to do a grounded theory study: a worked example of a study of dental practices . BMC Med Res Methodol 2011 ; 11 : 128 – 128 .
Charmaz K. ‘ Discovering’ chronic illness: using grounded theory . Soc Sci Med 1990 ; 30 : 1161 – 1172 .
Thornberg R , Dunne C. Literature review in grounded theory. In Bryant A , Charmaz K , eds. The SAGE Handbook of Current Developments in Grounded Theory . London : SAGE Publications ; 2019 .
Glaser BG. Doing Grounded Theory: Issues and Discussions . California : Sociology Press ; 1998 .
Bergman E , Berterö C. ‘ Grasp Life Again’. A qualitative study of the motive power in myocardial infarction patients . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2003 ; 2 : 303 – 310 .
Strauss A , Corbin J. Basics of Qualitative Research: Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques . 2nd ed. California : Sage ; 1998 .
Salminen-Tuomaala M , Åstedt-Kurki P , Rekiaro M , Paavilainen E. Coping—seeking lost control . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2012 ; 11 : 289 – 296 .
Charmaz K. Constructing Grounded Theory . 2nd ed. Los Angeles : SAGE ; 2014 .
Odell A , Grip L , Hallberg LRM. Restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): experiences from the patients' perspective . Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2006 ; 5 : 150 – 157 .
Probyn J , Greenhalgh J , Holt J , Conway D , Astin F. Percutaneous coronary intervention patients’ and cardiologists’ experiences of the informed consent process in Northern England: a qualitative study . BMJ Open 2017 ; 7 : e015127 .
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to Your Librarian
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1873-1953
- Print ISSN 1474-5151
- Copyright © 2024 European Society of Cardiology
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 19, Issue 2
- What is grounded theory?
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Helen Noble 1 ,
- Gary Mitchell 2
- 1 School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens's University Belfast , Belfast , UK
- 2 Four Seasons Health Care , Belfast , UK
- Correspondence to : Dr Helen Noble , School of Nursing and Midwifery, Queens's University Belfast, Belfast BT9 7BL, UK; Helen.noble{at}qub.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2016-102306
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Grounded theory (GT) is a research method concerned with the generation of theory, 1 which is ‘grounded’ in data that has been systematically collected and analysed. 2 It is used to uncover such things as social relationships and behaviours of groups, known as social processes. 3 It was developed in California, USA by Glaser and Strauss during their study—‘Awareness of Dying’. 1 It is a general methodology for developing theory that is grounded in data which is systematically gathered and analysed.
Features of GT
Data collection and analysis occur simultaneously.
Categories and analytic codes developed from data. Pre-existing conceptualisations not to be used—this is known as theoretical sensitivity (see below).
Theoretical sampling used to refine categories.
Abstract categories constructed inductively.
Social processes discovered in the data.
Analytical memos used between coding and writing.
Categories integrated into a theoretical framework. 4
Carrying out a GT study
Theoretical sampling.
Glaser and Strauss (1967) first mentioned theoretical sampling and described a process of generating theory from data which includes collecting the data, then coding and analysing the data. 1 Next the researcher makes a conscious decision about what further detail they feel needs exploring as the new theory develops. It usually takes place after some initial key concepts or categories have been identified, for example, you might decide to interview patients about their experience of heart failure. They may talk about systematic errors occurring in the general practice surgery. From this analysis of the data you may decide to approach and interview GPs to explore their views on patients’ comments. Theoretical sampling therefore, is used to produce more data to endorse or refute the categories that have been identified in the previous analysis. 6
Theoretical sensitivity
Theoretical sensitivity refers to the insight of the researcher. It concerns the researcher being able to give meaning to data, understand what the data says, and being able to separate out what is relevant and what is not. By being theoretically sensitive and using insight, the researcher is able to develop a theory that is grounded, theoretically dense, and cohesive. 7 Sensitivity comes from several sources including (1) literature—in depth reading offers a rich understanding of the phenomena being studied; (2) professional and personal experience—offers an understanding of the events and topics being explored; (3) the analytic process—allows for insight and understanding of the phenomena. 8
Analysis of data in GT
There are three stages of data analysis in GT: 8
Open coding: this involves line by line coding where concepts and key phrases are identified and highlighted and moved into subcategories, then categories. This breaks the data down into conceptual components and the researcher can start to theorise or reflect on what they are reading and understanding—making sense of the data. The data from each participant will be ‘constantly compared’ for similarities.
Axial coding: at this stage relationships are identified between the categories, and connections identified.
Selective coding: this involves identifying the core category and methodically relating it to other categories. The relationships must be authenticated and categories refined. Categories are then integrated together and a GT identified.
Analytical notes are encouraged. These are notes to oneself to explain thought patterns in relation to the data analysis. Final theory is usually generated from the integration of several analytical memos.
The core category
The core category is the chief phenomena around which the categories are built. Theory is generated around a core category. The core category should account for the variation found in the data, that is, the categories will relate to it in some way. The categories demonstrate how the core category is situated in the lives of those participating in the study.
Example of a GT case study
As illustrated, GT methodologies involve the construction of new theory through the analysis of data. In a study carried out by Beech et al , 9 the authors sought to explore patient participant experiences of recovery following surgical intervention for colorectal cancer. Beech et al 9 opted to use GT because previous studies had sought to answer this research question by measuring quantifiable biomedical markers, such as symptoms of pain, insomnia or fatigue. According to the authors, there was a paucity of empirical literature around the topic from a holistic perspective, for example social, psychological and cultural aspects of a person's well-being.
Twelve participants were interviewed four times, over a 1-year period. The authors used theoretical sampling to guide the researcher as data were collected. It helped facilitate the development of theory as it emerged, not once data collection was complete. 1 Initial participants were selected based on ‘subject area’, as is recommended in theoretical sampling. Each had undergone a surgical procedure to remove a tumour in their bowel or rectum and had not received prescribed chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The authors initially asked patient participants to describe their experiences to date.
Data analysis of the interviews was carried out according to the steps described by Strauss and Corbin. 10 The authors began by coding each line of each patient participant transcript. Similar codes were then grouped together to form subcategories and within these subcategories categories were identified. The authors then grouped together the categories to form theory related to patient participant experiences of recovery following surgical intervention for colorectal cancer. The process of data collection continued until each category was saturated and no new data emerged.
Patient participants described their recovery in three phases identified from three categories; disrupting the self, repairing the self and restoring the self. The authors also noted how the process was linear in that all participants went through the stages, for example, phase one began at prediagnosis and ended at the conclusion of surgery; phase two commonly lasted between 3 and 6 months and phase three, from 6 months onwards, was related to a person's fluctuating level of wellness and illness. Notably, these three categories were underpinned by various subcategories, which were generated from initial codes. For example, the second category Beech et al 4 identified, ‘disrupting the self’, was made up of the three subcategories; body repair, autonomy and re-establishing personal identity ( figure 1 ).
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Grounded theory data analysis.
Importantly, the authors encapsulated the three categories to present a pertinent theory related to patient participant experiences of recovery following surgical intervention for colorectal cancer. They found that recovery is more than physical repair. It is a process of restoring a sense of wellness demonstrated through an awareness and enjoyment of the physical, emotional, social and spiritual aspects of life, in other words, holistic health. 9
By using GT and adhering to this as a research method, a theory will be produced that is grounded in your data. 10 It is a research method which uses strict procedures for data analysis and will enable you to search for and conceptualise the hidden social and collective patterns and constructions in your area of interest.
- Glaser BG ,
- Strauss A ,
- Faithfull S
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

What is Grounded Theory in Qualitative Research?

- April 15, 2022
You may have come across the term “ grounded theory ” in qualitative and quantitative research. Typically, grounded theory is discussed in academic research, though as market researchers, we find that we often use this framework when developing studies. In this post, we’ll try to break grounded theory down for market research usage and help provide an understanding of how impactful this mode of framing research can be for B2B and B2C studies.
First off, what is grounded theory – in real-speak?
Let’s explain grounded theory in non-academic jargon to make this simple to digest:
Use grounded theory methods when you’re not sure what you’re looking for in a study or there is no clear theory as to why certain behaviors or patterns are occurring.
Or to make it even more clear:
Use grounded theory methods when you don’t know what you don’t know.
In typical research methods (both quantitative and qualitative), teams come together with a clear hypothesis about what they’re studying.
For example, “When travelers are booking flights online, they will go for the best prices and flight times.”
That’s a clear hypothesis, likely based on previous data and studies. The research team may be tasked with investigating this hypothesis further and adding more details to it – or even disproving it, to uncover whether there are other factors at play in how people choose and book airline flights. To test the hypothesis, the research team would design a user experience study, where they observe how people book flights online (with screensharing), while asking them questions as the traveler goes through the process. This will help gather essential data that can be analyzed, thematically, to further prove or disprove the initial hypothesis.
However, that’s not what grounded theory would do, because in this case we just described, the hypothesis was set from the beginning.
What if, however, the researchers instead had a situation such as this: A product team wants to understand how people react to working from home exclusively during the pandemic so that they can develop software tools for remote teams.
In this example, the team doesn’t have a clear hypothesis to work from. For this specific case, the study question was posed in early 2020, when working from home for entire teams was new. The pandemic situation was unprecedented in the modern tech age, so the development team wasn’t sure exactly what hypothesis question to pose – or, to put it more simply – they didn’t know what they were looking for exactly, but they did know that there were likely software tools they could develop that could be helpful for remote teams.
This is a perfect example of when to apply grounded theory research. Let’s explore this example further, through the lens of grounded theory.
How to set up a grounded theory study
When you’re not sure exactly what you’re looking for, using grounded theory methods helps you explore themes, in an iterative research style.
So let’s go back to our remote-team software example.
Because the research team wasn’t sure exactly how people were adapting to at-home work, they first assembled a small sample to study. Using mobile ethnographies , the team had a sample of at-home workers record their daily work patterns. They were asked more general questions about highs and lows, efficiencies, and inefficiencies, and where they were feeling frustrated or lost by not having in-person collaboration. They also explored “workarounds” that teams were doing to stay productive.
Once they received the data back and did follow-up in-depth interviews with the participants, the team then sorted the themes into “codes.” Codes essentially sum up patterns in the data that are reoccurring. For example “ workers are less efficient when brainstorming new creative ideas” was a code that came out of the initial round.
From the initial round, some ideas started to take place and patterns emerged. The research team realized they needed to expand their participant pool to also include in-house designers, and not just product managers. The research team then devised a second round of research, also using mobile ethnographies and in-depth interviews, but this time with in-house designers and product managers.
After this second round, even more themes and codes emerged, and the product design team felt like they were getting closer to specific issues that they could develop software to address.
But they needed more data.
After analyzing the second round, the research team decided to hone in on a specific topic: in this case, how to improve brainstorming and enhance the creative process for remote teams. So they developed a third round of research, and they pulled in creative design teams, product managers, and upper-level managers.
The questions the researchers posed in this third round were now quite specific, and they designed exercises around remote creative brainstorming (also using mobile ethnographies and in-depth interviews). This round was especially illuminating because they now were much closer to proving and disproving new hypotheses that had emerged from the initial research rounds.
After analyzing the third round, the product team felt ready to design software prototypes that would address some of the issues they found in the exploratory research phases. In short: They had come up with a hypothesis, which was “Remote teams are struggling to collaborate creatively using their current software.” Now they had a hypothesis (a problem statement) and a mission for their software design work.
Let’s now break down that case study to uncover the steps of grounded theory research
We just took you through a real-world example of using grounded theory research methods to uncover patterns and arrive at a hypothesis. Grounded theory, as you can see from this example, is the opposite of typical research projects, where teams know what they’re looking for, so they recruit participants, design specific questions and exercises, and then spend the bulk of the research proving or disproving the hypothesis they’re testing.
In grounded theory, it’s exploratory, from the very beginning. Teams start with some initial ideas, recruit samples to test, and from the early tests, start to see patterns. They then may have to shift and recruit different personas and start to ask questions specific to the themes from the first round of research. In each subsequent round of research, the team uncovers ideas and then tests and poses hypotheses based on what they’re learning.
Grounded theory is a great method for specific types of research issues
Grounded theory is best applied when research teams come into a problem with uncertainty about the full landscape and situation. Because it requires multiple rounds of research, it’s more costly and time-consuming than studies where the hypothesis and testing is clear, from the very beginning. However, hopefully as the example we used illustrated, it’s a fantastic method to generate new product ideas. The key is to have an open mind and be able to first cast a wide net of ideas, before narrowing down on emerging themes to test.
Do you have a study that could benefit from grounded theory research? Request a proposal today >
- Request Proposal
- Participate in Studies
- Our Leadership Team
- Our Approach
- Mission, Vision and Core Values
- Qualitative Research
- Quantitative Research
- Research Insights Workshops
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Millennial & Gen Z Market Research
- Market Research Services
- Our Clients
- InterQ Blog
10 Grounded Theory Examples (Qualitative Research Method)

Grounded theory is a qualitative research method that involves the construction of theory from data rather than testing theories through data (Birks & Mills, 2015).
In other words, a grounded theory analysis doesn’t start with a hypothesis or theoretical framework, but instead generates a theory during the data analysis process .
This method has garnered a notable amount of attention since its inception in the 1960s by Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss (Corbin & Strauss, 2015).
Grounded Theory Definition and Overview
A central feature of grounded theory is the continuous interplay between data collection and analysis (Bringer, Johnston, & Brackenridge, 2016).
Grounded theorists start with the data, coding and considering each piece of collected information (for instance, behaviors collected during a psychological study).
As more information is collected, the researcher can reflect upon the data in an ongoing cycle where data informs an ever-growing and evolving theory (Mills, Bonner & Francis, 2017).
As such, the researcher isn’t tied to testing a hypothesis, but instead, can allow surprising and intriguing insights to emerge from the data itself.
Applications of grounded theory are widespread within the field of social sciences . The method has been utilized to provide insight into complex social phenomena such as nursing, education, and business management (Atkinson, 2015).
Grounded theory offers a sound methodology to unearth the complexities of social phenomena that aren’t well-understood in existing theories (McGhee, Marland & Atkinson, 2017).
While the methods of grounded theory can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, the rich, robust theories this approach produces make it a valuable tool in many researchers’ repertoires.
Real-Life Grounded Theory Examples
Title: A grounded theory analysis of older adults and information technology
Citation: Weatherall, J. W. A. (2000). A grounded theory analysis of older adults and information technology. Educational Gerontology , 26 (4), 371-386.
Description: This study employed a grounded theory approach to investigate older adults’ use of information technology (IT). Six participants from a senior senior were interviewed about their experiences and opinions regarding computer technology. Consistent with a grounded theory angle, there was no hypothesis to be tested. Rather, themes emerged out of the analysis process. From this, the findings revealed that the participants recognized the importance of IT in modern life, which motivated them to explore its potential. Positive attitudes towards IT were developed and reinforced through direct experience and personal ownership of technology.
Title: A taxonomy of dignity: a grounded theory study
Citation: Jacobson, N. (2009). A taxonomy of dignity: a grounded theory study. BMC International health and human rights , 9 (1), 1-9.
Description: This study aims to develop a taxonomy of dignity by letting the data create the taxonomic categories, rather than imposing the categories upon the analysis. The theory emerged from the textual and thematic analysis of 64 interviews conducted with individuals marginalized by health or social status , as well as those providing services to such populations and professionals working in health and human rights. This approach identified two main forms of dignity that emerged out of the data: “ human dignity ” and “social dignity”.
Title: A grounded theory of the development of noble youth purpose
Citation: Bronk, K. C. (2012). A grounded theory of the development of noble youth purpose. Journal of Adolescent Research , 27 (1), 78-109.
Description: This study explores the development of noble youth purpose over time using a grounded theory approach. Something notable about this study was that it returned to collect additional data two additional times, demonstrating how grounded theory can be an interactive process. The researchers conducted three waves of interviews with nine adolescents who demonstrated strong commitments to various noble purposes. The findings revealed that commitments grew slowly but steadily in response to positive feedback, with mentors and like-minded peers playing a crucial role in supporting noble purposes.
Title: A grounded theory of the flow experiences of Web users
Citation: Pace, S. (2004). A grounded theory of the flow experiences of Web users. International journal of human-computer studies , 60 (3), 327-363.
Description: This study attempted to understand the flow experiences of web users engaged in information-seeking activities, systematically gathering and analyzing data from semi-structured in-depth interviews with web users. By avoiding preconceptions and reviewing the literature only after the theory had emerged, the study aimed to develop a theory based on the data rather than testing preconceived ideas. The study identified key elements of flow experiences, such as the balance between challenges and skills, clear goals and feedback, concentration, a sense of control, a distorted sense of time, and the autotelic experience.
Title: Victimising of school bullying: a grounded theory
Citation: Thornberg, R., Halldin, K., Bolmsjö, N., & Petersson, A. (2013). Victimising of school bullying: A grounded theory. Research Papers in Education , 28 (3), 309-329.
Description: This study aimed to investigate the experiences of individuals who had been victims of school bullying and understand the effects of these experiences, using a grounded theory approach. Through iterative coding of interviews, the researchers identify themes from the data without a pre-conceived idea or hypothesis that they aim to test. The open-minded coding of the data led to the identification of a four-phase process in victimizing: initial attacks, double victimizing, bullying exit, and after-effects of bullying. The study highlighted the social processes involved in victimizing, including external victimizing through stigmatization and social exclusion, as well as internal victimizing through self-isolation, self-doubt, and lingering psychosocial issues.
Hypothetical Grounded Theory Examples
Suggested Title: “Understanding Interprofessional Collaboration in Emergency Medical Services”
Suggested Data Analysis Method: Coding and constant comparative analysis
How to Do It: This hypothetical study might begin with conducting in-depth interviews and field observations within several emergency medical teams to collect detailed narratives and behaviors. Multiple rounds of coding and categorizing would be carried out on this raw data, consistently comparing new information with existing categories. As the categories saturate, relationships among them would be identified, with these relationships forming the basis of a new theory bettering our understanding of collaboration in emergency settings. This iterative process of data collection, analysis, and theory development, continually refined based on fresh insights, upholds the essence of a grounded theory approach.
Suggested Title: “The Role of Social Media in Political Engagement Among Young Adults”
Suggested Data Analysis Method: Open, axial, and selective coding
Explanation: The study would start by collecting interaction data on various social media platforms, focusing on political discussions engaged in by young adults. Through open, axial, and selective coding, the data would be broken down, compared, and conceptualized. New insights and patterns would gradually form the basis of a theory explaining the role of social media in shaping political engagement, with continuous refinement informed by the gathered data. This process embodies the recursive essence of the grounded theory approach.
Suggested Title: “Transforming Workplace Cultures: An Exploration of Remote Work Trends”
Suggested Data Analysis Method: Constant comparative analysis
Explanation: The theoretical study could leverage survey data and in-depth interviews of employees and bosses engaging in remote work to understand the shifts in workplace culture. Coding and constant comparative analysis would enable the identification of core categories and relationships among them. Sustainability and resilience through remote ways of working would be emergent themes. This constant back-and-forth interplay between data collection, analysis, and theory formation aligns strongly with a grounded theory approach.
Suggested Title: “Persistence Amidst Challenges: A Grounded Theory Approach to Understanding Resilience in Urban Educators”
Suggested Data Analysis Method: Iterative Coding
How to Do It: This study would involve collecting data via interviews from educators in urban school systems. Through iterative coding, data would be constantly analyzed, compared, and categorized to derive meaningful theories about resilience. The researcher would constantly return to the data, refining the developing theory with every successive interaction. This procedure organically incorporates the grounded theory approach’s characteristic iterative nature.
Suggested Title: “Coping Strategies of Patients with Chronic Pain: A Grounded Theory Study”
Suggested Data Analysis Method: Line-by-line inductive coding
How to Do It: The study might initiate with in-depth interviews of patients who’ve experienced chronic pain. Line-by-line coding, followed by memoing, helps to immerse oneself in the data, utilizing a grounded theory approach to map out the relationships between categories and their properties. New rounds of interviews would supplement and refine the emergent theory further. The subsequent theory would then be a detailed, data-grounded exploration of how patients cope with chronic pain.
Grounded theory is an innovative way to gather qualitative data that can help introduce new thoughts, theories, and ideas into academic literature. While it has its strength in allowing the “data to do the talking”, it also has some key limitations – namely, often, it leads to results that have already been found in the academic literature. Studies that try to build upon current knowledge by testing new hypotheses are, in general, more laser-focused on ensuring we push current knowledge forward. Nevertheless, a grounded theory approach is very useful in many circumstances, revealing important new information that may not be generated through other approaches. So, overall, this methodology has great value for qualitative researchers, and can be extremely useful, especially when exploring specific case study projects . I also find it to synthesize well with action research projects .
Atkinson, P. (2015). Grounded theory and the constant comparative method: Valid qualitative research strategies for educators. Journal of Emerging Trends in Educational Research and Policy Studies, 6 (1), 83-86.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2015). Grounded theory: A practical guide . London: Sage.
Bringer, J. D., Johnston, L. H., & Brackenridge, C. H. (2016). Using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software to develop a grounded theory project. Field Methods, 18 (3), 245-266.
Corbin, J., & Strauss, A. (2015). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory . Sage publications.
McGhee, G., Marland, G. R., & Atkinson, J. (2017). Grounded theory research: Literature reviewing and reflexivity. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 29 (3), 654-663.
Mills, J., Bonner, A., & Francis, K. (2017). Adopting a Constructivist Approach to Grounded Theory: Implications for Research Design. International Journal of Nursing Practice, 13 (2), 81-89.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 7 Key Features of 21st Century Learning
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Sociocultural Theory of Learning in the Classroom
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ The 4 Principles of Pragmatism in Education
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 17 Deep Processing Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

"Let the Fear Go and Trust the Process"—Experiencing Grounded Theory Over a Lifetime. Odis E. Simmons in Conversation With Astrid Gynnild
Odis simmons.
- Astrid Gynnild University of Bergen https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9502-1044
Odis SIMMONS was among the first students who learned grounded theory method (GTM) directly from the co-founders GLASER and STRAUSS. Except for GLASER himself, SIMMONS is probably the grounded theorist who has taught the method to most students globally. In this interview SIMMONS provides key insights into learning, doing, teaching, and applying classic grounded theory (GT) as a general research method. With his double background as a therapist and a teacher in higher education, SIMMONS elaborates on fears that students might have during the research process and how they are overcome. He explains the ideas behind his own approaches to grounded action and grounded therapy , which for a long time resided in the GTM background but are gradually getting more widespread. In the interview, he also brings new knowledge on the diverging perspectives of GLASER and STRAUSS which, according to him, existed from the beginning. He argues, in an including manner, why classic GTM and constructivist GTM should be considered two different methods and urges educators to openly discuss the differences.
Author Biographies
Odis E. SIMMONS enrolled at the University of California, San Francisco in 1970, and became an early student of both GLASER and STRAUSS after their seminal work "The Discovery of Grounded Theory" (1967) was published. SIMMONS got his PhD in sociology at the University of California, San Francisco in 1974. He has taught classic GTM to hundreds of students since he first started in 1971. His first academic position was at the University of Tulsa, Oklahoma. He then went to Yale University in Connecticut, where he directed the self-care program in the Medical School. From there he and his wife decided to take the plunge and move to the Northwest. After 14 years as a therapist, SIMMONS went on to a faculty position at Fielding Graduate University, where he developed his own program in classic GTM. He held the position at Fielding for 16 years until he formally retired in 2014. Following up on his teaching career, SIMMONS has written "Experiencing Grounded Theory: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning, Doing, Mentoring, Teaching, and Applying Grounded Theory," which was published in 2022. SIMMONS was a close friend of Barney G. GLASER until GLASER died in 2022, and he is a fellow of the Grounded Theory Institute.
Astrid Gynnild, University of Bergen
Astrid GYNNILD is a professor of media studies at the University of Bergen, Norway. She attended her first troubleshooting seminar with Barney GLASER in London in 2004. She got her PhD from the University of Bergen in 2006 with a grounded theory on creative processes of news professionals, with GLASER as external examiner. GYNNILD was a participant observer at more than a dozen of GLASER's troubleshooting seminars in Europe and in the USA 2004-2017. She was a visiting research scholar at the University of California, Berkeley 2011-2012, while also working closely with GLASER. She served as an editor of the non-profit journal Grounded Theory Review ( GTR ) 2012-2018 and turned the GTR into an open-access journal. GYNNILD co-authored "Grounded Theory: The Philosophy, Method and Work of Barney Glaser" with Vivian B. MARTIN (2012). She has published several classic grounded theories in both English and Norwegian. She is a reviewer in the GTR and a fellow of the Grounded Theory Institute.
Artinian, Barbara; Giske, Tove & Cone, Pamela (Eds.) (2009). Glaserian grounded theory in nursing research: Trusting emergence. New York, NY: Springer.
Charmaz, Kathy (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Charmaz, Kathy & Keller, Reiner (2016). A personal journey with grounded theory methodology. Kathy Charmaz in conversation with Reiner Keller. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 17(1), Art. 16, https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-17.1.2541 [Accessed: April 10, 2024].
Glaser, Barney G. (1978). Theoretical sensitivity: Advances in the methodology of grounded theory. Mill Valley, CA: Sociology Press.
Glaser, Barney G. (1992). Basics of grounded theory analysis: Emergence vs. forcing. Mill Valley, CA: Sociology Press.
Glaser, Barney G. (1998). Doing grounded theory. Issues and discussions. Mill Valley, CA: Sociology Press.
Glaser, Barney G. (2002). Constructivist grounded theory?. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 3(3), Art. 12, https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-3.3.825 [Accessed: April 10, 2024].
Glaser, Barney G. (2005). The grounded theory perspective III: Theoretical coding. Mill Valley, CA: Sociology Press.
Glaser, Barney G. (2014). Choosing grounded theory. Grounded Theory Review, 13(2), 3-19, https://groundedtheoryreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/CHOOSING-GROUNDED-THEORY-2014.pdf [Accessed: April 7, 2024].
Glaser, Barney G. with the assistance of Judith Holton (2004). Remodeling grounded theory. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 5(2), Art. 4, https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-5.2.607 [Accessed: April 21, 2024].
Glaser, Barney G. & Strauss, Anselm L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Chicago, IL: Aldine.
Gynnild, Astrid (2012a). Atmosphering for conceptual discovery. In Vivian B. Martin & Astrid Gynnild (Eds.), Grounded theory: The philosophy, method, and work of Barney Glaser (pp.31-51). Boca Raton, FL: BrownWalker Press.
Gynnild, Astrid (2012b). Living the ideas. A biographical interview with Barney Glaser. In Vivian B. Martin & Astrid Gynnild (Eds.), Grounded theory: The philosophy, method, and work of Barney Glaser (pp.237-255). Boca Raton, FL: BrownWalker Press.
Lyman, Stanford M. & Scott, Marvin B. (1970). A sociology of the absurd. New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
McCallin, Antoinette; Nathaniel, Alvita & Andrews, Tom (2011). Learning methodology minus mentorship. In Vivian B. Martin & Astrid Gynnild (Eds.), Grounded theory: The philosophy, method, and work of Barney Glaser (pp.237-255). Boca Raton, FL: BrownWalker Press.
Olson, Mitch M. (2008). Using grounded action methodology for student intervention—Driven succeeding: A grounded action study in adult education. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 9(1), Art. 9, https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-9.1.340 [Accessed: April 10, 2024].
Olson, Mitch M. & Raffanti, Michael. A. (2006). Leverage points, paradigms, and grounded action: Intervening in educational systems. World Futures, 62(7), 533-541.
Schatzman, Leonard & Strauss, Anselm L. (1972). Field research: Strategies for a natural sociology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Pearson.
Simmons, Odis (2012). Why classic grounded theory. In Vivian B. Martin & Astrid Gynnild (Eds.), Grounded theory: The philosophy, method, and work of Barney Glaser (pp.15-31). Boca Raton, FL: BrownWalker Press.
Simmons, Odis (2022). Experiencing grounded theory: A comprehensive guide to learning, doing, mentoring, teaching, and applying grounded theory. Boca Raton, FL: BrownWalker Press.
Simmons, Odis E., & Gregory, Tony. A. (2003). Grounded action: Achieving optimal and sustainable change. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 4(3), Art. 27, https://doi.org/10.17169/fqs-4.3.677 [Accessed: April 10, 2024].
Stern, Phyllis N. (1994). Eroding grounded theory. In Janice M. Morse (Ed.), Critical issues in qualitative inquiry (pp.212-223). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Strauss, Anselm L. & Corbin, Juliet M. (1990). Basics of qualitative research. Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Witter, B. (2020). Rodney Dangerfield's "i don't get no respect" was inspired by his rough childhood. biography.com, https://www.biography.com/actors/rodney-dangerfield-i-dont-get-no-respect [Accessed: April 10, 2024].
How to Cite
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)
Copyright (c) 2024 Astrid Gynnild, Odis Simmons

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Hilde Otteren, Astrid Gynnild, Remote Female Fixation—A Grounded Theory on Semi-Illegal Sharing of Nude Imagery Online , Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research: Vol. 22 No. 2 (2021): The Refiguration of Spaces and Cross-Cultural Comparison I

Make a Submission
Current issue, information.
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Usage Statistics Information
We log anonymous usage statistics. Please read the privacy information for details.
Developed By
2000-2024 Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung / Forum: Qualitative Social Research (ISSN 1438-5627) Institut für Qualitative Forschung , Internationale Akademie Berlin gGmbH
Hosting: Center for Digital Systems , Freie Universität Berlin Funding 2023-2025 by the KOALA project
Privacy Statement Accessibility Statement

- Study Protocol
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2024
Person-centred care and the work-related health and job satisfaction of health and social care professionals: protocol for a prospective longitudinal cohort study combined with qualitative studies (the PCC@Work project)
- Cornelia van Diepen 1 , 2 ,
- Qarin Lood 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Kristoffer Gustavsson 2 , 5 ,
- Malin Axelsson 6 ,
- Monica Bertilsson 7 ,
- Gunnel Hensing 7 &
- Andreas Fors 2 , 5 , 8
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 683 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The interplay of ethical stress, heavy workloads, and job dissatisfaction poses challenges to both the recruitment and retention of health and social care professionals. Person-centred care, rooted in ethical principles, involves collaborative care, and is expected to improve care and job satisfaction. However, prior research on the impact of person-centred care practices on professionals’ work-related health and job satisfaction has yielded mixed results, and most studies emanate from residential care. Understanding how person-centred care practices influence health and social care professionals across different care settings thus requires further exploration through rigorous methodology. The overall aim of PCC@Work is to follow, describe, assess, and explore the impact of person-centred care practices in hospital wards, primary care centres and municipal care on health and social care professionals’ work-related health and job satisfaction.
PCC@Work is designed as a prospective, longitudinal cohort study combined with qualitative studies. A web-based questionnaire will be distributed on five occasions within two years to health and social care professionals in the three care settings. In addition, focus groups and interviews will be conducted with a selection of health and social care professionals to explore their experiences of work-related health and job satisfaction in relation to person-centred practices.
PCC@Work will highlight some of the knowledge gaps on the impact of person-centred care practices regarding work-related health and job satisfaction of health and social care professionals. The uniqueness of the project lies in the multi-method design, combining a prospective longitudinal cohort study with qualitative studies, and the involvement of various professions and settings. This means we will be able to provide a comprehensive and representative understanding of person-centred care practices as a critical component for effective change in the working conditions of health and social care.
Peer Review reports
There is a growing interest in person-centred care (PCC) since authorities, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), have called for enabling patients to engage in their care and treatment [ 1 ]. PCC has also been endorsed by health and social care professionals and patient organisations [ 2 , 3 ]. In Sweden, PCC stands as a pivotal element in the “Good quality, local healthcare reform” [ 4 ]. This reform necessitates substantial organisational changes to ensure integrated, proactive, and health-promoting PCC across various care settings, responsive to each person’s resources and needs. PCC has been developed to frame care in a holistic and ethical way by establishing a partnership between health and social care professionals and persons in need of care. The concept of PCC is based on ethical principles and has its roots in the holistic paradigm, which highlights the importance of knowing each person as a capable human being with needs and resources [ 5 , 6 , 7 ].
The Gothenburg Centre for Person-Centred Care (GPCC) has developed a PCC framework for applying PCC, i.e., PCC practices, serving as a lens for embodying ethical values, guiding professional actions, and enhancing well-being and work performance [ 6 ]. This framework describes a model, summarising PCC into three main practices [ 6 , 8 ]:
Initiating personal narratives to get to know each patient as a person, to identify their previous experiences, present situation, needs, abilities, and resources.
Co-creating a personal plan in line with identified resources and barriers combined with medical, health, and social research evidence.
Documenting and monitoring the plan and adapting it to changes in the goals and/or other circumstances.
Previous research evaluating PCC has to a large extent focused on patients with chronic conditions, showing that PCC could, e.g., improve patients’ self-efficacy, symptom control, satisfaction with care and reduce length of hospital stay and healthcare costs [ 5 ]. PCC practices have also shown positive associations with work-related health among health and social care professionals, but the vast majority of the studies are performed in residential care and have mainly addressed registered nurses and nurse assistants [ 9 ]. What is less known is to what extent PCC practices are applied, and what impact they have on health and social care professionals’ work-related health and job satisfaction across diverse health and social care settings. This project, PCC@Work, is developed to fill this knowledge gap, focusing on the impact and experiences of applying PCC practices in hospital wards, primary care units, and municipal care.
The work environment for health and social care professionals is characterised by demanding conditions, including high workloads, low control, ethical dilemmas, unclear roles, and demanding schedules which may lead to increased stress and job dissatisfaction [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Additionally, an unsatisfactory and stressful work setting, along with ethically challenging situations, often prompt health and social care professionals to seek alternative employment [ 10 , 12 , 14 , 15 ]. Notably, it is concerning that both newly graduated and experienced professionals show a significant likelihood of considering leaving their current positions [ 10 , 12 , 16 ]. The shortage of skilled professionals has detrimental effects on the workload, quality of care and patient safety [ 10 , 13 , 17 , 18 ]. This situation is untenable and requires immediate attention to ensure adequate staffing in the future of health and social care.
In response, PCC@Work aligns itself with the overarching goal of promoting health and well-being in the workplace, aiming to proactively address mental health challenges and mitigate sickness-related absences. One potential remedy is transitioning towards more PCC practices, which could reduce ethical stress and foster more meaningful human interactions in health and social care [ 7 , 19 ]. PCC practices reportedly foster a heightened ethical consciousness regarding the quality of care, grant greater control over daily tasks, and encourage social collaboration [ 20 ]. This is supposed to empower health and social care professionals to align their actions with their personal and professional values by effectively organising and coordinating care with both colleagues and patients [ 21 ]. However, adopting PCC practices may also present challenges, particularly due to time constraints, with barriers including traditional culture and practices, sceptical attitudes, structural factors, the time-consuming nature of actively listening to patient narratives, and engaging in the co-creation of health and social care plans [ 22 ].
A recent review from our research group [ 23 ] illustrates how the introduction of a new professional role through PCC practices could lead to feelings of disorientation and uncertainty among health and social care professionals. These feelings might initially increase stress, and repeated measures with a longitudinal design are therefore essential to show if PCC practices could influence work-related health and job satisfaction in the long run. Significantly, the results showed positive experiences of job satisfaction, including a sense of meaningfulness, enhanced relationships between professionals and persons in need of health and social care, as well as increased appreciation and collaboration [ 23 ]. These findings, in combination with the findings from a previous review [ 9 ], prompt an inquiry into the degree to which the outcomes were influenced by the specific context of applying PCC practices. This underscores the imperative for comprehensive research in diverse health and social care settings, employing both quantitative and qualitative methodologies, to assess the impact and experiences of PCC practices from the professionals’ perspective. We hypothesise that a development towards increased PCC practises may enhance the work-related health of health and social care professionals, potentially mitigating sources of stress, excessive workloads, and job dissatisfaction.
Providing a comprehensive and transparent protocol is crucial as it enables the conduct and evaluation of research projects by effectively communicating pertinent information to key stakeholders. As such, our intention with this protocol is to convey the complexity of the design of this multi-method project. The longitudinal aspect of the PCC@Work project will ensure that the complex relationship between PCC practices, work-related health, and job satisfaction is thoroughly researched so that fluctuations over time can be captured. This allows for the impact of PCC practices to be monitored and evaluated. Development of PCC may increase health and social care professionals’ perceived levels of stress at an early stage.
Methods/design
Project aim.
The overall aim of PCC@Work is to follow, describe, assess, and explore the impact of PCC practices in hospital wards, primary care centres and municipal care on health and social care professionals’ work-related health and job satisfaction.
Study design and setting
This project has a multi-method design combining a prospective, longitudinal dynamic cohort study with qualitative studies. A web-based questionnaire will be distributed on five occasions within two years to health and social care professionals in hospital wards, primary care centres, and municipal care in Sweden. Employing dynamic cohorts allows participants to leave and enter during the study period. Theoretically and pragmatically, dynamic cohorts are a relevant choice in this project in which we monitor the gradual development of PCC practices. With dynamic cohorts, we can follow the participants at several data collection points. The design allows us to perform repeated cross-sectional analyses using the entire, dynamic, cohort (hospital wards, primary care centres and municipal care) at each data collection point. These different data collection points can be used as cross-sectional studies but can also be compared and give data on changes over time. Moreover, it is possible to make longitudinal analyses by creating a fixed closed cohort identified within the open cohort, to follow participants that stay at the same workplace during the study period. The study design is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
Open cohort study design. The blue arrows represent participants remaining at each care setting during the study period, and the yellow arrows represent examples of several possible scenarios for participants starting and quitting at each care setting during the period
The multi-method design includes focus group discussions [ 24 ] to generate qualitative data from health and social care professionals from the three settings. Based on a social constructivist approach, the focus groups aim to capture the collective understanding of work-related health and job satisfaction in relation to PCC practices among health and social care professionals in diverse care settings. In addition, there is room for individual interviews with key participants to create a deeper understanding of social processes and contextual influences related to PCC practices through grounded theory [ 25 ].
Participants and recruitment process
PCC@Work addresses health and social care professionals working directly with persons in need of health or social care in hospital wards, primary care centres, and municipal care. Study participants are reached through their work e-mail addresses provided to the research group by each care organisation. All potential participants receive an e-mail, including detailed information on study design, what participation entails, and ethical topics such as voluntariness, consent, and the possibility to withdraw at any time without any negative consequences to participants’ employment. The e-mail also includes a personal link to a web-based questionnaire. Three reminders are sent to participants to facilitate and promote participation. The web-based questionnaires are operated in collaboration with a company with vast experience in using web-based questionnaires.
There is a baseline data collection for the longitudinal study which will have followed-up after six, 12, 18 and 24 months. The impact of PCC practices will be measured after the third (12 months follow-up) and fifth data collection point (24 months follow-up). Repeated cross-sectional analyses will be conducted at each data collection point to explore associations between PCC practices, work-related health, and job satisfaction. In addition, a subsample of these participants will be asked to participate in the focus groups.
Prospective longitudinal cohort study measures
Exposure variable.
The Person - Centred Care Assessment Tool (P‐CAT) [ 26 ] is chosen as the exposure variable representing self-reported levels of PCC. P-CAT comprises 13 items aimed at capturing the extent to which professionals perceive PCC practices in their daily work [ 26 ]. P-CAT consists of two subscales: the extent of personalising care (EPC; 8 items) and organisational and environmental support (OES; 5 items) [ 26 , 27 ]. A 5‐point scale from 1 (completely disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) is used for evaluation purposes. The sum score ranges from 13 to 65, with a high score indicating a greater extent of perceived PCC. P‐CAT has shown satisfactory validity and reliability in a Swedish aged care context [ 27 ], and has recently been modified by our research group for use in other care settings showing good internal consistency [ 28 ].
Outcome variables
The Stress of Conscience Questionnaire (SCQ) [ 29 ] is a 9-item measurement for assessing stressful situations and the degree to which they trouble the conscience. This questionnaire was designed in Sweden to explore perceived stress related to not providing the care or activities one wants to provide within a care setting [ 29 ]. It consists of nine items, each divided into two parts: an A question that evaluates the frequency of a selected stressful situation using a scale ranging from 0 (never) to 5 (every day), and a B question that evaluates the perceived degree of troubled conscience generated by the situation using a scale ranging from 0 (no troubled conscience at all) to 5 (a very troubled conscience). The A score is multiplied by the B score to reflect the total stress of conscience, ranging from 0 to 25 for each item. Adding the scores for all items gives a total score ranging from 0 to 225. A higher total score signifies a higher perceived stress of conscience. Satisfactory psychometric properties have been reported for the SCQ in a Swedish healthcare population [ 29 ].
The Copenhagen Psychosocial Questionnaire (COPSOQ III) [ 30 ] is a widely used and scientifically tested questionnaire for examining the organisational and social work environment, covering a broad range of domains which can be adopted depending on the aim [ 30 ]. We focus on the COPSOQ III domains Demands at Work (6 items), Work Organisation and Job Contents (6 items), Interpersonal Relations and Leadership (7 items), and Work-Individual Interface (5 items). These domains include questions on job strain, demand/control, job satisfaction, meaningfulness, and intent to leave. The item response alternatives correspond to a five-point Likert scale where the mean score between 0 and 100 is calculated for included scales. If > 50% of item responses in a scale are not recorded, the scale measurement will be considered missing. Studies across different professions have corroborated the internal consistency reliability and construct validity of the scales [ 30 ].
The Work Ability Index (WAI), developed by [ 31 ], has been widely used in research in different countries and settings and can be used to assess self-reported individual work ability regarding perceived resources, health, and physical and mental demands [ 32 ]. Four out of the seven items from the WAI are applicable to this project and included in the questionnaire. The index has shown very good predictive abilities for measuring nurses’ workability [ 33 ], and satisfactory values in a general Swedish population [ 34 ].
The Capacity to Work index (C2WI-cmd) [ 35 ] was developed for assessing capacity to work in relation to common mental disorders in general working populations. C2WI-cmd consists of 12 items. The items include statements covering the capacity to work the last week. The respondent reports to which degree they agree, with the five response alternatives ‘Not at all’; ‘To a low degree’; ‘To a moderate degree’; ‘To a high degree’; or ‘Not relevant’. Our research group tested the C2WI-cmd for reliability, validity and user-friendliness in a Swedish working sample including healthcare professionals [ 35 ].
The WHO mental well-being index (WHO-5) [ 36 ] is a measure of how the respondent has felt in the last two weeks regarding the more positive aspects of their emotional state. Increasingly, well-being has been shown to be important in relation to health and everyday functioning. WHO-5 has shown validity in assessing well-being over time and comparing well-being between groups. Apart from the positive aspects, WHO-5 also prove validity in screening for depression [ 36 ].
Demographics
Other parts of the questionnaire concern the demographic and confounding factors; gender, age, profession, workplace, type of employment, working hours, shift work, overtime, years working in health or social care and at their organisation, experience and opinion of PCC practices, sickness absence, general health and ongoing implementations or reorganisations in the care setting. All of these will be incorporated into the analyses.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis will focus on repeated cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses to assess changes over time within groups. Statistical analysis will be done at each data collection point. Regression analyses (linear, ANOVA, ANCOVA) will be applied. The primary efficacy analysis centres on the baseline to two-year change in SCQ with the P-CAT as exposure, with Fisher’s non-parametric permutation test for paired observations. Results will be presented at a 5% significance level on aggregated levels.
Power calculation
For the quantitative studies, a change of 5 units in the Stress of Conscience Questionnaire (SCQ) was considered an acceptable effect, in each of the three cohorts (hospital wards, primary care centres, and municipal care), from baseline to 24 months with a power of 80% with Fisher’s non-parametric permutation test for paired observations, and a significance level of 0.05. Thus, 285 health and social care professionals must be included in each of the three cohorts (= 855 in total). We expect a response rate of approximately 40% and therefore aim to invite a minimum of 2200 health and social care professionals at baseline to allow for both staff turnover and withdrawals. The standard deviation for change in SCQ (total score range from 0 to 225) has been estimated to be 30 based on the literature [ 37 ].
Qualitative studies
To allow for a deeper and broader understanding of PCC practices in relation to work-related health and job satisfaction, the e-mail sent out for the 12-month follow-up data collection will invite participants to focus group discussions. Participants interested in contributing to a focus group discussion will then be contacted by the research group for more detailed information and for setting up a time and place for the focus group. Homogeneity will be strived for in terms of care setting and profession, and heterogeneity will be strived for in terms of work experience, national background, age, and sex, to capture a diversity of experiences and broaden the discussions [ 24 ].
For the focus group discussions, our intention is to conduct at least two focus groups with health and social care professionals per care setting (a total of at least six focus groups), and we will strive for four to six professionals per group ( n = 24–36). For the grounded theory study, an open sampling of approximately 15–20 health and social care professionals is estimated.
The focus groups will preferably be conducted in a venue accessible for the participants, or digitally if needed, and they are expected to last 60–90 min. Led by a moderator and co-moderator, discussions centre on key questions formulated by the research group to align with the study’s aim. The moderator guides the discussion, while the co-moderator observes, takes notes, and asks follow-up questions. Sessions begin with an introduction to the study’s aim and structure, followed by open-topic discussions. The moderators’ role is to ensure participant engagement, identify common themes, and pose specific questions to deepen the discussions. All sessions will be audio-recorded and transcribed for subsequent analyses. The grounded theory study will have a similar approach.
The focus groups will be iteratively analysed using a method developed explicitly for focus groups [ 24 ]. Focus group data will undergo multiple stages of analysis. Initially, repeated listening establishes an overall understanding. Each transcript is then independently examined to capture essential data. Preliminary themes are created by the researchers, guided by the study’s aim. Raw data is categorised, and descriptive statements are formed. Systematising data under themes involves aligning discussions with relevant categories. This continuous process ensures meaningful communication of discussion meanings. Finally, data is summarised and interpreted collaboratively to foster shared understanding. This analytical continuum transforms raw discussions into condensed, interpretable summaries, forming the basis for a collectively agreed-upon final interpretation. In addition, the individual interviews will be analysed by applying grounded theory [ 25 ], in which data collection and analysis will be conducted as simultaneous processes characterised by constant comparisons of data.
There are some limitations to this project. Various factors, including time constraints, lack of direct connection to researchers, survey fatigue, and insufficient interest or motivation, impact participation rates in research, particularly among care professionals [ 38 , 39 , 40 ]. Moreover, language barriers contribute to lower questionnaire participation rates for persons born outside the country of residence, affecting municipal care, where over one-third of care professionals are foreign-born [ 41 , 42 ].
For longitudinal research, fixed cohorts are ideal, but the dynamic nature of work-related studies, especially those involving PCC practices, necessitates following groups with similar exposure combinations. Additionally, uneven distribution among health and social care professionals, with assistant nurses being the largest group, poses challenges to achieve representative sampling. Sensitivity analyses comparing assistant nurses with other professionals can address this issue, and oversampling certain groups may be considered.
The definition of PCC varies across organisations and professions, emphasising the importance of using the P-CAT in the questionnaire to establish a common understanding. Ultimately, the study aims to uncover new insights into the impact of PCC practices on work-related health and job satisfaction among health and social care professionals in hospital wards, primary care centres, and municipal care.
Data availability
The datasets produced and analysed in this project are not publicly accessible to uphold the confidentiality commitments made to participants during the informed consent process. However, de-identified data can be provided upon reasonable request for review purposes.
Abbreviations
Person-Centred Care
Gothenburg centre for Person-Centred Care
Person- Centred Care Assessment Tool
Stress of Conscience Questionnaire
Copenhagen Psychosocial Questionnaire
Capacity to Work index
The WHO mental well-being index (5 statement version)
WHO. WHO global strategy on people-centred and integrated health services: Interim report [Internet]. 2015. http://www.who.int/servicedeliverysafety/areas/people-centred-care/global-strategy/en/ .
EPF. Manifesto 2019: Putting what matters to patients at the heart of EU health policy. European Patients Forum; 2019 p. 8.
European Committee for Standardization (CEN). CEN/TC 450 -Minimum requirements of patient involvement in person-centred care. [Internet]. European Commity for Standardization; 2020 p. EN 17398:2020. https://iteh.fr/catalog/tc/cen/bc1d2237-3a90-46e8-a976-89c0ae53 c7cc/cen-tc-450.
God och nära. vård – en reform för ett hållbart hälso- och sjukvårdssystem. SOU 2020:19.
Britten N, Ekman I, Naldemirci Ö, Javinger M, Hedman H, Wolf A. Learning from Gothenburg model of person centred healthcare. BMJ (Clinical Res ed). 2020;370(Fig 1):m2738.
Google Scholar
Ekman I, Swedberg K, Taft C, Lindseth A, Norberg A, Brink E, et al. Person-centered care - ready for prime time. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2011;10(4):248–51.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
McCormack B, Dewing J. International Community of Practice for Person-centred Practice: position statement on person-centredness in health and social care. International Practice Development Journal [Internet]. 2019 May [cited 2024 Feb 5];9(1). https://www.proquest.com/docview/2233067266/abstract/1699B4147B244C70PQ/1 .
Britten N, Moore L, Lydahl D, Naldemirci Ö, Elam M, Wolf A. Elaboration of the Gothenburg model of person-centred care. Health Expect. 2016;20(3):407–18.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Van Diepen C, Fors A, Ekman I, Hensing G. Association between person-centred care and healthcare providers’ job satisfaction and work-related health: a scoping review. BMJ Open. 2020;10(12):e042658.
Aiken LH, Sloane DM, Bruyneel L, Van den Heede K, Sermeus W. Nurses’ reports of working conditions and hospital quality of care in 12 countries in Europe. Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50(2):143–53.
Anskär E, Lindberg M, Falk M, Andersson A. Time utilization and perceived psychosocial work environment among staff in Swedish primary care settings | SpringerLink. BMC Health Services Research [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 May 3];18(166). https://link.springer.com/article/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-2948-6 .
Halter M, Boiko O, Pelone F, Beighton C, Harris R, Gale J, et al. The determinants and consequences of adult nursing staff turnover: a systematic review of systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):824.
Kaihlanen AM, Ruotsalainen S, Väisänen V, Corneliusson L, Pesonen T, Sinervo T. Job demand and job resource factors explaining stress and job satisfaction among home care nurses – a mixed-methods sequential explanatory study. BMC Nurs. 2023;22(1):404.
Porter S, Lexén A. Swedish occupational therapists’ considerations for leaving their profession: outcomes from a national survey. Scand J Occup Ther. 2022;29(1):79–88.
Van den Bulcke B, Metaxa V, Reyners AK, Rusinova K, Jensen HI, Malmgren J, et al. Ethical climate and intention to leave among critical care clinicians: an observational study in 68 intensive care units across Europe and the United States. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(1):46–56.
Koch P, Zilezinski M, Schulte K, Strametz R, Nienhaus A, Raspe M. How perceived quality of care and job satisfaction are Associated with Intention to leave the Profession in Young Nurses and Physicians. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(8):2714.
Hall LH, Johnson J, Watt I, Tsipa A, O’Connor DB. Healthcare Staff Wellbeing, Burnout, and Patient Safety: a systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(7):e0159015.
Poon YSR, Lin YP, Griffiths P, Yong KK, Seah B, Liaw SY. A global overview of healthcare workers’ turnover intention amid COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review with future directions. Hum Resour Health. 2022;20(1):70.
Ruggiano N, Edvardsson D. Person-centeredness in Home- and community-based long-term care: current challenges and new directions. Soc Work Health Care. 2013;52(9):846–61.
Sjögren K, Lindkvist M, Sandman PO, Zingmark K, Edvardsson D. To what extent is the work environment of staff related to person-centred care? A cross-sectional study of residential aged care. J Clin Nurs. 2015;24(9–10):1310–9.
Lood Q, Kirkevold M, Edvardsson D. Becoming part of an upwards spiral: meanings of being person-centred in nursing homes. Int J Older People Nurs. 2022;17(2):e12420.
Moore L, Britten N, Lydahl D, Naldemirci Ö, Elam M, Wolf A. Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of person-centred care in different healthcare contexts. Scand J Caring Sci. 2017;31(4):662–73.
Gustavsson K, van Diepen C, Fors A, Axelsson M, Bertilsson M, Hensing G. Healthcare professionals’ experiences of job satisfaction when providing person-centred care: a systematic review of qualitative studies. BMJ Open. 2023;13(6):e071178.
Krueger RA, Casey MA. Focus Group Interviewing. In: Handbook of Practical Program Evaluation [Internet]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2015 [cited 2024 Jan 26]. pp. 506–34. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119171386.ch20 .
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory: a practical guide through qualitative analysis. SAGE; 2006. p. 223.
Edvardsson D, Fetherstonhaugh D, Nay R, Gibson S. Development and initial testing of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22(1):101–8.
Sjögren K, Lindkvist M, Sandman PO, Zingmark K, Edvardsson D. Psychometric evaluation of the Swedish version of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2012;24(03):406–15.
Van Diepen C, Fors A, Ekman I, Bertilsson M, Hensing G. Associations between person- centred care and job strain, stress of conscience, and intent to leave among hospital personnel. J Clin Nurs. 2021;(March):1–11.
Glasberg AL, Eriksson S, Dahlqvist V, Lindahl E, Strandberg G, Söderberg A, et al. Development and initial validation of the stress of conscience questionnaire. Nurs Ethics. 2006;13(6):633–48.
Berthelsen H, Westerlund H, Bergström G, Burr H. Validation of the copenhagen psychosocial questionnaire version III and establishment of benchmarks for psychosocial risk management in Sweden. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):1–22.
Article Google Scholar
Tuomi K, Ilmarinen J, Jahkola A, Katajarinne L, Tulkki A. Work ability index. Safety Science. Volume 19. Helsinki: Institute of Occupational Health.; 1998. pp. 71–2.
Ilmarinen J, Tuomi K, Klockars M. By the work ability Index over an 11-Year period. Scandinavian J Work Environ Health. 2013;28(3):179–88.
Romero-Sánchez JM, Porcel-Gálvez AM, Paloma-Castro O, García-Jiménez J, González-Domínguez ME, Palomar-Aumatell X, et al. Worldwide prevalence of inadequate work ability among hospital nursing personnel: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2022;54(4):513–28.
Lundin A, Leijon O, Vaez M, Hallgren M, Torgén M. Predictive validity of the work ability index and its individual items in the general population. Scand J Public Health. 2017;45(4):350–6.
Hensing G, van Diepen C, Boström M, Bertilsson M. Validity of the Capacity to Work Index: Development of an Instrument to Measure Work Capacity in Relation to Depression and Anxiety in the General Working Population. J Occup Rehabil [Internet]. 2023 Nov 8 [cited 2023 Nov 9]; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10926-023-10150-2 .
Topp CW, Østergaard SD, Søndergaard S, Bech P. The WHO-5 well-being index: a systematic review of the literature. Psychother Psychosom. 2015;84(3):167–76.
Tuvesson H, Eklund M, Wann-Hansson C. Stress of Conscience among psychiatric nursing staff in relation to environmental and individual factors. Nurs Ethics. 2012;19(2):208–19.
Shiyab W, Ferguson C, Rolls K, Halcomb E. Solutions to address low response rates in online surveys. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2023;22(4):441–4.
Timmins F, Ottonello G, Napolitano F, Musio ME, Calzolari M, Gammone M, et al. The state of the science—the impact of declining response rates by nurses in nursing research projects. J Clin Nurs. 2023;32(7–8):e9–11.
PubMed Google Scholar
Wenemark M, Persson A, Brage HN, Svensson T, Kristenson M. Applying motivation theory to achieve increased response rates, Respondent satisfaction and data quality. J Official Stat. 2011;27(2):393–414.
Falk E, Sandelin F, Weissenbilder M. Den nationella SOM-undersökningen 2020 - En metodöversikt. SOM-institutet; 2021. Report No.: SOM-rapport nr 2021:2.
SKR. Välfärdens kompetensförsörjning. Sveriges Kommuner och Regioner; 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This project is supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working life and Welfare (reference number 2022 − 00278). The Council employs an external peer-review process before decision on grants. Thus, the project application with study design and methodology has been peer-reviewed. The funding source has no role in the writing of this manuscript or the decision to it for publication.
Open access funding provided by University of Gothenburg.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Erasmus School of Health Policy & Management, Erasmus University Rotterdam, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Cornelia van Diepen
Centre for Person-Centred Care (GPCC), University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Cornelia van Diepen, Qarin Lood, Kristoffer Gustavsson & Andreas Fors
Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, Department of Health and Rehabilitation, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Centre for Ageing and Health - AgeCap, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Institute of Health and Care Sciences, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Goteborg, Sweden
Kristoffer Gustavsson & Andreas Fors
Department of Care Science, Faculty of Health and Society, Malmö University, Malmö, Sweden
Malin Axelsson
School of Public Health and Community Medicine, Institute of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Monica Bertilsson & Gunnel Hensing
Research, Education, Development and Innovation, Region Västra Götaland, Primary Health Care, Gothenburg, Sweden
Andreas Fors
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors were involved in the design of the protocol. CvD drafted the manuscript with critical input from all authors. AF is the principal investigator and grant holder of the investigation. All authors reviewed, edited, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cornelia van Diepen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The project will be performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Swedish Ethical Review Authority (Dnr: 2019 − 01287, 2021–02821, 2021–05094, 2023-05980-02) has already approved recruitment and all other procedures involved in the study prior to any recruitment. The project participation is voluntary; participants receive adequate information about the specific study and data protection measures before giving consent. In the consent for participation in the project, participants will give permission to use their anonymised data for publication purposes. No third parties will access data, stored securely at the University of Gothenburg. All results will be presented on a group level, ensuring anonymity. Handling of personal data complies with the EU General Data Protection (GDPR EU 2016/679), highlighting our commitment to ethical standards and participant confidentiality.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
van Diepen, C., Lood, Q., Gustavsson, K. et al. Person-centred care and the work-related health and job satisfaction of health and social care professionals: protocol for a prospective longitudinal cohort study combined with qualitative studies (the PCC@Work project). BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 683 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11148-z
Download citation
Received : 12 March 2024
Accepted : 24 May 2024
Published : 30 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11148-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Study protocol
- Person-centred care
- Health and social care professionals
- Cohort study
- Job satisfaction
- Stress of conscience
- Psychosocial work environment
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Grounded theory provided an outlook that questioned the view of the time that quantitative methodology is the only valid, unbiased way to determine truths about the world. 11 Glaser and Strauss 5 challenged the belief that qualitative research lacked rigour and detailed the method of comparative analysis that enables the generation of theory.
Grounded Theory. Definition: Grounded Theory is a qualitative research methodology that aims to generate theories based on data that are grounded in the empirical reality of the research context. The method involves a systematic process of data collection, coding, categorization, and analysis to identify patterns and relationships in the data.
Grounded theory is a systematic methodology that has been largely applied to qualitative research conducted by social scientists.The methodology involves the construction of hypotheses and theories through the collecting and analysis of data. Grounded theory involves the application of inductive reasoning.The methodology contrasts with the hypothetico-deductive model used in traditional ...
Since Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss' (The discovery of grounded theory: strategies for qualitative research. New York: Adline De Gruyter, 1967) publication of their groundbreaking book, The Discovery of Grounded Theory, grounded theory methodology (GTM) has been an integral part of health social science.GTM allows for the systematic collection and analysis of qualitative data to ...
Abstract. Since being developed as a research methodology in the 1960s, grounded theory (GT) has grown in popularity. In spite of its prevalence, considerable confusion surrounds GT, particularly in respect of the essential methods that characterize this approach to research. Misinformation is evident in the literature around issues such as the ...
The term "grounded theory" first came to prominence with the publication of The Discovery of Grounded Theory (hereafter Discovery) by Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss in 1967.Since that time, the term itself has come to encompass a family of related approaches to research that reaches across many disciplines, including the social sciences, psychology, medicine, and many others.
The logic of grounded theory. Glaser and Strauss (Citation 1967) developed grounded theory by explaining the methods they used to construct their remarkable qualitative studies of death and dying in hospitals (Glaser & Strauss, Citation 1965, Citation 1968).In this methodological treatise, they introduced the innovative and systematic strategy of simultaneous data collection and analysis.
The grounded theory approach is especially relevant for research on issues for which limited prior research has been conducted and for which theory building is needed (Bryant & Charmaz, 2007 ...
Grounded Theory for Qualitative Research. : Straightforward and accessible, this pragmatic guide takes you step-by-step through doing grounded theory research. With hands-on advice focussed around designing real projects, it demonstrates best practice for integrating theory building and methods. Its extensive examples and case studies are drawn ...
Background: Grounded theory is a well-known methodology employed in many research studies. Qualitative and quantitative data generation techniques can be used in a grounded theory study. Grounded theory sets out to discover or construct theory from data, systematically obtained and analysed using comparative analysis.
Grounded theory is a systematic qualitative research method that collects empirical data first, and then creates a theory 'grounded' in the results. The constant comparative method was developed by Glaser and Strauss, described in their book, Awareness of Dying (1965). They are seen as the founders of classic grounded theory.
Grounded theory (GT) is a widely applied research method that is spelled out in several books including the foundational work by Glaser and Strauss (1967); the current editions of pathbreaking works by Charmaz (2014), Clarke (2005), and Corbin and Strauss (2015); and the comprehensive outline by Bryant (2017).In these and other contributions, the GT method takes a number of different forms ...
Grounded theory is a systematic methodology in the social sciences emphasizing generation of theory from data in the process of conducting research. It is mainly used for qualitative research, but is also applicable to other data (e.g., quantitative data; Glaser, 1967, chapter VIII)
Grounded theory is a qualitative research methodology that involves developing theories directly from the data collected during the research process instead of relying on pre-existing theories or hypotheses. This approach aims to generate insights and understanding about a particular phenomenon by systematically analyzing and coding the data to ...
Grounded theory provided an outlook that questioned the view of the time that quantitative methodology is the only valid, unbiased way to determine truths about the world. 11 Glaser and Strauss 5 challenged the belief that qualitative research lacked rigour and detailed the method of comparative analysis that enables the generation of theory.
Introduction. Qualitative research is a cornerstone in cardiovascular research. It gives insights in why particular phenomena occur or what underlying mechanisms are. 1 Over the past 2 years, the European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing published 20 qualitative studies. 2-21 These studies used methods such as content analysis, ethnography, or phenomenology.
Abductive Research Methods. B.D. Haig, in International Encyclopedia of Education (Third Edition), 2010 Grounded Theory. Grounded theory (GT) is probably the most widely known methodological perspective on how to conduct qualitative research in the social sciences. Originally introduced by sociologists Barney Glaser and Anselm Strauss (Glaser and Strauss, 1967), GT is used extensively in ...
Grounded theory (GT) is a research method concerned with the generation of theory,1 which is 'grounded' in data that has been systematically collected and analysed.2 It is used to uncover such things as social relationships and behaviours of groups, known as social processes.3 It was developed in California, USA by Glaser and Strauss during their study—'Awareness of Dying'.1 It is a ...
Grounded theory is a great method for specific types of research issues. Grounded theory is best applied when research teams come into a problem with uncertainty about the full landscape and situation. Because it requires multiple rounds of research, it's more costly and time-consuming than studies where the hypothesis and testing is clear ...
Grounded theory is a qualitative research method that involves the construction of theory from data rather than testing theories through data (Birks & Mills, 2015). In other words, a grounded theory analysis doesn't start with a hypothesis or theoretical framework, but instead generates a theory during the data analysis process.
Glaserian grounded theory in nursing research: Trusting emergence. New York, NY: Springer. Charmaz, Kathy (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Charmaz, Kathy & Keller, Reiner (2016). A personal journey with grounded theory methodology.
Grounded theory (GT) and thematic analysis (TA) are commonly used in qualitative healthcare research. Published by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, GT was the first set of qualitative research strategies described. TA has since been compared with selected GT strategies.
Grounded theory was first introduced more than 50 years ago, but researchers are often still uncertain about how to implement it. This is not surprising, considering that even the two pioneers of this qualitative design, Glaser and Strauss, have different views about its approach, and these are just two of multiple variations found in the literature.
Grounded theory is on e of the data collection approach in qualitative research. methods which is totally based on data rather than try to em erge theory from data. There are b ulk of books and ...
Grounded theory, as a qualitative research approach, is discovered, developed, and provisionally verified through systematic data collection and analysis of data pertaining to the phenomenon (p. 23). It provides researchers with a framework to generate a theory from the context of a phenomenon and offers a process to develop a model to be used ...
Be the first to add your personal experience. Grounded theory methodology is a powerful tool for business management research, offering a systematic approach to data collection and analysis aimed ...
The multi-method design includes focus group discussions [] to generate qualitative data from health and social care professionals from the three settings.Based on a social constructivist approach, the focus groups aim to capture the collective understanding of work-related health and job satisfaction in relation to PCC practices among health and social care professionals in diverse care settings.
Grounded theory may not be suitable for situations where access to participants for data collection is limited, as the theory development relies heavily on iterative analysis of rich data. Discourse Analysis Discourse Analysis (DA) is a qualitative research method that goes beyond the surface meaning of language.
The yield of grounded theory projects is the clarification of most of the necessary and sufficient conditions for the findings to occur, which tests and limits the applicability of study concepts and/or midlevel theory. Other models of generalization from concepts and theory may offer less detail and clarity to the reader/consumer regarding the ...